UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark one)
☒ ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended October 29, 2023
or
☐ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from ____ to ____
Commission file number 1-4121
DEERE & COMPANY
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware |
|
36-2382580 |
(State of incorporation) |
|
(IRS Employer Identification No.) |
One John Deere Place, Moline, Illinois |
|
61265 |
|
(309) 765-8000 |
(Address of principal executive offices) |
|
(Zip Code) |
|
(Telephone Number) |
SECURITIES REGISTERED PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OF THE ACT
Title of each class |
|
Trading symbol |
|
Name of each exchange on which registered |
Common stock, $1 par value |
|
DE |
|
New York Stock Exchange |
6.55% Debentures Due 2028 |
|
DE28 |
|
New York Stock Exchange |
SECURITIES REGISTERED PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(g) OF THE ACT: NONE
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
|
|
|
|
Large accelerated filer ☒ |
|
Accelerated filer ☐ |
|
Non-accelerated filer ☐ |
|
Smaller reporting company ☐ |
|
|
|
Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate quoted market price of voting stock of the registrant held by non-affiliates at April 28, 2023 was $110,752,079,592. At November 30, 2023, 280,255,442 shares of common stock, $1 par value, of the registrant were outstanding.
Documents Incorporated by Reference. Portions of the proxy statement for the annual meeting of stockholders to be held on February 28, 2024 are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
|
Page |
PART I |
|
|
2 |
||
14 |
||
24 |
||
24 |
||
24 |
||
24 |
||
|
|
|
PART II |
|
|
25 |
||
26 |
||
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
26 |
|
26 |
||
26 |
||
CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
26 |
|
26 |
||
27 |
||
DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS |
27 |
|
|
|
|
PART III |
|
|
27 |
||
27 |
||
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
27 |
|
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
27 |
|
27 |
||
|
|
|
PART IV |
|
|
28 |
||
28 |
1
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS.
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements that are subject to risks and uncertainties. All statements other than statements of historical fact included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements provide our current expectations and projections relating to our financial condition, results of operations, plans, objectives, future performance, and business. You can identify forward-looking statements as they do not relate to historical or current facts and by words such as “believe,” “expect,” “estimate,” “anticipate,” “will,” “aim,” “should,” “plan,” “forecast,” “target,” “guide,” “project,” “intend,” “could,” and similar words or expressions.
All forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from those that we expected. Important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from our expectations, or cautionary statements, and other important information about forward-looking statements are disclosed under Item 1A, “Risk Factors,” and Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations–Forward-Looking Statements,” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
As used herein, the terms “John Deere,” “we,” “us,” “our,” or “the Company” refer to Deere & Company and its subsidiaries unless designated or identified otherwise. All amounts are presented in millions of dollars, unless otherwise specified.
Products
The John Deere enterprise has manufactured agricultural equipment since 1837. Deere & Company was incorporated under the laws of Delaware in 1958. Our business is managed through the following four business segments: production and precision agriculture (PPA), small agriculture and turf (SAT), construction and forestry (CF), and financial services (John Deere Financial or FS).
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
BUSINESS SEGMENT |
|
PRODUCTION AND PRECISION AGRICULTURE |
|
SMALL AGRICULTURE AND TURF |
|
CONSTRUCTION AND FORESTRY |
|
FINANCIAL SERVICES |
PRODUCTS |
|
●
Large and Certain
Mid-Size Tractors ●
Combines
●
Cotton Pickers and Cotton Strippers
●
Sugarcane Harvesters
●
Sugarcane Loaders and Pull Behind Scrapers
●
Soil Preparation, Seeding, Application, and Crop Care Equipment
●
Tillage Equipment
|
|
●
Certain Mid-Size, Utility, and Compact Utility Tractors
●
Self-Propelled Forage Harvesters
●
Hay and Forage Equipment
●
Rotary Mowers
●
Utility Vehicles
●
Riding Lawn Equipment and Commercial Mowing Equipment
●
Golf Course Equipment
|
|
●
Backhoe Loaders
●
Crawler Dozers and Loaders
●
Four-Wheel-Drive Loaders and Compact Track Loaders
●
Excavators and Compact Excavators
●
Equipment used in Timber Harvesting
●
Road Building and Road Rehabilitation Equipment
●
Articulated Dump Trucks and Motor Graders
|
|
●
Retail Notes
●
Revolving Charge Accounts
●
Wholesale Receivables
●
Leases
●
Extended Warranties
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
CROPS/FUNCTION |
|
●
Corn and Soy
●
Small Grain
●
Cotton
●
Sugarcane
|
|
●
Dairy and Livestock
●
Lawn and Property Maintenance
●
Golf Course Maintenance
●
High-Value Crop Solutions
|
|
●
Earthmoving
●
Forestry
●
Roadbuilding
|
|
●
Financial Solutions
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
2
Smart Industrial Operating Model and Leap Ambitions
In fiscal year 2020, we announced our Smart Industrial Operating Model. The model is based on the following three focus areas:
| 1. | Production Systems. A strategic alignment of products and solutions around our customers’ production systems. Production systems refer to the series of steps our customers take to execute different tasks, operations, and projects to grow an agricultural product or execute a project. |
| 2. | Technology Stack. Investments in technology, as well as research and development, that deliver intelligent solutions to our customers through hardware and devices, embedded software, connectivity, data platforms, and applications. The technology stack leverages the core technologies mentioned in the previous sentence across the enterprise, including digital capabilities, automation, autonomy, and alternative power technologies. The stack has the potential to unlock economic and sustainable value for customers by optimizing jobs, strengthening decision-making, and better connecting the steps of a production system. |
| 3. | Lifecycle Solutions. The enterprise integration of our aftermarket and support capabilities to more effectively manage customer equipment, service, and technology needs across the full lifetime of a John Deere product, and with a specific lifecycle solution focus on the ownership experience. This integrated support seeks to enhance customer value through proactive and reactive support, easy access to parts, value-add services, and precision upgrades, regardless of when a customer purchases our equipment. |
Building upon the Smart Industrial Operating Model, we announced our Leap Ambitions framework in fiscal year 2022. The Leap Ambitions are designed to boost economic value and sustainability for our customers. The ambitions align across our customers’ production systems seeking to optimize their operations to deliver better outcomes with fewer resources.
The Leap Ambitions framework has three components: (i) size the incremental market opportunity, quantifying the value that can be created; (ii) identify the key actions required to guide investment in digitalization, autonomy, automation, and alternative power technologies; and (iii) define the desired financial and sustainable outcomes we hope to achieve to help investors and stakeholders understand the opportunities that can be unlocked in the future through present investments. Applying this framework, the Leap Ambitions set goals to measure the results under our Smart Industrial Operating Model. Current financial and sustainability goals for the Leap Ambitions relate to workforce safety, agriculture customer outcomes, product circularity, environmental footprint, Solutions as a Service, and equipment operations operating return on sales (OROS).
We aim to deliver ongoing value across our product lines by digitally connecting certain equipment we produce, enabling our customers to leverage technology for better economic and more sustainable outcomes in their businesses. We are introducing viable alternative power technologies for various product families. We also plan to enhance how we deliver value by introducing and scaling a Solutions as a Service business model.
We also aim to enable our agriculture customers to be more sustainable in their production steps by providing technology solutions that help to improve their nitrogen use efficiency, increase their crop protection efficiency, and reduce their CO2e emissions.
We believe we will deliver ongoing value to our SAT customers by increasing the connectivity of their equipment, offering electric options where feasible in our product families, and working toward production of a fully autonomous, battery powered electric agricultural tractor. For our CF customers, we aim to deliver ongoing value by offering electric and hybrid-electric options where feasible in our product families and increasing the use of grade management control for earthmoving customers, intelligent boom control for forestry customers, and precision roadbuilding solutions for our roadbuilding customers.
We anticipate enabling sustainable outcomes for our customers. Specifically, we aim to enable our agriculture customers to be more sustainable in their production steps by providing technology solutions that help to improve their nitrogen use efficiency, increase their crop protection efficiency, and reduce their CO2e emissions.
Available Information
Our internet address is http://www.deere.com. Our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports are available on our website free of charge as soon as reasonably practicable after they are filed or furnished with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC or Commission). The information contained on our website is not included in, nor incorporated by reference into, this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Equipment Operations
Our equipment operations consist of three of our business segments: PPA, SAT, and CF. In fiscal year 2023, PPA generated $26,790 net sales and revenue, or 48 percent of equipment operations net sales and revenues; SAT generated $13,980 net sales and revenues, or 25 percent of equipment operations net sales and revenues; and CF generated $14,795 net sales and revenues, or 27 percent of equipment operations net sales.
3
Production and Precision Agriculture
As compared with fiscal year 2022, PPA net sales for fiscal year 2023 were:
(In millions of dollars) |
2023 |
2022 |
% Change |
Net Sales |
$26,790 |
$22,002 |
22% |
The PPA segment is committed to meeting the fundamental needs of our customers through a combination of equipment and technology designed to enable our customers to overcome some of their biggest challenges: doing more with less, labor shortages, volatile input costs, and executing jobs in tighter timeframes. This segment defines, develops, and delivers global equipment and technology solutions for production-scale growers of crops like large grains (such as corn and soy), small grains (such as wheat, oats, and barley), cotton, and sugarcane. Equipment manufactured and distributed by the segment includes large and certain mid-size tractors, combines, cotton pickers, cotton strippers, sugarcane harvesters, related harvesting front-end equipment, and pull-behind scrapers. In addition, the segment includes tillage, seeding, and application equipment, including sprayers and nutrient management and soil preparation machinery.
We have been bringing innovations to agriculture for nearly 200 years and continue to invest in the development and production of advanced technology through integrated agricultural solutions and precision technologies across our portfolio of equipment. We have developed a differentiated, production system-level approach that helps us understand how customers operate, focusing on their costs, identifying the opportunities for them to reduce inputs, and increasing productivity, yield improvement, and sustainability. This approach directs our work. Advancements such as precise global navigation satellite systems technology, advanced connectivity and telematics, on-board sensors and computing power, automation software, digital tools, applications, and analytics provide seamless integration of information designed to improve customer decision-making and job execution. Our advanced telematics systems remotely connect equipment owners, business managers, and dealers to equipment in the field. This provides real-time alerts and information about equipment location, utilization, performance, and maintenance to improve productivity and efficiency, as well as to monitor agronomic job execution.
We aim to support our customers and their equipment throughout the entire equipment lifecycle. To prevent downtime, we offer a wide variety of aftermarket and customer solutions to keep equipment running, including machine monitoring, remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance alerts, and e-commerce solutions.
Examples of recent developments to unlock customer value and address challenges in the field include ExactShot™ and FurrowVision, which help customers reduce inputs during planting applications, generating cost savings, and lowering their environmental footprint; our fully autonomous 8R tillage tractor with a GPS guidance system and stereo cameras to execute tillage work without an in-cab operator, which helps to address farmers’ labor challenges and time constraints; and See & Spray™ Ultimate, which targets the application of non-residual herbicides on weeds in corn, soybean, and cotton fields.
In addition to John Deere brand names, the table below provides a list of PPA products and their associated brand names:
PRODUCT |
BRAND NAME |
Sprayers |
Hagie, Mazzotti |
Planters and Cultivators |
Monosem |
Sprayers and Planters |
PLA |
Carbon Fiber Sprayer Booms |
King Agro |
Sugarcane Harvester Aftermarket Parts |
Unimil |
Aftermarket Parts for PPA Products |
Vapormatic, A&I, Unimil, Alternatives by John Deere |
4
Small Agriculture and Turf
As compared with fiscal year 2022, SAT net sales for fiscal year 2023 were:
(In millions of dollars) |
2023 |
2022 |
% Change |
Net Sales |
$13,980 |
$13,381 |
4% |
SAT is committed to meeting the needs of our customers through defining, developing, and delivering global equipment and technology solutions designed to unlock customer value and sustainability for dairy and livestock producers, high-value crop producers, and turf and utility customers. The segment works to provide product leadership while extending integrated agricultural solutions and precision technologies across its portfolio of equipment to unlock incremental value for customers. Similar to PPA, the SAT segment aims to support customers and their equipment through the entire equipment lifecycle.
Equipment manufactured and distributed by the segment includes certain mid-size, small and utility tractors, and related loaders and attachments; turf and utility equipment, including riding lawn equipment, commercial mowing equipment, golf course equipment, utility vehicles, implements for mowing, tilling, snow and debris handling, aerating, and other residential, commercial, golf, and sports turf care applications; and hay and forage equipment, including self-propelled forage harvesters and attachments, balers, and mowers. SAT equipment is sold primarily through independent retail dealer networks, although the segment also builds turf products for sale by mass retailers, including The Home Depot and Lowe’s. Our turf equipment is sold primarily in North American, Western European, and Australian markets.
In the small agriculture market, we have introduced autonomous solutions, connectivity capabilities, and a path to electrifying our future by delivering a portfolio that helps current customers meet sustainability goals while finding innovative ways to serve new customers and unlock new markets for mechanization, at scale. For example, our joint venture with GUSS Automation, LLC in fiscal year 2022 added to our portfolio an autonomous sprayer to target our high value crop customers’ needs. In fiscal year 2023, we announced the acquisition of Smart Apply, Inc., a precision spraying equipment company. The Smart Apply Intelligent Spray Control System™ stacked with GUSS Automation’s remote sprayer is aimed at the needs of our high-value crop customers to improve their productivity and optimize inputs. On the turf side of the business, in fiscal year 2023 we launched two battery-powered walk behind mowers and announced certain hybrid innovations.
In addition to John Deere brand names, the table below provides a list of SAT products and their associated brand names:
PRODUCT |
BRAND NAME |
Equipment Attachments |
Frontier, Kemper, GreenSystem, Smart Apply |
Aftermarket Parts for SAT |
Vapormatic, A&I, Sunbelt, Alternatives by John Deere |
Agriculture and Turf Operations
Smart Industrial Operating Model. Our PPA and SAT segments offer a full line of agriculture and turf equipment and related service parts. As part of our Smart Industrial Operating Model, the segments are aligned around production systems, enabling focus on delivering equipment, technology, and solutions across all the jobs customers execute during a season. Sales and marketing support for both the PPA and SAT segments continues to be organized around four geographic regions: U.S., Canada, and Australia; Latin America and South America; Europe, Middle East, and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS); and Africa and Asia.
Business Environment. Sales of agricultural equipment are affected by total farm cash receipts, which reflect levels of farm commodity prices, acreage planted, crop yields, and government policies, including global trade policies, the amount and timing of government payments, and policies related to climate change. Sales also are influenced by general economic conditions, farmland prices, farmers’ debt levels and access to financing, interest and exchange rates, agricultural trends, including the production of and demand for renewable fuels, labor availability and costs, energy costs, tax policies, and other input costs associated with farming. Other key factors affecting new agricultural equipment sales are the value, age, and level of used equipment, including tractors, harvesting equipment, self-propelled sprayers, hay and forage equipment, and seeding equipment. Weather and climatic conditions also can affect buying decisions of agricultural equipment purchasers.
Innovations in machinery and technology also influence agricultural equipment purchasing. For example, larger, more productive equipment is well accepted where farmers are striving for more efficiency in their operations. Large, cost-efficient, highly mechanized agricultural operations account for an important share of worldwide farm output. These customers are increasingly adopting and integrating precision agricultural technologies like guidance, telematics, automation, and data management in their operations. The large-size agricultural equipment used on such farms has been particularly important to us.
5
A large proportion of the equipment operations’ total agricultural equipment sales in the U.S. and Canada, as well as in many countries outside the U.S. and Canada, are comprised of tractors over 100 horsepower, self-propelled combines, self-propelled cotton pickers, self-propelled forage harvesters, self-propelled sprayers, and seeding equipment. However, small tractors are also an important part of our global business. Further, we offer a number of harvesting solutions to support development of the mechanized harvesting of grain, oilseeds, cotton, sugarcane, forage, and biomass.
Retail sales of lawn and garden tractors, compact utility tractors, residential and commercial mowers, utility vehicles, and golf and turf equipment are influenced by the housing market, weather conditions, consumer spending patterns, and general economic conditions like unemployment, interest, and inflation rates.
Seasonality. Seasonal patterns in retail demand for agricultural equipment can result in substantial variations in the volume and mix of products sold to retail customers during the year. Seasonal demand must be estimated in advance, and equipment must be manufactured in anticipation of such demand to achieve efficient utilization of personnel and facilities throughout the year. The PPA and SAT segments can incur substantial seasonal variations in cash flows to finance production and inventory of agricultural and turf equipment. The segments also incur costs to finance sales to dealers in advance of seasonal demand.
For certain equipment, we offer early order programs, which can include discounts to retail customers that place orders well in advance of the use season. Production schedules are based, in part, on these early order programs; however, during periods of high demand, some factories may still produce after the use season. New combine and cotton harvesting equipment has been sold under early order programs with waivers of retail finance charges available to customers who take delivery of machines during non-use seasons.
In Australia, Canada, and the U.S., there are typically several used equipment trade-in transactions that take place in connection with most new agricultural equipment sales. To provide support to our dealers in these countries for carrying and ultimately selling this used inventory to retail customers, we provide these dealers with pools of funds awarded as a percentage of the dealer cost for eligible new equipment sales at the time of the new equipment settlement.
Retail demand for turf and utility equipment is normally higher in the second and third fiscal quarters. We have pursued a strategy of building and shipping such equipment as close to retail demand as possible. Consequently, to increase asset turnover and reduce the average level of field inventories throughout the year, production and shipment schedules of these product lines are normally proportionately higher in the second and third fiscal quarters of each year, corresponding closely to the seasonal pattern of retail sales. However, the patterns of seasonality have been affected by the supply chain disruptions experienced during fiscal year 2022.
Construction and Forestry
As compared with fiscal year 2022, CF net sales for fiscal year 2023 were:
(In millions of dollars) |
2023 |
2022 |
% Change |
Net Sales |
$14,795 |
$12,534 |
18% |
Our CF segment is committed to meeting the need for smart and more sustainable solutions to help our customers meet industry challenges, including jobsite safety, a shortage of skilled labor, volatile input costs, reducing rework, maximizing uptime, and minimizing their environmental footprint. CF also aims to support customers and their equipment through the entire equipment lifecycle (see PPA section above).
To address these challenges and unlock value for customers, we deliver a robust portfolio of construction, roadbuilding, and forestry products with precision technology solutions. Our smart solutions such as SmartWeigh™, grade control offerings, machine and system automation, and operations center, are designed to allow customers to complete more functions with fewer inputs, reduce rework and guesswork, and transform data into insights to allow for better decisions. Obstacle detection solutions such as SmartDetect™ supplements operator visibility on the jobsite through a combination of cameras, radar, and machine learning. Additionally, we plan to deliver hybrid-electric and battery electric equipment solutions to help customers reduce tailpipe emissions without sacrificing power and performance. We currently have the 644X four-wheel-drive loader and 944X four-wheel-drive loader in production with an electric drive coupled with a diesel engine.
Our primary construction products include excavators, wheel loaders, motor graders, dozers, backhoes, articulated dump trucks, compact construction equipment including skid steers, compact excavators, and compact track loaders, along with a variety of attachments. Our Wirtgen roadbuilding products include milling machines, pavers, compactors, rollers, crushers, screens, and asphalt plants. Similar to the construction product lineup, the Wirtgen brand also provides a technology stack aimed at allowing customers to make smarter and more sustainable decisions. Technology offerings include Wirtgen Performance Tracker, Mill Assist, Level Pro, Vögele Roadscan, Smart Compact, WITOS Paving, Spective Connect, AutoTrac™, and John Deere Connected Support™.
6
In forestry, our primary products include skidders, wheeled and tracked feller bunchers, forwarders, knuckleboom loaders, wheeled and tracked harvesters, swing machines, and precision forestry technology solutions such as Intelligent Boom Control, TimberMatic™ maps, and TimberManager™. These solutions allow customers to closely track jobsite progress and provide visibility into fleet location, utilization, performance, and maintenance information.
We have a number of initiatives in the rent-to-rent, or short-term rental, market for construction, earthmoving, roadbuilding, and material handling equipment. These include specially designed rental programs for our dealers and expanded cooperation with major national equipment rental companies.
We own retail forestry sales operations in Australia, Brazil, Finland, Ireland, New Zealand, Norway, Sweden, and the United Kingdom. In addition, the Wirtgen Group sells its products primarily through company-owned sales and service subsidiaries in many markets worldwide (most significantly in Europe, India, and Australia). In most other geographies, we sell through an independent dealer channel.
The prevailing levels of residential, commercial, and public construction, investment in infrastructure, and the condition of the forestry products industry influence retail sales of our construction, roadbuilding, and forestry equipment. General economic conditions, interest rate levels, the availability of credit, and certain commodity prices, such as those applicable to oil and gas, pulp, paper, and saw logs, also influence sales.
In addition to John Deere brand names, the table below provides a list of CF products and their associated brand names:
PRODUCT |
BRAND NAME |
Roadbuilding Equipment |
Wirtgen, Vögele, Hamm, Kleemann, Benninghoven, and Ciber |
Forestry Attachments |
Waratah |
Competition
The equipment operations sell products and services in a variety of competitive global and regional markets. The principal competitive factors in all markets include product performance, innovation, quality, distribution, sustainability, customer service, and value. John Deere’s brand recognition is a competitive factor in North America and many other parts of the world.
The agricultural equipment industry continues to change and is becoming even more competitive through the emergence and expanding global capability of many competitors. The competitive environment for the agriculture and turf operations includes some global competitors, including AGCO Corporation, CLAAS KGaA mbH, CNH Industrial N.V., Kubota Tractor Corporation, Mahindra & Mahindra Limited, and The Toro Company, as well as many regional and local competitors. These competitors have varying numbers of product lines competing with our products and each has varying degrees of regional focus. Additional competition within the agricultural equipment industry has come from a variety of short-line and specialty manufacturers, as well as local or regional competitors, with differing manufacturing and marketing methods. As technology increasingly enables enhanced productivity in agriculture, the industry is also attracting non-traditional competitors, including technology-focused companies and start-up ventures.
Our forestry and roadbuilding businesses operate globally. The construction business operates in competitive markets in North and South America, as well as other global markets. Global competitors of the CF segment include Caterpillar Inc., CNH Industrial N.V., Doosan Infracore Co., Ltd. and its subsidiary Doosan Bobcat Inc., Fayat Group, GOMACO Corporation, Hitachi Construction Machinery, Komatsu Ltd., Kubota Tractor Corporation, Ponsse Plc, SANY Group Co., Ltd., Terex, Tigercat Industries Inc., Volvo Construction Equipment (part of Volvo Group AB), and XCMG.
Manufacturing and Assembly
Common manufacturing processes and techniques are used in producing components for PPA, SAT, and CF equipment sold by us and our dealers. The equipment operations also pursue external sales of selected parts that can be manufactured and supplied to third parties on a competitive basis, including engines, power train components, and electronic components. The equipment operations’ manufacturing strategy involves four elements: Build a Stronger Business, Deliver Innovation, Excite the Customer, and Live the Team.
Build a Stronger Business refers to our ability to execute lean initiatives supported by safety, quality, delivery, and productivity goals.
Deliver Innovation refers to implementing our digitally connected factory projects to improve efficiency and differentiated value. We implement technology solutions to support our factories across the globe to increase our speed of manufacturing innovation and allow the workforce to focus on high-value tasks.
7
Excite the Customer refers to designing operations to be flexible and accommodate product design changes to meet market conditions and changing customer requirements.
Live the Team refers to building a safety culture by ensuring that employees are safe at work.
To utilize manufacturing facilities and technology more effectively, the equipment operations pursue continuous improvements in manufacturing processes, including steps to streamline manufacturing processes and enhance responsiveness to customers. Our flexible assembly lines can accommodate a wider product mix and deliver products in line with dealer and customer demand. Additionally, considerable effort is being directed to manufacturing cost reduction through process improvement and improvements in product design, advanced manufacturing technology, and supply management and logistics, as well as compensation incentives related to productivity and organizational structure.
See Item 2 “Properties” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for more information about our manufacturing facilities.
Patents, Trademarks, Copyrights, and Trade Secrets
We own a significant number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and intellectual property licenses related to our products and services and expect the number to grow as we continue to pursue technological innovations. We further our competitive position by filing patent and trademark applications in the U.S. and internationally to protect technology, improvements considered important to the business, and our brand. We believe that, taken together, our rights under these patents and licenses are important to our operations and competitive position, but do not regard any of our businesses as being dependent upon any single patent or family of patents. See “Risk Factors- Our business could be adversely affected by the infringement or loss of intellectual property rights” for more information.
Sales and Distribution
Through the U.S. and Canada, we market products to approximately 2,050 independent dealer locations. Of these, approximately 1,600 sell agricultural equipment, while approximately 450 sell construction, earthmoving, material handling, roadbuilding, and/or forestry equipment. In addition, roadbuilding equipment is sold at approximately 90 roadbuilding-only locations that may carry products that compete with our construction, earthmoving, material handling, and/or forestry equipment. Turf equipment is sold at most John Deere agricultural equipment locations, a few construction, earthmoving, material handling, roadbuilding, and/or forestry equipment locations, and about 280 turf-only locations, many of which also sell dissimilar lines of non-John Deere products. In addition, certain lawn and garden product lines are sold through The Home Depot and Lowe’s.
Outside the U.S. and Canada, our agriculture and turf equipment is sold to distributors and dealers for resale in over 100 countries. Sales and administrative offices are in Argentina, Australia, Brazil, China, France, Germany, India, Italy, Mexico, Poland, Singapore, Sweden, South Africa, Spain, Ukraine, and the United Kingdom. Turf equipment sales outside the U.S. and Canada occur primarily in Western Europe and Australia. Construction, earthmoving, material handling, and forestry equipment is sold to distributors and dealers primarily by sales offices located in Australia, Brazil, Finland, New Zealand, Singapore, and the United Kingdom. Some of these dealers are independently owned while we own others. Roadbuilding equipment is sold directly to retail customers and independent distributors and dealers for resale. As of November 1, 2022, we did not renew dealer agreements in Russia, and in October 2023, we sold our roadbuilding business in Russia. Consequently, we no longer sell equipment in Russia. The Wirtgen Group operates company-owned sales and service subsidiaries in Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, China, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Hungary, India, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Latvia, Lithuania, Malaysia, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Romania, South Africa, Sweden, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, Ukraine, and the United Kingdom. The equipment operations operate centralized parts distribution warehouses in the U.S., Brazil, and Germany in coordination with regional parts depots and distribution centers in Argentina, Australia, China, India, Mexico, South Africa, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
We market engines, power trains, and electronic components worldwide through select sales branches or directly to regional and global original equipment manufacturers and independently owned engine distributors.
Raw Materials
We purchase raw materials, manufactured components, and replacement parts for our equipment, engines, and other products from leading suppliers both domestically and internationally. These materials and components include a variety of steel products, metal castings, forgings, plastics, hydraulics, electronics, and ready-to-assemble components made to certain specifications. We also purchase various goods and services used for production, logistics, offices, and research and development. We develop and maintain sourcing strategies for our purchased materials and emphasize long-term supplier relationships at the core of these strategies. We use a variety of agreements with suppliers intended to drive innovation, ensure availability and delivery of industry-leading quality raw materials and components, manage costs on a globally competitive basis, protect our intellectual property, and minimize other supply-related risks. We actively monitor supply chain risks to minimize the likelihood of business disruptions caused by the supply base, including supplier financial viability, capacity, business continuity, labor availability, quality, delivery, cybersecurity, weather-related events, and natural disasters.
8
We have implemented mitigation efforts to minimize the impact of potential and actual supply chain disruptions on our customers. Examples include working with the supply base to prioritize allocations to improve material availability, multi-sourcing selected parts and materials, entering long term contracts for some critical components, and using alternative freight carriers to expedite delivery.
Backlog Orders
The dollar amount of backlog orders as of October 29, 2023 was approximately $7.9 billion for the PPA segment and $3.3 billion for the SAT segment, compared with $9.7 billion and $4.6 billion, respectively, at October 30, 2022. The agriculture and turf backlog are generally highest in the second and third quarters due to seasonal buying trends in these industries. The dollar amount of backlog orders for the CF segment was approximately $6.4 billion at October 29, 2023, compared with $8.2 billion at October 30, 2022, including, for both periods, backlog orders for roadbuilding equipment, which had not historically been included in discussions of the CF segment’s backlog orders. Backlog orders for equipment operations include all orders deemed to be firm as of the referenced date. Backlog orders decreased as demand has declined.
Financial Services
U.S. and Canada. The financial services segment primarily provides and administers financing for retail purchases from our dealers of new equipment manufactured by our agricultural and turf and construction and forestry markets, as well as used equipment taken in trade for this equipment. The Company and John Deere Construction & Forestry Company (a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company) are referred to as the “sales companies.” John Deere Capital Corporation (Capital Corporation), a U.S. financial services subsidiary, generally purchases retail installment sales and loan contracts (retail notes) from the sales companies. In Canada, John Deere Financial Inc., a Canadian financial services subsidiary, purchases and finances retail notes acquired by John Deere Canada ULC, our Canadian sales company. The terms of retail notes and the basis on which the financial services operations acquire retail notes from the sales companies are governed by agreements with the sales companies. The financial services segment also finances and services revolving charge accounts, in most cases acquired from and offered through merchants in the agricultural and turf markets. Additionally, the financial services operations provide wholesale financing to dealers of our agriculture and turf equipment and construction and forestry equipment (wholesale notes), primarily to finance inventories of equipment for those dealers. The various financing options offered by the financial services operations are designed to enhance sales of our products and generate financing income for the financial services operations. In the U.S. and Canada, certain subsidiaries included in the financial services segment offer extended equipment warranties.
Retail notes acquired by the sales companies are immediately sold to the financial services operations. The equipment operations are the financial services operations’ major source of business, although many retail purchasers of our products finance their purchases outside our organization through a variety of sources, including commercial banks and finance and leasing companies.
The financial services operations offer retail leases to equipment users in the U.S. A small number of leases are executed with units of local governments. Leases are usually written for periods ranging from less than one year to seven years, and typically contain an option permitting the customer to purchase the equipment at the end of the lease term. Retail leases also are offered in a generally similar manner to customers in Canada.
The financial services operations’ terms for financing equipment retail sales (other than smaller items financed with unsecured revolving charge accounts) generally provide for retention of a security interest in the equipment financed. Finance charges are sometimes waived for specified periods or reduced on certain John Deere products sold or leased in advance of the season of use or in other sales promotions. The financial services operations generally receive compensation from the sales companies at approximate market interest rates for periods during which finance charges are waived or reduced on the retail notes or leases. The cost is accounted for as a deduction in arriving at net sales by the equipment operations.
We have an agreement with Capital Corporation to make payments to Capital Corporation such that its consolidated ratio of earnings to fixed charges is not less than 1.05 to 1 for any four consecutive fiscal quarterly periods. We also have committed to continuing to own, directly or through one or more wholly-owned subsidiaries, at least 51 percent of the voting shares of capital stock of Capital Corporation and to maintain Capital Corporation’s consolidated tangible net worth at not less than $50 million. Our obligations to make payments to Capital Corporation under this agreement are independent of whether Capital Corporation is in default on its indebtedness, obligations, or other liabilities. Further, our obligations under the agreement are not measured by the amount of Capital Corporation’s indebtedness, obligations, or other liabilities. Our obligations to make payments under this agreement are expressly stated not to be a guaranty of any specific indebtedness, obligation, or liability of Capital Corporation and are enforceable only by or in the name of Capital Corporation. As of October 29, 2023, we were in compliance with all of our obligations, and no payments were required under this agreement in fiscal year 2023 or fiscal year 2022. At October 29, 2023, we indirectly owned 100 percent of the voting shares of Capital Corporation’s capital stock and Capital Corporation’s consolidated tangible net worth was $5,901.6 million.
9
Outside the U.S. and Canada. The financial services operations also offer financing, primarily for our products, in Argentina, Australia, Brazil, China, India, Mexico, New Zealand, and in several other countries in Africa, Asia, Europe, and Latin America. John Deere Financial sold its financial services business in Russia during the second quarter of fiscal year 2023. In certain markets, financing is offered through cooperation agreements or joint ventures with other financial institutions. The way the financial services operations offer financing in these countries is affected by a variety of country-specific laws, regulations, and customs, including those governing property rights and debtor obligations, which are subject to change, and which may introduce greater risk to the financial services operations.
The financial services operations also offer to select customers and dealers credit enhanced international export financing primarily for the purchase of our products.
Additional information on the financial services operations is provided in the “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” (MD&A) section in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Environmental Matters
We are subject to a variety of local, state, and federal environmental laws and regulations in the U.S., as well as the environmental laws and regulations of other countries in which we conduct business. We strive to comply with applicable laws and regulations; however, in the event of noncompliance, we could be subject to fines and other penalties. Compliance with these laws and regulations adds to the cost of our production operations. Compliance with emissions regulations adds to the cost of our products. However, we do not expect to incur material capital expenditures for environmental control facilities during fiscal year 2024. In addition to ensuring compliance with laws and regulations, we aim to reduce our environmental footprint through our Leap Ambitions framework and seek opportunities to reduce environmental impacts on the communities where we operate.
The U.S., the European Union (EU), India, and other governments throughout the world have enacted, and continue to enact, laws and regulations to reduce off-road engine emissions. Compliance with these regulations requires significant investments in the development of new engine technologies and after-treatment systems.
Governments also are implementing laws regulating products across their life cycles, including raw material sourcing and the storage, distribution, sale, use, and disposal of products at their end-of-life. These laws and regulations include requirements to develop less hazardous chemical substances and products, right-to-know, restriction of hazardous substances, and product take-back laws.
We are evaluating, cleaning-up, or conducting corrective action at a limited number of sites. We do not expect that these matters or other expenses or liabilities we may incur in connection with any noncompliance with environmental laws, regulations, or the clean-up of any additional properties, will have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations, cash flows, or competitive position.
We continue to monitor and review developing sustainability frameworks, standards, and global regulations and work to incorporate those most applicable to our business into our sustainability reporting.
With respect to properties and businesses that have been or will be acquired, we conduct due diligence into potential exposure to environmental liabilities but cannot be certain that we have identified, or will identify, all adverse environmental conditions. Compliance with these laws and regulations adds to the cost of our production operations. Compliance with emissions regulations adds to the cost of our products. However, we do not expect to incur material capital expenditures for environmental controls facilities during fiscal year 2024. In addition to ensuring compliance with laws and regulations, we aim to reduce our environmental footprint through our Leap Ambitions framework and seek opportunities to reduce environmental impacts on the communities where we operate.
New regulations applicable to John Deere products
California promulgated regulations prohibiting the use of small off-road spark-ignition engines under 25 horsepower. These regulations go into effect in 2024 and will impact some of our products, such as our turf care and golf course maintenance products. Even though we do not expect a material impact to our business from these regulations, to comply with new laws and regulations that limit off-road gasoline and diesel-powered engines, we intend to offer an electric option in each turf and compact utility tractor product family by 2026. However, compliance with emissions regulations has added, and will continue to add, to the cost of our products.
10
Government Regulations
We are subject to a wide variety of local, state, and federal laws and regulations in the countries where we operate. These laws and regulations include a range of trade, product, foreign exchange, employment, tax, environmental, safety, data privacy, antitrust, and other laws and regulations.
Compliance with these laws and regulations often requires the dedication of time and effort of our employees, as well as financial resources. In fiscal year 2023, compliance with the regulations applicable to us did not have a material effect on our capital expenditures, earnings, or competitive position. At this time, we do not expect to incur material capital expenditures related to compliance with regulations during fiscal year 2024. Additional information about the impact of government regulations on our business is included in Item 1A, “Risk Factors – Strategic Risks” and “Legal and Compliance Risks.”
Human Capital
Higher Purpose
Our employees are guided by our higher purpose: We run so life can leap forward. Employees are further guided by our Code of Business Conduct (Code), which helps them to uphold and strengthen the standards of honor and integrity that have defined us since our founding. Our world and business may change, yet we continue to be guided by our core values— integrity, quality, commitment, and innovation.
Employees
At October 29, 2023, we had approximately 83,000 employees, including approximately 33,800 employees in the U.S. and Canada. We also retain consultants, independent contractors, temporary, and part-time workers. Unions are certified as bargaining agents for approximately 80 percent of our U.S. production and maintenance employees. Approximately 11,500 of our active U.S. production and maintenance workers are covered by a collective bargaining agreement with the International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America (UAW), with an expiration date of November 1, 2027. A small number of U.S. production employees are represented by the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers (IAM). Collective bargaining agreements covering our employees in the U.S. expire between 2024 and 2027. Unions also represent the majority of employees at our manufacturing facilities outside the U.S.
There is no guarantee that we will be able to renew collective bargaining agreements or whether such agreements will be on terms satisfactory to us. For further discussion, see “Risk Factors—Disputes with labor unions may adversely affect our ability to operate in our facilities as well as impact our financial results.”
Code of Business Conduct
We are committed to conducting business in accordance with the highest ethical standards. We require all employees to complete training on our Code and, where permitted by law, also require that employees regularly certify compliance with the Code. The Code provides specific guidance to all our employees, outlining how they can and must uphold and strengthen the integrity that has defined John Deere since its founding. In addition, we maintain a global compliance hotline to allow for concerns of potential violations of the Code, global policies, or the law to be brought forward.
Health and Safety
We strive to achieve safety excellence through increased focus on leading indicators, risk reduction, health and safety management systems, and prevention. We have made progress on implementing best practices and leading indicators for enabling employee safety over recent years with our Health and Safety Management System.
We utilize a safety balanced scorecard, which includes leading and lagging indicators, and is designed to enable continuous measurement of safety performance and drive continuous improvement. Leading indicators include incident corrective action closure rates, ergonomic scorecard, and risk reduction from safety and ergonomic risk assessment projects. Lagging indicators include total recordable incident rate, ergonomic recordable case rate, and near-miss rate. Leading indicators are tracked by most of our manufacturing facilities and internally reported. In fiscal year 2023, we reported a total recordable incident rate of 2.08 and a lost time frequency rate of 0.65. To improve our total recordable incident rate, we will prioritize risk and injury reduction strategies, improve ergonomic programs, and focus on prevention through design.
We also updated our new employee onboarding in fiscal year 2023 to include training labs, hands-on-training, tooling and process exposures on the shop floor, operator checklists, and training videos of workstations.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)
We adhere to the principle of equal employment opportunity and we believe that a diverse workforce is essential to our long-term success and solving our customers’ most pressing challenges. We strive to foster a diverse, equitable, and inclusive culture. We embrace employees’ differences in race, color, religion, age, sex, sexual orientation, gender, gender identity and expression, marital or partnership status, family status, citizenship, national origin, ancestry, geographic background, military or veteran status, disability (mental or physical), and any other characteristics that make our employees unique.
11
Our leadership team works to set a consistent and transparent tone on DEI issues and strategy. We also create spaces for open conversations and learning through our Employee Resources Groups (ERGs) speaker series and micro-learnings. We sponsor 13 ERGs that are run by employees, open to all employees, and are a key driver of inclusion. ERGs build organization-wide networks that allow employees to come together and discuss shared interests. The global chapters work with local teams to support efforts to attract, retain, and develop the best talent. In addition, our global DEI strategy focuses on embedding DEI into world-wide business operations and people processes.
In addition to recruiting from a wide array of colleges and universities, we partner with several professional organizations to support our diversity recruitment strategy, including AnitaB.org – a global organization for women in technology, Minorities in Agriculture Natural Resources and Related Sciences, the National Association of Black Accountants, Inc., the National Black MBA Association, Inc., the National Society of Black Engineers, the Society of Women Engineers, the Thurgood Marshall College Fund Leadership Institute, and the Society of Hispanic Professional Engineers. Our broad recruiting strategy helps us identify talent from all backgrounds.
Compensation & Benefits
Our total rewards are intended to be competitive, meet the varied needs of our global workforce, and reinforce our values. We are committed to providing comprehensive and competitive pay and benefits to our employees. We invested, and continue to invest, in employees through growth and development and well-being initiatives.
Our work environment is designed to promote innovation, well-being, and reward performance. Our total rewards for employees include a variety of components that aim to support sustainable employment and the ability to build a strong financial future, including competitive market-based pay and comprehensive benefits. In addition to earning base pay, eligible employees are compensated for their contributions to our goals with both short-term cash incentives and long-term equity-based incentives.
Eligible full-time employees in the U.S. have access to medical, dental, and vision plans; savings and retirement plans; parental leave and paid time off; and other resources, such as the Employee Assistance Program, which provides mental health and wellness services. We also offer a variety of working arrangements to eligible employees, including flexible schedules, remote work, and job sharing to help employees manage home and work-life situations. Programs and benefits differ internationally for a variety of reasons, such as local legal requirements, market practices, and negotiations with works councils, trade unions, and other employee representative bodies.
Training and Development
Employees are critical to the long-term success of our business. We encourage employees to identify the paths that can build the skills, experience, knowledge, and competencies needed for career advancement. We support employees by creating purpose-driven work opportunities, comprehensive performance reviews and development plans, mentoring opportunities, and professional and personal development opportunities.
We encourage employees to provide feedback across the enterprise through our internal voluntary employee experience survey, ad-hoc “pulse” surveys, and new-hire and exit surveys. Reports from these surveys help equip us to address needs across the employee lifecycle to improve the overall experience and engagement of our workforce.
Around the world, we offer internships, training, upskilling, apprenticeships, and leadership development at all stages of an employee’s career. Training programs are tailored to different geographic regions and job functions and include topics such as technical operation of equipment, equipment assembly, relationships with customers and dealers, our culture and values, compliance with the Code, compliance with anti-bribery/corruption laws and policies, compliance with management of private data and cybersecurity, conflicts of interest, discrimination and workplace harassment policies, sexual harassment policies, and leadership development.
Human Rights and Our Code of Conduct
We honor human rights and respect the individual dignity of all persons globally. Our commitment to human rights requires that we understand and fulfill our responsibilities consistent with our values and practices. We strive to ensure that human rights are upheld for our employees and workers in our supply chain. Our commitment to human rights is defined in the Code, our Supplier Code of Conduct, our Dealer Code of Conduct, related policies and procedures, and our statement “Support of Human Rights in our Business Practice,” each of which is available on our website under “Governance.” These documents establish guidelines for our employees, suppliers, and dealers. We do not tolerate human rights abuses, such as forced labor, unlawful child labor, and human trafficking.
12
INFORMATION ABOUT OUR EXECUTIVE OFFICERS
The following are our executive officers as of December 6, 2023. All executive officers are elected or appointed by the Board of Directors and hold office until the meeting of the Board of Directors following the annual meeting of stockholders each year.
Name (Age) |
Present Deere Position (Effective Date) |
Business Experience (Effective Date) |
John C. May (54) |
Chairman, Chief Executive Officer, and President (2020) |
-
Chief Executive Officer and President (2019)
-
President and Chief Operating Officer (2019)
-
President, Worldwide Agriculture & Turf Division Global Harvesting and Turf Platforms, Ag Solutions Americas, and Australia (2018)
|
Joshua A. Jepsen (46) |
Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (2022) |
-
Deputy Financial Officer (2022)
-
Director, Investor Relations (2018)
|
Ryan D. Campbell (49) |
President, Worldwide Construction & Forestry Division and Power Systems (2022) |
-
Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (2019)
-
Deputy Financial Officer (2018)
|
Jahmy J. Hindman (48) |
Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer (2023) |
-
Chief Technology Officer (2020)
-
Global Director Tractor Platform Engineering (2018)
-
Global Manager, Architecture, Systems, Modules (2018)
|
Mary K.W. Jones (55) |
Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Worldwide Public Affairs (2019) |
-
Senior Vice President and General Counsel (2013)
|
Rajesh Kalathur (55) |
President, John Deere Financial, and Chief Information Officer (2022) |
-
President, John Deere Financial and Senior Vice President, Global Information Technology and Chief Financial Officer (2022)
-
President, John Deere Financial, and Chief Information Officer (2019)
-
Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Information Officer (2018)
|
Deanna M. Kovar (45) |
President, Worldwide Agriculture & Turf Division, Small Ag & Turf, Sales and Marketing Regions of Europe, CIS, Asia, and Africa (2023) |
-
Vice President, Production Systems, Production & Precision Ag (2023)
-
Vice President, Production Systems (2020)
-
Director, Operation Station (2018)
|
Felecia J. Pryor (49) |
Senior Vice President and Chief People Officer (2022) |
-
Executive Vice President & Chief Human Resources Officer, BorgWarner Inc (2022)
-
Global Vice President Human Resources, BorgWarner, Inc. - Morse Systems (2019)
-
Vice President Human Resources ASEAN, Ford Motor Company (2016)
|
Cory J. Reed (53) |
President, Worldwide Agriculture & Turf Division, Production & Precision Ag, Sales and Marketing Regions of the Americas and Australia (2020) |
-
President, Worldwide Agriculture & Turf Division, Americas and Australia, Global Harvesting and Turf Platforms, Agricultural Solutions (2019)
-
President, John Deere Financial (2016)
|
Justin R. Rose (44) |
President, Lifecycle Solutions, Supply Management, and Customer Success (2022) |
-
Senior Partner and Managing Director at the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) (2020)
-
Various roles of increasing responsibility from Associate to Partner and Managing Director at BCG (2002)
|
13
ITEM 1A.RISK FACTORS.
The following risks are considered material to our business based upon current knowledge, information, and assumptions. This discussion of risk factors should be considered closely in conjunction with the MD&A, including the risks and uncertainties described in the Forward-Looking Statements, and the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. These risk factors and other forward-looking statements relate to future events, expectations, trends, and operating periods. They involve certain factors that are subject to change and important risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially. Some of these risks and uncertainties could affect particular lines of business, while others could affect all our businesses. Although the risks are organized by headings and each risk is discussed separately, many are interrelated. The risks described in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and the Forward-Looking Statements in this report are not the only risks faced by us.
STRATEGIC RISKS
We may face risks associated with international, national, and regional trade laws, regulations, and policies, and government farm programs and policies which could significantly impair our profitability and growth prospects.
International, national, and regional laws, regulations, and policies directly or indirectly related to or restricting the import and export of our products, services, and technology, or those of our customers, or for the benefit of favored industries or sectors, could harm our global business. We are subject to various regulatory risks including, but not limited to, the following:
| ● | Restricted access to global markets could impair our ability to export goods and services from various manufacturing locations around the world. Restricted access could limit the ability to access raw materials and high-quality parts and components at competitive prices on a timely basis. For example, expanding export controls or limits on foreign investment can impact global supply of key materials and components, and actions taken within the US-China trade conflict can impact business in China, as well as sales, import/exports, and/or business engagement with Chinese entities globally. |
| ● | Trade restrictions, negotiation of new trade agreements, non-tariff trade barriers, local content requirements, and imposition of new or retaliatory tariffs against certain countries or covering certain products, including developments in U.S.-China trade relations, export control and sanctions against Russia, have limited, and could continue to limit, our ability to capitalize on current and future growth opportunities in international markets. These trade restrictions, and changes in, or uncertainty surrounding global trade policies, may affect our competitive position. |
| ● | Trade restrictions could impede those in developing countries from achieving a higher standard of living, which could negatively impact our future growth opportunities arising from increasing global demand for food, fuel, and infrastructure. |
| ● | Policies impacting exchange rates and commodity prices, or those limiting the export or import of commodities, could have a material adverse effect on the international flow of agricultural and other commodities that may result in a corresponding negative effect on the demand for agricultural and forestry equipment in many areas of the world. Our agricultural equipment sales could be harmed by such policies because farm income influences sales of agricultural equipment around the world. |
| ● | Changes in government farm programs and policies can influence demand for agricultural equipment as well as create unequal competition for multinational companies relative to domestic companies. |
We may be unable to manage increasing political, economic, and social uncertainty in certain regions of the world, which could significantly change the dynamics of our competition, customer base, and product offerings globally.
Efforts to grow our businesses depend in part upon access and developing market share and profitability in additional geographic markets, including, but not limited to, Argentina, Brazil, China, India, and South Africa. There are various risks associated with our global footprint, including, but not limited to, the following:
| ● | In some cases, these countries have greater political and economic volatility, greater vulnerability to infrastructure and labor disruptions, and differing customer product preferences and requirements than our other markets. In fiscal year 2023, as a result of the war in Ukraine, we suspended shipments of machines and service parts to Russia. The suspension of shipments to Russia reduced actual and forecasted revenue for the region and resulted in impairments of most long-lived assets, among other impacts. In addition, we initiated a voluntary separation program for employees in Russia in the third quarter of fiscal year 2022. |
| ● | Having business operations in various regions and countries exposes us to multiple and potentially conflicting business practices and legal and regulatory requirements that are subject to change. These practices and legal requirements are often complex and difficult to navigate, including those related to tariffs and trade regulations, investments, property ownership rights, taxation, repatriation of earnings, and advanced technologies. |
14
| ● | Expanding business operations globally also increases exposure to currency fluctuations, which can materially affect our financial results. |
| ● | While we maintain a positive corporate image and our brands are widely recognized and valued in our traditional markets, the brands are less known in some emerging markets, which could impede our efforts to successfully compete in these markets. |
| ● | Changing U.S. export controls and sanctions on various foreign countries and on various parties could affect our ability to collect receivables, provide aftermarket warranty support for our equipment, sell products, and otherwise impact our reputation and business. |
We may be impacted by general negative economic conditions and outlook, causing weakened demand for our equipment and services, limiting access to funding, and resulting in higher funding costs.
The demand for our products and services depends on the fundamentals in the markets in which we operate and can be significantly reduced in an economic environment characterized by high unemployment, high interest rates, cautious consumer spending, inflation, lower corporate earnings, and lower business investment. Negative or uncertain economic conditions that cause our customers to lack confidence in the general economic outlook can significantly reduce their likelihood of purchasing our equipment. These economic events adversely affected and may continue to adversely affect our operations.
Sustained general negative economic conditions and outlook also affect housing starts, energy prices and demand, and other construction, which dampens demand for certain construction equipment. Our turf operations and our construction and forestry segments are dependent on construction activity and have also been affected by recent adverse economic conditions. Decreases in construction activity and housing starts could have a material adverse effect on our financial results.
If negative economic conditions affect the overall farm economy, there could be a similar effect on our agricultural equipment sales. Uncertain or negative outlook with respect to pervasive U.S. fiscal issues as well as general economic conditions and outlook, such as market volatility and continuing interest rate increases by the Federal Reserve, have caused and could continue to cause significant changes in market liquidity conditions. Such changes could impact access to funding and associated funding costs, which could reduce our earnings and cash flows.
We may be affected by changing worldwide demand for food and different forms of renewable energy, which could impact the price of farm commodities and consequently the demand for our equipment. This could result in higher research and development costs related to changing machine fuel requirements.
Changing worldwide demand for farm outputs to meet the world’s growing food and renewable energy demands, driven in part by government policies, including those related to climate change, and a growing world population, are likely to result in fluctuating agricultural commodity prices, which directly affect sales of agricultural equipment. Lower agricultural commodity prices directly affect farm incomes, which could negatively affect sales of agricultural equipment and result in higher credit losses. While higher commodity prices benefit our crop-producing agricultural equipment customers, they could result in greater feed costs for livestock and poultry producers, which in turn may result in lower levels of equipment purchased by these customers. In addition, changing energy renewable demands may cause farmers to change the types or quantities of the crops they raise, with corresponding changes in equipment demands. Finally, changes in governmental policies regulating bio-fuel utilization could affect commodity demand and commodity prices, demand for our diesel-fueled equipment, and result in higher research and development costs related to equipment fuel standards.
We may not realize the anticipated benefits of our Smart Industrial Operating Model and Leap Ambitions.
Failure to realize the anticipated benefits of our Smart Industrial Operating Model and related business strategies in production systems, precision technologies, and aftermarket support could adversely affect results of our operations and financial condition. Several factors could impact our ability to successfully execute our Smart Industrial Operating Model, including, among other things:
| ● | Failure to accurately assess market opportunities and the technology required to address such opportunities; |
| ● | Failure to develop and introduce new technologies or lack of adoption of such technologies by our customers; |
| ● | Failure to holistically provide lifecycle solutions; and |
| ● | Failure to optimize our capital allocation in connection with the Smart Industrial Operating Model. |
15
Similarly, we may not realize the anticipated benefits of our Leap Ambitions and related goals within the expected timelines, or at all. As part of our Leap Ambitions we adopted various goals we expect to achieve by 2026 or 2030. We may not be able to achieve these goals for a variety reasons, some of which may be beyond our control. Examples include:
| ● | Our estimates and assumptions related to efficiency of our products and the adoption of precision technology may not be accurate; |
| ● | Certain materials, such as quality battery cells and cameras, may become unavailable or too costly; |
| ● | The infrastructure required to achieve our goals, such as sufficient charging stations or fuel availability, may become too costly or may not be developed on the expected timeline; and |
| ● | The actual or perceived failure to achieve our Leap Ambitions could negatively impact our ability to execute the Smart Industrial Operating Model. |
We may not realize all anticipated benefits of acquisitions, joint ventures, and divestitures, or these benefits may take longer to realize than expected.
From time to time, we make strategic acquisitions and divestitures and participate in joint ventures. Acquisitions and joint ventures we have entered, or may enter in the future, may involve significant challenges and risks, including that the acquisitions or joint ventures do not advance our business strategy, or fail to produce satisfactory returns on investment. Other risks include:
| ● | We may encounter difficulties in integrating acquisitions with our operations, applying internal control processes to these acquisitions, managing strategic investments, assimilating new capabilities to meet the future needs of our businesses, and/or combining business cultures; |
| ● | We may choose not to fully integrate businesses and may face regulatory or compliance exposure until appropriate processes and controls are put in place; |
| ● | Integrating acquisitions is often costly and may require significant attention from management and personnel; |
| ● | We may not realize all the anticipated benefits of acquisitions or joint ventures, or the realized benefits may be significantly delayed; and |
| ● | Due diligence evaluations of potential transactions include business, legal, and financial reviews with the goal of identifying and evaluating the material risks involved. These due diligence reviews may not identify all of the issues necessary to accurately estimate the cost and potential risks of a particular acquisition or joint venture, including potential exposure to regulatory sanctions resulting from an acquisition target’s or joint venture partner’s previous activities or costs associated with any quality issues with an acquisition target’s or joint venture’s products or services. |
We may also decide to divest businesses if in the best interests of our shareholders and joint ventures may be terminated at or before their stated expiration. For example, in March and October 2023, we sold our financial services and roadbuilding businesses in Russia following the outbreak of the war in Ukraine. Divestitures of businesses or dissolutions of joint ventures may involve significant challenges and risks, including failure to advance our business strategy, costs or disruptions to us, and negative effects on our product offerings, which may adversely affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition. Divestitures of businesses and dissolutions of joint ventures may result in ongoing financial or legal involvement in the divested business through indemnifications or other financial arrangements, such as retained liabilities, which could affect our future financial results.
Our ability to understand our customers’ preferences and requirements and to develop, manufacture, and market products that meet customer demand could significantly affect our business results.
Our ability to match new product offerings to global customers’ preferences for different types and sizes of equipment and various equipment features and functionality, at affordable prices, is critical to our success. This requires a thorough understanding of our existing and potential customers on a global basis, particularly in growth markets such as Argentina, Brazil, and India. Failure to deliver quality products that meet customer needs at competitive prices could have an adverse effect on our business.
In addition, customer preferences in the markets we serve are changing as a result of ongoing social and regulatory focus on sustainability as these markets transition to less carbon-intensive business models. As regulations and social pressure drive change, we must continue to proactively monitor trends and develop alternatives and enhancements that elevate and complement our product offerings. For example, even though we plan to offer electric, hybrid-electric, and battery electric equipment solutions, we may be unable to keep up with the rising demand for electric agriculture, turf, and construction equipment.
16
The development of alternative farming techniques, carbon sequestration technologies, and new low-carbon biofuels are changing farmers’ business models and equipment needs. If we fail to continue to develop or invest in emerging technologies to meet changing customer demands, we will be at risk of losing potential sources of revenue, which could affect our future financial results.
If we are unable to deliver precision technology and agricultural solutions to our customers, it could affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
Our approach to precision technology involves hardware and software, guidance, connectivity and digital solutions, automation and machine intelligence, and autonomy. Customers continue to adopt technology integrated in our portfolio of “smart” machines, systems, and solutions. We expect this trend to persist for the foreseeable future. To create and maintain a competitive differentiation, we need to successfully develop and introduce new precision technology solutions that improve profitability and sustainability for our customers. We may make significant investments in research and development, connectivity solutions, digital security for precision technology solutions, and dealer and employee training. These investments may not produce solutions that provide the desired results for customers’ profitability or sustainability outcomes. We utilize automation and machine learning and intelligence in some of our products. While the use of these emerging technologies can present significant benefits, it also creates risks and challenges. Data sourcing, technology, integration and process issues, program bias into decision-making algorithms, security problems, and the protection of privacy could impair the adoption and acceptance of autonomous machine solutions. If the output from these solutions is deemed to be inaccurate or questionable, our brand and reputation may be harmed and we may be subject to legal liability claims. Automation and machine learning and intelligence may also become the subject of local, state, federal, and foreign regulatory efforts limiting the features and capabilities of the technology. If we are not able to deliver precision technology solutions with differentiated features and functionality, or these solutions are not effective, customers may not adopt technology solutions, which could have a material adverse effect on our reputation and business.
We could be impacted by changes to or reallocation of radio frequency (RF) bands which could disrupt or degrade the reliability of our high precision augmented Global Positioning System (GPS) or other RF technology, which could impair our ability to develop and market GPS- and RF-based technology solutions, as well as significantly reduce agricultural and construction customers’ profitability.
Our current and planned integrated agricultural business and equipment management systems, as well as our fleet management telematics solutions for construction equipment, depend upon the use of RF signals. These signals include, but are not limited to, GPS signals, other GPS-like satellite signals, augmented GPS services, and other RF technologies that link equipment, operations, owners, dealers, and technicians. These radio services depend on frequency allocations governed by international and national government agencies. Any international or national reallocation of frequency bands, including frequency bands segmentation and band spectrum sharing, or other modifications concerning the regulation of frequency bands, could significantly disrupt or degrade the utility and reliability of our GPS-based products, which could negatively affect our ability to develop and market GPS-based technology solutions.
In addition, disruptions with GPS signals or the failure of telecommunications network operators to supply the bandwidth we need to support our products could interfere with the speed, availability, and usability of our equipment and services. If these GPS signals or RF signals become unavailable, our customers could be unable to use their equipment indefinitely. For our agricultural customers, this could result in lower crop yields, decreased operational efficiency, and higher equipment maintenance, seed, fertilizer, fuel, and wage costs. For construction customers, this could result in higher fuel and equipment maintenance costs, as well as lower construction design and project management efficiencies. These cost increases could significantly reduce customers’ profitability, sustainability, and demand for our products. As a result, our sales and revenue could significantly decrease, which would have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and our business.
Our ability to adapt in highly competitive markets could affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
We compete in a variety of highly competitive global and regional markets with other manufacturers and distributors that produce and sell similar products. In addition, our industry is attracting non-traditional competitors, including technology-focused companies and start-up ventures. We compete on product performance, innovation and quality, distribution, sustainability, customer service, and price. Aggressive pricing or other strategies of competitors, unanticipated product or manufacturing delays, or our failure to price products competitively could adversely affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
We rely on a network of independent dealers to manage the distribution of our products and services. If dealers are unsuccessful with their sales and business operations, it could have an adverse effect on our overall sales and revenue.
We rely on the capability of our dealers to develop and implement effective sales plans to create demand among purchasers for the equipment and related products and services that dealers purchase from us. If our dealers are unsuccessful in these endeavors, we will be unable to grow our sales and revenue, which would have an adverse effect on our financial condition.
17
In addition, the dealer channel’s ability to support and service precision technology solutions and emerging power solutions may affect customers’ acceptance and adoption rates of these products. The unavailability of specialized technicians to service our equipment may result in overburdening dealers’ servicing capacity.
Dealers may have trouble funding their day-to-day cash flow needs and paying their obligations due to adverse business conditions resulting from negative economic effects or other factors. Dealers may exit or we may seek to terminate relationships with certain dealers if they are unable to meet customer needs. The unplanned loss of any of our dealers could lead to inadequate market coverage, negative customer impressions, and may adversely impact our ability to collect receivables that are associated with that dealer.
ENVIRONMENTAL, CLIMATE, AND WEATHER RISKS
Unfavorable weather conditions or natural catastrophes that reduce agricultural production and demand for agriculture and turf equipment could directly and indirectly affect our business.
The purchasing decisions of our customers, particularly the purchasers of agriculture and turf equipment, can be significantly affected by poor or unusual weather conditions. Such conditions include:
| ● | Insufficient levels of rain, which prevent farmers from planting new crops and may cause growing crops to die or result in lower yields; |
| ● | Excessive rain or flooding can prevent planting from occurring at optimal times and may cause crop loss through increased disease or mold growth; |
| ● | Temperatures outside normal ranges, which can cause crop failure or decreased yields and may also affect disease incidence; |
| ● | Natural disasters such as regional floods, hurricanes or other storms, droughts, diseases, wildfires, and pests, either as a physical effect of climate change or otherwise, which have had, and could in the future have, significant negative effects on agricultural and livestock production; |
| ● | Adverse weather conditions in a particular geographic region, particularly during the important spring selling season; and |
| ● | Drought conditions can adversely affect sales of certain mowing equipment and can similarly cause lower sales volume. |
Each of these conditions could have a negative impact on farm income which can affect demand for agricultural equipment and the financial condition and credit risk of our dealers and customers.
Governmental actions designed to address climate change based on the emergence of new technologies and business models in connection with the transition to a lower-carbon economy could adversely affect John Deere and our customers.
There is global scientific consensus that greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions continue to alter the composition of Earth’s atmosphere in ways that are affecting and are expected to continue to affect the global climate. These considerations have led to new international, national, regional, and local legislative and regulatory responses. Various stakeholders, including legislators and regulators, shareholders, and non-governmental organizations, as well as companies in many business sectors, including us, are continuing to look for ways to reduce GHG emissions. The regulation of GHG emissions from certain stationary or mobile sources or the imposition of carbon pricing mechanisms could result in additional costs to us in the form of taxes or emission allowances, required facilities improvements, and increased energy costs. These results would increase our operating costs through higher utility, transportation, and materials cost and could prevent us from selling products into certain markets. Increased input costs, such as fuel and fertilizer, and compliance-related costs could also affect customer operations and demand for our equipment.
Further, our financial services segment is subject to additional international and national European regulations relating to climate and environmental risk, which are continually evolving and could affect the financing operations and climate-risk processes developed by the segment. Regulators in Europe and the U.S. have also focused efforts on increased disclosure related to climate change and mitigation efforts. The EU recently adopted the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) that will impose disclosure of the risks and opportunities arising from social and environmental issues, and on the impact of companies’ activities on people and the environment. The CSRD will need to be transposed into Member State law before it becomes effective, which is expected to occur in 2024. Similarly, the State of California recently passed the Climate Corporate Data Accountability Act and the Climate-Related Financial Risk Act that will impose broad climate-related disclosure obligations on certain companies doing business in California, including us, starting in 2026. The SEC has included in its regulatory agenda potential rulemaking on climate change disclosures that, if adopted, could significantly increase compliance burdens and associated regulatory costs and complexity.
18
Increasingly stringent engine emission regulations or bans on internal combustion engines may impact our ability to manufacture and distribute certain engines or equipment, which could negatively affect business results.
Our equipment operations must meet increasingly stringent engine emission reduction regulations throughout the world, including the European Union’s Stage V standard, which limits the amount of certain substances in exhaust gases that off-road engines can emit into the environment. Governmental agencies throughout the world are enacting more stringent laws and regulations to reduce off-road engine emissions. These laws and regulations are applicable to engines we manufacture, including those used in agriculture and CF equipment.
We have incurred, and continue to incur, substantial research and development costs related to the implementation of these more rigorous laws and regulations. While we have developed and are executing comprehensive plans to meet these requirements, these plans are subject to variables that could delay or otherwise affect our ability to manufacture and distribute certain equipment or engines, which could negatively impact business results. Additionally, in certain locations governments have banned, or may in the future ban, internal combustion engines for some types of products completely. To the extent these bans affect products manufactured and sold by us, our business, results of operations, and financial condition could be negatively affected.
FINANCIAL RISKS
Changes in government banking, monetary, and fiscal policies could have a negative effect on us.
Policies of the U.S. and other governments regarding banking, monetary, and fiscal policies intended to promote or maintain liquidity, stabilize financial markets, and/or address local deficit or structural economic issues could have a material impact on our customers and markets. Central bank policy interest rates continued to increase in fiscal year 2023. Most of our retail receivables are fixed rate, while wholesale financing receivables are variable rate. We have both fixed and variable rate borrowings. Historically, rising interest rates impact our borrowings sooner than the benefit is realized from the financing receivable and equipment on operating lease portfolios.
Our operations and results could also be affected by financial regulatory reform that could, among other things, have an adverse effect on the financial services segment and on our customers by limiting their ability to enter hedging transactions or to finance purchases of our products. Government policies on spending can also affect us, especially the CF segment, due to the impact of government spending on infrastructure development. Our operations, including those outside of the U.S., may also be affected by non-U.S. regulatory reforms being implemented to further regulate non-U.S. financial institutions and markets.
Changes in tax rates, tax legislation, or exposure to additional tax liabilities could have a negative effect on our business.
We are subject to income taxes in the U.S. and numerous foreign jurisdictions. Our domestic and international tax liabilities are dependent upon the location of earnings among these different jurisdictions. Tax rates in various jurisdictions may be subject to significant change. Our effective tax rates could be affected by changes in the mix of earnings in countries with differing statutory tax rates, changes in the valuation of deferred tax assets and liabilities, or changes in tax laws or their interpretations. If our effective tax rates were to increase, or if the ultimate determination of taxes owed is for an amount more than amounts previously accrued, our operating results, cash flows, and financial condition could be adversely affected.
Our consolidated financial results are reported in U.S. dollars while certain assets and other reported items are denominated in foreign currencies, creating currency exchange and translation risk.
We are a global company with transactions denominated in a variety of currencies. We are subject to currency exchange risk to the extent that our costs are denominated in currencies other than those in which we earn our revenues.
Additionally, the reporting currency for our consolidated financial statements is the U.S. dollar. Certain of our assets, liabilities, expenses, and revenues are denominated in other countries’ currencies, which are then translated into U.S. dollars at the applicable exchange rates and reported in our consolidated financial statements. Therefore, fluctuations in foreign exchange rates affect the value of those items as reflected in our consolidated financial statements, even if their value remains unchanged in the original currencies. While the use of currency hedging instruments may provide us with some protection from adverse fluctuations in currency exchange rates, by utilizing these instruments we potentially forego any benefits that may result from favorable fluctuations in such rates. In Argentina, we have employed mechanisms to convert Argentine pesos into U.S. dollars to the extent possible. These mechanisms are short-term in nature, leaving us exposed to long-term currency fluctuations.
Changes in interest rates or market liquidity conditions could adversely affect our financials and our earnings and/or cash flows.
Central bank policy interest rates continued to increase in fiscal year 2023. Rising interest rates could have a dampening effect on overall economic activity and/or the financial condition of our customers, either or both of which could negatively affect customer demand for our equipment and customers’ ability to repay their obligations to us. Rising interest rates may cause credit market dislocations, that can impact funding costs, which can affect the financial services segment’s ability to offer customers competitive financing rates.
19
While we strive to match the interest rate characteristics of our financial assets and liabilities, changing interest rates have had an adverse effect on our net interest rate margin—the difference between the yield we earn on our assets and the interest rates we pay for funding, which has affected our net interest income and earnings.
In addition, actions by credit rating agencies, such as downgrades or negative changes to ratings outlooks, can affect the availability and cost of funding for us and can increase our costs of capital and hurt our competitive position.
Because the financial services segment provides financing for a significant portion of our sales worldwide, negative economic conditions in the financial industry could materially impact our operations and financial results.
Negative economic conditions could have an adverse effect on the financial industry in which the financial services segment operates. The financial services segment provides financing for a significant portion of our sales worldwide. The financial services segment is exposed to the risk that customers and others will default on contractual obligations and may experience credit losses that exceed our expectations and adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. The financial services segment’s inability to access funds at cost-effective rates to support our financing activities could have a material adverse effect on our business. The financial services segment’s liquidity and ongoing profitability depend largely on timely access to capital to meet future cash flow requirements and to fund operations and costs associated with engaging in diversified funding activities. Additionally, negative market conditions could reduce customer confidence levels, resulting in declines in credit applications and increases in delinquencies and default rates, which could materially impact the financial services segment’s write-offs and provision for credit losses. The financial services segment may also experience residual value losses that exceed our expectations caused by lower pricing for used equipment and higher-than-expected equipment returns at lease maturity.
We may sustain increases in funding obligations under our pension plans which may impair our liquidity or financial condition.
We maintain certain defined benefit pension plans for certain employees, which impose funding obligations. We use various assumptions in calculating our future payment obligations under these plans. Significant adverse changes in credit or market conditions could result in actual rates of return on pension investments being lower than expected. Regulatory changes could cause a deterioration in the statutory funded status of our plans. We may be required to make significant contributions to our pension plans in the future. These factors could significantly increase our payment obligations under the plans and adversely affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
MANUFACTURING AND OPERATIONAL RISKS
We may be unable to accurately forecast customer demand for products and services, and to adequately manage inventory, which could adversely affect our operating results.
To ensure adequate inventory supply, we must forecast inventory needs and expenses and place orders sufficiently in advance with suppliers and contract manufacturers. These forecasts are based on estimates of future demand for products and services. Failure to accurately forecast our needs may result in unmet market demand, parts shortages, manufacturing delays, increased costs, or excess inventory. In fiscal year 2022, supply chain disruptions resulted in higher inventory levels. Although production schedules in fiscal year 2023 were more aligned with the customers’ seasonal use of our products, marking a return to historical seasonal production patterns, our ability to accurately forecast demand in the future could be affected by many factors, including changes in customer demand for our products and services, changes in demand for the products and services of competitors, unanticipated changes in general market conditions, and the weakening of economic conditions or customer confidence in future economic conditions. If the forecasts used to manage inventory are not accurate, we may experience excess inventory levels, shortage of available products, or reduced manufacturing efficiencies.
Changes in the availability and price of certain raw materials, components, and whole goods have resulted and could continue to result in disruptions to the supply chain causing production disruptions, increased costs, and lower profits on sales of our products.
We require access to various raw materials, components, and whole goods at competitive prices to manufacture and distribute our products. The price and availability of these materials have varied significantly in the last 36 months. For example, in fiscal year 2022, supply chain disruptions impacted many aspects of our business, including receiving past due deliveries from suppliers, parts availability, increased production costs, and higher inventory levels. We experienced supply chain improvements in fiscal year 2023 with a return to normal in the second half of the fiscal year.
While we have seen stabilization in the supply chain and some commodity pricing improvements, we anticipate potential fluctuations due to inflation, geopolitical and economic uncertainty, and regulatory and policy instability, including import tariffs and trade agreements. The latter have the potential to significantly increase production and logistics costs and have a material negative effect on the profitability of the business, particularly if we are unable to recover the increased costs due to market considerations or other factors.
20
We have experienced changes in the availability and prices of these raw materials, components, whole goods, and freight over the past several years, especially in fiscal years 2021 and 2022.Global logistics network challenges resulted in delays, shortages of key manufacturing components, increased order backlogs, increased transportation costs, and production inefficiencies from a higher number of partially completed machines in inventory, which increased our overall production and overhead costs. Increases in such costs have had an adverse effect on our business operations.
We rely on our suppliers to acquire the raw materials, components, and whole goods required to manufacture their products. Significant disruptions to the supply chain resulting from shortages of raw materials, components, and whole goods have and could continue to adversely affect our ability to meet commitments to our customers. In addition, certain materials and components used in our products are acquired from a single supplier or are proprietary in nature and cannot be alternatively sourced expeditiously. Furthermore, if our customers are unwilling to accept price increases for our products, or if we are unable to offset the increases in costs, raw material costs or shortages could have a material adverse effect on our operational or financial results.
Disputes with labor unions may adversely affect our ability to operate in our facilities as well as impact our financial results.
Many of our production and maintenance employees are represented by labor unions under various collective bargaining agreements with different expiration dates. Our failure to successfully renegotiate labor agreements as they expire has from time to time led, and could in the future lead, to work stoppages or other disputes with labor unions. For example, the UAW initiated a labor strike that had an adverse effect on our results of operations in fiscal 2022 because of reduced productions and shipments. Certain of our labor agreements expire as early as 2024. Disruptions to our manufacturing and parts-distribution facilities through various forms of labor disputes could adversely affect us. Any strike, work stoppage, or other dispute with a labor union distracts management from operating the business, may displace employees from ordinary job positions to fill in vacant positions, may affect our reputation, and could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
Our business may suffer if our equipment fails to perform as expected.
If our equipment does not perform as expected, we may receive warranty claims and have to perform post-sales repairs or recalls. We may also be subject to regulatory requirements and penalties that will impact our ability to develop, market, and sell equipment. This may result in product delivery delays. It could also lead to product liability, breach of warranty, and consumer protection claims. These claims and warranty expenses could be significant. As a manufacturer of equipment, we must manage the cost and risk associated with product warranties, post-sale repairs and recalls, regulatory penalties, and product liability, breach of warranty, and consumer protection claims with respect to our products. In addition to post-sale repairs or recalls initiated by us for various reasons, investigations into our products by government regulators may compel us to initiate product recalls or may result in negative public perceptions about the safety of our products, even if we disagree with the regulator’s determination. Such post-sale repairs or recalls, whether voluntary or involuntary, could result in significant expense, supply chain complications, and may harm our brand, business, prospects, financial condition, and operating results.
RESOURCES RISKS
Our ability to attract, develop, engage, and retain qualified employees could affect our ability to execute our strategy.
Our continued success depends, in part, on our ability to identify and attract qualified candidates with the requisite education, background, and experience as well as our ability to develop, engage, and retain qualified employees. Failure to attract, develop, engage, and retain qualified employees, whether as a result of an insufficient number of qualified applicants, difficulty in recruiting new employees, or inadequate resources to train, integrate, and retain qualified employees, could impair our ability to execute our business strategy and could adversely affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition. In addition, while we strive to reduce the impact of the departure of employees, our operations or ability to execute our business strategy and meet our business objectives may be affected by the loss of employees, particularly when departures involve larger numbers of employees, such as those we could experience if a surge occurs in the number of employees voluntarily leaving their jobs. Higher rates of employee separations may adversely affect us through decreased employee morale, the loss of knowledge of departing employees, and the devotion of resources to recruiting and onboarding new employees.
Security breaches and other disruptions to our information technology infrastructure could interfere with our operations and could compromise our information as well as information of our employees, customers, suppliers, and/or dealers, exposing us to liability that could cause our business and reputation to suffer.
In the ordinary course of business, we rely upon information technology networks and systems, some of which are managed by third parties, to process, transmit, and store electronic information and to manage or support a variety of business processes and activities, including supply chain, manufacturing, distribution, invoicing, and collection of payments from dealers and other purchasers of our equipment and from customers of the financial services segment. We use information technology systems to record, process, and summarize financial information and results of operations for internal reporting purposes and to comply with regulatory financial reporting, legal, and tax requirements.
21
Additionally, we collect and store sensitive data, including intellectual property, proprietary business information, and the proprietary business information of our customers, suppliers, and dealers, as well as personally identifiable information of our customers and employees in data centers which are often owned by third parties and on information technology networks. The secure operation of these information technology networks and the processing and maintenance of this information is critical to our business operations and strategy.
Despite security measures, including a vulnerability disclosure program, and business continuity plans, our information technology networks and infrastructure have been and may be vulnerable to intrusion, damage, disruptions, or shutdowns due to attacks by cyber criminals, employees’, suppliers’, or dealers’ error or malfeasance, supply chain compromise, disruptions during the process of upgrading or replacing computer software or hardware, power outages, computer viruses, ransomware or other malware, telecommunication or utility failures, terrorist acts, natural disasters, or other events. Although we have not suffered any significant cyber incidents that resulted in material business impact, we have from time to time been the target of malicious cyber threat actors. The occurrence of any significant event could compromise our networks, and the information stored there could be accessed, obtained, publicly disclosed, lost, altered, misused, or stolen. Any such access, disclosure, alteration, misuse, or other loss of information could result in legal claims or proceedings, government investigations, liability or regulatory penalties, disruption or shut down of our operations, and damage to our reputation, which could adversely affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition. Furthermore, as security threats continue to evolve and increase in frequency and sophistication, we may need to invest additional resources to protect information security.
Any unauthorized control or manipulation of our products’ systems could result in loss of confidence in us and our products.
Some of our products include connectivity hardware and software typically used for remote system updates. While we have implemented security measures intended to protect against unauthorized remote access to these products, malicious threat actors have attempted, and may attempt in the future, to gain unauthorized access to such products in order to gain control of the products, change the products’ functionality, user interface, or performance characteristics, interfere with the products’ operations, or gain access to data stored in or generated by the products or to systems to which they connect. In addition, reports of unauthorized access to our products, systems, and data, regardless of their reliability, may result in the perception that the products, systems, or data are vulnerable to malicious or unauthorized modifications. Any unauthorized access to or control of our products or systems, any loss of data, or any perception that products, systems, or data are vulnerable could result in legal claims or proceedings against us, government investigations, liability, or regulatory penalties, which could adversely affect our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
Our business could be adversely affected by the infringement or loss of intellectual property rights.
We protect our intellectual property with a combination of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secret laws, and legal agreements. We heavily rely on certain trademarks to protect our identity and customer recognition of our products and services, including, but not limited to, the “John Deere” mark, the leaping deer logo, the “Nothing Runs Like a Deere” slogan, and the green and yellow color combination. These trademarks, as well as the many patents that protect innovations used in our products, are integral to our business, and their loss could have a material adverse effect on us.
Additionally, third parties may initiate legal proceedings to challenge the validity of our intellectual property or allege that we infringe on their intellectual property. We may incur substantial costs if third parties initiate such legal proceedings, or if we initiate legal proceedings to protect or enforce our intellectual property. If the outcome of any such legal proceedings is unfavorable to us, our business could be adversely affected.
LEGAL AND COMPLIANCE RISKS
Our global operations are subject to complex and changing laws and regulations, the violation of which could expose us to potential liabilities, increased costs, and other adverse effects.
We are subject to numerous international, federal, state, and local laws and regulations, many of which are complex, frequently changing, and subject to varying interpretations. These laws and regulations cover a variety of subjects, including advertising, anti-money laundering, antitrust, consumer finance, environmental, climate-related, health and safety, foreign exchange controls and cash repatriation restrictions, foreign ownership and investment, import/export and trade, human rights, labor and employment, product liability reporting, cybersecurity, data privacy, telematics, and connectivity.
These laws may vary substantially within the different markets in which we operate. Compliance with these laws and regulations is expensive and may further increase the cost of conducting our global operations. In addition, we must comply with the U.S.
22
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and all applicable foreign anti-corruption laws, including the U.K. Bribery Act. These laws generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments or providing anything of value to improperly influence government officials or private individuals for the purpose of obtaining or retaining a business advantage, regardless of whether those practices are culturally expected in a particular jurisdiction. Although we have a compliance program in place designed to reduce the likelihood of potential violations of these laws and regulations, there can be no assurance that our employees, contractors, or agents will not violate such laws and regulations or our policies and procedures. Violations of these laws and regulations could result in criminal or civil sanctions and have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, results of operations, and financial condition.
Changes to existing laws and regulations, or changes to how they are interpreted, or the implementation of new, more stringent laws or regulations, could adversely affect our business by increasing compliance costs, limiting our ability to offer a product or service, requiring changes to our business practices, or otherwise making our products and services less attractive to customers. Legislative and regulatory changes, and other actions that could potentially affect our business may be announced with little or no advance notice and we may not be able to effectively mitigate all adverse effects from such measures.
We are subject to governmental laws, regulations, and other legal obligations related to privacy and data protection. Any inability or perceived inability of addressing these requirements could adversely affect our business.
The legislative and regulatory framework for privacy and data protection issues worldwide is rapidly evolving and is likely to remain uncertain for the foreseeable future. We collect personal information and other data as integral parts of our business processes and activities. This data is subject to a variety of U.S. and foreign laws and regulations, including oversight by various regulatory and other governmental bodies. Many foreign countries and governmental bodies, including the EU, China, Canada, and other relevant jurisdictions where we conduct business, have laws and regulations concerning the collection and use of personal information and other data obtained from their residents or by businesses operating within their jurisdictions. The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Privacy Act, and the China Personal Information Protection Law, among others, impose stringent data protection requirements and provide significant penalties for noncompliance. New privacy laws will continue to come into effect around the world in the future. Any inability or perceived inability to adequately address privacy and data protection concerns (even if unfounded), or comply with applicable laws, regulations, policies, industry standards, contractual obligations, or other legal obligations (including at newly acquired companies) could result in additional cost and liability to us, damage our reputation, inhibit sales, and otherwise adversely affect our business.
Legal proceedings and disputes in which we are, and may in the future be, involved could harm our business, financial condition, reputation, and brand.
We routinely are a party to claims and legal actions incidental to our business. These include claims for personal injury or property by users of our equipment, environmental, health, and safety claims, disputes with distributors, vendors and others with respect to commercial matters, and disputes with taxing and other governmental authorities regarding the conduct of our business. The defense of lawsuits and government inquiries or investigations has resulted and may result in expenditures of significant financial resources and the diversion of management’s time and attention away from business operations.
We are currently subject to a consolidated multidistrict class action lawsuit in the Northern District of Illinois alleging that we have engaged in attempted monopolization, exclusionary conduct, and restraint of the market for repair services for John Deere brand agricultural equipment by limiting repair resources only to our authorized technicians or independent authorized John Deere dealers. In addition, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is investigating whether we have violated laws in connection with the repair of John Deere brand agriculture equipment, as well as our information security practices and statements as they relate to the risk of unauthorized access to our computer systems, products, and services. We are fully cooperating with the FTC. We are currently unable to predict the outcome of these matters. The development and resolution of these matters could have a material adverse effect on our business, operations, and financial results.
GENERAL RISKS
Our reputation and brand could be damaged by negative publicity.
Our brand has worldwide recognition and significantly contributes to the success of our business. Our reputation is critical to growing our customer base. Our brand depends on the ability to maintain a positive customer perception of the business, including the core values of integrity, quality, innovation, and commitment. Negative claims or publicity involving us, our products or services, our culture and values, our stance on environmental, social, and governance topics, customer data, or any of our key employees or suppliers, could damage our reputation and brand image, regardless of whether such claims are accurate. In addition, our stance on environmental, social, and governance topics damage to our reputation could adversely impact the ability to attract new and maintain existing customers, employees, dealers, and business relationships. For example, we have been the subject of negative media articles relating to our customers’ right to maintain and safely repair their equipment.
23
Additionally, negative or inaccurate postings, articles, or comments on social media and the internet about us could generate negative publicity that could damage the reputation of our brand. Further, adverse publicity about regulatory or legal action against us, or legal proceedings initiated by us, could also damage our reputation and brand image, undermine customer confidence, and reduce long-term demand for equipment, even if the regulatory or legal action is unfounded or not material to our operations. If the reputation, culture, or image of our brands are damaged, or we receive negative publicity, then our sales, financial condition, and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
Unexpected events have increased and may in the future increase our cost of doing business or disrupt our operations.
The occurrence of one or more unexpected events, including war, acts of terrorism, epidemics and pandemics (such as the COVID pandemic), civil unrest, fires, tornadoes, tsunamis, hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, and other forms of severe weather in the United States or in other countries in which we operate, or in which our suppliers are located, have adversely affected and could in the future adversely affect our operations and financial performance. Such events have caused and could cause complete or partial closure of one or more of our manufacturing facilities or distribution centers, temporary or long-term disruptions in the supply of component products from some local and international suppliers, and disruption and delay in the transport of products to dealers, end-users, and distribution centers. Existing insurance coverage may not provide protection from all the costs that may arise from such events.
The potential physical impacts of climate change on our facilities, suppliers, and customers, and therefore on our operations, are highly uncertain and will be particular to the circumstances developing in various geographic regions. These potential physical effects may adversely affect the demand for our products and the cost, production, sales, and financial performance of our operations.
ITEM 1B. |
UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS. |
None.
ITEM 2. |
PROPERTIES. |
In the U.S. and Canada, the equipment operations own and operate 23 factory locations and lease and operate another 3 locations. Outside of the U.S. and Canada, the equipment operations own or lease and operate 45 factory locations in Argentina, Austria, Brazil, China, Finland, France, Germany, India, Israel, Italy, Mexico, the Netherlands, New Zealand, and Spain.
In addition, the equipment operations own or lease 12 facilities comprised of three locations supporting centralized parts distribution and nine regional parts depots and distribution centers throughout the U.S. and Canada. Outside the U.S. and Canada, the equipment operations also own or lease and occupy 11 total facilities with centralized parts distribution centers in Brazil, Germany, and India and regional parts depots and distribution centers in Argentina, Australia, China, India, Mexico, South Africa, Sweden, and the United Kingdom. We also own or lease eight facilities for the manufacture and distribution of other brands of replacement parts.
Our manufacturing facility in Russia was shut down in 2022. Our Eurasian parts distribution center in Russia was also closed, and the leased premises were returned to the landlord in the second quarter of fiscal year 2023. Premises owned by Wirtgen in Russia operating in the roadbuilding business were sold in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2023.
We own or lease 53 administrative offices and research facilities globally as well as many other smaller, miscellaneous facilities.
Overall, we own approximately 70.0 million square feet of facilities and lease approximately 13.1 million additional square feet in various locations. These properties are adequate and suitable for our business as presently conducted and are well maintained.
ITEM 3. |
LEGAL PROCEEDINGS. |
We are subject to various unresolved legal actions that arise in the normal course of business, the most prevalent of which relate to product liability (including asbestos related liability), retail credit, employment, patent, trademark, and antitrust matters. Currently we believe the reasonably possible range of losses for other unresolved legal actions would not have a material effect on our financial statements; however, the outcome of any current or future proceedings, claims, or investigations cannot be predicted with certainty. Adverse decisions in one or more of these proceedings, claims, or investigations could require us to pay substantial damages or fines, undertake service actions, initiate recall campaigns, or take other costly actions. It is therefore possible that legal judgements could give rise to expenses that are not covered, or not fully covered by our insurance programs and could affect our financial position and results.
ITEM 4. |
MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES. |
Not applicable.
24
PART II
ITEM 5. |
MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES. |
| (a) | Our common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the symbol “DE.” We have a history of paying quarterly cash dividends. While we currently expect a cash dividend to be paid in the future, future dividend payments will depend on our earnings, capital requirements, financial condition, and other factors considered relevant by our Board of Directors. See the information concerning the number of stockholders in Note 21 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
| (b) | Not applicable. |
| (c) | Purchases of our common stock during the fourth quarter of 2023 were as follows: |
ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Number of |
|
Number of Shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares Purchased |
|
that May Yet Be |
|
|
|
Total Number of |
|
|
|
|
as Part of Publicly |
|
Purchased under |
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
|
Announced Plans |
|
the Plans or |
|
|
|
|
Purchased (2) |
|
Average Price |
|
or Programs (1) |
|
Programs (1) |
|
|
Period |
|
(thousands) |
|
Per Share |
|
(thousands) |
|
(millions) |
|
|
Jul 31 to Aug 27 |
|
682 |
|
$ |
424.30 |
|
681 |
|
42.3 |
|
Aug 28 to Sept 24 |
|
2,204 |
|
|
410.43 |
|
2,204 |
|
39.8 |
|
Sept 25 to Oct 29 |
|
3,593 |
|
|
384.94 |
|
3,593 |
|
35.9 |
|
Total |
|
6,479 |
|
|
|
|
6,478 |
|
|
|
| (1) | We have a share repurchase plan that was announced in December 2022 to purchase up to $18.0 billion of shares of our common stock. The maximum number of shares that may yet be repurchased under this plan was 35.9 million based on the closing price of our common stock on the NYSE as of the end of the fourth quarter of $361.15 per share. At the end of the fourth quarter of 2023, $13.0 billion of common stock remains to be repurchased under this plan. |
| (2) | In the fourth quarter of 2023, 1 thousand shares were acquired from a plan participant at a market price of $431.68 to pay payroll taxes on the vesting of a restricted stock award. |
STOCK PERFORMANCE GRAPH
The graph compares the total shareholder returns (TSR) of Deere & Company, the Standard & Poor’s (S&P) 500 Construction Machinery & Heavy Transportation Equipment Index, the S&P 500 Industrials, and the S&P 500 Stock Index over a five-year period. It assumes $100 was invested on October 26, 2018 and that dividends were reinvested. Our stock price at October 27, 2023, was $361.15. Going forward, we intend to use the S&P 500 Industrials to replace the S&P 500 Construction Machinery & Heavy Transportation Equipment. We believe the S&P 500 Industrials provides a better benchmark to compare our cumulative total returns against the industry because it comprises those companies included in the S&P 500 that are classified as members of the GICS industrials sector, and therefore, have many characteristics similar to us, regardless of the specific types of products they offer. In contrast, the S&P’s 500 Construction Machinery & Heavy Transportation Equipment Index is made up of only four companies (Caterpillar (CAT), Cummins (CMI), Paccar (PCAR), and Wabtec (WAB)). The stock performance shown in the graph is not intended to forecast and does not necessarily indicate future price performance.
25
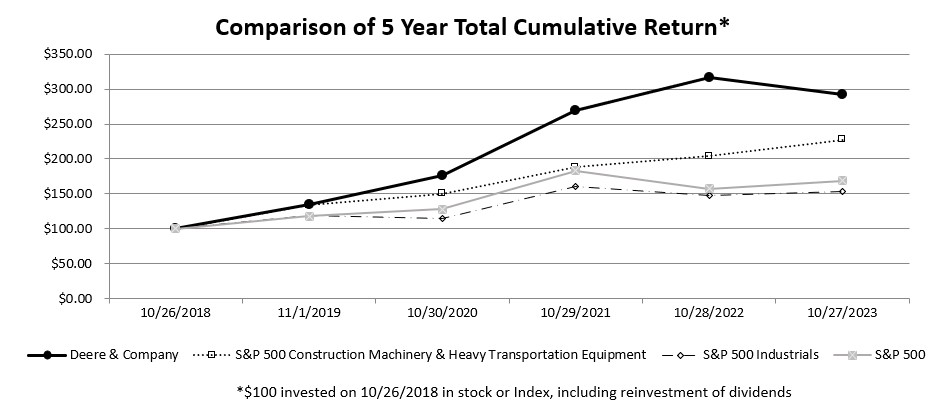
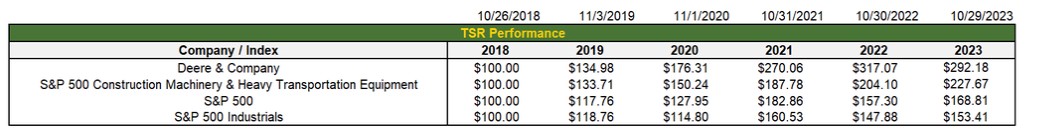
ITEM 6. |
[RESERVED] |
ITEM 7. |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS. |
See the information under the caption “Management’s Discussion and Analysis.”
ITEM 7A. |
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK. |
We are exposed to a variety of market risks, including interest rates and currency exchange rates. We attempt to actively manage these risks. See the information under “Management’s Discussion and Analysis,” under “Financial Instrument Market Risk Information” and in Note 26 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
ITEM 8. |
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. |
See the Consolidated Financial Statements and notes thereto and supplementary data.
ITEM 9. |
CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE. |
Not applicable.
ITEM 9A. |
CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES. |
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our principal executive officer and our principal financial officer have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the Exchange Act)) were effective as of October 29, 2023, based on the evaluation of these controls and procedures required by Rule 13a-15(b) or 15d-15(b) of the Exchange Act.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Our internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
26
All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
Management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of October 29, 2023, using the criteria set forth in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on that assessment, management concluded that, as of October 29, 2023, our internal control over financial reporting was effective.
Our independent registered public accounting firm has issued an audit report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. That report is included herein.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
During the fourth quarter, there were no changes that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. |
OTHER INFORMATION. |
Director and Executive Officer Trading Arrangements
None.
ITEM 9C. |
DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS. |
Not applicable.
PART III
ITEM 10. |
DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE. |
The information regarding directors required by this Item 10 will be set forth in the definitive proxy statement for our 2024 annual meeting of stockholders (proxy statement) to be filed with the Commission in advance of such meeting. Information regarding executive officers is presented in Item 1 of this report under the caption "Information about our Executive Officers."
We have adopted a code of ethics that applies to our executives, including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, and principal accounting officer. This code of ethics and our corporate governance policies are posted on our website at http://www.deere.com/governance. We intend to satisfy disclosure requirements regarding amendments to or waivers from our code of ethics by posting such information on this website. The charters of the Audit Review, Corporate Governance, Compensation, and Finance committees of our Board of Directors are available on our website as well. This information is also available in print free of charge to any person who requests it.
ITEM 11. |
EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION. |
The information required by this Item 11 will be set forth in the proxy statement to be filed with the Commission.
ITEM 12. |
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS. |
The information required by this Item 12 will be set forth in the proxy statement to be filed with the Commission.
ITEM 13. |
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE. |
The information required by this Item 13 will be set forth in the proxy statement to be filed with the Commission.
ITEM 14. |
PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES. |
Information required by this Item 14, including aggregate fees billed to us by our principal accountant, Deloitte & Touche LLP (PCAOB ID No. 34), will be set forth in the proxy statement to be filed with the Commission.
27
PART IV
ITEM 15. |
EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES. |
|
|
Page |
(1) |
Financial Statements |
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 |
46 |
|
|
|
|
47 |
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
|
|
49 |
|
|
|
|
(2) |
Exhibits |
|
|
|
|
|
See the “Index to Exhibits” on pages 83 – 86 of this report |
|
|
|
|
|
Certain instruments relating to long-term borrowings constituting less than 10 percent of registrant’s total assets are not filed as exhibits herewith pursuant to Item 601(b)4(iii)(A) of Regulation S-K. Registrant agrees to file copies of such instruments upon request of the Commission. |
|
|
|
|
Financial Statement Schedules Omitted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following schedules for the company and consolidated subsidiaries are omitted because of the absence of the conditions under which they are required: I, II, III, IV, and V. |
|
ITEM 16.FORM 10-K SUMMARY.
None.
28
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (MD&A) is intended to promote understanding of our financial condition and results of operations. The MD&A is provided as a supplement to, and should be read in conjunction with, the consolidated financial statements and the accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. All amounts are presented in millions of dollars, unless otherwise specified. For comparison of 2022 to 2021 results, refer to the “Management’s Discussion and Analysis” section of our 2022 Form 10-K.
OVERVIEW |
|
Deere & Company is a global leader in the production of agricultural, turf, construction, and forestry equipment and solutions. John Deere Financial provides financing for John Deere equipment, parts, service, and other input costs customers need to run their operations. Our operations are managed through the production and precision agriculture (PPA), small agriculture and turf (SAT), construction and forestry (CF), and financial services operating segments. References to “equipment operations” include PPA, SAT, and CF, while references to “agriculture and turf” include both PPA and SAT.
Net Sales and Revenues by Segment in 2023
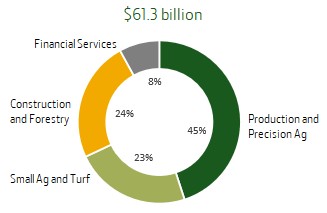
Smart Industrial Operating Model and Leap Ambitions
We announced the Smart Industrial Operating Model in 2020. This operating model is based on three focus areas:
| (a) | Production systems: A strategic alignment of products and solutions around our customers’ operations. |
| (b) | Technology stack: Investments in technology, as well as research and development, that deliver intelligent solutions to our customers through digital capabilities, automation, autonomy, and alternative power technologies. |
| (c) | Lifecycle solutions: The integration of our aftermarket and support capabilities to more effectively manage customer equipment, service, and technology needs across the full lifetime of a John Deere product. |
Our Leap Ambitions were launched in 2022. These ambitions are designed to boost economic value and sustainability for our customers. The ambitions align across our customers’ production systems seeking to optimize their operations to deliver better outcomes with fewer resources.
TRENDS & ECONOMIC CONDITIONS |
|
Industry Sales Outlook for Fiscal 2024
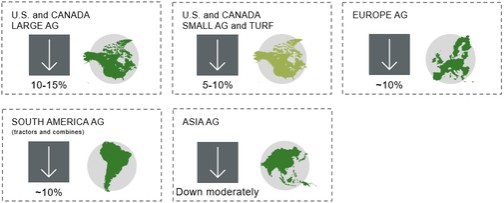

Company Trends – Customers seek to improve profitability, productivity, and sustainability through technology. Integration of technology into equipment is a persistent market trend. Our Smart Industrial Operating Model and Leap Ambitions are intended to capitalize on this market trend. These technologies are incorporated into products within each of our operating segments. We expect this trend to persist for the foreseeable future. The investments in these technologies and in establishing a Solutions as a Service business model might increase our operating costs and may decrease operating margins during the transition period. Most notably in 2023, we introduced See & Spray™ Ultimate and a new model of See & Spray™ Premium. These technologies were introduced on a limited basis and did not represent a significant percentage of our sales in 2023.
Company Outlook for 2024
| ● | Demand is expected to decline in 2024. |
| ● | Production volumes will decline to more normal levels in 2024. |
Agriculture and Turf Outlook for 2024
| ● | We expect large agricultural equipment sales to decline in 2024 in North America, Europe, and South America. |
| ● | Demand for small agricultural equipment is expected to moderate in Europe. |
| ● | Turf and utility equipment product sales are expected to be lower due to the overall U.S. economic condition and elevated interest rates. |
Market Conditions:
| ● | Agricultural fundamentals are expected to moderate in 2024 due to lower commodity prices and elevated interest rates, offset by declining input costs and improved customer financials. |
29
| ● | The dairy and livestock sector continues to benefit from elevated protein and hay prices. |
| ● | Farm input costs in Europe are declining. Grain prices vary from favorable in Western Europe to depressed in Eastern Europe due to the Russia/Ukraine war. |
| ● | Dealer inventories are elevated in Brazil due to inventory oversupply driven by weakening demand in the second half of 2023. |
| ● | Industry sales in Asia are impacted by moderating demand in India, the world’s largest tractor market by number of units. |
| ● | The fleet average age is older than in prior business cycles. Combines are in line with the historical average age, while tractors are slightly older than historical averages. |
Construction and Forestry Outlook for 2024
Market Conditions:
| ● | Construction equipment industry sales are forecasted to be down from 2023 levels. |
| ● | Benefits from rental fleet replenishment, the energy industry, and U.S. infrastructure spending are expected to partially offset moderation in residential home, office, and retail construction. |
| ● | Roadbuilding demand remains strong, similar to 2023 in the U.S., largely offset by softening demand in Europe. |
Financial Services Outlook for 2024
Net Income |
|
Up moderately |
|
||||
+ Nonrecurring prior period special items |
|
Favorable |
|
||||
+ Higher average portfolio |
|
Favorable |
|
||||
(-) Financing spreads |
|
Unfavorable |
|
||||
(-) Recoveries on operating lease dispositions |
|
Unfavorable |
|
||||
Additional Trends – We experienced supply chain disruptions and inflationary pressures in 2022. While these issues moderated in 2023, the effect on production schedules and central bank policy interest rates continued in 2023. These changes are discussed below.
Supply Chain Impact on Production Schedules. We experienced supply chain improvements compared to 2022, with a return to normal in 2023. The ease in supply chain disruptions contributed to higher levels of production compared to prior year. As a result, our production schedules in 2023 were more aligned with the customers’ seasonal use of our products, marking a return to historical seasonal production patterns and on-time product delivery. Additionally, supply chain improvements contributed to reductions in premium freight costs, moderation in material cost increases, and disciplined inventory management in 2023. In 2022, supply chain disruptions impacted many aspects of our business, including receiving past due deliveries from suppliers, parts availability, increased production costs, and higher inventory levels.
Interest Rates. Central bank policy interest rates increased in 2022 and 2023. Increased rates impacted us in several ways, primarily affecting the financing spreads for the financial services operations, and may impact future demand for our products.
Most retail customer receivables are fixed rate. Wholesale financing receivables generally are variable rate. Both types of
receivables are financed with fixed and floating rate borrowings. We manage our exposure to interest rate fluctuations by matching our receivables with our funding sources. We also enter into interest rate swap agreements to match our interest rate exposure.
Rising interest rates have historically impacted our borrowings sooner than the benefit is realized from receivable and lease portfolios. As a result, our financial services operations experienced $170 (after-tax) less favorable financing spreads in 2023 compared to 2022. If interest rates continue to rise, we expect to continue experiencing spread compression in 2024.
Demand for our products is negatively impacted by rising interest rates. We expect higher borrowing costs for our customers to primarily affect discretionary and residential product sales in 2024.
Rising interest rates are driven by factors outside of our control, and as a result, we cannot reasonably foresee when this condition will subside.
Agricultural Market Business Cycle. The agricultural market is affected by various factors including commodity prices, acreage planted, crop yields, and government policies. These factors affect farmers’ income and may result in lower demand for equipment. We may experience any of the following effects during unfavorable market conditions: lower net sales, higher sales discounts, higher receivable write-offs, or losses on equipment on operating leases. A potential benefit is that customers may invest in integrated technology solutions and precision agriculture to lower input costs and improve margins.
Other Items of Concern and Uncertainties – Other items that could impact our results are:
| ● | global and regional political conditions, including the war in Ukraine and the Israel-Hamas war, |
| ● | economic, tax, and trade policies, |
| ● | new or retaliatory tariffs, |
| ● | capital market disruptions, |
| ● | foreign currency and capital control policies, |
| ● | regulations and legislation regarding right to repair, |
| ● | weather conditions, |
| ● | marketplace adoption and monetization of technologies we have invested in, |
| ● | our ability to strengthen our digital capabilities, automation, autonomy, and alternative power technologies, |
| ● | changes in demand and pricing for new and used equipment, |
| ● | significant fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, |
| ● | volatility in the prices of many commodities, and |
| ● | slower economic growth or possible recession. |
30
CONSOLIDATED RESULTS |
2023 compared to 2022 |
Highlights
| ● | Net income rose in 2023 compared to 2022, driven by strong market conditions. |
| ● | We continue to focus on structural profitability and strategically investing in solutions that deliver value to our customers. |
Net Sales and Revenues

Net Sales (Equipment Operations)

| ● | Favorable industry fundamentals and strong demand for farm and construction equipment drove the sales increases in 2023. |
Net Income (Attributable to Deere & Company)

Diluted Earnings Per Share (EPS) ($ per share)

| ● | Net income and diluted EPS grew at a faster rate than sales due to our ability to keep cost increases below price realization. |
Other Significant Statement of Consolidated Income Changes –
An explanation of the cost of sales to net sales ratio and other significant statement of consolidated income changes follows:
Deere & Company |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
% Change |
|
||
Cost of sales to net sales |
|
|
67.9% |
|
|
73.7% |
|
-8 |
|
+ Price realization |
|
Favorable |
|
||||||
(-) Production costs |
|
Unfavorable |
|
||||||
Price realization was 12 percent driven by strong demand. Production costs increased due to a moderate rise in material cost and manufacturing overhead. These factors were partially offset by lower freight costs and production efficiencies generated by easing supply chain disruptions. |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other income |
|
$ |
1,003 |
|
$ |
1,295 |
|
-23 |
|
Other income was lower due to a non-cash gain on the remeasurement of the previously held equity investment in the Deere-Hitachi joint venture in 2022. |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development expenses |
|
|
2,177 |
|
|
1,912 |
|
+14 |
|
Research and development expenditures were higher due to continued focus on developing new technology solutions and new product introductions. |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Selling, administrative and general expenses |
|
|
4,595 |
|
|
3,863 |
|
+19 |
|
Selling, administrative and general expenses rose due to higher salary expenses driven by inflationary conditions, profit-sharing incentives, and an increase in expenses to support the Leap Ambitions framework. Also impacting the current year was a cumulative correction of the accounting treatment for financing incentives offered to John Deere dealers (see Note 4). |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense |
|
|
2,453 |
|
|
1,062 |
|
+131 |
|
Interest expense increased due to higher average borrowing rates and higher average borrowings. |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other operating expenses |
|
|
1,292 |
|
|
1,275 |
|
+1 |
|
See Note 9 for more information. |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
|
2,871 |
|
|
2,007 |
|
+43 |
|
Consistent with higher pretax income. |
|
||||||||
31
BUSINESS SEGMENT RESULTS |
2023 compared to 2022 |
Each equipment operation segment experienced price realization during 2023, as orderbooks were full and most product lines were on allocation. These factors contributed to higher shipment volumes for large agriculture and construction equipment.
Production costs were unfavorable in 2023 due to higher material costs, profit-sharing incentive compensation, and manufacturing overhead costs, partially offset by lower freight costs and improved production efficiency. Material costs were higher in the first three quarters of 2023 but continued to moderate through the year. In the fourth quarter of 2023, material costs were lower than in the prior year.
Production and Precision Agriculture Operations
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
% Change |
|
||
Net sales |
|
$ |
26,790 |
|
$ |
22,002 |
|
+22 |
|
Sales volume and other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+7 |
|
Price realization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+15 |
|
Currency translation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating profit |
|
|
6,996 |
|
|
4,386 |
|
+60 |
|
Operating margin |
|
|
26.1% |
|
|
19.9% |
|
|
|
Sales volumes increased 10 percent in the U.S. and Canada, 32 percent in Australia, and 9 percent in Western Europe, partially offset by the effect of suspension of shipments to Russia. Price realization was 17 percent in the U.S. and Canada and 12 percent outside the U.S. and Canada, driven by strong demand. Prior period results were impacted by special items (see Note 4).
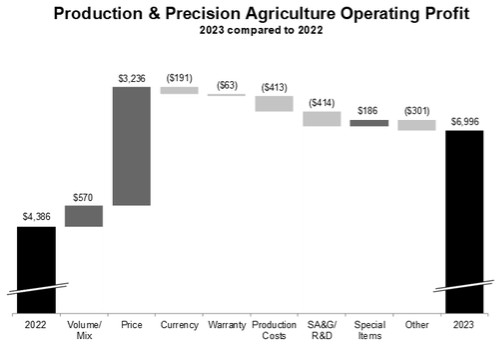
Small Agriculture and Turf Operations
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
% Change |
|
||
Net sales |
|
$ |
13,980 |
|
$ |
13,381 |
|
+4 |
|
Sales volume and other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-4 |
|
Price realization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+9 |
|
Currency translation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-1 |
|
Operating profit |
|
|
2,472 |
|
|
1,949 |
|
+27 |
|
Operating margin |
|
|
17.7% |
|
|
14.6% |
|
|
|
Sales volumes decreased 8 percent in the U.S. and Canada but increased 18 percent in Mexico and 2 percent in Western Europe.
Price realization was 8 percent in the U.S. and Canada driven by inflation and 12 percent in Western Europe driven by strong demand.
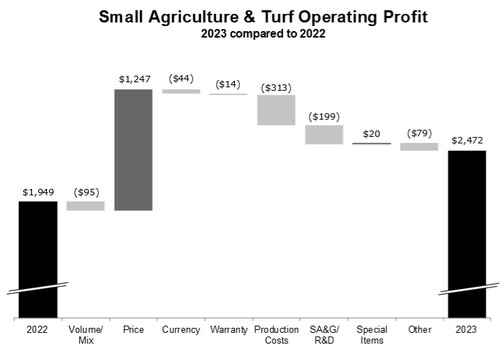
Construction and Forestry Operations
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
% Change |
|
||
Net sales |
|
$ |
14,795 |
|
$ |
12,534 |
|
+18 |
|
Sales volume and other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+9 |
|
Price realization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+10 |
|
Currency translation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-1 |
|
Operating profit |
|
|
2,695 |
|
|
2,014 |
|
+34 |
|
Operating margin |
|
|
18.2% |
|
|
16.1% |
|
|
|
Sales volumes increased 18 percent in the U.S. and Canada but decreased 6 percent outside the U.S. and Canada driven by lower sales in Brazil and the suspension of shipments to Russia. Price realization was 12 percent in the U.S. and Canada driven by strong demand, and 7 percent outside the U.S. and Canada. Results in both periods were impacted by special items (see Note 4).
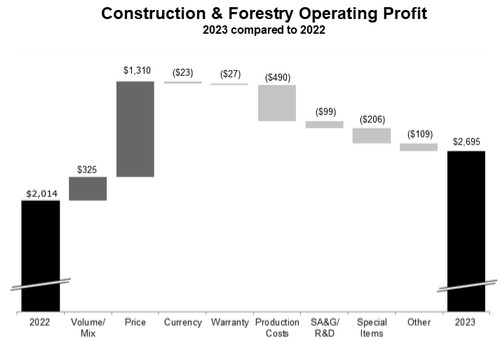
32
Financial Services Operations
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
% Change |
|
||
Revenue (including intercompany) |
|
$ |
5,554 |
|
$ |
4,085 |
|
+36 |
|
Average balance of receivables and leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+19 |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
2,362 |
|
|
799 |
|
+196 |
|
Average borrowings |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+20 |
|
Average borrowing rates |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+143 |
|
Net income |
|
|
619 |
|
|
880 |
|
-30 |
|
Average wholesale receivables increased 72 percent and retail notes increased 13 percent driven by higher equipment sales. Revenue also increased due to higher average financing rates. Net income declined as a result of unfavorable financing spreads and a correction of the accounting treatment for financing incentives offered to John Deere dealers (see Note 4). In 2022, financial services increased the provision for credit losses in Russia and recorded an intercompany benefit from the equipment operations, which guarantees financial services’ investments in certain international markets, including Russia (see Note 4). The Russia-related impacts are displayed in the “Other” bar below.
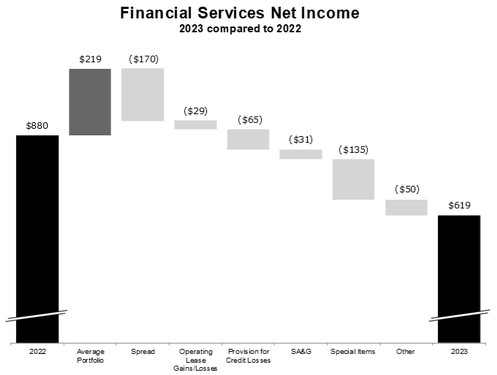
BUSINESS SEGMENT RESULTS |
2022 compared to 2021 |
Please refer to the “Management’s Discussion and Analysis” section of our 2022 Form 10-K.
CAPITAL RESOURCES AND LIQUIDITY |
2023 compared to 2022 |
We have access to global markets at a reasonable cost. Sources of liquidity include:
| ● | cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities on hand, |
| ● | funds from operations, |
| ● | the issuance of commercial paper and term debt, |
| ● | the securitization of retail notes, and |
| ● | bank lines of credit. |
We closely monitor our cash requirements. Based on the available sources of liquidity, we expect to meet our funding needs in the short term (next 12 months) and long term (beyond 12 months). We
are forecasting lower operating cash flows in 2024 compared with 2023 as identified previously in Trends and Economic Conditions.
We operate in multiple industries, which have unique funding requirements. The equipment operations are capital intensive. Historically, these operations have been subject to seasonal variations in financing requirements for inventories and receivables from dealers. However, the patterns of seasonality have been affected by the supply chain disruptions experienced during fiscal year 2022.
The financial services operations rely on their ability to raise substantial amounts of funds to finance their receivable and lease portfolios.
Key Metrics and Balance Sheet Changes
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Marketable Securities

| ● | See the detailed cash flow discussion in the next section. |
| ● | The increase was primarily driven by higher operating cash flow. |
Trade Accounts and Notes Receivable – Net

| ● | Receivables are generated from the sales of goods to customers. |
| ● | The increase was driven by higher sales. |
Financing Receivables and Equipment on Operating Leases

| ● | Acquisition volumes were 30 percent higher driven by higher retail volumes due to increased retail sales and higher wholesale receivables. |
Inventories

| ● | Inventories decreased due to easing of supply disruption constraints and moderation of future demand. |
Property and Equipment

| ● | Cash expenditures were $1.5 billion in 2023. |
| ● | Capital expenditures are forecast to be $1.9 billion in 2024. |
33
Borrowings

| ● | Borrowings increased corresponding with the level of the financing receivable and lease portfolios. |
Unused Credit Lines

| ● | The decrease in unused credit lines was due to an increase in commercial paper outstanding to fund growth in the receivable portfolios. |
Financial Services Ratio of Interest-Bearing Debt to Stockholder’s Equity

CASH FLOWS |
2023, 2022, and 2021 |
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
$ |
8,589 |
|
$ |
4,699 |
|
$ |
7,726 |
|
Net cash used for investing activities |
|
|
(8,749) |
|
|
(8,485) |
|
|
(5,750) |
|
Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities |
|
|
2,808 |
|
|
826 |
|
|
(1,078) |
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
|
|
31 |
|
|
(224) |
|
|
55 |
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
|
$ |
2,679 |
|
$ |
(3,184) |
|
$ |
953 |
|
Operating cash flows in 2023 were higher due to an increase in net income and lower inventory offset by higher receivables related to sales, while operating cash flows in 2022 were impacted by a $1 billion other postretirement benefit (OPEB) contribution.
Cash outflows from investing activities were $8.7 billion in 2023 due to growth in the financing receivable and lease portfolios, and purchases of property and equipment.
Cash inflows from financing activities were $2.8 billion in 2023, as higher borrowings were partially offset by repurchases of common stock and dividends paid.
Cash Returned to Shareholders

Cash returned to shareholders increased $3.7 billion in 2023.
DEBT RATINGS |
|
To access debt markets, we rely on credit rating agencies to assign short-term and long-term credit ratings to our debt. These ratings are an indicator of credit quality for fixed income investors. A debt rating is not a recommendation by the rating agency to buy, sell, or hold. A credit rating agency may change or withdraw company ratings based on its assessment of our current and future ability to meet interest and principal repayment obligations. Lower credit ratings or negative changes to ratings outlooks generally result in higher borrowing costs, including costs of derivative transactions, and reduced access to debt capital markets, and may adversely impact our liquidity.
The senior long-term and short-term debt ratings and outlook currently assigned to unsecured company securities by the rating agencies engaged by us are as follows:
|
|
Senior |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long-Term |
|
Short-Term |
|
Outlook |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fitch Ratings |
|
A+ |
|
F1 |
|
Stable |
Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. |
|
A2 |
|
Prime-1 |
|
Positive |
Standard & Poor’s |
|
A |
|
A-1 |
|
Stable |
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS AND CASH REQUIREMENTS |
2024 and Beyond |
Our material cash requirements include the following:
Borrowings – As of October 29, 2023, we had $21.2 billion of payments due on borrowings and securitization borrowings in the next year, along with interest payments of $2.2 billion. The securitization borrowing payments are based on the expected liquidation of the retail notes. See Notes 12 and 19 for additional borrowing details. These payments will likely be replaced with new borrowings to finance the receivable and lease portfolio, which is expected to grow in 2024.
Purchase Obligations – As of October 29, 2023, our outstanding purchase obligations were $4.5 billion, with $4.1 billion payable within one year. These purchase obligations are noncancelable.
Other Cash Requirements – In addition to our contractual obligations, we have the following commitments:
| ● | capital expenditures of $1.9 billion are planned for 2024, |
| ● | expected quarterly cash dividend throughout 2024 (subject to change at the discretion of our Board of Directors), and |
| ● | total pension and OPEB contributions in 2024 are expected to be approximately $225. |
Share repurchases will be considered as a means of deploying excess cash to shareholders, once the previously mentioned requirements are met.
34
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES |
|
The timely preparation of financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions. Those estimates affect reported amounts in these financial statements. Changes in those estimates and assumptions could have a significant effect. The following estimates are the most critical to our financial statements:
| ● | sales incentives, |
| ● | product warranties, |
| ● | postretirement benefit obligations, |
| ● | allowance for credit losses, |
| ● | operating lease residual values, and |
| ● | income taxes. |
These items require the most difficult, subjective, or complex judgments. Our accounting policies are described primarily in Note 2 of our consolidated financial statements.
Sales Incentives
We provide sales incentives to dealers. These incentives are offered in two forms:
| ● | volume bonuses – awarded based on a dealer’s sales volume and performance, and |
| ● | retail sales incentive programs – discounts or financing programs that are due when the dealer sells the equipment to a retail customer. |
The estimated cost of these programs is based on:
| ● | historical data, |
| ● | announced and expected incentive programs, |
| ● | field inventory levels, and |
| ● | forecasted sales volumes. |
At the time a sale is recognized, we record an estimate of the sales incentive costs. The final cost is determined at the end of the volume bonus measurement period or at the time of the retail sale.
There are numerous programs available at any time, and new programs may be announced after we record the equipment sale to the dealer. Changes in the mix and types of sales incentive programs affect these estimates, which are reviewed quarterly. Actual cost differences from the original cost estimate are recognized in “Net sales.”
Sales Incentive Accruals
The accruals recorded against receivables relate to programs where we have the contractual right and the intent to offset against existing receivables. The increase in each of 2023 and 2022 primarily resulted from higher retail sales. Additional factors in
2023 were higher incentives for dealer market share and incentives provided to offset elevated interest rates.
A key assumption of the retail sales incentive accrual is the predictive value of the historical percent of retail sales incentive costs to retail sales. Over the last five fiscal years, this percent has varied by an average of .7 percent. Holding other assumptions constant, .7 percent change would have modified the sales incentive accrual by $105.
Product Warranties
A standard warranty is provided as an assurance that our equipment will function as intended. The standard warranty period varies by product and region.
At the time a sale is recognized, we record an estimate of future warranty costs, based on the following calculation:
| ● | historical claims rate experience – multiplied by – |
| ● | the estimated population. |
The historical claims rate is determined by a review of five-year claims costs. The estimated population is based on dealer inventories and retail sales. These estimates are reviewed quarterly. Adjustments are also made for current quality developments.
Product Warranty Accruals

The increase in each of 2023 and 2022 related to higher sales volumes, partially offset by a decrease in the warranty rate.
Product warranty accrual estimates are affected by the historical percent of warranty claims costs as a percentage of gross sales. During this time, the percent has varied plus or minus .12 percent. Holding all other assumptions constant, if this estimated cost experience percent would have increased or decreased .12 percent, the warranty accrual at October 29, 2023 would have changed by approximately $81.
Postretirement Benefit Obligations
The pension and OPEB plan obligations (defined benefit) and expenses require the use of estimates. The main estimate is the present value of the projected future benefit payments. These future benefit payments extend several decades.
The estimates are based on existing retirement plan provisions. No assumption is made regarding any potential changes to benefit provisions beyond those to which we are presently committed (e.g., in existing labor contracts).
The key assumptions used by our actuaries to calculate the estimates include:
| ● | discount rates, |
| ● | health care cost trend rates, |
| ● | expected long-term return on plan assets, |
| ● | compensation increases, |
35
| ● | retirement rates, |
| ● | mortality rates, and |
| ● | expected contributions. |
Assumptions are set each year-end. These assumptions are not changed during the year unless there is a significant plan event. Actual results that differ from the assumptions affect future expenses and obligations.
The key pension and OPEB amounts follow:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Pension and OPEB net (benefit) cost |
|
$ |
(13) |
|
$ |
176 |
|
$ |
197 |
|
Long-term expected return on pension and OPEB plan assets (as a percent) |
|
|
6.2 |
|
|
5.0 |
|
|
5.9 |
|
Long-term expected return on pension and OPEB plan assets |
|
|
995 |
|
|
836 |
|
|
876 |
|
Actual return (loss) on pension and OPEB plan assets |
|
|
(395) |
|
|
(3,565) |
|
|
3,616 |
|
Pension assets, net of pension liabilities |
|
|
2,076 |
|
|
2,690 |
|
|
2,665 |
|
OPEB liabilities, net of OPEB assets |
|
|
1,001 |
|
|
1,205 |
|
|
3,175 |
|
The reduction in the 2023 pension and OPEB net (benefit) cost was due to increased expected long-term return rates on plan assets and increased discount rates.
The effect of hypothetical changes to selected assumptions on our major U.S. retirement benefit plans would be as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
October 29, 2023 |
|
2024 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
Increase |
|
Increase |
|
||
|
|
Percentage |
|
(Decrease) |
|
(Decrease) |
|
||
Assumptions |
|
Change |
|
PBO/APBO* |
|
Expense |
|
||
Pension |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discount rate** |
|
+/-.5 |
|
$ |
(414)/456 |
|
$ |
3/(3) |
|
Expected return on assets |
|
+/-.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
(63)/63 |
|
OPEB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discount rate** |
|
+/-.5 |
|
|
(120)/130 |
|
|
(4)/5 |
|
Expected return on assets |
|
+/-.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
(10)/10 |
|
Health care cost |
|
+/-1.0 |
|
|
231/(202) |
|
|
39/(34) |
|
* |
Projected benefit obligation (PBO) for pension plans and accumulated postretirement benefit obligation (APBO) for OPEB plans. |
** |
Pretax impact on service cost, interest cost, and amortization of gains or losses. |
Allowance for Credit Losses
The allowance for credit losses is an estimate of the credit losses expected over the life of the receivable portfolio. The allowance is measured on a collective basis for receivables with similar risk characteristics. Receivables that do not share risk characteristics are evaluated on an individual basis. Risk characteristics include:
| ● | finance product category, |
| ● | market, |
| ● | geography, |
| ● | credit risk, and |
| ● | remaining balance. |
We utilize the following loss forecast models to estimate expected credit losses:
| ● | Transition matrix models are used for large and complex retail customer receivable pools. These models are used for more than 90 percent of retail customer receivables. Historical portfolio performance and current delinquency levels are used to forecast future defaults. Estimated recovery rates are applied to the estimated default balance to calculate the expected credit losses. |
| ● | Weighted average remaining maturity (WARM) models are used for smaller and less complex retail customer receivable pools. |
| ● | Historical loss rate models are used on wholesale receivables, with consideration of current economic conditions and dealer financial risk. |
The model output is adjusted for forecasted economic conditions, which may include the following economic indicators:
| ● | commodity prices, |
| ● | industry equipment sales, |
| ● | unemployment rates, and |
| ● | housing starts. |
Management reviews each model’s output quarterly, and qualitative adjustments are incorporated as necessary.
Allowance for Credit Losses

The allowance decreased in 2023 due to the disposition of the receivable portfolio in Russia (see Note 11). Excluding the portfolio in Russia, the allowance increased slightly as higher portfolio balances and higher expected losses on turf and construction customer accounts. The allowance increased in 2022 due to higher reserves related to the economic uncertainty in Russia.
While we believe our allowance is sufficient to provide for losses over the life of our existing receivable portfolio, different assumptions would result in changes to the allowance for credit losses, specifically:
| ● | For the wholesale receivable portfolio: Changes in economic conditions have historically had limited impact on credit losses. |
| ● | Within the retail customer receivable portfolio: Credit loss estimates are dependent on a number of factors, including historical portfolio performance, current economic conditions, current delinquency levels, and estimated recoveries on defaulted accounts. |
36
Holding all other factors constant, a 10 percent increase in the transition matrix models’ forecasted defaults and a simultaneous 10 percent decrease in recovery rates would have resulted in a $53 increase to the allowance for credit losses at October 29, 2023.
Operating Lease Residual Values
Equipment on operating leases is depreciated to the estimated residual value over the lease term. The residual values are based on several factors, including:
| ● | lease term, |
| ● | expected hours of usage, |
| ● | historical wholesale sales prices, |
| ● | return experience, |
| ● | intended equipment use, |
| ● | market dynamics and trends, and |
| ● | dealer residual value guarantees. |
We review residual value estimates during the lease term. Depreciation is adjusted over the remaining lease term if residual estimates are revised. Impairments are recorded when events or circumstances necessitate.
At the end of the majority of leases, the equipment is disposed in the following sequence:
| ● | The lessee has the option to purchase the equipment for the contractual residual value. |
| ● | The dealer has the option to purchase the equipment. |
| ● | The equipment is sold to a third party at the equipment’s fair value. In this situation, we may record a gain or a loss for the difference between the residual value and the sale price. |
Operating Lease Residual Values

Hypothetically, if (a) future market values for this equipment were to decrease 10 percent from our present estimates and (b) all the equipment on operating leases were returned to us for remarketing at the end of the lease term, the total unfavorable impact after consideration of dealer residual value guarantees would be approximately $90. This amount would be recognized as higher depreciation expense over the remaining term of the operating leases, or potentially as an impairment.
Income Taxes
We are subject to federal, state, and foreign income taxes. These tax laws can be complex. Significant judgment and interpretation is required to implement them. Changes in tax laws could materially affect our consolidated financial statements. We record our tax positions in the following categories:
| ● | current taxes, |
| ● | deferred taxes, and |
| ● | uncertain tax positions. |
Deferred income taxes represent temporary differences between the tax and the financial reporting basis of assets and liabilities.
This will result in taxable or deductible amounts in the future. Loss carryforwards and tax credits are significant components of deferred tax asset balances. These assets are reviewed regularly for the following:
| ● | the likelihood of recoverability from future taxable income, |
| ● | reversal of deferred tax liabilities, and |
| ● | tax planning strategies. |
Valuation allowances are established when we determine that the deferred tax benefit may not be realized. The recoverability analysis requires significant judgment and relies on estimates. The valuation allowance as of October 29, 2023 was $1.6 billion. Changes in foreign income tax laws, income for certain jurisdictions, or our tax structure could impact the valuation allowance balance.
Some tax positions contain significant uncertainties. These positions may be challenged or disallowed by taxing authorities. If it is likely the position will be disallowed, no tax benefit is recorded. If it is likely the position will be sustained, a tax benefit is recognized. The ultimate resolution could take many years. This may result in a payment that is significantly different from the original estimate.
See Note 8 for further information on income taxes.
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Certain statements contained herein, including in the section entitled “Overview” relating to future events, expectations, and trends constitute “forward-looking statements” as defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 and involve factors that are subject to change, assumptions, risks, and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially. Some of these risks and uncertainties could affect all lines of our operations generally while others could more heavily affect a particular line of business.
Forward-looking statements are based on currently available information and current assumptions, expectations, and projections about future events and should not be relied upon. Except as required by law, we expressly disclaim any obligation to update or revise our forward-looking statements. Many factors, risks, and uncertainties could cause actual results to differ materially from these forward-looking statements. Among these factors are risks related to:
| ● | changes in U.S., foreign and international laws, regulations, and policies relating to trade, spending, taxing, banking, monetary, environmental (including climate change and engine emission), and farming policies; |
| ● | political, economic, and social instability of the geographies in which we operate, including the ongoing wars between Russia and Ukraine and between Israel and Hamas; |
| ● | adverse macroeconomic conditions, including unemployment, inflation, rising interest rates, changes in consumer practices due to slower economic growth or possible recession, and regional or global liquidity constraints; |
37
| ● | growth and sustainability of non-food uses for crops (including ethanol and biodiesel production); |
| ● | the ability to execute business strategies, including our Smart Industrial Operating Model, Leap Ambitions, and mergers and acquisitions; |
| ● | the ability to understand and meet customers’ changing expectations and demand for our products and solutions; |
| ● | accurately forecasting customer demand for products and services and adequately managing inventory; |
| ● | our ability to integrate new technology, including automation and machine learning, and deliver precision technology and solutions to customers; |
| ● | changes to governmental communications channels (radio frequency technology); |
| ● | our ability to adapt in highly competitive markets; |
| ● | dealer practices and their ability to manage distribution of our products and support and service precision technology solutions; |
| ● | changes in climate patterns, unfavorable weather events, and natural disasters; |
| ● | governmental and other actions designed to address climate change in connection with a transition to a lower-carbon economy; |
| ● | higher interest rates and currency fluctuations which could adversely affect the U.S. dollar, customer confidence, access to capital, and demand for our products and solutions; |
| ● | stress in the banking sector may have adverse impacts on vendors or customers as well as on our ability to access cash deposits; |
| ● | availability and price of raw materials, components, and whole goods; |
| ● | delays or disruptions in our supply chain; |
| ● | labor relations and contracts, including work stoppages and other disruptions; |
| ● | the ability to attract, develop, engage, and retain qualified personnel; |
| ● | security breaches, cybersecurity attacks, technology failures, and other disruptions to our information technology infrastructure and products; |
| ● | loss of or challenges to intellectual property rights; |
| ● | compliance with evolving U.S. and foreign laws, including economic sanctions, data privacy, and environmental laws and regulations; |
| ● | legislation introduced or enacted that could affect our business model and intellectual property, such as so-called right to repair or right to modify legislation; |
| ● | investigations, claims, lawsuits, or other legal proceedings; |
| ● | events that damage our reputation or brand; |
| ● | world grain stocks, available farm acres, soil conditions, harvest yields, prices for commodities and livestock, input costs, and availability of transport for crops; and |
| ● | housing starts and supply, real estate and housing prices, levels of public and non-residential construction, and infrastructure investment. |
Further information concerning our businesses, including factors that could materially affect our financial results, is included in our filings with the SEC (including, but not limited to, the factors discussed in Item 1A. “Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K). There also may be other factors that we cannot anticipate or that are not described herein because we do not currently perceive them to be material.
38
SUPPLEMENTAL CONSOLIDATING DATA
The supplemental consolidating data presented on the subsequent pages is presented for informational purposes. The equipment operations represents the enterprise without financial services. The equipment operations includes production and precision agriculture operations, small agriculture and turf operations, construction and forestry operations, and other corporate assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses not reflected within financial services. Transactions between the “equipment operations” and “financial services” have been eliminated to arrive at the consolidated financial statements.
The equipment operations and financial services participate in different industries. The equipment operations generate earnings and cash flows by manufacturing and selling equipment, service parts, and technology solutions to dealers and retail customers. Financial services finances sales and leases by dealers of new and used equipment that is largely manufactured by us. Those earnings and cash flows generally are the difference between the finance income received from customer payments less interest expense, and depreciation on equipment subject to an operating lease. The two businesses are capitalized differently and have separate performance metrics. The supplemental consolidating data is also used by management due to these differences.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INCOME STATEMENTS |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For the Years Ended October 29, 2023, October 30, 2022, and October 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unaudited |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
EQUIPMENT |
|
FINANCIAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
OPERATIONS |
|
SERVICES |
|
ELIMINATIONS |
|
CONSOLIDATED |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Net Sales and Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net sales |
|
$ |
55,565 |
|
$ |
47,917 |
|
$ |
39,737 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
55,565 |
|
$ |
47,917 |
|
$ |
39,737 |
|
|
|
Finance and interest income |
|
|
636 |
|
|
213 |
|
|
133 |
|
$ |
5,055 |
|
$ |
3,583 |
|
$ |
3,442 |
|
$ |
(1,008) |
|
$ |
(431) |
|
$ |
(279) |
|
|
4,683 |
|
|
3,365 |
|
|
3,296 |
|
1 |
|
Other income |
|
|
858 |
|
|
1,261 |
|
|
941 |
|
|
499 |
|
|
502 |
|
|
352 |
|
|
(354) |
|
|
(468) |
|
|
(302) |
|
|
1,003 |
|
|
1,295 |
|
|
991 |
|
2, 3 |
|
Total |
|
|
57,059 |
|
|
49,391 |
|
|
40,811 |
|
|
5,554 |
|
|
4,085 |
|
|
3,794 |
|
|
(1,362) |
|
|
(899) |
|
|
(581) |
|
|
61,251 |
|
|
52,577 |
|
|
44,024 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Costs and Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of sales |
|
|
37,739 |
|
|
35,341 |
|
|
29,119 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(24) |
|
|
(3) |
|
|
(3) |
|
|
37,715 |
|
|
35,338 |
|
|
29,116 |
|
4 |
|
Research and development expenses |
|
|
2,177 |
|
|
1,912 |
|
|
1,587 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,177 |
|
|
1,912 |
|
|
1,587 |
|
|
|
Selling, administrative and general expenses |
|
|
3,611 |
|
|
3,137 |
|
|
2,887 |
|
|
994 |
|
|
735 |
|
|
504 |
|
|
(10) |
|
|
(9) |
|
|
(8) |
|
|
4,595 |
|
|
3,863 |
|
|
3,383 |
|
4 |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
411 |
|
|
390 |
|
|
368 |
|
|
2,362 |
|
|
799 |
|
|
687 |
|
|
(320) |
|
|
(127) |
|
|
(62) |
|
|
2,453 |
|
|
1,062 |
|
|
993 |
|
1 |
|
Interest compensation to Financial Services |
|
|
687 |
|
|
299 |
|
|
217 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(687) |
|
|
(299) |
|
|
(217) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
Other operating expenses |
|
|
217 |
|
|
350 |
|
|
181 |
|
|
1,396 |
|
|
1,386 |
|
|
1,453 |
|
|
(321) |
|
|
(461) |
|
|
(291) |
|
|
1,292 |
|
|
1,275 |
|
|
1,343 |
|
5, 6 |
|
Total |
|
|
44,842 |
|
|
41,429 |
|
|
34,359 |
|
|
4,752 |
|
|
2,920 |
|
|
2,644 |
|
|
(1,362) |
|
|
(899) |
|
|
(581) |
|
|
48,232 |
|
|
43,450 |
|
|
36,422 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income before Income Taxes |
|
|
12,217 |
|
|
7,962 |
|
|
6,452 |
|
|
802 |
|
|
1,165 |
|
|
1,150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13,019 |
|
|
9,127 |
|
|
7,602 |
|
|
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
|
2,685 |
|
|
1,718 |
|
|
1,386 |
|
|
186 |
|
|
289 |
|
|
272 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,871 |
|
|
2,007 |
|
|
1,658 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income after Income Taxes |
|
|
9,532 |
|
|
6,244 |
|
|
5,066 |
|
|
616 |
|
|
876 |
|
|
878 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,148 |
|
|
7,120 |
|
|
5,944 |
|
|
|
Equity in income of unconsolidated affiliates |
|
|
4 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
18 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income |
|
|
9,536 |
|
|
6,250 |
|
|
5,084 |
|
|
619 |
|
|
880 |
|
|
881 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,155 |
|
|
7,130 |
|
|
5,965 |
|
|
|
Less: Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
|
(11) |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(11) |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
Net Income Attributable to Deere & Company |
|
$ |
9,547 |
|
$ |
6,251 |
|
$ |
5,082 |
|
$ |
619 |
|
$ |
880 |
|
$ |
881 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
10,166 |
|
$ |
7,131 |
|
$ |
5,963 |
|
|
|
1 Elimination of intercompany interest income and expense.
2 Elimination of equipment operations’ margin from inventory transferred to equipment on operating leases (see Note 6).
3 Elimination of financial services’ income related to intercompany guarantees of investments in certain international markets and intercompany service revenues.
4 Elimination of intercompany service fees.
5 Elimination of financial services’ lease depreciation expense related to inventory transferred to equipment on operating leases.
6 Elimination of equipment operations’ expense related to intercompany guarantees of investments in certain international markets and intercompany service expenses.
39
SUPPLEMENTAL CONSOLIDATING DATA (continued)
CONDENSED BALANCE SHEETS |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
As of October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unaudited |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
EQUIPMENT |
|
FINANCIAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
OPERATIONS |
|
SERVICES |
|
ELIMINATIONS |
|
CONSOLIDATED |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
|
|
||||||||
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
5,720 |
|
$ |
3,767 |
|
$ |
1,738 |
|
$ |
1,007 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
7,458 |
|
$ |
4,774 |
|
|
|
Marketable securities |
|
|
104 |
|
|
61 |
|
|
842 |
|
|
673 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
946 |
|
|
734 |
|
|
|
Receivables from Financial Services |
|
|
4,516 |
|
|
6,569 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
(4,516) |
|
$ |
(6,569) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
Trade accounts and notes receivable – net |
|
|
1,320 |
|
|
1,273 |
|
|
8,687 |
|
|
6,434 |
|
|
(2,268) |
|
|
(1,297) |
|
|
7,739 |
|
|
6,410 |
|
8 |
|
Financing receivables – net |
|
|
64 |
|
|
47 |
|
|
43,609 |
|
|
36,587 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43,673 |
|
|
36,634 |
|
|
|
Financing receivables securitized – net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7,335 |
|
|
5,936 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7,335 |
|
|
5,936 |
|
|
|
Other receivables |
|
|
1,813 |
|
|
1,670 |
|
|
869 |
|
|
832 |
|
|
(59) |
|
|
(10) |
|
|
2,623 |
|
|
2,492 |
|
8 |
|
Equipment on operating leases – net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,917 |
|
|
6,623 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,917 |
|
|
6,623 |
|
|
|
Inventories |
|
|
8,160 |
|
|
8,495 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8,160 |
|
|
8,495 |
|
|
|
Property and equipment – net |
|
|
6,843 |
|
|
6,021 |
|
|
36 |
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,879 |
|
|
6,056 |
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
3,900 |
|
|
3,687 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,900 |
|
|
3,687 |
|
|
|
Other intangible assets – net |
|
|
1,133 |
|
|
1,218 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,133 |
|
|
1,218 |
|
|
|
Retirement benefits |
|
|
2,936 |
|
|
3,666 |
|
|
72 |
|
|
66 |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
(2) |
|
|
3,007 |
|
|
3,730 |
|
9 |
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
2,133 |
|
|
940 |
|
|
68 |
|
|
45 |
|
|
(387) |
|
|
(161) |
|
|
1,814 |
|
|
824 |
|
10 |
|
Other assets |
|
|
1,948 |
|
|
1,794 |
|
|
559 |
|
|
626 |
|
|
(4) |
|
|
(3) |
|
|
2,503 |
|
|
2,417 |
|
|
|
Total Assets |
|
$ |
40,590 |
|
$ |
39,208 |
|
$ |
70,732 |
|
$ |
58,864 |
|
$ |
(7,235) |
|
$ |
(8,042) |
|
$ |
104,087 |
|
$ |
90,030 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term borrowings |
|
$ |
1,230 |
|
$ |
1,040 |
|
$ |
16,709 |
|
$ |
11,552 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
17,939 |
|
$ |
12,592 |
|
|
|
Short-term securitization borrowings |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,995 |
|
|
5,711 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,995 |
|
|
5,711 |
|
|
|
Payables to Equipment Operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,516 |
|
|
6,569 |
|
$ |
(4,516) |
|
$ |
(6,569) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
14,862 |
|
|
12,962 |
|
|
3,599 |
|
|
3,170 |
|
|
(2,331) |
|
|
(1,310) |
|
|
16,130 |
|
|
14,822 |
|
8 |
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
452 |
|
|
380 |
|
|
455 |
|
|
276 |
|
|
(387) |
|
|
(161) |
|
|
520 |
|
|
495 |
|
10 |
|
Long-term borrowings |
|
|
7,210 |
|
|
7,917 |
|
|
31,267 |
|
|
25,679 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38,477 |
|
|
33,596 |
|
|
|
Retirement benefits and other liabilities |
|
|
2,032 |
|
|
2,351 |
|
|
109 |
|
|
108 |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
(2) |
|
|
2,140 |
|
|
2,457 |
|
9 |
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
25,786 |
|
|
24,650 |
|
|
63,650 |
|
|
53,065 |
|
|
(7,235) |
|
|
(8,042) |
|
|
82,201 |
|
|
69,673 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitments and contingencies (Note 20) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Redeemable noncontrolling interest (Note 3) |
|
|
97 |
|
|
92 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
97 |
|
|
92 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Deere & Company stockholders’ equity |
|
|
21,785 |
|
|
20,262 |
|
|
7,082 |
|
|
5,799 |
|
|
(7,082) |
|
|
(5,799) |
|
|
21,785 |
|
|
20,262 |
|
11 |
|
Noncontrolling interests |
|
|
4 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
Financial Services' equity |
|
|
(7,082) |
|
|
(5,799) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7,082 |
|
|
5,799 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
Adjusted total stockholders' equity |
|
|
14,707 |
|
|
14,466 |
|
|
7,082 |
|
|
5,799 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21,789 |
|
|
20,265 |
|
|
|
Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity |
|
$ |
40,590 |
|
$ |
39,208 |
|
$ |
70,732 |
|
$ |
58,864 |
|
$ |
(7,235) |
|
$ |
(8,042) |
|
$ |
104,087 |
|
$ |
90,030 |
|
|
|
7 Elimination of receivables / payables between equipment operations and financial services.
8 Primarily reclassification of sales incentive accruals on receivables sold to financial services.
9 Reclassification of net pension assets / liabilities.
10 Reclassification of deferred tax assets / liabilities in the same taxing jurisdictions.
11 Elimination of financial services’ equity.
40
SUPPLEMENTAL CONSOLIDATING DATA (continued)
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For the Years Ended October 29, 2023, October 30, 2022, and October 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unaudited |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
EQUIPMENT |
|
FINANCIAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
OPERATIONS |
|
SERVICES |
|
ELIMINATIONS |
|
CONSOLIDATED |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Cash Flows from Operating Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
9,536 |
|
$ |
6,250 |
|
$ |
5,084 |
|
$ |
619 |
|
$ |
880 |
|
$ |
881 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
10,155 |
|
$ |
7,130 |
|
$ |
5,965 |
|
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision (credit) for credit losses |
|
|
7 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
(23) |
|
|
189 |
|
|
(13) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(16) |
|
|
192 |
|
|
(6) |
|
|
|
Provision for depreciation and amortization |
|
|
1,123 |
|
|
1,041 |
|
|
1,043 |
|
|
1,016 |
|
|
1,050 |
|
|
1,140 |
|
$ |
(135) |
|
$ |
(196) |
|
$ |
(133) |
|
|
2,004 |
|
|
1,895 |
|
|
2,050 |
|
12 |
|
Impairments and other adjustments |
|
|
18 |
|
|
88 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
173 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
191 |
|
|
88 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
Share-based compensation expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
130 |
|
|
85 |
|
|
82 |
|
|
130 |
|
|
85 |
|
|
82 |
|
13 |
|
Gain on remeasurement of previously held equity investment |
|
|
|
|
|
(326) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(326) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distributed earnings of Financial Services |
|
|
215 |
|
|
444 |
|
|
555 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(215) |
|
|
(444) |
|
|
(555) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
Provision (credit) for deferred income taxes |
|
|
(959) |
|
|
8 |
|
|
(369) |
|
|
169 |
|
|
(74) |
|
|
(72) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(790) |
|
|
(66) |
|
|
(441) |
|
|
|
Changes in assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Receivables related to sales |
|
|
(58) |
|
|
(189) |
|
|
(105) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(4,195) |
|
|
(2,294) |
|
|
1,074 |
|
|
(4,253) |
|
|
(2,483) |
|
|
969 |
|
15, 17, 18 |
|
Inventories |
|
|
474 |
|
|
(1,924) |
|
|
(1,835) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(195) |
|
|
(167) |
|
|
(662) |
|
|
279 |
|
|
(2,091) |
|
|
(2,497) |
|
16 |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
1,352 |
|
|
1,444 |
|
|
1,589 |
|
|
449 |
|
|
143 |
|
|
57 |
|
|
(971) |
|
|
(454) |
|
|
238 |
|
|
830 |
|
|
1,133 |
|
|
1,884 |
|
17 |
|
Accrued income taxes payable/receivable |
|
|
8 |
|
|
166 |
|
|
13 |
|
|
(31) |
|
|
(25) |
|
|
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(23) |
|
|
141 |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
Retirement benefits |
|
|
(164) |
|
|
(1,016) |
|
|
30 |
|
|
(6) |
|
|
1 |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(170) |
|
|
(1,015) |
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
367 |
|
|
250 |
|
|
(162) |
|
|
(51) |
|
|
(287) |
|
|
(25) |
|
|
(64) |
|
|
53 |
|
|
(183) |
|
|
252 |
|
|
16 |
|
|
(370) |
|
12, 13, 16 |
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
|
11,919 |
|
|
6,239 |
|
|
5,900 |
|
|
2,315 |
|
|
1,877 |
|
|
1,965 |
|
|
(5,645) |
|
|
(3,417) |
|
|
(139) |
|
|
8,589 |
|
|
4,699 |
|
|
7,726 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Investing Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Collections of receivables (excluding receivables related to sales) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24,128 |
|
|
22,400 |
|
|
20,527 |
|
|
(1,077) |
|
|
(1,493) |
|
|
(1,568) |
|
|
23,051 |
|
|
20,907 |
|
|
18,959 |
|
15 |
|
Proceeds from sales of equipment on operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,981 |
|
|
2,093 |
|
|
2,094 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,981 |
|
|
2,093 |
|
|
2,094 |
|
|
|
Cost of receivables acquired (excluding receivables related to sales) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(29,229) |
|
|
(26,903) |
|
|
(25,305) |
|
|
457 |
|
|
603 |
|
|
1,652 |
|
|
(28,772) |
|
|
(26,300) |
|
|
(23,653) |
|
15 |
|
Acquisitions of businesses, net of cash acquired |
|
|
(82) |
|
|
(498) |
|
|
(244) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(82) |
|
|
(498) |
|
|
(244) |
|
|
|
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
|
(1,494) |
|
|
(1,131) |
|
|
(845) |
|
|
(4) |
|
|
(3) |
|
|
(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1,498) |
|
|
(1,134) |
|
|
(848) |
|
|
|
Cost of equipment on operating leases acquired |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3,234) |
|
|
(2,879) |
|
|
(2,627) |
|
|
264 |
|
|
225 |
|
|
895 |
|
|
(2,970) |
|
|
(2,654) |
|
|
(1,732) |
|
16 |
|
Increase (decrease) in investment in Financial Services |
|
|
(870) |
|
|
7 |
|
|
(8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
870 |
|
|
(7) |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
Decrease (increase) in trade and wholesale receivables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(5,783) |
|
|
(3,601) |
|
|
1,364 |
|
|
5,783 |
|
|
3,601 |
|
|
(1,364) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
Collateral on derivatives – net |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
5 |
|
|
(7) |
|
|
(11) |
|
|
(647) |
|
|
(274) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(12) |
|
|
(642) |
|
|
(281) |
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
(290) |
|
|
(213) |
|
|
70 |
|
|
(160) |
|
|
(81) |
|
|
(84) |
|
|
3 |
|
|
37 |
|
|
(31) |
|
|
(447) |
|
|
(257) |
|
|
(45) |
|
18 |
|
Net cash used for investing activities |
|
|
(2,737) |
|
|
(1,830) |
|
|
(1,034) |
|
|
(12,312) |
|
|
(9,621) |
|
|
(4,308) |
|
|
6,300 |
|
|
2,966 |
|
|
(408) |
|
|
(8,749) |
|
|
(8,485) |
|
|
(5,750) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net proceeds (payments) in short-term borrowings (original maturities three months or less) |
|
|
(113) |
|
|
136 |
|
|
65 |
|
|
4,121 |
|
|
3,716 |
|
|
753 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,008 |
|
|
3,852 |
|
|
818 |
|
|
|
Change in intercompany receivables/payables |
|
|
2,090 |
|
|
(1,633) |
|
|
(354) |
|
|
(2,090) |
|
|
1,633 |
|
|
354 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from borrowings issued (original maturities greater than three months) |
|
|
342 |
|
|
138 |
|
|
11 |
|
|
15,087 |
|
|
10,220 |
|
|
8,711 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15,429 |
|
|
10,358 |
|
|
8,722 |
|
|
|
Payments of borrowings (original maturities greater than three months) |
|
|
(901) |
|
|
(1,356) |
|
|
(94) |
|
|
(7,012) |
|
|
(7,089) |
|
|
(6,996) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7,913) |
|
|
(8,445) |
|
|
(7,090) |
|
|
|
Repurchases of common stock |
|
|
(7,216) |
|
|
(3,597) |
|
|
(2,538) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(7,216) |
|
|
(3,597) |
|
|
(2,538) |
|
|
|
Capital investment from Equipment Operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
870 |
|
|
(7) |
|
|
8 |
|
|
(870) |
|
|
7 |
|
|
(8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
Dividends paid |
|
|
(1,427) |
|
|
(1,313) |
|
|
(1,040) |
|
|
(215) |
|
|
(444) |
|
|
(555) |
|
|
215 |
|
|
444 |
|
|
555 |
|
|
(1,427) |
|
|
(1,313) |
|
|
(1,040) |
|
14 |
|
Other |
|
|
(7) |
|
|
6 |
|
|
87 |
|
|
(66) |
|
|
(35) |
|
|
(37) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(73) |
|
|
(29) |
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities |
|
|
(7,232) |
|
|
(7,619) |
|
|
(3,863) |
|
|
10,695 |
|
|
7,994 |
|
|
2,238 |
|
|
(655) |
|
|
451 |
|
|
547 |
|
|
2,808 |
|
|
826 |
|
|
(1,078) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of Exchange Rate Changes on Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash |
|
|
24 |
|
|
(209) |
|
|
41 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
(15) |
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
(224) |
|
|
55 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash |
|
|
1,974 |
|
|
(3,419) |
|
|
1,044 |
|
|
705 |
|
|
235 |
|
|
(91) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,679 |
|
|
(3,184) |
|
|
953 |
|
|
|
Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash at Beginning of Year |
|
|
3,781 |
|
|
7,200 |
|
|
6,156 |
|
|
1,160 |
|
|
925 |
|
|
1,016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,941 |
|
|
8,125 |
|
|
7,172 |
|
|
|
Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash at End of Year |
|
$ |
5,755 |
|
$ |
3,781 |
|
$ |
7,200 |
|
$ |
1,865 |
|
$ |
1,160 |
|
$ |
925 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
7,620 |
|
$ |
4,941 |
|
$ |
8,125 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Components of Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
5,720 |
|
$ |
3,767 |
|
$ |
7,188 |
|
$ |
1,738 |
|
$ |
1,007 |
|
$ |
829 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
7,458 |
|
$ |
4,774 |
|
$ |
8,017 |
|
|
|
Restricted cash (Other assets) |
|
|
35 |
|
|
14 |
|
|
12 |
|
|
127 |
|
|
153 |
|
|
96 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
162 |
|
|
167 |
|
|
108 |
|
|
|
Total Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash |
|
$ |
5,755 |
|
$ |
3,781 |
|
$ |
7,200 |
|
$ |
1,865 |
|
$ |
1,160 |
|
$ |
925 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
7,620 |
|
$ |
4,941 |
|
$ |
8,125 |
|
|
|
12 Elimination of depreciation on leases related to inventory transferred to equipment on operating leases (see Note 6).
13 Reclassification of share-based compensation expense.
14 Elimination of dividends from financial services to the equipment operations, which are included in the equipment operations operating activities.
15 Primarily reclassification of receivables related to the sale of equipment.
16 Reclassification of direct lease agreements with retail customers.
17 Reclassification of sales incentive accruals on receivables sold to financial services.
18 Elimination and reclassification of the effects of financial services partial financing of the construction and forestry retail locations sales and subsequent collection of those amounts.
19 Elimination of investment from equipment operations to financial services.
41
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2020 |
|
2019 |
|
2018 |
|
2017 |
|
2016 |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
||||||||||
Net sales and revenues |
|
$ |
61,251 |
|
$ |
52,577 |
|
$ |
44,024 |
|
$ |
35,540 |
|
$ |
39,258 |
|
$ |
37,358 |
|
$ |
29,738 |
|
$ |
26,644 |
|
$ |
28,863 |
|
$ |
36,067 |
|
Net sales |
|
|
55,565 |
|
|
47,917 |
|
|
39,737 |
|
|
31,272 |
|
|
34,886 |
|
|
33,351 |
|
|
25,885 |
|
|
23,387 |
|
|
25,775 |
|
|
32,961 |
|
Finance and interest income |
|
|
4,683 |
|
|
3,365 |
|
|
3,296 |
|
|
3,450 |
|
|
3,493 |
|
|
3,107 |
|
|
2,732 |
|
|
2,511 |
|
|
2,381 |
|
|
2,282 |
|
Research and development expenses |
|
|
2,177 |
|
|
1,912 |
|
|
1,587 |
|
|
1,644 |
|
|
1,783 |
|
|
1,658 |
|
|
1,373 |
|
|
1,394 |
|
|
1,410 |
|
|
1,437 |
|
Selling, administrative and general expenses |
|
|
4,595 |
|
|
3,863 |
|
|
3,383 |
|
|
3,477 |
|
|
3,551 |
|
|
3,455 |
|
|
3,098 |
|
|
2,791 |
|
|
2,868 |
|
|
3,266 |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
2,453 |
|
|
1,062 |
|
|
993 |
|
|
1,247 |
|
|
1,466 |
|
|
1,204 |
|
|
899 |
|
|
764 |
|
|
680 |
|
|
664 |
|
Net income* |
|
|
10,166 |
|
|
7,131 |
|
|
5,963 |
|
|
2,751 |
|
|
3,253 |
|
|
2,368 |
|
|
2,159 |
|
|
1,524 |
|
|
1,940 |
|
|
3,162 |
|
Return on net sales |
|
|
18.3% |
|
|
14.9% |
|
|
15.0% |
|
|
8.8% |
|
|
9.3% |
|
|
7.1% |
|
|
8.3% |
|
|
6.5% |
|
|
7.5% |
|
|
9.6% |
|
Return on beginning Deere & Company stockholders’ equity |
|
|
50.2% |
|
|
38.7% |
|
|
46.1% |
|
|
24.1% |
|
|
28.8% |
|
|
24.8% |
|
|
33.1% |
|
|
22.6% |
|
|
21.4% |
|
|
30.8% |
|
Comprehensive income* |
|
|
10,099 |
|
|
6,629 |
|
|
8,963 |
|
|
2,819 |
|
|
2,081 |
|
|
3,222 |
|
|
3,221 |
|
|
627 |
|
|
994 |
|
|
2,072 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income per share – basic* |
|
$ |
34.80 |
|
$ |
23.42 |
|
$ |
19.14 |
|
$ |
8.77 |
|
$ |
10.28 |
|
$ |
7.34 |
|
$ |
6.76 |
|
$ |
4.83 |
|
$ |
5.81 |
|
$ |
8.71 |
|
– diluted* |
|
|
34.63 |
|
|
23.28 |
|
|
18.99 |
|
|
8.69 |
|
|
10.15 |
|
|
7.24 |
|
|
6.68 |
|
|
4.81 |
|
|
5.77 |
|
|
8.63 |
|
Dividends declared per share |
|
|
5.05 |
|
|
4.36 |
|
|
3.61 |
|
|
3.04 |
|
|
3.04 |
|
|
2.58 |
|
|
2.40 |
|
|
2.40 |
|
|
2.40 |
|
|
2.22 |
|
Dividends paid per share |
|
|
4.83 |
|
|
4.28 |
|
|
3.32 |
|
|
3.04 |
|
|
2.97 |
|
|
2.49 |
|
|
2.40 |
|
|
2.40 |
|
|
2.40 |
|
|
2.13 |
|
Average number of common shares outstanding (in millions) – basic |
|
|
292.2 |
|
|
304.5 |
|
|
311.6 |
|
|
313.5 |
|
|
316.5 |
|
|
322.6 |
|
|
319.5 |
|
|
315.2 |
|
|
333.6 |
|
|
363.0 |
|
– diluted |
|
|
293.6 |
|
|
306.3 |
|
|
314.0 |
|
|
316.6 |
|
|
320.6 |
|
|
327.3 |
|
|
323.3 |
|
|
316.6 |
|
|
336.0 |
|
|
366.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
104,087 |
|
$ |
90,030 |
|
$ |
84,114 |
|
$ |
75,091 |
|
$ |
73,011 |
|
$ |
70,108 |
|
$ |
65,786 |
|
$ |
57,918 |
|
$ |
57,883 |
|
$ |
61,267 |
|
Trade accounts and notes receivable – net |
|
|
7,739 |
|
|
6,410 |
|
|
4,208 |
|
|
4,171 |
|
|
5,230 |
|
|
5,004 |
|
|
3,925 |
|
|
3,011 |
|
|
3,051 |
|
|
3,278 |
|
Financing receivables – net |
|
|
43,673 |
|
|
36,634 |
|
|
33,799 |
|
|
29,750 |
|
|
29,195 |
|
|
27,054 |
|
|
25,104 |
|
|
23,702 |
|
|
24,809 |
|
|
27,422 |
|
Financing receivables securitized – net |
|
|
7,335 |
|
|
5,936 |
|
|
4,659 |
|
|
4,703 |
|
|
4,383 |
|
|
4,022 |
|
|
4,159 |
|
|
5,127 |
|
|
4,835 |
|
|
4,602 |
|
Equipment on operating leases – net |
|
|
6,917 |
|
|
6,623 |
|
|
6,988 |
|
|
7,298 |
|
|
7,567 |
|
|
7,165 |
|
|
6,594 |
|
|
5,902 |
|
|
4,970 |
|
|
4,016 |
|
Inventories |
|
|
8,160 |
|
|
8,495 |
|
|
6,781 |
|
|
4,999 |
|
|
5,975 |
|
|
6,149 |
|
|
3,904 |
|
|
3,341 |
|
|
3,817 |
|
|
4,210 |
|
Property and equipment – net |
|
|
6,879 |
|
|
6,056 |
|
|
5,820 |
|
|
5,817 |
|
|
5,973 |
|
|
5,868 |
|
|
5,068 |
|
|
5,171 |
|
|
5,181 |
|
|
5,578 |
|
Short-term borrowings |
|
|
17,939 |
|
|
12,592 |
|
|
10,919 |
|
|
8,582 |
|
|
10,784 |
|
|
11,062 |
|
|
10,035 |
|
|
6,911 |
|
|
8,425 |
|
|
8,018 |
|
Short-term securitization borrowings |
|
|
6,995 |
|
|
5,711 |
|
|
4,605 |
|
|
4,682 |
|
|
4,321 |
|
|
3,957 |
|
|
4,119 |
|
|
4,998 |
|
|
4,585 |
|
|
4,553 |
|
Long-term borrowings |
|
|
38,477 |
|
|
33,596 |
|
|
32,888 |
|
|
32,734 |
|
|
30,229 |
|
|
27,237 |
|
|
25,891 |
|
|
23,703 |
|
|
23,775 |
|
|
24,318 |
|
Total Deere & Company stockholders’ equity |
|
|
21,785 |
|
|
20,262 |
|
|
18,431 |
|
|
12,937 |
|
|
11,413 |
|
|
11,288 |
|
|
9,557 |
|
|
6,520 |
|
|
6,743 |
|
|
9,063 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Book value per share* |
|
$ |
77.37 |
|
$ |
67.82 |
|
$ |
59.83 |
|
$ |
41.25 |
|
$ |
36.45 |
|
$ |
35.45 |
|
$ |
29.70 |
|
$ |
20.71 |
|
$ |
21.29 |
|
$ |
26.23 |
|
Capital expenditures |
|
$ |
1,537 |
|
$ |
1,176 |
|
$ |
867 |
|
$ |
762 |
|
$ |
1,084 |
|
$ |
969 |
|
$ |
586 |
|
$ |
668 |
|
$ |
655 |
|
$ |
1,004 |
|
Number of employees (at year end) |
|
|
82,956 |
|
|
82,239 |
|
|
75,550 |
|
|
69,634 |
|
|
73,489 |
|
|
74,413 |
|
|
60,476 |
|
|
56,767 |
|
|
57,180 |
|
|
59,623 |
|
* Attributable to Deere & Company.
42
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENT MARKET RISK INFORMATION
We are naturally exposed to various interest rate and foreign currency risks. As a result, we enter into derivative transactions to manage this exposure and not for speculative purposes.
From time to time, we enter into interest rate swap agreements to manage our interest rate exposure. We also have foreign currency exposures at some of our foreign and domestic operations related to buying, selling, and financing in currencies other than the functional currencies. We have entered into derivative agreements related to the management of these foreign currency transaction risks.
Interest Rate Risk
Results of Operations – Central bank policy rates increased in 2022 and 2023. Rising interest rates have historically impacted our borrowings sooner than the benefit is realized from the financing receivable and equipment on operating lease portfolios. As a result, our financial services operations experienced spread compression in 2023. If interest rates continue to rise, we expect to continue experiencing spread compression in 2024.
Fair Value Measurement – Quarterly, we use a combination of cash flow models to assess the sensitivity of our financial instruments with interest rate exposure to changes in market interest rates. The models calculate the effect of adjusting interest rates as follows:
| ● | cash flows for financing receivables are discounted at the current prevailing rate for each receivable portfolio, |
| ● | cash flows for marketable securities are discounted at the applicable benchmark yield curve plus market credit spreads, |
| ● | cash flows for unsecured borrowings are discounted at the applicable benchmark yield curve plus market credit spreads for similarly rated borrowers, |
| ● | cash flows for securitized borrowings are discounted at the swap yield curve plus a market credit spread for similarly rated borrowers, and |
| ● | cash flows for interest rate swaps are projected and discounted using forward rates from the swap yield curve at the repricing dates. |
The net impact in these financial instruments’ fair values which would be caused by decreasing or increasing the interest rates by 10 percent from the market rates at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 would have been approximately $10 and $50, respectively.
Reference Rate Reform – We transitioned our financing, funding, and hedging portfolios from the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) to alternative reference rates in 2023. In 2024, we will transition certain portfolios from the Canadian Dollar Offered Rate (CDOR) to an alternative reference rate. These transition activities did not / are not expected to have a material impact on our financial statements.
Foreign Currency Risk
In the equipment operations, the practice is to hedge significant currency exposures. Worldwide foreign currency exposures are reviewed quarterly. Based on the anticipated and committed foreign currency cash inflows, outflows, and hedging policy for the next twelve months, we estimate that a hypothetical 10 percent strengthening of the U.S. dollar relative to other currencies through 2024 would increase the 2024 expected net cash inflows by approximately $25. At October 29, 2023, a hypothetical 10 percent strengthening of the U.S. dollar under similar assumptions and calculations indicated a potential $125 decrease on the 2023 net cash inflows. The estimated impacts by currency follow:
|
|
2024 |
|
2023 |
|
||
Australian dollar |
|
$ |
(75) |
|
$ |
(100) |
|
Brazilian real |
|
|
25 |
|
|
(150) |
|
British pound |
|
|
(50) |
|
|
(25) |
|
Canadian dollar |
|
|
|
|
|
(25) |
|
Euro |
|
|
75 |
|
|
50 |
|
Japanese yen |
|
|
75 |
|
|
125 |
|
Mexican peso |
|
|
25 |
|
|
25 |
|
Polish Zloty |
|
|
(25) |
|
|
(25) |
|
All other |
|
|
(25) |
|
|
|
|
Total increase (decrease) |
|
$ |
25 |
|
$ |
(125) |
|
In the financial services operations, our policy is to manage foreign currency risk through hedging strategies if the currency of the borrowings does not match the currency of the receivable portfolio. As a result, a hypothetical 10 percent adverse change in the value of the U.S. dollar relative to all other foreign currencies would not have a material effect on the financial services cash flows.
43
DEERE & COMPANY
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED INCOME
For the Years Ended October 29, 2023, October 30, 2022, and October 31, 2021
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net Sales and Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net sales |
|
$ |
55,565 |
|
$ |
47,917 |
|
$ |
39,737 |
|
Finance and interest income |
|
|
4,683 |
|
|
3,365 |
|
|
3,296 |
|
Other income |
|
|
1,003 |
|
|
1,295 |
|
|
991 |
|
Total |
|
|
61,251 |
|
|
52,577 |
|
|
44,024 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Costs and Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of sales |
|
|
37,715 |
|
|
35,338 |
|
|
29,116 |
|
Research and development expenses |
|
|
2,177 |
|
|
1,912 |
|
|
1,587 |
|
Selling, administrative and general expenses |
|
|
4,595 |
|
|
3,863 |
|
|
3,383 |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
2,453 |
|
|
1,062 |
|
|
993 |
|
Other operating expenses |
|
|
1,292 |
|
|
1,275 |
|
|
1,343 |
|
Total |
|
|
48,232 |
|
|
43,450 |
|
|
36,422 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income of Consolidated Group before Income Taxes |
|
|
13,019 |
|
|
9,127 |
|
|
7,602 |
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
|
2,871 |
|
|
2,007 |
|
|
1,658 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income of Consolidated Group |
|
|
10,148 |
|
|
7,120 |
|
|
5,944 |
|
Equity in income of unconsolidated affiliates |
|
|
7 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income |
|
|
10,155 |
|
|
7,130 |
|
|
5,965 |
|
Less: Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
|
(11) |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
2 |
|
Net Income Attributable to Deere & Company |
|
$ |
10,166 |
|
$ |
7,131 |
|
$ |
5,963 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per Share Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
34.80 |
|
$ |
23.42 |
|
$ |
19.14 |
|
Diluted |
|
|
34.63 |
|
|
23.28 |
|
|
18.99 |
|
Dividends declared |
|
|
5.05 |
|
|
4.36 |
|
|
3.61 |
|
Dividends paid |
|
|
4.83 |
|
|
4.28 |
|
|
3.32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average Shares Outstanding (In millions of shares) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
292.2 |
|
|
304.5 |
|
|
311.6 |
|
Diluted |
|
|
293.6 |
|
|
306.3 |
|
|
314.0 |
|
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of this statement.
44
DEERE & COMPANY
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Years Ended October 29, 2023, October 30, 2022, and October 31, 2021
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net Income |
|
$ |
10,155 |
|
$ |
7,130 |
|
$ |
5,965 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Comprehensive Income (Loss), Net of Income Taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Retirement benefits adjustment |
|
|
(456) |
|
|
645 |
|
|
2,884 |
|
Cumulative translation adjustment |
|
|
443 |
|
|
(1,116) |
|
|
118 |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives |
|
|
(29) |
|
|
63 |
|
|
16 |
|
Unrealized loss on debt securities |
|
|
(16) |
|
|
(109) |
|
|
(18) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Comprehensive Income (Loss), Net of Income Taxes |
|
|
(58) |
|
|
(517) |
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive Income of Consolidated Group |
|
|
10,097 |
|
|
6,613 |
|
|
8,965 |
|
Less: Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
|
(2) |
|
|
(16) |
|
|
2 |
|
Comprehensive Income Attributable to Deere & Company |
|
$ |
10,099 |
|
$ |
6,629 |
|
$ |
8,963 |
|
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of this statement.
45
DEERE & COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
As of October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
7,458 |
|
$ |
4,774 |
|
Marketable securities |
|
|
946 |
|
|
734 |
|
Trade accounts and notes receivable – net |
|
|
7,739 |
|
|
6,410 |
|
Financing receivables – net |
|
|
43,673 |
|
|
36,634 |
|
Financing receivables securitized – net |
|
|
7,335 |
|
|
5,936 |
|
Other receivables |
|
|
2,623 |
|
|
2,492 |
|
Equipment on operating leases – net |
|
|
6,917 |
|
|
6,623 |
|
Inventories |
|
|
8,160 |
|
|
8,495 |
|
Property and equipment – net |
|
|
6,879 |
|
|
6,056 |
|
Goodwill |
|
|
3,900 |
|
|
3,687 |
|
Other intangible assets – net |
|
|
1,133 |
|
|
1,218 |
|
Retirement benefits |
|
|
3,007 |
|
|
3,730 |
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
1,814 |
|
|
824 |
|
Other assets |
|
|
2,503 |
|
|
2,417 |
|
Total Assets |
|
$ |
104,087 |
|
$ |
90,030 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term borrowings |
|
$ |
17,939 |
|
$ |
12,592 |
|
Short-term securitization borrowings |
|
|
6,995 |
|
|
5,711 |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
16,130 |
|
|
14,822 |
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
520 |
|
|
495 |
|
Long-term borrowings |
|
|
38,477 |
|
|
33,596 |
|
Retirement benefits and other liabilities |
|
|
2,140 |
|
|
2,457 |
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
82,201 |
|
|
69,673 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitments and contingencies (Note 20) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Redeemable noncontrolling interest (Note 3) |
|
|
97 |
|
|
92 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, $1 par value (authorized – 1,200,000,000 shares; issued – 536,431,204 shares in 2023 and 2022), at paid-in amount |
|
|
5,303 |
|
|
5,165 |
|
Common stock in treasury, 254,846,927 shares in 2023 and 237,659,289 shares in 2022, at cost |
|
|
(31,335) |
|
|
(24,094) |
|
Retained earnings |
|
|
50,931 |
|
|
42,247 |
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
(3,114) |
|
|
(3,056) |
|
Total Deere & Company stockholders’ equity |
|
|
21,785 |
|
|
20,262 |
|
Noncontrolling interests |
|
|
4 |
|
|
3 |
|
Total stockholders’ equity |
|
|
21,789 |
|
|
20,265 |
|
Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity |
|
$ |
104,087 |
|
$ |
90,030 |
|
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of this statement.
46
DEERE & COMPANY
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOWS
For the Years Ended October 29, 2023, October 30, 2022, and October 31, 2021
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Cash Flows from Operating Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
10,155 |
|
$ |
7,130 |
|
$ |
5,965 |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision (credit) for credit losses |
|
|
(16) |
|
|
192 |
|
|
(6) |
|
Provision for depreciation and amortization |
|
|
2,004 |
|
|
1,895 |
|
|
2,050 |
|
Impairments and other adjustments |
|
|
191 |
|
|
88 |
|
|
50 |
|
Share-based compensation expense |
|
|
130 |
|
|
85 |
|
|
82 |
|
Gain on remeasurement of previously held equity investment |
|
|
|
|
|
(326) |
|
|
|
|
Credit for deferred income taxes |
|
|
(790) |
|
|
(66) |
|
|
(441) |
|
Changes in assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Receivables related to sales |
|
|
(4,253) |
|
|
(2,483) |
|
|
969 |
|
Inventories |
|
|
279 |
|
|
(2,091) |
|
|
(2,497) |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
830 |
|
|
1,133 |
|
|
1,884 |
|
Accrued income taxes payable/receivable |
|
|
(23) |
|
|
141 |
|
|
11 |
|
Retirement benefits |
|
|
(170) |
|
|
(1,015) |
|
|
29 |
|
Other |
|
|
252 |
|
|
16 |
|
|
(370) |
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
|
8,589 |
|
|
4,699 |
|
|
7,726 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Investing Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Collections of receivables (excluding receivables related to sales) |
|
|
23,051 |
|
|
20,907 |
|
|
18,959 |
|
Proceeds from sales of equipment on operating leases |
|
|
1,981 |
|
|
2,093 |
|
|
2,094 |
|
Cost of receivables acquired (excluding receivables related to sales) |
|
|
(28,772) |
|
|
(26,300) |
|
|
(23,653) |
|
Acquisitions of businesses, net of cash acquired |
|
|
(82) |
|
|
(498) |
|
|
(244) |
|
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
|
(1,498) |
|
|
(1,134) |
|
|
(848) |
|
Cost of equipment on operating leases acquired |
|
|
(2,970) |
|
|
(2,654) |
|
|
(1,732) |
|
Collateral on derivatives – net |
|
|
(12) |
|
|
(642) |
|
|
(281) |
|
Other |
|
|
(447) |
|
|
(257) |
|
|
(45) |
|
Net cash used for investing activities |
|
|
(8,749) |
|
|
(8,485) |
|
|
(5,750) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net proceeds in short-term borrowings (original maturities three months or less) |
|
|
4,008 |
|
|
3,852 |
|
|
818 |
|
Proceeds from borrowings issued (original maturities greater than three months) |
|
|
15,429 |
|
|
10,358 |
|
|
8,722 |
|
Payments of borrowings (original maturities greater than three months) |
|
|
(7,913) |
|
|
(8,445) |
|
|
(7,090) |
|
Repurchases of common stock |
|
|
(7,216) |
|
|
(3,597) |
|
|
(2,538) |
|
Dividends paid |
|
|
(1,427) |
|
|
(1,313) |
|
|
(1,040) |
|
Other |
|
|
(73) |
|
|
(29) |
|
|
50 |
|
Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities |
|
|
2,808 |
|
|
826 |
|
|
(1,078) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of Exchange Rate Changes on Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash |
|
|
31 |
|
|
(224) |
|
|
55 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash |
|
|
2,679 |
|
|
(3,184) |
|
|
953 |
|
Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash at Beginning of Year |
|
|
4,941 |
|
|
8,125 |
|
|
7,172 |
|
Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash at End of Year |
|
$ |
7,620 |
|
$ |
4,941 |
|
$ |
8,125 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Components of Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
7,458 |
|
$ |
4,774 |
|
$ |
8,017 |
|
Restricted cash (Other assets) |
|
|
162 |
|
|
167 |
|
|
108 |
|
Total Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Restricted Cash |
|
$ |
7,620 |
|
$ |
4,941 |
|
$ |
8,125 |
|
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of this statement.
47
DEERE & COMPANY
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN CONSOLIDATED STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
For the Years Ended October 31, 2021, October 30, 2022, and October 29, 2023
|
|
|
|
|
Total Stockholders’ Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Deere & Company Stockholders |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
Redeemable |
|
||||
|
|
Stockholders’ |
|
Common |
|
Treasury |
|
Retained |
|
Comprehensive |
|
Noncontrolling |
|
|
Noncontrolling |
|
|||||||
|
|
Equity |
|
Stock |
|
Stock |
|
Earnings |
|
Income (Loss) |
|
Interests |
|
|
Interest |
|
|||||||
Balance November 1, 2020 |
|
$ |
12,944 |
|
$ |
4,895 |
|
$ |
(18,065) |
|
$ |
31,646 |
|
$ |
(5,539) |
|
$ |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ASU No. 2016-13 adoption |
|
|
(35) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(35) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
|
5,965 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,963 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
Other comprehensive income |
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Repurchases of common stock |
|
|
(2,538) |
|
|
|
|
|
(2,538) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Treasury shares reissued |
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends declared |
|
|
(1,127) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1,125) |
|
|
|
|
|
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
Share based awards and other |
|
|
155 |
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(4) |
|
|
|
|
|
Balance October 31, 2021 |
|
|
18,434 |
|
|
5,054 |
|
|
(20,533) |
|
|
36,449 |
|
|
(2,539) |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acquisitions (see Note 3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
104 |
|
Net income (loss) |
|
|
7,133 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7,131 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
(3) |
|
Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
(517) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(517) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(15) |
|
Repurchases of common stock |
|
|
(3,597) |
|
|
|
|
|
(3,597) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Treasury shares reissued |
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends declared |
|
|
(1,329) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1,327) |
|
|
|
|
|
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
Share based awards and other |
|
|
105 |
|
|
111 |
|
|
|
|
|
(6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
Balance October 30, 2022 |
|
|
20,265 |
|
|
5,165 |
|
|
(24,094) |
|
|
42,247 |
|
|
(3,056) |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
92 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
|
10,168 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,166 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
(13) |
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
(58) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(58) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
Repurchases of common stock |
|
|
(7,274) |
|
|
|
|
|
(7,274) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Treasury shares reissued |
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends declared |
|
|
(1,477) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1,472) |
|
|
|
|
|
(5) |
|
|
|
|
|
Share based awards and other |
|
|
132 |
|
|
138 |
|
|
|
|
|
(10) |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
Balance October 29, 2023 |
|
$ |
21,789 |
|
$ |
5,303 |
|
$ |
(31,335) |
|
$ |
50,931 |
|
$ |
(3,114) |
|
$ |
4 |
|
|
$ |
97 |
|
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of this statement.
48
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note Listing |
Page |
|
1. |
49 |
|
2. |
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies and New Accounting Standards |
49 |
3. |
52 |
|
4. |
54 |
|
5. |
55 |
|
6. |
57 |
|
7. |
57 |
|
8. |
61 |
|
9. |
62 |
|
10. |
63 |
|
11. |
63 |
|
12. |
67 |
|
13. |
68 |
|
14. |
68 |
|
15. |
68 |
|
16. |
68 |
|
17. |
68 |
|
18. |
69 |
|
19. |
69 |
|
20. |
69 |
|
21. |
70 |
|
22. |
70 |
|
23. |
71 |
|
24. |
73 |
|
25. |
74 |
|
26. |
76 |
|
27. |
77 |
|
28. |
78 |
|
1. ORGANIZATION AND CONSOLIDATION
References to “Deere & Company”, “John Deere”, “Deere”, “we”, “us”, or “our” include our consolidated subsidiaries. We manage our business through the following operating segments: production and precision agriculture (PPA), small agriculture and turf (SAT), construction and forestry (CF), and financial services (FS). References to “equipment operations” include PPA, SAT, and CF, while references to “agriculture and turf” include both PPA and SAT.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements represent the consolidation of all companies in which Deere & Company has a controlling interest. Certain variable interest entities (VIEs) are consolidated since we are the primary beneficiary. The primary beneficiary has both the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the VIEs’ economic performance and the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits that could potentially be significant to the VIEs. We consolidate certain VIEs related to retail note securitizations (see Note 12).
We record our investment in each unconsolidated affiliated company (20 to 50 percent ownership) at cost, plus or minus our share of the profit or loss after acquisition, and further reduced for any dividends (see Note 16). Other investments (less than 20 percent ownership) are recorded at cost.
Fiscal Year
We use a 52/53 week fiscal year ending on the last Sunday in the reporting period, which generally occurs near the end of October. An additional week is included in the fourth fiscal quarter every five or six years to realign our fiscal quarters with the calendar. The fiscal year ends for 2023, 2022, and 2021 were October 29, 2023, October 30, 2022, and October 31, 2021, respectively. Fiscal years 2023, 2022, and 2021 contained 52 weeks. Unless otherwise stated, references to particular years, quarters, or months refer to our fiscal years and the associated periods in those fiscal years.
Presentation of Amounts
All amounts are presented in millions of dollars, unless otherwise specified.
Argentina
We have equipment operations and financial services operations in Argentina. The U.S. dollar has historically been the functional currency for our Argentina operations, as our business is indexed to the U.S. dollar due to the highly inflationary conditions. The Argentine government has certain capital and currency controls that restrict our ability to access U.S. dollars in Argentina and remit earnings from our Argentine operations. As of October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022, our net investment in Argentina was $766 and $742, respectively. Net sales and revenues from our Argentine operations represented approximately 1 percent of consolidated net sales and revenues for 2023 and 2022. We have employed mechanisms to convert Argentine pesos into U.S. dollars to the extent possible. These mechanisms are short-term in nature, leaving us exposed to long-term currency fluctuations. As of October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022, the gross peso exposure was $30 and $133, respectively, while the net peso exposure (after considering the impact of short-term hedges) was $5 and $53, respectively. Argentine peso-denominated monetary assets and liabilities are remeasured at each balance sheet date using the official currency exchange rate.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND NEW ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
The following are significant accounting policies in addition to those included in other notes to the consolidated financial statements.
Use of Estimates in Financial Statements
Certain accounting policies require management to make estimates and assumptions in determining the amounts reflected in the financial statements and related disclosures. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Revenue Recognition
General
Sales of equipment and service parts are recognized when we transfer control of the good to the independent customer, which generally occurs upon shipment. In most situations, the independent customer is a dealer, which subsequently sells the equipment and service parts purchased from us to a retail customer, who can finance the equipment with the financial services segment or another source of financing. In some situations, we sell directly to a retail customer.
49
The term “customer” includes both dealers and retail customers to whom we make direct sales.
Interest-Free Periods and Past-Due Interest
We charge dealers interest on outstanding balances from the earlier of when goods are sold to a retail customer by the dealer or the expiration of the interest-free period granted at the time of the sale to the dealer. Interest-free periods are determined based on the type of equipment sold and the time of year of the sale. These periods range from one to twelve months for most equipment. Interest-free periods may not be extended. Interest charged may not be forgiven, and past due interest rates are charged at higher rates. If the interest-free or below market interest rate period exceeds one year, we adjust the expected sales revenue for the effects of the time value of money using a current market interest rate. The revenue related to the financing component is recognized in “Finance and interest income” using the interest method. We do not adjust the sales price to account for a financing component if the expected interest-free or below market period is one year or less.
Right of Return
Generally, no right of return exists on sales of equipment. Dealers cannot cancel purchases after we recognize a sale and are responsible for payment even if the equipment is not sold to a retail customer. Service parts and certain attachment returns are estimable and accrued at the time a sale is recognized. The estimated returns are based on historical return rates, current dealer inventory levels, and current economic conditions. The estimated returns are recorded in “Other assets” for the inventory value of estimated returns, adjusted for restocking fees. The estimated dealer refund liability, adjusted for restocking fees, is recorded in “Accounts payable and accrued expenses.”
Remanufacturing
We remanufacture used engines and components (cores) that are sold to dealers and retail customers for maintenance and repair parts. Revenue for remanufactured components is recognized using the same criteria as other parts sales. When a remanufactured part is sold, we collect a deposit that is repaid if the customer returns a core that meets certain specifications within a defined time period. The deposit received from the customer is recognized as a liability in “Accounts payable and accrued expenses” and the used component that is expected to be returned is recognized in “Other assets.” When a customer returns a core, the deposit is repaid, the liability reversed, and the returned core is recorded in inventory to be remanufactured and sold to another customer. If a core is not returned within the required time, the deposit is recognized as revenue in “Net sales,” and the cost of the core is recorded as an expense in “Cost of sales.”
Bundled Technology
Certain equipment is sold with precision guidance, telematics, and other information gathering and analyzing capabilities. These technology solutions require hardware, software, and may include an obligation to provide services for a period of time. These solutions are mostly bundled with the sale of the equipment but
can also be purchased or renewed separately. The revenue related to the hardware and embedded software is recognized at the time of the equipment sale and recorded in “Net sales.” The revenue for the future services and usage-based software is deferred and recognized over the service period. The deferred revenue is recorded as a contract liability in “Accounts payable and accrued expenses.”
Financing Revenue and Origination Costs
Financing revenue and deferred costs on the origination of financing receivables are recorded over the lives of the related receivables using the interest method. Deferred costs are recognized as a reduction to “Finance and interest income.” Income and deferred costs on the origination of operating leases are recognized on a straight-line basis over the scheduled lease terms in “Finance and interest income.”
Sales Incentives
We offer sales incentive programs to promote the sale of our products from the dealer to the retail customer. At the time of the sale to a dealer, we record an estimated cost for the sales incentive programs as a reduction to the sales price. The estimated cost is based on historical data, announced and expected incentive programs, field inventory levels, and forecasted sales volumes. The final cost of these programs is determined at the end of the measurement period for volume-based incentives or when the dealer sells the equipment to a retail customer. Actual cost differences from the original cost estimate are recognized in “Net sales.”
Product Warranties
For equipment and service parts sales, we provide a standard warranty. At the time a sale is recognized, the estimated future warranty costs are recorded. The warranty liability is estimated based on historical warranty claims rate experience and the estimated amount of equipment still under warranty. The historical claims rate is primarily determined by a review of five-year claims costs while also taking into consideration current quality developments. The amount of equipment still under warranty is estimated based on dealer inventories and retail sales.
We also offer extended warranty arrangements for purchase at the customer’s option. The premiums for extended warranties are recognized in “Other income” primarily in proportion to the costs expected to be incurred over the contract period. The unamortized extended warranty premiums (deferred revenue) are recorded in “Accounts payable and accrued expenses” (see Note 18).
Sales and Transaction Taxes
We collect and remit taxes for revenue producing transactions as necessary based on various tax laws. These taxes include sales, use, value-added, and some excise taxes. We elected to exclude these taxes from the determination of the sales price. These taxes are not included in revenues.
Contract Costs
Incremental costs of obtaining an equipment revenue contract are recognized as an expense when incurred since the amortization period would be one year or less.
50
Advertising Costs
Advertising costs are charged to “Selling, administrative and general expenses” as incurred. Advertising costs were $244 in 2023, $227 in 2022, and $212 in 2021.
Depreciation and Amortization
Property and equipment, capitalized software, and other intangible assets are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation or amortization. These assets are depreciated over their estimated useful lives using the straight-line method. Equipment on operating leases is depreciated over the terms of the leases using the straight-line method. Property and equipment expenditures for new and revised products, increased capacity, and the replacement or major renewal of significant items are capitalized. Expenditures for maintenance, repairs, and minor renewals are charged to expense as incurred.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider investments with purchased maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
Receivables and Allowances
All financing and trade receivables are reported on the balance sheet at outstanding principal and accrued interest, adjusted for:
| ● | write-offs, |
| ● | allowance for credit losses, and |
| ● | unamortized deferred fees or costs on originated financing receivables. |
The allowance is a reduction to the receivable balances, and the provision is recorded in “Selling, administrative and general expenses.” The allowance for credit losses is an estimate of the credit losses expected over the life of the receivable portfolio. The allowance is measured on a collective basis for receivables with similar risk characteristics. Receivables that do not share risk characteristics are evaluated on an individual basis. Risk characteristics include:
| ● | finance product category, |
| ● | market, |
| ● | geography, |
| ● | credit risk, and |
| ● | remaining balance. |
We utilize the following loss forecast models to estimate expected credit losses:
| ● | Transition matrix models are used for large and complex retail customer receivable pools. These models are used for more than 90 percent of retail customer receivables. Historical portfolio performance and current delinquency levels are used to forecast future defaults. Estimated recovery rates are applied to the estimated default balance to calculate the expected credit losses. |
| ● | Weighted average remaining maturity (WARM) models are used for smaller and less complex retail customer receivable pools. |
| ● | Historical loss rate models are used on wholesale receivables, with consideration of current economic conditions and dealer financial risk. |
The model output is adjusted for forecasted economic conditions, which may include the following economic indicators:
| ● | commodity prices, |
| ● | industry equipment sales, |
| ● | unemployment rates, and |
| ● | housing starts. |
Management reviews each model’s output quarterly, and qualitative adjustments are incorporated as necessary (see Note 11).
Long-Lived Assets, Goodwill, and Other Intangible Asset Impairment
We evaluate the carrying value of long-lived assets (including equipment on operating leases, property and equipment, goodwill, and other intangible assets) when events or circumstances warrant such a review. Goodwill and unamortized intangible assets are tested for impairment annually at the end of the third quarter of each fiscal year, and more often if events or circumstances may have caused the fair value to fall below the carrying value. If the carrying value of the long-lived asset is considered impaired, the long-lived asset is written down to its fair value (see Notes 4 and 25).
Goodwill is allocated and reviewed for impairment by reporting unit. Goodwill is allocated to the reporting unit in which the business that created the goodwill resides. To test for goodwill impairment, the carrying value of each reporting unit is compared with its fair value. If the carrying value of the goodwill is considered impaired, the impairment is measured as the reporting unit’s carrying value minus the fair value.
Derivative Financial Instruments
It is our policy to use derivative transactions only to manage exposures from the normal course of business. We do not execute derivative transactions for the purpose of creating speculative positions or trading. Our financial services operations have interest rate and foreign currency exposure between (a) the receivable or lease portfolio and (b) how those portfolios are funded. We also have foreign currency exposures at some of our foreign and domestic operations related to buying, selling, and financing in currencies other than the functional currencies. In addition, we have interest rate and foreign currency exposure at certain equipment operations units for sales incentive programs.
All derivatives are recorded at fair value on the consolidated balance sheets. Cash collateral received or paid is not offset against the derivative fair values on the balance sheets. The cash flows from the derivative contracts are recorded in operating activities in the statements of consolidated cash flows. Each derivative is designated as a cash flow hedge, fair value hedge, or remains undesignated.
Changes in the fair value of derivatives are recorded as follows:
| ● | Cash flow hedges: Recorded in other comprehensive income (OCI) and reclassified to the income statement when the effects of the item being hedged are recognized in the income statement. These amounts offset the effects of interest rate changes on the related borrowings in interest expense. |
51
| ● | Fair value hedges: Recorded in interest expense, and the gains or losses are offset by the fair value gains or losses on the hedged items (fixed-rate borrowings), which are also recorded in interest expense. |
| ● | Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: Changes in the fair value of undesignated hedges are recognized as they occur in the income statement. |
All designated hedges are formally documented as to the relationship with the hedged item as well as the risk-management strategy. Both at inception and on an ongoing basis, the hedging instrument is assessed for its effectiveness. If and when a derivative is determined not to be highly effective as a hedge, the underlying hedged transaction is no longer likely to occur, the hedge designation is removed, or the derivative is terminated, hedge accounting is discontinued (see Note 26).
Foreign Currency Translation
The functional currencies for most of our foreign operations are their respective local currencies. The assets and liabilities of these operations are translated into U.S. dollars using the exchange rates at the end of the period. The revenues and expenses are translated at weighted-average rates for the period. The gains or losses from these translations are recorded in OCI.
Foreign currency gains or losses and foreign exchange components of derivative contracts are included in net income, with trade flow activity recorded in “Cost of sales,” sales incentive activity recorded in “Net sales,” and all other activity recorded in “Other operating expenses.” The pretax net loss for foreign exchange in 2023, 2022, and 2021 was $159, $175, and $134, respectively.
New Accounting Standards
We closely monitor all Accounting Standard Updates (ASUs) issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and other authoritative guidance. We adopted the following standards in 2023, none of which had a material effect on our consolidated financial statements:
New Accounting Standards Adopted |
|
No. 2021-10 — Government Assistance (Topic 832): Disclosures by Business Entities about Government Assistance |
|
No. 2021-05 — Leases (Topic 842): Lessors – Certain Leases with Variable Lease Payments |
|
No. 2021-04 — Issuer's Accounting for Certain Modifications or Exchanges of Freestanding Equity Classified Written Call Options |
|
We will adopt the following standards in future periods, none of which are expected to have a material effect on our consolidated financial statements.
New Accounting Standards to be Adopted |
|
No. 2022-04 — Liabilities — Supplier Finance Programs (Subtopic 405-50): Disclosure of Supplier Finance Program Obligations |
|
No. 2022-02 — Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326): Troubled Debt Restructurings and Vintage Disclosures |
|
No. 2022-01 — Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): Fair Value Hedging – Portfolio Layer Method |
|
No. 2021-08 — Business Combinations (Topic 805): Accounting for Contract Assets and Contract Liabilities from Contracts with Customers |
|
3. ACQUISITIONS AND DISPOSITIONS
During the presented periods, we completed acquisitions to support our Leap Ambitions, which focus on advancing our capabilities in technology.
Acquisitions
2023 Acquisitions
In 2023, we acquired SparkAI Inc. (Spark AI) and Smart Apply, Inc. (Smart Apply) to accelerate the integration of smart technology innovation in our products. The combined cost of these acquisitions was $82, net of cash acquired of $2. Spark AI was assigned to the PPA segment, while Smart Apply was assigned to the SAT segment. Most of the purchase price for these acquisitions was allocated to goodwill.
2022 Acquisitions
Kreisel
In February 2022, we acquired majority ownership in Kreisel Electric Inc. (Kreisel), a pioneer in the development of immersion-cooled battery technology. The Austrian company manufactures high-density, high-durability electric battery modules and packs for high-performance and off-highway applications and has created a battery-buffered, high-powered charging infrastructure platform.
The transaction includes a call option to purchase the remaining ownership interest in Kreisel in 2027. The minority interest holders also have a put option that would require us to purchase the holders’ ownership interests in 2027. The put and call options cannot be separated from the noncontrolling interest. Due to the redemption features, the minority interest is classified as redeemable noncontrolling interest in our consolidated balance sheets.
The total cash purchase price was $276, consisting of $253 for the acquired equity interests, $21 to reduce the option price, and customary working capital adjustments, net of cash acquired. The fair values assigned to the assets and liabilities of the acquired entity, which are based on information as of the acquisition date and available at October 30, 2022, follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
February 2022 |
|
|
Trade accounts and notes receivable |
|
$ |
2 |
|
Other receivables |
|
|
11 |
|
Inventories |
|
|
11 |
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
11 |
|
Goodwill |
|
|
218 |
|
Other intangible assets |
|
|
178 |
|
Other assets |
|
|
6 |
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
437 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
$ |
26 |
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Redeemable noncontrolling interest |
|
$ |
96 |
|
The identifiable intangible assets were related to technology, trade name, and customer relationships with a weighted average amortization period of 12 years. The goodwill is not deductible for income tax purposes. Kreisel is allocated amongst the PPA, SAT, and CF segments.
52
Excavator Factories
In March 2022, we acquired full ownership of three former Deere-Hitachi joint venture factories and began new license and supply agreements with Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd. (Hitachi). The two companies also ended their joint venture manufacturing and marketing agreements. The former joint venture factories continue to manufacture Deere-branded construction excavators and forestry equipment. Through a new supply agreement with Hitachi, Deere continues to offer a full portfolio of excavators. Deere’s marketing arrangement for Hitachi-branded construction excavators and mining equipment in the Americas ended with Hitachi assuming distribution and support of these products. John Deere dealers may continue to support their existing field population of Hitachi-branded excavators.
With the completion of this acquisition, we now have complete control over the excavator design, product, and feature updates, making it possible to more rapidly respond to customer requirements and integrate excavators with other construction products in the John Deere product portfolio. We can leverage technology developed for other product lines and production systems across the enterprise and extend those advanced solutions to Deere-designed excavators, strengthening the entire product portfolio. The total invested capital is as follows:
|
|
March 2022 |
|
|
Cash consideration for factories |
|
$ |
205 |
|
Cash consideration for license agreement |
|
|
70 |
|
Deferred consideration |
|
|
271 |
|
Total purchase price consideration |
|
|
546 |
|
Less: Cash obtained |
|
|
(187) |
|
Less: Settlement of intercompany balances |
|
|
(113) |
|
Net purchase price consideration |
|
|
246 |
|
Fair value of previously held equity investment |
|
|
444 |
|
Total invested capital |
|
$ |
690 |
|
The total purchase price consideration includes deferred consideration that will be paid as we purchase Deere-branded excavators, components, and service parts from Hitachi under the new supply agreement with a duration that ranges from 5 to 30 years. The deferred consideration represents the price increases under the new supply arrangement. Excluding inflation adjustments, the price increases for products to be acquired by us from Hitachi are as much as 27 percent higher than the prior supply arrangement. We financed the acquisition and associated transaction expenses from cash on hand. The fair value of the previously held equity investment created a non-cash gain of $326 (pretax and after-tax), which was recorded in “Other income” and included in the CF segment’s operating profit.
Prior to the acquisition, we purchased Deere- and Hitachi-branded excavators, components, and parts from the Deere-Hitachi joint venture factories for sale to John Deere dealers. These purchases were included in Cost of sales, while the sales to John Deere dealers were included in Net sales. Cost of sales also included profit-sharing payments to Hitachi in accordance with the previous marketing agreements. Following the acquisition, Net sales only
includes the sale of Deere-branded excavators to John Deere dealers, while Cost of sales reflects market pricing to purchase and manufacture excavators, as well as the related components and service parts.
The fair values assigned to the assets and liabilities of the acquired factories, which are based on information as of the acquisition date and available at October 30, 2022, follow:
|
|
March 2022 |
|
|
Other receivables |
|
$ |
29 |
|
Inventories |
|
|
286 |
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
180 |
|
Goodwill |
|
|
529 |
|
Other intangible assets |
|
|
70 |
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
56 |
|
Other assets |
|
|
3 |
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
1,153 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
$ |
300 |
|
Long-term borrowings |
|
|
163 |
|
Total liabilities |
|
$ |
463 |
|
The identifiable intangible assets were related to technology with a 10-year amortization period. The goodwill is not deductible for income tax purposes. The excavator factories are reported in the CF segment.
Other Acquisitions
In 2022, we acquired AgriSync Inc. (AgriSync), a technology service provider; an 80 percent stake in both SureFire Ag Systems, Inc. and SureFire Electronics, LLC (renamed after acquisition and collectively referred to as SurePoint), which design and manufacture liquid fertilizer application and spray tendering systems; an equity method investment in GUSS Automation LLC (GUSS Automation), a pioneer in semi-autonomous orchard and vineyard sprayers; LGT, LLC (Light), which specializes in depth sensing and camera-based perception for autonomous vehicles; and an equity method investment in InnerPlant, Inc. (InnerPlant), an early-stage biotech company. The combined cost of these acquisitions was $134, net of cash acquired of $3. The asset and liability fair values at the respective acquisition dates follow:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
October 2022 |
|
|
Trade accounts and notes receivable |
|
$ |
8 |
|
Inventories |
|
|
8 |
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
4 |
|
Goodwill |
|
|
53 |
|
Other intangible assets |
|
|
21 |
|
Other assets |
|
|
60 |
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
154 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
$ |
6 |
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
5 |
|
Total liabilities |
|
$ |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Redeemable noncontrolling interest |
|
$ |
9 |
|
53
The identifiable intangible assets were related to trade name, technology, and customer relationships with a weighted average amortization period of 7 years. AgriSync was allocated amongst the PPA, SAT, and CF segments, while SurePoint, Light, and InnerPlant were allocated to the PPA segment. GUSS Automation was assigned to the SAT segment.
2021 Acquisitions
Bear Flag
In August 2021, we acquired Bear Flag Robotics, Inc. (Bear Flag) to further accelerate Deere’s development and delivery of advanced technology. Bear Flag’s technology is complementary to other Deere technology efforts and enables autonomous tractor operations. The total cash purchase price before final adjustments, net of cash acquired of $4, was $225, with an additional $25 to be recognized as compensation expense over the four-year post-acquisition service period. In addition to the cash purchase price, $19 of liabilities were assumed. The asset and liability fair values at the acquisition date follow:
|
|
August 2021 |
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
$ |
1 |
|
Goodwill |
|
|
189 |
|
Other intangible assets |
|
|
54 |
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
244 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
$ |
1 |
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
18 |
|
Total liabilities |
|
$ |
19 |
|
The identified intangible was related to technology with a seven-year amortization period. The goodwill is not deductible for income tax purposes.
For the acquisitions, the goodwill was the result of future cash flows and related fair value exceeding the fair value of the identified assets and liabilities. The results of these operations have been included in our consolidated financial statements, and the pro forma results of operations as if these acquisitions had occurred at the beginning of the current or comparative fiscal year would not differ significantly from the reported results.
Dispositions
In October 2023, we sold our roadbuilding business in Russia. At the time of the sale, total assets were $32, consisting primarily of restricted cash, total liabilities were $1, and the cumulative translation loss was $11. Total proceeds from the sale include $16 of cash and $8 of deferred consideration. A pretax and after-tax loss of $18 was recorded in “Other operating expenses” in the CF segment.
In March 2023, we sold our financial services business in Russia (registered in Russia as a leasing company) to Insight Investment Group. The total proceeds, net of restricted cash sold, were $36. The operations were included in the financial services operating segment through the date of sale. At the disposal date, the total assets were $31, consisting primarily of financing receivables, the total liabilities were $5, and the cumulative translation loss was $10. In the first quarter of 2023, we reversed the allowance for
credit losses and recorded a valuation allowance on the assets held for sale in “Selling, administrative and general expenses.” We did not incur additional gains or losses upon disposition.
4. SPECIAL ITEMS
We were impacted by the following infrequent items. These items should not be considered recurring in nature.
2023 Special Items
Sale of Russian Roadbuilding Business
In the fourth quarter of 2023, we sold our Russian roadbuilding business, recognizing a loss of $18 (pretax and after-tax). The loss was recorded in “Other operating expenses” in the construction and forestry operations.
Brazil Tax Ruling
In the third quarter of 2023, the Brazil Superior Court of Justice published a favorable tax ruling regarding taxability of local incentives, which allowed us to record a $243 reduction in the provision for income taxes and $47 of interest income.
Financial Services Financing Incentives Correction
In the second quarter of 2023, we corrected the accounting treatment for financing incentives offered to John Deere dealers, which impacted the timing of expense recognition and the presentation of incentive costs in the consolidated financial statements. The cumulative effect of this correction, $173 pretax ($135 after-tax), was recorded in the second quarter of 2023. Prior period results for Deere & Company were not restated, as the adjustment was considered immaterial to our financial statements.
2022 Special Items
UAW Collective Bargaining Agreement
In November 2021, employees represented by the International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America (UAW) approved a new collective bargaining agreement. The agreement, which has a term of six years, covers the wages, hours, benefits, and other terms and conditions of employment for our UAW-represented employees at 14 U.S. facilities. The labor agreement included a lump sum ratification bonus payment of $8,500 per eligible employee, totaling $90 million, and an immediate wage increase of 10 percent plus further wage increases over the term of the contract. The lump sum payment was expensed in the first quarter of 2022.
Impact of Events in Russia / Ukraine
We suspended shipments of machines and service parts to Russia due to the events in Russia / Ukraine. The suspension of shipments reduced the forecasted revenue for the region, which made it probable future cash flows would not cover the carrying value of certain assets. As a result, an impairment was recorded for most long-lived assets in Russia, and our U.S. senior management decided to initiate a voluntary employee-separation program. We also recorded a reserve on inventory, and increased our allowance for credit losses, reflecting economic uncertainty in Russia.
The financial services operations received an intercompany benefit from the equipment operations, which guarantees the financial services’ investments in certain international markets, including Russia.
54
The Russian government imposed certain restrictions on companies’ abilities to repatriate or remit cash from their Russian-based operations to locations outside of Russia. Cash in excess of what was required to fund operations in Russia was reclassified as restricted. A summary of the reserves, impairments, and voluntary-separation costs recorded in 2022 follows. See Note 25 for fair value measurement information.
|
|
PPA |
|
SAT |
|
CF |
|
FS |
|
Total |
|
|||||
Inventory reserve – Cost of sales |
|
$ |
14 |
|
$ |
2 |
|
$ |
3 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
19 |
|
Fixed asset impairment – Cost of sales |
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
|
Intangible asset impairment – Cost of sales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
Allowance for credit losses – Financing receivables – SA&G expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
153 |
|
|
153 |
|
Voluntary-separation program: |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
– SA&G expenses |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
11 |
|
Intercompany agreement |
|
|
82 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
62 |
|
|
(153) |
|
|
|
|
Total Russia/Ukraine events pretax expense |
|
$ |
133 |
|
$ |
11 |
|
$ |
110 |
|
$ |
1 |
|
|
255 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net tax impact |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(40) |
|
Total Russia/Ukraine events after-tax expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
215 |
|
Gain on Previously Held Equity Investment
In March 2022, we acquired full ownership of three former Deere-Hitachi joint venture factories and began new license and supply agreements with Hitachi. The fair value of the previous equity investment resulted in a non-cash gain of $326 (pretax and after-tax; see Note 3).
Summary of 2023 and 2022 Special Items
The following table summarizes the operating profit impact of the special items recorded in 2023 and 2022:
|
|
PPA |
|
SAT |
|
CF |
|
FS |
|
Total |
|
|||||
2023 Expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Russian roadbuilding sale - Other operating expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
18 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
18 |
|
Financing incentive – SA&G expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
173 |
|
|
173 |
|
Total expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
173 |
|
|
191 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022 Expense (benefit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gain on remeasurement of equity investment – Other income (Note 3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(326) |
|
|
|
|
|
(326) |
|
Total Russia/Ukraine events pretax expense |
|
$ |
133 |
|
$ |
11 |
|
|
110 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
255 |
|
UAW ratification bonus – Cost of sales |
|
|
53 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
90 |
|
Total expense (benefit) |
|
|
186 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
(188) |
|
|
1 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year over year change |
|
$ |
(186) |
|
$ |
(20) |
|
$ |
206 |
|
$ |
172 |
|
$ |
172 |
|
5. REVENUE RECOGNITION
Our net sales and revenues by primary geographic market, major product line, and timing of revenue recognition follow:
|
|
PPA |
|
SAT |
|
CF |
|
FS |
|
Total |
|
|||||
2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Primary geographic markets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
United States |
|
$ |
13,917 |
|
$ |
7,796 |
|
$ |
9,109 |
|
$ |
3,283 |
|
$ |
34,105 |
|
Canada |
|
|
1,738 |
|
|
687 |
|
|
1,221 |
|
|
641 |
|
|
4,287 |
|
Western Europe |
|
|
2,640 |
|
|
2,824 |
|
|
1,725 |
|
|
132 |
|
|
7,321 |
|
Central Europe and CIS |
|
|
1,218 |
|
|
530 |
|
|
353 |
|
|
36 |
|
|
2,137 |
|
Latin America |
|
|
5,608 |
|
|
707 |
|
|
1,429 |
|
|
453 |
|
|
8,197 |
|
Asia, Africa, Oceania, and Middle East |
|
|
2,166 |
|
|
1,679 |
|
|
1,183 |
|
|
176 |
|
|
5,204 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
27,287 |
|
$ |
14,223 |
|
$ |
15,020 |
|
$ |
4,721 |
|
$ |
61,251 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Major product lines: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production agriculture |
|
$ |
26,450 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
26,450 |
|
Small agriculture |
|
|
|
|
$ |
10,122 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,122 |
|
Turf |
|
|
|
|
|
3,505 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,505 |
|
Construction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
6,842 |
|
|
|
|
|
6,842 |
|
Compact construction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,451 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,451 |
|
Roadbuilding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,794 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,794 |
|
Forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,429 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,429 |
|
Financial products |
|
|
219 |
|
|
96 |
|
|
58 |
|
$ |
4,721 |
|
|
5,094 |
|
Other |
|
|
618 |
|
|
500 |
|
|
446 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,564 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
27,287 |
|
$ |
14,223 |
|
$ |
15,020 |
|
$ |
4,721 |
|
$ |
61,251 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue recognized: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At a point in time |
|
$ |
26,969 |
|
$ |
14,092 |
|
$ |
14,915 |
|
$ |
111 |
|
$ |
56,087 |
|
Over time |
|
|
318 |
|
|
131 |
|
|
105 |
|
|
4,610 |
|
|
5,164 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
27,287 |
|
$ |
14,223 |
|
$ |
15,020 |
|
$ |
4,721 |
|
$ |
61,251 |
|
55
|
|
PPA |
|
SAT |
|
CF |
|
FS |
|
Total |
|
|||||
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Primary geographic markets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
United States |
|
$ |
10,975 |
|
$ |
7,741 |
|
$ |
7,103 |
|
$ |
2,419 |
|
$ |
28,238 |
|
Canada |
|
|
1,387 |
|
|
676 |
|
|
1,238 |
|
|
601 |
|
|
3,902 |
|
Western Europe |
|
|
2,188 |
|
|
2,478 |
|
|
1,576 |
|
|
102 |
|
|
6,344 |
|
Central Europe and CIS |
|
|
1,207 |
|
|
488 |
|
|
545 |
|
|
49 |
|
|
2,289 |
|
Latin America |
|
|
4,991 |
|
|
578 |
|
|
1,467 |
|
|
303 |
|
|
7,339 |
|
Asia, Africa, Oceania, and Middle East |
|
|
1,570 |
|
|
1,608 |
|
|
1,136 |
|
|
151 |
|
|
4,465 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
22,318 |
|
$ |
13,569 |
|
$ |
13,065 |
|
$ |
3,625 |
|
$ |
52,577 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Major product lines: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production agriculture |
|
$ |
21,685 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
21,685 |
|
Small agriculture |
|
|
|
|
$ |
10,027 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,027 |
|
Turf |
|
|
|
|
|
3,027 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,027 |
|
Construction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
5,864 |
|
|
|
|
|
5,864 |
|
Compact construction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,667 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,667 |
|
Roadbuilding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,441 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,441 |
|
Forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,308 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,308 |
|
Financial products |
|
|
60 |
|
|
52 |
|
|
32 |
|
$ |
3,625 |
|
|
3,769 |
|
Other |
|
|
573 |
|
|
463 |
|
|
753 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,789 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
22,318 |
|
$ |
13,569 |
|
$ |
13,065 |
|
$ |
3,625 |
|
$ |
52,577 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue recognized: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At a point in time |
|
$ |
22,178 |
|
$ |
13,493 |
|
$ |
12,980 |
|
$ |
105 |
|
$ |
48,756 |
|
Over time |
|
|
140 |
|
|
76 |
|
|
85 |
|
|
3,520 |
|
|
3,821 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
22,318 |
|
$ |
13,569 |
|
$ |
13,065 |
|
$ |
3,625 |
|
$ |
52,577 |
|
|
|
PPA |
|
SAT |
|
CF |
|
FS |
|
Total |
|
|||||
2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Primary geographic markets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
United States |
|
$ |
8,223 |
|
$ |
6,505 |
|
$ |
5,697 |
|
$ |
2,389 |
|
$ |
22,814 |
|
Canada |
|
|
853 |
|
|
498 |
|
|
1,047 |
|
|
617 |
|
|
3,015 |
|
Western Europe |
|
|
2,086 |
|
|
2,433 |
|
|
1,807 |
|
|
103 |
|
|
6,429 |
|
Central Europe and CIS |
|
|
1,322 |
|
|
475 |
|
|
828 |
|
|
39 |
|
|
2,664 |
|
Latin America |
|
|
2,916 |
|
|
456 |
|
|
903 |
|
|
247 |
|
|
4,522 |
|
Asia, Africa, Oceania, and Middle East |
|
|
1,417 |
|
|
1,679 |
|
|
1,331 |
|
|
153 |
|
|
4,580 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
16,817 |
|
$ |
12,046 |
|
$ |
11,613 |
|
$ |
3,548 |
|
$ |
44,024 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Major product lines: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production agriculture |
|
$ |
16,248 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
16,248 |
|
Small agriculture |
|
|
|
|
$ |
8,619 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8,619 |
|
Turf |
|
|
|
|
|
2,853 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,853 |
|
Construction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
4,684 |
|
|
|
|
|
4,684 |
|
Compact construction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,489 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,489 |
|
Roadbuilding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,749 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,749 |
|
Forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,280 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,280 |
|
Financial products |
|
|
55 |
|
|
46 |
|
|
20 |
|
$ |
3,548 |
|
|
3,669 |
|
Other |
|
|
514 |
|
|
528 |
|
|
391 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,433 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
16,817 |
|
$ |
12,046 |
|
$ |
11,613 |
|
$ |
3,548 |
|
$ |
44,024 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue recognized: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At a point in time |
|
$ |
16,659 |
|
$ |
11,969 |
|
$ |
11,522 |
|
$ |
105 |
|
$ |
40,255 |
|
Over time |
|
|
158 |
|
|
77 |
|
|
91 |
|
|
3,443 |
|
|
3,769 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
16,817 |
|
$ |
12,046 |
|
$ |
11,613 |
|
$ |
3,548 |
|
$ |
44,024 |
|
Following is a description of the elements of net sales and revenues for our major product lines:
Production Agriculture – Includes net sales of large and certain mid-size tractors and associated attachments, combines, cotton pickers, cotton strippers, sugarcane harvesters, sugarcane loaders and pull behind scrapers, tillage, seeding, and application equipment, including sprayers and nutrient management and soil preparation machinery, and related attachments and service parts.
Small Agriculture – Includes net sales of mid-size, utility, and compact utility tractors, self-propelled forage harvesters, hay and forage equipment, balers, mowers, and related attachments and service parts.
Turf – Includes net sales of turf and utility equipment, including riding lawn equipment, golf course equipment, utility vehicles, and commercial mowing equipment, along with a broad line of associated implements, other outdoor power products, and related attachments and service parts.
Construction – Includes net sales of a broad range of machines used in construction, earthmoving, and material handling, including backhoe loaders, crawler dozers and loaders, four-wheel-drive loaders, excavators, motor graders, articulated dump trucks, and related attachments and service parts.
Compact Construction – Includes net sales of smaller construction equipment, including compact excavators, compact track loaders, compact wheel loaders, skid steers, landscape loaders, and related attachments and service parts.
Roadbuilding – Includes net sales of equipment used in roadbuilding and renovation, including milling machines, recyclers, slipform pavers, surface miners, asphalt pavers, compactors, tandem and static rollers, mobile crushers and screens, mobile and stationary asphalt plants, and related attachments and service parts.
Forestry – Includes net sales of equipment used in timber harvesting, including log skidders, feller bunchers, log loaders, log forwarders, log harvesters, and related attachments and service parts.
Financial Products – Includes finance and interest income from retail notes related to sales of John Deere equipment to retail customers, wholesale financing to dealers of John Deere equipment, and revolving charge accounts; lease income from retail leases of John Deere equipment; and revenue from extended warranties.
Other – Includes sales of components to other equipment manufacturers that are included in “Net sales;” revenue earned over time from precision guidance, telematics, and other information enabled solutions; revenue from service performed at company owned dealerships and service centers; gains on disposition of property and businesses; trademark licensing revenue; and other miscellaneous revenue items that are included in “Other income.”
56
We invoice in advance of recognizing the sale of certain products and the revenue for certain services. These relate to extended warranty premiums, advance payments for future equipment sales, and subscription and service revenue related to precision guidance, telematic services, and other information enabled solutions. These advanced customer payments are presented as deferred revenue, a contract liability, in “Accounts payable and accrued expenses.” The deferred revenue received, but not recognized in revenue was $1,697 and $1,423 at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022, respectively. The contract liability is reduced as the revenue is recognized. Revenue recognized from deferred revenue that was recorded as a contract liability at the beginning of the fiscal year was $547 in 2023, $609 in 2022, and $485 in 2021.
The total amount of unsatisfied performance obligations for contracts with an original duration greater than one year and the estimated revenue to be recognized by fiscal year at October 29, 2023 follows:
Year |
|
Net Sales and Revenues |
|
|
2024 |
|
$ |
457 |
|
2025 |
|
|
382 |
|
2026 |
|
|
268 |
|
2027 |
|
|
161 |
|
2028 |
|
|
97 |
|
Later years |
|
|
126 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
1,491 |
|
As permitted, we elected only to disclose remaining performance obligations with an original contract duration greater than one year. The contracts with an expected duration of one year or less are for sales to dealers and retail customers for equipment, service parts, repair services, and certain telematics services.
6. SUPPLEMENTAL CASH FLOW INFORMATION
All cash flows from receivables related to sales are included in operating activities. This includes all changes in trade accounts and notes receivables, as well as some financing receivables. Financing receivables that are related to loans on equipment sold by independent dealers are included in investing activities.
Our short-term borrowings mature or may require payment within three months or less. During 2023, we issued $4.5 billion and retired $3.2 billion of retail note securitization borrowings, which are presented in “Net proceeds (payments) in short-term borrowings (original maturities three months or less).”
Restricted cash, recorded in “Other assets,” relates to securitization of financing receivables (see Note 12) and cash held in Russia.
Supplemental cash flow information follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Cash paid for interest |
|
$ |
2,227 |
|
$ |
1,101 |
|
$ |
1,041 |
|
Cash paid for income taxes |
|
|
3,578 |
|
|
1,940 |
|
|
2,075 |
|
Inventory transferred to equipment on operating leases |
|
|
195 |
|
|
167 |
|
|
662 |
|
Accounts payable related to purchases of property and equipment |
|
|
211 |
|
|
165 |
|
|
121 |
|
7. PENSION AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS
We have several funded and unfunded defined benefit pension plans and other postretirement benefit (OPEB) plans. These plans cover U.S. employees and certain foreign employees. The measurement date of our plans is October 31. The funded status as of October 31, 2023 of the significant plans follows:
|
|
Funded |
|
Enrollment |
|
|
|
|
Status |
|
Status |
|
|
Pensions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. salaried qualified |
|
$ |
1,511 |
|
Closed |
|
U.S. hourly qualified |
|
|
1,042 |
|
Open |
|
Other |
|
|
(477) |
|
Varies |
|
Total |
|
$ |
2,076 |
|
|
|
OPEB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. salaried |
|
$ |
(1,086) |
|
Closed |
|
U.S. hourly |
|
|
178 |
|
Closed |
|
Other |
|
|
(93) |
|
Varies |
|
Total |
|
$ |
(1,001) |
|
|
|
The components of net periodic pension and OPEB cost excluding the service component are included in the line item “Other operating expenses.”
The components of net periodic pension (benefit) cost and the related assumptions consisted of the following:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Pensions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Service cost |
|
$ |
246 |
|
$ |
349 |
|
$ |
332 |
|
Interest cost |
|
|
533 |
|
|
330 |
|
|
276 |
|
Expected return on plan assets |
|
|
(878) |
|
|
(726) |
|
|
(799) |
|
Amortization of actuarial (gain) loss |
|
|
(13) |
|
|
132 |
|
|
259 |
|
Amortization of prior service cost |
|
|
38 |
|
|
34 |
|
|
12 |
|
Settlements/curtailment |
|
|
37 |
|
|
45 |
|
|
21 |
|
Net (benefit) cost |
|
$ |
(37) |
|
$ |
164 |
|
$ |
101 |
|
Weighted-average assumptions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discount rates - service cost |
|
|
5.2% |
|
|
3.0% |
|
|
2.5% |
|
Discount rates - interest cost |
|
|
5.1% |
|
|
2.6% |
|
|
2.1% |
|
Rate of compensation increase |
|
|
3.8% |
|
|
3.7% |
|
|
3.7% |
|
Expected long-term rates of return |
|
|
6.3% |
|
|
5.1% |
|
|
6.0% |
|
Interest crediting rate - U.S. cash balance plans |
|
|
4.3% |
|
|
2.1% |
|
|
1.7% |
|
In November 2021, employees represented by the UAW approved a new collective bargaining agreement. We remeasured the U.S. hourly pension plan, which increased the 2022 pension expense by nearly $80 with $35 negatively impacting operating profit.
The 2024 net periodic pension benefit is expected to increase by $130 due to an increase in the expected long-term rates of return on plan assets (estimated to be 7.0 percent) and the Canadian pension settlement charge recognized in 2023, described below.
57
The components of net periodic OPEB cost and the assumptions related to the cost consisted of the following:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
OPEB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Service cost |
|
$ |
27 |
|
$ |
45 |
|
$ |
48 |
|
Interest cost |
|
|
176 |
|
|
99 |
|
|
102 |
|
Expected return on plan assets |
|
|
(117) |
|
|
(110) |
|
|
(77) |
|
Amortization of actuarial (gain) loss |
|
|
(59) |
|
|
(18) |
|
|
27 |
|
Amortization of prior service credit |
|
|
(3) |
|
|
(4) |
|
|
(4) |
|
Net cost |
|
$ |
24 |
|
$ |
12 |
|
$ |
96 |
|
Weighted-average assumptions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discount rates - service cost |
|
|
6.1% |
|
|
3.6% |
|
|
3.4% |
|
Discount rates - interest cost |
|
|
5.4% |
|
|
2.3% |
|
|
2.1% |
|
Expected long-term rates of return |
|
|
5.7% |
|
|
4.4% |
|
|
5.4% |
|
The benefit plan obligations, funded status, and the assumptions related to the obligations at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 follow:
|
|
Pensions |
|
OPEB |
|
||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||||
Change in benefit obligations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Beginning of year balance |
|
$ |
(10,529) |
|
$ |
(14,525) |
|
$ |
(3,341) |
|
$ |
(4,930) |
|
Service cost |
|
|
(246) |
|
|
(349) |
|
|
(27) |
|
|
(45) |
|
Interest cost |
|
|
(533) |
|
|
(330) |
|
|
(176) |
|
|
(99) |
|
Actuarial gain |
|
|
504 |
|
|
4,122 |
|
|
285 |
|
|
1,492 |
|
Prior service cost |
|
|
|
|
|
(505) |
|
|
|
|
|
(12) |
|
Benefits paid |
|
|
838 |
|
|
757 |
|
|
260 |
|
|
282 |
|
Health care subsidies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(27) |
|
|
(33) |
|
Settlement |
|
|
112 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign exchange and other |
|
|
(74) |
|
|
301 |
|
|
(3) |
|
|
4 |
|
End of year balance |
|
|
(9,928) |
|
|
(10,529) |
|
|
(3,029) |
|
|
(3,341) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Change in plan assets (fair value) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Beginning of year balance |
|
|
13,219 |
|
|
17,190 |
|
|
2,136 |
|
|
1,755 |
|
Actual loss on plan assets |
|
|
(387) |
|
|
(3,070) |
|
|
(8) |
|
|
(495) |
|
Employer contribution |
|
|
70 |
|
|
85 |
|
|
158 |
|
|
1,155 |
|
Benefits paid |
|
|
(838) |
|
|
(757) |
|
|
(260) |
|
|
(282) |
|
Settlement |
|
|
(112) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign exchange and other |
|
|
52 |
|
|
(229) |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
End of year balance |
|
|
12,004 |
|
|
13,219 |
|
|
2,028 |
|
|
2,136 |
|
Funded status |
|
$ |
2,076 |
|
$ |
2,690 |
|
$ |
(1,001) |
|
$ |
(1,205) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-average assumptions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discount rates |
|
|
5.9% |
|
|
5.4% |
|
|
6.0% |
|
|
5.6% |
|
Rate of compensation increase |
|
|
3.8% |
|
|
3.8% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest crediting rate - U.S. cash balance plans |
|
|
4.9% |
|
|
4.4% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The actuarial gain for pension for 2023 was due to an increase in discount rates. The actuarial gain for OPEB for 2023 was due to changes to health care assumptions. The actuarial gains for pension and OPEB for 2022 were due to an increase in discount rates. The pension prior service cost for 2022 was due to the new UAW collective bargaining agreement.
During 2023, we irrevocably transferred to an insurance company $112 of a Canadian pension plan’s defined benefit obligations and related plan assets. The transaction resulted in no changes to the benefits to be received by the retired participants. We recognized a one-time, non-cash, pretax pension settlement charge of $36 related to the accelerated recognition of actuarial losses included within “Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss).”
The discount rate assumptions used to determine the pension and OPEB obligations for all periods presented were based on hypothetical AA yield curves represented by a series of annualized individual discount rates. These discount rates represent the rates at which our benefit obligations could effectively be settled at the October 31 measurement dates.
The mortality assumptions for the 2023 and 2022 U.S. benefit plan obligations used the most recent tables and scales issued by the Society of Actuaries at that time. The 2023 and 2022 mortality assumptions included an adjustment to the scale related to COVID for some plans.
The weighted-average annual rates of increase in the per capita cost of covered health care benefits (the health care cost trend rates) for medical and prescription drug claims for pre- and post-65 age groups used to determine the October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 accumulated postretirement benefit obligations were as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
Initial year |
|
18.7% (2023 to 2024) |
|
0.0% (2022 to 2023) |
|
Second year |
|
8.8% (2024 to 2025) |
|
12.6% (2023 to 2024) |
|
Ultimate |
|
4.7% (2032 to 2033) |
|
4.7% (2032 to 2033) |
|
An increase in Medicare Advantage premiums and prescription drug trends impacted the weighted-average annual rates of increase for the initial year in 2023. A decrease in Medicare Advantage premiums impacted the weighted-average annual rates of increase for the initial year in 2022.
Information related to pension plans benefit obligations at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Total accumulated benefit obligations for all plans |
|
$ |
9,453 |
|
$ |
10,068 |
|
Plans with accumulated benefit obligation exceeding fair value of plan assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated benefit obligations |
|
|
1,147 |
|
|
1,116 |
|
Fair value of plan assets |
|
|
704 |
|
|
672 |
|
Plans with projected benefit obligation exceeding fair value of plan assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Projected benefit obligations |
|
|
1,261 |
|
|
1,225 |
|
Fair value of plan assets |
|
|
729 |
|
|
692 |
|
58
The pension and OPEB amounts recognized in the balance sheet at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 consisted of the following:
|
|
Pensions |
|
OPEB |
|
||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||||
Noncurrent asset |
|
$ |
2,608 |
|
$ |
3,223 |
|
$ |
399 |
|
$ |
507 |
|
Less: Current liability |
|
|
59 |
|
|
42 |
|
|
40 |
|
|
39 |
|
Less: Noncurrent liability |
|
|
473 |
|
|
491 |
|
|
1,360 |
|
|
1,673 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
2,076 |
|
$ |
2,690 |
|
$ |
(1,001) |
|
$ |
(1,205) |
|
The retirement benefits and other liabilities recognized in the balance sheet at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 consisted of the following:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Deferred compensation - current |
|
$ |
25 |
|
$ |
30 |
|
Deferred compensation and other - noncurrent |
|
|
183 |
|
|
182 |
|
Pensions and OPEB - current |
|
|
99 |
|
|
81 |
|
Pensions and OPEB - noncurrent |
|
|
1,833 |
|
|
2,164 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
2,140 |
|
$ |
2,457 |
|
The amounts recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income ‒ pretax at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 consisted of the following:
|
|
Pensions |
|
OPEB |
|
||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||||
Net actuarial (gain) loss |
|
$ |
1,660 |
|
$ |
926 |
|
$ |
(921) |
|
$ |
(820) |
|
Prior service (credit) cost |
|
|
406 |
|
|
446 |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
(4) |
|
Total |
|
$ |
2,066 |
|
$ |
1,372 |
|
$ |
(922) |
|
$ |
(824) |
|
Actuarial gains and losses are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). To the extent unamortized gains and losses exceed 10 percent of the higher of the market-related value of assets or the benefit obligation, the excess is amortized as a component of net periodic (benefit) cost over the remaining service period of the active participants. For plans in which all or almost all of the plan’s participants are inactive, the amortization period is the remaining life expectancy of the inactive participants.
Contributions
We make any required contributions to the plan assets under applicable regulations and voluntary contributions after evaluating our liquidity position and ability to make tax-deductible contributions. Total contributions to the plans were $228 in 2023 and $1,240 in 2022, which included both required and voluntary contributions and direct benefit payments. 2022 OPEB contributions included a voluntary contribution of $1,000 to a U.S. plan.
We expect to contribute approximately $85 to our pension plans and approximately $140 to our OPEB plans in 2024. The contributions include required and voluntary contributions and direct benefit payments from company funds. We have no significant required contributions to U.S. pension plan assets in 2024 under applicable funding regulations.
Expected Future Benefit Payments
The expected future benefit payments at October 29, 2023 were as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pensions |
|
OPEB* |
|
||
2024 |
|
$ |
746 |
|
$ |
249 |
|
2025 |
|
|
726 |
|
|
252 |
|
2026 |
|
|
727 |
|
|
257 |
|
2027 |
|
|
720 |
|
|
257 |
|
2028 |
|
|
708 |
|
|
257 |
|
2029 to 2033 |
|
|
3,564 |
|
|
1,251 |
|
* Net of prescription drug group benefit subsidy under Medicare Part D.
Plan Asset Information
The fair values of the pension plan assets at October 29, 2023 follow:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
Level 1 |
|
Level 2 |
|
Level 3 |
|
||||
Cash and short-term investments |
|
$ |
513 |
|
$ |
470 |
|
$ |
43 |
|
|
|
|
Equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. equity securities |
|
|
342 |
|
|
330 |
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
International equity securities and funds |
|
|
199 |
|
|
197 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
Fixed Income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Government and agency securities |
|
|
1,017 |
|
|
759 |
|
|
258 |
|
|
|
|
Corporate debt securities |
|
|
4,389 |
|
|
|
|
|
4,389 |
|
|
|
|
Mortgage-backed securities |
|
|
285 |
|
|
|
|
|
285 |
|
|
|
|
Private equity |
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
18 |
|
Other investments |
|
|
50 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
Derivative contracts - assets |
|
|
53 |
|
|
17 |
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
|
Derivative interest rate contracts - liabilities |
|
|
(309) |
|
|
(215) |
|
|
(94) |
|
|
|
|
Receivables, prepaids, and payables |
|
|
(137) |
|
|
(137) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Securities lending collateral |
|
|
615 |
|
|
|
|
|
615 |
|
|
|
|
Securities lending liability |
|
|
(615) |
|
|
|
|
|
(615) |
|
|
|
|
Securities sold short |
|
|
(73) |
|
|
(69) |
|
|
(4) |
|
|
|
|
Total of Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 assets |
|
|
6,347 |
|
$ |
1,382 |
|
$ |
4,947 |
|
$ |
18 |
|
Investments at net asset value: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term investments |
|
|
362 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. equity funds |
|
|
92 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
International equity funds |
|
|
151 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fixed income funds |
|
|
1,418 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Real estate funds |
|
|
462 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hedge funds |
|
|
491 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Private equity |
|
|
1,306 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Venture capital |
|
|
1,341 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other investments |
|
|
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total net assets |
|
$ |
12,004 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
59
The fair values of the OPEB health care assets at October 29, 2023 follow:
|
|
Total |
|
Level 1 |
|
Level 2 |
|
|||
Cash and short-term investments |
|
$ |
76 |
|
$ |
76 |
|
|
|
|
Fixed Income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Government and agency securities |
|
|
637 |
|
|
596 |
|
$ |
41 |
|
Corporate debt securities |
|
|
515 |
|
|
|
|
|
515 |
|
Mortgage-backed securities |
|
|
89 |
|
|
|
|
|
89 |
|
Other |
|
|
8 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
3 |
|
Securities lending collateral |
|
|
122 |
|
|
|
|
|
122 |
|
Securities lending liability |
|
|
(122) |
|
|
|
|
|
(122) |
|
Total of Level 1 and Level 2 assets |
|
|
1,325 |
|
$ |
677 |
|
$ |
648 |
|
Investments at net asset value: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fixed income funds |
|
|
392 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Real estate funds |
|
|
104 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hedge funds |
|
|
104 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Private equity |
|
|
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Venture capital |
|
|
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other investments |
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total net assets |
|
$ |
2,028 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The fair values of the pension plan assets at October 30, 2022 follow:
|
|
Total |
|
Level 1 |
|
Level 2 |
|
|||
Cash and short-term investments |
|
$ |
338 |
|
$ |
283 |
|
$ |
55 |
|
Equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. equity securities |
|
|
311 |
|
|
290 |
|
|
21 |
|
International equity securities and funds |
|
|
196 |
|
|
195 |
|
|
1 |
|
Fixed Income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Government and agency securities |
|
|
1,296 |
|
|
1,053 |
|
|
243 |
|
Corporate debt securities |
|
|
4,587 |
|
|
|
|
|
4,587 |
|
Mortgage-backed securities |
|
|
213 |
|
|
|
|
|
213 |
|
Other investments |
|
|
49 |
|
|
31 |
|
|
18 |
|
Derivative contracts - assets |
|
|
92 |
|
|
54 |
|
|
38 |
|
Derivative contracts - liabilities |
|
|
(209) |
|
|
(106) |
|
|
(103) |
|
Receivables, prepaids, and payables |
|
|
(207) |
|
|
(207) |
|
|
|
|
Securities lending collateral |
|
|
684 |
|
|
|
|
|
684 |
|
Securities lending liability |
|
|
(684) |
|
|
|
|
|
(684) |
|
Securities sold short |
|
|
(64) |
|
|
(58) |
|
|
(6) |
|
Total of Level 1 and Level 2 assets |
|
|
6,602 |
|
$ |
1,535 |
|
$ |
5,067 |
|
Investments at net asset value: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term investments |
|
|
633 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. equity funds |
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
International equity funds |
|
|
125 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fixed income funds |
|
|
1,736 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Real estate funds |
|
|
592 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hedge funds |
|
|
569 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Private equity |
|
|
1,322 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Venture capital |
|
|
1,553 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other investments |
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total net assets |
|
$ |
13,219 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The fair values of the OPEB health care assets at October 30, 2022 follow:
|
|
Total |
|
Level 1 |
|
Level 2 |
|
|||
Cash and short-term investments |
|
$ |
79 |
|
$ |
79 |
|
|
|
|
Fixed Income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Government and agency securities |
|
|
629 |
|
|
597 |
|
$ |
32 |
|
Corporate debt securities |
|
|
516 |
|
|
|
|
|
516 |
|
Mortgage-backed securities |
|
|
83 |
|
|
|
|
|
83 |
|
Other |
|
|
(4) |
|
|
(7) |
|
|
3 |
|
Securities lending collateral |
|
|
98 |
|
|
|
|
|
98 |
|
Securities lending liability |
|
|
(98) |
|
|
|
|
|
(98) |
|
Total of Level 1 and Level 2 assets |
|
|
1,303 |
|
$ |
669 |
|
$ |
634 |
|
Investments at net asset value: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. equity funds |
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
International equity funds |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fixed income funds |
|
|
347 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Real estate funds |
|
|
140 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hedge funds |
|
|
188 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Private equity |
|
|
41 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Venture capital |
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other investments |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total net assets |
|
$ |
2,136 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investments at net asset value in the preceding tables are measured at fair value using the net asset value per share practical expedient and are not classified in the fair value hierarchy. Fair value measurement levels in the preceding tables are defined in Note 25.
Fair values are determined as follows:
Cash and Short-Term Investments – The investments include (1) cash accounts that are valued based on the account value, which approximates fair value; (2) investments that are valued at quoted prices in the active markets in which the investment trades or using a market approach (matrix pricing model) in which all significant inputs are observable or can be derived from or corroborated by observable market data; and (3) investment funds that are valued based on a constant fund net asset value, which is based on quoted prices in the active market in which the investment fund trades, or the fund’s net asset value using the net asset value per share practical expedient (NAV), which is based on the fair value of the underlying securities.
Equity Securities and Funds – The values are determined by quoted prices in the active market in which the equity investment trades, or the fund’s NAV, based on the fair value of the underlying securities.
Fixed Income Securities and Funds and Other Funds – The securities are valued using either a market approach (matrix pricing model) in which all significant inputs are observable or can be derived from or corroborated by observable market data such as interest rates, yield curves, volatilities, credit risk, and prepayment speeds, or they are valued using the quoted prices in the active market in which the fixed income investment trades. Fixed income and other funds are valued using the fund’s NAV, based on the fair value of the underlying securities.
60
Real Estate, Venture Capital, Private Equity, and Hedge Funds – The investments that are structured as limited partnerships, excluding the private equity investments classified as Level 3, are valued at estimated fair value based on their proportionate share of the limited partnership’s fair value that is determined by the respective general partner. These investments are valued using the fund’s NAV, which is based on the fair value of the underlying investments. Valuations may be lagged up to six months. The NAV is adjusted for cash flows (additional investments or contributions, and distributions) and any known substantive valuation changes through year end. The private equity investments classified as Level 3 are valued based on the current market pricing of the assets related to an expected secondary sale. The investments were transferred into Level 3 as of October 29, 2023.
Derivative Instruments – The derivatives are valued using either an income approach (discounted cash flow) using market observable inputs, including swap curves and both forward and spot exchange rates, or a market approach (quoted prices in the active market in which the derivative instrument trades).
The investment objective for the pension and health care plan assets is to fulfill the projected obligations to the beneficiaries over a long period of time, while meeting our fiduciary responsibilities. The asset allocation policy is the most important decision in managing the assets, and it is reviewed regularly. The asset allocation policy considers our long-term asset class risk/return expectations for each plan since the obligations are long-term in nature. The target asset allocations as of October 29, 2023 are as follows:
|
|
Pension |
|
Health Care |
|
|
|
Assets |
|
Assets |
|
Equity |
|
5% |
|
9% |
|
Debt |
|
68% |
|
83% |
|
Real estate |
|
4% |
|
2% |
|
Other investments |
|
23% |
|
6% |
|
The assets are diversified and are managed by professional investment firms as well as by investment professionals who are company employees. As a result of our diversified investment policy, there were no significant concentrations of risk.
A market related value of plan assets is used to calculate the expected return on assets. The market related value recognizes changes in the fair value of pension plan assets systematically over a five-year period. The market related value of the health care plan assets equals fair value.
The expected long-term rate of return on plan assets reflects management’s expectations of long-term average rates of return on funds invested to provide for benefits included in the projected benefit obligations. The expected return is based on the outlook for inflation and for returns in multiple asset classes, while also considering historical returns, asset allocation, and investment strategy. Our approach has emphasized the long-term nature of the return estimate such that the return assumption is not changed significantly unless there are fundamental changes in capital markets that affect our expectations for returns over an
extended period of time (i.e., 10 to 20 years). The average annual return of our U.S. pension fund was approximately 6.8 percent during the past ten years and approximately 7.8 percent during the past 20 years.
We have created a Voluntary Employees’ Beneficiary Association trust (VEBA) for the funding of hourly postretirement health care benefits. The future expected asset returns for the VEBA is lower than the expected return on the other pension and health care plan assets due to investment in a higher proportion of liquid securities. These assets are in addition to the other postretirement health care plan assets that have been funded under Section 401(h) of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code and maintained in a separate account in the John Deere Pension Trust.
Defined Contribution Plans
We have defined contribution plans related to employee investment and savings plans primarily in the U.S. Our contributions and costs under these plans were $288 in 2023, $263 in 2022, and $207 in 2021. The contribution rate varies based on employee participation in the plans.
8. INCOME TAXES
We are subject to income taxes in a number of jurisdictions. We determine our income tax provision using the asset and liability method. The provision for income taxes by taxing jurisdiction and by significant component consisted of the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Current: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S.: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal |
|
$ |
1,803 |
|
$ |
514 |
|
$ |
899 |
|
State |
|
|
386 |
|
|
136 |
|
|
183 |
|
Foreign |
|
|
1,472 |
|
|
1,423 |
|
|
1,017 |
|
Total current |
|
|
3,661 |
|
|
2,073 |
|
|
2,099 |
|
Deferred: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S.: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal |
|
|
(485) |
|
|
29 |
|
|
(303) |
|
State |
|
|
(65) |
|
|
24 |
|
|
(45) |
|
Foreign |
|
|
(240) |
|
|
(119) |
|
|
(93) |
|
Total deferred |
|
|
(790) |
|
|
(66) |
|
|
(441) |
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
$ |
2,871 |
|
$ |
2,007 |
|
$ |
1,658 |
|
Based upon the location of our operations, the consolidated income before income taxes in the U.S. in 2023, 2022, and 2021 was $7.8 billion, $5.0 billion, and $4.1 billion, respectively, and in foreign countries was $5.2 billion, $4.1 billion, and $3.5 billion, respectively. Certain foreign operations are branches or partnerships of Deere & Company and are subject to U.S. as well as foreign income tax regulations. The pretax income by location and the preceding analysis of the income tax provision by taxing jurisdiction are not directly related.
61
A comparison of the statutory and effective income tax provision and reasons for related differences follow:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
U.S. federal income tax provision at the U.S. statutory rate (21 percent) |
|
$ |
2,734 |
|
$ |
1,917 |
|
$ |
1,597 |
|
State and local taxes, net of federal effect |
|
|
266 |
|
|
133 |
|
|
119 |
|
Other impacts of Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 |
|
|
(58) |
|
|
(29) |
|
|
(85) |
|
Rate differential on foreign subsidiaries |
|
|
142 |
|
|
121 |
|
|
148 |
|
Research and business tax credits |
|
|
(107) |
|
|
(65) |
|
|
(48) |
|
Excess tax benefits on equity compensation |
|
|
(49) |
|
|
(55) |
|
|
(79) |
|
Valuation allowances |
|
|
9 |
|
|
179 |
|
|
18 |
|
Other - net |
|
|
(66) |
|
|
(194) |
|
|
(12) |
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
$ |
2,871 |
|
$ |
2,007 |
|
$ |
1,658 |
|
At October 29, 2023, undistributed profits of subsidiaries outside the U.S. of approximately $5.1 billion are considered indefinitely reinvested. Determination of the amount of a foreign withholding tax liability on these unremitted earnings is not practicable.
Deferred income taxes arise because there are certain items that are treated differently for financial accounting than for income tax reporting purposes. An analysis of the deferred income tax assets and liabilities at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||||||||
|
|
Deferred |
|
Deferred |
|
Deferred |
|
Deferred |
|
||||
|
|
Tax |
|
Tax |
|
Tax |
|
Tax |
|
||||
|
|
Assets |
|
Liabilities |
|
Assets |
|
Liabilities |
|
||||
Accrual for employee benefits |
|
$ |
439 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
304 |
|
|
|
|
Accrual for sales allowances |
|
|
884 |
|
|
|
|
|
579 |
|
|
|
|
Allowance for credit losses |
|
|
79 |
|
|
|
|
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
Amortization of R&D expenditures |
|
|
492 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred compensation |
|
|
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
Goodwill and other intangible assets |
|
|
|
|
$ |
166 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
178 |
|
Lessee lease transactions |
|
|
68 |
|
|
61 |
|
|
62 |
|
|
57 |
|
Lessor lease transactions |
|
|
|
|
|
581 |
|
|
|
|
|
310 |
|
OPEB - net |
|
|
193 |
|
|
|
|
|
213 |
|
|
|
|
Pension - net |
|
|
|
|
|
424 |
|
|
|
|
|
532 |
|
Share-based compensation |
|
|
38 |
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
|
|
|
|
Tax loss and tax credit carryforwards |
|
|
1,518 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,405 |
|
|
|
|
Tax over book depreciation |
|
|
|
|
|
198 |
|
|
|
|
|
174 |
|
Unearned revenue |
|
|
177 |
|
|
|
|
|
154 |
|
|
|
|
Other items |
|
|
681 |
|
|
278 |
|
|
487 |
|
|
254 |
|
Less: valuation allowances |
|
|
(1,612) |
|
|
|
|
|
(1,545) |
|
|
|
|
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities |
|
$ |
3,002 |
|
$ |
1,708 |
|
$ |
1,834 |
|
$ |
1,505 |
|
Deere & Company files a consolidated federal income tax return in the U.S., which includes the wholly-owned financial services subsidiaries. These subsidiaries account for income taxes as if they filed separate income tax returns, with a modification for realizability of certain tax benefits.
At October 29, 2023, tax loss and tax credit carryforwards of $1,518 were available with $1,031 expiring from 2024 through 2043 and $487 with an indefinite carryforward period.
A reconciliation of unrecognized tax benefits at October 29, 2023, October 30, 2022, and October 31, 2021 follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Beginning of year balance |
|
$ |
891 |
|
$ |
811 |
|
$ |
668 |
|
Increases to tax positions taken during the current year |
|
|
68 |
|
|
98 |
|
|
81 |
|
Increases to tax positions taken during prior years |
|
|
164 |
|
|
29 |
|
|
100 |
|
Decreases to tax positions taken during the current year |
|
|
(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decreases to tax positions taken during prior years |
|
|
(209) |
|
|
(18) |
|
|
(23) |
|
Decreases due to lapse of statute of limitations |
|
|
(10) |
|
|
(7) |
|
|
(12) |
|
Other |
|
|
(4) |
|
|
2 |
|
|
(3) |
|
Foreign exchange |
|
|
10 |
|
|
(24) |
|
|
|
|
End of year balance |
|
$ |
907 |
|
$ |
891 |
|
$ |
811 |
|
The amount of unrecognized tax benefits at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 that would impact the effective tax rate if the tax benefits were recognized was $329 and $303, respectively. The remaining liability was related to tax positions for which there are offsetting tax receivables, or the uncertainty was only related to timing. We expect that any reasonably possible change in the amounts of unrecognized tax benefits in the next twelve months would not be significant.
We file our tax returns according to the tax laws of the jurisdictions in which we operate, which includes the U.S. federal jurisdiction and various state and foreign jurisdictions. The U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has completed the examination of our federal income tax returns for periods prior to 2015. The federal income tax returns for years 2015 to 2020 are currently under examination. Various state and foreign income tax returns also remain subject to examination by taxing authorities.
9. OTHER INCOME AND OTHER OPERATING EXPENSES
The major components of other income and other operating expenses consisted of the following:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Other income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues from services |
|
$ |
312 |
|
$ |
283 |
|
$ |
322 |
|
Extended warranty premiums earned |
|
|
312 |
|
|
289 |
|
|
227 |
|
Trademark licensing income |
|
|
95 |
|
|
89 |
|
|
87 |
|
Operating lease disposition gains |
|
|
33 |
|
|
72 |
|
|
65 |
|
Gain on previously held equity investment |
|
|
|
|
|
326 |
|
|
|
|
Investment income |
|
|
29 |
|
|
14 |
|
|
41 |
|
Other |
|
|
222 |
|
|
222 |
|
|
249 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
1,003 |
|
$ |
1,295 |
|
$ |
991 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other operating expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation of equipment on operating leases |
|
$ |
853 |
|
$ |
827 |
|
$ |
983 |
|
Extended warranty claims |
|
|
309 |
|
|
267 |
|
|
235 |
|
Cost of services |
|
|
227 |
|
|
214 |
|
|
202 |
|
Pension and OPEB benefit, excluding the service cost component |
|
|
(286) |
|
|
(218) |
|
|
(183) |
|
Foreign exchange loss |
|
|
122 |
|
|
132 |
|
|
59 |
|
Other |
|
|
67 |
|
|
53 |
|
|
47 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
1,292 |
|
$ |
1,275 |
|
$ |
1,343 |
|
62
10. MARKETABLE SECURITIES
Most marketable securities are classified as available-for-sale. Realized gains or losses are based on specific identification.
The amortized cost and fair value of marketable securities at the end of 2023 and 2022 follow:
|
|
|
|
|
Gross |
|
Gross |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Amortized |
|
Unrealized |
|
Unrealized |
|
Fair |
|
||||
|
|
Cost |
|
Gains |
|
Losses |
|
Value |
|
||||
2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
International equity securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
3 |
|
International mutual funds securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101 |
|
U.S. equity fund |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
86 |
|
U.S. fixed income fund |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
Total equity securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
222 |
|
Corporate debt securities |
|
$ |
285 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
41 |
|
|
244 |
|
International debt securities |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
1 |
|
Mortgage-backed securities* |
|
|
225 |
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
185 |
|
Municipal debt securities |
|
|
87 |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
75 |
|
U.S. government debt securities |
|
|
260 |
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
|
|
219 |
|
Total debt securities |
|
$ |
862 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
138 |
|
|
724 |
|
Marketable securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
946 |
|
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
International equity securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
3 |
|
U.S. equity fund |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
Total equity securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
73 |
|
Corporate debt securities |
|
$ |
236 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
36 |
|
|
200 |
|
International debt securities |
|
|
64 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
60 |
|
Mortgage-backed securities* |
|
|
186 |
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
155 |
|
Municipal debt securities |
|
|
74 |
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
63 |
|
U.S. government debt securities |
|
|
220 |
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
183 |
|
Total debt securities |
|
$ |
780 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
119 |
|
|
661 |
|
Marketable securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
734 |
|
* Primarily issued by U.S. government sponsored enterprises.
The purchases, maturities, and sale proceeds for marketable securities during 2023, 2022, and 2021 follow:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Purchases |
|
$ |
491 |
|
$ |
250 |
|
$ |
194 |
|
Maturities and sale proceeds |
|
|
186 |
|
|
79 |
|
|
109 |
|
Equity Securities
Proceeds of equity securities sold during 2023, 2022, and 2021 were not material. Unrealized gain (loss) on equity securities during 2023 and 2022 follow:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Net gain (loss) recognized on equity securities |
|
|
|
|
$ |
(11) |
|
Less: Net gain (loss) on equity securities sold |
|
$ |
(1) |
|
|
|
|
Unrealized gain (loss) on equity securities |
|
$ |
1 |
|
$ |
(11) |
|
Debt Securities
The contractual maturities of debt securities at October 29, 2023 follow:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortized |
|
Fair |
|
||
|
|
Cost |
|
Value |
|
||
Due in one year or less |
|
$ |
20 |
|
$ |
19 |
|
Due after one through five years |
|
|
147 |
|
|
136 |
|
Due after five through 10 years |
|
|
249 |
|
|
214 |
|
Due after 10 years |
|
|
221 |
|
|
170 |
|
Mortgage-backed securities |
|
|
225 |
|
|
185 |
|
Debt securities |
|
$ |
862 |
|
$ |
724 |
|
Actual maturities may differ from contractual maturities because some securities may be called or prepaid. Mortgage-backed securities contain prepayment provisions and are not categorized by contractual maturity.
The following debt security items were not material in 2023, 2022, and 2021:
| ● | realized gains, |
| ● | realized losses, and |
| ● | unrealized losses that have been continuous for over twelve months. |
Unrealized losses at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 were not recognized in income due to the ability and intent to hold to maturity. There were no significant impairment write-downs in the periods reported.
11. RECEIVABLES
Trade Accounts and Notes Receivable
Trade accounts and notes receivable arise from sales of goods to independent dealers. See Note 2 for our revenue recognition policy. We evaluate and assess dealers’ credit worthiness on an ongoing basis. Receivables are secured with collateral or other credit enhancements. Trade accounts and notes receivable at the end of 2023 and 2022 follow:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Trade accounts and notes receivable: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production & precision ag |
|
$ |
2,642 |
|
$ |
2,397 |
|
Small ag & turf |
|
|
2,344 |
|
|
2,065 |
|
Construction & forestry |
|
|
2,753 |
|
|
1,948 |
|
Trade accounts and notes receivable – net |
|
$ |
7,739 |
|
$ |
6,410 |
|
These receivables have significant concentrations of credit risk in the agriculture and turf and construction and forestry markets. Credit losses have been historically low. There is not a disproportionate concentration of credit risk with any single dealer. On a geographic basis, 53 percent of our trade accounts and notes receivable are located in the U.S. and Canada at October 29, 2023.
At October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 trade and notes receivables balances outstanding greater than 12 months were $107 and $49, respectively.
63
The allowance for credit losses on trade accounts and notes receivable at October 29, 2023, October 30, 2022, and October 31, 2021, as well as the related activity, follow:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Beginning of year balance |
|
$ |
36 |
|
$ |
41 |
|
$ |
39 |
|
ASU No. 2016-13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2) |
|
Provision |
|
|
7 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
10 |
|
Write-offs |
|
|
(8) |
|
|
(5) |
|
|
(7) |
|
Translation adjustments |
|
|
|
|
|
(1) |
|
|
1 |
|
End of year balance |
|
$ |
35 |
|
$ |
36 |
|
$ |
41 |
|
The equipment operations sell a significant portion of their trade receivables to financial services. Compensation is provided to financial services at market interest rates.
Financing Receivables ‒ Overall
Financing receivables originate under the following circumstances:
| ● | Retail customers purchase (or lease) equipment from a dealer and finance the equipment through John Deere Financial. |
| ● | We sell the equipment to a dealer under trade terms. Trade terms end, and the dealer finances the equipment on a wholesale receivable. Shown as wholesale notes in “Financing Receivables related to the Sale of Equipment.” |
| ● | A dealer finances the purchase of used equipment through John Deere Financial. |
| ● | We sell (or lease) the equipment directly to a retail customer with terms typically greater than 12 months. Shown as retail notes or sales-type leases in the “Financing Receivables related to the Sale of Equipment.” |
| ● | The customer utilizes a revolving credit product to finance parts, service, or input costs. |
Financing receivables at the end of 2023 and 2022 follow:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||||||||
|
|
Unrestricted/Securitized |
|
Unrestricted/Securitized |
|
||||||||
Retail notes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
$ |
26,955 |
|
$ |
6,052 |
|
$ |
23,830 |
|
$ |
4,868 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
4,623 |
|
|
1,442 |
|
|
4,396 |
|
|
1,179 |
|
Total |
|
|
31,578 |
|
|
7,494 |
|
|
28,226 |
|
|
6,047 |
|
Wholesale notes |
|
|
6,947 |
|
|
|
|
|
3,285 |
|
|
|
|
Revolving charge accounts |
|
|
4,789 |
|
|
|
|
|
4,316 |
|
|
|
|
Financing leases (direct |
|
|
2,906 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,832 |
|
|
|
|
Total financing receivables |
|
|
46,220 |
|
|
7,494 |
|
|
38,659 |
|
|
6,047 |
|
Less: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unearned finance income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Retail notes |
|
|
1,906 |
|
|
137 |
|
|
1,358 |
|
|
95 |
|
Wholesale notes |
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
Revolving charge accounts |
|
|
91 |
|
|
|
|
|
61 |
|
|
|
|
Financing leases |
|
|
350 |
|
|
|
|
|
285 |
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
2,372 |
|
|
137 |
|
|
1,716 |
|
|
95 |
|
Allowance for credit losses |
|
|
175 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
309 |
|
|
16 |
|
Financing receivables – net |
|
$ |
43,673 |
|
$ |
7,335 |
|
$ |
36,634 |
|
$ |
5,936 |
|
Assets managed by financial services continue to be evaluated by market, rather than by operating segment. Financing receivables have significant concentrations of credit risk in the agriculture and turf and construction and forestry markets. On a geographic basis,
84 percent of our financing receivables were located in the U.S. and Canada at October 29, 2023. There is no disproportionate concentration of credit risk with any single customer or dealer. We retain as collateral security in the equipment associated with most financing receivables. Theft and physical damage insurance are required for this equipment.
Financing Receivables ‒ Related to the Sale of Equipment
Financing receivables related to the sale of equipment are presented in the operating section of the cash flow statement. The balances at the end of 2023 and 2022 were as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Retail notes*: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
$ |
1,084 |
|
$ |
1,392 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
320 |
|
|
304 |
|
Total |
|
|
1,404 |
|
|
1,696 |
|
Wholesale notes |
|
|
6,947 |
|
|
3,285 |
|
Direct financing and sales-type leases* |
|
|
494 |
|
|
799 |
|
Total |
|
|
8,845 |
|
|
5,780 |
|
Less: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unearned finance income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Retail notes |
|
|
137 |
|
|
133 |
|
Wholesale notes |
|
|
25 |
|
|
12 |
|
Direct financing and sales-type leases |
|
|
60 |
|
|
67 |
|
Total |
|
|
222 |
|
|
212 |
|
Financing receivables related to our sales of equipment |
|
$ |
8,623 |
|
$ |
5,568 |
|
* These balances arise from sales and direct financing leases of equipment by company-owned dealers or through direct sales.
Financing Receivables ‒ Contractual Installment Payments
Financing receivable installments, including unearned finance income, at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 were scheduled as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||||||||
|
|
Unrestricted/Securitized |
|
Unrestricted/Securitized |
|
||||||||
Due in months: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 – 12 |
|
$ |
22,176 |
|
$ |
2,820 |
|
$ |
17,032 |
|
$ |
2,226 |
|
13 – 24 |
|
|
8,646 |
|
|
2,089 |
|
|
7,975 |
|
|
1,667 |
|
25 – 36 |
|
|
6,692 |
|
|
1,509 |
|
|
5,987 |
|
|
1,209 |
|
37 – 48 |
|
|
4,844 |
|
|
824 |
|
|
4,297 |
|
|
709 |
|
49 – 60 |
|
|
2,920 |
|
|
241 |
|
|
2,559 |
|
|
227 |
|
Thereafter |
|
|
942 |
|
|
11 |
|
|
809 |
|
|
9 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
46,220 |
|
$ |
7,494 |
|
$ |
38,659 |
|
$ |
6,047 |
|
Financing Receivables ‒ Credit Quality Analysis
We monitor the credit quality of financing receivables based on delinquency status, defined as follows:
| ● | Past due balances represent any payments 30 days or more past the due date. |
| ● | Non-performing financing receivables represent receivables for which we have stopped accruing finance income. This generally occurs when receivables are 90 days delinquent. |
| ● | Write-offs generally occur when receivables are 120 days delinquent. In these situations, the estimated uncollectible amount is written off to the allowance for credit losses. Any expected recovery is presented as non-performing. |
64
Finance income for non-performing receivables is recognized on a cash basis. Accrual of finance income is resumed when the receivable becomes contractually current and collections are reasonably assured.
The credit quality analysis of retail notes, financing leases, and revolving charge accounts (collectively, retail customer receivables) by year of origination was as follows:
|
|
October 29, 2023 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2020 |
|
||||
Retail customer receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
$ |
15,191 |
|
$ |
8,430 |
|
$ |
5,120 |
|
$ |
2,334 |
|
30-59 days past due |
|
|
62 |
|
|
75 |
|
|
39 |
|
|
21 |
|
60-89 days past due |
|
|
18 |
|
|
26 |
|
|
18 |
|
|
10 |
|
90+ days past due |
|
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
3 |
|
Non-performing |
|
|
30 |
|
|
78 |
|
|
62 |
|
|
33 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
2,927 |
|
|
1,961 |
|
|
1,084 |
|
|
353 |
|
30-59 days past due |
|
|
49 |
|
|
34 |
|
|
27 |
|
|
9 |
|
60-89 days past due |
|
|
19 |
|
|
14 |
|
|
12 |
|
|
5 |
|
90+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
Non-performing |
|
|
42 |
|
|
80 |
|
|
55 |
|
|
23 |
|
Total retail customer receivables |
|
$ |
18,340 |
|
$ |
10,705 |
|
$ |
6,421 |
|
$ |
2,791 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
October 29, 2023 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2019 |
|
Prior Years |
|
Revolving Charge Accounts |
|
Total |
|
||||
Retail customer receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
$ |
853 |
|
$ |
280 |
|
$ |
4,526 |
|
$ |
36,734 |
|
30-59 days past due |
|
|
9 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
29 |
|
|
238 |
|
60-89 days past due |
|
|
4 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
87 |
|
90+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
Non-performing |
|
|
22 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
255 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
84 |
|
|
29 |
|
|
119 |
|
|
6,557 |
|
30-59 days past due |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
127 |
|
60-89 days past due |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
54 |
|
90+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
Non-performing |
|
|
9 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
214 |
|
Total retail customer receivables |
|
$ |
987 |
|
$ |
341 |
|
$ |
4,698 |
|
$ |
44,283 |
|
|
|
October 30, 2022 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2020 |
|
2019 |
|
||||
Retail customer receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
$ |
13,500 |
|
$ |
7,984 |
|
$ |
4,091 |
|
$ |
1,875 |
|
30-59 days past due |
|
|
46 |
|
|
63 |
|
|
36 |
|
|
17 |
|
60-89 days past due |
|
|
14 |
|
|
25 |
|
|
13 |
|
|
6 |
|
90+ days past due |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-performing |
|
|
27 |
|
|
60 |
|
|
44 |
|
|
28 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
2,964 |
|
|
1,974 |
|
|
842 |
|
|
292 |
|
30-59 days past due |
|
|
53 |
|
|
52 |
|
|
23 |
|
|
9 |
|
60-89 days past due |
|
|
19 |
|
|
16 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
3 |
|
90+ days past due |
|
|
1 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
3 |
|
Non-performing |
|
|
25 |
|
|
61 |
|
|
34 |
|
|
19 |
|
Total retail customer receivables |
|
$ |
16,650 |
|
$ |
10,239 |
|
$ |
5,091 |
|
$ |
2,252 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
October 30, 2022 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2018 |
|
Prior Years |
|
Revolving Charge Accounts |
|
Total |
|
||||
Retail customer receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
$ |
785 |
|
$ |
200 |
|
$ |
4,111 |
|
$ |
32,546 |
|
30-59 days past due |
|
|
7 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
191 |
|
60-89 days past due |
|
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
66 |
|
90+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
Non-performing |
|
|
18 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
204 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
73 |
|
|
12 |
|
|
108 |
|
|
6,265 |
|
30-59 days past due |
|
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
143 |
|
60-89 days past due |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
47 |
|
90+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
Non-performing |
|
|
7 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
149 |
|
Total retail customer receivables |
|
$ |
895 |
|
$ |
240 |
|
$ |
4,255 |
|
$ |
39,622 |
|
65
The credit quality analysis of wholesale receivables by year of origination was as follows:
|
|
October 29, 2023 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2020 |
|
||||
Wholesale receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
$ |
631 |
|
$ |
93 |
|
$ |
21 |
|
$ |
4 |
|
30+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-performing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
23 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
30+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-performing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total wholesale receivables |
|
$ |
654 |
|
$ |
98 |
|
$ |
41 |
|
$ |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
October 29, 2023 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2019 |
|
Prior Years |
|
Revolving |
|
Total |
|
||||
Wholesale receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
$ |
1 |
|
$ |
160 |
|
$ |
5,175 |
|
$ |
6,085 |
|
30+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-performing |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
76 |
|
|
712 |
|
|
836 |
|
30+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-performing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total wholesale receivables |
|
$ |
2 |
|
$ |
236 |
|
$ |
5,887 |
|
$ |
6,922 |
|
|
|
October 30, 2022 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
2020 |
|
2019 |
|
||||
Wholesale receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
$ |
387 |
|
$ |
64 |
|
$ |
27 |
|
$ |
4 |
|
30+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-performing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
7 |
|
|
29 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
|
30+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-performing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total wholesale receivables |
|
$ |
394 |
|
$ |
93 |
|
$ |
29 |
|
$ |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
October 30, 2022 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2018 |
|
Prior Years |
|
Revolving |
|
Total |
|
||||
Wholesale receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
$ |
2 |
|
$ |
2,371 |
|
$ |
2,855 |
|
30+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-performing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
377 |
|
|
417 |
|
30+ days past due |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-performing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total wholesale receivables |
|
|
|
|
$ |
3 |
|
$ |
2,748 |
|
$ |
3,273 |
|
Financing Receivables ‒ Allowance for Credit Losses
An analysis of the allowance for credit losses and investment in financing receivables follows:
|
|
Retail Notes |
|
Revolving |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
& Financing |
|
Charge |
|
Wholesale |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Leases |
|
Accounts |
|
Receivables |
|
Total |
|
||||
2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Allowance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Beginning of year balance |
|
$ |
299 |
|
$ |
22 |
|
$ |
4 |
|
$ |
325 |
|
Provision |
|
|
97 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
119 |
|
Provision transferred to held for sale |
|
|
(142) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(142) |
|
Provision (credit) |
|
|
(45) |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
(23) |
|
Write-offs |
|
|
(84) |
|
|
(45) |
|
|
|
|
|
(129) |
|
Recoveries |
|
|
21 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
|
Translation adjustments |
|
|
(19) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(19) |
|
End of year balance* |
|
$ |
172 |
|
$ |
21 |
|
$ |
4 |
|
$ |
197 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financing receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
End of year balance |
|
$ |
39,585 |
|
$ |
4,698 |
|
$ |
6,922 |
|
$ |
51,205 |
|
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Allowance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Beginning of year balance |
|
$ |
138 |
|
$ |
21 |
|
$ |
7 |
|
$ |
166 |
|
Provision (credit) |
|
|
197 |
|
|
(2) |
|
|
(3) |
|
|
192 |
|
Write-offs |
|
|
(61) |
|
|
(27) |
|
|
|
|
|
(88) |
|
Recoveries |
|
|
22 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
52 |
|
Translation adjustments |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
End of year balance* |
|
$ |
299 |
|
$ |
22 |
|
$ |
4 |
|
$ |
325 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financing receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
End of year balance |
|
$ |
35,367 |
|
$ |
4,255 |
|
$ |
3,273 |
|
$ |
42,895 |
|
2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Allowance: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Beginning of year balance |
|
$ |
133 |
|
$ |
43 |
|
$ |
8 |
|
$ |
184 |
|
ASU No. 2016-13 |
|
|
44 |
|
|
(13) |
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
Provision (credit) |
|
|
|
|
|
(17) |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
(18) |
|
Write-offs |
|
|
(60) |
|
|
(28) |
|
|
|
|
|
(88) |
|
Recoveries |
|
|
20 |
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
56 |
|
Translation adjustments |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
End of year balance* |
|
$ |
138 |
|
$ |
21 |
|
$ |
7 |
|
$ |
166 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financing receivables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
End of year balance |
|
$ |
32,233 |
|
$ |
3,825 |
|
$ |
2,566 |
|
$ |
38,624 |
|
* Individual allowances were not significant.
We monitor the economy as part of the allowance setting process, including potential impacts of inflation and rising interest rates. Adjustments to the allowance are incorporated, as necessary.
During 2023, we determined that the financial services business in Russia met the held for sale criteria. The financing receivables in Russia were reclassified to “Other assets” and the associated allowance for credit losses was reversed. These operations were sold in the second quarter of 2023 (see Note 3). Excluding the portfolio in Russia, the allowance increased in 2023, primarily driven by growth in the retail notes and financing lease portfolios and higher expected losses on turf and construction customer accounts.
66
In 2022, the allowance for credit losses on retail notes and financing lease receivables increased due to higher reserves related to the events in Russia / Ukraine and higher portfolio balances. These increases were partially offset by continued positive agricultural market conditions. The revolving portfolio experienced low write-offs and solid recoveries.
Financing receivable analysis metrics follow:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Percent of the overall financing receivable portfolio: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Past-due amounts |
|
|
1.02 |
|
|
1.07 |
|
Non-performing |
|
|
.92 |
|
|
.83 |
|
Allowance for credit losses |
|
|
.38 |
|
|
.76 |
|
Deposits held as credit enhancements |
|
$ |
154 |
|
$ |
158 |
|
The allowance for credit losses as a percent of the overall financing receivable portfolio follow:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
Deere & Company |
|
.38 |
|
.76 |
|
.43 |
|
Closest comparators* |
|
.90 |
|
.93 |
|
1.15 |
|
* Peer companies from the 6153 and 6159 standard industrial classification (SIC) codes.
Financing Receivables ‒ Troubled Debt Restructurings
Infrequently, a customer experiences financial difficulties, and we grant a concession. These concessions may include:
| ● | a reduction of the stated interest rate, |
| ● | an extension of the maturity dates, |
| ● | a reduction of the amount of the debt, or |
| ● | a reduction of accrued interest. |
A troubled debt restructuring is a significant modification of the receivable. The following table quantifies troubled debt restructurings:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Number of receivable contracts |
|
|
209 |
|
|
276 |
|
|
397 |
|
Pre-modification balance |
|
$ |
10 |
|
$ |
12 |
|
$ |
18 |
|
Post modification balance |
|
|
9 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
17 |
|
Troubled debt restructurings for the presented periods related to retail notes. In 2023, 2022, and 2021, there were no significant troubled debt restructurings that subsequently defaulted and were written off. At October 29, 2023, we had no commitments to lend to customers whose accounts were modified in troubled debt restructurings.
Other Receivables
Other receivables at the end of 2023 and 2022 consisted of:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Taxes receivable |
|
$ |
1,626 |
|
$ |
1,450 |
|
Collateral on derivatives |
|
|
667 |
|
|
709 |
|
Receivables from unconsolidated affiliates |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
327 |
|
|
333 |
|
Other receivables |
|
$ |
2,623 |
|
$ |
2,492 |
|
12. SECURITIZATION OF FINANCING RECEIVABLES
Our funding strategy includes receivable securitizations, which allows us to receive cash for financing receivables immediately. While these securitization programs are administered in various forms, they are accomplished in the following basic steps:
| 1. | We transfer financing receivables into a bankruptcy-remote special purpose entity (SPE). |
| 2. | The SPE issues debt to investors. The debt is secured by the financing receivables. |
| 3. | Investors are paid back based on cash receipts from the financing receivables. |
As part of step 1, these receivables are legally isolated from the claims of our general creditors. This ensures cash receipts from the financing receivables are accessible to pay back securitization program investors. The structure of these transactions does not meet the accounting criteria for a sale of receivables. As a result, they are accounted for as a secured borrowing. The receivables and borrowings remain on our balance sheet and are separately reported as “Financing receivables securitized – net” and “Short-term securitization borrowings,” respectively.
We offer securitization programs to institutional investors and other financial institutions through public issuances or privately through a revolving credit agreement. At October 29, 2023, the revolving agreement had a financing limit of up to $1,500. At October 29, 2023, $1,281 of securitization borrowings were outstanding under the revolving agreement. In November 2023, the agreement was renewed for one year with a capacity of $2,000.
Restricted cash held by the SPE serves as a credit enhancement. It would be used to satisfy receivable payment deficiencies, if any. The cash restriction is removed either after all secured borrowing payments are made or proportionally as the secured receivables are collected and the borrowing obligations are reduced.
The components of the securitization programs were as follows at the end of 2023 and 2022:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Financing receivables securitized (retail notes) |
|
$ |
7,357 |
|
$ |
5,952 |
|
Allowance for credit losses |
|
|
(22) |
|
|
(16) |
|
Other assets (primarily restricted cash) |
|
|
152 |
|
|
155 |
|
Total restricted securitized assets |
|
$ |
7,487 |
|
$ |
6,091 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term securitization borrowings |
|
$ |
6,995 |
|
$ |
5,711 |
|
Accrued interest on borrowings |
|
|
13 |
|
|
6 |
|
Total liabilities related to restricted securitized assets |
|
$ |
7,008 |
|
$ |
5,717 |
|
The weighted-average interest rates on short-term securitization borrowings at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 were 4.7 percent and 2.8 percent, respectively.
Although these securitization borrowings are classified as short-term since payment is required if the financing receivables are liquidated early, the payment schedule for these borrowings at October 29, 2023 based on the expected liquidation of the retail notes is as follows: 2024 - $3,278, 2025 - $2,076, 2026 - $1,187, 2027 - $417, 2028 - $44, and later years - $4.
67
13. INVENTORIES
Inventories were valued at the lower of cost or net realizable value, as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Raw materials and supplies |
|
$ |
4,080 |
|
$ |
4,442 |
|
Work-in-process |
|
|
1,010 |
|
|
1,190 |
|
Finished goods and parts |
|
|
5,435 |
|
|
5,363 |
|
Total FIFO value |
|
|
10,525 |
|
|
10,995 |
|
Excess of FIFO over LIFO |
|
|
2,365 |
|
|
2,500 |
|
Inventories |
|
$ |
8,160 |
|
$ |
8,495 |
|
Percent valued on LIFO basis |
|
|
53% |
|
|
57% |
|
14. PROPERTY AND DEPRECIATION
A summary of property and equipment at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 follows:
|
|
Useful Lives* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Years) |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Land |
|
|
|
$ |
338 |
|
$ |
274 |
|
Buildings and building equipment |
|
22 |
|
|
4,735 |
|
|
4,386 |
|
Machinery and equipment |
|
11 |
|
|
6,613 |
|
|
6,208 |
|
Dies, patterns, tools, etc. |
|
8 |
|
|
1,658 |
|
|
1,558 |
|
All other |
|
5 |
|
|
1,323 |
|
|
1,205 |
|
Construction in progress |
|
|
|
|
1,266 |
|
|
818 |
|
Total at cost |
|
|
|
|
15,933 |
|
|
14,449 |
|
Less: accumulated depreciation |
|
|
|
|
9,054 |
|
|
8,393 |
|
Property and equipment - net |
|
|
|
$ |
6,879 |
|
$ |
6,056 |
|
* Weighted-averages
Property and equipment additions and depreciation follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Additions |
|
$ |
1,597 |
|
$ |
1,197 |
|
$ |
897 |
|
Depreciation |
|
|
838 |
|
|
806 |
|
|
830 |
|
For property and equipment, more than 10 percent resides in the U.S. and Germany, separately disclosed below:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
U.S. |
|
$ |
3,807 |
|
$ |
3,452 |
|
Germany |
|
|
1,192 |
|
|
991 |
|
Other countries |
|
|
1,880 |
|
|
1,613 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
6,879 |
|
$ |
6,056 |
|
15. GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLE ASSETS – NET
The changes in amounts of goodwill by operating segments were as follows. There are no accumulated goodwill impairment losses.
|
|
PPA |
|
SAT |
|
CF |
|
Total |
|
||||
October 31, 2021 |
|
$ |
542 |
|
$ |
265 |
|
$ |
2,484 |
|
$ |
3,291 |
|
Acquisitions (Note 3) |
|
|
132 |
|
|
69 |
|
|
599 |
|
|
800 |
|
Translation adjustments and other |
|
|
(28) |
|
|
(16) |
|
|
(360) |
|
|
(404) |
|
October 30, 2022 |
|
|
646 |
|
|
318 |
|
|
2,723 |
|
|
3,687 |
|
Acquisitions (Note 3) |
|
|
41 |
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
81 |
|
Translation adjustments and other |
|
|
15 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
112 |
|
|
132 |
|
October 29, 2023 |
|
$ |
702 |
|
$ |
363 |
|
$ |
2,835 |
|
$ |
3,900 |
|
The components of other intangible assets were as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Customer lists and relationships |
|
$ |
501 |
|
$ |
493 |
|
Technology, patents, trademarks, and other |
|
|
1,387 |
|
|
1,301 |
|
Total at cost |
|
|
1,888 |
|
|
1,794 |
|
Less accumulated amortization: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer lists and relationships |
|
|
195 |
|
|
166 |
|
Technology, patents, trademarks, and other |
|
|
560 |
|
|
410 |
|
Total accumulated amortization |
|
|
755 |
|
|
576 |
|
Other intangible assets - net |
|
$ |
1,133 |
|
$ |
1,218 |
|
Actual amortization expense for the past three years and the estimated amortization expense for the next five years follows:
Year |
|
Amortization |
|
|
2021 |
|
$ |
116 |
|
2022 |
|
|
145 |
|
2023 |
|
|
169 |
|
Estimated - 2024 |
|
|
170 |
|
2025 |
|
|
142 |
|
2026 |
|
|
119 |
|
2027 |
|
|
117 |
|
2028 |
|
|
85 |
|
16. OTHER ASSETS
Other assets at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 consisted of the following:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Operating lease asset (Note 24) |
|
$ |
283 |
|
$ |
299 |
|
Capitalized software, net |
|
|
450 |
|
|
372 |
|
Investment in unconsolidated affiliates |
|
|
126 |
|
|
117 |
|
Deferred charges (including prepaids) |
|
|
426 |
|
|
383 |
|
Derivative assets (Note 26) |
|
|
292 |
|
|
373 |
|
Prepaid taxes |
|
|
167 |
|
|
185 |
|
Parts return asset |
|
|
127 |
|
|
119 |
|
Restricted cash |
|
|
162 |
|
|
167 |
|
Matured lease & repossessed inventory |
|
|
59 |
|
|
44 |
|
Other |
|
|
411 |
|
|
358 |
|
Other Assets |
|
$ |
2,503 |
|
$ |
2,417 |
|
Capitalized software has an estimated useful life of three years. Amortization of these software costs in 2023, 2022, and 2021 was $144, $117, and $121, respectively.
17. SHORT-TERM BORROWINGS
Short-term borrowings at the end of 2023 and 2022 consisted of:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Commercial paper |
|
$ |
9,100 |
|
$ |
4,703 |
|
Notes payable to banks |
|
|
483 |
|
|
402 |
|
Finance lease obligations due within one year |
|
|
25 |
|
|
21 |
|
Long-term borrowings due within one year |
|
|
8,331 |
|
|
7,466 |
|
Short-term borrowings |
|
$ |
17,939 |
|
$ |
12,592 |
|
68
The weighted-average interest rates at the end of 2023 and 2022 were:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
Short-term borrowings: |
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial paper |
|
5.4% |
|
3.4% |
|
Notes payable to banks |
|
31.6% |
|
11.9% |
|
Notes payable to banks, excluding Argentina |
|
8.8% |
|
6.6% |
|
Worldwide lines of credit were $10.5 billion at October 29, 2023, consisting primarily of:
| ● | a 364-day credit facility agreement of $5.0 billion, expiring in the second quarter of 2024, |
| ● | a credit facility agreement of $2.5 billion, expiring in the second quarter of 2027, and |
| ● | a credit facility agreement of $2.5 billion, expiring in the second quarter of 2028. |
At October 29, 2023, $.8 billion of these worldwide lines of credit were unused. For the purpose of computing the unused credit lines, commercial paper and short-term bank borrowings were considered to constitute utilization. The credit agreements governing these lines of credit require us to maintain certain covenants. All of these credit agreement requirements have been met during the periods included in the consolidated financial statements.
18. ACCOUNTS PAYABLE AND ACCRUED EXPENSES
Accounts payable and accrued expenses at the end of 2023 and 2022 consisted of the following:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Accounts payable: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trade payables |
|
$ |
3,467 |
|
$ |
3,894 |
|
Dividends payable |
|
|
388 |
|
|
343 |
|
Operating lease liabilities |
|
|
281 |
|
|
302 |
|
Deposits withheld from dealers and merchants |
|
|
163 |
|
|
163 |
|
Payables to unconsolidated affiliates |
|
|
6 |
|
|
11 |
|
Other |
|
|
153 |
|
|
214 |
|
Accrued expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Employee benefits |
|
|
2,152 |
|
|
1,528 |
|
Product warranties |
|
|
1,610 |
|
|
1,427 |
|
Accrued taxes |
|
|
1,558 |
|
|
1,255 |
|
Derivative liabilities |
|
|
1,130 |
|
|
1,231 |
|
Dealer sales discounts |
|
|
1,243 |
|
|
1,044 |
|
Extended warranty premium |
|
|
1,021 |
|
|
866 |
|
Unearned revenue (contractual liability) |
|
|
676 |
|
|
557 |
|
Unearned operating lease revenue |
|
|
451 |
|
|
399 |
|
Accrued interest |
|
|
434 |
|
|
288 |
|
Other |
|
|
1,397 |
|
|
1,300 |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
$ |
16,130 |
|
$ |
14,822 |
|
Amounts are presented net of eliminations, which primarily consist of dealer sales incentives with a right of set-off against trade receivables of $2,228 at October 29, 2023 and $1,280 at October 30, 2022. Other eliminations were made for accrued taxes and other accrued expenses.
19. LONG-TERM BORROWINGS
Long-term borrowings at the end of 2023 and 2022 consisted of:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Underwritten term debt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. dollar notes and debentures: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.75% notes due 2025 |
|
$ |
700 |
|
$ |
700 |
|
6.55% debentures due 2028 |
|
|
200 |
|
|
200 |
|
5.375% notes due 2029 |
|
|
500 |
|
|
500 |
|
3.10% notes due 2030 |
|
|
700 |
|
|
700 |
|
8.10% debentures due 2030 |
|
|
250 |
|
|
250 |
|
7.125% notes due 2031 |
|
|
300 |
|
|
300 |
|
3.90% notes due 2042 |
|
|
1,250 |
|
|
1,250 |
|
2.875% notes due 2049 |
|
|
500 |
|
|
500 |
|
3.75% notes due 2050 |
|
|
850 |
|
|
850 |
|
Euro notes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.375% notes due 2024 (€800 principal) |
|
|
|
|
|
797 |
|
1.85% notes due 2028 (€600 principal) |
|
|
634 |
|
|
598 |
|
2.20% notes due 2032 (€600 principal) |
|
|
634 |
|
|
598 |
|
1.65% notes due 2039 (€650 principal) |
|
|
687 |
|
|
648 |
|
Serial issuances |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Medium-term notes |
|
|
29,638 |
|
|
24,604 |
|
Other notes and finance lease obligations |
|
|
1,769 |
|
|
1,223 |
|
Less: debt issuance costs and debt discounts |
|
|
(135) |
|
|
(122) |
|
Long-term borrowings |
|
$ |
38,477 |
|
$ |
33,596 |
|
Medium-term notes due through 2033 are offered by prospectus. All outstanding notes and debentures are senior unsecured borrowings and rank equally with each other. The outstanding principal and average interest rates at the end of 2023 and 2022 follow:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Medium-term notes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Principal |
|
$ |
30,902 |
|
$ |
25,629 |
|
Average interest rates |
|
|
4.9% |
|
|
2.9% |
|
The principal amounts of our long-term borrowings maturing in each of the next five years are as follows: 2024 - $8,319, 2025 - $9,195, 2026 - $7,867, 2027 - $3,724, and 2028 - $6,080.
20. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
A standard warranty is provided as assurance that the equipment will function as intended. The standard warranty period varies by product and region. At the time a sale is recognized, we record an estimate of future warranty costs based on historical claims rate experience and estimated population under warranty. The warranty reconciliation follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Beginning of year balance |
|
$ |
1,427 |
|
$ |
1,312 |
|
Warranty claims paid |
|
|
(1,181) |
|
|
(951) |
|
New product warranty accruals |
|
|
1,347 |
|
|
1,090 |
|
Foreign exchange |
|
|
17 |
|
|
(24) |
|
End of year balance |
|
$ |
1,610 |
|
$ |
1,427 |
|
The costs for extended warranty programs are recognized as incurred. See Note 9 for extended warranty claim costs.
In certain international markets, we provide guarantees to banks for the retail financing of John Deere equipment. At the end of 2023, the notional value of these guarantees was $239.
69
We may repossess the equipment collateralizing the receivables. At October 29, 2023, the accrued losses under these guarantees were not material.
We also had other miscellaneous contingent liabilities totaling approximately $105 at October 29, 2023. The accrued liability for these contingencies was not material.
At October 29, 2023, we had commitments of approximately $634 for the construction and acquisition of property and equipment.
We have commitments to extend credit to customers. The commitments are in the form of lines of credit and other pre-approved credit arrangements. We have the right to cancel or amend the terms of these commitments at any time. These commitments are not expected to be fully drawn upon; therefore, the total commitment amounts likely do not represent a future cash requirement. The commitments to extend credit at October 29, 2023 were:
| ● | $9.3 billion to John Deere dealers, and |
| ● | $32.4 billion to retail customers. |
We are subject to various unresolved legal actions. The accrued losses on these matters are not material. We believe the reasonably possible range of losses for these unresolved legal actions would not have a material effect on our financial statements. The most prevalent legal claims relate to:
| ● | product liability (including asbestos-related matters), |
| ● | retail credit, |
| ● | employment, |
| ● | patent, |
| ● | trademark, and |
| ● | antitrust matters. |
21. CAPITAL STOCK
Our stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol “DE.” At the end of 2023, there were 17,158 holders of record of our common stock.
The number of common shares we are authorized to issue is 1.2 billion. The common shares issued at October 29, 2023, October 30, 2022, and October 31, 2021 were 536.4 million. 281.6 million common shares were outstanding at October 29, 2023, with the remainder held in treasury stock.
The number of authorized preferred shares is 9 million. No preferred shares have been issued.
In December 2022, the Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $18.0 billion of common stock. At the end of fiscal year 2023, this repurchase program had $13.0 billion (35.9 million shares based on our fiscal year end closing NYSE common stock price of $361.15 per share) remaining to be repurchased. Repurchases of our common stock under this plan are made from time to time, at our discretion, in the open market.
A reconciliation of basic and diluted net income per share attributable to Deere & Company follows in millions, except per share amounts:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net income attributable to Deere & Company |
|
$ |
10,166 |
|
$ |
7,131 |
|
$ |
5,963 |
|
Average shares outstanding |
|
|
292.2 |
|
|
304.5 |
|
|
311.6 |
|
Basic per share |
|
$ |
34.80 |
|
$ |
23.42 |
|
$ |
19.14 |
|
Average shares outstanding |
|
|
292.2 |
|
|
304.5 |
|
|
311.6 |
|
Effect of dilutive stock options |
|
|
1.4 |
|
|
1.8 |
|
|
2.4 |
|
Total potential shares outstanding |
|
|
293.6 |
|
|
306.3 |
|
|
314.0 |
|
Diluted per share |
|
$ |
34.63 |
|
$ |
23.28 |
|
$ |
18.99 |
|
Shares excluded as antidilutive |
|
|
.1 |
|
|
.2 |
|
|
|
|
22. SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION
We issue stock options and restricted stock units to key employees. Restricted stock units are also issued to nonemployee directors for their services as directors. Restricted stock units consist of service-based and performance/service-based awards.
In 2023, we changed the accounting treatment of the Long-Term Incentive Cash that is granted to certain employees. As the performance metric related to this incentive plan is based, in part, on the price of our shares, we now account for it in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718. At October 29, 2023, we are authorized to grant an additional 16.6 million shares related to stock options or restricted stock units. We currently use shares that have been repurchased through our stock repurchase programs to satisfy share option exercises. The stock awards vesting periods and the dividend equivalents earned during the vesting period follow:
|
|
Vesting |
|
Dividend |
|
|
|
Period |
|
Equivalents |
|
Stock options |
|
1-3 years |
|
Not included |
|
Service-based RSUs |
|
1-3 years |
|
Included |
|
Performance/service-based RSUs |
|
3 years |
|
Not included |
|
Stock options expire ten years from the grant date. Performance/service-based awards are subject to a performance metric. The performance metric is based on our compound annual revenue growth rate, compared to a benchmark group of companies. The performance/service-based units award common stock in a range of zero to 200 percent for each unit granted based on the level of the metric achieved.
The fair value of stock options and restricted stock units is determined using our closing price on the grant date. These awards are expensed over the shorter of the award vesting period or the employee’s retirement eligibility period. The performance/service-based units’ expense is adjusted quarterly for the probable number of shares to be awarded. We recognize the effect of award forfeitures as an adjustment to compensation expense in the period the forfeiture occurs.
70
The total share-based compensation expense, recognized income tax benefits, and total grant-date fair values of stock options and restricted stock units vested consisted of the following:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Share-based compensation expense |
|
$ |
130 |
|
$ |
85 |
|
$ |
82 |
|
Income tax benefits |
|
|
21 |
|
|
17 |
|
|
16 |
|
Stock options and restricted stock units vested |
|
|
84 |
|
|
74 |
|
|
93 |
|
At October 29, 2023, there was $93 of total unrecognized compensation cost from share-based compensation arrangements. This compensation is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of approximately 1.5 years.
Stock Options
The fair value of each stock option award was estimated on the date of grant using a binomial lattice option valuation model. The assumptions used for the binomial lattice model to determine the fair value of options follow:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
Risk-free interest rate* |
|
2.68% |
|
1.27% |
|
.47% |
|
Expected dividends |
|
1.1% |
|
1.2% |
|
1.2% |
|
Volatility* |
|
33.0% |
|
32.0% |
|
31.0% |
|
Expected term (in years)* |
|
5.1 |
|
5.1 |
|
5.5 |
|
* Weighted-averages
The risk-free rates are based on U.S. Treasury security yields at the time of grant. Expected volatilities are based on implied volatilities from traded call options on our stock. We use historical data to estimate option exercise behavior representing the weighted-average period that options granted are expected to be outstanding.
The activity for outstanding stock options at October 29, 2023, and changes during 2023 follow:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remaining |
|
Aggregate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise |
|
Contractual |
|
Intrinsic |
|
||
|
|
Shares |
|
Price* |
|
Term |
|
Value |
|
||
|
|
(millions) |
|
(per share) |
|
(years) |
|
(millions) |
|
||
Outstanding at beginning of year |
|
2.0 |
|
$ |
153.11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granted |
|
.2 |
|
|
438.44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised |
|
(.5) |
|
|
118.54 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at end of year |
|
1.7 |
|
|
190.08 |
|
4.62 |
|
$ |
302.3 |
|
Exercisable at end of year |
|
1.3 |
|
|
144.71 |
|
3.66 |
|
|
292.3 |
|
* Weighted-averages
The amounts related to stock options were as follows in millions of dollars unless otherwise noted:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Weighted-average grant date fair value (per share) |
|
$ |
136.46 |
|
$ |
89.20 |
|
$ |
62.73 |
|
Intrinsic value of options exercised |
|
|
153 |
|
|
169 |
|
|
318 |
|
Cash received from exercises |
|
|
60 |
|
|
63 |
|
|
148 |
|
Tax benefit from exercises |
|
|
34 |
|
|
39 |
|
|
71 |
|
Restricted Stock Units
The weighted-average grant date fair values were as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Service-based |
|
$ |
428.35 |
|
$ |
347.59 |
|
$ |
258.86 |
|
Performance/service-based |
|
|
424.93 |
|
|
331.47 |
|
|
245.73 |
|
Our restricted stock units at October 29, 2023 and changes during 2023 in dollars and thousands of shares follow:
|
|
|
|
Grant-Date |
|
|
|
|
Shares |
|
Fair Value* |
|
|
Service-based |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nonvested at beginning of year |
|
404 |
|
$ |
251.42 |
|
Granted |
|
126 |
|
|
428.35 |
|
Vested |
|
(211) |
|
|
211.03 |
|
Forfeited |
|
(9) |
|
|
333.29 |
|
Nonvested at end of year |
|
310 |
|
|
348.82 |
|
Performance/service based |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nonvested at beginning of year |
|
143 |
|
|
227.70 |
|
Granted |
|
41 |
|
|
424.93 |
|
Vested |
|
(130) |
|
|
160.81 |
|
Performance change |
|
65 |
|
|
160.81 |
|
Nonvested at end of year |
|
119 |
|
|
331.78 |
|
* Weighted-averages
23. OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME ITEMS
The after-tax components of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) follow:
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
Retirement benefits adjustment |
|
$ |
(845) |
|
$ |
(389) |
|
$ |
(1,034) |
|
Cumulative translation adjustment |
|
|
(2,151) |
|
|
(2,594) |
|
|
(1,478) |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives |
|
|
(8) |
|
|
21 |
|
|
(42) |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) on debt securities |
|
|
(110) |
|
|
(94) |
|
|
15 |
|
Total accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
$ |
(3,114) |
|
$ |
(3,056) |
|
$ |
(2,539) |
|
71
The following tables reflect amounts recorded in other comprehensive income (loss), as well as reclassifications out of other comprehensive income (loss).
|
|
Before |
|
Tax |
|
After |
|
|||
|
|
Tax |
|
(Expense) |
|
Tax |
|
|||
|
|
Amount |
|
Credit |
|
Amount |
|
|||
2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cumulative translation adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized translation gain (loss) |
|
$ |
424 |
|
$ |
(2) |
|
$ |
422 |
|
Reclassification of realized (gain) loss to: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SA&G expenses |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
Other operating expenses |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
Net unrealized translation gain (loss) |
|
|
445 |
|
|
(2) |
|
|
443 |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized hedging gain (loss) |
|
|
25 |
|
|
(5) |
|
|
20 |
|
Reclassification of realized (gain) loss to: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts – Interest expense |
|
|
(62) |
|
|
13 |
|
|
(49) |
|
Net unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives |
|
|
(37) |
|
|
8 |
|
|
(29) |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) on debt securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized holding gain (loss) |
|
|
(20) |
|
|
4 |
|
|
(16) |
|
Net unrealized gain (loss) on debt securities |
|
|
(20) |
|
|
4 |
|
|
(16) |
|
Retirement benefits adjustment: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net actuarial gain (loss) |
|
|
(589) |
|
|
139 |
|
|
(450) |
|
Reclassification to Other operating expenses through amortization of: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Actuarial (gain) loss |
|
|
(81) |
|
|
20 |
|
|
(61) |
|
Prior service (credit) cost |
|
|
37 |
|
|
(9) |
|
|
28 |
|
Settlements |
|
|
37 |
|
|
(10) |
|
|
27 |
|
Net unrealized gain (loss) on retirement benefits adjustment |
|
|
(596) |
|
|
140 |
|
|
(456) |
|
Total other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
$ |
(208) |
|
$ |
150 |
|
$ |
(58) |
|
|
|
Before |
|
Tax |
|
After |
|
|||
|
|
Tax |
|
(Expense) |
|
Tax |
|
|||
|
|
Amount |
|
Credit |
|
Amount |
|
|||
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cumulative translation adjustment |
|
$ |
(1,105) |
|
$ |
(11) |
|
$ |
(1,116) |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized hedging gain (loss) |
|
|
89 |
|
|
(19) |
|
|
70 |
|
Reclassification of realized (gain) loss to: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts – Interest expense |
|
|
(9) |
|
|
2 |
|
|
(7) |
|
Net unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives |
|
|
80 |
|
|
(17) |
|
|
63 |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) on debt securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized holding gain (loss) |
|
|
(140) |
|
|
30 |
|
|
(110) |
|
Reclassification of realized (gain) loss – Other income |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
Net unrealized gain (loss) on debt securities |
|
|
(139) |
|
|
30 |
|
|
(109) |
|
Retirement benefits adjustment: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net actuarial gain (loss) |
|
|
1,192 |
|
|
(298) |
|
|
894 |
|
Prior service credit (cost) |
|
|
(517) |
|
|
124 |
|
|
(393) |
|
Reclassification to Other operating expenses through amortization of: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Actuarial (gain) loss |
|
|
116 |
|
|
(29) |
|
|
87 |
|
Prior service (credit) cost |
|
|
30 |
|
|
(7) |
|
|
23 |
|
Settlements/curtailment |
|
|
45 |
|
|
(11) |
|
|
34 |
|
Net unrealized gain (loss) on retirement benefits adjustment |
|
|
866 |
|
|
(221) |
|
|
645 |
|
Total other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
$ |
(298) |
|
$ |
(219) |
|
$ |
(517) |
|
|
|
Before |
|
Tax |
|
After |
|
|||
|
|
Tax |
|
(Expense) |
|
Tax |
|
|||
|
|
Amount |
|
Credit |
|
Amount |
|
|||
2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cumulative translation adjustment: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized translation gain (loss) |
|
$ |
112 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
112 |
|
Reclassification of realized (gain) loss to: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity in (income) loss of unconsolidated affiliates |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
Net unrealized translation gain (loss) |
|
|
118 |
|
|
|
|
|
118 |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized hedging gain (loss) |
|
|
8 |
|
$ |
(2) |
|
|
6 |
|
Reclassification of realized (gain) loss to: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts – Interest expense |
|
|
13 |
|
|
(3) |
|
|
10 |
|
Net unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives |
|
|
21 |
|
|
(5) |
|
|
16 |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) on debt securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized holding gain (loss) |
|
|
(21) |
|
|
3 |
|
|
(18) |
|
Net unrealized gain (loss) on debt securities |
|
|
(21) |
|
|
3 |
|
|
(18) |
|
Retirement benefits adjustment: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net actuarial gain (loss) |
|
|
3,492 |
|
|
(845) |
|
|
2,647 |
|
Reclassification to Other operating expenses through amortization of: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Actuarial (gain) loss |
|
|
283 |
|
|
(69) |
|
|
214 |
|
Prior service (credit) cost |
|
|
8 |
|
|
(2) |
|
|
6 |
|
Settlements |
|
|
22 |
|
|
(5) |
|
|
17 |
|
Net unrealized gain (loss) on retirement benefits adjustment |
|
|
3,805 |
|
|
(921) |
|
|
2,884 |
|
Total other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
$ |
3,923 |
|
$ |
(923) |
|
$ |
3,000 |
|
72
24. LEASES
We are both a lessee and a lessor. We lease for our own use warehouse facilities, office space, production equipment, information technology equipment, and vehicles. The financial services operations lease equipment produced or sold by us and a limited amount of other equipment to retail customers. We determine if an arrangement is or contains a lease at the contract inception.
Lessee
The amounts of the lease liability and right of use asset are determined at lease commencement and are based on the present value of the lease payments over the lease term. The lease payments are discounted using our incremental borrowing rate since the rate implicit in the lease is not readily determinable. We determine the incremental borrowing rate for each lease based on the lease term and the economic environment of the country where the asset will be used, adjusted as if the borrowings were collateralized. Leases with contractual periods greater than one year and that do not meet the finance lease criteria are classified as operating leases.
We have elected to combine lease and nonlease components, such as maintenance and utilities costs included in a lease contract, for all asset classes. Leases with an initial term of one year or less are expensed on a straight-line basis over the lease term and recorded in short-term lease expense. Variable lease expense includes warehouse facilities leases with payments based on utilization exceeding contractual minimum amounts and leases with payments indexed to inflation when the index changes after lease commencement.
The lease expense by type consisted of the following:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Operating lease expense |
|
$ |
129 |
|
$ |
114 |
|
$ |
116 |
|
Short-term lease expense |
|
|
49 |
|
|
55 |
|
|
29 |
|
Variable lease expense |
|
|
80 |
|
|
74 |
|
|
53 |
|
Finance lease: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation expense |
|
|
28 |
|
|
26 |
|
|
26 |
|
Interest on lease liabilities |
|
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
Total lease expense |
|
$ |
288 |
|
$ |
270 |
|
$ |
225 |
|
Operating and finance lease right of use assets and lease liabilities follow:
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
Operating leases: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other assets |
|
$ |
283 |
|
$ |
299 |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
281 |
|
|
302 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Finance leases: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property and equipment — net |
|
$ |
66 |
|
$ |
49 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term borrowings |
|
|
25 |
|
|
21 |
|
Long-term borrowings |
|
|
49 |
|
|
30 |
|
Total finance lease liabilities |
|
$ |
74 |
|
$ |
51 |
|
The weighted-average remaining lease terms in years and discount rates follows:
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
Weighted-average remaining lease terms: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating leases |
|
|
7 |
|
|
7 |
|
Finance leases |
|
|
4 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-average discount rates: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating leases |
|
|
3.1% |
|
|
2.4% |
|
Finance leases |
|
|
3.6% |
|
|
1.9% |
|
Lease payment amounts in each of the next five years at October 29, 2023 follow:
|
|
Operating |
|
Finance |
|
||
Due in: |
|
Leases |
|
Leases |
|
||
2024 |
|
$ |
103 |
|
$ |
27 |
|
2025 |
|
|
71 |
|
|
22 |
|
2026 |
|
|
36 |
|
|
14 |
|
2027 |
|
|
24 |
|
|
8 |
|
2028 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
3 |
|
Later years |
|
|
45 |
|
|
6 |
|
Total lease payments |
|
|
301 |
|
|
80 |
|
Less: imputed interest |
|
|
20 |
|
|
6 |
|
Total lease liabilities |
|
$ |
281 |
|
$ |
74 |
|
Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities follows:
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
Operating cash flows for operating leases |
|
$ |
132 |
|
$ |
127 |
|
$ |
104 |
|
Operating cash flows for finance leases |
|
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
Financing cash flows for finance leases |
|
|
31 |
|
|
28 |
|
|
25 |
|
Right of use assets obtained in exchange for lease liabilities follow:
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
Operating leases |
|
$ |
97 |
|
$ |
135 |
|
Finance leases |
|
|
54 |
|
|
17 |
|
Lessor
We lease equipment manufactured by us through John Deere Financial. Sales-type and direct financing leases are reported in “Financing receivables ‒ net.” Operating leases are reported in “Equipment on operating leases ‒ net.”
At the end of the majority of leases, the lessee has the option to purchase the underlying equipment for the contractual residual value or return it to the dealer. If the equipment is returned to the dealer, the dealer also has the option to purchase the equipment or return it to us for remarketing.
We estimate the residual values for operating leases at lease inception based on several factors, including lease term, expected hours of usage, historical wholesale sale prices, return experience, intended use of the equipment, market dynamics and trends, and dealer residual guarantees. We review residual value estimates during the lease term and test the carrying value of our operating lease assets for impairment when events or circumstances necessitate. The depreciation is adjusted on a straight-line basis over the remaining lease term if residual value estimates change. Lease agreements include usage limits and specifications on machine condition, which allow us to assess lessees for excess use or damages to the underlying equipment.
73
We have elected to combine lease and nonlease components. The nonlease components relate to preventative maintenance and extended warranty agreements financed by the retail customer. We have also elected to report consideration related to sales and value added taxes net of the related tax expense. Property taxes on leased assets are recorded on a gross basis in “Finance and interest income” and “Other operating expenses.” Variable lease revenues relate to property taxes on leased assets in certain markets and late fees.
Lease revenues earned by us follow:
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
Sales-type and direct finance lease revenues |
|
$ |
165 |
|
$ |
154 |
|
$ |
145 |
|
Operating lease revenues |
|
|
1,312 |
|
|
1,318 |
|
|
1,423 |
|
Variable lease revenues |
|
|
16 |
|
|
26 |
|
|
30 |
|
Total lease revenues |
|
$ |
1,493 |
|
$ |
1,498 |
|
$ |
1,598 |
|
At the time of accepting a lease that qualifies as a sales-type or direct financing lease, we record the gross amount of lease payments receivable, estimated residual value of the leased equipment, and unearned finance income. The unearned finance income is recognized as revenue over the lease term using the interest method.
Sales-type and direct financing lease receivables by market follow:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
$ |
1,078 |
|
$ |
1,118 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
1,048 |
|
|
1,167 |
|
Total |
|
|
2,126 |
|
|
2,285 |
|
Guaranteed residual values |
|
|
723 |
|
|
491 |
|
Unguaranteed residual values |
|
|
57 |
|
|
56 |
|
Less: unearned finance income |
|
|
(350) |
|
|
(285) |
|
Financing lease receivables |
|
$ |
2,556 |
|
$ |
2,547 |
|
Scheduled payments, including guaranteed residual values, on sales-type and direct financing lease receivables at October 29, 2023 follow:
Due in: |
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
$ |
1,453 |
|
2025 |
|
|
642 |
|
2026 |
|
|
378 |
|
2027 |
|
|
214 |
|
2028 |
|
|
142 |
|
Later years |
|
|
20 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
2,849 |
|
Lease payments from operating leases are recorded as income on a straight-line method over the lease terms. Operating lease assets are recorded at cost and depreciated to their estimated residual value on a straight-line method over the terms of the leases.
The cost of equipment on operating leases by market follow:
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
Agriculture and turf |
|
$ |
7,168 |
|
$ |
6,912 |
|
Construction and forestry |
|
|
1,212 |
|
|
1,342 |
|
Total |
|
|
8,380 |
|
|
8,254 |
|
Less: accumulated depreciation |
|
|
(1,463) |
|
|
(1,631) |
|
Equipment on operating leases - net |
|
$ |
6,917 |
|
$ |
6,623 |
|
Operating lease residual values |
|
$ |
4,864 |
|
$ |
4,640 |
|
First-loss residual value guarantees |
|
|
1,188 |
|
|
1,025 |
|
The equipment is depreciated on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease. The corresponding depreciation expense was $853 in 2023, $827 in 2022, and $983 in 2021.
Lease payments for operating leases are scheduled as follows:
Due in: |
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
$ |
1,044 |
|
2025 |
|
|
797 |
|
2026 |
|
|
490 |
|
2027 |
|
|
258 |
|
2028 |
|
|
65 |
|
Later years |
|
|
10 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
2,664 |
|
25. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. To determine fair value, we use various methods including market and income approaches. We utilize valuation models and techniques that maximize the use of observable inputs. The models are industry-standard models that consider various assumptions including time values and yield curves as well as other economic measures. These valuation techniques are consistently applied.
Level 1 measurements consist of quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. Level 2 measurements include significant other observable inputs such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; identical assets or liabilities in inactive markets; observable inputs such as interest rates and yield curves; and other market-corroborated inputs. Level 3 measurements include significant unobservable inputs.
Fair values of the financing receivables that were issued long-term were based on the discounted values of their related cash flows at interest rates currently being offered by us for similar financing receivables. The fair values of the remaining financing receivables approximated the carrying amounts.
Fair values of long-term borrowings and short-term securitization borrowings were based on current market quotes for identical or similar borrowings and credit risk, or on the discounted values of their related cash flows at current market interest rates.
74
The fair values of financial instruments that do not approximate the carrying values at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 follow:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||||||||
|
|
Carrying |
|
Fair |
|
Carrying |
|
Fair |
|
||||
|
|
Value |
|
Value* |
|
Value |
|
Value* |
|
||||
Financing receivables – net |
|
$ |
43,673 |
|
$ |
42,777 |
|
$ |
36,634 |
|
$ |
35,526 |
|
Financing receivables securitized – net |
|
|
7,335 |
|
|
7,056 |
|
|
5,936 |
|
|
5,698 |
|
Short-term securitization borrowings |
|
|
6,995 |
|
|
6,921 |
|
|
5,711 |
|
|
5,577 |
|
Long-term borrowings due within one year** |
|
|
8,331 |
|
|
8,156 |
|
|
7,466 |
|
|
7,322 |
|
Long-term borrowings** |
|
|
38,428 |
|
|
36,873 |
|
|
33,566 |
|
|
31,852 |
|
* Fair value measurements above were Level 3 for all financing receivables and Level 2 for all borrowings.
** |
Values exclude finance lease liabilities that are presented as borrowings (see Note 24). |
Assets and liabilities measured at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 at fair value on a recurring basis follow, excluding our cash equivalents, which were carried at a cost that approximates fair value and consisted of money market funds and time deposits:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||
Level 1: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Marketable securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
International equity securities |
|
$ |
3 |
|
$ |
3 |
|
International mutual funds securities |
|
|
101 |
|
|
|
|
U.S. equity fund |
|
|
86 |
|
|
70 |
|
U.S. fixed income fund |
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
|
U.S. government debt securities |
|
|
78 |
|
|
62 |
|
Total Level 1 marketable securities |
|
|
300 |
|
|
135 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Level 2: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Marketable securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Corporate debt securities |
|
|
244 |
|
|
200 |
|
International debt securities |
|
|
1 |
|
|
60 |
|
Mortgage-backed securities* |
|
|
185 |
|
|
155 |
|
Municipal debt securities |
|
|
75 |
|
|
63 |
|
U.S. government debt securities |
|
|
141 |
|
|
121 |
|
Total Level 2 marketable securities |
|
|
646 |
|
|
599 |
|
Other assets - Derivatives |
|
|
292 |
|
|
373 |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses - Derivatives |
|
|
1,130 |
|
|
1,231 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Level 3: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses – Deferred consideration |
|
|
186 |
|
|
236 |
|
* Primarily issued by U.S. government sponsored enterprises.
Fair value, nonrecurring level 3 measurements from impairments at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 follow:
|
|
Fair Value |
|
Losses |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 1 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||||
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
$ |
19 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
19 |
|
|
|
|
Property and equipment – net |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
|
$ |
44 |
|
Other intangible assets – net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
1 Related to assessments on the Russian operations, performed at May 1, 2022 and updated on July 31, 2022 and October 30, 2022.
The following is a description of the valuation methodologies we use to measure certain financial instruments on the balance sheets at fair value. For more information on asset impairments, see Note 4.
Marketable securities – The portfolio of investments is valued on a market approach (matrix pricing model) in which all significant inputs are observable or can be derived from or corroborated by observable market data such as interest rates, yield curves, volatilities, credit risk, and prepayment speeds. Funds are valued using the fund’s net asset value, based on the fair value of the underlying securities.
Derivatives – Our derivative financial instruments consist of interest rate contracts (swaps), foreign currency exchange contracts (futures, forwards and swaps), and cross-currency interest rate contracts (swaps). The portfolio is valued based on an income approach (discounted cash flow) using market observable inputs, including swap curves and both forward and spot exchange rates for currencies.
Financing receivables – Specific reserve impairments are based on the fair value of the collateral, which is measured using a market approach (appraisal values or realizable values). Inputs include a selection of realizable values (see Note 11).
Inventories – The impairment was based on net realizable value, less reasonably predictable selling and disposal costs.
Property and equipment – net – The valuations were based on cost and market approaches. The inputs include replacement cost estimates adjusted for physical deterioration and economic obsolescence, or quoted prices when available.
Other intangible assets – net – In 2022, we considered external valuations based on our probability weighted cash flow analysis.
Other assets – In 2021, the impairments were measured at the fair value of a right of use operating lease asset.
75
26. DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS
Fair values of our derivative instruments and the associated notional amounts at the end of 2023 and 2022 were as follows. Assets are recorded in “Other assets,” while liabilities are recorded in “Accounts payable and accrued expenses.”
|
|
|
|
Fair Value |
|
|||||
|
|
Notional |
|
Assets |
|
Liabilities |
|
|||
2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flow hedges: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts |
|
$ |
1,500 |
|
$ |
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair value hedges: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts |
|
|
12,691 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
970 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Not designated as hedging instruments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts |
|
|
13,853 |
|
|
169 |
|
|
98 |
|
Foreign exchange contracts |
|
|
8,117 |
|
|
75 |
|
|
54 |
|
Cross-currency interest rate contracts |
|
|
176 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flow hedges: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts |
|
$ |
1,950 |
|
$ |
87 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair value hedges: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts |
|
|
10,112 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
1,004 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Not designated as hedging instruments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts |
|
|
10,568 |
|
|
212 |
|
|
107 |
|
Foreign exchange contracts |
|
|
8,185 |
|
|
66 |
|
|
118 |
|
Cross-currency interest rate contracts |
|
|
260 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
2 |
|
The amounts recorded, at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022, in the consolidated balance sheets related to borrowings designated in fair value hedging relationships were as follows. Fair value hedging adjustments are included in the carrying amount of the hedged item.
|
|
Active Hedging |
|
Discontinued Hedging |
|
||||||||
|
|
Relationships |
|
Relationships |
|
||||||||
|
|
Carrying |
|
Cumulative |
|
Carrying |
|
Cumulative |
|
||||
|
|
Amount of |
|
Fair Value |
|
Amount of |
|
Fair Value |
|
||||
|
|
Hedged |
|
Hedging |
|
Formerly |
|
Hedging |
|
||||
|
|
Item |
|
Amount |
|
Hedged Item |
|
Amount |
|
||||
2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term borrowings |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
1,814 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
Long-term borrowings |
|
$ |
11,660 |
|
$ |
(976) |
|
|
7,144 |
|
|
(288) |
|
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term borrowings |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
2,515 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
Long-term borrowings |
|
$ |
9,060 |
|
$ |
(1,006) |
|
|
5,520 |
|
|
(19) |
|
The classification and gains (losses), including accrued interest expense, related to derivative instruments on the statements of consolidated income consisted of the following:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Fair Value Hedges |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts – Interest expense |
|
$ |
(542) |
|
$ |
(1,144) |
|
$ |
(236) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Flow Hedges |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Recognized in OCI: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts – OCI (pretax) |
|
$ |
25 |
|
$ |
89 |
|
$ |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reclassified from OCI: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts – Interest expense |
|
|
62 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
(13) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Not Designated as Hedges |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest rate contracts – Net sales |
|
$ |
1 |
|
$ |
53 |
|
$ |
13 |
|
Interest rate contracts – Interest expense |
|
|
40 |
|
|
81 |
|
|
14 |
|
Foreign exchange contracts – Net sales |
|
|
(6) |
|
|
(6) |
|
|
|
|
Foreign exchange contracts – Cost of sales |
|
|
8 |
|
|
(64) |
|
|
(101) |
|
Foreign exchange contracts – Other operating expenses |
|
|
100 |
|
|
402 |
|
|
(262) |
|
Total not designated |
|
$ |
143 |
|
$ |
466 |
|
$ |
(336) |
|
The amount of gain recorded in OCI at October 29, 2023 that is expected to be reclassified to “Interest expense” or “Other operating expenses” in the next twelve months if interest rates or exchange rates remain unchanged is $31 after-tax. There were no gains or losses reclassified from OCI to earnings based on the probability that the original forecasted transaction would not occur.
Counterparty Risk and Collateral
Derivative instruments are subject to significant concentrations of credit risk to the banking sector. We manage individual counterparty exposure by setting limits that consider the credit rating of the counterparty, the credit default swap spread of the counterparty, and other financial commitments and exposures between us and the counterparty banks. All interest rate derivatives are transacted under International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA) documentation. Some of these agreements include credit support provisions. Each master agreement permits the net settlement of amounts owed in the event of default or termination.
Certain of our derivative agreements contain credit support provisions that may require us to post collateral based on the size of the net liability positions and credit ratings. The aggregate fair value of all derivatives with credit-risk-related contingent features that were in a net liability position at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022, was $1.1 billion and $1.1 billion, respectively. In accordance with the limits established in these agreements, we posted $659 of cash collateral at October 29, 2023 and $701 at October 30, 2022. In addition, we paid $8 of collateral that was outstanding at both October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 to participate in an international futures market to hedge currency exposure, not included in the table below.
76
Derivatives are recorded without offsetting for netting arrangements or collateral. The impact on the derivative assets and liabilities related to netting arrangements and collateral at October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022 follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross Amounts |
|
Netting |
|
|
|
Net |
|
||||
|
|
Recognized |
|
Arrangements |
|
Collateral |
|
Amount |
|
||||
2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assets |
|
$ |
292 |
|
$ |
(152) |
|
|
|
|
$ |
140 |
|
Liabilities |
|
|
1,130 |
|
|
(152) |
|
$ |
(659) |
|
|
319 |
|
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assets |
|
$ |
373 |
|
$ |
(179) |
|
$ |
(54) |
|
$ |
140 |
|
Liabilities |
|
|
1,231 |
|
|
(179) |
|
|
(701) |
|
|
351 |
|
27. SEGMENT DATA
Our operations are presently organized and reported in four business segments. This presentation is consistent with how the chief operating decision maker (the CEO) assesses the performance of the segments and makes decisions about resource allocations.
The PPA segment defines, develops, and delivers global equipment and technology solutions to unlock customer value for production-scale growers of large grains, small grains, cotton, and sugarcane. The main products include large and certain mid-size tractors, combines, cotton pickers, sugarcane harvesters and loaders, and soil preparation, seeding, application, and crop care equipment.
The SAT segment defines, develops, and delivers global equipment and technology solutions to unlock customer value for dairy and livestock producers, high-value crop producers, and turf and utility customers. The segment’s primary products include certain mid-size, utility, and compact utility tractors, as well as hay and forage equipment, riding and commercial lawn equipment, golf course equipment, and utility vehicles.
The CF segment defines, develops, and delivers a broad range of machines and technology solutions organized along the earthmoving, forestry, and roadbuilding production systems. The segment’s primary products include crawler dozers and loaders, four-wheel-drive loaders, excavators, skid-steer loaders, milling machines, and log harvesters.
The products and services produced by the segments above are marketed through independent retail dealer networks and major retail outlets. For roadbuilding products in certain markets outside the U.S. and Canada, the products are sold through company-owned sales and service subsidiaries.
The financial services segment finances sales and leases by John Deere dealers of new and used production and precision agriculture equipment, small agriculture and turf equipment, and construction and forestry equipment. In addition, the financial services segment provides wholesale financing to dealers of the foregoing equipment, finances retail revolving charge accounts, and offers extended equipment warranties.
Because of integrated manufacturing operations and common administrative and marketing support, a substantial number of allocations must be made to determine operating segment data.
Identifiable assets assigned to the operating segments are those the units actively manage, consisting of trade receivables, inventories, property and equipment, intangible assets, and certain other assets. Corporate assets are managed collectively, including cash and cash equivalents, retirement benefit net assets, goodwill, and deferred income tax assets.
Information relating to operations by operating segment follows for the years ended October 29, 2023, October 30, 2022, and October 31, 2021.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATING SEGMENTS |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net sales and revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unaffiliated customers: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production & precision ag net sales |
|
$ |
26,790 |
|
$ |
22,002 |
|
$ |
16,509 |
|
Small ag & turf net sales |
|
|
13,980 |
|
|
13,381 |
|
|
11,860 |
|
Construction & forestry net sales |
|
|
14,795 |
|
|
12,534 |
|
|
11,368 |
|
Financial services revenues |
|
|
4,721 |
|
|
3,625 |
|
|
3,548 |
|
Other revenues* |
|
|
965 |
|
|
1,035 |
|
|
739 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
61,251 |
|
$ |
52,577 |
|
$ |
44,024 |
|
* Other revenues are primarily the production and precision ag, small ag and turf, and construction and forestry revenues for finance and interest income and other income.
Operating profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production & precision ag |
|
$ |
6,996 |
|
$ |
4,386 |
|
$ |
3,334 |
|
Small ag & turf |
|
|
2,472 |
|
|
1,949 |
|
|
2,045 |
|
Construction & forestry |
|
|
2,695 |
|
|
2,014 |
|
|
1,489 |
|
Financial services* |
|
|
795 |
|
|
1,159 |
|
|
1,144 |
|
Total operating profit* |
|
|
12,958 |
|
|
9,508 |
|
|
8,012 |
|
Interest income |
|
|
559 |
|
|
159 |
|
|
82 |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
(411) |
|
|
(390) |
|
|
(368) |
|
Foreign exchange gain (loss) from equipment operations’ financing activities |
|
|
(114) |
|
|
(103) |
|
|
(45) |
|
Pension and OPEB benefit (cost), excluding service cost component |
|
|
286 |
|
|
218 |
|
|
183 |
|
Corporate expenses – net |
|
|
(252) |
|
|
(255) |
|
|
(241) |
|
Income taxes |
|
|
(2,871) |
|
|
(2,007) |
|
|
(1,658) |
|
Total |
|
|
(2,803) |
|
|
(2,378) |
|
|
(2,047) |
|
Net income |
|
|
10,155 |
|
|
7,130 |
|
|
5,965 |
|
Less: Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
|
(11) |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
2 |
|
Net income attributable to Deere & Company |
|
$ |
10,166 |
|
$ |
7,131 |
|
$ |
5,963 |
|
* Operating profit of the financial services business segment includes the effect of its interest expense and foreign exchange gains or losses.
77
OPERATING SEGMENTS |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||
Interest income* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production & precision ag |
|
$ |
29 |
|
$ |
22 |
|
$ |
21 |
|
Small ag & turf |
|
|
35 |
|
|
24 |
|
|
21 |
|
Construction & forestry |
|
|
13 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
10 |
|
Financial services |
|
|
3,731 |
|
|
2,245 |
|
|
1,999 |
|
Corporate |
|
|
559 |
|
|
159 |
|
|
82 |
|
Intercompany |
|
|
(1,008) |
|
|
(431) |
|
|
(279) |
|
Total |
|
$ |
3,359 |
|
$ |
2,027 |
|
$ |
1,854 |
|
* Does not include finance rental income for equipment on operating leases.
Interest expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production & precision ag |
|
$ |
282 |
|
$ |
122 |
|
$ |
84 |
|
Small ag & turf |
|
|
236 |
|
|
105 |
|
|
87 |
|
Construction & forestry |
|
|
169 |
|
|
72 |
|
|
46 |
|
Financial services |
|
|
2,362 |
|
|
799 |
|
|
687 |
|
Corporate |
|
|
411 |
|
|
390 |
|
|
368 |
|
Intercompany |
|
|
(1,007) |
|
|
(426) |
|
|
(279) |
|
Total |
|
$ |
2,453 |
|
$ |
1,062 |
|
$ |
993 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation* and amortization expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production & precision ag |
|
$ |
581 |
|
$ |
523 |
|
$ |
495 |
|
Small ag & turf |
|
|
241 |
|
|
236 |
|
|
245 |
|
Construction & forestry |
|
|
301 |
|
|
282 |
|
|
303 |
|
Financial services |
|
|
1,016 |
|
|
1,050 |
|
|
1,140 |
|
Intercompany |
|
|
(135) |
|
|
(196) |
|
|
(133) |
|
Total |
|
$ |
2,004 |
|
$ |
1,895 |
|
$ |
2,050 |
|
* Includes depreciation for equipment on operating leases.
Identifiable operating assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production & precision ag |
|
$ |
8,734 |
|
$ |
8,414 |
|
$ |
7,021 |
|
Small ag & turf |
|
|
4,348 |
|
|
4,451 |
|
|
3,959 |
|
Construction & forestry |
|
|
7,139 |
|
|
6,754 |
|
|
6,457 |
|
Financial services |
|
|
70,732 |
|
|
58,864 |
|
|
51,624 |
|
Corporate |
|
|
13,134 |
|
|
11,547 |
|
|
15,053 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
104,087 |
|
$ |
90,030 |
|
$ |
84,114 |
|
Capital additions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production & precision ag |
|
$ |
896 |
|
$ |
649 |
|
$ |
458 |
|
Small ag & turf |
|
|
386 |
|
|
329 |
|
|
253 |
|
Construction & forestry |
|
|
311 |
|
|
217 |
|
|
183 |
|
Financial services |
|
|
4 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
1,597 |
|
$ |
1,197 |
|
$ |
897 |
|
78
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the stockholders and the Board of Directors of Deere & Company:
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Deere & Company and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022, the related statements of consolidated income, consolidated comprehensive income, changes in consolidated stockholders’ equity and consolidated cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended October 29, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of October 29, 2023 and October 30, 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended October 29, 2023, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of October 29, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated December 15, 2023, expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current‐period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
Sales Incentives — Refer to Note 2 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
The Company provides retail discount or financing sales incentives programs to dealers that are due when the dealer sells the equipment to a retail customer.
The estimated cost of these programs is based on:
| ● | historical data, |
| ● | announced and expected incentive programs, |
| ● | field inventory levels, and |
| ● | forecasted sales volumes. |
At the time a sale is recognized, the Company records an estimate of the sales incentive costs. The final cost is determined at the time of the retail sale.
There are numerous programs available at any time, and new programs may be announced after the Company records the equipment sale to the dealer. Changes in the mix and types of sales incentive programs affect these estimates, which are reviewed quarterly. Actual cost differences from the original cost estimate are recognized in “Net sales.” A key assumption is the predictive value of the historical percentage of retail sales incentive costs to retail sales.
We identified the United States and Canada sales incentive accrual as a critical audit matter because estimating sales incentive costs requires significant judgment by management and changes in historical percentage of sales incentive costs to retail sales by dealers could have a material impact on the sales incentive accrual. Auditing management’s assumptions about the predictive nature of historical sales incentive costs involves a high degree of auditor judgment and an increased extent of effort to evaluate the reasonableness of management’s estimates.
79
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures related to testing management’s assumption that historical sales incentive costs are predictive of future incentive costs included the following, among others:
| ● | We tested the effectiveness of management’s controls over the assumptions used to estimate the sales incentive accrual. |
| ● | We evaluated management’s ability to accurately forecast future incentive costs by performing a retrospective review that involved comparing actual incentive costs to management’s historical forecasts. |
| ● | We tested the completeness of the population used in the accrual calculation by inspecting incentive program communications to dealers to ensure programs offered were appropriately included in the calculation. We tested the accuracy of sales incentives transactions by verifying amounts settled with dealers. |
| ● | We evaluated the reasonableness of management’s assumption that historical sales incentive costs are predictive of future incentive costs by: |
| o | Considering the impact of changes in the current economic conditions and competitive environment. |
| o | Comparing historical and current sales incentive data for eligible products in the following manner: |
| ◾ | Type and number of programs |
| ◾ | Geography |
| ◾ | Program size and duration |
Allowance for Credit Losses – Refer to Notes 2 and 11 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
The allowance for credit losses is an estimate of the credit losses expected over the life of the Company’s receivable portfolio. The allowance is measured on a collective basis for receivables with similar risk characteristics. Receivables that do not share risk characteristics are evaluated on an individual basis. Risk characteristics include:
| ● | finance product category, |
| ● | market, |
| ● | geography, |
| ● | credit risk, and |
| ● | remaining balance. |
The Company utilizes loss forecast models to estimate expected credit losses. Transition matrix models are used for large and complex retail customer receivable pools. These models are used for more than 90 percent of retail customer receivables. Historical portfolio performance and current delinquency levels are used to forecast future defaults. Estimated recovery rates are applied to the estimated default balance to calculate the expected credit losses.
The model output is adjusted for forecasted economic conditions, which may include the following economic indicators:
| ● | commodity prices, |
| ● | industry equipment sales, |
| ● | unemployment rates, and |
| ● | housing starts. |
Management reviews each model’s output quarterly, and qualitative adjustments are incorporated as necessary.
We identified the allowance for credit losses estimated for the Company’s United States and Canada receivable portfolios by the transition matrix models and related reasonable and supportable forecasts and qualitative adjustments as a critical audit matter because determining the appropriate methodology and assumptions used in the estimate requires significant judgment by management. Given the subjective nature and judgment applied by management to determine the allowance for credit losses, auditing the methodology and assumptions requires a high degree of auditor judgment and an increased extent of effort, including the need to involve credit specialists.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures to test the allowance for credit losses estimated for the Company’s United States and Canada receivable portfolios by the transition matrix models and related reasonable and supportable forecasts and qualitative adjustments included the following, among others:
| ◾ | We tested the effectiveness of management’s controls over the methodology, data and assumptions used to estimate the allowance for credit losses. |
| ◾ | We tested the accuracy and evaluated the relevance of the underlying historical data used in the Company’s transition matrix models. |
80
| ◾ | With the assistance of our credit specialists, we evaluated the reasonableness and accuracy of the transition matrix models used to estimate the allowance for credit losses, including model assumptions and the selection and application of relevant risk characteristics and use of qualitative adjustments. |
| ◾ | We evaluated qualitative adjustments to the model estimate. Our evaluation included: |
| o | Comparison of qualitative factors used by the Company to source data provided by the Company and/or to externally available data. |
| o | Consideration and evaluation of contradictory evidence. |
| ◾ | We evaluated management’s ability to accurately forecast credit losses by performing a retrospective review, which involved comparing actual credit losses to historical estimates. |
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
Chicago, Illinois
December 15, 2023
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1910.
81
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the stockholders and the Board of Directors of Deere & Company:
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Deere & Company and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of October 29, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of October 29, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended October 29, 2023 of the Company and our report dated December 15, 2023, expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
Chicago, Illinois
December 15, 2023
82
Index to Exhibits
3.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
3.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
Certain instruments relating to long-term debt constituting less than 10 percent of the registrant’s total assets are not filed as exhibits herewith pursuant to Item 601(b)(4)(iii)(A) of Regulation S-K. The registrant will furnish copies of such instruments to the Commission upon request. | ||
|
|
|
10.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
83
10.6† |
|
Deere & Company Voluntary Deferred Compensation Plan, as amended October 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
10.7† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.8† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.9† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.10† |
|
Form of Terms and Conditions for John Deere Nonqualified Stock Options granted fiscal 2023 |
|
|
|
10.11† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.12† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.13† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.14† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.15† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.16† |
|
Form of John Deere Restricted Stock Unit Grant for Directors granted fiscal 2023 |
|
|
|
10.17† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.18† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.19† |
|
John Deere Defined Contribution Restoration Plan, as amended October 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
10.20† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.21† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.22† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.23† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.24† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.25† |
|
Deere & Company Nonemployee Director Deferred Compensation Plan, as amended October 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
84
10.26† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.27† |
|
Incentive Compensation Recovery Policy effective August 29, 2023 |
|
|
|
10.28† |
|
|
|
|
|
10.29 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.30 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.31 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.32 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.33 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.34 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.35 |
|
|
|
|
|
21. |
|
|
|
|
|
22. |
|
List of Guarantors and Subsidiary Issuers of Guaranteed Securities |
|
|
|
23. |
|
|
|
|
|
24. |
|
|
|
|
|
31.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
31.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
32. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.INS |
|
Inline XBRL Instance Document (the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document) |
85
|
|
|
101.SCH |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
|
|
|
101.CAL |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
101.DEF |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
101.LAB |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
101.PRE |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
104. |
|
Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) |
* |
Incorporated by reference. |
† |
Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
86
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
DEERE & COMPANY |
|
|
|
|
By: |
/s/ John C. May |
|
|
John C. May |
|
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
|
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
Date: December 15, 2023
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the date indicated.
Each person signing below also hereby appoints John C. May, Joshua A. Jepsen, and Edward R. Berk, and each of them singly, his or her lawful attorney-in-fact with full power to execute and file any and all amendments to this report together with exhibits thereto and generally to do all such things as such attorney-in-fact may deem appropriate to enable Deere & Company to comply with the provisions of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and all requirements of the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Signature |
|
Title |
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Leanne G. Caret |
|
Director |
) |
|
December 15, 2023 |
Leanne G. Caret |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ Tamra A. Erwin |
|
Director |
) |
|
|
Tamra A. Erwin |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ Alan C. Heuberger |
|
Director |
) |
|
|
Alan C. Heuberger |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ Charles O. Holliday, Jr. |
|
Director |
) |
|
|
Charles O. Holliday, Jr. |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ L. Neil Hunn |
|
Director |
) |
|
|
L. Neil Hunn |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ Joshua A. Jepsen |
|
Senior Vice President and |
) |
|
|
Joshua A. Jepsen |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
) |
|
|
|
|
(Principal Financial Officer and Principal |
) |
|
|
|
|
Accounting Officer) |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ Michael O. Johanns |
|
Director |
) |
|
|
Michael O. Johanns |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ Clayton M. Jones |
|
Director |
) |
|
|
Clayton M. Jones |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
87
/s/ John C. May |
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
) |
|
|
John C. May |
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ Gregory R. Page |
|
Director |
) |
|
|
Gregory R. Page |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ Sherry M. Smith |
|
Director |
) |
|
|
Sherry M. Smith |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ Dmitri L. Stockton |
|
Director |
) |
|
|
Dmitri L. Stockton |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
/s/ Sheila G. Talton |
|
Director |
) |
|
|
Sheila G. Talton |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
88
Exhibit 10.6
DEERE & COMPANY
VOLUNTARY DEFERRED COMPENSATION PLAN
Adopted 28 August 1985
Amended 11 December 1986
Amended 26 May 1993 – Effective 1 July 1993
Amended 7 December 1994 – Effective 1 January 1995
Amended 4 December 1996 – Effective 1 January 1997
Amended 26 August 1998
Amended by Supplement 30 August 2006
Amended and Restated 13 2007 – Effective 1 January 2008
Amended 28 January 2014 – Effective 1 November 2013
Amended 30 October 2015 – Effective 1 November 2015
Amended 31 October 2016 – Effective 1 November 2015
Amended 31 October 2017 – Effective 1 November 2016
Amended 31 October 2018 – Effective 1 November 2017
Amended: 31 October 2019 – Effective 1 November 2018
Amended: 31 October 2020 – Effective 1 November 2019
Amended: 31 October 2021 – Effective 1 November 2020
Amended: 31 October 2022 – Effective 1 November 2021
Amended: 31 October 2023 – Effective 1 November 2022
(For special rules applicable to deferrals after 2004
see the supplement beginning on page 12)

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
SECTION 1. ESTABLISHMENT AND PURPOSE
SECTION 2. DEFINITIONS
SECTION 3. ELIGIBILITY FOR PARTICIPATION
SECTION 4. ELECTION TO DEFER
SECTION 5. DEFERRED ACCOUNTS
SECTION 6. PAYMENT OF DEFERRED AMOUNTS
SECTION 7. BENEFICIARY
SECTION 8. RIGHTS OF EMPLOYEES, PARTICIPANTS
i
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
SECTION 9. ADMINISTRATION
SECTION 10. AMENDMENT, MODIFICATION AND TERMINATION OF THE PLAN
SECTION 11. MERGER OR CONSOLIDATION
SECTION 12. REQUIREMENTS OF LAW
SECTION 13. WITHHOLDING TAXES
SECTION 14. EFFECTIVE DATE OF THE PLAN
SUPPLEMENT APPLICABLE TO DEFERRALS AFTER 2004
ii
DEERE & COMPANY
VOLUNTARY DEFERRED COMPENSATION PLAN
-1-
-2-
-3-
Notwithstanding amounts elected by the Participant for deferral from the John Deere Performance Bonus Plan award, the total deferred portion shall not be less than $1,000 in any given calendar year. In the event the total deferred amount is less than $1,000, it shall be paid pursuant to the normal payout schedule for the John Deere Performance Bonus Plan.
Amounts of less than $1,000 per calendar quarter shall not be deferred from salary.
In all other cases, the distribution must begin on a date specified by the Participant in the election (whether the distribution is scheduled to begin before or after the date of retirement) but no later than ten years following the date of retirement. The Participant may elect to have distribution made in up to ten annual installments from the date distribution is to begin, but such distribution must be completed within ten years following retirement.
If the Participant wishes to designate a distribution after retirement, the Participant may designate in the election that distribution shall begin at retirement or begin at a specified point in time, or during a specified month, following the date of retirement, (Example #1: Distribution to begin three months after retirement.
-4-
Example #2: Distribution to begin the January of the year following retirement.)
-5-
-6-
-7-
acquires a right to receive payments under this Plan, such right shall be no greater than the right of any unsecured general creditor of the Company.
as long as the amount distributed shall not be in excess of that amount which is necessary for the Participant to meet the financial hardship.
Severe financial hardship will be deemed to have occurred in the event of the Participant's impending bankruptcy, a dependent's long and serious illness, other events of similar magnitude or the invalidation of a deferral election by the Internal Revenue Service. The Committee's decision in passing on the severe financial hardship of the Participant and the manner in which, if at all, the payment of deferred amounts shall be altered or modified shall be final, conclusive and not subject to appeal.
-8-
death, and any distributions remaining upon the beneficiary's death shall be made to the beneficiary's estate.
A Participant may from time to time during his lifetime change his beneficiary or beneficiaries on file with the Recordkeeper. In the event a Participant shall not designate a beneficiary or beneficiaries pursuant to this Section, or if for any reason such designation shall be ineffective, in whole or in part, the distribution that otherwise would have been paid to such Participant shall be paid to his estate and in such event, the term “beneficiary” shall include his estate.
-9-
determination of the Committee, interpretation or other action made or taken pursuant to the provisions of the Plan, shall be final and shall be binding and conclusive for all purposes and upon all persons.
-10-
Amounts calculated under either (a) or (b) above shall be paid in full as soon as practicable following any termination of the Plan.
-11-
-12-
SUPPLEMENT TO
DEERE & COMPANY
VOLUNTARY DEFERRED COMPENSATION PLAN
APPLICABLE TO AMOUNTS DEFERRED AFTER DECEMBER 31, 2004
The following provisions will apply only to amounts deferred under the Plan after December 31, 2004 and not to amounts deferred under the Plan that were both earned and vested before January 1, 2005. Amounts deferred under the Plan prior to January 1, 2005 will be subject to the terms of the Plan without regard to this supplement. Except to the extent amended hereby, the terms of the Plan shall continue to apply to amounts deferred pursuant to the Plan.
1.The following definitions are added to Section 2 (Definitions).
2.1(b) |
“Change in Control Event” means a change in ownership, a change in effective control, or a change in the ownership of a substantial portion of the assets of the Company within the meaning of the default rules under Section 409A. |
2.1(e) |
“Disability” means a participant is unable to engage in any substantial gainful activity by reason of any medically determinable physical or mental impairment which can be expected to result in death or can be expected to last for a continuous period of not less than 12 months or is, by reason of any medically determinable physical or mental impairment which can be expected to result in death or can be expected to last for a continuous period of not less than 12 months, receiving income replacement benefits for a period of not less than 3 months under a disability or an accident and health plan covering employees of the Company. |
2.1(i) |
“Retirement” means a Separation from Service by a Participant who is then eligible for a normal retirement benefit or an early retirement benefit within the meaning of the terms of the John Deere Pension Plan for Salaried Employees in effect as of 1 January 2007. |
2.1(j) |
“Section 409A” means Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code and the regulations and other guidance thereunder. |
2.1(k) |
“Section 409A Compliance” shall have the meaning ascribed to such term in Section 8.3. |
2.1(l) |
“Separation from Service” means, with respect to a Participant, a separation from service within the meaning of the default rules of Section 409A; provided that for purposes of determining which entities are treated as a single “service recipient” with the Company, the phrase “at least 20 percent” shall be substituted for the phrase “at least 80 percent” each place it appears in |
-13-
Sections 1563(a)(1), (2) and (3) of the Code and Section 1.414(c)-2 of the Treasury Regulations, as permitted under Section 1.409A-1(h)(3) of the Treasury Regulations
2.1(n) |
“Unforeseeable Emergency” means a severe financial hardship to the Participant resulting from (i) an illness or accident of the Participant or his spouse, dependent (within the meaning of Section 152 of the Code, but without giving effect to Section 152(b)(1), (b)(2) and (d)(1)(B) (“Dependent”)), (ii) the loss of the Participant’s property due to casualty (including the need to rebuild a home following damage to a home not otherwise covered by insurance, for example, not as a result of a natural disaster), (iii) the imminent foreclosure of or eviction from the Participant’s primary residence, (iv) the need to pay for medical expenses, including non-refundable deductibles, as well as for the costs of prescription drug medication, (v) the need to pay for the funeral expenses of a spouse, Dependent or beneficiary, or (vi) other similar extraordinary and unforeseeable circumstances arising as a result of events beyond the control of the Participant. The purchase of a primary residence and the payment of college tuition shall not constitute Unforeseeable Emergencies. |
2. Subsections 2.1(b) and (c) are renumbered as 2.1(c) and (d), respectively.
3.Subsection 2.1(d) is renumbered as 2.1(f).
4.Subsection 2.1(e) is renumbered as 2.1(h).
5.Subsection 2.1(f) is renumbered as 2.1(m).
6.Section 4 (Election to Defer) is restated in its entirety as follows:
4.1Deferral Amount
(a) |
Any Participant may elect to defer any part (in 5% increments up to 95%) of an award to be paid under the provisions of the John Deere Short-Term Incentive Bonus Plan. Such election must be made in writing prior to the beginning of the Fiscal Year upon which the award is based. Notwithstanding the Participant's election, enough of the award must be paid in cash to cover all withholding taxes. If not, the Company shall be authorized to reduce the Participant's elected deferral in such amount as is necessary to satisfy all applicable withholding taxes. |
(b) |
Any Participant may elect to defer any part (in 5% increments up to 70%) of base salary beginning with the first calendar quarter of each year. Such election must be made in writing prior to the beginning of the calendar year in which the deferrals are to commence and shall |
-14-
remain in effect for the remainder of the calendar year. Notwithstanding the Participant's election, enough salary must be paid in cash to cover all withholding taxes. If not, the Company shall be authorized to reduce the Participant's elected deferral in such amount as is necessary to satisfy all applicable withholding taxes, and the reduced deferral percent shall remain in effect until the beginning of the next pay period, at which time it shall revert to the Participant's stated deferral percent subject to the same reduction potential.
(c) |
Any Participant may elect to defer any part (in 5% increments up to 95%) of any other cash incentive award that is authorized by the Committee to be deferred pursuant hereto. Such election must be in writing (i) in the case of non-performance-based compensation or compensation for services performed for less than 12 months, not later than the close of the Participant’s taxable year preceding the taxable year in which services related to the award are performed; or (ii) in the case of performance-based compensation (as determined by the Committee pursuant to Section 409A) based on services performed over a period of at least 12 months, prior to the close of the Fiscal Year immediately preceding the calendar year of payment but in no event later than 6 months before the end of the performance period. Notwithstanding the Participant's election, enough of the award must be paid in cash to cover all withholding taxes. If not, the Company shall be authorized to reduce the Participant's elected deferral in such amount as is necessary to satisfy all applicable withholding taxes. |
(d) |
Any Participant that first becomes eligible to participate in the Plan during a calendar year may, within thirty days following the Participant’s earliest eligibility date, irrevocably elect to defer the compensation described in Sections 4.1(a) – (c) to the extent that the compensation is attributable to services performed after the effective date of the deferral election. The effective date of the deferral election described in the preceding sentence shall be the first day of the month immediately following the date that is thirty days after the Participant’s earliest eligibility date. |
4.2 |
Deferral Period and Payment Method. If the Participant defers any amount pursuant to Section 4.1, the Participant shall also designate the period and payment method for the deferral in the election. The Participant may elect to have distribution made in a lump sum or in up to ten annual installments, provided that the payments must in either case be completed within (i) ten years following the year to which the deferral relates, with respect to an election made on or after October 1, 2022 to designate a specific date for the |
-15-
commencement of payment or (ii) ten years following the year of Retirement, with respect to an election to designate the commencement of payment upon or following Retirement. Payments of the deferral amounts, plus any Investment Return thereon, shall commence on the first business day of the calendar quarter specified by the Participant in the election; provided, however, that if the Participant elects for the distribution to begin after Retirement, payment of the deferral amounts, plus any Investment Return thereon, shall commence on the first business day of the third or later calendar quarter (as elected by the Participant) following the calendar quarter of Retirement.
Notwithstanding the Participant’s deferral election, if death, Disability or Separation from Service occurs before Retirement, all remaining deferrals plus any Investment Return, shall be distributed as a single lump sum payment in January of the calendar year following the date of such death, Disability or Separation from Service. Additionally, no distribution upon Separation from Service (including upon Retirement or other termination but excluding upon Disability or death) may be made before the first business day of the first calendar quarter that begins at least six (6) months after such Participant’s date of Separation from Service, or, if earlier, the date of the Participant’s death, and any distribution that would be made but for application of this provision shall instead be aggregated with, and paid together with, the first distribution scheduled to be made after the end of such six-month period (or, if earlier, the date of the Participant’s death).
4.3 |
Irrevocable Elections. The elections in Sections 4.1 and 4.2 shall become irrevocable on the day prior to the beginning of the Fiscal Year or calendar year, as applicable, and may not be modified or terminated with respect to such Fiscal Year or calendar year by the Participant or his beneficiary. Elections that provide for distributions to begin after Retirement (but not elections that provide for distributions to begin in a calendar quarter specified by the Participant) shall also apply to each succeeding Fiscal Year or calendar year, as applicable, until such election is modified or terminated as provided in the following sentence. A Participant may modify or discontinue such deferrals, or may change his or her investment choices, for future Fiscal Years or calendar years by providing an irrevocable written election delivered to the Company not later than the close of the Fiscal Year or calendar year preceding the Fiscal Year or calendar year in which the changes are to take effect. Elections that provide for distributions to begin in a calendar quarter specified by the Participant shall apply only to amounts deferred during the Fiscal Year or calendar year with respect to which such election is made. Notwithstanding anything in this Section 4.3 to the contrary, the deferral elections described in Section 4.1(d) shall become irrevocable on the 30th day following the Participant’s earliest eligibility date. |
-16-
7.Subsection 5.1 (Deferred Accounts - Participant Accounts) is amended by changing the phrase “John Deere Equity Incentive Plan” to “John Deere Mid-Term Incentive Bonus Plan”.
8.Subsection 6.2 (Payment of Deferred Amounts - Unforeseeable Emergency) is restated in its entirety as follows:
6.2 |
Unforeseeable Emergency. The Committee, at its sole discretion, may alter the timing or manner of payment of deferred amounts in the event that the Participant establishes, to the satisfaction of the Committee, the occurrence of an Unforeseeable Emergency. In such event, the Committee may: |
(a) |
provide that all or a portion of the amount previously deferred by the Participant shall be paid immediately in a lump sum cash payment, or |
(b) |
provide that all or a portion of the installments payable over a period of time shall be paid immediately in a lump sum, |
as long as, as determined under regulations of the Secretary of the United States Treasury, the amount distributed shall not be in excess of that amount which is reasonably necessary to satisfy the Unforeseeable Emergency (which may include amounts necessary to pay taxes reasonably anticipated as a result of such distribution(s)), after taking into account the extent to which such hardship is or may be relieved through reimbursement or compensation by insurance or otherwise, or by liquidation of the Participant’s assets to the extent liquidation of such assets would not cause severe financial hardship, or by cessation of deferrals under the Plan and any other plan that would be aggregated with the Plan for purposes of Section 409A. If a Participant requests and receives a distribution on account of Unforeseeable Emergency, the Participant’s deferrals under the Plan shall cease and his elections under the Plan shall be canceled. Any new deferral election following cancellation of a prior deferral election due to Unforeseeable Emergency shall be subject to the timing requirements of Sections 4.1 and 4.2 and Section 409A.
The Committee's decision in passing on the occurrence of an Unforeseeable Emergency for the Participant and the manner in which, if at all, the payment of deferred amounts shall be altered or modified shall be final, conclusive and not subject to appeal.
9. Subsection 8.3 (Rights of Employees, Participants - No Acceleration of Distributions) is added as follows:
8.3 |
No Acceleration of Distributions. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary herein, this Plan does not permit the acceleration of the time or schedule of |
-17-
any distribution under the Plan, except as would not result in the imposition on any person of additional taxes, penalties or interest under Section 409A.
10.Section 10.1 (Amendment, Modification and Termination of the Plan) is amended by adding thereto:
“If the Plan is terminated, the Participant’s account shall be paid in accordance with time and form of payment otherwise specified hereunder, provided that the Board of Directors or the Committee, in its discretion and in full and complete settlement of the Company’s obligations under this Plan, may cause the Company to distribute the full amount of a Participant’s account to the Participant in a single lump sum to the extent that such distribution may be effected in a manner that will not result in the imposition on any person of additional taxes, penalties or interest under Section 409A.”
In addition, there is added immediately following Section 10.1 a new Section 10.2 (Section 409A Amendments) as follows:
“10.2Section 409A Amendments. Notwithstanding any provision in this Plan to the contrary the Board, the Committee or the Vice President of Human Resources of the Company shall have the unilateral right to amend or modify the Plan to the extent the Board, the Committee or the Vice President of Human Resources of the Company deems such action to be necessary or advisable to avoid the imposition on any person of adverse or unintended tax consequences under Section 409A, including recognition of income in respect of any benefits under this Plan before such benefits are paid or the imposition of additional taxes, penalties or interest. Any determinations made by the Board, the Committee, or the Vice President of Human Resources of the Company under this Section 10.2 shall be final, conclusive and binding on all persons.”
11.Section 11 (Merger or Consolidation) is restated in its entirety as follows:
Section 11. Change in Control
11.1 |
Change in Control. If the Company shall experience a Change in Control Event, the Committee may: |
(a) |
terminate the Plan and all other plans of the same type that would be aggregated with the Plan under Section 409A within the twelve months following the Change in Control Event, and all amounts deferred, plus interest additions shall be distributed in full as soon as practicable, but in no event later than twelve months, following the date the aggregated plans are terminated, notwithstanding any other provisions to the contrary; or |
-18-
(b) |
permit the Plan to continue, making any necessary adjustments or modifications to reflect any impact of the Change in Control Event, as determined by the Committee; provided that such adjustments or modifications do not result in the imposition on any person of additional taxes, penalties or interest under Section 409A. |
-19-
SCHEDULE A
Notional Investment Options
BTC LIFEPATH RET G
BTC LIFEPATH 2025 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2030 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2035 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2040 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2045 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2050 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2055 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2060 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2065 G
S & P 500 STOCK INDEX, CLASS F
SMALL/MID STOCK INDEX, CLASS F
INTERNATIONAL STOCK INDEX, CLASS F
U.S. TIPS BOND INDEX, CLASS F
U.S. BOND INDEX, CLASS F
COMMODITY INDEX, CLASS F
REAL ESTATE INDEX, CLASS F
FIDELITY GROWTH COMPANY COMMINGLED POOL CLASS #3
BOSTON PARTNERS LARGE CAP VALUE FUND SHARE CLASS E
QMA US SMALL CAP CORE EQUITY FD CL
INTERNATIONAL STOCK INDEX CLASS F (Replaced on December 17,2020)
-20-
U.S. EQUITY FUND (effective November 1, 2023
ALLSPRING EMERGING MARKETS EQUITY CIT E2
CIT-ALLSPRING ENHANCED CORE BOND E2
FIDELITY® INVESTMENTS MONEY MARKET FUNDS GOVERNMENT PORTFOLIO INSTITUTIONAL CLASS
-21-
Exhibit 10.10
JOHN DEERE STOCK OPTIONS
Terms and Conditions
Granted [Date]
(Nonqualified)
Vesting
These stock options will become exercisable over a three-year period with 34% becoming exercisable one year after the grant date and 33% becoming exercisable on each of the second and third years after the grant date. Vesting is accelerated upon retirement or disability (each as defined under the John Deere 2020 Equity and Incentive Plan (Plan)), allowing you to exercise these stock options six months after the grant date. If you die while actively employed, the entire stock option amount will be exercisable immediately by your beneficiaries or heirs.
Expiration
These stock options will expire ten years after the grant date. If you retire on or before October 31, ____, a prorated number of these stock options will be forfeited based on the percentage determined by dividing: (i) the number of calendar months from and including the month of retirement pursuant to applicable Company plans to and including October _____; by (ii) 12. Subject to the preceding sentence, if you retire or become disabled (as defined under the Plan), you or your beneficiaries or heirs, as the case may be, can exercise these stock options within five years of separation or ten years from the date of grant, whichever comes first. If you die after retirement or becoming disabled, the exercise period may be extended to one year from date of death. If you die while actively employed, your beneficiaries or heirs can exercise these stock options within one year after the date of death or ten years from the date of grant, whichever comes first. Stock options will be cancelled upon the date of termination of employment for reasons other than death, disability or retirement. Stock options are subject to being suspended and terminated if your employment is suspended or you are placed on a leave of absence. Regardless of the circumstance, all unexercised stock options will expire ten years from the date of grant.
Calculation
The option price of your grant is the closing price of Deere & Company common stock on the New York Stock Exchange at the conclusion of regular trading hours on the date of grant.
Expenses
Commissions, fees, and other expenses connected with the exercise and sale of this stock option grant are payable by you. No commissions or fees are charged if you purchase and hold the shares.
Procedures
Stock options are currently exercised through Fidelity. Information regarding the exercise process is available via the Internet at ________ or by calling __________in the U.S. Toll-free codes for calling from outside the U.S. can be accessed via the Internet at ____________.
Non-transferability
You may not voluntarily or involuntarily sell, transfer, gift, pledge, assign or otherwise alienate the stock options, including but not limited to transfers related to estate planning, dissolution of marriage, collection, execution, attachment, and any other voluntary or involuntary transfer. Any attempt to do so contrary to the provisions hereof shall be null and void.
Plan Information
These stock options were granted under and are subject to the terms of the Plan, for which a prospectus is available at _____________. Any inconsistencies between these terms & conditions and the Plan shall be resolved in accordance with the terms of the Plan. A paper copy of the prospectus is also available upon request from Deere & Company Global Compensation, One John Deere Place, Moline, Illinois, 61265-8098. The latest Deere & Company Annual Report and Proxy Statement are available electronically at http://www.deere.com/stock or in hard copy upon request from Deere & Company Investor Relations.
[Type here]
Beneficiary Form
The Plan (the John Deere 2020 Equity and Incentive Plan) was approved in February 2020. Grants under this Plan require a new Beneficiary Designation Form and are not covered by a Beneficiary Designation Form for the prior John Deere Omnibus Equity and Incentive Plan. Beneficiary Designation Forms for completing and returning to Fidelity are available at:
United States Participants:
Outside the United States Participants:
Your beneficiary designations for the Plan will remain in effect until changed by you and will apply to this and all future grants under the Plan.
Agreement
Due to a recent change in Illinois law, the non-compete clause in our terms and conditions requires Deere to inform you of the right to consult an attorney prior to accepting your grant(s). You are not required to accept your grant(s) until 14 days after receiving this message. You will be considered to have agreed to the terms and conditions of this grant, including the non-compete and consulting obligations described in Section 8.2 of the Plan, if you have not notified Deere & Company of any issues or problems within 150 days of the date of this notification.
Grants are made by and at the discretion of the Deere & Company Board of Directors Compensation Committee. This grant does not:
By agreeing to the terms hereof, you agree also to the collection, processing and transfer of personal data to and from plan administrators, banks, brokers and government agencies as necessary for grant administration.
Additional Terms Applicable to Participants in Salary Grade 19 and Above
You will be considered to have agreed to the terms of the Executive Incentive Award Recoupment Policy if you have not notified Deere & Company of any issues or problems within thirty days of the date of this notification.
Additional Terms Applicable to Participants in India
At the time of each stock option exercise you acknowledge and confirm that:
| ● | the exercise is for your own account and you are not acting on behalf of, or as agent for, any other person; |
| ● | you have been informed of the conditions that must be met to benefit from the stock options and declare that you qualify for the benefits; |
| ● | the exercise is final and irrevocable; |
| ● | you will ensure and be solely responsible for providing all necessary documentation for the purpose of any action under the Plan; |
| ● | your employer is offering the services to arrange for the remittance of exercise amounts only for your convenience and is not responsible for liability of any kind related to such services; and |
| ● | the exercise will be invalid if any of your representations are incorrect. |
Exhibit 10.11

Deere & Company
One John Deere Place, Moline, Illinois 61265 USA
JOHN DEERE RESTRICTED STOCK UNITS AND PERFORMANCE STOCK UNITS
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
GRANTED [Date] (“Grant Date”)
Deere & Company Restricted Stock Equivalents (also known as Restricted Stock Units) (“RSUs”) and Performance Stock Units (“PSUs”) are granted pursuant to the John Deere 2020 Equity and Incentive Plan (“Plan”). These terms and conditions (“Terms”), together with the Plan, contain the terms of your grant. You should read these Terms carefully. While you will be provided with at least 14 days to review and consider these Terms, please note that for the award to fully vest, you are required to actively accept the award and agree to these Terms by doing so on the Fidelity administration website (____________) prior to the RSUs and PSUs being converted to shares of Common Stock. Failure to actively accept the award and Terms will result in the award being forfeited.
RSUs and PSUs are elements of total executive compensation designed as long-term incentives to encourage ownership and focus on stockholder value.
RSUs and PSUs are common stock equivalents and represent the right to receive an equivalent number of shares of Deere & Company (“Company”) $1 par common stock (“Common Stock”) if and when certain vesting, performance and retention requirements, as detailed below, are satisfied.
Individual awards are determined by the Deere & Company Board of Directors Compensation Committee (“Committee”).
Due to a recent change in Illinois law, the non-compete clause in our Terms requires Deere to inform you of the right to consult an attorney prior to accepting your grant(s).
Your RSUs and PSUs are subject to the following provisions:
(1) |
Vesting Period. Except as provided in section (5) below and subject to your acceptance of these Terms, your RSUs will vest over three years with 34% of the RSUs vesting on the first anniversary of the Grant Date, 33% of the RSUs vesting on the second anniversary of the Grant Date, and 33% of the RSUs vesting on the third anniversary of the Grant Date (each, an “RSU Vesting Date”), subject to your continued employment through the applicable RSU Vesting Date. Except as provided in section (5) below and subject to your acceptance of these Terms, your PSUs will vest on the third anniversary of the Grant Date (“PSU Vesting Date”), subject to your continued employment through the PSU Vesting Date. The number of PSUs that vest, if any, will be determined based on the Company’s performance relative to the metrics described in section (2) below, as determined by the Committee. The period beginning on the Grant Date and ending on the third anniversary thereof is referred to as the “Vesting Period”. |
Within five days following the applicable RSU Vesting Date or PSU Vesting Date, as applicable, you will receive a number of shares of Common Stock equal to the number of your vested RSUs and vested PSUs, as applicable (in each case net of any shares of Common Stock withheld for taxes), and such vested RSUs and vested PSUs will terminate.
If you have not met your stock ownership guideline requirements at the time of the conversion, you are required to continue to hold the shares of Common Stock (net of any shares withheld for taxes) received upon conversion of your vested RSUs and PSUs until your stock ownership guidelines are met.
Stock ownership guidelines currently apply to salary grades 16 and above. In order to help meet ownership requirements, you can elect to pay the withholding taxes on your award in cash by contacting the Executive Compensation by no later than 14 days prior to the applicable RSU Vesting Date or PSU Vesting Date, as applicable.
You may not voluntarily or involuntarily sell, transfer, gift, pledge, assign or otherwise alienate the RSUs or PSUs, including but not limited to transfers related to estate planning, dissolution of marriage, collection, execution, attachment, and any other voluntary or involuntary transfer. Any attempt to do so contrary to the provisions hereof shall be null and void.
(2) |
Performance Metrics for PSUs. |
A. |
Relative Revenue Growth. The payout for your PSUs will be determined based on the Company’s compounded annual growth rate of revenues during the three-year performance period beginning on the first day of the Company’s 2023 fiscal year and ending on the final day of the Company’s 2025 fiscal year (“Performance Period”) relative to the revenue growth for the performance peer group as it is comprised on 15 November 2025 (“Comparator Group”). Revenue growth for a company will be calculated by dividing (i) total net sales and revenues on a consolidated basis as reported (“Revenues”) for the final year of the Performance Period by (ii) Revenues for the year prior to the start of the Performance Period; raising the quotient to the one-third power; then subtracting one from the result. For members of the Comparator Group, Revenues for a year are based on the last four quarters of data available from the Company’s independent data service as of 15 November 2025. Comparator Group companies will be approved by the Committee. |
| B. | Payout Table. The number of PSUs vested and converted to shares of Common Stock can range from zero to two hundred percent of the number of PSUs granted depending on relative performance as described in section (2)(A) according to the following table. Amounts for interim points will be interpolated. |
Revenue Growth vs. |
Percent of PSU Grant Vested |
Below 25th percentile |
0% |
At 25th percentile |
25% |
At 50th percentile |
100% |
At or above 75th percentile |
200% |
(3)Voting Rights. You have no voting rights with respect to the RSUs or PSUs.
(4) |
Dividends and Other Distributions. You are entitled to receive cash payments on your RSUs equal to any cash dividends paid with respect to the corresponding number of shares of Common Stock from the Grant Date until the date the vested RSUs are converted to Common Stock. Dividend equivalents shall be accrued and paid in cash at the time the vested RSUs are converted to Common Stock. If any RSUs are forfeited, the corresponding cash dividend equivalents will also be forfeited. You are not entitled to receive cash payments on the PSUs for any cash dividends paid during the Vesting Period with respect to the Common Stock. If shares of Common Stock are withheld for taxes, the number of RSUs on which dividend equivalents are accrued and paid shall be reduced by the number of shares withheld. If any stock splits or stock dividends are paid in shares of |
2
Common Stock before the RSUs and PSUs are converted to Common Stock, you will receive additional RSUs or PSUs equal to the number of Common Stock shares paid with respect to the corresponding number of shares of Common Stock. These additional RSUs and PSUs will convert to shares of Common Stock at the same time as the underlying RSUs or PSUs to which they relate.
(5) |
Termination of Employment. |
| A. | Retirement on or Before October 31, [year]. In the event of your termination of employment due to retirement pursuant to the John Deere Pension Plan for Salaried Employees or any successor or similar plan of the Company or its Subsidiaries (“Retirement”) on or before October 31, [year], you will forfeit a prorated number of your RSUs and PSUs equal to the product resulting from the total number of your RSUs and/or your PSUs, as applicable, multiplied by the percentage determined by dividing: (i) the number of calendar months from and including the month of Retirement, to and including October 2023; by (ii) 12. In such event, the number of PSUs vested and converted to shares can range from zero to two hundred percent of the number of non-forfeited PSUs depending on relative performance according to section (2) above. |
| B. | Retirement: RSUs. In the event of your Retirement before the RSUs are fully vested, then, subject to section (5)(A) above and sections (6) and (7) below: (i) your unvested RSUs will vest on the date of your Retirement; and (ii) such vested RSUs will be converted into shares of Common Stock following the applicable RSU Vesting Dates as set forth in section (1). |
| C. | Disability or Death: RSUs. In the event of your disability under the John Deere Long-Term Disability Plan for Salaried Employees or any successor or similar plan of the Company (“Disability”) or death before the RSUs are fully vested, then, subject to the section (5)(A) and sections (6) and (7) below: (i) your unvested RSUs will vest on the date of your Disability or death, as applicable; and (ii) your RSUs will be converted into shares of Common Stock following the applicable RSU Vesting Dates as set forth in section (1). |
| D. | Retirement, Disability or Death: PSUs. In the event of your Retirement, Disability, or death, during the Vesting Period then, subject to section (5)(A) above and sections (6) and (7) below, your unvested PSUs will continue to vest over the Vesting Period and, depending on the performance of the Company relative to the metrics described in section (2) above, will be converted into shares of Common Stock following the PSU Vesting Date as set forth in section (1). |
| E. | Other Terminations. If you terminate employment with the Company and its 50 percent or greater owned Subsidiaries during the Vesting Period due to your termination for cause or for any other reasons not specifically mentioned herein, all unvested RSUs and PSUs held by you at that time shall be forfeited along with any accrued dividend equivalents. RSUs and PSUs and accrued dividend equivalents are subject to forfeiture if your employment is suspended or you are placed on a leave of absence. |
The Committee may, at its sole discretion, waive any automatic forfeiture provisions or apply new restrictions to the RSUs or PSUs. There shall be no acceleration of the lapse of restrictions except as would not result in the imposition on any person of additional taxes, penalties, or interest under Section 409A of the Code or by regulations of the Secretary of the United States Treasury.
3
(6) |
Non-Compete Condition. In the event that your employment terminates during the Vesting Period with the consent of the Committee or by reason of Retirement or Disability, your rights to receive shares of Common Stock in respect of your vested or unvested RSUs and continued vesting of the PSUs shall be subject to the conditions that until the RSUs and PSUs, as applicable, are converted to shares of Common Stock, you shall (a) not engage, either directly or indirectly, in any manner or capacity as advisor, principal, agent, partner, officer, director, employee, member of any association or otherwise, in any business or activity which is at the time competitive with any business or activity conducted by the Company and (b) be available, except in the event of your death or incapacity, at reasonable times for consultations (which shall not require substantial time or effort) at the request of the Company's management with respect to phases of the business with which you were actively connected during employment, but such consultations shall not (except if your place of active service was outside of the United States) be required to be performed at any place or places outside of the United States of America or during usual vacation periods or periods of illness or other incapacity. In the event that either of the above conditions is not fulfilled, you shall forfeit all rights to any vested or unvested RSUs and/or PSUs and related dividend equivalents on the date of the breach of the condition. Any determination by the Committee, which shall act upon the recommendation of the Chairman, that you are, or have, engaged in a competitive business or activity as aforesaid or have not been available for consultations as aforesaid shall be conclusive. |
(7) |
Executive Incentive Compensation Recoupment Condition. This award and prior and future Incentive Compensation (as defined in the Policy) is subject to and conditioned on your agreement to the terms of the Company’s Executive Incentive Compensation Recoupment Policy, as amended from time to time, or any successor policy thereto (“Policy”). |
(8) |
No Employment Rights. Nothing herein confers any right or obligation on you to continue in the employ of the Company or any Subsidiary, nor shall this document affect in any way your right or the right of the Company or any Subsidiary, as the case may be, to terminate your employment at any time. Nothing herein creates an employment agreement or becomes part of remuneration for purposes of determining other benefits. Receipt of this award does not entitle you to any future awards or other considerations even if the Committee decides to continue making such awards to other employees. |
(9) |
Change of Control Events. For purposes of Article VII of the Plan as it applies to the RSUs and PSUs hereby awarded, notwithstanding the definitions in Article VII, a “Change of Control” shall have the meanings assigned to “Change in Control Events” under Section 409A of the Code and related regulations of the Secretary of the United States Treasury. Article VII of the Plan shall be administered with respect to the RSUs and PSUs so that it complies in all respects with Section 409A and related regulations. Upon a Change of Control and a Qualifying Termination, as defined in accordance herewith, unvested PSUs will be cashed out assuming the Company performance metric applied in section (2) is 100% and based of the Change of Control Price measured on the date of the Change of Control. |
(10) Severability. If all or any part of these Terms or the Plan is declared by any court or governmental authority to be unlawful or invalid, such unlawfulness or invalidity shall not invalidate any portion of these Terms or the Plan not declared to be unlawful or invalid. Any part of these Terms so declared to be unlawful or invalid shall, if possible, be construed in a manner that will give effect to the terms thereof to the fullest extent possible while remaining lawful and valid. To the extent a court of competent jurisdiction determines that the non-compete condition set forth in paragraph (6) of these Terms is overly broad in duration or scope, the parties expressly agree that the court may modify paragraph (6) so as to comply with applicable law.
4
(11) Amendment. These Terms may be amended only by a writing executed by the Company and you that specifically states that it is amending these Terms. Notwithstanding the foregoing, these Terms may be amended solely by the Committee by a writing which specifically states that it is amending these Terms, so long as a copy of such amendment is delivered to you, and provided that no such amendment adversely affecting your rights hereunder may be made without your written consent. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the Committee reserves the right to change, by written notice to you, the provisions of the RSUs, PSUs or these Terms in any way it may deem necessary or advisable (i) to carry out the purpose of the grant as a result of any change in applicable laws or regulations or any future law, regulation, ruling, or judicial decision, (ii) to ensure that you are not required to recognize taxable income with respect to your RSUs and PSUs prior to the time that they are converted into shares of Common Stock and are not subject to any additional taxes, penalties, or interest under Section 409A of the Code or (iii) to exercise the Committee’s discretion to eliminate or decrease the amount of the award as reserved in the Plan; provided that any such change shall be applicable only to RSUs and PSUs which are then subject to restrictions as provided herein.
(12) Consent to Personal Data. By agreeing to the terms hereof, you also agree to the collection, processing, use and worldwide transfer of your personal data to and from Deere & Company and its Subsidiaries, banks, brokers, plan servicers, grant administrators and government agencies as necessary for grant and Plan administration.
(13) Withholding Tax Election. Upon conversion of RSUs and PSUs to Common Stock, the default election will be to withhold whole shares of stock to be issued upon the conversion and applied to the required withholding taxes. In order to help meet ownership requirements, you can elect to pay the withholding taxes on your award in cash by contacting the Executive Compensation by no later than 14 days prior to the applicable RSU Vesting Date or PSU Vesting Date, as applicable. In the event the RSU or PSU award becomes subject to withholding taxes prior to the conversion date, the Company may either (i) withhold RSUs and apply their value to the required withholding taxes and any additional withholding taxes created by the withholding or (ii) withhold payroll due to the Participant and apply it to the required withholding taxes.
.
(14) Expenses. Commissions, fees, and other expenses connected with the sale of shares following conversion of the RSUs and PSUs are payable by you. No commissions or fees are charged for holding the RSUs and PSUs and shares in the 3rd party service provider brokerage account.
(15) Conformity with Plan. Your award is issued pursuant to Article III (Performance Shares and Units) and Article IV (Restricted Stock and Restricted Stock Equivalents) of the Plan and is intended to conform in all respects with the Plan. Inconsistencies between these Terms and the Plan shall be resolved in accordance with the terms of the Plan. By accepting this award, you agree to be bound by all the terms of the Plan and these Terms. All definitions stated in the Plan shall be fully applicable to these Terms. A Plan prospectus is available at the Plan Administrator website. A paper copy of the prospectus is also available upon request from Deere & Company Global Compensation, One John Deere Place, Moline, Illinois 61265 or by contacting ExecComp@JohnDeere.com.
5
(16) Beneficiary. The Plan (the John Deere 2020 Equity and Incentive Plan) was approved in February 2020. Grants under this Plan require a new Beneficiary Designation Form and are not covered by a Beneficiary Designation Form for the prior John Deere Omnibus Equity and Incentive Plan. Beneficiary Designation Forms for completing and returning to Fidelity are available at:
United States Participants:
Outside the United States Participants:
Your beneficiary designations for the Plan will remain in effect until changed by you and will apply to this and all future grants under the Plan.
(17) Section 409A. This grant of RSUs and PSUs is intended to be exempt from or comply with the applicable requirements of Section 409A of the Code and shall be administered in accordance with Section 409A of the Code. Notwithstanding anything in these Terms to the contrary, if the RSUs or PSUs constitute “deferred compensation” under Section 409A of the Code and the RSUs or PSUs become settled upon your separation from service, payment with respect to the RSUs shall be delayed for a period of six months after your separation from service if you are a “specified employee” as defined under Section 409A of the Code (as determined by the Committee), if required pursuant to Section 409A of the Code. If payment is delayed, the shares of Common Stock shall be distributed within 30 days of the date that is the six-month anniversary of your termination of employment. If you die during the six-month delay, such shares shall be distributed in accordance with your will or under the applicable laws of descent and distribution. Notwithstanding any provision to the contrary herein, payments made with respect to this grant of RSUs and PSUs may only be made in a manner and upon an event permitted by Section 409A of the Code, and all payments to be made upon a termination of employment hereunder may only be made upon a “separation from service” as defined under Section 409A of the Code. To the extent that any provision of these Terms would cause a conflict with the requirements of Section 409A of the Code, or would cause the administration of the RSUs or PSUs to fail to satisfy the requirements of Section 409A of the Code, such provision shall be deemed null and void to the extent permitted by applicable law. In no event shall you, directly or indirectly, designate the calendar year of payment.
6
Exhibit 10.16
Deere & Company World Headquarters
One John Deere Place, Moline, IL 61265 USA
John C. May
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer

[Date]
Dear Board Member:
I am pleased to advise that on [Date] (Grant Date) you were awarded ___ Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) pursuant to the 2022 Deere & Company Nonemployee Director Stock Ownership Plan (2022 Plan). This award consists of the regular annual award of RSUs equivalent to $165,000 with the number of RSUs based on the fair market value of Deere & Company (Deere) common stock on [Date]. Please note that acceptance of your award is required.
Participation in the 2022 Plan is limited to members of the Deere Board of Directors who are not currently employees of Deere. It is designed to encourage your personal interest in Deere growth and focus on stockholder value.
Fidelity Stock Plan Services (Fidelity), a division of Fidelity Investments®, is the administrative services provider for the 2022 Plan. Acceptance of your award will be done through the Fidelity online system. You will receive an email from Fidelity with instructions on how to log into [ ] and accept your award.
Fidelity also manages the Beneficiary Designation Forms (each, a Form) for the 2022 Plan. You will receive an email from Fidelity with a link to the Form should you want to update your beneficiaries with Fidelity. If you want to review your current beneficiaries, please reach out to [contact], whose contact information is below.
If you have any questions regarding acceptance of your grant, completion of your Form, or other beneficiary designations, please reach out to [contact], [title] at [phone] or by email at [email address].
Very truly yours, John C. May AMENDED: 12 January 2000 EFFECTIVE: 1 January 2000
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
Exhibit 10.19
JOHN DEERE DEFINED CONTRIBUTION RESTORATION PLAN
EFFECTIVE 1 JANUARY 1997
AMENDED: 28 November 2000
EFFECTIVE: 1 January 2001
AMENDED: 1 DECEMBER 2005
EFFECTIVE: 1 JANUARY 2005
AMENDED: 13 DECEMBER 2007
EFFECTIVE: 1 JANUARY 2008
AMENDED: 15 DECEMBER 2008
EFFECTIVE: 1 JANUARY 2009
AMENDED: 4 MARCH 2013
EFFECTIVE: 1 JANUARY 2013
AMENDED: 26 JUNE 2015
EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2015
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2016
EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2015
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2017
EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2016
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2018
EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2017
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2019
EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2018
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2020
EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2019
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2021
EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2020
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2022
EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2021
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2023
EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2022
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
ARTICLE I. ESTABLISHMENT, PURPOSE AND CONSTRUCTION
ARTICLE II. PARTICIPATION
ARTICLE III. CONTRIBUTIONS
ARTICLE IV. ACCOUNTS AND RATE OF RETURN
ARTICLE V. VESTING
ARTICLE VI. DISTRIBUTIONS
ARTICLE VII. ADMINISTRATION, AMENDMENT AND TERMINATION
ARTICLE VIII. DEFINITIONS
SCHEDULES
JOHN DEERE DEFINED CONTRIBUTION RESTORATION PLAN
Effective as of 1 January 2007 (unless otherwise provided herein), the Plan was amended pursuant to Section 409A of the Code. Amendments to the Plan adopted in 2007 are intended to align Plan provisions with prior operational changes and avoid the imposition on any Participant of taxes and interest pursuant to Section 409A of the Code. Interpretation of any portion of the Plan, if necessary, shall be consistent with this intent.
The Plan is intended to qualify as an unfunded deferred compensation plan for a select group of management or highly compensated employees, within the meaning of Sections 201(2), 301(a)(3), and 401(a)(1) of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended, and the rulings and regulations thereunder (“ERISA”).
| (a) | Effective as of 1 January 2023, any eligible employee who is hired or rehired by the Company on or after 1 January 2023 and who is eligible to receive Employer retirement contributions pursuant to Article III, Sections 3.1(c) and (d) of the SIP shall be eligible for Employer retirement contributions as described in Section 3.2(b) below. |
| (b) | Effective as of 1 January 2006, any employee not participating in the Traditional Option under the SIP who is an active employee on 31 October of a calendar year shall be eligible to make a Deferral Allocation (as defined in Section 3.3(a)(i) hereof) under the Plan during the subsequent calendar year, provided they have eligible Compensation for the calendar year of participation in excess of the limit under Section 401(a)(17) of the Code that was in effect for the immediately preceding calendar year. |
| (c) | Prior to 2006, any employee participating in the Contemporary Option under the SIP whose salary deferral and matching contribution under the SIP are reduced by the limitations imposed by Sections 401(a)(17), 402(g) and 415 of the Code shall be eligible to participate in the Plan. |
| (a) | Effective 1 January 2007. Effective as of 1 January 2007, pursuant to one or more deferral agreements in force under this Plan and subject to this Article III, the maximum amount of Deferral Allocations (as defined in Section 3.3(a)(i) hereof) that may be allocated during a calendar year to a Participant’s Account under this Plan is determined as follows: |
| (i) | the deferral percentage elected under this Plan not to exceed 6%, multiplied by, |
| (ii) | eligible Compensation for a calendar year in excess of the limit under Section 401(a)(17) of the Code that was in effect for the immediately preceding calendar year. |
A Participant's deferrals under the Plan shall not commence until such Participant's Compensation from such calendar year exceeds the amount determined pursuant to Section 3.1(a)(ii).
| (b) | Prior to 2007. Prior to January 1, 2007, pursuant to a salary deferral agreement in force under the SIP and subject to the provisions hereof, any amount of contribution up to 6% of Compensation for a calendar year that is restricted under Section 401(a)(17), Section 402(g) or 415 of the Code shall be allocated to a Participant’s salary deferral account under the Plan. |
| (c) | Eligible Compensation. For purposes of Sections 3.1(a)(ii) and 3.3: |
| (i) | “Compensation” for purposes of Deferral Allocations (as defined in Section 3.3(a)(i) hereof) under the Plan shall be Compensation as defined under the terms of the SIP in effect on 1 January 2007, which is paid to a Participant during the period beginning on the date on which such Participant first commences participation in the Plan and ending on the date of such Participant’s Separation from Service; provided, however, that such definition of Compensation under the SIP shall be applied without giving effect to the exclusion of amounts deferred under nonqualified deferred compensation plans, which are not considered “compensation” within the meaning of Section 415 of the Code and are not included in the definition of Compensation under the terms of the SIP; provided, further, that for avoidance of doubt, amounts received while a Participant is on a Special Paid Leave of Absence shall be considered Compensation for purposes of this Plan; and provided, further, that for avoidance of doubt, amounts received by a Participant after such Participant’s Separation from Service are not considered Compensation for purposes of this Plan, whether or not such amounts are received in respect of services performed prior to the Participant’s Separation from Service. |
| (ii) | Compensation payable after 31 December of a calendar year for services performed during the final payroll period of such calendar year containing such 31 December shall be treated as Compensation for the subsequent calendar year; |
| (iii) | Compensation for Participants who participate in the Contemporary Option under the SIP shall include Performance-Based Compensation received under the John Deere Short-Term Incentive Bonus Plan; and |
| (iv) | Sales commissions shall be deemed earned in the calendar year in which the customer remits to the Company the payment to which such Compensation relates. |
| (v) | Compensation shall include salary continuation benefits paid to a Disabled Participant during the 12-month period beginning on the Participant’s absence from work due to Disability and ending on the date on which benefits commence under the Company’s long-term disability plan, plus any Performance-Based Compensation received under the John Deere Short-Term Incentive Bonus Plan during such period, if any. |
(a)Employer Matching Contributions. Employer matching contributions, if any, corresponding to Deferral Allocations under Section 3.1 above shall be allocated to a matching account under this Plan. Employer matching contributions under this Plan will be determined as described in Article IV, Section 4.1(b) of the SIP.
(b) Employer Retirement Contributions. Regardless of whether a Participant is eligible to make or has made a Deferral Allocation under this Plan for any calendar year, Employer retirement contributions shall be allocated to an Employer retirement contribution account under this Plan for Participants who are hired or rehired by the Company on or after 1 January 2023 and are eligible to receive Employer retirement contributions pursuant to Article III, Sections 3.1(c) and (d) of the SIP. Employer retirement contributions under the Plan will be determined as described in Article IV, Section 4.1(c) of the SIP; provided, that Employer retirement contributions shall be determined on the basis of Retirement Contribution Earnings (as such term is defined in the SIP) that are in excess of the limit under Section 401(a)(17) of the Code.
| (a) | Effective 1 January 2007. |
| (i) | A Participant's deferral allocation under the Plan (the “Deferral Allocation”) with respect to Performance-Based Compensation for services performed during a Plan Year commencing on or after 1 November 2006 and with respect to all other Compensation for services performed during a calendar year commencing on or after 1 January 2007 that is not Performance-Based Compensation (including commission compensation earned during the |
| calendar year) shall be irrevocably determined pursuant to such Participant's deferral agreement in effect under this Plan as of 31 October preceding the beginning of the Plan Year (in the case of Performance-Based Compensation) and the beginning of the calendar year (for all other Compensation); provided, however, that the Deferral Allocation under the Plan shall not exceed 6% of the Participant's Compensation; and provided further that the Participant’s deferral agreement shall remain in effect for subsequent years until revoked or modified. Any such revocation or modification executed during a Plan Year shall become effective for Performance-Based compensation for the subsequent Plan Year and for other Compensation earned in the calendar year commencing after the end of the Plan Year in which the revocation or modification occurs. |
| (ii) | Effective for calendar years commencing on or after 1 January 2007 and Plan Years commencing on or after 1 November 2006, an eligible employee who does not have a Deferral Allocation in place on 31 October shall not be permitted to make a Deferral Allocation under the Plan during the following calendar year or Plan Year. |
| (iii) | A Participant’s elections with respect to his deferral agreement under the SIP shall have no effect on such Participant's Deferral Allocation under the Plan. |
| (b) | 1 January 2006 to 31 December 2006. With respect to the calendar year commencing 1 January 2006 and the Plan Year commencing 1 November 2005, a Participant's Deferral Allocation shall be based on the Participant's deferral agreement under the SIP in effect as of 31 December 2005. |
| (c) | 1 January 2005 to 31 December 2005. |
With respect to the calendar year beginning 1 January 2005 and the Plan Year beginning 1 November 2004, a Participant shall be permitted, through 15 March 2005, pursuant to Q&A 21 in Notice 2005-1, to make a new Deferral Allocation election or increase an existing Deferral Allocation with respect to amounts that have not been paid or that have not become payable at the time of such election; provided that the Participant's deferral agreement under the SIP in effect as of 15 March 2005 shall determine such Participant's Deferral Allocations under the Plan for the remainder of the 2005 calendar year; and provided further that such election with respect to the Plan shall not exceed 6% of the Participant's Compensation and shall be in accordance with procedures established by the Plan Administrator.
| (d) | Prior to 1 January 2005. Effective 1 January 1997 or the first day of any subsequent month through December 1, 2004, an eligible employee may elect to defer Compensation by completing a written election no later than the last work day of any month authorizing the Company to defer a percentage of Compensation under Section 4.8 of the SIP, provided that such employee is participating in the Contemporary Option under the SIP. Such election will remain in force until |
| changed or revoked by the employee or the employee ceases to be eligible to participate according to Article II of this Plan. |
| (a) | The rate of return for a Participant’s Account shall be the average of Prime Rate plus two percent as determined by the Federal Reserve statistical release for the month immediately preceding the month for which such rate shall be credited to Account balances for Deferral Allocations, Employer matching contributions and Employer retirement contributions under this Plan. |
Alternatively, a Participant may elect a rate of return equal to the average of the S&P 500 Index for the month immediately preceding the month for which such rate shall be credited to Account balances for Deferral Allocations, Employer matching contributions and Employer retirement contributions under this Plan.
Effective 1 November 2015, the above two notional investment options are frozen to future contributions and exchanges into these two notional investment options. Notwithstanding the preceding sentence, exchanges out of these two notional investment options will still be permitted.
| (b) | Effective 2 November 2015 the notional options listed on Schedule A shall become available for exchanges and effective 3 November 2015, the same notional investment options shall be available to future contributions. The Administrator may from time to time in its discretion modify the list of notional investment options set forth on Schedule A and, as so modified, such list shall constitute the notional investment options available for exchanges and future contributions occurring after the effective date of such modification. |
| (a) | Participants Retirement Eligible as of 31 December 2005. |
| (i) | A Participant who is Retirement Eligible as of 31 December 2005 and incurs a Separation from Service on or after 1 January 2006 shall be permitted, subject to Sections 6.4 and 6.5, to irrevocably elect the form of distribution for his Account, pursuant to Section 6.3 and this Section 6.1(a)(i), paid, at the Participant's election, either (A) the first day of the month containing the date that is six months and one day after his Separation from Service, plus one day for each day of Vacation, (B) one or more years after his Separation from Service or (C) on a date specified by the Participant, provided that if such specified date is a date prior to the Participant's Separation from Service, then such specified date shall be disregarded and the Account shall be distributed on the date that is six months and one day after the Separation from Service, plus one day for each day of Vacation. Elections pursuant to this Section 6.1(a)(i) shall be made by no later than 31 December 2005 in accordance with procedures established by the Administrator and shall provide that distribution of the Account shall begin no later than 1 January of the calendar year following the calendar year in which the Participant attains age 75. An election made pursuant to this Section 6.1(a)(i) shall apply to a Participant’s entire Account, including amounts credited to the Account after 31 December 2005. |
| (ii) | If a Participant described in Section 6.1(a)(i) does not make a timely election pursuant to Section 6.1(a)(i), his Account shall be paid in accordance with Section 6.1(b). |
| (b) | Participants Retirement Eligible After 31 December 2005 Who Separate from Service After Becoming Retirement Eligible. Effective as of 1 January 2006, the Account of a Participant (i) who becomes Retirement Eligible after 31 December 2005, and (ii) whose Separation from Service occurs after he becomes Retirement Eligible, shall be paid in five annual installments. The amount and timing of each annual installment shall be determined as follows: |
| (i) | The initial annual installment shall be an amount that is substantially equal to one-fifth of the value of the Participant's Account determined as of the last valuation date of the month immediately preceding the Measurement Date, and shall be paid on the last day of the month following the month which contains the Measurement Date. For purposes of Section 6.1, “Measurement Date” means the date that is the first anniversary of the Participant's Separation from Service, plus one day for each day of Vacation. |
| (ii) | The second annual installment shall be an amount that is substantially equal to one-fourth of the value of the Participant's Account determined as of the last valuation date of the month immediately preceding the date that is the first anniversary of the Measurement Date, and shall be paid on the last day of the month following the month which contains the first anniversary of the Measurement Date. |
| (iii) | The third annual installment shall be an amount that is substantially equal to one-third of the value of the Participant's Account determined as of the last valuation date of the month immediately preceding the date that is the second anniversary of the Measurement Date, and shall be paid on the last day of the month following the month which contains the second anniversary of the Measurement Date. |
| (iv) | The fourth annual installment shall be an amount that is substantially equal to one-half of the value of the Participant's Account determined as of the last valuation date of the month immediately preceding the date that is the third anniversary of the Measurement Date, and shall be paid on the last day of the month following the month which contains the third anniversary of the Measurement Date. |
| (v) | The fifth annual installment shall be an amount that is equal to the entire remaining balance in the Participant's Account and shall be paid on the date that is the fourth anniversary of the Measurement Date. |
| (c) | Participants Not Retirement Eligible When Separated. Effective as of 1 January 2006, the Account of a Participant (i) who is not Retirement Eligible as of 31 |
| December 2005, and (ii) whose Separation from Service occurs after 31 December 2005 and prior to the date on which he becomes Retirement Eligible shall be paid in a single lump sum on the last day of the month following the month in which the first anniversary of such Participant's Separation from Service occurs. |
| (a) | General Rule. A Participant who incurs a Separation from Service between 1 January 2005 and 31 December 2005 inclusive shall be permitted to elect, in accordance with procedures established by the Administrator to receive his 409A Account in any of the payment forms specified in Section 6.3. The 409A Account shall be distributed at the time (or over a period of years) specified by the Participant; provided that the Participant shall not be permitted to elect a date that is earlier than 30 days following (i) the last day of the month in which the Participant’s Separation from Service occurs (ii) plus one day for each day of Vacation in the case of Retirement or no later than 1 January of the year following the year in which the Participant attains age 75. If a Participant elects to receive his 409A Account in the form of installments of decrementing amounts or a specified amount, each installment subsequent to the first shall be paid on the anniversary of first installment. The election pursuant to this Section 6.2(a) shall be made by no later than 31 December 2005. |
| (b) | No Election. If a Participant described in Section 6.2(a) does not make a timely election, his 409A Account shall be paid in accordance with Section 6.1(c). |
| (c) | Grandfathered Account. During calendar year 2005, a Participant’s Grandfathered Account shall be distributed in accordance with Section 6.3. |
| (d) | Section 409A Transition Rules. Notwithstanding anything in the Plan, effective, unless otherwise provided, as of 1 January 2005 with respect to the 409A Account of a Participant and 1 January 2006 with respect to the Account: |
| (i) | Timing of Elections and Plan Amendments. Except as otherwise provided in Section 6.2(d)(ii), to the extent that any Participant makes, on or prior to 31 December 2005, a payment election or the Company amends, on or prior to 31 December 2007, Plan provisions regarding the time and form of payment of a Participant's 409A Account, with respect to all or a portion of the amounts previously deferred that are subject to Section 409A, such election and amendment shall be deemed to be made pursuant to Q&A 19(c) in Notice 2005-1. |
| (ii) | Termination of Participation; Cancellation of Deferral. To the extent that a Participant receives in the 2005 calendar year a distribution of all, or any portion, of his 409A Account or prospectively cancels or reduces in the 2005 calendar year all or any portion of his Salary Deferral Allocation election under the SIP, as the case may be, such distribution or cancellation shall be deemed a whole or partial (as the case may be) (i) termination of such |
| Participant's 409A Account or (ii) cancellation of such Participant's deferral election under the Plan, each pursuant to Q&A 20(a) of Notice 2005-1. |
| (a) | Time and Manner. Distribution of a Participant’s Account shall commence as soon as practicable after the valuation date at the end of the month following 30 days after the Participant’s termination of employment or 60 days following a Participant’s death in accordance with the election in 6.3(b) below and form of distribution shown in 6.3(c). Termination of employment for the purposes of this Plan shall include retirement and Long-Term Disability status on or after 1 November 1998. Distribution must begin no later than 1 January of the year following the year the Participant reaches age 75. |
| (b) | Election. A Participant shall make an irrevocable election regarding the time and manner of distribution no later than 30 days following termination of employment. Termination of employment for the purposes of this Plan shall include retirement and Long-Term Disability status on or after 1 November 1998. If the Participant’s employment is terminated by death, any eligible beneficiary shall make such irrevocable election within 60 days following the Participant’s death. |
| (c) | Form of Distribution. |
| (i) | A single lump sum payment |
| (ii) | A specified dollar amount each year until Account balance reaches zero. |
| (iii) | A decrementing yearly withdrawal over a specific period of time which results in a zero Account balance. |
In the event of the death of the Participant or a Qualified Domestic Relations Order, such beneficiaries or the Alternate Payee must take distribution as a single lump sum payment within 180 days following the event.
6.8 Employment Taxes due Upon Vesting. To the extent permitted under Section 409A, the Company may distribute an amount from a Participant’s Account to cover employment taxes payable on account of employer matching contributions (and earnings thereon) as well as related income tax withholding due on such distribution.
| (a) | This Plan shall be administered by the Administrator. The Administrator shall have the power to construe and interpret this Plan, decide all questions of eligibility and determine the amount, manner, and time of payment of any benefits hereunder. All determinations of the Administrator shall be final, binding, and conclusive on all persons. |
| (b) | The Administrator shall not accelerate or delay payment under the Plan except to the extent that such acceleration (including as a result of a “change in control” within the meaning of the default provisions of Section 409A and the final |
| regulations promulgated thereunder) or delay shall not cause any person to incur additional taxes, interest or penalties under Section 409A (“Section 409A Compliance”). |
| (a) | If the Plan is terminated pursuant to Section 7.8, payment of Participant Accounts shall be made in accordance with Article VI, except to the extent that the Board of Directors of the Company or the Management Compensation Committee of the Company determines, in its sole discretion and in full and complete settlement of the Company’s obligations under this Plan, to distribute the full amount of a Participant’s Account to the Participant; provided that such distribution may be effected in a manner that will result in Section 409A Compliance. |
| (b) | If a participating subsidiary or affiliate withdraws from the Plan pursuant to Section 7.11, payment of Participant Accounts shall be made in accordance with Section 6.1 or 6.2, as applicable. |
If during its affiliation with the Plan, a subsidiary or an affiliate's ownership by the Company falls below the 80 percent required level, such subsidiary or affiliate is automatically dropped from participation in this Plan and its employees are similarly dropped from being Participants in this Plan.
If a subsidiary or affiliate of Deere & Company which is covered by this Plan ceases to be a subsidiary or affiliate, the participation in this Plan by the employees of such subsidiary or affiliate shall terminate, and no employees of such former affiliate or subsidiary shall accrue or be entitled to a benefit under this Plan on and after the date such company ceases to be a subsidiary or affiliate of Deere & Company (other than former employees who were receiving benefit payments as of such date).
“409A Account” means the portion of a Participant’s account under the Plan the right to which is not both earned and vested on December 31, 2004.
“Account” means, effective as January 1, 2006, a Participant’s Grandfathered Account and 409A Account.
“Administrator” means the Company.
“Deferral Allocation” means, with respect to a Participant, the deferral allocation election under the Plan applicable to Performance-Based Compensation and all other eligible Compensation.
“Disability” means an absence from work due to a disability as determined under the long-term disability plan or practice of the Company for 12 months or longer, or, if earlier, the date on which a Participant's reemployment with the Company ceases to be guaranteed.
“Grandfathered Account” means the portion of a Participant’s account under the Plan the right to which is both earned and vested on December 31, 2004. The Grandfathered Account shall be subject to the Prior Plan.
“Notice 2005-1” means Notice-2005-1 promulgated by the U.S. Treasury Department and the Internal Revenue Service., as clarified and expanded by Final Regulations under Section 409A and Notice 2006-79.
“Performance-Based Compensation” means performance-based compensation within the meaning of Section 409A.
“Prior Plan” means the terms of the Plan in effect immediately prior to 1 January 2005, as set forth in the Company’s written documents, rules, practices and procedures applicable to this Plan (but without regard to any amendments thereto after 3 October 2004 that would result in any material modification, within the meaning of Section 409A and Notice 2005-1, of the Grandfathered Benefit).
“Retirement Eligible” means eligible for a normal retirement benefit or an early retirement benefit within the meaning of the terms of the John Deere Pension Plan for Salaried Employees--Contemporary Option in effect as of 1 January 2007.
“Section 409A” means Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and the rulings and regulations thereunder.
“Separation from Service” means, with respect to a Participant, a separation from service within the meaning of the default rules of Section 409A; provided, however, that, notwithstanding anything in Section 7.12 to the contrary, for purposes of determining which entities are treated as a single “service recipient” with the Company, the phrase “at least 20 percent” shall be substituted for the phrase “at least 80 percent” each place it appears in Sections 1563(a)(1), (2) and (3) of the Code and Section 1.414(c)-2 of the Treasury Regulations, as permitted under Section 1.409A-1(h)(3) of the Treasury Regulations; and provided further that, solely for purposes of an Account consisting exclusively of a Grandfathered Account, “Separation from Service” shall be determined in accordance with the terms of the Prior Plan.
“Vacation” means one or more days, as the case may be, of such vacation to which the Participant is entitled pursuant to the policies and practices of the Company then in effect and (i) as of the date of the Participant’s Separation from Service, deferred from a prior anniversary year and unused as of such Separation from Service, (ii) earned in the current anniversary year and unused as of such Separation from Service and (iii) if a Participant’s Vacation described in clause (i) or (ii) of this definition is used in the anniversary year following the anniversary year in which such Separation from Service occurs, earned in such following anniversary year, whether or not used by the Participant.
SCHEDULE A
Notional Investment Options
BTC LIFEPATH RET G
BTC LIFEPATH 2025 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2030 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2035 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2040 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2045 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2050 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2055 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2060 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2065 G
S & P 500 STOCK INDEX, CLASS F
SMALL/MID STOCK INDEX, CLASS F
INTERNATIONAL STOCK INDEX, CLASS F
U.S. TIPS BOND INDEX, CLASS F
U.S. BOND INDEX, CLASS F
COMMODITY INDEX, CLASS F
REAL ESTATE INDEX, CLASS F
FIDELITY GROWTH COMPANY COMMINGLED POOL CLASS #3
BOSTON PARTNERS LARGE CAP VALUE FUND SHARE CLASS E
QMA US SMALL CAP CORE EQUITY FD CL
INTERNATIONAL EQUITY FUND
U.S. EQUITY FUND (effective November 1, 2023)
ALLSPRING EMERGING MARKETS EQUITY CIT E2
CIT-ALLSPRING ENHANCED CORE BOND E2
BLENDED INTEREST FUND
SHORT-TERM INVESTMENT FUND W
Exhibit 10.25
DEERE & COMPANY
NONEMPLOYEE DIRECTOR DEFERRED COMPENSATION PLAN
EFFECTIVE DATE: 01 JANUARY 1997
REVISED: 26 MAY 1999
AMENDED BY SUPPLEMENT: 30 AUGUST 2006
AMENDED: 29 NOVEMBER 2006
AMENDED AND RESTATED 13 DECEMBER 2007: EFFECTIVE 1 JANUARY 2008
AMENDED: 25 FEBRUARY 2009EFFECTIVE: 25 FEBRUARY 2009
AMENDED: 30 OCTOBER 2015 EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2015
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2016 EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2015
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2017 EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2016
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2017 EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2017
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2019 EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2018
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2020 EFFECTIVE: 1 NOVEMBER 2019
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2021 EFFECTIVE 1 NOVEMBER 2020
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2022 EFFECTIVE 1 NOVEMBER 2021
AMENDED: 31 OCTOBER 2023 EFFECTIVE 1 NOVEMBER 2022
(For special rules applicable to deferrals after 2004
see the supplement beginning on page 14)
DEERE & COMPANY
NONEMPLOYEE DIRECTOR DEFERRED COMPENSATION PLAN
I. |
Purpose |
The purposes of the Deere & Company Nonemployee Director Deferred Compensation Plan (“Plan”) are to attract and retain highly qualified individuals to serve as Directors of Deere & Company (“Company”) and to relate Nonemployee Directors’ interests more closely to the Company’s performance and its shareholders’ interests.
II. |
Eligibility |
Each member of the Board of Directors (“Board”) of the Company who is not an employee of the Company or any of its subsidiaries (“Nonemployee Director”) is eligible to participate in the Plan.
III. |
Definitions |
(a) |
Committee. The Nominating Committee of the Board or any successor committee of the Board. |
(b) |
Common Stock. The publicly traded $1 par value common stock of the Company or any successor. |
(c) |
Compensation. Amounts payable for services as a Nonemployee Director, excluding reimbursed expenses. |
(d) |
Deferred Account. The bookkeeping account maintained for each participating Nonemployee Director which will be credited with Deferred Amounts pursuant to the terms hereof. |
(e) |
Deferred Amounts. All amounts credited to a Nonemployee Director’s Deferred Account pursuant to the Plan. |
(f) |
Elective Deferrals. Compensation voluntarily deferred by a Nonemployee Director under the Plan after 31 December 1996 (other than Lump-Sum Deferral defined below). |
(g) |
Investment Return. Any amounts (positive or negative) attributable to the Interest Alternative or the Equity Alternative (as such terms are defined in Section VII(c)) and any return (positive or negative) attributable to Notional Investments determined pursuant to VII(j). |
(h) |
Lump-Sum Deferral. A one-time lump-sum amount for each Nonemployee |
2
Director serving on 31 December 1996, which amount is deferred under the Plan as described in Section V, below, as a result of the termination of the John Deere Pension Benefit Plan for Directors (“Retirement Plan”).
(i) |
Notional Investment Options. The mutual funds and other investment vehicles designated by the Committee to be used to measure the return (positive or negative) to be attributed to deferred amounts |
(j) |
Participant. A Nonemployee Director for whom a Lump-Sum Deferral occurs on the Effective Date, or who elects to participate in the Plan. |
(k) |
Pre-1997 Elective Deferrals. Compensation deferred by a Nonemployee Director prior to 1 January 1997 under the predecessor Directors’ Deferred Compensation Plan approved 30 January 1973, as amended from time to time. |
(l) |
Recordkeeper. The entity which the Employer has selected to recordkeep the Nonemployee Director Deferred Compensation Plan. |
(m) |
Secretary. The Secretary of the Company. |
(n) |
Transition Date. 7 October 2016 |
IV. |
Effective Date |
The effective date of the Plan is 1 January 1997 (“Effective Date”).
V. |
Lump-Sum Deferral |
As of the Effective Date, the Retirement Plan will be eliminated and the present value of the life annuity offered under the Retirement Plan for each Nonemployee Director who is both a participant in the Retirement Plan and a member of the Board on the Effective Date will be deposited into the Deferred Account of such Nonemployee Director. The present value will be determined by using a discount factor which shall be the rate for 10-year treasury stripped bonds in effect as of 31 December 1996 and by using the 1984 Unisex Pension Mortality tables published in the Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation Regulation 2619, Appendix A.
VI. |
Elective Deferral |
(a) |
Participants may elect to defer a part or all of their annual Compensation by making an irrevocable deferral election in writing on a form provided by the Company and delivered to the Company not later than the Company may direct. Elective Deferrals will become effective on the first day of the following calendar quarter, at which time they become irrevocable. Notwithstanding the preceding sentence, any person who first becomes a |
3
Nonemployee Director during a calendar quarter, may elect, before his or her term begins, to defer a part or all of his or her compensation that would otherwise be payable to him or her during the remainder of such calendar quarter and each succeeding calendar quarter until such election is modified or terminated as provided herein. A Participant may discontinue deferrals, or may change his or her investment choices, for future quarters by providing a written election delivered to the Company not later than the Company may direct. These changes will become effective on the first day of the following calendar quarter.
(b) |
If the amount of a Participant’s Compensation is changed, the deferral percentage and investment alternative elections shall continue to be applied to the new Compensation amount after the change. |
VII. |
Deferred Account |
(a) |
The Recordkeeper shall establish a separate Deferred Account for each Participant. |
(b) |
Unless and until reallocated pursuant to Section VII(j), pre-1997 Elective Deferrals and the interest earned thereon shall be credited to the Deferred Account and will continue to be invested in the Interest Alternative described below. |
(c) |
As of the Effective Date and continuing for periods ending on the Transition Date, two investment alternatives will be available: an interest-bearing alternative (the “Interest Alternative”) and an equity alternative denominated in units of Deere Common Stock (the “Equity Alternative”). Additional investment alternatives may be added by subsequent amendment of the Plan. |
(d) |
For deferral elections made prior to the Transition Date, at the time of Elective Deferral, Participants may direct their deferrals into either the Interest Alternative or the Equity Alternative, or a combination of the two, in increments of 5%. |
(e) |
Effective October 1, 2022, deferred amounts credited to the Interest Alternative will be credited daily with interest at the interest rate equal to the average of Prime Rate plus two percent, as determined by U.S. Federal Reserve Statistical Release for the month immediately preceding the month for which such rate shall be credited. |
(f) |
Deferred Amounts credited into the Equity Alternative shall be expressed and credited to each Participant’s Deferred Account in units (“Units”) determined as hereinafter provided. As of each date on which Deferred Amounts are credited into the Equity Alternative, the Recordkeeper shall |
4
credit to such Deferred Account a number of Units and fractional Units, rounded to three decimal places, determined by dividing such Deferred Amounts by the Unit Value (as defined below) of one share of Common Stock. The “Unit Value” of one share of Common Stock shall be the closing price of the Common Stock on the New York Stock Exchange on the date on which Deferred Amounts are credited to the Deferred Account or a payment is to be valued under Section VIII (b) below, as the case may be; or if there were no sales on that day, then Unit Value shall be the closing price on the New York Stock Exchange Composite Tape on the most recent preceding day on which there were sales. The Lump-Sum Deferral shall be credited as of the Effective Date.
(g) |
When dividends are paid with respect to the Company’s Common Stock, the Recordkeeper shall calculate the amount which would have been payable on the Units in each Participant’s Deferred Account on each dividend record date as if each Unit represented one issued and outstanding share of the Company’s Common Stock. The applicable number of Units and fractional Units equal to the amount of such dividends (based on the Unit Value of one share of the Company’s Common Stock on the dividend payment date) shall be credited to each Participant’s Deferred Account. In the event of any capital stock adjustment to the Company’s Common Stock or other similar event, the number of Units or fractional Units credited to Deferred Accounts shall be adjusted to appropriately reflect such event. |
(h) |
Participants credited with Units hereunder shall not have any voting rights in respect thereof. |
| (i) | For periods beginning on or after the Transition Date, a Participant’s account shall continue to be valued as provided in the foregoing Sections VII(b) through (h), except that the account shall be valued in such manner only on the portion of the account that is not allocated to other Notional Investment Options pursuant to Section VII(j). |
(j) |
For periods beginning on the Transition Date, the Committee has established the Notional Investment Options listed on Schedule A which shall be available for exchanges and future contributions. The Committee may from time to time in its discretion modify the list of Notional Investment Options set forth on Schedule A and, as so modified, such list shall constitute the Notional Investment Options available for exchanges and future contributions occurring after the effective date of such modification. A Participant may reallocate the Participant’s account balance among the available Notional Investment Options on a daily basis pursuant to procedures established by the Committee. If a Participant fails to allocate the Participant’s account balance among the Notional Investment Options, the Participant’s deferrals on or after October 1, 2022 shall be allocated to |
5
the BTC LifePath Fund that is closest to the Participant’s 65th birthday, until modified by the Participant in accordance with this Section VII(j).
(k) |
Unless otherwise determined by the Committee, neither the Interest Alternative nor the Equity Alternative shall be available as a Notional Investment Option for amounts deferred after 31 December 2016. All such deferrals shall instead be allocated to one or more Notional Investment Options pursuant to a Participant’s election made pursuant to Section VII(j) above and shall thereafter be available for reallocation as specified therein. With respect to amounts deferred before 1 January 2017: (I) no such amount (including return thereon) that has been allocated from the Interest Alternative or the Equity Alternative to another Notional Investment Option may be reallocated back to either such alternative at any time. |
(l) |
A Participant’s account shall be credited (or debited) with returns (positive or negative) on the Notional Investment Options to which the Participant’s account is allocated. The Recordkeeper shall from time to time calculate each Participant’s account value based on the Participant’s deferred amounts and elections with respect to the deemed allocation of the Participant’s account among the Notional Investment Options available to the Participant. Such calculation will be based on the best information available to the Recordkeeper as of the date of determination, which information may include estimates. |
(m) |
The Committee may, from time to time, change the Notional Investment Options available to Participants. Nothing in the Plan shall be construed to confer on a Participant the right to continue to have any particular Notional Investment Option available for purposes of measuring the value of the Participant’s account. |
(n) |
The value of a Participant’s account is subject to risk at all times based upon the performance of the Notional Investment Options to which the Participant’s account is allocated. If the value of a Participant’s Notional Investment Options decreases in the future, the value of the Participant’s account may be lower than the Participant’s original deferred amounts. Although a Participant will not be an investor in the elected Notional Investment Options, a Participant’s account will be subject to gains and losses attributable to the performance of the elected Notional Investment Options. Payment of the Participant’s account is also subject to the risks associated with the Participant’s status as an unsecured general creditor of the Company as described in Section XI. |
6
VIII. |
Payment of Benefits |
(a) |
The value of a Participant’s Deferred Account shall be payable solely in cash, either in (i) a lump sum, or (ii) in up to ten equal annual installments, in accordance with an election made by the Participant by written notice delivered to the Recordkeeper prior to the calendar year in which payments are to be made or commence. Such payment or payments shall be made or commence, as the case may be, on the first business day of the calendar year following the year of the termination of service as Director. |
(b) |
Any lump sum payment shall be valued as of the end of the most recent calendar month prior to the payment date. The amount of each installment payment shall be determined by dividing the aggregate value credited to the Participant’s Deferred Account (as of the end of the most recent calendar month prior to the payment date) by the remaining number of unpaid installments; provided, however, that the Committee may, in its absolute discretion, approve any other method of determining the amount of each installment payment in order to achieve approximately equal installment payments over the installment period. |
(c) |
The Company shall have the right to deduct from all payments under this Plan the amount necessary to satisfy any Federal, state, or local withholding tax requirements. |
(d) |
The Committee, at its sole discretion, may alter the timing or manner of payment of Deferred Amounts in the event that the Participant establishes, to the satisfaction of the Board, severe financial hardship. In such event, the Committee may: |
(1) |
provide that all or a portion of the amount previously deferred by the Participant shall be paid immediately in a lump-sum cash payment; |
(2) |
provide that all or a portion of the installments payable over a period of time shall be paid immediately in a lump sum; or |
(3) |
provide for such other installment payment schedules as it deems appropriate under the circumstances. |
It is expressly provided that the amount distributed shall not be in excess of that amount which is necessary for the Participant to meet the financial hardship. Severe financial hardship will be deemed to have occurred in the event of the Participant’s impending bankruptcy, the long and serious illness of Participant or a dependent, other events of similar magnitude, or the invalidation of a deferral election by the Internal Revenue Service. The Committee’s decision in passing on the severe financial hardship of the Participant and the manner in which, if at all, the payment of Deferred Amounts shall be altered or modified shall be final, conclusive and not subject to appeal.
7
IX. |
Death of Participant |
(a) |
In the event of the death of a Participant, any amounts remaining in the Deferred Account will be paid to the Participant’s designated beneficiary in accordance with the distribution choices (e.g., lump sum or installments) elected by the Participant. These payments will commence on the first business day of the calendar year following the Participant’s death. Amounts unpaid after the death of both the Participant and the designated beneficiary will be paid in a lump sum to the executor or administrator of the estate of the last of them to die. In the event that a Participant had not properly filed a beneficiary designation with the Recordkeeper prior to his or her death or, in the event a beneficiary predeceases the Participant, any unpaid deferrals will be paid in a lump sum to the Participant’s estate. |
(b) |
No beneficiary hereunder shall have any right to assign, alienate, pledge, hypothecate, anticipate, or in any way create a lien upon any part of this Plan, nor shall the interest of any beneficiary or any distributions due or accruing to such beneficiary be liable in any way for the debts, defaults, or obligations of such beneficiary, whether such obligations arise out of contract or tort. |
X. |
Change of Control |
The following acceleration and valuation provisions shall apply in the event of a “Change of Control” or “Potential Change of Control,” as defined in this Section X.
(a) |
In the event that: |
(i) |
a “Change of Control” as defined in paragraph (b) of this Section X occurs; or |
(ii) |
a “Potential Change of Control” as defined in paragraph (c) of this Section X occurs and the Committee or the Board determines that the provisions of this paragraph (a) should be invoked; |
then, unless otherwise determined by the Committee or the Board in writing prior to the occurrence of such Change of Control, the value of all Units credited to a Participant’s Deferred Account shall be converted to cash based on the “Change of Control Price” (as defined in paragraph X(d)) and the aggregate amount credited to the Participant’s Deferred Account under the Plan shall be paid in one lump-sum payment as soon as practicable following the date the Change of Control or Potential Change of Control occurs, but in no event more than 90 days after such date.
8
(b) |
For purposes of paragraph (a) of this Section X, a “Change of Control” means a change in control of a nature that would be required to be reported in response to Schedule 14A of Regulation 14A promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (“Exchange Act”) whether or not the Company is then subject to such reporting requirement, provided that, without limitation, such a Change of Control shall be deemed to have occurred if: |
(i) |
any “person” (as defined in Sections 13(d) and 14(d) of the Exchange Act), other than a Participant in the Plan or group of Participants in the Plan, is or becomes the “beneficial owner” (as defined in Rule 13(d)(3) under the Exchange Act), directly or indirectly, of securities of the Company representing 30% or more of the combined voting power of the Company’s then outstanding securities; |
(ii) |
during any period of two consecutive years, there shall cease to be a majority of the Board comprised as follows: individuals who at the beginning of such period constitute the Board and any new director(s) whose election by the Board or nomination for election by the Company’s stockholders was approved by a vote of at least _ of the directors then still in office who either were directors at the beginning of the period or whose election or nomination for election was previously so approved; |
(iii) |
the shareholders of the Company approve a merger or consolidation of the Company with any other company, other than a merger or consolidation which would result in the voting securities of the Company outstanding immediately prior thereto continuing to represent (either by remaining outstanding or by being converted into voting securities of the surviving entity) at least 80% of the combined voting power of the voting securities of the Company or such surviving entity outstanding immediately after such merger of consolidation; or |
(iv) |
the shareholders of the Company approve a plan of complete liquidation of the Company or an agreement for the sale or disposition by the Company of all or substantially all of the Company’s assets. |
(c) |
For purposes of paragraph (a) of this Section X, a “Potential Change of Control” means the happening of any of the following: |
9
(i) |
the entering into an agreement by the Company (other than with a Participant in the Plan or group of Participants in the Plan), the consummation of which would result in a Change of Control of the Company as defined in paragraph (b) of this Section X; or |
(ii) |
the acquisition of beneficial ownership, directly or indirectly, by any entity, person or group (other than a Participant or group of Participants, the Company or a majority owned subsidiary of the Company, or any of the Company’s employee benefit plans including its trustee) of securities of the Company representing 5% or more of the combined voting power of the Company’s outstanding securities and the adoption by the Board of a resolution to the effect that a Potential Change of Control of the Company has occurred for purposes of the Plan. |
(d) |
For purposes of this Section X, “Change of Control Price” means the highest price per share of the Common Stock paid in any transaction reported on the New York Stock Exchange Composite Tape, or offered in any transaction related to a Potential or actual Change of Control of the Company at: |
(i) |
the date the Change of Control occurs; |
(ii) |
the date the Potential Change of Control is determined to have occurred; or |
(iii) |
such other date as the Committee may determine before the Change of Control occurs, or before or at the time the Potential Change of Control is determined to have occurred or the Committee or the Board determines that the provisions of paragraph X(a) shall be invoked, or at any time selected by the Committee during the 60 day period preceding such date. |
(e) |
Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in the Plan, in the event of a Change of Control (i) the Plan may not be amended to reduce the formulas contained in paragraph VII(e) which determine the rate at which amounts equivalent to interest accrue with respect to cash amounts credited to a Participant’s Deferred Account, including cash amounts attributable to the conversion of Units in a Participant’s Deferred Account pursuant to paragraph X(a), and (ii) the successor Plan Administrator referred to in paragraph XI(d) shall determine the rates under the interest formulas contained in paragraph VII(e). |
XI. |
Miscellaneous |
(a) |
The right of a Participant to receive any amount credited to the Participant’s |
10
Deferred Account shall not be transferable or assignable by the Participant, in whole or in part, either directly or by operation of law or otherwise, including, but not by way of limitation, execution, levy, garnishment, attachment, pledge, bankruptcy, or in any other manner, and no right or interest established herein shall be liable for, or subject to, any obligation or liability of the Participant, except by will or by the laws of descent and distribution. To the extent that any person acquires a right to receive any amount credited to a Participant’s Deferred Account hereunder, such right shall be no greater than that of an unsecured general creditor of the Company. Except as expressly provided herein, any person having an interest in any amount credited to a Participant’s Deferred Account under the Plan shall not be entitled to payment until the date the amount is due and payable. No person shall be entitled to anticipate any payment by assignment, alienation, sale, pledge, encumbrance or transfer in any form or manner prior to actual or constructive receipt thereof.
(b) |
The amounts credited to the Deferred Account shall constitute an unsecured claim against the general funds of the Company. The Company shall not be required to reserve or otherwise set aside funds or shares of Common Stock for the payment of its obligations hereunder. The Plan is unfunded, and the Company will make Plan benefit payments solely from the general assets of the Company as benefit payments come due from time to time. |
(c) |
Except as herein provided, this Plan shall be binding upon the parties hereto, their designated beneficiaries, heirs, executors, administrators, successors (including but not limited to successors resulting from any corporate merger, purchase, consolidation or otherwise of all or substantially all of the business or assets of the Company) or assigns. |
(d) |
In the event of a Change in Control, the Committee shall interpret the Plan and make all determinations, construe any ambiguity, supply any omission, and reconcile any inconsistency, deemed necessary or desirable for the Plan’s implementation. The determination of the Committee shall be conclusive. The Committee may obtain such advice or assistance as it deems appropriate from persons not serving on the Committee. The Secretary or other appropriate officer of the Company shall, in the event of any Change in Control, name as successor Plan Administrator any person or entity (including, without limitation, a bank or trust company). Following a Change in Control, the successor Plan Administrator shall interpret the Plan and make all determinations deemed necessary or desirable for the Plan’s implementation. The determination of the successor Plan Administrator shall be conclusive. The Company shall provide the successor Plan Administrator with such records and information as are necessary for the proper administration of the Plan. The successor Plan Administrator shall rely on such records and other information as the |
11
successor Plan Administrator shall in its judgment deem necessary or appropriate in determining the eligibility of a Participant and the amount payable to a Participant under the Plan.
(e) |
The Board, upon recommendation of the Committee, may at any time amend or terminate the Plan provided that no amendment or termination shall impair the rights of a Participant with respect to amounts then credited to the Participant’s Deferred Account, except with his or her consent. |
(f) |
Each Participant will receive a quarterly statement indicating the amounts credited to the Participant’s Deferred Account as of the end of the preceding calendar quarter. |
(g) |
If adjustments are made to outstanding shares of Common Stock as a result of stock dividends, stock splits, recapitalizations, reorganizations, mergers, consolidations and other changes in the corporate structure of the Company affecting the Common Stock, an appropriate adjustment shall also be made in the number and type of Units credited to the Participant’s Deferred Account to prevent dilution or enlargement of rights. The Committee’s or Board’s determination as to what adjustments shall be made, and the extent thereof, shall be final. |
(h) |
This Plan and all elections hereunder shall be construed in accordance with and governed by the laws of the State of Illinois. |
(i) |
Except where otherwise indicated by the context, any term used herein connoting gender also shall include both the masculine and feminine; the plural shall include the singular, and the singular shall include the plural. |
(j) |
In the event any provision of the Plan shall be held illegal or invalid for any reason, the illegality or invalidity shall not affect the remaining parts of the Plan, and the Plan shall be construed and enforced as if the illegal or invalid provision had not been included. |
(k) |
Nothing in the Plan shall be deemed to create any obligation on the part of the Board to nominate any Nonemployee Director for reelection by the Company’s shareholders, or rights to any benefits not specifically provided by the Plan. |
(l) |
The crediting of Units and the payment of cash under the Plan shall be subject to all applicable laws, rules, and regulations, and to such approvals by any governmental agencies as may be required. |
(m) |
The Company may impose such other restrictions on any Units credited pursuant to the Plan as it may deem advisable including, without limitation, restrictions intended to achieve compliance with the Securities Act of 1933, |
12
as amended, Section 16 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, with the requirements of any stock exchange upon which Common Stock is listed, and with any blue sky or other securities laws applicable to such Units.
(n) |
With respect to any Participants subject to Section 16 of the Securities Exchange Act, transactions under the Plan are intended to comply with all applicable conditions of Rule 16b-3 or its successors. To the extent any provision of the Plan or action by the Board fails to so comply, it shall be deemed null and void to the extent permitted by law and deemed advisable by the Board. |
13
SUPPLEMENT TO
DEERE & COMPANY
NONEMPLOYEE DIRECTOR DEFERRED COMPENSATION PLAN
APPLICABLE TO AMOUNTS DEFERRED AFTER DECEMBER 31, 2004
The following provisions will apply only to amounts deferred under the Plan after December 31, 2004 and not to amounts deferred under the Plan that were both earned and vested before January 1, 2005. Amounts deferred under the Plan prior to January 1, 2005 will be subject to the terms of the Plan without regard to this supplement. Except to the extent amended hereby, the terms of the Plan shall continue to apply to amounts deferred pursuant to the Plan.
1. |
The following definitions are added to Section III (Definitions). |
(a) |
Change in Control Event. A change in ownership, a change in effective control, or a change in the ownership of a substantial portion of the assets of the Company within the meaning of the default rules under Section 409A. |
(l) |
Section 409A. Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code and the regulations and other guidance thereunder. |
(m) |
Separation from Service. With respect to a Participant, a separation from service as a director or independent contractor within the meaning of the default rules of Section 409A. |
(n) |
Unforeseeable Emergency. A severe financial hardship to the Participant resulting from (i) an illness or accident of the Participant or his spouse, dependent (within the meaning of Section 152 of the Internal Revenue Code, but without giving effect to Section 152(b)(1), (b)(2) and (d)(1)(B) (“Dependent”)) or beneficiary, (ii) the loss of the Participant’s property due to casualty (including the need to rebuild a home following damage to a home not otherwise covered by insurance, for example, not as a result of a natural disaster), (iii) the imminent foreclosure of or eviction from the Participant’s primary residence, (iv) the need to pay for medical expenses, including non-refundable deductibles, as well as for the costs of prescription drug medication, (v) the need to pay for the funeral expenses of a spouse, Dependent or beneficiary, or (vi) other similar extraordinary and unforeseeable circumstances arising as a result of events beyond the control of the Participant. The purchase of a primary residence and the payment of college tuition shall not constitute Unforeseeable Emergencies. |
14
2. |
Subsections (a) through (j) of Section III (Definitions) are renumbered as subsections (b) through (k). |
3. |
Section VI(a) (Elective Deferral) is restated in its entirety as follows: |
| (a) | Participants may elect to defer a part or all of their annual Compensation by making an irrevocable deferral election in writing on a form provided by the Company and delivered to the Company not later than the last day of the calendar year preceding the calendar year in which the deferrals are to commence, at which time the deferral election becomes irrevocable. Notwithstanding the preceding sentence, any person who first becomes a Nonemployee Director during a calendar year, may elect, before or within 30 days after his or her term begins, to defer a part or all of his or her compensation that would otherwise be payable to him or her during the remainder of such calendar year, except that no such election shall be available to a Nonemployee Director if prior to becoming eligible to participate in the Plan, the Nonemployee Director was eligible to participate in any other arrangement of the Company or its subsidiaries or affiliates that is an “elective account balance” plan (as such term is defined for purposes of Section 409A) for directors or independent contractors, other than a separation pay arrangement. Elections made pursuant to this Section 3(a) shall apply to the calendar year in which the deferrals are to commence and to each succeeding calendar year until such election is modified or terminated as provided in the following sentence. A Participant may modify or discontinue deferrals, or may change his or her investment choices, for future calendar years by providing an irrevocable written election delivered to the Company not later than the close of the calendar year preceding the calendar year in which the changes are to take effect. |
4. |
Section VIII (Payment of Benefits) is restated in its entirety as follows: |
(a) |
The value of a Participant’s Deferred Account attributable to amounts deferred in respect of any calendar year (including related investment returns) shall be payable solely in cash, either in (i) a lump sum, or (ii) in up to ten equal annual installments, in accordance with an election made by the Participant by written notice delivered to the Recordkeeper prior to the calendar year for which the services to the Company are rendered. Such payment or payments shall be made or commence, as the case may be, on the first business day of the calendar year following the year of the Participant’s Separation from Service. |
(b) |
Notwithstanding anything else herein to the contrary, to the extent that a Participant is a “specified employee” within the meaning of Section 409A(a)(2)(B)(i) of the Internal Revenue Code, as determined under the |
15
Company’s established methodology for determining specified employees, on the date on which the Participant incurs a Separation from Service, no distribution upon Separation from Service (including upon retirement or other termination) may be made before the first business day of the first calendar quarter that begins at least six (6) months after such Participant’s date of Separation from Service, or, if earlier, the date of the Participant’s death, and any distribution that would be made but for application of this provision shall instead be aggregated with, and paid together with, the first distribution scheduled to be made after the end of such delay period (or, if earlier, the date of the Participant’s death).
(c) |
Any lump sum payment shall be valued as of the end of the most recent calendar month prior to the payment date. The amount of each installment payment shall be determined by dividing the aggregate value credited to the Participant’s Deferred Account (as of the end of the most recent calendar month prior to the payment date) by the remaining number of unpaid installments. |
(d) |
The Company shall have the right to deduct from all payments under this Plan the amount necessary to satisfy any Federal, state, or local withholding tax requirements. |
(e) |
The Committee, at its sole discretion, may alter the timing or manner of payment of Deferred Amounts in the event that the Participant establishes, to the satisfaction of the Board, that there has occurred an Unforeseeable Emergency. In such event, the Committee may: |
(i) |
provide that all or a portion of the amount previously deferred by the Participant shall be paid immediately in a lump-sum cash payment; or |
(ii) |
provide that all or a portion of the installments payable over a period of time shall be paid immediately in a lump sum. |
It is expressly provided that, as determined under regulations of the Secretary of the United States Treasury, the amount distributed shall not be in excess of that amount which is reasonably necessary to satisfy the Unforeseeable Emergency (which may include amounts necessary to pay taxes reasonably anticipated as a result of such distribution(s)), after taking into account the extent to which such hardship is or may be relieved through reimbursement or compensation by insurance or otherwise, or by liquidation of the Participant’s assets to the extent liquidation of such assets would not cause severe financial hardship, or by cessation of deferrals under the Plan. If a Participant requests and receives a distribution on account of Unforeseeable Emergency, the Participant’s deferrals under the Plan shall cease and his election under the Plan shall be canceled.
16
Any new deferral election following cancellation of a prior deferral election due to Unforeseeable Emergency shall be subject to the timing requirements of Section VI and Section 409A.
The Committee’s decision in passing on the occurrence of an Unforeseeable Emergency for the Participant and the manner in which, if at all, the payment of Deferred Amounts shall be altered or modified shall be final, conclusive and not subject to appeal.
(f) |
Notwithstanding anything to the contrary herein, this Plan does not permit the acceleration of the time or schedule of any distribution under the Plan, except as would not result in the imposition on any person of additional taxes, penalties or interest under Section 409A. |
5. |
Subsection (a) of Section IX (Death of Participant) is restated in its entirety as follows: |
(a)In the event of the death of a Participant, any amounts remaining in the Deferred Account will be paid to the Participant’s designated beneficiary in a single lump sum on the first business day of the calendar year following the Participant’s death. In the event that a Participant had not properly filed a beneficiary designation with the Recordkeeper prior to his or her death, or if the beneficiary dies prior to the payment date set forth in the preceding sentence, the balance of the Participant’s Deferred Account will be paid to his or her estate on such payment date.
6. |
Section X (Change in Control) is restated in its entirety as follows: |
The following acceleration and valuation provisions shall apply in the event of a Change in Control Event.
(a)In the event that a Change in Control Event occurs, then the value of all Units credited to a Participant’s Deferred Account shall be converted to cash, determined by multiplying the number of Units credited to the Participant’s Deferred Account on the date of the Change in Control Event by the “Change in Control Price” (as defined in paragraph X(b)), and the aggregate amount credited to the Participant’s Deferred Account under the Plan shall be paid in one lump-sum payment as soon as practicable following the date the Change in Control Event occurs, but in no event more than 90 days after such date.
(b)For purposes of this Section X, “Change in Control Price” means the closing selling price of a share of Common Stock on the date the Change in Control Event occurs, or if there are no sales on the date the Change in Control Event occurs, the closing selling price of a share of Common Stock on the trading day immediately preceding the date the Change in Control Event occurs, in either case as reported on the composite tape for securities listed on the NYSE, or such other national securities exchange as may be designated by the Committee.
17
(c)Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in the Plan, in the event of a Change in Control Event (i) the Plan may not be amended to reduce the formulas contained in paragraph VII(e), which determine the rate at which amounts equivalent to interest accrue with respect to cash amounts credited to a Participant’s Deferred Account, including cash amounts attributable to the conversion of Units in a Participant’s Deferred Account pursuant to paragraph X(a), and (ii) the successor Plan Administrator referred to in paragraph XI(d) shall determine the rates under the interest formulas contained in paragraph VII(e).
7. Subsection XI(b) (Miscellaneous) is amended by adding the following after the initial sentence thereof:
“No Participant or beneficiary shall have any interest whatsoever in any specific asset of the Company.
8. Subsection XI(d) (Miscellaneous) is amended by replacing each occurrence of the term “Change in Control” with “Change in Control Event”.
9. Subsection XI(e) (Miscellaneous) is amended by adding thereto:
“If the Plan is terminated, the balance of the Participant’s Deferred Account shall be paid in accordance with normal time and form of payment specified hereunder, provided that the Committee, in its discretion and in full and complete settlement of the Company’s obligations under this Plan, may cause the Company to distribute the full amount of a Participant’s Deferred Account to the Participant in a single lump sum to the extent that such distribution may be effected in a manner that will not result in the imposition on any person of additional taxes, penalties or interest under Section 409A.
Notwithstanding any provision in this Plan to the contrary, the Board, the Committee or the Vice President of Human Resources of the Company shall have the unilateral right to amend or modify the Plan to the extent the Board, the Committee or the Vice President of Human Resources of the Company deems such action to be necessary or advisable to avoid the imposition on any person of adverse or unintended tax consequences under Section 409A, including recognition of income in respect of any benefits under this Plan before such benefits are paid or the imposition of additional taxes, penalties or interest. Any determinations made by the Board, the Committee or the Vice President of Human Resources of the Company in this regard shall be final, conclusive and
18
binding on all persons.”
19
SCHEDULE A
Notional Investment Options
BTC LIFEPATH RET G
BTC LIFEPATH 2025 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2030 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2035 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2040 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2045 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2050 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2055 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2060 G
BTC LIFEPATH 2065 G (AVAILABLE ON NOVEMBER 15, 2019)
S & P 500 STOCK INDEX, CLASS F
SMALL/MID STOCK INDEX, CLASS F
INTERNATIONAL STOCK INDEX, CLASS F
U.S. TIPS BOND INDEX, CLASS F
U.S. BOND INDEX, CLASS F
COMMODITY INDEX, CLASS F
REAL ESTATE INDEX, CLASS F
FIDELITY GROWTH COMPANY COMMINGLED POOL CLASS #3
BOSTON PARTNERS LARGE CAP VALUE FUND SHARE CLASS E
QMA US SMALL CAP CORE EQUITY FD CL
INTERNATIONAL STOCK INDEX CLASS F
U.S. EQUITY FUND (effective November 1, 2023)
20
ALLSPRING EMERGING MARKETS EQUITY CIT E2
CIT-ALLSPRING ENHANCED CORE BOND E2
FIDELITY® INVESTMENTS MONEY MARKET FUNDS GOVERNMENT PORTFOLIO INSTITUTIONAL CLASS
21
Exhibit 10.27
DEERE & COMPANY
INCENTIVE COMPENSATION RECOVERY POLICY
Effective August 29, 2023
The Compensation Committee (the “Compensation Committee”) of the Board of Directors of Deere & Company (the “Company”) has adopted this Incentive Compensation Recovery Policy, which provides for the recoupment of certain executive compensation in the event that the Company is required to prepare an accounting restatement due to material noncompliance with any financial reporting requirement under the federal securities laws (this “Policy”). This Policy is designed to comply with Section 10D of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), the rules promulgated thereunder, and the Listed Company Manual of the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”).
Covered Executives. This Policy applies to current and former executive officers, as determined by the Compensation Committee in accordance with Section 10D of the Exchange Act, the rules promulgated thereunder, and the Listed Company Manual of the NYSE, and such other senior executives or employees who may from time to time be deemed subject to this Policy by the Compensation Committee (collectively, the “Covered Executives”).
Recovery Obligation. In the event that the Company is required to prepare an accounting restatement of its financial statements due to the Company’s material noncompliance with any financial reporting requirement under the securities laws, including any required accounting restatement to correct an error in previously issued financial statements that is material to the previously issued financial statements, or that would result in a material misstatement if the error were corrected in the current period or left uncorrected in the current period (each an “Accounting Restatement”), the Compensation Committee will reasonably promptly recover the Overpayment (as defined below) received by any Covered Executive during the three (3) completed fiscal years immediately preceding the date on which the Company is required to prepare an Accounting Restatement (or any transition period that results from a change in the Company’s fiscal year within or immediately following those three (3) completed fiscal years).
Incentive-Based Compensation. For purposes of this Policy, “Incentive-Based Compensation” means any compensation that is granted, earned, or vested based wholly or in part upon the attainment of a financial reporting measure. A financial reporting measure is: (i) any measure that is determined and presented in accordance with the accounting principles used in preparing financial statements, or any measure derived wholly or in part from such measure and (ii) stock price and total shareholder return. Incentive-Based Compensation and financial reporting measures are further defined in Exhibit A.
Overpayment. The amount to be recovered will be the amount of Incentive-Based Compensation received that exceeds the amount of Incentive-Based Compensation that otherwise would have been received had it been determined based on the restated amounts (or as otherwise determined in accordance with Section 10D of the Exchange Act, the rules promulgated thereunder, and the Listed Company Manual of the NYSE), and must be computed without regard to any taxes paid or withheld (the “Overpayment”).
Method of Recovery. The Compensation Committee shall determine, in its sole discretion, the manner in which any Overpayment shall be recovered. Methods of recovery may include, without limitation: (i) seeking repayment of cash Incentive-Based Compensation previously paid; (ii) seeking recovery of any gain realized on the vesting, exercise, settlement, sale, transfer, or other disposition of any equity-based awards; (iii) offsetting a portion of the Overpayment from any compensation otherwise owed by the Company to the Covered Executive; (iv) cancelling outstanding vested or unvested equity awards; (v) taking any other recovery action permitted by law; and/or (vi) any combination of the foregoing.
Limitation on Recovery. The right to recovery will be limited to Overpayments paid or distributed to individuals who served as Covered Executives during the three (3) years prior to the date on which the Company is required to prepare an Accounting Restatement (or during any transition period that results from a change in the Company’s fiscal year within or immediately following those three (3) completed fiscal years), and if applicable, limited by the date such Covered Executive began service as a Covered Executive.
Impracticability. The Compensation Committee shall recover any Overpayment in accordance with this Policy except to the extent that the Compensation Committee determines such recovery would be impracticable, as determined in accordance with Section 10D of the Exchange Act, the rules promulgated thereunder, and the Listed Company Manual of the NYSE.
No Additional Payment. The Company shall not be required to award Covered Executives an additional payment if the restated financial results would have resulted in a higher Incentive-Based Compensation payment.
No Indemnification. No Covered Executive shall receive indemnification from the Company or any of its affiliates for any loss associated with amounts that are or may be recovered by the Company pursuant to this Policy.
Administration; Interpretation. The Compensation Committee shall be the administrator of this Policy. The Compensation Committee is authorized to interpret and construe this Policy and to make all determinations necessary, appropriate, or advisable for the administration of this Policy. Determinations made by the Compensation Committee shall be final and binding. It is intended that this Policy be interpreted in a manner that is consistent with the requirements of Section 10D of the Exchange Act and the applicable rules or standards adopted by the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) or the Listed Company Manual of the NYSE.
Effective Date. This Policy shall be effective as of the date it is adopted by the Compensation Committee (the “Effective Date”) and shall apply to Incentive-Based Compensation (including Incentive-Based Compensation granted pursuant to arrangements existing prior to the Effective Date).
Amendment or Termination. The Compensation Committee reserves the right to amend this Policy from time to time in its discretion. The Compensation Committee may terminate this Policy at any time.
2
Other Recovery Rights. The Compensation Committee intends that this Policy will be applied to the fullest extent of the law. The Compensation Committee may require that any employment or service agreement, equity award agreement, or similar agreement entered into on or after the Effective Date shall, as a condition to the grant of any benefit thereunder, require a Covered Executive to agree to abide by the terms of this Policy. Any right of recovery under this Policy is in addition to, and not in lieu of, any other remedies or rights of recoupment that may be available to the Company pursuant to the terms of any similar policy in any employment or service agreement, equity award agreement, or similar agreement and any other legal remedies available to the Company; provided, however, that there is no intention to, nor shall there be, any duplicative recovery of the same compensation under more than one policy, plan, award, or agreement.
Successors. This Policy shall be binding and enforceable against all Covered Executives and their beneficiaries, heirs, executors, administrators, or other legal representatives.
3
EXHIBIT A
“Incentive-Based Compensation” means any compensation that is granted, earned, or vested based wholly or in part upon the attainment of a financial reporting measure, including, but not limited to: (i) non-equity incentive plan awards that are earned solely or in part by satisfying a financial reporting measure performance goal; (ii) bonuses paid from a bonus pool, where the size of the pool is determined solely or in part by satisfying a financial reporting measure performance goal; (iii) other cash awards based on satisfaction of a financial reporting measure performance goal; (iv) restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock options, stock appreciation rights, and performance share units that are granted or vest solely or in part on satisfying a financial reporting measure performance goal; and (v) proceeds from the sale of shares acquired through an incentive plan that were granted or vested solely or in part on satisfying a financial reporting measure performance goal.
Compensation that would not be considered Incentive-Based Compensation includes, but is not limited to: (i) salaries; (ii) bonuses paid solely on satisfying subjective standards, such as demonstrating leadership, and/or completion of a specified employment period; (iii) non-equity incentive plan awards earned solely on satisfying strategic or operational measures; (iv) wholly time-based equity awards; and (v) discretionary bonuses or other compensation that is not paid from a bonus pool that is determined by satisfying a financial reporting measure performance goal.
Financial reporting measures include, but are not limited to: revenues; net income; operating income; profitability of one or more reportable segments; financial ratios (e.g., accounts receivable turnover and inventory turnover rates); net assets or net asset value per share; earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization; funds from operations and adjusted funds from operations; liquidity measures (e.g., working capital, operating cash flow); return measures (e.g., return on invested capital, return on assets); earnings measures (e.g., earnings per share); sales per square foot or same store sales, where sales is subject to an accounting restatement; revenue per user, or average revenue per user, where revenue is subject to an accounting restatement; cost per employee, where cost is subject to an accounting restatement; any of such financial reporting measures relative to a peer group, where the Company’s financial reporting measure is subject to an accounting restatement; and tax basis income. A financial reporting measure need not be presented within the financial statements or included in a filing with the SEC.
4
EXHIBIT 21
DEERE & COMPANY
AND CONSOLIDATED SUBSIDIARIES
SUBSIDIARIES OF THE REGISTRANT
As of October 29, 2023
Subsidiary companies of Deere & Company are listed below. Except where otherwise indicated, 100 percent of the voting securities of the companies named is owned directly or indirectly by Deere & Company.
|
Name of subsidiary |
Organized under the laws of |
Subsidiaries included in consolidated financial statements * |
|
Deere Credit Services, Inc. |
Delaware |
Hamm AG |
Germany |
John Deere Asia (Singapore) Private Limited |
Singapore |
John Deere Brasil Ltda. |
Brazil |
John Deere Canada ULC |
Canada |
John Deere Capital Corporation |
Delaware |
John Deere Cash Management |
Luxembourg |
John Deere Construction & Forestry Company |
Delaware |
John Deere GmbH & Co. KG |
Germany |
John Deere Holding (Barbados) SRL |
Barbados |
John Deere Holding France S.A.S. |
France |
John Deere India Private Limited |
India |
John Deere International Manufacturing S.à.r.l. |
Luxembourg |
John Deere Limited |
Australia |
John Deere Limited |
Scotland |
John Deere Luxembourg Investment S.à.r.l. |
Luxembourg |
John Deere Sales Hispanoamerica, S. de R.L. de C.V. |
Mexico |
John Deere Shared Services LLC |
Iowa |
John Deere Technologies S.C.S. |
Luxembourg |
John Deere Walldorf GmbH & Co. KG |
Germany |
John Deere Walldorf International GmbH & Co. KG |
Germany |
Joseph Vögele Aktiengesellschaft |
Germany |
Wirtgen GmbH |
Germany |
Wirtgen America, Inc. |
Tennessee |
____________________________ |
|
|
|
* One-hundred ninety-six consolidated subsidiaries and twenty-three unconsolidated affiliates, whose names are omitted, considered in the aggregate as a single subsidiary, would not constitute a significant subsidiary. | |
| |
EXHIBIT 22
LIST OF SUBSIDIARY ISSUERS OF GUARANTEED SECURITIES
From time to time, the following 100%-owned subsidiaries of Deere & Company, a Delaware corporation (the “Company”), may issue debt securities that are fully and unconditionally guaranteed by the Company under a registration statement on Form S-3 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Name of Subsidiary Issuer |
Jurisdiction |
Deere Funding Canada Corporation |
Ontario |
Exhibit 23
CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
We consent to the incorporation by reference in Registration Statement No. 333-273045 on Form S‐3 and Registration Statement Nos. 333‐165069, 333‐62669, 333‐132013, 333‐140980, 333‐140981, 333‐202299 and 333‐236655 on Form S‐8 of our reports dated December 15, 2023, relating to the consolidated financial statements of Deere & Company, and the effectiveness of Deere & Company’s internal control over financial reporting, appearing in this Annual Report on Form 10‐K for the year ended October 29, 2023.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP |
Chicago, Illinois |
|
December 15, 2023 |
Exhibit 31.1
CERTIFICATIONS
I, John C. May, certify that:
1.I have reviewed this annual report on Form 10-K of Deere & Company;
2.Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3.Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4.The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have:
(a) Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b) Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c) Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d) Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and
5.The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b) Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
Date: December 15, 2023 |
By: |
/s/ John C. May |
|
|
John C. May |
|
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
|
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
Exhibit 31.2
CERTIFICATIONS
I, Joshua A. Jepsen, certify that:
1.I have reviewed this annual report on Form 10-K of Deere & Company;
2.Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3.Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4.The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have:
(a) Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b) Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c) Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d) Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and
5.The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b) Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
Date: December 15, 2023 |
By: |
/s/ Joshua A. Jepsen |
|
|
Joshua A. Jepsen |
|
|
Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
Exhibit 32
STATEMENT PURSUANT TO
18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350
AS REQUIRED BY
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of Deere & Company (the “Company”) on Form 10-K for the period ended October 29, 2023, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), the undersigned hereby certify that to the best of our knowledge:
1. |
The Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and |
2. |
The information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company. |
December 15, 2023 |
/s/ John C. May |
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
|
John C. May |
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
December 15, 2023 |
/s/ Joshua A. Jepsen |
|
Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal |
|
Joshua A. Jepsen |
|
Accounting Officer) |
A signed original of this written statement required by Section 906 has been provided to Deere & Company and will be retained by Deere & Company and furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission or its staff upon request.