UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 40-F
| ☐ | Registration statement pursuant to Section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
| or | |
| ☒ | Annual report pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
| For the fiscal year ended September 30, 2025 |
Commission File Number 001-41726 |
Electrovaya Inc.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
N/A
(Translation of Registrant’s name into English (if applicable))
| Ontario, Canada | 3692 | N/A | ||
| (Province or other jurisdiction of | (Primary Standard Industrial Classification | (I.R.S. Employer | ||
| incorporation or organization) | Code Number) | Identification Number) |
6688 Kitimat Road
Mississauga, Ontario L5N 1P8
(905) 855-4627
(Address and telephone number of Registrant’s principal executive offices)
Cogency Global Inc.
122 East 42nd Street, 18th Floor
New York, NY 10168
1-800-221-0102
(Name, address (including zip code) and telephone number (including
area code) of agent for service in the United States)
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol | Name of each exchange on which registered | ||
| Common Shares, no par value | ELVA | The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Securities for which there is a reporting obligation pursuant to Section 15(d) of the Act: None
For annual reports, indicate by check mark the information filed with this Form:
| ☒ Annual information form | ☒ Audited annual financial statements |
Indicate the number of outstanding shares of each of the registrant’s classes of capital or common stock as of the close of the period covered by the annual report: 42,108,920 outstanding as of September 30, 2025.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports); and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. ☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). ☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is an emerging growth company as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
☒ Emerging growth company
If an emerging growth company that prepares its financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards† provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
| † | The term “new or revised financial accounting standard” refers to any update issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board to its Accounting Standards Codification after April 5, 2012. |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☐
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
EXPLANATORY NOTE
Electrovaya Inc. is a “foreign private issuer” as defined in Rule 3b-4 under Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), and is a Canadian issuer eligible to file its Annual Report pursuant to Section 13 of the Exchange Act on Form 40-F pursuant to the multi-jurisdictional disclosure system (the “MJDS”) adopted by the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). The Company’s common shares are listed in the United States on the Nasdaq Capital Market (“NASDAQ”) under the trading symbol “ELVA” and in Canada on the Toronto Stock Exchange (“TSX” or the “Exchange”) under the trading symbol “ELVA”.
In this Annual Report, references to “we,” “our,” “us,” the “Registrant,” the “Company,” or “Electrovaya,” mean Electrovaya Inc. unless the context suggests otherwise.
FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
The Exhibits filed with this Annual Report of the Registrant contain forward-looking statements, including statements that relate to, among other things, revenue, purchase orders, revenue guidance of more than 30% revenue growth (exceeding $83 million) over FY 2025 in FY 2026, order growth and customer demand in FY 2026, mass production schedules, , the Company’s ability to start production of cells at the Jamestown, New York facility by end of FY 2026, future business opportunities, use of proceeds, ability to deliver to customer requirements and revenue growth forecasts for the fiscal year ending September 30, 2026. Forward-looking statements can generally, but not always, be identified by the use of words such as “may”, “will”, “could”, “should”, “would”, “likely”, "possible", “expect”, “intend”, “estimate”, “anticipate”, “believe”, “plan”, “objective” and “continue” (or the negative thereof) and words and expressions of similar import. Although the Company believes that the expectations reflected in such forward-looking statements are reasonable, assumptions and analyses made by the Company in light of the experience and perception of historical trends, current conditions and expected future developments and other factors it believes are appropriate are necessarily applied in making forward looking statements and such statements are subject to risks and uncertainties, therefore actual results may differ materially from those expressed or implied in such statements and undue reliance should not be placed on such statements. Material assumptions made in disclosing the forward-looking statements included in the news release include, but are not limited to assumptions that the Company’s customers will deploy its products in accordance with communicated timing and volumes, that the Company’s customers will complete new distribution centers in accordance with communicated expectations, intentions and plans, the sum of anticipated new orders in FY 2026 based on customers’ historical patterns and additional demand communicated to the Company and its partners but not yet provided as a purchase order with the Company’s current firm purchase order backlog totaling approximately $100-125 million, a discount of approximately 25% used in the revenue modeling applied to the overall expected order pipeline to account for potential delays in customer orders, expected decreases in input and material costs combined with stable selling prices in FY 2026, and a stable political climate with respect to exports from Canada to the United States, the start up time for manufacturing in Jamestown NY is estimated towards the end of FY 2026 or first quarter of FY 2027, the ability to leverage IRA45X credits, the ability to receive incentives from the state of New York, the ability to improve margins from domestic manufacturing, and the ability to attract additional customers through domestic manufacturing. Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from expectations include but are not limited to customers not placing orders roughly in accordance with historical ordering patterns and communicated intentions resulting in annual revenue growth in FY 2026 of more than 30% over FY 2025 (exceeding $83 million), the predictability of sales and success of the Company’s products in verticals other than material handling, the imposition of a tariff regime on Canadian exports by the United States, macroeconomic effects on the Company and its business and on the lithium battery industry generally, the Company’s liquidity and cash availability in excess of its operational requirements, and the ability to generate and sustain sales orders. Additional information about material factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from expectations and about material factors or assumptions applied in making forward-looking statements may be found in the Company’s Annual Information Form for the year ended September 30, 2025 under “Risk Factors”, in the Company’s base shelf prospectus dated September 17, 2024, and in the Company’s most recent annual and interim Management’s Discussion and Analysis under “Qualitative And Quantitative Disclosures about Risk and Uncertainties” as well as in other public disclosure documents filed with Canadian and American securities regulatory authorities. The Company does not undertake any obligation to update publicly or to revise any of the forward-looking statements contained in this document, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.
The revenue for the periods described herein constitute future-oriented financial information and financial outlooks (collectively, “FOFI”), and generally, is, without limitation, based on the assumptions and subject to the risks set out above under “Forward-Looking Statements”. Although management believes such assumptions to be reasonable, a number of such assumptions are beyond the Company’s control and there can be no assurance that the assumptions made in preparing the FOFI will prove accurate. FOFI is provided for the purpose of providing information about management’s current expectations and plans relating to the Company’s future performance and may not be appropriate for other purposes.
The FOFI does not purport to present the Company’s financial condition in accordance with IFRS, and it is expected that there may be differences between audited results and preliminary results, and the differences may be material. The inclusion of the FOFI in this news release disclosure should not be regarded as an indication that the Company considers the FOFI to be a reliable prediction of future events, and the FOFI should not be relied upon as such.
Readers are cautioned that the above list of cautionary statements is not exhaustive.
No assurance can be given that these expectations will prove to be correct and such forward-looking statements in the Exhibits filed with this Annual Report should not be unduly relied upon. The Registrant’s forward-looking statements contained in the Exhibits filed with this Annual Report are made as of the respective dates set forth in such Exhibits. Such forward-looking statements are based on the beliefs, expectations, and opinions of management on the date the statements are made. In preparing this Annual Report, the Registrant has not updated such forward-looking statements to reflect any change in circumstances or in management’s beliefs, expectations or opinions that may have occurred prior to the date hereof. Nor does the Registrant assume any obligation to update such forward-looking statements in the future as stated above. For the reasons set forth above, investors should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements.
NOTICE TO UNITED STATES READERS - DIFFERENCES IN UNITED STATES AND CANADIAN REPORTING PRACTICES
The Registrant is permitted, under the MJDS, to prepare this Annual Report in accordance with Canadian disclosure requirements, which are different from those of the United States. The Registrant has historically prepared its consolidated financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”), as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”), in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and auditor independence standards. Financial statements prepared in IFRS may differ from financial statements prepared in United States GAAP (“U.S. GAAP”) and from practices prescribed by the SEC. Therefore, the Registrant’s financial statements filed with this Annual Report may not be comparable to financial statements of United States companies prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
Unless otherwise indicated, all dollar amounts in this Annual Report are in United States dollars.
PRINCIPAL DOCUMENTS
The following documents have been filed as part of this Annual Report:
A. Annual Information Form
The Registrant’s Annual Information Form for the fiscal year ended September 30, 2025 is filed as Exhibit 99.1 to this Annual Report.
B. Audited Annual Financial Statements
The Registrant’s consolidated audited annual financial statements for the fiscal years ended September 30, 2025 and 2024, including the reports of the independent registered public accounting firm with respect thereto, is filed as Exhibit 99.2 to this Annual Report.
C. Management’s Discussion and Analysis
The Registrant’s Management’s Discussion and Analysis for the year ended September 30, 2025 is filed as Exhibit 99.3 to this Annual Report.
TAX MATTERS
Purchasing, holding or disposing of securities of the Registrant may have tax consequences under the laws of the United States and Canada that are not described in this Annual Report.
DISCLOSURE CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
The information provided in the sections entitled “Disclosure Controls” and “Internal Control Over Financial Reporting” in the Management’s Discussion and Analysis for the year ended September 30, 2025 filed as Exhibit 99.3 to this Annual Report.
MANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON
INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
The information provided in the sections entitled “Disclosure Controls” and “Internal Control Over Financial Reporting” in the Management’s Discussion and Analysis for the year ended September 30, 2025 filed as Exhibit 99.3 to this Annual Report.
ATTESTATION REPORT OF THE REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
This Annual Report does not include an attestation report of the Registrant’s registered public accounting firm. The Registrant qualifies as an “emerging growth company,” as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”), and therefore is exempt from the requirement under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 that a public company’s registered public accounting firm provide an attestation report on management’s assessment of internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, no such attestation report is included in, or filed with, this Annual Report.
CHANGES IN INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
There have been no changes in the Registrant’s internal control over financial reporting during the fiscal year ended September 30, 2025, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
NOTICES PURSUANT TO REGULATION BTR
None.
CODE OF ETHICS
The Registrant has adopted a written “code of ethics” (as defined by the rules and regulations of the SEC), entitled “Code of Conduct” (the “Code”) that applies to all members of the board of directors, officers, employees, representatives and other associates of the Company and its subsidiaries worldwide. Adherence to this code is a condition of employment with or providing services to the Company.
The Code may be obtained upon request from Electrovaya Inc.’s head office at 6688 Kitimat Rd, Mississauga, Ontario, L5N 1P8, Canada or by viewing the Registrant’s web site at https://electrovaya.com/financial-summary/.
All amendments to the Code, and all waivers of the Code with respect to any director, executive officer or principal financial and accounting officers, will be posted on the Registrant’s web site within five business days following the date of the amendment or waiver and any amendment will be provided in print to any shareholder upon request.
AUDIT COMMITTEE
Our Board of Directors has established the Audit Committee in accordance with Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act and Rule 5605(c) of the Nasdaq Marketplace Rules for the purpose of overseeing our accounting and financial reporting processes and the audits of our annual financial statements.
The Audit Committee is comprised of Dr. James K. Jacobs (Chair), Steven Berkenfeld, and Kartick Kumar. Our Board of Directors has determined that the Audit Committee satisfies the composition requirements of Rule 5605(c)(2) of the Nasdaq Marketplace Rules and that each member of the Audit Committee is independent within the meaning of Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act and Rule 5605(a)(2) of the Nasdaq Marketplace Rules.
All three members of the Audit Committee are financially literate, meaning they are able to read and understand the Registrant’s financial statements and to understand the breadth and level of complexity of the issues that can reasonably be expected to be raised by the Registrant’s financial statements.
Our Board of Directors has determined that Steven Berkenfeld qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” (as defined in paragraph (8)(b) of General Instruction B to Form 40-F).
The SEC has indicated that the designation or identification of a person as an audit committee financial expert does not make such person an “expert” for any purpose, impose any duties, obligations or liability on such person that are greater than those imposed on members of the audit committee and the board of directors who do not carry this designation or identification, or affect the duties, obligations or liability of any other member of the audit committee or board of directors.
PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The required disclosure is included under the heading “Audit Committee” in the Company’s Annual Information Form for the fiscal year ended September 30, 2025, filed as Exhibit 99.1 to this Annual Report.
PRE-APPROVAL OF AUDIT AND NON-AUDIT SERVICES PROVIDED BY
INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The Audit Committee Charter sets out responsibilities regarding the provision of non-audit services by the Registrant’s external auditors and requires the Audit Committee to pre-approve all permitted non-audit services to be provided by the Registrant’s external auditors, in accordance with applicable law.
OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS
The Registrant currently has no off-balance sheet arrangements.
TABULAR DISCLOSURE OF CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS
The following table lists, as of September 30, 2025, information with respect to the Registrant’s known contractual obligations (in thousands):
| Payments due by period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Less than | More than | |||||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations | Total | 1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | 5 years | |||||||||||||||
| Long-Term Debt Obligations | $ | 22,517 | $ | — | $ | 20,579 | $ | 969 | $ | 969 | ||||||||||
| Capital Finance Lease Obligations | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Operating Lease Obligations | $ | 3,156 | $ | 761 | $ | 2,206 | $ | 189 | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Purchase Obligations | $ | 9,555 | $ | 9,555 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Other Long-Term Liabilities Reflected on Balance Sheet | $ | 1,390 | $ | 196 | $ | 703 | $ | 225 | $ | 266 | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 36,618 | $ | 10,512 | $ | 23,488 | $ | 1,383 | $ | 1,235 | ||||||||||
NASDAQ CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The Registrant is a foreign private issuer and its common shares are listed on the NASDAQ.
NASDAQ Rule 5615(a)(3) permits a foreign private issuer to follow its home country practice in lieu of the requirements of the Rule 5600 Series, the requirement to distribute annual and interim reports set forth in Rule 5250(d), and the Direct Registration Program requirement set forth in Rules 5210(c) and 5255; provided, however, that such a company shall comply with the Notification of Material Noncompliance requirement (Rule 5625), the Voting Rights requirement (Rule 5640), have an audit committee that satisfies Rule 5605(c)(3), and ensure that such audit committee’s members meet the independence requirement in Rule 5605(c)(2)(A)(ii).
The Registrant has reviewed the NASDAQ corporate governance requirements and confirms that except as described below, the Registrant is in compliance with the NASDAQ corporate governance standards in all significant respects:
The Registrant does not follow Rule 5605(b)(2), which requires the company to have regularly scheduled meetings at which only independent directors present (“executive sessions”). In lieu of following Rule 5605(b)(2), the Registrant follows Canadian securities laws and the rules of the TSX.
The Registrant has a formal Audit Committee charter but does not follow Rule 5605(c)(1), which requires a company’s Audit Committee charter to include the items enumerated in Rule 5605(c)(1) and have the Audit Committee review and reassess the Charter on an annual basis. In lieu of following Rule 5605(c)(1), the Registrant follows applicable Canadian securities laws and the rules of the TSX with respect to audit committee charters.
The Registrant does not follow Rule 5605(d)(1), which requires companies to adopt a formal written compensation committee charter and have a compensation committee review and reassess the adequacy of the charter on an annual basis. In lieu of following Rule 5605(d)(1), the Registrant follows applicable Canadian securities laws and the rules of the TSX.
The Registrant does not follow Rule 5620(c), under which the Nasdaq minimum quorum requirement for a shareholder meeting is 33-1/3% of the outstanding shares of common stock. A quorum for a meeting of shareholders of the Registrant is two shareholders or proxyholders that hold or represent, as applicable, not less than 25% of the issued and outstanding shares entitled to be voted at the meeting. In lieu of following Rule 5620(c) (shareholder quorum), the Registrant follows applicable Ontario and Canadian corporate and securities laws and the rules of the TSX.
The foregoing is consistent with the laws, customs, and practices in the province of Ontario and Canada.
Further information about the Registrant’s governance practices is included on the Registrant’s website.
MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS
The Registrant has adopted a compensation recovery policy (the “Clawback Policy”) as required by Nasdaq listing standards and pursuant to Rule 10D-1 of the Exchange Act. The Clawback Policy is incorporated by reference as Exhibit 97.
At no time during or after the fiscal year ended September 30, 2025, was the Registrant required to prepare an accounting restatement that required recovery of erroneously awarded compensation pursuant to the Clawback Policy. As of September 30, 2025, there was no outstanding balance of erroneously awarded compensation to be recovered from the application of the Clawback Policy to a prior restatement.
RECOVERY OF ERRONEOUSLY AWARDED COMPENSATION
None.
UNDERTAKING
The Registrant undertakes to make available, in person or by telephone, representatives to respond to inquiries made by the SEC staff, and to furnish promptly, when requested to do so by the SEC staff, information relating to: the securities registered pursuant to Form 40-F; the securities in relation to which the obligation to file an annual report on Form 40-F arises; or transactions in said securities.
CONSENT TO SERVICE OF PROCESS
The Registrant has previously filed with the SEC a written consent to service of process on Form F-X. Any change to the name or address of the Registrant’s agent for service shall be communicated promptly to the SEC by amendment to the Form F-X referencing the file number of the Registrant.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Additional information relating to the Registrant may be found on the SEDAR+ System for Electronic Document Analysis and Retrieval at www.sedarplus.ca and on the SEC’s Electronic Data Gathering, Analysis and Retrieval (EDGAR) system at www.sec.gov.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Exchange Act, the Registrant certifies that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form 40-F and has duly caused this Annual Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| ELECTROVAYA INC. | |||
| By: | /s/ Raj Das Gupta | ||
| Name: | Raj Das Gupta | ||
| Title: | Chief Executive Officer | ||
Date: December 19, 2025
EXHIBIT INDEX
- 1 -
Exhibit 99.1

ELECTROVAYA INC.
ANNUAL INFORMATION FORM
FOR THE YEAR ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2025
DECEMBER 10, 2025
-
ELECTROVAYA INC.
ANNUAL INFORMATION FORM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| 1. | CORPORATE STRUCTURE | 2 | |
| 1.1 Name, Address and Incorporation | |||
| 1.2 Our Mission and Values | |||
| 1.3 Intercorporate Relationships | |||
| 2. | GENERAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE BUSINESS | 3 | |
| 2.1 Summary of the Business | |||
| 2.2 Three-Year History | |||
| 2.3 Narrative Description of the Business | |||
| 3. | CAPITAL STRUCTURE AND MARKET FOR SHARES | 11 | |
| 4. | DIVIDEND POLICY | 13 | |
| 5. | DIRECTORS AND OFFICERS | 14 | |
| 6. | TRANSFER AGENT AND REGISTRAR | 16 | |
| 7. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS AND REGULATORY ACTIONS | 17 | |
| 8. | INTEREST OF MANAGEMENT AND OTHERS IN MATERIAL TRANSACTIONS | 17 | |
| 9. | MATERIAL CONTRACTS | 19 | |
| 10. | INTERESTS OF EXPERTS | 19 | |
| 11. | RISK FACTORS | 19 | |
| 12. | ADDITIONAL INFORMATION | 32 | |
| 13. | AUDIT COMMITTEE | 33 | |
| APPENDIX “A” AUDIT COMMITTEE CHARTER | A-1 | ||
ELECTROVAYA INC.
ANNUAL INFORMATION FORM
Unless otherwise indicated herein, the information set out in this annual information form (“AIF”) is current to December 10, 2025 and is presented in US dollars.
This AIF contains forward-looking statements including statements with respect to the effects of pandemics, geopolitical tensions, supply chains customer demand and order flow, other factors impacting revenue, the competitive position of the Company’s products, global trends in technology supply chains, the Company’s strategic objectives and financial plans, including the operations and strategic direction of Electrovaya Labs, the Company’s products, including high voltage battery systems for electric bus, truck and energy storage applications and low voltage battery systems for electric lift truck and robotic applications and the potential for revenue from new applications , cost implications, continually increasing the Company’s intellectual property portfolio, additional capital raising activities, the adequacy of financial resources to continue as a going concern, and also with respect to the Company’s markets, objectives, goals, strategies, intentions, beliefs, expectations and estimates generally. Forward-looking statements can generally be identified by the use of words such as “may”, “will”, “could”, “should”, “would”, “likely”, “possible”, “expect”, “intend”, “estimate”, “anticipate”, “believe”, “plan”, “objective” and “continue” (or the negatives thereof) and words and expressions of similar import. Readers and investors should note that any announced estimated and forecasted orders and volumes provided by customers and potential customers to Electrovaya also constitute forward-looking information and Electrovaya does not have (a) knowledge of the material factors or assumptions used by the customers or potential customers to develop the estimates or forecasts or as to their reliability and (b) the ability to monitor the performance of the business its customers and potential customers in order to confirm that the forecasts and estimates initially represented by them to Electrovaya remain valid. If such forecasts and estimates do not remain valid, or if firm irrevocable orders are not obtained, the potential estimated revenues of Electrovaya could be materially and adversely impacted.
Although the Company believes that the expectations reflected in such forward-looking statements are reasonable, the outcome of such statements involve and are dependent on risks and uncertainties, and undue reliance should not be placed on such statements. Certain material factors or assumptions are applied in making forward-looking statements, and actual results may differ materially from those expressed or implied in such statements. Material assumptions used to develop forward-looking information in this AIF include, among other things, that that current customers will continue to make and increase orders for the Company’s products; that the Company’s alternate supply chain will be adequate to replace material supply and manufacturing; that the Company’s products will remain competitive with currently-available alternatives in the market; that the alternative energy market will continue to grow and the impact of that market on the Company; the purchase orders actually placed by customers of Electrovaya; customers not terminating or renewing agreements; general business and economic conditions (including but not limited to inflation, currency rates and creditworthiness of customers); the relative effect of the global geopolitical and supply chain challenges on the Company’s business, its customers, and the economy generally; the Company’s technology enabling a new category of solid state battery that meets the requirements for broader market adoption; the Company’s liquidity and capital resources, including the availability of additional capital resources to fund its activities; industry competition; changes in laws and regulations; legal and regulatory proceedings; the ability to adapt products and services to changes in markets; the ability to retain existing customers and attract new ones; the ability to attract and retain key executives and key employees; the granting of additional intellectual property protection; and the ability to execute strategic plans. Information about risks that could cause actual results to differ materially from expectations and about material factors or assumptions applied in making forward-looking statements may be found herein under the heading “Risk Factors”, and in other public disclosure documents filed with Canadian securities regulatory authorities. The Company does not undertake any obligation to update publicly or to revise any of the forward-looking statements contained or incorporated by reference in this document, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.
-
| 1. | Corporate Structure |
| 1.1 | Name, Address and Incorporation |
The company’s full corporate name is Electrovaya Inc. (the “Company” or “Electrovaya”), which, as used herein, refers to Electrovaya Inc., its predecessor corporations and all its subsidiaries (unless the context otherwise requires).
Our registered and head office is located at 6688 Kitimat Road, Mississauga, Ontario L5N 1P8. Our telephone number and website address are (905) 855-4610 and www.electrovaya.com, respectively.
Electrovaya was incorporated under the Business Corporations Act (Ontario) in September 1996. The Company listed on the Toronto Stock Exchange in November 2000 under the ticker “EFL”. The Company changed the ticker symbol on the TSX to ELVA and began trading on the Nasdaq Stock exchanged on July 6, 2023.
Electrovaya is a leader in advanced lithium-ion battery technology, leveraging proprietary materials science and a robust intellectual property portfolio to deliver industry-leading safety and exceptional cycle life. Our solutions power mission-critical, heavy-duty applications—including material handling, robotics, heavy duty vehicles, and defense systems. Supported by a multidisciplinary team of engineers, we provide fully integrated energy solutions that combine cutting-edge cell design, battery management systems, and system-level innovation to meet the most demanding performance requirements.
| 1.2 | Our Mission and Values |
Electrovaya’s mission is to deliver the world’s best battery solutions for mission-critical applications, enabling the global energy transition and supporting resilient energy security. We aim to accelerate electrification across industrial, transportation, and defense sectors while creating long-term value for our shareholders. Through continuous innovation in advanced materials and proprietary technologies, we strive to enhance safety, performance, and longevity in every product we deliver.
-
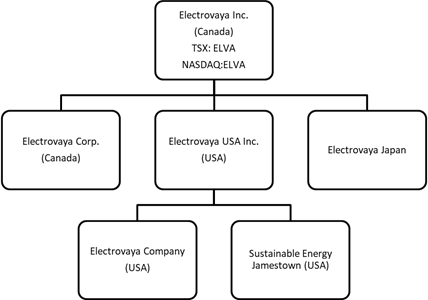
| 1.3 | Intercorporate Relationships |
The following diagram illustrates the intercorporate relationships between the Company and its material subsidiaries, and the percentage of votes attached to all voting securities of the material subsidiary owned, controlled, or directed, directly or indirectly, by the Company, and the subsidiary’s respective jurisdiction of formation.
| 2. | General Development of the Business |
| 2.1 | Summary of the Business |
Electrovaya is a technology-focused lithium-ion battery company engaged in the design, development and manufacturing of advanced battery cells, modules and systems. The Company’s products primarily are based on its proprietary Infinity Battery Technology, which incorporates ceramic-enhanced lithium-ion cell constructions and advanced materials that deliver high safety performance, long cycle life and strong durability in demanding operating environments. These characteristics make Electrovaya’s products suitable for mission-critical applications, including material-handling equipment, robotic and autonomous vehicles, heavy-duty electric vehicles, defense-related platforms and stationary energy-storage systems.
Electrovaya’s development activities draw upon capabilities in electrochemistry, materials science, mechanical and electrical engineering, and battery-management software. The Company maintains an expanding intellectual-property portfolio related to advanced materials, cell designs, ceramic components, separator technologies and system-level battery architectures. Electrovaya is also engaged in programs related to next-generation solid-state and hybrid solid-state battery technologies, as well as improvements to its existing Infinity platform.
-
The Company’s commercial offerings include low-voltage and high-voltage battery systems supplied to a range of industrial and transportation markets. These include material-handling equipment, robotic vehicles, airport ground-support equipment, construction and mining equipment, electric buses and trucks, and grid-connected or behind-the-meter energy-storage installations. While the material-handling sector has historically represented a significant share of the Company’s revenue, Electrovaya continues to expand into adjacent markets where long operating life, enhanced safety and reliable high-power performance are essential.
Electrovaya sells its products through a combination of original equipment manufacturer relationships, dealer networks and direct sales to large fleet operators and industrial customers. The Company is expanding its commercial reach in North America and internationally, targeting applications in which performance, safety and operational reliability serve as key purchasing criteria.
Electrovaya maintains research, engineering and manufacturing operations in Mississauga, Ontario. To support anticipated growth, as well as emerging energy-security and domestic-manufacturing priorities in North America, the Company is developing a lithium-ion cell and battery manufacturing facility located on a 52-acre site near Jamestown, New York. The site includes a 137,000-square-foot building that is intended to serve as the Company’s first U.S. cell manufacturing location. The project is supported in part by government incentives, including a direct loan from the Export-Import Bank of the United States. Following completion and commissioning, the facility is expected to increase production capacity and provide U.S.-based manufacturing capabilities aligned with evolving supply-chain and national energy-security objectives.
Additional information can be found in the Company’s Management’s Discussion and Analysis for the year ended September 30, 2025.
| 2.2 | Three-Year History |
During the last three years, Electrovaya has developed advanced lithium-ion battery cells and systems with unique performance attributes for use in a variety of heavy duty and mission critical applications. The first target market for these products was the material handling sector as it was an existing market that was relatively mature and willing to pay higher costs for better performing battery products. As of today, the majority of our battery systems are being utilized in the material handling industry. The Company demonstrated continuous improvements in the energy density of its commercial cell technologies and also has launched an increasing list of battery systems. These include battery systems for multiple classes of material handling vehicles, customized systems for robotic applications, airport ground equipment, high voltage battery systems that are targeting the electric bus, truck and energy storage applications and finally customized solutions for defense applications. Many of these battery systems have also gone through UL safety testing certification and the Company has maintained ISO9001 certification since 2022. Electrovaya has started making more deliveries to sectors other than material handling and is expecting these sectors to grow to become more material in future years. The company continues research and development activities for new battery systems, advances in battery management system technology and next generation solid state battery technology.
-
Listing on NASDAQ
In Fiscal 2023, Electrovaya achieved a significant milestone by listing its common shares on the Nasdaq Capital Market, enhancing the Company’s visibility and access to U.S. capital markets.
EXIM loan for Jamestown facility
Electrovaya has positioned itself to increase its domestic manufacturing capacity and support overall anticipated growth in demand for its products. In March 2025, the company was able to close the term loan from The Export-Import Bank of the United States (“EXIM”) for the amount of $50.8 million to support Electrovaya’s expansion in Jamestown New York. The Company made the first draw from EXIM facility in the month of September 30, 2025. The project is expected to be completed by the last quarter of FY 2026 or first quarter of FY 2027.
Bank of Montreal working capital facility
In March 2025, the Company also refinanced its working capital facility with the Bank of Montreal with a three-year senior secured asset-based lending facility. The facility provides an initial US $20 million with a further US $5 million accordion to support further growth. The facility lowers the Company’s cost of capital with reduced interest rates and fees, strengthening its financial position
Equity raises in the market
Over the past three years the Company has been active in the equity markets.
During the month of November 2023, the Company issued shares and warrants via private placement and raised $10.5 million in cash for the Company.
During the month of December 2024, the company issued additional 5,951,250 shares in a brokered offering in the market and raised a total of $12.8 million (net receipts).
During the month of November 2025 (i.e. FY 2026), the company issued 5,405,000 shares to the investors in a brokered offering, raising a total of $28.2 million.
OEM Partners
The Material Handling vertical has represented the largest segment for Electrovaya and over the last three years accounts for over 95% of its sales.
Electrovaya has developed extensive relationships with OEMs to support both the distribution of Electrovaya battery systems as well as the integration of Electrovaya battery products into specific vehicle programs.
In December 2020, Electrovaya and Raymond Corporation signed a Strategic Supply Agreement making Raymond Corporation, the Company’s partner in the material handling industry. In November 2023, the Company announced a new three year agreement that included the addition of Toyota Material Handling. This new agreement increased sales volumes and also included the capability to supply to additional affiliated companies.
-
In April 2024, Electrovaya announced a partnership with Sumitomo Corporation Power and Mobility (“SCPM”). Through this relationship Electrovaya and SCPM are actively marketing Electrovaya’s solutions to OEMs in Japan and elsewhere. The partnership resulted in an initial supply agreement with a global construction equipment manufacturer.
Product Launches
In 2024, Electrovaya developed customized battery systems for specific vehicle development programs for two of its OEM partners. These vehicles are expected to be launched in 2026.
On July 2025, the Company announced that it has launched multiple battery system products for a variety of robotic vehicle platforms. These battery systems developed in collaboration with three major OEM partners, with 2 based in the USA and 1 in Japan for a variety of robotic vehicle applications ranging from material handling to surveillance applications. Initial deliveries to all three OEMs will begin in the current quarter with anticipated commercial deliveries accelerating from FY 2026 onwards.
On July 29, 2025, the Company announced the launch of multiple battery system products designed specifically for airport ground support equipment (GSE). Developed in collaboration with a major original equipment manufacturer (OEM) supplier, these innovative systems support a broad range of electrified ground support equipment (GSE) applications, including airplane tuggers, baggage tractors, belt loaders, cargo loaders, and more.
Improvement in overall financial health of the Company
The Company has demonstrated a strong improvement in adjusted EBITDA performance over the past two fiscal years. In Fiscal 2025, Electrovaya achieved several significant financial milestones, including generating positive adjusted EBITDA of $8.8 million and net income of $3.3 million. Revenue for the year was $64 million, representing an increase of approximately 43% compared to the prior year. In addition, the successful equity raise of approximately $28 million in November 2025 has further strengthened the Company’s liquidity position and supported a solid overall financial foundation.
| 2.3 | Narrative Description of the Business |
| 2.3.1 | Overview of Products & Services |
Electrovaya developed and commercialized a lithium-ion battery technology that management believes enables significant enhancements to battery cycle life (longevity) and safety performance. Electrovaya has considerable internal data backing up these claims in addition to third party test data. The Company has been marketing the technology as its “Infinity Battery Technology” and has focused on applications that require either or both performance differentiations. This technology owned by the Company and is protected by a variety of patents and know-how based intellectual property and includes unique ceramic separator and cell design features amongst other proprietary attributes. The core building block of the technology is demonstrated at the lithium-ion cell level, where independent third party testing has validated the performance differentiation. While the Company does provide cell level products to some customers, the vast majority of sales are derived from battery systems which are electromechanical systems made up of multiple lithium-ion cells in combination with electronics and electromechanical components. These systems are customized for a variety of applications, the most mature being Material Handling Electric Vehicles (“MHEV”).
-
Battery System Products
Over the last 7 years, Electrovaya has developed an increasing number of battery systems based on its Infinity Technology. For MHEV applications, the Company provides over 50 distinct battery models, most of which have received UL 2580 or another type of certification. These systems include a variety of voltage classes and capacities and are designed to be compatible with various Class 1-5 material handling vehicles. The Company has deployed over 10,000 battery systems in this category and they are in use at some of the world’s largest companies’ distribution center networks.
Other products that the Company has recently developed include a variety of battery systems designed for airport ground support equipment (“GSE”), battery systems tailored for robotic applications and some specialized battery systems designed for mission critical defense applications. These other products are at relative infancy and are expected to be scaled in production over the coming years.
Products under Development
Electrovaya is developing new products including both new cell technologies and new battery systems. New cell technologies include a proprietary solid state battery development which has been underway for the last several years. The Company has filed multiple patents for this technology and has plans to file additional patents. Currently the solid state battery effort has led to small cells being produced and the Company is currently investing to scale these efforts to enable pre-commercial test samples to strategic customers. Electrovaya’s solid state cells feature proprietary ceramic separator technology that leverages some of the existing technology know-how from the Company’s existing technology portfolio. The advantages of the solid state battery technology include much higher energy density making the technology attractive for applications like airborne drones, aerospace and defense applications and consumer electronics. Management believes the technology is complimentary to the Infinity Technology and would serve distinct applications.
Other cell based development efforts include a high power version of its Infinity Battery technology to enable sub five minute charge rates. The Company believes that there is strong demand for this type of product for certain robotic applications.
Electrovaya continues to invest into new battery system products based on its core Infinity Technology. This includes new products to serve energy storage, robotic, defense and other speciality applications.
-
2.3.2 Sale of Products
Electrovaya’s largest vertical by sales volume continues to be the MHEV vertical. While the Company has focused the majority of its sales efforts primarily on this sector, we have recently developed new products designed to serve new verticals including heavy duty vehicles, robotics, airport ground support equipment (GSE) and energy storage systems. Our primary geographical focus is North America, however we have had recent sales activities in South America, Asia and Australia.
For our batteries powering MHEVs, there are two main market sales channels; the OEM Partners sales channel and the Direct sales channel. The Company also maintains strong relationships with the end users of its products even if the sale of its products was conducted by a distributer or OEM partner. These direct relationships are key to maintaining long term commitments and visibility for demand. The Company is actively pursuing additional OEM and distributer relationships for robotics, airport ground support equipment, electric bus, truck, diesel generator replacement and defense applications. The Company anticipates some contribution to revenue from these new market segments from the 2026 fiscal year, however with more significant contributions in 2027 and beyond due to production schedules of the targeted OEMs.
2.3.3 Competition
The battery industry is highly competitive. Electrovaya competes with a large number of market participants including pure-play battery providers, diversified technology and industrial vendors and strategic joint ventures. Our primary competitors are included in the following summary below:
| ● | MHEVs including forklifts and Automated Guided Vehicles. Competition in this group includes alternative power sources such as lithium ion batteries, lead acid batteries, hydrogen fuel cells and other power sources including fossil fuels. Our lead acid battery competitors include EnerSys, East Penn Manufacturing Company and Exide Technologies Inc. Our hydrogen fuel cell competitors include Plug Power, Ballard as well as forklift manufacturers Hyster Yale and Linde. Competitors in the lithium ion battery sector include East Penn, Flux Power and EnerSys. |
| ● | High Voltage Vehicle Battery Systems. Competition includes manufacturers and battery system integrators including Proterra, Nikola, Microvast, Akasol, Forsee Power, Toshiba and others. |
| ● | Stationary Energy Storage. Competition includes manufacturers and system integrators. We compete primarily with LG Chem, Panasonic, Tesla, SAFT, BYD, Fluence, Samsung, SK Innovation, Toshiba, Leclanche, and others. |
| ● | Other Electric Vehicle Battery Systems. We compete primarily with LG Chem, Johnson Controls, SAFT, Samsung, SK Innovation, BYD, CATL, Enersys, Panasonic, and others. |
| ● | Batteries for Robotic Applications: Electrovaya is launching battery systems for robotic applications. The competition for these solutions includes but is not limited to Toshiba, LG, Panasonic and others. |
-
| ● | Batteries for Airport Ground Equipment: Electrovaya is launch battery systems for airport ground equipment. The competition for these solutions includes but is not limited to Flux Power, Enersys, East Penn and others. |
To compete successfully, we intend to continue to build on the advantages offered by our technology.
2.3.4 Research and Development
Electrovaya continues to research, develop and commercialize improved lithium-ion batteries and associated technologies with longer life, higher energy density and increased safety. The Company primarily uses “NCM” (nickel cobalt manganese) based cells. When combined with other Electrovaya technologies including specialized electrolytes and ceramic composite separators, the end result is a cell with competitive advantages in performance, cycle life and safety. The Company also launched a cell product based on Lithium Iron Phosphate “LFP” cathodes targeting markets that call for this technology and also enabling lower cost alternatives to its core NMC based products.
Electrovaya is committed to investing in developing better products for our customers and pursuing research activities that prepare us for the future. To date, Electrovaya has invested more than $100 million in research & development and manufacturing advances and continues to invest in current and future technologies.
At the system level, our team of engineers continues to develop the mechanical, thermal, electrical, and control systems for innovative battery systems for our clients, enabling us to offer a complete solution for their specific power or energy requirements. Electrovaya has expanded its engineering team in the current fiscal year and is pursuing an aggressive product development plan.
The Electrovaya Labs division continues research into next generation cells and batteries in the areas of solid-state cells, electrode production, rapid charging and higher energy density batteries, and will generate additional intellectual property and patent applications in connection with the same. Electrovaya expanded the team at this division in 2024 and 2025 and expects to continue this trend. The Company continues to invest in a few key areas for this division including for solid state batteries and next generation ceramic separator development. These investments include both capital equipment and personnel.
2.3.5 Intellectual Property
Electrovaya has a program to enhance its intellectual properties and owns many patents. These patents cover our fundamental structural technology innovations, our system level designs including our intelligent battery management system for transportation, as well as some nanomaterial developments. Our patents are issued globally and typically across the United States and Canada. In some cases, we do file into other jurisdictions such as Europe, India, China, Japan and other countries where potential markets and/or manufacturing activities make patent protection desirable and economically justifiable. Electrovaya recently also acquired about 30 patents mainly on ceramic composite separators and lithium ion cells.
-
We seek to protect our intellectual property, including our technological innovations, products, software, manufacturing processes, business methods, know-how, trade secrets, trademarks and trade dress by law through patents, copyright and trademark law, by contract through non-disclosure agreements, and through safeguarding of trade secrets.
Our patent portfolio, trade secrets and proprietary know-how are an important component in protecting our battery innovations and our manufacturing processes. We further protect our trade secrets and proprietary know-how by keeping our facilities physically secure, disclosing relevant information only on a need-to-know basis and entering into non-disclosure agreements with our potential customers, employees, consultants and potential strategic partners, and by treating and marking the confidential information as confidential.
We will continue to apply for patents resulting from ongoing research and development activities, acquire, or license patents from third parties, if appropriate, and further develop the trade secrets related to our manufacturing processes and the design and operation of the equipment we use in our manufacturing processes.
2.3.6 Employees
As of September 30, 2025 we had approximately 123 full-time employees as well as contract employees and consultants. We believe we enjoy a good and productive relationship with our employees.
2.3.7 Manufacturing
The Company has a battery and battery systems research and manufacturing facility in Mississauga, Ontario. The location comprises approximately 62,000 square feet and is designed to enhance the Company’s productivity and efficiency. The facilities are focused on lithium ion battery production, which includes the assembly, integration and testing of lithium ion batteries as well as development and testing of new products and enhancements by our engineering team.
During the last quarter of FY 2026 or first quarter of FY2027, the Company anticipates that it will begin operations at its 137,000 square feet facility in Jamestown, New York. The facility will be focused on cell, pack and module manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries. The facility will produce both the Infinity and Infinity-HV battery lines and provide additional capacity as the Company expands into new verticals.
2.3.8 Safety
Safety is of paramount importance to the Company not only for our products but more importantly for our people. We have robust safety protocols in all areas. We have a Joint Health and Safety Committee which includes employees across disciplines and at all levels. This Committee regularly meets to ensure safety protocols are followed and updated when necessary.
Our products are designed and manufactured with safety as the primary concern. All components are vigorously tested prior to being included in the manufacturing process. Our products are assembled to the highest standard and are subject to a comprehensive end of line testing to ensure they adhere to our demanding safety standards.
-
Electrovaya recently achieved the UL2580 certification on a variety of battery systems, with UL LLC completing multiple system level tests on Electrovaya’s batteries, including fire propagation at both ambient and elevated temperatures, and other electrical and mechanical tests. Furthermore, UL completed full functional testing and provided UL991 and UL1998 certifications relating to Electrovaya’s latest battery management systems. Furthermore, Electrovaya achieved UL recognition for its latest NMC and LFP cells.
2.3.9 Quality
Quality is also an integral part of our culture and processes. We believe we have differentiated ourselves in the market by having the highest quality and safest product available.
Electrovaya received ISO9001:2015 Quality Management certification in 2022. Furthermore, our quality assurance management system has been tested and validated by a number of third parties including Toyota Material Handling and Raymond Corporation.
Our processes and systems are focused on ensuring that every product that is shipped to our customers conforms to our rigorous quality standards while being produced in a safe and environmentally conscious manner.
2.3.10 Sustainability
Our Company was founded 29 years ago with the express purpose to develop clean technology for a greener planet. Electrovaya is focused on contributing to the prevention of climate change through supplying the safest and longest lasting Li-Ion batteries in the marketplace. Our goal is to be a global leader in the supply of advanced lithium ion battery technologies.
Our processes and facilities embody our focus on sustainability. Waste is minimized and recycled where possible. Steps have been introduced to reduce our energy and water use.
| 3. | Capital Structure and Market for Shares |
Our authorized share capital consists of an unlimited number of common shares. Holders of common shares are entitled to receive notice of any meetings of our shareholders, to attend and to cast one vote per common share at all such meetings. The holders of our common shares are entitled to vote at all meetings of our shareholders, and each common share carries the right to one vote in person or by proxy. The holders of the common shares are also entitled to receive any dividends we may declare, and to receive our remaining property upon liquidation, dissolution or wind-up.
-
In June 2023, the Company, with the approval of shareholders, carried out a share consolidation at a ratio of 5 to 1. Subsequent to this, in July 2023, the Company listed its common shares on Nasdaq.
Our common shares are listed for trading on the Toronto Stock Exchange under the symbol “ELVA.TO” and on the Nasdaq under the symbol “ELVA”. The table below sets forth information relating to the trading of the common shares on the TSX and Nasdaq for the months indicated.
TSX (CDN)
| Date | High | Low | Volume |
| Sep 2025 | 10.43 | 7.88 | 3,209,400 |
| Aug 2025 | 8.47 | 5.86 | 1,361,900 |
| Jul 2025 | 7.00 | 4.22 | 1,112,600 |
| Jun 2025 | 5.00 | 4.09 | 597,200 |
| May 2025 | 4.60 | 3.62 | 386,900 |
| Apr 2025 | 3.85 | 3.13 | 208,000 |
|
Mar 2025
|
4.15 | 2.85 | 460,200 |
| Feb 2025 | 3.79 | 3.09 | 294,700 |
| Jan 2025 | 4.10 | 3.39 | 438,800 |
| Dec 2024 | 4.10 | 3.02 | 710,900 |
| Nov 2024 | 3.94 | 2.80 | 472,600 |
| Oct 2024 | 3.94 | 2.84 | 175,800 |
-
NASDAQ
| Date | High | Low | Volume |
| Sep 2025 | 7.49 | 5.71 | 11,655,900 |
| Aug 2025 | 6.20 | 4.16 | 5,457,500 |
| Jul 2025 | 5.14 | 3.11 | 4,270,600 |
| Jun 2025 | 3.71 | 2.98 | 1,909,400 |
| May 2025 | 3.44 | 2.55 | 1,440,200 |
| Apr 2025 | 2.77 | 2.25 | 562,700 |
| Mar 2025 | 2.92 | 1.80 | 1,498,600 |
| Feb 2025 | 2.68 | 2.11 | 1,089,100 |
| Jan 2025 | 2.89 | 2.31 | 1,938,900 |
| Dec 2024 | 2.91 | 2.11 | 2,697,800 |
| Nov 2024 | 2.78 | 1.73 | 1,762,200 |
| Oct 2024 | 2.36 | 2.05 | 301,600 |
| 4. | Dividend Policy |
We have never declared or paid any dividends on our common shares in the past; however, we may declare and pay dividends on our common shares in the future depending upon our financial performance.
-
| 5. | Directors and Officers |
The following table sets forth the names and municipalities of residence of our directors and officers, the position they hold with us and their principal occupation during the last five years:
| Name, Office (if any) and Principal Occupation | Director Since | Common Shares Beneficially Owned | Stock Options Held | Warrants |
|
Dr. Sankar Das Gupta, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada
Executive Chairman
|
1996 | 10,295,751 | 605,000 | 1,420,000 |
|
Dr. Carolyn M. Hansson(1)(2)
Director
Professor of Materials Engineering, Department of Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering, University of Waterloo
|
2017 | 50,000 | 57,000 | — |
|
Dr. James K. Jacobs(1)(2), Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Director
Retired
|
2018 | 478,107 | 46,000 | — |
|
Kartick Kumar(1)(2)
Director
Managing Director, Climate Investments, King Philanthropies
|
2021 | 2 | 32,000 | — |
|
Dr. Rajshekar Das Gupta Oakville, Ontario, Canada
Director, Chief Executive Officer
|
2022 | 671,048 | 2,059,000 | 38,884 |
|
Steven Berkenfeld
New York, New York
USA
Director
|
2023 | — | 70,000 | — |
|
John Gibson
Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Secretary and Chief Financial Officer
|
N/A
|
3,444
|
204,000
|
— |
| (1) | Audit Committee member. |
| (2) | Nominating, Corporate Governance and Compensation Committee member. |
All directors hold office until the close of the next annual meeting of the shareholders or until their successors are duly elected or appointed.
As of September 30, 2025, the directors and officers of the Company, as a group, beneficially own, directly or indirectly, or exercise control or direction over, an aggregate of 11,498,352 or approximately 27% of the issued and outstanding common shares of the Company.
In October, 2023, the board of directors accepted the nomination of Steven Berkenfeld to join as a director of the Company.
-
Cease Trade Orders, Bankruptcies, Penalties or Sanctions
Except as described below, to the best of management’s knowledge, no officer or director:
| (a) | is, as at the date of this AIF, or has been, within 10 years before the date of this AIF, a director, chief executive officer or chief financial officer of any company (including the Company) that: |
| (i) | was subject to an order that was issued while the proposed director was acting in the capacity as director, chief executive officer or chief financial officer; or |
| (ii) | was subject to an order that was issued after the proposed director ceased to be a director, chief executive officer or chief financial officer and which resulted from an event that occurred while that person was acting in the capacity as director, chief executive officer or chief financial officer; or |
| (b) | is, as at the date of this AIF, or has been within 10 years before the date of the AIF, a director or executive officer of any company (including the Company) that, while that person was acting in that capacity, or within a year of that person ceasing to act in that capacity, became bankrupt, made a proposal under any legislation relating to bankruptcy or insolvency or was subject to or instituted any proceedings, arrangement or compromise with creditors or had a receiver, receiver manager or trustee appointed to hold its assets; or |
| (c) | has, within the 10 years before the date of the AIF, become bankrupt, made a proposal under any legislation relating to bankruptcy or insolvency, or become subject to or instituted any proceedings, arrangement or compromise with creditors, or had a receiver, receiver manager or trustee appointed to hold the assets of the officer or director. |
On January 25, 2018, Litarion GmbH (“Litarion”), a former subsidiary of Electrovaya, commenced a voluntary structured insolvency process and an Administrator was put in place for the sale of the business. On April 30, 2018, the Administrator commenced insolvency proceedings and assumed control of the assets of Litarion. Sankar Das Gupta, Executive Chairman of the Corporation, was a managing director of Litarion until the Administrator’s appointment.
In June, 2021, the administrator of Litarion and the Company and its officers agreed to mutually settle all claims as part of the termination of the insolvency proceedings.
Except as described below, to the best of management’s knowledge, no officer or director has been subject to:
| (a) | any penalties or sanctions imposed by a court relating to securities legislation or by a securities regulatory authority or has entered into a settlement agreement with a securities regulatory authority; or |
| (b) | any other penalties or sanctions imposed by a court or regulatory body that would likely be considered important to a reasonable security holder in deciding whether to make an investment decision in the Company’s common shares. |
-
On June 30, 2017, the Company and Sankar Das Gupta, Executive Chairman of the Corporation, entered into a Settlement Agreement (the “Agreement”) with Staff of the Ontario Securities Commission (“OSC”) resolving issues the OSC identified with respect to the Company’s continuous disclosure between December 2015 and September 2016 (the “Time Period”). The Agreement settled allegations by the OSC regarding unbalanced news releases that did not adequately disclose the nature and risks of newly-announced business arrangements issued by the Company during the Time Period, that the Company did not update previously announced forward-looking information in its Management Discussion and Analysis during the Time Period, and that the Company did not provide an accurate description of its business in its annual information form filed during the Time Period.
The Company did not face a financial penalty in relation to the Agreement. Dr. Das Gupta agreed to pay an administrative penalty and upgrade his personal knowledge of continuous disclosure standards. Under the terms of the Agreement, the Company agreed to additional steps to comply with continuous disclosure requirements, including
| ● | a review of the Company’s corporate governance framework by an independent consultant and adopting all recommended changes that are accepted by OSC Staff; |
| ● | instituting a disclosure committee comprising 4 directors (2 of whom were required to be independent) for a period of 20 months, which committee was to approve all public disclosure made by the Corporation; |
| ● | naming an independent director as Chair of the disclosure committee for a period of 20 months; and |
| ● | naming an independent director as Chair of the Board for a period of 20 months. |
Under the terms of the Settlement Agreement, Dr. Das Gupta agreed to:
| ● | pay an administrative penalty of Cdn$250,000; |
| ● | a prohibition on acting as a director or officer of any reporting issuer, other than the Company or an affiliate, for a period of one year; |
| ● | pay the costs of the corporate governance consultant’s review; and |
| ● | participate in, and pay for, a corporate governance course on disclosure issues acceptable to staff of the OSC. |
| 6. | Transfer Agent and Registrar |
The transfer agent and registrar for the common shares of the Company is TSX Trust Company at its principal office in Toronto, Ontario.
-
| 7. | Legal Proceedings and Regulatory Actions |
The Company is not involved in any legal proceeding or regulatory action which it expects would have a material effect on the Company.
| 8. | Interest of Management and Others in Material Transactions |
Other than as disclosed in this AIF, no director, executive officer, person or company that beneficially owns or controls more than 10% of any class of the Company’s outstanding voting securities, or any associates or affiliates of persons had any material interest, direct or indirect, in any transaction within the three most recently completed financial years or during the current financial year that has materially affected or is reasonably expected to materially affect the company.
Purchase of Jamestown Property
On October 15, 2021, the Company, as purchaser, agreed to purchase the property municipally known as 1 Precision Way, Jamestown, NY 14701 (the “Property”) for a purchase price of $5 million. Among other factors, the Property was of interest to the Company for various reasons, including access to Government incentives, increased capacity, and access to the US market.
Prior to closing, it was determined that the Company would not have access to sufficient capital to finance the building purchase. The vendor had another buyer, therefore, in May 2022, prior to closing, the Company, as assignor, and Sustainable Energy Jamestown LLC (“SEJ”), as assignee, entered into an agreement to assign the agreement of purchase and sale for the Property to SEJ, with the intention that SEJ would complete the purchase of the Property. SEJ completed the purchase of the property in May 2022.
On November 1, 2022, the Company entered into an agreement with Sustainable Energy Jamestown (“SEJ”), a party related to shareholders of the Company for the purchase of the building at 1 Precision Way, Jamestown, NY. The purchase agreement sets the purchase price at $5,500 less any expenses incurred on behalf of the related party to date and the repayment of the deposit of $550.
On March 31, 2023, the Company completed the purchase of the membership interest in SEJ. The purchase of the site includes 52 acres of land, including a building previously utilized for the manufacturing of electronic components. The purchase price was paid by way of a $1.05 million Promissory Note payable to the members of Sustainable Energy Jamestown LLC with a term of 365 days bearing interest at 7.5% per annum payable at maturity and the assumption of a $4.4 million vendor promissory note (“VPN”) issued on July 1, 2022 with a 2 year term bearing interest at 2% per annum and secured against the property. At the time of the transaction, the balance of the VPN was $3.95 million with a payment due on maturity of $2.4 million. As part of the security interests granted to the Company’s existing lender for its consent to the transaction, Dr. Sankar Das Gupta pledged 7,000,000 Common Shares (1,400,000 post consolidation) of the Company.
In March 2025, the Company secured the direct loan for the amount of $50.8 million from Export-Import Bank of the United States. This financing will fund Electrovaya's battery manufacturing buildout including equipment, engineering and setup costs for the facility. Electrovaya has rapidly increasing demand for its products from a wide range of heavy duty and mission critical electrified applications, and it has been a priority of the Company to expand its manufacturing operations in the United States for these vital products. The Company’s manufacturing facility in Jamestown is scheduled to produce Electrovaya’s proprietary Infinity lithium-ion ceramic cells, which offer industry leading longevity and safety.
-
Personal Guarantees
On February 16, 2024, the Executive Chairman and Chief Executive Officer both exercised options of Electrovaya Inc. A sum of $507 from the Promissory Note was utilized to cover a portion of the options' purchase price. The remaining balance of the promissory note, amounting to $519, was then substituted with a new Promissory Note on February 28, 2024, carrying a 14% interest rate and maturing on July 31, 2025. The Promissory Note including interest accrued was repaid in full on December 30, 2024.
| September 30, | ||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||
| Promissory Note | $nil | $519,000 | ||
Electrovaya Labs – Facility Usage Agreement
In May 2021, Electrovaya entered a month-to-month Facility Usage Agreement for the use of space and allocated staff of a third party research firm providing access to laboratory facilities, primarily for research associated with its Electrovaya Labs segment. The term of the agreement was for six months and could be terminated by either party upon 90 days notice.
In July 2021, the facility was acquired by an investor group controlled by the family of Dr. Das Gupta, the Chairman of the Company and a controlling shareholder, and which group included the Company’s current CEO, Dr. Raj Das Gupta. The Facility Usage Agreement was not changed on the change of ownership and remains in effect between the Company and the owner, such that the monthly payment of $25,000 is now with a related party of Electrovaya.
In June 2023, the Facility Usage Agreement was retroactively extended from January 1, 2023, for an additional three years. The agreement maintains a 2.5% annual rent increment while keeping all other terms and conditions unchanged.
Performance Option Grants
In September 2021, on the recommendation of the Compensation Committee of the Corporation, a committee composed entirely of independent directors, the Board of Directors of the Corporation determined that it is advisable and in the best interests of the Corporation to amend the terms of the compensation of certain key personnel to incentivize future performance, to encourage retention of their services, and to align their interests with those of the Corporation’s shareholders.
Dr. Sankar Das Gupta was granted 700,000 options which vest in two tranches of 200,000 options and one tranche of 300,000 options, based on reaching specific target market capitalizations. The fair value of these options on the day of grant is calculated using the Monte Carlo method of option valuation and expensed over the mean vesting period in accordance with IFRS 2.
-
Dr. Rajshekar Das Gupta was granted 900,000 options which vest in three tranches of 300,000 options based on reaching specific target market capitalizations. The fair value of these options on the day of issuance was calculated using the Monte Carlo method of option valuation and expensed over the mean vesting period in accordance with IFRS 2.
In April 2023, following the suggestion of the Company's Compensation Committee, consisting entirely of independent directors, the Company's Board of Directors awarded Dr. Rajshekar Das Gupta a total of six hundred thousand options. These options will vest in two phases: three hundred thousand options and three hundred thousand options, contingent upon achieving certain target market capitalizations.
| 9. | Material Contracts |
The Company does not have any material contracts that were required to be filed under section 12.2 of National Instrument 51-102 - Continuous Disclosure Obligations.
| 10. | Interests of Experts |
The auditor of the Company is MNP LLP (“MNP”), Chartered Accountants, Suite 1900, 1 Adelaide St East, Toronto, Ontario M5C 2V9. There are no registered or beneficial interests, direct or indirect, in any securities or other property of the Company or any of its subsidiaries held or received by MNP. MNP is independent in accordance with the auditors’ rules of Professional conduct in Canada.
| 11. | Risk Factors |
Our business of designing, developing and manufacturing lithium-ion advanced battery and battery systems for the transportation, electric grid stationary storage and mobile markets faces many risks of varying degrees of significance, which could affect our ability to achieve our strategic objectives. The risk factors described below are not the only risks and uncertainties that we face. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently consider immaterial may also impair our business operations. These risk factors could materially affect our future operating results and could cause actual events to differ materially from those described in our forward-looking statements. Additional risks the Company faces are disclosed in the Company’ Management’s Discussion and Analysis for the year ended September 30, 2025.
There is no assurance that we will be able to produce or generate and fulfill orders for large quantities of our products.
Electrovaya may not be able to establish anticipated levels of high-volume production on a timely, cost-effective basis, or at all. It has never manufactured batteries in substantially large quantities and it may not be able to maintain future commercial production at planned levels. As a result of the risks discussed within this AIF, among others, Electrovaya may not be able to generate or fulfill new sales orders or deliver them in a timely manner, which could have a material effect on its business and results of operations.
-
Our ability to generate positive cash flows
To rapidly develop and expand our business, we have made significant up-front investments in our manufacturing capacity and incurred research and development, sales and marketing and general and administrative expenses. In addition, our growth has required a significant investment in working capital and significant debt finance over the last several years. In the financial year ending September 30, 2025 and financial year ending September 30, 2024, the Company was able to generate positive cash flows from the operations. However, due to the nature of our business coupled with timing of collection of accounts receivables and changing government regulations especially in North America, our ability to generate positive cash flows from operations and overall cash flow may vary on a year to year basis. We, as a business, will continue to incur debt service costs, increased research and development, sales and marketing, and general and administrative expenses, as well as acquisition expenses. Our business will continue to require significant amounts of working capital to support our growth. Therefore, we may not achieve sufficient revenue growth to generate positive future cash flow and may need to raise additional capital from investors or other finance sources to achieve our future growth.
Our failure to raise additional capital necessary to expand our operations and invest in our products and manufacturing facilities could reduce our ability to compete successfully.
We regularly require additional capital and we may not be able to obtain additional debt or equity financing on favorable terms, if at all. If we raise additional equity financing, our shareholders may experience significant dilution of their ownership interests, and the per-share value of our common shares could decline. If we engage in debt financing, we may be required to accept terms that restrict our ability to incur additional indebtedness and force us to maintain specified liquidity or other ratios. We also seek Canadian and U.S. federal, provincial and state grants, loans and tax incentives, some of which we intend to use to expand our operations. We may not be successful in obtaining these funds or incentives. If we need additional capital and cannot raise or otherwise obtain it on acceptable terms, we may not be able to, among other things:
| ● | develop or enhance our products or introduce new products; |
| ● | continue to expand our development, sales and marketing and general and administrative organizations and manufacturing operations; |
| ● | attract top-tier companies as customers or as our technology and product development partners; |
| ● | acquire complementary technologies, products or businesses; |
| ● | expand our operations, in Canada, U.S. or internationally; |
| ● | expand and maintain our manufacturing capacity; |
| ● | hire, train and retain employees; |
| ● | respond to competitive pressures or unanticipated working capital requirements: or |
| ● | continue as a going concern. |
Financial outlooks are inherently forward-looking and the Company’s actual financial results may differ, possibly materially, from any expected results presented in a financial outlook.
From time to time, the Company may disclose financial outlooks. Financial outlooks constitute forward-looking information, which is necessarily based on certain assumptions about future circumstances and results of operations. The Company believes it bases its financial outlooks from time to time on assumptions that are reasonable in the circumstances, but the achievement of actual results is subject to a number of risks that could cause the information in the forward-looking statement to differ from the statements as presented, possibly materially.
-
There is no guarantee that actual results will be as presented in any financial outlook, and may materially differ. Investors and other market participants may base their expectations on a financial outlook provided by management. Differences in financial and operating results as compared to any financial outlook may cause the trading price of the Common Shares to decrease, possibly materially.
Sales under the Material Handling OEM Strategic Supply Agreement
In December 2020, the Company entered into the Raymond Strategic Supply Agreement. In November 2023, the Company announced a new three year strategic supply agreement which included Toyota Material Handling. More recently, Raymond and Toyota Material Handling have merged under the Toyota Material Handling North America (TMHNA) name. The 2023 agreement increased the minimum sales volumes required to maintain exclusivity and also included capability to supply additional affiliated companies. The Strategic Supply Agreement includes a provision where the OEMs can have an exclusive arrangement with the Company if it makes minimum purchases. The Company based its financial outlook (including revenue forecasts) in its base shelf prospectus dated September 17, 2024 on the basis that TMHNA would be incentivized to maintain the exclusive relationship and provide purchase orders in at least an amount required to maintain exclusivity, given feedback on the products received to date, interpretation of such a clause, and an evaluation of TMHNA’s financial capability to complete such orders and the materiality of the value of such orders in the context of Raymond’s enterprise as a whole. While the Company believes it is reasonable to assume that the minimum quantity required to maintain exclusivity under the Strategic Supply Agreement will be purchased, there is no guarantee these sales will be made and the achievement of such sales is subject to a number of assumptions and factors including those described in the section “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Information. The failure of TMHNA to fulfill a material amount of orders under the Strategic Supply Agreement, the expiry or termination of the agreement, could have both positive or a material adverse effect on the Company’s ability to meet the sales and revenue projections in any financial outlook provided herein, and on the Company’s results of operations.
We manufacture a complex product including components from various suppliers. Failures in components or the finished product could result in product recalls, and rework of the product could lead to claims and additional costs. Our products carry warranties, and this exposes us to undeterminable cost should product failures occur.
While we have in place quality controls for ourselves and our suppliers, there is no assurance that a fault will not occur occasionally. As such there is a risk of a warranty claim and recall of products, that could have a negative effect on our business and results of operations.
-
Our principal competitors have, and any future competitors may have, greater financial and marketing resources than we do, and may develop batteries or other technologies similar or superior to ours or otherwise compete more successfully than we do.
Competition in the battery industry is intense. The industry consists of major domestic and international companies, most of which have existing relationships in the markets into which we sell as well as financial, technical, marketing, sales, manufacturing, scaling capacity, distribution and other resources, and name recognition substantially greater than ours. With respect to large energy storage systems specifically, this is a relatively new product offering for the Company, and competition for sales of such products includes both battery companies listed elsewhere and large multinational companies, and Electrovaya may not be able to compete with such entities due to inability to match scale, expertise, geographical reach, or other factors. These companies may develop batteries or other technologies that perform as well as or better than our batteries, activities into which the Company has limited knowledge and visibility. We believe that our primary battery competitors are existing suppliers of cylindrical lithium-ion, nickel cadmium, nickel metal-hydride and in some cases, non-starting/lighting/ignition lead-acid batteries. Potential customers may choose to do business with our more established competitors, because of their perception that our competitors are more stable, are more likely to complete various projects, can scale operations more quickly, have greater manufacturing capacity, are more likely to continue as a going concern, and may lend greater credibility to any joint venture. If we are unable to compete successfully against manufacturers of other batteries or technologies in any of our targeted applications, our business could suffer, and we could lose or be unable to gain market share.
From time to time, the Company may enter into contracts or other arrangements with customers, and may disclose estimates of future sales and revenue associated with such contracts or arrangements. Contracts with our customers typically do not provide for firm price or volume commitments, or “take or pay” arrangements with respect to product orders. As a result, our business development and partnering efforts may fail to generate revenue in meaningful amounts, or at all, and actual revenue generated from any such contracts may be materially less than estimated and announced.
From time to time, the Company will negotiate sales or supply contracts for its products. Typically, such contracts provide for a master framework for sales to a customer under which product will be sold pursuant to purchase orders, but without any minimum volumes or other purchase or payment obligations under the contract. Therefore, the Company is subject to the requirements of such customers as to if, as, when, and in what volume they wish to ultimately purchase the product.
From time to time, the Company may estimate future revenue expectations based on forecasts for orders during the life of such contract provided to the Company by the customers, and may announce such expectations publicly. However, execution of the orders remains solely at the discretion of the customers. Accordingly, Electrovaya’s actual revenues under any contract or other customer arrangement could be materially less than initially estimated or announced. Any such customer order forecasts constitute forward-looking information of the customer, and the Company does not have knowledge of the material factors or assumptions used by the customers to develop the order forecasts, and cannot assess their reliability. The Company also does not have the ability to monitor the performance of the customers’ business in order to confirm that the volumes initially represented by them in any forecasts remain valid. If such forecasts do not remain valid, or if firm irrevocable orders are not obtained, the Company’s potential estimated revenues could be materially and adversely impacted, which could have a material effect on its business and results of operations.
-
The Company’s actual results of operations may differ materially from the expected results announced based on arrangements with customers that are not definitive agreements. The Company may not be able to fulfill certain requirements of customer arrangements.
From time to time, the Company may enter into and announce understandings or other arrangements other than contracts with customers. Any understandings or other arrangements may be subject to additional risks including that the arrangements may still be subject to negotiation and there is no assurance a definitive agreement will be reached, or that if such agreement is reached, such agreement will be on the same terms as disclosed in the understanding. For example, product specifications may not yet have been agreed to and therefore a definitive agreement cannot be entered into, nor deliveries commenced until product specifications are agreed and a definitive arrangement is signed. Any definitive agreement with a customer, if entered into at all, may be on terms materially different than as disclosed in any announcement of an understanding or other arrangement that is not a definitive agreement. The actual results of the Company’s business may be materially different than as expected pursuant to any understanding that is not a definitive agreement, therefore undue reliance should not be placed on any agreement that is not a definitive agreement.
Electrovaya occasionally receives purchase orders that contain a series of milestones or deliverables, all or a portion of which may need to be completed in serial fashion before each subsequent activity and revenue generating milestones can be achieved. If each required milestone is not achieved, the entire amount of the purchase order may not be realized.
Pandemic outbreaks may have significant and far-reaching negative effects on our operations and our customers.
The global COVID-19 global pandemic created a number of risks in the Company’s business, not all of which may be quantifiable to or immediately identifiable by the Company. Future widespread outbreaks of disease may have similar effects on the Company’s business. The effects of lockdowns, lower efficiency and productivity from affected employees and due to regulations, costs of compliance with mitigation, such as physical separation or air quality installations, or personal protective equipment, disruptions to suppliers and increased costs, border and shipping restrictions, decreased customer engagement, and effects of disease outbreaks on customers’ business and the downstream effect of their purchases of battery products from us can all have a detrimental effect on our business and results of operations.
We may not be able to successfully recruit and retain skilled employees, particularly scientific, technical and management professionals.
We believe that our future success will depend in large part on our ability to attract and retain highly skilled technical, managerial and marketing personnel who are familiar with our key customers and experienced in the battery industry. Industry demand for such employees, especially employees with experience in battery chemistry and battery manufacturing processes, exceeds the number of personnel available, and the competition for attracting and retaining these employees is intense. This competition will intensify if the advanced battery market continues to grow, possibly requiring increases in compensation for current employees over time. We compete in the market for personnel against numerous companies, including larger, more established competitors who have significantly greater financial resources than we do and may be in a better financial position to offer higher compensation packages to attract and retain human capital. We cannot be certain that we will be successful in attracting and retaining the skilled personnel necessary to operate our business effectively in the future. Because of the highly technical nature of our batteries and battery systems, the loss of any significant number of our existing engineering and project management personnel could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
-
Our working capital requirements involve estimates based on demand expectations and may decrease or increase beyond those currently anticipated, which could harm our operating results and financial condition.
In order to fulfill the product delivery requirements of our customers, we plan for working capital needs in advance of customer orders. As a result, we base our funding and inventory decisions on estimates of future demand. If demand for our products does not increase as quickly as we have estimated or drops off sharply, our inventory and expenses could rise, and our business and operating results could suffer. Alternatively, if we experience sales in excess of our estimates, our working capital needs may be higher than those currently anticipated. Our ability to meet this excess customer demand depends on our ability to arrange for additional financing for any ongoing working capital shortages, since it is likely that cash flow from sales will lag behind these investment requirements.
Laws regulating the manufacture or transportation of batteries may be enacted which could result in a delay in the production of our batteries or the imposition of additional costs that could harm our ability to be profitable.
Laws and regulations exist today, and additional laws and regulations may be enacted in the future, which impose environmental, health and safety controls on the storage, use and disposal of certain chemicals and metals used in the manufacture of lithium-ion batteries. Complying with any laws or regulations could require significant time and resources from our technical staff and possible redesign of one or more of our products, which may result in substantial expenditures and delays in the production of one or more of our products, all of which could harm our business and reduce our future profitability. The transportation of lithium and lithium-ion batteries is regulated both domestically and internationally. Compliance with these regulations, when applicable, increases the cost of producing and delivering our products.
Electrovaya does not have a collaborative partner to assist it in the development of its batteries, which may limit its ability to develop and commercialize its products on a timely basis.
Electrovaya believes that the formation of strategic partnerships will be critical for the Company to meet its business objectives. It will continue to seek arrangements with potential partners to mitigate development and commercialization risks going forward, balanced by its objective to maximize market share and penetration by not entering into exclusivity arrangements with a single partner.
-
The Company expects to continue to incur significant costs and invest considerable resources designing and testing batteries for use with, or incorporation into, specific products, which may not translate into revenue for long periods of time, or ever.
The development by the Company of new applications for its rechargeable batteries is a complex and time-consuming process. New battery designs and enhancements to existing battery models can require long development and testing periods. Significant delays in new product releases or significant problems in creating new products could negatively impact the Company’s revenues. Significant revenue from these investments may not be achieved for a number of years, if at all. Moreover, these applications may never be profitable and even if they are profitable, operating margins may be low.
We depend on contract manufacturing.
There are many risks associated with contract manufacturing. Trade wars and associated tariffs, as well as other associated factors, such as Russia’s invasion of Ukraine could make contract manufacturing too expensive to operate. Our intellectual property is more difficult to control in contract manufacturing. Contract manufacturing could lead to products with inferior quality, especially as we will have to depend on the quality practices of the contract manufacturer. There is also potential loss of control of the supply chain, potential supplier credit risk, and third-party product and financial liability.
Our products depend on intellectual property, which may be subject to challenge or failures to adequately protect it.
Our success depends, in part, on our ability to protect our proprietary methodologies, processes, know-how, tools, techniques and other intellectual property that we use to manufacture and sell our products. If we fail to protect our proprietary technology, we may lose any competitive advantage it provides. Others may claim that the Company’s products infringe on their intellectual property rights, which could result in significant expenses for litigation, developing new technology or licensing existing technologies from third parties. If we are unable to maintain registration of our trademarks, or if our trademarks or trade name are found to violate the rights of others, the Company may have to change its trademarks or name and lose any associated goodwill.
We have had a history of losses, and we may be unable to achieve or sustain profitability.
We have had a history of losses. We are continuously expanding our business and manufacturing capacity and therefore, we expect to incur expenses as we grow.
We may incur significant losses in the future for a number of reasons, including the risks described in this AIF, and we may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays and other unknown events. Accordingly, there will be an element of uncertainty around us achieving or sustaining profitability.
The Company manufactures products which can become hazardous in some circumstances.
Electrovaya is exposed to certain risks as a result of being in an industry that manufactures devices or products containing energy. All lithium-ion polymer batteries can become hazardous under some circumstances. In the event of a short circuit or other physical, electrical or thermal damage to these batteries, chemical reactions may occur that release excess heat or gases, which could create dangerous situations, including fire, explosions and releases of toxic fumes. The Company’s batteries may emit smoke, catch fire or emit gas, any of which may expose Electrovaya to product liability litigation. In addition, these batteries incorporate potentially hazardous materials, which may require special handling, and safety problems may develop in the future. Product failure or improper use of lithium-ion polymer battery products, such as the improper management of the charging/discharging system, may also result in dangerous situations. The identification of any health or safety concerns could affect the Company’s reputation and sales. Changes in environmental or other regulations affecting the manufacture, transportation or sale of Electrovaya’s products could also adversely affect the Company’s ability to manufacture or sell its products or result in increased costs or liability.
-
Electrovaya may be required to devote significant financial and management resources to processing and remedying warranty claims. If product liability issues arise, the Company could incur significant expenses and suffer damage to its reputation and the market acceptance of its products.
Our sales volume is not assured, and we depend on a limited number of customers for a significant portion of our sales.
The Company expects to continue to sell its products directly to corporate customers, but if these parties do not purchase these products or purchase them in lower quantities or over longer time periods than expected, Electrovaya’s revenue profile and cash flows may be severely affected. The Company continues to rely upon a limited number of customers for a significant portion of its sales and the loss of any customer could have a material adverse effect on its sales and operating results and make it more difficult to attract and retain other customers.
If overall market demand for the Company’s products and clean energy sources declines significantly, and consumer and corporate spending for such products declines, Electrovaya’s revenue growth will be adversely affected. Additionally, the Company’s revenues would be unfavorably impacted if customers reduce their purchases of new products or upgrades to the Company’s existing product lineup if such new offerings are not perceived to add significant new functionality or other value to prospective purchasers.
Electrovaya depends on the supply of certain raw materials and components for the manufacture of anodes, cathode and separators, the supply of which is beyond our control. Such raw materials, especially lithium salts, may be in short supply. As demand for lithium-ion batteries escalates there could be significant raw material shortages and the company may be unable to produce or deliver products to its customers or meet its cost targets due to escalation of prices of its raw materials.
Lithium salts vary in price as the demand for lithium-ion batteries moves, and the development of additional lithium salt supply to meet demand is not assured. In addition, Electrovaya’s battery management systems contain electronics and microchips. Prices for raw materials critical to the Company’s products could fluctuate and the price and delivery of electronic components and micro-chips can have high volatility. If the Company is unable to source critical raw materials and components in a cost-effective manner or at all, the Company may not be able to produce its products in the anticipated volume or at all, or charge a competitive price for its products, which could have a material adverse effect on its business and results of operations. Contract manufacturing reduces some of these risks to Electrovaya and moves it to the contract manufacturer.
-
Letters of Intent and Memoranda of Understanding Entered into by Electrovaya are non-binding and no definitive agreements may be executed.
Non-binding MoUs entered into by Electrovaya are subject to a number of risks including: (i) the arrangements are still in the negotiation phase and there is no assurance a definitive agreement will be reached or if reached, such agreement will be on the same terms as disclosed in the MoU, (ii) product specifications have not yet been agreed and thus Electrovaya cannot enter into a definitive agreement nor commence deliveries until the product specifications are agreed and a definitive arrangement is signed; (iii) no sales are assured under the MoUs and no firm irrevocable commitments have been obtained from the potential customer; and (iv) the MoUs and any definitive agreement entered into in furtherance thereof, may be subject to the same risk factors as the Contracts.
Our international operations and sales activities subject us to a number of risks, including unfavorable political, regulatory, labor and tax conditions.
Risks inherent to international operations and sales, include, but are not limited to, the following:
| ● | difficulty in enforcing agreements, judgments and arbitration awards in foreign legal systems; |
| ● | impediments to the flow of foreign exchange capital payments and receipts due to exchange controls instituted by certain foreign governments and the fact that the local currencies of these countries are not freely convertible; |
| ● | inability to obtain, maintain or enforce intellectual property rights; |
| ● | changes in general economic and political conditions; |
| ● | changes in foreign government regulations and technical standards, including additional regulation of rechargeable batteries, power technology, or the transport of lithium or phosphate, which may reduce or eliminate our ability to sell or license in certain markets; |
| ● | requirements or preferences of foreign nations for domestic products could reduce demand for our products; |
| ● | trade barriers such as export requirements, tariffs, taxes and other restrictions and expenses, which could increase the prices of our products and make us less competitive; and |
| ● | longer payment cycles typically associated with international sales and potential difficulties in collecting accounts receivable, which may reduce the future profitability of foreign sales. |
Our business in foreign jurisdictions (including the United States) requires us to respond to rapid changes in market conditions in these countries. Our overall success as a global business depends on our ability to succeed in different legal, regulatory, economic, social and political situations and conditions. We may not be able to develop and implement effective policies and strategies in each foreign jurisdiction where we do business.
-
Our strategic plan includes growth, which we may not be able to manage effectively.
If the Company fails to manage growth successfully, it could experience delays, cost overruns or other problems. Similarly, the Company is in a specialized industry where qualified, key personnel may be difficult to retain or replace on a cost-effective basis.
The shift into large energy storage product lines exposes us to elevated levels of system failure and therefore reputational and product liability risk, as larger products have longer lives and greater voltage capacities, and are therefore relied on more heavily.
Electrovaya has plans to build and deliver large MWh sized energy storage systems for grid energy storage. Safety concerns are further heightened in these systems as they are necessarily larger and with greater voltages, yet are contained in a small space. Furthermore, these systems are for expected use in utilities and other electrical energy delivery applications where typical service life is longer than automotive or similar applications. There is a risk that our systems will not meet utility and similar industry standards.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish or cease publishing research or reports about us, our business or our market, or if they change their recommendations regarding our shares adversely, our share price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common shares will be influenced by the research and reports that industry or securities analysts may publish about us, our business, our market or our competitors. If any of the analysts who may cover us change their recommendation regarding our shares adversely, or provide more favorable relative recommendations about our competitors, our share price would likely decline. If any analyst who may cover us were to cease coverage of our company or fail to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause our share price or trading volume to decline.
We are exposed to risks associated with the fluctuation of currency values.
The Company is exposed to foreign currency risk. The Company’s functional currency is the US dollar and while the majority of its revenue is derived in United States dollars, a significant portion of the Company’s purchases and payroll are in Canadian dollars. Also, operations are located primarily in Canada. Any fluctuations in the value of any of these currencies relative to the US dollar or to each other may result in a material effect on the results of the Company’s operations.
Our share price may be volatile.
The market price of our common shares could be subject to significant fluctuations, and it may decline below the price at which you purchased it. Market prices for securities of early stage companies have historically been particularly volatile. As a result of this volatility, you may not be able to sell your common shares at or above the price you paid. Some of the factors that may cause the market price of our common shares to fluctuate include:
| ● | fluctuations in our quarterly financial results or the quarterly financial results of companies perceived to be similar to us; |
-
| ● | fluctuations in our recorded revenue, even during periods of significant sales order activity; |
| ● | changes in estimates of our future financial results or recommendations by securities analysts; |
| ● | failure of any of our products to achieve or maintain market acceptance; |
| ● | product liability issues involving our products or our competitors’ products; |
| ● | changes in market valuations of similar companies; |
| ● | success of competitive products or technologies; |
| ● | changes in our capital structure, such as future issuances of securities or the incurrence of debt; |
| ● | announcements by us or our competitors of significant services, contracts, acquisitions or strategic alliances; |
| ● | regulatory developments in Canada, the United States or foreign countries; |
| ● | litigation involving us, our general industry or both; |
| ● | additions or departures of key personnel; |
| ● | investors’ general perception of us and our business; and |
| ● | changes in general economic, industry and market conditions. |
In addition, if the market for technology stocks or the stock market in general experiences a loss of investor confidence, the trading price of our common shares could decline for reasons unrelated to our business, financial condition or results of operations. The occurrence of any of the foregoing, without limitation, could cause the trading price of our shares to fall and may expose us to class action lawsuits that, even if unsuccessful, could be costly to defend and a distraction to management.
We do not expect to declare any dividends in the foreseeable future.
We do not anticipate declaring any cash dividends to holders of our common shares in the foreseeable future. Consequently, investors may need to rely on sales of their common shares after price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize any future gains on their investment. Investors seeking cash dividends should not purchase our common shares.
Adverse business or financial conditions affecting the electromotive and energy storage industries may have a material adverse effect on our development and marketing partners and our battery business.
Our financial results may vary significantly from period-to-period due to the long and unpredictable sales cycles for some of our products and changes in the mix of products we sell during a period, which may lead to volatility in our operating results and share price.
Much of our business depends on and is directly affected by the general economic state of Canada and the United States and the global material handling and energy storage industry. Possible effects could include reduced spending on alternative energy systems, a delay in the introduction of new, or the cancellation of new and existing, hybrid and electric vehicles and programs, and a delay in the conversion of existing batteries to lithium-ion batteries, each of which would have a material adverse effect on our business.
-
The size and timing of our revenue from sales to our customers is difficult to predict and is market dependent. Our sales efforts often require us to educate our customers about the use and benefits of our products, including their technical and performance characteristics. Customers typically undertake a significant evaluation process that has in the past resulted in a lengthy sales cycle for us, typically many months. In some markets such as the transportation market, there is usually a significant lag time between the design phase and commercial production. We spend substantial amounts of time and money on our sales efforts and there is no assurance that these investments will produce any sales within expected time frames or at all. Given the potentially large size of battery development and supply contracts, the loss of or delay in the signing of a contract or a customer order could significantly reduce our revenue in any period. Since most of our operating and capital expenses are incurred based on the estimated number of design wins and their timing, they are difficult to adjust in the short term. As a result, if our revenue falls below our expectations or is delayed in any period, we may not be able to reduce proportionately our operating expenses or manufacturing costs for that period, and any reduction of manufacturing capacity could have long-term implications on our ability to accommodate future demand.
Our profitability from period-to-period may also vary significantly due to the mix of products that we sell in different periods. As we expand our business we expect to sell new battery and battery system products into new markets and applications. These products are likely to have different cost profiles and will be sold into markets governed by different business dynamics. Consequently, sales of individual products may not necessarily be consistent across periods, which could affect product mix and cause revenues and profit or loss to vary significantly.
As a result of these factors, we believe that quarter-to-quarter comparisons of our operating results are not meaningful in every circumstance and that these comparisons cannot be relied upon as indicators of future performance. Moreover, our operating results may not meet expectations of equity research analysts or investors. If this occurs, the trading price of our common shares could fall substantially either suddenly or over time.
We are dependent upon customers who manufacture their own finished products for our sales, and the actions and risks affecting these customers may also affect us, which risks we may not be able to effectively mitigate.
To be commercially useful, battery products must be integrated into products manufactured by customers, such as OEMs. We can offer no guarantee that such customers will manufacture appropriate, durable or safe products incorporating our products. Any integration, design, manufacturing or marketing problems encountered by such OEMs could adversely affect our reputation and therefore the market for our products and our financial results. The Company does not have visibility into the operating and business processes of its customers.
We may face potential delays in construction and commissioning of the Jamestown, New York facility.
The Company is in the process of developing a lithium-ion battery cell and system manufacturing facility located near Jamestown, New York. Construction, equipment installation, commissioning and validation activities at this facility are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties that may result in delays, increased costs or changes in the expected timing or scope of the project. These risks include, but are not limited to, the availability and timely delivery of specialized manufacturing equipment, contractor and labour availability, supply chain disruptions, regulatory or permitting delays, utility-service readiness, and variability in construction and commissioning schedules. Any material delay in construction, commissioning or commencement of operations at the Jamestown facility could affect the Company’s ability to scale production, meet customer demand, or realize anticipated operational, financial or strategic benefits from the facility. There can be no assurance that the Jamestown project will be completed within the anticipated schedule or budget, or that operational milestones will be achieved as planned.
-
Electrovaya Solid State Battery developments may not result in any commercially viable technology.
The Company may be unsuccessful in demonstrating viability, performance and manufacturability of its Solid State platform.
US Incentives related to the Inflation Reduction Act are Retracted.
The Company believes that the Inflation Reduction Act provides a strong incentive to manufacture batteries in its planned manufacturing site in Jamestown, New York. Changes to this legislation could adversely impact the business case for these operations.
The Company’s business is subject to risks associated with doing business in foreign jurisdictions including, but not limited to: trade protection measures such as the imposition of or increase in tariffs, import and export licensing and control requirements; potentially negative consequences from changes in tax laws (both foreign and domestic); difficulties associated with transacting business with parties in a foreign jurisdiction including increased costs and uncertainties associated with enforcing contractual obligations; and unexpected or unfavorable changes in other regulations and applicable regulatory requirements. Future changes to trade or investment policies, treaties and tariffs, fluctuations in exchange rates, or the perception that these changes could occur could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations. In addition, actions by foreign markets to implement further trade policy changes, including limiting foreign investment or trade, increasing regulatory scrutiny, imposing quotas or supply limitations or taking other actions which could apply to the jurisdictions in which the Company operates, could negatively impact the Company’s business.
The recent changing tariff policy between the United States and Canada adds a degree of uncertainty around the Company’s ability to move goods freely across the border and utilize its Canadian based manufacturing sites for US exports. As a mitigating factor, Electrovaya is able to build battery systems at its Jamestown New York facility, which would reduce the impact of these potential tariffs.
Potential expiry, withdrawal or renegotiation of the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA).
The United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement (“USMCA”) governs a significant portion of North American trade activity, including the movement of raw materials, components and finished goods used in the Company’s operations. Under the agreement’s review mechanism, any Party may elect to withdraw from or decline to renew USMCA, and the agreement may also be subject to renegotiation or amendments. There is no assurance that USMCA will remain in effect in its current form.
-
Any expiry, withdrawal or material modification of USMCA could result in the imposition of new tariffs, duties, customs barriers, rules-of-origin requirements, or other trade restrictions affecting goods moving between Canada, the United States and Mexico. Such changes could increase the Company’s cost of importing materials or equipment, affect the pricing and competitiveness of battery systems manufactured in Canada or the United States, disrupt established supply chains, or require modifications to sourcing, manufacturing or logistics strategies. These effects could be heightened given the Company’s ongoing development of its U.S. manufacturing facility in Jamestown, New York, as well as its reliance on cross-border trade for equipment, components, and customer deliveries.
Changes to USMCA could also create uncertainty for customers operating integrated North American logistics or manufacturing operations, which may affect purchasing decisions or the timing of commercial programs involving the Company’s products. The Company may incur additional costs or delays in responding to new regulatory or customs requirements and may not be able to fully mitigate the impact of any adverse changes.
There can be no assurance that USMCA will remain in force, be renewed on existing terms, or be replaced by an agreement offering comparable trade protections. Any material adverse change to the USMCA framework could negatively affect the Company’s operations, cost structure, and financial performance.
Electric vehicles are a significant target industry that is subject to evolving and unforeseen changes.
The Company targets sales of its products to the electric vehicle industry, which is rapidly evolving and may not develop as anticipated. The regulatory frameworks, in Canada and in foreign jurisdictions, governing the industry are currently uncertain and may remain uncertain for the foreseeable future. The deployment of incentives by governments encouraging the adoption of electric vehicles have been variable over time and there can be no certainty that similar incentives will be available to customers going-forward, which could decrease demand for electric vehicles and their components. Developments in alternative technologies, such as advanced diesel, ethanol, fuel cells or compressed natural gas, or improvements in the fuel economy of the internal combustion engine, may materially and adversely affect the Company’s business, financial condition, and operating results.
| 12. | Additional Information |
Additional information including directors’ and officers’ remuneration and indebtedness, principal holders of our securities, securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans, and interests of insiders in material transactions, where applicable, is contained in the management information circular for our most recent annual meeting of shareholders that involved the election of directors. Additional information is also included in our consolidated financial statements and MD&A for our most recently completed financial year. The foregoing and other information about the Company can be found on the SEDAR website for Canadian regulatory filings at www.sedar.com and on the Company’s website at www.Electrovaya.com.
-
| 13. | Audit Committee |
The text of the Company’s Audit Committee Charter is appended as Appendix “A”.
The members of the Audit Committee of the Company are indicated in the listing of Directors in the section above entitled “Directors and Officers”. All members of the Audit Committee are financially literate and independent.
In addition to carrying out its statutory legal responsibilities (including review of the Company’s annual consolidated financial statements prior to their presentation to the Board) the Audit Committee reviews all financial reporting, including interim financial statements and management’s discussion and analysis. The Audit Committee meets or confers with the Company’s external auditors and with members of management at least four times a year (and more frequently as necessary) to assist it in the effective discharge of its duties. The Audit Committee also recommends to the Board the auditors to be appointed as the Company’s auditors at the annual meeting and the terms of their remuneration.
Pursuant to the Audit Committee’s charter, any non-audit services to be provided to the Company must be approved by the Audit Committee prior to the auditors’ engagement. Non-audit services are approved on an engagement-by-engagement basis.
The following summarizes the fees paid for professional services rendered to the Company for the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024:
| Audit Fees | 2025* | 2024* | ||||||
| Audit fees | $ | 345,360 | $ | 440,118 | ||||
| Audit related fees | $ | 55,682 | $ | 23,643 | ||||
| Tax compliance | $ | — | $ | 4,416 | ||||
| Other audit related | — | — | ||||||
| Total | $ | 401,042 | $ | 468,177 | ||||
* Converted into US dollars at the average rate for the fiscal year ended September 30, 2025 and 2024 respectively (2024:1.3986 Cdn dollars per US dollar 2023: 1.3587 Cdn dollars per US dollar;)
- A-
Appendix
“A”
Audit Committee Charter
ELECTROVAYA INC.
| 1. | General |
It is the policy of Electrovaya Inc. (the “Corporation”) to establish and maintain an Audit Committee (the “Committee”), composed entirely of independent directors, to assist the board of directors (the “Board”) in carrying out its oversight responsibility for the Corporation’s internal controls, financial reporting and risk management processes. The Committee will be provided with resources commensurate with the duties and responsibilities assigned to it by the Board, including administrative support. If determined necessary by the Committee, it will have the discretion to institute investigations of improprieties, or suspected improprieties within the scope of its responsibilities, including the standing authority to retain special counsel or experts.
| 2. | Composition of the Committee |
| 2.1 | The Committee shall consist of at least three directors. The Board shall appoint the members of the Committee. The Committee shall appoint one member to be the chair of the Committee (the “Chair”). |
| 2.2 | Each director appointed to the Committee by the Board shall be an outside director who is unrelated. An outside, unrelated director is a director who is independent of management and is free from any interest, any business or other relationship which could, or could reasonably be perceived, to materially interfere with the director’s ability to act with a view to the best interests of the Corporation, other than interests and relationships arising from shareholdings. In determining whether a director is independent of management, the Board shall make reference to the then current legislation, rules, policies and instruments of applicable regulatory authorities. Notwithstanding these guidelines, determination of independence is to be decided by the Board, whose decision is final. |
| 2.3 | Each member of the Committee shall be “financially literate”. A director appointed by the Board to the Committee shall be a member of the Committee until replaced by the Board or until his or her resignation. |
| 3. | Meetings of the Committee |
| 3.1 | The Committee shall convene a minimum of four times each year at such times and places as may be designated by the Chair and whenever a meeting is requested by the Board, a member of the Committee, the auditors, or a senior officer of the Corporation. Meetings of the Committee shall also correspond with the review of the quarterly financial statements and management’s discussion and analysis. |
| 3.2 | Notice of each meeting of the Committee shall be given to each member of the Committee and to the auditors, who shall be entitled to attend each meeting of the Committee and shall attend whenever requested to do so by a member of the Committee. However, no notice of a meeting shall be necessary if all of the members are present either in person or by means of telephone or web conference, or other communication equipment, or if those absent waive notice or otherwise signify their consent to the holding of such meeting. |
- A-
| 3.3 | Notice of a meeting of the Committee shall: |
| 3.3.1 | be in writing; |
| 3.3.2 | state the nature of the business to be transacted at the meeting in reasonable detail; |
| 3.3.3 | to the extent practicable, be accompanied by copies of documentation to be considered at the meeting; and |
| 3.3.4 | be given at least two business days prior to the time stipulated for the meeting or such shorter period as the members of the Committee may permit. |
| 3.4 | A quorum for the transaction of business at a meeting of the Committee shall consist of a majority of the members of the Committee. However, it shall be the practice of the Committee to require review, and, if necessary, approval of certain important matters by all members of the Committee. |
| 3.5 | Any matter to be determined by the Committee shall be decided by a majority of the votes cast at a meeting of the Committee called for such purpose. Any action of the Committee may also be taken by an instrument or instruments in writing signed by all of the members of the Committee (including in counterparts, by facsimile or other electronic signature) and any such action shall be as effective as if it had been decided by a majority of the votes cast at a meeting of the Committee called for such purpose. |
| 3.6 | A member or members of the Committee may participate in a meeting of the Committee by means of such telephonic, electronic or other communication facilities, as permits all persons participating in the meeting to communicate adequately with each other. A member participating in such a meeting by any such means is deemed to be present at the meeting. |
| 3.7 | In the absence of the Chair, the members of the Committee shall choose one of the members present to be chair of the meeting. In addition, the members of the Committee shall choose one of the persons present to be the secretary of the meeting. |
| 3.8 | The chairman of the Board, senior management of the Corporation and other parties may attend meetings of the Committee; however, the Committee (i) shall meet with the external auditors independent of management, as necessary, in the sole discretion of the Committee, but in any event, not less than quarterly; and (ii) may meet separately with management. |
- A-
| 3.9 | The Committee shall hold an in-camera session without any senior officers present at each meeting of the Committee, unless such a session is not considered necessary by the members present. |
| 3.10 | Minutes shall be kept of all meetings of the Committee and shall be signed by the chair and the secretary of the meeting. |
| 4. | Committee Responsibilities |
The Committee’s primary responsibilities are to:
| 4.1 | identify and monitor the management of the principal risks that could impact the financial reporting of the Corporation; |
| 4.2 | monitor the integrity of the Corporation’s financial reporting process and system of internal controls regarding financial reporting and accounting compliance; |
| 4.3 | engage independent counsel and other advisors as it determines necessary to carry out its duties; |
| 4.4 | set and pay the compensation for any advisors employed by the audit committee |
| 4.5 | monitor the independence and performance of the Corporation’s external auditors; |
| 4.6 | communicate directly with the internal and external auditors; |
| 4.7 | deal directly with the external auditors to approve external audit plans, other services (if any) and fees; |
| 4.8 | directly oversee the external audit process and results; |
| 4.9 | provide an avenue of communication among the external auditors, management and the Board; and, |
| 4.10 | ensure that there is an appropriate standard of corporate conduct relating to the internal controls and financial reporting of the Corporation. |
| 5. | Duties |
| 5.1 | The Committee shall: |
| 5.1.1 | review the audit plan with the Corporation’s external auditors and with management; |
| 5.1.2 | discuss with management and the external auditors any proposed changes in major accounting policies or principles, the presentation and impact of significant risks and uncertainties and key estimates and judgments of management that may be material to financial reporting; |
- A-
| 5.1.3 | review with management and with the external auditors significant financial reporting issues arising during the most recent fiscal period and the resolution or proposed resolution of such issues; |
| 5.1.4 | review any problems experienced or concerns expressed by the external auditors in performing an audit, including any restrictions imposed by management or significant accounting issues on which there was a disagreement with management; |
| 5.1.5 | review with senior management the process of identifying, monitoring and reporting the principal risks affecting financial reporting; |
| 5.1.6 | consider whether the Corporation’s financial disclosures are complete, accurate, prepared in accordance with IFRS and fairly present the financial position of the Corporation; |
| 5.1.7 | obtain timely reports from the external auditors describing critical accounting policies and practices applicable to the Corporation, the alternative treatment of information in accordance with IFRS that were discussed with the CFO of the Corporation, the ramifications thereof, and the external auditor’s preferred treatment, and should review any material written communications between the Corporation and the external auditor; |
| 5.1.8 | review and discuss with senior officers of the Corporation any guidance being provided on the expected future results and financial performance of the Corporation, and provide its recommendations on such guidance to the Board; |
| 5.1.9 | review the procedures which are in place for the review of the public disclosure by the Corporation of financial information extracted or derived from the financial statements of the Corporation and periodically assess the adequacy of such procedures; |
| 5.1.10 | review audited annual financial statements and related documents in conjunction with the report of the external auditors and obtain an explanation from management of all significant variances between comparative reporting periods; |
| 5.1.11 | consider and review with management, the internal control memorandum or management letter containing the recommendations of the external auditors and management’s response, if any, including an evaluation of the adequacy and effectiveness of the internal financial controls of the Corporation and subsequent follow-up to any identified weaknesses; |
| 5.1.12 | review with financial management and the external auditors the quarterly unaudited financial statements and management’s discussion and analysis before release to the public; |
| 5.1.13 | before release, review and if appropriate, recommend for approval by the Board, all public disclosure documents containing audited or unaudited financial information, including any prospectuses or securities offering documents (including documents incorporated by reference therein), annual reports, annual information forms, management’s discussion and analysis and press releases containing financial information; |
- A-
| 5.1.14 | review, consider and if appropriate, approve any transactions between the Corporation and related parties of the Corporation and specifically reviewing the actions taken by, and especially non-management expenditures proposed by Board members to certify that these are correctly in the best interests of the Company and not just in the interest of a Board member or group of Board members; |
| 5.1.15 | oversee any of the financial affairs of the Corporation, its subsidiaries or affiliates, and, if deemed appropriate, make recommendations to the Board, external auditors or management; |
| 5.1.16 | evaluate the independence and performance of the external auditors and annually recommend to the Board the appointment of the external auditors or the discharge of the external auditors when circumstances are warranted; |
| 5.1.17 | consider the recommendations of management in respect of the appointment of the external auditors; |
| 5.1.18 | pre-approve all non-audit services to be provided to the Corporation or its subsidiary entities by its external auditors, or the external auditors of the Corporation’s subsidiary entities (if any); |
| 5.1.19 | approve the engagement letter for non-audit services to be provided by the external auditors or affiliates, together with estimated fees, and consider the potential impact of such services on the independence of the external auditors; |
| 5.1.20 | review the fees paid by the Corporation to the external auditor in respect of audit and non-audit services on an annual basis; |
| 5.1.21 | when there is to be a change of external auditors, review all issues and provide documentation related to the change, including the information to be included in the Notice of Change of Auditors and documentation required pursuant to National Instrument 51-102 — Continuous Disclosure Obligations (or any successor instrument) of the Canadian Securities Administrators and the planned steps for an orderly transition period; |
| 5.1.22 | review and approve the Corporation’s hiring policies regarding partners, employees and former partners and employees of the external auditors and any former external auditors; |
| 5.1.23 | review all reportable events, including disagreements, unresolved issues and consultations, as defined by applicable securities policies, on a routine basis, whether or not there is to be a change of external auditors; and |
- A-
| 5.1.24 | review with management at least annually, the financing strategy and plans of the Corporation. |
| 5.2 | The Committee has the authority to: |
| 5.2.1 | inspect any and all of the books and records of the Corporation, its subsidiaries and affiliates (to the extent necessary); |
| 5.2.2 | discuss with the management of the Corporation, its subsidiaries and affiliates and senior staff of the Corporation, any affected party and the external auditors, such accounts, records and other matters as any member of the Committee considers necessary and appropriate; |
| 5.2.3 | engage independent counsel and other advisors as it determines necessary to carry out its duties; |
| 5.2.4 | to set and pay the compensation for any advisors employed by the Committee; |
| 5.2.5 | conduct any investigation considered appropriate by the Committee; and |
| 5.2.6 | at any meeting, request the presence of the auditor, a member of senior management or any other person who could contribute to the subject of the meeting. |
| 5.3 | The Committee shall, at the earliest opportunity after each meeting, report to the Board the results of its activities and any reviews undertaken and make recommendations to the Board as deemed appropriate. |
| 6. | Chair of the Committee |
| 6.1 | The Committee will appoint one member who is qualified for such purpose to be Chair, to serve until the next annual election of directors or otherwise until his or her successor is duly appointed. If, following the election of directors, in any year, the Board does not appoint a Chair, the incumbent Chair will continue in office until a successor is appointed. |
| 6.2 | The Chair should: |
| 6.2.1 | provide leadership to the Committee and oversee the functioning of the Committee; |
| 6.2.2 | chair meetings of the Committee (unless not present), including in-camera sessions, and report to the Board following each meeting of the Committee on the activities and any recommendations and decisions of the Committee, and otherwise at such times and in such manner as the Chair considers advisable; |
| 6.2.3 | ensure that the Committee meets at least quarterly in each financial year of the Corporation, and otherwise as is considered advisable; |
| 6.2.4 | in consultation with the Chairman of the Board and the members of the Committee, establish dates for holding meetings of the Committee; |
- A-
| 6.2.5 | set the agenda for each meeting of the Committee, with input from other members of the Committee, the Chairman of the Board, and any other appropriate individuals; |
| 6.2.6 | ensure that Committee materials are available to any director upon request; |
| 6.2.7 | act as a liaison, and maintain communication, with the Chairman of the Board, and the Board to coordinate input from the Board and to optimize the effectiveness of the Committee; |
| 6.2.8 | report annually to the Board on the role of the Committee and the effectiveness of the Committee in contributing to the effectiveness of the Board; |
| 6.2.9 | assist the members of the Committee to understand and comply with the responsibilities contained in this mandate; |
| 6.2.10 | foster ethical and responsible decision making by the Committee; |
| 6.2.11 | together with the Board, oversee the structure, composition and membership of, and activities delegated to, the Committee from time to time; |
| 6.2.12 | ensure appropriate information is provided to the Committee by the senior officers of the Corporation to enable the Committee to function effectively and comply with this mandate; |
| 6.2.13 | ensure that appropriate resources and expertise are available to the Committee; |
| 6.2.14 | ensure that the Committee considers whether any independent counsel or other experts or advisors retained by the Committee are appropriately qualified and independent in accordance with the applicable laws; |
| 6.2.15 | facilitate effective communication between the members of the Committee and the senior officers of the Corporation, and encourage an open and frank relationship between the Committee and the external auditor; |
| 6.2.16 | attend, or arrange for another member of the Committee to attend, each meeting of the shareholders of the Corporation to respond to any questions from shareholders that may be asked of the Committee; and |
| 6.2.17 | perform such other duties as may be delegated to the Chair by the Committee or the Board from time to time. |
| 7. | Removal and Vacancies |
Any member of the Committee may be removed and replaced at any time by the Board, and will automatically cease to be a member as soon as he or she resigns or ceases to meet the qualifications set out above. The Board will fill vacancies on the Committee by appointment from among qualified members of the Board on the recommendation of the Committee. If a vacancy exists on the Committee, the remaining members will exercise all of its powers so long as a quorum remains in office.
- A-
| 8. | Assessment |
At least annually, the Committee will assess its effectiveness in fulfilling its responsibilities and duties as set out in this Mandate and in a manner consistent with the Board mandate to be adopted by the Board.
| 9. | Review and Disclosure |
The Committee will review this Mandate at least annually and submit it to the Board for approval with such further proposed amendments as it deems necessary and appropriate.
| 10. | Access to Outside Advisors |
The Committee may retain any outside advisor, at the expense of the Corporation at any time and has the authority to determine any such advisor’s fees and other retention terms. The Committee, and any outside advisors retained by it, will have access to all records and information relating to the Corporation and its subsidiaries which it deems relevant to the performance of its duties.
Exhibit 99.2

CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Expressed in U.S. dollars)
ELECTROVAYA INC.
FOR
THE YEARS ENDED September 30, 2025 and 2024
|
|
| REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM |  |
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of Electrovaya Inc.
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position of Electrovaya Inc. (the “Company”) as at September 30, 2025 and 2024, and the related consolidated statements of income (loss), comprehensive income (loss), changes in equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended September 30, 2025, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”).
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of the Company as at September 30, 2025 and 2024, and the results of its consolidated operations and its consolidated cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended September 30, 2025, in conformity with IFRS® Accounting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Chartered Professional Accountants
Licensed Public Accountants
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2023.
Toronto, Canada
December 10, 2025
MNP LLP 1930

|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Financial Position
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars)
As at September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| As at | As at | ||||||||||
| Notes | September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||||
| Assets | |||||||||||
| Current assets | |||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 6,358 | 781 | |||||||||
| Restricted cash | 656 | — | |||||||||
| Trade and other receivables | Note 5 | 16,474 | 11,292 | ||||||||
| Inventories | Note 6 | 12,451 | 9,698 | ||||||||
| Prepaid expenses | Note 7 | 6,017 | 7,647 | ||||||||
| Total current assets | 41,956 | 29,418 | |||||||||
| Non-current assets | |||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | Note 8 | 13,043 | 9,974 | ||||||||
| Long-term deposit | 257 | 90 | |||||||||
| Deposits for Jamestown equipment | Note 7 | 6,608 | — | ||||||||
| Deferred income tax asset | Note 23 | 2,067 | — | ||||||||
| Total non-current assets | 21,975 | 10,064 | |||||||||
| Total assets | 63,931 | 39,482 | |||||||||
| Liabilities and Equity | |||||||||||
| Current liabilities | |||||||||||
| Trade and other payables | Note 9, 22 | 9,555 | 9,460 | ||||||||
| Working capital facilities | Note 10 (a) | — | 16,283 | ||||||||
| Promissory notes | Note 10 (b) | — | 519 | ||||||||
| Short term loans | Note 11 | — | 1,630 | ||||||||
| Derivative liability | Note 19 | 144 | 155 | ||||||||
| Relief and recovery fund payable | Note 17 | 21 | 13 | ||||||||
| Lease liability | Note 13 | 358 | 471 | ||||||||
| Total current liabilities | 10,078 | 28,531 | |||||||||
| Non-current liabilities | |||||||||||
| Lease liability | Note 13 | 1,457 | 1,871 | ||||||||
| Long term loan | Note 10b) | 20,744 | — | ||||||||
| Government assistance payable | Note 17 | 216 | 152 | ||||||||
| Other payables | Note 22 | 309 | 343 | ||||||||
| Total non-current liabilities | 22,726 | 2,366 | |||||||||
| Equity | |||||||||||
| Share capital | Note 14 | 134,866 | 116,408 | ||||||||
| Contributed surplus | 11,508 | 10,904 | |||||||||
| Warrants | Note 14 | 4,725 | 4,725 | ||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | 5,909 | 5,792 | |||||||||
| Deficit | (125,881 | ) | (129,244 | ) | |||||||
| Total equity | 31,127 | 8,585 | |||||||||
| Total liabilities and equity | 63,931 | 39,482 | |||||||||
| See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements. | |
Signed on behalf of the Board of Directors |
|
| Chair of the Board | Sankar Das Gupta, Director |
| Chair of Audit Committee | James K Jacobs, Director |
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Income (loss)
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| Notes | September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||||
| Revenue | Note 21 | 63,826 | 44,615 | ||||||||
| Direct manufacturing costs | Note 6(b) | 44,106 | 30,926 | ||||||||
| Gross margin | 19,720 | 13,689 | |||||||||
| Expenses | |||||||||||
| Research and development | 4,379 | 3,038 | |||||||||
| Government assistance | Note 18 | (89 | ) | (316 | ) | ||||||
| Sales and marketing | 2,928 | 2,935 | |||||||||
| General and administrative | 3,679 | 3,939 | |||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 1,756 | 2,155 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 1,527 | 1,209 | |||||||||
| Operating expenses | 14,180 | 12,960 | |||||||||
| Income from operations | 5,540 | 729 | |||||||||
| Finance charges | Note 12 | 2,755 | 3,700 | ||||||||
| Loss (gain) from fair value changes in derivative liability | Note 12 | 915 | (1,334 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign exchange loss (gain) and interest income | 560 | (152 | ) | ||||||||
| Income (loss) before income tax | 1,310 | (1,485 | ) | ||||||||
| Income tax recovery | Note 23 | 2,053 | — | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) for the year | 3,363 | (1,485 | ) | ||||||||
| Basic income (loss) per share | 0.09 | (0.04 | ) | ||||||||
| Diluted income (loss) per share | 0.08 | (0.04 | ) | ||||||||
| Weighted average number of shares – basic | 39,077,512 | 34,012,383 | |||||||||
| Weighted average number of shares – diluted | 41,374,979 | 34,012,383 | |||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Net Income (loss) for the year | 3,363 | (1,485 | ) | |||||
| Items that may be reclassified to Income and Loss | ||||||||
| Cumulative translation adjustment | 117 | (98 | ) | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) for the year | 117 | (98 | ) | |||||
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year | 3,480 | (1,583 | ) | |||||
| See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements. | ||||||||
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| Share Capital | Contributed Surplus | Warrants | Accumulated other Comprehensive Income | Deficit | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance – October 01, 2023 | 115,041 | 9,249 | 4,725 | 5,890 | (127,759 | ) | 7,146 | |||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | — | 2,155 | — | — | — | 2,155 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of shares | 169 | — | — | — | — | 169 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of options | 1,198 | (500 | ) | — | — | — | 698 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss for the year | — | — | — | (98 | ) | — | (98 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Net loss for the year | — | — | — | — | (1,485 | ) | (1,485 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance – September 30, 2024 | 116,408 | 10,904 | 4,725 | 5,792 | (129,244 | ) | 8,585 | |||||||||||||||||
| Balance – October 01, 2024 | 116,408 | 10,904 | 4,725 | 5,792 | (129,244 | ) | 8,585 | |||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | — | 1,756 | — | — | — | 1,756 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of shares | 11,582 | — | — | — | — | 11,582 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of options | 2,699 | (1,152 | ) | — | — | — | 1,547 | |||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of warrants | 4,177 | — | — | — | — | 4,177 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income for the year | — | — | — | 117 | — | 117 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income for the year | — | — | — | — | 3,363 | 3,363 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Balance – September 30, 2025 | 134,866 | 11,508 | 4,725 | 5,909 | (125,881 | ) | 31,127 | |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| Notes | September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents provided by (used in) | ||||||||||
| Operating activities | ||||||||||
| Net income (loss) for the year | 3,363 | (1,485 | ) | |||||||
| Add: | ||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 1,454 | 1,209 | ||||||||
| Loss on disposal of assets | 73 | — | ||||||||
| Stock based compensation expense | 1,756 | 2,155 | ||||||||
| Interest expense and other financing charges | Note 12 | 3,670 | 2,366 | |||||||
| Non-cash foreign exchange (gain) loss | 576 | (67 | ) | |||||||
| Gain on debt extinguishment | — | (936 | ) | |||||||
| Income tax recovery | (2,053 | ) | — | |||||||
| Bad debt expense | — | 51 | ||||||||
| Cash provided by operating activities | 8,839 | 3,293 | ||||||||
| Net changes in the working capital | Note 16 | (7,122 | ) | (2,255 | ) | |||||
| Cash from operating activities | 1,717 | 1,038 | ||||||||
| Investing activities: | ||||||||||
| Purchase of property, plant and equipment | Note 8 | (4,611 | ) | (125 | ) | |||||
| Deposits for Jamestown equipment | (6,608 | ) | (541 | ) | ||||||
| Change in long term deposits | (167 | ) | — | |||||||
| Change in restricted cash | (656 | ) | — | |||||||
| Cash (used in) investing activities | (12,042 | ) | (666 | ) | ||||||
| Financing activities | ||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of shares, net of issuance cost | 11,582 | — | ||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of warrants | 3,249 | — | ||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of options | 1,547 | 131 | ||||||||
| Proceeds from working capital facilities | Note 10(a) | 79,757 | 52,247 | |||||||
| Repayment of working capital facilities | Note 10(a) | (77,895 | ) | (47,805 | ) | |||||
| Debt issuance cost paid on working capital facilities | Note 10(a) | (1,505 | ) | — | ||||||
| Repayment of vendor take back loan | Note 11 | (1,630 | ) | (1,879 | ) | |||||
| Proceeds from EXIM loan | Note 10(a) | 4,373 | — | |||||||
| Repayment of promissory note | Note 10(b), 11 | (519 | ) | — | ||||||
| Interest and other finance cost | Note 12 | (2,122 | ) | (2,533 | ) | |||||
| Government assistance | (203 | ) | (55 | ) | ||||||
| Lease payments | Note 13 | (732 | ) | (735 | ) | |||||
| Cash from (used in) financing activities | 15,902 | (629 | ) | |||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 5,577 | (257 | ) | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year | 781 | 1,032 | ||||||||
| Effect of movements in exchange rates on cash held | — | 6 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | 6,358 | 781 | ||||||||
| Supplemental cash flow disclosures: | ||||||||||
| Interest paid | 2,122 | 2,233 | ||||||||
| Income tax paid | — | — | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| 1. | Reporting Entity |
Electrovaya Inc. (the “Company”) is domiciled in Ontario, Canada, and is incorporated under the Business Corporations Act (Ontario). The Company’s registered office is at 6688 Kitimat Road, Mississauga, Ontario, L5N 1P8, Canada. The Company’s common shares trade on the Toronto Stock Exchange and NASDAQ under the symbol ELVA.TO and ELVA, respectively. The Company has no immediate or ultimate controlling parent.
These consolidated financial statements comprise the Company and its subsidiaries (together referred to as the “Group” or “Company”). The Company is primarily involved in the design, development, manufacturing and sale of Lithium-Ion batteries, battery systems and battery-related products for energy storage, clean electric transportation, and other specialized applications.
| 2. | Basis of Presentation |
| a. | Statement of Compliance |
These consolidated financial statements have been prepared based on the principles of IFRS® Accounting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”) and the Interpretations of the International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (“IFRIC”). The consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a historical cost basis, except for property, plant and equipment and derivative financial instruments that have been measured at fair value.
These consolidated financial statements were authorized for issuance by the Company’s Board of Directors on December 10, 2024.
| b. | Basis of Accounting |
These consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the going concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and settlement of liabilities as they fall due in the normal course of business.
| c. | Functional and Presentation Currency |
These consolidated financial statements are presented in U.S. dollars and have been rounded to the nearest thousands, except per share amounts and when otherwise indicated. The functional currency of the Electrovaya Inc. is the Canadian dollar and the functional currencies of all the companies within the Group is US dollars. Below are the companies within Group –
Electrovaya Corp., Electrovaya Company, Sustainable Energy Jamestown LLC, Electrovaya USA Inc.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| d. | Use of Judgements and Estimates |
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with of IFRS® Accounting Standards as issued by requires management to make judgements, estimates and assumptions that affect the application of accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to accounting estimates are recognized in the period in which the estimates are revised and in any future periods affected.
Information about significant areas of estimation uncertainty that have the most significant effect on the amounts recognized in the consolidated financial statements relate to the following (assumptions made are disclosed in individual notes throughout the consolidated financial statements where relevant):
| ● | Estimates used in determining the net realizable values of inventories, taking into account the most reliable evidence available at each reporting date. The future realization of these inventories may be affected by future technology or other market-driven changes that may reduce future selling prices. |
| ● | Estimates used in testing non-financial assets for impairment including determination of the recoverable amount of a cash generating unit. |
| ● | Estimates used in determining the fair value of stock option grants and warrants. These estimates include assumptions about the volatility of the Company’s stock and forfeiture. |
| ● | Deferred tax assets are recognised for unused tax losses to the extent that it is probable that taxable income will be available against which the losses can be utilised. Significant management judgement is required to determine the amount of deferred tax assets that can be recognised, based upon the likely timing and the level of future taxable income, together with future tax planning strategies. Information on tax losses carried forward is presented in Note 23. |
Allowance for expected credit losses
The allowance for expected credit losses is based on the assessment of the collectability of customer accounts and the aging of the related invoices and represents the best estimate of probable credit losses in the existing trade accounts receivable. The Company regularly reviews the allowance by considering factors such as historical experience, credit quality, the age of the account receivable balances, and current economic conditions that may affect a customer’s ability to pay.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company account for stock-based compensation costs in accordance with the accounting standards for stock-based compensation, which require that all stock-based payments to employees be recognized in the consolidated statements of income (loss) based on their fair values. The fair value of stock options on the grant date is estimated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model using the single-option approach and the Monte Carlo valuation method depending on the type of option granted. The Black Scholes and Monte Carlo option pricing models require the use of highly subjective and complex assumptions, including the option’s expected term and the price volatility of the underlying stock, to determine the fair value of the award.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
Warrants
The Company accounts for warrants in accordance with the accounting standards for warrants, which requires all warrants to be recognized in the consolidated statement of financial position based on their fair values. The fair value of warrants on the grant date is estimated using the Black-Scholes pricing model approach. The Black Scholes pricing model requires the use of highly subjective and complex assumptions, including the warrant’s expected term and the price volatility of the underlying stock, to determine the fair value of the award.
| 3. | Material Accounting Policies |
The accounting policies below are in compliance with of IFRS® Accounting Standards as issued by and have been applied consistently to all periods presented in these consolidated financial statements.
| a. | Basis of consolidation |
| i. | Subsidiaries |
These consolidated financial statements include direct and indirect subsidiaries, all of which are wholly owned. Any subsidiaries that are formed or acquired during the year are consolidated from their respective dates of formation or acquisition. Inter-company transactions and balances are eliminated on consolidation.
Subsidiaries are entities controlled by the Company. The financial results of subsidiaries are included in the consolidated financial statements from the date that control commences until the date that control ceases. The accounting policies of subsidiaries have been changed when necessary to align them with the policies adopted by the Company. All subsidiaries have the same reporting dates as their parent Company.
| ii. | Transactions eliminated on consolidation |
Intra-company balances and transactions, and any unrealized income and expenses arising from intra-company transactions, are eliminated in preparing the consolidated financial statements.
| b. | Foreign currency |
Each subsidiary of the Company maintains its accounting records in its functional currency. A Company’s functional currency is the currency of the principal economic environment in which it operates.
| i. | Foreign currency transactions |
Transactions carried out in foreign currencies are translated using the exchange rate prevailing at the transaction date. Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in a foreign currency at the reporting date are translated at the exchange rate at that date. The foreign currency gain or loss on such monetary items is recognized as income or expense for the period. Non-monetary assets and liabilities denominated in a foreign currency are translated at the historical exchange rate prevailing at the transaction date.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| ii. | Translation of financial statements of foreign operations |
The assets and liabilities of subsidiaries whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar are translated into U.S. dollars at the exchange rate prevailing at the reporting date. The income and expenses of foreign operations whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar are translated to U.S dollars at the exchange rate prevailing on the date of transaction. Foreign currency differences on translation are recognized in other comprehensive income (loss) in the cumulative translation account net of income tax.
Foreign exchange gains or losses arising from a monetary item receivable from or payable to a foreign operation, the settlement of which is neither planned nor likely to occur in the foreseeable future and which in substance is considered to form part of the net investment in the foreign operation, are recognized in other comprehensive income (loss) in the cumulative translation adjustment account.
| c. | Financial instruments |
Recognition
Financial assets and financial liabilities are recognized in the Company’s consolidated statement of financial position when the Company becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument. On initial recognition, all financial assets and financial liabilities are recorded at fair value, net of attributable transaction costs, except for financial assets and liabilities classified as at fair value through profit or loss (‘FVTPL’). The directly attributable transactions costs of financial assets and liabilities as at FVTPL are expensed in the period in which they are incurred.
Subsequent measurement of financial assets and liabilities depends on the classification of such assets and liabilities.
Classification and Measurement
The Company determines the classification of its financial instruments at initial recognition. Financial assets and financial liabilities are classified according to the following measurement categories:
| ● | those to be measured subsequently at fair value either through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) or through other comprehensive income (“FVTOCI”); and, |
| ● | those to be measured subsequently at amortized cost. |
The classification and measurement of financial assets after initial recognition at fair value depends on the business model for managing the financial asset and the contractual terms of the cash flows. Financial assets that are held within a business model whose objective is to collect the contractual cash flows, and that have contractual cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal outstanding, are generally measured at amortized cost at each subsequent reporting period. All other financial assets are measured at their fair values at each subsequent reporting period, with any changes recorded through FVTPL or through FVTOCI (which designation is made as an irrevocable election at the time of recognition).
After initial recognition at fair value, financial liabilities are classified and measured at either:
| ● | amortized cost. |
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| ● | FVTPL, if the Company has made an irrevocable election at the time of recognition, or when required (for items such as instruments held for trading or derivatives); or, |
| ● | the Company reclassifies financial assets when and only when its business model for managing those assets changes. Financial liabilities are not reclassified. |
The Company’s financial assets consist of cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, trade and other receivables, prepaid expenses and deposits of Jamestown equipment, which are classified and subsequently measured at amortized cost. The Company’s financial liabilities consist of trade and other payables, working capital facilities, promissory notes, short term loans, lease liability, relief and recovery fund payable, and other payables, which are classified and measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method. Derivative liability is classified and measured at fair value through profit and loss. Interest expense is reported in income or loss.
| d. | Cash equivalents |
Cash equivalents include short-term investments with original maturities of three months or less.
| e. | Inventories |
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost and net realizable value. Cost of raw material is determined using the average cost method. Cost of semi-finished and finished goods are determined using the First in First out (FIFO) method. Cost includes all expenses directly attributable to the manufacturing process as well as appropriate portions of related production overheads. Net realizable value is the estimated selling price in the ordinary course of business less any applicable selling expenses.
| f. | Property, plant and equipment |
Recognition and measurement
Items of property, plant and equipment (other than land) are measured at cost less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses. Cost includes the cost of material and labor and other costs directly attributable to bringing the asset to a working condition for its intended use.
When significant components of an item of property, plant and equipment have different useful lives, they are accounted for as separate items of property, plant and equipment.
Gains and losses on disposal of an item of property, plant and equipment are determined by comparing the proceeds from disposal with the carrying amount of property, plant and equipment, and are recognized net within income or loss.
The Company capitalizes borrowing costs directly attributable to the acquisition, construction or production of qualifying property, plant and equipment as part of the cost of that asset, if applicable. Capitalized borrowing costs are amortized over the useful life of the related asset.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
Subsequent costs
The cost of replacing a part of an item of property, plant and equipment is recognized in the carrying amount of the item if it is probable that the future economic benefits embodied within the part will flow to the Company, and its cost can be measured reliably. The carrying amount of the replaced part is derecognized. Maintenance and repair costs are expensed as incurred, except where they serve to increase productivity or to prolong the useful life of an asset, in which case they are capitalized.
Depreciation is provided on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets.
The following useful lives are applied:
Schedule Of Property, Plant and Equipment Useful Lives
| Item | Life (in years) |
| Leasehold improvements | 3 |
| Battery technology and certifications | 3-8 years |
| Production equipment | 2-15 |
| Office furniture and equipment | 2-5 |
| Building | 20 |
| Right of use assets | Over the lease term |
Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed at each reporting date and adjusted prospectively, if appropriate.
| g. | Leases |
Where the Company has entered a lease, the Company has recognized a right-of-use asset representing its rights to use the underlying assets and a lease liability representing its obligation to make lease payments. The right-of-use asset, where it relates to an operating lease, has been presented net of accumulated depreciation and is disclosed in the consolidated statement of financial position. The lease liability has been disclosed as a separate line item, allocated between current and non-current liabilities. The lease liability associated with all leases is measured at the present value of the expected lease payments at inception and discounted using the interest rate implicit in the lease. If the rate cannot be readily determined, the Company’s incremental borrowing rate is used to discount the lease liability. Judgement is required to determine the incremental borrowing rate.
| h. | Impairment |
| ● | Financial assets |
The Company recognizes an allowance for credit losses equal to lifetime credit losses for trade and other receivables. None of these assets include a financing component. Significant receivable balances are assessed for impairment individually based on information specific to the customer. The remaining receivables are grouped, where possible, based on shared credit risk characteristics, and assessed for impairment collectively. The allowance assessment incorporates past experience, current and expected future conditions.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| ● | Non-financial assets |
The carrying amounts of the Company’s non-financial assets, other than inventories and deferred tax assets are reviewed at each reporting date to determine whether there is any indication of impairment. If any such indication exists, then the asset’s recoverable amount is estimated. For intangible assets that are not yet available for use, the recoverable amount is estimated each year at the same time.
An impairment loss is recognized if the carrying amount of an asset or its CGU exceeds its estimated recoverable amount. Impairment losses are recognized in income (loss). Impairment losses recognized in respect of CGUs are allocated to the carrying amounts of the assets in the unit (group of units).
In respect of other assets, impairment losses recognized in prior periods are assessed at each reporting date for any indications that the loss has decreased or no longer exists. An impairment loss is reversed if there has been a change in the estimates used to determine the recoverable amount. An impairment loss is reversed only to the extent that the asset’s carrying amount does not exceed the carrying amount that would have been determined, net of depreciation, if no impairment loss had been recognized.
| i. | Provisions |
Legal
Provisions are recognized for present legal or constructive obligations arising from past events when the amount can be reliably estimated, and it is probable that an outflow of resources will be required to settle an obligation. Provisions are measured at the estimated expenditure required to settle the present obligation, based on the most reliable evidence available at the reporting date, including the risks and uncertainties associated with the present obligation. Where there are a number of similar obligations, the likelihood that an outflow will be required in settlement is determined by considering the class of obligations as a whole. Provisions are discounted to their present values, where the time value of money is material.
At the end of each reporting period, the Company evaluates the appropriateness of the remaining balances. Adjustments to the recorded amounts may be required to reflect actual experience or to reflect the current best estimate.
In the normal course of operations, the Company may be subject to lawsuits, investigations and other claims, including environmental, labor, product, customer disputes and other matters. The ultimate outcome or actual cost of settlement may vary significantly from the original estimates. Material obligations that have not been recognized as provisions, as the outcome is not probable or the amount cannot be reliably estimated, are disclosed as contingent liabilities, unless the likelihood of outcome is remote.
| j. | Share-based payments |
The Company accounts for all share-based payments to employees and non-employees using the fair value-based method of accounting. The Company measures the compensation cost of stock-based option awards to employees at the grant date using the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of the options. The share-based compensation cost of the options is recognized as stock-based compensation expense over the relevant vesting period of the stock options.
Under the Company`s stock option plan, all options granted under the plan have a maximum term of 10 years and have an exercise price per share of not less than the market value of the Company’s common shares on the date of grant. The Board of Directors has the discretion to accelerate the vesting of options or stock appreciation rights granted under the plan in accordance with applicable laws and the rules and policies of any stock exchange on which the Company’s common shares are listed.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
The Company has an option plan whereby options are granted to employees and consultants as part of the Company’s incentive plans. Stock options vest in installments over the vesting period. Stock options typically vest one third each year over 3 years or immediately as approved by the Board. The Company treats each installment as a separate grant in determining stock-based compensation expense.
The grant date fair value of options granted to employees is recognized as stock-based compensation expense, with a corresponding charge to contributed surplus, over the vesting period. The expense is adjusted to reflect the estimated number of options expected to vest at the end of the vesting period, adjusted for the estimated forfeitures during the period. Any cumulative adjustment prior to vesting is recognized in the current period. No adjustment is made to any expense recognized in the prior periods if share options ultimately exercised are different to that estimated on vesting. The fair value of options is measured using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. Measurement inputs include the price of Common shares on the measurement date, exercise price of the option, expected volatility (based on weighted average historic volatility), weighted average expected life of the option (based on historical experience and general option holder behavior), expected dividends, estimated forfeitures and the risk-free interest rate.
Upon exercise of options, the proceeds received net of any directly attributable transaction costs up to the nominal value of the shares issued are allocated to share capital with any excess being recorded in retained earnings or deficit.
| k. | Income taxes |
Tax expense recognized in income or loss comprises the sum of deferred tax and current tax not recognized in other comprehensive income or directly in equity. Current income tax assets and/or liabilities comprise those obligations to, or claims from, fiscal authorities relating to the current or prior reporting periods, that are unpaid at the reporting date. Current tax is payable on taxable income, which differs from income or loss in the consolidated financial statements. Calculation of current tax is based on tax rates and tax laws that have been enacted or substantively enacted by the end of the reporting period.
Deferred income taxes are calculated using the liability method on temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax bases. However, deferred tax is not provided on the initial recognition of goodwill on the initial recognition of an asset or liability unless the related transaction is a business combination or affects tax or accounting income or transactions that at the time of the transaction, does not give rise to equal taxable and deductible temporary differences. Deferred tax on temporary differences associated with investments in subsidiaries and joint ventures is not provided if reversal of these temporary differences can be controlled by the Company and it is probable that reversal will not occur in the foreseeable future. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are calculated, without discounting, at tax rates that are expected to apply to their respective period of realization, provided they are enacted or substantively enacted by the end of the reporting period. Deferred tax assets are recognized to the extent that it is probable that they will be able to be utilized against future taxable income, based on the Company’s forecast of future operating results which is adjusted for significant non-taxable income and expenses and specific limits to the use of any unused tax loss or credit.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset only when the Company has a right and intention to set off current tax assets and liabilities from the same taxation authority. Changes in deferred tax assets or liabilities are recognized as a component of tax income or expense in income or loss, except where they relate to items that are recognized in other comprehensive income or directly in equity, in which case the related deferred tax is also recognized in other comprehensive income or equity, respectively. A valuation allowance is recorded against any deferred income tax asset if it is more likely than not that the asset will be realized.
| l. | Revenue |
Revenue arises from the sale of goods and the rendering of services. It is measured by reference to the fair value of consideration received or receivable, excluding sales taxes, rebates, and trade discounts. The Company often enters sales transactions involving a range of the Company’s products and services, for example for the delivery of battery systems and related services.
Sale of goods
Sale of goods and services is recognized when the Company has transferred to the buyer the significant risks and rewards of ownership, generally when the customer has taken undisputed delivery of the goods and services. For contracts that permit the customer to return an item, revenue is recognized to the extent that it is highly probable that a significant reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur. Therefore, the amount of revenue recognized is adjusted for expected returns, which are estimated based on the historical data for specific types of products.
Advance payments by customers - Any advance receipts from customers are included in contract liabilities until the revenue recognition criteria is met.
Warranty provision
A provision for warranty costs is recorded on product sales at the time the sale is recognized. In establishing the warranty provision, management estimates the likelihood that products sold will experience warranty claims and the estimated cost to resolve claims received, taking into account the nature of the contract and past and projected experience with the products.
Government Grants
Government grants are recognized when there is reasonable assurance that the Company has met the requirements of the approved grant program and there is reasonable assurance that the grant will be received. Government grants that compensate for expenses already incurred are recognized in income on a systematic basis in the same year in which the expenses are incurred. Government grants for immediate financial support, with no future related costs, are recognized in income when receivable. Government grants that compensate the Company for the cost of an asset are recognized on a systematic basis over the useful life of the asset. Government grants consisting of investment tax credits are recorded as a reduction of the related expense or cost of the asset acquired. If a government grant becomes repayable, the repayment is treated as a change in estimate. Where the original grant related to income, the repayment is applied first against any related deferred government grant balance, and any excess as an expense. Where the original grant related to an asset, the repayment is treated as an increase to the carrying amount of the asset or as a reduction to the deferred government grant balance.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| m. | Research and development |
Expenditure on research is recognized as an expense in the period in which it is incurred.
Costs that are directly attributable to the development phase are recognized as intangible assets provided, they meet the following recognition requirements:
| ● | completion of the intangible asset is technically feasible so that it will be available for use or sale. |
| ● | the Company intends to complete the intangible asset and use or sell it. |
| ● | the Company has the ability to use or sell the intangible asset. |
| ● | the intangible asset will generate probable future economic benefits. Among other things, this requires that there is a market for the output from the intangible asset or for the intangible asset itself, or, if it is to be used internally, the asset will be used in generating such benefits. |
| ● | there are adequate technical, financial and other resources to complete the development and to use or sell the intangible asset. |
| ● | the expenditure attributable to the intangible asset during its development can be measured reliably. Development costs not meeting these criteria for capitalization are expensed in income or loss as incurred. |
| n. | Finance income and expense, foreign currency gains and losses |
Interest income is reported on an accrual basis using the effective interest method.
Finance costs are comprised of interest expense on promissory notes, short term loans and working capital facilities. Borrowing costs that are not directly attributable to the acquisition, construction or production of a qualifying asset are recognized in income or loss using the effective interest method. Foreign currency gains and losses are reported on a net basis.
| o. | Earnings per share (EPS) |
The Company presents basic and diluted earnings per share (“EPS”) data for its common shares. Basic EPS is calculated by dividing the income or loss attributable to common shareholders of the Company by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted EPS is determined by adjusting the income or loss attributable to common shareholders and the weighted average number of common shares outstanding, adjusted for own shares held, for the effects of all dilutive potential common shares, which comprise share options granted to employees. In a period of losses, the dilutive instruments comprising warrants and stock options are excluded for the determination of dilutive net loss per share because their effect is anti-dilutive.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| p. | Segment reporting |
An operating segment is a component of the Company that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses, including revenues and expenses that relate to transactions with any of the Company’s other components. All operating segments’ operating results are regularly reviewed by the Company’s chief operating decision maker to make decisions about resources to be allocated to the segment and assess its performance, and for which discrete financial information is available.
| 4. | Standards issued but not yet effective |
The following new and amended standards and interpretations have been issued but are not yet effective for the Company’s current reporting period. The Company intends to adopt these standards in its consolidated financial statements for the periods in which they become effective. Management is currently assessing the potential impact of these standards on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
IFRS 18 – Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements
Issued in April 2024 and replacing IAS 1, IFRS 18 introduces a new defined structure for the statement of income or loss, requiring classification of income and expenses into five categories (operating, investing, financing, income taxes, and discontinued operations). It also requires disclosure of management-defined performance measures (MPMs) in a single note, enhances aggregation/disaggregation guidance across all primary statements and notes, and mandates that “operating income or loss” be used as the starting point for operating cash flows under the indirect method. Effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2027, with retrospective application permitted. The Company is evaluating the impact of IFRS 18 on its presentation and disclosures.
| 5. | Trade and Other Receivables |
Trade and Other Receivables
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Trade receivables, gross | 13,796 | 10,577 | ||||||
| Expected credit losses | (82 | ) | (64 | ) | ||||
| Trade receivables | 13,714 | 10,513 | ||||||
| Other receivables | 2,760 | 779 | ||||||
| Trade and other receivables | 16,474 | 11,292 | ||||||
Financial year ending September 30, 2025
Accounts receivable
| Particulars | Current | 31-60 | 61-90 | 91-120 | >120 | Total |
| % | 81.31 | 7.52 | 0.41 | 0.34 | 10.42 | 100 |
| Gross Trade receivable | 11,218 | 1,038 | 57 | 46 | 1,437 | 13,796 |
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| Particulars | Current | 31-60 | 61-90 | 91-120 | >120 | Total |
| Trade receivable (Gross) | 11,218 | 1,038 | 57 | 46 | 1,437 | 13,796 |
| Expected loss rate (%) | 0.20 | 0.53 | 1.70 | 3.14 | 3.55 | 0.59 |
| Expected loss provision | 23 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 51 | 82 |
Financial year ending September 30, 2024
| Particulars | Current | 31-60 | 61-90 | 91-120 | >120 | Total |
| % | 78.52 | 20.61 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.75 | 100 |
| Gross Trade receivable | 8,305 | 2,180 | 11 | 4 | 77 | 10,577 |
| Particulars | Current | 31-60 | 61-90 | 91-120 | >120 | Total |
| Trade receivable (Gross) | 8,305 | 2,180 | 11 | 4 | 77 | 10,577 |
| Expected loss rate (%) | 0.05 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 1.06 | 70.13 | 0.61 |
| Expected loss provision | 4 | 6 | — | — | 54 | 64 |
The movement in the allowance for credit losses can be reconciled as follows:
Allowance for Credit Losses
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Beginning balance | 64 | 257 | ||||||
| Write off | (2 | ) | (244 | ) | ||||
| Allowance provided | 20 | 51 | ||||||
| Ending balance | 82 | 64 | ||||||
| 6. | Inventories |
| a. | Total inventories on hand as at September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024 are as follows: |
Schedule of Inventories
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Raw materials | 11,348 | 8,433 | ||||||
| Semi-finished | — | 324 | ||||||
| Finished goods | 1,103 | 941 | ||||||
| Total | 12,451 | 9,698 | ||||||
| b. | During the year ended September 30, 2025, the provision for slow moving and obsolete inventories amounted to $218 (September 30, 2024: $225), which was also included in direct manufacturing costs. |
| c. | During the year ended September 30, 2025, material amounting to $41,390 (September 30, 2024: $29,250) was expensed through direct manufacturing costs. |
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| 7. | Prepaid expenses |
Schedule of Prepaid Expenses
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Prepaid expenses | 187 | 612 | ||||||
| Prepaid insurance | 5 | 54 | ||||||
| Prepaid purchases | 5,825 | 6,981 | ||||||
| Deposits for Jamestown equipment | 6,608 | — | ||||||
| Total | 12,625 | 7,647 | ||||||
Prepaid purchases are comprised of vendor deposits on inventory orders for the future acquisition of inventories.
| 8. | Property, plant and equipment |
Schedule Of Property, Plant and Equipment
| September 30, 2025 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land | Buildings | Right of use asset | Leasehold improvement | Production equipment | Office furniture & equipment | Capital work in progress | Battery technology and certifications | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross carrying amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance beginning | 215 | 7,485 | 3,209 | 76 | 1,809 | 105 | — | 935 | 13,834 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additions | — | — | (96 | ) | 253 | 1,213 | 20 | 2,049 | 1,076 | 4,515 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disposals | — | — | — | — | (509 | ) | — | — | 11 | (498 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exchange differences | — | — | (4 | ) | — | — | (5 | ) | — | (6 | ) | (15 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance ending | 215 | 7,485 | 3,109 | 329 | 2,513 | 120 | 2,049 | 2,016 | 17,836 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and impairment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance beginning | — | (793 | ) | (1,584 | ) | (48 | ) | (1,194 | ) | (72 | ) | — | (169 | ) | (3,860 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation | — | (374 | ) | (393 | ) | (31 | ) | (279 | ) | (21 | ) | — | (271 | ) | (1,369 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Disposals | — | — | — | — | 435 | — | — | — | 435 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exchange differences | — | — | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance ending | — | (1,167 | ) | (1,977 | ) | (79 | ) | (1,038 | ) | (92 | ) | — | (440 | ) | (4,793 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Book Value ending | 215 | 6,318 | 1,132 | 250 | 1,475 | 28 | 2,049 | 1,576 | 13,043 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| September 30, 2024 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land | Buildings | Right of use asset | Leasehold improvement | Production equipment | Office furniture & equipment | Battery technology and certifications | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross carrying amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance beginning | 215 | 7,485 | 3,197 | 76 | 1,712 | 73 | 401 | 13,159 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additions | — | — | — | — | 94 | 31 | 539 | 664 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exchange differences | — | — | 12 | — | 3 | 1 | — | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance ending | 215 | 7,485 | 3,209 | 76 | 1,809 | 105 | 940 | 13,839 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and impairment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance beginning | — | (419 | ) | (1,127 | ) | (33 | ) | (970 | ) | (60 | ) | (31 | ) | (2,640 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation | — | (374 | ) | (454 | ) | (15 | ) | (221 | ) | (11 | ) | (137 | ) | (1,212 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Exchange differences | — | — | (9 | ) | — | (3 | ) | (1 | ) | — | (13 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance ending | — | (793 | ) | (1,590 | ) | (48 | ) | (1,194 | ) | (72 | ) | (168 | ) | (3,865 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Net Book Value ending | 215 | 6,692 | 1,619 | 28 | 615 | 33 | 772 | 9,974 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
During the financial year ending September 30, 2025, the Company incurred loan fees of $472 (September 30, 2024: $ NIL) in connection with the EXIM financing facility. As the related borrowing is directly attributable to the construction of a qualifying asset, the loan fee has been capitalized to “capital work in progress” (CWIP) in accordance with IAS 23 – Borrowing Costs. The capitalized amount forms part of the cost of the qualifying asset and will be amortized over the useful life of the asset once it is available for its intended use. Refer Note 10(b) for more details
| 9. | Trade and Other Payables |
Schedule of Trade and Other Payables
| Note | September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | ||||||||
| Trade payables | 6,754 | 7,037 | ||||||||
| Accruals | 2,046 | 1,732 | ||||||||
| TPC (short term) | Note 22 | 23 | 36 | |||||||
| Employee payables | 732 | 655 | ||||||||
| Total | 9,555 | 9,460 | ||||||||
Warranty provision continuity schedule is as follows:
Schedule of Warranty Provisions
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Opening provision | 1,072 | 250 | ||||||
| Warranty expenses during the year | (665 | ) | (672 | ) | ||||
| Additional provision during the year | 785 | 1,494 | ||||||
| Closing balance | 1,192 | 1,072 | ||||||
| 10. | Working Capital Facilities |
| a. | Revolving Credit Facility |
As of September 30, 2025, the balance owing under the facility is $17,672 (Cdn $24,612). The maximum credit available under the facility is $25,000.
Cortland
The interest on the revolving credit facility is the greater of a) 7.05% per annum above the Prime Rate or b) 12% per annum. Interest is payable monthly.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
Bank of Montreal
The interest rate is 7.45%, interest which is payable monthly.
Schedule of Revolving Credit Facility
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Opening balance | 16,283 | 11,821 | ||||||
| Exchange difference | (12 | ) | 20 | |||||
| Payments made during the year | (77,895 | ) | (47,805 | ) | ||||
| Loan fees (net of amortization: $104) | (461 | ) | — | |||||
| Cash drawn during the year | 79,757 | 52,247 | ||||||
| Closing balance | 17,672 | 16,283 | ||||||
On September 29, 2023, the Company renewed its revolving facility with Cortland and extended the term of the facility by three months to December 29, 2023. In exchange for this renewal, the Company issued 10,443 shares at Cdn $3.83 (as determined by five-day volume weighted average) as compensation for Cdn $40 (US $29.59) amendment fee. This was included within finance costs on the statement of income (loss). All other terms and conditions are unchanged.
On February 12, 2024, the Company revised its revolving facility, expanding its maximum principal amount to $22,000 and extending its term to July 29, 2025. As part of this adjustment, a commitment fee of Cdn $303 (US $225) was paid in cash on the closing date and amortised over the term of the facility.
On March 07, 2025, the Company entered a three-year credit agreement with Bank of Montreal as lender to provide working capital facilities with outstanding amount not exceeding $20,000 and a $5,000 accordion. As a part of this agreement, the balance outstanding with Cortland working capital facility was paid off in full. The company paid an early termination fee to Cortland for $375. Legal and professional fees in relation to the new facility have been capitalised and will be amortised over the period of the facility. The working capital facility provides the Bank with security over the assets of the Company. Interest accrued up to September 30, 2025, is $100 (September 30, 2024: $ NIL).
Export-Import Bank of United States
During March 2025, a loan was approved from Export–Import Bank of the United States for $50,853 for the Jamestown facility with a term of 6.5 years and interest rate of 4.90%. The prepayment of EXIM loan comments in the month of March 2027.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
As of September 30, 2025, the Company has drawn the following amount:
Schedule of amount drawn under Revolving Credit Facility
| September 30, | ||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Opening balance | — | — | ||||||
| Loan amount withdrawn during the year | 4,373 | — | ||||||
| Debt issuance cost | (1,309 | ) | — | |||||
| Loan fees | 472 | — | ||||||
| Payments made during the year | — | — | ||||||
| Closing balance | 3,536 | — | ||||||
Loan fees of $472 is capitalised as part of “capital work in progress” (CWIP) (Refer Note 8 for more details).
| b. | Promissory note |
Schedule of Promissory Note
| September 30, | ||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Promissory note opening balance | 519 | 1,026 | ||||||
| Finance costs | 14 | 37 | ||||||
| Repayment of Promissory note(i) | (533 | ) | (507 | ) | ||||
| Repayment of Promissory note(i) | — | (37 | ) | |||||
| Promissory note ending balance | — | $ | 519 | |||||
| i. | On February 16, 2024, the Executive Chairman and Chief Executive Officer both exercised options of the Company. A sum of $507 from the promissory note was utilized to cover portion of the options' purchase price. The remaining balance of the promissory note, amounting to $519, was then substituted with a new promissory note on February 28, 2024, carrying a 14% interest rate and paid off in the month of December 2024. |
| ii. | On March 31, 2023, the Company purchased 100% of the membership interest in Sustainable Energy Jamestown LLC (‘SEJ”), a New York incorporated company controlled by the majority shareholders of the Company. In return, the Company issued a promissory note for $1,050 to the members of SEJ, with a term of 365 days bearing interest at 7.5% annually payable at maturity. Interest recorded for the year is $1 (September 30, 2024: $76). |
| 11. | Short term loans |
On May 16, 2022, the Company acquired the assets and liabilities of Sustainable Energy Jamestown (“SEJ”), including a Vendor Take Back (‘VTB”) note relating to the purchase of the property by SEJ. The secured VTB had a two-year term with repayment starting on July 1, 2022, and expiring on December 18, 2024, and carried interest at 2% per annum. The VTB note was secured against the real estate property that was acquired as part of the SEJ transaction. On October 1, 2024, the VTB was further extended to December 18, 2024.
The company paid back the VTB liability along with interest in the month of December 2024.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
Schedule of Short Term Loans
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Vendor take back | — | 1,630 | ||||||
The VTB continuity is as follows:
Schedule of Short Term VTB Liability
| Opening balance as at September 30, 2023 (Short term: $673. Long term: $3,457) | 4,130 | |||
| Repaid in year | (750 | ) | ||
| Interest accretion | 77 | |||
| Closing balance as at September 30, 2023 (Short term: $3,457. Long term: $nil) | 3,457 | |||
| Repaid in year | (1,879 | ) | ||
| Interest accretion | 52 | |||
| Closing balance as at September 30, 2024 (Short term: $1,630 Long term: $nil) | 1,630 | |||
| Interest accretion | 16 | |||
| Repaid in year | (1,646 | ) | ||
| Closing balance as at September 30, 2025 | — |
| 12. | Finance costs |
During the year, the Company incurred both cash and non-cash finance costs. The following table shows the split as included on the statement of income (loss).
Schedule of Cash and Non-Cash Finance Costs
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash | Non-Cash | Total | Cash | Non-Cash | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Working capital facility | 2,092 | 22 | 2,114 | 2,134 | — | 2,134 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Issued to lender (note 14a) | — | — | — | — | 30 | 30 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued to consultants | — | — | — | — | 169 | 169 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest on VTB loan (note 11) | 16 | — | 16 | 96 | 52 | 148 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Promissory notes, accretion on promissory note and settlement fee on promissory note | 14 | — | 14 | — | 76 | 76 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lease interest (note 13) | — | 279 | 279 | — | 348 | 348 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Changes in FV of derivative warrants | — | 915 | 915 | — | (1,334 | ) | (1,334 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Accretion on government assistance | — | 67 | 67 | — | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accretion on government loans – TPC | — | 114 | 114 | 3 | 487 | 490 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other finance cost | — | 151 | 151 | 301 | — | 301 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Finance Costs | 2,122 | 1,548 | 3,670 | 2,534 | (168 | ) | 2,366 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| 13. | Lease liability |
As of September 30, 2025, lease liability consists of:
Schedule of Lease Liability
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Current | 358 | 471 | ||||||
| Non-current | 1,457 | 1,871 | ||||||
| Carrying amount - lease liability | 1,815 | 2,342 | ||||||
Information about leases for which the Company is a lessee is as follows:
Schedule of Lease
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Interest on lease liabilities | 279 | 348 | ||||||
| Incremental borrowing rate at time of transition | 14 | % | 14 | % | ||||
| Cash outflow for the lease | 732 | 735 | ||||||
The Company’s future minimum lease payments for the years ended September 30, 2025, for the continued operations are as under:
Schedule of Future Lease Payments
| Year | Amount |
| 2026 | 761 |
| 2027 | 719 |
| 2028 | 735 |
| 2029 | 752 |
| 2030 | 189 |
The Company entered into a lease agreement for 61,327 sq. ft for its premises as its headquarters in Mississauga, Ontario at 6688 Kitimat Road. The lease is for 10 years starting January 1, 2020, with expiry December 31, 2029. In addition, the Company is required to pay certain occupancy costs.
The lease agreement for the Company's lab facility has been renewed for an additional three years, commencing from January 2023.
The terms of the renewed lease entail a fixed monthly rent as follows:
| ● | CAD $25,625 for the first year, |
| ● | CAD $26,265 for the second year, and |
| ● | CAD $26,922 for the third year. |
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| 14. | Share capital |
| a. | Authorized and issued capital stock |
| Schedule of Authorized and Issued Capital Stock | Common Shares | |||||||||||
| Number | Amount | |||||||||||
| Balance, September 30, 2023 | Note | 33,832,784 | 115,041 | |||||||||
| Issuance of shares | (i) | 10,024 | 30 | |||||||||
| Issuance of shares | (ii) | 42,157 | 169 | |||||||||
| Transfer from contributed surplus | — | 501 | ||||||||||
| Exercise of options | 252,700 | 667 | ||||||||||
| Balance, September 30, 2024 | 34,137,665 | 116,408 | ||||||||||
| Issuance of shares | (iii) | 5,951,250 | 11,582 | |||||||||
| Transfer from contributed surplus | — | 2,080 | ||||||||||
| Exercise of warrants | (iv) | 845,000 | 3,249 | |||||||||
| Exercise of options | Note 14(b) | 1,175,005 | 1,547 | |||||||||
| Balance, September 30, 2025 | 42,108,920 | 134,866 | ||||||||||
| i. | In December 2023, additional shares were issued as extension fee for the revolving facility on December 20, 2023. All terms and conditions were unchanged. In exchange for the extension, the Company issued 10,024 shares at Cdn $3.99 (as determined by a five-day volume weighted average) as compensation for Cdn $40 extension fee (US $ 30.01). |
| ii. | On March 07, 2024, the Company issued 42,157 shares for consulting for investor relations. The Company issued the shares at Cdn $ 5.43 as compensation. |
| iii. | The company issued 5,175,000 common shares at $2.15 for a total equity raise of $11,789 and share issuance cost of $206. The proceeds were recognised net of legal and consulting fees. Over allotment option for the option shares 776,250 was exercised by the underwriters in the month of December 2024. |
| iv. | On August 11, 2025, the warrants classified as derivative warrants were exercised by the investors at the price of CDN 5.30. As a result, the Company received US $3,249 in total proceeds. Fair valuation was done under Black Scholes model and the assumptions on the date of exercise included Risk-free interest rate (based on U.S. government bond yields) of 2.68%, expected volatility of the market price of shares (based on historical volatility of share price) of 65.05%, and the expected warrant life (in years) of 0.24 years. |
| b. | Stock Options |
Options to purchase common shares of the Company under its stock option plan may be granted by the Board of Directors of the Company to certain full-time and part-time employees, directors and consultants of the Company and its affiliates. Stock options are non-assignable and may be granted for terms of up to 10 years. Stock options vest at various periods from zero to three years. As a result of the reverse stock split, very five options were consolidated into one option without any action from option holders, reducing the number of outstanding options from approximately 23.5 million to 4.7 million.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
On February 17, 2021, at a Special Meeting of the Shareholders, a resolution was passed to (i) authorize amendments to the Company’s Stock Option Plan to increase the maximum number of common shares issuable upon the exercise of stock options thereunder from 3,020,000 to 4,600,000.
On March 25, 2022, at a Special Meeting of the Shareholders, a resolution was passed to (i) authorize amendments to the Company’s Stock Option Plan to increase the maximum number of common shares issuable upon the exercise of stock options thereunder from 4,600,000 to 6,000,000.
| Schedule of Stock Options | Note | Number outstanding | Weighted average exercise price (US $) |
|||||||||
| Outstanding, September 30, 2023 | 4,714,388 | 2.44 | ||||||||||
| Exercised during the year | (252,700 | ) | 2.65 | |||||||||
| Expired during the year | (24,400 | ) | 2.87 | |||||||||
| Granted | 443,000 | 3.42 | ||||||||||
| Outstanding, September 30, 2024 | 4,880,288 | 2.52 | ||||||||||
| Exercised during the year | Note 14(a) | (1,175,005 | ) | 1.31 | ||||||||
| Expired during the year | Note 14(a) | (34,399 | ) | 3.34 | ||||||||
| Granted | 854,000 | 3.37 | ||||||||||
| Outstanding, September 30, 2025 | 4,524,884 | 3.44 | ||||||||||
| Exercise price | Number outstanding |
Weighted average remaining life (years) |
Number exercisable |
Weighted average (US $) |
|
| $4.67 | (Cdn 6.51) | 340,000 | 0.25 | 340,000 | 4.67 |
| $2.44 | (Cdn 3.4) | 514,000 | 9.53 | 163,333 | 2.44 |
| $3.36 | (Cdn 4.68) | 414,666 | 8.51 | 178,673 | 3.36 |
| $3.84 | (Cdn 5.35) | 992,715 | 7.53 | 272,391 | 3.84 |
| $2.05 | (Cdn 2.85) | 235,000 | 6.72 | 235,000 | 2.05 |
| $4.13 | (Cdn 5.75) | 20,000 | 6.16 | 20,000 | 4.13 |
| $3.59 | (Cdn 5) | 1,494,667 | 5.95 | 694,667 | 3.59 |
| $2.37 | (Cdn 3.3) | 238,268 | 4.95 | 238,268 | 2.37 |
| $1.08 | (Cdn 1.5) | 99,000 | 3.83 | 99,000 | 1.08 |
| $1.01 | (Cdn 1.4) | 55,180 | 2.40 | 55,180 | 1.01 |
| $4.38 | (Cdn 6.1) | 10,667 | 1.83 | 10,667 | 4.38 |
| $7.65 | (Cdn 10.65) | 101,121 | 1.25 | 101,121 | 7.65 |
| $2.84 | (Cdn 3.95) | 9,600 | 0.36 | 9,600 | 2.84 |
| 4,524,884 | 2,417,900 | 3.44 | |||
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
For the options exercised, the share price at the time of exercise was between CDN $3.54-$8.20. Total stock-based compensation expense recognized during the year ended September 30, 2025, was $1,756 (2024: $2,155).
The Company amortizes the estimated grant date fair value of stock options to expense over the vesting period (generally three years). The grant date fair value of outstanding stock options was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model which uses highly subjective and complex assumptions, including the option's expected term and the price volatility of the underlying stock based on historical stock prices, to determine the fair value of the option.
| i. | The following table summarizes the assumptions used with the Black-Scholes valuation model for the determination of the stock-based compensation costs for the stock options granted during the year ended September 30, 2025: |
| Grant date | April 14, 2025 | |||
| No of options | 514,000 | |||
| Share price | $ | 2.44 | ||
| Exercise price | $ | 2.44 | ||
| Average expected life in years | 10 | |||
| Volatility | 84.59 | % | ||
| Risk-free weighted interest rate | 2.96 | % | ||
| Dividend yield | — | |||
| Fair-value of options granted | $ | 1,066 | ||
| Grant date | August 15, 2025 | |||
| No of options | 340,000 | |||
| Share price | $ | 4.67 | ||
| Exercise price | $ | 4.67 | ||
| Average expected life in years | 0.25 | |||
| Volatility | 61.17 | % | ||
| Risk-free weighted interest rate | 4.5 | % | ||
| Dividend yield | — | |||
| Fair-value of options granted | $ | 244 |
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| ii. | The following table summarizes the assumptions used with the Black-Scholes valuation model for the determination of the stock-based compensation costs for the stock options granted during the year ended September 30, 2024: |
| Grant date | April 05, 2024 | |||
| No of options | 443,000 | |||
| Share price | $ | 3.44 | ||
| Exercise price | $ | 3.44 | ||
| Average expected life in years | 10 | |||
| Volatility | 87.98 | % | ||
| Risk-free weighted interest rate | 3.58 | % | ||
| Dividend yield | — | |||
| Fair-value of options granted | $ | 1,316 | ||
| c. | Warrants |
Details of Share Warrants
| Schedule of Warrants | Number Outstanding | Exercise Price | |||||||
| Outstanding, September 30, 2023 | 1,711,924 | $ | 2.38 | ||||||
| Expired | (291,924 | ) | $ | 5.92 | |||||
| Outstanding, September 30, 2024 | 1,420,000 | $ | 2.38 | ||||||
| Outstanding, September 30, 2025 | 1,420,000 | $ | 0.63 | ||||||
Additionally, the number of derivative warrants outstanding as at September 30, 2025, were 67,841 (September 30, 2024: 912,841).
The grant date fair value of outstanding share warrants was determined using the Black-Scholes pricing model using the following assumptions in the year of the grant:
Risk-free interest rate (based on U.S. government bond yields) of 2.49% (September 30, 2024: 2.94%), expected volatility of the market price of shares (based on historical volatility of share price) of 87.03%, (September 30, 2024: 52.72%) and the expected warrant life (in years) of 0.11 years (September 30, 2024: 1.1). A 10% of change in any assumption would result in the change in derivative warrant liability between $1 (September 30, 2024: ($51)) and $(1) (September 30, 2024: $51).
Warrant continuity schedule is as follows:
| Schedule of Warrant continuity | Units | Fair Value ($) | ||||||
| Opening valuation as at Nov 9, 2022 | 1,754,340 | 3,259 | ||||||
| Warrants exercised as at July 28, 2023 | (841,499 | ) | (1,409 | ) | ||||
| Fair value adjustment | — | (361 | ) | |||||
| Closing balance (September 30, 2023) | 912,841 | 1,489 | ||||||
| Fair value adjustment | — | (1,334 | ) | |||||
| Closing balance (September 30, 2024) | 912,841 | 155 | ||||||
| Warrants exercised as on August 11, 2025 | (845,000 | ) | (926 | ) | ||||
| Fair value adjustment | — | 915 | ||||||
| Closing balance (September 30, 2025) | 67,841 | 144 | ||||||
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| d. | Details of Compensation options: |
| Number Outstanding | Exercise Price (CDN $) | |||||||
| Outstanding, September 30, 2023 | 17,522 | 4.95 | ||||||
| Expired during the year | (17,522 | ) | 6.70 | |||||
| Outstanding, September 30, 2024, and 2025 | — | — | ||||||
| 15. | Related Party Transactions: |
Management compensation
Key management compensation comprises the following:
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Salaries, bonus and other benefits | 989 | 1,185 | ||||||
| Share based compensation | 681 | 969 | ||||||
| Key Management Personnel Compensation | 1,670 | 2,154 | ||||||
Share based compensation includes a portion of options that are granted but have not vested and are valued using the Monte Carlo valuation method. See details in Special Option Grants below:
Promissory note
Schedule of accrued interest
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Promissory Note (note 10(b)) | — | 519 | ||||||
Research Lab – Facility Usage Agreement
In May 2021, Electrovaya entered a month-to-month Facility Usage Agreement for the use of space and allocated staff of a third-party research firm providing access to laboratory facilities, primarily for research. The laboratory and pilot plant facilities have certain equipment and permits for research and developments with chemicals. The term of the agreement was for six months and could be terminated by either party upon 90 days notice.
In July 2021, the facility was acquired by an investor group controlled by the family of Dr. Sankar Das Gupta, which includes its CEO, Dr. Rajshekar Das Gupta. The Facility Usage Agreement was not changed on the change of ownership and remains in effect between the Company and the owner, such that the monthly payment of Cdn $26,922 is now made to a related party of Electrovaya.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
On June 7, 2023, the Facility Usage Agreement was retroactively extended from January 1, 2023, for an additional three years. The lease has been recognized as a lease liability, with a corresponding right of use asset. Total amount of rent paid to the related party in the financial year ending September 30, 2025, is $229 (September 30, 2024 : $231).
Special Options Grants
In September 2021, on the recommendation of the Compensation Committee of the Company, a committee composed entirely of independent directors, the Board of Directors of the Company determined that it is advisable and in the best interests of the Company to amend the terms of the compensation of certain key personnel to incentivize future performance, to encourage retention of their services, and to align their interests with those of the Company’s shareholders.
Dr. Sankar Das Gupta was granted 700,000 options which vest in two tranches of 200,000 options and one tranche of 300,000 options, based on reaching specific target market capitalizations. The fair value of these options on the day of grant is calculated using the Monte Carlo method of option valuation and expensed over the mean vesting period in accordance with IFRS 2. During the year ended September 30, 2025, the Company recognised stock-based compensation expense of $257 (September 30, 2024: $456).
Dr. Rajshekar Das Gupta was granted 900,000 options which vest in three tranches of 300,000 options based on reaching specific target market capitalizations. These fair value of these options on the day of issuance is calculated using the Monte Carlo method of option valuation and expensed over the mean vesting period in accordance with IFRS 2. During the year ended September 30, 2025, the Company recognised stock-based compensation expense of $Nil (September 30, 2024: $Nil).
In April 2023, following the suggestion of the Company's Compensation Committee, consisting entirely of independent directors, the Company's Board of Directors awarded Dr. Rajshekar Das Gupta a total of 600,000 options. These options will vest in two phases: 300,000 options and 300,000 options, contingent upon achieving certain target market capitalizations. During the year ended September 30, 2025, the Company recognised stock-based compensation expense of $79 (September 30, 2024: $512).
| 16. | Change in Non-Cash Operating Working Capital |
Schedule Of Change in Non-Cash Operating Working Capital
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Trade and other receivables | (5,182 | ) | (732 | ) | ||||
| Inventories | (3,043 | ) | (1,418 | ) | ||||
| Prepaid expenses and other | 1,035 | (1,693 | ) | |||||
| Trade and other payables | 68 | 1,588 | ||||||
| Total | (7,122 | ) | (2,255 | ) | ||||
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| 17. | Relief and Recovery Fund Payable |
The Relief and recovery fund is created by the Ministry of Economic Development to support the Company to recover from economic disruption associated with the COVID-19 outbreak. An amount of $300 (Cdn 380) was received as at September 30, 2021. The funding bears no interest, and the Company is required to repay in equal monthly payments for 5 years starting from April 1, 2023. The Company discounted the loan to the present value using the discount rate of 50%. Interest expense booked for the financial year ending September 30, 2025 is $41 (September 30, 2024: $48).
| 18. | Government Assistance |
The government assistance is related to specific Government supported research and development programs undertaken by Electrovaya. The National Research Council of Canada Industrial Research Assistance Program (IRAP) has provided $66 (Cdn $93) and Innovation Asset MSP contribution $23 (Cdn $32). This total was recorded within Government Grants in the consolidated statement of income (loss).
| 19. | Financial Instruments |
Derivative Liabilities
Warrants as derivative liability is fair valued using Black Scholes Model ("BSM"). Using this approach, the fair value of the warrants on November 09, 2022, was determined to be $3,265. Key valuation inputs and assumptions used in the BSM are stock price of CAD $4.55, expected life of 3 years, annualized volatility of 85.58%, annual risk-free rate of 3.87%, and annual dividend yield of 0.0%.
For the financial year ending September 30, 2025, key valuation inputs and assumptions used in the BSM when valuing the warrants as at September 30, 2025, were, stock price Cdn $8.20 (September 30, 2024 : Cdn $3.16), expected life of 0.11 years (September 30, 2024 : 1.1 years), annualized volatility of 87.03% (September 30, 2024 : 52.72%), annual risk-free rate of 2.49 % (September 30, 2024 : 2.94%), and dividend yield of 0.0 % (September 30, 2024 : 0.0%).
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
Fair Value
IFRS 13 “Fair Value Measurement” provides guidance about fair value measurements. Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value are required to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The fair value hierarchy is based on three levels of inputs. The first two levels are considered observable and the last unobservable. These levels are used to measure fair values as follows:
| ● | Level 1 – Quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities, either directly or indirectly. |
| ● | Level 2 – Inputs, other than Level 1 inputs that are observable for assets and liabilities, either directly or indirectly. Level 2 inputs include quoted market prices for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in markets that are not active; or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities. |
| ● | Level 3 – Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. |
Schedule Of Warrant Fair Value
| Fair Value | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||||||
| Warrants | 144 | — | 144 | — | ||||||||||||
There were no transfers between Level 1 and Level 2 during 2025.
Risk Management
The Company may be exposed to risks of varying degrees of significance which could affect its ability to achieve its strategic objectives. The main objectives of the Company’s risk management processes are to ensure that the risks are properly identified and that the capital base is adequate in relation to those risks. The principal risks to which the Company is exposed are described below. There have been no changes in risk exposure since the prior year unless otherwise noted.
Capital risk
The Company manages its capital to ensure that there are adequate capital resources for the Company to maintain and develop its products. The capital structure of the Company consists of shareholders’ equity and depends on the underlying profitability of the Company’s operations.
The Company manages its capital structure and makes adjustments to it, based on the funds available to the Company, in order to support the development, manufacture and marketing of its products. The Board of Directors does not establish quantitative return on capital criteria for management, but rather relies on the expertise of the Company’s management to sustain future development of the business.
The Company's capital management objectives are:
| ● | to ensure the Company's ability to continue as a going concern. |
| ● | to provide an adequate return to shareholders by pricing products and services commensurately with the level of risk. |
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
The Company monitors capital based on the carrying amount of equity plus its short-term debt comprised of the promissory notes, less cash and cash equivalents as presented on the face of the consolidated statement of financial position.
The Company sets the amount of capital in proportion to its overall financing structure, comprised of equity and long-term debt. The Company manages the capital structure and makes adjustments to it in the light of changes in economic conditions and the risk characteristics of the underlying assets. In order to maintain or adjust the capital structure, the Company issues new shares or increases its long-term debt.
Credit risk and Concentration risk
Credit risk is the risk that the counterparty fails to discharge an obligation to the Company. The Company is exposed to this risk due to its cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash and , trade and other receivables.
The Company manages its credit risk related to trade and other receivables by establishing procedures to establish credit limits and approval policies. The balance in trade and other receivables is primarily attributable to trade accounts receivables. In the opinion of management, the credit risk is moderate and minimum credit losses are expected. Management is taking appropriate action to mitigate this risk by adjusting credit terms.
The Company is exposed to credit risk in the event of default by its customers. Trade receivables are recorded at the invoiced amount, do not bear interest, and do not require collateral. For the year ended September 30, 2025, two customers accounted for $52,978 or 83% of revenue (September 30, 2024: two customers accounted for $38,900 or 87.21%). As of September 30, 2025, two customers accounted for 88 % of accounts receivable (September 30, 2024: 96%). Refer Note 5 for expected credit loss provision.
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company may not have cash available to satisfy its financial obligations as they come due. The majority of the Company's financial liabilities recorded in accounts payable, accrued and other current liabilities and provisions are due within 90 days. The Company manages liquidity risk by maintaining a portfolio of liquid funds and having access to a revolving credit facility. The Company believes that cash flow from operating activities, together with cash on hand, cash from its trade and other receivables, and borrowings available under the revolving facility are sufficient to fund its currently anticipated financial obligations and will remain available in the current environment.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
The following are the undiscounted contractual maturities of significant financial liabilities and the total contractual obligations of the Company as at September 30, 2025:
Schedule Of financial liabilities
| 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 & beyond | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Trade and other payables | 9,555 | — | — | — | — | 9,555 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lease liability | 761 | 719 | 735 | 752 | 189 | 3,156 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Long term loan | — | 969 | 18,641 | 969 | 1,938 | 22,517 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other payable | 196 | 239 | 239 | 225 | 491 | 1,390 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total financial liabilities | 10,512 | 1,927 | 19,615 | 1,946 | 2,618 | 36,618 | ||||||||||||||||||
The following are the undiscounted contractual maturities of significant financial liabilities and the total contractual obligations of the Company as at September 30, 2024:
| 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 & beyond | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Trade and other payables | 9,460 | — | — | — | — | 9,460 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lease liability | 760 | 598 | 555 | 571 | 588 | 3,072 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Short term loan | 1,630 | — | — | — | — | 1,630 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Promissory note | 519 | — | — | — | — | 519 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Working capital facility | 16,283 | — | — | — | — | 16,283 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other payable | 211 | 188 | 208 | 218 | 610 | 1,435 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total financial liabilities | 28,863 | 786 | 763 | 789 | 1,198 | 32,399 | ||||||||||||||||||
Market risk
Market risk incorporates a range of risks. Movement in risk factors, such as market price risk and currency risk, affect the fair value of financial assets and liabilities. The Company is exposed to these risks as the ability of the Company to develop or market its products and the future profitability of the Company is related to the market price of its primary competitors for similar products.
Interest rate risk
The Company has variable interest debt as described in Note 10 and 12. Changes in interest rates will affect future interest expense and cash flows. The Company does not enter derivative instruments to reduce this exposure. A 10% change in interest rate would result in change in finance cost by $209 (September 30, 2024: $213).
Foreign currency risk
The Company is exposed to foreign currency risk. The Company’s functional currency is the United States dollar (Electrovaya Inc.'s functional currency is CAD) and the financial statements are presented in United States dollars. Changes in the relative values of these currencies will give rise to changes in other comprehensive income.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
Purchases are transacted in Canadian dollars, United States dollars and Euro. Management believes the foreign exchange risk derived from any currency conversions may have a material effect on the results of its operations. The financial instruments impacted by a change in exchange rates include exposures to the above financial assets or liabilities denominated in nonfunctional currencies. Cash held by the Company in US dollars at September 30, 2025, was $1,590 (September 30, 2024: $159).
If the US dollar to Canadian foreign exchange rate changed by 2% this would change the recorded net gain(loss) by $285 (September 30, 2024: $174).
| 20. | Contingencies |
| a. | Refundable Ontario Investment Tax Credits |
On July 22, 2022, the Company received a Notice of Confirmation from the CRA relating to the 2014 and 2015 SRED reassessment for $299 (Cdn$386) and $302 (Cdn$389) including interest, respectively. The balance owing has been fully provided for in other payables, and the Company is pursuing the next appropriate step in the appeal process and believes the amounts may be reversed or substantially reduced. The outcome cannot be determined.
| b. | Ministry of Energy |
On May 28, 2018, the Province of Ontario issued a claim against Electrovaya Corp. claiming $655 (Cdn $830) related to a dispute regarding funding and fulfilment of the Intelligent Energy Storage System under the Smart Grid Fund program. A Statement of Defense disputing the claim in its entirety was filed on March 21, 2019. No further steps have been taken by the province to pursue the claim.
| c. | Other Contingencies |
In the normal course of business, the Company is party to business related claims. The potential outcomes related to existing matters faced by the Company are not determinable at this time. The Company intends to defend these actions, and management believes that the resolution of these matters will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition.
| 21. | Segment and Customer Reporting |
The Company develops, manufactures and markets power technology products. There is only a single segment applicable to the Company.
Given the size and nature of the products produced, the Company’s sales are segregated based on large format batteries, with the remaining smaller product line categorized as “Other”.
There has been no change in either the determination of the Company's segments, or how segment performance is measured, from that described in the Company’s consolidated financial statements as at and for the year ended September 30, 2025.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
Schedule Of segment performance
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Large format batteries | 63,336 | 42,970 | ||||||
| Other | 490 | 1,645 | ||||||
| Total of Large format batteries | 63,826 | 44,615 | ||||||
Revenues can also be analyzed as follows based on the nature of the underlying deliverables:
Schedule Of Revenues
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Revenue with customers | ||||||||
| Sale of batteries and battery systems | 63,336 | 42,970 | ||||||
| Sale of services | 240 | 983 | ||||||
| Grant income | ||||||||
| Research grant | 250 | 26 | ||||||
| Others | — | 636 | ||||||
| Total of Revenue with customers | 63,826 | 44,615 | ||||||
Revenues attributed to geographical regions based on the location of the customer were as follows:
Schedule of Revenues Based on Geographical Region
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Canada | 2,499 | 1,655 | ||||||
| United States | 60,718 | 42,784 | ||||||
| Others | 609 | 176 | ||||||
| Total | 63,826 | 44,615 | ||||||
| 22. | Other payables |
Technology Partnerships Canada (“TPC”) projects were long-term (up to 30 years) commencing with an R&D phase, followed by a benefits phase – the period in which a product, or a technology, could generate revenue for the Company. In such cases, repayments would flow back to the program according to the terms and conditions of the Company’s contribution agreement.
In June 2018, the contribution agreement was amended and is included at its net present value in other payables. Further, in September 2024, the agreement was further amended with amended terms and conditions for the repayment of the debt with new payment schedule. Consequently, the old debt was de-recognised in the books of accounts and the new debt was introduced with first payment starting in July 2025 and final payment to be discharged in July 2031.
The following table represents changes in the provision for repayments to Industry Canada.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
Schedule Of Other payables
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Opening balance | 379 | 984 | ||||||
| Interest accretion | 114 | 490 | ||||||
| Foreign exchange | (12 | ) | — | |||||
| Payment made during the year | (149 | ) | — | |||||
| Debt extinguishment | — | (1,474 | ) | |||||
| Recognition of new debt | — | 370 | ||||||
| Interest accretion on new debt | — | 9 | ||||||
| Ending balance | 332 | 379 | ||||||
| Less: current portion of the provision (included in Trade and other payables) | (23 | ) | (36 | ) | ||||
| Ending balance of long-term portion | 309 | 343 | ||||||
Following is the payment schedule for TPC:
Schedule Of latest repayment
| Year | Amount | ||||
| 2026 | 132 | ||||
| 2027 | 132 | ||||
| 2028 | 132 | ||||
| 2029 | 132 | ||||
| 2030 | 132 | ||||
| 2031 | 132 | ||||
| 23. | Income-tax |
The income tax recovery differs from the amount computed by applying the Canadian statutory income tax rate of 26.50% (2024 – 26.50%) to the loss before income taxes as a result of the following:
Schedule of Income Tax
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Income (Loss) before income taxes | 1,310 | (1,485 | ) | |||||
| Expected recovery of income taxes based on | 347 | (394 | ) | |||||
| statutory rates | ||||||||
| Reduction in income tax recovery resulting from: | ||||||||
| Foreign tax rate differential | (96 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||
| Other permanent differences | 772 | 246 | ||||||
| Share issue costs allocated to equity | (427 | ) | — | |||||
| Expiry of losses | 372 | — | ||||||
| Deferred tax benefit not recognized | — | 157 | ||||||
| Deferred tax benefits previously unrecognised | (3,021 | ) | — | |||||
| Income tax recovery | (2,053 | ) | — | |||||
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
The components of deferred income taxes as at September 30, 2025 and 2024 are as follows:
Schedule of components of deferred tax
| Opening, October 1, 2024 | Recognized in P&L | Recognized in OCI | Closing, September 30, 2025 | |||||||||||||
| Deferred Tax Assets: | ||||||||||||||||
| Canadian non-capital loss carry forwards | 452 | 1,734 | (2 | ) | 2,184 | |||||||||||
| US net operating losses | 348 | (58 | ) | — | 290 | |||||||||||
| Deferred tax assets recognized | 800 | 1,676 | (2 | ) | 2,474 | |||||||||||
| Deferred Tax Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized foreign exchange | 1 | (1 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | (801 | ) | 378 | 16 | (407 | ) | ||||||||||
| (800 | ) | 377 | 16 | (407 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net Deferred tax asset (liability) | — | 2,053 | 14 | 2,067 | ||||||||||||
| Opening, October 1, 2023 | Recognized in P&L | Closing, September 30, 2024 | ||||||||||
| Deferred Tax Assets | ||||||||||||
| Canadian non-capital loss carry forwards | 602 | (150 | ) | 452 | ||||||||
| US net operating losses | 408 | (60 | ) | 348 | ||||||||
| Deferred tax assets recognized | 1,010 | (210 | ) | 800 | ||||||||
| Deferred Tax Liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Unrealized foreign exchange | (11 | ) | 12 | 1 | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | (999 | ) | 198 | (801 | ) | |||||||
| (1,010 | ) | 210 | (800 | ) | ||||||||
| Net Deferred tax asset (liability) | — | — | — | |||||||||
In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the future tax assets will be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of deferred taxable income during the year in which those temporary differences become deductible.
Management considers projected future taxable income, uncertainties related to the industry in which the Company operates and tax planning strategies in making this assessment.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
The Company concluded that there is uncertainty regarding the future recoverability of Company’s deferred income tax assets in future periods. Therefore, deferred tax assets have not been recognized in the financial statements with respect to the following deductible temporary differences:
Schedule Of operating deferred tax assets
| September 30, 2025 | September 30, 2024 | |||||||
| Canadian non-capital loss carry forwards | 26,055 | 41,904 | ||||||
| Canadian capital loss carry forwards | 18 | 69 | ||||||
| US net operating losses | 4,681 | 5,332 | ||||||
| Lease liabilities | 1,815 | 2,342 | ||||||
| Disallowed interest carry forwards | 1,952 | 1,780 | ||||||
| Unclaimed research and development expenses | 15,378 | 15,852 | ||||||
| Non-refundable research and development credits | 15,427 | 19,524 | ||||||
| Share issuance cost | 1,829 | — | ||||||
| Other | 1,192 | 1,121 | ||||||
| Total | 68,347 | 87,924 | ||||||
The Company has Unrecognized losses that expire as early as 2026 as follows:
Schedule of Unrecognized losses
| Year of expiry | Canada | USA | ||||||
| 2026 | 141 | 192 | ||||||
| 2027 | 403 | 678 | ||||||
| 2028 | 3,736 | 49 | ||||||
| 2029 | — | 356 | ||||||
| 2030 | 303 | 665 | ||||||
| 2031 | — | 1,083 | ||||||
| 2032 | 615 | 195 | ||||||
| 2033 | 966 | 149 | ||||||
| 2034 | — | 29 | ||||||
| 2035 | 2,134 | — | ||||||
| 2036 | 1,585 | 14 | ||||||
| 2037 | 2,114 | 2 | ||||||
| 2038 | 5,928 | — | ||||||
| 2039 | 2,128 | — | ||||||
| 2040 | 533 | — | ||||||
| 2041 | 4,953 | — | ||||||
| 2042 | 516 | — | ||||||
| 2043 | — | — | ||||||
| 2044 | — | — | ||||||
| 2045 | — | — | ||||||
| Indefinite | — | 1,269 | ||||||
| 26,055 | 4,681 | |||||||
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated)
For the years ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024
| 24. | Subsequent events |
On November 05, 2025, the Company announced underwritten marketed offering of common shares in the capital of the Company. The Company announced the pricing of the Offering at a price of $5.20 per Common Share (the Offering Price”). The Company closed the Offering on November 6, 2025, issuing an aggregate of 5,405,000 Common Shares (including 705,000 Common Shares issued pursuant to the full exercise of the Over-Allotment Option at the Offering Price for aggregate gross proceeds to the Company of $28,106,000.
|
|
Exhibit 99.3

ELECTROVAYA INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS FOR THE YEAR ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2025
DECEMBER 10, 2025
ELECTROVAYA INC. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
| 1. | OUR BUSINESS | 5 |
| 2. | OUR STRATEGY | 5 |
| 3. | RECENT DEVELOPMENTS | 6 |
| 4. | SELECTED ANNUAL FINANCIAL INFORMATION | 10 |
| 5. | LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES | 18 |
| 6. | OUTSTANDING SHARE DATA | 19 |
| 7. | OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS | 19 |
| 8. | RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS | 19 |
| 9. | CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES | 19 |
| 10. | CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND RECENT ACCOUNTING PRONOUNCEMENTS | 20 |
| 11. | FINANCIAL AND OTHER INSTRUMENTS | 20 |
| 12. | DISCLOSURE CONTROLS | 20 |
| 13. | INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING | 20 |
| 14. | QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT RISKS AND UNCERTAINTIES | 21 |
| 15. | OTHER RISKS | 25 |
| ● | Introduction |
Management’s discussion and analysis (“MD&A”) provides our viewpoint on our Company, performance and strategy. “We,” “us,” “our,” “Company” and “Electrovaya” include Electrovaya Inc. and its wholly owned or controlled subsidiaries, as the context requires.
Our Board of Directors, on the recommendation of its Audit Committee, approved the content of this MD&A on December 10, 2025, and it is, therefore, dated as at that date. This MD&A includes the operating and financial results for the quarters and year ending September 30, 2025, and 2024, and should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements. It includes comments that we believe are relevant to an assessment of and understanding of the Company’s consolidated results of operations and financial condition. The financial information herein is presented in thousands of US dollars unless otherwise noted (except per share amounts, which are presented in US dollars unless otherwise noted), in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”). Additional information about the Company, including Electrovaya’s current annual information form, can be found on the SEDAR website for Canadian regulatory filings at www.sedar.com and the EDGAR website for SEC regulatory filings at sec.gov/EDGAR.
|
|
| ● | Forward-looking statements |
This MD&A contains forward-looking statements, including statements that relate to, among other things, revenue, purchase orders, revenue guidance of more than 30% revenue growth (exceeding $83 million) over FY 2025 in FY 2026, order growth and customer demand in FY 2026, mass production schedules, , the Company’s ability to start production of cells at the Jamestown, New York facility by end of FY 2026, future business opportunities, use of proceeds, ability to deliver to customer requirements and revenue growth forecasts for the fiscal year ending September 30, 2026. Forward-looking statements can generally, but not always, be identified by the use of words such as “may”, “will”, “could”, “should”, “would”, “likely”, “possible”, “expect”, “intend”, “estimate”, “anticipate”, “believe”, “plan”, “objective” and “continue” (or the negative thereof) and words and expressions of similar import. Although the Company believes that the expectations reflected in such forward-looking statements are reasonable, assumptions and analyses made by the Company in light of the experience and perception of historical trends, current conditions and expected future developments and other factors it believes are appropriate are necessarily applied in making forward looking statements and such statements are subject to risks and uncertainties, therefore actual results may differ materially from those expressed or implied in such statements and undue reliance should not be placed on such statements. Material assumptions made in disclosing the forward-looking statements included in the news release include, but are not limited to assumptions that the Company’s customers will deploy its products in accordance with communicated timing and volumes, that the Company’s customers will complete new distribution centers in accordance with communicated expectations, intentions and plans, the sum of anticipated new orders in FY 2026 based on customers’ historical patterns and additional demand communicated to the Company and its partners but not yet provided as a purchase order with the Company’s current firm purchase order backlog totaling approximately $100-125 million, a discount of approximately 25% used in the revenue modeling applied to the overall expected order pipeline to account for potential delays in customer orders, expected decreases in input and material costs combined with stable selling prices in FY 2026, and a stable political climate with respect to exports from Canada to the United States, the start up time for manufacturing in Jamestown NY is estimated towards the end of FY 2026 or first quarter of FY 2027, the ability to leverage IRA45X credits, the ability to receive incentives from the state of New York, the ability to improve margins from domestic manufacturing, and the ability to attract additional customers through domestic manufacturing. Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from expectations include but are not limited to customers not placing orders roughly in accordance with historical ordering patterns and communicated intentions resulting in annual revenue growth in FY 2026 of more than 30% over FY 2025 (exceeding $83 million), the predictability of sales and success of the Company’s products in verticals other than material handling, the imposition of a tariff regime on Canadian exports by the United States, macroeconomic effects on the Company and its business and on the lithium battery industry generally, the Company’s liquidity and cash availability in excess of its operational requirements, and the ability to generate and sustain sales orders. Additional information about material factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from expectations and about material factors or assumptions applied in making forward-looking statements may be found in the Company’s Annual Information Form for the year ended September 30, 2025 under “Risk Factors”, in the Company’s base shelf prospectus dated September 17, 2024, and in the Company’s most recent annual and interim Management’s Discussion and Analysis under “Qualitative And Quantitative Disclosures about Risk and Uncertainties” as well as in other public disclosure documents filed with Canadian securities regulatory authorities. The Company does not undertake any obligation to update publicly or to revise any of the forward-looking statements contained in this document, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.
|
|
The revenue for the periods described herein constitute future-oriented financial information and financial outlooks (collectively, “FOFI”), and generally, is, without limitation, based on the assumptions and subject to the risks set out above under “Forward-Looking Statements”. Although management believes such assumptions to be reasonable, a number of such assumptions are beyond the Company’s control and there can be no assurance that the assumptions made in preparing the FOFI will prove accurate. FOFI is provided for the purpose of providing information about management’s current expectations and plans relating to the Company’s future performance and may not be appropriate for other purposes.
The FOFI does not purport to present the Company’s financial condition in accordance with IFRS, and it is expected that there may be differences between audited results and preliminary results, and the differences may be material. The inclusion of the FOFI in this news release disclosure should not be regarded as an indication that the Company considers the FOFI to be a reliable prediction of future events, and the FOFI should not be relied upon as such.
|
|
ELECTROVAYA INC. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
| 1. | OUR BUSINESS |
Electrovaya is a technology-focused lithium-ion battery company engaged in the design, development and manufacturing of advanced battery cells, modules and systems. The Company’s products primarily are based on its proprietary Infinity Battery Technology, which incorporates ceramic-enhanced lithium-ion cell constructions and advanced materials that deliver high safety performance, long cycle life and strong durability in demanding operating environments. These characteristics make Electrovaya’s products suitable for mission-critical applications, including material-handling equipment, robotic and autonomous vehicles, heavy-duty electric vehicles, defense-related platforms and stationary energy-storage systems.
Electrovaya’s development activities draw upon capabilities in electrochemistry, materials science, mechanical and electrical engineering, and battery-management software. The Company maintains an expanding intellectual-property portfolio related to advanced materials, cell designs, ceramic components, separator technologies and system-level battery architectures. Electrovaya is also engaged in programs related to next-generation solid-state and hybrid solid-state battery technologies, as well as improvements to its existing Infinity platform.
The Company has a battery and battery systems research and manufacturing facility in Mississauga, Ontario at 6688 Kitimat Road. The location, which comprises approximately 62,000 square feet, is designed to enhance the Company’s productivity and efficiency. The Company also owns a 52-acre site including a 137,000 square foot manufacturing site at 1 Precision Way in Jamestown New York. This site is intended to be Electrovaya’s US headquarters and a key manufacturing hub. The setup of the Jamestown manufacturing hub started in later part of FY2025 and will continue through FY 2026 with aim of commercial cell manufacturing in early FY 2027. Following completion and commissioning, the facility is expected to increase production capacity and provide U.S.-based manufacturing capabilities aligned with evolving supply-chain and national energy-security objectives. The Company maintains research, engineering and manufacturing operations and has operating personnel in both Canada and the USA.
The Company’s commercial offerings include low-voltage and high-voltage battery systems supplied to a range of industrial and transportation markets. These include material-handling equipment, robotic vehicles, airport ground-support equipment, speciality defense applications, construction and mining equipment, electric buses and trucks, and grid-connected or behind-the-meter energy-storage installations. While the material-handling sector has historically represented a significant share of the Company’s revenue, Electrovaya continues to expand into adjacent markets where long operating life, enhanced safety and reliable high-power performance are essential.
| 2. | OUR STRATEGY |
We have developed a highly proprietary and specialized lithium-ion technology that provides superior cycle life and safety. Given these advantages, the Company is focused on applications where those two performances differentiators provide the greatest benefits which has led to a focus on heavy duty and mission critical applications. These often require battery systems to provide around the clock operational capability, longer life and better safety and include material handling, robotics, transit, aerospace and other intensive electrified applications. We developed cells, modules, battery management systems, software and firmware necessary to deliver systems for these intensive applications. We also developed supply chains which can produce needed components including separators, electrolytes with appropriate additives, cells and cell assembly, modules, electronic boards, electrical and mechanical components as needed for our battery systems. Our goal is to utilize our battery and systems technology to develop and commercialize mass-production levels of battery systems for our targeted end markets.
|
|
To achieve these strategic objectives, we intend to:
| ● | Establish global strategic relationships in order to broaden the market potential of our products and services. |
| ● | Develop and commercialize leading-edge technology for heavy duty and mission critical electrified applications, as well as partnering with key large organizations to bring them to market. |
| ● | Invest in research and development initiatives related to new technologies that reduce the costs of our products, but enhance the operating performance, of our current and future products; and, |
| ● | Focus on intensive use and mission critical applications such as the logistics and e-commerce industry, automated guided vehicles, electric buses, energy storage and similar other applications. |
| 3. | RECENT DEVELOPMENTS |
On October 17, 2024, the Company announced a CDN$2 million investment from the Government of Canada through the Federal Economic Development Agency for Southern Ontario. The funding will be used to support investments in automation, AI and capacity enhancements at the Company’s Mississauga, Ontario manufacturing facility.
On November 12, 2024, the Company announced it had received a purchase order valued at approximately US$3.5 million for immediate delivery of its batteries from one of its OEM sales channels. The batteries will be used by a leading Fortune 100 e-commerce company in the United States and Australia for powering material handling electric vehicles in its warehouse operations.
On November 14, 2024, the Company announced that it has secured a direct loan in the amount of US$50.8 million from the Export-Import Bank of the United States (“EXIM”) under the bank’s ‘Make More in America’ initiative. This financing will fund Electrovaya’s battery manufacturing buildout in Jamestown, New York including equipment, engineering and setup costs for the facility.
On December 3, 2024, the Company announced it had received a purchase order valued at approximately US$4.1 million for immediate delivery of its batteries. The batteries will be used by a leading Fortune 500 retailer in the United States for powering material handling electric vehicles in two existing warehouse sites. Additional sites are also being planned for conversion on top of the two orders received.
|
|
On December 16, 2024, the Company announced that its Infinity Series Lithium-Ion Phosphate (LFP) based cell had successfully achieved UL2580 recognition. This milestone underscores the exceptional safety and reliability of Electrovaya’s battery technology, meeting the rigorous safety standards set by UL2580, including the stringent external fire test (projectile test).
On December 18, 2024, the Company announced that in connection with its previously completed public offering of 5,175,000 common shares in the capital of the Company (the “Common Shares”) at the price of US$2.15 per Common Share (the “Offering Price”) for gross proceeds of approximately US$11.1 million (the “Offering”) that Roth Capital Partners, acting as sole book-running manager, and Raymond James Ltd. and Craig-Hallum Capital Group LLC acting as the co-lead book-running managers in the Offering, have purchased an additional 776,250 Common Shares at the Offering Price, for additional gross proceeds to the Company of US$1,668,937.50, before deducting the underwriting commissions, pursuant to their exercise in full of the over-allotment option (the “Over-Allotment Option”). After giving effect to the full exercise of the Over-Allotment Option, the Company sold 5,951,250 Common Shares under the Offering, for aggregate gross proceeds of US$12,795,188.00.
On March 4, 2025, the Company announced it has received a purchase order through its OEM sales channel valued at approximately US$4.2 million. The batteries will be used by a rapidly growing cold storage third party logistics operator in the United States for powering material handling electric vehicles. The end user currently operates six facilities with Electrovaya’s Infinity Battery Technology.
On March 6, 2025, the Company announced that it has received orders from a second global construction OEM through its partnership with Sumitomo Corporation Power & Mobility (“SCPM”), a 100% subsidiary of Sumitomo Corporation (TYO:8053). This order is for high voltage battery systems for a leading global Japanese headquartered construction equipment manufacturer. The orders were placed under Electrovaya’s existing Supply Agreement with SCPM and will be delivered in Japan in 2025.
On March 10, 2025, the Company announced that it has closed a direct loan in the amount of US$50.8 million from the Export-Import Bank of the United States (“EXIM”) under the bank’s ‘Make More in America’ initiative.
On March 10, 2025, the Company announced that it has closed a credit agreement with the Bank of Montreal Corporate Finance (“BMO”) for a senior secured asset based lending facility (the “Facility”) which includes a three year term and which includes the following features:
| ● | Revolving asset based facility of US $20.0 Million |
| ● | Accordion of US $5.0 million to support further growth when required |
| ● | Ancillary
credit products for foreign currency hedging and credit cards |
On March 27, 2025, the Company announced it had received purchase orders through its OEM sales channel valued at approximately US$7.3 million. The batteries will be used by a leading Fortune 100 e-commerce company in the United States and Canada for powering material handling electric vehicles in multiple distribution centers. This order followed a recent $3.5 million order from the same end customer that was placed in November 2024.
|
|
On April 1, 2025, the Company announced it had received a purchase order valued at approximately US$8.7 million. The batteries
will be used by a leading Fortune 500 retailer in the United States for powering material handling electric vehicles in three
existing warehouse sites. This order followed a recent $4.1million order from the same end customer for two distribution centers
that was placed in December 2024.
On April 30, 2025, the Company announced that it received the Make More in America Deal of the Year award from the Export Import Bank of the United States.
On May 7, 2025, the Company announced that it had begun battery systems manufacturing operations out of its Jamestown New York facility. It also announced that it had placed over $40 million worth of capital equipment orders to prepare for cell and module manufacturing, slated to begin in mid 2026.
On June 3, 2025, the Company announced that it has received a repeat order valued at approximately $6.3 million from a Fortune 100 e-commerce customer for infinity battery systems.
3.1 Business Highlights, Subsequent Events and 2026 Outlook
Business Highlights - Q4 FY 2025
On July 8, 2025, the Company announced that it has entered into a Commercial Supply Agreement with Janus Electric Holdings Limited (ASX:JNS), an Australia based pioneer in the electrification of heavy transport vehicles.
On July 15, 2025, the Company announced the receipt of new purchase orders totaling approximately US$4.5 million through its OEM sales channel.
On July 22, 2025, The Company announced that it has launched multiple battery system products for a variety of robotic vehicle platforms. These battery systems developed in collaboration with three major OEM partners, with 2 based in the USA and 1 in Japan for a variety of robotic vehicle applications ranging from material handling to surveillance applications. Initial deliveries to all three OEMs will begin in the current quarter with anticipated commercial deliveries accelerating from FY 2026 onwards.
On July 29, 2025, the Company announced the launch of multiple battery system products designed specifically for airport ground support equipment (GSE). Developed in collaboration with a major original equipment manufacturer (OEM) supplier, these innovative systems support a broad range of electrified ground support equipment (GSE) applications, including airplane tuggers, baggage tractors, belt loaders, cargo loaders, and more.
On September 3, 2025, the Company announce that it has successfully completed shipment of its first battery modules to Japan from its Canadian manufacturing facility.
On September 9, 2025, the Company announced the commercial launch of its next-generation Energy Storage Systems (“ESS”), developed to address the growing demand for safe, durable, and cost-effective stationary energy storage solutions.
|
|
On September 17, 2025, the Company announced that it has commenced drawdowns on its $50.8 million EXIM debt Facility (“Facility”) which is tied to capital and engineering expenses at its Jamestown, NY facility.
Subsequent Events
On October 31, 2025, the Company announced the establishment of a subsidiary in Japan. The new entity, Electrovaya Japan, will serve as a local platform to expand the Company’s commercial activities and to support its growing customer base and strategic relationships across the Japanese market.
On November 4, 2025, the Company announced that it was commencing an underwritten public offering (the “Offering”) of its common shares (the “Common Shares”). The Company expects to grant the underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to an additional 15% of Common Shares at the public offering price. All of the Common Shares are being offered by the Company.
On November 5, 2025, the Company announced the pricing of its previously announced public offering (the “Offering”) of 4,700,000 common shares of the Company (“Common Shares”) at a price to the public of US$5.20 per Common Share. The Company has granted the underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to an additional 705,000 Common Shares at the public offering price, less underwriting discounts and commissions.
On November 6, 2025, the Company announced the closing of its previously announced public offering (the “Offering”) of 4,700,000 common shares of the Company (“Common Shares”) at a price to the public of US$5.20 per Common Share. The underwriters elected to exercise the overallotment option in full, resulting in an additional 705,000 Common Shares being issued today for aggregate gross proceeds, before deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and other offering expenses payable by Electrovaya, of approximately US$28.1 million.
Positive Financial Outlook:
The Company anticipates strong growth into FY2026 with estimated revenues growth to exceed 30% over FY 2025 (in excess of $83 million) driven by continuing demand from the Company’s largest end users of material handling batteries and our entry into additional market verticals. This guidance is prepared by taking into account its existing purchase orders, along with anticipated pipeline from its key end users and customers. This guidance also takes into consideration a percentage of anticipated revenue that potentially may be deferred to FY 2027. This guidance is subject to change and is made barring any unforeseen circumstances. See “Forward-Looking Statements”.
|
|
| 4. | SELECTED ANNUAL FINANCIAL INFORMATION |
| 4.1 | Operating Segments |
The Company has reviewed its operations and determined that it operates in one business segment and has only one reporting unit. The Company develops, manufactures and markets power technology products.
| 4.2 | Selected Annual Financial Information for the Years Ended September 30, 2025, 2024 and 2023 |
Results of Operations
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars)
| Year Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | ||||||||||
| Total Revenue | 63,826 | 44,615 | 44,059 | |||||||||
| Direct manufacturing costs | 44,106 | 30,926 | 32,203 | |||||||||
| Gross margin | 19,720 | 13,689 | 11,856 | |||||||||
| GM% | 30.9 | % | 30.7 | % | 26.9 | % | ||||||
| Expenses | ||||||||||||
| Research & development | 4,379 | 3,038 | 3,382 | |||||||||
| Government assistance | (89 | ) | (316 | ) | (387 | ) | ||||||
| Sales & marketing | 2,928 | 2,935 | 1,897 | |||||||||
| General & administrative | 3,679 | 3,939 | 3,687 | |||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 1,756 | 2,155 | 1,167 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 1,527 | 1,209 | 907 | |||||||||
| 14,180 | 12,960 | 10,653 | ||||||||||
| Income from operations | 5,540 | 729 | 1,203 | |||||||||
| Finance Cost | 2,755 | 3,700 | 2,835 | |||||||||
| Change in derivative liability | 915 | (1,334 | ) | (361 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign exchange (gain)/loss | 560 | (152 | ) | 887 | ||||||||
| 1,310 | (1,485 | ) | (2,158 | ) | ||||||||
| Income tax recovery | 2,053 | — | 679 | |||||||||
| Net income (loss) for the year | 3,363 | (1,485 | ) | (1,479 | ) | |||||||
Revenue
Revenue increased to $63.8 million, compared to $44.6 million for the years ended September 30, 2025 and 2024 respectively, an increase of $19.21 million or 43.1%. A significant increase over both years. Revenue was predominantly from the sale of batteries and battery systems for MHEVs. Batteries and battery systems accounted for $63.34 million or 99.2% of revenue for FY 2025 and $42.9 million or 96.3% for FY2024. Sale of engineering services, research grants, and other sources of revenue, including Government assistance, accounted for the remaining $0.49 million or 0.8% in FY 2025 and $1.6 million or 3.7% in FY 2024.
|
|
| Year Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | ||||||||||
| Battery Systems | 63,336 | 42,970 | 42,168 | |||||||||
| Services | 240 | 983 | 216 | |||||||||
| Research Grants | 250 | 26 | 693 | |||||||||
| Other Revenue | — | 636 | 982 | |||||||||
| 63,826 | 44,615 | 44,059 | ||||||||||
Direct Manufacturing Costs and Gross Margin
Direct manufacturing costs are comprised of materials, labour and manufacturing overhead, excluding amortization, associated with the production of batteries and battery packs for Electric Vehicles, stationary grid applications and research and engineering service revenues.
The gross margin increased to $19.7 million, compared to $13.7 million for the year ended September 30, 2025 and September 30, 2024, respectively, an increase of $6.0 million or 44.1%. The gross margin percentage was 30.9% for the year ended September 30, 2025, compared to 30.7% for the prior year.
| Year ended September 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | ||||||||||
| Total revenue | 63,826 | 44,615 | 44,059 | |||||||||
| Direct manufacturing cost | 44,106 | 30,926 | 32,203 | |||||||||
| Gross margin | 19,720 | 13,689 | 11,856 | |||||||||
| GM% | 30.9 | % | 30.7 | % | 26.9 | % | ||||||
When reviewing gross margin by revenue stream, the main driver of revenue, Battery Systems, shows a gross margin of 30.9% for the year.
| Year Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||
| Revenue | GM % | GM $ | ||||||||||
| Battery Systems | 63,336 | 30.9 | % | 19,579 | ||||||||
| Services | 240 | 30.0 | % | 72 | ||||||||
| Other Revenue | 250 | 27.6 | % | 69 | ||||||||
| 63,826 | 30.9 | % | 19,720 | |||||||||
Our margin varies from period to period due to a number of factors including the product mix, special customer pricing, material cost, shipping costs and foreign exchange movement. In the current fiscal year, we have been able to take advantage of strong operational efficiencies and some economies of scale to help improve margins. The Company continues to monitor gross margin closely and has implemented measures to increase it for fiscal year 2026.
|
|
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses include:
| ● | Research and Development (“R&D”): Research and development expenses consist primarily of compensation and premises costs for research and development personnel and activities, including independent contractors and consultants, and direct materials; |
| ● | Government Assistance: The company applied for and received funding from the Industrial Research Assistance Program during the year; |
| ● | Sales and Marketing: Sales and marketing expenses are comprised of the salaries and benefits of sales and marketing personnel, marketing activities, advertising and other costs associated with the sales of Electrovaya’s product lines; |
| ● | General and Administrative: General and administrative expenses include salaries and benefits for corporate personnel, insurance, professional fees, reserves for bad debts and facilities expenses. The Company’s corporate administrative staff includes its executive officers and employees engaged in business development, financial planning and control, legal affairs, human resources and information technology; |
| ● | Stock based compensation: Recognizes the value based on Black-Scholes option pricing model of stock based compensation expensed over the relevant vesting period; |
| ● | Depreciation and Amortization: Expenses relating to the depreciation and amortization of capital equipment, leasehold improvements and other assets. |
Total operating expenses are $14.2 million compared to $12.9 million for the years ended September 30, 2025, and September 30, 2024, respectively, resulting in an increase of $1.2 million or 9.4% and $3.5 million or 33.1%. Within the year, R&D expenses increased by $1.3 million laying emphasises on the Company’s consistent commitment to address the growing number of projects, the engineering requirements of additional sales verticals, and on-going research in the areas of solid-state batteries, separator development and higher energy density batteries. The R&D expense will vary period to period as staff are utilized in R&D or production activities. Other movements in the year included a decrease in government assistance by $0.2 million, a decrease in general & administrative costs by $0.3 million. Stock based compensation decreased in 2025 by $0.4 million. Sales and marketing costs remained flat year over year despite the significant increase in revenue. Due to capital additions in FY 2025, there is increase in depreciation and amortization charge by $0.3 million.
Net profit
The Company earned net profit in FY 2025 to the amount of $3.4 million which changed significantly from the losses incurred by the Company in FY 2024 to the amount of $(1.49) million, an increase in profitability of $4.9 million over each of the prior two fiscal years. The Company concluded FY 2025 with positive earnings per share of $0.09. Net profit was significantly affected by one off costs during the year. Finance costs include $0.4 million of charges relating to the termination of the previous debt. The exercise of warrants during the year also generated a significant adjustment to the income statement for the fair value of the derivative liability of $0.9 million. Excluding these one-off items, would generate a net profit of $4.7 million and earnings per share of $0.11.
|
|
Key Performance Indicators
In addition to operating results and financial information described above, management reviews the following measures (which are not measures defined under IFRS):
Adjusted EBITDA1
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars)
| Adjusted EBITDA1 | |||||||||||||
| Year Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | |||||||||||
| Income (Loss) from operations | 5,540 | 729 | 1,203 | ||||||||||
| Less: | Stock based compensation | 1,756 | 2,155 | 1,167 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 1,527 | 1,209 | 907 | ||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA1 | 8,823 | 4,093 | 3,277 | ||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA1 % | 14 | % | 9 | % | 7 | % | |||||||
1 Non-IFRS Measure: Adjusted EBITDA is defined as profit/(loss) from operations, plus stock-based compensation costs and depreciation and amortization. Adjusted EBITDA does not have a standardized meaning under IFRS. We believe that certain investors and analysts use Adjusted EBITDA to measure the performance of the business and is an accepted measure of financial performance in our industry. It is not a measure of financial performance under IFRS, and may not be defined and calculated in the same manner by other companies and should not be considered in isolation or as an alternative to Income (loss) from operations.
Adjusted EBITDA1 increased by $4.7 million from FY 2024, and $5.5 million from the FY 2023. The Company has had ten consecutive quarters of positive EBITDA and Management is committed to continue this trend.
Adjusted EBITDA1 will improve primarily through increased sales, maintaining gross margin percentage and controlling operating expenses. We continue our efforts for sales growth, control of manufacturing costs and reduction operating expenses.
Summary Financial Position
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars)
| Year Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | ||||||||||
| Total current assets | $ | 48,564 | $ | 29,418 | $ | 25,906 | ||||||
| Total non-current assets | 15,367 | 10,064 | 10,608 | |||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 63,931 | $ | 39,482 | $ | 36,514 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 10,078 | 28,531 | 26,611 | |||||||||
| Total non-current liabilities | 22,726 | 2,366 | 2,757 | |||||||||
| Equity (Deficiency) | 31,127 | 8,585 | 7,146 | |||||||||
| Total liabilities and equity (deficiency) | $ | 63,931 | $ | 39,482 | $ | 36,514 | ||||||
|
|
In the three-year period commencing September 30, 2023 and ending September 30, 2025 current assets have increased by $22.7 million, current liabilities have decreased by $16.5 million and the equity has increased by $23.9 million. The Company also finished the fiscal year with a positive current ratio 4.82.
Management is focused on continuing to improve the company’s financial position through the prudent use of debt and equity but most importantly achieving a profitable position and strong working capital management.
Summary Cash Flow
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars)
| Year Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) for the year | $ | 3,363 | $ | (1,485 | ) | $ | (1,479 | ) | |||||
| Less: | Depreciation and amortization | 1,454 | 1,209 | 907 | |||||||||
| Loss on disp[osal of assets | 73 | — | — | ||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 1,756 | 2,155 | 1,167 | ||||||||||
| Financing costs | 3,670 | 2,339 | 2,474 | ||||||||||
| Foreign exchange | 576 | (40 | ) | 1 | |||||||||
| Income tax recovery | (2,053 | ) | — | — | |||||||||
| Gain on debt extinguishment | — | (936 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Bad debt recovery (expense) | — | 51 | — | ||||||||||
| Premium on purchase of SEJ | — | — | 495 | ||||||||||
| Deferred tax recovery | — | — | (679 | ) | |||||||||
| Cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 8,839 | $ | 3,293 | $ | 2,886 | |||||||
| Net change in working capital | (7,122 | ) | (2,255 | ) | (8,121 | ) | |||||||
| Cash from (used in) operating activities | 1,717 | 1,038 | (5,235 | ) | |||||||||
| Cash (used in) investing activities | (12,042 | ) | (666 | ) | (903 | ) | |||||||
| Cash from (used in) financing activities | 15,902 | (629 | ) | 6,553 | |||||||||
| Increase/(decrease) in cash | 5,577 | (257 | ) | 415 | |||||||||
| Exchange difference | — | 6 | (9 | ) | |||||||||
| Cash, beginning of year | 781 | 1,032 | 626 | ||||||||||
| Cash at end of year | $ | 6,358 | $ | 781 | $ | 1,032 | |||||||
The Company ended September 30, 2025, with $7.0 million of cash (including restricted cash of $0.7 million) as compared to $0.8 million for September 30, 2024. The Company showed a positive cash generated from operations of $1.7 million compared to cash generated from operations of $1.0 million for September 2024. Although the Company showed an increase in negative net changes in working capital compared to the prior year, the overall cash position of the company has significantly strengthened over the last year due to increasing revenue and general cost control measures adopted by the company.
|
|
4.3 Quarterly Financial Results
Results of Operations
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars
| 2025 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Yr | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Revenue | 11,169 | 15,018 | 17,133 | 20,506 | 63,826 | |||||||||||||||
| Direct Manufacturing Costs | 7,761 | 10,345 | 11,856 | 14,144 | 44,106 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross Margin | 3,408 | 4,673 | 5,277 | 6,362 | 19,720 | |||||||||||||||
| GM% | 30.5 | % | 31.1 | % | 30.8 | % | 31.0 | % | 30.9 | % | ||||||||||
| Expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Research & development | 984 | 1,070 | 1,169 | 1,156 | 4,379 | |||||||||||||||
| Government assistance | (65 | ) | (19 | ) | (1 | ) | (4 | ) | (89 | ) | ||||||||||
| Sales & marketing | 780 | 504 | 582 | 1,062 | 2,928 | |||||||||||||||
| General & administrative | 1,167 | 1,106 | 634 | 772 | 3,679 | |||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 415 | 288 | 543 | 510 | 1,756 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 317 | 328 | 388 | 494 | 1,527 | |||||||||||||||
| 3,598 | 3,277 | 3,315 | 3,990 | 14,180 | ||||||||||||||||
| Gain (Loss) from operations | (190 | ) | 1,396 | 1,962 | 2,372 | 5,540 | ||||||||||||||
| Finance cost | 685 | 691 | 453 | 926 | 2,755 | |||||||||||||||
| Change in derivative liability | 17 | (59 | ) | 138 | 819 | 915 | ||||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange (gain)/loss | (472 | ) | (64 | ) | 464 | 632 | 560 | |||||||||||||
| 230 | 568 | 1,055 | 2,377 | 4,230 | ||||||||||||||||
| Income tax recovery | — | — | — | 2,053 | 2,053 | |||||||||||||||
| Net income/(loss) | (420 | ) | 828 | 907 | 2,048 | 3,363 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
| 2024 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Yr | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Revenue | 12,091 | 10,695 | 10,274 | 11,555 | 44,615 | |||||||||||||||
| Direct Manufacturing Costs | 8,562 | 6,970 | 6,815 | 8,579 | 30,926 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross Margin | 3,529 | 3,725 | 3,459 | 2,976 | 13,689 | |||||||||||||||
| GM% | 29.2 | % | 34.8 | % | 33.7 | % | 25.8 | % | 30.7 | % | ||||||||||
| Expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Research & development | 964 | 642 | 1,037 | 395 | 3,038 | |||||||||||||||
| Government assistance | (58 | ) | (29 | ) | (34 | ) | (195 | ) | (316 | ) | ||||||||||
| Sales & marketing | 730 | 708 | 934 | 563 | 2,935 | |||||||||||||||
| General & administrative | 1,334 | 921 | 928 | 756 | 3,939 | |||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 369 | 480 | 820 | 486 | 2,155 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 290 | 300 | 358 | 261 | 1,209 | |||||||||||||||
| 3,629 | 3,022 | 4,043 | 2,266 | 12,960 | ||||||||||||||||
| Gain (Loss) from operations | (100 | ) | 703 | (584 | ) | 710 | 729 | |||||||||||||
| Finance Cost | 19 | 1,535 | 356 | 1,790 | 3,700 | |||||||||||||||
| Change in derivative liability | — | — | — | (1,334 | ) | (1,334 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange (gain)/loss | 89 | 7 | (616 | ) | 368 | (152 | ) | |||||||||||||
| 108 | 1,542 | (260 | ) | 824 | 2,214 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Profit (Loss) | (208 | ) | (839 | ) | (324 | ) | (114 | ) | (1,485 | ) | ||||||||||
For the three-month period ended September 30, 2025, total revenue was $20.5 million. This represents an increase of $8.9 million over Q4 FY2024. The increase is attributable to the Company’s long-term commitment to sustainable growth in revenue. In line with the movement in revenue, gross margin increased by $3.4 million to $6.4 million for Q4 2025. Total operating expenses for Q4 2025 increased to $3.9 million compared to $2.3 million for Q4 2024, an increase of $1.7 million. In comparison to the prior year, research and development and sales and marketing costs both increase by $0.8 million and $0.5 million respectively.
Quarterly Adjusted EBITDA1
| 2025 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Yr | |||||||||||||||||
| Gain (Loss) from operations | (190 | ) | 1,396 | 1,962 | 2,372 | 5,540 | |||||||||||||||
| Less: | Stock based compensation | 415 | 288 | 543 | 510 | 1,756 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 317 | 328 | 388 | 494 | 1,527 | ||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA1 | 542 | 2,012 | 2,893 | 3,376 | 8,823 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
| 2024 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Yr | |||||||||||||||||
| Gain (Loss) from operations | (100 | ) | 703 | (584 | ) | 710 | 729 | ||||||||||||||
| Less: | Stock based compensation | 369 | 480 | 820 | 486 | 2,155 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 290 | 300 | 358 | 261 | 1,209 | ||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA1 | 559 | 1,483 | 594 | 1,457 | 4,093 | ||||||||||||||||
1 Non-IFRS Measure: Adjusted EBITDA is defined as profit/loss from operations, plus stock-based compensation costs and depreciation and amortization. Adjusted EBITDA does not have a standardized meaning under IFRS. We believe that certain investors and analysts use Adjusted EBITDA to measure the performance of the business and is an accepted measure of financial performance in our industry. It is not a measure of financial performance under IFRS, and may not be defined and calculated in the same manner by other companies and should not be considered in isolation or as an alternative to Income (loss) from operations.
Quarterly Adjusted EBITDA shows an improving trend from fiscal 2024 to fiscal 2025, driven by increased revenue and operational efficiencies.
Quarterly Comparative Summaries
Quarterly revenue from continued operations are as follows:
| (USD $ thousands) | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 |
| 2025 | $11,169 | $15,018 | $17,133 | $20,506 |
| 2024 | $12,091 | $10,695 | $10,274 | $11,555 |
| 2023 | $8,562 | $8,470 | $10,597 | $16,430 |
Quarterly net income (losses) from continued operations are as follows:
| (USD $ thousands) | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 |
| 2025 | $(420) | $828 | $907 | $2,048 |
| 2024 | $(208) | $(839) | $(324) | $(114) |
| 2023 | $(2,581) | $(303) | $(557) | $1,962 |
Quarterly net income (losses) per common share from continued operations are as follows:
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | |
| 2025 | $(0.01) | $0.02 | $0.02 | $0.06 |
| 2024 | $(0.00) | (0.03) | $(0.01) | $(0.00) |
| 2023 | $(0.08) | $(0.01) | $(0.02) | $0.06 |
Quarterly Revenue and Seasonality
In recent periods, revenue has been weighted towards the second half of the fiscal year, and management expects this trend to continue into FY 2026. This primarily reflects the higher weighting of end customers of the Company’s material handling products who are large retailers that typically avoid receiving battery deliveries during their peak season.
|
|
The lithium ion forklift battery has a long sales cycle as many customers are large companies, the technology is relatively new to the forklift market, and customers need time to familiarize themselves with and validate the benefits as compared to the incumbent technology of lead acid batteries. In some cases, the process involves receiving a demonstrator battery for testing and trial. This causes a somewhat long and “lumpy”, or uneven, sales cycle. As customers become more comfortable with the product and place repeat orders, it is management’s view that the sales will grow in a more predictable and consistent fashion.
| 5. | LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES |
During the year ended September 30, 2025, the Company generated cash from operations of $1.7 million (September 30, 2024: $1.0 million. As of September 30, 2025, the Company has working capital of $31.9 million (September 30, 2024: $0.9 million) and a net profit of $1.3 million (2024: $1.5 million).
The Company has begun the construction of its gigafactory in Jamestown, New York (the “Gigafactory”), after securing financing from Export-Import Bank of the United States (EXIM) for $50.8. million which was approved on November 14, 2024. The Company has also secured support from the State of New York including $2 million in grants and $4.5 million in refundable tax credits. The first phase of construction is expected to take place within the existing 135,000 square foot manufacturing facility for the production of cells and batteries, with an estimated capital expenditure of approximately US$50 million.
Further, the Company continuously aims to improve its manufacturing process, equipment and facilities. The Company also anticipates gross margins to improve or remain consistent in fiscal year 2026 due to decreasing costs of key materials including but not limited to cell materials, separators, and other high value items. These anticipated improved margins, when combined with expected overall sales growth should result in improved overall financial performance.
On September 30, 2025, the Company has the following contractual obligations:
| 2026 | 10,518 |
| 2027 | 963 |
| 2028 | 19,621 |
| 2029 | 1,951 |
| 2023 and beyond | 3,588 |
|
|
| 6. | OUTSTANDING SHARE DATA |
The authorized and issued capital stock of the Company consists of an unlimited authorized number of common shares as follows:
| Common Shares Number | Amount | |||||||
| Balance, September 30, 2023 | 33,832,784 | 115,041 | ||||||
| Issuance of shares | 10,024 | 30 | ||||||
| Issuance of shares | 42,157 | 169 | ||||||
| Transfer from contributed surplus | — | 501 | ||||||
| Exercise of options | 252,700 | 667 | ||||||
| Balance, September 30, 2024 | 34,137,665 | 116,408 | ||||||
| Issuance of shares | 5,951,250 | 11,582 | ||||||
| Transfer from contributed surplus | — | 2,080 | ||||||
| Exercise of warrants | 845,000 | 3,249 | ||||||
| Exercise of options | 1,175,005 | 1,547 | ||||||
| Balance, September 30, 2025 | 42,108,920 | 134,866 | ||||||
| 7. | OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS |
The Company does not have any off-balance sheet arrangements for the quarter ended September 30, 2025.
| 8. | RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS |
Please refer to Note 15 to the September 30, 2025 Financial Statements for details on related party transactions.
| 9. | CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES |
The Company’s management makes judgments in the process of applying the Company’s accounting policies in the preparation of its consolidated financial statements. In addition, the preparation of financial information requires that the Company’s management make assumptions and estimates of effects of uncertain future events on the carrying amounts of the Company’s assets and liabilities at the end of the reporting period and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results may differ from those estimates as the estimation process is inherently uncertain. Estimates are reviewed on an ongoing basis based on historical experience and other factors that are considered to be relevant under the circumstances. Revisions to estimates and the resulting effects on the carrying amounts of the Company’s assets and liabilities are accounted for prospectively.
The critical judgments, estimates and assumptions applied in the preparation of Company’s financial information are reflected in Note 3 of the Company’s September 30, 2025 consolidated financial statements.
|
|
| 10. | CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND RECENT ACCOUNTING PRONOUNCEMENTS |
Our accounting policies and information on the adoption and impact of new and revised accounting standards the Company was required to adopt are disclosed in Note 4 of our consolidated financial statements and their related notes for the year ended September 30, 2025.
| 11. | FINANCIAL AND OTHER INSTRUMENTS |
Please refer to Note 19 of the September 30, 2025 Financial Statements for details of Financial and Other Instruments.
| 12. | DISCLOSURE CONTROLS |
We have established disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that the information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports that it files or submits under securities legislation is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in such rules and forms and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer (who are our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, respectively) as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating our disclosure controls and procedures, management recognized that disclosure controls and procedures can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the disclosure controls and procedures are met.
Our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures. Based on this evaluation and as described below under “Internal Control over Financial Reporting”, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of September 30, 2025.
| 13. | INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING |
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the CEO and the CFO and effected by the Board of Directors, management and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of consolidated financial statements for external purposes in accordance with IFRS.
Our management, including our CEO and CFO, believes that any disclosure controls and procedures or internal control over financial reporting, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. Further, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, they cannot provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, have been prevented or detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty, and that breakdowns can occur because of a simple error or mistake. Additionally, controls can be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by unauthorized override of the control. The design of any system of controls is based in part on certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Accordingly, because of the inherent limitations in a cost-effective control system, misstatements due to error or fraud might occur and not be detected.
|
|
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting on September 30, 2025, based on the criteria set forth in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission as published in 2013, and determined that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective. Also, management determined there were no material weaknesses in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting on September 30, 2024.
| 14. | QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT RISKS AND UNCERTAINTIES |
The Company may be exposed to risks of varying degrees of significance which could affect its ability to achieve its strategic objectives. The main objectives of the Company’s risk management processes are to ensure that the risks are properly identified and that the capital base is adequate in relation to those risks. The principal risks to which the Company is exposed are described below.
Capital risk
The Company manages its capital to ensure that there are adequate capital resources for the Company to maintain and develop its products. The capital structure of the Company consists of shareholders’ equity and depends on the underlying profitability of the Company’s operations.
The Company manages its capital structure and makes adjustments to it, based on the funds available to the Company, in order to support the development, manufacture and marketing of its products. The Board of Directors does not establish quantitative return on capital criteria for management, but rather relies on the expertise of the Company’s management to sustain future development of the business.
The Company’s capital management objectives are:
| ● | to ensure the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. |
| ● | to provide an adequate return to shareholders by pricing products and services commensurately with the level of risk. |
The Company monitors capital on the basis of the carrying amount of equity plus its short-term debt composed of the Promissory note, less cash and cash equivalents as presented on the face of the statement of financial position.
|
|
The Company sets the amount of capital in proportion to its overall financing structure, comprising equity and long-term debt. The Company manages the capital structure and makes adjustments to it in the light of changes in economic conditions and the risk characteristics of the underlying assets. In order to maintain or adjust the capital structure, the Company issues new shares or increases its long-term debt.
Capital for the reporting periods under review is summarized as follows:
| September 30, | ||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Total Equity | 31,127 | 8,585 | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | (7,014 | ) | (781 | ) | ||||
| Equity | 24,113 | 7,804 | ||||||
| Total Equity | 31,127 | 8,585 | ||||||
| Promissory Note | — | 519 | ||||||
| Short-term loan | — | 1,630 | ||||||
| Working capital facilities | — | 16,283 | ||||||
| Other Long-term liabilities | 22,726 | 2,366 | ||||||
| Overall Financing | 53,853 | 29,383 | ||||||
| Capital to Overall financing Ratio | 0.45 | 0.27 | ||||||
Credit risk
Credit risk is the risk that the counterparty fails to discharge an obligation to the Company. The Company is exposed to this risk for various financial instruments, for example, by granting loans and receivables to customers, placing deposits, etc. The Company’s maximum exposure to credit risk is limited to the carrying amount of financial assets recognized at the reporting date, as summarized below:
| Year ended September 30, | ||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 7,014 | 781 | ||||||
| Trade and other receivables | 16,474 | 11,292 | ||||||
| Carrying amount | 23,488 | 12,073 | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents are comprised of the following:
| Year ended September 30, | ||||||||
| 2025 | 2024 | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 6,358 | 781 | ||||||
| Restricted cash | 656 | — | ||||||
| 7,014 | 781 | |||||||
The Company’s current portfolio consists of certain banker’s acceptance and high interest yielding savings accounts deposits. The majority of cash and cash equivalents are held with financial institutions, each of which had at September 30, 2025 a rating of R-1 mid or above.
|
|
The Company manages its credit risk by establishing procedures to establish credit limits and approval policies. The balance in trade and other receivables is primarily attributable to trade accounts receivables. In the opinion of management, the credit risk is moderate as some receivables are falling into arrears. Management is taking appropriate action to mitigate this risk by adjusting credit terms.
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that we may not have cash available to satisfy our financial obligations as they come due. The majority of our financial liabilities recorded in accounts payable, accrued and other current liabilities and provisions are due within 90 days. We manage liquidity risk by maintaining a portfolio of liquid funds and having access to a revolving credit facility. We believe that cash flow from operating activities, together with cash on hand, cash from our A/R, and borrowings available under the Revolver are sufficient to fund our currently anticipated financial obligations, and will remain available in the current environment.
Market risk
Market risk incorporates a range of risks. Movement in risk factors, such as market price risk and currency risk, affect the fair value of financial assets and liabilities. The Company is exposed to these risks as the ability of the Company to develop or market its products and the future profitability of the Company is related to the market price of its primary competitors for similar products.
Interest rate risk
The Company has floating and fixed interest-bearing debt ranging from prime plus 4.9% to 7.45%. The Company’s current policy is to invest excess cash in investment-grade short-term deposit certificates issued by its banking institutions.
Foreign currency risk
The Company is exposed to foreign currency risk. The Company’s functional currency is the US dollar and a majority of its revenue is derived in US dollars. Purchases are transacted in Canadian dollars, United States dollars and Euro. Management believes the foreign exchange risk derived from any currency conversions may have a material effect on the results of its operations. The financial instruments impacted by a change in exchange rates include our exposures to the above financial assets or liabilities denominated in non functional currencies. Cash held by the Company in US dollars on September 30, 2025, was $1,590 (September 30, 2024: $159).
If the US dollar to Canadian foreign exchange rate changed by 2% this would change the recorded net gain by $285 (September 30, 2024: $174).
Price risk
The Company is exposed to price risk. Price risk is the risk that the commodity prices that the Company charges are significantly influenced by its competitors and the commodity prices that the Company must charge to meet its competitors may not be sufficient to meet its expenses. The Company reduces the price risk by ensuring that it obtains information regarding the prices set by its competitors to ensure that its prices are appropriate to the unique attributes of our product. In the opinion of management, the price risk is low and is not material.
|
|
Disclosure control risks
The Company’s management, with the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer of the Company, have designed disclosure controls and procedures (“DC&P”), or caused them to be designed under their supervision, to provide reasonable assurance that material information relating to the issuer, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known, particularly during the period in which interim or annual filings are being prepared, and information required to be disclosed by the Company in its annual filings, interim filings or other reports filed or submitted by it under securities legislation is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in securities legislation. Although certain weaknesses have been identified, these items do not constitute a material weakness or a weakness in DC&P that are significant. A control system, no matter how well conceived or operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. DC&P are reviewed on an ongoing basis.
Internal control risks
The Company’s management, with the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer of the Company, have designed such internal control over financial reporting (“ICFR”), or caused it to be designed under their supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with IFRS. Such design also uses the framework and criteria established in Internal Control over Financial Reporting - Guidance for Smaller Public Companies, issued by The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company relies on entity-wide controls and programs including written codes of conduct and controls over initiating, recording, processing and reporting significant account balances and classes of transactions. Other controls include centralized processing controls, including a shared services environment and monitoring of operating results. Based on the evaluation of the design and operating effectiveness of the Company’s ICFR, the CEO and CFO concluded that the company’s ICFR was effective as at September 30, 2025.
The Company does not believe that it has any material weakness or a weakness in ICFR that are significant, other than those reported in the September 30, 2025 audited financial statements. Control deficiencies have been identified within the Company’s accounting and finance departments and its financial information systems over segregation of duties and user access respectively. Specifically, certain duties within the accounting and finance departments were not properly segregated due to the small number of individuals employed in these areas. To our knowledge, none of the control deficiencies has resulted in a misstatement to the financial statements. However, these deficiencies may be considered a material weakness resulting in a more-than remote likelihood that a material misstatement of the Company’s annual or interim financial statements would not be prevented or detected.
As the Company incurs future growth, we plan to expand the number of individuals involved in the accounting function. At the present time, the CEO and CFO oversee all material transactions and related accounting records. In addition, the Audit Committee reviews on a quarterly basis the financial statements and key risks of the Company and queries management about significant transactions, there is a quarterly review of the company’s condensed interim unaudited financial statements by the Company’s auditors and daily oversight by the senior management of the Company.
|
|
| 15. | OTHER RISKS |
Other Risk Factors.
The risks described above are not the only risks and uncertainties that we face. Additional risks the Company faces are described under the heading “Risk Factors” in the Company’s AIF for the year ended September 30, 2025.
Other additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently consider immaterial may also impair our business operations. These risk factors could materially affect our future operating results and could cause actual events to differ materially from those described in our forward-looking statements.
Additional information relating to the Company, including our AIF for the year ended September 30, 2025, is available on SEDAR and EDGAR.
|
|
EXHIBIT 99.4
CERTIFICATION
I, Dr. Rajshekar DasGupta, Chief Executive Officer of Electrovaya Inc., certify that;
| 1. | I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 40-F of Electrovaya Inc.; | |
| 2. | Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report; | |
| 3. | Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this Annual Report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report; | |
| 4. | The registrant’s other certifying officers and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have: |
|
| a) | Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; | |
| b) | Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles: | |
| c) | Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and | |
| d) | Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by the annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and | |
| 5. | The registrant’s other certifying officers and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions): | |
| a) | All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal controls over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and | |
| b) | Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting. | |
Date: December 19, 2025
By: /s/ Dr. Rajshekar DasGupta
Name: Dr. Rajshekar DasGupta
Title: Chief Executive Officer
EXHIBIT 99.5
CERTIFICATION
I, John Gibson, Chief Financial Officer of Electrovaya Inc., certify that;
| 1. | I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 40-F of Electrovaya Inc.; | |
| 2. | Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report; | |
| 3. | Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this Annual Report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report; | |
| 4. | The registrant’s other certifying officers and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have: |
|
| a) | Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; | |
| b) | Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles: | |
| c) | Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and | |
| d) |
Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by the annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and
|
|
| 5. | The registrant’s other certifying officers and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions): | |
| a) | All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal controls over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and | |
| b) | Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting. | |
Date: December 19, 2025
By: /s/ John Gibson
Name: John Gibson
Title: Chief Financial Officer
EXHIBIT 99.6
CERTIFICATION OF CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER
PURSUANT TO
18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
I, Dr. Rajshekar DasGupta, Chief Executive Officer of Electrovaya Inc. (the “Company”), hereby certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to the best of my knowledge:
| a. | the Annual Report on Form 40-F of the Company for the fiscal year ended September 30, 2025 (the “Annual Report”) fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended; and | |
| b. | the information contained in the Annual Report fairly presents in all material respects the financial condition and results of operations of the Company. |
| Date: December 19, 2025 | |
|
By: Name: Dr. Rajshekar DasGupta Title: Chief Executive Officer |
EXHIBIT 99.7
CERTIFICATION OF CHIEF FINANCIAL OFFICER
PURSUANT TO
18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
I, John Gibson, Chief Financial Officer of Electrovaya Inc. (the “Company”), hereby certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to the best of my knowledge:
| a. | the Annual Report on Form 40-F of the Company for the fiscal year ended September 30, 2025 (the “Annual Report”) fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended; and | |
| b. | the information contained in the Annual Report fairly presents in all material respects the financial condition and results of operations of the Company. |
| Date: December 19, 2025 | |
|
By: Name: John Gibson Title: Chief Financial Officer |
Exhibit 99.8

CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
We consent to the use of our auditor’s report dated December 10, 2025 with respect to the consolidated financial statements of Electrovaya Inc. (the “Company”) as at September 30, 2025 and 2024 and for each of the years in the two-year period ended September 30, 2025, included in the Annual Report on Form 40-F of the Company for the year ended September 30, 2025, as filed with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
We also consent to the incorporation by reference in the Registration Statement No. 333-278139 on Form F-10, of our auditor’s report dated December 10, 2025, with respect to the consolidated financial statements of the Company as at September 30, 2025 and 2024 and for each of years in the two-year period ended September 30, 2025, as included in the Annual Report on Form 40-F for the year ended September 30, 2025, as filed with the SEC on December 19, 2025.
We also consent to the reference to our firm under the headings “Interest of Experts” and “Auditors, Transfer Agent and Registrar” in the Registration Statement No. 333-278139 on Form F-10.
Chartered Professional Accountants
Licensed Public Accountants
Toronto, Canada
December 19, 2025
MNP LLP
| 1 Adelaide Street East, Suite 1900, Toronto ON, M5C 2V9 | 1.877.251.2922 T: 416.596.1711 F: 416.596.7894 |