UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 20-F
☐ |
REGISTRATION STATEMENT PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OR (g) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
OR
☒ |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
OR
☐ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
OR
☐ |
SHELL COMPANY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File Number 001-38354
CORPORACIÓN AMÉRICA AIRPORTS S.A. |
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) |
|
Not Applicable |
(Translation of registrant’s name into English) |
|
Grand Duchy of Luxembourg |
(Jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
|
Jorge Arruda Filho, Chief Financial Officer |
(Name, Telephone, E-mail and or Facsimile number and Address Company Contact Person)) |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class |
|
Trading Symbol |
|
Name of each exchange in which registered |
Common Shares, U.S.$1.00 nominal value per share |
|
CAAP |
|
New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Securities for which there is a reporting obligation pursuant to Section 15(d) of the Act: None
Indicate the number of outstanding shares of each of the issuer’s classes of capital or common stock as of the close of the period covered by the annual report
163,222,707 Common Shares, as of December 31, 2023
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes ☐ No ☒
If this report is an annual or transition report, indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer |
☐ |
Accelerated filer |
☒ |
Non-Accelerated filer |
☐ |
Emerging growth company |
☐ |
If an emerging growth company that prepares its financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark which basis of accounting the registrant has used to prepare the financial statements included in this filing:
U.S. GAAP ☐ |
International Financial Reporting Standards as issued |
Other ☐ |
If “Other” has been checked in response to the previous question, indicate by check mark which financial statement item the registrant has elected to follow.
Item 17 ☐ Item 18 ☐
If this is an annual report, indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act)
Yes ☐ No ☒
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
|
Page |
|
|
|
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT WITH RESPECT TO FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS |
2 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
||
|
|
|
4 |
||
|
|
|
6 |
||
|
|
|
6 |
||
|
|
|
6 |
||
|
|
|
6 |
||
|
|
|
37 |
||
|
|
|
133 |
||
|
|
|
133 |
||
|
|
|
181 |
||
|
|
|
188 |
||
|
|
|
191 |
||
|
|
|
199 |
||
|
|
|
199 |
||
|
|
|
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES REGARDING MARKET RISK |
213 |
|
|
|
|
213 |
||
|
|
|
214 |
||
|
|
|
MATERIAL MODIFICATIONS TO THE RIGHTS OF SECURITY HOLDERS AND USE OF PROCEEDS |
214 |
|
|
|
|
214 |
||
|
|
|
215 |
||
|
|
|
215 |
||
|
|
|
215 |
||
|
|
|
215 |
||
|
|
|
216 |
||
|
|
|
PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES BY THE ISSUER AND AFFILIATED PURCHASERS |
216 |
|
|
|
|
216 |
||
|
|
|
216 |
||
|
|
|
218 |
||
|
|
|
DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS |
218 |
|
|
|
|
218 |
||
|
|
|
218 |
||
|
|
|
220 |
||
|
|
|
221 |
||
|
|
|
222 |
||
|
|
|
|
223 |
|
i
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT WITH RESPECT TO FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This annual report contains forward-looking statements about our expectations, beliefs and intentions regarding, among other things, our products and services, development efforts, business, financial condition, results of operations, strategies, plans and prospects. Forward-looking statements can be identified by the use of forward-looking words such as “believe,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” “may,” “should,” “could,” “might,” “seek,” “target,” “will,” “project,” “forecast,” “continue” or “anticipate” or their negatives or variations of these words or other comparable words or by the fact that these statements do not relate strictly to historical matters. Forward-looking statements relate to anticipated or expected events, activities, trends or results as of the date they are made. Because forward-looking statements relate to matters that have not yet occurred, these statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ materially from any future results expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. Many factors could cause our actual activities or results to differ materially from the activities and results anticipated in forward-looking statements, including, but not limited to, the factors listed below:
| ● | our business strengths and future results of operation; |
| ● | delays or unexpected casualties related to construction under our investment plans and master plans; |
| ● | our ability to generate or obtain the required capital to fully develop and operate our airports; |
| ● | impact of epidemics, pandemics, and public health crises; |
| ● | general economic, political, demographic and business conditions in the geographic markets we serve; |
| ● | decreases in passenger traffic; |
| ● | changes in the fees we may charge under our concession agreements; |
| ● | inflation and hyperinflation, depreciation, and devaluation of the AR$, EUR, BRL, UYU or AMD, against the U.S. dollar; |
| ● | the early termination, revocation, or failure to renew or extend any of our concession agreements; |
| ● | the right of the Argentine Government to buy out the AA2000 Concession Agreement (as defined herein); |
| ● | changes in our investment commitments or our ability to meet our obligations thereunder; |
| ● | existing and future governmental regulations; |
| ● | natural disaster-related losses which may not be fully insurable; |
| ● | the ongoing war events; and |
| ● | cyberterrorism in the international markets we serve. |
We believe these forward-looking statements are reasonable; however, these statements speak only as of the date of this annual report and are subject to known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our or our industry’s actual results, levels of activity, performance, or achievements to be materially different from those anticipated by the forward-looking statements. We discuss these risks in this annual report in greater detail under the heading “Risk Factors.” Given these uncertainties, you should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events.
Unless required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events, or developments or otherwise.
2
CERTAIN CONVENTIONS
Corporación América Airports S.A. (“CAAP”) was incorporated under the laws of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (“Luxembourg”) on December 14, 2012. The Company owns no material assets other than its direct and indirect ownership of the issued share capital of other intermediate holding companies for all our operating subsidiaries. Except where the context otherwise requires or where otherwise indicated, all references to the “Company,” “CAAP,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to Corporación América Airports S.A. and its consolidated subsidiaries, as well as those businesses we account for using the equity method.
In this annual report, unless otherwise specified or the context otherwise requires:
| ● | “U.S.$” and “U.S. dollar” each refers to the United States dollar; |
| ● | “AR$” refers to the Argentine peso; |
| ● | “€,” “EUR” or “euro” each refers to the euro, the single currency established for members of the European Economic and Monetary Union since January 1, 1999; |
| ● | “R$” or “BRL” each refers to the Brazilian real; |
| ● | “$U” or “UYU” each refers to the Uruguayan peso; and |
| ● | “AMD” refers to the Armenian dram. |
We have translated some of the local currency amounts contained in this annual report into U.S. dollars for convenience purposes only. The U.S. dollar-equivalent information presented in this annual report is provided solely for convenience and should not be construed as implying that the amounts represent, or could have been or could be converted into, U.S. dollars at such rates or at any other rate. See “Item 3. Key Information— Risk Factors— Depreciation or fluctuation of the currencies of the countries where we operate could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.”
Certain numbers and percentages included in this annual report have been subject to rounding adjustments. Accordingly, figures shown for the same category presented in various tables or other sections of this annual report may vary slightly, and figures shown as totals in certain tables may not be the arithmetic aggregation of the figures that precede them.
3
PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL INFORMATION
This annual report contains our audited consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for our fiscal years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 (our “Audited Consolidated Financial Statements”).
We prepare our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”), as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”). We have applied all IFRS Accounting Standards adopted by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) effective at the time of preparing our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements. Our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements have been audited by Price Waterhouse & Co. S.R.L. (“PwC”), a member firm of the PricewaterhouseCoopers global network, and an independent registered public accounting firm, whose report dated March 20, 2024, is also included in this annual report.
Our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements are presented in U.S. dollars. Our fiscal year ends on December 31 of each year. Accordingly, all references to a particular year are to the year ended December 31 of that year.
Our Segments
As of and for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, we have identified six reportable segments: Argentina, Italy, Brazil, Uruguay, Ecuador and Armenia. See Note 4 to our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and “Adjusted Segment EBITDA and Adjusted Segment EBITDA excluding Construction Services.”
In December 2021, we transferred our 50% ownership interest in Aeropuertos Andinos del Perú S.A. (“AAP”) to Andino Investment Holding S.A. See “Business Overview—Our Airports by Country in Which We Operate—Peru.” The elimination of any intersegment revenues and other significant intercompany operations are included in the “Intrasegment Adjustments” column. AAP was not previously classified as an asset held for sale or as a discontinued operation. All the financial and operational information provided for our Peruvian segment for the year ended December 31, 2021 includes our financial information and results of operation until December 16, 2021, date on which the transfer of our interest in AAP was completed.
Factors Affecting Comparability of Prior Periods
During 2020 and 2021, the Company’s operations were significantly affected due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the related measures that affected passenger traffic. The significant decrease in our results of operations due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent rebound in our results of operations after the termination of measures affecting passenger traffic, affected the comparability of the figures reported for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 with the corresponding period in 2021.
Adjusted Segment EBITDA and Adjusted Segment EBITDA excluding Construction Services
“Adjusted Segment EBITDA” is defined, with respect to each segment, as income/(loss) from continuing operations before financial income, financial loss, income tax expense, depreciation, and amortization for such segment. Adjusted Segment EBITDA excludes certain items that are not considered part of our core operating results. Specifically, we do not allocate financial income, financial loss, income tax expense, depreciation, and amortization to our reportable segments. Our management also reviews a metric of performance, denominated “Adjusted Segment EBITDA excluding Construction Services,” which only differs with the Adjusted Segment EBITDA measure by excluding the Construction Services margin.
Although Adjusted EBITDA, and consequently, Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services, are commonly viewed as non-IFRS measures in other contexts, pursuant to IFRS 8, “Segment Information,” these are treated as IFRS measures in the manner in which we utilize them. We use Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services for purposes of making decisions about allocating resources to our segments and to internally evaluate their financial performance because we believe they reflect current core operating performance and provide an indicator of the segment’s ability to generate cash.
Non-IFRS Information
Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services
“Adjusted EBITDA” is a non-IFRS financial measure defined as net income/(loss) from continuing operations before financial income, financial loss, income tax expense, depreciation, and amortization. “Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services” only differs with the previously mentioned measure by excluding Construction Services margin.
4
Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services are not defined under IFRS and have important limitations as analytical tools. You should not consider them in isolation or as a substitute for analysis of our results as reported under IFRS. For example, Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services have the following limitations:
| ● | exclude certain tax payments that may represent a reduction in cash available to us; |
| ● | do not reflect any cash capital expenditure requirements for the assets being depreciated and amortized that may have to be replaced in the future; |
| ● | do not reflect changes in, or cash requirements for, our working capital needs; and |
| ● | do not reflect the significant interest expense, or the cash requirements, necessary to service our debt. |
We believe that the presentation of Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services enhances investors’ understanding of our performance. We believe these measures are useful metrics for investors to assess our operating performance from period to period by excluding certain items that we believe are not representative of our core business. We present Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services to provide supplemental information that we consider relevant for the readers of our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this annual report, and such information is not meant to replace or supersede IFRS measures.
In addition, our management believes Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services are useful because they allow us to evaluate our operating performance and compare the results of our operations from period to period without regard to our financing methods, capital structure or income taxes more effectively. We exclude the items listed above from income for the year in arriving at Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services because these amounts can vary substantially from company to company within our industry depending upon accounting methods and book values of assets, capital structures and the method by which the assets were acquired.
Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services should not be considered as alternatives to, or more meaningful than, consolidated net income for the year as determined in accordance with IFRS or as indicators of our operating performance from continuing operations.
Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services may not be the same as similarly titled measures used by other companies.
We have included the reconciliation of Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services to consolidated net income from continuing operations for all the periods presented. See “Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Operating Results—Adjusted EBITDA Reconciliation to Net Income/(Loss) from Continuing Operations.”
Capital Increase
As part of the management share compensation plan (see “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—Compensation—Management Compensation Plan”), on October 9, 2020, the board of directors of the Company increased the Company’s share capital by the amount of U.S.$3,200,445 through the issuance of 3,200,445 new shares having a nominal value of U.S.$1.00 each. As a result of the issuance of these new shares, which were subscribed by A.C.I. Airports S.à r.l., the Company’s controlling shareholder, the outstanding share capital of the Company as of December 31, 2023 is 163,222,707 shares. The shares were subscribed for a total subscription price of U.S.$6,144,854.40 (i.e., a subscription price of U.S.$1.92 per new share, being the market price per share as of October 8, 2020), and paid for through the incorporation of the corresponding amount which was allocated to the Company’s free distributable reserves. The new shares were, subsequently and on the same date, transferred by the controlling shareholder to the Company to be held in treasury until their allocation to key employees in accordance with the management share compensation plan. As of the date of this annual report, 949,322 shares have been delivered to key employees under the management share compensation plan and the remaining outstanding 2,251,123 shares are still held in treasury.
5
PRESENTATION OF INDUSTRY AND MARKET DATA
In this annual report, we rely on, and refer to, information regarding our business and the markets in which we operate and compete. The market data and certain economic and industry data and forecasts used in this annual report were obtained from internal surveys, market research, governmental and other publicly available information, and independent industry publications. Industry publications, surveys, and forecasts generally state that the information contained therein has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, but that the accuracy and completeness of such information is not guaranteed. We believe that these industry publications, surveys, and forecasts are reliable, but we have not independently verified them and cannot guarantee their accuracy or completeness.
Certain market share information and other statements presented herein regarding our position relative to our competitors are not based on published statistical data or information obtained from independent third parties but reflect our best estimates. We have based these estimates upon information obtained from publicly available information from our competitors in the industry in which we operate.
ITEM 1. IDENTITY OF DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND ADVISERS
Not applicable.
ITEM 2. OFFER STATISTICS AND EXPECTED TIMETABLE
Not applicable.
ITEM 3. KEY INFORMATION
A.Reserved
B.CAPITALIZATION AND INDEBTEDNESS
Not applicable.
C.REASONS FOR THE OFFER AND USE OF PROCEEDS
Not applicable.
D.RISK FACTORS
You should carefully consider the risks and uncertainties described below, together with the other information contained in this annual report, before making any investment decision. Any of the following risks and uncertainties could have a material adverse effect on our business, prospects, results of operations and financial condition. The market price of our common shares could decline due to any of these risks and uncertainties, and you could lose all or part of your investment. The risks described below are those that we currently believe may materially affect us.
Summary of Risk Factors
The following is a series of concise statements highlighting the principal, but not all, risk factors that we face. The list is followed by a discussion of the Company’s risk factors, including those highlighted below.
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
| ● | Our concessions may be terminated under various circumstances, some of which are beyond our control. |
| ● | We may be subject to monetary penalties or early termination if we fail to comply with the terms of our concession agreements. |
| ● | Our revenue is highly dependent on levels of air traffic, which depend in part on factors beyond our control, including economic and political conditions in the countries where we operate our airports. |
6
| ● | Outbreaks of diseases as well as any other public health crises that may arise in the future, have had, and may continue to have a negative impact on passenger traffic levels, air traffic operations and in our results of operations, financial position, and cash flows. |
| ● | Geopolitical uncertainties and an increase of trade protectionism could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operation and financial condition. |
| ● | We are dependent on information and communication technologies, and our systems and infrastructures face certain risks, including cybersecurity risks. |
Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement
| ● | The Argentine Government extended the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement until 2038 subject to our compliance with certain commitments, which if we fail to comply with, could result in the imposition of fines or the termination or revocation of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. |
| ● | Pursuant to the AA2000 Concession Agreement, since February 2018, the Argentine Government may buy out our concession, which would materially affect our revenues and operations. |
| ● | The Organismo Regulador del Sistema Nacional de Aeropuertos (“ORSNA”) may adjust the fees we charge for aeronautical services, the payments we are required to make to the Argentine Government and our investment plan in a way that is detrimental to us or fail to adjust them to restore the AA2000 Concession Agreement’s economic equilibrium. |
| ● | If the ORSNA does not approve the capital expenditures already made under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we could be required to make additional capital expenditures, which may affect our cash flows and financial condition. |
Risks Related to Our Other Principal Operations and Other Principal Markets in Which We Operate
| ● | Italy. If the approval process from local and national authorities of the master plan for the Florence Airport is further delayed, our financial results from the operation of such airport will be negatively impacted. |
| ● | Uruguay. A deterioration in the economic conditions of our neighboring markets, particularly Argentina has the potential to affect the number of passengers at our Uruguayan airports mainly Punta del Este airport. |
| ● | Armenia. The ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine has and will likely continue to disrupt or impact the connecting flights between our Armenian Airports and Russia, which could affect our results of operation. |
Risks Related to Our Common Shares
| ● | We issued, and may further issue, options, restricted shares, and other forms of share-based compensation, which have the potential to dilute shareholder value and cause the price of our common shares to decline. |
| ● | A significant portion of our common shares may be sold into the public market, which could cause the market price of our common stock to drop significantly, even if our business is doing well. |
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
Our concessions may be terminated under various circumstances, some of which are beyond our control.
Our business consists of acquiring, developing and operating airport concessions. These concessions are granted by governmental authorities for a limited period of time and subject to several conditions and obligations.
7
Our concessions may be terminated under various circumstances, some of which are beyond our control. In general, our concession agreements may be terminated at any time by the relevant governments or agencies for public interest reasons. Concession agreements may also be terminated due to our material and repeated breach of the concession terms. The termination of one or more of our concessions could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
If an applicable governmental authority terminates any of our concessions, with or without cause, we may be entitled to seek claims for compensation from such terminating governmental authority. Although termination payments vary by concession, they usually include a claim for indemnification equal to the value of the non-amortized investments made by us for purposes of operating the airports and rendering the services agreed under the concession agreements. If the applicable governmental authority terminates one of our concessions due to our material and repeated breach or failure to make the committed investments, we may assert claims for indemnification equal to those non-amortized investments we made for purposes of operating the relevant airports and rendering of the services agreed under the relevant concession agreements. If the concession is terminated by the relevant government or agency for public interest reasons or without cause, we may assert claims for indemnification equal to the non-amortized investments plus loss of profits. Collecting on such claims may be difficult and time-consuming, and any amounts collected in respect of such claims may not provide us with the expected level of returns, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
In the AA2000 Concession Agreement, our largest concession operations, the Argentine Government has the right to buy out the concession agreement upon prior notification to us and indemnify us for certain investments we incurred for purposes of operating the airports and rendering the services agreed thereunder. See “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement—Pursuant to the AA2000 Concession Agreement, since February 2018, the Argentine Government may buy out our concession, which would materially affect our revenues and operations.”
We may be subject to monetary penalties or early termination if we fail to comply with the terms of our concession agreements.
We may be subject to monetary penalties if we violate or otherwise fail to comply with the terms of our concessions. Some violations of a concession agreement may provide for cure periods or other remedial action, while other violations, whenever they are substantial and repeated, can result in the immediate termination of the relevant concession. If we experience difficulties, we may encounter problems in satisfying our obligations under our concession agreements and the relevant governmental authorities may impose sanctions on us. For a description of the consequences that may result from the violation of various terms of our concessions, or local laws and regulations related to such concessions, see “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework.” Monetary penalties could negatively affect our results of operations.
In addition, under all our concession agreements, we are required to establish and comply with an investment plan for the airports covered under such concession agreements. If we do not fulfill our investment commitments on a timely basis or obtain necessary financing to complete the projects, such failures could lead to a breach of the relevant concession agreement, which may subject us to monetary fines or the early termination of our concession agreements.
Our revenue and profitability may be affected if we fail to win new concession agreements, acquire companies with existing concession agreements, or otherwise improve or expand our current operations.
Our growth strategy relies upon identifying and winning new concession agreements, acquiring companies with existing concession agreements, or improving and expanding our current operations. Our future growth may also depend on new (greenfield) development projects, which may require significant time and upfront financial commitments for construction and development. While we anticipate having opportunities to bid for concession agreements or purchase existing concessionaires in the future, we cannot predict the frequency or accuracy of such opportunities. We must also strategically identify which concession agreements and existing concessionaires to target based on numerous factors such as number of passengers, size of the relevant airport(s), type, location, and quality of the available airports and subconcession space, rental structure, financial return, regulatory requirements, and the competitive landscape within such market. We may not be able to successfully expand, as we may not correctly analyze the suitability of airport locations, anticipate all the challenges imposed by expanding our operations or succeed in executing our growth plan efficiently. We also may fail to expand within budget, on a timely basis or expand at all. In addition, to win a particular concession contract, we may be required to make investments or incur other expenses that would render such concession less economically attractive.
Our growth strategy and the substantial investment associated with the acquisition of each new concession agreement, existing concessions or expansion of existing concessions may cause our operating results to fluctuate and be unpredictable.
8
Outbreaks of diseases as well as any other public health crises that may arise in the future, have had, and may continue to have a negative impact on passenger traffic levels, air traffic operations and in our results of operations, financial position, and cash flows.
Future outbreaks of existing or future diseases as well as any other public health crises, or the fear of such events and governmental responses to such events, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, could provoke responses that negatively affect passenger air traffic. The COVID-19 pandemic that resulted in several cities being placed under quarantine, increased travel restrictions from and to several countries, and extended shutdowns of certain businesses in certain regions, also forced airlines to cancel flights and disrupted the frequency and pattern of air travel worldwide. New strains of the COVID-19 virus, as well as, future public health crises similar to the outbreak of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (known as SARS) between 2002 and 2003, the outbreak of the A/H1N1 virus in 2009, the Ebola outbreak in 2014 and 2015 and the outbreak of the Zika virus in 2018 and 2019, could have a negative impact on our business and our revenue which is largely dependent on the level of passenger traffic in our airports. Any outbreaks of health epidemics could result in decreased passenger traffic and increased costs for the air travel industry and, as a result, could have a material adverse effect on our business revenues and results of operations.
Our business, operating results and growth rates may be adversely affected by current or future unfavorable economic and market conditions and adverse developments in the global economy.
Our business depends on the economic health of the global economy. If the conditions of the global economy remain uncertain or continue to be volatile, or if they deteriorate, including as a result of the impact of military conflict, such as the war between Russia and Ukraine and the conflict between Israel and Hamas, terrorism or other geopolitical events, our business, our operating results and our financial condition may be materially adversely affected.
In the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States and global markets have encountered a material increase in the level of inflation. Increases in inflation rates raise our costs for commodities, labor, materials and services and other costs required to grow and operate our business, and failure to secure these on reasonable terms may adversely impact on our financial condition. Additionally, increases in inflation rates have caused, and may cause in the future, global economic uncertainty and uncertainty about the interest rate environment, which may make it more difficult, costly or dilutive for us to secure additional financing. A failure to adequately respond to these risks could have a material adverse impact on our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
There can be no assurance that future credit and financial market instability and a deterioration in confidence in global economic conditions will not occur. Our general business strategy may be adversely affected by any such economic downturn, liquidity shortages, volatile business environment or continued unpredictable and unstable market conditions. If the current equity and credit markets deteriorate, or if adverse developments are experienced by financial institutions, it may cause short-term liquidity risk and also make any necessary debt or equity financing more difficult, more costly, more onerous with respect to financial and operating covenants and more dilutive. Failure to secure any necessary financing in a timely manner and on favorable terms could have a material adverse effect on our growth strategy, financial performance and stock price and could require us to alter our operating plans. In addition, there is a risk that one or more of our service providers, financial institutions, manufacturers, suppliers and other partners may be adversely affected by the foregoing risks, which could directly affect our ability to attain our operating goals on schedule and on budget.
Geopolitical uncertainties and an increase of trade protectionism could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operation and financial condition.
Russia’s war against neighboring Ukraine continues to disrupt international travel from and to Russia and Ukraine and other destinations. Additionally, as a response to the ban of flights to Russia by Western countries and the European Union, Russia has closed its skies for carriers registered in Western countries and carriers also avoid overflying the war zone, disrupting global supply chains (including aircraft components), and adversely affecting air travel (including air travel routs and accessibility to airports).
In addition to travel restrictions, in response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the European Union, the U.K. and the U.S. introduced extensive sanctions on Russia (as well as Belarus for its role in Russia’s invasion) comprised of targeted, restrictive measures on certain individuals and entities, export controls, restrictions on economic relations, trade and other financial transactions. These sanctions have had, and are expected to continue to have, a significant disruptive effect on global markets, including oil and gas markets. Geopolitical events may lead to further instability across Europe and worldwide.
9
The imposition of tariffs on certain imported products by the U.S. has triggered retaliatory actions from certain foreign governments and may trigger retaliatory actions by other foreign governments, potentially resulting in a “trade war”. Certain foreign governments have instituted or are considering imposing trade sanctions on certain U.S. goods. Others are considering the imposition of sanctions that will deny U.S. companies access to critical raw materials.
Relatedly, global markets and supply chains have been further disrupted by Hamas attack on October 7, 2023. Hamas, an organization designated by the U.S. as a terrorist organization, launched a series of coordinated attacks from the Gaza Strip onto Israel. On October 8, 2023, Israel formally declared war on Hamas, and the armed conflict is ongoing as of the date of this filing. Hostilities between Israel and Hamas could escalate and involve surrounding countries in the Middle East. To date, we have not experienced any material disruptions and interruptions in our infrastructure, supplies, technology systems, or networks needed to support our operations as a result of the conflict between Israel and Hamas, but cannot discard the possibility of future disruptions and interruptions as a result of this conflict.
We cannot predict the progress, outcome or consequences of the conflicts between Russia and Ukraine, or Israel and Hamas, or their impacts in Ukraine, Russia, Belarus, Europe, the U.S., or the Middle East. The length, impact, and outcome of ongoing military conflicts is highly unpredictable and could lead to significant market and other disruptions, including significant volatility in commodity prices and supply of energy resources, instability in financial markets, supply chain disruptions, political and social instability, trade disputes or trade barriers, changes in consumer or purchaser preferences, as well as an increase in cyberattacks and espionage. The above geopolitical and trade uncertainty and tensions have resulted in fuel price increases, and have affected, and may continue to affect, our profitability. Sanctions, trade wars between certain countries or blocks of countries, or other governmental action related to tariffs or international trade agreements, could have a material adverse effect on passenger traffic on our airports as well as on our services, costs and suppliers or world economy or certain sectors thereof and, consequently, on our business and financial results.
We could be subject to acts of terrorism or war, which could have a negative impact on air travel and result in increased security requirements.
Our airports operate within a stringent and complex security regime, as required by the relevant governmental authorities, which may impose additional security measures from time to time. The consequences of the Russian and Ukraine war, the Israel and Hamas conflict, as well as any future terrorist action, threat or war may include the cancellation or delay of flights, fewer airlines and passengers using our airports, liability for damage or loss and the costs of repairing damage. If as a consequence of conflict or terrorist attack one of the airports we operate is affected, the airport in question could be closed, in whole or in part, for the time needed to care for victims, investigate the circumstances of the attack, rebuild any damaged areas or otherwise, with a subsequent decrease in the revenue and increase in costs for the reconstruction of the affected areas (to the extent these are not covered by insurance policies).
Moreover, if an accident, act of terrorism or threat affects the safety standard perception on customers thereof or were to occur in a country in which we operate, even if not at our airports, the perception of safety by airport users could decrease, and, consequently, there could be a reduction in passenger air traffic for an indefinite period of time, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Furthermore, the implementation of additional security measures at our airports in the future could lead to additional limitations on airport capacity or retail space, overcrowding, increases in operating costs and delays to passenger movement through the airport, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Our business may also be affected by the outbreak of wars or armed conflicts in any region of the world, including, for example, the Russian and Ukraine war, and the Israel and Hamas conflict. Among other things, wars can lead to increased prices of fuel, supplies, and interest rates for aircraft leases, which could, in turn, lead to increased prices of airline tickets and a decline in demand for air transportation in general. Likewise, the occurrence of armed conflicts could result in increased security measures, thereby increasing security costs.
10
We are dependent on information and communication technologies, and our systems and infrastructures face certain risks, including cybersecurity risks.
The operation of complex infrastructures, such as airports, and the coordination of the many actors involved in its operation require the use of several highly specialized information systems, including both our own information technology systems and those of third-party service providers, such as systems that monitor our operations or the status of our facilities, communication systems to inform the public, access control systems and closed circuit television security systems, infrastructure monitoring systems, passenger ticketing and boarding, automated baggage handling, points of sale, terminals and radio and voice communication systems used by our personnel. In addition, our accounting and fixed assets, payroll, budgeting, human resources, supplier and commercial, hiring, payments and billing systems and our websites are key to the functioning of our airports. The proper functioning of these systems is critical to our operations and business management. These systems may, from time to time, require modifications or improvements as a result of changes in technology, the growth of our business and the functioning of each of these systems.
Attempts to gain unauthorized access to our information technology systems have become more sophisticated over time. The risk of cyber - crime has been increasing, especially as infiltrating technology continues to become increasingly sophisticated. We and certain of our service providers may from time to time be subject to cyberattacks and security incidents. While we have not experienced any significant system failure, accident or security breach to date, if such an event were to occur and cause interruptions in our and our critical third parties’ operations, it could result in material disruptions to our programs, our operations, and ultimately, our financial results. In particular, if we are unable to contain or minimize the effects of a significant cyber - attack, such attack could materially affect the number of passengers at our airports, cause the loss or exposure of information, damage our reputation and lead to regulatory penalties and financial losses. Any security compromise affecting us, our service providers, strategic partners, other contractors, consultants, or our industry, whether real or perceived, could harm our reputation, erode confidence in the effectiveness of our security measures and lead to regulatory scrutiny. To the extent that any disruption or security breach were to result in a loss of, or damage to, our data or systems, or inappropriate disclosure of confidential or proprietary or personal information, we could incur liability, including litigation exposure, penalties and fines, we could become the subject of regulatory action or investigation, our competitive position could be harmed and the further development and commercialization of our products and services could be delayed. If such an event were to occur and cause interruptions in our operations, it could result in a material disruption of our business.
In order to face these issues, we created a global information security department which reports to the Executive Committee. We also hired a global information security manager and reinforced the global information security department with multicultural security specialists in different locations. This new area focuses on cybersecurity, contingency procedures, security governance, access and identity management, infrastructure protection and monitoring, researching and deploying new technology to improve protection of information and communication systems.
Additionally, we are implementing a global security monitoring service (SOC) including a new incident response and threat intelligence service. This service allows us to respond more quickly and efficiently to any potential security breach. On the other hand, we are implementing and strengthening security measures to maintain and improve protection of information, increasing endpoint and perimeter protection, vulnerability management processes in order to improve the global posture of the company in terms of information security. However, these information technology systems cannot be completely protected against certain events such as natural disasters, fraud, computer viruses, hacking, communication failures, equipment breakdown, software errors and other technical problems. The occurrence of any of these events could disrupt our operations, result in an increase in costs and a decrease in revenue and damage our public image and our business in general.
The loss or impairment of our relationship with governments and their agencies in the markets in which we operate could adversely affect our business, future revenues, and growth prospects.
Our principal assets are concession rights granted by governments in the countries in which we operate. Our business depends to a large extent on our ability to manage relationships with the relevant governments and their agencies. During the term of our concessions, we are in continuous communications with the relevant governments and their agencies regarding, among other things, the terms and conditions of the concession, compliance with the concession agreement, the applicable master plan and works to be performed at the airports, including works not specifically required by the terms of the relevant concession, and the establishment of tariffs. Our business, prospects, financial condition, or operating results could be materially harmed if we were suspended or debarred from contracting with any such government or government agency or if our reputation or relationship with any such government or agency is impaired.
11
Our revenue is highly dependent on levels of air traffic, which depend in part on factors beyond our control, including economic and political conditions in the countries where we operate our airports.
Our revenue is closely linked to passenger and cargo traffic volumes and the number of air traffic movements at our airports. These factors directly determine our aeronautical revenue and indirectly determine our commercial revenue. Passenger and cargo traffic volumes and air traffic movements depend, in part, on many factors beyond our control. Such factors include economic conditions and the political situation in the countries where we operate our airports, epidemics, pandemics and other public health crises, terrorism, fluctuations in petroleum prices (which can have a negative impact on traffic as a result of fuel surcharges or other measures adopted by airlines in response to increased fuel costs), currency exchange rate fluctuations, hyperinflation, geopolitical considerations and changes in regulatory policies applicable to the aviation industry. The occurrence of any of these risks may result in a reduction of passenger air traffic levels and air traffic movements globally and in the regions in which we operate. A significant decline in passenger and cargo traffic volumes and the number of air traffic movements at our airports could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We face risks related to our dependence on the revenue from Ezeiza Airport.
During the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, the Ministro Pistarini International Airport (“Ezeiza Airport”) generated U.S.$253.7 million or 18.2% of our consolidated revenue, U.S.$278.1 million or 20.2 % of our consolidated revenue, and U.S.$123.3 million or 17.4% of our consolidated revenue, respectively, for each of such periods. As a result of the substantial contribution to our revenue from the Ezeiza Airport, any event or condition affecting this airport (in addition to any potential termination or buyout of the AA2000 Concession Agreement) could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations. For example, an economic recession in Argentina, a reduction in the operations of Ezeiza Airport, competition from other airports or a decrease in the number of passengers traveling to Buenos Aires as tourists could cause a decrease in our revenue from this airport which, in turn, could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Increases in international fuel prices could reduce demand for air travel.
The price of fuel may be subject to fluctuations resulting from a reduction or increase in output of petroleum, voluntary or otherwise, by oil producing countries, other market forces, any future terrorist attacks, a general increase in international hostilities, including, for example, the Russian and Ukraine war, and the Israel and Hamas conflict. In the past, increased fuel costs were among the factors leading to cancellations of routes, decreases in frequencies of flights and, in some cases, even contributed to filings for bankruptcy by some airlines. Although fuel is a widely traded global commodity, in the event of a significant increase in fuel prices in one or more of the countries in which we operate, or in one or more countries that provide significant numbers of international air passengers to the countries in which we operate, the effects of a localized price increase may be more significant than a general, worldwide increase in fuel prices. Significant fluctuations may result in higher airline ticket prices and in a decrease in demand for air travel generally, both of which could have an adverse effect on our revenues and results of operations.
Extended interruptions or disruptions at the airports where we operate due to natural disasters, prolonged weather conditions and other adverse incidents could affect our business and results of operations.
A significant extended interruption or disruption in service at the airports where we operate could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. Our operations could be impacted by flight cancellations and airport closures caused by weather and natural disasters. Severe weather conditions, particularly heavy snowfall, increases in the frequency, severity, and duration of natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, volcanic activity, earthquakes, and tsunamis, can significantly disrupt service, cause cancellation of flights and negatively affect passenger traffic at airports, which may result in decreased revenues and increased costs. The disaster recovery and business continuity plans we have in place may prove inadequate in the event of a serious disaster or similar event. We may incur substantial expenses as a result of the limited nature of our disaster recovery and business continuity plans, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Competition from other destinations could adversely affect our business.
The principal factor affecting our business is the number of passengers that use our airports. Our passenger traffic volume may be adversely affected by the attractiveness, affordability, and accessibility of competing destinations. In addition, our passenger traffic volume may be adversely affected by the level of business activity in each destination or the likelihood of airlines using any of those destinations as a hub or base for their operations. If business activity and tourism levels and, therefore, the number of passengers using our airports, is negatively impacted by competing airports and hubs in the geographic regions in which we operate, such development could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, or results of operations.
12
We are subject to the risk of union disputes and work stoppages at our locations, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Some of our employees are members of labor unions. For example, as of December 31, 2023, approximately 63% and 32.7% (64.8% and 48.9 %, as of December 31, 2022) of our employees in Argentina and Italy, respectively, were members of labor unions. Negotiating labor contracts, either for new locations or to replace expiring contracts, is time consuming or may not be accomplished on a timely basis. In addition, we negotiate some of our collective bargaining agreements on an annual basis. If we are unable to satisfactorily negotiate those labor contracts with the labor unions on terms acceptable to us or without a strike or work stoppage, the effects on our business could be materially adverse. Any strike or work stoppage could disrupt our business, adversely affecting our results of operations and our public image could be materially adversely affected by such labor disputes. In addition, existing labor contracts may not prevent a strike or work stoppage, and any such work stoppage could have a material adverse effect on our business.
The operations of our airports may be adversely affected by actions or inactions of third parties that are beyond our control.
In most of our airports, our operations are largely dependent on the services provided by governments and other third parties who render services to passengers and airlines, such as meteorology, air traffic control, security, electricity, and immigration and customs services. In addition, in some of our airports we are dependent on third-party providers of certain complementary services such as baggage handling, fuel services, catering and aircraft maintenance and repair. While we are responsible for adopting security measures at some of our airports, we do not control the management or operation of security, which is controlled by government agencies or third parties. We are not responsible for, and cannot control, any of these services. Any disruption in, or other adverse situation related to, such services, including work strikes or other similar events, could cause the cancellation of flights and negatively affect passenger traffic at our airports, which may ultimately result in decreased revenues and have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, or results of operations.
The loss of one or more of our aeronautical customers or the interruption of their operations could result in a loss of a significant amount of our passenger traffic.
None of our agreements with our aeronautical customers obligate them to provide service at or to our airports. If any of our aeronautical customers were to reduce their use of our airports or cease to operate at them for any reason, including merger, bankruptcy, or due to regulatory restrictions or the impact of any disease outbreak, or impacts of the Russia and Ukraine war or the Israel and Hamas conflict, among other factors, the remaining airlines may not increase their flight frequency to replace the flights that our aeronautical customers could no longer operate. Our business and revenue, and our ability to recover receivables, could be adversely affected if we are unable to replace the business of our main aeronautical customers.
Our main aeronautical customers are Aerolíneas Argentinas Group and LATAM Group. For the year ended December 31, 2023, Aerolíneas Argentinas Group and LATAM Group accounted for 11.1% and 13.1% of our consolidated aeronautical revenue, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2022, Aerolíneas Argentinas Group and LATAM Group accounted for 15.8% and 10.8% of our consolidated aeronautical revenue, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2021, Aerolíneas Argentinas Group and LATAM Group accounted for 8.7% and 10.1% of our consolidated aeronautical revenue, respectively.
Consequently, we have a significant concentration of aeronautical customers, which may expose us to a material adverse effect if one or more of our large aeronautical customers were to significantly suspend or interrupt payments to us for any reason. Furthermore, a delay in payment or non-payment by a major aeronautical customer could materially and adversely affect the results of our operations.
An aircraft accident or other material factors beyond our control, such as disasters, climate - related catastrophes, among others, may affect the operation of our runways.
Our runways may require unscheduled repair, renovation or reconstruction due to natural disasters, climate - related catastrophes, aircraft accidents and other factors beyond our control. The closure of any runway for a significant period of time could have a material adverse effect on the number of passengers that use our airports, and therefore, a material adverse effect on our operations and financial results.
13
Ongoing and proposed construction, renovation or repair work at our airports could have a negative impact on our revenues.
At any time, we may be in the process of constructing, renovating and/or repairing a number of our airports. These works may sometimes affect the passenger experience, which may ultimately adversely affect our commercial revenue. The operations of our other airports may decrease or be adversely affected by future construction, renovations, or repairs, and this could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
We are exposed to certain risks in connection with the use of certain spaces by subconcessionaires at our airports.
We are exposed to risks related to the spaces subconcessioned to third parties, such as non-payment by subconcessionaires of certain fees and other lease arrangements or a weakening demand for the use of the spaces allocated to subconcessionaires. For example, many of our subconcessionaires’ locations are situated beyond the security checkpoints at airports, and they rely heavily on their customers spending a significant amount of time in the terminal and waiting areas of the airport terminals in which they have subconcessioned space. Changes in customers’ travel habits prior to departure, including an increase in the availability or popularity of airline business and first-class lounges, or an increase in the efficiency of ticketing, transportation safety procedures and air traffic control systems could reduce the amount of time that customers spend at such subconcessioned locations, which could materially reduce the revenue they are able to generate and which, in turn, could reduce the amount of fees and rent we can collect from our subconcessionaires. Any material reduction in the fees and lease payments that we are able to charge to our subconcessionaires could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our insurance policies may not provide sufficient coverage against all liabilities.
We are required to maintain insurance under all our concession agreements, and we seek to ensure all risks for which insurance coverage is available on commercially reasonable terms. We can offer no assurance that our insurance policies will cover all our liabilities in the event of an accident, natural disaster, terrorist attack or other incident. The insurance market for airport liability coverage generally, and for airport construction in particular, is limited and a change in the coverage policy by the insurance companies involved could reduce our ability to obtain and maintain adequate or cost-effective coverage. For example, insurance alternatives in Armenia are limited, therefore, we could incur in higher costs in obtaining insurance policies as required under the concession.
Similarly, for some of our airports, we do not currently carry business interruption insurance or property insurance against terrorism and related risks. Consequently, any substantial interruption of our business or terrorist attacks could have a material adverse effect in our results of operations and our financial condition.
We are exposed to liability to third parties for injuries or damages.
We are obligated to protect the public and to reduce the risk of accidents at our airports. As with any company dealing with the security of individuals, we must implement measures for the protection of the public, such as hiring private security services, maintaining our airports’ infrastructure and fire safety in public spaces, and providing emergency medical services. These obligations could expose us to liability to third parties for personal injury or property damage and, to the extent not adequately covered by insurance, could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
Most of our operations are in emerging markets.
Our existing concessions are mostly in countries with emerging economies and investing in developing economies generally involves risks. These risks include political, social, and economic events, any of which could impact our operations or the market value of our common shares and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. These risks and instability are caused by many different factors, including the following:
| ● | adverse external economic factors; |
| ● | inconsistent fiscal and monetary policies (including currency devaluation); |
| ● | dependence on external financing; |
| ● | changes in governmental economic and tax policies and regulations; |
| ● | high levels of inflation; |
14
| ● | fluctuations in currency values; |
| ● | high interest rates; |
| ● | wage increases and price controls; |
| ● | limitation on imports; |
| ● | exchange rates and capital controls; |
| ● | political and social tensions; |
| ● | fluctuations in central bank reserves; and |
| ● | trade barriers. |
Emerging markets have historically experienced uneven periods of economic growth, as well as recession, periods of high inflation and economic instability. Adverse economic conditions in any of these countries could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Some of the countries in which we operate have experienced, or are currently experiencing, high rates of inflation. In an effort to control inflation, governments of these countries often maintain a tight monetary policy with high interest rates, thereby restricting the availability of credit and retarding economic growth. Inflation, measures to combat inflation and public speculation about possible additional actions have also contributed significantly to economic uncertainty in many of these countries and to heightened volatility in their securities markets. Periods of higher inflation may also slow the growth rate of local economies. Inflation is also likely to increase some of our costs and expenses, which we may not be able to fully transfer to our clients, which could adversely affect our operating margins and operating income in some of the emerging markets in which we operate.
Depreciation or fluctuation of the currencies of the countries where we operate could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Many of the countries where we operate have experienced volatility in the exchange rate of their currency against the U.S. dollar. Because we present our financial statements in U.S. dollars, this volatility may reduce the revenues we report or increase the expenses we report in any given period. These effects may in turn have an adverse effect on the market of our common shares. In addition, because we have a substantial amount of dollar-denominated indebtedness, exchange rate volatility may result in increased debt service costs. Finally, in some instances we receive revenues in a currency different from that in which we pay expenses, in which case currency volatility can affect the profitability of our operations.
We are subject to various environmental laws, regulations and authorizations that affect our operations and may expose us to significant costs, liabilities, obligations, or restrictions.
We, our subconcessionaires and our aeronautical customers are subject to various environmental laws, regulations and authorizations governing, among other things, the generation, use, transportation, management and disposal of hazardous materials, the emission and discharge of hazardous materials into the ground, air or water, and human health and safety. Failure to comply with these environmental requirements, including the terms of our concession agreements, could result in our being subject to litigation, fines, or other sanctions. We could also incur significant capital or other compliance costs relating to such requirements. We could also be held responsible for contamination, human exposure to hazardous materials or other environmental damage at our airports or otherwise related to our operations. Environmental claims have been asserted against us, and additional claims may be asserted against us in the future. See “Item 8. Financial Information—Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information—Legal Proceedings—Argentine Proceedings—Environmental Proceedings.” We are unable to determine our potential liability under these pending or possible future claims. We only have environmental insurance coverage for environmental damages at a limited number of our airports.
These environmental requirements, and the enforcement and interpretation thereof, change frequently and have tended to become more stringent over time. Future environmental laws, regulations and authorizations may require us to incur additional costs in order to bring our airports into, and maintain, compliance. Our costs, liabilities, obligations, and restrictions relating to environmental matters could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
15
We are subject to review by taxing authorities, and an incorrect interpretation by us of tax laws and regulations may have a material adverse effect on us.
Taxes payable by companies in many of the countries in which we operate are substantial and include value-added tax, excise duties, profit taxes, payroll related taxes, property taxes, and other taxes. In certain countries in which we operate, such as Brazil or Argentina, the tax system is highly complex and the interpretation of the tax laws and regulations is commonly controversial, leading to disputes which are sometimes subject to prolonged evaluation periods until a final resolution is reached. In addition, there may be changes that result from enactment of additional tax reforms or changes to the manner in which current tax laws are applied that cannot be quantified and there can be no assurance that any such reforms or changes would not have an adverse effect upon our revenues. For instance, most jurisdictions in which we operate have recently adopted new transfer pricing measures. If tax authorities impose significant additional tax liabilities as a result of transfer pricing adjustments, it could have an adverse effect on us.
Over the past few years, tax administrations around the world have put in place a number of initiatives to facilitate communication and information exchange among each other, have become more rigid in exercising any discretion they may have, and have increased their scrutiny of company tax filings. In this regard, the G20 / OECD Inclusive Framework has been working on addressing a number of tax challenges such as transparency, exchange of information, coherence, and substance, and to this end has proposed numerous tax law changes under its Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) Action Plans. Particularly, in December 2021, the OECD released the Pillar Two model rules (the Global Anti-Base Erosion Proposal, or ‘GloBE’ rules) for a new global minimum tax framework introducing a minimum tax regime for multinationals. At the EU level, the European Council formally adopted the directive implementing Pillar Two and Member States were obliged to transpose the directive into national laws before 31 December 2023 (the five Member States that have not done it within the deadline are now expected to do so soon, as penalties from the CJEU can be imposed). The EU has also adopted a number of Directives (namely, the Anti-Tax Avoidance Directives, or ATAD), which seek to prevent tax avoidance by companies and to ensure that companies pay appropriate taxes in the markets where profits are effectively made, and business is effectively performed.
In establishing a provision for income tax expense and filing returns, we must make judgments and interpretations about the application of these inherently complex tax laws that may be interpreted differently by the competent tax authorities and courts. For example, applying the GloBE rules and determining the impact are likely to be very complex and pose a number of practical challenges. While disclosing quantitatively the full effect of these laws is realistically not possible at this stage, we believe that they could have an adverse effect on us, as the new rules could result in new taxes and/or additional costs for the Company when complying with the new reporting obligations.
In addition, in some jurisdictions where we operate, the interpretations of tax laws by the taxing authorities are sometimes unpredictable and frequently involve litigation, introducing further uncertainty and risk to our tax liability. It is also possible that tax authorities in the countries in which we operate will introduce additional revenue raising measures. If the judgment, estimates and assumptions we use in preparing our tax returns are subsequently determined to be incorrect, there could be a material adverse effect on us, which may ultimately affect our revenues. See “Item 8. Financial Information—Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information—Legal Proceedings” and “Item 8. Financial Information—Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information—Legal Proceedings—Argentine Proceedings— Tax Proceedings Related to Technical Assistance Agreements.”
Any of these events occurring, alone or jointly, could lead to an increase of our tax burden and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Our acquisition strategy could involve additional risks to us, many of which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We continue to examine opportunities to acquire or invest in existing or new concessions that complement or expand our business. These opportunities may involve government-owned entities as well as private sector companies. Any future acquisitions may result in a dilutive issuance of equity securities, incurrence of additional debt, reduction of existing cash balances, amortization of expenses related to goodwill and other intangible assets or other charges to operations. Additional leverage could require us to dedicate cash flow to fund debt service requirements, thus decreasing the funds available to us to finance working capital and business operations generally. All of the foregoing factors could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects.
16
Future concession or acquisitions could involve numerous risks, including that we may recognize lower relative operating margins associated with such acquisitions, and we may recognize impairment charges with respect to future acquired assets due to the performance of such assets. Our results of operations may also be affected by the timing of acquisitions, the timing and amount of integration costs related to such acquisitions and the degree to and the rate at which the economic benefits of integration are realized.
Future growth may also place additional demands on our personnel and other resources, including an increased level of responsibility for management. Our ability to manage growth effectively will require us to continue to improve our operational, management and financial systems and controls and to successfully train, motivate and manage our employees. If our management is unable to manage growth effectively, our business could be adversely affected.
Our inability to raise additional financing may limit our operations.
We may have limited ability to incur additional financing for some of our concession agreements, which may entail important consequences for investors, among them (i) limiting our capacity to satisfy our future investment obligations with respect to the airports we operate pursuant to the terms and conditions of our concession agreements, or other capital expenditures required for the operation of such airports; and (ii) limiting our flexibility to take advantage of opportunities for new business within the markets we operate or potential new markets. Any of these situations may ultimately affect our operations and financial results.
Many of our most significant subsidiaries have substantial non - controlling interests owned by third-parties, and any substantial conflict with minority shareholders may have an adverse effect on our business.
We indirectly own 82.7%, and 51.0% of our principal Argentina and Brazil operating subsidiaries, respectively, which are namely Aeropuertos Argentina 2000 S.A. (“AA2000”) and ICAB. Likewise, we indirectly own 75.0% of Corporación América Italia S.p.A. (“CA Italy”) who owns 62.3% of our principal Italian operating subsidiary, Toscana Aeroporti S.p.A. (“TA”). Because we control these entities, we record all their revenues and expenses and then allocate net income between controlling and non-controlling interest. The other shareholders of these entities, including, in the case of Italy, public shareholders, may have interests different from ours, and any substantial conflict with minority shareholders may have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
We may have conflicts of interest with ACI Airports S.à r.l., our majority shareholder, and we may not be able to resolve such conflicts on terms favorable to us.
We are currently controlled by A.C.I. Airports S.à r.l., a holding company incorporated in Luxembourg (the “Majority Shareholder”). Conflicts of interest may arise between our Majority Shareholder and us in a number of areas relating to our past and ongoing relationships. Potential conflicts of interest that we have identified include, among others, allocation of business and investment opportunities and/or the acquisition of airport assets outside of our existing corporate structure. Generally, the Majority Shareholder may from time to time make strategic decisions that it believes are in the best interest of the business as a whole, including its ownership interest in our business. These decisions may be different from the decisions that we would have made on our own and may not be aligned with your interests. We may not be able to resolve any potential conflicts and, even if we do, the resolution may be less favorable to us than if we were dealing with an unaffiliated party.
We have been advised by the Southern Cone Foundation (“SCF”), our ultimate controlling shareholder, that it does not intend to participate in any significant future acquisitions of airport concession assets or airport-related companies, except through us.
The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration or another regulatory agency could downgrade the aviation safety rating of any of the countries in which we operate, which could have a negative impact on passenger traffic.
Under the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration regulations, the aviation safety rating of any of the countries in which we operate could be downgraded. Airlines from such countries could be prevented from expanding or changing their current operations to and from the United States, except under certain limited circumstances, code-sharing arrangements between such airlines and U.S. airlines could be suspended, and operations by such airlines flying to the United States could be subjected to greater administrative oversight. Any such additional regulatory requirements could result in reduced passenger traffic originating in or with destination to the United States by non-U.S. airlines operating at our airports or, in some cases, in an increase in that cost of service, which could result in decrease in demand for travel. The Federal Aviation Administration may downgrade the air safety rating of any of the countries in which we operate in the future. The European Aviation Safety Agency and other regulatory agencies may take similar actions, either independently or in response to any such action by the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration. Such actions might reduce our revenues and have a negative impact on passenger traffic.
17
We are subject to anti-corruption laws in the jurisdictions in which we operate.
We are subject to and bound by U.S. and foreign anti-corruption laws and regulations, such as the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, the Argentine Anticorruption Law of 2018 (Law No. 27,401), the Italian Corruption Law of 2012 (Law No. 190), the Brazil Clean Company Act of 2013 (Law No. 12,846), the Uruguayan Anticorruption Law of 1998 (Law No. 17.060) and the Criminal Code (Law 9.155) and the Armenia Law on the Committee for Preventing Corruption (Law No. HO-96-N). These anti-corruption laws generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments to local and foreign officials for the purpose of obtaining or keeping business and/or other benefits. Many jurisdictions have recently implemented new anti-corruption laws (such as in the case of Argentina and Brazil) or have broadened the scope of existing anti-corruption laws (such as in the case of Italy).
On February 17, 2021, Ecuadorian Organic Law Reformation of the Comprehensive Organic Criminal Code on Anti-Corruption was published, incorporating regulatory compliance and good corporate governance systems as well as new criminal figures related to corruption in the private sector.
The Brazilian Clean Company Act holds companies strictly liable for the corrupt acts of their employees and intermediaries, which means that a company may be held liable for such acts, without a finding of fault on the part of the company. See “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Other Principal Operations and Other Principal Markets in Which We Operate—Brazil— ” and “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Other Principal Operations and Other Principal Markets in Which We Operate—Brazil —” Our business requires that we maintain continuous contact with governments and agencies from the initial bid process for any concession and throughout the entire term of any concession we are awarded. Despite the existence of our compliance program together with our ongoing efforts to ensure compliance with anti-corruption laws, there can be no assurance that our employees, agents, and the companies to which we outsource certain of our business operations, will not take actions in violation of our policies, for which we may be ultimately held responsible. If we are not in compliance with anti-corruption laws and other laws governing the conduct of business with government entities (including local laws), we may be subject to criminal and civil penalties and other remedial measures, which could harm our reputation and have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. Any investigation of any actual or alleged violations of such laws could also harm our reputation or have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Increasing scrutiny from stakeholders on ESG matters, including our ESG reporting, exposes us to reputational and other risks.
There is an increasing focus from certain investors, customers, employees and other stakeholders concerning ESG matters. If our ESG practices fail to meet regulatory requirements or investor, customer, employee or other stakeholders’ evolving expectations and standards for responsible corporate citizenship in areas including environmental stewardship, support for local communities, board of directors and employee diversity, human capital management, employee health and safety practices, service quality, supply chain management, corporate governance and transparency, our reputation, brand and employee retention may be negatively impacted, and our customers and suppliers may be unwilling to continue to do business with us. As public interest and legislative pressure related to public companies’ ESG practices continues to grow, the related legislative landscape in the European Union and the United States has been evolving accordingly.
In the European Union, Directive (EU) 2022/2464 (the “CSRD”) entered into force on January 5 2023. This new directive strengthens the rules on the social and environmental information that companies must report. It expands the scope of companies required to report ESG information and increases the depth of required disclosures. The CSRD also introduces a ‘double materiality’ analysis, which requires companies to report on how sustainability issues might create financial risks for the company and on the company’s own impacts on people and the environment. The CSRD applies to large EU companies, EU parent companies of a “large group” and listed EU small or medium-sized companies. It also applies to non-EU companies that meet certain criteria, including an EU turnover threshold and a subsidiary. The specific information to be reported is set out in the European Sustainability Reporting Standards. In our case, the CSRD will apply as of financial year 2025, to be reported in 2026.
18
In the United States, in 2022, the SEC proposed extensive rules aimed at enhancing and standardizing climate-related disclosures in an effort to foster greater consistency, comparability and reliability of climate-related information. The rules were adopted on March 6, 2024 and require domestic registrants and foreign private issuers to include certain climate-related information in their registration statements and annual reports, including data regarding greenhouse gas emissions and information regarding climate-related risks and opportunities and related financial impacts, governance, and strategy. The rules established phased-in compliance dates which, in the case of accelerated filers such as us, will start with the annual report for the fiscal year ending on December 31, 2026, to be filed in early 2027. Further, on several challenges against the new SEC climate disclosure rules were consolidated for review by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit. Given the recent adoption of the rules and the several challenges against them, we are still uncertain about the ultimate impact of the rules on our business, which, may result in increased legal, accounting and financial compliance costs and make some activities more difficult, time-consuming and costly.
Moreover, the SEC has also announced that it is working on proposals for mandatory disclosure of certain other ESG-related matters, including with respect to board diversity and human capital management. At this time, there is uncertainty regarding the scope of such proposals or when they would become effective. As regulations develop, we will consider the implications for our business of the overlapping global measures, and how they fit together. Compliance with any new laws or regulations increases our regulatory burden and could make compliance more difficult, increase the risk that we are subject to enforcement, affect the manner in which we or our portfolio companies conduct our businesses, adversely affect our profitability, require us to incur significant additional costs to comply, and impose increased oversight obligations on our management and board of directors. If we do not adapt to or comply with new regulations, or fail to meet evolving investor, industry or stakeholder expectations and concerns regarding ESG issues, investors may reconsider their capital investment in our Company, we may become subject to penalties, and customers and consumers may choose to stop purchasing our services, which could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business or financial condition.
Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement
The Argentine Government extended the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement until 2038 subject to our compliance with certain commitments, which if we fail to comply with, could result in the imposition of fines or the termination or revocation of the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
The Technical Conditions of the Extension approved by Decree No. 1009/2020 (“Technical Conditions of the Extension”) established the following commitments to be complied by AA2000: (i) allocate an amount equal to U.S.$132.0 million (VAT included) as direct investment to complete 2020 and 2021 ongoing works (the “2020/2021 Direct Investment Commitment”); (ii) use its best efforts to obtain the greatest leverage possible, before December 31, 2021, to have an early inflow of up to (a) U.S.$85.0 million in the “Trust Fund for Works of Group A of Airports of the National Airport System” (the “Development Trust”) and (b) U.S.$124.0 million in the “Additional Fund for Substantial Investments in Group A of Airports” (the “Development Trust Leverage Commitment”) (iii) secure, before March 31, 2022, or, provided that there are justified reasons and subject to ORSNA’s approval, before December 2022, certain level of funds available in an aggregate amount of U.S.$406.5 million (VAT included), which shall be applied to: (a) works considered as direct investment, to be carried out preferably during 2022/2023 (the “2022/2023 Commitment”) and (b) the redemption of preferred shares of the Argentine Government to be performed by AA2000 before March 31, 2022 (the “Redemption of the Preferred Shares Commitment”, and jointly with the 2022/2023 Commitment, the “Availability of Funds Commitment”); and (iv) to make direct investments for U.S.$200.0 million (VAT included), between the years 2024 and 2027, at an annual average of U.S.$50.0 million (VAT included), in addition to any direct investment balance carried forward from the 2021/2023 period (the “2024-2027 Commitment). With respect to the capital expenditures to be performed under the 2022/2023 Commitment and the 2024-2027 Commitment, Resolution No. 60/ 2021 of the ORSNA established that AA2000’s capital expenditures under the Technical Conditions of the Extension amount to approximately U.S.$500 million plus VAT, to be performed in two phases: (i) phase 1, approximately U.S.$336 million plus VAT to be performed preferably in 2022 and 2023 (the “Phase 1 Commitment”), and (ii) phase 2, annual investments of approximately U.S.$41 million plus VAT between 2024 and 2027, for a total of approximately U.S.$164 million plus VAT (the “Phase 2 Commitment”). The financial projection of income and expenses attached to the Technical Conditions of the Extension include the estimated dates in which the referred commitments and capital expenditures would need to be performed.
As of the date of this annual report, AA2000 has fully complied with the 2020/2021 Direct Investment Commitment and the Availability of Funds Commitment. Regarding this latter commitment, on May 10, 2022, ORSNA issued Note No. NO-2022-46520010-APN-ORSNA through which it confirmed that AA2000 had fulfilled the Availability of Funds Commitment in the amount of U.S.$406.5 million for its application to the Mandatory Capex Program (including the Redemption of the Preferred Shares Commitment performed in March 2022).
19
With respect to the Development Trust Leverage Commitment, in December 2022 and January 2023, AA2000 informed the ORSNA that it had complied with its best efforts obligation under this commitment. On May 22, 2023, in response to the filing made by AA2000, the ORSNA took note of the best efforts performed by AA2000 in compliance with the Development Trust Leverage Commitment and requested to AA2000 its collaboration so that, if the ORSNA deems it appropriate and the financial landscape improves, other financing options for the Development Trust may be sought. In light of this, on May 23, 2023, AA2000 expressed its agreement to fully collaborate with the ORSNA to that end.
Regarding the Phase 1 Commitment, the Company is currently executing the infrastructure works in the terms provided by the Technical Conditions of the Extension and Resolution No. 60/2021, while the Phase 2 Commitment is pending. With respect to the Phase 1 Commitment, on February 5, 2024, AA2000 informed the ORSNA about the status of the referred commitments as of December 31, 2023. Works amounting to U.S.$262.1 million (VAT included) have been initiated, of which U.S.$190.3 million (VAT included) have been executed. Considering the amount utilized for the Redemption of the Preferred Shares Commitment, totaling U.S.$174.2 million, the total amount committed under the Phase 1 Commitment amounts to U.S.$436.3 million (VAT included), which surpasses the required commitment amount for this phase (U.S.$336 million). As of the date of this report, U.S.$364.5 million (VAT included) (out of the U.S.$436.3 million (VAT included) committed) have been executed. As of the date of this annual report, the ORSNA has not issued a response to the filing made by AA2000.
As of the date of this annual report, AA2000 has substantially complied with the commitments under the Technical Conditions of the Extension. However, failure to fully comply with the pending commitments (in particular, the Phase 2 Commitment) could result in the imposition of fines or the termination or revocation of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. Termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement would constitute a default under the Argentine Notes Series 2017, the Argentine Notes Series 2020, the Argentine Notes Series 2021, New Money 2021 Notes (as defined herein), the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan (as defined herein) and the ICBC Dubai Loan (as defined herein).
Pursuant to the AA2000 Concession Agreement, since February 2018, the Argentine Government may buy out our concession, which would materially affect our revenues and operations.
Pursuant to the AA2000 Concession Agreement, since February 13, 2018, the Argentine Government has the right to “buy-out” (“rescatar”) the AA2000 Concession Agreement for public interest reasons and upon prior notification to us. In the event that the Argentine Government were to exercise this option, it would be required to indemnify us in an amount equal to the value of the non-amortized aeronautical investments we have made as of the time of the buy-out, multiplied by 1.10, plus the value of all other investments we have made and which have not been amortized. The Argentine Government would not be required to indemnify us for investments that were not included in our investment plan or that were not approved by the ORSNA. The Argentine Government would also not be required to indemnify us for lost revenue or lost profits. The Argentine Government would be required to assume in full any debts incurred by us to acquire goods or services for purposes of providing airport services, except for debts incurred in connection with the investment plan for which we would be compensated as part of the payment made to us by the Argentine Government. Furthermore, the buy-out of the AA2000 Concession Agreement would constitute an event of default under (i) our Argentine Notes Series 2017, Argentine Notes Series 2020, Argentine Notes Series 2021 and the New Money 2021 Notes, (ii) the syndicated bimonetary loan granted by Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (Argentina) S.A., the branch of Citibank N.A. established in the Republic of Argentina, Banco de Galicia y Buenos Aires S.A.U. and Banco Santander Argentina S.A. which provided for disbursements in pesos and/or U.S. dollars (the “Syndicated Bimonetary Loan”), and (iii) the offshore credit facility dated July 25, 2022 entered by and between AA2000 and Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Limited, Dubai Branch (“ICBC Dubai”), as lender, and the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (“ICBC”), as onshore custodian agent (“ICBC Dubai Loan”), which will result in automatic acceleration of the notes, the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan and the ICBC Dubai Loan. As of December 31, 2023, the total amount outstanding under the Argentine Notes Series 2017, the Argentine Notes Series 2020, the Argentine Notes Series 2021, the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan and the ICBC Dubai Loan is U.S.$58.7 million, U.S.$16.3, U.S.$272.9 million, U.S.$62.0 million, U.S.$9.8 million, and U.S.$10.0 million, respectively. The Argentine Government’s indemnification obligations in combination with the collateral structure under the notes, the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan and the ICBC Dubai Loan may not be adequate to repay the holders of such notes. See “Item 5. Operating and Financial review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Indebtedness.”
During the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, the revenue derived from our operation of the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement represented 45.1%, 55.0% and 51.2%, respectively, of our total consolidated revenue. If the Argentine Government exercises its right to buy-out the AA2000 Concession Agreement, such buy-out would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
20
The ORSNA may adjust the fees we charge for aeronautical services, the payments we are required to make to the Argentine Government and our investment plan in a way that is detrimental to us or fail to adjust them to restore the AA2000 Concession Agreement’s economic equilibrium.
Under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the ORSNA is required to conduct an annual review of AA2000’s financial projections and, if necessary, to re-establish economic equilibrium by adjusting (i) the fees we charge airlines and passengers for aeronautical services, (ii) certain payments we make to the Argentine Government pursuant to the AA2000 Concession Agreement, and/or (iii) our investment obligations. On January 13, 2021, the ORSNA, through Resolution No. 4/2021, increased the fees that AA2000 may charge to international passengers from U.S.$51.00 to U.S.$57.00. In December 2022, the ORSNA issued Resolution No. 98/2022 by virtue of which a new increase of the use fee charged to domestic passengers was approved, establishing a use fee of AR$1,100 effective as of January 2023. In November 2023, the ORSNA issued Resolution No. 84/2023 by virtue of which a new increase of the use fee charged to domestic passengers was approved, establishing a use fee of AR$2,540 for Category I airports, AR$1,771 for Category II airports and AR$1,551 for Categories III and IV airports, effective as of January 2024. If the ORSNA applies adjustments to the Specific Allocation of Revenues and to the fees we may charge or that we must pay under the AA2000 Concession Agreement in a way that is detrimental to us, or if the ORSNA fails to adjust such fees in order to restore the AA2000 Concession Agreement’s economic equilibrium, or if the ORSNA seeks to modify our rights under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, any of such actions or failures to act may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If the ORSNA does not approve the capital expenditures already made under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we would be required to make additional capital expenditures, which may affect our cash flows and financial condition.
The ORSNA reviews our capital expenditures to monitor our compliance with the investment plan under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, and to determine whether it can record such expenditures in the registry maintained by the ORSNA. If a capital expenditure is approved by the ORSNA, it is then entered into its registry. The ORSNA only approves investments that are supported by a certificate that reflects the completion of the relevant works and does not approve investments made in connection with the start of the works.
Accordingly, we may record capital expenditures during a period that has not yet been (and may never be) approved by the ORSNA. If the ORSNA does not approve our capital expenditures under the investment plan of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we will be required to make additional capital expenditures. This may require us to obtain additional financing, which we may not be able to obtain on terms favorable to us, or at all. Our capital expenditures for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019 and 2018 are currently under review by the ORSNA. See “Argentina—Our Airports in Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement—Economic Equilibrium.”
Political events occurring, and political measures taken, in Argentina could affect the country’s economy in general, and the aeronautical sector in particular.
Since taking office, the new government has announced various significant economic and political reforms. In this regard, on December 21, 2023, Urgency Decree No. 70/2023 (the “Decree 70/2023”) was published in the Official Gazette, declaring a state of public emergency in economic, financial, fiscal, administrative, social security, tariffs, health and social matters until December 31, 2025. Decree 70/2023 aims to lay the groundwork for a profound state reform, including the privatization of numerous state-owned enterprises. To this end, Decree 70/2023 repeals several laws related to state intervention in the economy, such as the “Gondolas” Law No. 27,545 (and its amendments), the Supply Law No. 20,680 (and its amendments), Observatory of Prices Law No. 26,992 (and its amendments), and State Enterprises Law No. 20,075 (and its amendments), with the goal of liberalizing trade, services, and industry, and eliminating restrictions on the supply of goods and services which distort market prices.
In this line, Decree 70/2023 contemplates significant changes for the country’s aeronautical policy with the objective of further developing the aeronautical industry and promoting free competition in the market. See “Argentina—Our Airports in Argentina—Aeronautical Policy.”
Furthermore, Decree 70/2023 amends various legal frameworks, including the Civil and Commercial Code of the Nation, reinforcing freedom of contract, the principle of party autonomy, and the legality and enforceability of contracts in foreign currency; the Customs Code, liberalizing foreign trade; the Labor Contract Law, flexibilizing individual and collective labor relations; the health system, facilitating the hiring of social works and prepaid health services; and the credit card regime, eliminating the caps applicable to fees and interest rates.
21
Decree 70/2023 came into effect on December 29, 2023. However, in accordance with the provisions of Law No. 26,122, the Permanent Bicameral Commission of the Congress must submit a report to each chamber of congress regarding the validity or invalidity of the Decree 70/2023, assessing the decree’s compliance with the constitutionally established, formal and substantial requirements for its issuance within 10 days. Once this term has expired, if the Bicameral Commission has not issued an opinion, the Chambers of Deputies and Senators may deal with the DNU directly. With the deadline met, on March 14, 2024, Decree 70/2023 was rejected by the Senate. However, in accordance with Law No. 26,122, Decree 70/2023 will only become ineffective if it is expressly rejected by both legislative chambers. To the date of this annual report, the Chamber of Deputies has not set a date for deliberating on the approval or rejection of Decree 70/2023.
In addition, since its issuance by the Executive Branch, Decree 70/2023 has faced numerous challenges regarding its constitutionality, leading to the filing of several injunctions before the national labor courts and the federal courts, among others. As of the date of this annual report, some of these injunctions have been accepted by the relevant courts, and various precautionary measures with diverse effects and scopes have been granted. For example, the Confederación General del Trabajo (“CGT” for its Spanish acronym) and the Central de Trabajadores y Trabajadoras de Argentina (“CTA” for its Spanish acronym) requested the suspension of the applicability of Title IV “Labor” of Decree 70/2023. Both injunctions were granted by the Chamber of Labor Appeals. Additionally, the National Chamber of Appeals in Civil and Commercial Federal accepted an action filed against Decree 70/2023, as a collective injunction. In that case, the claimant seeks to maintain the validity of sections 5, g) and 17 of Law 26,682/2011, linked to the price of the installments of prepaid medicine contracts. As to the date of this report, no measure has been issued yet. Furthermore, the Province of La Rioja requested before the Supreme Court the issuance of a precautionary measure suspending the effects of Decree 70/2023 and instructing the Executive Branch not to apply any of its provisions until the definitive resolution of the present case, which, as of the date of this annual report, has not been granted.
Simultaneously, through Decree 76/2023, the Executive Branch convened extraordinary legislative sessions to address, among other issues, an omnibus bill “Bases y Puntos de Partida para la Libertad de los Argentinos” which proposes to deepen the reforms introduced by Decree 70/2023. In this context, it reaffirms the declaration of the state of public emergency until December 31, 2025, extendable by the Executive Branch for two additional years. Likewise, during the emergency, the project proposes the delegation of legislative powers to the Executive Branch, in accordance with article 76 of the National Constitution. Similar to Decree 70/2023, the bill proposes a comprehensive reform of the state and a strong deregulation of the economy. As of the date of this annual report, the bill has not been passed by the Congress.
As of the date of this annual report, there is uncertainty regarding the impact that these measures and any other future measures of the new government may have on the Argentine economy in general and on the aeronautical and infrastructure sectors in particular. We believe that the effect of economic liberalization will be positive for the country’s business environment, but we cannot predict such effects with certainty.
Several measures proposed by the new government have generated political and social unrest, which may hinder the new administration from implementing these measures as proposed. Since the ruling party does not have its own quorum in either chamber of Congress, the new government will need to seek alliances and political support from other parties, to obtain approval for its proposals. This increases uncertainty regarding the new government’s ability to approve any measures it intends to implement.
The political uncertainty as well as the consequences of the new policies adopted in Argentina concerning the Argentine economy could adversely affect our operating results in Argentina, and, consequently, our financial position.
Our operations in Argentina depend on macroeconomic conditions in Argentina.
Our business and financial results in Argentina depend to a significant degree on macroeconomic, political, regulatory, and social conditions therein. The Argentine economy has experienced significant volatility in recent decades, characterized by periods of low or negative growth, high levels of inflation and currency devaluation, and may experience further volatility in the future.
Over the last years, Argentina has experienced a period of severe political, economic, and social crises, which have caused a significant economic contraction and have led to radical changes in government policies. Among other things, the crises resulted in Argentina defaulting on its sovereign foreign debt obligations, a significant devaluation of the Argentine peso and ensuing inflation, and the introduction of emergency measures that affected many sectors of the economy. Likewise, the decline in international demand for Argentine products, the lack of stability and competitiveness of the Argentine peso against other currencies, the decline in confidence among consumers and foreign and domestic investors, and the higher rate of inflation and future political uncertainties, among other factors, have affected the development of the Argentine economy.
22
The former administration adopted several economic and policy reforms aimed at stabilizing the economy. For instance, as of the date of this annual report, the Argentine Government has entered into a Stand By Agreement with the International Monetary Fund (“IMF”) for an aggregate outstanding amount of U.S.$40.6 billion.
In March 2023, continuing with the restructuring of the Argentine Government debt, the Ministry of Economy announced a new exchange of bonds and Treasury bills denominated in Argentine pesos with maturities in the short term, which obtained a 64% support.
In June 2023, the renewal of the currency swap between China and Argentina was finalized and a gradual extension to U.S.$10 billion was agreed. In July 2023, the Andean Development Corporation (“CAF”) approved a bridge loan to Argentina in the amount of U.S.$1.0 billion to cover the debt until the IMF board approves the refinancing of the program.
In August 2023, the government announced that Qatar granted a special drawing rights loan to Argentina for the equivalent of U.S.$770 million. In addition, Argentina obtained approval of the fifth and sixth reviews of the agreement signed with the IMF for a U.S.$7.5 billion disbursement. The new administration made a first payment for U.S.$960 million to the IMF through a loan granted by the Development Bank of Latin America. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the new Minister of Economy, Luis Caputo, announced that he intends to renegotiate the terms of the agreement with the IMF.
Although these restructuring and reprofiling processes have been successful, it cannot be assured that Argentina will be able to comply with the commitments assumed with these creditors within the framework of such processes. It is also not possible to assure what the foreign policy of the new administration will be, or what relations with the creditors and foreign investors of the country will look like. Under such terms, if the Argentine Government fails to comply with the agreed covenants and fiscal and economic goals, Argentina might once again fall into default and, in turn, the country’s financial and economic situation might be adversely affected.
The aeronautical policy reforms proposed by the Decree 70/2023 may affect our business and result of operations.
Decree 70/2023 introduces significant changes to the aeronautical policy of the country and attempts to develop the aeronautical industry and promote free competition in the market. The main changes provided by Decree 70/2023 are the following:
| ● | Decree-Law No. 12,507/56 (national policy on aeronautics), Law No. 19,030 (national policy for air transport), and Decree No. 1654/02 (on the emergency of air transport), were repealed; |
| ● | civil commercial aviation is deemed an essential service; |
| ● | the aeronautical authority shall regulate and oversee airport services (defined as all services provided within an airport, excluding air navigation services), based on the principles of ensuring safety, free competition, and market access (however the airport services captured by the AA2000 Concession Agreement and those airport services subject to the supervision of ORSNA are not modified by Decree 70/2023 and remain unchanged as of the date of this annual report); |
| ● | ramp services in general are classified as essential airport services; |
| ● | both manned and unmanned aircrafts are considered devices or mechanisms capable of navigating in airspace and suitable for transporting people or goods; |
| ● | operation of air commercial activities by foreign flag companies would be subject to prior clearance and must comply with international rules and agreements to which the Argentine Republic is a party; |
| ● | air transport services will no longer be subject to concession by the Executive Branch but only to authorization; moreover, the Argentine Aeronautical Code no longer expressly requires a prior public hearing for their granting; |
| ● | individuals operating domestic air transport routes are no longer required to be Argentines (a legal domicile in the country would suffice for these purposes); |
| ● | the requirements established for companies providing domestic air commercial services under which, at least more than 50% of the partners must be Argentine with legal domicile in the country, were abrogated; |
23
| ● | to ensure a proper balance between the interests of passengers and carriers, the aeronautical authorities shall issue regulations regarding passenger rights and their protection; and |
| ● | Laws No. 26,412 and 26,466 were amended enabling the transfer of shares of Aerolíneas Argentinas S.A. and Austral Líneas Aéreas – Cielos del Sur S.A., and their controlled companies, to the employees of these companies under an Employee Ownership Program. |
Additionally, the amendments proposed by Decree 70/2023 require further regulation by the Argentine ANAC (as defined herein), the Secretary of Transportation and other regulatory bodies. We cannot predict what such further regulation may entail. As of the date of this annual report, we cannot predict how the changes proposed by Decree 70/2023 or how further regulation from the aeronautical regulatory bodies may affect our business and our results of operations. Regarding the potential repeal by Congress of Decree 70/2023, please see “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement—Political events and political measures taken in Argentina could affect the country’s economy and the aeronautical sector in particular.”
The emergency declared by Decree 70/2023 and the new measures that the new administration might implement, could adversely affect our business and result of operations.
The emergency declared by Decree 70/2023 is intended to stabilize the economy, achieve significant deregulation of economic activity and minimize government intervention. As of the date of this annual report, we cannot predict the impact of the measures that may be adopted under the state of emergency either at the federal or provincial level, or the effect that such measures may have on the Argentine economy and Argentina’s ability to meet its financial obligations, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, we can give no assurance that economic, regulatory, social and political developments in Argentina will not affect our business, financial condition or results of operations. Regarding the potential repeal by Congress of Decree 70/2023, please see “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement—Political events and political measures taken in Argentina could affect the country’s economy and the aeronautical sector in particular.”
Current Argentine exchange controls and the implementation of further exchange controls could adversely affect our results of operations.
The prior administration and the Argentine Central Bank implemented certain measures that control and restrict the ability of companies and individuals to access the foreign exchange market. Those measures include, among others: (i) restricting access to the Argentine foreign exchange market for the purchase or transfer of foreign currency abroad for any purpose, including the payment of dividends to non-resident shareholders; (ii) restricting the acquisition of any foreign currency to be held as cash in Argentina; (iii) requiring exporters to repatriate all the proceeds of their exports of goods and services and to settle them in pesos, in the local exchange market; (iv) limitations on the transfer of securities into and from Argentina; (v) restrictions on the payment of imports of goods and services; (see “—AA2000’s foreign financial indebtedness and debt denominated in foreign currency with access to the Foreign Exchange Market could be affected by the mandatory refinancing regime enacted by the Argentine Central Bank”); and (vi) the implementation of taxes on certain transactions involving the acquisition of foreign currency (the so called “PAIS Tax”).
Although the new administration stated its intention to deregulate the economy and allow the free flow of foreign currency, exchange controls on the inflow and outflow of foreign currency funds are still in force, due to the low level of reserves of the Argentine Central Bank (the “BCRA” for its acronym in Spanish). In line with the restrictions in force during the prior administration, the BCRA’s new regulations established limitations on the flow of foreign currency into and out of the Foreign Exchange Market (the “MULC” for its Spanish acronym), with the purpose of stabilizing the Argentine economy.
24
As of the date of this annual report, subject to certain requirements, the BCRA regulations grant access to the MLC to repay principal or interest (at maturity) on foreign financial indebtedness as well as new commercial debt corresponding to imports of goods and services incurred from December 13, 2023, provided that advance payments are subject to BCRA’s prior clearance, unless certain exceptions are met. In turn, the stock of commercial debt corresponding to imports of goods and services is subject to BCRA’s prior clearance, unless certain exceptions are met. Similarly, the BCRA designed a scheme of issuance of dollar-denominated notes (“BOPREAL”) with the intention to regularize the significant level of outstanding commercial debt owed by Argentine importers (which as of January 24, 2024 amounted to U.S.$.42.6 billion). On January 31, 2024, the allocation of BOPREAL Series 1 was completed, reaching the maximum available amount for this series of U.S.$5.0 billion. AA2000 had subscribed an aggregate amount of U.S.$1,083,470 of BOPREAL Series 1. Additionally, on February 22, 2024, the allocation of BOPREAL Series 2 was also completed, reaching the maximum amount of U.S.$2.0 billion offered under this Series. The offering of BOPREAL Series 3 is currently ongoing, which has an offering maximum amount of up to U.S.$3.0 billion.
In addition, the BCRA issued regulations allowing micro, small and medium enterprises registering outstanding commercial debt for an amount less than or equal to U.S.$500,000 to access the MLC to cancel their debts with foreign suppliers according to a schedule to access the MLC subject to certain caps and maximum amounts. The BCRA also established that this micro, small and medium enterprises will have priority to subscribe the BOPREAL Series 2.
There can be no assurance that the BCRA or other government agencies will not increase or relax such controls or restrictions, make modifications to these regulations, impose mandatory refinancing plans related to our indebtedness payable in foreign currency (as established in the past), establish more severe restrictions on currency exchange, or maintain the current foreign exchange regime or create multiple exchange rates for different types of transactions, substantially modifying the applicable exchange rate at which we acquire currency to service our outstanding liabilities denominated in currencies other than the Peso, all of which could affect our ability to comply with our financial obligations when due, raise capital, refinance our debt at maturity, obtain financing, execute our capital expenditure plans, and/or undermine our ability to pay dividends to foreign shareholders. Consequently, these exchange controls and restrictions could materially adversely affect the Argentine economy and our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Government measures, as well as pressure from labor unions, could require salary increases or additional employee benefits, all of which could increase companies’ operating costs.
Most industrial and commercial activities in Argentina are regulated by specific collective bargaining agreements that group together companies according to industry sectors and trade unions. Argentine employers, both in the public and private sectors, have experienced significant pressure from their employees and labor organizations to increase wages and to provide additional employee benefits. Due to the high levels of inflation, employees and labor organizations are demanding wage increases. In the past, the Argentine Government enacted laws, regulations and decrees requiring companies in the private sector to maintain minimum wage levels and to provide specified benefits to employees. Pursuant to Resolution No. 15/2023 of the National Council for Employment, Productivity and the Minimum Adjustable Wage, issued on September 29, 2023, the adjustable minimum wage was increased as follows: (i) on October 1, 2023, to AR$132,000; (ii) in November 2023, to AR$146,00061,953; and (iii) in December 2023, to AR$156,000 (minimum amount to be maintained until a new update is approved).
In the future, the Argentine Government could take new measures requiring salary increases or additional employee benefits, and the labor force and labor unions may demand employers to implement those measures. Increases in wages or employee benefits could result in added costs and adversely affect our results of operations in Argentina.
Increased public expenditures could result in long-lasting adverse consequences for the Argentine economy.
In recent years, the Argentine Government has substantially increased public expenditures. In November 2023, public sector expenditures increased by 113.1% as compared to November 2022, the Argentine Government reported a primary fiscal deficit of 2.9% of the gross domestic product (“GDP”), according to the Argentine Ministry of Treasury. Although the new administration has stated its intention to implement sharp cuts in public expenditures and public debt, there are no assurances that the new administration will not face resistance from Congress, convince stakeholders of its proposed changes, and, consequently, be able to implement its plans and reforms. Future fiscal deficits could negatively affect the Argentine Government’s ability to access the long-term financial markets and could, in turn, result in more limited access to such markets by Argentine companies, including us.
25
The Argentine economy could be adversely affected by economic developments in other global markets and by more general “contagion” effects.
Argentina’s economy is vulnerable to external shocks that could be caused by adverse developments affecting its principal trading partners. A significant decline in the economic growth of any of Argentina’s major trading partners (including Brazil, the European Union, China, and the United States) could have a material adverse impact on Argentina’s balance of trade and adversely affect Argentina’s economic growth.
The Argentine economy continues to be vulnerable to external shocks that may be generated by adverse events in the region or globally.
Changes in social, political, regulatory, or economic conditions in Argentina’s principal trading partners or in foreign trade laws or policies may generate uncertainty in international markets and have a negative effect on standalone economies, including the Argentine economy, which may, in turn, have a negative impact on our operations.
Global economic conditions may also result in depreciation of regional currencies and exchange rates, including the Argentine peso, which would likely also cause volatility in Argentina. The effect of global economic conditions on Argentina could reduce exports and foreign direct investment, resulting in a decline in tax revenues and a restriction on access to the international capital markets, which could, adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations. A new global economic and/or financial crisis or the effects of deterioration in the current international context, could affect the Argentine economy and, consequently, our results of operations and financial condition.
Significant fluctuation in the value of the Argentine peso may adversely affect the Argentine economy as well as our financial condition and results of operations.
The Argentine peso has suffered and may continue to suffer devaluation against the U.S. dollar. Despite the positive effects of the decline of the Argentine peso on the competitiveness of certain sectors of the Argentine economy, it can also have far-reaching negative impacts on the Argentine economy and on businesses and individuals’ financial condition.
Exchange rate uncertainty intensified during the electoral scenario. After the primary elections a 20% depreciation of the peso against the U.S. dollar took place. Among its first measures, the new administration implemented a devaluation of the peso against the U.S. dollar of around 118% approximately (from AR$366 per U.S.$1 to AR$800 per U.S.$1.00) aiming to reduce the significant gap between the official exchange rate and the implicit exchange rate applicable to the blue-chip swap transactions (the alternative mechanism to outflow foreign currency abroad) which by the time the new administration took office was around 157,6% and was reduced to 50% as of January 31, 2024.
As of December 31, 2023, the official exchange rate was AR$808.45 to U.S.$1.00. A significant increase in the value of the peso against the U.S. dollar also presents risks to the Argentine economy. If the peso continues to depreciate, all of the negative effects on the Argentine economy related to such depreciation could resurface, which could result in a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations due to our financial commitments in U.S. dollars. A significant real appreciation of the peso would adversely affect exports, which could have a negative effect on GDP growth and employment, as well as reduce Argentine public sector revenues by reducing tax collection in real terms, given its high dependence on taxes and exports.
A significant further depreciation of the peso against the U.S. dollar could have an adverse effect on the ability of Argentine companies to make timely payments on their debts denominated in or indexed or otherwise connected to a foreign currency, generate very high inflation rates, reduce real salaries significantly, and have an adverse effect on companies focused on the domestic market, such as public utilities and the financial industry. Such potential depreciation could also adversely affect the Argentine Government’s capacity to honor its foreign debt, which could affect AA2000’s capacity to meet obligations denominated in a foreign currency, which, in turn, could have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
International and regional passenger use fees are denominated in U.S. dollars and are payable in both U.S. dollars and Argentine pesos. Currency exchange rate volatility directly affects conversions of U.S. dollars into Argentine pesos. Any appreciation in the value of the Argentine peso against the U.S. dollar may reduce our cash flows. Conversely, any depreciation in the value of the Argentine peso against the U.S. dollar may increase our cash flows.
26
The overall cost increase of international travel as a result of fluctuations in currency exchange rates could potentially lead to decreased passenger traffic volume as a result of increases in travel costs. A large decrease in the value of a particular foreign currency relative to the value of the Argentine peso or the U.S. dollar, as applicable, could have an adverse effect on the number of international air passengers originating from nations that use such devalued currency.
Continuing high inflation may impact the Argentine economy and adversely affect our results of operations.
Inflation has materially undermined, and in the future may continue to undermine, the Argentine economy and the Argentine Government’s ability to foster conditions that would permit stable economic growth. In recent years, Argentina has confronted inflationary pressures, evidenced by a significant increase in fuel, energy, and food prices, among other factors. According to the most recent publicly available information, the inflation rate was 50.9% in 2021, 94.8% in 2022 and 211.4% in 2023.
The prior administration, through the Ministry of Economy and the BCRA, adopted several measures to deaccelerate inflation and control the devaluation of the Argentine peso against the U.S. dollar. These measures included, among others: (i) restrictions on the access of individuals and entities to the MLC; (ii) taxation to certain operations which imply acquisition of foreign currency (the PAIS tax); (iii) negotiations with creditors in order to restructure the Argentine external debt; and (iv) price freezes on hundreds of products. Nevertheless, the Argentine economy continued to experience high levels of inflation.
In an attempt to manage inflation, the new administration has eliminated price controls implemented by the prior administration, in order to allow prices in the economy to be determined by supply and demand. However, the foreign exchange controls remain in place due to the lack of BCRA’s reserves. In addition, certain prices, such as public transportation and public services tariffs, will be subject to progressive deregulation, to ease transition and prevent social turmoil.
We cannot predict whether the measures announced by the new administration will reduce high inflation rates. If inflation is not controlled, high inflation could undermine Argentina’s foreign competitiveness by diluting the effects of the depreciation of the Argentine peso, negatively affecting the level of economic activity and employment, and undermining confidence in Argentina’s banking system, which could further limit the availability of domestic and international financing to businesses. Furthermore, a portion of Argentina’s sovereign debt is subject to adjustment by the Stabilization Coefficient (Coeficiente de Estabilización de Referencia), a currency index that is strongly related to inflation. Therefore, any further significant increase in inflation could cause an increase in Argentina’s external debt and, consequently, in Argentina’s financial obligations, which could aggravate pressures on the Argentine economy. If inflation remains high or continues to increase, Argentina’s economy may be negatively affected, and our results of operations could be materially affected.
Failure to adequately address actual and perceived risks of institutional deterioration and corruption may adversely affect Argentina’s economy and financial condition and, consequently, our business.
A lack of a solid and transparent institutional framework for contracts with the Argentine Government and its agencies and corruption allegations have affected and continue to affect Argentina. Argentina ranked 98 of 180 in Transparency International’s 2023 Corruption Perceptions Index, and 126 of 190 in the 2020 Ease of Doing Business Report of the World Bank.
The failure to address these issues could increase the risk of political instability, distort decision-making processes, and adversely affect Argentina’s international reputation and ability to attract foreign investment. The Argentine Government’s ability to implement initiatives to strengthen Argentina’s institutions and to reduce corruption is uncertain as it would be subject to independent review by the judicial branch, as well as legislative support from opposition parties.
We cannot give any assurance that the Argentine Government will implement any of these initiatives nor if implemented, that any of such initiatives would be successful in halting institutional deterioration and corruption.
27
Risks Related to Our Other Principal Operations and Other Principal Markets in Which We Operate
Italy
If the approval process from local and national authorities of the master plan for the Florence Airport is further delayed, our financial results from the operation of such airport could be negatively impacted.
The master plan for the period 2014 through 2029 was approved by the Italian Civil Aviation Authority (“ENAC” for its Italian acronym) in November 2015, by the Italian Ministry of the Environment in December 2017 and by the Italian Ministry of Infrastructures and Transport in April 2019. However, on May 27, 2019, upon request of the Environmental Association (Associazione VAS Vita Ambiente) and other local municipalities, such approval was repealed through judgment No. 793. On July 25, 2019, TA, jointly with the Ministry of Environment, ENAC and other authorities, appealed such judgement.
On February 14, 2020, TA has been notified by the Council of State that the appeal has been rejected. Therefore, we received the obligation to undertake a new procedure regarding the environmental compliance of the Florence airport master plan. During 2022, a project review of the master plan was performed and the investments forecasts (traffic and infrastructures) were defined until 2035 (the “2035 TA Master Plan”). In October 2022, TA initiated a public debate process as required under applicable law which concluded on February 6, 2023. The 2035 TA Master Plan was presented to ENAC on March 2023 and received its technical approval in May 2023. In June 2023, ENAC asked the Italian Ministry of the Environment to apply the “Integrated Environmental Procedure” (both, Environmental Impact Assessment and Environmental Strategic Assessment) as permitted by local statutes.
The first phase of the Integrated Environmental Procedure (called scoping) was carried out during 2023 and was concluded in January 2024 (with minutes from the National Committee EIA-EAS issued on December 29, 2023). The second phase of such procedure should start in April 2024 and should be concluded by the summer of 2024. The permit/authorization process is expected to start in autumn 2024 and will be concluded by the end of 2024, allowing the start of the construction phase.
Our ability to increase revenues and profits derived from the operation of the Florence Airport may be adversely affected if the 2035 TA Master Plan is rejected or its approval is delayed.
The exercise of the special powers of the Italian Government may restrict our ability to transfer, or take certain corporate actions in respect of, our shareholding in TA or restrict the ability of investors to acquire a significant stake in our share capital.
Certain regulations concerning legal restrictions on transfer of assets of strategic national importance may apply to us, as controlling shareholder of TA, the operator of our Italian Airports (as defined herein).
Provisions of Law Decree No. 21 of March 15, 2012 (“Law Decree 21/2012”), as converted with amendments into Law No. 56 of May 11, 2012, and subsequently amended from time to time, which granted the Italian Government special powers (the “Golden Powers”), could be triggered in the event that: (i) we attempt to transfer our shareholding in TA and/or the Italian Airports to a third party; or (ii) a stake of TA’s share capital is transferred to a third party in the future; or (iii) TA’s corporate bodies attempt to approve and/or implement certain resolutions, acts or transactions resulting in changes to the ownership, control, or availability of the assets of TA (including, inter alia, mergers, demergers, establishment and enforcement of security interests over shares/assets of TA).
Below is a description of the procedure that would apply in such a case. As of the date of this annual report, we are not aware that our initial public offering has indeed triggered any procedures pursuant to Law Decree 21/2012.
Pursuant to current laws and regulations, (i) the approval of specific corporate resolutions by companies operating, inter alia, in the energy, transport, and communications sectors, which are understood to be of strategic importance to the nation, and (ii) the acquisition of significant shareholdings in such companies by investors, are subject to the Golden Powers. Article 2 of Law Decree 21/2012 specifically regulates the special powers of the Italian Government over the strategic assets of companies operating in the transport sector. In particular, these provisions state that, in relation to companies that own one or more of such strategic assets, the Italian Government may:
| ● | veto any resolutions, acts and transactions that would (i) result in a change of ownership, control, or purpose of such assets, (ii) result in an exceptional situation not regulated by national or European laws applicable to the sector, or (iii) constitute a threat of a serious prejudice to the interest of public safety (Article 2, paragraph 3); |
28
| ● | impose conditions requiring certain buyers to provide guarantees in any purchase, (Article 2, paragraph 5), if such a purchase poses a serious threat to public interest (Article 2, paragraph 6); and |
| ● | oppose to the purchase, if such a purchase entails exceptional risks to the protection of public interest, which cannot be mitigated by the buyer providing the guarantee (Article 2, paragraph 6). |
Article 2 of the Decree of the President of the Council of Ministers No. 180 of December 23, 2020, has identified airports as “strategic assets.” Therefore, the Italian Airports are subject to these Decrees.
As a result, our ability to enter into certain commercial transactions may be further restricted by the Italian Government’s decision to exercise its Golden Powers with respect to the management of strategic transport assets in Italy. This may limit our ability, as TA’s shareholder, to benefit from the proceeds of certain proposed asset sales or acquisitions or business combinations and may limit our shareholder’s ability to benefit from possible premiums connected to a proposed change in control transaction or tender offer.
If the Italian Government exercises these Golden Powers in the future with respect to any transaction involving, directly or indirectly, TA and/or the Italian Airports, such exercise could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects in the future.
However, it should be noted that in 2023 the operation (still ongoing) regarding the new financing for investments in the Pisa Airport and the refinancing of previous TA’s debts was submitted to the Italian Government. The Italian Government gave its consent for these transactions.
Coordinating compliance with regulatory obligations may strain our resources and divert management’s attention.
TA is listed on the Milan Stock Exchange. As a public company, TA is subject to the reporting requirements of local regulations in Italy and other applicable securities rules and regulations. Compliance with these rules and regulations involves legal and financial compliance costs, makes some activities more difficult, time-consuming, or costly and increases demand on TA’s systems and resources. Coordination between TA and us to comply with our respective regulatory and filings procedures can be burdensome, divert management’s attention and affect our daily operations and business.
In addition, the interests of TA’s public shareholders may not be the same as the interest of our Majority Shareholder. This conflict of interest may affect our operations and business.
Brazil
We have identified payments made by ICAB that may not have had any proper purpose and that could expose us to fines and sanctions as well as reputational harm and other adverse effects.
We have identified three payments totaling approximately R$0.8 million made by ICAB during 2014, when Infravix was still an indirect shareholder of ICAB, to individuals or entities that the press has suggested made illegal payments to government officials on behalf of corporate clients. We have been unable to identify a proper purpose for some of these payments. The case reported by the press has been under investigation by the Supreme Court for approximately three years, but neither of ICAB’s current executives nor ICAB has been subject of any criminal investigations.
Moreover, on September 14, 2019, Receita Federal (Brazilian Tax authority) identified the mentioned payments and considered those did not have a proper purpose, therefore, imposed a R$1.3 million fine on ICAB. ICAB is contesting the fine through an administrative procedure. The outcome of this procedure is still uncertain.
We could be exposed to reputational harm and other adverse effects in connection with these payments. If these payments are ultimately found to have been improper, we could be subject to additional fines and sanctions, as well as other penalties. Any of the foregoing effects could have a material adverse effect on our business.
29
We expect to incur losses in our Brasilia Airport for the next several years due to the accretion of the financial liability recognized as a result of the committed fixed concession fee.
Under the Brazilian Concession Agreements for the operation of the Brasilia Airport, we are obligated to pay an annual fixed concession fee which is adjusted by inflation. Initially, we recognized this contractual obligation as a financial liability at fair value in acquisition accounting. Following a revision of the interest rate of discount, we now measure the liability at an amortized cost utilizing a discount rate of 6.81% (real), which is the regulatory weighted average cost of capital (“WACC”) applicable at the time we entered into the Brasilia Concession Agreement. Any change in the current discount rate used to discount the estimated cash outflows, as well as an increase in the liability that reflects the passage of time (also referred to as the unwinding of a discount or accretion) is recognized as expense, period over period. During the years ended December 31, 2022, 2021 and 2020, we recognized losses of U.S.$101.2 million, U.S.$108.8 million and U.S.$69.7 million, respectively, relating to these effects. See Note 23 to our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements. We expect the accretion described above to occur in a similar magnitude in the next several years.
During 2021, ICAB suspended payment of 50% of the annual fixed concession fee based on the re-schedule request that was made before the Brazilian ANAC. Such request was recently rejected by ANAC. See “Brazilian Proceedings—ICAB—Administrative Proceedings before the Brazilian ANAC.” As of the date of this annual report, a court injunction has suspended all actions against ICAB for lack of payment of the annual fixed concession fee. Therefore, unless such injunction is cancelled or lifted, ICAB could not be forced to pay such remaining 50% of the annual fixed concession fee. If such injunction is lifted or cancelled, ICAB would be forced to pay such outstanding 50%. Also, if not paid, the Brasilia Concession Agreement may be terminated which would have a negative impact on our results of operations.
Furthermore, if the injunction is cancelled or lifted, ICAB will be in automatic default under the BNDES Refinancing (as defined below). See “Item 5 Operating and Financial review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Indebtedness—Brazilian Refinancing Transactions.” Upon such default, BNDES would be entitled to request the guarantors of the Brasilia airport indebtedness to post additional collateral as security of the obligations assumed thereunder. If such additional collateral is not timely and adequately posted, BNDES could declare all amounts due and payable, which would affect our results of operations and liquidity.
Regarding the concession fee for the year ended December 31, 2022, a partial payment of R$81.6 million (approximately U.S.$15.3 million) was made through the application of re-equilibrium credits. With respect to the remainder of such concession fee, on November 21, 2022, ICAB made an offer to the Ministry of Infrastructure to pay through the delivery of federal bonds, which is in process of analysis by the Ministry. In December 2022, the Ministry issued an Official Letter confirming that while the Federal bonds are being analyzed, ICAB will be deemed to be in compliance with its obligations.
The commercial area at the Brasilia Airport may not attract the numbers of customers we anticipate, which would ultimately affect our results of operations.
A key part of our strategy to expand and increase our commercial revenues in the Brasilia Airport is the development of an area with commercial offerings within the airport.
On December 13, 2019, ICAB entered into a lease agreement with a leading Brazilian real estate group pursuant to which such group agreed to build and develop, with its own capital, a new shopping center of approximately 350,000 square feet of gross leasable areas. If this project fails to attract the number of customers that we anticipate, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
The ongoing economic uncertainty and political instability in Brazil may adversely affect our economic and financial condition.
Brazil’s political environment has historically influenced, and continues to influence, the performance of the country’s economy. Political crises have affected and continue to affect the confidence of investors and the general public, which have historically resulted in economic deceleration and heightened volatility in the securities issued by Brazilian companies.
30
The recent economic instability in Brazil has contributed to a decline in market confidence in the Brazilian economy as well as to a deteriorating political environment. In addition, various ongoing investigations into allegations of money laundering and corruption being conducted by the Office of the Brazilian Federal Prosecutor, including the Car Wash Affair, have negatively affected the Brazilian economy and political environment. Members of the Brazilian Government as well as senior officers of large state-owned companies have faced or are currently facing allegations of corruption and money laundering as a result of the Car Wash Affair. These individuals are alleged to have accepted and/or offered bribes by means of kickbacks on contracts granted by the Brazilian Government to several infrastructures, oil and gas and construction companies. These kickbacks allegedly financed the political campaigns of political parties forming the previous government’s coalition that was led by former President Dilma Rousseff, which funds were unaccounted for or not publicly disclosed.
Exchange rate instability may have adverse effects on the Brazilian economy and our results of operations.
The Brazilian currency has been historically volatile and has been devalued frequently over the past three decades. Throughout this period, the Brazilian Government has implemented various economic plans and used various exchange rate policies, including sudden devaluations, periodic mini devaluations (during which the frequency of adjustments has ranged from daily to monthly), exchange controls, dual exchange rate markets and a floating exchange rate system. Although long-term depreciation of the Brazilian real is generally linked to the rate of inflation in Brazil, depreciation of the Brazilian real occurring over shorter periods of time has resulted in significant variations in the exchange rate between the Brazilian real, the U.S. dollar and other currencies. The Brazilian real/U.S. dollar exchange rate reported by the Brazilian Central Bank was R$5.5802 per U.S. dollar on December 31, 2021, R$5.2174 per U.S. dollar on December 31, 2022, and R$4.8410 per U.S. dollar on December 31, 2023, but there can be no assurance that the Brazilian real will not again depreciate against the U.S. dollar or other currencies in the future, which could lead to fluctuations in our consolidated earnings and cash flow as measured in U.S. dollars.
Uruguay
A deterioration in the economic conditions of our neighboring markets, particularly Argentina has the potential to affect the number of passengers at our Uruguayan airports mainly Punta del Este airport.
The number of passengers and cargo volume at the airports in Uruguay is primarily a fraction of the number of passengers coming from or going to Brazil and Argentina. Passengers and cargo volume at our Uruguayan airports are also a reflection of the economic situation of Brazil and Argentina. The state of affairs in Argentina, particularly in relation to its economy and with respect to foreign exchange restrictions, could negatively impact the number of passengers and consequently affect our operation and financial results mostly at the Punta del Este Airport.
Our operations in Uruguay remain highly linked to the numbers of passengers using the airports in Uruguay’s main trading partners, such as Brazil and Argentina. Therefore, any deterioration of a neighboring market could have a material impact on the number of passengers at our Uruguayan airports which, in turn, could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Ecuador
The political environment of Ecuador is uncertain which could have adverse effect on our results of operations.
On May 17, 2023, former president Mr. Guillermo Lasso dissolved congress and called for presidential elections. On November 23, 2023, Mr. Daniel Noboa was elected as new president of Ecuador, and on January 8, 2024, Mr. Noboa declared a state of emergency for a term of 60 days. The state of emergency, together with the political, economic and social crisis in Ecuador, could negatively affect activity at our Ecuadorian airports and ultimately our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Armenia
The ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine has and will likely continue to disrupt or impact the flights schedules and supply chains, which could affect our results of operation.
It is not clear how long the ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine will last. Such conflict has, and will likely continue to, disrupt supply chains, and cause changes in the flights schedule.
31
While it is difficult to anticipate the indirect impact that the war between Russia and Ukraine or the sanctions announced to date may have on our business, any additional sanctions imposed or actions taken by the U.S., EU nations or other countries, and any retaliatory measures taken by Russia, such as restrictions flights from and to Russia and Armenia, could have an adverse impact on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Furthermore, the war in the Middle East continues to escalate and even if future developments are unpredictable, any escalation in international hostilities could have a negative impact on us too. For example, a conflict with Azerbaijan could negatively affect our operations.
Even though the Armenian authorities announced that they are going to proceed with constitutional reforms and that they continue the negotiations to reach a peace treaty where the US is acting as active mediator, there have been some aggressive statements coming from Azerbaijan which could affect our operations in case they hinder the execution of the peace treaty.
Risks Related to Our Common Shares
The price of our common shares may be highly volatile.
We cannot predict the extent to which investor interest in our common shares will create or be able to maintain an active trading market, or how liquid that market will be in the future. The market price of our common shares may be volatile and may be influenced by many factors, some of which are beyond our control, including:
| ● | the failure of financial analysts to cover our common shares or changes in financial estimates by analysts; |
| ● | actual or anticipated variations in our operating results; |
| ● | changes in financial estimates by financial analysts, or any failure by us to meet or exceed any of these estimates, or changes in the recommendations of any financial analysts that elect to follow our common shares or the shares of our competitors; |
| ● | announcements by us or our competitors of significant contracts or acquisitions; |
| ● | future sales of our common shares; and |
| ● | investor perceptions of us and the industries in which we operate. |
In addition, the equity markets in general have experienced substantial price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of particular companies affected. These broad market and industry factors may materially harm the market price of our common shares, regardless of our operating performance. In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of certain companies’ securities, securities class action litigation has been instituted against these companies. This litigation, if instituted against us, could adversely affect our financial condition or results of operations.
We issued, and may further issue, options, restricted shares, and other forms of share-based compensation, which have the potential to dilute shareholder value and cause the price of our common shares to decline.
In 2020, we implemented a long-term management share compensation plan. See “Item 6 Directors, Senior Management and Employees —Compensation — Management Compensation Plan.” We may offer additional share options, restricted shares, and other forms of share-based compensation to our directors, officers, and employees in the future. If any options that we issue are exercised, or any shares that we may issue vest, and those shares are sold into the public market, the market price of our common shares may be adversely affected.
32
A significant portion of our common shares may be sold into the public market, which could cause the market price of our common stock to drop significantly, even if our business is doing well.
Our officers, directors, and the Majority Shareholder are able to sell our common shares in the public market. In addition, pursuant to a registration rights and indemnification agreement, the Majority Shareholder and any affiliate transferees have the right, subject to certain conditions, to require us to register the sale of their common shares under the Securities Act. By exercising their registration rights and selling a large number of shares, our existing owners could cause the prevailing market price of our common shares to decline. The common shares covered by registration rights would represent approximately 80.5% of our outstanding capital stock. Registration of any of these outstanding common shares would result in such shares becoming freely tradable without compliance with Rule 144 upon effectiveness of the registration statement. Sales of a substantial number of such common shares or the perception that such sales may occur could cause our market price to fall or make it more difficult for you to sell your common shares at a time and price that you deem appropriate.
We may need additional capital and we may not be able to obtain it.
We believe that our existing cash and cash equivalents, cash flows from operations and ability to raise financing are and will be sufficient to meet our anticipated cash needs for the foreseeable future. We may, however, require additional cash resources due to changed business conditions or other future developments, including any investments or acquisitions we may decide to pursue. If these resources are insufficient to satisfy our cash requirements, we may seek to sell additional equity or debt securities or obtain other sources of financing. The sale of additional equity securities could result in dilution to our shareholders. The incurrence of indebtedness could result in increased debt service obligations and could require us to agree to operating and financing covenants that would restrict our operations.
Our ability to obtain additional capital on acceptable terms is subject to a variety of uncertainties, including:
| ● | conditions of the U.S. capital markets and other capital markets in which we may seek to raise funds; |
| ● | our future results of operations and financial condition; |
| ● | government regulation of foreign investment in the United States, Europe, and Latin America; and |
| ● | global economic, political, and other conditions in jurisdictions in which we do business. |
Our business and results of operations may be adversely affected by the increased strain on our resources from complying with the reporting, disclosure, and other requirements applicable to public companies in the United States promulgated by the U.S. Government, New York Stock Exchange, or other relevant regulatory authorities.
Compliance with existing, new, and changing corporate governance and public disclosure requirements adds uncertainty to our compliance policies and increases our costs of compliance. Changing laws, regulations and standards include those relating to accounting, corporate governance, and public disclosure, including the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, new U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) regulations and the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) listing guidelines. In particular, compliance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“Section 404”) and related regulations regarding required assessment of internal controls over financial reporting and our external auditor’s audit of internal controls over financial reporting, requires the commitment of significant financial and managerial resources.
Our efforts to comply with evolving laws, regulations and standards have resulted in, and are likely to continue to result in, increased general and administrative expenses. Further, our board members and senior management could face an increased risk of personal liability in connection with their performance of duties. As a result, we may face difficulties attracting and retaining qualified board members and senior management, which could harm our business. If we fail to comply with new or changed laws or regulations and standards differ, our business and reputation may be harmed.
33
If we fail to maintain an effective system of internal controls over financial reporting, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results or prevent fraud.
As a public company in the United States, we are subject to reporting obligations under the U.S. securities laws. The SEC, as required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, adopted rules requiring every public company to include a management report on such company’s internal control over financial reporting in its annual report, which contains management’s assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. In addition, an independent registered public accounting firm must attest to and report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. We became subject to these requirements for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019.
Our management has concluded that our internal control over financial reporting is effective as of December 31, 2023. Our independent registered public accounting firm has issued an attestation report, which has concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2023. See “Item 15. Controls and Procedures.” However, if we fail to maintain effective internal control over financial reporting in the future, our management and our independent registered public accounting firm may not be able to conclude that we have effective internal control over financial reporting at a reasonable assurance level. This could in turn result in loss of investor confidence in the reliability of our financial statements and negatively impact the trading price of our common shares. Furthermore, we are committed to invest considerable costs, management time and other resources in an effort to comply with Section 404 and other requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
Our exemption as a “foreign private issuer” from certain rules under the U.S. securities laws will result in less information about us being available to investors than for U.S. companies, which may result in our common shares being less attractive to investors.
As a “foreign private issuer” in the United States, we are exempt from certain rules under the U.S. securities laws and are permitted to file less information with the SEC than U.S. companies. As a “foreign private issuer,” we are exempt from certain rules under the Exchange Act, that impose certain disclosure obligations and procedural requirements for proxy solicitations under Section 14 of the Exchange Act. In addition, our officers, directors, and principal shareholders are exempt from the reporting and “short-swing” profit recovery provisions of Section 16 of the Exchange Act and the rules under the Exchange Act with respect to their purchases and sales of our common shares. Moreover, we are not required to file periodic reports and financial statements with the SEC as frequently or as promptly as companies that are not “foreign private issuers” whose securities are registered under the Exchange Act. In addition, we are not required to comply with Regulation FD promulgated by the SEC under the Exchange Act, which restricts the selective disclosure of material information. As a result, our shareholders may not have access to information they deem important, which may result in our common shares being less attractive to investors.
Our ability to pay dividends is restricted under Luxembourg law
Our articles of association and the Luxembourg law of August 10, 1915, on commercial companies as amended from time to time (loi du 10 août 1915 sur les sociétés commerciales telle que modifiée), require a general shareholders meeting to approve any dividend distribution, except as set forth below.
Our ability to declare dividends under Luxembourg corporate law is subject to the availability of distributable earnings or available reserves, including, among other things, a share premium. Moreover, we may not be able to declare and pay dividends more frequently than annually. As permitted by Luxembourg corporate law, our articles of association authorize the declaration of dividends more frequently than annually by the board of directors in the form of interim dividends so long as the amount of such interim dividends does not exceed total net profits made since the end of the last financial year for which the annual accounts have been approved, plus any profits carried forward and sums drawn from reserves available for this purpose, less the aggregate of the prior financial year’s accumulated losses, the amounts to be set aside for the reserves required by Luxembourg law or by our articles of association for the prior financial year, and the estimated tax due on such earnings.
34
We are a holding company and depend on the ability of our subsidiaries to distribute funds to us in order to satisfy our financial obligations and to make dividend payments, which they may not be able to do.
We are a holding company, and our subsidiaries conduct all of our operations. We own no material assets other than the equity interests in our subsidiaries. As a result, our ability to make dividend payments depends on our subsidiaries and their ability to distribute funds to us. The ability of a subsidiary to make these distributions could be affected by covenants included in most of the concession agreements in which we act as concessionaires, such as the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the Uruguayan Concession Agreements, the Armenian Concession Agreement, the Italian Concession Agreements, and the Brazilian Concession Agreements, or by the financing agreements we have entered into, or by the law and regulation in force in their respective jurisdictions of incorporation, including, for example, foreign exchange controls on the inflow and outflow of foreign currency flows. See “Item 3 Key Information—Risk Factors— Current Argentine exchange controls and the implementation of further exchange controls could adversely affect our results of operations.” See also “Item 5 Operating and Financial review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Indebtedness.” If we are unable to obtain funds from our subsidiaries, we will be unable to distribute dividends. We do not intend to seek to obtain funds from other sources to pay dividends.
Our shareholders may have more difficulty protecting their interests than they would as shareholders of a U.S. corporation, which could adversely impact trading in our common shares and our ability to conduct equity financings.
Our corporate affairs are governed by our articles of association and the laws of Luxembourg, including the laws governing public limited liability companies (sociétés anonymes). The rights of our shareholders and the responsibilities of our directors and officers under Luxembourg law are different from those applicable to a corporation incorporated in the United States. In addition, Luxembourg law governing the securities of Luxembourg companies may not be as extensive as those in effect in the United States, and Luxembourg law and regulations in respect of corporate governance matters may not be as protective of minority shareholders as state corporation laws in the United States. Therefore, our shareholders may have more difficulty in protecting their interests in connection with actions taken by our directors and officers or our principal shareholders than they would as shareholders of a corporation incorporated in the United States.
Neither our articles of association nor Luxembourg law provide for appraisal rights for dissenting shareholders in certain extraordinary corporate transactions that may otherwise be available to shareholders under certain U.S. state laws. As a result of these differences, our shareholders may have more difficulty protecting their interests than they would as shareholders of a U.S. issuer.
Holders of our common shares may not be able to exercise their pre-emptive subscription rights and may suffer dilution of their shareholding in the event of future common share issuances.
Under Luxembourg law, our shareholders benefit from a pre-emptive subscription right on the issuance of common shares for cash consideration. However, shareholders may, at a general shareholders’ meeting and in accordance with Luxembourg law and our articles of association, waive or suppress and authorize the board to waive, suppress or limit any shareholders’ pre-emptive subscription rights provided by Luxembourg law to the extent the board deems such waiver, suppression or limitation advisable for any issuance or issuances of common shares within the scope of our authorized share capital prior to the pricing for a period of up to five years following the publication of the deed granting such authorization on the Luxembourg Official Gazette (Recueil Electronique des Sociétés et Associations (RESA)) which period may be renewed for one or several periods of up to five years. Such common shares may be issued above, at or below market value as well as by way of incorporation of available reserves (including, among other things, a share premium). In addition, a shareholder may not be able to exercise the shareholder’s pre-emptive right on a timely basis or at all, unless the shareholder complies with the requirements set forth under Luxembourg corporate law and applicable laws in the jurisdiction in which the shareholder is resident, particularly in the United States. As a result, the shareholding of such shareholders may be materially diluted in the event common shares are issued in the future. Moreover, in the case of an increase in capital by a contribution in kind, no pre-emptive rights of the existing shareholders exist.
35
We are organized under the laws of Luxembourg and it may be difficult for you to obtain or enforce judgments or bring original actions against us or our executive officers and directors in the United States.
We are organized under the laws of Luxembourg. The majority of our assets are located outside the United States. Furthermore, the majority of our directors and officers and some experts named in this annual report reside outside the United States and a substantial portion of their assets are located outside the United States. Investors may not be able to effect service of process within the United States upon us or these persons or to enforce judgments obtained against us or these persons in U.S. courts, including judgments in actions predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities laws. Likewise, it may also be difficult for an investor to enforce in U.S. courts judgments obtained against us or these persons in courts located in jurisdictions outside the United States, including judgments predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities laws. It may also be difficult for an investor to bring an original action in a Luxembourg court predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities laws against us or these persons. Furthermore, Luxembourg law does not recognize a shareholder’s right to bring a derivative action on behalf of the company, except in limited cases. Minority shareholders holding securities entitled to vote at the general meeting and holding at least 10.0% of the voting rights of the company may bring an action against the directors on behalf of the company. Minority shareholders holding at least 10.0% of the voting rights of the company may also ask the directors questions in writing concerning acts of management of the company or one of its subsidiaries, and if the company fails to answer these questions within one month, these shareholders may apply to the Luxembourg courts to appoint one or more experts instructed to submit a report on these acts of management.
As there is no treaty in force on the reciprocal recognition and enforcement of judgments in civil and commercial matters between the United States and Luxembourg, courts in Luxembourg will not automatically recognize and enforce a final judgment rendered by a U.S. court. A valid judgment in civil or commercial matters obtained from a court of competent jurisdiction in the United States may be entered and enforced through a court of competent jurisdiction in Luxembourg, subject to compliance with the enforcement procedures (exequatur). The enforceability in Luxembourg courts of judgments rendered by U.S. courts will be subject prior any enforcement in Luxembourg to the procedure and the conditions set forth in the Luxembourg procedural code, which conditions may include the following as of the date of this annual report (which may change):
| ● | the judgment of the U.S. court is final and enforceable (exécutoire) in the United States; |
| ● | the U.S. court had jurisdiction over the subject matter leading to the judgment (that is, its jurisdiction was in compliance with both Luxembourg private international law rules and with the applicable domestic U.S. federal or state jurisdictional rules); |
| ● | the U.S. court has applied to the dispute the substantive law that would have been applied by Luxembourg courts; |
| ● | the judgment was granted following proceedings where the counterparty had the opportunity to appear and, if it appeared, to present a defense, and the decision of the foreign court must not have been obtained by fraud, but in compliance with the rights of the defendant; |
| ● | the U.S. court has acted in accordance with its own procedural laws; |
| ● | the judgment of the U.S. court does not contravene Luxembourg international public policy; and |
| ● | the U.S. court proceedings were not of a criminal or tax nature. |
We indemnify our directors for and hold them harmless against all claims, actions, suits, or proceedings brought against them, subject to limited exceptions. The rights and obligations among or between us and any of our current or former directors and officers will be generally governed by the laws of Luxembourg and subject to the jurisdiction of the Luxembourg courts, unless such rights or obligations do not relate to or arise out of their capacities listed above. Although there is doubt as to whether U.S. courts would enforce such provision in an action brought in the United States under U.S. federal or state securities laws, such provision could make enforcing judgments obtained outside Luxembourg more difficult to enforce against our assets in Luxembourg or jurisdictions that would apply Luxembourg law.
36
Luxembourg insolvency laws may offer our shareholders less protection than they would have under U.S. insolvency laws.
As a company organized under the laws of Luxembourg and with its registered office in Luxembourg, we are subject to Luxembourg insolvency laws in the event any insolvency proceedings are initiated against us including, among other things, Council Regulation (EC) No. 2015/848 of May 20, 2015, on insolvency proceedings (recast), as amended. Should courts in another European country determine that the insolvency laws of that country apply to us in accordance with and subject to such EU regulations, the courts in that country could have jurisdiction over the insolvency proceedings initiated against us. Insolvency laws in Luxembourg or the relevant other European country, if any, may offer our shareholders less protection than they would have under U.S. insolvency laws and make it more difficult for them to recover the amount they could expect to recover in a liquidation under U.S. insolvency laws.
Holders generally will be subject to a 15.0% withholding tax on payment of dividend distributions made on the common shares under current Luxembourg tax law.
Under current Luxembourg tax law, payments of dividends made on the common shares generally are subject to a 15.0% Luxembourg withholding tax. Certain exemptions or reductions in the withholding tax may apply, but it will be up to the holders to claim any available refunds from the Luxembourg tax authority. For more information on the taxation implications, see “Item 10 Additional Information—Taxation—Luxembourg Tax Considerations.”
We are subject to complex tax rules in various jurisdictions, and our interpretation and application of these rules may differ from those of relevant tax authorities, which could result in a liability to material additional taxes, interest, and penalties.
We operate in a number of territories and will accordingly be subject to tax in several jurisdictions. The tax rules to which the Company and its subsidiaries are subject are complex, and we must make judgement (including based on external advice) as to the interpretation and application of these rules. Our tax affairs will in the ordinary course be reviewed by tax authorities. Those tax authorities may disagree with our interpretation and/or application of relevant tax rules. A challenge by a tax authority in these circumstances might require us to incur costs in connection with litigation against the relevant tax authority or reaching a settlement with the tax authority and, if the tax authority’s challenge is successful, could result in additional taxes (perhaps together with interest and penalties) being assessed on us, and as a result an increase in the amount of tax payable by us.
Additionally, dividends and other intra-group payments made by our subsidiaries may be subject to withholding taxes imposed by the jurisdiction in which the entity making the payment is organized or tax resident. Unless such taxes are fully creditable or refundable, dividends and other intra-group payments may increase the amount of tax paid by us. Although the Company and its subsidiaries arrange themselves and their affairs with a view to minimizing the incurrence of such taxes, there can be no assurance that we will succeed.
Holders of our common shares who sell or transfer common shares acquired after January 1, 2018 representing 10% or more of our equity may be subject to Argentine capital gains tax under the new Argentine tax law.
Under Argentine tax law, non-Argentine residents who sell or transfer shares or other participations in foreign entities, which shares were acquired after January 1, 2018, may be subject to capital gains tax in Argentina if 30% or more of the value of the foreign entity is derived from assets located in Argentina and the shares being sold or transferred represent 10% or more of the equity interests of such foreign entity. Therefore, any non-Argentine resident holders of our common shares who sell or transfer common shares acquired after January 1, 2018 and which shares being sold or transferred represent 10% or more of our equity interests, may be subject to the Argentine capital gains tax. See “Item 10 Additional Information—Taxation—Argentine Tax Considerations.”
ITEM 4. COMPANY INFORMATION
The Company makes its filings in electronic form under the EDGAR filing system of the SEC. Its filings are available through the EDGAR system at www.sec.gov. The Company’s filings are also available to the public through the Internet at CAAP’s website at http://investors.corporacionamericaairports.com. The Company’s website is provided for informational purposes only and the information contained on its website or that can be accessed through its website is not part of this annual report.
37
A. |
HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT OF THE COMPANY |
We have been operating since 1998 and have become a leading global airport concession operator.
| ● | In 1998, as part of the AA2000 consortium, we were awarded the national and international public bid conducted by the Argentine Government for the concession rights related to the operation of 33 airports in Argentina, including the two largest airports, the Ministro Pistarini International Airport ( or the Ezeiza Airport as previously defined in Item 3.D.), located at Ezeiza, Buenos Aires, and the Jorge Newbery Aeroparque Airport (“Aeroparque Airport”), located in Buenos Aires. |
| ● | In 2001, as part of the Aeropuertos del Neuquén S.A. (“NQN”) consortium, we were awarded the concession to operate Aeropuerto de Neuquén (“Neuquén Airport”), our 34th airport in Argentina. |
| ● | In 2002, our subsidiary Armenia International Airports CJSC (“AIA”) was awarded the concession to operate the Zvartnots International Airport (“Zvartnots Airport”), located 12 kilometers from downtown Yerevan, Armenia’s capital. |
| ● | In 2003, in a public auction conducted by the Uruguayan Government, we purchased the shares of Puerta del Sur S.A. (“Puerta del Sur”), owner of the concession that operates the General Cesáreo Berisso International Airport (“Carrasco Airport”) in Carrasco, Uruguay, located 19 kilometers from downtown Montevideo, Uruguay’s capital. |
| ● | In 2004, as part of the Terminal Aeroportuaria de Guayaquil S.A. (“TAGSA”) consortium, we were awarded the concession to operate the José Joaquín de Olmedo International Airport (“Guayaquil Airport”), located five kilometers from downtown Guayaquil, Ecuador. |
| ● | In 2007, we executed an amendment to the Zvartnots Airport concession agreement to include Shirak Airport in Gyumri (“Shirak Airport”), the second largest civil airport in Armenia. |
| ● | In 2008, in a private transaction, we acquired all of the equity interests of Consorcio Aeropuertos Internacionales S.A. (“CAISA”), which owns the concession that operates the Carlos A. Curbelo Airport (“Punta del Este Airport”) located in Maldonado, by Punta del Este, Uruguay. |
| ● | In 2008, as part of the consortium Aeropuerto de Bahía Blanca S.A. (“BBL”), we were awarded the concession to operate Aeropuerto de Bahía Blanca (“Bahía Blanca Airport”), our 35th airport in Argentina. |
| ● | In 2011, as part of the consortium AAP, we were awarded the concession to operate six principal airports in southern Peru (the “AAP Airports”). |
| ● | In 2011, as part of the consortium Aeropuertos Ecológicos de Galápagos S.A. (“ECOGAL”), we were awarded the concession to operate the Seymour Airport (“Galapagos Airport”), located in Baltra Island, Galapagos Archipelago, our second airport in Ecuador. |
| ● | In 2011, as part of the consortium ICASGA, we were awarded the concession to operate the International Airport of São Gonçalo do Amarante (“Natal Airport”), located in Natal, Brazil. |
| ● | In 2012, pursuant to an agreement between AA2000 and the Argentine province of Santiago del Estero, we began operating the Termas de Río Hondo Airport, our 36th airport in Argentina, which pursuant to ORSNA’s Resolution No. 27/2021 has also been incorporated into the AA2000 Concession Agreement. |
| ● | In 2012, as part of the consortium ICAB, we were awarded the concession to operate the Presidente Juscelino Kubitschek International Airport (“Brasilia Airport”), located 11 kilometers from downtown Brasilia, Brazil’s capital. |
| ● | In 2012, we formed A.C.I. Airports International S.à r.l. to hold, either directly or indirectly, our interests in various companies that own our airport concessions. |
38
| ● | In 2014, we acquired controlling interests in the companies that own the Aeroporto Galileo Galilei di Pisa (“Pisa Airport”) located in Pisa, Italy, and the Aeroporto di Firenze (“Florence Airport,” and together with Pisa Airport, the “Italian Airports”) located in Florence, Italy, through a number of private acquisitions with former shareholders as well as the consummation of two public tender offers. In 2015, we merged the two companies that operated the Italian Airports to form TA, a company publicly listed on the Milan Stock Exchange (Borsa Italiana) and of which we own 46.71% of the issued and outstanding common stock. The concessions for the Pisa Airport and the Florence Airport have been transferred to TA. |
| ● | In 2014, we executed an amendment to the concession agreement of the Carrasco Airport extending the term by 10 years to 2033. |
| ● | In 2015, we completed the corporate consolidation through which we acquired direct interest in ICASGA and indirect interest in ICAB through Inframerica. |
| ● | In 2017, as part of the AA2000 consortium, we were awarded the concession rights related to the operation of the El Palomar Airport (“El Palomar Airport”), located in the province of Buenos Aires, our 37th airport in Argentina. |
| ● | On February 1, 2018, we completed our initial public offering, in which we and the Majority Shareholder sold an aggregate of 28,571,429 common shares to the public. |
| ● | In 2018, by means of two separate transactions, we acquired an additional 11.08% interest in TA, increasing our ownership to 62.28% of its issued and outstanding common stock. |
| ● | In 2018, we sold and transferred 25% of CA Italy’s issued and outstanding common stock to Investment Corporation of Dubai, reducing our ownership in CA Italy to 75%. |
| ● | In 2018, we executed an amendment to the Guayaquil Concession Agreement extending the concession term for additional five years. |
| ● | In June 2019, we executed an amendment to the Punta del Este Concession Agreement extending the concession term for additional 14 years, until March 31, 2033. |
| ● | In July 2020, the Italian Government passed a law in relation with the COVID-19 pandemic emergency measures, granting a two-year concession extension for airport operators. |
| ● | In November 2020, we executed an irrevocable amendment for the termination Natal Airport concession. |
| ● | In December 2020, we executed an amendment to the AA2000 Concession Agreement extending the concession term for additional ten years, until February 13, 2038. |
| ● | In July 2021, we executed an amendment to the TAGSA Concession Agreement extending the concession term for additional two years, until July 27, 2031. |
| ● | In October 2021, the amendment of the Neuquén Airport Concession Agreement with the Argentinian Government was approved, extending the concession through 2026. |
| ● | In November 2021, we executed an amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement (the “Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement”) extending the concession term for additional 20 years, until 2053 and incorporating the following six new airports to the scope of the Carrasco Concession Agreement (the “Uruguay New Airports”): Aeropuerto Internacional de Rivera, the Aeropuerto Internacional de Salto, the Aeropuerto Internacional de Carmelo, the Aeropuerto Internacional de Durazno, the Aeropuerto Internacional de Melo and the Aeropuerto Internacional de Paysandú. |
| ● | In December 2021, we transferred our 50% ownership in AAP to Andino Investment Holding S.A. Following this transaction, Andino Investment Holding S.A. now owns 100% of AAP. Therefore, as of the date of this annual report, we no longer operate the airports under the AAP Concession Agreement. |
39
| ● | In November 2022, we were notified that the consortium formed by the Company, Mota Engil Africa and Mota Engil Nigeria, was selected as preferred bidder for the Nnamdi Azikiwe International Airport (NAIA) Abuja, and Mallam Aminu Kano International Airport (MAKIA) Kano, both located in Nigeria, Africa. |
| ● | On December 30, 2022, TA completed the sale of 80% of the share capital of Toscana Aeroporti Handling (“TAH”) to Alisud S.p.A. for €750,000 (the “disposal of the handling business”). The transaction includes an option for TA to exercise, starting from January 1, 2025, a sell option for the remaining 20% share of TAH’s share capital to Alisud for a price of €250,000. In addition, when the performance targets set by TAH’s business plan are achieved, Alisud will pay an additional earn-out price of at least €200,000 to TA. |
| ● | On December 31, 2023, ICASGA was absorbed by ACI do Brasil S.A. (in which we hold 99.99% of the equity interest and the remaining 0.01% is held by the Majority Shareholder). |
The following table lists our concessions by country, together with their commencement date and extension details (if any):
|
|
|
|
CAAP |
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effective |
|
Number of |
|
Concession |
|
Concession |
|
Extension |
Country |
|
Concession |
|
Ownership |
|
Airports |
|
Start Date |
|
End Date |
|
Details |
Argentina |
|
AA2000 |
|
82.7 |
% |
35 |
|
1998 |
|
2038 |
|
— |
|
|
NQN |
|
75.5 |
% |
1 |
|
2001 |
|
2026 |
|
|
|
|
BBL |
|
82.6 |
% |
1 |
|
2008 |
|
2033 |
|
Extendable for 10 years(1) |
Italy |
|
TA (SAT)(2) |
|
46.7 |
% |
1 |
|
2006 |
|
2048 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2014) |
(3) |
|
|
— |
|
|
TA (ADF)(2) |
|
46.7 |
% |
1 |
|
2003 |
|
2045 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2014) |
(4) |
|
|
— |
Brazil |
|
ICASGA |
|
99.9 |
%(5) |
1 |
|
2012 |
(6) |
|
|
—(7) |
|
|
ICAB |
|
51.0 |
% |
1 |
|
2012 |
|
2037 |
|
5 years, extendable for additional 5 years if required to reestablish economic equilibrium |
Uruguay |
|
Puerta del Sur(8) |
|
100 |
% |
7 |
|
2003 |
|
2053 |
|
— |
|
|
CAISA |
|
100 |
% |
1 |
|
1993 |
|
2033(9) (10) (11) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2008) |
|
|
|
— |
Ecuador |
|
TAGSA |
|
50.0 |
% |
1 |
|
2004 |
|
2031 |
|
— |
|
|
ECOGAL |
|
99.9 |
% |
1 |
|
2011 |
|
2026 |
|
— |
Armenia |
|
AIA |
|
100 |
% |
2 |
|
2002 |
|
2032 |
|
Option to renew every 5 years |
| (1) | Subject to certain terms and conditions, including governmental approval. |
| (2) | Both SAT and ADF have merged with TA, of which CA Italy currently owns a 62.28% equity interest. We own 75% of CA Italy’s equity interest. |
| (3) | We began operating the Pisa Airport in 2014. |
| (4) | We began operating the Florence Airport in 2014. |
| (5) | Our effective ownership is 99.98%. |
| (6) | The concession for the Natal Airport was awarded in August 2011, which became effective in January 2012. The Natal Airport began operating in June 2014. |
| (7) | In November 2020, we executed an amendment for the termination of the Natal Airport concession. As of the date of this report, we no longer operate the Natal Airport. |
| (8) | Includes the Uruguay New Airports, which were incorporated to the Carrasco Concession Agreement by means of the amendment executed in November 2021. |
| (9) | We acquired the shares of CAISA in 2008. |
| (10) | We began operating the Punta del Este Airport in 2008, the amendment to the concession agreement approving the extension of the Punta del Este Concession Agreement was executed on June 28, 2019. |
| (11) | Renewable at our sole discretion for an indefinite number of 5-year extension periods. |
40
B.BUSINESS OVERVIEW
Overview
We acquire, develop, and operate airport concessions. We are a leading private airport operator in the world. As of the date of this annual report, we operate 52 airports globally in Latin America, Europe, and Eurasia. Since 1998, when we acquired the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we have expanded the environments and geographies in which we operate by acquiring airport concessions in Armenia, Uruguay, Ecuador, Brazil, Italy, and additional concessions in Argentina.
We operate some of the largest and most important airports in the countries where we conduct operations, including a large international airport, such as Ezeiza Airport in Argentina, domestic airports, such as Brasilia Airport in Brazil and Aeroparque Airport in Argentina, airports in tourist destinations, such as Bariloche and Iguazu in Argentina, Galapagos Ecological Airport in Ecuador, and Florence Airport in Italy, as well as mid-sized domestic and tourist destination airports.
Argentina is our largest and longest established market where we operate and manage 37 of the 56 airports in Argentina’s national airport system, including the Argentina’s two largest airports, Ezeiza and Aeroparque. In each year since we acquired the rights under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, our airports in Argentina have handled over 95.6% of Argentina’s total commercial passenger traffic.
Our Revenue Sources
A significant portion of our revenue depends directly or indirectly on the level of passenger traffic at our airports and the number of aircraft movements (takeoffs and landings) conducted in the airports we operate. We classify our revenue in the following categories: aeronautical revenue, commercial revenue, construction service revenue and other revenue.
Aeronautical Revenue
Aeronautical revenue is derived from the use of our airport facilities by aircrafts and passengers.
Our concession agreements establish or otherwise regulate the rates that we may charge to aircraft operators and passengers for aeronautical services. We charge each departing passenger a fee for the use of our airports which varies depending upon whether the passenger’s flight is an international, regional, or domestic flight, and whether the passenger is in transit or not. Some of our concession agreements also allow us to charge additional fees to passengers for services such as enhanced security measures and reduced mobility assistance, among others. We charge customers our aeronautical fees for aircraft landing and parking, which depend on whether the flight is international or domestic, the maximum take-off weight of the aircraft, the time slot and take-off time, among other factors. International fees are generally higher than domestic or transit fees.
Non-Aeronautical Revenue
Our Non-Aeronautical Revenue is comprised of commercial revenue, construction service revenue and other revenue.
Commercial Revenue
The majority of our commercial revenue is derived from fees resulting from warehouse usage (which includes cargo storage, storage and warehouse services and related international cargo services), services and retail stores, duty free shops, car parking facilities, catering, hangar services, food and beverage services, retail stores, including royalties collected from retailers’ revenue, and rent of space, advertising, fuel, airport counters, vip lounges and fees collected from other miscellaneous sources, such as telecommunications, car rentals and passenger services.
Construction Service Revenue
We treat our investments related to improvements and upgrades to be performed in connection with our concession agreements under the intangible asset model established by IFRIC 12. As a result, we define all expenditures associated with investments required by the concession agreements as revenue generating activities given that they ultimately provide future benefits, and subsequent improvements and upgrades made to the concession are recognized as intangible assets based on the principles of IFRIC 12.
41
Therefore, we recognize revenue and the associated costs of improvements to concession assets in relation with the concessions’ obligations to perform improvements as established in the respective concession agreements. Revenue represents the value of the exchange between us and the respective governmental authorities with respect to the improvements, given that we construct or provide improvements to the airports as obligated under the respective concession agreements, and in exchange, the governmental authorities grant us the right to obtain benefits for services provided using those assets, which are recognized as intangible assets. We recognize the revenue and expense in profit or loss when the expenditures are performed. The cost for such additions and improvements to concession assets is based on actual costs incurred by us in the execution of the additions or improvements, considering the investment requirements in the concession agreements. Through bidding processes, we contract third parties to carry out such construction or improvement services. The amount of revenues for these services is equal to the amount of costs incurred plus a reasonable margin. The amounts paid are set at market value.
Other Revenue
Other revenue includes revenue that is not otherwise classified as aeronautical revenue, commercial revenue, or construction service revenue.
Our Concession Agreements
Our business consists of acquiring, developing and operating airport concessions, which are granted by governmental authorities for a limited period of time. There are three different concession models within our portfolio: single till model in Argentina (AA2000) and Armenia, dual till model in our Italian airports and inflation-based model in our Ecuador, Uruguay and Brazil airports.
| ● | Single till model: a certain return shall be achieved over the life of the concession, and for the calculation, all revenues (aeronautical and commercial) as well as operating expenses and capital expenditures are considered. In order to achieve economic equilibrium, the regulator can adjust passenger and aircraft tariffs, reduce concession fees, reduce capital investment commitments, or a combination thereof. |
| ● | Dual till model: which provides a guaranteed return in connection with its aeronautical activities. Only aeronautical revenues are considered to cover aeronautical operating expenses and capital expenditures. There is an established WACC for the regulated part of the business. |
| ● | Inflation based model: there is no guaranteed return for the concession, and tariffs adjust on an annual basis, considering domestic inflation or a combination between domestic and US inflation. |
Main Operations and Financial Consolidated Metrics
For the year ended December 31, 2023, we had total consolidated revenue of U.S.$1.4 billion, net income from continuing operations of U.S.$226.5 million, Adjusted EBITDA of U.S.$677.7 million and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services of U.S.$671.3 million, and our airports handled 849,473 total aircraft movements and served 81.1 million total passengers (of which approximately 35.0% were international, approximately 56.3% were domestic and approximately 8.8% were transit passengers). For the year ended December 31, 2022, we had total consolidated revenue of U.S.$1.4 billion, net income from continuing operations of U.S.$165.6 million, Adjusted EBITDA of U.S.$456.7 million and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services of U.S.$454.8 million, and our airports handled 738,211 total aircraft movements and served 65.6 million total passengers (of which approximately 32.5% were international, approximately 57.6% were domestic and approximately 9.8% were transit passengers). For the year ended December 31, 2021, we had total consolidated revenue of U.S.$0.7 billion, net loss from continuing operations of U.S.$159.8 million, Adjusted EBITDA of U.S.$149.3 million and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services of U.S.$147.0 million, and our airports handled 497,189 total aircraft movements and served 35.7 million total passengers (of which approximately 23.1% were international, approximately 63.1% were domestic and approximately 13.8% were transit passengers). See “Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Operating Results—Adjusted EBITDA Reconciliation to Net Income/(Loss) from Continuing Operations.”
42
Our Airports by Country in Which We Operate
Argentina
Our largest operations are in Argentina, where we operate a total of 37 of the 56 airports in the Argentine national airport system, including the two largest airports in the country, Ezeiza Airport and Aeroparque Airport. Ezeiza Airport is our largest airport in terms of contribution to revenue and Argentina’s second largest airport in terms of passenger traffic, while Aeroparque Airport is Argentina’s largest airport in terms of passenger traffic.
Our airports are located in 22 of the 23 Argentine provinces and in the City of Buenos Aires and currently serve major metropolitan areas in several Argentine provinces (such as Buenos Aires, Córdoba and Mendoza) and the City of Buenos Aires, tourist destinations (such as Bariloche, Mar del Plata and Iguazú), regional centers (such as Córdoba, Santa Rosa, San Luis, San Juan, La Rioja, Santiago del Estero and Catamarca) and border province cities (such as Mendoza, Iguazú, Salta and Bariloche).
Of the 37 airports we operate in Argentina, 19 have been designated as “international airports” under applicable local law, meaning that they are or may potentially be equipped to receive international flights.
The table below shows passenger traffic (in thousands) as reported by our subsidiaries:
|
|
Passenger traffic |
|
||||||
|
|
International |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
or national |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
Airport |
|
designation |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|
|
(In Thousands) |
|
||||||
“Aeroparque Jorge Newbery” |
|
International |
|
15,627.8 |
|
12,909.6 |
|
4,524.2 |
|
Aeropuerto Internacional de Ezeiza, “Ministro Pistarini” |
|
International |
|
10,826.2 |
|
7,513.4 |
|
3,196.9 |
|
Aeropuerto Internacional de Córdoba, “Ing. A. Taravella” |
|
International |
|
2,971.6 |
|
2,149.0 |
|
717.3 |
|
Aeropuerto de San Carlos de Bariloche “Teniente Luis Candelaria” |
|
International |
|
2,603.3 |
|
2,050.4 |
|
1,128.9 |
|
Aeropuerto de Mendoza, “El Plumerillo” |
|
International |
|
2,426.1 |
|
1,738.5 |
|
667.9 |
|
Aeropuerto Internacional de Salta, “Martín Miguel de Güemes” |
|
International |
|
1,484.9 |
|
1,223.9 |
|
545.3 |
|
Aeropuerto de Cataratas del Iguazú, “Mayor D. Carlos Eduardo Krause” |
|
International |
|
1,567.2 |
|
1,187.2 |
|
422.7 |
|
Aeropuerto de Neuquén, “Presidente Perón” |
|
International |
|
1,138.1 |
|
898.9 |
|
389.4 |
|
Aeropuerto de Tucumán, “Tte. Benjamin Matienzo” |
|
International |
|
855.7 |
|
718.2 |
|
318.3 |
|
Aeropuerto de Comodoro Rivadavia, “Geral. Enrique Mosconi” |
|
International |
|
579.3 |
|
465.9 |
|
188.2 |
|
Aeropuerto de San Juan, “Domingo Faustino Sarmiento” |
|
National |
|
221.5 |
|
197.0 |
|
79.0 |
|
Aeropuerto de Bahía Blanca, “Comandante Espora” |
|
National |
|
277.8 |
|
174.4 |
|
61.7 |
|
Aeropuerto de Río Gallegos, “Piloto Civil Norberto Fernández” |
|
International |
|
246.6 |
|
210.1 |
|
93.7 |
|
Aeropuerto de Jujuy, “Gobernador Horacio Guzmán” |
|
International |
|
599.0 |
|
480.8 |
|
203.8 |
|
Aeropuerto de Resistencia, “José de San Martín” |
|
International |
|
201.2 |
|
247.1 |
|
72.4 |
|
Aeropuerto Internacional de Mar del Plata, “Astor Piazzolla” |
|
International |
|
321.3 |
|
286.2 |
|
88.6 |
|
43
|
|
Passenger traffic |
||||||
|
|
International |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|
or national |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
Airport |
|
designation |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Aeropuerto de Posadas, “Libertador General D. José de San Martín” |
|
International |
|
409.9 |
|
230.9 |
|
142.8 |
Aeropuerto de Río Grande “Gobernador Ramon Trejo Noel” |
|
International |
|
161.0 |
|
129.6 |
|
67.7 |
Aeropuerto Internacional de Formosa, “El Pucu” |
|
International |
|
107.1 |
|
88.9 |
|
12.4 |
Aeropuerto de San Luis, “Brigadier Mayor César R Ojeda” |
|
National |
|
76.1 |
|
75.8 |
|
24.7 |
Aeropuerto de Santiago del Estero, “Vcom. Ángel de la Paz Aragonés” |
|
National |
|
240.3 |
|
182.2 |
|
75.4 |
Aeropuerto de La Rioja, “Capitán Vicente Almandos Almonacid” |
|
National |
|
91.2 |
|
68.9 |
|
23.8 |
Aeropuerto de San Rafael, “S.A. Santiago Germano” |
|
National |
|
46.1 |
|
54.6 |
|
24.3 |
Aeropuerto de Puerto Madryn, “El Tehuelche” |
|
National |
|
207.3 |
|
120.7 |
|
23.5 |
Aeropuerto de Catamarca, “Coronel Felipe Varela” |
|
National |
|
86.2 |
|
65.9 |
|
27.9 |
Aeropuerto de Esquel “Brigadier General Antonio Parodi” |
|
National |
|
90.4 |
|
81.7 |
|
38.8 |
Aeropuerto de Paraná, “General Urquiza” |
|
National |
|
53.1 |
|
33.9 |
|
11.4 |
Aeropuerto de Santa Rosa |
|
National |
|
52.0 |
|
35.4 |
|
19.4 |
Aeropuerto de San Fernando |
|
International |
|
10.9 |
|
47.6 |
|
34.4 |
Aeropuerto de Viedma, “Gobernador Castello” |
|
National |
|
43.3 |
|
42.4 |
|
18.3 |
Aeropuerto Termas de Río Hondo |
|
National |
|
14.7 |
|
24.7 |
|
13.8 |
Aeropuerto de Río Cuarto, “Área de Material” |
|
National |
|
27.9 |
|
31.1 |
|
13.6 |
Aeropuerto de General Pico |
|
National |
|
0.0 |
|
0.2 |
|
0.2 |
Aeropuerto de Reconquista “Teniente Daniel Jukic” |
|
National |
|
5.9 |
|
0.5 |
|
0.5 |
Aeropuerto de Malargüe, “Comodoro D Ricardo Salomón” |
|
National |
|
0.6 |
|
2.7 |
|
0.1 |
Aeropuerto de Villa Reynolds |
|
National |
|
0.0 |
|
2.4 |
|
0.9 |
Aeropuerto El Palomar |
|
International |
|
0.0 |
|
2.2 |
|
2.5 |
Main Operating and Financial Metrics
In Argentina, our main concession is the AA2000 Concession Agreement, which accounted for approximately 42.3 million passengers, or 96.8% of the total 43.7 million total passengers we served during the year ended December 31, 2023. Approximately 10.8 million of our passengers were at Ezeiza Airport and 15.6 million at Aeroparque Airport. For the year ended December 31, 2022, the airports under AA2000 Concession Agreement served, approximately 32.7 million passengers, or 96.8% of the total 33.8 million total passengers we served during the year ended December 31, 2022. Approximately 7.5 million of our passengers were at Ezeiza Airport and 12.9 million at Aeroparque Airport. For the year ended December 31, 2021, the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement served approximately 12.8 million passengers, or 96.6% of the total 13.3 million total passengers we served during the year ended December 31, 2021. Approximately 3.2 million of our passengers were at Ezeiza Airport and 4.5 million at Aeroparque Airport.
In our Argentina segment, AA2000 represented over 99.2% of our total revenues, 96.8% of our passengers and 96.4% of our air traffic movements during the year ended December 31, 2023. On a consolidated basis, AA2000 represented over 45.4% of our consolidated revenues, 52.1% of our total passengers and 52.1% of our air traffic movements during the year ended December 31, 2023.
The following table provides summary data for our operations in Argentina for the periods indicated:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31,(1) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
Revenue (in millions of U.S.$) |
|
$ |
640.6 |
|
45.8 |
% |
$ |
762.6 |
|
55.3 |
% |
$ |
362.9 |
|
51.3 |
% |
Number of passengers (in millions) |
|
|
43.7 |
|
53.8 |
% |
|
33.8 |
|
51.5 |
% |
|
13.3 |
|
37.2 |
% |
Air traffic movements (in thousands) |
|
|
458.6 |
|
54.0 |
% |
|
384.7 |
|
52.1 |
% |
|
227.3 |
|
45.7 |
% |
| (1) | We have included information for our three concessions in Argentina: AA2000, Bahía Blanca and Neuquén. We currently indirectly own 82.7% of the ordinary share capital of AA2000, 82.6% of the share capital of Bahía Blanca, and 75.5% of the share capital of Neuquén. |
Our Argentina segment had Adjusted EBITDA of U.S.$232.0 million, U.S.$277.9 million, and U.S.$65.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively, and had Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Service of U.S.$231.9 million, U.S.$277.7 million, and U.S.$65.4 million, for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
44
AA2000 Concession Agreement Key Terms
Key terms are described below, for a full description of the concession terms, see “Item 4 Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement.”
| ● | Term: The AA2000 concession agreement started in 1998 and expires in 2038, considering the new concession term after the extension granted by the Argentine Government in December 2020. |
| ● | Concession fee: AA2000 must pay 15% of total revenues excluding construction service to the Argentine State. |
| ● | AA2000’s capital expenditures under the Technical Conditions of the Extension amounts to the aggregate amount of approximately U.S.$500 million plus VAT, to be performed in two phases: (i) phase 1, approximately U.S.$336 million plus VAT to be performed preferably within 2022 and 2023, and (ii) phase 2, annual investments of approximately U.S.$41 million plus VAT between 2024 and 2027, for a total of approximately U.S.$164 million plus VAT. Investments between 2028 and 2038 will be determined based on the operational needs of the airport system and will take into consideration the economic equilibrium of the concession. |
| ● | Redemption of preferred shares: As established in the agreement for the extension, if AA2000 redeems the preferred shares before March 31, 2022, the amount redeemed can be credited towards the reduction of the phase 1 capex program. In February and March 2022, respectively, AA2000’s board of directors and the shareholders, by means of an extraordinary shareholders meeting, decided to redeem such preferred shares. See “AA2000 Ownership Structure.” |
| ● | Economic equilibrium: The concession operates under a single-till model, which sets the economic equilibrium that needs to be achieved by the end of the concession. The economic equilibrium is based on the IRR that is derived from the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses, which considers actual numbers for previous years and ORSNA’s projections for future years. The ORSNA must verify the economic equilibrium on a yearly-basis and adjust the variables in case the IRR is below the target IRR. The adjustments could be made through increasing tariffs, reducing the concession fee or reducing the capital expenditure commitments. |
AA2000 Ownership Structure
We currently indirectly own 82.7% of the share capital and voting stock of AA2000’s share capital. The Argentine Government owns 15.0% of AA2000’s share capital and voting stock.
On March 10, 2022, an extraordinary general meeting of AA2000 approved the redemption of the preferred shares, the reduction of the capital stock and the amendment of Article 2.01 of AA2000’s bylaws. The total redemption value amounted ARS17,225,719,240 (equivalent to approximately U.S.$155.2 million), which adjusted by inflation as of December 31, 2022, amounts to ARS32,302,581,376 (equivalent to approximately U.S.$182.3 million).
As of December 31, 2022, the preferred shares have been fully settled in cash by AA2000. The payments adjusted by inflation since the date of each disbursement amounts to ARS30,476,665,719 (equivalent to approximately U.S.$172.0 million).
Italy
In Italy, we operate and manage the Florence Airport and the Pisa Airport, the leading airports in the Tuscany region, one of Italy’s most touristic regions. Florence Airport is an important world-class touristic destination serving full-cost carriers, while Pisa Airport has a proven low-cost carriers business model.
Main Operating and Financial Metrics
Of the approximately 8.2 million total passengers in the TA airports during the year ended December 31, 2023, approximately 5.1 million were in Pisa Airport and 3.1 million were in the Florence Airport. Of the approximately 6.7 million total passengers in the TA airports during the year ended December 31, 2022, approximately 4.5 million were in Pisa Airport and 2.2 million were in the Florence Airport. Of the approximately 2.8 million total passengers in the TA airports during the year ended December 31, 2021, approximately 2.0 million were in Pisa Airport and 0.8 million were in the Florence Airport.
45
The following table provides summary data for our operations in Italy for the periods indicated:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
Revenue (in millions of U.S.$) |
|
$ |
133.4 |
|
9.6 |
% |
$ |
117.2 |
|
8.5 |
% |
$ |
70.5 |
|
10.0 |
% |
Number of passengers (in millions) |
|
|
8.2 |
|
10.1 |
% |
|
6.7 |
|
10.2 |
% |
|
2.8 |
|
7.9 |
% |
Air traffic movements (in thousands) |
|
|
77.9 |
|
9.2 |
% |
|
68.9 |
|
9.3 |
% |
|
39.6 |
|
8.0 |
% |
Our Italy segment had Adjusted Segment EBITDA of U.S.$39.1, U.S.$21.2 million, and U.S.$0.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively, and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services of U.S.$32.9, U.S.$19.5 million, and U.S.$(1.8) million, for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Italian Concession Agreements Key Terms
Key terms are described below, for a full description of the concession terms, see “Item 4 Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Italy—The Pisa Concession Agreement,” and “Item 4 Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Italy—The Florence Concession Agreement.”
Term: The Florence airport concession started in 2003 and is expected to expire in 2045, while the Pisa concession agreement started in 2006 and is expected to expire in 2048. Both concession terms include the two-year extension granted by the Italian Government in July 2020, following a law in relation with the COVID - 19 pandemic emergency measures.
Concession fee: TA is required to pay annual fees, based on a workload unit criterion, where each unit corresponds to one passenger or 100 kg of goods or post. The canon is to be paid in two separate semi-annual installments, due in July and January of each year. The value of the minimum canon is adjusted on an annual basis according to inflation. For the year ended December 31, 2023, TA paid an annual canon of €3.9 million under the Pisa concession and €1.8 million under the Florence concession. For the year ended December 31, 2022, TA paid an annual canon of €1.4 million under the Pisa concession and €0.5 million under the Florence concession. For the year ended December 31, 2021, TA paid an annual canon of €1.0 million under the Pisa concession and €0.6 million under the Florence concession.
Operating agreement: In 2015, ENAC and TA entered into an operating agreement (contratto di programma) which states TA’s obligations regarding, among others, the following items of the Pisa and Florence airports: airport traffic level forecasts, new construction and extraordinary maintenance works and TA’s performance of the obligations under the four-year intervention plan, as well as its quality and environmental protection plan.
Master Plan: Florence Airport
Currently, this airport cannot service long-haul flights given the short length of its runway. Additionally, since the runway was built in the direction of the prevailing wind and mainly operates in one-way direction, Florence Airport has a relatively high number of flight cancellations due to adverse weather conditions that are rerouted to Pisa Airport (when possible, to avoid passenger loss). Passengers can also be rerouted to Bologna Airport, if needed. Plans are underway (project review process) to optimize the infrastructural layout of the airport, including the construction of a new runaway and a new passenger terminal. The new infrastructure should allow Florence Airport to carry out a sustainable development and reach its full potential and complement Pisa Airport’s offerings. In 2014, the 2014-2029 Florence airport master plan was defined, and in 2015, it received the technical approval by ENAC. In March 2015, ENAC started the environmental procedure at the Ministry of Environment and on December 28, 2017, the same Ministry approved the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) procedure. In April 2018, ENAC started the permit procedure under the master plan. The master plan was also approved by the Infrastructure Ministry in April 2019.
However, on May 27, 2019, upon request of the Environmental Association (Associazione VAS Vita Ambiente) and other local municipalities, such approval was repealed through judgment No. 793. On July 25, 2019, TA, jointly with the Ministry of Environment, ENAC and other national, regional and local authorities, appealed such judgement. On February 14, 2020, TA was notified of the rejection of the appeal by the Council of State. Therefore, ENAC (and TA) was forced to re-start the whole administrative process for the approval of the master plan.
46
During 2022, a project review of the master plan was performed and the new 2035 TA master plan was defined. In October 2022, TA initiated a public debate process as required under the new applicable law (D. Lgs 50/2016, D.P.C.M. 76/2018). This process was completed in February 2023, and in April 2023, TA submitted to ENAC the new 2035 Florence airport master plan. It received the technical approval by ENAC on May 2023, and at the beginning of June 2023 ENAC required the Ministry of Environment to start the new EIA-ESA procedure (a new integrated environmental procedure introduced by law in 2020). The scoping-phase of the EIA-ESA procedure was concluded in December 2023. The next integrated assessment-phase is expected to be carried out in 2024 and completion of such process is expected to occur by the end of the Summer 2024.
Once finished the above environmental procedure at the Ministry of the Environment, ENAC will ask the Ministry of Infrastructure to start the authorization process for the assessment of urban planning compliance. The procedure will be carried out in autumn 2024 and will conclude by the end of November 2024.
Master Plan: Pisa Airport
In connection with the Pisa Airport, on October 24, 2017, ENAC approved and signed our 2014-2028 master plan. Further investments in capital expenditures will allow the airport to reach between 6.5 and 7.0 million passengers capacity in the short term. During 2022, we initiated the preliminary works, and during 2023, the construction design for expansion and renovation of the passenger terminal was concluded. The works will start in the first quarter of 2024.
Economic equilibrium: our Italian airports operate under a dual-till model, that establishes a guaranteed return for the aeronautical activities, based on an established WACC. Therefore, aeronautical tariffs are adjusted in order to cover for aeronautical operating expenses as well as the allowed remuneration on capital expenditures.
TA Ownership Structure
TA is the result of the merger of Società Aeroporto Toscano (“SAT”), Galileo Galilei S.p.A. and Aeroporto di Firenze S.p.A. (“ADF”) on June 1, 2015, and is headquartered in Florence. As a result of the merger, CA Italy had a controlling stake of 51.1% of TA. In 2018, by means of two separate transactions, we acquired an additional 4.50% and 6.58%, respectively, in TA, increasing CA Italy’s ownership to 62.28% of its issued and outstanding common stock. Later in 2018, we sold and transferred 25% of CA Italy’s issued and outstanding common stock to Investment Corporation of Dubai, reducing our ownership in CA Italy to 75% and, consequently, our indirect ownership in TA to 46.71%.
TA is listed on Euronext Milan of Borsa Italiana S.p.A. under the ticker TYA. The year-end price for 2023 was €11.5 per share, representing a market cap of €214.0 million. Corporate capital amounted to €30.7 million, which is comprised of 18,611,966 ordinary shares with no nominal value.
Brazil
In Brazil, we operate the Brasilia Airport which is located 12 kilometers (8.5 miles) from downtown Brasilia, Brazil’s capital city. It is the only airport in South America capable of operating two runways simultaneously, which provides the largest runway capacity in Brazil.
The Brasilia Airport is Brazil’s third largest airport in terms of passenger traffic. Because of its geographic location in the central region of the country and its location in the federal capital of Brazil, the Brasilia Airport is one of the only airports with direct and daily flights to all 26 Brazilian state capitals. The Brasilia Airport also offers some international routes.
We also operated the Natal Airport, but in November 2020, we executed an irrevocable amendment for the termination of the Natal Concession Agreement. Pursuant to the terms of the amendment agreement, upon the execution of a new concession agreement with a new operator, an indemnification payment should be made to ICASGA. On January 18, 2023, the “Tribunal de Contas da União” (TCU), a government-related entity, gave clearance for the government to carry out the tender process for the Natal airport. On February 8, 2023, the tender documents were published and the auction date was set for May 19, 2023. ANAC conducted the new bidding process for the airport which was awarded to Zurich Airports.
On December 27, 2023, the Brazilian National Congress enacted a bill enabling a budgetary amendment and approving the payment by the Federal Government of the portion of the indemnification owed to ICASGA and subject to direct payment by the Federal Government. The other portion of the indemnification, also owed by the Federal Government, was to be paid by Zurich Airports.
47
After that bill was passed, an amicable process for the termination of the concession to ICASGA was effectively established, and ICASGA lost the right of exploitation of the airport.
On December 28, 2023, ICASGA and ANAC entered into an agreement whereby ICASGA was absorbed by ACI do Brasil S.A.
For bureaucratic and operational reasons, the regulatory legal framework and the concession contract required a reduced operational transition period, during ACI do Brasil S.A. and Zurich Airports shared the operation of the Natal Airport, to ensure operational safety and quality of service to passengers during the transition. During that period, ACI do Brasil S.A. acted as a transition agent between the granting authority, who granted the right of exploitation to the new concessionaire, and Zurich Airports, which already held the right of exploitation through a valid and effective concession contract. In consequence, as from the date of this report, we no longer operate the Natal Airport.
Main Operating and Financial Metrics
For the year ended December 31, 2023, of the approximately 17.1 million total passengers in Brazil, approximately 14.9 million were in the Brasilia Airport and 2.2 million were in the Natal Airport. For the year ended December 31, 2022, of the approximately 15.7 million total passengers in Brazil, approximately 13.4 million were in the Brasilia Airport and 2.3 million were in the Natal Airport. For the year ended December 31, 2021, of the approximately 12.3 million total passengers in Brazil, approximately 10.5 million were in the Brasilia Airport and 1.8 million were in the Natal Airport.
The following table provides summary data for our operations in Brazil for the periods indicated:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
Revenue (in millions of U.S.$) |
|
$ |
110.6 |
|
7.9 |
% |
$ |
89.3 |
|
6.5 |
% |
$ |
58.4 |
|
8.3 |
% |
Number of passengers (in millions) |
|
|
17.1 |
|
21.1 |
% |
|
15.7 |
|
24.0 |
% |
|
12.3 |
|
34.5 |
% |
Air traffic movements (in thousands) |
|
|
158.4 |
|
18.6 |
% |
|
144.6 |
|
19.6 |
% |
|
117.9 |
|
23.7 |
% |
Our Brazil segment had Adjusted EBITDA of U.S.$218.3 million, U.S.$32.1 million, and U.S.$19.0 million, for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively, and had Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services of U.S.$218.3 million, U.S.$32.1 million, and U.S.$19.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Inframerica, concessionaire of Natal airport, has filed a request for concession termination, as set forth in law 13.448/2017. The request was filed in March 2020, before World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a world pandemic.
Several factors give origin to the decision to terminate the concession granted by the government. First factor relates to passenger traffic, as such has been negatively impacted. Compared to valuation studies (EVTEA) from the time where concession was originally granted, the results obtained are not close to what was projected, and it does not even result in half of the value expectancies. Secondly, aeronautical tariffs have decreased 35% compared with other airports that have been delivered for operation to private companies. Lastly, tower control tariff is 301% lower than other tariff from tower controls in general.
During the period that the government has to analyze the returning request and until they proceed with a new concessionaire, Inframerica will keep the airport operating with the same quality and preserving its safety, honoring the commercial deals, and keeping its employees’ salaries and benefits. The return request is related only to Natal Airport.
On May 26, 2020, the ANAC confirmed the technical and legal feasibility of the request regarding the re-bidding process initiated by ICASGA. On June 3, 2020, the process was approved by the Ministério da Infraestrutura, and on June 10, 2020, the Conselho do Programa de Parcerias de Investimentos of the Ministério da Economia expressed a favorable opinion and submitted the request for proposal for re-bidding to the President of Brazil.
48
On August 24, 2020, the Natal Airport was qualified to go through the re-bidding process. On November 20, 2020, ICASGA and ANAC signed a concession agreement amendment setting forth the rules and proceedings for the re-bidding effective until August 24, 2022 or until the new operator wins the re-bidding, whichever occurs first. On June 2, 2022, the Investment Partnership Program Committee gave a favorable opinion to extend the project’s re-bidding qualification until August 24, 2023. In case the re-bidding remains vacant on or after August 24, 2023, the Brazilian Government could extend the term. In case this term is not extended, the concessionaire will be responsible for continuing with the operation of the airport under the same conditions in place before the amendment.
Brazilian Concession Agreements Key Terms
Key terms are described below, for a full description of the concession terms, see “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Brazil—Brasilia Concession Agreement,” and “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Brazil—Natal Concession Agreement”
Term: The Natal Airport concession was awarded in August 2011 to ICASGA and would have expired in 2040. On March 5, 2020, however, the Company made public that ICASGA filed a non-binding request to the Brazilian Federal Government to commence the termination process of the Natal Airport, and on November 19, 2020, CAAP announced the execution of the amendment. On December 28, 2023, ICASGA and ANAC entered into an agreement whereby ICASGA was absorbed by ACI do Brasil S.A. After the completion of successful bidding process, the operation of the Natal Airport was transferred to Zurich Airports (the new concessionaire). The Brasilia Concession Agreement started in 2012 and is expected to expire in 2037, which may be extended for an additional 5 years, if necessary, to reestablish economic equilibrium.
Concession fees: The Brasilia airport is required to pay the ANAC an annual fixed payment. The amount is R$90.0 million for 2020, R$180.0 million for the years 2021 through 2031 (for 2021, the company is still having a judicial discussion to reduce 50% of the amount, reprograming the futures payments from 2030 to 2037), R$301.4 million for 2032 and R$270.1 million for the years 2033 through 2037, as well as a variable payment, adjusted by the Consumer Price Inflation Index (Índice Nacional de Preços ao Consumidor Amplo; or “IPCA”). Brasilia Airport is also subject to an annual variable payment, equal to: (i) 2% of the perceived annual gross revenues, for annual gross revenue of up to R$422.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, R$448.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, R$469.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, and R$491.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023; plus (ii) 4.5% of the annual gross revenues, including the gross revenue of its wholly owned subsidiaries, for annual gross revenues above R$422.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, R$448.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, R$469.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, and R$491.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, if any. As of December 31, 2021, a 50% of the concession fee to be paid in 2021 by ICAB was pending as a re-scheduling of such fee was requested. Regarding the concession fee to be paid in 2022, a partial payment of R$81.6 million (equivalent to U.S.$15 million) was made through the application of re-equilibrium credits. To pay the remaining amount, ICAB presented on November 21, 2022, an offer of court payment orders to the Ministry of Infrastructure, which is still under analysis. In December 2022, the Ministry issued an official letter confirming that, during the time it takes to issue a final opinion, ICAB will be considered to be in compliance with its obligations. Regarding the concession fee to be paid in 2023, a partial payment of R$104.5 million (equivalent to U.S.$21.6 million) was made through the application of re-equilibrium credits. The remaining amount of R$248.2 million (equivalent to U.S.$51.3 million) was paid in cash.
Tariff Adjustment: The Brazilian concessions operate under an inflation-based model. Tariffs shall be adjusted annually by IPCA, upon the application of a specific formula that considers the IPCA and the effects of the Q and X Factors, as defined in the Brazilian Concession Agreements. The Brazilian ANAC adopted Factor X as a mechanism to measure positive and negative productivity and efficiency variations.
Extraordinary review: an extraordinary review is intended to restore the economic and financial equilibrium of the Brazilian Concession Agreements when costs, revenues or gains of ICASGA or ICAB are unbalanced as a result of events with respect to which the Brazilian ANAC is required to bear the risk. We may request an extraordinary review of the Brazilian Concession Agreement to re-establish the economic and financial equilibrium of the concession if one or more events occurs (i.e. changes in any law or rule related to (a) the services that the concessionaire must provide or (b) any security procedure; operational restrictions resulting from any act (or omission thereof) by any governmental body; mandatory changes in tariffs or granting of tariff benefits; changes in the tax regime that causes additional costs for the concessionaire (excluding income tax); and a Force Majeure event). The review will be based, among others, on the marginal cash flow related to every event generating economic and financial disequilibrium. We requested and were granted an economic re-equilibrium as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic impact in 2020, considered a force majeure event. See “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—COVID-19 Virus Impact.”
49
Brazilian airport Ownership Structure
The Brasilia Airport Concession is owned by ICAB, a subsidiary of Inframerica. As of the date of this annual report, we own 99.98% of the equity interests of Inframerica, which holds 51.0% of the equity interests of ICAB. Infraero, a state-owned company affiliated with the Civil Aviation Secretariat of Brazil, is the owner of the remaining 49.0% interest in ICAB.
Inframerica was originally owned by Infravix and Corporación América S.A. (“CASA”). In 2015, we and the Majority Shareholder (A.C.I. Airports S.à r.l.) acquired Infravix’s shareholding in Inframerica. In 2015, CAAP acquired CASA’s stake in Inframerica.
We operated the Natal Airport through our 99.98% ownership of ICASGA. ICASGA was originally owned by Infravix (50.0%) and CASA (50.0%). In 2015, we acquired from Infravix a 49.95% interest in ICASGA and the Majority Shareholder acquired the remaining 0.05% interest in ICASGA. Also as of the date of this annual report, ICASGA has been fully absorbed by ACI do Brasil S.A., and the concession for the Natal Airport has been fully transferred to Zurich Airports (see “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Our Airports by Country in Which We Operate—Brazil”).
Uruguay
Our operations in Uruguay consist of the operation and maintenance of the two main Uruguayan airports that receive commercial flights, the Carrasco Airport and the Punta del Este Airport, and the Uruguay New Airports which were incorporated into the scope of the Carrasco Concession Agreement pursuant to the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement. The Carrasco Airport, located near Montevideo, is Uruguay’s largest airport in terms of passenger traffic and serves as the country’s primary gateway for international travel. Carrasco Airport has the capacity to handle up to 4.5 million passengers annually. It currently serves regional centers, tourist destinations and certain major cities throughout Europe and the Americas. The Punta del Este Airport is not material to our business. Upon the execution of the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement, Puerta del Sur also operates, develops and maintains the Uruguay New Airports.
We also own TCU S.A. (“TCU”) through which we operate the cargo terminal at the Carrasco Airport. We own 100% of Puerta del Sur, the holder of the concession agreement through the execution of a comprehensive management agreement with the Uruguayan Ministry of Defense (the “Carrasco Concession Agreement”) to operate the Carrasco Airport and, following the execution of the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement, the Uruguay New Airports. Additionally, we own 100% of CAISA, the holder of the concession agreement (“Punta del Este Concession Agreement,” and together with the Carrasco Concession Agreement, the “Uruguayan Concession Agreements”) with the Uruguayan Ministry of Defense to operate the Punta del Este Airport.
In 2003, our wholly-owned subsidiary Cerealsur S.A. acquired 100% of the outstanding shares of Puerta del Sur, the holder of the Carrasco Concession Agreement. The original concession agreement was for a period of 20 years ending in November 2023, which term was extended for an additional period of 10 years, until 2033. In November 2021 we executed an amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement extending the concession term for additional 20 years, until 2053 and incorporating the Uruguay New Airports to the scope of the concession.
Main Operating and Financial Metrics
For the year ended December 31, 2023, of the approximately 2.0 million total passengers in Uruguay, approximately 1.8 million were in the Carrasco Airport and 134 thousand were in the Punta del Este Airport. For the years ended December 31, 2022, of the approximately 1.4 million total passengers in Uruguay, approximately 1.3 million were in the Carrasco Airport and 119.5 thousand were in the Punta del Este Airport. For the year ended December 31, 2021, of the approximately 0.5 million total passengers in Uruguay, approximately 0.5 million were in the Carrasco Airport and 25.4 thousand were in the Punta del Este Airport.
50
The following table provides summary data for our operations in Uruguay for the periods indicated:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2023(1) |
|
2022(2) |
|
2021(3) |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
Revenue (in millions of U.S.$) |
|
$ |
157.0 |
|
11.2 |
% |
$ |
105.3 |
|
7.6 |
% |
$ |
51.3 |
|
7.3 |
% |
Number of passengers (in millions) |
|
|
2.0 |
|
2.4 |
% |
|
1.4 |
|
2.2 |
% |
|
0.5 |
|
1.4 |
% |
Air traffic movements (in thousands) |
|
|
32.0 |
|
3.8 |
% |
|
27.9 |
|
3.8 |
% |
|
17.8 |
|
3.6 |
% |
| (1) | Includes revenues for TCU and reflects intersegment adjustments of U.S.$8.2 million. |
| (2) | Includes revenues for TCU and reflects intersegment adjustments of U.S.$7.5 million. |
| (3) | Includes revenues for TCU and reflects intersegment adjustments of U.S.$6.8 million. |
Our Uruguay segment had Adjusted EBITDA of U.S.$50.0 million, U.S.$35.3 million, and U.S.$13.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively, and had Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services of U.S.$50.0 million, U.S.$35.3 million, and U.S.$13.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Uruguayan Concession Agreements Key Terms
Key terms are described below, for a full description of the concession terms, see “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Uruguay—The Carrasco Concession Agreement,” and “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Uruguay—The Punta del Este Concession Agreement”.
Term: The initial term of the Carrasco Concession Agreement was for 20 years commencing in November 2003, which in August 2014 was extended for an additional 10-year period, until 2033, and further extended in November 2021, upon execution of the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement, for an additional 20-year period until 2053. The Punta del Este Concession Agreement was executed in 1993 and was extended in 2019 for an additional 14-year period, until 2033.
Concession fee: Puerta del Sur is required to pay annual concession fees, consisting of (a) basic fees, equal to the higher of (i) a fixed annual amount of U.S.$4.8 million and (ii) U.S.$4.46 per total annual passengers (some limits and exceptions apply), plus applicable cargo fees, and (b) additional fees, as long as the number of passengers exceed 1.5 million passengers per year, which is are calculated by multiplying the number of passengers by a fix coefficient, depending on the volume of passengers. The concession fee is to be made in two separate semi-annual installments, due July and December each year.
Tariff adjustment: The Uruguayan concessions operate under an inflation-based model. The tariffs charged to the airlines per aircraft movements and passenger use tariffs are adjusted pursuant to the formula described in the Carrasco Concession Agreement, considering a combination between domestic and US inflation rates.
Puerta del Sur and CAISA Ownership Structure
We own 100% of Puerta del Sur, the holder of the Carrasco Concession Agreement, which incorporated the Uruguay New Airports, and 100% of CAISA, the holder of Punta del Este Concession Agreement.
Ecuador
Our operations in Ecuador consist of the operation and maintenance of the Guayaquil Airport, in the City of Guayaquil, the second largest airport in the country, and the Galapagos Airport, located in Baltra Island, Galapagos Archipelago.
The Galapagos Airport has been recognized as the first ecological and sustainable airport in the world by the U.S. Green Building Council. The airport terminal was entirely planned, designed and built taking into account its relationship with the surrounding environment to reduce its environmental impact. The terminal also received Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certification, GOLD level.
Additionally, on June 23, 2015, the Galapagos Airport received the Carbon Footprint Reduction accreditation from the Airport Carbon Accreditation program. The program, implemented by Airports Council International Europe, is aimed at evaluating and recognizing airports that make outstanding efforts to reduce and compensate for greenhouse gas emissions. The Galapagos Airport is the first airport in South America and in Latin America and the Caribbean to receive a carbon footprint reduction accreditation. Currently, we are in level 3+, “Compensation” and we are working towards moving to the next level, “Reduction.”
51
Main Operating and Financial Metrics
The following table provides summary data for our operations in Ecuador for the periods indicated:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31,(1) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
Revenue (in millions of U.S.$) |
|
$ |
105.2 |
|
7.5 |
% |
$ |
96.2 |
|
7.0 |
% |
$ |
65.2 |
|
9.2 |
% |
Number of passengers (in millions) |
|
|
4.8 |
|
6.0 |
% |
|
4.2 |
|
6.4 |
% |
|
2.5 |
|
7.0 |
% |
Air traffic movements (in thousands) |
|
|
78.5 |
|
9.2 |
% |
|
77.0 |
|
10.4 |
% |
|
55.9 |
|
11.2 |
% |
| (1) | We have included 100% of operational information of ECOGAL, with respect to number of passengers and air traffic movements, for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021. The revenue information for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 includes only the consolidated revenue of TAGSA, our other concession in the Ecuador segment. |
For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, our Ecuador segment had Adjusted EBITDA of U.S.$32.0 million, U.S.$29.0 million, and U.S.$16.1 million, respectively, and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services of U.S.$32.0 million, U.S.$29.0 million, and U.S.$16.1 million, respectively.
Ecuadorian Concession Agreements Key Terms
Key terms are described below, for a full description of the concession terms, see “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Ecuador—The Guayaquil Concession Agreement,” and “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Uruguay—The Galápagos Concession Agreement.”
Term: The Guayaquil Concession Agreement was executed in 2004. TAGSA and AAG signed the Eighth Amendment of the Concession Agreement on July 20, 2021, through which the economic-financial equilibrium of the concession was reestablished, due to the force majeure and/or fortuitous event caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and its effects through time. Pursuant to this amendment, TAGSA was compensated for the losses suffered from March 17, 2020, through December 31, 2020, by a two-year extension, ending July 31, 2031. The Eighth Amendment of the Concession Agreement sets forth a compensation procedure for the following years starting in 2021.
Concession fee: TAGSA is required to pay an annual concession amount equal to 50.25% of the aggregate gross revenue from tariffs and charges, and certain other commercial revenues (e.g., fuel, parking spaces and use of convention center) derived from the operation of the Guayaquil Airport, for 2022, and will be 50.25% until the economic-financial equilibrium is fully reestablished.
Tariff adjustment: The Ecuadorian concessions operate under an inflation-based model. The tariffs charged to the airlines per aircraft movements and passenger use tariffs are adjusted pursuant to the formula described in the Guayaquil Concession Agreement, considering a combination between domestic and US inflation rates.
Capital expenditure commitments: as a result of the concession extension, the Guayaquil Concession Agreement includes an obligation to execute new works and investments that will culminate in the year 2024, for a total reference amount of U.S.$32.2 million, of which U.S.$26.3 million were already invested as of December 31, 2023.
The Galápagos Concession Agreement expires in 2026. ECOGAL is still in the negotiation process with the Dirección General de Aviación Civil (“DGAC”) to obtain the economic-financial equilibrium of the concession agreement.
TAGSA and ECOGAL Ownership Structure
We own 50.0% of TAGSA, which operates and maintains the Guayaquil Airport, and 99.9% of ECOGAL, which operates and maintains the Galapagos Airport.
Armenia
In Armenia, we operate the only two airports for scheduled commercial flights in Armenia: the Zvartnots Airport, located in the capital city of the country, and the Shirak Airport.
52
Main Operating and Financial Metrics
For the year ended December 31, 2023, of the approximately 5.4 million total passengers in Armenia, approximately 5.3 million were in the Zvartnots Airport and 0.1 million were in the Shirak Airport. For the year ended December 31, 2022, of the approximately 3.7 million total passengers in Armenia, approximately 3.6 million were in the Zvartnots Airport and 0.05 million were in the Shirak Airport. For the year ended December 31, 2021, of the approximately 2.4 million total passengers in Armenia, approximately 2.3 million were in the Zvartnots Airport and 0.1 million were in the Shirak Airport.
The following table provides summary data for our operations in Armenia for the periods indicated:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
Revenue (in millions of U.S.$) |
|
$ |
252.5 |
|
18.0 |
% |
$ |
207.5 |
|
15.1 |
% |
$ |
98.4 |
|
13.9 |
% |
Number of passengers (in millions) |
|
|
5.4 |
|
6.7 |
% |
|
3.7 |
|
5.6 |
% |
|
2.4 |
|
6.7 |
% |
Air traffic movements (in thousands) |
|
|
44.1 |
|
5.2 |
% |
|
35.2 |
|
4.8 |
% |
|
21.3 |
|
4.3 |
% |
For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, our Armenia segment had Adjusted EBITDA of U.S.$99.7 million, U.S.$68.9 million, and U.S.$44.3 million, respectively, and Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services of U.S.$99.6 million, U.S.$68.8 million, and U.S.$44.1 million, respectively.
Armenian Concession Agreement Key Terms
Key terms are described below, for a full description of the concession terms, see “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Armenia—Armenian Concession Agreement.”
Term: The Armenian Concession Agreement was executed in 2002 and expires in 2032, with the option at our sole discretion, to indefinitely extend the term for additional periods of five years.
Concession fee: no concession fee is required to pay under the Armenian Concession Agreement.
Master Plan: The Master Plan contains the works to be executed for each five-year period and must be updated every five years and extended to cover the 30-year term of the concession.
Internal Rate of Return: The concession operates under a single-till model, which sets the economic equilibrium that needs to be achieved by the end of the concession. Under the concession agreement, we have the right to receive an annual internal rate of return of 20%. The internal rate of return and is calculated as the annual net after tax internal rate of return on the actual capital investments valued in US dollars, including equity, equity equivalents, subordinate loans and/or convertible loans and any other capital contribution.
AIA Ownership Structure
We own 100% of AIA which owns the concession to operate and maintain the Zvartnots Airport and the Shirak Airport.
Peru
Our operations in Peru consisted of the operation, use and maintenance of five airports in southern Peru, including the Arequipa Airport, which is the third largest airport in Peru in terms of passenger traffic, through our 50.0% participation in AAP. AAP was incorporated by public deed dated November 22, 2010, for the sole purpose of acting as the concessionaire of the AAP Concession Agreement. We accounted for the results of operations of AAP using the equity method and therefore, such results are not included in the total revenue for our operations.
53
On December 16, 2021 we transferred our 50% ownership interest in AAP to Andino Investment Holding S.A. Following this transaction, Andino Investment Holding S.A. now owns 100% of AAP. Therefore, as of the date of this annual report, we no longer operate the airports under the AAP Concession Agreement. Our decision to no longer operate in Peru is part of a long-term strategic plan that seeks to concentrate efforts and resources towards core and relevant assets in jurisdictions with long-term meaningful growth opportunities.
| ● | For the transfer of the interest in AAP, the Company received U.S.$5 thousand, while it committed to make a payment to Andino Investment Holding S.A. for assumed liabilities and future capital expenditures commitments of AAP amounting to U.S.$17.2 million, which, as of the date of this annual report, have already been paid in full. |
| ● | The Company issued the following guarantees: three standby letters of credit with Morgan Stanley for a total amount of U.S.$2.25 million, U.S.$0.5 million and U.S.$0.1 million, respectively, to guarantee concession contract fulfilment, works to be performed and equipment and an irrevocable first demand guarantee letter in the amount of U.S.$5.25 million in favor of VolcomCapital Deuda Perú II Fondo de Inversión (administered and managed by VolcomCapital Administradora General de Fondos S.A.) (“Volcom”) related to a loan entered by AAP. |
| ● | In December 2022, after the Company paid to Andino the agreed payment for assumed obligations and future capital expenditures commitments, all of the abovementioned guarantees were lifted or replaced. |
Main Customers
Main Aeronautical Customers
For the year ended December 31, 2023 our main aeronautical customers were LATAM Group, Aerolíneas Argentinas Group, Copa, Gol Transportes Aereos, Avianca Group, Iberia Lineas Aereas Espana, American Airlines, FB Líneas Aéreas S.A., and Lufthansa Group. For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, the aeronautical revenue received from LATAM Group totaled U.S.$84.7 million, U.S.$66.0 million, and U.S.$26.6 million, respectively representing 13.1%, 10.8% and, 10.1% respectively, of our total consolidated aeronautical revenue. For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, aeronautical revenue received from Aerolíneas Argentinas Group totaled U.S.$71.4 million, U.S.$96.6 million, and U.S.$22.9 million, respectively, representing 11.1%, 15.8%, and 8.7%, respectively, of our total consolidated aeronautical revenue.
The following table sets forth our main aeronautical customers for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, based on the total amount of aeronautical revenue.
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
(in millions |
|
Aeronautical |
|
(in millions |
|
Aeronautical |
|
(in millions |
|
Aeronautical |
|
|||
Main Aeronautical Customers |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
|||
LATAM Group |
|
|
84.7 |
|
13.1 |
% |
|
66.0 |
|
10.8 |
% |
|
26.6 |
|
10.1 |
% |
Aerolíneas Argentinas Group(1) |
|
|
71.4 |
|
11.1 |
% |
|
96.6 |
|
15.8 |
% |
|
22.9 |
|
8.7 |
% |
Copa |
|
|
40.2 |
|
6.2 |
% |
|
44.1 |
|
7.2 |
% |
|
19.7 |
|
7.5 |
% |
Gol Transportes Aéreos |
|
|
37.1 |
|
5.8 |
% |
|
31.8 |
|
5.2 |
% |
|
8.9 |
|
3.4 |
% |
Avianca Group |
|
|
27.6 |
|
4.3 |
% |
|
24.1 |
|
4.0 |
% |
|
8.6 |
|
3.3 |
% |
Iberia Lineas Aereas España |
|
|
23.8 |
|
3.7 |
% |
|
24.4 |
|
4.0 |
% |
|
11.2 |
|
4.3 |
% |
American Airlines |
|
|
23.5 |
|
3.6 |
% |
|
32.3 |
|
5.3 |
% |
|
22.0 |
|
8.4 |
% |
FB Líneas Aereas S.A |
|
|
17.8 |
|
2.8 |
% |
|
16.8 |
|
2.8 |
% |
|
1.7 |
|
0.6 |
% |
Lufthansa Group |
|
|
14.0 |
|
2.2 |
% |
|
19.1 |
|
3.1 |
% |
|
8.6 |
|
3.3 |
% |
Others |
|
|
304.4 |
|
47.2 |
% |
|
254.7 |
|
41.8 |
% |
|
132.7 |
|
50.5 |
% |
Total |
|
|
644.5 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
609.8 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
262.8 |
|
100.0 |
% |
| (1) | See “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business and Industry—The loss of one or more of our aeronautical customers or the interruption of their operations could result in a loss of a significant amount of our passenger traffic.” |
54
Main Commercial Customers
For the year ended December 31, 2023, our main commercial customers were Dufry and Flyone Armenia. In the year ended December 31, 2023, we invoiced U.S.$82.2 million to Dufry and U.S.$26.5 million to Flyone Armenia, representing 13.6% and 4.4%, respectively, of our total consolidated commercial revenue.
For the year ended December 31, 2022, our main commercial customers were Dufry and Flyone Armenia. In the year ended December 31, 2022, we invoiced U.S.$68.7 million to Dufry and U.S.$13.1 million to Flyone Armenia, representing 11.2% and 2.1%, respectively, of our total consolidated commercial revenue.
For the year ended December 31, 2021, our main commercial customers were Dufry and Aerolíneas Argentinas Group. In the year ended December 31, 2021, we invoiced U.S.$27.3 million to Dufry and U.S.$12.3 million to Aerolíneas Argentinas Group, representing 7.5% and 3.4%, respectively, of our total consolidated commercial revenue.
In 2011, we sold our duty-free operations in Argentina, Uruguay, Ecuador and Armenia to Dufry Group. Dufry Group, therefore, became the exclusive duty-free operator at these airports. In Brazil and Italy, countries in which we acquired the concessions agreements after 2011, we have separate duty-free concession agreements with Dufry Group. In December 2023, CAAP became holder of 49% of the equity shares of Navinten S.A., which operates the duty free shops in the airports of Uruguay; as of that date, Navinten S.A. is an associated company.
Our duty-free concession agreements are primarily long-term contracts and include a variable payment, as well as a required minimum fee. Variable payments are calculated as a percent of revenues. New contracts may include an upfront payment once executed. We also charge a separate fee for use of retail and warehouse space. The terms of each agreement with Dufry vary, depending on the jurisdiction and size of the airport where it operates.
The following table sets forth our main commercial services providers for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, based on the percentage of total amounts invoiced by us (net from value added tax) to all commercial services providers during the periods indicated:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
(in millions |
|
Commercial |
|
(in millions |
|
Commercial |
|
(in millions |
|
Commercial |
|
|||
Main Commercial Customers |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
|||
Dufry |
|
|
82.2 |
|
13.6 |
% |
|
68.7 |
|
11.2 |
% |
|
27.3 |
|
7.5 |
% |
Flyone Armenia |
|
|
26.5 |
|
4.4 |
% |
|
13.1 |
|
2.1 |
% |
|
0.1 |
|
0.0 |
% |
Aeroflot Group |
|
|
11.8 |
|
2.0 |
% |
|
9.0 |
|
1.5 |
% |
|
5.0 |
|
1.4 |
% |
Aerolíneas Argentinas Group |
|
|
10.2 |
|
1.7 |
% |
|
11.2 |
|
1.8 |
% |
|
12.3 |
|
3.4 |
% |
Priority Pass |
|
|
9.5 |
|
1.6 |
% |
|
7.1 |
|
1.2 |
% |
|
3.0 |
|
0.8 |
% |
Red Wings |
|
|
7.6 |
|
1.3 |
% |
|
12.5 |
|
2.0 |
% |
|
0.5 |
|
0.1 |
% |
Wizz Air |
|
|
7.6 |
|
1.3 |
% |
|
2.5 |
|
0.4 |
% |
|
0.2 |
|
0.1 |
% |
Armenian Airlines LLC |
|
|
5.2 |
|
0.9 |
% |
|
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
% |
|
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
% |
Armenian National Airlines CJSC |
|
|
5.1 |
|
0.8 |
% |
|
1.3 |
|
0.2 |
% |
|
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
% |
Others |
|
|
437.8 |
|
72.5 |
% |
|
487.1 |
|
79.6 |
% |
|
313.7 |
|
86.6 |
% |
Total |
|
|
603.7 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
612.5 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
362.1 |
|
100.0 |
% |
Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG)
CAAP qualifies as a “large undertaking” on a stand-alone basis and as a “parent undertaking” of a large economic group as defined in the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (“CSRD”) adopted by the European Commission. Thus, we are subject to the reporting obligations set forth under the CSRD. The legal reporting obligations under the CSRD, include, among others:
| ● | provide information on the Company and its subsidiaries’ value chain impact on sustainability matters as well as how sustainability matters affect the Company and its subsidiaries’ value chain, development, performance and position, according to the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (“ESRS”); and |
55
| ● | obtain from the Company’s statutory auditor an opinion, based on a limited assurance engagement, on the compliance of the Company’s consolidated sustainability reporting pursuant to the requirements set forth in the CSRD and the ESRS, among others. |
Once the CSRD becomes enforceable in Luxembourg, the Company will fall within the “second tranche” of companies that will need to report in line with the final ESRS. This means that the Company will have to report in line with the ESRS and CSRD requirements for the first time in 2026, for the financial year ending on December 31, 2025.
For this purpose, in 2023, the Company assigned an ESG officer to prepare for compliance with the CSRD conducted a certified “double materiality” analysis (impact and financial materiality) of the 20 material topics relevant for the business. This exercise has adjusted and validated the list of “ESG KPIs” that will have to be prioritized, managed and reported in a consolidated manner. All of the ESG KPIs identified respond to a previous assessment of the impacts, risks and opportunities associated to the 20 material topics, in line with the Company’s risk matrix.
Moreover, the Company’s strategy contemplates the implementation, in the near future, of the following steps:
| ● | conduct a gap assessment analysis of the status of every ESG KPIs needed in all of its subsidiaries to comply with the CSRD; and |
| ● | develop an ESG-focused roadmap that includes: |
| (i) | a strategy for the prioritized material topics of the “double materiality assessment” regarding its ESG KPIs, addressing its impacts risks and opportunities with targets; |
| (ii) | a strategy for the management of the ESG KPIs that are currently not being measured in the manner that the CSRD demands; |
| (iii) | development of a strategy to implement internal ESG policies and processes to assure compliance at a consolidated level, and allocate responsibilities across the group entities and teams; and |
| (iv) | the provision of regular sustainability and ESG related trainings to board members, executive teams and persons responsible for collecting sustainability-related information across the Company. |
56
Regulatory and Concessions Framework
Introduction
As of December 31, 2023, we hold concessions in Argentina, Italy, Brazil, Uruguay, Ecuador and Armenia and are subject to regulations in each one of these countries. The following table sets out aspects of our concession agreements, along with their respective term and extension provisions, and the corresponding regulatory governmental authority.
|
|
Concession agreement |
|
Governmental authority |
|
Term and extension provisions |
|
Argentina |
|
AA2000 Concession Agreement |
|
Argentine Government; ORSNA |
|
30-year original term. It was extended for 10 additional years on December 17, 2020 (ending February 13, 2038). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NQN Concession Agreement |
|
Government of the Province of Neuquén; ORSNA |
|
20-year original term (ending October 24, 2021). It was extended until 2026. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BBL Concession Agreement |
|
Municipality of Bahía Blanca; ORSNA |
|
25-year term (ending May 22, 2033). Concession may be extended for 10 years upon governmental approval. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Italy |
|
Pisa Concession Agreement |
|
ENAC |
|
40-year original term. A two-year extension was granted by the Government in July 2020 (ending December 7, 2048). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Florence Concession Agreement |
|
ENAC |
|
40-year original term. A two-year extension was granted by the Government in July 2020 (ending February 10, 2045). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Brazil |
|
Natal Concession Agreement |
|
Brazilian ANAC |
|
28 year term (ending January 24, 2040). An amendment to terminate the Natal Concession Agreement was executed in August 2020. As of the date of this report we no longer operate the Natal Airport. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Brasilia Concession Agreement |
|
Brazilian ANAC |
|
25-year term (ending July 24, 2037); may be extended for an additional 5 years if necessary to reestablish economic equilibrium. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Uruguay |
|
Carrasco Concession Agreement and |
|
Defense Ministry |
|
Extension recently executed. Concession set to terminate on November 20, 2053). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Punta del Este Concession Agreement |
|
Defense Ministry |
|
40-year term (ending March 31, 2033). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ecuador |
|
Guayaquil Concession Agreement |
|
AAG; Municipality of Guayaquil |
|
27-year and 5-month term (ending July 27, 2031). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Galapagos Concession Agreement |
|
DGAC; STAC (as defined herein) |
|
15-year term (ending July 6, 2026). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Armenia |
|
Armenian Concession Agreement |
|
Armenian Ministry of Territorial Administration and Infrastructure, CAC (as defined herein) |
|
30-year term (ending June 8, 2032), with option to extend the term of the agreement by 5-year periods if in good standing. |
|
57
Argentina
Our Airports in Argentina
|
|
Name |
|
Location |
|
International or |
|
Category(1) |
1. |
|
Aeropuerto de San Carlos de Bariloche “Teniente Luis Candelaria” |
|
San Carlos de Bariloche |
|
International |
|
I |
2. |
|
Aeropuerto de Catamarca, “Coronel Felipe Varela” |
|
Catamarca |
|
National |
|
I |
3. |
|
“Aeroparque “Jorge Newbery” |
|
Ciudad A. Buenos Aires |
|
International |
|
I |
4. |
|
Aeropuerto de Comodoro Rivadavia, “Gral. Enrique Mosconi” |
|
Comodoro Rivadavia |
|
International |
|
I |
5. |
|
Aeropuerto Internacional de Córdoba, “Ing. A. Taravella” |
|
Córdoba |
|
International |
|
I |
6. |
|
Aeropuerto de Esquel “Brigadier General Antonio Parodi” |
|
Esquel |
|
National |
|
I |
7. |
|
Aeropuerto Internacional de Ezeiza, “Ministro Pistarini” |
|
Ezeiza |
|
International |
|
I |
8. |
|
Aeropuerto Internacional de Formosa, “El Pucu” |
|
Formosa |
|
International |
|
I |
9. |
|
Aeropuerto de General Pico |
|
General Pico |
|
National |
|
II |
10. |
|
Aeropuerto de Cataratas del Iguazú, “Mayor D. Carlos Eduardo Krause” |
|
Puerto Iguazú |
|
International |
|
I |
11. |
|
Aeropuerto de Jujuy, “Gobernador Horacio Guzmán” |
|
Jujuy |
|
International |
|
I |
12. |
|
Aeropuerto de La Rioja, “Capitán Vicente Almandos Almonacid” |
|
La Rioja |
|
National |
|
I |
13. |
|
Aeropuerto de Malargüe, “Comodoro D Ricardo Salomón” |
|
Malargüe |
|
National |
|
II |
14. |
|
Aeropuerto Internacional de Mar del Plata, “Astor Piazzolla” |
|
Mar del Plata |
|
International |
|
I |
15. |
|
Aeropuerto Internacional de Mendoza, “El Plumerillo” |
|
Mendoza |
|
International |
|
I |
16. |
|
Aeropuerto de Paraná, “General Urquiza” |
|
Paraná |
|
National |
|
I |
17. |
|
Aeropuerto de Posadas, “Libertador General D. José de San Martín” |
|
Posadas |
|
International |
|
I |
18. |
|
Aeropuerto de Puerto Madryn, “El Tehuelche” |
|
Puerto Madryn |
|
National |
|
II |
19. |
|
Aeropuerto de Reconquista “Teniente Daniel Jukic” |
|
Reconquista |
|
National |
|
II |
20. |
|
Aeropuerto de Resistencia, “José de San Martín” |
|
Resistencia |
|
International |
|
I |
21. |
|
Aeropuerto de Río Cuarto, “Área de Material” |
|
Las Higueras |
|
National |
|
II |
22. |
|
Aeropuerto de Río Gallegos, “Piloto Civil Norberto Fernández” |
|
Río Gallegos |
|
International |
|
I |
23. |
|
Aeropuerto de Río Grande “Gobernador Ramon Trejo Noel” |
|
Río Grande |
|
International |
|
I |
24. |
|
Aeropuerto Internacional de Salta, “Martín Miguel de Güemes” |
|
Salta |
|
International |
|
I |
25. |
|
Aeropuerto de San Fernando |
|
San Fernando |
|
International |
|
II |
26. |
|
Aeropuerto de San Luis, “Brigadier Mayor César R Ojeda” |
|
San Luis |
|
National |
|
I |
27. |
|
Aeropuerto de San Rafael, “S.A. Santiago Germano” |
|
San Rafael |
|
National |
|
II |
28. |
|
Aeropuerto de San Juan, “Domingo Faustino Sarmiento” |
|
San Juan |
|
National |
|
I |
29. |
|
Aeropuerto de Santa Rosa |
|
Santa Rosa |
|
National |
|
I |
30. |
|
Aeropuerto de Santiago del Estero, “Vcom. Ángel de la Paz Aragonés” |
|
Santiago del Estero |
|
National |
|
I |
31. |
|
Aeropuerto de Tucumán, “Tte. Benjamín Matienzo” |
|
San Miguel de Tucumán |
|
International |
|
I |
32. |
|
Aeropuerto de Viedma, “Gobernador Castello” |
|
Viedma |
|
National |
|
I |
33. |
|
Aeropuerto de Villa Reynolds |
|
Villa Reynolds |
|
National |
|
I |
34. |
|
Aeropuerto El Palomar |
|
El Palomar |
|
International |
|
I |
35. |
|
Aeropuerto de Neuquén, “Presidente Perón”(2) |
|
Neuquén |
|
International |
|
I |
36. |
|
Aeropuerto de Bahía Blanca, “Comandante Espora”(2) |
|
Bahía Blanca |
|
National |
|
I |
37. |
|
Aeropuerto Termas de Río Hondo (3) |
|
Termas de Río Hondo |
|
National |
|
I |
| (1) | The category determines the maximum fees we may charge. See in “Item 4 Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement,” the “Passenger Use Fees,” “Landing Fees,” and “Parking Fees.” |
58
| (2) | In addition to the airports operated under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we also operate the Neuquén Airport and the Bahia Blanca Airport which are not subject to the AA2000 Concession Agreement. These airports are subject to Province of Neuquén and Municipality of Bahia Blanca regulations as well as to the ORSNA resolutions, respectively. See “—Other Airports we operate in Argentina.” |
| (3) | Pursuant to ORSNA’s Resolution No. 27/2021, the Termas de Río Hondo Airport has also been incorporated into the AA2000 Concession Agreement. |
Sources of Regulation
We are subject to numerous regulations that govern the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the concession agreements for the Neuquén and the Bahía Blanca Airports, as well as our business and the operation of the airports, issued by the Argentine Congress, the Executive Branch, the Ministry of Transportation (currently, the Secretary of Transportation, under the Ministry of Infrastructure in accordance with the provisions of Decree No. 8/2023), the ORSNA and the Administration of National Civil Aviation (Administración Nacional de Aviación Civil or the “Argentine ANAC”).
Title III of Law No. 17,285, dated May 17, 1967 (as amended from time to time, including, but not limited to, the amendment contemplated by the Decree No. 70/2023, the “Argentine Aeronautical Code”), as amended, and Regulation No. 1/2017 of the Airport Infrastructure and Services General Bureau (Dirección General de Infraestructura y Servicios Aeroportuarios), set forth the basic framework for the regulation of airports in Argentina. The Argentine Aeronautical Code also provided for the creation of both international and national airports and established concepts such as public and private airports. Decree No. 375/97 created the Argentine National Airport System and established the general framework for regulating the use, operation and management of the Argentine airport facilities that are part of the Argentine National Airport System. Under Decree No. 375/97, the Argentine Government may grant concessions to operate and manage some or all of the airports in the Argentine National Airport System subsequent to a public bidding process that is open to both national and international entities. Decree No. 375/97 provides that the Argentine National Airport System is regulated by the ORSNA, with respect to matters generally involving management and maintenance, and by the Argentine ANAC with respect to matters generally involving airport safety and air travel.
Argentina has a federal government system with 23 provinces and the City of Buenos Aires with local laws. Under the Argentine Constitution, all powers which are not granted to the Argentine Government remain with the provinces and the City of Buenos Aires. Laws related to civil, commercial, criminal, mining, interjurisdictional transportation, labor and social security matters are exclusively regulated by the National Congress. Pursuant to Article 75, Subsection 30) of the Argentine Constitution, national airports are considered “premises of national interest” (establecimientos de utilidad nacional), therefore, federal legislation is applicable, with the sole exception for tax and police powers of each of the Argentine Provinces, insofar as they do not interfere with the federal interest.
Aeronautical Policy
On December 20, 2023, the Executive Branch issued the Urgency Decree No. 70/2023, which was published in the Official Gazette on December 21, 2023 (the “Decree 70/2023”).
The Decree 70/2023, among other matters, (i) declares the public emergency in economic, financial, fiscal, administrative, pension, tariff, health, and social matters until December 31, 2025; (ii) abrogates several laws related to government intervention in the economy; and (iii) implements amendments and changes to several laws and regulations aiming to deregulate the economy.
In this line, Decree 70/2023 contemplates relevant changes regarding the aeronautical policy of the country attempting to develop the aeronautical industry and promote free competition in the market.
The main changes contemplated by Decree 70/2023 are the following:
(i) Decree-Law No. 12,507/56 (national policy on aeronautics), Law No. 19,030 (national policy for air transport), and Decree No. 1654/02 (on the emergency of air transport), were abrogated;
59
(ii) civil air commercial aviation is deemed an essential service; (iii) the aeronautical authority shall regulate and oversee airport services (defined as all services provided within an airport, excluding air navigation services), based on the principles of ensuring safety, free competition, and market access (however the airport services captured by the AA2000 Concession Agreement and those airport services subject to the supervision of the ORSNA are not modified by Decree 70/2023 and remain unchanged as of the date of this annual report);
(iv) ramp services in general are classified as essential airport services;
(v) both manned and unmanned aircrafts are considered devices or mechanisms capable of navigating in airspace and suitable for transporting people or goods;
(vi) operation of air commercial activities by foreign flag companies would be subject to prior clearance and must comply with international rules and agreements to which the Argentine Republic is a party;
(vii) air transport services will no longer be subject to concession by the Executive Branch but only to authorization; moreover, the Argentine Aeronautical Code no longer expressly requires a prior public hearing for their granting;
(viii) individuals operating domestic air transport routes are no longer required to be Argentine (a legal domicile in the country would suffice for these purposes);
(ix) the requirements established for companies providing domestic air commercial services under which, at least more than 50% of the partners must be Argentine with legal domicile in the country, were abrogated;
(x) to ensure a proper balance between the interests of passengers and carriers, the aeronautical authorities shall issue regulations regarding passenger rights and their protection; and
(xi) Laws No. 26,412 and 26,466 were amended enabling the transfer of shares of Aerolíneas Argentinas S.A. and Austral Líneas Aéreas – Cielos del Sur S.A., and their controlled companies, to the employees of these companies under an Employee Ownership Program.
Decree 70/2023 came into force on December 29, 2023, without the need for any additional formalities. Notwithstanding this, the decree must be reviewed by a permanent bicameral commission of the Congress and can only be invalidated if both Chambers of the Congress expressly reject it. A repeal of Decree 70/2023, due to the rejection of both Chambers of the Congress will not have retroactive effect and, therefore, all rights acquired and legal relationships established during the validity of the decree will be valid.
The amendments proposed by the Decree 70/2023 require further regulation by the Argentine ANAC, the Secretary of Transportation and other regulatory bodies. Many of the changes of the aeronautical policy contemplated by the Decree 70/2023 will have an impact in AA2000’s business and its operations. As of the date of this annual report, we cannot predict how these changes will affect our business and our results of operations, since this assessment would be subject to the rules and regulations to be issued by the relevant regulatory authorities. See “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement—The aeronautical policy reforms proposed by the Decree 70/2023 may affect our business and result of operations.”
Governmental Authorities
Role of the ORSNA
The Organismo Regulador del Sistema Nacional de Aeropuertos (ORSNA, as previously defined for its Spanish acronym) is the principal regulator of our airports under Argentine law and is an agency under the authority of the Ministry of Transportation (currently, the Secretary of Transportation, under the Ministry of Infrastructure, in accordance with the provisions of Decree No. 8/2023). The ORSNA is responsible for establishing the rules and procedures that govern our management and maintenance of the airports we operate and for enforcing our compliance with Argentine laws and the terms of the concession agreements in Argentina, including our fulfillment of our investment plan and master plans. The ORSNA and the Argentine ANAC are jointly responsible for establishing the criteria for our development of airport safety manuals, airport operations manuals, emergency plans and maintenance programs.
All disputes arising in connection with the operation or management of our airports must be submitted to the ORSNA prior to submitting them before federal courts. If we challenge any of ORSNA’s decisions, we may seek final judgment on the matter from the Ministry of Transportation (currently, the Secretary of Transportation, under the Ministry of Infrastructure, in accordance with the provisions of Decree No. 8/2023) and subsequently from the Argentine federal court system.
60
Role of the Argentine ANAC
Under the authority of the Ministry of Transportation, the Argentine (currently, the Secretary of Transportation, under the Ministry of Infrastructure, in accordance with the provisions of Decree No. 8/2023), ANAC is responsible for providing services relating to aeronautical activities, including air traffic control and flight protection services. Since July 2009, the Argentine ANAC has been exclusively in charge of civil aeronautical functions, which were previously provided by the Argentine Air Force, the ORSNA and the Sub-Secretariat of Aerocommercial Transportation.
The Argentine ANAC has the power to audit and control civil aviation activities, including public and private airports and airdromes, air traffic and communications and air navigation and aeronautical services. In addition, it may develop regulatory projects in connection with such activities.
Under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the Argentine ANAC is responsible for providing in our airports, among other functions, operating functions (including air traffic control and communications), supervisory functions (including supervision of airport infrastructure, aviation personnel and flight equipment) and safety functions (including direction and supervision of search and rescue operations) at our airports. The Argentine ANAC charges the airlines and is responsible for the collection of general security, flight route security and aircraft landing support charges.
Additional Argentine Agencies
The Ministry of Interior operates the Argentine Migrations Bureau and, under the Ministry of the Economy, operates the Argentine General Customs Bureau (Dirección General de Aduanas) which performs all immigration and customs functions for all airports in Argentina. The Argentine Migrations Bureau imposes and collects certain charges relating to immigration. In addition, security functions are provided by the Airport Security Police (Policía de Seguridad Aeroportuaria), which is under the authority of the Ministry of Security.
The AA2000 Concession Agreement
Pursuant to Administrative Decision No. 60/98, AA2000 was awarded the concession for the operation of 33 of the airports of the Argentine National Airport System set forth and covered by the AA2000 Concession Agreement. The AA2000 Concession Agreement was approved by Decree No. 163/98, dated February 11, 1998. In December 2020, the Argentine Government extended the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement until February 2038 through Decree No. 1009/2020.
Because of the period of severe political, economic and social crisis that Argentina experienced during 2001 and 2002, the Congress enacted Law No. 25,561, which was subsequently amended and expanded, and which declared a public emergency in social, economic, administrative, financial and exchange matters and provided for, among other things, the renegotiation of public services and works contracts, such as the AA2000 Concession Agreement. Decree No. 311/03 established that the renegotiation of public services and works contracts would be carried out by the Public Service Contract Analysis and Renegotiation Unit (Unidad de Renegociación y Análisis de Contratos de Servicios Públicos) and that the renegotiation process would be presided over by the former Ministry of Economy and Production and the Ministry of Planning.
Within the renegotiation framework established by Decree No. 311/03, on July 20, 2005, we executed a memorandum of understanding with the Argentine Government which sets forth the guidelines for the renegotiation of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. The renegotiation of the AA2000 Concession Agreement resulted in a preliminary memorandum of agreement, which after being negotiated and reviewed by the proper authorities, was executed by the Argentine Government and us on April 3, 2007, and was confirmed by the Executive Branch by Decree No. 1799, dated December 4, 2007, which approved the renegotiated agreement (“Final Memorandum of Agreement”).
In 2012, pursuant to an agreement between AA2000 and the Province of Santiago del Estero, we began operating Termas de Río Hondo Airport. On March 21, 2013, the Argentine Government issued Decree No. 303/2013, which resulted in including this airport to the AA2000 Concession Agreement. See “-Other Airports we Operate in Argentina.”
On December 27, 2017, AA2000 was awarded the concession for the operation of the El Palomar Airport, which was brought under the AA2000 Concession Agreement pursuant to Decree No. 1107/2017 and Resolution No. 894/2018 of the former Ministry of Transportation (currently, the Secretary of Transportation). As of the date of this annual report, the El Palomar Airport has no operations. As of the date of this annual report, we operate 35 airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
61
Unless otherwise stated, the term “AA2000 Concession Agreement” refers to the AA2000 Concession Agreement modified by the Final Memorandum of Agreement.
In addition to the regulatory structure set forth under Argentine law and regulations governing the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the majority of our rights and obligations with respect to the concession are regulated by the specific terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement as set forth below.
Our General Obligations
In general, under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we are responsible for the following functions in connection with the airports, among others:
| ● | ensuring equality, freedom of access and nondiscrimination with respect to the use of airport services and facilities on the terms established under the relevant bidding documentation; |
| ● | ensuring that the operations of the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement comply with community interests, environmental protection, anti-drug trafficking laws and national defense; |
| ● | implementing the master plans approved by the ORSNA; |
| ● | operating airport services and facilities in a reliable manner, in accordance with applicable national and international standards; |
| ● | investing in airport infrastructure in accordance with the applicable investment plan; |
| ● | the maintenance of airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, except for those facilities used by the Argentine Government in the areas assigned to and/or reserved for it; |
| ● | the installation, operation and maintenance of the airport facilities and/or equipment in such manner as to prevent them from constituting a public safety hazard; |
| ● | compliance with the relevant environmental protection standards and assessment of the environmental impact that may result from proposed works; |
| ● | providing the ORSNA with all documents and information necessary or requested for verifying compliance with the AA2000 Concession Agreement and any applicable laws and regulations; |
| ● | providing, in the areas under our control, firefighting services for the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement; |
| ● | ensuring the ability of the Argentine Government to exercise its relative powers necessary for the operation of the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement; and |
| ● | controlling and coordinating operations and activities on each apron, under the supervision of the Argentine ANAC. |
62
Term
The AA2000 Concession Agreement was for an initial period of 30 years through February 13, 2028. In December 2020, the Argentine Government extended the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement until February 2038 through Decree No. 1009/2020 (the “Technical Conditions of the Extension”) see “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement— The Argentine Government extended the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement until 2038 subject to our compliance with certain commitments”). This extension was part of an agreement entered with the ORSNA with an aim to mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in our operations and further includes our commitment to incremental capital expenditures as discussed below in “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement—Technical Conditions of the Extension.” The ORSNA may require us to continue complying with the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement for a term of no more than 12 months following the termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. In such a case, the ORSNA shall expressly notify us of its decision no less than six months prior to the termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
Technical Conditions of the Extension
In December 2020, the Argentine Government extended the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement until February 13, 2038. Pursuant to the Technical Conditions of the Extension, AA2000 required to comply with the following commitments:
| ● | assign funds equal to U.S.$132 million as direct investment to complete works pending for the years 2020 and 2021 (also previously defined herein as the 2020/2021 Direct Investment Commitment): |
| ● | do its best efforts to secure, before December 31, 2021, funding, to enable AA2000 to have an early inflow of up to (a) U.S.$85 million in the “Trust Fund for Works of Group A of Airports of the National Airport System;” and (b) U.S.$124 million in the “Additional Fund for Substantial Investments in Group A of Airports”; (also previously defined herein as the Development Trust Leverage Commitment) |
| ● | secure availability of funds, before March 31, 2022, or, provided that there are justified reasons and subject to ORSNA’s approval, before December 2022, for an aggregate amount of U.S.$406.5 million (VAT included), which must be applied to: (a) works considered as direct investment, to be carried out, preferably, during the years 2022 and 2023 (also previously defined herein as the 2022/2023 Commitment); and (b) the redemption of preferred shares of the Argentine Government to be performed by AA2000 before March 31, 2022 (also previously defined herein as the Redemption of the Preferred Shares Commitment, and together with the 2022/2023 Commitment, the Availability of Funds Commitment); and |
| ● | make direct investments for U.S.$200 million (VAT included) between the years 2024 and 2027, at an annual average of U.S.$50 million (VAT included), provided that this volume of investment shall be complementary to any direct investment balance carried forward from the 2021/2023 period (also previously defined herein as the 2024-2027 Commitment). |
With respect to the capital expenditures to be performed under the 2022/2023 Commitment and the 2024-2027 Commitment,, Resolution No. 60/ 2021 of the ORSNA established that AA2000’s capital expenditures under the Technical Conditions of the Extension amounts to the aggregate amount of approximately U.S.$500 million plus VAT, to be performed in two phases: (i) phase 1, approximately U.S.$336 million plus VAT to be performed preferably within 2022 and 2023 (also previously defined herein as the Phase 1 Commitment), and (ii) phase 2, annual investments of approximately U.S.$41 million plus VAT between 2024 and 2027, for a total of approximately U.S.$164 million plus VAT (also previously defined herein as the Phase 2 Commitment).
We have filed the Technical Conditions of the Extension as exhibit to the annual report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2020, and filed on April 9, 2021. Although this document is available to the public in Argentina, we are filing it in English as an exhibit to this annual report for ease of reference to our investors.
As of the date of this annual report, AA2000 has fully complied with the 2020/2021 Direct Investment Commitment and the Availability of Funds Commitment. Regarding this latter commitment, on May 10, 2022, ORSNA issued Note No. NO-2022-46520010-APN-ORSNA through which it confirmed that AA2000 had fulfilled the Availability of Funds Commitment in the amount of U.S.$406.5 million for its application to the Mandatory Capex Program (including the Redemption of the Preferred Shares Commitment, which was complied with in March 2022).
63
With respect to the Development Trust Leverage Commitment, in December 2022 and January 2023, AA2000 informed the ORSNA that is has complied with its best efforts obligation under this commitment. On May 22, 2023, in response to the filing made by AA2000, the ORSNA took note of the best efforts performed by AA2000 in compliance with the Development Trust Leverage Commitment and requested to AA2000 its collaboration so that, if the ORSNA deems it appropriate and the financial landscape improves, other financing options for the Development Trust may be sought. In light of this, on May 23, 2023, AA2000 expressed its agreement to fully collaborate with the ORSNA to that end.
Regarding the Phase 1 Commitment, the Company is currently executing the infrastructure works in the terms provided by the Technical Conditions of the Extension and Resolution No. 60/2021, while the Phase 2 Commitment is pending. On February 5, 2024, AA2000 informed the ORSNA about the status of the Phase 1 Commitment as of December 31, 2023. Works amounting to U.S.$262.1 million (VAT included) have been initiated, of which U.S.$190.3 million (VAT included) have been executed. Considering the amount utilized for the Redemption of the Preferred Shares Commitment, totaling U.S.$174.2 million, the total amount committed under the Phase 1 Commitment amounts to U.S.$436.3 million (VAT included), which surpasses the required commitment amount for this phase (U.S.$336 million). As of the date of this report, U.S.$364.5 million (VAT included) (out of the U.S.$436.3 million (VAT included) committed) have been executed. As of the date of this annual report, the ORSNA has not issued a response to the filing made by AA2000.
As of the date of this annual report, AA2000 has substantially complied with the commitments under the Technical Conditions of the Extension. However, failure to fully comply with the ongoing commitments (in particular, the Phase 2 Commitment) could result in the imposition of fines or the termination or revocation of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. Termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement would constitute a default under the Argentine Notes Series 2017, the Argentine Notes Series 2020, the Argentine Notes Series 2021, New Money 2021 Notes, the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan and the ICBC Dubai Loan. See “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement—The Argentine Government extended the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement until 2038 subject to our compliance with certain commitments” and “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement—Lack of financing alternatives may adversely impact AA2000’s ability to comply with the commitments under the Technical Conditions of the Extension to the AA2000 Concession Agreement.”
Pursuant to the provisions of the Technical Conditions of the Extension and Resolution No. 60/2021, the Company withdrew all claims and lawsuits filed or in progress against the Argentine Government and/or its decentralized entities, whether in administrative, arbitration or judicial venues. See “Legal Procedures”.
Property
Pursuant to the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the Argentine Government transferred to us all of its personal property and the right to use real property in connection with the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement for the term of the concession. Under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we are required to use the real property to satisfy all airport service needs and we are required to provide for the ongoing maintenance of the property. However, we have the right to grant sub - concessions or otherwise allow third parties to use the real property, subject to the prior notification to the ORSNA. In the event of the destruction of all or part of the real property, we are responsible for the payment of all expenses related to the repair or replacement of the property except for damages that occur in connection with acts of God or a force majeure event or if the damaged property is not necessary for complying with our obligations under the AA2000 Concession Agreement. If any event occurs during the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement that makes the continued use of any property impossible, we are required to return such property to the Argentine Government and will have no recourse against the Argentine Government for the damages we suffer. We are also required under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement to grant to the Argentine Air Force free of charge the space necessary at each airport under the AA2000 Concession Agreement to conduct its assigned duties under the AA2000 Concession Agreement and Argentine law. The Argentine ANAC is responsible for all costs and maintenance in connection with the space provided to it. At the end of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we are required to transfer all personal and real property, together with any improvements thereto, back to the Argentine Government.
Under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we may suggest the substitution of one or more airports by building new airports during the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, when such substitution is beneficial for customers in terms of price and service quality, subject to the ORSNA’s prior authorization. In such cases, the airports being substituted shall be returned to the Argentine Government simultaneously with the new airport’s commencement of operations. In addition, the ORSNA may add or remove airports from the AA2000 Concession Agreement with our prior consent. Airports may also be removed from AA2000 Concession Agreement when they are no longer in use.
64
Exclusivity
Under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the Argentine Government cannot, under any circumstances, affect our exclusive rights or affect the economic equilibrium of the AA2000 Concession Agreement to the extent we comply with certain requirements.
Pursuant to the provisions of the Technical Conditions of the Extension, the exclusivity established by the AA2000 Concession Agreement was maintained. However, the exclusivity with respect to certain areas of influence, outside the city of Buenos Aires which includes the Ezeiza, Aeroparque, San Fernando and El Palomar airports, was cancelled. Likewise, exclusivity in the areas of influence will be maintained throughout the national territory for the activity of tax warehouses (“depósitos fiscales”).
Finally, the metropolitan area of Buenos Aires, Argentina, which includes the Ezeiza, Aeroparque, San Fernando and El Palomar Airports, is excluded from both the exclusivity as well as from the area of influence established by the AA2000 Concession Agreement regarding future infrastructure airport projects when due to the characteristics of such projects, they cannot be financed and operated by AA2000.
Liabilities
Under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we are liable for all damages caused to the Argentine Government and/or third parties as a consequence of our performance of the AA2000 Concession Agreement and our failure to perform our obligations thereunder.
Penalties
Under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, on December 13, 2004, the ORSNA issued Resolution No. 88/2004, approving the Rules on Penalties for Infringements of the Concessionaire of the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement (Régimen de Sanciones de Aplicación al Concesionario del Grupo “A” de Aeropuertos del Sistema Nacional de Aeropuertos). In the event that we breach any of our obligations under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the ORSNA has the right to impose monetary fines as it deems appropriate. In addition, in accordance with the provisions of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, delays in implementing the investment plan according to the schedule would result in the ORSNA’s imposition of a penalty equal to 10% of the value of the work that is delayed, which could be collected directly by the ORSNA against the performance guarantee, as discussed further below. Any monetary fines imposed by the ORSNA would only become due and payable after a final administrative decision.
Service Standards
Under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we have agreed to adopt certain standards for our airports regarding design, construction, operation, administration, maintenance, renewal, improvement, development, equipment and systems as reasonably established by the ORSNA in accordance with guidelines developed by the International Air Transport Association (“IATA”) and the International Civil Aviation Organization (“ICAO”) using similar airports as a reference based on their type, size and passenger traffic. In connection with monitoring our compliance with these standards, the ORSNA has the right to inspect all the airports managed by us. The ORSNA is not required to notify us in advance of its inspection. Such inspections are to be carried out at least annually for each airport with passenger traffic greater than 750,000 per year.
Performance Guarantee and Guarantee for the Performance of the Works Foreseen in the AA2000 Concession Agreement
Under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we are required to maintain a performance guarantee in the amount of at least AR$30 million as security for the timely fulfillment of all of our obligations under the AA2000 Concession Agreement. In the event that the ORSNA collects part or all of the guarantee, we are required to restore the full amount of the guarantee within 30 days from the date of collection and to pay the Argentine Government interest in an amount equal to LIBOR plus 2.0% from the fifth day following such collection until the date that the guarantee is restored. We may, with the approval of the ORSNA, pledge securities, assets, mortgages and surety bonds to satisfy our guarantee requirement. In this regard, we obtained a surety bond which currently amounts to AR$6,499,206,349.21 and will be renewed on an annual basis.
In addition, we are required to annually establish, prior to March 31 of each year, a guarantee in the amount of 50% of the annual investment plan required under the AA2000 Concession Agreement in order to guarantee our compliance with the investment plan for such year. We may, with the approval of the ORSNA, pledge securities, assets, mortgages and surety bonds to satisfy our guarantee requirement. We obtained a surety bond in the amount of U.S.$130,000,000 to comply with our obligation for 2023.
65
Technical Expert Requirement
Under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we are required to have as a shareholder, at all times, a technical expert who has expertise in operating and managing airports. Under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, any shareholder who has held at least 10.0% of our share capital for a minimum of five years is considered a technical expert. Any substitution of a shareholder that qualifies as a technical expert must be previously approved by the ORSNA. Since CASA and CAS have owned at least 45.9% and 29.8% of AA2000’s common shares, respectively, for over five years, they are deemed technical experts.
Maintenance of Insurance
The Concession Agreement requires us to maintain a civil insurance policy covering personal and property damages, loss or injury in an amount equal to at least AR$300.0 million throughout the term of the concession. We are also required to maintain worker’s compensation insurance in accordance with Argentine law. We have contacted a civil liability insurance policy in the amount of U.S.$300.0 million covering liabilities that may arise under civil law in connection with the management of our airports and the development of works in our airports.
Collateral Assignment of Revenue
We may collaterally assign revenue derived from the concession, in order to obtain the necessary resources for the fulfillment of our obligations. Such assignment cannot affect the Specific Allocation of Revenue, as defined in the AA2000 Concession Agreement and described in “—Specific Allocation of Revenue,” or the resources foreseen for the financing of the investment plan detailed in the Final Memorandum of Agreement. In addition, collateral assignment of revenue that is made into a trust may remain in effect even upon an early termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, as long as the application of the funds thereunder is audited by the Argentine Government and/or by a consulting firm hired for such purpose that is satisfactory to the Argentine Government. Such collateral assignment must be previously authorized by a resolution of the ORSNA, which is responsible for the auditing of the application of the funds. On January 17, 2017, April 24, 2020, and October 15, 2021 the ORSNA issued Resolutions No. 1/2017, No. 21/2020 and No. 66/2021, pursuant to which it authorized the collateral assignment of revenue under the international passenger use tariff for an amount equal to U.S.$400 million for (i) the benefit of, and pari passu among, holders of the Argentine Notes Series 2017, the Argentine Notes Series 2020 and the Argentine Notes Series 2021; and (ii) the benefit of the lenders of the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan, the holders of New Money 2021 Notes, the holders of Class 5 Notes and the lender under ICBC Dubai Loan, which are subordinated to the right of the holders of the Argentine Notes Series 2017, the Argentine Notes Series 2020 and the Argentine notes series 2021: in both cases, as long as after such assignment AA2000 would have sufficient funds to cover basic operating costs (the “Tariff Trust”). On August 8, 2019, August 18, 2020, March 16, 2021, June 17, 2021 and October 15, 2021, the ORSNA issued Resolutions Nos. 61/2019, 57/2020, 2/2021, 3/2021 and 66/2021 pursuant to which it authorized the collateral assignment for the benefit of, (x) pari passu among, each of the lenders under Syndicated Bimonetary loan, the holders of the New Money 2021 Notes and Class 5 Notes, the lender under the ICBC Dubai Loan, and the lenders or relevant holders under new debt incurred by AA2000 to fund infrastructure works for a total amount of up to U.S.$235 million and (y) the holders of the Argentine Notes Series 2021, in this case subordinated to the creditors detailed in (x), of (i) certain collection rights of AA2000 vis a vis Terminal de Cargas Argentinas S.A. (business unit of AA2000), excluding 15% of the revenues under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, (ii) any residual rights AA2000 could be entitled to receive as final beneficiary (fideicomisario) to and under (but none of its obligations under or relating to) the AA2000 Concession Agreement, contracts and applicable laws in respect to the rights to receive payments in the event of termination, expropriation or redemption of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, including the right to receive and withhold payment pursuant thereto, which have been transferred and assigned in trust to the Tariff Trust; (iii) the residual rights, as beneficiary or final beneficiary (fideicomisario), of AA2000 under the Tariff Trust exclusively relatively to the non-assigned portion of such assets net of the amounts destined to fund the Series 2021 Offshore Reserve Account (the “Cargo Trust”). Once the Argentine Notes Series 2017 and the Argentine Notes Series 2020 are cancelled in full, AA2000 will amend and restate the Cargo Trust and the Tariffs Trust, so that the Argentine Notes Series 2021 become secured by the Cargo Trust on a pro rata and pari passu basis with the existing beneficiaries of the Cargo Trust, and these other beneficiaries under the Cargo Trust become secured by the Tariffs Trust on a pro rata pari passu basis with the Argentine Notes Series 2021. Pursuant to Resolution No. 66/2021 the ORSNA authorized the amendment and restatement of the Tariff Trust and the Cargo Trust.
66
Additionally, according to the AA2000 Concession Agreement, a collateral assignment cannot, under any circumstances, decrease the quality of our services or affect the fulfillment of our contractual obligations. Moreover, the collateral assignment must recognize the powers and privileges of the Argentine Government set forth in the AA2000 Concession Agreement and must guarantee that no rights or actions that jeopardize the continuity of the aeronautical public services are exercised. According to the AA2000 Concession Agreement, while a collateral assignment remains in place, we shall have no right to indemnification for the investments secured by the relevant collateral assignment. Once the collateral assignment is terminated, we shall be paid the relevant indemnification amount corresponding to such investments net of the amounts transferred to and applied by the trust.
Assignment of Concession Agreement
The AA2000 Concession Agreement may not be assigned to any third party without the prior consent of the ORSNA and the Argentine Government. We are authorized to grant concessions relating to commercial operation of the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement to third parties during the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, including the execution of subcontracts with, and the granting of permits to, third parties in order to exploit AA2000’s rights emerging from the provision of the commercial services under the AA2000 Concession Agreement. We are required to inform the ORSNA of our intentions prior to the execution of subcontracts or the granting of the permits. The ORSNA may object to any assignment if it considers it to be insufficient or against the best interests of the management, operation or functioning of the airports.
Previous Sub-concessions
Pursuant to the bidding documentation for our concessions in Argentina, we were required to maintain in effect certain sub-concessions granted by the Argentine Government for the provision of commercial activities within our airports that were in effect at the time we commenced our activities at the airports until the expiration of such agreements’ terms. After the expiration of their terms, such sub-concessions will belong to us. We may decide to continue such activities ourselves, continue with the existing providers or enter into new agreements with third parties to provide such services. We describe below the most important agreements that are currently in effect.
| ● | Agreement with Intercargo: On November 20, 1990, the Argentine Government granted a concession to Intercargo for a period of 20 years for Intercargo to provide assistance with the connection of aircraft to terminals through passenger walkways, for arriving and departing passengers, in 16 of our airports. Intercargo also provides additional services such as ramp services, loading and unloading of luggage, mail and cargo, among other services. |
Intercargo had executed an agreement with the Argentine Government providing for the payment of monthly fees of U.S.$156,000 for ramp services and U.S.$8,000 for the use of space within our airports. Such agreements were assigned to us when we took over the operations of the airports. As a result of certain negotiations following the Argentina peso devaluation, Intercargo currently pays to us an additional monthly fee of U.S.$156,740 and, every six (6) months, pays us the difference between such amounts and the amount resulting from the calculation using the current market exchange rate.
If the Argentine Government decides to terminate, cancel or conclude the concession contract for the service rendered by Intercargo, the concession for such services shall be transferred to AA2000, who shall render the services on its own or through a third party or parties hired for that purpose.
| ● | Agreement with Interbaires: On April 24, 1990, the Argentine Government granted a 20-year concession to Interbaires, which may be automatically extended for an additional 10-year term. Interbaires operates the duty free shops at Ezeiza, Aeroparque and the airports of Córdoba, Bariloche, Mendoza, Mar del Plata and Iguazú. AA2000 agreed to extend the concession on May 4, 2010. The additional term under which Interbaires will continue providing services to us consists of an additional 17 years, two months and 29 days, and expires on February 8, 2028. Interbaires pays us a monthly royalty fee equal to 15% of its total gross revenue, net of VAT. |
67
| ● | Agreement with Gate Gourmet (previously Buenos Aires Catering): In 2005, we entered into an agreement with Gate Gourmet, which granted such company an exploitation and commercial use permit for the provision of catering services in aircraft, laundry services, catering for third parties delivered outside the airports and training courses, among other services. Such agreement is expected to expire on February 29, 2028. Pursuant to such agreement, Gate Gourmet is required to pay us a monthly fee of 10% of the gross amounts invoiced by such company for the provision of catering services, 5% of the gross amounts invoiced for laundry services, 1.5% of the gross amounts invoiced for the renting of space for training courses and 1.5% of the gross amounts invoiced for catering to third parties delivered outside the airports. |
Share Transfer Restrictions
AA2000’s shares may not be pledged or encumbered without prior authorization from the ORSNA. The pledging or refraining from pledging shares or other assets may not be regarded as a condition precedent for fulfillment of investment commitments and may not serve as justification for failing to fulfill the commitments assumed under the AA2000 Concession Agreement in a proper and timely manner.
The shareholders of AA2000 can only change their stake ownership or sell their shares upon prior authorization from the ORSNA. AA2000 cannot merge or spin off during the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
Applicable Law and Jurisdiction
The AA2000 Concession Agreement is governed and interpreted in accordance with the laws of Argentina. The parties to the AA2000 Concession Agreement agree to accept the jurisdiction of the competent federal courts of the City of Buenos Aires.
Miscellaneous Provisions
Under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we and the Argentine Government have additional rights and obligations, including the following:
| (i) | we are permitted to use and manage airports other than the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement with the prior authorization of the Argentine Government; |
| (ii) | in order to encourage the performance of new works in the airports, we may stipulate in agreements with third parties aimed at rendering services which require the performance of new works, upon the prior authorization of the ORSNA that these agreements shall continue in effect in the event of an early termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. In such a case, the Argentine Government or its assignee shall be subrogated in our rights and obligations under such agreements; and |
| (iii) | the Argentine Government, through the Secretary of Transportation, is required to establish a procedure for governing slot allocation at each apron. |
Specific Allocation of Revenue
Under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we are required to, on a monthly basis, allocate an amount equal to 15% (in Argentine pesos) of the total revenue derived from the concession (“Specific Allocation of Revenue”), pursuant to the following percentages:
| ● | 11.25% of total revenue to a trust for the development of the Argentine National Airport System to fund capital expenditures for the Argentine National Airport System, as determined by ORSNA. |
| ● | 1.25% of total revenue to a fund to study, control and regulate the AA2000 Concession Agreement, which shall be administered and managed by the ORSNA. |
| ● | 2.5% of total revenue to a trust for investment commitments for the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement. |
68
The Specific Allocation of Revenue is set forth in a trust agreement for the development of the Argentine National Airport System executed on December 29, 2009, between us and Banco Nación, as trustee (“Development Trust”). See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement—Development Trust” below.
However, for the purpose of calculating the Specific Allocation of Revenue, we do not take into account our revenue derived from reimbursement of expenses by our sub - concessionaire’s, revenue derived from Construction Services under IFRIC 12, and the revenue resulting from our contributions to the Development Trust aimed at investments in our airports equivalent to 2.5% of the total revenue derived from the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
Investment Plan
Investment Commitments
Under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement and the Technical Conditions of the Extension, we are required to make capital expenditures in accordance with our investment plan, which sets forth the amount of our required investment commitments for the period from 2006 through the end of the AA2000 Concession Agreement in 2038.
Prior to the approval of the Technical Conditions of the Extension, our total required investment commitments from January 2006 until 2028 were AR$2.2 billion (at constant values corresponding to December 2005). As of December 31, 2021, we had invested AR$2.9 billion (at values corresponding to December 2005) under our investment plan. Our capital expenditures for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019 and 2018 are currently under review by the ORSNA. See “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement—If the ORSNA does not approve the capital expenditures already made under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we would be required to make additional capital expenditures, which may affect our cash flows and financial condition.” Our investments have thus far been financed by cash generated by our operations, funds from the Development Trust and the net proceeds from our issuance of indebtedness.
Pursuant to the Technical Conditions of the Extension, AA2000 is obliged to comply with the 2020/2021 Direct Investment Commitment, the Development Trust Leverage Commitment, the Availability of Funds Commitment and the 2024 - 2027 Commitment (among other obligations assumed by AA2000, see “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement—Technical Conditions of the Extension”).
The amount of capital expenditures for the 2028-2038 period will be established by the ORSNA according to the operating needs of the aeronautical system and the equilibrium of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. In addition, the Technical Conditions of the Extension includes as an exhibit the indicative Financial Projection of Income and Expenses up to the year 2038 (calculated in December 2019 values).
With respect to the capital expenditures to be performed under the 2022/2023 Commitment and the 2024-2027 Commitment, Resolution No. 60/2021 of the ORSNA established that AA2000’s capital expenditures under the Technical Conditions of the Extension amounts to the aggregate amount of approximately U.S.$500 million plus VAT, to be performed in two phases: Phase 1 Commitment and Phase 2 Commitment.
69
As of December 31, 2022, we have invested AR$75 million (VAT included) (at values corresponding to December 2019). Our capital expenditures for the year ended December 31, 2022 are currently under review by the ORSNA. In addition, with respect to AA2000’s commitments under the Technical Conditions of the Extension and Resolution No. 60/2021, as of the date of this annual report: (i) AA2000 has fully complied with the 2020/2021 Direct Investment Commitment and the Availability of Funds Commitment; (ii) with respect to the Development Trust Leverage Commitment, in December 2022 and January 2023, AA2000 informed the ORSNA that is has complied with its best efforts obligation under this commitment. On May 22, 2023, in response to the filing made by AA2000, the ORSNA took note of the best efforts performed by AA2000 in compliance with the Development Trust Leverage Commitment and requested to AA2000 its collaboration so that, if the ORSNA deems it appropriate and the financial landscape improves, other financing options for the Development Trust may be sought. In light of this, on May 23, 2023, AA2000 expressed its agreement to fully collaborate with the ORSNA to that end; and (iii) regarding the Phase 1 Commitment, the Company is currently executing the infrastructure works in the terms provided by the Technical Conditions of the Extension and Resolution No. 60/2021, while the Phase 2 Commitment is pending. With respect to the Phase 1 Commitment, on February 5, 2024, AA2000 informed the ORSNA about the status of the referred commitments as of December 31, 2023. Works amounting to U.S.$262.1 million (VAT included) have been initiated, of which U.S.$190.3 million (VAT included) have been executed. Considering the amount utilized for the Redemption of the Preferred Shares Commitment, totaling U.S.$174.2 million, the total amount committed under the Phase 1 Commitment amounts to U.S.$436.3 million (VAT included), which surpasses the required commitment amount for this phase (U.S.$336 million). As of the date of this report, U.S.$364.5 million (VAT included) (out of the U.S.$436.3 million (VAT included) committed) have been executed. As of the date of this annual report, the ORSNA has not issued a response to the filing made by AA2000. See “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Argentina and the AA2000 Concession Agreement—If the ORSNA does not approve the capital expenditures already made under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we would be required to make additional capital expenditures, which may affect our cash flows and financial condition.”
Compliance with the Investment Plan
The investments contemplated in the five-year plans submitted to the ORSNA will be directed, in all cases, to cover operating needs and capacity and demand increases, as well as the fulfillment of international quality and safety standards within our airports. We may not commence works that are not authorized by the ORSNA and included in the applicable investment plan. All works authorized by ORSNA, even in excess of the required amount, are considered for the purposes of the economic equilibrium, as described below. We must submit to the ORSNA, in accordance with the procedure established by said regulatory authority, each five - year investment plan before January 31 of the year preceding the year in which the investment plan will be performed. If the ORSNA makes observations on the investment plan, AA2000 must implement the relevant amendments, otherwise it will be considered a violation of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. Likewise, the ORSNA will specify the rules that govern the authorization of related constructions.
Under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the ORSNA may revise the timing of the works contemplated in the applicable investment plan and may also modify the investment plan to require additional works, provided that such modifications may not require investment commitments in excess of those already contemplated for the relevant annual period.
Works performed in accordance with the investment plan are entered in an investment registry maintained by the ORSNA, which catalogues both the physical progress and economic investments made under the investment plan. We are required to provide all the necessary documentation and any other data or reports requested by the ORSNA with respect to the investment registry.
Master Plan
Under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we are also required to establish a master plan for each of our airports, which shall be approved and can only be subsequently amended by the ORSNA. Each master plan sets forth the investment commitments to be received by each airport over the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, considering the expected demand for aeronautical and commercial services.
70
Economic Equilibrium
The Technical Conditions of the Extension sets forth financial projections (“Financial Projection of Income and Expenses”) of our income, operational expenses, investment obligations and the procedure for paying balances and mutual claims for the period January 1, 2006 through February 13, 2038 (expressed in December 2019 values). The “economic equilibrium” derives from, and is determined in accordance with, the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses which establishes fund flows for each year during the AA2000 Concession Agreement. Under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the ORSNA must annually review the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses in order to verify and preserve the equilibrium of the variables on which it was originally based. During each annual review, amounts previously included in the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses as projections are replaced with our actual results of operations and investments for each relevant period. Our actual results of operations and investments for any year are adjusted to eliminate the effects of inflation for such year in accordance with a formula set forth in the Final Memorandum of Agreement, in order for the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses to be restated in constant values. The ORSNA then determines a new set of projections through the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement which, together with our past results of operations, may result in an economic equilibrium. The three principal factors that determine economic equilibrium are the payments we make to the Argentine Government, the fees we charge for aeronautical services (such as passenger use fees and aircraft landing and parking fees) and the investments that we are required to make under the AA2000 Concession Agreement. The ORSNA then determines the adjustments to be made to these three factors that would be needed, if any, to achieve economic equilibrium through the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. The only factors that have been adjusted in the past have been the fees that we are permitted to charge for aeronautical services and the additional investment commitments. The AA2000 Concession Agreement contemplates annual revisions to be made during March of each year. All changes to the projections are contemplated to be effective as of April 1 of the same year, although as of the date of this annual report, the yearly adjustments for 2018, 2019, 2020, 2021 and 2022 were not yet effective, which were postponed until 2023 according to the Resolution No. 60/2021.
In September 2021, the ORSNA deferred to June 30, 2023, the yearly adjustments of the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses, based on the detrimental effects that the COVID-19 pandemic had on the air traffic. In July 2023, the ORSNA issued Resolution No. 56/2023, by virtue of which the conditions and conclusions established in the report prepared by the Gerencia de Regulación Económica y Financiera regarding the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses for the period 2019 - 2023 were approved. According to the provisions of Resolution No. 56/2023 and the report referred therein, the comprehensive review of the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses for the period 2019 - 2023 will be considered by the ORSNA upon the recovery of international passenger traffic to values similar to those registered in 2019.
The provisions of Resolution No. 56/2023 were challenged by AA2000 through the filing of a lawsuit against the ORSNA, “Aeropuertos Argentina 2000 S.A. –. ORSNA - Res. 56/23 s/ proceso de conocimiento”, Docket No. CAF 32610/2023), heard by the National Federal Administrative Litigation Court No. 9, Secretariat No. 17. In the referred proceeding, among other petitions, AA2000 requested the ORSNA to (i) proceed to complete the review process of the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses for the period 2018-2022, and consequently (ii) order the relevant tariff adjustments to restore the economic equation of the concession granted to AA2000 in the terms contractually required to achieve the final result of the internal rate of return of 16.45% established in Technical Conditions of the Extension.
In addition, in the context of Resolution No. 56/2023 and within the review process of the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses for the period 2018-2022, the ORSNA issued Resolutions 65/2023 and 66/2023. AA2000 filed with the ORSNA a motion for reconsideration (“recurso de reconsideración”) against these resolutions and requested the suspension of their effects.
In November, 2023, the ORSNA and AA2000 entered into an agreement whereby they agreed: (i) to suspend the proceeding detailed above until June 30, 2024; (ii) that AA2000 must, at its cost, engage a passenger traffic consulting study; (iii) to postpone until May 30, 2024, the annual ordinary review of the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses, corresponding the period 2018-2023. The court ratified the suspension of the proceeding agreed with ORSNA. As of the date of this annual report, AA2000 has fulfilled the commitments assumed under the referred agreement.
In addition, we may propose additional charges not included in the AA2000 Concession Agreement whenever such charges are for technical and financial improvements to the rendering of services to users and air operators. In the event we engage in or offer new or additional services not expressly contemplated in the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we may also request the ORSNA to approve such services and set additional fees for such services when the application of such additional fees would result in better service for the airlines and the passengers using our airports.
71
Since 2009, the ORSNA has reviewed the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses nine times and has issued resolutions in respect of each such revision, the last of which was issued in 2019. Pursuant to Resolution No. 92/2019, the ORSNA retroactively approved the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses for the period of 2017, according to the following rules:
| ● | to re-balance the variables included in the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses through an increase in aeronautical fees; and |
| ● | to maintain the benefit airlines paying on time are entitled to under Resolution No. 10/09, dated January 28, 2009, pursuant to which such airlines pay fees equivalent to 70.0% of the international aeronautical charges set forth in Annex II of the Final Memorandum of Agreement. |
By means of Resolution No. 93/2019, also issued on October 21, 2019, the ORSNA approved a new tariff scheme, according to the following detail: (i) a fee for the international passenger use of U.S.$51.00; and (ii) a fee for the domestic passenger use of AR$195.00, effective for flights as of January 1st, 2020.
In line with the provisions of the Technical Conditions of the Extension (see “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement—Technical Conditions of the Extension” above), Resolution No. 4/2021 of the ORSNA was published in the Official Gazette. The referred resolution establishes the following:
| ● | an increase of U.S.$6 (from U.S.$51 to U.S.$57) in the international passenger fee for travelers departing from AA2000 airports. This tariff increase became effective on January 14, 2021, for flights as of March 15, 2021; |
| ● | domestic passenger fees remain unchanged until the end of 2021 (being applicable the fees approved by Resolution No. 93/2019); |
| ● | aircraft fees remain unchanged for both domestic and international air operators (being applicable the provisions of Resolution No. 92/2019); and |
| ● | on December 29, 2021, the ORSNA issued Resolution No. 83/2021 by virtue of which it approved an increase of the domestic passenger use of AR$419, from AR$195 to AR$614, for flights departing from Category I Airports. The increase is in force as from January 1, 2022, for flights tickets issued as from March 1, 2022. In December 2022, the ORSNA issued Resolution No. 98/2022 by virtue of which an increase of the use fee for the domestic passenger was approved, establishing a fee of AR$1,100 effective as of January 2023. In November 2023, the ORSNA issued Resolution No. 84/2023 by virtue of which a new increase of the use fee for the domestic passenger was approved, establishing a fee of AR$2,540 for Category I airports, AR$1,771 for Category II airports and AR$1,551 for Categories III and IV airports. |
We filed the December 30, 2008 resolution containing the Mechanisms for the Revision of the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses and the August 5, 2008 resolution containing the Manual of Regulatory Accounting, as exhibits to the annual report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2018. We filed Resolution 75/2019 in relation with the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses for the year 2016, Resolutions 92/2019 and 93/2019 in relation with the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses for the year 2017 on October 24, 2019 and Resolution No. 4/2021 under cover of Form 6-K and we intend to file each future resolution of ORSNA relating to these periodic revisions of Financial Projections of Income and Expenses under the same cover.
Withdrawal and Settlement of Claims
As a result of Argentina’s 2001/2002 economic crises, we and the Argentine Government, among other parties, had several claims against each other for breach of payment obligations under the AA2000 Concession Agreement. As a result of the withdrawal of such claims, we and the Argentine Government agreed that the total amount to be paid by us to the Argentine Government was AR$849.1 million, which we reflected in AA2000’s Audited Consolidated Financial Statements for the year ended December 31, 2006. We also agreed that this amount would be settled as follows:
| ● | 23.0% (AR$195.0 million), was fully satisfied in 2011; |
| ● | 18.6% (AR$158.0 million) through the issue of convertible notes, which were converted into shares of AA2000 in December 2011; and |
72
| ● | 58.4% (AR$496.1 million) was capitalized through the delivery to the Argentine Government of 496,161,413 preferred shares which are convertible into common shares of AA2000. Such preferred shares have a nominal value of AR$1 and have no voting rights. In addition, such shares are redeemable by us at any time at nominal value plus accrued interest. Beginning in 2020, the Argentine Government is able to convert all of the preferred shares into common shares of AA2000 with a nominal value of one peso each, up to a maximum amount of 12.5% per year of the total amount of the initial preferred shares issued to the Argentine Government to the extent we have not previously redeemed such an annual percentage for that year. At the time of exercising any conversion rights, the Argentine Government shall execute an agreement with other shareholders of AA2000 to secure and maintain the Argentine Government’s level of participation in common shares as a consequence of the conversion. The preferred shares accrue an annual dividend of 2% of the nominal value of the preferred shares, which shall be paid in kind with delivery of additional preferred shares and will be accumulated in the event we do not have sufficient retained earnings during a given fiscal period. In addition, the preferred shares have a priority over common shares in the event of liquidation. |
The preferred shares will be considered part of the shareholder’s equity of AA2000 so long as they are not redeemed by us. The debts and commitments are reflected in our Audited Combined Consolidated Financial Statements. In March 2022, the shareholders approved the redemption of the preferred shares.
In addition, as a condition of effectiveness of the extension of the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, AA2000 was required to evidence with the Argentine Government its waiver of all claims, remedies and filed or ongoing lawsuits against the Argentine Government and/or its decentralized entities (i.e. the ORSNA), or, if applicable, it shall demonstrate it has obtained the corresponding judicial approval whenever the parties involved deem it necessary. Such waiver shall not be understood as an acknowledgment of the legitimacy of such fines. As of the date of this annual report, AA2000 has waived all the ongoing claims against the Argentine Government and the ORSNA.
Regulation of Fees
The AA2000 Concession Agreement establishes the maximum fees that we may charge to aircraft operators and passengers for aeronautical services that principally consist of passenger use fees for the use of the airports, which are charged to each departing passenger and vary depending on whether the passenger’s flight is an international, regional or domestic flight, and aircraft fees, which are charged for aircraft landing and aircraft parking and vary depending on whether the flight is international or domestic, among other factors. In accordance with its annual review of our financial projections, the ORSNA may adjust the maximum fees which we may charge, considering increases in air traffic, improvements in efficiency, increases in taxes, the level of services provided, as well as projected investment levels under the master plan and the need to preserve the economic equilibrium of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement—Economic Equilibrium” above. The implementation of such fees generally occurs over different periods of time following the effectiveness of the resolution authorizing such fees. In addition, from time to time as established by the ORSNA, we may set fees for arrangements not contemplated under the AA2000 Concession Agreement when the implementation of such additional charges represents technical and financial improvements in the provision of services to airlines and passengers. Under Argentine law, we have the right to collect all passenger use fees and aircraft fees.
Pursuant to ORSNA Resolutions Nos. 10/09, 126/11, 117/12, 45/14, 168/15, 168/15 101/16, 93/2019, 04/2021 and 83/2021 airlines that pay aircraft landing fees on time benefit from a 70.0% discount of the international aeronautical fees set forth in Annex II of the Final Memorandum of Agreement. As of the date of this annual report, the discount entails a 48.42% effective discount on landing fees, and a 42.78% effective discount on parking fees.
73
Passenger Use Fees
The table below sets forth the maximum fees that, effective as of January 1, 2022 (except for domestic flights which are effective as from January 3, 2024), we may charge for passenger use fees by airport category under the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
|
|
Airport Category |
||||||||||
Use Fees Per Departing Passenger |
|
I |
|
II |
|
III |
|
IV |
||||
International flights(1) |
|
U.S.$ |
57.00 |
|
U.S.$ |
37.97 |
|
U.S.$ |
39.66 |
|
U.S.$ |
39.66 |
Domestic flights(2) |
|
AR$ |
2,540.00 |
|
AR$ |
1,771.00 |
|
AR$ |
1,551.00 |
|
AR$ |
1,551.00 |
| (1) | By means of Resolution No. 81/2023 issued by the ORSNA on November 16, 2023, the ORSNA amended the Use Fees for the “MyD. Carlos Eduardo Krause” Airport in the city of Puerto Iguazú, Province of Misiones, for direct international flights originating from the city of Puerto Iguazú Airport with direct international destinations, without connections to other national airports, setting it at the amount of U.S.$15 per passenger for tickets issued as November 21, 2023, to be used from January 1, 2024. The Company filed with the ORSNA a motion for clarification and reconsideration (“recurso de aclaratoria y reconsideración”) against said resolution. |
| (2) | Tariffs established by Resolution No. 84/2023 issued by the ORSNA on November 30, 2023 and published in the Official Gazette on December 4, 2023. |
Regional passenger use fees are a variation of the international flight passenger use fees and are applied only to international flights which cover a distance of less than 300 kilometers (187.5 miles), including international flights between the City of Buenos Aires and Uruguay. Regional passenger use fees are set at U.S.$25.16.
Passenger use fees on international flights are not charged for: (i) children under the age of 2, (ii) diplomats and (iii) transfer and transit passengers. Passenger use fees on domestic flights are not charged for: (i) children under the age of 3 and (ii) transfer and transit passengers.
Landing Fees
The table below sets forth the maximum amounts that, effective as of January 1, 2020, we may collect from aircraft operators by airport category under the AA2000 Concession Agreement in respect of international and domestic aircraft landing fees.
International Flights
|
|
Airport Category |
|
||||||
|
|
I |
|
II |
|
III |
|
IV |
|
|
|
(U.S.$ per ton, except percentages) |
|
||||||
Aircraft weight |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 – 12 tons |
|
29.32 |
|
17.39 |
|
9.99 |
|
9.99 |
|
Minimum fee |
|
184.89 |
|
92.38 |
|
39.57 |
|
39.57 |
|
12 – 30 tons |
|
6.27 |
|
3.73 |
|
2.24 |
|
2.24 |
|
31 – 80 tons |
|
7.16 |
|
4.48 |
|
2.62 |
|
2.62 |
|
81 – 170 tons |
|
8.81 |
|
5.37 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
> 170 tons |
|
9.76 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
Minimum fee |
|
81.50 |
|
48.51 |
|
29.11 |
|
29.11 |
|
Surcharge for operation out of the normal timetable |
|
352.82 |
|
255.12 |
|
162.84 |
|
162.84 |
|
Surcharge for night airfield lightning |
|
30 |
% |
30 |
% |
30 |
% |
30 |
% |
74
Domestic Flights
|
|
Airport Category |
|
||||||
|
|
I |
|
II |
|
III |
|
IV |
|
|
|
(AR$ per ton, except percentages) |
|
||||||
Aircraft weight |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 – 12 tons |
|
20.37 |
|
15.18 |
|
8.82 |
|
4.54 |
|
Minimum fee |
|
142.73 |
|
108.34 |
|
62.15 |
|
31.53 |
|
12 – 30 tons |
|
1.05 |
|
0.67 |
|
0.43 |
|
0.26 |
|
31 – 80 tons |
|
1.14 |
|
0.76 |
|
0.52 |
|
— |
|
81 – 170 tons |
|
1.26 |
|
0.88 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
> 170 tons |
|
1.47 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
Minimum fee |
|
13.65 |
|
8.71 |
|
5.59 |
|
3.38 |
|
Surcharge for operation out of the normal timetable |
|
260.00 |
|
188.00 |
|
120.00 |
|
68.00 |
|
Surcharge for night airfield lightning |
|
30 |
% |
50 |
% |
30 |
% |
30 |
% |
Per ton aircraft fees are charged for international and domestic flights to all commercial and private aircraft, with the exception of aircrafts that weigh less than two tons. Aircraft weighing between two and twelve tons pay the minimum fee set forth in the table above. A rush-hour landing surcharge, equal to 50% of the landing fee applicable to such aircraft, is charged to all domestic and international flights that land at Aeroparque between 6:00 a.m. and 10:00 am, and between 6:30 p.m. and 9:30 p.m., daily.
Parking Fees
The table below sets forth the maximum amounts that, effective as of January 1, 2020, we may collect from aircraft operators, by airport category, under the AA2000 Concession Agreement with respect to international and domestic aircraft parking fees.
International Flights
|
|
Airport Category |
||||||||
|
|
Ezeiza/ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeroparque |
|
I |
|
II |
|
III |
|
IV |
|
|
(U.S.$ per ton per hour or fraction) |
||||||||
Aircraft weight (tons) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 – 12 tons |
|
3.84 |
|
1.92 |
|
1.43 |
|
1.12 |
|
1.12 |
Minimum fee |
|
55.46 |
|
36.99 |
|
13.18 |
|
13.18 |
|
13.18 |
12 – 80 tons |
|
0.34 |
|
0.17 |
|
0.13 |
|
0.10 |
|
0.10 |
81 – 170 tons |
|
0.48 |
|
0.20 |
|
0.14 |
|
0.11 |
|
— |
> 170 tons |
|
0.98 |
|
0.22 |
|
0.14 |
|
— |
|
— |
Minimum fee |
|
7.33 |
|
4.89 |
|
2.44 |
|
2.44 |
|
2.44 |
Domestic Flights
|
|
Airport Category |
||||||||
|
|
Ezeiza/ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeroparque |
|
I |
|
II |
|
III |
|
IV |
|
|
(AR$ per ton per hour or fraction) |
||||||||
Aircraft weight (tons) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 – 12 tons |
|
4.45 |
|
2.65 |
|
2.1 |
|
1.6 |
|
1.05 |
Minimum fee |
|
124.44 |
|
81.9 |
|
51.9 |
|
37.8 |
|
23.64 |
12 – 80 tons |
|
0.85 |
|
0.50 |
|
0.40 |
|
0.30 |
|
0.20 |
81 – 170 tons |
|
1.15 |
|
0.65 |
|
0.50 |
|
0.40 |
|
— |
> 170 tons |
|
1.50 |
|
0.85 |
|
0.60 |
|
— |
|
— |
Minimum fee |
|
39.5 |
|
26.00 |
|
16.50 |
|
12.00 |
|
7.50 |
75
Aircraft parking fees for international flights are charged to all commercial and private aircrafts, with the exception of aircrafts that weigh less than five tons. Aircraft parking fees for domestic flights are charged to all commercial and private aircraft, with the exception of aircraft that weigh less than five tons. Aircrafts that weigh less than five tons pay the minimum fee set forth above, only when parking time is greater than 15 days within a one-month period. Aircraft parking fees for international and domestic flights for Ezeiza Airport and Aeroparque Airport are charged to aircrafts parked in an operative apron; aircraft parking fees for international and domestic flights for aircraft parked in a remote apron are charged the fees corresponding to Category I. Free parking time is not applicable, irrespective of whether the flight is international or domestic, or commercial (whether in regular flight or not) or private.
Commercial Revenue
Fees for commercial services may be freely established by us. However, all terms of agreements with third parties for the provision of commercial services must be notified to the ORSNA. If the ORSNA objects to the terms of an agreement, it may request that the agreement be terminated. Either we or the third party may challenge such request in an administrative proceeding to be decided by the ORSNA, which is subject to further administrative proceedings and judicial review.
Termination by the Argentine Government upon breach by AA2000
The Argentine Government may terminate the AA2000 Concession Agreement upon the existence of the following conditions:
| ● | if we repeatedly breach, as determined by the ORSNA, any of our obligations under the AA2000 Concession Agreement (including our obligations under the Technical Conditions of the Extension) and the breach is not cured within the time period specified by the ORSNA in its notice of the breach; |
| ● | if the cumulative amount of fines (affirmed by final administrative ruling) imposed on us exceeds 20% of our annual gross revenue, net of taxes and charges, as calculated by the ORSNA at the end of each fiscal year; |
| ● | if any of our shareholders encumber or allow to be encumbered in any manner AA2000’s shares without the ORSNA’s consent, and do not secure the discharge of the encumbrance within a time period specified by the ORSNA; |
| ● | if we fail to pay the Specific Allocation of Revenue in due manner and time; |
| ● | if AA2000’s shareholders approve, without the ORSNA’s consent, an amendment to our bylaws or a stock issuance that alters or permits alterations of the shareholdings existing at the time of incorporation, on the terms established under the AA2000 Concession Agreement; or |
| ● | if our shares are transferred and no technical expert remains a shareholder without the prior approval from the ORSNA. |
If the Argentine Government elects to terminate the AA2000 Concession Agreement (even due to our breach), it is required to pay us the value of the aeronautical investments we have made that have not been amortized as of the time the termination is ordered, after deducting the following percentages as compensation for damages incurred:
| ● | 50.0% during the first 10 years of the AA2000 Concession Agreement; |
| ● | 45.0% during the second 10-year period of the AA2000 Concession Agreement; and |
| ● | 40.0% during the third 10-year period of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. |
Aeronautical investments include those investments that are contemplated under the AA2000 Concession Agreement or that are specifically authorized by the ORSNA as aeronautical investments within our airports’ premises, but do not include investments not originally contemplated under the investment plan that are not expressly authorized by the ORSNA. In the event that the Argentine Government elects to terminate the AA2000 Concession Agreement for one of the reasons stated above, the Argentine Government and the ORSNA may also foreclose on and collect the full amount of the performance guarantees.
Termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement would constitute a default under the Argentine Notes Series 2017, the Argentine Notes 2020, the Argentine Notes Series 2021, the New Money 2021 Notes, the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan and the ICBC Dubai Loan.
76
Buy-out of the AA2000 Concession Agreement
Under Argentine public law, the Argentine Government has the right to buy out or otherwise terminate concessions, including the AA2000 Concession Agreement, at any time if such buy out or termination is made in the public interest. If the Argentine Government elects to buy out the AA2000 Concession Agreement, it is required to indemnify us in an amount equal to the value of the aeronautical investments we have made that have not been amortized as of the time of the buy-out, multiplied by 1.10 plus the value of all other investments made that have not been amortized. The Argentine Government will not indemnify us for investments not foreseen in our investment plan, investments that have not been authorized by the ORSNA or for lost revenue. In addition, the Argentine Government must assume in full any debts incurred by us to acquire goods or services for purposes of providing airport services, except for debts incurred in connection with the investment plan (such as the issuance of the Argentine Notes, the Argentine Additional Notes and the Argentine 2021 Notes) for which we would be compensated as part of the indemnification to us by the Argentine Government. However, in accordance with section 30.4 of the Final Memorandum of Agreement, while a collateral assignment of revenue that is made into a trust remains in effect, we will have no right to indemnification for the investments secured by the relevant collateral assignment.
The buy-out of the AA2000 Concession Agreement by the Argentine Government would constitute a default under the Argentine Notes Series 2017, the Argentine Notes 2020, the Argentine Notes Series 2021, the New Money 2021 Notes, the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan and the ICBC Dubai Loan.
In addition, in case the Argentine Government decides to buy out the AA2000 Concession Agreement, it is our understanding that the economic equilibrium of the concession needs to be met since the beginning of the concession until the date of the termination.
Termination by AA2000 upon breach by the Argentine Government
We may demand termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement if the Argentine Government breaches its obligations in such a manner that prevents us from providing the services required of us under the AA2000 Concession Agreement or which permanently affects the same and if the Argentine Government does not remedy the situation giving rise to such breach within 90 days following notice from us.
Upon our termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we shall be entitled to the following damages from the Argentine Government:
| ● | if terminated during the first 10-year period of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the amount of our aeronautical investments that have not been amortized as of the time of the termination multiplied by 1.30; |
| ● | if terminated during the second 10-year period of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the amount of our aeronautical investments that have not been amortized as of the time of the termination multiplied by 1.20; and |
| ● | if terminated during the third 10-year period of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the amount of our aeronautical investments that have not been amortized as of the time of the termination multiplied by 1.10. |
Additionally, if the Argentine Government’s breach of the AA2000 Concession Agreement that gives rise to our termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement is caused by the negligence, fault or willful misconduct of the individuals acting on behalf of the Argentine Government, we shall have the right to demand compensation for all damages, with the exception of lost profits.
Termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement shall be deemed a default under the Argentine Notes Series 2017, the Argentine Notes Series 2020, the Argentine Notes Series 2021, the New Money 2021 Notes, the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan and the ICBC Dubai Loan.
End of Concession
Upon the termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we will be required to (i) turn over the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement to the Argentine Government and all property thereof, together with any improvements thereto, at no charge and in good condition, subject to normal wear and tear; (ii) undertake responsibility for payment of all of our debts, which cannot be transferred to the Argentine Government; and (iii) transfer to the Argentine Government or the new grantee of the concession the performance of all services in connection with the AA2000 Concession Agreement, including developments and technological breakthroughs and other services related to the performance of the services under the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
77
In addition, under the terms of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, no agreement entered into by us and in effect as of such date will be transferred to the Argentine Government upon the end of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. We are required to include provisions in any such agreements whereby the providers of goods or services undertake to continue with the performance of the relevant agreements for at least 180 days following the end of the AA2000 Concession Agreement. Such agreements shall also provide for the Argentine Government’s right to terminate the same.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, pursuant to section 30.4 of the Final Memorandum of Agreement, a collateral assignment of revenue that is made into a trust may remain in effect even upon an early termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, as long as the application of funds thereunder is audited by the Argentine Government and/or by a consulting firm, hired for such purpose and satisfactory to the Argentine Government. The collateral assignment of revenue must be previously authorized by a resolution of the ORSNA who is also responsible for auditing the application of the funds. On January 17, 2017 April 24, 2020, and October 15, 2021 the ORSNA issued Resolutions No. 1/2017, 21/2020, and No. 66/2021, respectively, pursuant to which it authorized the collateral assignment of revenue under the Tariff Trust. On August 8, 2019, August 18, 2020, March 16, 2021, June 17, 2021, and October 15, 2021, the ORSNA issued Resolutions Nos. 61/2019, 57/2020, 2/2021, 3/2021 y 66/2021, respectively, pursuant to which it authorized the collateral assignment of revenues and rights established by the Cargo Trust. Once the Argentine Notes Series 2017 and the Argentine Notes Series 2020 are cancelled in full, AA2000 will amend and restate the Cargo Trust and the Tariffs Trust, so that the Argentine Notes Series 2021 become secured by the Cargo Trust on a pro rata and pari passu basis with the existing beneficiaries of the Cargo Trust, and these other beneficiaries become secured by the Tariffs Trust on a pro rata pari passu basis with the Argentine Notes Series 2021. Pursuant to Resolution No. 66/2021 the ORSNA authorized the amendment and restatement of the Tariff Trust and the Cargo Trust. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement—Collateral Assignment of Revenue.”
Development Trust
On December 29, 2009, we, as trustor, and Banco Nación, as trustee, entered into the Development Trust, aimed at managing and allocating the funds to be transferred by us under the Specific Allocation of Revenue and the Allocated Revenues under the Mutual Claim Settlement Procedure. The Secretary of Transportation and the ORSNA also executed the Development Trust acknowledging and providing their consent with the terms and conditions therein.
Under the Development Trust, the following trust funds were established:
| ● | “Trust Fund to Study, Control and Regulate the Concession,” consisting of the assignment in trust of 1.25% of AA2000’s total revenues, which shall be designated to carry out studies on the control and regulation of the concession as required by the ORSNA. The trust was terminated in 2011; |
| ● | “Trust Fund for the Payment of the Unpaid Amounts Arising from Mutual Claims,” consisting of Allocated Revenues under the Mutual Claim Settlement Procedure, which shall be designated to pay the amount of AR$195.0 million plus interest at a 2% annual rate, owed to the Argentine Government according to the provisions set forth in the Final Memorandum of Agreement. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement—Withdrawal and Settlement of Claims.” In turn, such funds shall be used in connection with infrastructure projects at airports of the Argentine National Airport System not operated by us; |
| ● | “Trust Fund for Funding Infrastructure works of the Argentine National Airport System,” consisting of the assignment in trust of 11.25% of AA2000’s total revenues, 70.0% of which is to be contributed to finance infrastructure airport works and to improve the services provided in airports of the Argentine National Airport System and 30.0% of which is to be contributed directly to ANSES; |
| ● | “Trust Fund for Funding Infrastructure Works in airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement,” consisting of the assignment in trust of 2.5% of AA2000’s total revenues derived from services under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, which shall be designated to finance works included in each five-year investment plan; and |
78
| ● | “Trust Fund for Infrastructure Airport Works Derived from Potential Charges and Tariff Increases for Specific Allocations,” consisting of the assignment in trust of 100% of the amounts deriving from specific charges and tariff increases that may be set in the future, net of collection expenses, which shall be designated to finance airport infrastructure works as it shall be detailed in the regulations under which such specific tariff and charges are created. Pursuant to Resolutions No. 118/12, as amended, and 45/14, the ORSNA created two specific trust funds: (a) “Trust Fund for Works of 2012 Project” and (b) “Trust Fund for the Reinforcement of Significant Works in airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement.” In 2021, the Trust Fund for Works of 2012 Project ceased to exist and its funds were transferred to the “Trust Fund for the Reinforcement of Significant Works in airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement.” Under the “Trust Fund for the Reinforcement of Significant Works in airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement,” after giving effect to the Specific Allocation of Revenue detailed above, we needed to assign: 10.72% of the passenger use fees approved by the ORSNA for the 2011–2012 revision period, for the “Trust Fund for the Reinforcement of Significant Works in airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement” (which include works that were not previously specified in the AA2000 Concession Agreement, nor in the Final Memorandum of Agreement), until the expiration of the concession or the expiration of a 30-year period, whichever occurs first. By Resolution No. 83/2023 dated November 30, 2023, the ORSNA ordered the closure of the “Trust Account of the Trust Fund for the Reinforcement of Significant Works in Airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement” and established that (i) AA2000 must ensure the completion of ongoing construction works and those still pending that are incorporated in the financial commitments programmed under the “Trust Account of the Trust Fund for the Reinforcement of Significant Works in Airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement”; and (ii) the funds deposited in said account, as well as the funds owed to it by AA2000, shall be transferred to the “Trust Fund for Funding Infrastructure Works in airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement,” and shall be computed as additional direct investments to the amounts that AA2000 must transfer to the referred trust fund, added to the expenses planned as direct investment for the years 2024-2027. |
The term of the above-mentioned trust funds shall not exceed 30 years and shall be terminated if the concession is terminated for any cause, except for the “Trust Fund for Infrastructure Airport Works Derived from Potential Charges and Tariff Increases for Specific Allocations,” which shall have the duration set forth under the regulations pursuant to which such tariff and charges are created.
The ORSNA shall calculate the amounts that we shall transfer on a monthly basis to Banco Nación pursuant to the procedure for Specific Allocation of Revenues approved by ORSNA Resolution No. 64/2008, dated August 7, 2008. The amount calculated shall be communicated to us and to Banco Nación during the first 15 days of each month. We shall deposit the respective amounts during the following 48 business hours after being notified of the amount by the ORSNA. In the event of payment default, the amounts will accrue interest at a rate equal to one and a half times the discount rate for commercial transactions of Banco Nación in pesos.
The Development Trust sets forth that we are not obligated to make any additional capital contributions to the above-mentioned trust funds. In the event such trust funds are insufficient to meet their purpose due to a cause not related to us, the amounts required to fulfill the commitments undertaken shall be paid by the Argentine Government.
Contributions to the Development Trust
Pursuant to the Development Trust, the Specific Allocation of Revenue and the Allocated Revenues under the Mutual Claim Settlement Procedure retroactively accrued from January 1, 2006, through the execution date of the Development Trust would be transferred to the Development Trust pursuant to the conditions and methodologies to be set forth by the ORSNA, with the approval of the Secretary of Transportation.
79
The Development Trust provides that we may pay the amounts in cash payable to the Development Trust through the assignment of credits owed to us originated in aeronautical services and/or commercial services within the AA2000 Concession Agreement, subject to the ORSNA’s prior authorization. In light of this, in February 2021, AA2000 requested authorization to the ORSNA to implement the agreement reached with Aerolíneas Argentinas under which AA2000 will assign to the Development Trust the credit against Aerolíneas Argentinas and Austral Líneas Aéreas for the aggregate amount of AR$120 million and U.S.$36 million corresponding to the debt owed by these companies as of March 31, 2020 (the “Assignment of Aerolíneas Argentinas Credit”). On July 21, 2021, AA2000 sent the ORSNA a detailed allocation of the assigned credit to the different accounts of the Development Trust. The amounts assigned to the Development Trust will be allocated to cancel (i) the 2020 Specific Allocation of Revenue outstanding as of November 2020; and (ii) the amounts owed by AA2000 under the “Trust Fund for Works of 2012 Project” and the “Trust Fund for the Reinforcement of Significant Works in airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement.” On April 5, 2022, the former Ministry of Transportation (currently, the Secretary of Transportation) took the planned intervention. On June 14, 2022, the ORSNA notified AA2000 that the Ministry of Transportation had completed its intervention and approved the assignment in the terms described.
As of the date of this annual report, AA2000 has notified both, Aerolíneas Argentinas, as assigned debtor, and Banco de la Nación Argentina, as trustee under the Development Trust, about the assignment. Also, in 2022, AA2000 received a payment in cash from Aerolíneas Argentinas, for an amount of approximately U.S.$15 million, and additional payments in cash in 2023 for an aggregate amount of approximately U.S.$27.5 million, including both outstanding debt and current amounts.
Other Airports we Operate in Argentina
In addition to the airports operated under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, we also operate the Neuquén Airport and the Bahía Blanca Airport.
In 2001, the Government of the Province of Neuquén together with the ORSNA awarded to us the concession agreement to operate the Neuquén Airport for an initial term of 20 years, which was set to expire in 2021. By virtue of Decree No. 1820/2021, issued by the Executive Branch of the Province of Neuquén, the concession was extended for an additional term of five years, expected to terminate in 2026. In 2008, the Municipality of Bahia Blanca together with the ORSNA awarded to us the concession to operate the Bahía Blanca Airport for an initial term of 26 years, which is set to expire in 2033. Both concession agreements provide the possibility of extension upon approval. The Neuquén Airport and the Bahía Blanca Airport are not material to our business.
Italy
Headquartered in Florence, TA is the result of the merger of SAT, Galileo Galilei S.p.A. and ADF on June 1, 2015. As a result of the merger, CA Italy, which is 75% owned by CAAP, has a controlling stake of 62.28% of TA. We indirectly own 46.71% of TA’s issued and outstanding common stock Prior to the merger, SAT and ADF were granted concessions for the management of the Pisa Airport and the Florence Airport, respectively. After the merger, the concessions were transferred to TA. Set forth below is a description of their main terms and conditions, as well as of the relevant regulatory framework.
Sources of Regulation
Set forth below are the main laws and regulations that govern the concession agreements entered into by ENAC with SAT and ADF, as well as the operation and management of the airport operation and business:
| ● | Law No. 537/1993 and Decree Law No. 251/1995 (converted into law with modifications by Law No. 351/1995, as subsequently supplemented and amended) set forth the regulations that apply to the management of airports and the realization of the relative infrastructure. |
| ● | Legislative Decree No. 250/97, as subsequently supplemented and amended, which regulates the responsibilities of ENAC. |
| ● | In implementation of Law No. 537/1993, Ministerial Decree No. 521/1997 provided that the granting of full airport management under concession is conditioned upon the execution of a concession agreement. |
| ● | Regulation of the Ministry of Transportation and Navigation and the Ministry of the Interior No. 85/1999, implementing Decree Law No. 9/1992, converted with modifications by Law No. 217/1992, as subsequently supplemented and amended, sets forth provisions concerning the granting of concessions relating to security services. |
80
| ● | The Ministry of Transportation and Navigation (currently named “Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport”), in implementation of the abovementioned Ministerial Decree No. 521/1997, issued the Directive No. 141-T/2000 sets forth the guidelines for the granting of concessions, subsequently repealed and replaced by Ministerial Guidelines No. 8736/2003. |
On March 16, 2004, ENAC issued certain guidelines for procedures concerning the granting of concessions.
| ● | Law No. 265/2004 provided certain innovations to the applicable framework of rules concerning the granting of airport management concessions. |
| ● | Decree Law No. 203/2005, as subsequently supplemented and amended and converted into law by Law No. 248/2005, introduced certain provisions for the rationalization and improvement of the efficiency of the airport management sector. |
| ● | Decree Law No. 96/2005, as supplemented and amended, implemented the provisions set forth with Law No. 265/2004 and revised the aviation section of the Italian navigation code. |
| ● | Directive 96/67/EC on access to the ground handling market at European Union airports and the relative implementation of Legislative Decree No. 18/1999, as subsequently amended and supplemented. |
| ● | Article 71, paragraph 2, of Law Decree No. 1/2012, as subsequently supplemented and amended, established the Transport Regulation Authority (Autorità di Regolazione dei Trasporti) and granted it with the powers, inter alia, of supervision and financial regulation in relation to the airport operation and business. |
| ● | Article 71, paragraph 3, of Law Decree No. 1/2012, as subsequently supplemented and amended, established the criteria and models for the determination of the tariffs applicable in relation to the airport business and the relative approval process. |
| ● | Article 705 of Italian Navigation Code (Royal Decree No. 327/1942, as subsequently supplemented and amended) sets forth the rules concerning the determination of airport management and the relative responsibilities. |
| ● | Law No. 324/1976, as subsequently supplemented and amended, provided the regulations concerning the use of airports open to civil air traffic. |
| ● | Law No. 77, enacted on July 17, 2020, extended the term under the Italian Concessions Agreements for two additional years. |
Powers Reserved to the Italian Government with Respect to Strategic Transport Assets
Pursuant to current laws and regulations, (i) the approval of specific corporate resolutions by companies operating in the energy, transport, and communications sectors, which are understood to be of strategic importance to the nation, and (ii) the acquisition of significant shareholdings in such companies by investors, are subject to special “Golden Powers” of the Italian Government provided under Law Decree No. 21/2012. Article 2 of Law Decree No. 21/2012 specifically regulates the special powers of the Italian Government concerning the strategic assets of companies operating in the transport sector. In particular, Article 2 of Law Decree No. 21/2012 includes the following regulations for identifying:
| ● | strategic assets in the transport sector, such as ports and airports, including those necessary to ensure the minimum provision and operation of essential public services, the assets and relationships of strategic importance to the national interest in the transport sector; |
| ● | the types of acts or transactions within the same group of companies to which the Italian Government’s special powers do not apply; and |
| ● | the procedures for exercising the special powers in the transport sector. |
81
The “strategic assets” in the transport sector have been defined by Article 2 of Presidential Decree No. 85 of March 25, 2014 (the “Presidential Decree 85/2014”) as large networks and plants of national interest, intended to ensure the main trans-European corridors and the related conventional reports, including:
| ● | ports of national interest; |
| ● | airports of national interest; and |
| ● | national railroad networks of relevance for trans-European networks. |
Such regulations apply to TA by virtue of its being an entity that operates the Italian Airports of national interest located in Pisa and Florence. In particular, these provisions state that, in relation to companies that own one or more of these strategic assets, the Italian Government, having assessed the relevant transaction and identified a threat concerning said strategic assets, may:
| ● | impose specific conditions on, or (in case the specific conditions are not adequate to protect the essential national interests of defense and national security) veto any resolutions, acts and transactions by any company owning strategic assets that would determine a change in the ownership, control, availability or transferability of those assets themselves or change their use (including merger or demerger, transfer of the registered office to a foreign country, change of the relevant company’s business purpose, winding up, amendments to the company’s articles of association concerning the limits to the voting rights attaching to the company’s interest or the maximum shareholding which each shareholder may own, transfer of the entire business or of a business division which include the strategic assets, assignment of the strategic assets by way of security, and resolutions concerning the sale of subsidiaries which own strategic assets), where such resolutions, acts or transactions result in an exceptional situation not regulated by national or European laws applicable to the sector which constitute a threat of a serious prejudice to the interest of public safety and operation of the networks and installations, and the continued provision of services (Article 2, paragraph 3); |
| ● | impose conditions requiring certain buyers outside the European Union to give guarantees in any purchase and for any reason, (Article 2, paragraph 5), of shareholdings in an amount that would give the buyer control of the purchased company, pursuant to Article 2359 of the Italian Civil Code and the Consolidated Financial Services Act, if such a purchase poses a serious threat to public interest in the security and operation of networks and installations and the continued provision of services (Article 2, paragraph 6); and |
| ● | oppose the purchase described before, if such a purchase entails exceptional risks to the protection of public interest relating to the security and operation of networks and installations and continued provision of services, which cannot be mitigated by the buyer committing to guarantee the protection of such interests (Article 2, paragraph 6). |
To exercise these special powers, Article 2 of Law Decree No. 21/2012 provides that:
| ● | the operator has an obligation to disclose both any resolutions, acts and transactions that could be subject to the actions described before, and any purchases or transactions that could be subject to the actions described before; and |
| ● | the Italian Government shall abide by objective and non-discriminatory evaluation criteria in exercising its special powers. The Italian Government is required, in relation to any transaction, to consider the following: (i) in relation to the official position of the European Union, whether there is any reason to believe (a) that connections may exist between the buyer and other countries that do not recognize the principles of democracy or the rule of law, and which may not comply with international law, or that have acted in a way that poses as a threat to the international community, as evidenced by their alliances; or (b) that the buyer has relationships with criminal or terrorist organizations or with persons or entities otherwise related to them; (ii) the suitability of the structure resulting from the legal deed or transaction, considering conditions for financing the acquisition and the economic, financial, technical, and organizational capacity of the buyer to guarantee the security and continuity of provision of services, or provide adequate security and operation of the networks and installations. |
82
Without prejudice to the disclosure obligations set out in Article 2, paragraphs 2 and 5 of Law Decree No. 21/2012, Article 4 of Presidential Decree No. 85/2014 provides that:
| ● | the special powers apply to the extent that protection of the essential national interests, including those relating to adequate infrastructure development, is not guaranteed by the existence of specific sector regulation, either in the form of a convention connected with a specific concession relationship or otherwise; |
| ● | certain transactions are excluded from the scope of the special powers, including transactions carried out within the same corporate group, such as mergers, demergers, takeovers, or sales and transfers, including, in certain cases, the sale and transfer of shares; and |
| ● | such an exclusion is not available when there is information indicating a threat of serious harm to the public interest in the security and operation of the networks and installations and continued provision of services. |
The procedures for exercising such special powers in the transport sector have been established by Presidential Decree No. 86 of March 25, 2014 (the “Presidential Decree 86/2014”).
As discussed above, the Italian Government may exercise its veto power in relation to the adoption of shareholders’ meeting or management body meeting resolutions of companies that own strategic assets in the transport sector in the matters indicated in Article 2, paragraph 2, of Law Decree No. 21/2012. Accordingly, the company that owns these strategic assets must notify the Prime Minister’s Office (Presidenza del Consiglio dei Ministri) within ten days of the implementation of any such resolution and must provide the complete set of information concerning the resolution itself (Article 5, Presidential Decree 86/2014). The Prime Minister’s Office will announce any veto it may issue within 15 business days after being so notified. If additional information is requested by the Prime Minister’s Office, the deadline for giving notice of any veto is postponed once until such requested information is received. The Italian Government’s veto power may also be exercised by imposing specific requirements or conditions if such requirements and conditions are considered to be sufficient to ensure protection of the public interest in the security and operation of the networks and installations and continuous provision of services. If the deadline for announcing any veto expires without any order having been issued, the transaction is deemed approved and can be executed.
Resolutions or acts adopted in violation of the abovementioned veto power are null and void. The Prime Minister’s Office may also require the company and any counterparty to unwind any such transaction at its own expense. Unless the act constitutes a criminal offense, anyone who fails to comply with the measures associated with the exercise of the veto power is subject to monetary administrative fine up to twice the value of the transaction, and at any rate not less than 1% of the total revenues realized by the companies involved during the last financial year in which a financial statement has been approved.
The Italian Government has the power to impose conditions or oppose the acquisition of significant shareholdings attributing control of companies that own assets of strategic importance in the transport sector to a party outside the European Union pursuant to Article 2, paragraph 5, of Law Decree No. 21/2012. Accordingly, the person or entity outside the European Union that acquires a significant shareholding constituting control of a company that owns strategic assets in the transport sector (Article 4, paragraph 1, Presidential Decree 86/2014) must disclose such a purchase within ten days after the execution of any such transaction to the Prime Minister’s Office, together with all information providing a general description of the merger plan, the buyer, and the scope of its operations. The Prime Minister’s Office will notify the buyer of any conditions it deems necessary to impose or exercise its veto power within 15 business days after such disclosure. Until the expiry of this deadline, the voting rights and those rights other than ownership associated with the shares representing the significant shareholding are suspended.
If the Prime Minister’s Office exercises its power to impose conditions, in the event of breach or violation of such conditions, the voting rights or rights other than ownership of the shares which represent a significant shareholding are suspended for the entire period that the breach or violation continues. Any resolutions adopted with the deciding vote of such shares and the resolutions and acts adopted in violation or in breach of the imposed conditions, are null and void. A buyer that fails to comply with the imposed conditions, unless the act constitutes a criminal offense, is subject to a monetary administrative fine up to twice the value of the transaction and, in any event, no less than 1% of the total revenues realized in the last financial year for which a financial statement has been approved (Article 8, Presidential Decree 86/2014). If the power to oppose the acquisition of the shareholding is exercised, the buyer may not exercise its voting rights of such shares and must sell these shares within one year. If it fails to comply with this obligation, the courts, on request from the Prime Minister’s Office, will order the sale of these shares according to the procedures provided for in Article 2359 of the Italian Civil Code. Any shareholders’ meeting resolutions adopted with the deciding vote of such shares are null and void.
83
On October 2, 2014, the Prime Ministerial Decree (Decreto del Presidente del Consiglio dei Ministri) of August 6, 2014 was published in the Official Gazette of the Republic of Italy (General Series No. 229). It contains rules for the coordination of the activities of the Prime Minister’s Office necessary to exercise the special powers over company ownership structures in the defense and national security sectors, and over strategic activities in the energy, transport, and telecommunication sectors. These rules specify the Department of the Prime Minister’s Office to which these notifications must be sent, as well as the relevant procedures, and also provide a simplified procedure in the case of intercompany transactions.
Governmental Authorities
Transport Regulatory Authority (Autorità di Regolazione dei Trasporti)
The Transport Regulatory Authority (“TRA”) was established pursuant to Article 37 of Decree-Law No. 6 December 2011, No. 201 (converted into law, with modifications, by Law No 214 of December 22, 2011).
It is responsible for regulation in the transport sector and access to its infrastructure and ancillary services. Among its tasks are also the definition of the quality levels of transport services and the minimum content of the rights that users can claim against the operators.
In the airport sector, the TRA undertakes supervisory duties (Article 71 et seq., Decree-Law No. 1/2012), approving the airport regulatory system and the amount of airport charges.
ENAC
ENAC was established on July 25, 1997, under Legislative Decree No. 250/97 as the national authority committed to oversee the technical regulation, oversight and control of civil aviation.
ENAC is responsible for many aspects of the civil aviation regulation including the control and vigilance of the application of the regulatory regimes, and the regulation of the administrative and economic aspects of the air transport system.
Other aspects of the aviation sector that fall within the institutional mandate of ENAC include safety, security control and enforcement of international law, and guaranteeing the quality of the services provided to the user and the protection of the rights of the passenger.
The Pisa Concession Agreement
With the Inter-managerial Decree (decreto interdirigenziale) No. 002/2004, the Pisa Airport was assigned to ENAC. After a temporary concession which started in 2001, the current concession for Pisa Airport (“Pisa Concession”) was approved on December 7, 2006, with the Inter-Ministerial Decree issued by the Ministry of Transportation, the Ministry of the Economy and the Ministry of Defense.
On October 9, 2015, ENAC and TA entered into an operating agreement (contratto di programma) in order to define TA’s obligations with respect to (i) airport traffic level forecasts, (ii) new construction and extraordinary maintenance works, (iii) the quality levels with respect to environmental protection, (iv) the status of TA’s performance of the obligations arising under the relevant operating agreement for TA’s four-year intervention plan, as well as its quality and environmental protection plan and (v) the fines that would apply to TA in the case of delay in carrying out its obligations arising under the operating agreement, or failure to fulfill such obligations.
Obligations Assumed by TA as Concessionaire
Under the terms of the Pisa Concession Agreement, TA is responsible for developing, managing, exploiting, operating and maintaining Pisa Airport, which includes, inter alia, the performance of the following obligations and activities:
| ● | paying the annual concession fee; |
| ● | performing the works provided by the plan of works (programma d’intervento) and the ordinary and extraordinary maintenance works; |
84
| ● | entering into an operating agreement (contratto di programma) with ENAC; |
| ● | adopting all appropriate measures in favor of the neighboring territorial communities and their security; |
| ● | organizing and managing the airport business, ensuring the optimal use of available resources for the purpose of providing an adequate level of services and activities, to be carried out in compliance with the principles of security, efficiency, cost effectiveness and environmental protection; |
| ● | providing its services under conditions of continuity and regularity, in compliance with the impartiality principle and in accordance with the applicable non-discrimination rules; |
| ● | obtaining prior authorization from ENAC to appoint subconcessionaires to carry out airport activities and to give prior written communication to ENAC of the subconcession of other activities (e.g., commercial activities), in any case ensuring that the relative third-party subconcessionaires obtain insurance policies to cover the risks related to their respective activities; |
| ● | providing all of the necessary support for the relevant public administrations to carry out their emergency and health services within the context of the airport business and management; |
| ● | adopting all necessary measures to ensure the provision of the fire-fighting service; |
| ● | ensuring the carrying out of airport security control services; |
| ● | complying with the relevant obligations provided under the applicable framework and periodically communicating data on the quality of offered services to ENAC; |
| ● | preparing and presenting to ENAC a report on the implementation status of the operations program and related investment plan; and |
| ● | guaranteeing the suitability of the standards of offered services. |
85
Fees
The table below sets forth the maximum amounts that we were permitted to collect as of January 2023, under the Pisa Concession:
|
|
2023 (1) |
|
|
|
(in Euros) |
|
Takeoff/Landing |
|
|
|
Landing and take offs (< 25 t) |
|
2.34 |
|
Landing and take offs (> 25 t (each subsequent ton)) |
|
3.23 |
|
Parking (per hour or fraction besides the first two hours) |
|
0.27 |
|
Cargo embarking/ Disembarking |
|
0.0238 |
|
Check-in desks |
|
1.45 |
|
Assets for exclusive use/offices |
|
66.35 |
|
Fueling |
|
0.0057 |
|
Passengers charges (EU adult) |
|
5.98 |
|
Passengers charges (EU child) |
|
2.99 |
|
Passengers charges (EXTRA EU, adult) |
|
6.86 |
|
Passengers charges (EXTRA EU, child) |
|
3.43 |
|
Body Check & Hand Baggage Security |
|
2.25 |
|
Hold Baggage Security |
|
0.73 |
|
Deicing |
|
0.13 |
|
Loading bridge (till 1 hour) |
|
85.88 |
|
Loading bridge (after the 1st hour) |
|
171.76 |
|
Assets for exclusive use-offices |
|
199.06 |
|
Assets for exclusive use – technical operating room |
|
66.35 |
|
Assets for exclusive use – airside areas |
|
19.91 |
|
PRM |
|
1.09 |
(2) |
(1) |
These tariffs were approved by the Italian Regulatory Transport Authority through regulation No. 26839/22 dated December 22, 2022. |
(2) |
Effective as of February 1, 2021. |
Concession Fees
As consideration for the airport concession granted by ENAC, TA is required to pay annual fees to be determined by the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport pursuant to Law No. 662/1996.
Canon payments are to be made in two separate installments, the first one to be made each July 31 and the second one each January 31 of each year during the concession agreement. The following year, each payment shall be equivalent to 50% of the annual canon payments. The value of the minimum canon is adjusted on an annual basis according to inflation. For the year ended December 31, 2023, TA paid an annual canon equal to €3.9 million under the Pisa Airport Concession Agreement.
The fees are established by Inter-managerial Decree (decreto interdirigenziale) dated June 30, 2003, which provides the adoption of a workload unit criterion, where each unit corresponds to one passenger or 100 kg of goods or post.
Revenue
Under the terms of the Pisa Concession Agreement, TA is entitled to collect, inter alia:
| ● | the aeronautical, commercial and cargo revenue related to services rendered at Pisa Airport; |
| ● | the embarkation and debarkation charges on transported goods; and |
| ● | the fees for security control services. |
86
Investment Plan
Under the terms of our Pisa Concession Agreement, TA is required to present a long-term master plan for each individual airport. The master plan projections (including traffic, operating expenses, investment commitments, etc.) are used by ENAC to determine airport tariffs and are revised every four years. Once approved by ENAC, the investment commitments in the master plan become binding obligations under the terms of the respective concession. On October 24, 2017, ENAC approved and signed our 2015-2028 master plan for Pisa Airport.
Guarantees
Under the Pisa Concession Agreement and for the purpose of securing its performance obligations, TA is required to provide a bank guarantee (fideiussione bancaria) and/or insurance policy for an amount equal to a yearly concession fee (to be updated on the basis of the yearly recalculations of the concession fee). TA currently has an aggregate of €2.8 million in guarantees outstanding for both the Pisa Concession and the Florence Concession.
On the expiration, revocation or termination of the Pisa Concession Agreement, ENAC shall authorize TA to release the security following an assessment concerning the fulfilment of TA’s obligations and ascertaining that no legal proceedings are in place due to actions or omissions attributable to TA.
ENAC may proceed, without prior formal notice or filing before the courts, to withdraw the amount of the security should TA fail to pay a yearly concession fee. ENAC may also enforce such guarantee in payment of damages incurred as a result of TA’s actions.
Insurance
Under the Pisa Concession Agreement, TA shall obtain an insurance policy, for an amount to be determined in agreement with ENAC, in order to cover a series of risks related to the assets used either directly or indirectly in the airport management business (e.g., fires, aircraft crashes, damages due to transported goods, machinery or natural events). The relevant policy must provide that ENAC shall be named as a loss payee under such policy, and only upon prior authorization from ENAC may the relevant payment be made to TA (in this case, TA being responsible for the reparation of the relevant damages).
Furthermore, TA is also required to obtain an insurance policy to cover the risks connected to the performance of its business and damages that may be incurred by public administrations and entities and/or third parties present in the Pisa Airport.
In order to comply with regulatory and/or security requirements, ENAC may give directions to TA concerning the insurance policy to be obtained, including the extension of the covered risks.
Termination, Revocation and Forfeiture
The Pisa Concession Agreement will expire on December 7, 2048.
Termination upon Breach by TA
If ENAC determines that TA is in breach of the relevant provisions of the Italian Navigation Code or of the Pisa Concession Agreement, TA shall be liable for the payment of a penalty equal to 20% of the annual concession fee (in any case, not less than €50,000). If TA repeats a breach of the same nature within a period of two years, the relative penalty shall be equal to 40.0% of the annual concession fee (in any case, not less than €100,000). In the instance of multiple violations within the period of two years, the penalty shall be equal to 70.0% of the annual concession fee (in any case, to a sum not less than €170,000). The abovementioned penalty shall also be applied should TA fail to deliver the required plans and programs or not achieve the relevant quality objectives within the provided deadlines.
If TA breaches any of the relevant provisions concerning security, the penalty shall be equal to 30% of the annual concession fee (in any case, not less than €75,000 and if a violation of the same nature be repeated within a period of two years, 60.0% of the annual concession fee (in any case, not less than €150,000).
87
Revocation and Forfeiture
The Pisa Concession Agreement provides that, in the event needs of public interest arise, TA may request that the Pisa Concession be revoked, at which time TA will assume the burden of making all compensatory payments to be determined with the relevant third parties and after consulting ENAC.
The concession granted may be forfeited before its expiration date upon the occurrence of specified events of default, as provided under the Pisa Concession, including: (i) prevailing reasons of public interest; (ii) serious and repeated violations of the Italian navigation code or the Pisa Concession Agreement; (iii) a breach of the security regulations or the loss of requirements for certification as provided under the relevant ENAC regulations for the construction and operation of airports; (iv) a failure to implement the operations program and investment plan; (v) events that indicate that TA is no longer capable of operating the Pisa Airport; (vi) over 12 month delays in payment of the applicable concession fee; or (vii) a TA bankruptcy.
If the Pisa Concession is revoked before its expiration, whether through a forfeiture or termination due to an event of default, ENAC shall regain the rights over the assets which were assigned to TA.
For the projects which it has financed, TA shall have the right to an indemnity which shall not exceed the value of the relevant project at the moment of revocation minus any amortizations. In any case, TA shall be liable for any damages that derive from its actions or omissions and, in the event of forfeiture of the Pisa Concession, TA shall have no right to reimbursement for the completed works or for the costs it may have incurred.
Governing Law
The Pisa Concession Agreement is governed by the laws of Italy.
Dispute Resolution
Under the Pisa Concession Agreement, ENAC and TA may elect to have a dispute concerning the Pisa Concession Agreement be decided by an arbitration panel, without prejudice to their right to file their claims before the competent courts. The arbitration panel shall be composed of three members, of which TA and ENAC may appoint one each and the chairman being appointed by the two selected by TA and ENAC. Should the two arbiters fail to reach an agreement on the appointment of the chairman of the panel, the relative appointment shall be made by the chairman of the Italian State Council (Consiglio di Stato). ENAC has no liability in the disputes between or among TA, subconcessionaires and third parties that arise in relation to the Pisa Concession Agreement.
The Florence Concession Agreement
After a temporary three-year concession which started in 2001, the concession for the Florence Airport was approved on March 11, 2003, with the Inter-Ministerial Decree issued by the Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport and the Ministry of the Economy and Finance (the “Florence Concession Agreement” and jointly with the Pisa Concession Agreement, the “Italian Concession Agreements”).
In order to meet the urgent need to implement the relevant legal framework, the abovementioned Inter-Ministerial Decree provided the extension of the duration of the Florence Concession Agreement to 40 years.
On October 9, 2015, ENAC and TA entered into an operating agreement (contratto di programma) in order to define TA’s obligations with respect to (i) airport traffic level forecasts; (ii) new construction and extraordinary maintenance works; (iii) the quality levels with respect to environmental protection; (iv) the status of TA’s performance of the obligations arising under the relevant operating agreement for TA’s four-year intervention plan, as well as its quality and environmental protection plan; and (v) the fines that would apply to TA in the case of delay in carrying out its obligations arising under the operating agreement, or failure to fulfill such obligations.
Obligations Assumed by TA as Concessionaire
Under the terms of the Florence Concession Agreement, TA is responsible for developing, managing, exploiting, operating and maintaining the Florence Airport, which includes the performance of the following obligations and activities:
| ● | paying the annual concession fee; |
88
| ● | performing the works provided by the plan of works (programma d’intervento) and the ordinary and extraordinary maintenance works; |
| ● | entering into an operating agreement (contratto di programma) with ENAC; |
| ● | adopting all appropriate measures in favor of the neighboring territorial communities and their security; |
| ● | organizing and managing the airport business, ensuring the optimal use of available resources for the purpose of providing an adequate level of services and activities, to be carried out in compliance with the principles of security, efficiency, cost effectiveness and environmental protection; |
| ● | providing its services under conditions of continuity and regularity, in compliance with the impartiality principle and in accordance with the applicable non-discrimination rules; |
| ● | obtaining prior authorization from ENAC to appoint subconcessionaires to carry out airport activities and to give prior written communication to ENAC of the subconcession of other activities (e.g., commercial activities), in any case ensuring that the relative third-party subconcessionaires obtain insurance policies to cover the risks related to their respective activities; |
| ● | providing all of the necessary support for the relevant public administrations to carry out their emergency and health services within the context of the airport business and management; |
| ● | adopting all necessary measures to ensure the provision of the fire-fighting service; |
| ● | ensuring the carrying out of airport security control services; |
| ● | complying with the relevant obligations provided under the applicable framework and periodically communicating data on the quality of offered services to ENAC; |
| ● | preparing and presenting to ENAC a report on the implementation status of the operations program and related investment plan; and |
| ● | guaranteeing the suitability of the standards of offered services. |
89
Fees
The table below sets forth the maximum amounts that we were permitted to collect as of January 1, 2023, under the Florence Concession Agreement:
|
|
2023 |
|
|
|
(in Euros) |
|
Landing and takeoff fees (from 1 ton to 25 ton) |
|
4.81 |
|
Landing and takeoff fees (each subsequent ton) |
|
6.45 |
|
Aircraft parking (per hour or fraction after first two hours) |
|
0.22 |
|
Passengers charges (EU adult) |
|
11.07 |
|
Passengers charges (EXTRA EU adult) |
|
13.40 |
|
Passengers charges (intra EU flights, child) |
|
5.54 |
|
Passengers charges (EXTRA EU, child) |
|
6.70 |
|
Cargo embarking/disembarking charges |
|
0.246 |
|
Body check and hand baggage security |
|
1.73 |
|
Hold baggage security |
|
0.99 |
|
PRM |
|
1.56 |
(2) |
Assets for exclusive use – offices |
|
267.42 |
|
Assets for exclusive use -technical operating room |
|
53.48 |
|
Assets for exclusive use – air side areas |
|
21.39 |
|
Assets for exclusive use – offices fueler |
|
258.50 |
|
Assets for exclusive use - Technical operating room fueler |
|
51.70 |
|
Assets for exclusive use – fueler air side areas |
|
19.61 |
|
Assets for exclusive use – self check-in |
|
356.55 |
|
Check-in desks |
|
3.06 |
|
Deicing |
|
— |
(1) (3) |
| (1) | These tariffs were approved by the Italian Regulatory Transport Authority through regulation No. 26843/22 dated December 22, 2022. |
| (2) | Effective as of February 12, 2023. |
| (3) | Will be invoiced based on actual consumption. No fixed fee. |
Concession Fees
As consideration for the airport concession granted by ENAC, TA is required to pay annual fees to be determined pursuant to Law No. 662/1996, which provides that the relevant fees shall be the subject of the joint determination of the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport. The fees are established by Inter-managerial Decree (decreto interdirigenziale) dated June 30, 2003, which provides the adoption of a workload unit criterion where each unit corresponds to one passenger or 100 kg of goods or post.
Canon payments are to be made in two separate installments, the first one to be made each July 31 and the second one each January 31 of each year during the concession agreement. The following year, each payment shall be equivalent to 50% of the annual canon payments. The value of the minimum canon is adjusted on an annual basis according to inflation. For the year ended December 31, 2023, TA paid €1.8 million in annual canon under the Florence Concession Agreement.
Revenue
Under the terms of the Florence Concession Agreement, TA is entitled to collect, inter alia:
| ● | the aeronautical, commercial and cargo revenue related to services rendered at Florence Airport; |
| ● | the embarkation and debarkation charges on transported goods; and |
| ● | the fees for security control services. |
90
Investment Plan
Under the terms of our Florence Concession Agreement, TA is required to present a long-term master plan for each individual airport. The master plan projections (including traffic, operating expenses, investment commitments, etc.) are used by ENAC to determine airport tariffs, and are revised every four years. Once approved by ENAC, the investment commitments in the master plan become binding obligations under the terms of the respective concession.
The initial investment plan for the Florence Airport covered years 2014-2029. Following the COVID-19 pandemic, TA prepared a project review of the previous master plan, and a proposal for the 2035 TA Master Plan was defined. In October 2022, TA initiated a public debate process as required by statute. This process was completed on February 2023, and on April 2023, TA submitted to ENAC the new 2035 Florence airport master plan. It received the technical approval by ENAC on May 2023, and at the beginning of June 2023, ENAC required the Ministry of Environment to start the new EIA – ESA procedure (a new integrated environmental procedure introduced by the law on 2020). The scoping-phase of the EIA – ESA procedure was concluded in December 2023. The next integrated assessment-phase will be carried out during 2024 and completion of such process is expected by the end of the summer 2024. Once finished the above environmental procedure at the Ministry of the Environment, ENAC will ask the Ministry of Infrastructure to start the authorization process for the assessment of urban planning compliance. The procedure will be carried out in autumn 2024 and will be concluded by the end of November 2024.
Guarantees
Under the Florence Concession Agreement and to secure its performance obligations thereunder, TA is required to provide a bank guarantee (fideiussione bancaria) and/or insurance policy for an amount equal to a yearly concession fee (to be updated on the basis of the yearly recalculations of the concession fee). TA currently has an aggregate of €2.8 million in guarantees outstanding for both the Pisa Concession and the Florence Concession. On the expiration, revocation or termination of the Florence Concession Agreement, ENAC shall authorize TA to release the security following a determination that TA has fulfilled its obligations thereunder and a determination that no legal proceedings are in place due to actions or omissions attributable to TA.
ENAC may proceed, without prior formal notice or filing before the courts, to withdraw the amount of the security should TA fail to pay a yearly concession fee. ENAC may also enforce such guarantee in payment of damages incurred as a result of TA’s actions.
Insurance
Under the Florence Concession Agreement, TA shall obtain an insurance policy, for an amount to be determined in agreement with ENAC, in order to cover a series of risks related to the assets used either directly or indirectly in the airport management business (e.g., fires, aircraft crashes, damages due to transported goods, machinery or natural events). The relevant policy must provide that ENAC shall be named as a loss payee under such policy, and only upon prior authorization from ENAC may the relevant payment be made to TA (in this case, TA being responsible for the reparation of the relevant damages).
Furthermore, TA is also required to obtain an insurance policy to cover the risks connected to the carrying out of its business and damages that may be incurred by public administrations and entities and/or third parties present in the Florence Airport.
Termination, Revocation and Forfeiture
The Florence Concession Agreement will expire on February 10, 2045.
Revocation and Forfeiture
Pursuant to Article 2 of the Florence Concession Agreement, as necessary for public interest, TA may revoke the Florence Concession Agreement, at which time TA will assume the burden of making all compensatory payments to be determined with the relevant third parties and after consultation with ENAC.
91
The concession granted may be revoked before its expiration date upon the occurrence of specific events of default, and the Florence Concession Agreement shall be forfeited by TA (and ENAC shall proceed to appoint an officer for the management of the airport) upon the occurrence of the following: (i) the instances provided under the Italian Navigation Code; (ii) serious and breach of the security regulations; (iii) a failure to implement the operations program and investment plan; and (iv) events that indicate that TA is no longer capable of operating the Florence Airport. Furthermore, the Florence Concession Agreement may be automatically forfeited should TA fail to pay the relevant concession fee for a period exceeding 12 months from the provided due date or in the instance of TA being declared bankrupt.
In the instance of forfeiture, ENAC shall regain the rights over the assets which were assigned to TA and shall appoint an officer for the management of the airport. Moreover, TA shall have no right to reimbursement neither for the carried out works nor for the costs it may have incurred in the event of forfeiture.
Should ENAC not determine that a declaration of forfeiture is necessary, the same authority may provide a fine in relation to TA for the payment of a sum equal to a maximum of 50% of the concession fee, plus the payment of security and control costs.
Governing Law
The Florence Concession Agreement is governed by the laws of Italy.
Dispute Resolution
Under the Florence Concession Agreement, ENAC and TA may elect to have a dispute concerning the Florence Concession Agreement be decided by an arbitration panel, without prejudice to their right to file their claims before the competent courts. The arbitration panel shall be composed of three members, of which TA and ENAC may appoint one each and the chairman being appointed by the two selected by TA and ENAC. Should the two arbiters fail to reach an agreement on the appointment of the chairman of the panel, the relative appointment shall be made by the chairman of the Italian State Council (Consiglio di Stato).
ENAC has no liability in the disputes between TA, sub - concessionaires and third parties that arise in relation to the Florence Concession Agreement.
Brazil
Sources of Regulation
The Brazilian Federal Constitution provides that the Brazilian Government shall, directly or by concessions, authorizations or permissions, explore air and space navigation and all airports’ infrastructures.
In 1997, Federal Law No. 9,491/1997 was enacted and created the National Privatization Program (Programa Nacional de Desestatização) which established the framework for privatizations in Brazil. Since the enactment of the National Privatization Program, the Brazilian privatization process has undergone constant change as economic and political realities shifted.
Starting in 2010, upon the enactment of Presidential Decrees Nos. 7,205/2010, 7,531/2011, 7,896/2013 and 8,517/2015, the following airports were included in the National Privatization Program and began to be operated by third parties under concession agreements: Natal–Aluízio Alves; São Paulo–Guarulhos; Campinas–Viracopos; Brasilia–Juscelino Kubitschek; Rio de Janeiro–Galeão; Cofins–Tancredo Neves; Porto Alegre–Salgado Filho; Salvador–Luís Eduardo Magalhães; Florianópolis–Hercílio Luz; and Fortaleza–Pinto Martíns.
Although currently Infraero has responsibility to manage, directly or through concession agreements with third parties, a substantial portion of the Brazilian medium and large airport infrastructure, Brazilian laws provide that the Brazilian ANAC has responsibility for creating a standard model for concessions for airport infrastructure and authority to enter into the relevant concession agreements. The Brazilian ANAC was established in 2005 pursuant to Federal Law No. 11,182/2005 that integrates the Federal Public Administration, and since 2016, the Ministry of Transport, Ports and Civil Aviation has been responsible for the regulation and inspection of the civil aviation in Brazil. Notwithstanding the recent privatization of airports in Brazil, the privatization and concession models vary considerably and no definitive privatization standard for airport concessions has been defined by the relevant governmental authorities.
92
Recent developments
Certain recent rules have changed the regulation of the airport industry and may be applied to the concessions if requested by the relevant concessionaire.
| ● | On March 29, 2017, Directive No. 135 of the Ministry of Transport, Ports and Civil Aviation was enacted and established the terms and conditions in connection with the re-profiling of the fixed grant (concession fee) payments related to the concession agreements that have been executed prior to December 31, 2016. |
| ● | On April 7, 2017, Directive No. 143 of the Ministry of Transport, Ports and Civil Aviation was enacted and established the possibility of commercial agreements being executed with a term of effectiveness that exceeds the term of the concessions. |
| ● | On May 19, 2017, in order to further the implementation of Directive No. 135, Provisional Executive Order No. 779/2017 was published and provided for the conditions for amendments to the concession agreements executed prior to December 31, 2016, in connection with the re-profiling of the fixed grant (concession fee) payments related to the concession agreements. This Provisional Executive Order is still pending approval by the Brazilian Congress. |
| ● | On October 26, 2017, Federal Law No. 13,449 was published and established the conditions for amendments to the concession agreements executed prior to December 31, 2016, in connection with the re-profiling of the fixed grant (concession fee) payments. |
| ● | On June 25, 2017, Federal Law No. 13,448/2017 was published and brought new alternative solutions for ongoing concessions. Among such solutions is the re-tendering of concession projects, including public private partnerships (“PPPs”). Additionally, such Federal Law sets forth that Brazilian Concession Agreements between the Brazilian Government and concessionaires may be formally amended to contain an arbitration clause permitting resolution of specific claims permitted by law through arbitration. The relevant concessionaire will be required to deposit in advance the costs and expenses of the arbitration, but the final arbitral award may rule that the Brazilian Government shall reimburse the concessionaire for such costs and expenses. |
| ● | On August 6, 2019, Decree No. 9.957/2019 was published. It regulates the procedure for re-tendering of concession projects, including PPPs in the roads, rail and airport sectors covered by Federal Law No. 13,448/2017. |
| ● | On August 5, 2020, due to the financial impact caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, federal law No. 14,034 was published, amending federal law 13,499, dated October 26, 2017, allowing the deferral on payment of the concession fee. |
| ● | On October 20, 2020, Directive No. 157 of the Ministry of Infrastructure was enacted and established the terms and conditions for the re-profiling of the fixed grant (concession fee) payments due in 2020. |
| ● | On December 3, 2021, Directive No. 139 of the Ministry of Infrastructure was enacted and established the terms and conditions for the re-profiling of the fixed grant (concession fee) payments due in 2021. |
| ● | On June 14, 2022, Law No. 14,368 revoked provisions of various laws, and established that as of January 1, 2023, contributions to the National Civil Aviation Fund will not be due by airport concessionaries. |
Natal Concession Agreement
The concession agreement for the construction, operation and maintenance of the Natal Airport (the “Natal Concession Agreement”) was awarded in August 2011 to ICASGA and became effective on January 18, 2012. The initial term of the Natal Concession Agreement was for 28 years and could be extended for another five years.
On March 5, 2020, the Company made public that ICASGA filed a non-binding request to the Brazilian Federal Government to commence the re-bidding process of the Natal Airport under Law No. 13.448 of July 5, 2017 and ANAC Resolution No. 533 of November 7, 2019.
93
On November 20, 2020, ICASGA and ANAC executed an amendment to the Natal Concession Agreement setting forth the rules and proceedings for the re-bidding.
On May 19, 2023, ANAC conducted the new bidding process for the airport which was awarded to Zurich Airports.
On September 12, 2023, a contract between the new concessionaire and ANAC was executed. On December 27, 2023 the budget required for indemnification payment by the Government was approved by the National Congress and sanctioned by the President of Brazil, determining the final gross indemnification in the amount of R$609.5 million. On December 29, 2023, the Brazilian Government made a partial payment deducting all the obligations related to fixed and variable concession fees (a total net payment of R$199.7 million equivalent to U.S.$41.3 million), extinguishing all the concession fees obligations that ICAGSA maintained. On January 5, 2024, the remaining compensation was collected.
Brasilia Concession Agreement
The concession agreement for the construction, operation and maintenance of the Brasilia Airport (“Brasilia Concession Agreement”) was awarded in February 2012 to ICAB and became effective on July 24, 2012. The initial term of the Brasilia Concession Agreement is for 25 years and can be extended for an additional 5 years, if necessary, to reestablish economic equilibrium.
The Natal Concession Agreement and the Brasilia Concession Agreement are collectively referred to in this annual report as the “Brazilian Concession Agreements.”
Material Terms and Conditions of the Brazilian Concession Agreements
Under the Brasilia Concession Agreement, ICAB shall be responsible for (i) managing the expansion of Brasilia Airport to provide adequate infrastructure and improve its service level; and (ii) maintaining and operating Brasilia Airport in accordance with certain parameters provided for under Annex 2 of the Brasilia Concession Agreement (the “Brasilia Airport Development Plan”).
During the term of the Brasilia Concession Agreement, ICAB shall be responsible for, among other things:
| ● | providing adequate service to passengers and users of the airport, as defined in Article 6 of Federal Law No. 8.987/95 (the “Brazilian Concessions Law”), using all means and resources available, including, but not limited to, making any necessary investments to expand airport operations to sustain the required service levels, based on the existing demand and the provisions set forth in the Brasilia Airport Development Plan; |
| ● | implementing services and management programs, and offering training programs to its employees for purposes of improving services and the convenience of users in order to meet the requirements set forth in the Brasilia Airport Development Plan; |
| ● | providing proper service (according to what the Brasilia Airport Development Plan defines as regular, continuous, efficient, safe, up to date, broad and courteous service), at a fair price, to the general public and airport customers; |
| ● | performing all services, controls and activities related to the concession agreement, with due care and diligence, employing the best available practices in every task performed; |
| ● | presenting the Brazilian ANAC with an Infrastructure Management Plan every five years and an annual Service Quality Plan during the term of the ICAB Concession Agreement; |
| ● | submitting to the approval of the Brazilian ANAC any proposal for the implementation of service improvements and new technologies, as provided for under the Brasilia Concession Agreement and applicable regulations; |
| ● | developing and implementing plans for dealing with emergencies at the airports, maintaining, for such purposes, human resources and materials required by industry regulations and the Brasilia Airport Development Plan; and |
| ● | meeting minimum corporate capital requirements with respect to ICAB that is, a minimum subscribed and paid-in corporate capital in the amount of R$243.251 million. |
94
Concession Fees
Annual Fixed Payment
Under the Natal Concession Agreement, ICASGA was required to pay the Brazilian ANAC an annual fixed payment adjusted based on the base interest rate of the Central Bank of Brazil in the amount R$6.8 million for the years 2020 to 2032, and R$9.7 million for the years 2033 to 2040. Due to the re-bidding process, since 2021 ICASGA was authorized to defer payment of the concession fee owed to the Brazilian ANAC. On December 29, 2023, such deferred amounts, liquid credits with economic-financial rebalancing (R$87 million equivalent to U.S.$18.0 million), were discounted from government payments in the amount R$287 million (equivalent to U.S.$59.3 million) as compensation for ICASGA.
In December 2023, ICASGA received a gross indemnification in the amount of R$609.5 million (equivalent to U.S.$125.9 million. As of December 31, 2023, a net gain of R$825 million (equivalent to U.S.$166.5 million) was recognized mainly due to a gain for the reversal of impairment losses recognized in previous periods over intangible assets of R$514 million (equivalent to U.S.$103.8 million) and other operating income that includes the compensation of intangible assets of R$125 million (equivalent to U.S.$25.2 million) and a net gain from the offset of other assets and liabilities of the concession for a total of R$186 million (equivalent to U.S.$37.5 million).
Throughout these nearly four years of the amicable returning process, Inframerica ensured service excellence and maintained a cooperative and smooth collaboration with all parties involved. All financial commitments were met, and the administrator is expected to transfer the asset in good standing with all its partners and authorities.
The Concessionaire has been internally working with its employees to ensure a termination process that complies with all CLT (Consolidation of Labor Laws).
On December 31, 2023, Inframerica, the concessionaire of Natal Airport S.A., was absorbed by ACI do Brasil S.A., a subsidiary of CAAP.
Under the Brasilia Concession Agreement, ICAB is required to pay the Brazilian ANAC an annual fixed payment of the following amounts adjusted by the Consumer Price Inflation Index (Índice Nacional de Preços ao Consumidor Amplo; or “IPCA”): a fixed annual payment, as well as a variable payment, adjusted by IPCA. In relation to the annual payment for 2021, the company is still having a judicial discussion to reduce 50% of the amount, reprograming the futures payments from 2030 to 2037). Regarding the 2022 concession fee, a partial payment of R$81.6 million was made through the application of re-equilibrium credits. To pay the remaining amount, on November 21, 2022, ICAB presented to the Ministry of Infrastructure an offer of court payment orders, which is still in process of analysis. In December 2022, the Ministry issued an official letter confirming that, during the time it takes to issue a final opinion, ICAB is in compliance with its obligations. Regarding the 2023 concession fee, in December 2023. ICAB paid in full the concession fee in the amount of R$352.7 million, of which R$248.2 million was paid in cash while the remaining R$104.5 was made through the application of re-equilibrium credits.
Annual Variable Payment
ICAB is also subject to an annual variable payment, equal to: (i) 2% of the perceived annual gross revenues, for annual gross revenue of up to R$925.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023; plus (ii) 4.5% of the annual gross revenues, including the gross revenue of its wholly-owned subsidiaries, for annual gross revenues above R$925.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Monthly Payment
Pursuant to the Brasilia Concession Agreement (as amended), ICAB (amendment N° 02/2018) and ICASGA (amendment N° 06/2018) shall also pay a monthly payment equal to 26.4165% of all airport tariffs received by each company. Due to the re-bidding process, since 2021 ICASGA was authorized to defer payment of the concession fee owed to the Brazilian ANAC. Such deferred amounts were discounted from the compensation received from the government.
On June 14, 2022, Law No. 14,368, revoked provisions of various laws and established that as of January 1, 2023, contributions to the National Civil Aviation Fund will not be due by airport concessionaires. Consequently, monthly payments are no longer be required as of January 1, 2023.
95
Master Development Program
Under the terms of our Brasilia Concession Agreement, ICAB is required to present a master development program for approval by the Brazilian ANAC every five years. The Brazilian ANAC is the Brazilian Agency created in 2005 that integrates the Federal Public Administration and the Ministry of Transport, Ports and Civil Aviation in Brazil. The Brazilian ANAC is responsible for the regulation and inspection of civil aviation in Brazil, and is responsible for creating the standard model for carriers for airport infrastructure, and is the counterparty for the Brasilia Concession Agreement. The master development program (PGI – Plano de Gestão de Infraestrutura) includes planned investment (including capital expenditures and improvements) of the concession holder for the succeeding 5-year period.
The master development plan for Brasilia Airport for the 2018 to 2022 period was approved in 2017. The master development plan must set forth the investments necessary to comply with the dimension/quality parameters established in the Brasilia Concession Agreement (considering the concessionaire’s projections on air traffic growth), as well as any optional investments proposed by ICAB. Once reviewed and approved by the Brazilian ANAC, the investments proposed in the plan become binding commitments under the terms of the Brasilia Concession Agreement. However, ICAB may reduce or otherwise modify any investment in such plan so long as such investment is not related to ICAB’s compliance with the dimension/quality parameters established in the Brasilia Concession Agreement.
On October 24 2022, a new master development plan for Brasilia Airport with respect to the 2023 to 2027 period was submitted for ANAC’s approval.
Fees
As consideration for the investments and payment obligations assumed by ICASGA and ICAB under the Brazilian Concession Agreements, ICASGA and ICAB are entitled to charge the tariffs (fees contemplated by the Brazilian Concession Agreements and pursuant to applicable law and regulation) and non-tariffs (fees associated with the exploration of other commercial activities) described below:
Tariffs
ICAB is entitled to charge certain tariffs from users and airlines upon use of services, equipment, facilities and installations available at Brasilia Airports, including:
| ● | departure passenger charges; |
| ● | connection charges |
| ● | landing fees; |
| ● | aircraft parking fees; and |
| ● | cargo fees. |
ICAB are prohibited from charging any tariff not provided for in the Brazilian Concession Agreements, or the applicable law and regulation. In addition, Law 14.034/2020 revoked the FNAC fee as of January 1, 2021.
The tables below set forth the maximum amounts that we were permitted to collect as of July, 2023, under the Brasilia Concession Agreement:
Boarding Rate Group I
Nature |
|
Domestic |
|
International |
Concessionaire |
|
29.51 |
|
52.25 |
96
Connection Rate
Domestic (R$/passenger) |
|
International (R$/passenger) |
13.59 |
|
13.59 |
Landing Fee Group I
Domestic (R$/Ton) Final |
|
International (R$/Ton) Final |
9.2378 |
|
24.6287 |
Rate of Permanence of the Group I
|
|
Domestic |
|
International |
|
|
(R$) |
|
(R$) |
Rate of Permanence |
|
Final |
|
Final |
Maneuver Patio (PPM) |
|
1.8252 |
|
4.9170 |
Long Stay Patio (PPE) |
|
0.3875 |
|
1.0011 |
Adjustment
Tariffs shall be adjusted annually by IPCA, upon the application of a specific formula that considers the IPCA and the effects of the Q and X Factors, as defined in the Brazilian Concession Agreements. The Brazilian ANAC adopted Factor X as a mechanism to measure positive and negative productivity and efficiency variations and Factor Q as a mechanism to verify compliance with service levels. Adjustment of tariffs under Natal Concession Agreement also considers an additional Factor M, which allows the increase of tariffs when non-tariffs correspond to more than 35% of revenues.
Non-Regulated Revenue
Pursuant to the Brazilian Concession Agreements, ICASGA and ICAB may engage in commercial activities that generate non-regulated revenues, as provided under the relevant airport master plan, directly, through subsidiaries or through lease contracts with third parties.
The following airport-related commercial activities are authorized:
| ● | ground handling, catering and fueling; |
| ● | retail, duty free, food and beverage, banking services, lottery and vending machines; |
| ● | rental of office spaces, warehouses and export processing areas; |
| ● | car rental, parking, hotels and meeting rooms; and |
| ● | hotel transfers, city tour and telecommunication services. |
Review of the Concession Parameters
The review of the parameters of the Brazilian Concession Agreements shall be conducted every five years during the concession period and involves the determination of service quality indicators, the methodology of calculation of factors X, Q and the discount rate considered in the calculation of the marginal cash flow used in determining extraordinary reviews.
In January 2019, ICASGA initiated the proceedings regarding the review of the parameters of its Concession Agreement. In December 2019, the proceedings were finalized and therefore, the parameters are now effective as of January 1, 2020.
97
Extraordinary Review
The extraordinary review is intended to restore the economic and financial equilibrium of the Brazilian Concession Agreements when costs, revenues or gains of ICASGA or ICAB are unbalanced as a result of events with respect to which the Brazilian ANAC is required to bear the risk (e.g., changes in airport security requirements, change in certain rules and regulations, and the existence of archeological sites in the airport area).
In addition, the Natal Airport and Brasilia Airport may make a request for the restoration of economic and financial equilibrium under the Brazilian Concession Agreements if government entities do not complete the works required under the concession tender documents. A request for the restoration of equilibrium may also be made if there are latent defects in the then existing infrastructure.
The relevant concessionaire may request an extraordinary review of the Brazilian Concession Agreement to re-establish the economic and financial equilibrium of the concession if one or more events under Section V of the concession agreement occurs. The principal events are the following:
| ● | any changes in any law or rule related to (a) the services that the concessionaire must provide or (b) any security procedure; |
| ● | operational restrictions resulting from any act (or omission thereof) by any governmental body; |
| ● | mandatory changes in tariffs or granting of tariff benefits; |
| ● | changes in the tax regime that causes additional costs for the concessionaire (excluding income tax); and |
| ● | force majeure event. |
The restoration of the economic and financial equilibrium may be implemented by the Brazilian ANAC upon (i) changing the amount of tariffs; (ii) modifying the concession term or ICASGA or ICAB’s obligations; or (iii) adopting other measures it deems appropriate. The review will be based, among others, on the marginal cash flow related to every event generating economic and financial disequilibrium.
In the process of determining the compensation necessary to offset economic and financial changes, the Brazilian ANAC may request documents prepared by independent institutions, the cost of which shall be at ICASGA or ICAB’s expense, as the case may be.
Guarantees and other Financial Commitments
Performance bond
Under the Brazilian Concession Agreements, the Brazilian concessionaires are required to provide certain performance bonds for some events. Main performance bonds relate to “Phase I-B” and “Phase II” events under the Brazilian Concession Agreements. The current amount of Phase II is R$258.3 million (equivalent to approximately U.S.$53.4 million) in ICAB. The performance bond in ICAB was fulfilled by a guarantee letter issued by CAAP an entered into with BMG insurance company.
Financial commitments
The Brazilian Concession Agreements are subject to the general provisions set forth under the Brazilian Concessions Law (Federal Law No. 8,987/95), Public Procurements and Administrative Contracts Law (Federal Law No. 8,666/93), as well as MTPA and the Brazilian ANAC regulations.
Pursuant to Article 28 of the Brazilian Concessions Law, the Brazilian concessionaires may provide the rights arising from the concession as collateral for their financing arrangements, up to a limit that does not compromise the operations and continuity of the services provided by the concessionaire.
ICASGA and ICAB have complied with all the minimum financial commitments required under their respective Brazilian Concession Agreements. Any further investments would only be necessary in the event of increased demand.
98
Federal Law No. 13,499/17
Federal Law No. 13,499/17 (Provisional Measure MP779) provides that airport concessionaires in Brazil are permitted to prepay the applicable concession fees due by such concessionaire. By prepaying such concession fees, an equal amount of future concession fees is deferred. The deferred amount is adjusted at a rate equal to 6.81% plus inflation (measured by IPCA). We used part of the borrowings under the Banco Santander Bridge Loan Facility to prepay approximately 45% of the concession fees due in 2018 under the Brasilia Concession Agreement. We also prepaid 100% of the concession fees due in 2018 under the Natal Concession Agreement. On December 20, 2017, we entered into amendments of each of the Brasilia Concession Agreement and the Natal Concession Agreement in connection with such prepayments.
Penalties
Operational Intervention
Whenever contractual breaches are deemed to substantially affect the concessionaire’s ability to provide its services as provided for in the Brazilian Concession Agreements, the Brazilian ANAC may temporarily intervene in the operations to guarantee the quality of services and adherence to contractual provisions and regulations.
Termination of the Concessions
The Brazilian Concession Agreements will be deemed terminated upon any of the following events:
| ● | the end of the concession term, as provided for in the relevant Brazilian Concession Agreement; |
| ● | the expropriation of the concession by the Brazilian ANAC for reasons of public interest; |
| ● | forfeiture declaration by the Brazilian ANAC as a result of the breach of material contractual obligations by ICASGA and ICAB pursuant to Article 38 of the Brazilian Concessions Law; |
| ● | termination by a judicial order resulting from an action filed by ICASGA or ICAB based upon the breach of the Brazilian ANAC obligations; |
| ● | the annulment of the Brazilian Concession Agreements by a judicial or administrative order based on the discovery of illegalities or irregularities in the tender documents, in the bid process or in the Brazilian Concession Agreements; or |
| ● | bankruptcy or liquidation of ICASGA or ICAB, as the case may be. |
Upon termination of the Brazilian Concession Agreements, the Brazilian ANAC may:
| ● | assume the airport services and operations; |
| ● | occupy and use the premises, facilities, equipment, materials and human resources employed in the airport services and operations that are required for the continuity thereof; |
| ● | apply the pertinent penalties, especially those relating to the reversion of assets attached to the concessions in favor of the Brazilian ANAC; and |
| ● | retain and enforce guarantees or collateral to ensure payment of administrative fines and losses caused by the concessionaires. |
The amount of any indemnification payment due to ICASGA or ICAB in the event of the expropriation, or termination by a judicial order, of the relevant concession will include the outstanding balance under the loan agreements entered by ICASGA or ICAB with BNDES and/or CEF. In addition, ICAB is entitled to receive payment for (i) non-amortized investments; and (ii) all applicable demobilization costs, including fines, termination payments and indemnifications due to employees, suppliers and other creditors.
99
If the Brazilian Concession Agreements are terminated in connection with a forfeiture declaration issued by the Brazilian ANAC, then the amount of the indemnification payment will be limited to the non-amortized amount of assets reverted to the Brazilian Government less the amount of (i) any applicable losses; (ii) fines; and (iii) insurance payments received by ICASGA or ICAB, in each case, in connection with the events and circumstances that resulted in the forfeiture declaration.
Reverted Assets
ICASGA and ICAB are obliged to maintain an updated list of the assets attached to the Brazilian Concession Agreements, which shall be returned to the Brazilian ANAC upon the end of the relevant concession, in adequate working condition, sufficient to ensure the continuity of the Airports services and operations for at least three years, in the case of ICASGA, and two years in the case of ICAB.
Transfer of control and transfer of concession
The assignment of the concessions and the transfer of direct or indirect corporate control of ICASGA or ICAB depend on the prior and express approval from the Brazilian ANAC. During the first five years of the Brazilian Concession Agreements, the prior and express approval from the Brazilian ANAC will also be required in connection with: (i) changes to ICASGA ownership structure that do not imply transfer of control, (ii) transfer of ICAB shares owned by its private shareholder and (iii) changes to ICAB private shareholder ownership structure that do not imply transfer of control.
Penalties
The failure to comply with the Brazilian Concession Agreements, the applicable request for proposal and the rules and regulations issued by the Brazilian ANAC may result in the following penalties to the concessionaires, in addition to any other penalties provided for in the applicable law and regulation:
| ● | warning; |
| ● | fine; |
| ● | temporary suspension of participation in requests for proposals to obtain new concessions or authorizations for the operation of the airport infrastructure as well as restrictions for ICASGA or ICAB to enter into new contracts with the Brazilian Government; and/or |
| ● | forfeiture of the concession. |
Governing Law and Dispute Resolution
The Brazilian Concession Agreements are governed by the laws of Brazil. Any dispute, controversy or disagreement related to indemnification payments that may be due to a party upon the termination of the Brazilian Concession Agreements, including reverted assets, shall be settled by arbitration, in accordance with the Arbitration Rules of the International Chamber of Commerce, subject to the provisions of Federal Law No. 9,307, of September 23, 1996 (the Brazilian Arbitration Law). The Brazilian courts of the Federal District (Distrito Federal) have jurisdiction to resolve all other disputes related to the Brazilian Concession Agreements.
Uruguay
Sources of Regulation
The following are the main laws and regulations that govern the Uruguayan Concession Agreements:
| ● | Law No. 14,305 (“Uruguayan Aeronautical Code”) as regulated by the Executive Branch Decree No. 39/977. Title V of the Uruguayan Aeronautical Code sets forth the basic framework regarding airports in Uruguay establishing certain requirements that all airports, depending on their classification, have to comply with. |
| ● | Law No. 9,977 which provides that the Dirección Nacional de Aviación e Infraestructura Aeronáutica of Uruguay (“DINACIA”) an agency of the Defense Ministry, shall be the aeronautical authority having the responsibility of controlling, promoting and managing civil aviation. |
100
| ● | Executive Branch Decree No. 21/999, which regulates in further detail the responsibilities of DINACIA. |
| ● | Law No. 19,925 which created the National System of International Airports (known as “SINAI,” for its Spanish acronym) for purposes of developing certain airports within the country. This Law granted the Uruguayan Executive Power the authority to modify and supplement existing concessions for the construction, maintenance and exploitation, jointly or separately, of airports within the SINAI. |
The following are the main laws and regulations that govern the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement and the operation of the Carrasco Airport and the Uruguay New Airports:
| ● | Law No. 17,555 dated September 18, 2002, which authorized the Corporación Nacional para el Desarrollo (“CND”), a state - owned agency created by Law No. 15,785, to incorporate a company with the purpose of “managing, exploiting, operating, constructing and maintaining” Carrasco Airport. Pursuant to the aforementioned authorization, in 2003 the Uruguayan Government incorporated Puerta del Sur, and on February 6, 2003, Puerta del Sur entered into the Concession Agreement with the Defense Ministry to manage, exploit, operate, construct and maintain the Carrasco Airport for a 20-year term, extendable up to 30 more years, by paying an annual concession price or “fee.” |
| ● | Executive Branch Decree No. 376/002, dated September 28, 2002, which includes the Régimen de Gestión Integral, which regulates Law No. 17,555, and created the Unidad de Control, which acts as Puerta del Sur’s regulator. |
| ● | Executive Branch Decree No. 153/003, dated April 24, 2003, Executive Branch Decree No. 192/003, dated May 20, 2003, and Executive Branch Decree No. 317/003, dated August 13, 2003, which amended the terms of the auction of Puerta del Sur’s shares and certain requirements connected to the Concession Agreement. |
| ● | Resolution No. 284/005 issued by the Defense Ministry, pursuant to which the Defense Ministry approved certain amendments to the Carrasco Concession Agreement. |
| ● | Executive Branch Decree No. 303/005, dated September 13, 2005, Executive Branch Decree No. 469/007, dated December 3, 2007, Executive Branch Decree No. 491/009, dated October 19, 2009, Executive Branch Decree No. 20/012 dated January 27, 2012, Executive Branch Decree No. 148/2014, dated May 26, 2014, Executive Branch Decree No. 62/015, dated February 18, 2015, Executive Branch Decree No. 232/2017 dated August 28, 2017 and Executive Branch Decree No. 31/2018 dated February 2, 2018, all of which updated the tariffs set forth in the Carrasco Concession Agreement. |
| ● | Executive Branch Decree No. 409/08, which approved the regulations related to the treatment of Carrasco Airport as a “freeport.” |
| ● | Executive Branch Decree No. 229/014, dated August 6, 2014, which amended several aspects of the Carrasco Concession Agreement, providing the extension of the Carrasco Concession Agreement for an additional 10 year term in exchange for (i) payment of a fee of U.S.$20.0 million and an additional fee by Puerta del Sur which will be discussed further on, (ii) the return to the Ministry of Defense of the old Carrasco Airport passengers terminal, and (iii) commitment by Puerta del Sur to perform certain obligations. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Uruguay— Amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement—Obligations Assumed by Puerta del Sur as Concessionaire.” |
| ● | Resolution No. 27/015, dated March 11, 2015, issued by the Defense Ministry regarding the FBO-VIP zone. |
| ● | Resolution No. 96006, dated November 30, 2020, issued by the Uruguayan executive power, authorized an amendment of the Carrasco Concession Agreement in order to reduce 50% the canon to be paid by Puerta del Sur during the first semester of 2020 as a consequence of COVID’s impact. On December 19, 2020, the Ministry of Defense and Puerta del Sure entered into such amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement to provide for such canon reduction. |
101
| ● | Resolution No. 218/021, dated November 5, 2021, issued by the Execute Branch, which amended and extended the Carrasco Concession Agreement for an additional 20-year period, from November 2033 to November 2053 and incorporated the Uruguay New Airports located in the cities of Melo (Cerro Largo, Uruguay), Rivera (Rivera, Uruguay), Durazno (Durazno, Uruguay), Carmelo (Colonia, Uruguay), Paysandú (Paysandú, Uruguay) and Salto (Salto, Uruguay) into the scope of the Carrasco Concession Agreement. |
The following are the main regulations that govern the Punta del Este Concession Agreement and the operation of the Punta del Este Airport
| ● | Law No. 15,637 dated September 28, 1984, which authorizes the Executive Branch to grant concessions of public property to individuals, public or private legal entities, mix ownership companies, allowing the concessionaire to collect fees from the commercial exploitation. |
| ● | Resolution No. 960/993 issued by the Executive Power dated October 23, 1993, which awarded the Public Tender 4/991 for the reconstruction, maintenance and partial operation of the services of the Punta del Este Airport to Consorcio Aeropuertos Internacionales S.A. and authorized the Ministry of Defense to enter into the Punta del Este Concession Agreement with CAISA for a period of 20 years. |
| ● | Resolution No. 1866/001 issued by the Ministry of Defense dated December 14, 2001, which approved the amendment of the terms of the Punta del Este Concession Agreement. |
| ● | Resolution No. 1351/2019 issued by the Executive Power dated March 28, 2019, which approved the amendment of the Punta del Este Concession Agreement, extending its term until March 31, 2033. The amended agreement was executed on June 28, 2019. |
Governmental Authorities
Role of DINACIA
The former Directorate of Civil Aviation, currently called DINACIA, the Uruguayan aviation authority, was created by the Executive Branch Decree No. 21/999, dated January 26, 1999.
The goal of DINACIA is to implement civil aviation policies in Uruguay, according to current international standards and recommendations, thus continuously monitoring operational security, directing, and controlling civil aviation activities. DINACIA is also in charge of the safety, regularity and efficiency of the aeronautical operations and with providing services in accordance with international regulations and requirements in Uruguay.
DINACIA’s rights and obligations with respect to the Carrasco Concession Agreement are set forth under the Concession Agreement and applicable laws. DINACIA also provides the necessary resources for the functioning of the Unidad de Control and administrative support, infrastructure and material resources.
Uruguayan Executive Branch Decree No. 21/999 also regulates DINACIA’s organization and powers, which among others include the following: (i) execute the national aeronautics policies according to current regulations and directives; (ii) direct, coordinate, monitor and evaluate the activities assigned to other departments; (iii) advise, in compliance with current legal standards, in all matters related to civil aviation; (iv) issue, in its capacity as national aeronautical authority certain certificates (Certificados de Explotador Aéreo) to airline companies that must comply with the requirements established in the regulations of civil aviation; (v) issue instructions (Instructivos) to define policies to be developed in the areas of its competence in order to control compliance with all civil aviation activity; and (vi) issue rules (Circulares) regarding airport security and operations. Notwithstanding the foregoing, DINACIA has authority in all matters related to civil aviation and aeronautics, according to national statutes and international treaties.
Unidad de Control
The Unidad de Control was created by Executive Branch Decree No. 376/002 as the responsible body for the supervision and control of the fulfillment of airport concessionaires and the financial, legal, technical and operative supervision of the Uruguayan Concession Agreements. The Unidad de Control’s members inspect both the Carrasco Airport and the Punta del Este Airport regularly.
102
Under the terms of the Uruguayan Concession Agreements, certain tariffs and charges included in the Uruguayan Concession Agreements require the approval of the Executive Branch. Prices not included in the Carrasco Concession Agreement, applicable to the airlines, require the approval of the Unidad de Control. Other prices must only be notified to the Unidad de Control and they have to be based on market prices and private negotiations.
All disputes arising in connection with the operation or management of an airport must be submitted to the Unidad de Control. The Unidad de Control is the body responsible for suggesting to DINACIA all mitigations and sanctions that could apply in case of breach by the concessionaires of their obligations.
The Unidad de Control also controls compliance with the ICAO rules relating to maintenance and management of all airports, and is responsible for coordinating and controlling all activities related to the emergency plans of the airports.
Resolution No. 193/016 dated April 28, 2016, incorporated rules related to Emergency Plans at airports and Airports Certifications, which must be obtained by Puerta del Sur and CAISA. Before Resolution 193/016, both the Emergency Plan and the Airport Certification were obligations of the State. The completion of the Certification process is long and can last a couple of years.
The Carrasco Concession Agreement
In September 2002, the Uruguayan Government (through Law No. 17,555 and Executive Branch Decree No. 376/02) authorized the CND to incorporate a company with the purpose of “managing, exploiting, operating, constructing and maintaining” the Carrasco Airport. Pursuant to the aforementioned authorization, in 2003 the CND incorporated Puerta del Sur, which entered into the Carrasco Concession Agreement with the Defense Ministry to operate the Carrasco Airport. The initial term of the Carrasco Concession Agreement was for 20 years commencing in November 2003, which was extended for an additional 10-year period (i.e., until 2033) by Executive Branch Decree No. 229/2014 dated August 6, 2014.
In August 2003, our wholly-owned subsidiary Cerealsur S.A. acquired 100% of the issued and outstanding shares of Puerta del Sur in a public auction organized by the Uruguayan Government at the Uruguayan Stock Exchange. In November 2003, Puerta del Sur took the effective control of the Carrasco Airport.
In order to meet the operator expertise requirements under the Carrasco Concession Agreement, upon consent of the Executive Branch, Puerta del Sur entered into an operating agreement with Cedicor, with experience in the management and operations of airports around the world, including in Argentina, Ecuador, Peru, Brazil, Italy and Armenia, to manage the Carrasco Airport. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Uruguay—Amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement—Obligations Assumed by Puerta del Sur as Concessionaire—Airport Operator.”
Amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement
On December 18, 2020, the Uruguayan government passed Law No. 19,925 which created the National System of International Airports (known as “SINAI,” for its Spanish acronym) for purposes of developing certain airports within the country. This Law granted the Uruguayan Executive Power the authority to modify and supplement existing concessions for the construction, maintenance and exploitation, jointly or separately, of airports within the SINAI. Under the scope of the SINAI, the Uruguayan Executive Power, through the Ministry of Defense, negotiated with Puerta del Sur the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement.
The Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement was executed on November 8, 2021 and modified the existing Carrasco Concession Agreement by, among other things, (i) extending the term of the Carrasco Concession Agreement until November 20, 2053, (ii) incorporating into the concession six additional Uruguay New Airports located in Rivera, Salto, Carmelo, Durazno, Melo, Paysandú, and (iii) requiring Puerta del Sur to make capital expenditures in connection with the development of the Uruguay New Airports of U.S.$67 million, in the aggregate, between 2022 and 2028 with respect to the operation of such Uruguay New Airports. Such capital expenditures will need to be completed pursuant to the following investment schedule (“Investment Schedule”), which may be adjusted as a result of force majeure events and certain other particular circumstances: (i) U.S.$13 million during 2022, (ii) U.S.$32 million during 2023, (iii) U.S.$18 million during 2024; and (iv) U.S.$4 million during 2028. Additionally, the scope of works to be performed on the Uruguay New Airports are contemplated in the investment programs (programas de inversion) (“Investment Program”) which include the construction schedule.
Under the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement, the concession is expected to expire on November 20, 2053.
103
Except with respect to the Durazno International Airport in which operations will not start before January 1, 2025, the operation of the Uruguay New Airports by Puerta del Sur under the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement started progressively after meeting certain conditions.
The Uruguayan government consented to the amendment by Puerta del Sur of its by-laws to reflect the incorporation of the Uruguay New Airports under the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement.
The Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement does not change the concession fees that Puerta del Sur must pay under the Carrasco Concession Agreement. However, passengers departing from and arriving to the Uruguay New Airports will be taken into account for purposes of determining the fees to be actually paid, which depends on passenger traffic.
Obligations Assumed by Puerta del Sur as Concessionaire
Under the terms of the Carrasco Concession Agreement, Puerta del Sur is responsible for developing, managing, exploiting, operating and maintaining the Carrasco Airport, which includes performance of the following activities:
| ● | using Carrasco Airport facilities and the human and material resources associated with the aeronautical and commercial services regulated under the Carrasco Concession Agreement exclusively for such purposes; |
| ● | taking all necessary measures (other than those under the responsibility of the Uruguayan Government) in order for Carrasco Airport to be included in the following categories of the IATA: (a) Category 1 Instrumental; (b) Category 4E regarding the state of the landing strip; (c) Category 9 regarding fire protection; and (d) at least in Category C of IATA; |
| ● | maintaining Carrasco Airport operational 24 hours a day, seven days a week; |
| ● | complying with applicable security measures required by the ICAO, as well as other measures required by DINACIA; |
| ● | allowing the Uruguayan Government to comply with its duties under the Carrasco Concession Agreement as the regulator of the Carrasco Airport, including the services relating to air police, police enforcement, customs control, immigration, Interpol, meteorology, veterinary and healthcare; |
| ● | keeping and maintaining the facilities received under concession in perfect operating conditions and in full operations (24/7, 365 days a year) and replacing them as deemed necessary in the event of destruction or obsolescence and updating them to reflect the latest technological advances; |
| ● | implementing the necessary measures to ensure freedom of access and nondiscrimination; |
| ● | performing the works required by the Carrasco Concession Agreement. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Uruguay—Amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement—Obligations Assumed by Puerta del Sur as Concessionaire—Construction of a New Passenger Terminal”; |
| ● | reporting to the relevant authorities any breach of the Carrasco Concession Agreement and those which endanger or may endanger the security of Carrasco Airport, and cooperate with any investigations; |
| ● | maintaining the guarantees and insurance policies valid and current in accordance with the terms of the Carrasco Concession Agreement; |
| ● | reporting to DINACIA, the control entity of Carrasco Airport, any facts affecting the regulated airport activities; |
| ● | paying the concession fee; |
| ● | providing to the Unidad de Control all documents and information necessary to verify compliance with the Carrasco Concession Agreement; |
104
| ● | permitting DINACIA (without any restrictions) to use a limited space at the Carrasco Airport free of charge, and compensating the Uruguayan Government for the provision of transit, flight protection, radio navigation and communications services; and |
| ● | complying with all the obligations contained in the Régimen de Gestión Integral and all those inherent to a “reasonable” or “diligent” business owner. |
The control of the aeronautical transit, general flight operations and security measures are excluded from the Carrasco Concession Agreement and remain with DINACIA.
The Unidad de Control, an agency that consists of representatives of the Defense Ministry and the Ministries of Economy and Transportation, supervises Puerta del Sur’s compliance with its obligations as concessionaire of Carrasco Airport, and oversees the financial, legal, technical and operative supervision of the concession. Under the terms of the Carrasco Concession Agreement, Puerta del Sur has assumed the obligations described below.
Maintenance and Operation of the Airport Terminal and Uruguay New Airports
Under the Carrasco Concession Agreement, Puerta del Sur is required to take all measures to provide secure, regular, efficient and high-quality services, at the minimum cost to the users of Carrasco Airport and the Uruguay New Airports. Any change in the Carrasco Concession Agreement related to infrastructure, facilities or equipment will require the prior authorization of the Executive Branch.
Under the Carrasco Concession Agreement, Puerta del Sur is responsible for complying with all applicable legal requirements related to aeronautical, labor, fiscal, customs and other matters related to its activity.
Airport Operator
Under the Carrasco Concession Agreement, Puerta del Sur is required to engage and maintain an experienced and financially sound airport operator for the airport, who, in turn, is charged with providing advice to Puerta del Sur in the following areas: airplanes, passengers, mailing and cargo.
On February 2, 2017, Puerta del Sur replaced SEA as operator and entered into an operating agreement with Cedicor. Under the terms of the operating agreement between Puerta del Sur and Cedicor, Puerta del Sur pays Cedicor an annual fee of 2.5% of Puerta del Sur’s operating income with a minimum of U.S.$500,000 and a maximum of U.S.$2.0 million per calendar year. On January 17, 2022, Puerta del Sur and Cedicor signed an amendment under which Cedicor agreed to also operate the new airports.
The Carrasco Concession Agreement requires that any entity acting as the operator of Carrasco Airport and/or the new airports must be approved by the Executive Branch and must satisfy the following conditions:
| ● | Technical operational capacity: The operator must have at least eight years’ experience in airport management and operations with, at minimum, 40,000 tons of cargo and 2.4 million passengers per year, as certified by the competent aeronautical authority of the country in which it operates. If the operator is a holding company, the referenced technical capacity will be that of the controlled entity. Cedicor’s technical and operational capacity was certified by the Aeronautical Authority of Guayaquil and approved by Uruguay’s Executive Branch. |
| ● | Financial and economical capacity: The operator must have a minimum operating capital of U.S.$50.0 million in its most recently ended fiscal year, as evidenced by the audited balance sheet and income statement of the operator prepared in accordance with IFRS. Operating capital is calculated as the sum of net worth and short - term and long - term financial debt. |
Puerta del Sur must submit to DINACIA any request seeking the approval of the Executive Branch to approve an entity to become operator of Carrasco Airport. The Executive Branch must approve the proposed operator within a term of 20 days. If denied, Puerta del Sur will have 15 days to respond to any objections. Once approved, the agreement between Puerta del Sur and the operator will be in force during the effective term of the Carrasco Concession Agreement. Any termination of the operating agreement will require the consent of the Uruguayan Government.
105
If Puerta del Sur elects to replace the airport operator, it must submit to the Uruguayan Government the name of the replacement, together with evidence that the proposed operator meets all required conditions. Any proposed operator must be approved by the Uruguayan Government.
Landing Fees
|
|
Adjusted Price |
|
|
U.S.$ |
|
|
(U.S.$ per ton) |
Aircraft weight (tons)(1) |
|
|
Up to 10 tons |
|
69.48 |
10 – 20 tons |
|
354.32 |
20 – 30 tons |
|
442.28 |
30 – 70 tons |
|
662.30 |
70 – 170 tons |
|
935.54 |
> 170 tons |
|
1,273.65 |
(1) |
Landing fees increase by 20% for night landing. |
Parking Fees
|
|
PAD/h(1) |
In operative platform |
|
5% PAD/h |
Outside operative platform |
|
2.5% PAD/h |
Under repair (others) |
|
0 |
(1) |
PAD/h = daily landing price per hour or fraction. |
Boarding Services Fees
|
|
U.S.$ |
Connections |
|
26.0 |
International flights |
|
58.0 |
Security Tariff |
|
9.15 |
Handling Companies fees
|
|
In |
|
|
|
|
Transit |
|
Terminal |
|
|
|
|
|
Up to 10 seats |
|
6.95 |
|
11.55 |
11 – 30 seats |
|
20.87 |
|
31.25 |
31 – 90 seats |
|
41.68 |
|
52.03 |
91 – 150 seats |
|
62.53 |
|
83.35 |
151 – 250 seats |
|
125.05 |
|
166.75 |
> 251 seats |
|
187.58 |
|
208.43 |
Load Airplanes
|
|
In |
|
|
|
|
Transit |
|
Terminal |
|
|
|
|
|
5,700 kg MTOW |
|
11.57 |
|
23.19 |
Up to B-737, B-727 (or similar) |
|
83.35 |
|
93.87 |
B-767, DC-8 (or similar) |
|
104.22 |
|
125.10 |
DC-10, MD-11, B-747, A-340 (or similar) |
|
140.11 |
|
187.63 |
106
Concession Fees
As consideration for the Carrasco Concession Agreement, Puerta del Sur is required to pay annual fees to DINACIA for the concession of Carrasco Airport. These fees consist of: (a) basic fees and (b) additional fees.
Basic Fees
The basic fees are calculated annually for the period from November to November and are equal to the higher of (i) a fixed amount of U.S.$4.6 million and (ii) the amount resulting by multiplying the total number of passengers that use Carrasco Airport by U.S.$4.19 per passenger (passengers in transit that exceed 7.5% of the total number of passengers that use the services of Carrasco Airport are excluded from such calculation, as well as diplomats, members of the Defense Ministry assigned to United Nation’s peace keeping missions or other international organizations and children under the age of two), plus applicable cargo fees.
Additional Fees
In connection with the extension of the term of the Carrasco Concession Agreement, in September 2014 Puerta del Sur agreed to pay additional fees (effective as of September 1, 2017), which are calculated based on the number of passengers that use Carrasco Airport and that exceed 1.5 million passengers per year (transit passengers are not included in such calculation, nor are diplomats, members of the Defense Ministry assigned to United Nation’s peace keeping missions or other international organizations or children under the age of two) multiplied by the coefficient set forth in the following table.
Passengers from |
|
Passengers to |
|
Coefficient |
— |
|
1,500,000 |
|
— |
1,500,001 |
|
1,750,000 |
|
0.075 |
1,750,001 |
|
2,000,000 |
|
0.155 |
2,000,001 |
|
2,250,000 |
|
0.272 |
2,250,001 |
|
2,500,000 |
|
0.398 |
2,500,001 |
|
2,750,000 |
|
0.538 |
2,750,001 |
|
3,000,000 |
|
0.692 |
3,000,001 |
|
— |
|
0.861 |
Timing of Payment of Fees: Puerta del Sur must pay 50% of the annual fees to DINACIA in June of each year (as calculated for the previous November-to-November period), and the remaining 50% in the following December.
Delay in Payment of Fees: If Puerta del Sur fails to timely pay the annual fees, it shall incur default interest at a rate of LIBOR (180 days) plus 10.0%. In addition, such failure to pay would be a breach of the Concession Agreement and may lead to the termination of the Carrasco Concession Agreement.
Fees under the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement
The Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement does not change the concession fees that Puerta del Sur must pay under the Carrasco Concession Agreement. However, passengers departing from and arriving to the Uruguay New Airports will be taken into account for purposes of determining the fees to be actually paid, which depends on passenger traffic.
The Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement also contemplates the operation and exploitation by Puerta del Sur of free ports and special customs areas (zonas aduaneras primarias) within the area of each of the Uruguay New Airports.
107
Puerta del Sur Revenue
Under the terms of the Carrasco Concession Agreement, Puerta del Sur is entitled to collect, among others, all aeronautical, commercial and cargo revenue related to services rendered at Carrasco Airport and/or the Uruguay New Airports.
According to Executive Branch Decree No. 376/02, the Concessionaire is entitled to make a request to the Executive Branch of the Uruguayan Government for an annual adjustment of the prices charged at Carrasco Airport and/or the Uruguay New Airports for landing, aircraft parking, passenger use tariffs, cargo, handling and storage of containers. If the requested adjustments are approved by the Uruguayan Executive Branch, the new prices are the maximum that can be charged, but not the fees that Puerta del Sur must necessarily charge. These prices charged to the airlines per aircraft movements and passenger use tariffs are adjusted pursuant to the Carrasco Concession Agreement.
Other services provided by Puerta del Sur to airlines and not included above shall be proposed by Puerta del Sur and approved by the Unidad de Control. The current services that are being provided by Puerta del Sur to the airlines are included in the Concession Agreement and the Memorandum of Understanding and its amendments executed between the airline companies and Puerta del Sur which were ratified by the Unidad de Control.
Other commercial revenues relating to the operation of Carrasco Airport or the Uruguay New Airports and not included above are unregulated and may be fixed by Puerta del Sur without any restriction. However, the Carrasco Concession Agreement requires that the prices for such unregulated services be in line with local market prices, taking into account the quality and kind of services provided. Puerta del Sur must inform the Unidad de Control about the prices that it will charge for such services, and enclose comparative information about similar services in Uruguay and in the region. If the Unidad de Control rejects the proposed prices because they are not in line with local markets, Puerta del Sur would not be able to apply them. Prices are also published on the Puerta del Sur website and at DINACIA’s website.
The prices that Puerta del Sur charges for the use of spaces within the terminal (other than spaces granted for airline operations) are freely set between Puerta del Sur and its counterparties and not subject to review or approval by any authority.
Obligations Assumed by Puerta del Sur Under the 2014 Amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement
As consideration for the extension of the term of the Concession Agreement for an additional 10-year period that took place in September 2014, Puerta del Sur agreed to the following:
| ● | Extension Premium: Puerta del Sur agreed to pay to the Uruguayan Government U.S.$20.0 million simultaneously with the execution of the amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement, which amount has been already paid in full; |
| ● | Return of Old Passenger Terminal: The old passenger terminal has been detached from the Concession Agreement and was returned to the Defense Ministry; however, Puerta del Sur has assumed the obligation to pay U.S.$3.5 million in order to renovate the old terminal, which were duly paid at the execution of the amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement; |
| ● | Waiver of the Payment of Passenger Use Tariffs for Certain Governmental Authorities: Puerta del Sur has agreed to waive the payment of passenger use tariffs for diplomats, members of the Defense Ministry assigned to United Nations peace keeping missions or other international organizations and children under the age of two; |
| ● | Airport Security System: Puerta del Sur agreed to replace Carrasco Airport’s current security system with an integrated security system. The replacement will be initiated once the Executive Branch issues the Decrees imposing the obligation on the airlines to submit the advanced passenger information and passenger name record information to the Ministry of Interior; |
| ● | New Taxiway: Puerta del Sur agreed to build a new taxiway before the termination date of the Carrasco Concession Agreement, or earlier, if required by the ICAO regulations based on Carrasco Airport traffic statistics; currently the airport does not have sufficient traffic to require the construction of the taxiway, and Puerta del Sur expects to build the taxiway in the final years of the Carrasco Concession Agreement; and |
108
| ● | Change of Control of Puerta del Sur: In general terms, a change of control of Puerta del Sur is not subject to approval by the Uruguayan Government, nor would it require any type of permit or authorization. However, under the terms of the amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement, it was agreed that if the shares of Puerta del Sur are sold within 36 months after the execution of the amendment (August 6, 2014), Puerta del Sur will be required to pay to the Uruguayan Government 50% of the benefit resulting from the sale, which is defined as the total consideration to be obtained from the sale minus investment costs. As of the date of this annual report, such 36-months term has expired, therefore, the payment requirement upon sale of shares of Puerta del Sur is no longer enforceable. Puerta del Sur is prohibited from assigning the Carrasco Concession Agreement, in whole or in part, without the prior and express authorization of the Executive Branch. Any new concessionaire would have to comply with the terms of the Carrasco Concession Agreement. |
| ● | Additional Fees: Puerta del Sur agreed to pay additional fees (effective as of September 1, 2017) based on the number of passengers that use the Carrasco Airport and as long as the number of passengers exceed 1.5 million passengers per year. These additional fees are calculated by multiplying the number of passengers by a fix coefficient, depending on the volume of passengers. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Uruguay—Amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement—Additional Fees” above. |
Additional Obligations assumed by Puerta del Sur as Concessionaire under the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement
Puerta del Sur has agreed to the following obligations with respect to the Uruguay New Airports:
| ● | make capital expenditures in an amount equal to U.S.$67.0 million in the aggregate between 2022 and 2028, in accordance with the investment schedule, with respect to the operation of such Uruguay New Airports; |
| ● | developing, managing, exploiting, operating and maintaining the Uruguay New Airports until November 20, 2053; |
| ● | extend insurance coverage for the Uruguay New Airports; and |
| ● | provide the performance guarantees explained below. |
Master plan
The master plan is to be prepared considering projections of passengers and cargo traffic growth and it does not need to include investment projections. The last master plan for Carrasco Airport was prepared in connection with the extension of the Carrasco Concession Agreement’s term, covered the period 2011-2033 and was approved by Decree 229/14. Every year, Puerta del Sur has to corroborate the projections made for the past year and with that information be able to update the master plan every five years. Under the Resolution No. 218/021 of the Executive Branch and the amendment agreement signed on November 8, 2021, Puerta del Sur is going to invest an aggregate of U.S.$67 million in the new airports.
Guarantees
Under the Carrasco Concession Agreement, Puerta del Sur is required to provide the following guarantees:
| ● | A guarantee securing the completion of the construction works of the new terminal. A U.S.$1.5 million completion guarantee is in place concerning Group 1 and 2 works. |
| ● | A performance guarantee for U.S.$7.6 million. This guarantee will be returned six months after the expiration of the Concession Agreement. |
| ● | Guarantees securing the completion of each group of construction works related to the Uruguay New Airports, to be determined under the Investment Program and for the amounts set forth under the Investment Schedule. The guarantees will need to be for an amount equal to 5% of each group of construction work to be performed. |
109
We have obtained a surety bond with a local financial institution to support our guarantee obligations under the Carrasco Concession Agreement.
Insurance
Upon execution of the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement and takeover of the Uruguay New Airports, the existing insurance coverage under the Carrasco Concession Agreement has been extended to cover the Uruguay New Airports.
Termination
The Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement by its terms is expected to terminate on November 20, 2053.
Termination Upon Breach by Puerta del Sur
The Carrasco Concession Agreement may be terminated by the Defense Ministry (with prior approval of the Executive Branch) upon due notification to Puerta del Sur, upon repeated and material breaches of the Carrasco Concession Agreement by Puerta del Sur. The Carrasco Concession Agreement does not expressly set forth a definition of a material breach of the Concession Agreement; however, the Carrasco Concession Agreement provides certain examples, including:
| ● | delay in the payment of annual fees to DINACIA for the concession of Carrasco Airport; |
| ● | charging amounts over the maximum permitted under the Carrasco Concession Agreement; |
| ● | provision of services repeatedly in an incorrect or not efficient manner; and |
| ● | assignment of the Carrasco Concession Agreement without the prior approval of the Defense Ministry. |
Upon a breach of the Carrasco Concession Agreement by Puerta del Sur, the Defense Ministry will be entitled to:
| ● | foreclose upon all collateral posted by Puerta del Sur under the Carrasco Concession Agreement to guarantee performance of its obligations; |
| ● | take control of the Carrasco Airport and all its assets; and |
| ● | claim all damages suffered by Carrasco Airport as well as request payment of all credit owed to the Defense Ministry. |
Replacement of Puerta del Sur as party to the Carrasco Concession Agreement by the Uruguayan government
The Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement revises the provisions under the Carrasco Concession Agreement with respect to the right of the Uruguayan government to terminate the concession for public interest. Under the current terms of the Carrasco Concession Agreement, before the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement entered into effectiveness, the Defense Ministry could replace Puerta del Sur as party to the Carrasco Concession Agreement (prior approval from the Uruguayan executive power) due to reasons based on “public interest” that require the Concession Agreement to be terminated.
Upon replacement of Puerta del Sur as party to the Carrasco Concession Agreement, Puerta del Sur shall be entitled to receive a termination payment calculated as follows:
| ● | the performance guarantee posted under the Carrasco Concession Agreement, plus |
| ● | the value of all investments made in construction, reparation of buildings made in accordance with the Carrasco Concession Agreement, less accumulated depreciation, plus |
| ● | a portion of the amount paid in the auction in August 2003 (U.S.$34.0 million) to purchase shares of Puerta del Sur. |
Upon execution of the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement, the Uruguayan Ministry of Defense will still have the right, with prior authorization from the Uruguayan executive power, to terminate the Carrasco Concession Agreement due to reasons based on “public interest” but the indemnification amount to be paid shall be modified both in relation to the Uruguay New Airports and in relation to the Carrasco International Airport, in accordance with the following:
110
The early termination may be done either: (i) with respect to the Carrasco Airport and the Uruguay New Airports (“Full Termination”), or (ii) with respect to one or more of the Uruguay New Airports only (“Partial Termination”).
Upon a Full Termination, Puerta del Sur will be entitled to receive a termination payment calculated as follows:
| ● | the value of all investments made in construction, works and repairs of buildings at the Carrasco International Airport made in accordance with the Carrasco Concession Agreement, less accumulated depreciation as of the financial year in which the termination occurs, plus |
| ● | the adjusted amount of U.S.$34 million, paid in the public auction in August 2003 to purchase the shares of Puerta del Sur, less accumulated depreciation as of the financial year in which the termination occurs, provided however, that this amount will be fully amortized by 2023, plus |
| ● | the adjusted amount of U.S.$23.5 million paid in cash by Puerta del Sur in 2014 in connection with and exchange for the 10-year extension of the Carrasco Concession Agreement from 2023 to 2033, less accumulated depreciation as of the financial year in which the termination occurs, provided however, that this amount will be fully amortized by 2033, plus |
| ● | the value of all investments made in the Uruguay New Airports up to the date of the early termination, adjusted by the parametric formula outlined in the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement and, as from January 1, 2034, also adjusted by the accumulated depreciation as of the financial year-end in which the early termination occurs using the linear method (until the end of the Carrasco Concession Agreement term in 2053), plus |
| ● | the accumulated value of the expenses incurred (net of operating income from the Uruguay New Airports) incurred to operate and maintain the Uruguay New Airports from the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement effective date until, and including, December 31, 2033, adjusted by the fixed formula outlined in the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement. Starting January 1, 2034, the value will be reduced by a cumulative 5% until the year in which the early termination occurs. If there is a Full Termination on or after January 1, 2034, then there will be no compensation for the expenses incurred to operate and maintain the Uruguay New Airports as from January 1, 2034. |
Furthermore, the performance guarantee posted under the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement would be returned to Puerta del Sur.
Upon a Partial Termination, Puerta del Sur will not be entitled to receive a termination payment. If upon the occurrence of a Partial Termination, there are mandatory investments remaining in relation to the Uruguay New Airports being terminated then, with prior authorization of the Uruguayan executive power, Puerta del Sur will need to invest such outstanding investments in connection with the terminated Uruguay New Airports in the other still remaining Uruguay New Airports under the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement.
Termination Upon Terminal Destruction
In the event of force majeure (e.g., the destruction of Carrasco Airport or severe damage that prevents Carrasco Airport’s operations), the Defense Ministry will be entitled to terminate the Carrasco Concession Agreement without paying the termination payment to Puerta del Sur and collect all of the indemnification payments under all of Carrasco Airport’s insurance policies.
Alternatively, the Defense Ministry could request Puerta del Sur to re-build Carrasco Airport if the reconstruction of the airport does not alter the terms of the Carrasco Concession Agreement.
Termination Upon Agreement Between Puerta del Sur and the Defense Ministry
The Carrasco Concession Agreement may be terminated by mutual agreement (with prior approval of the Uruguayan Executive Branch). No termination fee is payable by any party in this circumstance.
111
Return of Facilities
Upon the expiration of the term, or termination, of the Carrasco Concession Agreement, the Carrasco Concession Agreement provides that the Uruguayan Government will take full possession of Carrasco Airport’s premises, and all of its facilities and installations. The works and equipment incorporated by Puerta del Sur will also be transferred to the Defense Ministry.
In the event that the facilities, installations or equipment become obsolete or are not of interest to the Uruguayan Government, Puerta del Sur may be required to remove, update or demolish the same. If Puerta del Sur fails to comply with the aforementioned obligation, the Defense Ministry may perform the mentioned activities at Puerta del Sur’s cost.
After the Carrasco Concession Agreement term has expired or been terminated, Puerta del Sur will have a period of 180 calendar days to deliver the premises in perfect condition, other than normal wear and tear.
Force Majeure
Pursuant to the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement, in an event of force majeure (e.g., strikes, pandemics, earthquakes, floods, terrorism, acts of the authorities, changes in law, borders closure, exceptional restrictions to air traffic, among others), none of the parties would be deemed in breach of the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement, in regards to the obligation to make capital expenditures in accordance with the Investment Schedule and the obligations of construction works in accordance with the Investment Program.
The party affected by force majeure must notify the other party and will have a period of time equal to the period during which the force majeure continues (up to 90 days) to remediate the situation. If after such period, remediation is not possible or there continues to be a force majeure situation, the parties will negotiate, within 60 days, adjustments to the Investment Schedule or Investment Program. If the parties do not reach an agreement within such 60-day period, then neither party may terminate the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement but they can request a technical arbitration to decide on the remediation to the Investment Program and the Investment Schedule, to the extent applicable.
Except for regulating force majeure events affecting the Investment Schedule and the Investment Program, the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement does not modify the effect of force majeure on the destruction of the terminal, which shall continue to be those described in “Termination - Termination Upon Terminal Destruction.”
Punta del Este Concession Agreement
In 2008, in a private purchase transaction, we acquired all of the equity interests of CAISA, which owns the concession that operates the Punta del Este Airport. The Punta del Este Concession Agreement was executed in 1993 and was scheduled to expire on March 31, 2019. In March 2019, the Executive Power of Uruguay through the Defense Ministry issued a resolution approving the extension of the Punta del Este Concession Agreement for additional 14 years, until March 31, 2033, authorizing the Ministry of Defense to grant the modification of the aforementioned contract. In 2019, an amendment to such concession was executed, pursuant to which CAISA committed to undertake investments in an amount of approximately U.S.$35.0 million. As of December 31, 2020, U.S.$12.5 million of this commitment had already been invested. The Punta del Este Airport is not material to our business.
Armenia
Sources of Regulation
The following are the main laws and regulations that govern the Armenian Concession Agreement, the business of AIA and the operation of Zvartnots and Shirak Airports in Armenia:
| ● | Republic of Armenia Government Resolution No. 17, dated January 8, 2002, approving the Armenian Concession Agreement by and between the Armenian Government and CASA, dated December 17, 2001, and designating the Minister of Justice to oversee the transition provisions of the Armenian Concession Agreement (Appendix E) and to adjust them in consultation with CASA, if necessary, before the possession date. |
112
| ● | Law No. HO-329 (the Republic of Armenia Law on Types of Activities Subject to Licensing in the Territory of Yerevan Zvartnots Airport), dated May 29, 2002, pursuant to which AIA, as the Concession Manager of Zvartnots Airport (the “Concession Manager”) was granted licenses to carry activities such as sale of medicines, foreign exchange bureau, operation of customs warehouses, duty-tax free shops, customs mediation, activities of customs carrier, casinos and other entertainment premises. Under this law, the Concession Manager is also entitled to assign its licenses or transfer parts thereof to other persons, who are eligible for such licenses. There are no other transfer restrictions set forth in the Law No. HO-329 nor in the Armenian Concession Agreement. |
| ● | Republic of Armenia Government Resolution No. 693-A, dated May 30, 2002, pursuant to which the Armenian Government approved an addendum to the Armenian Concession Agreement. The addendum was executed on May 17, 2002, to allow CASA to assign its rights and obligations under the Armenian Concession Agreement to American International Airports LLC, who then incorporated AIA. |
| ● | Republic of Armenia Government Resolution No. 2004-A, dated December 1, 2005, pursuant to which the Armenian Government authorized the Concession Manager to grant a subconcession to a third-party service provider, Zvartnots Handling Closed Joint-Stock Company, to operate ground handling services and aircraft towing at the Zvartnots Airport, among other services. |
| ● | Armenian Aviation Law No. HO-81-N, dated February 22, 2007 defining, among other things, the terms of the concession of Zvartnots Airport and the concessionaire’s rights and obligations. The Armenian Aviation Law also sets forth the basic framework for maintenance and operations of airports in Armenia and defines the powers of the GDCA. |
| ● | Republic of Armenia Government Resolution No. 965-N, dated August 2, 2007, pursuant to which the Armenian Government approved Addendum No. 3 of the Armenian Concession Agreement granting AIA a concession for the operation of the Shirak Airport. Addendum No. 3 was executed on November 16, 2007. |
| ● | Republic of Armenia Government Resolution No. 588-A, dated May 20, 2010, pursuant to which the Armenian Government approved Addendum No. 4 of the Armenian Concession Agreement terminating AIA’s ownership rights to the immovable property actually occupied by the company implementing Armenian air-navigation service. Addendum No. 3 was executed on June 10, 2010. |
| ● | Republic of Armenia Government Resolution No. 1532-N, dated December 27, 2018, pursuant to which the Armenian Government approved the master plan for 2018-2022 submitted by AIA, as the concessionaire of Zvartnots Airport and the Shirak Airport. In accordance with the Armenian Concession Agreement, the Master Plan is the document containing guidelines for the works to be done by the Concession Manager on Zvartnots Airport and the Shirak Airport for each five-year period during the term of the Armenian Concession Agreement. The Master Plan must be prepared by AIA and is subject to approval by the Armenian Government. The Master Plan for 2003-2007 had been previously approved by Government Resolution No. 392-N, dated April 10, 2003, the Master Plan for 2008-2012 by the Government Resolution No. 1559-N dated December 25, 2008, and the Master Plan for 2013-2017 by the Government Resolution 1495-N, dated December 26, 2013. |
| ● | The Republic of Armenia Territorial Administration and Infrastructure Minister’s Order No. 37-L, dated 10 June 2020 “On Approval the Charter of Civil Aviation Committee (CAC),” which defines the authority of the CAC. |
Governmental Authorities
Role of CAC
In the Republic of Armenia, the aviation policy (except military) is developed and implemented by relevant ministry (Ministry of Territorial Administration and Infrastructure) The state administrative body subordinated to the ministry is the civil aviation committee (“CAC”) in the field of air transport regulation, civil aviation and non-military state aviation activities, air traffic service, aviation security, flight safety, as well as safety and security regulation of aviation ground means and provided services, oversight of aviation services and aviation infrastructures existing in the Republic of Armenia.
113
Order No. 37-L dated 10 June 2020 and the Armenian Aviation Law (the “Armenian Aviation Law”) regulate CAC’s organization, powers and duties. CAC’s duties include, among others, oversight compliance with applicable regulation, develop new regulation in the air transportation industry, grants licenses and permits, etc.
The Armenian Concession Agreement
On December 17, 2001, the Armenian Concession Agreement was executed by and between the Armenian Government and CASA, and subsequently approved by the Armenian Government in January 2002. Under the Armenian Concession Agreement, CASA assumed all of the rights and obligations as the Concession Manager of Zvartnots Airport until such time as it established and registered an Armenian affiliate company to assume such rights and obligations.
On May 17, 2002, an Addendum to the Armenian Concession Agreement was executed which permitted CASA to assign to its affiliate, American International Airports LLC, all of the rights and obligations pertaining to CASA, stemming from the Armenian Concession Agreement. American International Airports LLC incorporated and registered AIA as a wholly-owned subsidiary in Armenia and assigned to it all of the rights and obligations of the Concession Manager of Zvartnots Airport under the Armenian Concession Agreement.
The Armenian Concession Agreement was further amended by the following addenda executed by and between the Armenian Government and AIA.
| ● | Addendum No. 1, executed on February 21, 2003, under which the Armenian Government and the Concession Manager agreed to certain mechanisms regarding the registration of property rights of the Concession Manager for real property in Zvartnots Airport; |
| ● | Addendum No. 2, executed on October 19, 2006, under which, commencing on January 1, 2007, AIA undertook to provide rescue and firefighting services and facilities in accordance with the standards of Annex 14, Chapter 9 of the ICAO (Emergency and Other Issues), as well as ICAO related manuals and applicable Armenian laws; |
| ● | Addendum No. 3, executed on November 16, 2007, under which the Armenian Government expanded the concession of Zvartnots Airport granted to AIA to include the concession of the Shirak Airport, which gave AIA the right to engage in certain types of aviation and non-aviation activities. As such, the terms of the Armenian Concession Agreement are also applicable to the Shirak Airport concession; and |
| ● | Addendum No. 4, executed on June 10, 2010, under which AIA agreed to terminate its rights under the Armenian Concession Agreement over certain real property operated by “Hayaeronavigatsia” CJSC, the local air traffic navigation company, at the Zvartnots Airport, including the land occupied by the newly built Air Traffic Control Tower building. As such, AIA no longer has the right to dispose of and use these real property units, even for purposes of rendering the services under the Armenian Concession Agreement. |
| ● | In December 2020, 100% of the share capital of AIA was transferred from American International Airports LLC to the Company pursuant to a Share Transfer Agreement duly registered in Armenia. As a consequence of this transfer, American International Airports LLC no longer holds any interest in AIA nor in any other Armenian entity. |
Rights of the Concession Manager
Pursuant to the terms and conditions of the Armenian Concession Agreement, the Concession Manager has the exclusive right to administer, operate and exploit Zvartnots Airport and Shirak Airport and was granted by the Armenian Government the exclusive right to use the airports and all real, personal, mixed, tangible and intangible property of any kind or nature which is now or in the future will be a part of the airport activities, and to conduct all businesses relating to the airports, with the exception of certain businesses and properties specifically indicated in the Armenian Concession Agreement. The Concession Manager holds all of the licenses related to management of the airports other than regulatory functions exclusively vested in the Armenian Government. The Concession Manager has the exclusive right to administer and to carry out activities relating to the airports, which include, among others:
Aviation services
| ● | aircraft guidance and escorting services; |
114
| ● | management of parking areas; |
| ● | provision and operation of escalators; |
| ● | telescopic bridge; |
| ● | ground handling services, including aircraft pulling services; |
| ● | electrical supply services; |
| ● | operational-technical maintenance services; |
| ● | aviation security and aircraft custody services; |
| ● | utility services for aircrafts; |
| ● | fuel and lubricants supply and fueling; and |
| ● | special vehicle transportation services. |
Commercial
| ● | rent of ground spaces for commercial purposes; |
| ● | advertising; |
| ● | duty-tax free shops; |
| ● | shopping centers; |
| ● | bank and exchange bureau and financial services; |
| ● | hotels; |
| ● | restaurants, snack-bars, coffee shops; |
| ● | duty paid shops such as clothing and fixtures, newspaper and magazine stands; |
| ● | casinos and other entertainment premises; |
| ● | car parking; |
| ● | baggage carts and lockers; |
| ● | telecommunication services; |
| ● | vip lounges; |
| ● | catering; and |
| ● | gas stations for automobiles. |
Other
| ● | customs warehouses; |
| ● | intermodal logistics platforms; |
115
| ● | free zones; |
| ● | ground transportation; and |
| ● | other services, to the extent not prohibited under the Armenian Concession Agreement, which are complementary or useful to the aeronautical operation and/or the commercial development of the airports, including, but not limited to, activities connected to the airports such as convention, art and exhibition centers, hotels and other leisure and tourism activities and transportation, which may be performed outside the airports. |
Air traffic control activities are not included in the Armenian Concession Agreement. The Concession Manager is not responsible for approximation, taxying, flight operations or any other activity related to air traffic control. Such activities are handled exclusively by Hayaeronavigatsia CJSC.
The Concession Manager is entitled to conduct the above-mentioned commercial activities on its own account or through any third parties. It may also grant to third parties the right to use certain ground spaces to carry out commercial activities authorized by the Concession Manager, either free of charge or for consideration, by way of a revocable instrument or agreement or by such other instrument the Concession Manager considers appropriate.
Obligations Assumed by the Concession Manager
Under the terms of the Armenian Concession Agreement, the Concession Manager shall:
| ● | undertake and warrant the normal and permanent rendering of aviation services; |
| ● | manage and operate the airports according to internationally accepted airport standards; |
| ● | comply with the Master Plan; |
| ● | obtain, at its own cost and risk, adequate financing and management resources to modernize the physical infrastructure of the airports, to ensure compliance with applicable regulatory standards and to improve the quality of their management; |
| ● | provide the Armenian Government with the ground spaces required for the performance of customs, migration, defense, security, safety, Phyto-zoo sanitary and bromatological controls and public health activities, as long as they are and remain activities directly performed by Armenian Government agencies and bodies. If the Armenian Government decides to delegate any of such activities to the private sector, the Concession Manager shall have a right of first refusal for the performance of such activities, which right must be exercised within a period of 30 days as from the announcement of any bid by a third party; |
| ● | provide the Armenian Government with an annual report (and such other reports as the Armenian Government may reasonably request) on the development of the management, exploitation and operation of the airports, which will include data regarding traffic, revenues and investments; |
| ● | manage, operate and exploit the airport activities, directly or through contracts with third parties, subject to the limitations set forth in the Armenian Concession Agreement; |
| ● | collect from all of the users (including the airlines and all other public or private persons performing activities or exercising any authority in the airports) the corresponding airport charges and the fees which the Concession Manager may establish from time to time; and |
| ● | construct, maintain and/or operate, on its own account or through any third parties, any hangars, fuel storage plants or aircraft supply plants, customs warehouses and/or any other warehouses or premises related to the handling of air cargoes or the aeronautical operation in general. |
116
Master Plan
Under the terms of our Armenian Concession Agreement, AIA is required to present a master development plan for approval by the director of the Ministry of Territorial Administration and Infrastructure every five years. Each master development plan includes investment commitments (including capital expenditures and improvements) applicable to the concession holder for the succeeding five-year period. Once approved by the government, which requires approval by the Prime Minister, these commitments become binding obligations under the terms of the respective concession. Since 2003, the Armenian government has approved our master development plan for the Armenian Concession Agreement as periodically revised.
The Master Plan and all revisions and extensions thereof will be made according to traffic projections, the internal rate of return agreed upon by the Armenian Government and the Concession Manager, the objective needs of the services and other conditions that the Concession Manager may deem appropriate according to standards applied in similar airports around the world. The Master Plan will be updated every five years and extended to cover the 30-year term of the Armenian Concession Agreement. The Master Plan may be revised from time to time at the Concession Manager’s request or based on the changing needs of the airports.
The Concession Manager is entitled, in its sole discretion, to establish the priority rank among the works described in the Master Plan, to postpone or anticipate the execution thereof to earlier or later periods than those originally foreseen in the Master Plan, and to prepare the corresponding projects for the implementation of the works, emphasizing safety concerns according to ICAO rules and taking into account service quality levels under the International Air Transport Association Class C category.
The Concession Manager is required to inform the Armenian Government on the performance and progress of the specific works described in the Master Plan. Nevertheless, there are no periodic reporting requirements.
Concession Fees
Under the Armenian Concession Agreement, the Concession Manager shall not pay any fee or other consideration of any kind whatsoever for the rights granted to it in the Armenian Concession Agreement.
Airport Charges and Fees
All of the activities carried out at the airports as well as the use of any property transferred to the Concession Manager by the Armenian Government shall entitle the Concession Manager to collect the relevant Airport Charges and the Fees which the Concession Manager establishes. The initial airport charges are stated in an appendix of the Armenian Concession Agreement. These charges were updated on April 1, 2022 and include the following:
Landing Charge
Landing Charge for Passenger Aircraft is €5.80 per Metric Ton or fraction.
| ● | Night Landing Additional Charge for Passenger Aircraft: 20% of the amount of the Landing Charge, calculated as described above will be added to each Passenger Aircraft landing occurred during nighttime (from 21:00 to 07:00). |
| ● | Special Flight Radio AID Control Landing Charge is free of charge. |
Take-Off Charges
Charges are imposed based on the maximum certified aircraft take-off weight.
Passenger aircraft Take-Off Charge
| ● | Take-Off Charge Passenger Aircraft is €5.80 per Metric Ton or fraction. |
| ● | Night Take-Off Additional Charge Passenger Aircraft: 20% of the amount of the Take-Off Charge, calculated as described above, will be added to each passenger aircraft take-off occurred during nighttime (from 21:00 to 07:00). |
117
Other services
Every special announcement made by the airport for the airline will be charged in the amount of €15 per each announcement/flight.
Manifest of Departing Passengers printed and/or prepared by the Airport will be charged €0.15 per each departing checked-in passenger.
Use of Airport Departure Control System will be charged EUR 1.50 per each departing checked-in passenger.
Use of Apron Access to all aircraft types will be charged according to the take-off weight of the aircraft, as follows:
| ● | Aircraft weight <= 50 Tons will be charged €13.15 per each flight. |
| ● | Aircraft weight 50-100 Tons inclusive will be charged €30.42 per each flight. |
| ● | Aircraft weight 100-200 Tons inclusive will be charged €60.34 per each flight. |
| ● | Aircraft weight 200-300 Tons inclusive will be charged €101.27 per each flight. |
| ● | Aircraft weight >300 Tons will be charged €187.20 per each flight. |
| ● | Requirement of Airport Supervisor assistance will be charged €22 per each person per each hour or fraction. |
| ● | Requirement of Airport Technician assistance will be charged €18 per each person per each hour or fraction. |
| ● | Requirement of Airport Personnel assistance will be charged €12 per each person per each hour or fraction. |
Use of Airport Local Departure Control System will be charged €1.10 per each departing checked-in passenger.
Take-Off Special Flight Radio AID Control
Special Flight Radio AID Control Take-Off Charge is free of charge.
Aircraft Parking Charge
Parking Charge for Passenger Aircraft
Passenger aircraft parking charge after the parking time free of charge is finished for airlines based at Zvartnots International Airport is €0.20 per ton, per hour or their fractions.
Passenger Aircraft Parking Charge for Other regular Airlines non based at Zvartnots International Airport, for all aircraft types:
| ● | Passenger aircraft parking time free of charge for non-based regular airlines is two hours and 30 minutes. |
| ● | Passenger aircraft parking charge after the parking time free of charge is finished for non-based regular airlines is €0.35 per ton, per hour or their fractions. |
| ● | Passenger aircraft parking charge after the parking time free of charge is finished for parking locations equipped with loading bridges is €360 per ton, per hour or their fractions. |
118
Parking Charge for General Aviation and Charter Flight’s Aircraft
General aviation and charter flight’s aircraft Parking Charge for airline based at Zvartnots International Airport for all aircraft types:
| ● | General aviation and charter flight’s aircraft parking time free of charge for airline based at Zvartnots International Airport is two hours and 30 minutes. |
| ● | General aviation and charter flight’s aircraft parking charge after the parking time free of charge is finished for airline based at Zvartnots International Airport is €0.50 per ton, per hour or their fractions. |
General aviation and charter flight’s aircraft Parking Charge for other airlines, for all aircrafts types:
| ● | General aviation and charter flight’s aircraft parking time free of charge for non-based airline is two hours and 30 minutes. |
| ● | General aviation and charter flight’s aircraft parking charge after the parking time free of charge is finished for non-based airline is €0.60 per ton, per hour or their fractions. |
Passenger aircraft parking charge after the parking time free of charge is finished for Private Jets is 0.10 per ton, per hour or their fractions.
Non-Commercial Aircraft performing Cargo Humanitarian Flight for goods Parking Charge:
| ● | Non-commercial aircraft performing cargo humanitarian flight parking time free of charge is six hours. |
| ● | Non-commercial aircraft performing cargo humanitarian flight parking charge after the parking time free of charge is finished is €0.20 per ton, per hour or their fractions. |
Parking Other Republics President aircraft on President Flight
| ● | Other Republics President aircraft on President Flight parking time free of charge is two hours and 30 minutes. |
| ● | Other Republics President aircraft on President Flight parking charge after the parking time free of charge is finished is €0.20 per ton, per hour or their fractions. |
| ● | Maximum Other Republic President aircraft on President Flight Parking Charge after the parking time free of charge is finished is €50 per each tranche of 48 hours of parking or fraction. |
Official Foreign Government Flight parking
| ● | Official Foreign Government Flight parking time free of charge is two hours and 30 minutes. |
| ● | Official Foreign Government Flight parking charge after the free parking time is expired is €0.20 per ton per hour or fraction. |
| ● | Maximum Official Foreign Government Flight parking charge after the parking time free of charge is finished is €120 per each tranche of 48 hours of parking or fraction. |
Parking Special Flight Radio AID Control
Special Flight Radio AID Control parking charge is free of charge.
119
Passenger Tariff
Passenger Handling Airport Tariff
| ● | Per each departing passenger €23 is charged as Passenger Handling Airport Tariff. (Starting from 1 April 2022- Per each departing passenger €25 shall be charged as Passenger Handling Airport Tariff) |
| ● | Per each transit passenger €8 is charged as Passenger Handling Airport Tariff. |
| ● | Per each departing infant under two years old No Passenger Handling Airport Tariff is charged. |
| ● | Per each departing infant under two years old traveling with a separate seat 50% of the Passenger Handling Airport Tariff is charged. |
| ● | Per each transit infant passenger under two years old No Passenger Handling Airport Tariff is charged. |
| ● | Per each transit infant under two years old, traveling with a separate seat 50% of the Passenger Handling Airport Tariff is charged. |
Departing Child
| ● | Per each departing child from two years old up to 12 years old inclusive, 50% of the Passenger Handling Airport Tariff is charged. |
| ● | Per each transit child passenger from two years old up to 12 years old inclusive, 50% of the Passenger Handling Airport Tariff is charged. |
Security Charge
Security service
Airport Security Charge is €2 per each departing passenger.
Departing Infant
| ● | Per each departing infant under two years old No Airport Security Charge is charged. |
| ● | Per each departing infant under two years old traveling with a separate seat Airport Security Charge is €2 |
| ● | Per each transit infant under two years old No Airport Security Charge is charged |
| ● | Per each transit infant under two years old traveling with a separate seat 50% of the Airport Security Charge is charged |
Transit Passenger
Per each transit passenger 50% of the Airport Security Charge is charged.
Loading Bridge Use Charge
| ● | Loading Bridge Use Charge is €80. |
| ● | Loading Bridge Use Charge on Arrival of the flight only is €40. |
| ● | Loading Bridge Use Charge on Departure of the flight only is €40. |
120
Note
Use of loading bridge at gates equipped with loading gates is mandatory.
Excess Luggage Charges
| ● | Per each Ton of excess luggage the airline will be charged €100. |
Centralized Power Supply Service Charges
The supply of centralized power will be charged per hour or fraction, according to the following tariffs Aircraft weight:
Metric Tons |
|
Charge per hour |
|
● 7.01.01. <= 50 |
|
€ |
32 |
● 7.01.02. 50 – 100 inclusive |
|
€ |
45 |
● 7.01.03. 100 – 200 inclusive |
|
€ |
54 |
● 7.01.04. 200 – 300 inclusive |
|
€ |
63 |
● 7.01.05. > 300 |
|
€ |
72 |
Use of alternative type of power supply (diesel, etc.) in parking lots with centralized power supply is prohibited.
Aircraft Special Security
| ● | Aircraft special security can be carried out if there is a special request of the air carrier. |
| ● | Airport Special Security Charge is 3% of applicable Landing Charge, per each hour of parking or fraction. |
| ● | Security charges for the airside parking within time limits are included in the following tariffs: |
| ● | In case of parking within time limits, in the landing and take-off Charges; |
| ● | In case of parking past the parking time limits, in the parking tariffs (both within and past time limits); |
| ● | Security charges provided at technical maintenance areas €4.30 per hour or fraction. |
Cargo Handling Tariffs
| ● | Import Cargo Handling Charge per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 32 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 6.4). |
| ● | Import Cargo Handling Minimum Charge for each Airway bill is 6,000 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,200). |
| ● | Cargo Handling Minimum Charge for Imported Dangerous Goods Cargo is 8,000 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,600) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Import Cargo Handling Additional Charge for Dangerous Goods Cargo per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 100 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 20). |
| ● | Import Cargo Handling Minimum Charge for Valuable Cargo is 8,000 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,600) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Import Cargo Handling Additional Charge for Valuable Cargo per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 200 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 40). |
| ● | Import Cargo Handling Minimum Charge for Imported Perishable Cargo is 4,000 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 800) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Import Cargo Handling Additional Charge for Imported Perishable Cargo per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 8 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1.6). |
121
| ● | Import Cargo Handling Minimum Charge for Livestock Cargo is 8,000 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,600) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Import Cargo Handling Additional Charge for Livestock Cargo is per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 20 Dram (plus 20% VAT – AMD 4). |
| ● | Export Cargo Handling Charge per each 1 (one) kilogram is 32 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 6.4). |
| ● | Export Cargo Handling Minimum Charge for each Airway bill is 6,000 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,200). |
| ● | Export Cargo Handling Minimum Charge for Dangerous Goods Cargo is 8,000 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,600) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Additional Export Cargo Handling Charge for exportation Dangerous Goods Cargo per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 100 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 20). |
| ● | Charge for completing dangerous goods acceptance checklist per each Airway Bill is 12,000 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 2,400). |
| ● | Minimum Export Cargo Handling Charge for exportation Valuable Cargo is 8,000 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,600) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Additional Export Cargo Handling Charge for exportation Valuable Cargo per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 200 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 40). |
| ● | Minimum Export Cargo Handling Charge for exportation Perishable Cargo is 4,000 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 800) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Additional Export Cargo Handling Charge for exportation Perishable Cargo per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 8 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1.6). |
| ● | Minimum Export Cargo Handling Charge for Livestock Cargo is 8,000 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,600) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Additional Export Cargo Handling Charge for Exported Livestock Cargo is per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 20 Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 4). |
| ● | Free Cargo Import Storage (except Valuable Cargo) will apply for up to 48hs (forty-eight hours) from arrival to the warehouse. |
| ● | Free Valuable Cargo Import Storage will apply for up to 12hs (twelve hours) from arrival to the warehouse. |
| ● | Free Cargo Import Storage will apply for up to 168hs (one hundred and sixty-eight hours) from arrival to the warehouse for goods imported by humanitarian organizations. |
| ● | Import Storage Charge (except Valuable Cargo) to the Consignee/Agent once the free storage period 48hs has expired is charged AMD 8 (plus 20% VAT AMD 1.6), per kilogram per day. |
| ● | Valuable Cargo Import Storage Charge to the Consignee/Agent once the free storage period 12hs has expired is charged AMD 116.4 (plus 20% VAT AMD 23.28), per kilogram per day. |
| ● | Minimum Import Storage Charge (except Valuable Cargo) to the Consignee/Agent AMD 5,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,000) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Minimum Valuable Cargo Import Storage Charge to the Consignee/Agent AMD 11,640 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 2,328) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Storage charges are per calendar day, independently of the hours used. |
122
| ● | Maximum storage time in the warehouse is 6 months. |
| ● | Free Cargo Export Storage (except Valuable Cargo) will apply for up to 24 (twenty-four) hours from arrival to warehouse. |
| ● | Free Valuable Cargo Export Storage will apply for up to 12 (twelve) hours from arrival to warehouse. |
| ● | Export Cargo Storage (except Valuable Cargo) is charged to the consignor/agent. AMD 8 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1.6) per kilogram per day, after 24 (twenty-four) hours from reception of the merchandise. |
| ● | Export Valuable Cargo Storage is charged to the consignor/agent. AMD 116.4 (plus 20% VAT - 23.28 AMD ) per kilogram per day, after 12 (twelve) hours from reception of the merchandise. |
| ● | Minimum Export Storage Charge (except Valuable Cargo) after the free cargo storage period is to the Forwander/Agent AMD 5,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,000) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Valuable Cargo Minimum Export Storage Charge after the free cargo storage period is to the Forwander/Agent AMD 11,640 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 2,328) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | Marking of each Cargo Pieces will be charged 20 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 4) per each piece. |
| ● | Labeling of each Cargo piece (upon request of air carrier or cargo consignor) will be charged 50 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 10) per each piece. |
| ● | Special Escort of Import Goods is AMD 30,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 6,000) per each shipment. |
| ● | Special Escort of Export Goods is AMD 30,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 6,000) per each shipment. |
| ● | Additional Import Cargo Handling Charge for handling cargo merchandise in the warehouse in order to take samples or examine is AMD 3,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 600) per each movement shipment. |
| ● | Cutting of each Airway bill will be charged AMD 2,500 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 500). |
| ● | AMD 4,000 Weighing Cargo Goods Charge (plus 20% VAT - AMD 800) for each weighing. |
| ● | Cargo handling charge for imported cargo by truck per each 1 (one) kilogram is AMD 16.40 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 3.28). |
| ● | Cargo handling minimum charge for imported cargo by truck AMD 6,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,200). |
| ● | Cargo handling minimum charge for imported Dangerous Goods cargo by truck AMD 8,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,600). |
| ● | By truck Cargo Handling Additional Charge for Dangerous Goods Cargo per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 100 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 20). |
| ● | Cargo handling minimum charge for imported Valuable cargo by truck AMD 8,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,600). |
| ● | By truck Cargo Handling Additional Charge for Valuable Cargo per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 100 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 20). |
| ● | Cargo handling minimum charge for imported Perishable cargo by truck AMD 4,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 800). |
| ● | By truck Cargo Handling Additional Charge for imported Perishable Cargo per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 8 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,6). |
| ● | Cargo handling minimum charge for imported Livestock cargo by truck AMD 8,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,600). |
123
| ● | By truck Cargo Handling Additional Charge for Livestock Cargo per each 1 (one) Kilogram is 20,00 RA Dram (plus 20% VAT - AMD 4). |
| ● | By truck free Cargo Import Storage will apply for up to 48hs (forty-eight hours) from arrival to the warehouse. |
| ● | By truck import Storage Charge to the Consignee/Agent once the free storage period has expired is charged AMD 8 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1.6), per kilogram per day. |
| ● | By truck minimum Import Storage Charge to the Consignee/Agent AMD 5,000 (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,000) per each Airway bill. |
| ● | AMD 3.35 Perishable Cargo Handling Charge (offloading and loading Truck) (plus 20% VAT - AMD 0.67) per each kilogram. |
| ● | AMD 0.85 Perishable Cargo Storage Charge in Refrigerator (plus 20% VAT - AMD 0.17) per each kilogram per day. |
| ● | AMD 1.5 Perishable Cargo Storage Charge in Freezer (plus 20% VAT - AMD 0.3) per each kilogram per day. |
| ● | AMD 12 Freight Unloading from surface transport vehicles (plus 20% VAT - AMD 2.4) per kg or fraction. |
| ● | AMD 12 Freight Loading on surface transport vehicles (plus 20% VAT - AMD 2.4) per kg or fraction. |
| ● | AMD 24 Freight Unloading/Loading from/on surface transport vehicles (plus 20% VAT - AMD 4.8) per kg or fraction. |
| ● | AMD 5,000 Courier and consolidated Cargo allocation and assortment minimum charge (plus 20% VAT - AMD 1,000) for each Airway Bill. |
| ● | AMD 25 Courier and consolidated Cargo allocation and assortment and handing charge (plus 20% VAT - AMD 5) per one kilogram. |
Any modifications to such airport charges may be carried out upon notice from the Concession Manager to the Armenian Government, subject to the Armenian Government’s right to object to any adjustment within a 15 day period as from the date of receipt of such notice. The Armenian Government cannot unreasonably withhold its approval to the adjustments to the airport charges.
The Concession Manager, at its sole discretion, may collect the airport charges and fees in U.S. dollars, euros or Armenian dram, to the extent permitted by Armenian Law.
Airport charges and fees shall be automatically adjusted by applying the following procedures:
| ● | airport charges and fees expressed in Armenian dram will be adjusted proportionally to the variations of the exchange ratio between the Armenian dram and the United States dollar; |
| ● | airport charges and fees expressed in United States dollars will be adjusted based on the Total Producer Price Index for Finished Goods seasonally adjusted (PPI), as published monthly by the Bureau of Labor Statistics of the United States Department of Labor, and verified by the index as of December 2001, which shall be considered the “PPI Base Year,” and the index as of December of the year to be updated; and |
| ● | airport charges and fees expressed in euros will be adjusted proportionally to the variations of the exchange ratio between the euro and the United States dollar. |
Exchange and inflation variations between the date of any invoice and the date of actual payment of the corresponding charge or fee may be billed by the Concession Manager separately.
Internal Rate of Return
Internal Rate of Return is calculated as the annual net after tax internal rate of return on the Concession Manager’s actual total airport capital investments valued in United States dollars, including equity, equity equivalents, subordinate loans and/or convertible loans and any other capital contribution as expressed in the Concession Manager’s accounting statements audited by an international auditing firm.
124
Pursuant to the terms of the Armenian Concession Agreement, the Concession Manager is granted the right to receive an annual Internal Rate of Return of 20%. At the end of each fiscal year, the Concession Manager may propose to the Armenian Government certain adjustments to the Master Plan to adhere to the Internal Rate of Return of 20%. If the approved adjustments to the Master Plan are insufficient to meet the agreed Internal Rate of Return, the Concession Manager shall be entitled to adjust the real value (taking into account inflation) of airport charges, provided that before each adjustment the Concession Manager informs the Armenian Government of the proposed adjustment. If the Concession Manager does not recover the agreed Internal Rate of Return after applying the foregoing procedures, the Concession Manager shall be entitled, in its sole discretion and the Armenian Government cannot oppose, to extend the term of the Armenian Concession Agreement to the extent it permits the Concession Manager to reach the target Internal Rate of Return.
In addition, if applicable taxes payable by Concession Manager increase, then the Concession Manager shall be entitled to immediately increase all airport charges and fees so as to reflect such increase. Tax increases include rate increases, elimination or reduction of any exemption or deduction and any other modification which causes any applicable tax liability to increase.
Termination
The Armenian Concession Agreement will terminate pursuant to its terms on June 9, 2032. If the Concession Manager is in good standing on such date, the Concession Manager shall have the option to indefinitely extend the term of the Armenian Concession Agreement for additional periods of five years.
The Armenian Concession Agreement may be terminated prior to the scheduled termination date upon the occurrence of any of the following events:
| ● | Concession Manager’s breach of certain obligations; |
| ● | bankruptcy of the Concession Manager; |
| ● | administrative discretionary act; |
| ● | the Armenian Government’s breach of any of its obligations; and |
| ● | Force Majeure Events. |
Termination of the Armenian Concession Agreement will not imply the termination of the agreements that the Concession Manager executed with third parties, which shall be automatically assigned to the Armenian Government unless otherwise provided for in those agreements.
Termination due to the Concession Manager’s Breach
The Armenian Government is entitled to terminate the Armenian Concession Agreement if:
| ● | the Armenian Concession Agreement is entirely or partially assigned to a third party by the Concession Manager, without obtaining the express authorization of the Armenian Government; or |
| ● | the Concession Manager abandons the facilities of the airports, meaning that it stops its operations at the airports for more than 10 days due to the Concession Manager’s fault and without reasonable cause. No clear definition of abandonment of the airports facilities is included in the Armenian Concession Agreement. In case of dispute, it may be submitted, at the Concession Manager’s discretion, to arbitration. |
Bankruptcy of the Concession Manager
The bankruptcy, insolvency or invocation of any laws for the protection from creditors or cessation of business of or by the Concession Manager will cause the termination of the Armenian Concession Agreement.
Administrative Discretionary Act
If the Armenian Government decides to terminate the Armenian Concession Agreement unilaterally other than for “cause,” as specified in the Armenian Concession Agreement, the Armenian Government shall pay the Concession Manager specific liquidated damages and shall indemnify and hold the Concession Manager harmless with respect to all adverse consequences caused by third parties and deriving from the termination of the Armenian Concession Agreement.
125
If the Armenian Government terminates the Agreement based on reasonable national defense considerations, it will be liable solely for the total amount of investments effectively made by the Concession Manager since the commencement of the Armenian Concession Agreement and until the date of termination, as well as the Concession Manager’s existing obligations regarding investments assumed under the Armenian Concession Agreement, which may not be revoked or assigned to the Armenian Government or a new manager.
Armenian Government’s Breach of Contract
The Concession Manager is entitled to terminate the Armenian Concession Agreement if the Armenian Government breaches any of its obligations thereunder, and fails to cure such breach within a 20-day period after being served with a notice of the breach by the Concession Manager. Upon such termination, the Armenian Government shall pay the Concession Manager certain liquidated damages and shall indemnify and hold the Concession Manager harmless with respect to all adverse consequences caused by third parties deriving from the termination of the Armenian Concession Agreement.
Termination due to Force Majeure Events
The Concession Manager shall have the right to terminate the Armenian Concession Agreement upon the occurrence of a force majeure event and with a six-months prior notice if the Concession Manager reasonably proves that during the last two years prior to the date of notice it has not been able to recover the Internal Rate of Return on the investments made by the Concession Manager until such moment.
Upon termination, the Concession Manager shall assist the Armenian Government in identifying actions necessary to ensure normal continuation of airport activities, and shall provide training, information and know-how to the Armenian Government, at the Armenian Government’s reasonable request.
Governing Law and Dispute Resolution
Pursuant to Article 9 of the “Agreement between the Argentine Republic and the Republic of Armenia for the Reciprocal Promotion and Protection of Investments,” dated October 10, 1994, any dispute regarding the validity, interpretation and/or enforcement of the Armenian Concession Agreement may be submitted, at the Concession Manager’s discretion, to arbitration with the International Center for Settlement of Investment Disputes in accordance with the supplementary mechanism of such body for the management of conciliation, arbitration or investigation procedures. The arbitration award shall be final and binding on the parties.
The International Center for Settlement of Investment Disputes shall resolve all disputes in accordance with the provisions of the Armenian Concession Agreement, the laws of the jurisdiction of the contracting parties involved in the dispute, including their rules on conflict of law, the terms of any specific agreement concluded in relation to the parties’ respective investments and the relevant principles of international law.
In the event the Concession Manager decides not to submit the dispute to arbitration, the ordinary courts of the Republic of Armenia shall have jurisdiction to solve the case, in accordance with Armenian law.
Ecuador
Sources of Regulation
The Guayaquil Concession Agreement was executed on February 27, 2004, by and among TAGSA, AAG and the Municipality of Guayaquil. The Guayaquil Concession Agreement has been amended ten times since the date of execution, the most significant of which relates to the unification of terminals and the use of other sites within the Guayaquil Airport, for commercial uses, the expansion of the terminals and the re-establishment of the economical equilibrium of the Guayaquil Concession Agreement and the increase in investment for new works as well as the increase in the contribution of regulated revenues from 50.25% to 55.25% as a consequence of the concession extension until July 27, 2029. Nevertheless, as a consequence of the Eighth Amendment to the Concession Agreement and the economic equilibrium reestablishment conducted in 2021, the contribution of regulated revenues decreased to 53.66%, and in 2022 decreased to 50.25%, until the economic equilibrium of the Guayaquil Concession Agreement is reestablished and agreed to extend the concession period until July 27, 2031. Terms of the Guayaquil Concession Agreement amendment also sets forth an increase of U.S.$524,600 in the administrative service fee, paid semiannually, as of February 2019.
126
The following are the main laws and regulations that govern the Guayaquil Concession Agreement and the operation of the Guayaquil Airport:
| ● | Article 249 of the Constitution of Ecuador of 1998 sets forth that the rendering of public services, directly or by delegation, was the responsibility of the Ecuadorian State. The Ecuadorian State is authorized to delegate the performance of public services to private companies through grants of concessions or other forms stipulated in the Ecuadorian legislation. |
| ● | Article 1 of the Civil Aviation Law enables the delegation to the private sector of airport public services, as well as the possibility of the Ecuador Government to transfer to the municipalities the ability to render airport public services directly or by delegation, as per article 249 of the Constitution of Ecuador of 1998. Based on this, by means of Executive Decree No. 871 dated October 18, 2000, the President of Ecuador authorized the Municipality of Guayaquil to delegate to the private sector the rendering of airport services. |
| ● | Article 43 of the Law on Modernization of the State defines the forms under which a delegation can be made, including concessions of public services or works, licenses, permits or other legal forms applicable under administrative law. |
The concession agreement for the operation of the Galapagos Airport was executed on April 15, 2011, by and among DGAC, ECOGAL, CASA and the Subsecretaria de Transporte Aeronáutico Civil (“STAC”). ECOGAL’s share capital is owned 99.9% by Yokelet S.L. and 0.1% by A.C.I Vip S.L.U. Yokelet S.L. is a wholly-owned subsidiary of CAAP. The parties amended the Galapagos Concession Agreement on May 13, 2013, April 15, 2014 and August 21, 2014, for purposes of updating the tariffs charged under the Galapagos Concession Agreement and other investment amounts.
The following are the main laws and regulations that govern the Galapagos Concession Agreement and that are related to the business and the operation of the Galapagos Airport:
| ● | Article 314 of the Constitution of Ecuador of 2008 sets forth that the Ecuadorian Government shall be responsible for the public services of port and airport infrastructure. Likewise, pursuant to Article 316, the Ecuadorian Government is authorized to delegate the performance of public services to private companies through grants of concessions or other forms stipulated in the Ecuadorian legislation. |
| ● | Article 41 of the Law on Modernization of the State also provides that the Ecuadorian Government can delegate to any local or foreign entity the maintenance and improvement of existing airports by means of a public tender. |
CASA presented a private initiative to the DGAC proposing to manage, operate and maintain the Galapagos Airport. DGAC accepted the proposal and awarded a concession to CASA pursuant to Resolution No. 159 A/2008, dated September 15, 2008.
The Guayaquil Concession Agreement
The concession of the Guayaquil Airport included three construction phases, each of which has been completed to the satisfaction of the Airport Authority of Guayaquil (“AAG”). The initial phase included complete re-asphalting (recapeo) of the runway and the construction of a new passenger terminal, terminal platform, taxiway and control tower, while the intermediate phase applied to the cargo terminal. The final phase included works and investments related mainly to commercial buildings, as well as the general aviation platform. In addition, the Guayaquil Concession Agreement includes an obligation on TAGSA to expand the national terminal and TAGSA is in the process of executing new works and investments for a total amount of U.S.$32.2 million.
On July 14, 2023, the Nineth Addendum to the Concession Contract was signed, where the tariffs corresponding to international commercial and charter flights were reduced by a 19%, and the tariffs of lighting and parking for international commercial and charter flights were reduced by a 12%, which was compensated by the increase of tariffs related to the departure of domestic flights.
127
On July 25, 2023, the Tenth Addendum to the Concession Contract was signed, through which it was determined that the remaining value to be invested, agreed in the Seventh Addendum, should be used to cover the works related to the capacity to receive general aviation aircraft in the sum of U.S.$2.9 million and the other committed works, unless the AAG and TAGSA agree otherwise. Under the terms of the Guayaquil Concession Agreement, TAGSA is responsible for transforming, operating and administrating the Guayaquil Airport, which includes the performance of the following activities:
| ● | preventive and corrective maintenance of the Guayaquil Airport, including (i) all necessary repairs of the facilities, equipment, and other assets built, acquired or incorporated by the TAGSA or pre-existing in the Guayaquil Airport and (ii) maintaining the facilities, equipment and other assets to prevent deterioration; |
| ● | taking all the necessary measures to protect the environment of the Guayaquil Airport and avoid or limit pollution disturbances to individuals and properties and other harmful results to the environment due to the rendering of aeronautic services and non-aeronautic services; |
| ● | design and construction of the works and investment specified in the Guayaquil Concession Agreement and its amendments during the initial, intermediate and final phases; |
| ● | provision of other non-aeronautic services, which include common commercial services such as food, beverages, counters, check-in desks at the terminal, etc., and facultative commercial services such as vip lounges, souvenirs sale, cargo, etc. Rates for such services are fixed directly by TAGSA; and |
| ● | TAGSA and AAG signed the Eighth Amendment of the Concession Agreement on July 20, 2021, through which the economic-financial equilibrium of the concession was reestablished, due to the force majeure and/or fortuitous event caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and its effects through time. Under the Eighth Amendment, TAGSA and AAG were compensated for the losses suffered from March through December 2020, through a two-year concession term, which will now expire on July 27, 2031. Also, TAGSA was conceded a reduction of the contribution over regulated revenues to 53.66%. On July 14, 2022, TAGSA signed the Act of Reestablishment Of The Economic-Financial Balance of the Guayaquil Airport System Concession Contract for the year 2021 and a reduction of the contribution of regulated revenues to 50.25% was also determined. The economic-financial equilibrium was fixed in a formula that considers revenues and expenses of 2019. On April 14, 2023, TAGSA signed the Act of Reestablishment Of The Economic - Financial Balance of the Guayaquil Airport System Concession Contract for the year 2022. |
Concession Fees
Pursuant to the terms of the Guayaquil Concession Agreement, TAGSA is required to pay an annual concession amount to a trust (“Trust”) which amounts to 53.66% of the aggregate gross revenue received by TAGSA from tariffs and charges, and certain other commercial revenues (e.g., fuel, parking spaces and use of convention center) derived from the operation of the Guayaquil Airport for 2021, and as from 2022, the contribution will decrease to 50.25% until the economic-financial equilibrium is fully reestablished.
128
Tariffs
The table below sets forth the maximum amounts that we were permitted to collect as of February 2024, under the Guayaquil Concession Agreement:
|
|
2024(1) |
|
|
(In U.S.$) |
INTERNATIONAL - Commercial and Charters |
|
|
Landing |
|
|
<= 50 tons |
|
14.75 |
50 to 100 tons |
|
15.39 |
> 100 to 150 tons |
|
16.03 |
> 150 tons |
|
16.68 |
Lighting |
|
|
< = 50 tons |
|
4.33 |
50 to 100 tons |
|
4.51 |
> 100 to 150 tons |
|
4.71 |
> 150 tons |
|
4.88 |
Parking(2) |
|
|
< = 50 tons |
|
2.2144 |
50 to 100 tons |
|
2.31 |
> 100 to 150 tons |
|
2.39 |
> 150 tons |
|
2.49 |
Passenger |
|
|
Departure |
|
32.97 |
Security |
|
6.23 |
Connection to the Embarkation / Disembarkation Bridge |
|
|
Departure / Security |
|
76.69 |
Use of bridge for every 15 minutes or fraction |
|
12.88 |
|
|
|
DOMESTIC - Commercial, Charter, Private and Cargo |
|
|
Landing |
|
|
> 25 to 50 tons |
|
1.27 |
> 50 to 100 tons |
|
1.37 |
> 100 to 150 tons |
|
1.45 |
> 150 tons |
|
1.51 |
Lighting |
|
|
> 25 to 50 tons |
|
0.55 |
> 50 to 100 tons |
|
0.58 |
> 100 to 150 tons |
|
0.58 |
> 150 tons |
|
0.59 |
Parking(3) (4) |
|
|
25 to 50 tons |
|
0.25 |
> 50 to 100 tons |
|
0.26 |
> 100 to 150 tons |
|
0.27 |
> 150 tons |
|
0.27 |
Passengers |
|
|
Departure |
|
11.55 |
Security |
|
6.23 |
Connection to the Embarkation / Disembarkation Bridge |
|
|
Departure / Security |
|
38.48 |
Use of bridge for every 15 minutes or fraction |
|
11.54 |
Domestic Annual Aeronautical Rate(5) |
|
|
From 0 to 6 tons |
|
164.84 |
> 6 to 12 tons |
|
824.13 |
> 12 to 18 tons |
|
1,236.23 |
> 18 to 25 tons |
|
1,846.06 |
| (1) | Maximum take-off weight in tons. |
| (2) | The international parking fee will be charged for 3-hour fractions or fractional periods thereafter. |
| (3) | The domestic parking fee will be charged for 4-hour fractions or fractional periods thereafter. |
129
| (4) | Any aircraft that remains on the ground for an uninterrupted period of more than 30 days will be subject to the parking fee plus a surcharge of fifty percent (50%). |
| (5) | The annual fee includes landing, lighting and parking. The fees apply on Ecuadorian civil aircrafts which maximum take-off weight is up to 25 tons. |
Master Plan
Under the terms of our Guayaquil Concession Agreement, the concessionaire is not required to present a master development program.
On July 6, 2018, TAGSA signed Addendum No. 07 which established new works for an amount of U.S.$32.2 million to be completed by TAGSA before 2024 As of December 31, 2022, U.S.$8.0 million remain pending. On July 25, 2023, the Tenth Addendum to the Concession Contract was signed, through which it was determined that the remaining value to be invested, agreed in the Seventh Addendum, should be used to cover the works related to the capacity to receive general aviation aircraft in the sum of $2.9 million and the other committed works, unless the AAG and TAGSA agree otherwise.
Guarantee and Performance Bonds
Under the terms of the Guayaquil Concession Agreement, we are required to maintain a performance bond in the amount of U.S.$3.0 million as security for the timely fulfillment of all of our obligations under the Concession Agreement.
In addition, TAGSA is required to maintain a performance bond for the payments to the Trust for the development of the new Guayaquil Airport that corresponds to an amount of 20.0% of the fees that are payable to the Trust minus the amount of the performance bond of the Guayaquil Concession Agreement. The current amount of the performance bond is U.S.$4.0 million.
Term and Termination
The new term of the Guayaquil Concession Agreement is 27 years and five months, expiring on July 27, 2031. The Guayaquil Concession Agreement may be terminated upon the occurrence of any of the following events, among others:
| ● | breach by TAGSA as a result of its failure to: (i) issue or extend bonds, (ii) comply with its obligation to perform the investments stipulated in the Guayaquil Concession Agreement or any amendments, (iii) comply with its payment obligations under the credit agreement executed for purposes of financing the works foreseen for the initial phase, when such breach affects the normal operation of the Guayaquil Airport and (iv) comply with the concessionaire company, verified by an arbitration tribunal or any other obligation included under the Guayaquil Concession Agreement; |
| ● | the transfer of the Control Group Shares of TAGSA, which represent the shares of TAGSA initially owned by CASA, currently owned by Corporacion Aeroportuaria S.A.; |
| ● | any amendment to the bylaws of TAGSA without prior authorization by AAG; |
| ● | if TAGSA fails to pay the required amounts to (i) the Trust for the development of the airport in Guayaquil, or (ii) AAG for the provision of administrative services; |
| ● | accumulation of fines or sanctions for breach of the levels of services and/or performance for amounts higher than U.S.$0.3 million in a consecutive period of 12 months; |
| ● | breach by AAG of its obligations under the Guayaquil Concession Agreement, as determined by an arbitration tribunal; |
| ● | acts or omissions of the AAG or the Municipality of Guayaquil that impede the efficient execution of the Guayaquil Concession Agreement and that produce substantial adverse effects over the rights of TAGSA, as determined by an arbitration tribunal; or |
| ● | mutual agreement of the parties. |
130
Governing Law and Dispute Resolution
The Guayaquil Concession Agreement is governed by the laws of Ecuador. The parties undertake to attempt to solve any dispute related to the Guayaquil Concession Agreement through mediation. In the event that any dispute is not solved in mediation, the parties must proceed to arbitration, in accordance with the terms and conditions of the Guayaquil Concession Agreement.
The Galapagos Concession Agreement
Under the terms of the Galapagos Concession Agreement, CASA is responsible for providing the Galapagos Airport with management, operation, maintenance and construction services, including the performance of the following activities:
| ● | Projects corresponding to the Redevelopment Plan, in accordance with the following phases: |
Phase 1: Construction of a new airport terminal, control tower and technical facilities, all of which were completed on August 29, 2013, upon issuance by the Resolution No. 2013-0272 accepting the completion of Phase 1.
Phase 2: Demolition of existing airport terminal, expansion of aircraft platform, remodeling of fire service building, relocation of existing hangars and remodeling of hangars for the cargo terminal, all of which were completed in March 2014.
Phase 3: Involves the development of certain works on the runway and platform, including reconstruction of the runway. Phase 3 also includes a general obligation to perform corrective and prevent maintenance of the runway and platform from 2014 through 2026. The last stage within Phase 3 was expected to commence on June 1, 2021. However, due to impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and ECOGAL request to restore the economic and financial balance under the concession, such phase has not yet commenced.
| ● | Projects corresponding to the new investments, including (i) asphalt reinforcement of part of the taxiway and intersections (as from June 1, 2015), (ii) asphalt reinforcement of the runway (as from June 1, 2017), (iii) installation of a system for beaconing and resurfacing of runway with asphalt (as from June 1, 2021) and (iv) corrective and preventive maintenance on the concrete sector of the runways and platform (from years 2014 until 2026). As of the date of this annual report, item (iii) is currently suspended due to force majeure in connection with the COVID-19 pandemic and it is part of the negotiation of the economic-financial equilibrium of the concession agreement with DGAC. |
| ● | Certain maintenance obligations, including all necessary repairs of the facilities, equipment and other concession assets. CASA must prepare and present to the DGAC a maintenance program after the conclusion of Phase 3 of the Redevelopment Plan. |
In addition, ECOGAL has the obligation to provide certain other services within the Galapagos Airport, including, among others, assignment of aircraft parking spaces. ECOGAL charges tariffs for these additional services from the airlines, private aircrafts, users or passengers, as applicable.
ECOGAL also provides services within the airport terminal, which include (i) common commercial services such as food, beverages, counters, check-in desks at the terminal, etc. and (ii) facultative commercial services such as vip lounges, souvenirs sale, cargo, etc. Rates for such services are fixed directly by ECOGAL and are considered as part of the determination of the Net Profit in favor of the DGAC. The rates are fixed based on the square meter used in each commercial area. Arrival and commercial establishments used for food industry have a higher rate (calculated using as a reference the prices charged in the Guayaquil Airport and in the city of Puerto Ayora, Galápagos). Offices used by airlines have a rate based on square meter, calculated using as a reference the prices charged in the Guayaquil Airport for similar purposes and rates applied by DGAC.
Master Plan
Under the terms of our Galapagos Concession Agreement, the concessionaire is not required to present a master development program.
On August 21, 2014, ECOGAL and DGAC entered into Addendum No. 03 to the Galapagos Concession Agreement, which established new investments and rescheduled certain existing investments for the remaining term of the concession agreement.
131
Fees
The Galapagos Concession Agreement sets forth the tariffs for the fees and services provided by ECOGAL in the Galapagos Airport; such tariffs are approved by the National Civil Aviation Council. The following table sets forth the current tariff rates:
Tariff |
|
(in U.S.$) |
Ecological tariff (by departing passengers) |
|
5.70 |
Tariff for terminal use (by departing passengers) |
|
25.98 |
Security tariff (by departing passengers) |
|
3.48 |
Tariff for cash fire and rescue (by departing passengers) |
|
3.98 |
Landing tariff 25 – 50 tons (in tons) |
|
0.86 |
Landing tariff 50-000 tons (in tons) |
|
0.92 |
Guarantees and other Performance Bonds
The Galapagos Concession Agreement requires the delivery of a bond of U.S.$700,000 by ECOGAL to the DGAC, which should be in place during the term of the Galapagos Concession Agreement. The bond was issued by Seguros Oriente S.A., an insurance company in Ecuador, and is in force until April 14, 2024. This bond will be renewed annually.
Term and Termination
The term of the Galapagos Concession Agreement is 15 years as from the compliance of the conditions precedent set forth in Clause 69 (approval of tariffs), which were satisfied on July 15, 2011.
The Galapagos Concession Agreement may be terminated upon the occurrence of any of the following events, among others:
| ● | mutual agreement by the parties; |
| ● | in the event ECOGAL commits an act of gross negligence, as determined by an arbitration tribunal; |
| ● | breach of DGAC’s respective obligations under the Galapagos Concession Agreement; or |
| ● | bankruptcy of ECOGAL. |
Governing Law and Dispute Resolution Regime
The Galapagos Concession Agreement is governed by the laws of Ecuador. The parties undertake to attempt to solve any dispute related to the Galapagos Concession Agreement through mediation. In the event that any dispute is not solved in mediation, the parties must proceed to arbitration, in accordance with the terms and conditions of the Galapagos Concession Agreement.
C. ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Corporación América International S.à r.l., a private limited liability company (société à responsabilité limitée) also incorporated in Luxembourg (“CAI”) holds the 100% of the Majority Shareholder. The Majority Shareholder currently controls 80.53% of our common shares.
CAI is wholly-owned by SCF, a foundation created under the laws of Liechtenstein, which manages assets for the benefit of the foundation’s beneficiaries. The potential beneficiaries of this foundation are certain members of the Eurnekian family as well as religious, charitable and educational institutions designated by the foundation’s board of directors. The board of directors of the foundation is currently composed of four individuals and decisions are taken by majority vote. The board of directors has broad authority to manage the affairs of the foundation and to designate its beneficiaries and additional board members.
Most of our operating subsidiaries have non-controlling interests, some of which are significant.
132
The following diagram reflects a simplified summary of our organizational structure as of March 27, 2024:
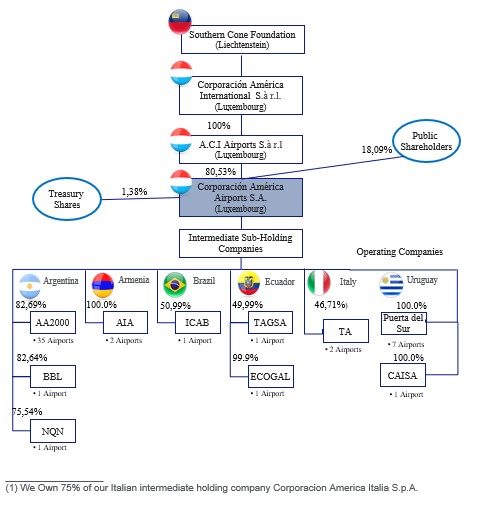
ITEM 4A. UNRESOLVED SEC STAFF COMMENTS
The Company has no unresolved comments from the staff of the SEC with respect to its periodic reports under the Exchange Act.
ITEM 5. OPERATING AND FINANCIAL REVIEW AND PROSPECTS
Our discussion and analysis of our results of operations and financial condition are based upon our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements, which have been prepared in accordance with IFRS. Our operating and financial review and prospects should be read in conjunction with our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements, the accompanying notes thereto and other financial information appearing elsewhere in this annual report.
133
A. OPERATING RESULTS
Factors Affecting Our Results of Operations
A number of factors have a significant impact on our business and results of operations, the most important of which are passenger traffic levels and air traffic operations, fluctuations in exchange rates in the currencies in which we operate, our capital investment plans and regulations.
Passenger Traffic Levels and Air Traffic Operations
A significant portion of our revenue depends directly or indirectly on the level of passenger traffic at our airports and the number of aircraft movements (takeoffs and landings) conducted in the airports we operate. Aeronautical revenue within our airports is directly dependent on aircraft movements. In addition, our commercial revenues depend significantly on the number of passengers passing through terminals, as well as on the nature of the traffic. For example, international passenger traffic generates more commercial revenue than domestic traffic.
From 2022 to 2023, air traffic increased 23.7% in terms of number of passengers, increased 15.1% in terms of aircraft movements, and increased 7.9% in terms of cargo volume handled. From 2021 to 2022, air traffic increased 83.7% in terms of number of passengers, increased 48.5% in terms of aircraft movements and increased 6.1% in terms of cargo volume handled.
Fluctuations in Exchange Rates in the Currencies in which We Operate
Our primary foreign currency exposure gives rise to market risks associated with exchange rate movements of the Argentine peso, the Brazilian real, the euro, the Uruguayan peso and the Armenian dram against the U.S. dollar; and the Euro against the Armenian dram. See “Item 11. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risk—Exchange Rate Risk.”
|
|
Closing Exchange Rate |
|
Average Exchange Rate |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
% change |
|
|
|
|
|
% change |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
against prior |
|
|
|
|
|
against prior |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
year |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
year |
|
UYU |
|
39.02 |
|
40.07 |
|
(2.6) |
% |
38.82 |
|
41.15 |
|
(5.7) |
% |
BRL |
|
4.84 |
|
5.22 |
|
(7.2) |
% |
5.0 |
|
5.16 |
|
(3.3) |
% |
EUR |
|
1.11 |
|
1.07 |
|
3.6 |
% |
1.08 |
|
1.06 |
|
2.0 |
% |
ARS |
|
808.45 |
|
177.16 |
|
356.3 |
% |
294.8 |
|
130.04 |
|
126.7 |
% |
AMD |
|
404.79 |
|
397.59 |
|
1.8 |
% |
392.54 |
|
434.74 |
|
(9.7) |
% |
Our Capital Investment Plans
We are in negotiations to implement infrastructure development plans in Italy and Armenia. In Italy, we and the Italian Government are currently in discussions to develop a EUR 528 million infrastructure plan for the Florence and Pisa Airports. Subject to further discussions and approvals as per the Italian regulatory framework, it is expected that this plan would include a total investment of EUR 440 million between 2024 and 2027 in the Florence Airport, including a new terminal of approximately 45,000 square meters and a new runway of approximately 2,200 meters in length; and a total investment of EUR 88 million between 2024 and 2027 in the Pisa Airport, including the expansion of the existing terminal by approximately 7,500 square meters and the renovation of about 12,000 square meters of existing terminal areas, as well as the restructuring/expansion of the existing aircraft parking area. In Armenia, we and the Armenian Government are currently in discussions to develop a U.S.$400 million infrastructure plan to be implemented before end of 2027. In Armenia, in addition to adding new boarding gates, check-in counters and stand positions, the infrastructure plan is also anticipated to expand the terminal area by approximately 40,000 square meters and the commercial space by approximately 6,200 square meters. See “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources.”
134
Regulations
Fees for aeronautical services are established under the terms of the relevant concession agreement, and the regulatory framework of the governmental authority in each jurisdiction where we operate. Our concession agreements establish or otherwise regulate the rates that we may charge to aircraft operators and passengers for aeronautical services, including fees for landing and transit of aircraft, departing passenger fees, and fees for aircraft parking. Some of our concession agreements also allow us to charge additional fees to passengers for services such as security and reduced mobility assistance, among others. These fees are invoiced to users of our airport infrastructure, principally airlines using our airports, either from their general revenue or as collected directly from airline passengers.
Our Segments
As of and for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, we have identified six reportable segments: Argentina, Italy, Brazil, Uruguay, Ecuador and Armenia. See Note 4 to our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and “Adjusted Segment EBITDA and Adjusted Segment EBITDA excluding Construction Services.”
In December 2021, we transferred our 50% ownership interest in AAP to Andino Investment Holding S.A. See “Business Overview—Our Airports by Country in Which We Operate—Peru.” The elimination of any intersegment revenues and other significant intercompany operations are included in the “Intrasegment Adjustments” column. AAP was not previously classified as an asset held for sale or as a discontinued operation.
All the financial and operational information provided for our Peruvian segment for the year ended December 31, 2021 includes our financial and results of operation until December 16, 2021, date on which the transfer of our interest in AAP was completed.
Our Associates
Under the terms of the concession agreement for the operation of the Galapagos Airport (the “Galapagos Concession Agreement”), the net profits generated by ECOGAL must be transferred entirely to the Dirección General de Aviación Civil. Because we are not entitled to receive dividends from the operations of ECOGAL, we record our percentage ownership interest in the shareholders’ equity of ECOGAL in “Investments in associates” and we account for our results of operations for ECOGAL under the equity method as “share of loss in associates.”
Certain of the operational information provided below with respect to passenger composition, cargo volume and aircraft movements includes results of AAP (until December 16, 2021) and ECOGAL. Revenue and expense information on a per segment basis for Ecuador includes the results of TAGSA but does not include the results of ECOGAL.
In December 2023, CAAP acquired 100% of the issued share capital of Navinten S.A. (“Navinten”), a non-listed company based in Uruguay which operates the duty free shops in the Uruguayan airports.
In December 2023, CAAP decreased its participation in Navinten to 49% after (i) selling a 10% of its participation in the company, and (ii) approving the issuance of new shares of Navinten, thus losing the control of Navinten, which became an associated company.
Macroeconomic Conditions
Argentina has historically been subject to inflation. The National Statistic and Census Institute (“INDEC”) reported an inflation increase of, 50.9% in 2021, 94.8% in 2022 and 211.4% in 2023. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Continuing high inflation may impact the Argentine economy and adversely affect our results of operations.”
135
We have determined that, as of July 1, 2018, the Argentine economy qualifies as a hyperinflationary economy according to the guidelines of the IAS 29, since the total cumulative inflation in Argentina in the 36 months prior to July 1, 2018, as measured by the wholesale price index published by the INDEC, exceeded 100%. Accordingly, IAS 29 guidance is applicable to our financial statements for periods ending after July 1, 2018. IAS 29 requires the financial information of an entity which functional currency is a currency of a hyperinflationary economy to be adjusted by applying a general price index and expressed in the measuring unit at the end of the reporting period and then such financial information to be translated into the presentation currency at the prevailing exchange rate. See Note 2 to our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report. See “Item 3. Key Information- Risk Factors- Continuing high inflation may impact the Argentine economy and adversely affect our results of operations.”
Likewise, our Argentine subsidiaries are operating in an economical context where main variables have recently experienced a strong volatility as a consequence of political and economic uncertainties, both in national and international environments. Considering this situation, we continue to assess the evolution of variables in order to identify the unforeseen potential impacts that could affect the Company’s business and performance.
Our Passenger Traffic, Cargo Volume and Aircraft Movements
Our revenue is highly dependent on levels of air traffic. Passenger traffic in our airports is composed of international, domestic and transit passengers. During the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 20201, approximately 56.3%, 57.6% and 63.1% respectively, of the passengers were domestic passengers, approximately 35.0%, 32.5%, and 23.1%, respectively, of our passengers were international passengers, and approximately 8.8%, 9.8%, and 13.8%, respectively, of our passengers were transit passengers. The majority of our aircraft movements consist of commercial airline traffic, which drives a substantial portion of our passenger traffic. General aviation, which includes private jets, is the second largest category of aircraft movements, but does not significantly contribute to passenger traffic. Cargo is generally transported through commercial aircraft movements, and to a lesser extent, through cargo flights. The principal factor affecting our cargo volume is macroeconomic conditions in the local and regional markets. The following table sets forth certain statistical data relating to our total passenger traffic, cargo volume and aircraft movements for the periods indicated:
|
|
Years ended December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
% change |
|
|
|
% change |
|
|
|
% change |
|
|
|
|
|
against prior |
|
|
|
against prior |
|
|
|
against prior |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
year |
|
2022 |
|
year |
|
2021 |
|
year |
|
Domestic Passengers (in millions) |
|
45.7 |
|
20.9 |
% |
37.8 |
|
67.7 |
% |
22.5 |
|
56.0 |
% |
International Passengers (in millions) |
|
28.4 |
|
32.9 |
% |
21.3 |
|
159.0 |
% |
8.2 |
|
16.5 |
% |
Transit passengers (in millions) |
|
7.1 |
|
10.1 |
% |
6.5 |
|
31.0 |
% |
4.9 |
|
33.0 |
% |
Total passengers (in millions) |
|
81.1 |
|
23.7 |
% |
65.6 |
|
83.7 |
% |
35.7 |
|
41.5 |
% |
Cargo volumes (in thousands of tons) |
|
370.2 |
|
7.9 |
% |
343.1 |
|
6.1 |
% |
323.5 |
|
26.6 |
% |
Total aircraft movements (in thousands) |
|
849.5 |
|
15.1 |
% |
738.2 |
|
48.5 |
% |
497.2 |
|
40.9 |
% |
136
Our Passenger Traffic, Cargo Volume and Aircraft Movements, per Segment
Set forth below is a summary (including our unconsolidated operations) of the passenger composition, cargo volume and aircraft movements for each of our segments:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
% Change |
|
|
|
|
|
% Change |
|
|
|
|
|
% Change |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Against |
|
|
|
|
|
Against |
|
|
|
|
|
Against |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
% of Total |
|
Prior Year |
|
2022 |
|
% of Total |
|
Prior Year |
|
2021 |
|
% of Total |
|
Prior Year |
|
Argentina |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic Passengers (in millions) |
|
30.5 |
|
66.8 |
% |
26.9 |
% |
24.1 |
|
63.7 |
% |
122.0 |
% |
10.8 |
|
48.1 |
% |
72.3 |
% |
International Passengers (in millions) |
|
11.7 |
|
41.3 |
% |
36.2 |
% |
8.6 |
|
40.4 |
% |
333.9 |
% |
2.0 |
|
24.1 |
% |
(40.0) |
% |
Transit passengers (in millions) |
|
1.4 |
|
19.9 |
% |
27.7 |
% |
1.1 |
|
17.2 |
% |
142.1 |
% |
0.5 |
|
9.3 |
% |
24.7 |
% |
Total passengers (in millions) |
|
43.7 |
|
53.8 |
% |
29.3 |
% |
33.8 |
|
51.5 |
% |
154.4 |
% |
13.3 |
|
37.2 |
% |
33.3 |
% |
Cargo volume (in thousands of tons) |
|
191.8 |
|
51.8 |
% |
5.6 |
% |
181.7 |
|
52.9 |
% |
4.2 |
% |
174.4 |
|
53.9 |
% |
21.2 |
% |
Aircraft movements (in thousands) |
|
458.6 |
|
54.0 |
% |
19.2 |
% |
384.7 |
|
52.1 |
% |
69.3 |
% |
227.3 |
|
45.7 |
% |
46.1 |
% |
Italy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic Passengers (in millions) |
|
1.7 |
|
3.8 |
% |
9.6 |
% |
1.6 |
|
4.2 |
% |
62.2 |
% |
1.0 |
|
4.3 |
% |
46.7 |
% |
International Passengers (in millions) |
|
6.4 |
|
22.7 |
% |
25.7 |
% |
5.1 |
|
24.0 |
% |
177.7 |
% |
1.8 |
|
22.4 |
% |
40.7 |
% |
Transit passengers (in millions) |
|
0.0 |
|
0.1 |
% |
64.8 |
% |
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
% |
112.4 |
% |
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
% |
166.4 |
% |
Total passengers (in millions) |
|
8.2 |
|
10.1 |
% |
21.9 |
% |
6.7 |
|
10.2 |
% |
137.7 |
% |
2.8 |
|
7.9 |
% |
42.7 |
% |
Cargo volume (in thousands of tons) |
|
12.9 |
|
3.5 |
% |
(13.2) |
% |
14.9 |
|
4.3 |
% |
(2.7) |
% |
15.3 |
|
4.7 |
% |
15.6 |
% |
Aircraft movements (in thousands) |
|
77.9 |
|
9.2 |
% |
13.1 |
% |
68.9 |
|
9.3 |
% |
74.1 |
% |
39.6 |
|
8.0 |
% |
31.2 |
% |
Brazil |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic Passengers (in millions) |
|
10.9 |
|
23.8 |
% |
8.4 |
% |
10.0 |
|
26.5 |
% |
28.6 |
% |
7.8 |
|
34.6 |
% |
39.1 |
% |
International Passengers (in millions) |
|
0.6 |
|
2.3 |
% |
38.7 |
% |
0.5 |
|
2.2 |
% |
373.4 |
% |
0.1 |
|
1.2 |
% |
(50.4) |
% |
Transit passengers (in millions) |
|
5.6 |
|
78.7 |
% |
6.2 |
% |
5.3 |
|
81.6 |
% |
19.0 |
% |
4.4 |
|
89.9 |
% |
34.4 |
% |
Total passengers (in millions) |
|
17.1 |
|
21.1 |
% |
8.6 |
% |
15.7 |
|
24.0 |
% |
27.9 |
% |
12.3 |
|
34.5 |
% |
35.5 |
% |
Cargo volume (in thousands of tons) |
|
66.6 |
|
18.0 |
% |
15.2 |
% |
57.8 |
|
16.9 |
% |
(3.6) |
% |
60.0 |
|
18.5 |
% |
72.2 |
% |
Aircraft movements (in thousands) |
|
158.4 |
|
18.6 |
% |
9.5 |
% |
144.6 |
|
19.6 |
% |
22.7 |
% |
117.9 |
|
23.7 |
% |
31.8 |
% |
Uruguay |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic Passengers (in millions) |
|
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
% |
23.9 |
% |
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
% |
32.4 |
% |
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
% |
207.4 |
% |
137
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31 |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
% Change |
|
|
|
|
|
% Change |
|
|
|
|
|
% Change |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Against |
|
|
|
|
|
Against |
|
|
|
|
|
Against |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
% of Total |
|
Prior Year |
|
2022 |
|
% of Total |
|
Prior Year |
|
2021 |
|
% of Total |
|
Prior Year |
|
International Passengers (in millions) |
|
1.9 |
|
6.8 |
% |
34.9 |
% |
1.4 |
|
6.7 |
% |
194.9 |
% |
0.5 |
|
5.9 |
% |
(20.2) |
% |
Transit passengers (in millions) |
|
0.0 |
|
0.3 |
% |
219.8 |
% |
0.0 |
|
0.1 |
% |
163.7 |
% |
0.0 |
|
0.1 |
% |
14.3 |
% |
Total passengers (in millions) |
|
2.0 |
|
2.4 |
% |
35.8 |
% |
1.4 |
|
2.2 |
% |
194.2 |
% |
0.5 |
|
1.4 |
% |
(19.9) |
% |
Cargo volume (in thousands of tons) |
|
31.2 |
|
8.4 |
% |
(2.9) |
% |
32.1 |
|
9.4 |
% |
5.5 |
% |
30.4 |
|
9.4 |
% |
5.3 |
% |
Aircraft movements (in thousands) |
|
32.0 |
|
3.8 |
% |
14.8 |
% |
27.9 |
|
3.8 |
% |
56.8 |
% |
17.8 |
|
3.6 |
% |
36.2 |
% |
Armenia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic Passengers (in millions) |
|
- |
|
- |
% |
- |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
International Passengers (in millions) |
|
5.4 |
|
19.1 |
% |
46.8 |
% |
3.7 |
|
17.3 |
% |
53.8 |
% |
2.4 |
|
29.1 |
% |
190.5 |
% |
Transit passengers (in millions) |
|
- |
|
- |
% |
- |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
Total passengers (in millions) |
|
5.4 |
|
6.7 |
% |
46.8 |
% |
3.7 |
|
5.6 |
% |
53.8 |
% |
2.4 |
|
6.7 |
% |
190.5 |
% |
Cargo volume (in thousands of tons) |
|
33.9 |
|
9.1 |
% |
45.0 |
% |
23.3 |
|
6.8 |
% |
34.7 |
% |
17.3 |
|
5.4 |
% |
10.1 |
% |
Aircraft movements (in thousands) |
|
44.1 |
|
5.2 |
% |
25.4 |
% |
35.2 |
|
4.8 |
% |
64.9 |
% |
21.3 |
|
4.3 |
% |
109.3 |
% |
Ecuador(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic Passengers (in millions) |
|
2.6 |
|
5.6 |
% |
19.5 |
% |
2.1 |
|
5.6 |
% |
102.5 |
% |
1.1 |
|
4.7 |
% |
51.3 |
% |
International Passengers (in millions) |
|
2.2 |
|
7.8 |
% |
9.5 |
% |
2.0 |
|
9.5 |
% |
42.3 |
% |
1.4 |
|
17.3 |
% |
74.8 |
% |
Transit passengers (in millions) |
|
0.1 |
|
1.0 |
% |
4.0 |
% |
0.1 |
|
1.1 |
% |
92.0 |
% |
0.0 |
|
0.7 |
% |
(5.6) |
% |
Total passengers (in millions) |
|
4.8 |
|
6.0 |
% |
14.5 |
% |
4.2 |
|
6.4 |
% |
68.3 |
% |
2.5 |
|
7.0 |
% |
62.2 |
% |
Cargo volume (in thousands of tons) |
|
33.8 |
|
9.1 |
% |
1.7 |
% |
33.3 |
|
9.7 |
% |
44.7 |
% |
23.0 |
|
7.1 |
% |
36.5 |
% |
Aircraft movements (in thousands) |
|
78.5 |
|
9.2 |
% |
2.0 |
% |
77.0 |
|
10.4 |
% |
37.7 |
% |
55.9 |
|
11.2 |
% |
34.4 |
% |
Peru(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic Passengers (in millions) |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
1.9 |
|
8.3 |
% |
56.5 |
% |
International Passengers (in millions) |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
0.0 |
|
0.1 |
% |
(10.6) |
% |
Transit passengers (in millions) |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
Total passengers (in millions) |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
1.9 |
|
5.3 |
% |
56.0 |
% |
Cargo volume (in thousands of tons) |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
3.0 |
|
0.9 |
% |
44.8 |
% |
Aircraft movements (in thousands) |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
— |
% |
17.5 |
|
3.5 |
% |
35.4 |
% |
| (1) | We have included ECOGAL’s operational data, although its results of operations are not consolidated. |
| (2) | We have included AAP’s operational data until December 16, 2021, although its results of operations are not consolidated. |
138
Our Revenue from Continuing Operations
We classify our revenue in the following categories: aeronautical revenue, commercial revenue, construction service revenue and other revenue. Our consolidated revenue does not include revenue of ECOGAL (Galapagos Airport) operations for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, as it was accounted for under the equity method.
Our total consolidated revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 is summarized below:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
||||||
|
|
(in millions |
|
% of Total |
|
(in millions of |
|
% of Total |
|
(in millions |
|
$ of Total |
|
|
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
Aeronautical revenue |
|
644.5 |
|
46.0 |
% |
609.8 |
|
44.2 |
% |
262.8 |
|
37.2 |
% |
Non-aeronautical Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
603.7 |
|
43.1 |
% |
612.5 |
|
44.4 |
% |
362.1 |
|
51.2 |
% |
Construction service revenue |
|
144.7 |
|
10.3 |
% |
149.8 |
|
10.9 |
% |
79.8 |
|
11.3 |
% |
Other Revenue |
|
7.2 |
|
0.5 |
% |
6.6 |
|
0.5 |
% |
2.3 |
|
0.3 |
% |
Total consolidated revenue |
|
1,400.0 |
|
100.0 |
% |
1,378.7 |
|
100.0 |
% |
706.9 |
|
100.0 |
% |
Our Expenses from Continuing Operations
Our expenses from continuing operations are cost of services, selling, general and administrative expenses, financial loss, inflation adjustments, other expense, and income tax. Other reportable expenses consist of impairment loss/ (reversal) and other operating expenses.
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
||||||
|
|
(in millions |
|
% of Total |
|
(in millions of |
|
% of Total |
|
(in millions |
|
$ of Total |
|
|
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Expenses |
|
U.S.$) |
|
Expenses |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Expenses |
|
Cost of services |
|
914.7 |
|
66.1 |
% |
963.0 |
|
73.3 |
% |
622.4 |
|
66.4 |
% |
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
138.7 |
|
10.0 |
% |
141.4 |
|
10.8 |
% |
102.1 |
|
10.9 |
% |
Financial loss |
|
406.6 |
|
29.4 |
% |
196.4 |
|
15.0 |
% |
131.3 |
|
14.0 |
% |
Inflation adjustment |
|
40.5 |
|
2.9 |
% |
(19.5) |
|
(1.5) |
% |
(6.7) |
|
(0.7) |
% |
Other expense |
|
(93.4) |
|
(6.8) |
% |
7.1 |
|
0.5 |
% |
18.8 |
|
2.0 |
% |
Income tax |
|
(24.2) |
|
(1.8) |
% |
24.9 |
|
1.9 |
% |
69.1 |
|
7.4 |
% |
Total expenses |
|
1,382.8 |
|
100.0 |
% |
1,313.2 |
|
100.0 |
% |
936.9 |
|
100.0 |
% |
Cost of Services
Our cost of services is composed primarily of salaries and social security contributions, construction service cost, maintenance, airport concession fees, the amortization of intangible assets, service fees, cost of fuel, royalties, fees and easements, airport operation costs and other miscellaneous items.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses from Continuing Operations
Our selling, general and administrative expenses consist primarily of taxes, salaries and social contributions, amortization and depreciation, utility services, office expenses, repair and replacement provisions, maintenance costs, advertising expenses, insurance costs, aircraft charter service costs, costs related to security, healthcare and firefighters, bad debt charges and other miscellaneous items.
139
Financial Loss from Continuing Operations
Our financial loss consists primarily of interest expense, net foreign exchange loss, adjustments with respect to our Brazilian operations and other expenses.
Adjusted EBITDA Reconciliation to Net Income/(Loss) from Continuing Operations
|
|
For the year ended December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|
(in millions of U.S.$) |
||||
Income from continuing operations |
|
226.5 |
|
165.6 |
|
(159.8) |
Financial income |
|
(101.6) |
|
(63.9) |
|
(28.1) |
Financial loss |
|
406.6 |
|
196.4 |
|
131.3 |
Inflation adjustment |
|
40.5 |
|
(19.5) |
|
(6.7) |
Income tax |
|
(24.2) |
|
24.9 |
|
69.1 |
Amortization and depreciation |
|
130.0 |
|
153.1 |
|
143.5 |
Adjusted EBITDA |
|
677.7 |
|
456.7 |
|
149.3 |
Construction services revenue |
|
(144.7) |
|
(149.8) |
|
(79.8) |
Construction services cost |
|
138.3 |
|
147.9 |
|
77.5 |
Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services |
|
671.3 |
|
454.8 |
|
147.0 |
See “Presentation of Financial Information—Non-IFRS Information—Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted Segment EBITDA excluding Construction Services.”
140
Summary Consolidated Results of Operations
The following table sets forth a summary of our consolidated results of operations, as well as the percentage change of each category from the prior year for the periods indicated:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
% of Change |
|
|
|
% of Change |
|
|
|
% of Change |
|
|
|
(in millions |
|
against |
|
(in millions |
|
against |
|
(in millions |
|
against |
|
|
|
of U.S.$) |
|
prior year |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
prior year |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
prior year |
|
Aeronautical revenue |
|
644.5 |
|
5.7 |
% |
609.8 |
|
132.0 |
% |
262.8 |
|
19.5 |
% |
Non-aeronautical Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
603.7 |
|
(1.5) |
% |
612.5 |
|
69.2 |
% |
362.1 |
|
39.4 |
% |
Construction service revenue |
|
144.7 |
|
(3.4) |
% |
149.8 |
|
87.8 |
% |
79.8 |
|
(36.6) |
% |
Other Revenue |
|
7.2 |
|
9.8 |
% |
6.6 |
|
191.1 |
% |
2.3 |
|
20.7 |
% |
Total consolidated revenue |
|
1,400.0 |
|
1.6 |
% |
1,378.7 |
|
95.0 |
% |
706.9 |
|
16.4 |
% |
Cost of Services |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Concession fees |
|
156.2 |
|
(1.4) |
% |
158.5 |
|
67.7 |
% |
94.5 |
|
24.1 |
% |
Amortization and depreciation |
|
123.7 |
|
(15.2) |
% |
145.8 |
|
7.9 |
% |
135.1 |
|
(22.3) |
% |
Cost of fuel |
|
113.1 |
|
5.5 |
% |
107.2 |
|
330.7 |
% |
24.9 |
|
90.3 |
% |
Salaries and social security contributions |
|
185.9 |
|
(9.7) |
% |
205.9 |
|
46.0 |
% |
141.0 |
|
13.3 |
% |
Taxes |
|
2.4 |
|
(32.8) |
% |
3.5 |
|
19.4 |
% |
2.9 |
|
(50.1) |
% |
Maintenance expenses |
|
105.6 |
|
(1.7) |
% |
107.5 |
|
28.1 |
% |
83.9 |
|
2.2 |
% |
Construction service costs |
|
138.3 |
|
(6.5) |
% |
147.9 |
|
90.9 |
% |
77.5 |
|
(37.8) |
% |
Services and fees |
|
56.6 |
|
(0.3) |
% |
56.8 |
|
26.8 |
% |
44.8 |
|
10.8 |
% |
Provision for maintenance cost |
|
4.4 |
|
26.5 |
% |
3.5 |
|
(26.7) |
% |
4.7 |
|
159.6 |
% |
Office expenses |
|
9.7 |
|
(9.4) |
% |
10.8 |
|
106.5 |
% |
5.2 |
|
40.1 |
% |
Others |
|
18.8 |
|
19.2 |
% |
15.7 |
|
102.1 |
% |
7.8 |
|
3.5 |
% |
Total Cost of Services |
|
914.7 |
|
(5.0) |
% |
963.0 |
|
54.7 |
% |
622.4 |
|
(4.8) |
% |
Salaries and Social Security contributions |
|
33.0 |
|
2.3 |
% |
32.3 |
|
52.6 |
% |
21.2 |
|
3.9 |
% |
Amortization and depreciation |
|
6.3 |
|
(14.1) |
% |
7.3 |
|
(12.4) |
% |
8.4 |
|
(11.6) |
% |
Services and fees |
|
39.7 |
|
(11.5) |
% |
44.8 |
|
45.1 |
% |
30.9 |
|
9.7 |
% |
Taxes |
|
37.0 |
|
(18.2) |
% |
45.3 |
|
82.8 |
% |
24.8 |
|
31.1 |
% |
Maintenance expenses |
|
2.1 |
|
12.6 |
% |
1.9 |
|
108.4 |
% |
0.9 |
|
(21.1) |
% |
Advertising |
|
1.5 |
|
(6.4) |
% |
1.7 |
|
81.1 |
% |
0.9 |
|
(41.7) |
% |
Office expenses |
|
4.9 |
|
32.2 |
% |
3.7 |
|
149.8 |
% |
1.5 |
|
20.7 |
% |
Insurance |
|
2.8 |
|
19.1 |
% |
2.4 |
|
10.0 |
% |
2.1 |
|
5.9 |
% |
Bad debts recovery |
|
(3.4) |
|
(81.1) |
% |
(18.2) |
|
119.0 |
% |
(8.3) |
|
184.7 |
% |
Bad debts |
|
5.0 |
|
(62.9) |
% |
13.4 |
|
(8.7) |
% |
14.7 |
|
(10.2) |
% |
Others |
|
9.7 |
|
43.1 |
% |
6.8 |
|
35.7 |
% |
5.0 |
|
(5.4) |
% |
Total selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
138.7 |
|
(1.9) |
% |
141.4 |
|
38.5 |
% |
102.1 |
|
0.3 |
% |
Impairment reversal/(loss) of non-financial assets |
|
102.8 |
|
(92,746.8) |
% |
(0.1) |
|
(70.1) |
% |
(0.4) |
|
(99.4) |
% |
Other operating income |
|
100.6 |
|
169.3 |
% |
37.3 |
|
(12.7) |
% |
42.8 |
|
(21.0) |
% |
Other operating expense |
|
(9.5) |
|
35.4 |
% |
(7.0) |
|
(62.1) |
% |
(18.4) |
|
144.5 |
% |
Operating income |
|
540.6 |
|
77.5 |
% |
304.6 |
|
4,614.8 |
% |
6.5 |
|
(103.9) |
% |
Share of income/(loss) in associates |
|
7.1 |
|
(832.8) |
% |
(1.0) |
|
54.2 |
% |
(0.6) |
|
(62.3) |
% |
Income before financial results and income tax |
|
547.7 |
|
80.4 |
% |
303.6 |
|
5,106.7 |
% |
5.8 |
|
(103.5) |
% |
Financial income |
|
101.6 |
|
59.1 |
% |
63.9 |
|
127.4 |
% |
28.1 |
|
(21.3) |
% |
Financial loss |
|
(406.6) |
|
107.0 |
% |
(196.4) |
|
49.6 |
% |
(131.3) |
|
(39.1) |
% |
Inflation adjustment |
|
(40.5) |
|
(308.4) |
% |
19.5 |
|
190.8 |
% |
6.7 |
|
(125.2) |
% |
Income/(loss) before income tax |
|
202.2 |
|
6.1 |
% |
190.5 |
|
(310.1) |
% |
(90.7) |
|
(75.6) |
% |
Income tax |
|
24.2 |
|
(197.4) |
% |
(24.9) |
|
(64.0) |
% |
(69.1) |
|
(583.4) |
% |
Income/(Loss) for continuing operations |
|
226.5 |
|
36.7 |
% |
165.6 |
|
(203.7) |
% |
(159.8) |
|
(55.3) |
% |
Loss from discontinued operations |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(21.2) |
|
371.9 |
% |
Income/(Loss) for the year |
|
226.5 |
|
36.7 |
% |
165.6 |
|
(191.5) |
% |
(181.0) |
|
(50.0) |
% |
Attributable to Owners of the parent |
|
239.5 |
|
42.4 |
% |
168.2 |
|
(242.8) |
% |
(117.8) |
|
(53.5) |
% |
Non-controlling interest |
|
(13.0) |
|
415.2 |
% |
(2.5) |
|
(96.0) |
% |
(63.2) |
|
(41.9) |
% |
141
Our Revenue by Segment
Set forth below is a summary of the total revenue for each of our reportable segments:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
||||||
|
|
(in millions |
|
% of Total |
|
(in millions |
|
% of Total |
|
(in millions of |
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
U.S.$) |
|
Revenue |
|
Argentina |
|
640.6 |
|
45.5 |
% |
762.6 |
|
55.3 |
% |
362.9 |
|
51.3 |
% |
Italy |
|
133.4 |
|
9.6 |
% |
117.2 |
|
8.5 |
% |
70.5 |
|
10.0 |
% |
Brazil |
|
110.6 |
|
7.9 |
% |
89.3 |
|
6.5 |
% |
58.4 |
|
8.3 |
% |
Uruguay |
|
157.0 |
|
11.3 |
% |
105.3 |
|
7.6 |
% |
51.3 |
|
7.3 |
% |
Armenia |
|
252.5 |
|
18.1 |
% |
207.5 |
|
15.1 |
% |
98.4 |
|
13.9 |
% |
Ecuador(1) |
|
105.2 |
|
7.5 |
% |
96.2 |
|
7.0 |
% |
65.2 |
|
9.2 |
% |
Unallocated |
|
0.7 |
|
0.1 |
% |
0.6 |
|
0.0 |
% |
0.3 |
|
0.0 |
% |
Total consolidated revenue(1) (2) |
|
1,400.0 |
|
100.0 |
% |
1,378.7 |
|
100.0 |
% |
706.9 |
|
100.0 |
% |
| (1) | We account for the results of operations of ECOGAL using the equity method. |
| (2) | We account for the results of operations of Navinten using the equity method. |
142
Revenue Classification by Segment
Set forth below is a summary of the aeronautical revenue and non-aeronautical revenue, including commercial services revenue, construction service revenue and other revenue from continuing operations, for each of our segments, which have intra - segment adjustments allocated to each corresponding segment:
|
|
For the year ended December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|
(in millions |
|
(in millions |
|
(in millions |
|
|
of U.S.$) |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
of U.S.$) |
Argentina |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical revenue |
|
296.4 |
|
330.3 |
|
94.9 |
Non-aeronautical Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
251.2 |
|
308.1 |
|
214.5 |
Construction service revenue |
|
93.0 |
|
124.2 |
|
53.5 |
Other revenue |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Total revenue |
|
640.6 |
|
762.6 |
|
362.9 |
Italy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical revenue |
|
70.1 |
|
70.4 |
|
37.5 |
Non-aeronautical Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
39.9 |
|
32.4 |
|
17.1 |
Construction service revenue |
|
16.2 |
|
7.8 |
|
13.7 |
Other revenue |
|
7.2 |
|
6.6 |
|
2.2 |
Total revenue |
|
133.4 |
|
117.2 |
|
70.5 |
Brazil |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical revenue |
|
45.7 |
|
36.6 |
|
24.1 |
Non-aeronautical Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
64.8 |
|
52.7 |
|
34.3 |
Construction service revenue |
|
0.2 |
|
— |
|
— |
Other revenue |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Total revenue |
|
110.6 |
|
89.3 |
|
58.4 |
Uruguay |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical revenue |
|
65.4 |
|
43.5 |
|
14.6 |
Non-aeronautical Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
59.8 |
|
48.6 |
|
31.4 |
Construction service revenue |
|
31.7 |
|
13.2 |
|
5.3 |
Other revenue |
|
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
Total revenue |
|
157.0 |
|
105.3 |
|
51.3 |
Ecuador |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical revenue |
|
78.3 |
|
68.4 |
|
46.5 |
Non-aeronautical Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
26.9 |
|
25.1 |
|
17.9 |
Construction service revenue |
|
0.0 |
|
2.8 |
|
0.8 |
Other revenue |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Total revenue |
|
105.2 |
|
96.2 |
|
65.2 |
Armenia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical revenue |
|
88.5 |
|
60.7 |
|
45.3 |
Non-aeronautical Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
160.4 |
|
145.1 |
|
46.5 |
Construction service revenue |
|
3.6 |
|
1.8 |
|
6.6 |
Other revenue |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Total revenue |
|
252.5 |
|
207.5 |
|
98.4 |
Unallocated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical revenue |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Non-aeronautical Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
0.7 |
|
0.6 |
|
0.3 |
Construction service revenue |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Other revenue |
|
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
Total revenue |
|
0.7 |
|
0.6 |
|
0.3 |
Total consolidated revenue for all segments |
|
1,400.0 |
|
1,378.7 |
|
706.9 |
143
Our Expenses by Segment
Set forth below is a summary of our total expenses from continuing operations by segment which consists of cost of services, selling general and administrative expenses and other operating expenses. Intra - segments adjustments have been allocated to each corresponding segment:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
||||||
|
|
(in millions |
|
% of Total |
|
(in millions |
|
% of Total |
|
(in millions |
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Expenses(1) |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Expenses(1) |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
Expenses(1) |
|
Argentina |
|
481.9 |
|
45.3 |
% |
587.9 |
|
52.9 |
% |
380.2 |
|
51.2 |
% |
Italy |
|
104.8 |
|
9.9 |
% |
111.6 |
|
10.0 |
% |
96.2 |
|
13.0 |
% |
Brazil |
|
90.9 |
|
8.6 |
% |
84.7 |
|
7.6 |
% |
69.8 |
|
9.4 |
% |
Uruguay |
|
112.8 |
|
10.6 |
% |
75.7 |
|
6.8 |
% |
49.1 |
|
6.6 |
% |
Armenia |
|
171.8 |
|
16.2 |
% |
156.5 |
|
14.1 |
% |
68.7 |
|
9.2 |
% |
Ecuador |
|
76.9 |
|
7.2 |
% |
70.9 |
|
6.4 |
% |
54.1 |
|
7.3 |
% |
Unallocated |
|
23.7 |
|
2.2 |
% |
24.0 |
|
2.2 |
% |
24.8 |
|
3.3 |
% |
Total segment expenses |
|
1,062.8 |
|
100.0 |
% |
1,111.3 |
|
100.0 |
% |
742.9 |
|
100.0 |
% |
| (1) | Excludes income tax, financial loss, impairment loss/ (reversal). |
144
Expenses Classification by Segment
Set forth below is a table of our total expenses from continuing operations, consisting of costs of services and selling, general and administrative expenses and other operating expenses for each of our segments which have intra - segments adjustments allocated to each corresponding segment:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|
(in millions |
|
(in millions |
|
(in millions |
|
|
of U.S.$) |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
of U.S.$) |
Argentina |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Services |
|
419.6 |
|
526.6 |
|
326.8 |
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses |
|
55.0 |
|
56.1 |
|
38.5 |
Other operating expenses |
|
7.3 |
|
5.2 |
|
14.9 |
Total Expenses |
|
481.9 |
|
587.9 |
|
380.2 |
Italy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Services |
|
91.6 |
|
94.6 |
|
83.2 |
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses |
|
13.1 |
|
17.0 |
|
13.1 |
Other operating expenses |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Total Expenses |
|
104.8 |
|
111.6 |
|
96.2 |
Brazil |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Services |
|
79.3 |
|
71.1 |
|
59.2 |
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses |
|
11.1 |
|
13.2 |
|
8.4 |
Other operating expenses |
|
0.5 |
|
0.4 |
|
2.2 |
Total Expenses |
|
90.9 |
|
84.7 |
|
69.8 |
Uruguay |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Services |
|
93.4 |
|
58.8 |
|
39.9 |
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses |
|
18.9 |
|
16.4 |
|
9.0 |
Other operating expenses |
|
0.5 |
|
0.5 |
|
0.2 |
Total Expenses |
|
112.8 |
|
75.7 |
|
49.1 |
Ecuador |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Services |
|
62.3 |
|
57.6 |
|
44.4 |
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses |
|
14.6 |
|
13.2 |
|
9.7 |
Other operating expenses |
|
0.0 |
|
0.1 |
|
0.0 |
Total Expenses |
|
76.9 |
|
70.9 |
|
54.1 |
Armenia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Services |
|
156.5 |
|
142.7 |
|
56.8 |
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses |
|
14.3 |
|
13.0 |
|
11.2 |
Other operating expenses |
|
1.0 |
|
0.8 |
|
0.7 |
Total Expenses |
|
171.8 |
|
156.5 |
|
68.7 |
Unallocated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of Services |
|
11.9 |
|
11.6 |
|
12.1 |
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses |
|
11.7 |
|
12.4 |
|
12.2 |
Other operating expenses |
|
0.0 |
|
0.0 |
|
0.4 |
Total Expenses |
|
23.7 |
|
24.0 |
|
24.8 |
Year Ended December 31, 2023 Compared with Year Ended December 31, 2022
Revenue from Continuing Operations
Our revenue was U.S.$1,400.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 1.6% increase from U.S.$1,378.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase in revenue of U.S.$21.4 million was principally derived from the revenue increase of U.S.$51.7 million in Uruguay, U.S.$45.0 million in Armenia, U.S.$21.3 million in Brazil, U.S.$16.2 million in Italy, and U.S.$9.0 million in Ecuador, offset by the decrease of U.S.$122.0 million in Argentina.
145
Argentina
Revenue from our Argentina segment was U.S.$640.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 16.0%, or U.S.$122.0 million decrease as compared to U.S.$762.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This decrease in revenues was mainly the outcome of:
| ● | a decrease of U.S.$33.9 million, or 10.3%, in aeronautical revenue mainly due to the impact of inflation and the devaluation of the Argentine peso against the U.S. dollar derived from the application of IAS 29. This decrease was partially offset by an increase in passenger traffic mostly reflected in international passenger traffic; |
| ● | a decrease of U.S.$56.9 million, or 18.5%, in commercial revenue derived mainly from the impact of inflation and the devaluation of the Argentine peso against the U.S. dollar derived from the application of IAS 29. This decrease was partially offset by: (i) an increase in duty free shop, retail stores, catering, food and beverage, among others, derived from the increase in passenger traffic, and (ii) the increase of cargo revenue due to the increase in cargo volume; and |
| ● | a decrease of U.S.$31.2 million, or 25.1%, in construction services revenue mainly associated with the impact of inflation and the devaluation of the Argentine peso against the U.S. dollar derived from the application of IAS 29. This decrease was partially offset by the construction works we performed in our airports in Argentina, see “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Capital Expenditures by Segment—Argentina.” |
Italy
Revenue from our Italy segment was U.S.$133.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 13.8% or U.S.$16.2 million increase as compared to U.S.$117.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase in revenue was mainly the result of: (i) an increase of U.S.$7.5 million, or 23.0%, in commercial revenue associated with parking facilities, food and beverage services, vip lounges, among others, derived from the increase in passenger traffic; (ii) an increase of U.S.$8.4 million, or 106.9%, in construction services revenue mainly associated with the construction works we performed at our airports in Italy (see “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Capital Expenditures by Segment—Italy.”); and (iii) the appreciation of the Euro against the U.S. dollar. This increase in revenue was partially offset by the decrease of U.S.$0.3 million, or 0.4%, in aeronautical revenue mainly due to the aggregate effect of the decrease in revenue resulting from the disposal of the handling business, offset by the increase in passenger traffic, and the recognitions by the Ministry of Economy and Finance of the CPI inflationary effect on airports fees for past years.
Brazil
Revenue from our Brazil segment was U.S.$110.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 a 23.9% or U.S.$21.3 million increase as compared to U.S.$89.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was mainly due to (i) an increase of U.S.$9.0 million, or 24.7%, in aeronautical revenue due to the increase in passenger traffic and the increase in tariffs that we are entitled to charge under the concessions, (ii) an increase of U.S.$12.1 million, or 23.0%, in commercial revenue mainly associated with vip lounges, duty free shops, parking facilities, food and beverages, among others, derived from the increase in passenger traffic, and (iii) the appreciation of the Real against the U.S. dollar.
Uruguay
Revenue from our Uruguay segment was U.S.$157.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 49.1% or U.S.$51.7 million increase compared to U.S.$105.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was mainly derived from (i) an increase of U.S.$22.0 million, or 50.6%, in aeronautical revenue due to the increase in passenger traffic and the increase in tariffs that we are entitled to charge under the concessions; (ii) an increase of U.S.$11.2 million, or 23.0%, in commercial revenue mainly associated with (a) duty free shops, vip lounges, parking facilities, among others, derived from the increase in passenger traffic, (b) the increase in warehouse use fees as a result of the increase in cargo volumes, and (c) the increase in fuel due to the new operation of the fuel business; and (iii) the increase of U.S.$18.5 million, or 140.8%, in construction services revenue mainly associated with the construction works we performed at the Uruguay New Airports, see “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Capital Expenditure by Segment—Uruguay.”
146
Ecuador
Revenue from our Ecuador segment was U.S.$105.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 9.4% or U.S.$9.0 million increase as compared to U.S.$96.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was mainly due to: (i) an increase of U.S.$10.0 million, or 14.6%, in aeronautical revenue mainly associated with the increase in passenger traffic and the increase in tariffs that we are entitled to charge under the concession, and (ii) an increase of U.S.$1.8 million, or 7.2%, in commercial revenue mainly associated with duty free shops and food and beverage stores derived from the increase in passenger traffic. This increase was partially offset by the decrease of U.S.$2.7 million, or 99.2%, in construction service revenue associated with the construction works we performed at our airport in Ecuador, see “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Capital Expenditure by Segment—Ecuador.”
Armenia
Revenue from our Armenia segment was U.S.$252.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 21.7% or U.S.$45.0 million increase as compared to U.S.$207.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase in revenue was mainly derived from: (i) an increase of U.S.$27.9 million, or 45.9%, in aeronautical revenue due to the increase in passenger traffic, (ii) an increase of U.S.$15.3 million, or 10.5%, in commercial revenue mainly due to duty free and other commercial revenues derived from the increase in passenger traffic, the increase in the sale of fuel at our Armenian airports, and the increase in cargo business due to increase in tariffs and cargo volumes.
Unallocated
Our unallocated revenue comprised a non-significant amount of commercial revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Cost of Services from Continuing Operations
Cost of services decreased 5.0% to U.S.$914.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to U.S.$963.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This decrease in cost of services of U.S.$48.3 million was derived from the U.S.$107.0 million in Argentina and U.S.$2.9 million in Italy. This decrease was partially offset by the increase of U.S.$8.2 million in Brazil, U.S.$34.6 million in Uruguay, U.S.$4.7 million in Ecuador, and U.S.$13.8 million in Armenia.
The sum of the cost of services reported for each of our segments equals the total amount of consolidated cost of services as per the statement of income.
Argentina
Cost of services from our Argentina segment was U.S.$419.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 20.3% or U.S.$107.0 million decrease as compared to U.S.$526.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This decrease in cost of services was primarily due to the decrease in construction services costs, concession fees, salaries and social security contributions, in all cases associated with the impact of inflation and the devaluation of the Argentine peso against the U.S. dollar derived from the application of IAS 29. This decrease was partially offset by (i) the increase in expenses resulting from increased airport operations, and (ii) the increase in capital expenditures.
Depreciation and amortization included in cost of services was U.S.$60.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 30.8% or U.S.$26.7 million decrease from U.S.$86.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Italy
Cost of services from our Italy segment was U.S.$91.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 3.1% or U.S.$2.9 million decrease as compared to U.S.$94.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This decrease in cost of services was mainly due to: the decrease in salaries and social contributions due to the disposal of the handling business. The decrease was partially offset by (i) the increase in construction services costs associated with the increase in capital expenditures, (ii) the increase in other cost of sales, mainly in provision for maintenance cost and vip lounges expenses, related to the increase in airport operations, and (iii) the increase in concession fees that we were required to pay to the concessionaire as a consequence of the increase in passenger traffic.
147
Depreciation and amortization included in cost of services was U.S.$7.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 a 4.5% or U.S.$0.3 million increase from U.S.$7.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Brazil
Cost of services from our Brazil segment was U.S.$79.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 11.5% or U.S.$8.2 million increase as compared to U.S.$71.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was primarily due to: (i) the increase in concession fee in line with the previously agreed passenger curve, (ii) the increase in services and fees due to the increase in fire services expenses and civil aviation protection services due to the increase in airports operations, and (iii) the appreciation of the Real against the U.S. dollar.
Depreciation and amortization included in cost of services was U.S.$12.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 7.4% or U.S.$0.8 million increase from U.S.$11.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Uruguay
Cost of services from our Uruguay segment was U.S.$93.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 58.9% or U.S.$34.6 million increase as compared to U.S.$58.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase in cost of services was mainly due to: (i) increase in construction services cost incurred in connection with the works performed at the Uruguay New Airports, (ii) the increase in salaries and social contributions due to the increase in airport operations, the increase in the number of employees related to the Uruguay New Airports and the appreciation of Uruguayan Peso against de U.S. Dollar, (iii) the increase in maintenance expenses due to the increase in airport operations and the Uruguay New Airports, and (iv) the increase in concession fees that we were required to pay the concessionaire as a consequence of the increase in revenue.
Depreciation and amortization included in cost of services was U.S.$7.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 12.4% or U.S.$0.8 million increase from U.S.$6.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Ecuador
Cost of services from our Ecuador segment was U.S.$62.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, an 8.2% or U.S.$4.7 million increase as compared to U.S.$57.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase in cost of services was mainly a consequence of (i) the increase in concession fees that we were required to pay the concessionaire as a consequence of the increase in regulated revenue, (ii) the increase in maintenance expenses due to the increase in airport operations, and (iii) the increase in salaries due to the increase in the number of employees related to the incorporation of the fire squad. This increase was partially offset by the decrease in construction services cost incurred in connection with the works performed at our airport in Ecuador.
Depreciation and amortization included in cost of services was U.S.$5.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 3.2% or U.S.$0.2 million increase from U.S.$5.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Armenia
Cost of services from our Armenia segment was U.S.$156.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 9.7% or U.S.$13.8 million increase as compared to U.S.$142.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase in cost of services was mainly due to: (i) the increase in cost of fuel to support the increase of fuel sales, (ii) the increase in salaries and social contributions due to increase in the number of employees, in line with the increase in airport operations, (iii) the increase in other cost of sales due to the increase in airport operations, and (iv) the increase of U.S.$1.8 million in construction services costs associated with the increase in capital expenditures.
Depreciation and amortization included in cost of services was U.S.$19.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 12.4% or U.S.$2.1 million decrease from U.S.$17.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Unallocated
Cost of services from our unallocated segment mainly contain the depreciation and amortization which have increased 2.6% or U.S.$0.3 million from U.S.$11.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022 to U.S.$11.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2023.
148
Gross Profit from Continuing Operations
Based on the above, our gross profit increased by 16.8% or U.S.$69.7 million to a gain of U.S.$485.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to a gain of U.S.$415.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses from Continuing Operations
Selling, general and administrative expenses decreased by 1.9% to U.S.$138.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to U.S.$141.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This decrease of U.S.$2.7 million primarily derived from the decrease of U.S.$3.9 million in Italy, U.S.$2.1 million in Brazil, and U.S.$1.1 million in Argentina. The decrease was partially offset by the increase of U.S.$2.4 million in Uruguay, U.S.$1.4 million in Ecuador, and U.S.$1.3 million in Armenia.
The sum of the selling, general and administrative expenses reported for each of our segments equals the total amount of consolidated selling, general and administrative expenses as per the statement of income.
Argentina
Selling, general and administrative expenses from our Argentina segment were U.S.$55.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 2.0% or U.S.$1.1 million decrease as compared to U.S.$56.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This decrease in selling, general and administrative expenses was primarily due to (i) a decrease in accrued taxes derived from the impact of inflation and the devaluation of the Argentine peso against the U.S. dollar derived from the application of IAS 29. This decrease was partially offset by aggregate effect of an increase in revenue and a decrease in bad debts recovery due to collection of debt in connection with Aerolíneas Argentina Group in 2022.
Our depreciation and amortization included in selling, general and administrative expenses for our Argentina segment during the year ended December 31, 2023 suffered non-significant variations as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022.
Italy
Selling, general and administrative expenses from our Italy segment were U.S.$13.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 22.7% or U.S.$3.9 million decrease as compared to U.S.$17.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This decrease was mainly associated to services and fees due to the decrease in gas and electricity fees.
Depreciation and amortization included in selling, general and administrative expenses was U.S.$3.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 18.0% or U.S.$0.7 million decrease from U.S.$4.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Brazil
Selling, general and administrative expenses from our Brazil segment were U.S.$11.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 16.1% or U.S.$2.1 million decrease as compared to U.S.$13.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This decrease resulted from (i) the decrease in services and fees, and (ii) the decrease in bad debt.
Our depreciation and amortization included in selling, general and administrative expenses for our Brazil segment during the year ended December 31, 2023 suffered non-significant variations as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022.
Uruguay
Selling, general and administrative expenses from our Uruguayan segment were U.S.$18.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 14.7% or U.S.$2.4 million increase as compared to U.S.$16.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was mainly due to: (i) the increase in other selling, general and administrative expenses associated to security services as a result of more traffic activity, and (ii) the increase in vip lounge expenses and airlines commissions derived from the increase in passenger traffic. The increase was partially offset by the decrease in services and fees in connection with the investment project presented to obtain tax benefits in 2022.
Our depreciation and amortization included in selling, general and administrative expenses for our Uruguay segment during the year ended December 31, 2023 suffered non-significant variations as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022.
149
Ecuador
Selling, general and administrative expenses from our Ecuador segment were U.S.$14.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 10.4% or U.S.$1.4 million increase as compared to U.S.$13.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was mainly due to: (i) an increase in salaries and social security contributions as a consequence of the increase in payment of legal bonus to employees as a result of the increase in annual net results, (ii) an increase in services and fees due to an increase in management fee incurred in connection with the increase in revenues.
Our depreciation and amortization included in selling, general and administrative expenses for our Ecuador segment during the year ended December 31, 2023 suffered non-significant variations as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022.
Armenia
Selling, general and administrative expenses from our Armenia segment were U.S.$14.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 9.7% or U.S.$1.3 million increase as compared to U.S.$13.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was mainly due to the increase in salaries and social security contributions and other selling, general and administrative expenses mainly due to increased airport operations.
Depreciation and amortization included in selling, general and administrative expenses was U.S.$0.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 37.6% or U.S.$0.2 million decrease from U.S.$0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Unallocated
Unallocated selling, general and administrative expenses were U.S.$11.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 5.2% or U.S.$0.6 million decrease from U.S.$12.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Depreciation and amortization included in selling, general and administrative expenses was U.S.$0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, a 5.5% decrease from U.S.$0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Impairment reversal/(Loss) of non-financial assets from Continuing Operations
In the year ended December 31, 2023, we recorded a reversal of impairment of U.S.$102.8 million mainly derived from the indemnification related to the friendly termination of the concession agreement in ICAGSA. In the year ended December 31, 2022, we recorded an impairment loss of U.S.$0.1 million.
Other Operating Income from Continuing Operations
Other operating income increased by 169.3% or U.S.$63.2 million to U.S.$100.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to U.S.$37.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was mainly due to (i) an increase of U.S.$62.7 million in Brazil derived from the indemnification related to the friendly termination of the concession agreement in ICAGSA, and (ii) the increase of U.S.$3.0 million in unallocated income mainly derived from the sale of part of the participation in Navinten S.A. which operates the duty free shop in Uruguay. These variations were partially offset by a decrease of U.S.$4.3 million in our Italian subsidiary, TA, mainly due to the government grant recognized in 2022 and a decrease in the grants to AA2000 for U.S.$2.4 million for the development of airport infrastructure derived from the increase in revenues.
Other Operating Expenses from Continuing Operations
Other operating expenses increased by 35.4% or U.S.$2.5 million to U.S.$9.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to U.S.$7.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was mainly due to the increase of U.S.$2.0 million in Argentina subsidiary AA2000.
Operating Income from Continuing Operations
As a result of the foregoing, our operating income increased by 77.5% or U.S.$236.1 million to a gain of U.S.$540.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to a gain of U.S.$304.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
150
Share of Income/Loss in Associates from Continuing Operations
Our share of income/loss in associated companies increased by 832.8% or U.S.$8.1 million to a gain of U.S.$7.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to a loss of U.S.$1.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, derived from accounting our results of operations for Navinten S. A. under the equity method.
Adjusted Segment EBITDA and Adjusted Segment EBITDA excluding Construction Services
We evaluate the performance of each of our segments based on Adjusted EBITDA, which is defined, with respect to each segment, as income from continuing operations before financial income, financial loss, income tax expense, and depreciation and amortization for such segment. See “Presentation of Financial Information—Adjusted Segment EBITDA and Adjusted Segment EBITDA excluding Construction Services” and “Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Operating Results—Adjusted EBITDA Reconciliation to Net Income/(Loss) from Continuing Operations.”
Therefore, each segment’s Adjusted EBITDA measure equals the segment’s operating income plus the segment’s share of losses in associates plus the segment’s depreciation and amortization included in each segment’s cost of services and selling, general and administrative expenses, as further discussed in the respective sections above.
The sum of each segment’s Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted Segment EBITDA excluding Construction Services equals the total consolidated Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted Segment EBITDA excluding Construction Services. See “Presentation of Financial Information—Non-IFRS Information—Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted Segment EBITDA excluding Construction Services.”
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Change |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
against |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
prior year |
|
% Change |
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
(in millions |
|
Adjusted |
|
(in millions |
|
Against |
|
(in millions |
|
Adjusted |
|
|
|
of U.S.$) |
|
EBITDA |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
prior year |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
EBITDA |
|
Argentina |
|
232.0 |
|
34.2 |
% |
(45.8) |
|
(16.5) |
% |
277.9 |
|
60.8 |
% |
Italy |
|
39.1 |
|
5.8 |
% |
18.0 |
|
84.8 |
% |
21.2 |
|
4.6 |
% |
Brazil |
|
218.3 |
|
32.2 |
% |
186.2 |
|
580.4 |
% |
32.1 |
|
7.0 |
% |
Uruguay |
|
50.0 |
|
7.4 |
% |
14.6 |
|
41.4 |
% |
35.3 |
|
7.7 |
% |
Armenia |
|
99.7 |
|
14.7 |
% |
30.8 |
|
44.7 |
% |
68.9 |
|
15.1 |
% |
Ecuador |
|
32.0 |
|
4.7 |
% |
3.0 |
|
10.4 |
% |
29.0 |
|
6.3 |
% |
Unallocated |
|
6.6 |
|
1.1 |
% |
14.2 |
|
(186.4) |
% |
(7.6) |
|
(1.7) |
% |
Total Adjusted EBITDA |
|
677.7 |
|
100.0 |
% |
221.0 |
|
48.4 |
% |
456.7 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Change |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
against |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
prior year |
|
% Change |
|
|
|
% of Total |
|
|
|
(in millions |
|
Adjusted |
|
(in millions |
|
Against |
|
(in millions |
|
Adjusted |
|
|
|
of U.S.$) |
|
EBITDA |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
prior year |
|
of U.S.$) |
|
EBITDA |
|
Argentina |
|
231.9 |
|
34.6 |
% |
(45.7) |
|
(16.5) |
% |
277.7 |
|
61.1 |
% |
Italy |
|
32.9 |
|
4.9 |
% |
13.4 |
|
68.9 |
% |
19.5 |
|
4.3 |
% |
Brazil |
|
218.3 |
|
32.5 |
% |
186.2 |
|
580.4 |
% |
32.1 |
|
7.1 |
% |
Uruguay |
|
50.0 |
|
7.4 |
% |
14.6 |
|
41.4 |
% |
35.3 |
|
7.8 |
% |
Armenia |
|
99.6 |
|
14.8 |
% |
30.8 |
|
44.7 |
% |
68.8 |
|
15.1 |
% |
Ecuador |
|
32.0 |
|
4.8 |
% |
3.0 |
|
10.4 |
% |
29.0 |
|
6.4 |
% |
Unallocated |
|
6.6 |
|
1.0 |
% |
14.2 |
|
(186.4) |
% |
(7.6) |
|
(1.7) |
% |
Total Adjusted EBITDA excluding construction services |
|
671.3 |
|
100.0 |
% |
216.5 |
|
47.6 |
% |
454.8 |
|
100.0 |
% |
151
Income before Financial Results and Income Tax from Continuing Operations
Our income before financial results and income tax increased by 80.4% or U.S.$244.1 million to a gain of U.S.$547.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to a gain of U.S.$303.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Financial Income from Continuing Operations
Our financial income increased by 59.1% to U.S.$101.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to financial income of U.S.$63.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase of U.S.$37.7 million in financial income was primarily due to (i) higher interest income mainly derived from the increase in financial investment in our subsidiary BSB, and (ii) the increase in foreign exchange income mainly in our subsidiaries in Argentina.
Financial Loss from Continuing Operations
Our financial loss increased by 107.0% to U.S.$406.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to financial loss of U.S.$196.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase of U.S.$210.2 million in financial loss was primarily due to (i) the increase of U.S.$283.7 million in foreign exchange expenses mainly in our Argentina subsidiaries due to the difference of devaluation of the Argentine peso, compared to the U.S. dollar, overinflation in 2023, which was lower than such difference in 2022. This increase was partially offset by (i) the decrease of U.S.$69.1 million in interest expenses mainly in AA2000 due to the interest accrued from the liabilities related to the redemption of the preferred shares in 2022 and the decrease in financial debts, and (ii) the decrease of U.S.$3.0 million in changes in liability for concessions in ICAB as a result of a decrease in the Brazilian index used to adjust the concession fee payable under the Brazilian Concession Agreements.
Inflation adjustment from Continuing Operations
Our inflation adjustment was a loss of U.S.$40.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 308.4% or U.S.$60.0 million decrease compared to inflation adjustment gain of U.S.$19.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2022 due to the application of IAS 29 and the translation mechanism in our Argentine subsidiaries.
Income before Income Tax from Continuing Operations
As a result of the foregoing, our income before income tax increased by 6.1% or U.S.$11.7 million to U.S.$202.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to the gain of U.S.$190.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Income Tax from Continuing Operations
Income tax gains were U.S.$24.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 197.4% variation from income tax expenses of U.S.$24.9 million recorded for the year ended December 31, 2022. This U.S.$49.1 million decrease in income tax expense was primarily due to the increase in gain in deferred income tax due to (i) the increase in deferred tax loss primarily due to the devaluation in the period of December 2023, and an inflation adjustment impacting the tax losses carried forward from previous years in the subsidiaries based in Argentina, and (ii) a write-off of deferred tax assets made in 2022 in our Brazilian subsidiary, ICAB, as a consequence of a decrease in projections. These variations were offset by the increase in current tax mainly in (i) our Armenian subsidiary due to the increase in airports operations, and (ii) Corporación Aeroportuaria S.A. and CAAP, due to withholding tax from dividend received.
Income from Continuing Operations
As a result of the foregoing, our income from continuing operations increased by 36.7% to U.S.$226.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, which reflects a difference in gain of U.S.$60.8 million compared to the gain from continuing operations of U.S.$165.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Loss from Discontinued Operations
Loss from discontinued operations represents losses we have incurred for AAP disposing during the periods presented. We incurred a loss from discontinued operations for the year ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 in the amount of U.S.$0.0 million, U.S.$0.0 million and U.S.$21.2 million, respectively.
152
Net Income
Our net income increased by 36.7% to U.S.$226.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, which reflects a difference in gain of U.S.$60.8 million compared to the U.S.$165.6 million in gain for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Year Ended December 31, 2022 Compared with Year Ended December 31, 2021
A comparison of the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 has been omitted from this annual report, but may be found in “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects” of our annual report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2022, filed with the SEC on March 31, 2023.
Capital Expenditures by Segment
Argentina
Under the terms of our AA2000 Concession Agreement, AA2000 is required to make capital expenditures in accordance with an investment plan. See “Item 4. Company Information - Business Overview - Regulatory and Concessions Framework – Argentina - The AA2000 Concession Agreement - Investment Plan.”
In the year ended December 31, 2023, we spent U.S.$93.3 million on capital expenditures in Argentina, primarily for (i) construction of a new departure terminal building at the Ezeiza Airport; (ii) expansion and remodeling of the passenger terminal at Termas de Rio Hondo Airport; (iii) remodeling the Aeroparque Airport mainly for exterior improvements such as sidewalks, landscaping and coastal filling; (iv) remodeling work of the passenger terminal at San Juan Airport; and (v) power supply to the Control Tower and Rehabilitation of Alpha Taxiing at Resistencia Airport.
During the next five years, AA2000 expects to incur additional capital expenditures as set forth under the Technical Conditions for Extension of the AA2000 Concession Agreement executed in December 2020. See “Item 4. Company Information- Business Overview- Regulatory and Concessions Framework – Argentina- The AA2000 Concession Agreement- Technical Conditions of the Extension.”
Italy
Under the terms of our Italian Concession Agreements, TA is required to present a long-term master plan for each individual airport. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Italy—The Pisa Concession Agreement,” and “Item 4 Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Italy—The Florence Concession Agreement.”
In the year ended December 31, 2023, TA spent U.S.$16.5 million on intangible assets and U.S.$1.0 million in property, plant and equipment (“PPE”), respectively. Intangible works focused primarily on preparatory works and designs for the expansion of the Pisa terminal, the design of Florence Airport new terminal, the update of the Master plan and the environmental impact assessment of Florence and redevelopment of commercial area in Pisa airport. PPE investments focused primarily on vehicles, hardware and equipment for metal detectors.
In the year ended December 31, 2022, TA spent U.S.$8.2 million on intangible assets and U.S.$1.5 million in property, PPE, respectively. Intangible works focused primarily on design of Florence Airport new terminal and Master plan. PPE investments focused primarily on parking system at Pisa Airport. In the year ended December 31, 2021, TA spent U.S.$16.1 million on intangible assets and U.S.$3.8 million in property, PPE, respectively. Intangible works focused primarily on flight infrastructure at the Florence Airport and the new baggage handling system both in Pisa and Florence Airports. PPE investments focused primarily on final supply of x-ray machines related to the new BHS, new operating machines, vehicles and electronic devices in both Pisa and Florence Airports.
In partnership with the Italian Government, we have developed an investment plan for Florence Airport to invest approximately EUR440 million in capital expenditures for intangible assets. Currently, this airport cannot service long-haul flights given the short length of its runway. Additionally, since the runway was built in the direction of the prevailing wind, and there are orographic obstacles along the same direction, Florence Airport has a relatively high number of flight cancellations due to adverse weather conditions. Plans are underway to build a new terminal and runway. During the next five years, we expect that our subsidiary TA will incur these capital expenditures, subject to final approval of the Florence Master Plan. We expect that approximately EUR150 million may be invested in connection with the new terminal and the runway to be assumed by governmental institutions.
153
CAAP and the Italian Government are currently in discussions to develop a EUR528 million infrastructure plan for both the Florence and Pisa Airports. Subject to further discussions and approvals as per the Italian regulatory framework, it is expected that this plan would include:
Florence Airport:
| ● | Amount: EUR440 million, of which approximately EUR290 million is expected to be financed with free cash flow and new borrowing, by TA and the balance to be financed with sovereign grants. |
| ● | Timing of execution: between 2024 and 2027. |
| ● | The plan is expected to include a new terminal of approximately 45,000 square meters (existing terminal area is approximately 19,420 square meters) and a new runway of approximately 2,200 meters in length (existing runway length is approximately 1,560 meters). |
Pisa Airport:
| ● | Amount: EUR88 million, which is expected to be entirely financed with free cash flow and new borrowing by TA. |
| ● | Timing of execution: between 2024 and 2027. |
| ● | The plan is expected to include the expansion of the existing terminal by approximately 7,500 square meters and the renovation of about 12,000 square meters of existing terminal areas (existing terminal area is approximately 32,115 square meters), as well as the restructuring/expansion of the existing aircraft parking area. |
Brazil
Under the terms of our Brasilia Concession Agreement, ICAB is required to present a master development program for approval by the Brazilian ANAC every five years. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Brazil—Brasilia Concession Agreement—Master Development Program.”
In the year ended December 31, 2023, we spent U.S.$1.6 million on capital expenditures at the Brasilia Airport, primarily for expansion of the vip lounge and paving of the landing and take-off runway. In the year ended December 31, 2022, we spent U.S.$1.8 million on capital expenditures at the Brasilia Airport, primarily for fixing remote gates within the Brasilia Airport. In the year ended December 31, 2021, we spent U.S.$1.8 million on capital expenditures at the Brasilia Airport, primarily for software acquisition and improvements for the relocation of rental spaces.
During the next five years, ICAB expects to incur additional mandatory investments in the amount of U.S.$9.4 million with respect to the Brasilia Airport. With respect to optional expenditures, ICAB may incur in optional capital expenditures in relation with the development of the commercial area at the Brasilia Airport. In connection with the development of this new commercial area at the Brasilia Airport, we are moving forward with the adjusted, lower-capital intensive model, that we believe will encompass a mix of commercial offerings funded and operated by third parties. We expect to receive a percentage of the net operating income derived from the operation of this area.
In the year ended December 31, 2023, we spent U.S.$111 thousand on capital expenditures at the Natal Airport, primarily to purchase generators, hoses, automatic door motors and fire system lining. In the year ended December 31, 2022, we spent U.S.$159 thousand on capital expenditures at the Natal Airport, primarily to purchase generators, UPS batteries and protective suits, for other general airport maintenance and operation matters. In the year ended December 31, 2021, we spent U.S.$41.5 thousand on capital expenditures at the Natal Airport, primarily due to the acquisition of fire trucks.
Uruguay
Under the terms of the Carrasco Concession Agreement, the relevant concessionaire is required to present a revised master development program for approval by the Ministry of National Defense every five years. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Uruguay—Amendment to the Carrasco Concession Agreement—Master Plan.”
154
In the year ended December 31, 2023, we spent U.S.$34.5 million on capital expenditures primarily for the National System of International Airports (SINAI), (U.S.$11.1 million for the Rivera Airport, U.S.$11 million for the Salto Airport, U.S.$1.7 million for the Carmelo Airport, U.S.$0.8 million for the Melo Airport, U.S.$0.8 million for the Paysandú Airport, U.S.$3.1 million for the Durazno Airport, and U.S.$2.6 million for advanced payments). In the year ended December 31, 2022, we spent U.S.$17.2 million on capital expenditures primarily for (i) construction of new terminal and runway and improving lightning and beaconing at Carmelo Airport and advance payment made to the National System of International Airports (known as SINAI) for works to be completed at the different airports. In the year ended December 31, 2021, we spent U.S.$0.1 million on capital expenditures at the Carrasco Airport, primarily for the works performed in the underground access gate.
In the year ended December 31, 2023, we spent U.S.$2.1 million on capital expenditures at the Punta del Este Airport, primarily for the acquisition of equipment for walkway and check in points and improvement in passenger’s terminal. In the year ended December 31, 2022, we spent U.S.$2.8 million on capital expenditures at the Punta del Este Airport, primarily for construction of three new hangars, beaconing and runway edge. In the year ended December 31, 2021, we spent U.S.$5.4 million on capital expenditures at the Punta del Este Airport, primarily for the construction of three new hangars, acquisition of fire trucks, security equipment and improvement in passenger’s terminal.
During the next five years, Puerta del Sur expects to incur additional capital expenditures in the amount of U.S.$41.5 million, as required by contract. We do not expect to incur in optional expenditures. Likewise, during the next five years and upon execution of the amendment to the Punta del Este Airport Concession Agreement in order to extend the concession term, CAISA expects to incur additional capital expenditures in the amount of U.S.$5.0 million in the Punta del Este Airport, all required by contract. We do not expect to incur in any optional expenditures.
Ecuador
Under the terms of each of our Guayaquil and Galapagos Concession Agreements, the concessionaire is not required to present a master development program. See in “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Ecuador” the “The Guayaquil Concession Agreement—Master Plan” and “The Galapagos Concession Agreement—Master Plan.”
In the year ended December 31, 2023, we spent U.S.$3.3 million on capital expenditures at the Guayaquil Airport, primarily for works related to Addendum 7 – Addendum 10 (works on platforms and the General Aviation Terminal expansion) of U.S.$2.0 million and the update of body scan and the closed-circuit television equipment. In the year ended December 31, 2022, we spent U.S.$1.8 million on capital expenditures at the Guayaquil Airport, primarily for the airport apron, machine and equipment and the purchase of electric vehicles. In the year ended December 31, 2021, we spent U.S.$0.8 million on capital expenditures at the Guayaquil Airport, primarily for works related with Addendum No. 07.
In the year ended December 31, 2023, we spent U.S.$374 thousand on capital expenditures at the Galapagos Airport, primarily for maintenance of runway and acquisition of safety and fire equipment. In the year ended December 31, 2022, we spent U.S.$122 thousands on capital expenditures at the Galapagos Airport, primarily for maintenance of airport roadway. In the year ended December 31, 2021, we spent U.S.$70 thousands on capital expenditures at the Galapagos Airport, primarily for the purchase of an electric vehicle and an electricity generator.
During the next five years, TAGSA expects to incur additional capital expenditures in the amount of U.S.$10.9 million in the Guayaquil Airport, of which U.S.$4.9 million are expenditures required by contract and U.S.$6.0 million are optional expenditures. Likewise, during the next five years, ECOGAL expects to incur additional capital expenditures in the amount of U.S.$10 million in the Galapagos Airport, all of which are expenditures required by contract.
ECOGAL is currently in negotiations with the Direccion General de Aviacion Civil to enter into an amendment of the Galapagos Concession Agreement to reassess and differ the capital investment required under such concession.
Armenia
Under the terms of our Armenian Concession Agreement, AIA is required to present a master development plan for approval by the director of the General Department of Civil Aviation (“GDCA”) every five years. See “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework—Armenia—The Armenian Concession Agreement—Master Plan.”
155
In the year ended December 31, 2023, we spent U.S.$6.5 million at the Zvartnots Airport and U.S.$0.6 million at the Shirak Airport on capital expenditures, primarily for the new security system installation, new parking and old parking reconstructions, acquisition of property and equipment at Zvartnots Airport, new hall constructions, and renovation work at Shirak Airport. In the year ended December 31, 2022, we spent U.S.$5.1 million at the Zvartnots Airport and U.S.$0.7 million at the Shirak Airport on capital expenditures, primarily for (i) remodeling works at the Shirak Airport which mainly included works made at the departure and arrival halls, (ii) construction works at the Zvartnots Airport which mainly included building reparation, and (iii) upgrade of systems and security equipment. In the year ended December 31, 2021, we spent U.S.$2.1 million at the Zvartnots Airport and U.S.$5.5 million at the Shirak Airport on capital expenditures, primarily for renovation works at the Shirak Airport, renovation of runway of C station in Zvartnots Airport and the acquisition of PPE, mainly on a snow cleaning machine, computer appliances and cameras.
CAAP and the Armenian Government are currently in discussions to develop a U.S.$400 million infrastructure plan expected to be implemented before end of 2027 in Zvartnots Airport and Shirak Airport. In addition to adding new boarding gates, check-in counters and stand positions, the infrastructure plan is also anticipated to expand the terminal area by approximately 40,000 square meters (existing terminal area is approximately 34,000 square meters) and the commercial space by approximately 6,200 square meters (existing commercial space is approximately 12,600 square meters).
Critical Accounting Policies
Critical accounting policies are those that are most important to the portrayal of our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows, and require management to make difficult, subjective or complex judgments, assumptions and estimates about matters that are inherently uncertain or where judgments, assumptions and estimates are significant. Our management bases its estimates on historical experience and other assumptions that it believes are reasonable based upon information available to us at the time that these judgments, assumptions and estimates are made. We continually evaluate our judgments, estimates and assumptions. Our actual results may differ from the judgments, assumptions and estimates made by our management. To the extent that there are material differences between these judgments, assumptions and estimates (on the one hand) and actual results (on the other hand), our future financial statement presentation, financial condition, results of operation and cash flows may be affected.
We have prepared our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements in accordance with IFRS Accounting Standards adopted by International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and interpretations issued by the International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee. The Audited Consolidated Financial Statements are presented in U.S. dollars.
In order to provide an understanding regarding the manner in which our management forms its judgments about future events, including the variables underlying our judgments, estimates and assumptions, we summarize our critical accounting policies in Note 2.X to our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
We summarize the recent accounting pronouncements in Note 2.A to our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements.
B. LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
General
As a holding company with no airport operations of our own, we are primarily dependent on dividends and distributions from our operating subsidiaries as a source of liquidity at the holding company level. Other sources of liquidity also include management fees received from certain subsidiaries.
Historically, we have covered most of its liquidity needs with cash flows generated by the operations of our subsidiaries, and through non-recourse debt issued at the subsidiary level secured by the assets of such subsidiary. Occasionally, we have made capital contributions directly into subsidiaries. Part of these capital contributions were required by the relevant concession agreements.
The primary use of our liquidity has been to fund operating expenses, our investment commitments under our concession agreements, to service our indebtedness and to make necessary capital expenditures to accommodate increases in total passengers and air traffic movements.
156
The financial condition and liquidity of our operating subsidiaries has been, and we expect will continue to be, influenced by a variety of factors, including:
| ● | our ability to generate cash flows from our operating activities; |
| ● | our investment commitments under our investment plan under our concession agreements and additional capital expenditures we decide to make; |
| ● | the level of our outstanding indebtedness and the interest that we are obligated to pay on our indebtedness, which affect our net financial expenses; and |
| ● | prevailing domestic and international interest rates at the time we incur indebtedness, which affect our debt services requirements. |
Our ability to generate cash is subject to our performance, general economic conditions, requirements of our concession agreements, industry trends, and other factors.
In those operations where our cash and cash equivalents and operating cash flows are insufficient to fund our future activities and requirements, we may need to raise additional funds through public or private equity, or debt financing. If we issue equity securities in order to raise additional funds, substantial dilution to existing shareholders may occur. If we raise cash through the issuance of indebtedness, we may be subject to additional contractual restrictions on our business. We cannot assure you that we would be able to raise additional funds on favorable terms, or at all.
COVID-19 Virus-Impact
Although COVID-19 virus had an impact in the global economy and in particular in the aviation industry during 2020 and 2021, there was an increase in traffic across all countries in 2022 compared with previous years as travel restrictions have been lifted mainly during the second semester of 2021 and continued during 2022.
In 2023, our passenger traffic increased 23.7% compared to 2022 with 81.1 million passengers served (65.6 million passengers served in 2022). Passenger traffic during 2023 increased in line with the recovery of the aviation industry.
Our Brazilian Segment
In connection with the BNDES Refinancing (see “Item 5. Operating and Financial review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Indebtedness—Brazil—ICAB”), the Majority Shareholder and CAAP have agreed not to create any encumbrances on their shares of Inframerica, and not to sell, acquire, merge or spin-off assets or undertake any other action that results or that may result in a change in the current corporate structure of Inframerica or any change of control in Inframerica, without the prior consent of BNDES. The Majority Shareholder has agreed not to undertake any change of control in CAAP without the prior consent of BNDES. In addition, the Majority Shareholder has agreed to maintain a minimum credit rating (the “Minimum Rating”) or a stand-alone rating (without including the sovereign rating), of at least B-/B3, which has been achieved in April 2022, being in compliance as of December 31, 2022 and 2023.
Additionally, as of December 31, 2021, ICAB did not pay in full the 2021 fixed concession fee and, therefore, was not in compliance with certain covenant under the BNDES Refinancing. See “Brazilian Proceedings—ICAB—Administrative Proceedings before the Brazilian ANAC.”
The forgoing has occurred because, pursuant to Portaria 139, ICAB requested to reprofile 50% of the amount due and payable of the fixed concession fee on December 31, 2021 and, even though, the Brazilian Ministry of Infrastructure granted its approval, ANAC denied ICAB’s request, and initiated administrative proceedings to declare ICAB’s payment obligations default.
Notwithstanding the process initiated by ANAC, ICAB initiated a judicial procedure. On February 2, 2022, a federal judge granted a writ of mandamus pursuant to which all actions against ICAB in connection with the lack of payment of the concession fee were automatically suspended. The process is still ongoing and although there can be no assurance as to the outcome of the proceedings, ICAB believes, based on the opinion of the ICAB’s external legal advisors, it is not likely that such writ of mandamus suspending actions against ICAB will be lifted or cancelled.
157
Impact of conflict between Russia and Ukraine
The ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine is disrupting international travel from and to Russia and Ukraine. This conflict has, and may continue to, disrupt supply chains, cause instability in the global economy and disrupt international travel from and to Russia affecting the countries generally served by the Company, mainly Armenia. Moreover, there has been an increase in the costs of raw materials and expenses for utilities, being caused mainly by the conflict.
In addition, following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, several sanctions have been announced against Russia, including, among others, travel bans and asset freezes impacting business and financial organizations in connection with Russia. Wider sanctions and other actions could be imposed if the conflict further escalate.
As a result of the above and considering the uncertainty of the extension of the war and the additional measures and sanctions that could be imposed, the full extent to which the war will impact the Company’s business, results of operations, financial position and liquidity is unknown. The company evaluated the potential risks and identified that the main affected operations could be that of Armenia, considering the current routes on which the group operates. The current routes from Russian airlines were taken over by other airlines. However, the Company is closely monitoring the situation. See Note 1 of our Consolidated Financial Statements and see Risk factor “Item 3.D Key Information—The ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine has and will likely continue to disrupt or impact the connecting flights between our Armenian Airports and Russia, which could affect our results of operation.”
Restrictions on Distribution of Dividends by Certain Subsidiaries
Statutory Restrictions
The ability of our operating subsidiaries to pay dividends is subject to accounting, tax, debt covenant restrictions, foreign exchange policies in place from time to time in the various countries where we operate, among other restrictions. Given these restrictions, significant cash or cash equivalent balances may be held from time to time at our international operating subsidiaries.
In order for operating subsidiaries to pay dividends, they must have positive retained earnings and net income, and enough cash on their balance sheet to make the relevant dividend payments. Subsidiaries must also satisfy requirements under local law to set aside a portion of their net income in each year to legal reserves. Additionally, there will be a tax effect because dividends from certain subsidiaries are subject to taxes, as described below:
In accordance with Argentine, Italian and Uruguayan company law, our operating subsidiaries incorporated in Argentina, in Italy or in Uruguay, as the case may be, must set aside at least 5% of their net income (determined on the basis of their statutory accounts) in each year to legal reserves, until such reserves equal 20% of their respected issued share capital. As of December 31, 2023, required legal reserves at our Argentine operating subsidiaries amounted to an aggregate of U.S.$15.7 million, of which U.S.$15.6 million had been reserved as of such date. As of December 31, 2023, required legal reserves at our Italian subsidiaries amounted to an aggregate of approximately U.S.$7.4 million, of which U.S.$6.4 million had been reserved as of such date. As of December 31, 2023, required legal reserves at our Uruguayan subsidiaries amounted to an aggregate of U.S.$13.8 million, of which U.S.$12.2 million had been reserved as of such date.
Argentine Law No. 27,630, published on 16 June 2021, amended the Income Tax Law with the introduction of new progressive corporate income tax rates, effective for fiscal years beginning 1 January 2021. This included the following progressive rates based on net taxable income: 25% (up to AR$5.0 million); 30% (over AR$5.0 million up to AR$50.0 million); and 35% (over AR$50.0 million). As from 1 January 2022, the bracket thresholds are to be adjusted for inflation based on the consumer price index.
Previously, Argentine Law No. 27,430, published on 30 December 2017 and Law No. 27,541, published on 23 December 2019, had reduced the single corporate tax rate from 30% to 25% and increased the remittance and dividend withholding tax rates from 7% to 13% from 1 January 2021, which was effectively undone with Law 27,630. A provision was also included to confirm that the single 30% corporate tax rate and the 7% remittance and dividend withholding tax rate apply for the three fiscal years beginning on 1 January 2018, whatever the fiscal period in which such dividends or profits are made available.
A 7% withholding tax rate is provided for dividends. This withholding rate applies to distributions made to shareholders qualifying as resident individuals or nonresidents. Therefore, in general, distributions to our Luxembourg parent companies from our Argentine subsidiaries will be subject to Argentine withholding tax.
158
With the combination of the corporate rate and dividend withholding rate on after-tax profit, for fiscal years starting in 2021, the combined tax rate would be between 30.25%; and 39.55%, depending on the applicable progressive rate.
In accordance with Brazilian law, each of our subsidiaries incorporated in Brazil must allocate 5% of its net profit to form a legal reserve, which may not exceed 20% of its capital. Our Brazilian subsidiaries may refrain from allocating resources to the legal reserve during any fiscal year in which the balance of such reserve exceeds 30% of its capital. We have not formed a legal reserve in our Brazilian subsidiaries due to the lack of net profit in the applicable fiscal years.
According to the legal requirements of Armenia and AIA’s charter, AIA is required to create a minimum non-distributable reserve from its retained earnings of an amount equal to 15% of its share capital for the purposes of covering future losses. As of December 31, 2023, required minimum non-distributable reserves for AIA amounted to an aggregate of U.S.$8.1 million, which has been fully set aside as of such date.
In accordance with Ecuadorian law, TAGSA must set aside at least 10% of its net income for each year to a legal reserve, until such reserve equals 50% of its issued share capital. As of December 31, 2023, required legal reserves for TAGSA amounted to an aggregate of approximately U.S.$9.0 million, all of which has been set aside as of such date.
These restrictions on the distributions of dividends do not materially impact our ability to meet our cash obligations at a holding company level.
Contractual Restrictions
The ability of our operating subsidiaries to pay dividends is also subject to contractual debt covenant restrictions (see “Item 5. Operating and Financial review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Indebtedness”).
Argentina Foreign Exchange Regulations
Although the new administration has announced several measures to promote foreign investments and deregulate the economy, given the lack of reserves of the Argentine Central Bank (for its acronym in Spanish, the “BCRA”) the foreign exchange restrictions applicable to inflow and outflow of funds into and from Argentina, reinstated since September 2019, remain substantially the same.
In this vein, access to the Foreign Exchange Market (“MLC”, for its Spanish acronym) for payments of dividends abroad, among other concepts, is subject to the BCRA prior clearance, unless certain limited exceptions are met. In practice this requirement and the difficulties for residents to fall under the scope of any of the exceptions provided thereby are considered an implied prohibition to access the MLC to transfer dividends offshore.
Below is a summary of the main foreign exchange restrictions currently contemplated by the foreign exchange regulations (Communiqué “A” 7953, as amended and supplemented from time to time, the “Foreign Exchange Regulations”) regarding payment of dividends, financial debts and imports. General Requirements to Access to the Foreign Exchange Market
As a general rule, and in addition to any rules regarding the specific purpose for access the MLC, certain general requirements must be met by a local company (such as AA2000) or individual for the purchase of foreign currency or its transfer abroad (i.e., payments of imports and other purchases of goods abroad, payment of services rendered by non-residents, remittances of profits and dividends, payment of principal and interest on foreign indebtedness, payments of interest on debts for the import of goods and services, among others) without need of the BCRA’s prior clearance.
Among others, the main restrictions include the following:
| (i) | not having performed, on the day in which the access to the MLC is required and in the previous 90 calendar days (in case the transactions detailed below are performed with securities governed by Argentine law) or 180 calendar days (in case the transactions detailed below are performed with securities governed by foreign law), and the commitment not to perform within the subsequent 90 or 180 calendar days (as applicable) (the “Blocking Period”), the following transactions (the “General Requirements”): |
| ● | sales of foreign-currency denominated securities in Argentina with settlement in foreign currency; |
| ● | exchange of securities issued by a resident for foreign assets; |
159
| ● | transfers of securities issued by a resident to depositories located abroad; |
| ● | purchase of securities issued by non-residents in Argentina with settlement in Pesos; |
| ● | purchase of Argentine deposit certificates representing foreign shares (CEDEARs); |
| ● | purchase of securities representing private debt issued in a foreign jurisdiction; and/or |
| ● | delivery of funds in Pesos or other Argentine assets (other than funds in foreign currency deposited in an Argentine bank account) to any individual or entity, resident or non-resident, affiliated or not, receiving as a previous or subsequent consideration, directly or indirectly, by itself or through an affiliated, controlled or controlling entity, foreign assets, crypto assets or securities deposited in a foreign jurisdiction. |
| (ii) | on the day of access to the MLC, all the foreign currency in Argentina must be on deposit at Argentine financial entities and the payor must have no “liquid external assets” and/or CEDEARs exceeding U.S.$100,000, except to the extent simultaneously applied to make payments allowed under the Foreign Exchange Regulations and unless such “liquid external assets” originate from certain transactions specified in the Foreign Exchange Regulations; |
| (iii) | commit to repatriate into Argentina and exchange into Argentine pesos through the MLC, within five business days from collection, any funds received under loans granted to third parties, time deposits or for the disposition of assets to the extent that the loans were granted, the deposits constituted, or the assets acquired after May 28, 2020; and |
| (iv) | if the entity requesting access to the MLC is a legal entity, it must submit a sworn statement indicating: |
| (a) | that in the previous 180 calendar days prior to the date requesting access to the MLC, the entity has not delivered Pesos or other local liquid assets to any individual or entity, related or not, except those deliveries directly associated with the ordinary course of business; or |
| (b) | in the event of having delivered Argentine pesos or other liquid local assets during the relevant terms indicated by the Foreign Exchange Regulations, the detail of is direct controlling entities and other members of its economic group (without restrictions regarding the activity or location of the respective related parties) and, alternatively, affidavits of: |
| (1) | the related entities who have received funds or local liquid assets during the relevant terms established by the Foreign Exchange Regulations, stating that they have not carried out and committing not to carry out the transactions listed in (i)(a) through (i)(g) above and stating that they have not delivered Argentine pesos or other local liquid assets to their direct controlling entities or to other members of the same economic group, except those directly associated with regular transactions between residents for the acquisition of goods and/or services; or |
| (2) | each related person, whether they have received funds or local liquid assets or not, stating, alternatively and during the applicable terms established by the Foreign Exchange Regulations: |
| (x) | not having conducted and committing not to conduct the transactions listed in (i)(a) through (i)(g) above; or |
| (y) | not having received Argentine pesos or other local liquid assets from the entity accessing the MLC or from any of its affiliates who have received, in turn, funds or local liquid assets from said entity, except those directly associated with regular transactions between residents for the acquisition of goods and/or services. |
160
Transfer of Funds Abroad for Payment of Dividends
According to the Foreign Exchange Regulations, payment of dividends is subject to the BCRA’s prior clearance unless certain exceptions are met and the General Requirements are complied with. Among other exceptions and requirements, the Foreign Exchange Regulations establish the following conditions in order to allow access to the MLC for the payment of dividends:
| ● | the dividends distribution shall arise from audited and approved financial statements; |
| ● | the aggregate amount to be paid under this concept shall not exceed the amount in Pesos due to the relevant shareholder according to the dividend distribution decided in the shareholders’ meeting; |
| ● | the company registers direct capital contributions which were exchanged into Pesos through the MLC since January 17, 2020; |
| ● | the aggregate amount of the transfers effected for this purpose through the MLC as of January 17, 2020, including the payment requested, shall not exceed a 30% of the value of the new capital contributions in the local company which were repatriated and exchanged into Pesos through the MLC as of the referred date; |
| ● | the acquisition of foreign currency must be effected after a minimum time period of 30 calendar days as of the exchange into Pesos of the last relevant contribution for the purpose of the computation of the value mentioned in item (c) above; |
| ● | the company must submit to the relevant foreign exchange trader: (a) the document that certify that the contributions were definitively converted into capital; or (b) a certificate of the request of registration of the capital increase made before the competent Public Registry of Commerce, provided that the documents that certify the definitive conversion of the contributions into capital are submitted within 365 calendar days as of said request of registration; and |
| ● | The company must have disclosed the aforementioned capital contributions in the last filing due under the Reporting Regime of External Assets and Liabilities. |
In addition, according to the provisions of the Foreign Exchange Regulations, in case the relevant company is a beneficiary under certain incentive schemes for exporters and oil and gas producers, access to the MLC would also be allowed to transfer dividends abroad. However, as of the date of this annual report, AA2000 is not a beneficiary of the referred schemes.
Transfer of Funds Abroad for Payment of Debt
The Foreign Exchange Regulations establish the obligation of repatriation and exchange into Argentine pesos through the MLC of external debts disbursed as of September 1, 2019 as a condition for subsequent access to the MLC, (unless certain exceptions are met, such as the case of exchanges or capitalization of interest) in order to cancel principal and interest services of said indebtedness.
Subject to the fulfillment of the General Requirements and the obligations described in the previous paragraph, access to the MLC is authorized for the repayment of the financial debt services abroad at their maturity date or up to three business days in advance. It is established that access to the Argentine Foreign Exchange Market for the payment of debt services abroad could also be granted to trustees of trusts established in the country to guarantee the payment of principal and interest services of said debt, to the extent it is verified that the debtor would have had access to the MLC for said payment.
Among other cases, Argentine residents are authorized to make payments of services of financial debts abroad or of local debt securities prior to the period allowed by the regulations (three days prior to expiration of the relevant service of principal or interest), subject to fulfillment of the following conditions: (i) it involves external financial debt authorized by the regulations to have access to the MLC for debt repayment purposes, and the related contracts provide for the crediting of funds in escrow accounts for future foreign debt servicing purposes, (ii) the funds acquired are deposited in foreign currency accounts of their ownership opened in local financial institutions constitution of the guarantees in offshore accounts shall only be authorized when this is the sole and exclusive alternative set forth in the financing agreements entered into before August 31, 2019, (iii) the accumulated amounts do not exceed the value of the next debt service, (iv) access is made for a daily amount that does not exceed 20% of the amount set forth in (iii), and (v) the bank must have verified that the indebtedness complies with the exchange regulations by which such access is admitted. Foreign currency funds not used in the cancellation of the committed debt service must be settled in the MLC within 5 business days after the expiration date of the respective debt service.
161
Likewise, among other cases, the Foreign Exchange Regulations also provide that prior approval of the BCRA will not be necessary to access the MLC for pre-payment with more than three business days prior to due date for the payment of principal and interest on financial debts abroad as long as all the following conditions are met: (i) the pre-payment is made simultaneously with the repatriation and exchange into pesos of the proceeds disbursed under new financial debt, (ii) the average life of the new indebtedness is greater than the average remaining life of the debt that is pre-paid, (iii) the maturity of the first principal service of the new indebtedness is not prior to the first expected future maturity of the principal service of the debt that is prepaid, and (iv) the amount of the first principal service of the new indebtedness does not exceed the amount of the first planned future principal service of the debt that is prepaid.
In addition, among other cases, no prior consent from the BCRA is required to pre-pay interest of external financial debt in the context of a process of exchange of debt securities with an anticipation of more than three business days, as long as (i) the prepayment is made in the context of an exchange of debt securities issued by the client requesting access to the MLC, (ii) the aggregate amount to be prepaid corresponds to accrued interest until the exchange closing date; (iii) the average life of the new securities is longer than the remaining average life of the securities subject to the exchange; and (iv) the aggregate principal amount of the new securities shall not exceed the aggregate principal amount outstanding under the securities subject to the exchange.
Limitations for the repayment of foreign-currency-denominated financial debt - Refinancing Plan
The Foreign Exchange Regulations required to submit to the BCRA, a refinancing plan following certain guidelines in order to access the MLC for, the repayment of principal maturing between October 15, 2020 and December 31, 2023 (the “Relevant Period”) corresponding to external financial indebtedness with non-related parties and foreign-currency-denominated securities issued in the local market (including, in both cases, indebtedness of financial institutions for own operation and excluding borrowings granted or guaranteed by international organizations and official credit agencies) (the “Mandatory Refinancing”).
According to item 3.17 of the Foreign Exchange Regulations, as a rule, under the Mandatory Refinancing at least:
60% of the outstanding principal amount under the relevant financing with maturities that fell during the Relevant Period should be refinanced with a new financing or debt restructuring with an average life of not less than two years while access to the MLC to repay the remaining 40% was allowed. In addition, certain exceptions to this rule were contemplated (e.g. repayments through the MLC not exceeding U.S.$2 million were allowed). As of the date of this annual report the relevant maturity dates contemplated by the Mandatory Refinancing were not extended; therefore, the requirement to submit the refinancing plan for principal maturities after December 31, 2023, is not applicable.
External financial debt with related parties
Subject to certain exceptions, repayment of principal of external financial debt with related parties is subject to the BCRA’s prior approval until December 31, 2024.
Other relevant Foreign Exchange Regulations
Blue-Chip Swap Transactions
The performance of blue-chip swap transactions can be an alternative lawful mechanism to perform payments abroad. As outflows, the blue-chip swap transactions consist in purchasing securities in an Argentine market and, afterwards, selling those securities in a foreign market (obtaining foreign currency outside of Argentina). The implicit exchange rate applicable to this type of transactions is higher with respect to the official foreign exchange rate.
According to the Foreign Exchange Regulations, the performance of this type of transactions by companies or individuals who regularly access to the MLC triggers the Blocking Period, except in the case of transactions performed with BOPREAL. See “—General Requirements to Access the MLC” and “—Payment of imports of goods and services-BCRA Notes.”
In addition, the Foreign Exchange Regulations establishes that the settlement of blue-chip swap transactions must be made through transfers to and from bank accounts of the relevant customer held in foreign financial institutions (with some exceptions, see “—Payment of imports of goods and services-BCRA Notes”).
If the relevant company or individual who intends to perform a blue-chip swap transactions benefits from any grant, subsidies or financing granted by the government as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, it would be impaired to conduct this type of transactions.
162
In addition, the CNV Rules provide for certain requisites applicable to the performance of blue-chip swap transactions, which include, among others, the following:
| (i) | a minimum parking period of the securities involved in the blue-chip swap transactions of one (1) business day; |
| (ii) | the submission of an affidavit stating that the entity performing the blue-chip swap transactions does not hold a position as a taker in repos and/or reverse repos, regardless of the settlement currency, either as a holder or joint holder, and in no registered broker-agent, and that it has not obtained any type of financing, either in funds and/or other securities; |
| (iii) | the obligation of the broker-agent involved to report information regarding each blue-chip swap transaction to be performed with five (5) business days in advance if: (a) the transaction is going to be performed by a non-resident; or (b) the transaction is going to be performed by residents and exceeds the amount of AR$200,000,000 per day; and |
| (iv) | a daily limit for blue-chip swap transactions to be performed by non-residents of AR$100,000,000. |
Payment of imports of goods and services
Elimination of the “SIRA” and “SIRASE” declarations as a requirement for access to the MLC. Creation of “SEDI”
On December 13, 2023, the BCRA issued Communiqué “A” 7917 which eliminates the need to have an approved “SIRA” or “SIRASE” declarations for the payment of imports of goods and services, respectively, and to validate payments through the “Single Foreign Trade Current Account for Foreign Trade” (“Cuenta Única de Comercio Exterior”).
In replacement of this system, on December 22, 2023, the AFIP and the Secretariat of Commerce issued the Joint General Resolution No. 5466/2023 (as amended and supplemented from time to time) (the “Joint Resolution”) by virtue a new system so called “SEDI” was created (“Sistema Estadístico de Importaciones”). An approved “SEDI” declaration is required exclusively for the customs clearance of imports of goods. This declaration will be valid for 360 calendar days, counted as from the date of its approval.
The Joint Resolution also eliminated the requirement of analysis of the importer’s financial economic capacity (“CEF” for its Spanish acronym) in order to authorize the SEDI declaration. In this sense, the AFIP -prior to the customs approval- will analyze’ the importer’s tax situation at the time of making the SEDI declaration, based on the information available in its records.
Access to the MLC for payment of imports of goods and services:
Communiqué “A” 7917 contemplates a differential treatment for imports of goods and services taking place on or after December 13, 2023, with respect to the regime applicable to the payment of commercial debt outstanding as of December 12, 2023 (the “Outstanding Debt”).
The payment of the Outstanding Debt through the MLC is subject to the BCRA’s prior approval: (i) when it corresponds to transactions financed or guaranteed by local or foreign financial entities or by international organizations or official credit agencies; or (ii) payments made within the framework of incentive schemes for exporters (which, as of the date of this annual report, AA2000 is not a beneficiary=. Additionally, the BCRA implemented an alternative payment mechanism through the subscription of notes to be issued by the BCRA (the “BOPREAL”), whose main characteristics are detailed “—BCRA Notes” below.
The access to the MLC for the payment of imports of goods and services made on or after December 13, 2023, is subject to compliance with the General Requirements and the following requisites:
| (i) | as a rule, advance payment of imports of goods or services is subject to the BCRA’s prior clearance; |
| (ii) | access to the MLC for the payment of imports of goods is allowed in quarters (25% of each installment) as from 30, 60, 90 and 120 calendar days from the nationalization of the goods (certain exceptions and specific terms are applicable to certain goods such as oil, energy, pharmaceuticals, automotive products); |
| (iii) | access to the MLC for the payment of imports of services is allowed after 30 days from the date of service provision (certain exceptions and specific terms are provided for certain types of services such as health services, travel, credit card payments, cultural and recreational services); and |
163
| (iv) | access to the MLC for the payment of imports of services provided by related parties is allowed after 180 days from the date of service provision (unless the services fall under any of the exceptions contemplated in the rule). |
BCRA Notes
On December 22, 2023, the BCRA issued Communiqué “A” 7925 (as amended) establishing the conditions for subscription of BOPREAL, which, in accordance with the provisions of Decree No. 72/2023 and the aforementioned BCRA regulations, may be used by importers to: (i) regularize the Outstanding Debt; and (ii) cancel certain tax and customs obligations. The BOPREAL may only be subscribed by importers who have Outstanding Debt.
The terms and conditions of the three series of BOPREAL offered by the BCRA are detailed in Communiqué “B” 12695. The notes can be subscribed in Argentine pesos at the reference exchange rate published by the BCRA according to Communiqué “A” 3500 of the day before the subscription date. Importers must subscribe BOPREAL through financial entities.
On January 31, 2024, the allocation of BOPREAL Series 1 was completed, reaching the maximum available amount for this series of U.S.$5 billion. AA2000 had subscribed an aggregate amount of U.S.$1,083,470 of BOPREAL Series 1. Additionally, on February 22, 2024, for the allocation of BOPREAL Series 2 was also completed, reaching the maximum amount offered under this series of U.S.$2.0 billion. The offering of Series 3 is currently ongoing for a maximum amount of up to U.S.$3.0 billion. The BOPREAL may be used as a mechanism to repay the Outstanding Debt, as follows:
(i) |
importers who subscribed Series 1 BOPREALs prior to January 31, 2024, and the aggregate amount of BOPREALs subscribed equals or exceeds 50% of the Outstanding Debt, can access to the MLC, beginning February 1, 2024; |
a. |
in an amount up to 5% of the aggregate amount of Series 1 BOPREALs subscribed by the importer |
b. |
in an amount up to 10% of the aggregate amount of Series 1 BOPREALs subscribed by the importer, provided that, simultaneously: |
i. |
repatriate and exchange into Pesos through the MLC an equivalent amount corresponding to collections from exports of goods that would have been due to be received from March 1, 2025, onwards; and |
ii. |
repatriate and exchange into Pesos through the MLC an equivalent amount corresponding to advance payments for exports of goods that will be offset with shipments whose collections would have been due from March 1, 2025, onwards, up to 10% of the total advances. |
(ii) |
importers who subscribe to BOPREAL Series 1 for an amount equal to or greater than 25% of the Outstanding Debt can access the MLC for up to 50% of the prepayments of exports of goods they settle simultaneously through the MLC, corresponding to shipments whose payments would have been due from March 1, 2025, for up to 10% of the total advances. |
(iii) |
swap (“canje”) and/or arbitrage (“arbitraje”) with funds deposited in a local account corresponding to principal and interest payments under any series of BOPREAL (i.e., amounts paid by the BCRA under the BOPREAL will be freely available to be transferred abroad); |
(iv) |
payment in kind of the Outstanding Debt through the delivery to the relevant foreign supplier (either a related or an unrelated party) of any series of BOPREAL; and |
(v) |
blue-chip swap transactions carried out by the importer with BOPREAL, which will not trigger the Blocking Period. In addition, BCRA Communiqué “A” 7935 allows the importer, as from April 1, 2024, to make blue chip swap transactions with other securities (other than BOPREAL) in order to cover the difference of the Outstanding Debt not cancelled with the proceeds obtained from the settlement of the blue-chip swap transactions performed with BOPREAL. In addition, through Communiqué “A” 7940 the BCRA also allowed the possibility of settling in the account of a third party abroad the blue-chip swap transactions performed with BOPREAL and other securities (in the latter case as from April 1, 2024). |
164
Registry of Commercial Debt for Imports with Foreign Suppliers
The Joint Resolution created the Registry of Commercial Debt for Imports with Foreign Suppliers (“Padrón de Deuda Comercial por Importaciones con Proveedores del Exterior”) (the “Registry”) in which the importers must register the Outstanding Debt. In accordance with the Resolution, if the importers cancel imports under the Outstanding Debt through other mechanisms that did not involve the transfer of currency, they should also register those imports in the Registry.
According to the referred rule, the importers should have completed the Registry in accordance with the guidelines available on the AFIP’s website, until January 24, 2024. The information recorded in the Registry shall be deemed a sworn statement. If the importer did not submit the information to the Register, or falsifies or adulterates the information provided therein, it will not be able to access to the payment mechanisms established by the new regulations (e.g., subscriptions of BOPREAL Series 2 and 3) and the relevant debt shall be subject to a further evaluation by the authorities. As of the date of this annual report, AA2000 completed the Registry.
MEMs will be able to access the MLC to cancel de Outstanding Debt for imports
Communiqué “A” 7952 allows Micro, Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (“MSMEs”) to access the MLC as from February 10, 2024, to cancel the Outstanding Debt, as long as they comply with the following requisites:
1. |
the MSMEs, must be subscribed in accordance with the BCRA rules on “Determination of the status of micro, small and medium-sized enterprises”; |
2. |
the aggregate amount of the Outstanding Debt is less than or equal to U.S.$500,000 (the “Maximum Amount”); |
3. |
the aggregate amount of the Outstanding Debt must have been registered in the Registry of Commercial Debt for Imports with Foreign Suppliers (“Padrón de Deuda Comercial por Importaciones con Proveedores del Exterior”); |
4. |
payments made through the MLC must not exceed the Maximum Amount and, in turn, must not exceed the following caps according to the schedule detailed below: |
a. |
from February 10, 2024, through March 9, 2024, the lesser of U.S.$50,000 or the Maximum Amount; |
b. |
from March 10, 2024, through April 9, 2024, the lesser of U.S.$150,000 or the Maximum Amount 3; and |
c. |
on or after April 10, 2024, no cap as long as the Maximum Amount is not exceeded; and |
5. |
the Outstanding Debt must be declared in the last due presentation of the “Survey of External Assets and Liabilities” established by Communiqué “A” 6401 (as amended and supplemented from time to time). |
Off-Balance Sheet Risks
Our off-balance sheet risk arises principally as a result of our contingent obligations to third-party guarantors that provide performance bonds, sureties and other guarantees that are required to secure the performance of our obligations under our concession agreements. For a discussion of the performance bonds, sureties and other guarantees provided in our concession agreements, please see the following sections of “Item 4. Company Information—Business Overview—Regulatory and Concessions Framework”: “Argentina—The AA2000 Concession Agreement—Performance Guarantee and Guarantee for the Performance of the Works Foreseen in the AA2000 Concession Agreement,” “Italy—The Pisa Concession Agreement—Guarantees,” “Italy—The Florence Concession Agreement—Guarantees,” “Brazil—The Brazilian Concession Agreement—Guarantees and Other Financial Commitments,” “Uruguay—The Carrasco Concession Agreement—Guarantees,” “Ecuador—Terminal Aeroportuaria de Guayaquil S.A. TAGSA Concession—Guarantee and Performance Bonds,” “Ecuador—Aeropuerto Ecológico de Galápagos S.A. ECOGAL—Guarantee and Other Performance Bonds,” and Note 26 to our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements.
165
We have entered into a registration rights and indemnification agreement with the Majority Shareholder. Pursuant to such registration rights and indemnification agreement, we agree to indemnify the Majority Shareholder for the pro rata portion of any losses, claims, damages, liabilities, joint or several, and expenses arising out of or based upon certain letters of guarantee provided by the Brazilian National Development Bank (Banco Nacional do Desenvolvimento Economico e Social “BNDES”) and Banco Citibank to ICAB, as determined by a final, non-appealable judgment of a court of competent jurisdiction. See “Item 7. Major Shareholders and Related-Party Transactions—Related Party Transactions—Other Transactions with Related-Parties—Registration Rights and Indemnification Agreement.”
Cash Flows
Years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Operating Activities
The net cash provided by operating activities was U.S.$356.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 17.8% or U.S.$53.8 million increase in net cash provided by operating activities as compared to U.S.$302.6 million in net cash provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2022, mainly as a result of (i) the increase of U.S.$57.9 million in cash provided by operating activities derived from the increase in our airports activity, and (ii) the aggregate effect of the decrease of U.S.$5.5 million in capital expenditures mainly in Argentina partially offset by the increase in capital expenditures in our subsidiaries in Uruguay and Italy, see “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Capital Expenditures by Segment.” The increase in net cash provided by operating activities was partially offset by a decrease of U.S.$9.6 million in grants received from local authorities in 2023, as compared to 2022.
Investing Activities
The net cash used in investing activities was U.S.$66.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, an 807.5% or U.S.$75.8 million variation as compared to U.S.$9.4 million provided by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2022. The variation was primarily due to the financial investing made during 2023 explained by the aggregate effect of (i) the decrease of U.S.$97.7 million in disposal of other financial assets mainly in AA2000, AIA, CASA and the release of restricted cash in the interest payment account in ACI Sudamérica in 2022, offset by the increase in disposal of other financial assets in TAGSA, Corporación Aeroportuaria S.A., and CAS Panamá in 2023. This variation from cash provided by investing activities in 2022 to cash used in investing activities in 2023, was partially offset by the decrease of U.S.$22.0 million in acquisition of other financial assets mainly in AA2000, CASA TAGSA and Corporación Aeroportuaria S.A.
The net cash used in discontinued investing activities was U.S.$14.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2022 due to the disbursement of the outstanding balance related to AAP disposal.
Financing Activities
The net cash used in financing activities was U.S.$201.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 13.9% or U.S.$32.7 million decrease as compared to U.S.$234.3 million in net cash used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2022 primarily as a result of:
(i) |
the payment of U.S.$172.0 million for the redemption of preferred shares under the AA2000 Concession Agreement in 2022; |
(ii) |
the decrease of U.S.$128.3 million in loans repaid mainly due to the decrease of: (a) U.S.$116.7 million derived from the decrease in payment of borrowings in AA2000, (b) the decrease of U.S.$31.5 million mainly derived from the prepayment made to Ameriabank C.J.S.C. in AIA in 2022, partially offset by (c) the increase of U.S.$18.9 million in Italy due to the SACE loan payments (See “Item 5. Operating and Financial review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Indebtedness”); |
(iii) |
the decrease of U.S.$27.6 million in interest paid mainly due to U.S.$30.1 million in AA2000 as a result of the decrease in debt, offset by the increase of U.S.$4.1 million in Italy (See “Item 5. Operating and Financial review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Indebtedness”); |
166
(iv) |
these variations were partially offset by: (a) the decrease of U.S.$284.1 million in proceeds from borrowings mainly due to the decrease of U.S.$275.4 million in AA2000 and the increase of U.S.$6.8 million in Italy (See “Item 5. Operating and Financial review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Indebtedness”), and (b) the decrease of U.S.$14.7 million in proceeds from cash contributions made by the non-controlling interest in ICAB. |
Years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021
A cash flow comparison of the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 has been omitted from this annual report, but may be found in “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects” of our annual report on Form 20-F for the period ended December 31, 2022, filed with the SEC on March 31, 2023.
Treasury policies, currencies of cash held, hedging and other miscellaneous items
We manage our cash needs on a decentralized basis, and manage our indebtedness to ensure compliance with any debt restrictions and limitations on dividends and distributions established in our debt agreements that include such restrictions. We do not currently enter into any hedging arrangements.
Indebtedness
Set forth below is a summary of certain terms and conditions of our financing agreements:
Argentina
Argentine Notes – Argentine Notes Series 2017
On February 6, 2017, AA2000 issued U.S.$400.0 million aggregate principal amount of 6.875% senior secured notes due 2027 (the “Argentine Notes Series 2017”). The Argentine Notes Series 2017 are senior obligations of AA2000 and rank pari passu in right of payment with any existing and future indebtedness of AA2000 that is not subordinated in right of payment to the Argentine Notes Series 2017. The Argentine Notes Series 2017, up to an amount equal to U.S.$400.0 million, are secured by the trust dated January 19, 2017 entered into by AA2000 and the trustee thereto, under which AA2000 transferred and assigned in trust (a) right, title and interest in, to and pursuant to (but none of its obligations under or relating to) each payment of the Usage Fees; and (b) the Company’s right, title and interest in, to and pursuant to (but none of its obligations under or relating to) 100% of the AA2000 rights under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, to receive payment in the event of termination, expropriation or surrender of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, including the right to receive and retain all payments thereunder and all other proceeds thereof;, subject to the condition that AA2000 has sufficient funds from proceeds not transferred to the trust to cover basic concession operating costs (the “Tariffs Trust”). The Tariffs Trust was approved by ORSNA up to the full principal amount of the Argentine Note Series 2017. AA2000 is not required to fully fund the Tariffs Trust.
Principal and interest on the Argentine Notes Series 2017 are payable quarterly on each February 1, May 1, August 1, and November 1, with the first payment of interest beginning on May 1, 2017, and the first payment of principal beginning on May 1, 2019. The Argentine Notes Series 2017 will mature on February 1, 2027.
AA2000 may redeem the Argentine Notes Series 2017 in whole or in part at the following redemption prices:
Date of Payment |
|
Multiplier |
|
On or after the fifth anniversary of the issuance date to but excluding the sixth anniversary of the issuance date |
|
103.438 |
% |
Thereafter to but excluding the seventh anniversary of the issuance date |
|
102.578 |
% |
Thereafter to but excluding the eighth anniversary of the issuance date |
|
101.719 |
% |
Thereafter to but excluding the ninth anniversary of the issuance date |
|
100.859 |
% |
Thereafter |
|
100.000 |
% |
In relation to the Argentine Notes Series 2017, AA2000 was subject to certain customary negative covenants, such as restrictions on debt it may incur, restrictions on payment of dividends, restrictions on encumbrances of its property, limitations on disposal of its assets and investments which it may make, as well as restrictions in relation to its ability to merge or consolidate with another entity. As detailed in “—Exchange Offer to Argentine Notes Series 2017”, in the context of the exchange offer completed in May 2020, substantially all of the restrictive covenants and events of default established by the indenture were eliminated with respect to the Argentine Notes Series 2017.
167
Termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement will trigger a default under the Argentine Notes Series 2017. In the event of termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, payment of the Argentine Notes Series 2017 will be automatically accelerated and shall be immediately due and payable.
Global Program
On February 27, 2020, the ordinary general meeting of shareholders of AA2000 approved the creation of a Global Program for the issuance of Notes. The aforementioned program establishes the issuance of simple Notes not convertible into shares with a nominal value of up to U.S.$500 million, or its equivalent in other currencies, with a duration of five years from the date of approval of the Argentine Comisión Nacional de Valores (“CNV”). On April 17, 2020, AA2000 obtained authorization from the CNV for the Global Program for the Issuance of Notes. The principal value was increased up to U.S.$1,500 million after an ordinary general meeting of holders held on June 15, 2021, and the approval of the CNV on July 11, 2021, which left unchanged the issuance period of five years from the date of the original approval.
Exchange Offer to Argentine Notes Series 2017
On May 19, 2020, AA2000 completed an exchange offer pursuant to which 86.73% of the aggregate original principal amount of the Argentine Notes Series 2017 were exchanged for newly issued 6.875% Cash/9.375% PIK Class I Series 2020 Additional Senior Secured Notes due 2027 (the “Argentine Notes Series 2020”).
The terms of the Argentine Notes Series 2020 are substantially identical to the terms of the Argentine Notes Series 2017, except that (i) the quarterly interest payment originally scheduled to be paid in cash on the Argentine Notes Series 2017 on May 1, 2020 was paid in cash in the form of an interest premium payment equal to U.S.$10 for each U.S.$1,000 outstanding principal amount of the Argentine Notes Series 2017, and/or in kind (as the case may be) by increasing the principal amount of any Argentine Notes Series 2020 issued on the settlement date (May 20, 2020), (ii) quarterly interest payments originally scheduled to be paid in cash on the Argentine Notes Series 2017 on August 1, 2020, November 1, 2020 and February 1, 2021 were and will be paid in kind by increasing the principal amount of any outstanding Argentine Notes Series 2020 at a rate of 9.375% per annum, (iii) quarterly amortization payments originally scheduled to be paid on the Argentine Notes Series 2017 on May 1, 2020 August 1, 2020, November 1, 2020 and February 1, 2021 were deferred to begin on May 1, 2021 pursuant to terms of the Argentine Notes Series 2020 and continue under a new principal amortization schedule until maturity, (iv) at any time after February 1, 2021, the Company has the right to exercise a one-time optional redemption to redeem, in whole or in part, an amount of Argentine Notes Series 2020 equal to the sum of (a) the aggregate amount of interest payments previously paid in kind on the Argentine Notes Series 2020 and (b) the aggregate amount of quarterly amortization payments originally scheduled to be paid on the Argentine Notes Series 2017 on May 1, 2020, August 1, 2020, November 1, 2020 and February 1, 2021 that is effectively deferred pursuant to the exchange of Argentine Notes for Argentine Notes 2020 in the exchange offer, and (v) substantially all of the restrictive covenants and events of default and related provisions under the indenture executed in connection with the Argentine Notes Series 2017 were eliminated solely with respect to the Argentine Notes Series 2017.
The Argentine Notes Series 2020 and the Argentine Notes Series 2017 are secured by the Tariffs Trust on a pro rata and pari passu basis in accordance with the indenture and the related collateral documents.
New Exchange to Argentine Notes Series 2017 and Argentine Notes Series 2020 and New Offering
On October 28, 2021, AA2000 issued U.S.$208.9 million aggregate principal amount of 8.5% Class I Series 2021 Additional Senior Secured Notes due 2031 (the “Argentine Notes Series 2021”) in exchange for 24.61% of the total original principal amount of the Argentine Notes Series 2017 and 66.83% of the original principal amount of the Argentine Notes Series 2020. Additionally, on November 4, 2021, AA2000 issued U.S.$64.0 million of newly issued Argentine Notes Series 2021 related to a new fund raising.
The Argentine Notes Series 2021, the Argentine Notes Series 2017 and the Argentine Notes Series 2020 not exchanged are secured by the Tariffs Trust on a pro rata and pari passu basis. In addition, to secure its obligations under the Argentine Notes Series 2021, AA2000, together with the relevant parties thereto, amended the “Cargo Trust” as defined below in “—The Credit Facilities”) in order to include holders of Argentine 2021 Notes as beneficiaries therein, granting them a security interest which is subordinated to (i) the rights of creditors under certain existing loans of AA2000, and (ii) any debt permitted to be incurred to finance or refinance any capital expenditures made or to be made pursuant to the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
168
Once the Argentine Notes Series 2017 and the Argentine Notes Series 2020 not exchanged in the exchange offer mature or are repaid in full, AA2000 is required to amend and restate the Cargo Trust and the “Tariffs Trust”, so that the Argentine Notes Series 2021 become secured under the Cargo Trust on a pro rata and pari passu basis with the existing beneficiaries of the Cargo Trust, and these beneficiaries in turn become secured under the Tariffs Trust on a pro rata and pari passu basis with the Argentine Notes Series 2021. In accordance with the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the collateral assignment of revenue must be authorized by the ORSNA. On October 15, 2021, the ORSNA approved the amendment of the Tariffs Trust and of the Cargo Trust to include the Argentine Notes Series 2021 as beneficiaries thereto (including their future amendment and restatement, once the Argentine Notes Series 2017 and Argentine Notes Series 2020 are repaid in full). Furthermore, AA2000 received the approval from the Argentine Central Bank to establish a non-interest-bearing U.S. dollar trust account in the United States to secure the Argentine 2021 Notes. The main covenants and guarantees remain unchanged. However, substantially all of the restrictive covenants and events of default and related provisions were eliminated solely with respect to the Argentine Notes Series 2020. Additionally, it has been established in the offering memorandum that the compliance of the financial ratios does not begin to apply until June 2023.
Termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement will trigger a default under the Argentine Notes Series 2017, the Argentine Notes Series 2020 and the Argentine Notes Series 2021. In the event of termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement, payment of any of those notes will be automatically accelerated and shall be immediately due and payable.
Additional New Money Offering
In addition to the exchange offer completed on October 28, 2021 (as described above), on November 4, 2021, AA2000 issued U.S.$62.0 million aggregate principal amount of Class 4 Senior Secured Notes related to a new money offering, having a maturity of seven years, this is November 1, 2028, bearing an annual interest rate of 9.500% (the “New Money 2021 Notes”). The New Money 2021 Notes are secured by a first priority lien on the Cargo Trust on a pari passu basis with the certain commercial bank lenders to AA2000 and new debt incurred by AA2000 to fund infrastructure works for a total amount of up to U.S.$235 million. (see “—The Credit Facilities”).
Argentine Notes – Series 2020 Class 2
On August 20, 2020, within the framework of the Global Program for the Issuance of Negotiable Obligations, AA2000 issued Class 2 Series 2020 negotiable obligations denominated in US dollars to be paid in pesos, for an amount of U.S.$40 million maturing on August 20, 2022, at an interest rate of 0% and with an issue price at par (100% of the nominal value). The amortization of the capital of the negotiable obligations was established in a single installment upon maturity, which will be payable at the Communication Reference “A” 3500 exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Argentine Republic (BCRA). In June 2022, AA2000 repurchased U.S.$2 million of dollar-linked Class 2 notes issued in August 2020. In August 2022, U.S.$25.4 million of these notes were exchanged for dollar-linked Class 9 Notes, while at the maturity date, in August 2022, AA2000 repaid the remaining U.S.$12.6 million.
Argentine Notes – Class 3
On September 8, 2021, AA2000 issued U.S.$30.5 million aggregate principal amount of 4.00% Class 3 Notes, repaid in a single payment in September 2023.
On July 5, 2023, A2000 completed an exchange offer pursuant to which 90.7% of the total original principal amount of the Argentine Notes – Class 3 were exchanged for newly issued Argentine Notes – Class 10 in kind according to the exchange ratio of U.S.$1.00 nominal value of Argentine Note Class 3 for U.S.$0.9065 nominal value of Argentine Notes – Class 10. On July 6, 2023, the notes of the holders who did not enter the exchange were redeemed paying to the holders the relevant redemption premium (101% on the outstanding amounts) and the accrued interest until the redemption date. The redemption of the notes was partially funded with the proceeds obtained by AA2000 under the issuance of 0.00% dollar-linked Argentine Notes – Additional Class 9 due 2026 and issued in July 2023.
169
Argentine Notes – Class 5 and 6
On February 21, 2022, AA2000 issued U.S.$174 million of dollar-linked notes, in the local market, in two tranches:
| ● | U.S.$138 million of Class 5 Notes, with an annual interest rate of 5.5%, five-year grace period and quarterly amortization, starting May 2027 (the “Class 5 Notes”). AA2000 will use these proceeds to fund infrastructure works in certain of the Group “A” airports, within the National Airports System; These notes are secured by a first priority lien on the Cargo Trust on a pari passu basis with certain commercial bank lenders to AA2000 and the New Money 2021 Notes; and |
| ● | U.S.$36 million of Class 6 Notes, with an interest rate of 2%, maturing in February 2025. In December 2023 and March 2024, AA2000 repurchased U.S.$1.6 million and U.S.$4.7 million, respectively, of the par value of Class 6 Notes. |
Argentine Notes – Class 7
On July 8, 2022, AA2000 issued U.S.$20 million of dollar-linked Class 7 Notes in the local market, at a 0% interest rate, repayable in a single installment in July 2025. In December 2023, Class 7 Notes were redeemed, paying to the holders the relevant redemption premium (102% on outstanding amounts).
Argentine Notes – Class 9
On August 19, 2022, AA2000 issued U.S.$30 million of dollar-linked Class 9 Notes in the local market, at a 0,00% interest rate, repayable in three installments of U.S.$10 million each, in February, May and August 2026 The integration of the nominal value amounted to U.S.$25.4 million through the exchange of Class 2 Notes while the remaining U.S.$4.6 million were in integrated in AR$. In March 2024, AA2000 repurchased dollar-linked Class 9 Notes for U.S.$1.6 million.
Argentine Notes - Class 9 Additional Notes
On July 5, 2023, within the framework of Global Program for the issuance of Notes, AA2000 issued an additional U.S.$2.7 million of Argentine Note - Additional Class 9, with an issue price above par (119% of the nominal value). The proceeds obtained under the Class 9 Additional Notes were applied to fund the redemption of Argentine Notes – Class 3 (see “—Argentine Notes - Class 3”).
Argentine Notes – Class 10
On July 5, 2023, within the framework of Global Program for the issuance of Notes, AA2000 issued U.S.$25.1 million with an issue price above par (110.65% of the nominal value). The notes were integrated 100% in kind according to the exchange ratio of U.S.$1.00 nominal value of Argentine Note Class 3 for U.S.$0.9065 nominal value of Argentine Notes – Class 10. In March 2024, AA2000 repurchased dollar-linked Class 10 Notes for U.S.$4.5 million.
The Credit Facilities
On August 9, 2019, AA2000 entered into two credit facility agreements: (a) the “onshore” credit facility agreement for a principal amount of U.S.$85.0 million (the “ Onshore Credit Facility”) and (b) the “offshore” credit facility agreement for a principal amount of U.S.$35.0 million (the “ Offshore Credit Facility”) and together with the Onshore Credit Facility, the “Credit Facilities”). The lenders were Citibank N.A. (“Citibank”), the Citibank N.A. branch established in Argentina (“Citibank Argentina”), Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (Argentina) S.A.U. (“ICBC”), Banco de Galicia y Buenos Aires S.A.U. (“Galicia”) and Banco Santander Argentina S.A.(“Santander”) (jointly, the “Lenders”).
The agreed term for the Credit Facilities was thirty-six months from August 8, 2019 (the Borrowing Date). The principal amount under the Credit Facilities was originally to be repaid in nine quarterly equal and regular installments, the first one being paid 12 months from the Borrowing Date. Principal amounts under the Credit Facilities bear interests as follows: (i) regarding the Onshore Credit Facility, at a fixed annual nominal rate of 9.75%, and (ii) regarding the Offshore Credit Facility, at a variable rate equivalent to (a) the LIBOR rate, plus (b) an applicable interest rate of an annual nominal 5,500%, plus (c) the applicable withholding tax.
170
The Credit Facilities are secured by a first priority lien on a pari passu and pro rata basis with the New Money 2021 Notes, Class 5 Notes, ICBC Dubai Loan (as defined below), the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan (as defined below) and new debt incurred by AA2000 to fund infrastructure works for a total amount of up to U.S.$235 million, pursuant to the argentine collateral trust agreement dated August 9, 2019 (as amended in October 2021) under which, AA2000 has transferred and assigned to the collateral trustee, all: (a) rights, title and interest in, to and under each payment of the cargo airport charges payable by the user of such services in connection with all proceeds derived from export and import services carried out by Terminal de Cargas Argentina S.A. (a business unit of AA2000); and (b) any residual amount that AA2000 could be entitled to receive pursuant to the Tariffs Trust, in respect of the rights to receive payment in the event of a termination, expropriation or redemption of the AA2000 Concession Agreement; including the right to receive and withhold all the payments pursuant to them and any other produced by them, assigned in trust to secure the Argentine Notes Series 2017, the Argentine Notes Series 2020 and the Argentine Notes Series 2021 issued by AA2000 (the “Cargo Trust”).
Between April 2020 and May 2021 AA2000 entered into a series of agreements to defer (in financial terms) the principal repayments of the Onshore Credit Facility and the Offshore Credit Facility, respectively, and to waive AA2000’s obligation to meet certain expected financial ratios. In accordance with these agreements, AA2000 entered into bilateral agreements with each of the financial institutions whose disbursements were made between August 2020 and August 2021, which established a quarterly installment of interest at a variable interest rate and an applicable margin (the “Bilateral Agreements”).
Additionally, in order to comply with the mandatory refinancing established by the Foreign Exchange Regulations (see “Argentina Foreign Exchange Regulations”) AA2000 agreed to extended 60% of the Offshore Credit Facility installments corresponding to Citibank maturing on November 19, 2020 and February 19, 2021, of U.S.$2,333,333 each that will be fully repaid on November 19, 2022 and February 19, 2023 respectively.
Syndicated Bimonetary Loan
On October 26, 2021, a framework agreement was signed to contemplate terms and conditions of a new refinancing of the Credit Facilities and the Bilateral Agreements. Through the framework agreement, the deferral (in financial terms) of principal amortization installments totaling U.S.$58,000,000 was agreed upon, as well as the deferral of the outstanding bilateral loans totaling AR$3,606,813,216.
On November 18, 2021, AA2000 implemented the framework agreement signed on October 26, 2021, by obtaining the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan. This loan is secured with a first priority lien on the Cargo Trust pari passu and on a pro rata basis with the lenders under the Credit Facilities, the New Money Notes 2021, the Class 5 Notes, the ICBC Dubai Loan (as defined below) and new debt incurred by AA2000 to fund infrastructure works for a total amount of up to U.S.$235 million. As from the date of amendment and reordering of the Tariffs Trust and the Cargo Trust (once the Argentine Notes Series 2017 and the Argentine Notes Series 2020 have been fully repaid), each and every one of the financings referred to in this section will be secured pro rata and pari pasu with the New Money 2021 Notes, the Class 5 Notes, the Argentine Notes Series 2021, the ICBC Dubai Loan (as defined below), and any other indebtedness secured by the Tariff Trust and the Cargo Trust.
Principal under the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan would be paid in eight equal and consecutive quarterly installments, with the first installment to be paid in February 2023.
The disbursements denominated in Argentine pesos will be paid quarterly, accruing interest at a variable rate equivalent to the BADLAR rate adjusted by Leliq plus an applicable margin of 10.00% per annum in the case of ICBC, Banco Galicia and Banco Santander. In the case of Citibank Argentina, a variable rate equivalent to the higher of: (i) the BADLAR rate; or (ii) the interest rate of the BCRA’s overnight deposit rate plus an applicable margin of 15.00% per annum.
The disbursements denominated in U.S. dollars bears an 8.5% nominal interest rate per annum.
The proceeds disbursed under the Argentine pesos and the U.S. Dollars tranches of the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan were applied to cancel (i) the Bilateral Agreements; and (ii) the remaining installments of the Credit Facilities.
Pursuant to the terms and conditions of the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan, AA2000 must comply with certain restrictions related to indebtedness, restricted payments (including dividends), creation of liens, among others, in line with the restrictive covenants provided by the terms and conditions of the Credit Facilities, the Argentine Notes Series 2021, and the New Money 2021 Notes.
171
As of December 31, 2023, (i) the Credit Facilities were repaid in full by AA2000; (ii) the Argentine pesos tranche of the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan was prepaid in full by AA2000; and (iii) U.S.$9.0 million remains outstanding under the U.S. Dollar tranche of the Syndicated Bimonetary Loan, plus the accrued interest thereunder.
Banco Ciudad Loan
On November 1, 2021 AA2000 signed a new loan agreement with Banco de la Ciudad de Buenos Aires for U.S.$5 million (the “Banco Ciudad Loan”).
The loan has a payment term of twenty-four months, a nominal annual interest rate of 6% and its principal amortizes 30% after twelve months and eighteen months, and 40% after twenty-four months. It is secured by assigned revenues from certain commercial contracts celebrated with Jorge Newbery Airport, Gate Gourmet Argentina S.A. and Sky Chefs Argentine INC. As of December 31, 2023, the Banco Ciudad Loan had been fully repaid.
The ICBC Dubai Loan
On July 29, 2022, AA2000 obtained the ICBC Dubai Loan, for a total amount of U.S.$10 million, accruing interest at a variable rate equivalent to three-month SOFR plus spread of 7.875% and withholding taxes. The loan will be repaid in three installments to be made in April, July and October 2025. The loan is secured by a first priority lien on the income generated in the cargo terminal on a pari passu basis with certain commercial bank lenders to AA2000 and the Class 4 Notes, and a second priority lien on the international and regional air station usage fees and concession compensation rights.
ICBC Import Financing
In March 2023, AA2000 obtained a loan from ICBC for a total amount of U.S.$1.2 million for financing imports, accruing interest rate of 12.90%, to be paid in one installment on the maturity date. On September 18, 2023, AA2000 canceled this loan.
In September 2023, AA2000 obtained a loan from ICBC for a total amount of U.S.$0.5 million for financing imports, accruing interest rate of 15.50%, to be paid in one installment on the maturity date. In January 2024, AA2000 repaid this loan in full.
Also, in September 2023, AA2000 obtained another a loan from ICBC for a total amount of U.S.$0.1 million for financing imports, accruing interest rate of 15.50%, to be paid in one installment on the maturity date, that is to say, December 2024.
Italy
CA Italy Note Issuance
On January 8, 2018, CA Italy issued €60.0 million aggregate principal amount of 4.556% secured notes due 2024 (the “Italian Notes”). The proceeds of the Italian Notes were used to refinance and replace the 6.250% secured notes due 2019 issued by CA Italy in December 2014. Interest on the Italian Notes is payable annually in arrears on June 30 of each year. The Italian Notes will mature on December 31, 2024.
In connection with the sale of the 25% interest in the share capital of CA Italy to Mataar Holdings 2 B.V., Dicasa Spain S.A.U. and Mataar Holdings 2 B.V. agreed, inter alia, to execute and deliver all documentation required to effect that such sale would constitute a permitted change of control under the terms and conditions of the Italian Notes.
The Italian Notes are secured by an economic first ranking pledge in respect of all the shares representing 100% of the share capital of CA Italy, 100% of the share capital of Dicasa Spain S.A.U. and the shares representing CA Italy’s holding in TA.
(i) Mandatory Redemption
CA Italy must redeem the Italian Notes in whole, upon: (i) suspension, cancellation, termination, revocation (in each case, without replacement), forfeiture, surrender or transfer of the Florence Concession or the Pisa Concession to the extent that such event constitutes or is reasonably likely to constitute a material adverse change, or (ii) upon the loss of CA Italy’s ability to directly appoint and/or remove the majority (by voting power) of the members of the governing body or its ability to control the ordinary dividend policy of TA, or (iii) if CA Italy ceases to hold at least 50.1% of the issued share capital in TA.
172
CA Italy must also redeem the Italian Notes in whole or if the amount of the mandatory redemption is less than the principal outstanding amount of the Italian Notes as at the date of the mandatory redemption, then in part, upon occurrence of: (i) sale, lease, license, transfer, loan or other disposal by CA Italy of any asset, other than the shares which it holds in TA or any disposal of the concessions by CA Italy, or (ii) the disposition by CA Italy of any shares held by it in TA (subject to the exception set forth under the terms and conditions of the Italian Notes).
(ii) Redemption at CA Italy’s Option
At the option of CA Italy, the Italian Notes may be redeemed in whole, but not in part, on any interest payment date, at their principal outstanding amount together with interest accrued to the date fixed for the redemption if (i) CA Italy, or Dicasa Spain S.A., its intermediate co-guarantor, has or will become obligated to pay additional amounts as a result of any change in, or amendment to, the laws or regulation of the Republic of Italy or the Kingdom of Spain or, in each case, any political subdivision or any authority having power to tax, or any change in the application or official interpretation of such laws or regulations, which change or amendment becomes effective on or after the issue date, and (ii) such obligation cannot be avoided by CA Italy (or Dicasa Spain S.A.U., or its intermediate co-guarantor, as the case may be) taking reasonable measures available to it, provided that no such notice of redemption shall be given earlier than 90 days prior to the earliest date on which CA Italy (or Dicasa Spain S.A.U., or its intermediate co-guarantor, as the case may be) would be obliged to pay such additional amounts were a payment in respect to the Italian Notes then due.
CA Italy may also redeem the Italian Notes in whole upon the occurrence of an equity cure event or if the applicable equity cure amount is less than the principal outstanding amount of the Italian Notes plus the relevant make-whole amount due under the terms and conditions of the Italian Notes as at the relevant equity cure redemption date, then in part and in each case on giving at least 5 and no more than 10 days’ irrevocable notice to the holders of the Italian Notes. The relevant equity cure amount must be used: (i) if from one calculation date under the terms and conditions of the Italian Notes to the following calculation date the EBITDA of CA Italy falls by 15% or less, to redeem a principal amount of the Italian Notes such that the total of the principal amount of the Italian Notes repaid (at 100% of their principal amount), interest accrued thereon and the make-whole amount equals the relevant equity cure amount; or (ii) if such EBITDA reduction is greater than 15%, to redeem a principal amount of the Italian Notes such that the total of the principal amount of the Italian Notes repaid (at 100% of their principal amount) and interest accrued thereon equals the relevant equity cure amount.
CA Italy may, on any business day prior to December 31, 2021, on giving not more than 10 nor less than 5 days’ irrevocable notice to the noteholders, redeem all, but not in part, of the Italian Notes at an amount equal to (i) 100% of the principal outstanding amount of the Italian Notes, together with interest accrued thereon to the date of redemption, plus (ii) the remaining scheduled interest on the redeemed Italian Notes. CA Italy may, on any business day after December 31, 2021, on giving not more than 10 nor less than 5 days’ irrevocable notice to the noteholders, redeem all, but not some only, of the Italian Notes, at 100% of their principal outstanding amount together with interest accrued to the date fixed for redemption.
(iii) Redemption at Noteholders’ Option
If CA Italy is unable to make permitted payments for two consecutive calculation dates, the holders of the Italian Notes have the option to require CA Italy to redeem or purchase, in whole or in part, as long as the proceeds from such redemption or purchase since the first calculation date minus €300,000, is less than the principal amount.
In the case of a change of control, holders of the Italian Notes have the option to require CA Italy to redeem or purchase all or a portion of their Italian Notes at 101% of its principal outstanding amount together with interest accrued to the date which is seven days after a change of control notice is given by CA Italy.
If the remuneration payable to the noteholders under the Italian Notes exceeds the maximum rate of interest permitted by Italian Usury Legislation, the noteholders will have the option to require CA Italy to redeem or purchase all or some of its Italian Notes at 101% of its principal outstanding amount together with interest accrued to the date upon which the relevant note is redeemed. If any event results in it becoming illegal under laws or regulations applicable to the holder of the Italian Notes to hold such Italian Notes (provided that such holder of Italian Notes has received a legal opinion so stating) (each, an “Illegality Event”), such holder of Italian Notes shall have the option to require CA Italy to redeem or, at CA Italy’s option, to purchase all or some of its Italian Notes within seven days of providing notice to the Issuer, at 100% of the principal outstanding amount, together with interest accrued to (but excluding) the date of such notice.
173
(iv) General Covenants
Except for certain permitted payments, CA Italy, inter alia, must not declare, make or pay any dividend, charge, fee or other distribution (or interest on any unpaid dividend, charge, fee or other distribution) (whether in cash or in kind) on or in respect of its share capital (or any class of its share capital) or repay or distribute any dividend or share premium reserve, among other restrictions. Such permitted payments are only those payments made by CA Italy to its holding company, provided that the following conditions are fulfilled: (a) all payments due and payable under all related transaction documents have been satisfied; (b) the distribution is identified and made within sixty (60) days of the delivery of the most recent compliance certificate; (c) any mandatory redemption amounts then due and payable have been paid; (d) no event of default, default or lock-up is continuing or would result from the making of the proposed payment; (e) CA Italy has confirmed that certain financial ratios are satisfied; and (f) such payment will not be made in the two years prior to the final maturity date.
The obligors of the Italian Notes are also prohibited from: (i) selling, transferring or otherwise disposing of any of their respective assets on terms whereby such assets are or may be leased to or re-acquired by an obligor of the Italian Notes or any other member of the group; (ii) selling, transferring or otherwise disposing of any of its receivables, creating or permitting liens over any of their assets (other than the liens under the Italian Notes or liens by operation of law); (iii) entering into guarantees (other than the guarantees contemplated under the Italian Notes); (iv) incurring any financial indebtedness (other than certain permitted indebtedness); (v) entering into sale-leaseback transactions or (vi) entering into agreements contemplating the establishment of bank account arrangements. CA Italy is also required to maintain a leverage ratio of less than 9.00:1 during each twelve-month period up to December 31, 2019 and 8.50:1 during each twelve-month period thereafter.
On November 2020, the holders of the Italian Notes waived any default and event of default that would otherwise arise as a result of the testing of the CA Italy’s leverage ratio in respect of the calculation dates falling on June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2020.
On June 2021, holders of the Italian Notes waived any default and event of default that would otherwise arise as a result of CA Italy’s leverage ratio in respect to the calculation dates June 30, 2021, and consequently no Lock-Up Event Put Option could be exercised.
On December 2021, holders of the Italian Notes waived any default and event of default that would otherwise arise as a result of CA Italy’s leverage ratio in respect of the calculation dates December 31, 2021 and June 30, 2022, and consequently no Lock-Up Event Put Option could be exercised.
On December 2022, holders of the Italian Notes waived any default and event of default that would otherwise arise as a result of CA Italy’s leverage ratio in respect of the calculation dates December 2022, and June 2023, and consequently no Lock-Up Event Put Option may be exercisable during such period.
As of December 31, 2023, there have been no events of defaults under the Italian Notes.
TA
On June 30, 2015, TA entered into the following bank loans (i) with MPS Capital Service for the principal amount of €12.8 million to mature on June 2022, and (ii) with “Banca Infrastruture Innovazione e Sviluppo” (“BIIS”), for the principal amount of €40.0 million to mature in September 2027. These loans were mainly used to finance and support infrastructure investments at the Florence and Pisa Airports.
Moreover, three loans have been subscribed by TA’ subsidiary, Jet Fuel. The aggregate amount under the first two loans is €0.5 million, and must be repaid before June 2023 and June 2024, respectively. The third loan amounts to €0.2 million and must be repaid before December 2023. These three loans were granted by Banco BPM in March 2017, January 2018 and July 2021, to support operating investment (aircraft refuellers). There are no financial parameters or covenants that need to be complied under these loans.
On November 6, 2020, the proceeds of a €85 million loan were disbursed to TA under a loan subscribed by Intesa Sanpaolo and BNL-BNP Paribas. The loan is 90% backed by SACE guarantees pursuant to the provisions of Decree-Law No. 23/2020 within the framework of the program “Garanzia Italia,” an Italian guarantee scheme intended to support Italian companies affected by the COVID-19 crisis. The financing has a term of six years, with a two-year grace period and TA is required to comply with certain financial covenants and restrictions. As a consequence of such financing, TA cannot distribute any equity reserves without the approval of the majority of the banks.
174
During 2022, TA subscribed the following short term loans: (i) with BPM S.p.A for the principal amount of €3.5 million which originally to matured in January 2023 but has been extended to August 2023, (ii) with Banca Nazionale del Lavoro S.p.A. for the principal amount of €5.0 million which will mature in May 2023, (iii) three different loans with Unicredit S.p.A. for the aggregate amount of €8.5 million, originally to matured by the end of March 2023 but will be extended to September 2023, (iv) with Intesa San Paolo for the principal amount of €11 million originally to matured in March 2023 but was extended to June 2023, (v) with Unicredit S.p.A. for the principal amount of €1.0 million originally to matured in March 2023 but was extended to June 2023, and (vi) with Monte dei Paschi di Siena for the principal amount of €11 million originally to mature in March 2023 but extended to September 2023.
During 2023, TA subscribed the following extensions to short term loans: (i) with BPM S.p.A for the principal amount of €3.5 million originally to mature in August 2023 but extended to April 2024, (ii) three different short term loans with Unicredit S.p.A. for the aggregate amount of €8.5 million, originally to mature by the end of December 2023 but extended to March 2024, (iii) with Intesa San Paolo for the principal amount of €11.0 million originally to mature in December 2023 but extended to January 2024, and (iv) with Monte dei Paschi di Siena for the principal amount of €11.0 million originally to mature in September 2023 but extended to June 2024.
Brazil
ICASGA
On December 21, 2012, ICASGA entered into a credit facility agreement with BNDES, as amended on September 25, 2013, February 3, 2014, October 1, 2014, July 8, 2016 and December 29, 2017, pursuant to which BNDES provided a loan to ICASGA in an aggregate principal amount of R$329.3 million to finance the construction of the Natal Airport. The loan was issued in nine tranches (Tranches A–I), each with varying interest rates and maturity dates. The loan is secured by (i) a pledge, granted by the Majority Shareholder and CAAP, of all ICASGA’s issued and outstanding shares, together with any dividends and distributions in connection therewith; (ii) an assignment of all of the present and future ICASGA rights arising from the Natal Concession Agreement and the amounts received in connection therewith, including indemnification payments, revenues and escrow deposits; and (iii) letters of guarantee issued by certain indirect shareholders and affiliates of ICASGA. On March 14, 2018, ICASGA made a prepayment of R$300.0 million under the debt with BNDES, which was a prerequisite for BNDES to grant a R$300.0 million credit to ICAB.
On December 29, 2023, upon a completion of a successful bidding process in the framework of the non-binding request to the Brazilian Federal Government to commence the re-bidding process of the Natal Airport, pursuant to which the operation of Natal Airport was transferred to a different operator. On January 15, 2024, the outstanding financial debt owing to BNDES for a total amount of R$75.9 million (equivalent to U.S.$15.7 million) was prepaid after which the related guarantees were released.
ICAB
ICAB entered into three credit facility agreements to finance investments in the expansion, maintenance and operation of Brasilia Airport as follows: (i) credit facility agreement entered with BNDES entered on February 7, 2014, in an aggregate principal amount of R$558 million, issued in two tranches (Tranche A and Tranche B), with varying interest rates and maturity dates; (ii) credit facility agreement entered with the Brazilian Federal Savings Bank (Caixa Econômica Federal—”CEF”) entered on February 12, 2014, in an aggregate principal amount of R$235.8 million, issued in three tranches (Tranches A, B and C), with varying interest rates and maturity dates; and (iii) credit facility agreement entered with CEF on February 12, 2014, in an aggregate principal amount of R$47.2 million, issued in three tranches (Tranches A, B and C), with varying interest rates and maturity dates, which funds are required to fund construction works and equipment relating to the “Aerocity” to be installed in Brasilia Airport (“ICAB Loans”).
ICAB Loans are secured by (i) the pledge, granted by Inframerica and Infraero, of all ICAB issued and outstanding shares, as well as any dividends and interest on equity payments in connection thereof; (ii) the pledge, granted by Inframerica’s direct shareholders of all Inframerica issued and outstanding shares, as well as any dividends and interest on equity payments in connection thereof; (iii) the fiduciary assignment of all of the present and future ICAB rights arising from the Brasilia Concession and the amounts received in connection thereof, including indemnifications, revenues and escrow deposits, as well as other ICAB receivables not related to Brasilia Concession; (iv) letters of guarantee issued by certain indirect shareholders and affiliates of ICAB; and (v) the insurance coverage required under the Brasilia Concession Agreement.
175
Before financial completion, payment by ICAB of dividends or distributions exceeding 25.0% of net profits requires prior authorization of BNDES and CEF. “Financial Completion” is defined as compliance with the following cumulative conditions: (i) maintenance of a Debt Service Coverage Ratio of at least 1.3:1.0 for at least two consecutive years, and an Equity Ratio of at least 25%, as determined in a balance sheet audited by an independent firm registered with the Brazilian Securities and Exchange Commission; (ii) creation and funding of reserve accounts provided for in the assignment of rights agreement; (iii) obtaining and maintaining governmental authorities required for the operation of Brasilia Airport; (iv) timely payment of 12 principal installments due under the Credit Facility Agreement entered between ICAB and BNDES; and (v) compliance of ICAB and its direct and indirect shareholders with their obligations under the Credit Facility Agreements and corresponding guarantee agreements, as well as with their obligations before the Brazilian ANAC.
After financial completion, payment of dividends or distributions exceeding 25% of net profits requires the maintenance of a Debt Service Coverage Ratio of at least 1.3:1.0, and an Equity Ratio of at least 25%, as determined by a balance sheet audited by an independent firm registered with the Brazilian Securities and Exchange Commission.
In accordance with the commitments assumed by the Majority Shareholder under the letter of guarantee, any merger, consolidation or disposition of all, or substantially all, of the Majority Shareholder’s assets requires prior and express authorization of BNDES and CEF.
In March 2018, CAAP and BNDES entered into an amendment to the ICAB Loans pursuant to which (i) the interest-only period and the final maturity date were extended for an additional two years, and (ii) BNDES granted ICAB an additional loan in an amount equal to R$300.0 million under the same terms and conditions as the existing ICAB Loans. In March 2018, ICAB also repaid the outstanding amount of R$274.4 million under the credit facility with the Brazilian Federal Savings Bank (Caixa Econômica Federal—”CEF”).
On June 5, 2019, ICAB entered into a loan with Banco Votorantim S.A. - Bahamas Branch for an amount of U.S.$8.9 million due in June 2020. This loan is secured with a guarantee signed by Banco Votorantim S.A. Brazil with ICAB (“Contrato de Prestação de Garantia”). This guarantee agreement, dated June 14, 2019, is secured by a guarantee letter issued by CAAP for a total amount of U.S.$8.9 million or its equivalent in Brazilian Real which cannot be lower than R$36 million plus interest. Future payments of the loan are protected from the exposure to U.S. dollars exchange rate fluctuation with a cash flow swap derivative with Banco Votorantim S.A. from Brazil that denominates future payments in Brazilian Real for a total amount of R$36 million.
On May 25, 2021, ICAB cancelled an existing loan in R$ and entered into a new loan in U.S. dollars with Banco Votorantim S.A. - Bahamas agency for $3.0 million due in June 2022. This loan was secured with a guarantee signed by Banco Votorantim S.A. Brasil with ICAB (“Contrato de Prestaçao de Garantía”). This guarantee agreement, dated May 25, 2021, was in turn secured by a guarantee letter issued by CAAP for a total amount of U.S.$3.0 million or its equivalent in Brazilian Real which cannot be lower than R$16.2 million-plus interest.
In January 2022, ICAB cancelled the loan and entered into a new loan in U.S. dollars with Banco Votorantim S.A. – Bahamas Branch for an amount of U.S.$2.7 million, which was fully repaid on March 20, 2023. This loan was secured by a guarantee letter issued by CAAP. Further payments under the loan were protected from the exposure to U.S. dollars exchange rate fluctuation with a cash flow swap derivative with Banco Votorantim S.A. Brazil.
Brazilian Refinancing Transactions
In December 2017, we entered into amendments and extension agreements with BNDES with respect to the ICAB Loans and the ICASGA Loans (the “BNDES Refinancing”).
With respect to the ICAB Loans, the BNDES Refinancing extended the final maturity and the interest-only payment terms of such loans for an additional two years, and provided an interest capitalization period for 50% of the interest due for two years. Also, the BNDES Refinancing increased the size of the credit facility commitments by an additional R$300.0 million. We repaid the Banco Santander Bridge Loan Facility and the Citibank Credit Agreement (as defined below) with new borrowings under the BNDES Refinancing, and the release of certain amounts held in the debt service reserve accounts as a result of the extension of the interest-only repayment terms under such BNDES credit facilities.
With respect to the ICASGA Loans, the BNDES Refinancing extended the final maturity of such loans for an additional two years, extended the interest-only payment terms of such loans for an additional three years and provided an interest capitalization period for 50% of the interest due for two years.
176
In connection with the BNDES Refinancing, the Majority Shareholder and CAAP have agreed not to create any encumbrances on their shares of Inframerica, and not to sell, acquire, merge or spin-off assets or undertake any other action that results or that may result in a change in the current corporate structure of Inframerica or any change of control in Inframerica, without the prior consent of BNDES. The Majority Shareholder has agreed not to undertake any change of control in CAAP without the prior consent of BNDES. In addition, the Majority Shareholder has agreed to maintain the Minimum Rating or a stand-alone rating (without including the sovereign rating) of at least B-/B3, which has been achieved in April 2022, being in compliance as of December 31, 2022. On June 28, 2023, a formal letter was filed with the BNDES, presenting the ACI rating report, declaring compliance with the contractual obligation to maintain the ACI rating equal to or higher than “B-,” for the year 2023.
Additionally, as of December 31, 2021, ICAB did not pay in full the 2021 fixed concession fee and, therefore, was not in compliance with certain covenant under the BNDES loan agreement. The forgoing has occurred because ICAB had requested to reprofile 50% of fixed concession fee which was due and payable on December 31, 2021 and, even though, the Brazilian Ministry of Infrastructure had granted such reprofile, ANAC denied ICAB’s request, and initiated administrative proceedings alleging ICAB’s breach of its payment obligations.
Therefore, ICAB initiated a judicial procedure and, on February 2, 2022, a writ of mandamus was granted by a Federal judge suspending any act or enforceability in connection with the unpaid portion of the concession fee due to ANAC. ANAC appealed, but in April 2022, the court of justice provisionally maintained the first instance judgment favorable to ICAB. In November 2023, the case was decided and the first instance ruling in favor of ICAB was confirmed, granting ICAB the right to reschedule payment of 50% of the 2021 fixed concession fee. The Brazilian ANAC appealed the ruling, and, as of December 31, 2023, the court of justice has not issued its decision. Although there can be no assurance as to the outcome of the proceedings, ICAB believes that based on the opinion of the ICAB’s external legal advisors, it is not likely that the writ of mandamus is rescinded by the justice.
Uruguay
ACI Airport Sudamérica S.A.U. Senior Secured Guaranteed Notes
On May 7, 2015, ACI Airport Sudamérica, S.A.U. (“ACI Sudamerica”) issued U.S.$200.0 million aggregate principal amount of 6.875% senior secured guaranteed notes due 2032 (“Uruguayan Notes”).
The Uruguayan Notes are senior obligations of ACI Sudamerica and rank equally in right of payment with any existing and future obligations of ACI Sudamerica that are not subordinated in right of payment to the Uruguayan Notes, senior in right of payment to all existing and future obligations of ACI Sudamerica that are subordinated to the Uruguayan Notes, senior in right of payment to all existing and future unsecured indebtedness of ACI Sudamerica to the extent of the value of the collateral securing the Uruguayan Notes, effectively subordinated to obligations of ACI Sudamerica preferred by statute or operation of law and, until such time as Puerta del Sur becomes a guarantor, structurally subordinated to the obligations of Puerta del Sur. The holders of the Uruguayan Notes benefit from a guarantee and security package. The security package includes: (i) the pledge of all of the shares in Puerta del Sur; (ii) a pledge of all of the shares in Cerealsur S.A.; (iii) an account of Cerealsur S.A. into which certain dividend payments and other distributions from Puerta del Sur to Cerealsur S.A. will be deposited and all amounts deposited therein; (iv) an account of ACI Sudamerica into which all dividend payments and other distributions from Cerealsur S.A., to ACI Sudamerica will be deposited and all amounts deposited therein; and (v) a debt service reserve account and all the amounts deposited therein. The Uruguayan Notes are fully and unconditionally guaranteed by Cerealsur S.A. Puerta del Sur also became guarantor of the Uruguayan Notes after making full payment of its 7.75% negotiable obligations due 2021 (obligaciones negociables) that were issued on April 30, 2007.
The Uruguayan Notes will mature on November 29, 2032. The principal balance of the Uruguayan Notes, together with accrued interest, will be repaid in 34 installments May 29 and November 29 of each year, commencing on May 29, 2016.
177
After November 29, 2022, ACI Sudamerica may redeem the Uruguayan Notes in whole or in part, at the redemption price set forth below, plus accrued and unpaid interest and additional amounts, if any; provided that if the Uruguayan Notes are redeemed in part only, at least U.S.$100.0 million principal amount shall remain outstanding after any such partial redemption.
Date of Payment |
|
Multiplier |
|
Beginning on November 29, 2022 and ending on November 28, 2023 |
|
103.438 |
% |
Beginning on November 29, 2023 and ending on November 28, 2024 |
|
102.292 |
% |
Beginning on November 29, 2024 and ending on November 28, 2025 |
|
101.146 |
% |
Beginning on November 29, 2025 and thereafter |
|
100.000 |
% |
Thereafter |
|
100.000 |
% |
ACI Sudamerica may pay dividends or make distributions so long as no retention event or event of default has occurred and is continuing, the distributions to debt service ratio is greater than or equal to 1.2:1.0, and the historical distributions to debt service ratio is greater than or equal to 1.2:1.0.
A retention event occurs when either the distributions or historical distributions to debt service ratio is less than 1.2:1.0, a default or event of default has occurred and is continuing, a default or event of default has occurred and is continuing under the Puerta del Sur Secured Guaranteed Notes and such event has not been cured within the applicable cure periods thereunder, or either Cerealsur S.A. or Puerta del Sur is not able, for any reason, to make such dividend payments.
The distributions to debt service ratio is the ratio of (i) the distributions or dividends of Puerta del Sur minus the fixed costs of Cerealsur and ACI Sudamerica, in each case for the most recently ended two interest periods under the Uruguayan Notes to (ii) debt service of ACI Sudamerica for the next two interest periods under the Uruguayan Notes.
Exchange Offer to the Uruguayan Notes
On May 26, 2020, ACI Sudamerica completed an exchange offer pursuant to which 93.60% of the total original principal amount of the Uruguayan Notes were exchanged for newly issued 6.875% Cash/7.875% PIK Senior Secured Guaranteed Notes due 2032 (the “Uruguayan Additional Notes”).
The Uruguayan Additional Notes will have terms that are identical in all material respects to the terms of the Uruguayan Notes except that: (i) interest and the principal amount of the Uruguayan Additional Notes will be repaid in 26 installments on May 29 and November 29 of each year, commencing on May 29, 2020; provided that for the period from and including May 26, 2020 (the “Settlement Date”) to, and including, the payment date falling on May 29, 2021 (the “PIK Period”), ACI Sudamerica may elect not to pay in cash principal and interest due on the Uruguayan Additional Notes, and may instead (a) pay any interest due in kind by increasing the principal balance on the Uruguayan Additional Notes by the amount of such interest (such amount, “PIK Interest Payment”) and (b) defer any principal due (such amount, a “PIK Principal Payment”) with such deferred amounts to be repaid on a new amortization schedule. Upon such election (i) each remaining scheduled principal payment on the Uruguayan Additional Notes will be increased by a pro rata amount equal to such aggregate amount of principal deferred and interest paid in kind during the PIK Period, and (ii) the interest rate on the Uruguayan Additional Notes will be increased to 7.875% per annum, with respect to any interest period for which ACI Sudamerica has made such election; (ii) ACI Sudamerica has elected that no principal or interest was to be paid in cash on the May 29, 2020 payment date with respect to the Uruguayan Additional Notes and each such payment was automatically be deemed a PIK Principal Payment and a PIK Interest Payment, as applicable; (iii) at any time and from time to time, ACI Sudamerica will have the right, at its option, to redeem the Uruguayan Additional Notes in an amount not to exceed the aggregate amount of all PIK Principal Payments and PIK Interest Payments then outstanding at a redemption price equal to: (a) 100% of the Uruguayan Additional Notes being redeemed, plus (b) accrued and unpaid interest and additional amounts, if any, to the redemption date; provided that the aggregate principal amount of any such redemption shall not be less than U.S.$1,000,000; and (iv) substantially all of the restrictive covenants and events of default and related provisions under the Indenture executed in connection with the Uruguayan Notes were eliminated solely with respect to the Uruguayan Notes.
The Uruguayan Additional Notes and the Uruguayan Notes are secured by the same collateral on a pro rata and pari passu basis in accordance with the indenture and the related collateral documents, other than with respect to (i) the Uruguayan Additional Notes debt service reserve account, a special, segregated account in the name of ACI Sudamerica established and maintained in New York City, New York and which was established for the benefit of the Uruguayan Additional Notes and (ii) the Uruguayan Notes debt service reserve account, a U.S. Dollar-denominated segregated trust account maintained by the Bank of New York Mellon in the name of ACI Sudamerica, which is established for the benefit of the Uruguayan Notes.
178
New Exchange Offer to the Uruguayan Notes
On November 12, 2021, ACI Sudamerica issued U.S.$180.8 million aggregate principal amount of newly issued 6.875% Senior Secured Guaranteed Notes due 2034 (the “Uruguayan Series 2021 Notes”) in exchange for 40.62% of the total original principal amount of the Uruguayan Notes (Series 2015 Notes) and 96.43% of the original principal amount of the Uruguayan Additional Notes. In the exchange offer, ACI Sudamerica also requested and obtained the necessary consents to enter and execute the Amended Carrasco Concession Agreement.
The Uruguayan Series 2021 Notes are secured on a pari passu basis by the collateral, except for (i) the pledge of all of the shares of ACI Sudamerica, which pledge is for the benefit of the Uruguayan Series 2021 Notes, the Uruguayan Additional Notes and the LC Parties (as defined below), (ii) a Series 2021 Debt Service Reserve Account established solely for the benefit of the Uruguayan Series 2021 Notes, (iii) a Series 2020 Debt Service Reserve Account established solely for the benefit of the Uruguayan Additional Notes, (iv) a Series 2015 Debt Service Reserve Account established solely for the benefit of the Uruguayan Notes, (v) a segregated account in the name of ACI Sudamerica to be established by The Bank of New York Mellon, as the Offshore Collateral Agent (the “Offshore Collateral Agent”), solely for the benefit of the Uruguayan Series 2021 Notes (the “Interest Payment Account”), to be funded with a portion of the proceeds of the issuance of the Uruguayan Series 2021 Notes, and (vi) a segregated account in the name of ACI Sudamerica to be established by Offshore Collateral Agent, solely for the benefit of the LC Parties.
In connection with exchange offer, ACI Sudamerica entered into a Letter of Credit Facility Agreement (the “LC Facility Agreement”) with the issuing banks and lenders party thereto (the “LC Parties”), Citibank, N.A., as Administrative Agent, and the Offshore Collateral Agent, for purposes of issuing one or more standby letters of credit, from time to time, to satisfy its obligation with respect to the Series 2021 Debt Service Reserve Account. ACI Sudamerica’s obligations under the LC Facility Agreement rank pari passu with the Uruguayan Series 2021 Notes, Uruguayan Additional Notes and the Uruguayan Notes, and is secured ratably by the collateral and be jointly and severally guaranteed by Cerelasur and Puerta del Sur.
Puerta del Sur Secured Guaranteed Notes
On April 30, 2007, Puerta del Sur issued U.S.$87.0 million aggregate principal amount of 7.75% secured guaranteed notes due 2021 (“Puerta del Sur Notes”). These Puerta del Sur Notes constituted direct obligations of Puerta del Sur. In 2021, Puerta del Sur exercised an option to prepay the entire principal amount and unpaid accrued interests.
Other borrowing
On April 16, 2021, Puerta del Sur obtained a loan of U.$.S10 million with Banco de la República Oriental del Uruguay (BROU) repayable in 60 monthly installments starting on April 2023. This loan is secured by a guarantee issued by CAAP and by a standby letter issued by Morgan Stanley Private Bank, National Association for U.$.S1.5 million guaranteed by Corporación America Sudamericana S.A.
CAISA
During 2020 and 2021, CAISA received different loans from Banco Santander S.A. in the total amount of up to U.S.$7.0 million to bear interest at an annual of 5.10% and maturing on April 30, 2027. The principal amount is to be paid in six annual installments in April of each year along with accrued interest, starting the first installment in April 2022.
Additionally, during 2020 and 2021, CAISA received different loans from Banco Itaú Uruguay S.A. in the total amount of up to U.S.$7.0 million, at a variable annual rate of LIBOR plus: (i) 2.5% until November 30, 2020, (ii) 2.84% from December 1, 2020 until October 31, 2021, and (iii) 3.8% from November 1, 2021 onwards, and maturing on April 30, 2027. The principal amount is to be paid in six annual installments in April of each year, starting the first installment in April 2022.
Ecuador
In November 2019, TAGSA entered into a credit facility agreement with Banco Bolivariano CA, which provided a loan in the aggregate principal amount of U.S.$9.0 million due in November 2024. Also, in December 2019, TAGSA entered into a credit facility agreement with Banco Guayaquil CA, which provided a loan in the aggregate principal amount of U.S.$10.0 million due in February 2026. Both loans have a variable interest rate (an initial interest rate of 8.75% adjustable every 90 days) and quarterly payments of principal and interest.
179
In December 2020, TAGSA entered into a credit facility agreement with Banco Bolivariano CA, which provided a loan in the aggregate principal amount of U.S.$8.5 million due in December 2025, and enter into a credit facility agreement with Banco Guayaquil CA, which provided a loan in the aggregate principal amount of U.S.$3.5 million due in December 2025. Both loans have a variable interest rate (an initial interest rate of 7,25% adjustable Banco Bolivariano every 360 days and Banco Guayaquil every 180 days) and quarterly payments of principal and interest.
Armenia
On December 15, 2015, AIA entered into a senior secured dual-currency credit facility agreement with Credit Suisse AG, London Branch, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, the Black Sea Trade and Development Bank and the German Investment Corporation for an aggregate principal amount of U.S.$160.0 million to refinance certain existing indebtedness and certain shareholder equity. The loan is secured by, inter alia: (i) the collateral assignment of all of the present and future rights arising from the Armenian Concession Agreement and other related agreements; (ii) a pledge over all present and future cash collateral bank accounts (iii) a pledge over all AIA shares, as well as all dividends which may be paid or become payable on such shares; and (iv) a pledge over certain movable and immoveable assets of AIA relating to the Zvartnots Airport. Principal is repaid in semi-annual installments, with final maturity on 84 months from the first disbursement under the credit facility agreement.
Under the facility agreement, AIA must maintain ratios of debt to EBITDA, debt service coverage and adjusted debt services coverage ratios at a certain level, and may not, inter alia (i) declare, make or pay any dividend or interest on any unpaid dividend or; (ii) repay or distribute any dividend or share premium reserve without the prior written consent of the facility agent; provided that AIA may make or pay such dividends if:
| ● | such distribution is a distribution made in accordance with the use of proceeds under the facility agreement, (i.e., to refinance shareholder’s equity); |
| ● | the distribution is constituted by payments to International Airports Management LLC (“IAM”) pursuant to certain management, know-how, technical and operations assistance agreement for so long as IAM remains a subsidiary of SCF, subject to a specified maximum amount; or |
| ● | the following conditions are each satisfied: (i) certain financial ratios are satisfied prior to the distribution, and AIA certifies that it projects, based on reasonable assumptions, that those financial ratios will be satisfied following such distribution; (ii) during the month prior to each payment date under the credit facility an amount at least equal to the aggregate amount of (1) interest and scheduled principal repayments under the facility agreement due and payable on or prior to that payment date; and (2) interest, fees and all other financial charges (including principal repayments) in respect of any other specified financial indebtedness on or prior to that payment date, stands to the credit of a specified bank account; and (iii) no event of default under the facility agreement is continuing or would result from the making of such distribution. |
On December 23, 2020, AIA changed its facility agent from Credit Suisse AG to Ameriabank C.J.S.C. re-structured the terms of the debt, including maturity date (which was extended to June 25, 2024), and additional clauses that modify the original restrictions and covenants, such as the fact that the borrower must, on or before the date any distribution is made, prepay the whole or part of the loans in the same amount as the Distribution Amount.
In December 2022, AIA prepaid the existing loan and entered into a new loan agreement with Ameriabank C.J.S.C. for up to €40 million of which €20 million were disbursed as of December 31, 2022 while the remaining €20 million were disbursed in April 30, 2023. This agreement has certain restrictions in payments, additional indebtedness, disposal of assets and transactions with affiliates, and has to maintain certain financial ratios. According to this agreement, these ratios must be met as of June 30 and December 31 of each year the loan is outstanding. As of December 31, 2023, no events of defaults have occurred under the loan.
According to loan repayment schedule attached to the loan agreement, the loan principal amount was repayable in equal installment up to 23 December 2025. However, AIA repaid €28 million on December 25, 2023, which has shortened the loan repayment date up to December 23, 2024.
As of December 31, 2023, AIA pledged to the bank cash held in bank accounts for U.S.$59 million. Additionally, the loan is secured by the pledge of shares of AIA and of certain collection rights.
180
C. RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT, PATENTS AND LICENSES, ETC.
Not applicable.
D. TREND INFORMATION
Other than as disclosed elsewhere in this annual report, we are not aware of any trends, uncertainties, demands, commitments or events since December 31, 2023, that are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on our revenues, income, profitability, liquidity or capital resources, or that would cause the reported financial information in this annual report to be not necessarily indicative of future operating results or financial conditions.
E. CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES.
We describe our significant accounting policies and estimates in Note 2.X to our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements contained elsewhere in this annual report. We believe that these accounting policies and estimates are critical in order to fully understand and evaluate our financial condition and results of operations.
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with IFRS Accounting Standards adopted by International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
In preparing these consolidated financial statements, management has made judgments, estimates and assumptions that affect the application of our accounting policies and the reported amounts recognized in the financial statements. On a periodic basis, we evaluate our estimates. We base our estimates on historical experience, authoritative pronouncements and various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
ITEM 6. DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND EMPLOYEES
A. DIRECTORS AND SENIOR MANAGEMENT
Set forth below is information concerning our current officers and directors as of the date of this annual report. There are no family relationships among the directors, executive officers or between any executive officer and director. Our executive officers are appointed by the board of directors to serve in their roles. Each executive officer is appointed for such term as may be prescribed by the board of directors or until a successor has been chosen and qualified or until such officer’s death, resignation or removal. According to the bylaws, Directors shall be elected for a term not exceeding six (6) years. Directors will hold their office until the general shareholders’ meeting that will approve the annual accounts of the Company for the financial year ending on December 31, 2026, date on which they may be eligible for re-appointment or replaced.
Unless otherwise indicated, the business address of all of our executive officers and directors is 128, Boulevard de la Pétrusse, L-2330, Luxembourg, Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
Name |
|
Date of Birth |
|
Position Held |
|
First Appointment |
Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
November 28, 1978 |
|
Director |
|
September 14, 2017 |
Máximo Luis Bomchil |
|
May 13, 1950 |
|
Director |
|
September 14, 2017 |
Roderick H. McGeoch |
|
October 2, 1946 |
|
Director |
|
September 14, 2017 |
David Arendt |
|
April 4, 1953 |
|
Independent Director |
|
September 14, 2017 |
Valérie Pechon |
|
November 10, 1975 |
|
Independent Director |
|
September 14, 2017 |
Carlo Alberto Montagna |
|
February 27, 1964 |
|
Independent Director |
|
September 14, 2017 |
Daniel Marx |
|
April 16, 1953 |
|
Director |
|
February 28, 2019 |
181
Background of Our Officers and Directors
Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian. Mr. Martín Eurnekian is the chairman of AA2000 and is also the Chief Executive Officer of CAAP. He is a member of the board of directors of most of the airport operating companies controlled by the group. Mr. Eurnekian has more than 15 years of experience in managing different businesses (retail, services and construction/engineering) in seven different countries (Argentina, Uruguay, Brazil, Ecuador, Peru, Italy and Armenia). In particular, Mr. Eurnekian has led the processes associated with evaluating, acquiring and constructing (or re-modeling), and is involved in the management of the following airports, in addition to Carrasco Airport: Punta del Este Airport, Guayaquil Airport, Brasilia Airport, Natal Airport, Pisa Airport and Florence Airport, among others. Mr. Eurnekian holds an Engineering degree in Information Technology from Universidad de Belgrano, Argentina.
Máximo Luis Bomchil. Mr. Bomchil is Honorary Chairman of the law firm Bomchil, former senior and managing partner of the firm and former head of the firm’s tax department. His practice focuses on general commercial and corporate law matters, with particular emphasis on corporate and tax matters, corporate acquisition arrangements and corporate restructuring. Mr. Bomchil is Chairman of HCA S.A., an important hotel business group in Argentina and member of the board of directors of Aeropuertos Argentina 2000 S.A. He is also a syndic of Central Vuelta de Obligado S.A., Termoeléctrica Manuel Belgrano S.A. and ENEL Generación El Chocón S.A. Mr. Bomchil has a law degree from the Catholic University of Argentina (Universidad Católica Argentina) (1973), a Juris Doctor from Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Germany (1976), and a Master of Laws from the University College of London University (1977). He is former chairman of the Alliance Française de Buenos Aires, former board member of the Foundation Alliance Française and has been decorated by the French government as Officier de la Legion d’Honneur.
Roderick H. McGeoch. On January 26, 2013 Mr. McGeoch became an Officer of the Order of Australia in recognition of his “distinguished service to the community through contributions to a range of organizations, and to sport, particularly through leadership in securing the Sydney Olympic Games.” He is a contributor in different social sectors including foreign representation, as Former Honorary Consul of Luxemburg in Australia; arts; Trans-Tasman; telecommunications; sports; international Finance; Australia/New Zealand Leadership Forum; entertainment; law; and media and marketing. Mr. McGeoch has been a member of the Advisory Board of American Infrastructure Holdings since November 1, 2013. He is also a consultant to Corporación América; a director of Destination New South; Chairman of Venues NSW (until November 2023) and in January 2005 was appointed Chairman of Vantage Private Equity Growth Limited. In May 2017 he was appointed Chairman of Chubb Insurance Australia; in July 2020 he was appointed Chairman of Australasia Media Company; in August 2020 he was appointed Chairman of the Board of Surevision. Mr. McGeoch’s previous appointments include on November 1, 2009 he was appointed as Chairman of BGP Holding Plc. Chairman of MediaWorks as of October 31, 2013; and a director of the board of Ramsay Health Care Limited. Lately, he has also been appointed as director of AAP Corporation Pty Limited. He did serve for many years on the Board of the Salvation Army Eastern Territories; was appointed to the Sky City Board of Directors in September 2002. Mr. McGeoch holds a Bachelor of Laws degree from the University of Sydney. He was appointed a Member of the Order of Australia by the Australian Government.
David Arendt. Mr. David Arendt is an independent director and sits on the boards and board committees of regulated entities based in Luxembourg (a bank, an insurance company, an insurance broker, an NYSE listed operating company), of the Luxembourg export credit agency Office du Ducroire, of general partners of private equity funds active in the fields of real estate, infrastructure, direct lending and agri-food. Pro-bono mandates include the Luxembourg Automobile Club, the largest (by number of members) Luxembourg non-for-profit association and the International School of Luxembourg. Prior to his activity of independent director, Mr. Arendt he worked in Europe and the United States in law, finance and business. His career started in Law with the leading Luxembourg law firm Arendt & Medernach. He then moved to New York where he earned an LLM at New York University and was an associate at Debevoise & Plimpton LLP and Shearman & Sterling LLP. His career in banking included positions in London, New York and Luxembourg at Prudential Securities, Merrill Lynch and Banque Générale du Luxembourg (now BGL BNP Paribas). His career in business includes executive management positions at Cargolux Airlines International SA, the all-cargo airline based in Luxembourg and Le Freeport Luxembourg (recently rebranded Luxembourg High Security Hub), a high tech/highly secure facility for storing and handling valuable goods. He is also the principal and Managing Director of Arendt Capital Advice S.à r.l., an economic consulting company (conseil économique) which he created in January 2017 to provide advisory and project management services in the fields of logistics and academia. Mr. Arendt holds a License in Law from Grenoble University (France), a Master of Laws degree from King’s College, London University and a Master of Laws degree from New York University, School of Law. He was a member of the Luxembourg and New York bars. He is a certified director by ILA (Institut Luxembourgeois des Administrateurs) and INSEAD (IDP-International Directors Program).
182
Valérie Pechon. Ms. Pechon is a founding member of Key Partners S.à r.l., a Luxembourg-based trust services provider, member of the Luxembourg Order of Chartered Accountants (Ordre des Experts-Comptables) and is an Independent and non-executive director in Luxembourg companies. From 2011 to 2016 she served as a domiciliation director (part of the extended Management Team) in Intertrust Luxembourg. She has also served as domiciliation manager in Alter Domus Luxembourg (2008-2010) and as audit assignment management–External Auditor in Deloitte Audit Luxembourg. She made a traineeship at Santiago de Chile Deloitte’s office (4 months) and was part of a case study regarding retirement fund techniques in Chile. Ms. Pechon has a four-year University degree in Business Administration (ULG-EAA) with an orientation in finance.
Carlo Alberto Montagna. Mr. Montagna is a Partner of The Directors’ Office, the leading practice of independent directors in Luxembourg, since September 2011. He is a member of the board of directors, a trustee or a member of audit committees of many European or International financial groups or corporations, most of them based in Luxembourg, with a particular focus in investment funds covering the entire spectrum of investment strategies, from long only to real assets, including infrastructure and alternative energy. He is a member of ALFI and ILA. He has also served as Managing Director, Client Executive for Investment Managers, Insurances, Foundations, Pension Funds in Continental Europe (2003-2007) at BNY Mellon, while he was a member of the board of directors of investments fund administered by BNY Mellon Luxembourg. He has also served at IMI Group (1993-2003), now known as IntesaSanPaolo Group; with IMI Bank (Lux) S.A. Luxembourg (2002-2003) as General Manager, while during the year 2003 he served as Member of the Securities Market Commission of the Luxembourg Banking Association as principal delegate of the Italian Banks’ Association in Luxembourg; from 2000 to 2002 he served as Director of the Investment Banking division in IMI Bank (Lux) S.A. Luxembourg, and from 1998 to 2000 as Head of Treasury at Banca IMI s.p.a. Milan, while he was also a Member of the Italian Banks Treasurers’ Committee at the Bank of Italy under the supervision of the European Central Bank; from 1993 to 1998 he served at IMI Bank (Lux) S.A. Luxembourg as Head of Treasury and from 1991 to 1993 as Senior Dealer, proprietary trader at Banca Nazionale del Lavoro in Rome. During his career, Carlo built up an extensive knowledge of trading strategies and managed various portfolios; he developed front office as well as back office solutions, launched investment funds, managed small and big size companies. He is a skilled relationship director and people manager. Mr. Montagna passed all examinations during his three years of study of Economics and Law at the University of Pavia, Italy, Faculty of Economics (1982-1985), he is specialized in Swaps valuation, hedging and trading strategies at ICMB Geneva in 1994. He speaks Italian, French, Dutch, basic Luxembourgish and Spanish.
Daniel Marx. Mr. Marx is the Executive Director of Quantum Finanzas, a financial advisory firm based in Buenos Aires. Mr. Marx has an extensive track record in both the private and public sectors, where he held executive positions. He was Board Member of the Central Bank of Argentina from 1986 to 1988 and Undersecretary of Finance of the Argentine Ministry of Economy from 2000 to 2001 and Chief Debt Negotiator from 1988 to 2003 in charge of the design and execution of sovereign debt restructuring, financing program and relationship with international financial institutions and private banks. He also advised on the initial public offerings by several major Argentine companies and served on the boards of directors of various companies. He holds a degree in Economics from the University of Buenos Aires.
Our Senior Management
Our senior management oversees our day-to-day operations to ensure that our overall strategic objectives are implemented and reports to our board of directors.
The following table sets forth certain relevant information about our officers and senior management:
Name |
|
Date of Birth |
|
Position |
|
First Appointment |
Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
November 28, 1978 |
|
Chief Executive Officer |
|
September 14, 2017 |
Jorge Arruda Filho |
|
April 9, 1968 |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
April 30, 2021 |
Roberto Naldi |
|
February 17, 1953 |
|
Head of European Business Development |
|
September 14, 2017 |
Andrés Zenarruza |
|
July 22, 1976 |
|
Head of Legal & Compliance |
|
September 14, 2017 |
Eugenio Perissé |
|
March 2, 1959 |
|
Head of Business Development |
|
September 14, 2017 |
Set forth below is a summary of the business experience of our senior management, except for the members of our senior management who are also directors, whose business experience is set forth above.
183
Jorge Arruda Filho. Mr. Arruda Filho is our Chief Financial Officer. He joined CAAP in 2014 and served as Head of Finance and M&A until April 30, 2021 when he was appointed as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer. He is also Chief Executive Officer of Inframerica Brazil. Mr. Arruda Filho has more than 20 years of investment banking experience, most recently serving as CEO and Head of Investment Banking at Nomura Securities Brazil.
Roberto Naldi. Mr. Naldi is our Head of European Business Development. He serves as the President of Corporación America Italia S.p.A. and is a member of the Board of Directors of the Florence Airport and Pisa Airport. Previously, he held several roles as Senior Advisor and Member of the Board across CAAP airports. Mr. Naldi holds a degree in Civil Engineering from University of Florence, Italy.
Andrés Zenarruza. Mr. Zenarruza is our Head of Legal & Compliance. Prior to joining us, Mr. Zenarruza practiced law in the legal department of the Corporate and Investment Bank of Citi in Argentina and as an associate at Baker and McKenzie’s Buenos Aires office. He received his law degree from the University of Buenos Aires (UBA) and a Master of Laws from the University of Cambridge in 2002. Mr. Zenarruza is a British Chevening Scholar and a Cambridge Overseas Trust Scholar.
Eugenio Perissé. Mr. Perissé is our Head of Business Development. Mr. Perissé has over 30 years of experience in airport planning, project coordination and on-site construction management. Mr. Perissé has an Architectural degree from Buenos Aires University.
Daily Manager
Martín Cossatti. Mr. Cossatti is our Head of Accounting, Planning and Tax and the Company’s daily manager. Mr. Cossatti has authority to act on behalf of the Company in all matters pertaining to the daily management and affaires of the Company. Mr. Cossatti holds a Public Accountant degree from the Universidad de la República, Uruguay and a Master of Business Administration degree from the Universidad Católica del Uruguay.
B. COMPENSATION
The compensation of our directors is reviewed and approved on an annual basis at our ordinary general shareholders’ meeting. In 2023, the total compensation payable to our directors and senior management was U.S.$4.2 million. The compensation plan applicable to CAAP’s directors was approved in May 2023 by the Annual General Meeting of the Shareholders.
Management Compensation Plan
On August 20, 2020, our board of directors adopted the Management Compensation Plan (the “Management Plan”), which we refer to as the Management Plan in this annual report. The purpose of the Management Plan is to permit executives and key employees of either the Company, or any of its subsidiaries or certain eligible affiliates acting as employers who are eligible to receive an annual incentive compensation consisting either of (i) a certain number of shares in the share capital of the Company or of (ii) contractual rights (not documented by a certificate or otherwise) to receive, at a certain point in time, a certain number of Shares, thereby encouraging the employees to focus on the long term growth and profitability of the Company.
The maximum number of shares allocable under the Management Plan is 2% of the total outstanding shares of the Company at all times during the validity of the Management Plan. The shares to be allocated may be (i) issued via the authorized but unissued share capital of the Company or (ii) transferred either (a) from shares repurchased by the Company and held in the treasury (actions de trésorerie) or (b) from shares purchased directly on the open market or otherwise.
184
The rights granted under the Management Plan are subject to the following terms and conditions and to such additional terms and conditions, not inconsistent with the terms of the Management Plan, as the Compensation Committee shall deem desirable at its sole discretion: provided however, that, changes adversely affecting the rights of an employee (at least the ones not in his/her favor) to receive rights need to be consented to by such employee:
| ● | Consideration. Each right shall give the right to receive 1 (one) share or its equivalent in cash, as defined above, and shall be granted in lieu of the employees’ payout or in lieu of other incentive compensation (being a portion of them or representing their entirety) as determined by the Committee at its sole discretion. The Committee shall determine the number of rights or the manner of determining the number of rights available to be granted, subject to the total number of rights available under the Management Plan for such year, and the amount or the method of determining the consideration to be given by each employee, taking into consideration appropriate factors in making such determinations, such as interest rates, volatility of the market price of the shares issued in the share capital of the Company and the term of the restriction affecting the disposal of the rights granted (if any). |
| ● | Vesting. Standard vesting period shall be three years. The Committee will determine when the rights shall become disposable in full. The Committee will further determine whether such rights upon vesting and becoming exercisable shall be payable by the Company -at their respective date of vesting- either by payment in shares or by payment in cash or a combination of them, as determined by the Committee in its sole discretion. |
| ● | Manner of Exercise. A completed, dated and signed Acceptance Letter must be delivered by the Employee to the Plan Administrator in order to receive the Rights or the Share(s) granted to him/her based on the exercise of his/her Rights. |
| ● | Time for Exercise. |
A. Termination of Employment.
| ● | Death, total disability (as determined by the public social security body the employee is subject to), or normal retirement of employee: if the employment contract of the employee with the Company is terminated by reason of the employee’s death, total disability, or normal retirement, the rights shall become disposable in full on the termination date. |
| ● | Termination at the initiative of the employee: if the employment contract of the employee with the Company is terminated at the initiative of the employee before his/her rights become exercisable/are exercised for any reason, the rights granted to him/her under the Management Plan shall be forfeited. |
| ● | Termination at the initiative of the Company without Cause: if the employment contract of the employee with the Company is terminated at the initiative of the Company without Cause before his/her rights become exercisable/are exercised for any reason, the rights shall become disposable in full on the employee’s termination date. |
| ● | Termination at the initiative of the Company with Cause: if the employment contract of the employee is terminated at the initiative of the Company for Cause (including without limitation due to an Act of Misconduct, bad performance, violation of the Company’s rules or the terms of the statutory documentation, etc.) before his/her rights become exercisable/are exercised for any reason, the rights granted to him/her under the Management Plan shall be forfeited. |
B. Delisting. In the event that the shares are delisted from the New York Stock Exchange, then on and after the delisting date, the Company reserves the right to (a) cancel any outstanding rights, unless the Committee determines otherwise in its sole discretion, and (b) repurchase any shares previously allocated to any employee, at the closing price of the shares on the trading day immediately preceding the delisting date, or otherwise at the price agreed by the Committee with such employee.
Clawback Policy
On November 15, 2023, the Company approved its claw-back policy providing for the recovery of erroneously awarded incentive-based compensation received by current and former executive officers in connection with a financial restatement, regardless of fault or misconduct, on or after October 2, 2023. A copy of our clawback policy is attached hereto as Exhibit No. 97.
185
C. BOARD PRACTICES
Companies listed on the NYSE must comply with certain corporate governance standards provided under Section 303A of the NYSE Listed Company Manual. NYSE listed companies that are foreign private issuers are permitted to follow home-country practices in lieu of Section 303A, except that such companies are required to comply with Sections 303A.06, 303A.11 and 303A.12(b) and (c) of the NYSE Listed Company Manual. Under Section 303A.06, foreign private issuers must have an audit committee that meets the independence requirements of Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act. Under Section 303A.11, such companies must disclose any significant ways in which their corporate governance practices differ from those followed by domestic companies under NYSE listing standards. Finally, under Section 303A.12(b) and (c), such companies must promptly notify the NYSE in writing after becoming aware of any non-compliance with any applicable provisions of this Section 303A and must annually make a written affirmation to the NYSE.
Board Committees
Our articles of association provide that the board of directors may establish committees, such as an audit committee, a compensation committee and a nomination committee, among others. The composition of any of these committees and any powers delegated thereto shall be determined by the board of directors.
Corporate Governance Code, Code of Conduct and Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers
We have adopted a Corporate Governance Code and Code of Conduct and related integrity policies applicable to all of our directors, officers and employees. We have also adopted an additional code of ethics applicable to our Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Controller and other persons performing similar functions. Our articles of association require any director to refrain from voting on or approving of any related-party agreement with such director or party related to such director. Our Corporate Governance Code, Code of Conduct and related integrity policies and Code of Ethics for senior financial officers provide additional procedures for the audit committee and the board of directors to identify, report, review and approve any related-party agreements with directors or senior management (or any affiliate other than us).
Audit Committee
The Audit Committee consists of the following three directors: Valérie Pechon (Member), David Arendt (President and Financial Expert) and Carlo Montagna (Member). Each member of the Audit Committee is required to meet the requirements of independence, experience and financial experience set forth in the listing standards of the NYSE and the requirements of Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act. David Arendt, member of our Audit Committee is a “financial expert” within the meaning of SEC rules and regulations. The Audit Committee will perform the duties set forth in our corporate governance code. The primary responsibilities of the Audit Committee include the following:
| ● | overseeing management’s establishment and maintenance of adequate systems of internal accounting, auditing and financial controls; |
| ● | reviewing the effectiveness of our legal, regulatory compliance, ethical standards and risk-management programs; |
| ● | reviewing certain related-party transactions in accordance with our corporate governance code; |
| ● | overseeing our financial reporting process, including the filing of financial reports; and |
| ● | selecting our independent auditors, evaluating their independence and performance and approving audit fees and the services provided by them. |
Executive Committee
The Executive Committee (comité de direction) consists of three members: Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian (Chief Executive Officer), Jorge Arruda Filho (Chief Financial Officer) and Andrés Zenarruza (Head of Legal & Compliance). Our Chief Executive Officer is the president of the Executive Committee. The Executive Committee performs the duties set forth in our corporate governance code. The primary responsibilities of the Executive Committee include the following, amongst others:
| ● | assessing and proposing business strategies, and implementing strategies and policies approved by the board of directors; |
186
| ● | developing processes for the identification, evaluation, monitoring and mitigation of risks; |
| ● | implementing appropriate internal control systems and follow-up of such system’s effectiveness, and reporting compliance with its goals to the board of directors; |
| ● | analyzing and proposing the full year budget following-up its evolution, and assessing mitigation of internal and market variables; |
| ● | identifying and implementing business synergies among Group companies; and |
| ● | proposing the delegation of powers to officers and supervising managers, which are consistent with the policies and procedures established by the board of directors. |
Acquisitions and Business Development Committee
The Acquisitions and Business Development Committee currently consists of five members: our Chief Executive Officer, our Chief Financial Officer, our Head of Legal and Compliance, our Head of Business Development, and our Head of European Business Development, as the regular members. The Acquisitions and Business Development Committee is currently comprised of Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian, Jorge Arruda Filho, Andrés Zenarruza, Eugenio Perissé and Roberto Naldi. The Acquisitions and Business Development Committee is chaired by our Chief Executive Officer (Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian). The Acquisitions and Business Development Committee performs the duties set forth in our corporate governance code and report indirectly to the Board through the Executive Committee. The primary responsibilities of the Acquisitions and Business Development Committee include the following:
| ● | evaluating and reporting on our acquisition and business development plans, in collaboration with the board of directors and the executive committee; |
| ● | assisting the executive committee with recommendations on acquisitions and business development agenda of the group; |
| ● | evaluating, reporting and recommending to the executive committee specific acquisitions or business opportunities; and |
| ● | approving new acquisitions or development opportunities within the powers delegated to the Acquisitions and Business Development Committee by the board of directors and the executive committee. |
Disclosure Committee
The Disclosure Committee currently consists of four members: our Chief Executive Officer, Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian, our Chief Financial Officer, Jorge Arruda Filho, our Head of Legal & Compliance, Andrés Zenarruza and our Head of Investor Relations, Patricio Esnaola. This Committee oversees and reviews all materials for which there is a disclosure requirement. This committee meets at regular intervals in order to review all data.
Compensation Committee
The Compensation Committee currently consists of three members: our Chief Executive Officer, Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian, the Chairman of the Board of Directors, Máximo Bomchil, and the Chairman of the Audit Committee This Committee oversees and reviews the specific awards to be granted, based on the proposal to be submitted by the plan administrator and administers the clawback policy by determining not to recover erroneously awarded compensation in circumstances where non-enforcement is expressly permitted by the clawback rules and in accordance with the clawback policy.
Information Security Incident Response Committee
The Information Security Incident Response Committee (the “ISIRC”) shall be summoned in case of a cybersecurity incident and will include by the Local IT Manager/Responsible (of the involved subsidiary), an Information Security Specialist (local and/or corporate), the Head of Legal and Compliance (representing CAAP’s Executive Committee) and, if necessary, members of other technology-related teams, or members of CAAP Executive Committee or other members of senior management.
187
D. EMPLOYEES
As of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, we had 6.1 thousand; 6.1 thousand and 5.8 thousand employees, respectively, of whom 5.4 thousand; 5.4 thousand and 5.2 thousand, respectively, worked on activities such as operations, maintenance, security, customer services, parking and fees collection sector; and 0.7 thousand, 0.7 thousand and 0.6 thousand, respectively, worked in sales and marketing, the finance sector, administration, human resources, legal department and other activities.
We have unionized employees in all of the jurisdictions in which we operate. As of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, 62.9%, 64.8% and 66.1%, respectively, of our employees in AA2000 were represented by two unions: (a) Union de Personal Civil de la Nación, and (b) Asociación de Personal Aeronáutico. The relationship between the unions and these employees is mainly governed by a collective bargaining agreement (CBA Nbr. 1,254/2011 “E”) between us and the unions, dated November 26, 2016. We negotiate this collective bargaining agreement, and the other labor agreements to which we are a party, on an annual basis. We have not experienced any significant labor conflicts during the last two years. We maintain a successful working relationship with each union’s delegates and representatives. See “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business and Industry—We are subject to the risk of union disputes and work stoppages at our locations, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.”
In addition, as of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, 0.1 thousand, 0.4 thousand and 0.4 thousand, respectively, of our employees in Italy (approximately 32.7%, 48.9% and 50.4%, respectively) are represented by transportation trade unions. In Italy, there are two levels of collective bargaining: the national employment contract, which every company is bound to apply, and the collective corporate contract.
As of December 31, 2023, 0.1 thousand of our employees in Brazil (approximately 16%) are represented by the National Union of Airport Employees (Sindicato Nacional do Aeroportuarios). We have not experienced any significant collective conflicts during the last two years. We maintain a successful working relationship with each union’s delegates and representatives in Brazil.
The following table provides information regarding the number of our employees as of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021:
|
|
Number of Employees |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
|
(in thousands) |
||||
Operations and infrastructure |
|
5.4 |
|
5.4 |
|
5.2 |
Administration |
|
0.7 |
|
0.7 |
|
0.6 |
Total |
|
6.1 |
|
6.1 |
|
5.8 |
E. SHARE OWNERSHIP
None of our directors, officers or members of our senior management owns any of our common shares.
F. DISCLOSURE OF A REGISTRANT’S ACTION TO RECOVER ERRONEOUSLY AWARDED COMPENSATION
Not applicable.
ITEM 7. MAJOR SHAREHOLDERS AND RELATED-PARTY TRANSACTIONS
A. MAJOR SHAREHOLDERS
The following table sets forth information with respect to the beneficial ownership of our shares as of December 31, 2023:
| ● | each shareholder, or group of affiliated shareholders, who we know beneficially owns more than 5% of our outstanding shares; |
| ● | each of our directors and executive officers individually; and |
| ● | all directors and executive officers as a group. |
188
As of December 31, 2023, we had 163,222,707 issued and outstanding common shares of which 2,251,123 are held as treasury shares. Beneficial ownership as exclusively determined in accordance with the rules of the SEC generally includes any shares over which a person exercises sole or shared voting and/or investment power. Shares subject to options and warrants currently exercisable or exercisable within 60 days are deemed outstanding for computing the percentage ownership of the person holding the options but are not deemed outstanding for computing the percentage ownership of any other person. Except as otherwise indicated, we believe the beneficial owners of the shares listed below, based on information furnished by them and as per the rules of the SEC, have sole voting and investment power with respect to the number of shares listed opposite their names. The address of each beneficial owner is 128, Boulevard de la Pétrusse, L-2330 Luxembourg, Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
|
|
Common shares Beneficially |
|
||
|
|
Owned |
|
||
|
|
as of December 31, 2023 |
|
||
|
|
Common Shares |
|
||
|
|
Number |
|
% |
|
A.C.I. Airports S.à r.l |
|
131,450,833 |
|
80.53 |
% |
Our executive officers and directors: |
|
|
|
|
|
Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
Máximo Bomchil |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
Roderick H. McGeoch |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
David Arendt |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
Valerie Pechon |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
Carlo Alberto Montagna |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
Daniel Marx |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
Jorge Arruda Filho |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
Roberto Naldi |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
Andres Zenarruza |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
Eugenio Perissé |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
All executive officers and directors as a group: |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
A.C.I. Airports S.à r.l., a private limited liability company (société à responsabilité limitée) incorporated in Luxembourg, is 100% controlled by CAI which is 100% controlled by SCF.SCF manages assets for the benefit of the foundation’s beneficiaries. The potential beneficiaries of this foundation are certain members of the Eurnekian family as well as religious, charitable and educational institutions designated by the foundation’s board of directors. The board of directors of the foundation is currently composed of four individuals and decisions are taken by majority vote. The board of directors has broad authority to manage the affairs of the foundation and to designate its beneficiaries and additional board members.
B.RELATED-PARTY TRANSACTIONS
We have engaged in, and we expect that we will continue to engage in, transactions with related parties, including, without limitation, the transactions described below. We believe the terms and conditions of these arrangements are generally equivalent to those which we could obtain from an unaffiliated third party, to the extent there are third parties which could provide comparable goods or services. For more information regarding our relationships and transactions with related parties, see Note 27 to our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this annual report.
Proden S.A.
Proden S.A., one of our affiliates, is a sociedad anónima organized under the laws of Argentina (“Proden”) that is currently directly controlled Corporación América Inmobiliaria S.A. which in turn is indirectly controlled by SCF. Proden provides technology outsourcing services to our following subsidiaries: AA2000, but until December 31, 2021 also provided services to AIA and CAISA. Proden also leases to AA2000 the building where AA2000 has its principal office. Pursuant to this lease agreement entered into on March 1, 2008, AA2000 pays Proden a monthly rental fee of U.S.$227,985. During the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, we recorded expenses of U.S.$2.3 million, U.S.$4.1 million and U.S.$4.5 million, respectively, in connection with the services provided to all of our subsidiaries and with the lease agreement.
189
Servicios Integrales América S.A.
Servicios Integrales América S.A., one of our affiliates, a sociedad anónima organized under the laws of Argentina (“SIASA”). SIASA is currently controlled by Casa Ventas S.A., which in turn is indirectly controlled by SCF. SIASA provides compliance, legal, accounting, investor relations and business development services to CAAP and technology outsourcing services to our following subsidiaries: AA2000, AIA, Puerta del Sur, CAISA, TCU, TAGSA, CASA, CAS Panamá, Corporación Aeroportuaria S.A., and Corporación América Sudamericana S.A. – Sucursal Ecuador “CASE”. During the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, we recorded expenses of U.S.$3.4 million, U.S.$3.8 million and U.S.$2.9 million, respectively, corresponding to these services rendered to all the aforementioned subsidiaries. As of December 31, 2023, we owed SIASA U.S.$0.2 million.
Helport S.A. and Compañía de Infraestructura y Construcción S.A.
Helport S.A. and Compañía de Infraestructura y Construcción S.A. our affiliates, are sociedades anónimas organized under the laws of Argentina (“Helport” and “CINC” respectively). Both companies are indirectly controlled by SCF and provide AA2000 with a broad range of construction services. During the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, AA2000 recorded expenses of U.S.$3.2 million, U.S.$2.9 million and U.S.$0.2 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, AA2000 owed Helport and CINC U.S.$0.7 million, U.S.$1.1 million and U.S.$35.1 thousand, respectively.
Financing Agreements
Compañía General de Combustibles S.A.
Compañía General de Combustibles S.A., one of our affiliates, is a sociedad anónima organized under the laws of Argentina (“CGC”). CGC is indirectly controlled by SCF. CGC entered into a loan agreement with Aeropuertos Argentina 2000 S.A. with an interest at a fixed annual rate of 4.5%, maturing in June 2024. As of December 31, 2023, CGC owed AA2000 U.S.$14.8 million. During the year ended December 31, 2023, AA2000 recorded an income of U.S.$0.2 million related to interests received from the loan agreement with CGC.
Other Financial Agreements
As of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 related parties owed CAAP and its subsidiaries U.S.$3.1 million, U.S.$3.0 million and U.S.$2.8 million, respectively, under other related party financing agreements. In each of the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, we had accrued interest income of U.S.$0.2 million, in respect of such related party financing agreements.
Other Transactions with Related-Parties
ECOGAL Management Support Agreement—Galapagos Airport
Between April 15, 2011 and December 31, 2019, ECOGAL, one of our associates, entered into a management support agreement with CASE, one of our subsidiaries. Pursuant to this management support agreement, CASE collected the fees of ECOGAL under the Galapagos Concession Agreement. Under this Agreement, ECOGAL paid CASE a fee equal to 5% of ECOGAL’s total annual revenue, excluding VAT. From January 1, 2020, ECOGAL signed a new management support agreement with Cedicor S.A. Sucursal Ecuador under the same conditions of the previous agreement. During the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, ECOGAL recorded expenses for an amount of U.S.$0.7 million and U.S.$0.6 million, respectively, with Cedicor S.A. Sucursal Ecuador. As of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 ECOGAL owed CASE U.S.$0.4 million, U.S.$1.0 million and U.S.$1.1 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2023, ECOGAL owed Cedicor Sucursal Ecuador U.S.$0.2 million.
Know How, Technical and Operational Assistance and Management Agreement—Armenia Airports
On January 1, 2014, AIA and IAM, one of our affiliates, entered into a Know How, Technical and Operational Assistance and Management Agreement which was later amended in April 2014.
190
Pursuant to this agreement, IAM provides AIA management services, as well as know-how, technical and operational assistance in connection with the development of national and international air traffic of passengers, freight and mail, the analysis of operations, ground handling and maintenance activities and budgets, and assistance concerning financial planning and access to financial resources, among other things. AIA paid IAM a fee equal to 5% of the aeronautical revenue of the airport until March 31, 2022 and from April 1, 2022 a fixed monthly fee of U.S.$0.15 million, payable within 30 days of the end of each calendar month. During the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, AIA recorded expenses for an amount of U.S.$1.8 million, U.S.$1.9 million and U.S.$2.3 million, respectively, in respect of such services. As of December 31 of 2023, 2022 and 2021, AIA owed IAM U.S.$0.2 million, U.S.$0.2 million and U.S.$0.2 million, respectively.
Cash and Equivalents
As of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, CAAP and its subsidiaries maintain cash and cash equivalents deposited in Converse Bank for U.S.$23.2 million, U.S.$4.7 million and U.S.$21.6 million, respectively.
Term deposits
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, AIA maintained term deposits in Converse Bank for U.S.$10.1 million and U.S.$9.8 million, respectively. There were no deposits maintained in Converse Bank during the year ended December 31, 2022.
Other Services Agreements
Within the ordinary operation of our airports, we entered into several related-party agreements in addition to the ones described above. During the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, related parties rendered services to us in an amount of U.S.$12.8 million, U.S.$10.8 million and U.S.$5.3 million, respectively. Overall, as of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 we were owed U.S.$4.9 million, U.S.$8.1 million and U.S.$6.3 million for related-party transactions, respectively.
Registration Rights and Indemnification Agreement
We have entered into a registration rights and indemnification agreement with our Majority Shareholder. This agreement provides to the Majority Shareholder and its affiliate transferees up to five “demand” registrations for the sale of our common shares. Additionally, the agreement provides the Majority Shareholder and its affiliate transferees customary “piggyback” registration rights. The registration rights and indemnification agreement also provide that we will pay certain expenses relating to such registrations and indemnify the Majority Shareholder and its affiliate transferees against certain liabilities which may arise under the Securities Act.
Pursuant to such registration rights and indemnification agreement, we agree to indemnify the Majority Shareholder for the pro rata portion of any losses, claims, damages, liabilities, joint or several, and expenses arising out of or based upon certain letters of guarantee provided by the Majority Shareholder under certain credit facilities provided by the BNDES and Banco Citibank to ICAB, in each case, as determined by a final non-appealable judgment of a court of competent jurisdiction (see “Item 5. Operating and Financial review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Indebtedness—Brazil—ICAB”). The pro rata portion of such liabilities equals the aggregate amount of such losses, claims, damages and liabilities multiplied by the aggregate percentage of our capital stock (on a fully-diluted basis) which is not otherwise held by the Majority Shareholder and any of its affiliates.
C. INTERESTS OF EXPERTS AND COUNSEL
Not applicable.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL INFORMATION
A. CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS AND OTHER FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The Company’s Audited Consolidated Financial Statements are included in Item 18.
Legal Proceedings
We are involved in certain legal proceedings from time to time that are incidental to the normal conduct of our business. The material proceedings are described below.
191
Argentine Proceedings
Environmental Proceedings
We, our sub concessionaires, and our aeronautical customers are subject to various environmental laws, regulations and authorizations governing, among other things, the generation, use, transportation, management and disposal of hazardous materials, the emission and discharge of hazardous materials into the ground, air or water, and human health and safety. We have incurred and expect to continue to incur in compliance costs relating to such requirements. In addition, we could be held responsible for contamination, human exposure to hazardous materials or other environmental damage at our airports or otherwise related to our operations, even if we were not at fault or if such matters were caused by a sub concessionaire, an aeronautical customer or other third party. Following the expiration or termination of our concession agreements, we could still be held liable for environmental damages that arise after such expiration, but which were caused while we were the concessionaire. Environmental claims have been asserted against us, and additional claims may be asserted against us in the future.
Pursuant to the Final Memorandum of Agreement entered into with the Argentine Government, dated April 3, 2007, we are required to assess and remediate environmental damage at our airports in Argentina. In accordance with section 22 of the Argentine Environmental Policies Law No. 25,675, we carry environmental insurance for Ezeiza Airport and Aeroparque Airports, which covers the cost of repairing environmental damages. We are not required to have environmental insurance for the rest of our airports in Argentina. However, in connection with any enlargements or remodeling projects undertaken at our airports, we may be required to prepare assessments of the projects’ potential environmental impacts.
In August 2005, a civil action was brought by Asociación de Superficiarios de la Patagonia, (“ASSUPA”) a non-governmental organization, against Shell Oil Company for alleged environmental damages caused by an oil spill at Ezeiza Airport and, in September 2006, AA2000 was called to intervene as a third party at the request of the plaintiff. The lawsuit alleges that AA2000 is jointly liable with Shell Oil Company due to the fact that AA2000 manages the real property at which the environmental damages occurred. AA2000 has asserted that Shell Oil Company is solely responsible for any damages. We have not made any provisions in our financial statements to cover risks related to this proceeding. Shell Oil Company and ORSNA are currently jointly working in the damage remediation activities.
In August 2011, ASSUPA brought a civil action against AA2000 in an Argentine administrative federal court in the City of Buenos Aires (Justicia Federal en lo Contencioso Administrativo de la Capital Federal), under the General Environmental Law No. 25,675, requesting compensation for environmental damage caused in all of the airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
As a solution, a “General Remediation Agreement” was subscribed with ASSUPA in which it was established the execution of specific agreements for each airport where remediation works should be conducted and in which the guidelines for each remediation work will be established. It was also agreed that these works will be financed with the “Patrimonio de Afectación para el Financiamiento de Obras en los Aeropuertos que conforman el Grupo “A” del Sistema Nacional De Aeropuertos (SNA) (2.5%).
On April 15, 2021, a specific agreement for the remediation of Ezeiza Airport was also subscribed. Both agreements subscribed with ASSUPA were submitted to ORSNA and approved by the Court on August 30, 2021.
In addition, an agreement regarding the lawyers’ fees involved in all past and present judicial activity until the process ends has also been subscribed. The amounts involved in this agreement are roughly U.S.$7 million of which U.S.$5 million are linked to the counterpart lawyer’s fees and U.S.$2 million are linked to the counterpart expert’s fees.
On February 23, 2022, a specific agreement for the environmental remediation of the San Fernando Airport was subscribed and submitted to ORSNA; and approved by the Court on December 29, 2022. The amount of the remediation is still under estimation.
On January 2, 2023, a specific agreement for the environmental remediation of the Aeroparque “Jorge Newbery” Airport was subscribed, submitted to ORSNA on January 25, 2023, and presented for court approval on February 2, 2023. The amount of the remediation is still under estimation.
The amounts to be paid in connection with the remediation works will be considered investments under the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
192
Civil Proceedings
In February 2021, Aerolíneas Argentinas submitted a debt recognition proposal for the amounts owed until March 31, 2020 (AR$120,586,290.10 or U.S.$36,542,036.83), by which such amounts would be assigned to the Trust for Strengthening of the National Airport System. On February 4, 2021, AA2000 accepted the aforementioned proposal and, in compliance with the provisions of Article 15 of the Trust Agreement dated December 29, 2009, requested ORSNA, prior intervention of the Ministry of Transportation, authorization for the assignment of such amounts.
On July 21, 2021, by note AA2000-ADM-1019/21, AA2000 sent the request for the application of the amounts to be integrated into the different accounts of the Trust for Strengthening of the National Airport System (FFSNA) for the purposes of the application of the assigned debt certificate. AA2000 agreed with ORSNA the way in which such assigned credits would be applied. On April 5, 2022, the Ministry of Transportation took the planned intervention. On June 14, 2022, the ORSNA notified AA2000 that the Ministry of Transportation has completed its intervention and approved the assignment in the terms described.
AA2000 notified both Aerolíneas Argentinas, as assigned debtor, and Banco de la Nación Argentina, as trustee under the Trust for Strengthening of the National Airport System, regarding the assignment. Also, AA2000 received in 2022 a payment in cash from Aerolíneas Argentinas, for an amount of approximately U.S.$15 million.
In 2023, Aerolíneas Argentinas made several payments in cash for a total amount of approximately U.S.$27.5 million, including both outstanding debt and current amounts.
On July 7, 2022, the first instance judgment rejected the claim and imposed the payment of the Court costs to the plaintiff, who appealed the decision.
On December 13, 2023, the Court of Appeals partially upheld the plaintiff’s appeal on the merits and reversed the first instance ruling, ordering NQN to pay the sum of U.S.$577,740 plus U.S.$250,534 in interest (set as of December 29, 2023, at an annual rate of 8%). The costs of both instances were imposed on NQN and amount, in total, to 53.3% of the amount of the judgment. These costs include the counsel’s fees which amount to the 15.6% of the judgment amount for his first instance works plus 30% of said percentage for his second instance works.
This ruling was appealed before the Supreme Court of Neuquen by NQN (both on the merits and the Court costs) and by its former counsel (just on the amount of fees). Both extraordinary appeals are pending.
The filing of the appeal does not prevent the beneficiaries of the sentence from requesting provisional seizures against NQN to ensure the collection of their fees if the judgement were confirmed. These seizures cannot be executed until the provincial extraordinary appeal is resolved and the execution will proceed only if the appeal is dismissed. If seizures are requested, it will be required to replace them by insurance policies. The counsel’s fees should be covered by the insurance policy previously filed in the proceedings.
Within the framework of the lawsuit, the court ordered a seizure on NQN’s account in the amount of U.S.$250,000, which was replaced by an insurance policy offered by the company in the amount of U.S.$500,000. A hearing was held on July 14, 2022 and the evidence offered by both parties is currently being reviewed.
Miscellaneous
The amount linked to this settlement, which had been notified by ORSNA, was approximately AR$234,866,430.19.
193
In September 2022 ORSNA proposed to collect the debt in 12 installments subject to payment of all the pending fines, increasing the amount owed to U.S.$4,289,643.15 and AR$183,333.10. AA2000 agreed to enter into this payment agreement. The agreement was signed on December 6, 2022. Payment of the total firm fines is established in 12 monthly installments, with the first installment due on 12/10/2022 and the last on 11/10/2023, applying the BADLAR interest rate.
The agreement was regularly complied, with the last instalment having been paid on September 11, and the ORSNA being informed of this situation. Consequently, the obligations of the convention have been fully fulfilled.
Brazilian Proceedings
Administrative Proceedings
In December 2021, ICAB requested ANAC to reschedule 50% of the 2021 fixed concession fee, as already approved by the Brazilian Ministry of Infrastructure, such request was denied by ANAC. In January 2022, ICAB decided to submit a formal claim against ANAC. In February 2022, a provisional decision was granted, suspending ANAC’s decision and ICAB’s default until a final decision. ANAC appealed, but in April 2022, the court of justice provisionally maintained the first instance judgement favorable to ICAB. In November 2023, the case was sentenced, and the first instance’s ruling in favor of ICAB was confirmed, granting ICAB’s right to reschedule 50% of the 2021 fixed concession fee. This ruling was appealed by ANAC, but the court of justice has not decided yet.
After ICAB partially deducted 2021 fixed concession fee and rescheduled 50% of the 2021 concession fee, ANAC started an administrative procedure to verify if ICAB was on default with the Concession Agreement payments. ICAB submitted a defense, and the procedure was suspended until a Federal Judge would grant a decision.
On March 3, 2022 ANAC rejected the petition for an extraordinary review of the Concession Agreement requested in connection with the COVID-19 pandemic impact. ANAC only intends to grant an economic re-equilibrium as previously done, year by year, after specific analysis, instead of long-term re-equilibriums.
On July 1, 2022, ICAB filed claims before the Brazilian ANAC requesting the economic re-equilibrium under the Brasilia Concession Agreement based on the losses and cost incurred in connection with the COVID-19 pandemic for 2022. On November 4, 2022, ICAB was granted the amount of R$70.1 million to be deducted from the 2022 fixed concession fee.
Regarding the 2022 fixed concession fee a partial payment of R$81.6 million (equivalent to U.S.$15 million) was made through the application of re-equilibrium credits in 2022. To pay the remaining amount, ICAB presented on November 21, 2022, to the Ministry of Infrastructure an offer of payment with judicial credits (“Precatorios”) and such Precatorios are still under analysis. In December 2022, the Ministry issued an official letter, confirming that, during the time it takes to analyze Precatorios and issue a final opinion, ICAB is in compliance with its obligations.
In March 2023, even though Constitutional authorization was still valid, the Brazilian attorney general, (“AGU”), revoked its own regulation on the acceptance of Precatorios for the payment of concession fees, and started the analysis to propose a new regulation regarding the due process for compensation.
194
On May 15, 2023, ICAB submitted a request to pay the variable concession fee with the Precatorios, but in June 2023 ANAC informed the non-recognition of the payment and initiated an administrative procedure to determine the default asking ICAB to make a new payment, on the basis that the Advocacy General of the Union - AGU revoked the regulation on the acceptance of Precatorios and initiated a study to propose a new regulation.
On June 15, 2023, ICAB submitted a legal claim requesting (a) ANAC to cease the requirement of the payment until the Precatorios analyses was complete and (b) a preliminary injunction to suspend of payment requirement. ICAB is still waiting for a final decision.
Due to this, ICAB did not meet one of the obligations set forth in the financing agreement with BNDES, and consequently, this resulted in the reclassification of non-current installments to current, due to the requirements of said agreement.
Even though ICAB had conviction on the validity and legality of the use of Precatorios for payment of concession fees, on August 15, 2023, ICAB paid in full the obligation of the variable concession fee for a total amount of R$9.1 million (equivalent to U.S.$1.9 million) through the application of re-equilibrium credits and in consequence ICAB withdraw the request to pay the variable concession fee with the Precatorios. The payment through the application of re-equilibrium credits was accepted, and in consequence the matter related with the payment of the variable concession fee is finalized.
Additionally, on December 7, 2023, ICAB was granted the amount of R$86.1 million to be deducted from the 2023 fixed concession fee.
Civil Proceedings
On September 9, 2020, Infraero informed ICAB about the audit results and although no evidence of excessive pricing was found on the main contract, Infraero mentioned the potential existence of certain irregularities on the four amendments to the agreement. On September 22, 2020, ICAB filed a response alleging the inexistence of the referred irregularities. Infraero is currently reviewing the document and a final determination about the case is still pending. If confirmed, Infraero could recommend ICAB to demand a reparation from Helvix from R$40 million to R$150 million.
195
Tax Proceedings
In June 2022, the Brazilian Supreme Court confirmed the decision of the Federal District Court excluding ICAB’s responsibility for the payment of IPTU and restricting this tax to the areas occupied by third parties who explore activities unrelated to the airport. This lawsuit was concluded.
The Federal District initiated a new lawsuit, demanding the payment of R$5 million on pending IPTU. On January 21, 2020, ICAB was notified about this new proceeding and in March 2020, ICAB filed a response arguing in the same rights as those raised in the prior proceeding.
In September 2022, the Federal District, again sued ICAB, claiming the payment of R$1.2 million of IPTU. ICAB answered the complaint under the same rights raised on prior lawsuits. As of the date of this letter, none of these claims have been ruled by the court of first instance.
Proceedings related to the Natal Airport
These proceedings were initiated by or against ICASGA. However, considering that on December 31, 2023 such company was absorbed by ACI do Brasil S.A., the former will replace ICASGA in all proceedings from such date.
Administrative Proceedings
Re-Equilibrium Requests
On July 9, 2020, ICASGA filed claims before the Brazilian ANAC, in the total amount of R$27,8 million, requesting the economic re-equilibrium of the Natal Concession Agreement based on the losses end cost management incurred due to COVID-19 pandemic. The amount is based on the loss of income and drastic reduction of revenues due to the unforeseeable circumstances created by the pandemic.
On May 31, 2022, ANAC granted ICASGA an economic re-equilibrium due to the pandemic in the amount of R$18.1 million. This amount is in line with the amount requested by ICASGA and is in connection with the losses suffered during the 2021 fiscal year and is going to be added to other ICASGA credits to be received along with the indemnity regarding the rebidding process.
On December 29, 2022, ANAC granted ICASGA an economic re-equilibrium of R$11.3 million due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic during 2022 fiscal year and is in line with the amount requested by ICASGA. This amount is going to be also added to the other ICASGA credits to be received along with the indemnity regarding the rebidding process.
On December 7, 2023, ANAC granted ICASGA an economic re-equilibrium of R$14.4 million due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic during 2023 fiscal year, in line with the amount requested by ICASGA.
On December 28, ICASGA and ANAC executed an agreement concerning the incorporation of ICASGA by ACI do Brasil S.A.
196
Re-Bidding Process
On March 5, 2020, ICASGA filed a request to the Brazilian Federal Government and ANAC to start the re-bidding process of the Natal Airport and transfer the operation of Natal Airport to a different operator after a new bidding process, according to the terms of Law No. 13.448 of July 5, 2017 and ANAC Resolution No. 533 of November 7, 2019.
On May 26, 2020, ANAC approved the technical and legal feasibility of the request for re-bidding being the first step in the procedure. On June 3rd, 2020 the Ministry of Infrastructure approved the compatibility of the request for re-bidding with the sector’s public policy. On June 10th, 2020 the Investment Partnership Program (PPI)Committee gave a favorable opinion to the qualification of the project’s re-bidding.
On November 20, 2020, ICASGA and ANAC signed a concession agreement amendment setting forth the rules and proceedings for the re-bidding.
On May 19, 2023, ANAC conducted the new bidding process for the airport which was awarded to Zurich Airports.
On September 12, 2023 Zurich Airports, ANAC and ICASGA entered into a new concession agreement.
On December 27, 2023 the budget required for indemnification payment to be paid by the Government was approved by the National Congress and sanctioned by the Brazilian President.
On December 31, 2023, ICASGA was absorbed by ACI do Brasil S.A., a subsidiary of the Company.
On December 29, 2023 and January 5, 2024, the Federal Government and Zurich Airport paid R$199.7 million, and R$323.4 million respectively, as indemnification payment.
Tax Proceedings
On November 1, 2017, ICASGA initiated a lawsuit before the Municipality of São Gonçalo do Amarante to dispute the legality of the IPTU collected by the City of São Gonçalo do Amarante.
On January 18, 2018, the Judge granted a provisional decision, by suspending the tax collection and on August 27, 2019, a further ruling found the collection as unfounded. The Municipality appealed and obtained a provisional decision, which allowed for the collection of such tax up to the amount of approximately R$17 million. On December 11, 2019, ICASGA appealed against that provisional decision, which was granted on May 27, 2020 and consequently, the tax collection was suspended. The Municipality appealed again before the Brazilian Supreme Court, and on June 16, 2020 such appeal was denied. The tax collection remains suspended until trial by the State Court is completed.
On November 17, 2020, the State Court made its final decision and denied the Municipality’s appeal. Therefore, the judgement dismissing the collection of IPTU against ICASGA was confirmed. The Municipality filed a final appeal at the Supreme Court, and on August 1, 2023 a first decision was granted, in favor of the City. The Minister decided to revoke the State Court’s last decision and ruled that the State Court had to analyze the lawsuit again. ICASGA submitted an appeal before the Supreme Court, asking this monocratic decision adopted in August to be reviewed by the other Minister. Such request which was granted on September 29, 2023. The Supreme Court partially changed its decision, and decided to keep IPTU immunity as a rule, but to allow the Municipality to collect this tax only over the areas occupied by third parties who exploit activities unrelated to the airport public service.
After the Supreme Court’s decision, in December 2023, the Municipality rectified the value of the tax demanded from R$80 million, to R$8 million, which is the total value of IPTU for all the concession years. ICASGA filed an administrative appeal, since it still considers that the amount is not correct and should not be charged to ICASGA.
197
Ecuadorian Proceedings
Tax Proceedings
The Servicio de Rentas Internas (“SRI”) determined that TAGSA has to pay roughly the amount of U.S.$3.3 million linked to income tax for 2017. On April 27, 2021, TAGSA submitted the request for a nullity, which was rejected on November 8, 2021 by the SRI. TAGSA exhausted the administrative instance, and since the outcome was not positive, TAGSA submitted a judicial claim on January 31, 2022, for an amount of U.S.$4.5 million. On July 13 and September 6, 2022, two hearings took place, and on October 18, 2022 a rule was issued in favor of TAGSA. On December 12, 2022, SRI submitted a cassation complaint against the ruling, which was accepted by the National Court on July 6, 2023. On July 14, 2023 TAGSA submitted its response and now the parties are waiting for the Court to schedule the hearing.
Italian Proceedings
TA entered into two preliminary sales contracts with NUOVE Iniziative Toscane (NIT) in 2018 with the commitment to purchase land and buildings located in the “Piana di Castello” near the Municipality of Florence. For the first contract, expected price was equal to EUR 75 million of which EUR 3 million were paid as a deposit at the time of the execution, while for the second the expected price was equal to EUR 90,000 of which EUR 9,000 had been paid at the time of the execution.
On September 10, 2021, NIT filed a claim before the Civil Court of Milan – claiming the fulfillment of the conditions precedent to obtain the issuance of a constitutive sentence pursuant to art. 2932 of the Italian Civil Code, condemning TA to pay the relative price (net of the deposits already paid, therefore EUR 72 million for the first contract and EUR 81,000 for the second contract), in addition to the costs it incurred and damages.
On January 20, 2022, TA answered the claim by rejecting, as inadmissible and unfounded, all the requests made by NIT, taking into consideration the non-occurrence of the conditions precedent, and consequently condemn NIT to immediately return the sums already paid by TA. Based on the opinion of TA’s counsel, no provision has been recognized for this matter.
In the court hearing on June 20, 2022, the proceeding was postponed to a new court which was supposed to be held on March 13, 2023, but was further postponed to September 2023. However, such hearing did not take place since the parties proceeded to submit their closing arguments in writing.
The Parties submitted their final briefs in December 2023, and it is expected that the resolution is issued within the first months of 2024.
Peruvian Proceedings
On July 13, 2017, the Government of Peru notified the unilateral decision to rescind the concession agreement for the Nuevo Aeropuerto International de Chinchero.
On June 21, 2018, an arbitration procedure request was submitted by Kuntur Wasi to the competent authority, ICSID (known as CIADI in Spanish). On the same date, Corporación América S.A. also submitted to ICSID a request for the arbitration procedure under the bilateral investment treaty framework. Both procedures before ICSID were carried out in a single docket.
On August 10, 2023, Kuntur Wasi received a notification from the ICSID Arbitral Court regarding a favorable resolution concerning the arbitration procedure due to unreasonably and arbitrary unilateral termination of the Concession Agreement by the Peruvian Ministry of Transports and Communications. The Arbitral Court has already determined the final award for damages and losses, and on February 28, 2024, both parties submitted further information that was required to calculate the business profit based on the invested amounts as well as the recognition of interests on the related amounts.
198
Dividend Distribution Policy
The declaration and payment of future dividends to holders of our common shares will be at the discretion of the annual general meeting and/or our board of directors, in case of interim dividend distributions, and will depend upon many factors, including our financial condition, earnings, distributable profits, legal requirements, restrictions in our debt agreements and other factors deemed relevant by our board of directors. In addition, as a holding company, our ability to pay dividends depends on our receipt of cash dividends from our operating subsidiaries, which may further restrict our ability to pay dividends as a result of the laws of their respective jurisdictions of organization, agreements of our subsidiaries or covenants under any present or future indebtedness that we or they may incur. For further information regarding the restrictions on our ability to declare and pay dividends, see “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors— Risks Related to Our Common Shares—Our ability to pay dividends is restricted under Luxembourg law,” and “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Indebtedness.”
In addition, under Luxembourg law and the articles of association of the Company, at least 5.0% of our net profits (if any) per year must be allocated to the creation of a legal reserve until such reserve has reached an amount equal to 10.0% of our issued share capital. If the legal reserve subsequently falls below 10.0% of our issued share capital, 5.0% of net profits again must be allocated toward the reserve until such reserve returns to 10.0% of our issued share capital. If the legal reserve exceeds 10.0% of our issued share capital, the legal reserve may be reduced. The legal reserve is not available for distribution.
B. SIGNIFICANT CHANGES
There have been no significant changes since the approval date of the financial statements included elsewhere in this annual report. Please see Note 34 of the Consolidated Financial Statements elsewhere in this annual report for details of events after the reporting period.
ITEM 9. THE OFFER AND LISTING
A. OFFER AND LISTING DETAILS
Our common shares trade solely on the NYSE under the symbol “CAAP.” Our common shares do not trade in any other market.
B. DISTRIBUTION PLAN
Not applicable.
C. MARKETS
Our common shares began trading on the NYSE under the symbol “CAAP,” in connection with our initial public offering, on February 1, 2018.
D. SELLING SHAREHOLDERS
Not applicable.
E. EXPENSES OF THE ISSUE
Not applicable.
ITEM 10. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
A. SHARE CAPITAL
Not applicable.
199
B. MEMORANDUM AND ARTICLES OF ASSOCIATION
The following is a summary of some of the terms of our common shares, based on our articles of association. The following summary is not complete and is subject to, and is qualified in its entirety by reference to, the provisions of our articles of association, and applicable Luxembourg law, including Luxembourg corporate law.
On May 22, 2019 the extraordinary general meeting of the shareholders of the Company, approved amendments to our articles of association to amend the following: (i) the convening procedure for general meetings; (ii) the signature power to sign extracts or copies of minutes of general meetings; (iii) the convening procedure for meetings of the board of directors; (iv) the signature power to sign extracts or copies of minutes of meetings of the board of directors; (v) the period during which certain documents shall remain available at the registered office of the Company prior to general shareholders’ meetings; (vi) adjust a clerical inaccuracy and add a definition of “General Meeting.”
On October 23, 2020 and further to the share capital increase by an amount of U.S.$3,200,445 (three million two hundred thousand four hundred forty-five US dollars) through the use of the authorized share capital and the issuance of 3,200,445 (three million two hundred thousand four hundred forty-five) shares having a nominal value of U.S.$1 (one US dollar) each decided by the compensation committee of the Company on October 9, 2020, article 5.1 of the articles of association was amended so as to read as follows:
“5.1 Issued share capital
The share capital is set at one hundred sixty-three million two hundred twenty-two thousand seven hundred and seven US dollars (U.S.D.163,222,707), represented by one hundred sixty-three million two hundred twenty-two thousand seven hundred and seven (163,222,707) shares having a nominal value of one US dollar (U.S.$1.00) each.”
On May 23, 2023, the extraordinary general meeting of the shareholders of the Company, approved amendments to our articles of association to implement the following: (i) renewal of the authorized share capital of the Company; (ii) amendment of the number of members of the executive committee (comité de direction) of the Company; (iii) amendment to the signatory powers in respect of the daily management (gestion journalière) of the Company; (iv) amendment of the term “chairman” by “chairperson” in the Articles.
A copy of the articles of association, as amended and currently in force, is furnished under Item 19, “Exhibits.”
General
We are a public limited liability company (société anonyme) incorporated under, and governed by, the laws of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. We are registered with the Luxembourg Trade and Companies Register (Registre de Commerce et des Sociétés de Luxembourg (RCS)) under the number B 174140. We were incorporated on December 14, 2012, under the name A.C.I. Airports International S.à r.l. The name changed to Corporación América Airports S.A. on September 14, 2017, upon conversion from a private limited liability company (société à responsabilité limitée) to a public limited liability company (société anonyme). Our registered office is currently located at 128, Boulevard de la Pétrusse, L-2330 Luxembourg, Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
Our agent for service of process in the United States is Puglisi & Associates, located at 850 Library Avenue, Suite 204, Newark, Delaware 19711. Since our incorporation, other than a capital increase by the conversion of reserves and the recent capital increase in connection with the Management Plan (see “Item 6. Compensation — Management Compensation Plan”), there have been no material changes to our share capital. We have not undergone any bankruptcy, receivership or similar proceedings.
Common Shares
Common shares are issued in registered form only and no certificates will be issued. The Company is entitled to treat the registered holder of any share as the absolute owner thereof and is not bound to recognize any equitable claim or other claim or interest in such share on the part of any other person.
200
Issuance of Common Shares
Our shareholders have renewed the initial authorization granted to the board of directors to issue common shares up to the maximum amount of the authorized unissued share capital of the Company for a period of five years from the date of the deed renewing such authorization (regardless of the date of its publication in the Luxembourg Official Gazette (Recueil électronique des sociétés et associations (RESA)), which period may be subsequently and indefinitely renewed, to such persons, and on such terms and for such consideration as the board of directors may determine.
Our authorized share capital consists of 225,000,000 common shares with a nominal value of U.S.$1.00 per share, out of which 61,777,293 common shares with a nominal value of U.S.$1.00 are left. We have 163,222,707 common shares issued and outstanding, of which 2,251,123 are held as treasury shares. All of our issued and outstanding common shares are fully paid and the board of directors cannot call on or compel our shareholders to contribute additional amounts to the Company.
Pre-emptive Rights
In the event of any capital increase whether in cash or in kind, the holders of our common shares shall have pre-emptive rights to subscribe for additional common shares proportionally to their existing equity in our share capital, except as noted below. The exercise period for such pre-emptive rights is determined by the board of directors, but must be at least 14 days from the date of the publication of the offering in the RESA and a journal published in Luxembourg. If holders of common shares do not elect to exercise their pre-emptive rights, the other holders of pre-emptive rights shall benefit from secondary pre-emptive subscription rights for unsubscribed shares; provided, however, that the general meeting (or the board of directors, as authorized by the general meeting) may limit or withdraw such pre-emptive subscription rights in accordance with applicable law and our articles of association. The board of directors is also authorized for a period of five years commencing on May 23, 2023, to cancel or limit the pre-emptive rights of the shareholders in accordance with our articles of association and in connection with the issuance of shares (i) for payment in cash or in kind, or (ii) in connection with a conversion of profits and reserves (including share premium).
Meetings of Shareholders
The board of directors shall convene at least one general shareholders meeting each calendar year (the “annual general meeting”) for the purpose of, among other things, approving the annual accounts, deciding on the allocation of the annual profit, if any, and, as the case may be, electing or renewing the mandates of directors. Under Luxembourg law, the annual general meeting must be held within six months of the end of the fiscal year. A general meeting can be adjourned at the request of one or more shareholders representing at least one tenth of the issued share capital.
The board of directors may convene any general meeting whenever in its judgment such a meeting is necessary. The board of directors must convene a general meeting within a period of one month upon notice, which notice must set forth certain information specified in the articles of association, to the Company from shareholders holding at least the 10.0% threshold on the date of such notice. In addition, one or more shareholders who together hold at least 10.0% of the issued share capital on the date of the notice to the Company, which notice must set forth certain information specified in the articles of association, may require that the Company include on the agenda of such general meeting one or more additional items. At least eight days’ notice to shareholders is required for a general meeting. No business may be transacted at a general meeting, other than business that is properly brought before the general meeting in accordance with our articles of association.
Voting Rights
Holders of our common shares are entitled to one vote per share on all matters submitted to a vote of holders of common shares. Luxembourg Law does not provide for cumulative voting in the election of directors. Voting of shareholders at a general meeting may be in person, by proxy or by voting bulletin. Our articles of association specify how the Company shall determine the shareholders of record entitled to notice of or to vote at any meeting of shareholders or any adjournment thereof.
201
Amendments of the Articles of Association
Except where our articles of association authorize the board of directors to approve an increase in share capital, approve a redemption and subsequent cancellation of shares and change the address of its registered office and subsequently record such change, if needed in the presence of a Luxembourg notary, our articles of association require a special resolution approved at an extraordinary general shareholders meeting to amend the articles of association. The agenda of the extraordinary general shareholders meeting must indicate the proposed amendments to the articles of association. Any resolutions to amend the articles of association must be taken before a Luxembourg notary and such amendments must be published in accordance with Luxembourg law. Resolutions to amend the articles of association may only be passed in a general meeting where at least one half of the share capital is represented, and the agenda indicates the proposed amendments to the articles of association, and the text of those which pertain to the purpose or the form of the Company. If the required quorum is not obtained, a second general meeting may be convened by an announcement filed with the RCS and published in the RESA and in a Luxembourg newspaper at least 15 days before the relevant meeting which shall deliberate validly regardless of the proportion of the capital represented. The applicable majority for both meetings shall be 66.67% of all votes validly cast.
Variation of Share Rights
Under Luxembourg law, where a resolution of an extraordinary general shareholders meeting will change the rights of our common shares or any other outstanding class of shares, the resolution must, in order to be valid, fulfill the quorum and voting requirements for an extraordinary general meeting with respect to each such class.
Permitted Transfers of Common Shares
The common shares are freely transferable subject to compliance with transfer formalities under applicable law.
Dividend Rights
Under Luxembourg law, dividends may only be declared from the freely available distributable reserves of the Company. Interim dividends may be declared by the board of directors, subject to certain mandatory legal requirements as detailed in the articles of association. The general shareholders meeting would in the normal course be asked to declare as final the interim dividends paid during the year. The shareholders may declare dividends at a general meeting.
Dividends may be paid in U.S. dollars, Euro or any other currency chosen by the board of directors and dividends may be paid at such places and times as may be determined by the board of directors within the limits of any decision made at the general shareholders meeting. Dividends may also be paid in kind in assets of any nature, and the valuation of those assets shall be established by the board of directors according to valuation methods determined in its discretion.
Distributions on winding up of the Company
The Company may be dissolved, at any time, by a resolution of the general meeting adopted in the manner required for amendment of the articles of association. In the event of dissolution of the Company, the liquidation shall be carried out by one or more liquidators (who may be physical persons or legal entities) appointed by the general meeting which authorized such liquidation. The general meeting shall also determine the powers and the remuneration of the liquidator(s). Under the liquidation of the Company, the surplus assets of the Company available for distribution among shareholders shall be distributed in accordance with the rules on distributions set forth in our articles of association, by way of advance payments or after payment (or provisions, as the case may be) of the Company’s liabilities.
Registration Rights and Indemnification Agreement
We have entered into a registration rights and indemnification agreement with the Majority Shareholder. This agreement provides to the Majority Shareholder up to five “demand” registrations for the sale of our ordinary shares. Additionally, the agreement provides the Majority Shareholder and its affiliate transferees customary “piggyback” registration rights. The registration rights and indemnification agreement also provide that we will pay certain expenses relating to such registrations and indemnify such holders of registrable securities against certain liabilities which may arise under the Securities Act.
202
Board of Directors
Our articles of association provide that our business is to be managed and conducted by or under the direction of our board of directors. In managing the business of the Company, the board of directors is vested with the broadest powers to perform or cause to be performed any actions necessary or useful in connection with the purpose of the Company. All powers not expressly reserved by the Luxembourg law or by the articles of association to the general shareholders meeting shall fall within the authority of the board of directors.
Our board of directors shall be composed of up to nine directors, appointed by the general shareholders meeting. The members of the board of directors shall be elected for a term not exceeding six years, and shall be eligible to stand for re-election. A director may be removed with or without cause and/or replaced, at any time, by a resolution adopted at the general shareholders meeting. The general shareholders meeting shall also determine the number of directors, the remuneration and their term of office. In the event of any director vacancy, the remaining directors may elect at a meeting of the board of directors, by majority vote, to fill such vacancy or vacancies, as the case may be, until the following general shareholders meeting.
Executive Committee
The management of the Company is delegated to an executive committee designated from time to time by the board of directors. The executive committee has the broadest powers possible under Luxembourg law and remains under the supervision and control of the board of directors.
Mergers and de-mergers
A merger by absorption whereby a Luxembourg company, after its dissolution without liquidation, transfers to the absorbing company all of its assets and liabilities in exchange for the issuance to the shareholders of the company being acquired of shares in the acquiring company, or a merger effected by transfer of assets to a newly incorporated company, must, in principle, subject to certain exceptions, be approved by a special resolution of shareholders of the Luxembourg company to be held before a notary. Similarly, a de-merger of a Luxembourg company is, in principle, subject to certain exceptions subject to the approval by a special resolution of shareholders.
Shareholder Suits and Information Rights
Class actions and derivative actions are generally not available to shareholders under Luxembourg law. Minority shareholders holding securities entitled to vote at the general meeting that resolved on the granting of discharge to the directors and holding at least 10.0% of the voting rights of the Company may bring an action against the directors on behalf of the Company.
Minority shareholders holding at least 10.0% of the voting rights of the Company may also ask the directors questions in writing concerning acts of management of the Company or one of its subsidiaries, and if the Company fails to answer these questions within one month, these shareholders may apply to the Luxembourg courts to appoint one or more experts instructed to submit a report on these acts of management. Furthermore, consideration would be given by a Luxembourg court in summary proceedings to acts that are alleged to constitute an abuse of majority rights against the minority shareholders.
Indemnification of Directors and Officers
We have amended our articles of association to provide that we will, to the extent permitted by law, indemnify our directors and officers against liability and expenses reasonably incurred or paid by them in connection with claims, actions, suits or proceedings in which they become involved as a party or otherwise by virtue of performing or having performed as a director or officer, and against amounts paid or incurred by them in the settlement of such claims, actions, suits or proceedings, if such person acted in good faith and in a manner the person reasonably believed to be in, and not opposed to, the best interests of the Company, and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe the person’s conduct was unlawful. The indemnification will extend, among other things, to legal fees, costs and amounts paid in the context of a settlement. We have entered into separate indemnification agreements with our directors and executive officers. Except for proceedings to enforce rights to indemnification or advancement of expenses, we shall not be obligated to indemnify any such officer or director in connection with a proceeding initiated by such person when such proceeding (or part thereof) was consented to by the board of directors.
203
Our articles of association provide that we may purchase and maintain insurance or furnish similar protection or make other arrangements, including, but not limited to, providing a trust fund, letter of credit or surety bond on behalf of our directors or officers against any liability asserted against them in their capacity as a director or officer.
Access to Books and Records and Dissemination of Information
The register of shareholders of the Company is open to inspection, at our registered office, by shareholders. Each year, the shareholders have the right to inspect, at the Company’s registered office, for at least eight calendar days prior to the annual general meeting, among other things, (i) the annual accounts, as well as the list of directors and of the statutory auditors, (ii) the report of the statutory auditors and (iii) in case of amendments to our articles of association, the text of the proposed amendments and the draft of the resulting consolidated articles of association. Each shareholder is entitled to obtain these free of charge, upon request. Under Luxembourg law, it is generally accepted that a shareholder has the right to receive responses to questions concerning items on the agenda for a general meeting of shareholders, if such responses are necessary or useful for a shareholder to make an informed decision concerning such agenda item, unless a response to such questions could be detrimental to our interests.
Registrar and Transfer Agent
We have appointed Equiniti Trust Company, LLC (formerly known as American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC) as our U.S. registrar and transfer agent, and all common shares and shareholders are transferred from the register held at our registered office to the register held by our U.S. registrar and transfer agent.
Repurchase of Common Shares
Pursuant to our articles of association, our board of directors may redeem our own common shares in accordance with Luxembourg law on such terms and in such manner as may be authorized by the general meeting of shareholders in an ordinary resolution, subject to the rules of any stock exchange on which our common shares are traded.
Reduction of Share Capital
The share capital of the Company may be reduced by a resolution adopted by the general meeting of shareholders in the manner required for the amendment of the articles of association.
Non-Distributable Reserve
Our articles of association provide for the creation of a non-distributable reserve. We recorded this non-distributable reserve in the amount of U.S.$1,353.7 million. The non-distributable reserve may be reduced by a resolution adopted by the general meeting of shareholders.
Annual Accounts
The board of directors shall draw up the annual accounts of the Company that shall be submitted to the approval of the shareholders at the annual general meeting. Except in some cases provided for by Luxembourg Law, our board of directors must also annually prepare management reports on the annual accounts and consolidated accounts. The annual accounts and consolidated accounts are audited by an approved statutory auditor (réviseur d’entreprises agréé).
The annual accounts and the consolidated accounts, after approval by the annual general meeting of shareholders, will be filed with the RCS.
C. MATERIAL CONTRACTS
We have not entered into any material contracts during the preceding two years which were outside the ordinary course of business.
D. EXCHANGE CONTROLS
None.
204
E. TAXATION
The following is a summary of the material Luxembourg, U.S. and Argentine federal income tax consequences of the ownership and disposition of our common shares by persons addressed herein.
Potential investors in our common shares should consult their own tax advisors concerning the specific Luxembourg and U.S. federal, state and local tax consequences of the ownership and disposition of our common shares in light of their particular situations as well as any consequences arising under the laws of any other taxing jurisdiction.
Luxembourg Tax Considerations
Introduction
The following information is of a general nature only and is based on the law currently in force in Luxembourg, though it is not intended to be, nor should it be construed to be, legal or tax advice. It does not purport to be a complete analysis of all possible tax situations that may be relevant to a decision to purchase, own or deposit our common shares.
Prospective purchasers of our common shares (“Shareholders”) should consult their own tax advisers as to the applicable tax consequences of the ownership of our common shares, based on their particular circumstances. Please be aware that the residence concept used under the respective headings below applies for Luxembourg income tax assessment purposes only. Any reference in this section to a tax, duty, levy impost or other charge or withholding of a similar nature refers to Luxembourg tax laws and/or concepts only. Also, please note that a reference to Luxembourg income tax encompasses corporate income tax (impôt sur le revenu des collectivités), municipal business tax (impôt commercial communal), a solidarity surcharge (contribution au fonds pour l’emploi) and personal income tax (impôt sur le revenu) generally. Corporate taxpayers may further be subject to net wealth tax (impôt sur la fortune), as well as other duties, levies or taxes. Corporate income tax, municipal business tax, net wealth tax as well as the solidarity surcharge invariably applies to most corporate taxpayers’ resident of Luxembourg for tax purposes. Individual taxpayers are generally subject to personal income tax and the solidarity surcharge. Under certain circumstances, where an individual taxpayer acts in the course of the management of a professional or business undertaking, municipal business tax may apply as well.
Taxation of the Company
A fixed registration duty of EUR75 will be due at the moment of the incorporation of the Company, in case of amendment to the articles of association, or upon transfer to Luxembourg of the registered office or the central administration of a civil or commercial company.
From a Luxembourg tax perspective, Luxembourg companies are considered as being resident in Luxembourg provided that they have either their registered office or their central administration in Luxembourg. The Company (a fully taxable company) will be considered as a resident of Luxembourg both for the purposes of Luxembourg domestic tax law and for the purposes of the double taxation treaties entered into by Luxembourg, and should therefore be able to obtain a residence certificate from the Luxembourg tax authorities.
The Company is liable to Luxembourg corporation taxes. The standard applicable rate of Luxembourg corporation taxes (which include corporate income tax, municipal business tax and the solidarity surcharge) is 24.94% for the fiscal year ending on December 31, 2023 for a company established in Luxembourg city. Liability to such corporation taxes extends to the Company’s worldwide income (including capital gains), subject to the provisions of any relevant double taxation treaty. The taxable income of the Company is computed by application of all rules of the Luxembourg income tax law of December 4, 1967, as amended (loi concernant l’impôt sur le revenu), as commented and currently applied by the Luxembourg tax authorities (LIR). Under the LIR, all income of the Company will be taxable in the fiscal period to which it economically relates, and all deductible expenses of the Company will be tax deductible in the fiscal period to which they economically relate. Under certain conditions, dividends received by the Company from qualifying participations and capital gains realized by the Company on the sale of such participations, may be exempt from Luxembourg corporation taxes under the Luxembourg participation exemption regime.
The Company is subject to net wealth tax levied annually at a 0.5% rate on an amount up to EUR500 million and 0.05% on the amount of taxable net wealth exceeding EUR500 million. Under certain conditions, qualifying participations may be exempt from net wealth tax under the Luxembourg participation exemption regime.
205
Notwithstanding the above, a minimum net wealth tax is levied on corporate entities having their statutory seat or central administration in Luxembourg. For entities for which the sum of financial assets, transferable securities and cash at bank exceeds 90% of their total gross assets and EUR350,000, the minimum net wealth tax is set at EUR4,815. For all other Luxembourg entities, the minimum net wealth ranges from EUR535 to 32,100, depending on their total gross assets.
Taxation of the Shareholders
Luxembourg tax residency of the holders of our common shares
A holder of our common shares will not become resident, nor be deemed to be resident, in Luxembourg by reason only of the holding and/or disposing of our common shares or the execution, performance or enforcement of his/her rights thereunder.
Withholding tax
Dividends paid by the Company to the Shareholders are as a rule subject to a 15% Luxembourg withholding tax of the gross dividend (17.65% of the net dividend if the Company bears the cost of the withholding tax, which is not mandatory under Luxembourg tax laws), unless a reduced withholding tax rate applies pursuant to an applicable double tax treaty or an exemption pursuant to the application of the participation exemption, and, to the extent withholding tax applies, the Company is responsible for withholding amounts corresponding to such taxation.
There is a double tax treaty between Luxembourg and the United States under which the Luxembourg withholding tax may be reduced to 5% if the beneficial owner of the dividend is a U.S. corporation that holds directly at least 10% of the voting stock of the Company (or to 0% if the beneficial owner holds at least 25% of the voting stock and certain other requirements are met). In addition, under Luxembourg domestic law, a dividend paid to a U.S. corporation may qualify for an exemption from Luxembourg withholding tax if it has held either (i) at least 10% of the stock of the Company or (ii) stock of the Company having an acquisition value of at least EUR1,200,000, for at least 12 months at the time of distribution. U.S. Holders (as defined below) should consult their own tax advisors regarding the availability to them of an exemption from Luxembourg withholding taxes.
Where the recipient of the dividend is not a U.S. corporation but is located elsewhere, a withholding tax exemption may apply under the participation exemption if cumulatively (i) the Shareholder is an eligible parent (“Eligible Parent”) and (ii) at the time the income is made available, the holder of our shares has held or commits itself to hold for an uninterrupted period of at least 12 months a direct participation of at least 10% of our share capital or a direct participation having an acquisition price of at least EUR1.2 million (or an equivalent amount in another currency). Holding participation through an entity treated as tax transparent from a Luxembourg income tax perspective is deemed to be a direct participation in proportion to the net assets held in this entity.
An Eligible Parent includes (a) a collective entity resident in a European Union (EU) Members State covered by Article 2 of Directive 2011/96/EU of November 30, 2011 on the common system of taxation applicable in the case of parent companies and subsidiaries of different EU Member States, as amended (the “EU Parent-Subsidiary Directive”) and which are not excluded to benefit from the EU Parent-Subsidiary Directive under its mandatory anti-abuse rule (“GAAR”) provided for by Council Directive 2015/121/EU, as implemented in Luxembourg, or a Luxembourg permanent establishment thereof, (b) a collective entity resident in a State having a double tax treaty with Luxembourg and subject to a tax corresponding to Luxembourg corporate income tax or a Luxembourg permanent establishment of such entity, (c) a joint-stock company or a cooperative company resident in the European Economic Area (EEA) other than an EU Member State and liable to a tax corresponding to Luxembourg corporate income tax or a Luxembourg permanent establishment of such company or (d) a Swiss joint-stock company which is effectively subject to corporate income tax in Switzerland without benefiting from an exemption or (e) a fully taxable Luxembourg resident collective entity or (f) the Luxembourg State, a Luxembourg municipality, an association of a Luxembourg municipality or an operation of Luxembourg public-law entity, (g) a permanent establishment of an entity referred to at letters (a), (e) or (f) above. No withholding tax is levied on capital gains and liquidation proceeds.
Taxation of Dividend Income
Shareholders who are either Luxembourg resident individuals or Luxembourg fully taxable resident companies (or foreign shareholders having a permanent establishment in Luxembourg through which such Shares are held), will in principle be subject to tax at the ordinary rates on the dividends received from the Company. However, under Luxembourg tax laws currently in force, 50% of the amount of such dividend may be tax exempt at the level of these Shareholders.
206
The Luxembourg withholding tax levied at source on the dividends paid may, under certain conditions, be credited against the Luxembourg income tax due on these dividends.
Furthermore, certain corporate Shareholders may benefit from an exemption of Luxembourg corporation taxes on dividend income under the following conditions:
| ● | the Shareholder receiving the dividends is either (i) a fully taxable Luxembourg resident collective entity, (ii) a Luxembourg permanent establishment of an EU resident collective entity falling within the scope of article 2 of the EU Parent-Subsidiary Directive, (iii) a Luxembourg permanent establishment of a joint-stock company that is resident in a State with which Luxembourg has concluded a double tax treaty, or (iv) a Luxembourg permanent establishment of a joint-stock company or of a cooperative company which is a resident of a EEA Member State (other than a EU Member State); and |
| ● | on the date on which the income is made available, the Shareholder holds or commits to hold directly (or even indirectly through certain entities) for an uninterrupted period of at least twelve months, a participation of at least 10% in the share capital of the Company (or with an acquisition price of at least EUR1.2 million). |
The Shareholder which is a Luxembourg resident entity governed by the law of 17 December 2010 on undertakings for collective investment, as amended, by the law of 13 February 2007 on specialized investment funds, as amended, by the law of 11 May 2007 on the family estate management company, as amended, or by the law of 23 July 2016 on reserved alternative investment funds and which does not fall under the special tax regime set out in article 48 thereof, is not subject to any Luxembourg corporation taxes in respect of dividends received from the Company. No tax credit is then available for Luxembourg withholding tax on dividends received from the Company.
Non-resident shareholders (not having a permanent establishment in Luxembourg through which the Shares are held) will in principle not be subject to Luxembourg income tax on the dividends received from the Company (except for the withholding tax mentioned above, if applicable).
Taxation of Capital Gains
Under current Luxembourg tax laws, capital gains realized by a Luxembourg resident individual Shareholder (acting in the course of the management of his/her private wealth) upon the disposal of his/her Shares are not subject to Luxembourg income tax, provided this disposal takes place more than six months after the Shares were acquired and he/she does not hold a substantial participation. The participation is considered as substantial (a “Substantial Participation”) if the Shareholder (i) holds or has held (either solely or together with his/her spouse or partner and minor children) directly or indirectly more than 10% of the share capital of the Company at any time during a period of five years before the realization of the capital gain or (ii) acquired his/her Shares for free during the five years preceding the disposal of his/her Shares and the previous holder of the Shares or, in the case of subsequent gratuitous transfers, one of the previous holders has held (either solely or together with his/her spouse or partner and minor children) directly or indirectly more than 10% of the share capital of the Company at any time during a period of five years before the realization of the capital gain.
Capital gains realized upon the disposal of Shares by a Luxembourg resident corporate Shareholder (fully subject to Luxembourg corporation taxes) are in principle fully taxable. However, an exemption from Luxembourg corporation taxes applies under the following conditions:
| ● | the Shareholder realizing the capital gains is either (i) a fully taxable Luxembourg resident collective entity, (ii) a Luxembourg permanent establishment of an EU resident collective entity falling within the scope of article 2 of the EU Parent-Subsidiary Directive, (iii) a Luxembourg permanent establishment of a joint-stock company that is resident in a State with which Luxembourg has concluded a double tax treaty, or (iv) a Luxembourg permanent establishment of a joint-stock company or of a cooperative company which is a resident of a EEA Member State (other than a EU Member State); and |
| ● | on the date on which the disposal takes place, the Shareholder has held for an uninterrupted period of at least twelve months, a participation of at least 10% in the share capital of the Company (or with an acquisition price of at least EUR6 million). |
207
The Shareholder which is a Luxembourg resident entity governed by the law of 17 December 2010 on undertakings for collective investment, as amended, by the law of 13 February 2007 on specialized investment funds, as amended, by the law of 11 May 2007 on the family estate management company, as amended, or by the law of 23 July 2016 on reserved alternative investment funds and which does not fall under the special tax regime set out in article 48 thereof, is not subject to any Luxembourg corporation taxes in respect of capital gains realized upon disposal of its Shares.
Under Luxembourg tax laws currently in force (subject to the provisions of double taxation treaties), capital gains realized by a Luxembourg non-resident Shareholder (not acting via a permanent establishment or a permanent representative in Luxembourg through which/whom the Shares are held) are not taxable in Luxembourg unless (a) the Shareholder holds a Substantial Participation in the Company and the disposal of the Shares takes place less than six months after the Shares were acquired or (b) the Shareholder has been a former Luxembourg resident for more than fifteen years and has become a non-resident, at the time of transfer, less than five years ago.
Net Wealth Taxation
A corporate Shareholder, whether it is resident of Luxembourg for tax purposes or, if not, it maintains a permanent establishment or a permanent representative in Luxembourg through which/whom such Shares are held, is subject (but an exemption may apply under the conditions stated below) to Luxembourg wealth tax on such Shares, except if the Shareholder is governed by the law of 11 May 2007 on the family estate management company, as amended, by the law of 17 December 2010 on undertakings for collective investment, as amended, by the law of 13 February 2007 on specialized investment funds, as amended, by the law of 23 July 2016 on reserved alternative investment funds, or is a securitization company governed by the law of 22 March 2004 on securitization, as amended, or is a capital company governed by the law of 15 June 2004 on venture capital vehicles, as amended.
The Shareholder which is (i) a Luxembourg resident fully taxable collective entity, (ii) a Luxembourg permanent establishment of an EU resident collective entity falling within the scope of article 2 of the EU Parent-Subsidiary Directive, (iii) a domestic permanent establishment of a joint-stock company that is resident in a State with which Luxembourg has concluded a double tax treaty, or (iv) a domestic permanent establishment of a joint-stock company or of a cooperative company which is a resident of a EEA Member State (other than a EU Member State), may be exempt from Luxembourg net wealth tax on its Shares if it holds a participation of at least 10% in the share capital of the Company (or with an acquisition price of at least EUR1.2 million).
An individual Shareholder, whether he/she is resident of Luxembourg or not, is not subject to Luxembourg wealth tax on his/her Shares.
Other Taxes
Under current Luxembourg tax laws, no registration tax or similar tax is in principle payable by the Shareholder upon the acquisition, holding or disposal of the Shares. Registration duties may be due in the case where the shares are physically attached to a public deed or to any other document subject to mandatory registration, as well as in the case of a registration of the Shares on a voluntary basis.
When the Shareholder is a Luxembourg resident for inheritance tax assessment purposes at the time of his/her death, the Shares are included in his/her taxable estate for Luxembourg inheritance tax assessment purposes.
Luxembourg gift tax may be due on a gift or donation of the Shares if embodied in a notarial deed executed before a Luxembourg notary or recorded in Luxembourg.
Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations
The following is a summary of the material U.S. federal income tax consequences to U.S. Holders (as defined below) of the ownership and disposition of our common shares. This summary assumes that the common shares are held as capital assets (generally, property held for investment), within the meaning of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), in the hands of a U.S. Holder at all relevant times. This summary is based upon U.S. federal income tax laws (including the Code, final, temporary and proposed Treasury regulations, rulings, judicial decisions and administrative pronouncements), all as of the date of this annual report and such authorities may be repealed, revoked or modified, possibly with retroactive effect, so as to result in U.S. federal income tax consequences different from those discussed below.
208
The discussion does not cover all aspects of U.S. federal income taxation that may be relevant to, or the actual tax effect that any of the matters described herein will have on, the acquisition, ownership or disposition of our common shares by particular investors (including consequences under the alternative minimum tax or net investment income tax), and does not address state, local, non-U.S. or other tax laws.
This summary also does not address all of the U.S. tax considerations that may apply to holders that are subject to special tax rules, such as U.S. expatriates, insurance companies, individual retirement accounts and other tax-deferred accounts, tax-exempt organizations, certain financial institutions, dealers and certain traders in securities, persons holding common shares as part of a straddle, hedging, conversion or other integrated transaction, persons who acquired their common shares pursuant to the exercise of employee shares options or otherwise as compensation, entities or arrangements classified as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes, persons whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar, persons that own or have owned directly, indirectly, or constructively, shares of the Company representing 10% or more of the voting power or value of the Company, or persons whose shares of the Company are effectively connected with a business carried on through a permanent establishment in Luxembourg. Such holders may be subject to U.S. federal income tax consequences different from those set forth below.
If an entity or arrangement treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds common shares, the tax treatment of a partner generally will depend upon the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. An entity or arrangement treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes, or partner in a partnership, is urged to consult its own tax advisor regarding the specific tax consequences of owning and disposing of the common shares.
As used herein, the term U.S. Holder means a beneficial owner of one or more of our common shares, that is for U.S. federal income tax purposes, one of the following:
| ● | an individual citizen or resident (as defined in Section 7701(b) of the Code) of the United States; |
| ● | a corporation (or other entity that is treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes) that is created or organized in or under the laws of the United States or any state or political subdivision thereof (including the District of Columbia); |
| ● | an estate the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income taxation regardless of its source; or |
| ● | trust if (1) a court within the United States can exercise primary supervision over it, and one or more United States persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust, or (2) the trust has a valid election in effect under applicable U.S. Treasury regulations to be treated as a United States person; |
| ● | who holds the common shares as capital assets for U.S. federal income tax purposes; |
| ● | who owns, directly, indirectly or by attribution, less than 10% of the share capital or voting shares of the Company; and |
| ● | whose holding is not effectively connected with a business carried on through a permanent establishment in Luxembourg. |
Except as otherwise noted, this summary assumes that the Company is not a passive foreign investment company (a “PFIC”) for U.S. federal income tax purposes, which the Company believes to be the case. The Company’s possible status as a PFIC must be determined annually and therefore may be subject to change. If the Company were to be a PFIC in any year, materially adverse consequences could result for U.S. Holders.
Potential investors in our common shares should consult their own tax advisors concerning the specific U.S. federal, state and local tax consequences of the ownership and disposition of our common shares in light of their particular situations as well as any consequences arising under the laws of any other taxing jurisdiction.
209
Taxation of distributions
Distributions received by a U.S. Holder on common shares, including the amount of any Luxembourg taxes withheld, generally will be subject to U.S. taxation as foreign source dividend income to the extent paid out of the Company’s current or accumulated earnings and profits (as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles). Distributions in excess of current and accumulated earnings and profits will be treated as a non-taxable return of capital to the extent of the U.S. Holder’s basis in the common shares and thereafter as capital gain. Because the Company does not maintain calculations of its earnings and profits under U.S. federal income tax principles, it is expected that such distributions (including any Luxembourg taxes withheld) will be reported to U.S. Holders as dividends. U.S. Holders should consult their own tax advisers with respect to the appropriate U.S. federal income tax treatment of any distribution received from the Company. Corporate U.S. Holders who own less than 10% of the share capital or voting shares of the Company will not be entitled to claim the dividends received deduction with respect to dividends paid by the Company. A non-corporate recipient of dividend income will generally be subject to tax on dividend income from a “qualified foreign corporation” at a reduced capital gains rate rather than the marginal tax rates generally applicable to ordinary income provided that the holding period requirement is met. A non-U.S. corporation (other than a corporation that is classified as a PFIC for the taxable year in which the dividend is paid or the preceding taxable year) generally will be considered to be a qualified foreign corporation if the shares of the non-U.S. corporation are readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States. The common shares of the Company are listed on the NYSE and should qualify as readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States so long as they are so listed. Therefore, the Company believes that it will be a qualified foreign corporation for purposes of the reduced tax rate, although no assurance can be given that it will continue to be treated as a qualified foreign corporation in the future. Non-corporate U.S. Holders should consult their own tax advisors to determine whether they are subject to any special rules that limit their ability to be taxed at this favorable rate.
Any dividends the Company pays to U.S. Holders generally will constitute non-U.S. source “passive category” income for U.S. foreign tax credit limitation purposes. Subject to certain generally applicable limitations (including a minimum holding period requirement), any Luxembourg tax withheld with respect to distributions made on our common shares may be treated as foreign taxes eligible for credit against a U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability. These generally applicable restrictions and conditions include new requirements adopted in Treasury regulations promulgated in December 2021, and subject to the discussion below, there can be no assurance that any taxes imposed by Luxembourg will satisfy these requirements. A recent notice from the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) provides temporary relief from such Treasury regulations by allowing taxpayers to apply a modified version of the Treasury regulations for taxable years ending before the date that a notice or other guidance withdrawing or modifying the temporary relief is issued (or any later date specified in such notice or other guidance), provided that the taxpayer consistently applies such modified version of the Treasury regulations and complies with specific requirements set forth in a previous notice. In the case of a U.S. Holder that either (i) is eligible for, and properly elects, the benefits of the tax treaty between Luxembourg and the United States or (ii) consistently elects to apply the modified version of the Treasury regulations in the manner described in the preceding sentence, the Luxembourg tax on dividends generally will qualify as a creditable tax. In the case of all other U.S. Holders, the application of these requirements to the Luxembourg tax on dividends is uncertain and we have not determined whether these requirements have been met. If the Luxembourg tax is not a creditable tax for a U.S. Holder or the U.S. Holder does not elect to claim a foreign tax credit for any foreign income taxes, the U.S. Holder may be able to deduct the Luxembourg tax in computing the U.S. Holder’s taxable income for U.S. federal income tax purposes, subject to applicable limitations and requirements. The rules governing the foreign tax credit are complex and involve the application of rules that depend upon a U.S. Holder’s particular circumstances. Accordingly, a U.S. Holder is urged to consult its tax advisor regarding the availability of the foreign tax credit under its particular circumstances.
Taxation upon sale or other disposition of common shares
A U.S. Holder generally will recognize U.S. source capital gain or loss on the sale or other disposition of common shares, which will be long-term capital gain or loss if the U.S. Holder has held such common shares for more than one year. The amount of the U.S. Holder’s gain or loss will be equal to the difference between such U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the common shares sold or otherwise disposed of and the amount realized on the sale or other disposition. Net long-term capital gains of non-corporate U.S. Holders, including individuals, are eligible for reduced rates of taxation. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations. Any gain or loss that a U.S. Holder recognizes generally will be treated as gain or loss from sources within the United States for U.S. foreign tax credit limitation purposes.
210
Passive foreign investment company rules
The Company believes that it was not a PFIC for its 2023 taxable year and does not expect to be a PFIC for its 2024 taxable year or in the foreseeable future. A non-U.S. corporation will be a PFIC in any taxable year in which, after taking into account the income and assets of the corporation and certain subsidiaries pursuant to applicable “look-through rules,” either (i) at least 75% of its gross income is “passive income” or (ii) at least 50% of the average value of its assets is attributable to assets which produce passive income or are held for the production of passive income. Although rental income generally is passive income, certain exceptions apply to allow a lessor to treat its rental income as non-passive. One exception provides that rental income earned by a lessor from leasing real property with respect to which the lessor, through its own officers or staff of employees, regularly performs active and substantial management and operational functions while the property is leased will be non-passive income. The Company believes that the rental income that it takes into account for purposes of the PFIC tests described above currently qualifies for this exception. However, because PFIC status depends upon the composition of the Company’s income and assets and the market value of its assets (including, among others, less than 25% owned equity investments) from time to time, there can be no assurance that the Company will not be considered a PFIC for any taxable year.
If the Company were a PFIC for any taxable year during which a U.S. Holder held common shares, unless the U.S. Holder makes a mark-to-market election as discussed below, gain recognized by a U.S. Holder on a sale or other disposition of a common shares would be allocated ratably over the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common shares. The amounts allocated to the taxable year of the sale or other disposition and to any year before the Company became a PFIC would be taxed as ordinary income. The amount allocated to each other taxable year would be subject to tax at the highest rate in effect for individuals or corporations, as appropriate, and an interest charge at the rates generally applicable to underpayments of tax payable in those years would be imposed on the resulting tax liability. The same treatment would apply to any distribution in respect of common shares to the extent such distribution exceeds 125% of the average of the annual distributions on common shares received by the U.S. Holder during the preceding three years or the U.S. Holder’s holding period, whichever is shorter. Certain elections may be available that would result in alternative treatments (such as mark-to-market treatment) of the common shares.
In addition, if the Company were treated as a PFIC in a taxable year in which it pays a dividend or in the prior taxable year, the reduced rate discussed above with respect to dividends paid to certain non-corporate U.S. Holders would not apply.
In certain circumstances, instead of being subject to the excess distribution rules discussed above, a U.S. Holder may make an election to include gain on the common shares of a passive foreign investment company as ordinary income under a mark-to-market method, provided that the common shares are regularly traded on a qualified exchange. Under current law, the mark-to-market election is only available for common shares that are regularly traded within the meaning of U.S. Treasury regulations on certain designated U.S. exchanges and foreign exchanges that meet trading, listing, financial disclosure and other requirements to be treated as a qualified exchange under applicable U.S. Treasury regulations. The NYSE is a qualified exchange.
If a U.S. Holder makes a mark-to-market election, the U.S. Holder will include each year as ordinary income, rather than capital gain, the excess, if any, of the fair market value of the U.S. Holder’s common shares at the end of the taxable year over such U.S. Holder’s adjusted basis in the common shares and will be permitted an ordinary loss in respect of the excess, if any, of the adjusted basis of these common shares over their fair market value at the end of the taxable year, but only to the extent of the net amount previously included in income as a result of the mark-to-market election. A U.S. Holder’s basis in the common shares will be adjusted to reflect any such income or loss amounts. Any gain or loss on the sale of the common shares will be ordinary income or loss, except that this loss will be ordinary loss only to the extent of the previously included net mark-to-market gain.
A U.S. Holder who owns, or is treated as owning, PFIC stock during any taxable year in which the Company is a PFIC may be required to file IRS Form 8621 annually. Prospective purchasers should consult their tax advisors regarding the requirement to file IRS Form 8621 and the potential application of the PFIC regime.
211
Information reporting and backup withholding
Under U.S. federal income tax law and the Treasury regulations, certain categories of U.S. Holders must file information returns with respect to their investment in, or involvement in, a foreign corporation. For example, U.S. Holders that hold certain specified foreign financial assets in excess of U.S.$50,000 are subject to U.S. return disclosure obligations (and related penalties). The definition of specified foreign financial assets includes not only financial accounts maintained in foreign financial institutions, but also, unless held in accounts maintained by a financial institution, any stock or security issued by a non-U.S. person, any financial instrument or contract held for investment that has an issuer or counterparty other than a U.S. person and any interest in a foreign entity. U.S. Holders may be subject to these reporting requirements unless their common shares are held in an account at a domestic financial institution. Penalties for failure to file certain of these information returns are substantial.
Payments of dividends and sales proceeds with respect to common shares by a U.S. paying agent or other U.S. intermediary will be reported to the IRS and to the U.S. Holder as may be required under applicable regulations. Backup withholding may apply to these payments if the U.S. Holder fails to provide a correct taxpayer identification number or certification that it is not subject to backup withholding. Certain U.S. Holders are not subject to backup withholding. The amount of any backup withholding from a payment to a U.S. Holder will be allowed as a credit against the U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability and may entitle such U.S. Holder to a refund, provided that the required information is timely furnished to the IRS. U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors about these rules and any other reporting obligations that may apply to the ownership or disposition of common shares, including requirements related to the holding of certain foreign financial assets.
Argentine Tax Considerations
The Income Tax Law contains rules on the indirect transfer of shares with effect from January 1, 2018.
As stated in the Income Tax Law, capital gains resulting from the sale or transfer by non-Argentine residents of shares or other participations in foreign entities which have been acquired on or after January 1, 2018 are taxable when the following two conditions are met: (i) 30% or more of the value of the foreign entity is derived from assets located in Argentina, and (ii) the participation being transferred represents (at the moment of the sale or transfer or during the 12 prior months) 10% or more of the equity of the foreign entity. The applicable tax rate would generally be 15% (calculated on the actual net gain or a presumed net gain equal to 90% of the sale price) of the proportional value that corresponds to the Argentine assets. However, this rate may be reduced for residents of certain jurisdictions with whom Argentina concluded a treaty for the avoidance of double taxation in force at the time of the tax event. This tax on indirect transfers only applies to participations in foreign entities acquired after the effective date of the tax reform.
Furthermore, transfers made within the same economic group are not taxable. Regulations published in December 2018 set forth that this requirement is met when (i) the transferors of the shares participate jointly, directly or indirectly, in 80% or more of the share capital of the acquirer, or (ii) one or more entities participate jointly, directly or indirectly, in 80% or more of the share capital of both the transferor and the acquirer. This requirement must be complied with for a two-year period prior to the transfer of the shares. If a subsequent transfer is then made to a third party, the acquisition cost of the shares is equal that which was computed by the original acquirer of the shares part of the economic group.
The regulations have included an anti-abuse rule which foresees that the exemption on capital gains on shares within the same economic group is not applicable when they were made with a tax oriented main purpose, including while considering the application of tax treaties.
Since our Argentine assets currently represent more than 30% of the value of our total assets on a consolidated basis, a holder that sells or transfers our common shares, acquired after January 1, 2018, would be subject to the Argentine capital gains tax to the extent such common shares represent 10% or more of our equity.
The General Resolution No. 4,227/18 issued by the Argentine Tax Authorities foresees that the tax will be payable either by: (i) the purchaser of the share capital of the foreign entity if it is an Argentine resident, or (ii) by a legal local representative or directly by the seller through an international wire transfer if the purchaser is not an Argentine tax resident.
If the recipient of the capital gain chooses to assess the tax considering the actual net gain method, the recipient shall inform the decision to the withholding agent (if applicable) and provide proof of the acquisition, sale and of what the cost and its adjustment is. The withholding agent or the legal representative, if applicable, shall keep such proof.
212
If the payment is made by a non-resident seller, the payment should be made within 10 (ten) working days as of the day of the sale. If the seller is a resident of a Non-Cooperating jurisdiction, as defined under Decree No. 862/2019, for purposes of fiscal transparency, then a 35% rate shall be applicable.
F. DIVIDENDS AND PAYING AGENTS.
Not applicable.
G. STATEMENT BY EXPERTS
Not applicable.
H. DOCUMENTS ON DISPLAY
The Company makes its filings in electronic form under the EDGAR filing system of the SEC. Its filings are available through the EDGAR system at www.sec.gov. The Company’s filings are also available to the public through the Internet at CAAP’s website at http://investors.corporacionamericaairports.com. Such filings and other information on its website are not incorporated by reference in this annual report. Interested parties may request a copy of this filing, and any other report, at no cost, by writing to the Company at the following address: 128, Boulevard de la Pétrusse, L-2330, Luxembourg, Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
I. SUBSIDIARY INFORMATION
Not applicable.
J. ANNUAL REPORT TO SECURITY HOLDERS
Not applicable.
ITEM 11. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES REGARDING MARKET RISK
We are exposed to market risks arising from our normal business activities. These market risks principally involve the possibility that exchanges in exchange rates will adversely affect the value of our financial assets and liabilities, or future cash flows and earnings. Market risk is the potential loss arising from adverse changes in market rates and prices.
For discussion and sensitivity analyses of our exposure to these risks, see Note 3.A to our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements included in this annual report.
ITEM 12. DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES OTHER THAN EQUITY SECURITIES
A. DEBT SECURITIES
Not applicable.
B. WARRANTS AND RIGHTS
Not applicable.
C. OTHER SECURITIES
Not applicable.
D. AMERICAN DEPOSITARY SHARES
Not applicable.
213
ITEM 13. DEFAULTS, DIVIDEND ARREARAGES AND DELINQUENCIES
None.
ITEM 14. MATERIAL MODIFICATIONS TO THE RIGHTS OF SECURITY HOLDERS AND USE OF PROCEEDS
Not applicable.
ITEM 15. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
A. DISCLOSURE CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (pursuant to Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of December 31, 2023. Based on this evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2023.
The Company has established disclosure controls and procedures to ensure that the information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms. Such information is accumulated and made known to the officers who certify the Company’s financial reports and to other members of senior management and the Disclosure Committee as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
The Disclosure Committee is composed of the Chief Executive Officer, Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian: the Chief Financial Officer, Jorge Arruda Filho; the Head of Legal & Compliance, Andrés Zenarruza and the Head of Investor Relations, Patricio Esnaola. This Committee oversees and reviews all materials for which there is a disclosure requirement, together with all data required to support the documents mentioned above. This committee meets at regular intervals in order to review all data.
Please see Exhibits 12.1 and 12.2 for the certifications required by this Item.
B. MANAGEMENT’S ANNUAL ASSESSMENT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
CAAP’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for CAAP as defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f). Our internal control over financial reporting was designed by management to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation and fair representation of its financial statements for external purposes in accordance with IFRS Accounting Standards adopted by International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
Because of its inherent limitation, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements or omissions. Therefore, effective control over financial reporting cannot, and does not, provide absolute assurance of achieving our control objectives. In addition, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness of the internal controls to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
CAAP’s management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of CAAP’s internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO 2013”). Based on its evaluation and as set forth in its report dated March 20, 2024, included in Item 18 of this annual report, CAAP’s management concluded that CAAP’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2023.
C. ATTESTATION REPORT OF THE REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, has been audited by Price Waterhouse & Co. S.R.L., an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which is included on page F-1 of our Audited Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
214
D. CHANGES IN INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
During the period covered under this annual report, there have not been any changes in our internal control over financial reporting that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 16. RESERVED
ITEM 16A. AUDIT COMMITTEE FINANCIAL EXPERT
See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—Board Practices—Board Committees—Audit Committee.” Our Board of Directors has determined that David Arendt qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” under applicable SEC rules.
ITEM 16B. CODE OF ETHICS
We have adopted a Corporate Governance Code and Code of Conduct and related integrity policies that applies to all subsidiaries and controlled affiliates of CAAP and to each of their respective board members, committee members, senior management, employees, interns and apprentices (hereinafter, “Colleagues”). It is also expected that all persons or entities who act as agents, partners, including business partners, representatives, intermediaries, consultants or who act on behalf of or provide services for CAAP (hereinafter “Third Parties”) will comply with such Code of Conduct. We have also adopted an additional Code of Ethics applicable to our Chief Executive Officer, the Chief Financial Officer, the Controller, Accounting & Tax Officer, or persons performing similar functions (collectively, the “Senior Financial Officers”) See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—Board Practices—Board Committees—Corporate Governance Code, Code of Conduct and Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers.”
We will provide a hard copy of those documents free of charge upon written request at the following address: 128, Boulevard de la Pétrusse, L-2330 Luxembourg, Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
ITEM 16C. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
Fees Paid to the Company’s Principal Accountant
In 2023, Price Waterhouse & Co. S.R.L. served as the principal external auditor for the Company. Fees paid to Price Waterhouse & Co. S.R.L. and other PwC member firms in 2023 and 2022 are detailed below:
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31 |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Audit fees |
|
1,871 |
|
2,202 |
Audit related fees |
|
95 |
|
40 |
Tax fees |
|
58 |
|
81 |
All other fees |
|
20 |
|
13 |
Total |
|
2,044 |
|
2,336 |
Audit Fees
Audit fees were paid for professional services rendered by the auditors for the audit of the consolidated financial statements of the Company and the statutory financial statements of the Company and its subsidiaries.
Audit-Related Fees
Audit-related fees are typically services that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of the consolidated financial statements and are not reported under the audit fee item above. This item includes fees for attestation services on financial information of the Company and its subsidiaries included in their annual reports that are filed with their respective regulators.
Tax Fees
Tax fees were paid for tax compliance and tax advice professional services.
215
All other fees
All other fees were paid for specific minor professional services not related to the above categories.
Audit Committee’s Pre-approval Policies and Procedures
The Company’s audit committee is responsible for, among other things, the oversight of the Company’s independent auditors. The audit committee has adopted a policy of pre-approval of audit and permissible non-audit services provided by its independent auditors in its charter.
Under the policy, the audit committee makes its recommendations through the Board of Directors to the shareholders’ meeting concerning the continuing appointment or termination of the Company’s independent auditors. On a yearly basis, the audit committee reviews together with management and the independent auditor, the audit plan, audit related services and other non-audit services and approves the related fees. Any changes to the approved fees must be reviewed and approved by the audit committee. In addition, the audit committee delegated to its Chairman the authority to consider and approve, on behalf of the Audit Committee, additional non-audit services that were not recognized at the time of engagement, which must be reported to the other members of the audit committee at its next meeting. No services outside the scope of the audit committee’s approval can be undertaken by the independent auditor.
Our audit committee has authorized all auditing and non-auditing services provided by our independent accountants during the year ended December 31, 2023 and the fees paid for such services.
ITEM 16D. EXEMPTIONS FROM THE LISTING STANDARDS FOR AUDIT COMMITTEES
Not applicable.
ITEM 16E. PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES BY THE ISSUER AND AFFILIATED PURCHASERS
None.
ITEM 16F. CHANGE IN REGISTRANT’S CERTIFYING ACCOUNTANT.
Not applicable.
ITEM 16G. CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Under the Corporate Governance Rules of the NYSE currently in effect, the Company is required to disclose any significant ways in which its corporate governance practices differ from those required to be followed by domestic companies under NYSE listing standards. These significant differences are summarized below.
Our corporate governance practices are governed by Luxembourg Companies Law and our articles of association. As a Luxembourg company and a foreign private issuer under the rules of the NYSE, we are required to comply with a more limited set of corporate governance rules than U.S. domestic issuers listed in the NYSE. We, however, believe that our corporate governance practices meet or exceed, in all material respects, the corporate governance standards that are generally required for U.S. domestic issuers listed in the NYSE but the following is a summary of the significant ways that our corporate governance practices differ from the corporate governance standards required by the NYSE of U.S. domestic issuers (provided that our corporate governance practices may differ in non-material ways from the standards required by the NYSE that are not detailed here):
Non-management Directors’ Meetings
Under NYSE standards, non-management directors must meet at regularly scheduled executive sessions without management present and, if such group includes directors who are not independent, a meeting should be scheduled once per year including only independent directors. Neither Luxembourg law nor our articles of association require the holding of such meetings and we do not have a set policy for these meetings. Our articles of association provide, however, that the board of directors shall meet as often as required by the interests of the Company and at least four times a year, upon notice by the chairperson or by any two directors.
216
In addition, NYSE-listed companies are required to provide a method for interested parties to communicate directly with the non-management directors as a group. While we do not have such a method, we have set up a compliance line for investors and other interested parties to communicate their concerns to members of our audit committee.
Audit Committee
Under NYSE standards, listed U.S. companies are required to have an audit committee composed of independent directors that satisfies the requirements of Rule 10A-3 promulgated under the Exchange Act. Our articles of association currently require the Company to have an audit committee. Pursuant to CAAP’s Corporate Governance Code, the audit committee is composed of three members which shall at all times comply with the independence and experience requirements set forth on Rule 10A-3 mentioned above. As of the date of this annual report, our audit committee complies with such requirements. In accordance with NYSE standards, we have an audit committee entirely composed of independent directors.
Under NYSE standards, all audit committee members of listed U.S. companies are required to be financially literate or must acquire such financial knowledge within a reasonable period and at least one of its members shall have experience in accounting or financial administration. In addition, if a member of the audit committee is simultaneously a member of the audit committee of more than three public companies, and the listed company does not limit the number of audit committees on which its members may serve, then in each case the board must determine whether the simultaneous service would prevent such member from effectively serving on the listed company’s audit committee and shall publicly disclose its decision. Although no comparable provisions on audit committee membership exist under Luxembourg law or our articles of association, these are indeed included in our Corporate Governance Code.
Standards for Evaluating Director Independence
Under NYSE standards, the board is required, on a case-by-case basis, to express an opinion with regard to the independence or lack of independence of each individual director. Neither Luxembourg law nor our articles of association require the board to express such an opinion nor to include a definition of “independent.”
Audit Committee Responsibilities
Pursuant to our articles of association, the audit committee shall assist the Board of Directors in fulfilling its oversight responsibilities relating to the integrity of the Company’s financial statements, including periodically reporting to the Board of Directors on its activity and the adequacy of the Company’s system of internal controls over financial reporting. As per the audit committee charter, as amended, the audit committee shall make recommendations for the appointment, compensation, retention and oversight of, and consider the independence of, the Company’s external auditors. The audit committee is required to review material transactions (as defined by the articles of association) between CAAP or its subsidiaries with related parties and also perform the other duties entrusted to it by the board.
The NYSE requires certain matters to be set forth in the audit committee charter of U.S. listed companies. Our audit committee charter provides for many of the responsibilities that are expected from such bodies under the NYSE standard; however, due to our equity structure and holding company nature, the charter does not contain all such responsibilities, including provisions related to setting hiring policies for employees or former employees of independent auditors, discussion of risk assessment and risk management policies, and an annual performance evaluation of the audit committee.
Shareholder Voting on Equity Compensation Plans
Under NYSE standards, shareholders must be given the opportunity to vote on equity-compensation plans and material revisions thereto, except for employment inducement awards, certain grants, plans and amendments in the context of mergers and acquisitions, and certain specific types of plans.
Disclosure of Corporate Governance Guidelines
NYSE-listed companies must adopt and disclose corporate governance guidelines. Neither Luxembourg law nor our articles of association require the adoption or disclosure of corporate governance guidelines. Our board of directors follows corporate governance guidelines consistent with our equity structure and holding company nature which are stated in our Corporate Governance Code.
217
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
Under NYSE standards, listed companies must adopt and disclose a code of business conduct and ethics for directors, officers and employees, and promptly disclose any waivers of the code for directors or executive officers. Neither Luxembourg law nor our articles of association require the adoption or disclosure of such a code of conduct. However, as stated in our Corporate Governance Code, we have adopted a Code of Conduct and related integrity policies that apply to all directors, officers and employees, which complies with the NYSE’s requirements, except that it does not require the disclosure of waivers of the code for directors and officers. In addition, we have adopted a supplementary Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers.
Chief Executive Officer Certification
A chief executive officer of a U.S. company listed on the NYSE must annually certify that he or she is not aware of any violation by the company of NYSE corporate governance standards. In accordance with NYSE rules applicable to foreign private issuers, our chief executive officer is not required to provide the NYSE with this annual compliance certification. However, in accordance with NYSE rules applicable to all listed companies, our chief executive officer must promptly notify the NYSE in writing after any of our executive officers becomes aware of any noncompliance with any applicable provision of the NYSE’s corporate governance standards. In addition, we must submit an executed written affirmation annually and an interim written affirmation each time a change occurs to the board or the audit committee.
ITEM 16H. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
ITEM 16I. DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS
Not applicable.
ITEM 16J. INSIDER TRADING POLICIES
On January 31, 2018 the Company approved its insider trading prevention policy (amended on August 22, 2018 and on March 23, 2022) which provides the guidelines to assist the members of the Board, the members of the Committees, the Senior Management, employees, interns and trainees of the Company and anyone who by his job, profession or function has access to non-public information of CAAP, to comply with their obligations under the securities and exchange laws and regulations of the Company’s jurisdiction and the jurisdictions in which the Company’s securities are traded. A copy of our insider trading prevention policy is attached hereto as Exhibit No. 11.1.
ITEM 16K. CYBERSECURITY
Definitions
For purposes of this section, “Cybersecurity Incident” means a violation, or imminent threat of violation, of our systems’ information confidentiality, integrity, or availability, including of our third-party service providers, or any violation of computer security policies, or acceptable use policies, or any cybersecurity event that could have a negative impact on our reputation, operations, or financial position.
Risk management and strategy
On November 15, 2023, the Board approved the Information Security Incident Management Policy (the “Cybersecurity Policy”) which establishes guidelines to identify, assess, manage and communicate material risks from cybersecurity incidents. The Cybersecurity Policy is applicable to the Company and its subsidiaries’ information systems and supporting infrastructure in all locations. It also covers processes to oversee and identify risks from cybersecurity threats associated with the use of third-party service providers, being an important part of the Company’s global risk management strategy. In addition to the Cybersecurity Policy, the Company has enacted a cybersecurity risk matrix (the “Cybersecurity Risk Matrix”) to determine cybersecurity risks and align projects to address such risks. Therefore, our actions, plans and projects are aligned with the risks identified within such Cybersecurity Risk Matrix which is reviewed annually by information security officers and authorized by the corporate information security manager.
218
All strategic information security projects are established in a global strategic plan, based on the analysis of the risks determined and classified in accordance with the Cybersecurity Risk Matrix. Critical risks are addressed by a combination of security services and technology. Also, a global security operation center and an incident response and threat intelligence service are in place. A combination of information security applications and monitoring controls are also used to detect and protect the information assets based on protection layers criteria. Global penetration testing and security reviews are regularly performed in our subsidiaries.
Also, the Cybersecurity Policy created the Information Security Incident Response Committee (the “ISIRC”) which is a non-permanent body, mainly responsible for coordinating and authorizing the strategy and tasks to contain a Cybersecurity Incident and restore normal operation. The members of the ISIRC are:
| (a) | local IT Manager/Responsible (of the involved subsidiary); |
| (b) | an Information Security Specialist (local and/or corporate); |
| (c) | the Head of Legal and Compliance (representing our Executive Committee); and |
| (d) | if necessary, members of other technology-related teams, or members of our Executive Committee or other members of senior management shall be included. |
According to the Cybersecurity Policy, Cybersecurity Incidents must be classified by the local security manager from a technical perspective in critical, high, medium, low, or very low based on the Incident Impact Calculation Matrix. Such classification is reviewed by the ISIRC, from a qualitative and quantitative perspective, and considers factors that are not taken into account in a mathematical calculation, in order to determine the severity of the incident.
The Cybersecurity Policy establishes an incident management process, which can be defined as a plan to manage Cybersecurity Incident and ensures that the Company takes immediate action in case of any incidents. The incident management process consists of the following phases: (i) detection; (ii) analysis and early communication; (iii) containment; (iv) eradication; (v) recovery; (vi) documentation and improvement proposals; and (vii) disclosure.
The phase of “detection” involves (i) data gathering and analysis; (ii) identification of indicators of an attack or compromise of the network; and (iii) correlating events and having the intelligence to identify early signs of an attack. Examples of detectable events include data breaches, an unusual number of locked accounts, encrypted files, among others. Upon detection of a Cybersecurity Incident, such incident is immediately reported to the Local Cybersecurity Manager/Responsible who then convenes an ISIRC meeting. As per the Cybersecurity Policy, once a Cybersecurity Incident is identified, the Local Cybersecurity Manager/Responsible shall classify it from a technical perspective based on the Incident Impact Calculation Matrix, prepare the corresponding Cybersecurity Incident Report and create a record of the information and documentation related to the incident. All the information related to the Cybersecurity Incident is then submitted to the ISIRC which shall review the classification provided by the Local Cybersecurity Manager/Responsible and define the severity of the incident.
The Cybersecurity Incidents which individually or in the aggregate are classified by the ISIRC as critical or high, must be reported by the ISIRC to our Executive Committee, which shall analyze if the incident must be disclosed. The Cybersecurity Policy also establishes that in case of detection of any Cybersecurity Incident, it shall be immediately reported to the local cybersecurity officer (local or corporate), who will call an ISIRC meeting. In case of critical or high incident, the Executive Committee must then report it to the Board of Directors of the Company.
In relation to the “containment” strategy, the Cybersecurity Policy establishes that it is dependent on the type of attack and its potential impact on the organization. In any case, after the Cybersecurity Incident has been successfully contained, any element or change produced because of the Cybersecurity Incident must be repaired. This could include, rebuilding affected servers, removing malware, or closing and resetting passwords of breached accounts.
On the phase of “recovery”, every affected system should be restored in order to reinstate regular operations.
219
After receiving information from the ISIRC, the Executive Committee must determine if a Cybersecurity Incident is material, or if any series of related Cybersecurity Incidents taken together are material, in which case it must decide the necessity and extent of any ongoing and annual disclosures. In order to determine the materiality of a Cybersecurity Incident or series of related cybersecurity incidents taken together, our Executive Committee must evaluate the impact of such incident from a quantitative and a qualitative perspective, as well as, if there is a substantial likelihood that a reasonable investor would have considered it important in making an investment decision or if it significantly alters the total mix of available information. As part of the materiality analysis, our Executive Committee may consider both the immediate fallout and any longer-term effects, including on our operations, finances, brand, reputation and customer relationships. If the Executive Committee deems it necessary, could report the Cybersecurity Incident to our Board of Directors, to be involved in the determination of materiality of the incident.
The Head of Legal and Compliance leads the disclosure process if the Cybersecurity Incident is material. In accordance with the terms and conditions of our third-party agreements, our providers are obliged to inform us immediately in the case of detection of a Cybersecurity Incident that could involve the Company in any manner, in which case the local cybersecurity manager must call a ISIRC who must define if it should be reported to the Executive Committee to determine if it is material.
Finally, although our business strategy, results of operations or financial condition have not been materially affected by Cybersecurity Incidents up to this date, we understand that the cybersecurity risks have been increasing, especially as infiltrating technology continues to become increasingly sophisticated, and while we have implemented several measures and procedures to mitigate such risk, such as the Cybersecurity Policy, we must remain vigilant and alert to such risks and keep our systems and procedures updated to the most recent trends.
For further information about the potential cybersecurity risks of the Company and how they could affect the Company, see “Item 3. Key Information—Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business and Industry—We are dependent on information and communication technologies, and our systems and infrastructures face certain risks, including cybersecurity risks.”
Governance
The Information Security Department of the Company (the “Information Security Department”) is responsible for implementing and maintaining an organization-wide information security framework, from the perspective of normative governance (policies, standards, and procedures) but also from the technological capabilities to achieve the necessary security standards to minimize the risk of the Company from cyber security attacks.
The Information Security Department reports to the Executive Committee through the Head of Legal and Compliance. The Head of Legal and Compliance is technically and strategically assisted by the Information Security Corporate Manager, who is also supported by a specialized group of information technology and security engineers and highly specialized worldwide leaders and researchers. See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—A. Directors and Senior Management—Background of Our Officers and Directors.”
The Information Security Corporate Manager has more than twenty years of progressive experience in all aspects of technology risk management, and has a deep understanding of strategic and tactical aspects of information technology security, internal control over information technology and operational processes over critical assets and infrastructure. The Information Security Corporate Manager is experienced in aspects as a comprehensive access management strategy, cybersecurity monitoring and governance, awareness programs, business continuity strategy, information technology general controls under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, among others.
The Information Security Plan, Budget and strategic projects are presented and explained, at least once per year, to the Board of Directors.
The Board of Directors has also decided to include cybersecurity as a permanent item of the agenda of its meetings and to receive a report with a summary of any cybersecurity event, even not material, on a quarterly basis. Additionally, and as required by internal policies, the Board of Directors must be informed of any critical or high impact security incident detected at any time.
Finally, in terms of governance, it is worth pointing out the role of the ISIRC, non-permanent body responsible for overseeing the risk management’s efforts and strategy of the Company in the event of a Cybersecurity Incident. The members of the ISIRC are mentioned above.
ITEM 17. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The Company has responded to Item 18 in lieu of responding to this item.
220
ITEM 18. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(1) |
Financial Statements |
Corporación América Airports S.A.
Audited Consolidated Financial Statements
221
ITEM 19. EXHIBITS
(b) List of Exhibits
The following exhibits are filed or incorporated by reference as part of this annual report:
Exhibit |
|
Description |
1.1. |
|
Amended Articles of Association of Corporacion America Airports S.A., as amended in May 2023* |
2.2 |
|
|
8.1. |
|
|
11.1 |
|
|
12.1. |
|
|
12.2. |
|
|
13.1. |
|
|
13.2. |
|
|
23 |
|
|
97 |
|
|
101.INS |
|
XBRL Instance Document. |
101.SCH |
|
iXBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
101.CAL |
|
iXBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
101.DEF |
|
iXBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
101.LAB |
|
iXBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
101.PRE |
|
iXBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
* |
Incorporated by reference, to the annual report on Form 20-F filed by Corporación América Airports S.A. on April 9, 2021 (File No. 001-38354). |
222
SIGNATURES
The registrant hereby certifies that it meets all of the requirements for filing Form 20-F and that it has duly caused and authorized the undersigned to sign this annual report on its behalf.
|
CORPORACIÓN AMERICA AIRPORTS S.A. |
|
|
|
|
|
By: |
/s/ Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
Name: |
Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
Title: |
Chief Executive Officer |
|
|
|
|
By: |
/s/ Jorge Arruda Filho |
|
Name: |
Jorge Arruda Filho |
|
Title: |
Chief Financial Officer |
|
|
|
Dated: March 28, 2024 |
|
|
223

Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of Corporación América Airports S.A.
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statement of financial position of Corporación América Airports S.A. and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). We also have audited the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023 in conformity with IFRS Accounting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the COSO.
Basis for Opinions
The Company’s management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management's Annual Assessment on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 15B. Our responsibility is to express opinions on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
Price Waterhouse & Co. S.R.L., Bouchard 557, 8th floor, C1106ABG - City of Buenos Aires
F-1

Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
T: +(54.11) 4850.0000, F: +(54.11) 4850.1800, www.pwc.com/ar A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (i) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the consolidated financial statements and (ii) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Brazilian Concession Assets Impairment Assessment
As described in Notes 2.D(1), 2X(a) and 12 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company’s consolidated concession assets balance was USD 2,508 million as of December 31, 2023, out of which USD 688.7 million correspond to the Brazilian Concession assets. Management reviews the carrying amounts of its property, plant and equipment and intangible assets with finite useful lives to determine whether there is any indication that those assets have suffered an impairment loss. For the purposes of assessing impairment, assets are grouped at the lowest levels for which there are largely independent cash inflows (cash-generating units or CGUs). Management performed impairment test for the Brazilian Concession assets (Brazilian CGU) based on the discounted cash flow model (value in use), considering significant assumptions related to passenger growth rates and discount rate.
F-2

The principal considerations for our determination that performing procedures relating to the Brazilian concession assets impairment assessment is a critical audit matter is the significant judgment applied by management when developing the value in use measurement of Brazilian CGU. This in turn led to a high degree of auditor judgment, subjectivity, and effort in performing procedures to evaluate management’s cash flow projections and significant assumptions related to passenger growth rates and the discount rate. In addition, the audit effort involved the use of professionals with specialized skill and knowledge to assist in performing these procedures and evaluating the audit evidence obtained.
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the consolidated financial statements. These procedures included testing the effectiveness of controls relating to management’s concession assets impairment assessments, including controls over the valuation of Brazilian CGU. These procedures also included, among others, testing management’s process for developing the value in use estimate; evaluating the appropriateness of the discounted cash flow model; testing the completeness, accuracy, and relevance of underlying data used in the model; and evaluating the significant assumptions used by management related to passenger growth rates and the discount rate. Evaluating management’s assumptions related to passenger growth rates and discount rate involved evaluating whether the assumptions used by management were reasonable considering (i) the current and past performance of the Brazilian CGU, (ii) the consistency with external market and industry data, and (iii) whether these assumptions were consistent with evidence obtained in other areas of the audit. Professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in the evaluation of the Company’s discounted cash flow model and the discount rate assumption.
/s/ Price Waterhouse & Co. S.R.L.
/s/ Juan Manuel Gallego Tinto
Partner
Buenos Aires, Argentina
March 20, 2024
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2017.
F-3
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
CAAP’s Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for CAAP as defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f). Our internal control over financial reporting was designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with IFRS Accounting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board. Internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
● pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of CAAP Group;
● provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with IFRS and that receipts and expenditures of CAAP Group are being made only in accordance with authorizations of Management and directors of CAAP Group; and
● provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of CAAP Group’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of CAAP Group’s internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control – Integrated Framework 2013 issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO 2013”). Based on its evaluation, Management concluded that the CAAP Group’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2023. The effectiveness of CAAP Group’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023 has been audited by Price Waterhouse & Co S.R.L., an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which is included herein.
Montevideo, Uruguay
March 20, 2024
By: |
/s/ Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
By: |
/s/ Jorge Arruda Filho |
Name: Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
Name: Jorge Arruda Filho |
||
Title: Chief Executive Officer |
|
Title: Chief Financial Officer |
||
F-4
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
Corporación América Airports S.A.
CONSOLIDATED
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022
and for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
R.C.S. Luxembourg B 174.140
128, Boulevard de la Pétrusse
L – 2330 Luxembourg
F-5
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF INCOME
|
|
|
|
For the year |
|
For the year |
|
For the year |
|
|
|
|
ended |
|
ended |
|
ended |
|
|
Notes |
|
December 31, 2023 |
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
December 31, 2021 |
Continuing operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
5 |
|
1,400,038 |
|
1,378,663 |
|
706,913 |
Cost of services |
|
6 |
|
(914,677) |
|
(962,978) |
|
(622,381) |
Gross profit |
|
|
|
485,361 |
|
415,685 |
|
84,532 |
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
7 |
|
(138,669) |
|
(141,355) |
|
(102,062) |
Impairment reversal / (loss) of non-financial assets |
|
12 |
|
102,838 |
|
(111) |
|
(371) |
Other operating income |
|
8 |
|
100,560 |
|
37,340 |
|
42,777 |
Other operating expense |
|
|
|
(9,453) |
|
(6,984) |
|
(18,416) |
Operating income |
|
|
|
540,637 |
|
304,575 |
|
6,460 |
Share of income / (loss) in associates |
|
10,15 |
|
7,108 |
|
(970) |
|
(629) |
Income before financial results and income tax |
|
|
|
547,745 |
|
303,605 |
|
5,831 |
Financial income |
|
9 |
|
101,598 |
|
63,859 |
|
28,080 |
Financial loss |
|
9 |
|
(406,570) |
|
(196,405) |
|
(131,271) |
Inflation adjustment |
|
9 |
|
(40,547) |
|
19,459 |
|
6,691 |
Income / (loss) before income tax |
|
|
|
202,226 |
|
190,518 |
|
(90,669) |
Income tax |
|
11 |
|
24,241 |
|
(24,883) |
|
(69,111) |
Income / (loss) from continuing operations |
|
|
|
226,467 |
|
165,635 |
|
(159,780) |
Loss from discontinued operations |
|
31 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(21,196) |
Income / (loss) for the year |
|
|
|
226,467 |
|
165,635 |
|
(180,976) |
Attributable to: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Owners of the parent |
|
|
|
239,506 |
|
168,166 |
|
(117,755) |
Non-controlling interest |
|
|
|
(13,039) |
|
(2,531) |
|
(63,221) |
|
|
|
|
226,467 |
|
165,635 |
|
(180,976) |
Earnings per share for profit from continuing operations attributable to the ordinary equity holders of the Group: |
|
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic earnings per share |
|
|
|
1.49 |
|
1.05 |
|
(0.60) |
Diluted earnings per share |
|
|
|
1.49 |
|
1.05 |
|
(0.60) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings per share for profit attributable to the ordinary equity holders of the Group: |
|
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic earnings per share |
|
|
|
1.49 |
|
1.05 |
|
(0.73) |
Diluted earnings per share |
|
|
|
1.49 |
|
1.05 |
|
(0.73) |
F-5
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
|
|
|
|
For the year |
|
For the year |
|
For the year |
|
|
|
|
ended |
|
ended |
|
ended |
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2023 |
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
December 31, 2021 |
Income / (loss) for the year |
|
|
|
226,467 |
|
165,635 |
|
(180,976) |
Items that will not be reclassified to profit or loss: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remeasurement of defined benefit obligation |
|
|
|
4 |
|
859 |
|
28 |
Items that may be reclassified to profit or loss: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share of other comprehensive (loss) / income from associates |
|
15 |
|
(70) |
|
43 |
|
55 |
Currency translation adjustment |
|
|
|
(281,684) |
|
91,105 |
|
137,719 |
Other comprehensive (loss) / income from continuing operations for the year, net of income tax |
|
|
|
(281,750) |
|
92,007 |
|
137,802 |
Currency translation adjustment from discontinued operations |
|
31 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
920 |
Other comprehensive income from discontinued operations for the year, net of income tax |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
920 |
Other comprehensive (loss) / income for the year |
|
|
|
(281,750) |
|
92,007 |
|
138,722 |
Total comprehensive (loss) / income for the year |
|
|
|
(55,283) |
|
257,642 |
|
(42,254) |
Attributable to: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Owners of the parent |
|
|
|
7,818 |
|
239,015 |
|
(22,132) |
Non-controlling interest |
|
|
|
(63,101) |
|
18,627 |
|
(20,122) |
|
|
|
|
(55,283) |
|
257,642 |
|
(42,254) |
Total comprehensive income / (loss) for the year attributable to owners of the parent arises from: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Continuing operations |
|
|
|
7,818 |
|
239,015 |
|
(1,856) |
Discontinued operations |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
(20,276) |
|
|
|
|
7,818 |
|
239,015 |
|
(22,132) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-6
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION
|
|
|
|
At |
|
At |
|
|
Notes |
|
December 31, 2023 |
|
December 31, 2022 |
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intangible assets, net |
|
12 |
|
2,520,965 |
|
2,960,002 |
Property, plant and equipment, net |
|
13 |
|
74,919 |
|
74,742 |
Right-of-use asset |
|
14 |
|
10,493 |
|
9,192 |
Investments in associates |
|
15 |
|
11,992 |
|
1,911 |
Other financial assets at fair value through profit or loss |
|
20 |
|
5,979 |
|
3,160 |
Other financial assets at amortized cost |
|
20 |
|
61,090 |
|
3,764 |
Derivative financial instruments |
|
|
|
69 |
|
67 |
Deferred tax assets |
|
16 |
|
62,712 |
|
54,882 |
Inventories |
|
18 |
|
318 |
|
254 |
Other receivables |
|
17 |
|
42,640 |
|
78,765 |
Trade receivables |
|
19 |
|
889 |
|
1,581 |
|
|
|
|
2,792,066 |
|
3,188,320 |
Current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inventories |
|
18 |
|
16,148 |
|
15,765 |
Other financial assets at fair value through profit or loss |
|
20 |
|
4,884 |
|
12,792 |
Other financial assets at amortized cost |
|
20 |
|
83,142 |
|
53,905 |
Other receivables |
|
17 |
|
145,549 |
|
57,800 |
Current tax assets |
|
|
|
3,779 |
|
10,852 |
Trade receivables |
|
19 |
|
126,560 |
|
111,089 |
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
21 |
|
369,848 |
|
385,265 |
|
|
|
|
749,910 |
|
647,468 |
Total assets |
|
|
|
3,541,976 |
|
3,835,788 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EQUITY |
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
Share capital |
|
|
|
163,223 |
|
163,223 |
Share premium |
|
|
|
183,430 |
|
183,430 |
Treasury shares |
|
|
|
(4,322) |
|
(4,600) |
Free distributable reserve |
|
|
|
378,910 |
|
378,910 |
Non-distributable reserve |
|
|
|
1,358,028 |
|
1,358,028 |
Currency translation adjustment |
|
|
|
(482,852) |
|
(251,145) |
Legal reserves |
|
|
|
3,676 |
|
1,081 |
Other reserves |
|
|
|
(1,313,888) |
|
(1,314,025) |
Retained earnings |
|
|
|
438,775 |
|
201,193 |
Total attributable to owners of the parent |
|
|
|
724,980 |
|
716,095 |
Non-controlling interests |
|
|
|
78,929 |
|
146,274 |
Total equity |
|
|
|
803,909 |
|
862,369 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Borrowings |
|
22 |
|
1,133,549 |
|
1,287,421 |
Deferred tax liabilities |
|
16 |
|
137,315 |
|
232,458 |
Other liabilities |
|
23 |
|
768,364 |
|
768,383 |
Lease liabilities |
|
14 |
|
10,294 |
|
5,531 |
Trade payables |
|
24 |
|
2,617 |
|
3,307 |
|
|
|
|
2,052,139 |
|
2,297,100 |
Current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Borrowings |
|
22 |
|
199,688 |
|
178,016 |
Other liabilities |
|
23 |
|
345,864 |
|
357,078 |
Lease liabilities |
|
14 |
|
3,687 |
|
3,278 |
Derivative financial instruments liabilities |
|
|
|
— |
|
51 |
Current tax liabilities |
|
|
|
23,921 |
|
13,794 |
Trade payables |
|
24 |
|
112,768 |
|
124,102 |
|
|
|
|
685,928 |
|
676,319 |
Total liabilities |
|
|
|
2,738,067 |
|
2,973,419 |
Total equity and liabilities |
|
|
|
3,541,976 |
|
3,835,788 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-7
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
|
|
Attributable to owners of the parent |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Free |
|
Non- |
|
|
|
Currency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share |
|
Share |
|
Treasury |
|
distributable |
|
distributable |
|
Legal |
|
translation |
|
Other |
|
Retained |
|
|
|
Non-controlling |
|
|
|
|
capital |
|
premium |
|
shares |
|
reserves |
|
reserves |
|
reserves |
|
adjustment |
|
reserves |
|
earnings (1) |
|
Total |
|
interests |
|
Total |
Balance at January 1, 2023 |
|
163,223 |
|
183,430 |
|
(4,600) |
|
378,910 |
|
1,358,028 |
|
1,081 |
|
(251,145) |
|
(1,314,025) |
|
201,193 |
|
716,095 |
|
146,274 |
|
862,369 |
Income / (loss) for the year |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
239,506 |
|
239,506 |
|
(13,039) |
|
226,467 |
Shareholders contributions (Note 25.e) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
9,424 |
|
9,424 |
Share-based payments reserve (Notes 25.a, 25.c and 30) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
278 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
106 |
|
671 |
|
1,055 |
|
— |
|
1,055 |
Other comprehensive income / (loss) for the year (Note 25.d) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(231,707) |
|
19 |
|
— |
|
(231,688) |
|
(50,062) |
|
(281,750) |
Transfer to legal reserve |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2,595 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(2,595) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Changes in non-controlling interests (Note 25.c and 25.e) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
12 |
|
— |
|
12 |
|
(13,668) |
|
(13,656) |
Balance at December 31, 2023 |
|
163,223 |
|
183,430 |
|
(4,322) |
|
378,910 |
|
1,358,028 |
|
3,676 |
|
(482,852) |
|
(1,313,888) |
|
438,775 |
|
724,980 |
|
78,929 |
|
803,909 |
Balance at January 1, 2022 |
|
163,223 |
|
183,430 |
|
(4,772) |
|
378,910 |
|
1,358,028 |
|
1,081 |
|
(321,647) |
|
(1,321,211) |
|
32,689 |
|
469,731 |
|
303,877 |
|
773,608 |
Income / (loss) for the year |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
168,166 |
|
168,166 |
|
(2,531) |
|
165,635 |
Shareholders contributions (Note 25.e) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
24,170 |
|
24,170 |
Share-based payments reserve (Notes 25.a, 25.c and 30) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
172 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
157 |
|
338 |
|
667 |
|
— |
|
667 |
Redemption of preferred shares (Notes 25.f) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(182,336) |
|
(182,336) |
Other comprehensive income for the year (Note 25.d) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
70,502 |
|
347 |
|
— |
|
70,849 |
|
21,158 |
|
92,007 |
Changes in non-controlling interests (Note 25.c and 25.e) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
6,682 |
|
— |
|
6,682 |
|
(18,064) |
|
(11,382) |
Balance at December 31, 2022 |
|
163,223 |
|
183,430 |
|
(4,600) |
|
378,910 |
|
1,358,028 |
|
1,081 |
|
(251,145) |
|
(1,314,025) |
|
201,193 |
|
716,095 |
|
146,274 |
|
862,369 |
Balance at January 1, 2021 |
|
163,223 |
|
183,430 |
|
(6,145) |
|
378,910 |
|
1,358,028 |
|
176 |
|
(417,272) |
|
(1,321,142) |
|
150,202 |
|
489,410 |
|
315,876 |
|
805,286 |
Loss for the year |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(117,755) |
|
(117,755) |
|
(63,221) |
|
(180,976) |
Shareholders contributions (Note 25.e) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
11,475 |
|
11,475 |
Transfer to legal reserve |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
905 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(905) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Share-based payments reserve (Notes 25.a, 25.c and 30) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1,373 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(1,500) |
|
1,147 |
|
1,020 |
|
— |
|
1,020 |
Other comprehensive income / (loss) for the year (Note 25.d) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
95,625 |
|
(2) |
|
— |
|
95,623 |
|
43,099 |
|
138,722 |
Changes in non-controlling interests (Note 25.c and 25.e) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1,433 |
|
— |
|
1,433 |
|
(3,352) |
|
(1,919) |
Balance at December 31, 2021 |
|
163,223 |
|
183,430 |
|
(4,772) |
|
378,910 |
|
1,358,028 |
|
1,081 |
|
(321,647) |
|
(1,321,211) |
|
32,689 |
|
469,731 |
|
303,877 |
|
773,608 |
(1) Retained Earnings calculated according to Luxembourg Law are disclosed in Note 26.c.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-8
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
|
|
|
|
For the year ended |
|
For the year ended |
|
For the year ended |
|
|
Notes |
|
December 31, 2023 |
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
December 31, 2021 |
Cash flows from operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income / (loss) for the year from continuing operations |
|
|
|
226,467 |
|
165,635 |
|
(159,780) |
Adjustments for: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization and depreciation |
|
12,13,14 |
|
151,593 |
|
172,480 |
|
160,633 |
Deferred income tax |
|
11 |
|
(62,697) |
|
4,415 |
|
50,027 |
Current income tax |
|
11 |
|
38,456 |
|
20,468 |
|
19,084 |
Share of loss in associates |
|
10 |
|
(7,108) |
|
970 |
|
629 |
Impairment (reversal) / loss of non-financial assets reversal |
|
12 |
|
(102,838) |
|
111 |
|
371 |
Income due to concession compensation |
|
8 |
|
(62,677) |
|
— |
|
— |
Loss on disposals of property, plant and equipment and intangible assets |
|
|
|
592 |
|
420 |
|
139 |
Gain on disposal of subsidiaries |
|
|
|
— |
|
(4,186) |
|
— |
Low value, short term and variable lease payments |
|
|
|
(3,082) |
|
(1,154) |
|
(1,204) |
Share-based compensation expenses |
|
30 |
|
1,055 |
|
667 |
|
1,020 |
Interest expense |
|
9 |
|
95,185 |
|
164,288 |
|
125,533 |
Other financial results, net |
|
|
|
(41,558) |
|
(41,055) |
|
(19,157) |
Net foreign exchange |
|
9 |
|
164,026 |
|
(90,603) |
|
(113,609) |
Government subsidies per Covid-19 context |
|
8 |
|
(21,511) |
|
(14,133) |
|
(33,366) |
Government grants collected |
|
|
|
383 |
|
10,020 |
|
11,790 |
Other accruals |
|
|
|
3,145 |
|
(5,043) |
|
7,450 |
Inflation adjustment |
|
|
|
54,170 |
|
6,969 |
|
(17,727) |
Acquisition of Intangible assets |
|
12,29 |
|
(149,436) |
|
(154,940) |
|
(83,212) |
Income tax paid |
|
|
|
(22,919) |
|
(22,631) |
|
(2,871) |
Unpaid concession fees |
|
|
|
49,992 |
|
46,084 |
|
65,360 |
Changes in liability for concessions |
|
9 |
|
98,480 |
|
101,488 |
|
109,103 |
Changes in working capital |
|
29 |
|
(53,303) |
|
(57,641) |
|
(12,255) |
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
|
|
356,415 |
|
302,629 |
|
107,958 |
Net cash used in discontinued operating activities |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from investing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash contribution in associates |
|
15 |
|
(84) |
|
(260) |
|
(741) |
Net acquisition of subsidiaries companies |
|
26.b |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(1,134) |
Net disposal of subsidiaries companies |
|
|
|
— |
|
(406) |
|
— |
Acquisition of other financial assets |
|
|
|
(128,899) |
|
(150,856) |
|
(37,120) |
Disposals of other financial assets |
|
|
|
72,571 |
|
170,235 |
|
55,207 |
Acquisition of Property, plant and equipment |
|
|
|
(9,661) |
|
(9,091) |
|
(7,665) |
Acquisition of Intangible assets |
|
12 |
|
(1,221) |
|
(732) |
|
(851) |
Proceeds from sale of Property, plant and Equipment |
|
|
|
264 |
|
233 |
|
535 |
Others |
|
|
|
626 |
|
263 |
|
1,395 |
Net cash (used in) / provided by investing activities |
|
|
|
(66,404) |
|
9,386 |
|
9,626 |
Net cash used in discontinued investing activities |
|
|
|
— |
|
(14,700) |
|
(2,495) |
Cash flows from financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from cash contributions |
|
25.e |
|
9,424 |
|
24,170 |
|
11,475 |
Proceeds from borrowings |
|
22 |
|
87,846 |
|
371,951 |
|
366,544 |
Principal elements of lease payments |
|
14 |
|
(3,118) |
|
(4,307) |
|
(4,729) |
Loans repaid |
|
22 |
|
(200,475) |
|
(328,775) |
|
(266,839) |
Interest paid |
|
22 |
|
(83,791) |
|
(111,387) |
|
(86,108) |
Debt renegotiation expenses capitalization |
|
22 |
|
(110) |
|
(2,011) |
|
(20,439) |
Debt renegotiation premium |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
(193) |
Guarantee deposit |
|
|
|
2,168 |
|
(512) |
|
(1,015) |
Dividends paid to non-controlling interests in subsidiaries |
|
25.e |
|
(13,656) |
|
(11,382) |
|
(2,361) |
Redemption of preferred shares |
|
25.f |
|
— |
|
(172,029) |
|
— |
Others |
|
|
|
86 |
|
(6) |
|
(4) |
Net cash used in financing activities |
|
|
|
(201,626) |
|
(234,288) |
|
(3,669) |
Net cash used in discontinued financing activities |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
88,385 |
|
77,727 |
|
113,915 |
Decrease in cash and cash equivalents from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
— |
|
(14,700) |
|
(2,495) |
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At the beginning of the year |
|
21 |
|
385,265 |
|
375,783 |
|
281,031 |
Effects of exchange rate changes and inflation adjustment on cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
(103,802) |
|
(53,545) |
|
(16,668) |
Increase in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
88,385 |
|
77,727 |
|
113,915 |
Decrease in cash and cash equivalents from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
— |
|
(14,700) |
|
(2,495) |
At the end of the year |
|
21 |
|
369,848 |
|
385,265 |
|
375,783 |
Information of non-cash transactions has been disclosed in Note 29.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-9
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
INDEX TO THE NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1 |
General information and significant event of the year |
2 |
Basis of presentation and accounting policies |
3 |
Financial risk management |
4 |
Segment information |
5 |
Revenue |
6 |
Cost of services |
7 |
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
8 |
Other operating income |
9 |
Financial results, net |
10 |
Share of results in associates |
11 |
Income tax |
12 |
Intangible assets, net |
13 |
Property, plant and equipment, net |
14 |
Leases |
15 |
Investments in associates |
16 |
Deferred income tax |
17 |
Other receivables |
18 |
Inventories |
19 |
Trade receivables |
20 |
Other financial assets |
21 |
Cash and cash equivalents |
22 |
Borrowings |
23 |
Other liabilities |
24 |
Trade payables |
25 |
Equity |
26 |
Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits |
27 |
Related party balances and transactions |
28 |
Business combinations, other acquisitions and investments |
29 |
Cash flow disclosures |
30 |
Share - based payments |
31 |
Discontinued operations |
32 |
Earnings per share |
33 |
Restricted net assets |
34 |
Subsequent events |
35 |
Condensed financial information of the Company |
F-10
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
1 General information and significant event of the year
1.1 General Information
Corporación América Airports S.A. (the “Company” or “CAAP”) is a holding company primarily engaged through its operating subsidiaries in the acquisition, development and operation of airport concessions. The Company and its operating subsidiaries are collectively referred to hereinafter as the “Group”.
The Company’s shares trade on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the symbol “CAAP”.
The Company was formed as a private limited liability company under the laws of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg on December 14, 2012. The Company is ultimately controlled by Southern Cone Foundation (“SCF”), a foundation organized under the laws of the Principality of Liechtenstein. The address of its registered office is in Vaduz.
The Company’s registered office address is 128, Boulevard de la Pétrusse, Luxembourg.
The Group currently has operations in Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay, Armenia, Italy, and Ecuador.
The fiscal year begins on January 1 and ends on December 31.
These Consolidated Financial Statements have been approved for issuance by the Board of Directors on March 20, 2024.
1.2 Significant event of the year
1.2.1 Re-bidding of the International Airport of São Gonçalo do Amarante (“Natal Airport”)
On March 5, 2020, CAAP announced that its subsidiary Inframérica Concessionária do Aeroporto de São Gonçalo do Amarante S.A. (“ICASGA”) filed a request to the Agência Nacional de Aviação Civil (“the Brazilian ANAC”) to commence the re-bidding process of the Natal Airport, pursuant to Law No. 13,448 of July 5, 2017, and the Brazilian ANAC Resolution No. 533 of November 7, 2019.
On May 26, 2020, the Brazilian ANAC confirmed the technical and legal feasibility of the request regarding the re-bidding process initiated by ICASGA. On June 3, 2020, the process was approved by the Ministério da Infraestrutura, and on June 10, 2020, the Conselho do Programa de Parcerias de Investimentos of the Ministério da Economia expressed a favorable opinion and submitted the request for proposal for re-bidding to the President of Brazil.
On August 24, 2020, Natal Airport was qualified to go through the re-bidding process. On November 20, 2020, ICASGA and the Brazilian ANAC signed a concession agreement amendment setting forth the rules and proceedings for the re-bidding (the “Amendment”) and the re-bidding process became irrevocable and irreversible. The Amendment imposed restrictions on the ICASGA’s actions, such as making investments, acquisition or disposal of reversible assets, without the prior express consent of the Brazilian ANAC.
However, despite the fact that ICASGA may no longer hold the right to operate Natal Airport until the end of the original term the re-bidding process was not effective until certain aspects beyond ICASGA’s control were confirmed, namely; i) that the re-bidding procedure for determining the new concessionaire be successfully completed and ii) that the bid offered by the winner of the bidding process be sufficient to pay the indemnity owed by the Brazilian ANAC to ICASGA.
The auction successfully took place on May 19, 2023. On September 12, 2023, a contract between the new concessionaire and the Brazilian ANAC was signed, starting the process of approval of the compensation payment to ICASGA. However, the conclusion of the re-bidding process was still uncertain, given that the amount determined by the new offer was not sufficient to pay the indemnity owing to ICASGA in full and the Brazilian legislation did not allow the Government to pay the outstanding balance unless there was a specific budget approval.
F-11
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
General information and significant event of the year (Cont.)
1.2 Significant event of the year (Cont.)
1.2.1 Re-bidding of the International Airport of São Gonçalo do Amarante (“Natal Airport”) (Cont.)
The residual part of the budget was finally approved by the National Congress and endorsed by the President of Brazil on December 27, 2023 crystalizing a final gross indemnification of R$ 609.5 million (equivalent to USD 125.9 million).
Considering that all conditions for the concession agreement amended to be effective were met, as of December 31, 2023, a net gain of USD 166.5 million was recognized in ICASGA, mainly due to a gain for the reversal of impairment losses recognized in previous periods over intangible assets of USD 103.8 million (Note 12) and other operating income that includes the compensation for the assets and liabilities of the concession for a total of USD 62.7 million (Note 8). The related concession assets, including the concession intangible asset, and liabilities were derecognized as of December 31, 2023. The transaction did not have an impact on income tax as unrecognized tax loss carry forwards were used to compensate the current tax expense for an amount of approximately R$ 36.8 million (equivalent to USD 7.4 million). Based on tax advice received, management considers that the deduction of 100% of the tax loss carryforwards can be applied.
On December 29, 2023, the Brazilian Government made a partial payment deducting all the obligations related to fixed and variable concession fees and including the receivables related to re-equilibriums (a total net payment of R$ 199.7 million equivalent to USD 41.3 million), extinguishing all the concession fees obligations that ICAGSA maintained. On January 5, 2024, the balance of the indemnification was collected (see Note 34).
Additionally, on December 31, 2023, following ICASGA’s absorption by ACI Do Brasil S.A. (“ACIB”), a Brazilian subsidiary of CAAP, all the rights and obligations of ICASGA were transferred to ACIB.
1.2.2 Conflict between Russia and Ukraine
Russia’s war against neighboring Ukraine continues to disrupt international travel from and to Russia and Ukraine and other destinations as the flights to Russia have been banned by Western countries and by the European Union, Russia has closed its skies for carriers registered in Western countries and carriers avoid overflying the war zone. It is likely that this war will continue to disrupt supply chains, cause instability in the global economy and disrupt international travel to/from airports operated by the Company, in particular those located in Europe.
In addition, following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, sanctions have been implemented against Russia, including, among others, travel bans and asset freezes impacting businesses, financial organizations and individuals of Russian origin some of which have been tightened as the war intensified. Wider sanctions and other actions could be imposed if the conflict further escalates.
During 2022 and 2023, there has been an increase in traffic in Armenia above internal projections and the traffic in Italy has not been affected by the conflict. Moreover, during 2022, there was an increase in the costs of raw materials and expenses for utilities, being caused mainly by the conflict. Considering the uncertainty of the extension of the war and the additional measures and sanctions that could be imposed, the full extent by which the war will impact the Company’s business, results of operations, financial position and liquidity is unknown. The Company is closely monitoring the situation.
F-12
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies
A Summary of material accounting policies information
The principal accounting policies applied in the preparation of these Consolidated Financial Statements are set out below. These policies have been consistently applied to all the periods presented, unless otherwise stated.
Basis of preparation
The Group’s Consolidated Financial Statements have been prepared in accordance with IFRS Accounting Standards (“IFRS”) and interpretations (“IFRIC”) issued by the IFRS Interpretations Committee applicable to companies reporting under IFRS. The Consolidated Financial Statements comply with IFRS as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”).
Presentation in the consolidated statement of financial position differentiates between current and non-current assets and liabilities. Assets and liabilities are regarded as current if they mature within one year or within the normal business cycle of the Group, or are held for sale.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with IFRS requires the use of certain critical accounting estimates. It also requires management to exercise its judgment in the process of applying the Group’s accounting policies. The areas involving a higher degree of judgment or complexity, or areas where assumptions and estimates are significant to the Consolidated Financial Statements are disclosed in Note 2.X.
Several balance sheet consolidated statements of financial position and consolidated statements of income items have been combined in the interests of clarity. These items are stated and explained separately in the notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. The statement of income is structured according to the function of the expense method (nature of the expenses is classified in notes).
These Consolidated Financial Statements are presented in thousands of U.S. dollars unless otherwise stated. All amounts are rounded off to thousands of U.S. dollars unless otherwise stated. As such, insignificant rounding differences may occur. A dash (“—”) indicates that no data was reported for a specific line item in the relevant financial year or period or when the pertinent figure, after rounding, amounts to nil.
New and amended standards adopted by the Group
The Group has adopted the following standards and interpretations that become applicable for annual period commencing on or after January 1, 2023:
- Narrow scope amendments to IAS 1, Practice statement 2 and IAS 8.
- Deferred tax related to assets and liabilities arising from a single transaction - Amendment to IAS 12.
- International Tax Reform – Pillar Two Model Rules – Amendments to IAS 12.
- During the year ended December 31, 2022, the Group has applied the following standards and amendments for the first time for their annual reporting period commencing on January 1, 2022:
- Property, Plant and Equipment: Proceeds before Intended Use – Amendments to IAS 16.
- Annual Improvements to IFRS Standards 2018-2020 – Amendments to IFRS 1, IFRS 9, IFRS 16 and IAS 41.
- Reference to the Conceptual Framework – Amendments to IFRS 3.
- Onerous Contracts – Cost of Fulfilling a Contract – Amendments to IAS 37.
The amendments listed above did not have any material impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-13
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
A Summary of material accounting policies information (Cont.)
The following accounting standards and interpretations have been published but the application are not mandatory for December 31, 2023 reporting periods and have not been early adopted by the Group:
- Non-current liabilities with covenants – Amendments to IAS 1.
- Classification of Liabilities as Current or Non-current – Amendments to IAS 1.
- Lease liability in sale and leaseback – amendments to IFRS 16.
- Sale or contribution of assets between an investor and its associate or joint venture – Amendments to IFRS 10 and IAS 28.
- Supplier Finance Arrangements – Amendments to IAS 7 and IFRS 7.
- Lack of exchangeability – Amendments to IAS 21.
The Group is currently assessing the impact these standards, amendments or interpretations will have in the current or future reporting periods and on foreseeable future transactions.
B Group accounting policies
(1) Subsidiaries and transactions with non-controlling interests
Subsidiaries are all entities over which the Group has control. The Group controls an entity when it is exposed to, or has rights to, variable returns from its involvement with the entity and has the ability to affect those returns through its power over the entity. Subsidiaries are fully consolidated from the date on which control is exercised by the Company and are no longer consolidated from the date control ceases.
The acquisition method is used to account for the business combinations. The consideration transferred for the acquisition of a subsidiary is the fair value of the assets transferred, the liabilities incurred or assumed at the date of exchange, and the equity interest issued by the Group. Acquisition-related costs are expensed as incurred. Identifiable assets acquired, liabilities and contingent liabilities assumed in a business combination are measured initially at their fair values at the acquisition date. Any non-controlling interest in the acquiree is measured either at fair value or at the non-controlling interest’s proportionate share of the acquiree’s net assets. Accounting treatment is applied on an acquisition by acquisition basis.The excess of the aggregate of the consideration transferred and the amount of any non-controlling interest in the acquiree over the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. If this consideration is lower than the fair value of the net assets of the subsidiary acquired, the difference is recognized directly in the Consolidated Statement of Income.
F-14
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
B Group accounting policies (Cont.)
(1) Subsidiaries and transactions with non-controlling interests (Cont.)
Transactions with non-controlling interests that do not result in a loss of control are accounted as equity transactions with owners of the Company. For purchases from non-controlling interests, the difference between any consideration paid and the relevant share acquired of the carrying value of net assets of the subsidiary is recorded in equity. Gains or losses on disposals to non-controlling interests are also recorded in equity. Material intercompany transactions, balances and unrealized gains and losses have been eliminated in consolidation. However, financial gains and losses from intercompany transactions may arise when the subsidiaries have different functional currencies. These financial gains and losses are included in the Consolidated Statement of Income under Financial income and Financial loss.
(2) Associates
Associates are all entities over which the Group has significant influence but not control, generally accompanying a shareholding of between 20% and 50% of the voting rights. Investments in associates are accounted for by the equity method of accounting and are initially recognized at cost, and the carrying amount is increased or decreased to recognize the investor`s share of profit or loss of the investment after the date of acquisition. Dividends received or receivable from associates are recognized as a reduction in the carrying amount of the investment. The Company’s investment in associates includes goodwill identified on acquisition, net of any accumulated impairment loss.
Where the Group’s share of losses in an equity-accounted investment equals or exceeds its interest in the entity, including any other unsecured long-term receivables, the Group does not recognize further losses, unless it has incurred obligations or made payments on behalf of the other entity.
Accounting policies of associates have been adjusted where necessary to ensure consistency with the policies adopted by the Group. The Company’s pro-rata share of earnings in associates is recorded in the Consolidated Statement of Income under Share of income / (loss) in associates and Share of other comprehensive (loss)/ income from associates. The Company’s pro-rata share of changes in other reserves is recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Changes in Equity under Other Reserves.
F-15
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
B Group accounting policies (Cont.)
(3) List of Subsidiaries
Detailed below are the subsidiaries of the Company, which have been consolidated in these Consolidated Financial Statements. The percentage of ownership refers to the direct and indirect ownership of CAAP in their subsidiaries at each period-end.
Holdings companies
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Percentage of ownership at |
|
||||
|
|
Country of |
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
||||
Company |
|
incorporation |
|
Local currency |
|
Main activity |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
Abafor S.A. |
|
Uruguay |
|
Uruguayan pesos |
|
Holding company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
ACI Airport Sudamérica S.A.U. (“ACI”) |
|
Spain |
|
Euros |
|
Holding company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
ACI Airports Italia S.A.U. |
|
Spain |
|
Euros |
|
Holding company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
America International Airports LLC (1) |
|
USA |
|
U.S. dollars |
|
Holding company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
Anabe ITG S.L. (9) |
|
Spain |
|
Euros |
|
Holding company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
— |
|
Barnsley ITG S.L. (11) |
|
Spain |
|
Euros |
|
Holding company |
|
99.98 |
% |
— |
|
— |
|
Cargo & Logistics S.A. (1) (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Holding company |
|
82.89 |
% |
82.89 |
% |
82.10 |
% |
Cedicor S.A. |
|
Uruguay |
|
Uruguayan pesos |
|
Holding company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
Cerealsur S.A. |
|
Uruguay |
|
Uruguayan pesos |
|
Holding company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
Corporación Aeroportuaria S.A. (“CAER”) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Holding company |
|
99.98 |
% |
99.98 |
% |
99.98 |
% |
Corporacion Africa Airports Nigeria Limited (“CAAN”) (9) |
|
Nigeria |
|
Naira |
|
Holding company |
|
51.00 |
% |
— |
|
— |
|
Corporación América Italia S.p.A. (“CAI”) |
|
Italy |
|
Euros |
|
Holding company |
|
75.00 |
% |
75.00 |
% |
75.00 |
% |
Corporación América S.A. (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Holding company |
|
97.22 |
% |
97.22 |
% |
96.18 |
% |
Corporación América Sudamericana S.A. (7) |
|
Panamá |
|
U.S. dollars |
|
Holding company |
|
96.53 |
% |
96.53 |
% |
95.50 |
% |
DICASA Spain S.A.U. (1) |
|
Spain |
|
Euros |
|
Holding company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
Inframérica Participaçoes S.A. (1) (8) |
|
Brazil |
|
Brazilian real |
|
Holding company |
|
99.98 |
% |
99.98 |
% |
99.97 |
% |
Yokelet S.L. |
|
Spain |
|
Euros |
|
Holding company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
F-16
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
B Group accounting policies (Cont.)
(3) List of Subsidiaries (Cont.)
Operating companies
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Percentage of ownership at |
|
||||
|
|
Country of |
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
||||
Company |
|
incorporation |
|
Local currency |
|
Main activity |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
|
Abuja Airport Concession Company (“AACC”) (10) |
|
Nigeria |
|
Naira |
|
Airports Operation |
|
51.00 |
% |
— |
|
— |
|
ACI do Brasil S.A. (“ACIB”) (12) |
|
Brazil |
|
Brazilian real |
|
Airports Operation(12) |
|
99.99 |
% |
99.99 |
% |
99.99 |
% |
Aerocombustibles Argentinos S.A. (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Fueling company |
|
94.79 |
% |
94.79 |
% |
93.78 |
% |
Aeropuerto de Bahía Blanca S.A. (“BBL”) (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Airports Operation |
|
82.64 |
% |
82.64 |
% |
81.75 |
% |
Aeropuertos Argentina 2000 S.A.(“AA2000”) (2) (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Airports Operation |
|
82.69 |
% |
82.69 |
% |
81.91 |
% |
Aeropuertos del Neuquén S.A. (“ANSA”) (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Airports Operation |
|
75.54 |
% |
75.54 |
% |
74.73 |
% |
Armenia International Airports C.J.S.C. (“AIA”) |
|
Armenia |
|
Dram |
|
Airports Operation |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
CAAirports International Services S.A. |
|
Uruguay |
|
Uruguayan pesos |
|
Service company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
Consorcio Aeropuertos Internacionales S.A. (“CAISA”) |
|
Uruguay |
|
Uruguayan pesos |
|
Airports Operation |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
Enarsa Aeropuertos S.A. (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Fuel plants |
|
77.77 |
% |
77.77 |
% |
76.95 |
% |
Inframérica Concessionária do Aeroporto de Brasilia S.A. (“ICAB”) (8) |
|
Brazil |
|
Brazilian real |
|
Airports Operation |
|
50.99 |
% |
50.99 |
% |
50.99 |
% |
Inframérica Concessionária do Aeroporto de São Gonçalo do Amarante S.A. (“ICASGA”) (12) |
|
Brazil |
|
Brazilian real |
|
Airports Operation |
|
— |
|
99.98 |
% |
99.98 |
% |
Kano Airport Concession Company Limited (“KACC) (10) |
|
Nigeria |
|
Naira |
|
Airports Operation |
|
51.00 |
% |
— |
|
— |
|
Paoletti América S.A. (3) (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Service company |
|
41.35 |
% |
41.35 |
% |
40.95 |
% |
Puerta del Sur S.A. (”PDS”) |
|
Uruguay |
|
Uruguayan pesos |
|
Airports Operation |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
Servicios y Tecnología Aeroportuaria S.A. (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Service company |
|
82.79 |
% |
82.79 |
% |
82.01 |
% |
Sinatus S.A. (13) |
|
Uruguay |
|
Uruguayan pesos |
|
Service company |
|
100.00 |
% |
— |
|
— |
|
TCU S.A. |
|
Uruguay |
|
Uruguayan pesos |
|
Service company |
|
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
100.00 |
% |
Terminal Aeroportuaria Guayaquil S.A. (“TAGSA”) (4) |
|
Ecuador |
|
U.S. dollars |
|
Airports Operation |
|
49.99 |
% |
49.99 |
% |
49.99 |
% |
Texelrío S.A. (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Service company |
|
57.88 |
% |
57.88 |
% |
57.34 |
% |
Toscana Aeroporti S.p.A. (“TA”) (5) (6) |
|
Italy |
|
Euros |
|
Airports Operation |
|
46.71 |
% |
46.71 |
% |
46.71 |
% |
Villalonga Furlong S.A. (7) |
|
Argentina |
|
Argentine pesos |
|
Service company |
|
82.90 |
% |
82.90 |
% |
82.12 |
% |
(1) These companies do not have relevant net assets other than the share of ownership in the operating companies included in the table below.
(2) Includes a 9.35% direct interest of Cedicor S.A. in AA2000.
(3) The Group has control over this company based on having majority representation in the board, power to direct the process of setting of financial and operating policies and execute the operational management of such Company.
(4) The Group has control over this company based on having power to direct the process of setting of financial and operating policies and execute the operational management of such Company.
(5) The Group has control over this company based on having a majority stake in Corporación América Italia S.p.A. that has 62.28% of ownership of TA, power to direct the process of setting of financial and operating policies and execute the operational management of such Company.
F-17
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
B Group accounting policies (Cont.)
(3) List of Subsidiaries (Cont.)
(6) The Group TA has control over the following companies: Jet Fuel Co. S.r.l., Parcheggi Peretola S.r.l., Toscana Aeroporti Engineering S.r.l. and Toscana Aeroporti Construzioni S.r.l. Additionally, the Group TA had control over Toscana Aeroporti Handling S.r.l. until December 30, 2022, when sold an 80% of its participation.
(7) In December, 2021, and December 2022 Cedicor S.A.’s contributions in Corporación América S.A. were capitalized increasing its participation from 95.80% to 96.18% in 2021 and from 96.18% to 97.22% in 2022, indirectly modifying the participation in the operating subsidiaries.
(8) During 2022 CAAP made contributions in Inframérica Participaçoes S.A.
(9) Holding company part of the structure related to the future Nigerian’s concessions (Note 26.b).
(10) Operating company part of the structure related to the future Nigerian’s concessions (Note 26.b).
(11) Holding company incorporated under CAER in December 2023, becoming shareholder of TAGSA.
(12) In December 2023, ACIB incorporated ICASGA (Note 1.2.1).
(13) Subsidiary incorporated under Abafor S.A.
F-18
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
B Group accounting policies (Cont.)
(3) List of Subsidiaries (Cont.)
Summarized financial information in respect of each of the Group’s subsidiaries that has most significant non-controlling interests is set below. The summarized financial information below represents amounts before intragroup elimination.
|
|
TA |
||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Non-current assets |
|
267,569 |
|
255,355 |
|
|
Current assets |
|
68,197 |
|
89,097 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
335,766 |
|
344,452 |
|
|
Non-current liabilities |
|
78,834 |
|
99,928 |
|
|
Current liabilities |
|
139,248 |
|
137,057 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
218,082 |
|
236,985 |
|
|
Equity |
|
117,684 |
|
107,467 |
|
|
Revenue |
|
133,422 |
|
117,209 |
|
70,469 |
Gross income |
|
41,783 |
|
22,633 |
|
(12,681) |
Operating income / (loss) |
|
28,418 |
|
10,306 |
|
(12,182) |
Financial results |
|
(7,350) |
|
(4,119) |
|
(3,061) |
Share of income in associates |
|
14 |
|
(258) |
|
91 |
Income tax |
|
(6,842) |
|
(1,528) |
|
8,704 |
Net income / (loss) |
|
14,240 |
|
4,401 |
|
(6,448) |
Other comprehensive income / (loss) for the year |
|
4,142 |
|
(5,827) |
|
(8,978) |
Total comprehensive income / (loss) for the year |
|
18,382 |
|
(1,426) |
|
(15,426) |
Dividends paid |
|
(7,838) |
|
(7,340) |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase / (decrease) in cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provided by / (used in) operating activities |
|
21,469 |
|
26,588 |
|
(13,249) |
Used in investing activities |
|
(1,388) |
|
(3,161) |
|
(4,909) |
Used in financing activities |
|
(52,221) |
|
(21,843) |
|
(8,522) |
F-19
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
B Group accounting policies (Cont.)
(3) List of Subsidiaries (Cont.)
|
|
TAGSA |
||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Non-current assets |
|
53,782 |
|
56,025 |
|
|
Current assets |
|
59,737 |
|
53,752 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
113,519 |
|
109,777 |
|
|
Non-current liabilities |
|
7,329 |
|
13,536 |
|
|
Current liabilities |
|
54,106 |
|
47,447 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
61,435 |
|
60,983 |
|
|
Equity |
|
52,084 |
|
48,794 |
|
|
Revenue |
|
105,228 |
|
96,199 |
|
65,155 |
Gross profit |
|
42,943 |
|
38,614 |
|
20,784 |
Operating income |
|
25,319 |
|
22,561 |
|
9,150 |
Financial results |
|
656 |
|
(316) |
|
(1,413) |
Income tax |
|
(2,455) |
|
(1,937) |
|
(971) |
Net income |
|
23,520 |
|
20,308 |
|
6,766 |
Other comprehensive income / (loss) for the year |
|
80 |
|
356 |
|
(205) |
Total comprehensive income for the year |
|
23,600 |
|
20,664 |
|
6,561 |
Dividends paid |
|
(20,308) |
|
(17,225) |
|
(3,000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase / (decrease) in cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provided by operating activities |
|
35,891 |
|
36,709 |
|
21,877 |
Used in investing activities |
|
(5,382) |
|
(10,152) |
|
(20,076) |
Used in financing activities |
|
(27,337) |
|
(24,399) |
|
(10,245) |
F-20
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
B Group accounting policies (Cont.)
(3) List of Subsidiaries (Cont.)
|
|
ICAB |
||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Non-current assets |
|
666,428 |
|
645,847 |
|
|
Current assets |
|
86,371 |
|
86,134 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
752,799 |
|
731,981 |
|
|
Non-current liabilities |
|
906,312 |
|
841,901 |
|
|
Current liabilities |
|
215,761 |
|
190,784 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
1,122,073 |
|
1,032,685 |
|
|
Equity |
|
(369,274) |
|
(300,704) |
|
|
Revenue |
|
100,252 |
|
79,713 |
|
51,706 |
Gross profit |
|
31,262 |
|
19,047 |
|
1,909 |
Operating income |
|
37,816 |
|
21,328 |
|
11,702 |
Financial results |
|
(102,953) |
|
(114,550) |
|
(124,815) |
Income tax |
|
3,250 |
|
(12,409) |
|
(9,320) |
Net loss |
|
(61,887) |
|
(105,631) |
|
(122,433) |
Other comprehensive (loss) / income for the year |
|
(25,918) |
|
(13,748) |
|
14,898 |
Total comprehensive loss for the year |
|
(87,805) |
|
(119,379) |
|
(107,535) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase / (decrease) in cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provided by / (used in) operating activities |
|
6,876 |
|
32,188 |
|
(585) |
Used in investing activities |
|
(16) |
|
(53) |
|
(459) |
(Used in) / provided by financing activities |
|
(12,784) |
|
17,003 |
|
457 |
F-21
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
B Group accounting policies (Cont.)
(3) List of Subsidiaries (Cont.)
|
|
AA2000 |
||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Non-current assets |
|
1,165,410 |
|
1,594,529 |
|
|
Current assets |
|
181,405 |
|
211,057 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
1,346,815 |
|
1,805,586 |
|
|
Non-current liabilities |
|
672,981 |
|
796,193 |
|
|
Current liabilities |
|
124,665 |
|
222,223 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
797,646 |
|
1,018,416 |
|
|
Equity |
|
549,169 |
|
787,170 |
|
|
Revenue |
|
635,563 |
|
758,111 |
|
362,128 |
Gross profit |
|
218,246 |
|
234,803 |
|
37,846 |
Operating income / (loss) |
|
170,714 |
|
190,446 |
|
(6,949) |
Financial results |
|
(211,898) |
|
35,866 |
|
61,322 |
Income tax |
|
52,912 |
|
2,900 |
|
(54,396) |
Net income / (loss) |
|
11,728 |
|
229,212 |
|
(23) |
Other comprehensive (loss) / income for the year |
|
(250,002) |
|
314,021 |
|
125,333 |
Total comprehensive (loss) / income for the year |
|
(238,274) |
|
543,233 |
|
125,310 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase / (decrease) in cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provided by operating activities |
|
192,164 |
|
146,789 |
|
62,937 |
(Used in) / provided by investing activities |
|
(64,305) |
|
8,338 |
|
11,516 |
(Used in) / provided by financing activities |
|
(74,050) |
|
(122,453) |
|
31,455 |
(4) Discontinued operations
A discontinued operation is a component of the entity that has been disposed and that represents a separate major line of business or geographical area of operations, is part of a single coordinated plan to dispose of such a line of business or area of operations, or is a subsidiary acquired exclusively with a view to resale. The results of discontinued operations are presented separately in the Consolidated Statement of Income and Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income, when applicable.
F-22
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
C Foreign currency translation
(1) Functional and presentation currency
Items included in the financial statements of each of the Group’s entities are measured using the currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity operates (“the functional currency”).
The Consolidated Financial Statements are presented in U.S. dollars, which is the Company’s functional currency and the Group’s presentation currency.
(2) Transactions in currencies other than the functional currency
Transactions in currencies other than the functional currency are translated into the functional currency using the exchange rates prevailing at the dates of the transactions or valuations where items are re-measured.
At the end of each reporting period: (i) monetary items denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are translated using the closing rates; (ii) non-monetary items that are measured in terms of historical cost in a currency other than the functional currency are translated using the exchange rates prevailing at the date of the transactions; and (iii) non-monetary items that are measured at fair value in a currency other than the functional currency are translated using the exchange rates prevailing at the date when the fair value was determined. If such transactions occurred in a company applying IAS 29, after the above-mentioned translation, transactions are re-expressed in terms of the measuring unit current at the end of the reporting period.
Foreign exchange gains and losses resulting from the settlement of such transactions and from the translation at year-end exchange rates of monetary assets and liabilities denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are recorded as follows:
- |
Exchange differences arising from foreign currency loans are recognized on a net aggregate basis in the Financial loss line of the Consolidated Statement of Income. |
- |
Other exchange differences are recognized on a net aggregate basis in Financial income or Financial loss in the Consolidated Income Statement, depending on whether they are gains or losses at net level on a quarterly basis. |
Foreign exchange gains and losses derived from the net monetary position in subsidiaries applying IAS 29 are presented in real (inflation-adjusted) terms.
(3) Translation of financial information in currencies other than the Company’s functional currency
Income and expenses of the subsidiaries whose functional currencies are not the U.S. dollar and are not in a hyperinflationary economy, are translated into U.S. dollars at average exchange rates on a quarterly basis. Assets and liabilities for each balance sheet presented are translated at the balance sheet date exchange rates.
All figures (income, expenses, assets and liabilities) of the subsidiaries whose functional currencies are the one of a hyperinflationary economy, are translated into U.S. dollars at the balance sheet date exchange rates, considering that all items are expressed in terms of the measuring unit current at the end of the reporting period.
Translation differences are recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income as “Currency translation adjustment”. As of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, the Company recognized a translation (loss)/income of USD (281.7) million, USD 91.1 million and USD 138.6 million, respectively, arising from the translation of the investments in Argentina, Brazil, Italy and Armenia. In the case of a sale or other disposal of any of such subsidiaries, any cumulative translation difference would be recognized in the Statement of Income as a gain or loss from the sale of such subsidiary.
F-23
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
D Intangible assets
(1) Concession Assets
The Group, through its subsidiaries has been awarded the concession for the administration and operation of the following airports:
- |
PDS and CAISA of major airports in Uruguay (Montevideo and Punta del Este) as well as six regional airports under the concession of PDS. |
- |
TA a merger of Aeroporto di Firenze S.p.A. (“ADF”) and Società Aeroporto Toscano Galileo Galilei S.p.A. (“SAT”) of Florence and Pisa airports, respectively. |
- |
ICAB and ICASGA of Brasilia and São Gonçalo do Amarante airports, respectively. As mentioned in Note 1.2.1, the concession of the São Gonçalo do Amarante airport was handle to a new concessionaire. |
- |
TAGSA of Guayaquil airport, “José Joaquin de Olmedo”. |
- |
AA2000 of 35 airports in Argentina. |
- |
BBL of Bahía Blanca airport in Argentina. |
- |
ANSA of Neuquén airport in Argentina. |
- |
AIA of the “Zvartnots” International Airport of Yerevan and Shirak Airport, Republic of Armenia. |
The concession agreements are accounted for in accordance with the principles included in IFRIC 12 “Service Concession Arrangements”. The Group recognized an intangible asset for:
a) |
Fixed fees payables as the result of the acquisition of the right (license) to charge users for the service of airport concession (see Note 23), |
b) |
Right to obtain benefits for services provided using the assets built under the concession contracts. |
In case that an unconditional contractual right to receive cash or another financial asset from or at the direction of the grantor for the construction services; the grantor has little, if any, discretion to avoid payment, usually because the agreement is enforceable by law, the Company recognizes as Other financial assets at fair value through profit or loss in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position.
Acquisitions correspond, according to the terms of the Concession contract, to the improvements of existing infrastructure assets to increase their useful life or capacity, or the construction of new infrastructure assets.
General and specific borrowing costs, attributable to the acquisition, construction or production of assets that necessarily take a substantial period to get ready for their intended use, rental or sale are added to the cost of such assets until the assets are substantially ready to be used, rented or sold.
As part of the obligations arising from the concession agreements, the Group provides construction or upgrade services. IFRIC 12 “Service Concession Arrangements” requires recognition of revenues and costs from the construction or upgrade services provided. The fair value of the construction or upgrade service is equal to the construction or upgrade costs plus a reasonable margin determined for each concession.
The intangible asset for infrastructure under each concession agreement is amortized over the contract term in accordance with an appropriate method reflecting the rate of consumption of the concession asset’s economic benefits as from the date the infrastructure is brought into service.
F-24
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
D Intangible assets (Cont.)
(1) Concession Assets (Cont.)
The concession fee paid to the grantor under the concession agreements is recognized depending on the terms defined in the concession agreement:
a) |
Fixed concession fee is recognized at the beginning of the concession as it is reliably measurable, as a counterpart an intangible asset is recognized, this type of fee is independent from the revenue. |
b) |
Variable fees payables that are defined as a percentage over certain revenue streams are recognized on a monthly basis in the Consolidated Statement of Income. |
Each operating company is responsible for obtaining the necessary guarantees for the commitments assumed in each concession. They are mostly covered by insurance that is paid in advance and it is recorded in Other receivables, and is accrued over the life of the coverage.
Main commitments under each concession agreement are included in Note 26 b.
(2) Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the acquisition cost over the fair value of the Group’s share of net identifiable assets, liabilities and contingent liabilities acquired as part of business combinations determined by management. Goodwill impairment reviews are performed annually or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate a potential impairment. An impairment loss is recognized for the amount by which the asset’s carrying amount exceeds its recoverable amount. The recoverable amount is the higher of an asset’s fair value less costs of disposal and value in use. Impairment losses on goodwill are not reversed. Goodwill, net of impairment losses, if any, is included on the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position under Intangible assets, net. For the purpose of impairment testing, goodwill acquired in a business combination is allocated to each cash-generating units (CGUs) of a subsidiary or group of subsidiaries that are expected to benefit from such business combination.
(3) Other intangible assets
An intangible asset purchased or produced internally is booked among Assets, as required by IAS 38, only if it can be identified and controlled, and if it is possible to predict the generation of future economic benefits and if its cost can be determined reliably.
Intangible assets with finite lives are valued at purchase or production cost less accumulated amortization and impairment losses. Amortization is determined by making reference to the period of its estimated useful life and starts when the asset is available for use.
E Property, plant and equipment
Property, plant and equipment is recognized at historical acquisition or construction cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment losses; historical cost includes expenses directly attributable to the acquisition of the items.
Major overhaul and rebuilding expenditures are capitalized as property, plant and equipment only when it is probable that future economic benefits associated with the item will flow to the Group and the investment enhances the condition of assets beyond its original condition.
F-25
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
E Property, plant and equipment (Cont.)
Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method to allocate the cost of each asset to its residual value over the estimated useful life, as follows:
Buildings and improvements |
|
25‑30 |
years |
Plant and production equipment |
|
3‑10 |
years |
Vehicles, furniture and fixtures, and other equipment |
|
4‑10 |
years |
The residual values and useful lives of significant property, plant and equipment are reviewed and adjusted, if appropriate, at each year-end date.
Gain and losses on disposals are determined by comparing the proceeds with the carrying amount and are included in Other operating income / (expense) in the Consolidated Statement of Income.
F Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost and net realizable value. Net realizable value is the estimated selling price in the ordinary course of business, less the estimated costs of completion and selling expenses. The cost of inventories is based on the weighted averaged principle and includes expenditure incurred in acquiring the inventories and bringing them to their existing location and condition.
If applicable, the Group establishes an allowance for obsolete or slow-moving inventory related to finished goods. For slow moving or obsolete finished products, an allowance is established based on management’s analysis of product aging.
G Trade and other receivables and contract assets
Trade and other receivables are initially recognized at the amount of consideration that is unconditional, unless they contain significant financing components when they are recognized at fair value. They are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method, less loss allowance. See Note 3.A(iii) for a description of the Group’s impairment policies.
A construction contract is a contract specifically negotiated for the construction of an asset. When the outcome of a construction contract can be reliably estimated, contract revenue and contract costs are acknowledged by the percentage of completion method. A contract asset is initially recognized for unbilled work in progress. Upon completion of the work and acceptance by the customer, the amount recognized as contract assets is reclassified to trade receivables.
H Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents are comprised of cash in banks, mutual funds and short-term investments with an original maturity of three months or less at the date of purchase which are readily convertible to known amounts of cash.
In the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position, bank overdrafts are included in Borrowings in current liabilities. For the purposes of the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows, cash and cash equivalents includes bank overdrafts if the overdraft is repayable on demand and is integral to the Group’s cash management.
F-26
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
I Equity
(1) Equity components
The Consolidated Statement of Changes in Equity includes:
- |
The share capital, share premium, legal reserve, free distributable reserves and non-distributable reserves calculated in accordance with Luxembourg Law; |
- |
The treasury shares, currency translation adjustment, other reserves, retained earnings and non-controlling interest. |
(2) Share capital
Share capital is stated at nominal value. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, share capital was USD 163 million (USD 1 per share).
All issued shares are fully paid.
The authorized capital of the Company is set at USD 225 million represented by a maximum of 225 million shares having a nominal value of USD 1 each.
Pursuant to Luxembourg regulations, contributions in kind made by shareholders must be at fair value and might be considered as Free Distributable Reserve.
(3) Dividends distribution by the Company to shareholders
Dividends distribution are recorded in the Company’s financial statements as a provision when Company’s shareholders have the right to receive the payment, or when interim dividends are approved by the Board of Directors in accordance with the by-laws of the Company. Dividends may be paid by the Company to the extent that it has distributable retained earnings, calculated in accordance with Luxembourg law (see Note 26.c).
(4) Other reserves
SCF’s airport business was historically conducted through a large number of entities as to which there was no single holding entity but which were separately owned by entities directly or indirectly controlled by SCF during all the periods presented. In order to facilitate the Company’s initial public offering, in 2016 SCF completed a reorganization (the “Reorganization”) whereby, each of the operating and holding entities under SCF’s common control, were ultimately contributed to the Company.
The reorganization was accounted for as a reorganization of entities under common control, using the predecessor cost method. The net effect was recorded in Equity under Other Reserves. Moreover, in 2016, and considering that the shares of America International Airports LLC were contributed to the Free Distributable Reserves of the Company at the fair value a significant negative amount was included in Other Reserves to reflect the reduction to the predecessor’s cost of the shares.
Other reserves also include the share-based payment reserve constituted in connection with the creation of a management share compensation program as explained in Note 30.
F-27
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
I Equity (Cont.)
(5) Non-controlling interest
The Group treats transactions with non-controlling interests that do not result in a loss of control as transactions with equity owners of the Group. A change in ownership interest results in an adjustment between the carrying amounts of the controlling and non-controlling interests to reflect their relative interests in the subsidiary. Any difference between the amount of the adjustment to non-controlling interests and any consideration paid or received is recognized in Other reserves within equity attributable to owners of the Company.
J Borrowings
Borrowings are recognized initially at fair value, net of transaction costs incurred. Subsequently borrowings are measured at amortized cost.
Fees paid on the establishment of loan facilities are recognized as transaction costs of the loan to the extent that it is probable that some or all of the facility will be drawn down. In this case, the fee is deferred until the draw-down occurs. To the extent there is no evidence that it is probable that some or all of the facility will be drawn down, the fee is capitalized as a prepayment for liquidity services and amortized over the period of the facility to which it relates.
In the event of debt renegotiations, if the exchange of debt instruments between the financial creditor and the Group is concluded under substantially different conditions or entails a substantial modification of the conditions, considering both quantitative and qualitative factors, the existing financial liability is de-recognized as an extinguishment of the original liability and a new liability is recognized. Otherwise, the original liability should not be extinguished, but should be considered as a modification, adjusting its measurement in relation to the new terms and conditions.
K Current and Deferred income tax
The tax expense for the year comprises current and deferred tax. Tax is recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Income, except for tax items recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income.
The current income tax charge is calculated on the basis of the tax laws enacted or substantively enacted at the reporting date in the countries where the Group entities operate and generate taxable income. Management periodically evaluates positions taken in tax returns with respect to situations in which applicable tax regulation is subject to interpretation and considers whether it is probable that a taxation authority will accept an uncertain tax treatment. The Group measures its tax balances either based on the most likely amount or the expected value, depending on which method provides a better prediction of the resolution of the uncertainty.
Deferred income taxes recognized applying the liability method on temporary differences arising between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their carrying amounts in the Consolidated Financial Statements. The principal temporary differences arise from intangible assets adjusted for the effects of IAS 29 in the Argentinian subsidiaries, and the effect of valuation on fixed assets, inventories and provisions. Deferred tax assets are also recognized for tax losses carry-forwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured at the tax rates that are expected to apply in the time period when the asset is realized or the liability is settled, based on tax laws that have been enacted or substantively enacted at the reporting date.
Deferred tax assets are recognized to the extent it is probable that future taxable income will be available against which the temporary differences can be utilized.
F-28
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
K Current and Deferred income tax (Cont.)
Deferred tax liabilities and assets are not recognized for temporary differences between the carrying amount and tax bases of investments in foreign operations where the company is able to control the timing of the reversal of the temporary differences and it is probable that the differences will not reverse in the foreseeable future.
At the end of each reporting period, CAAP reassesses unrecognized deferred tax assets. The Group recognizes a previously unrecognized deferred tax asset to the extent that it has become probable that future taxable income will allow the deferred tax asset to be recovered.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset where there is a legally enforceable right to offset current tax assets and liabilities and where the deferred tax balances relate to the same taxation authority. Current tax assets and tax liabilities are offset where the entity has a legally enforceable right to offset and intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the asset and settle the liability simultaneously.
In order to determine the net taxable income of Argentine subsidiaries at the end of each year, the tax inflation adjustment determined in accordance with articles No. 95 to No. 98 of the income tax law has been incorporated into the tax results, due to the fact that as of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 the accumulated price index variation for the last 36 months has already exceeded 100%.
L Employee benefits
Compensation to employees in the event of dismissal is charged to profit or loss of the year in which it becomes payable.
Short-term obligations
Liabilities for wages and salaries, including non-monetary benefits and annual leave that are expected to be settled wholly within twelve months after the end of the period in which the employees render the related service are recognized in respect of employees’ services up to the end of the reporting period and are measured at the amounts expected to be paid when the liabilities are settled. The liabilities are presented as current in Salary payable in Other liabilities.
Long-term employee benefits
Some entities of the Group have long term employee benefits that are unfunded defined benefit plan in accordance with IAS 19 - “Employee Benefits”.
The company calculates annually the provision for employee retirement cost based on actuarial calculations performed by independent professionals using the Projected Unit Credit Costs method. The present value of the defined benefit obligations at each year-end is calculated discounting estimated future cash outflows at an annual rate equivalent to the average rate of high-quality corporate bonds, which are denominated in the same currency in which the benefits will be paid, and whose terms approximate the terms of the pension obligations.
The net interest cost is calculated by applying the discount rate to the net balance of the defined benefit obligation.
Service cost and interest cost are recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Income, while actuarial gains and losses arising from changes in actuarial assumptions are recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income.
Actuarial assumptions include variables such as, in addition to the discount rate, death rate, age, sex, years of service, current and future level of salaries, turnover rates, among others.
F-29
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
L Employee benefits (Cont.)
Long-term employee benefits (Cont.)
Changes in the present value of the defined benefit obligation resulting from plan amendments or curtailments are recognized immediately in profit or loss as past service costs.
Share-based payments
Share-based compensation benefits are provided to employees via the Management Share Compensation Plan. Information related to this plan is set out in Note 30.
In the case the Company receives employees’ services as consideration for its own equity instruments the share-based payments transaction is considered equity-settled while if services are acquired by incurring a liability to transfer cash or other assets for those services based on the price of its own equity instruments the transaction is considered cash-settled.
The fair value of shares granted to employees under the share compensation plan is recognized as an expense over the relevant service period considering specified performance targets to be met while the employee is rendering the service required, being the year to which the service relates and the vesting period of the shares. The fair value is measured at the grant date of the shares, using the Company’s share market price, and is recognized in equity in the share-based payment reserve in line Other Reserves.
The number of shares expected to vest is estimated based on the non-market vesting conditions. The estimates are revised at the end of each reporting period, and adjustments are recognized in profit or loss and the share-based payment reserve.
Where shares are forfeited due to a failure by the employee to satisfy the service or performance conditions, any expenses previously recognized in relation to such shares are reversed effective from the date of the forfeiture.
The shares under the plan are held as treasury shares until they are delivered to employees.
F-30
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
M Provisions
Provisions for legal claims and other charges are recognized when: the Group has a present legal or constructive obligation as a result of past events; it is probable that an outflow of resources will be required to settle the obligation and; the amount has been reliably estimated.
Provisions are measured at the present value of the expenditures expected to be required to settle the obligation using a pre-tax rate that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the obligation. The increase in the provision due to passage of time is recognized as financial loss.
The concession agreements in the different jurisdictions include certain commitments to be complied by each company. These commitments can be grouped in two categories:
| - | Works that can be classified as standard maintenance of the infrastructure, which are expensed as incurred. |
| - | Major scheduled maintenance and refurbishments of the infrastructure in the future. |
Since IFRIC 12 does not recognize infrastructure as property, plant and equipment, rather as a right to charge customers for the use of the infrastructure, major refurbishments and renewals to be performed in future years to maintain or restore the infrastructure asset to its level of functionality, operation and safety should be recognized in accordance with IAS 37 - Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Assets (unless the grantor agrees to reimburse the operator). Provision is recorded at the best estimate of the amount of the expenditure expected to be incurred to perform the major overhaul or restoration work, discounted using a rate that reflects time value of money and risks involved.
N Trade payables
Trade payables are initially recognized at fair value, generally the nominal invoice amount and are subsequently measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method.
O Concession fee payable
Each concession agreement determines different types of concession fees to be paid to the corresponding regulatory authority. Fees could be fixed or variable. Some concession agreements establish both a minimum fixed payment, and an additional variable amount if certain conditions are met (such as a minimum number of passengers, among others).
For those concession agreements that require payment of a fixed amount, the Company recognized the obligation at present value. The increase in the provision due to the passage of time is recognized in financial results. The variable concession fees paid to the grantor derived from the concession agreements are recognized as cost of the period. The fixed concession fee payable is capitalized at the inception of the agreement as concession assets- intangible asset.
F-31
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
P Leases / Sub-concession of spaces
The Group as a lessee
The Group acts as a lessee renting various offices, equipment and cars.
Contracts may contain both lease and non-lease components. The Group allocates the consideration in the contract to the lease and non-lease components based on their relative stand-alone prices.
Leases are recognized as a right-of-use asset and a corresponding liability at the date at which the leased asset is available for use by the group. Each lease payment is allocated between the liability and finance cost. The finance cost is charged to profit or loss over the lease period so as to produce a constant periodic rate of interest on the remaining balance of the liability for each period. The right-of-use asset is depreciated over the lease term on a straight-line basis. If the Group is reasonably certain to exercise a purchase option, the right-of-use asset is depreciated over the underlying asset’s useful life.
Assets and liabilities arising from a lease are initially measured on a present value basis. Lease liabilities include the net present value of the following lease payments:
| - | fixed payments (including in-substance fixed payments), less any lease incentives receivable, |
| - | variable lease payment that are based on an index or a rate, |
| - | amounts expected to be payable by the lessee under residual value guarantees, |
| - | the exercise price of a purchase option if the lessee is reasonably certain to exercise that option, and |
| - | payments of penalties for terminating the lease, if the lease term reflects the lessee exercising that option. |
Lease payments to be made under reasonably certain extension options are also included in the measurement of the liability.
The lease payments are discounted using the interest rate implicit in the lease. If that rate cannot be determined, the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate is used, being the rate that the lessee would have to pay to borrow the funds necessary to obtain an asset of similar value in a similar economic environment with similar terms and conditions.
If a readily observable amortizing loan rate is available to the individual lessee (through recent financing or market data) which has a similar payment profile to the lease, then the group entities use that rate as a starting point to determine the incremental borrowing rate.
The Group is exposed to potential future increases in variable lease payments based on an index or rate, which are not included in the lease liability until they take effect. When adjustments to lease payments based on an index or rate take effect, the lease liability is reassessed and adjusted against the right-of-use asset.
Right-of-use assets are measured at cost comprising the following:
| - | the amount of the initial measurement of lease liability, |
| - | any lease payments made at or before the commencement date less any lease incentives received, |
| - | any initial direct costs, and |
| - | restoration costs. |
Payments associated with short-term leases, leases of low-value assets and variable leases that do not depend on an index or rate are recognized on a straight-line basis as an expense in profit or loss. Short-term leases are leases with a lease term of 12 months or less.
The Group as a lessor
The Group acts as a lessor regarding leases and sub-concession of spaces with third parties at its airports facilities.
F-32
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
P Leases / Sub-concession of spaces (Cont.)
The Group as a lessor (Cont.)
As a lessor the Group classifies its leases as either operating or finance leases. A lease is classified as a finance lease if it transfers substantially all the risks and rewards incidental to ownership of the underlying asset, and classified as an operating lease if it does not.
Lease income from operating leases where the Group is a lessor is recognized in income on a straight-line basis over the lease term. The respective leased assets are included in the balance sheet based on their nature.
Q Revenue recognition
Revenue is recognized when control over a good or service is transferred to customer and thus when the latter has the ability to direct the use and obtain the benefits from the good or service. Revenue is recognized either over time or at a point in time, when (or as) the Group satisfies performance obligations by transferring the promised services or goods to its customers.
Group revenue arises mainly from airports operations and includes:
Aeronautical revenues
These revenues are those generally regulated under each airport’s concession agreement. They consist of passengers’ departure fees, landing, parking and other fees paid by the airlines.
Revenue from aeronautical services, derived from the use of airports facilities by aircrafts and passengers, is recognized over time as the services are provided. The Group considers that it has completed its performance obligations when the services (for instance passenger fee rate, landing rates, platform use fees, among others) are rendered to its customers. The Group does not defer collection terms in excess of the normal market terms, so there is no need to distinguish between a commercial component and a revenue interest component.
Non-aeronautical revenues
| - | Commercial revenues: those are typically not regulated under the applicable concession agreement. Commercial revenues are leases and/or rent fees from retail (including duty free), food and beverage, services and car rental companies, advertising, car parking, fueling charges and cargo fees, among others. |
| - | Construction service revenues: IFRIC 12 requires to recognize revenues and costs from the construction or upgrade services provided. Construction service revenue equals the construction or upgrade costs plus a reasonable margin determined according to the analysis performed by each concession. |
Under the terms of IFRIC 12 “Service Concession Arrangements”, a concession operator may have a twofold activity:
| - | a construction activity in respect of its obligations to design, build and finance a new asset that it delivers to the grantor; |
| - | an operating and maintenance activity in respect of concession assets. |
Revenue from non-aeronautical activities such as commercial revenue (excluding sale of goods, leases and sub-concession of spaces) and construction services are recognized over time. The Group considers that it has completed its performance obligations when the services (such as warehouse use fees, parking facilities and VIP lounges) are rendered to its customers or construction costs are incurred.
F-33
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
Q Revenue recognition (Cont.)
Revenue from sale of goods, mainly fueling, is recognized at a point in time when control of the goods is transferred to the customer and the customer obtains the benefits from the goods. The Group considers that it has completed its performance obligations when the goods are supplied to its customers.
The Group recognizes contract liabilities for consideration received in respect of unsatisfied performance obligations and reports these amounts as Other liabilities in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position. Similarly, if the Group satisfies a performance obligation before it receives the consideration, the Group recognizes either a contract asset or a receivable in its Consolidated Statement of Financial Position, depending on whether something other than the passage of time is required before the consideration is due.
Revenue is shown net of value-added tax and discounts. Intercompany balances with subsidiaries have been eliminated in consolidation.
R Cost of services and other expenses
Cost of services and other expenses are accrued and recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Income.
Construction service cost: IFRIC 12 requires to recognize revenues and costs from the construction or upgrade services provided.
Commissions, freight and other selling expenses, including services and fees, office expenses and maintenance, are recorded in Selling, general and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statement of Income.
S Government grants
Government grants are recognized at their fair value where there is a reasonable assurance that the grant will be received and the Group will comply with all attached conditions.
Government grants relating to costs are deferred and recognized in profit or loss over the period necessary to match them with the costs that they are intended to compensate.
A government grant that becomes receivable as a compensation for expenses or losses already incurred, or for the purpose of giving immediate support to the Group, with no future related costs, shall be recognized in profit or loss of the period in which it becomes receivable.
Grants related to income are presented as part of profit or loss, either separately or under a general heading such as Other operating income; alternatively, they are deducted from the related expense.
Grants related to assets, including non-monetary grants at fair value, are presented in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position, either by setting up the grant as deferred income or by deducting the grant in arriving at the carrying amount of the asset.
F-34
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
T Financial instruments
Non-derivative financial instruments comprise investments in debt instruments, corporate bonds, time deposits, trade and other receivables, cash and cash equivalents, borrowings, and trade and other payables.
The Group classifies its financial assets in the following measurement categories:
(i) |
Amortized cost: Assets that are held for collection of contractual cash flows where those cash flows represent solely payments of principal and interest are measured at amortized cost. Interest income from these financial assets is included in financial income using the effective interest rate method. Any gain or loss arising on derecognition is recognized directly in profit or loss and presented in other gains/(losses) together with foreign exchange gains and losses. Impairment losses are presented as separate line item in the Consolidated Statement Income. |
(ii) |
Fair value through other comprehensive income (“FVOCI”): Assets that are held for collection of contractual cash flows and for selling the financial assets, where the assets’ cash flows represent solely payments of principal and interest, are measured at FVOCI. Movements in the carrying amount are taken through OCI, except for the recognition of impairment gains or losses, interest revenue and foreign exchange gains and losses which are recognized in profit or loss. When the financial asset is derecognized, the cumulative gain or loss previously recognized in OCI is reclassified from equity to profit or loss and recognized in other gains/(losses). Interest income from these financial assets is included in finance income using the effective interest rate method. Foreign exchange gains and losses are presented in other gains/(losses) and impairment expenses are presented as separate line item in the Consolidated Statement of Income. |
(iii) |
Fair value through profit or loss (“FVPL”): Assets that do not meet the criteria for amortized cost or FVOCI are measured at FVPL. A gain or loss on a debt investment that is subsequently measured at FVPL is recognized in profit or loss and presented net within other gains/(losses) in the period in which it arises. |
The classification depends on the Company’s business model for managing the financial assets and the contractual terms of the cash flows.
The Group assesses on a forward-looking basis the expected credit losses associated with its debt instruments carried at amortized cost and FVOCI. The impairment methodology applied depends on whether there has been a significant increase in credit risk.
U Derivative financial instruments
Derivatives are initially recognized at fair value on the date a derivative contract is entered into, and they are subsequently remeasured to their fair value at the end of each reporting period. The accounting for subsequent changes in fair value depends on whether the derivative is designated as a hedging instrument and, if so, the nature of the item being hedged.
Changes in the fair value of any derivative instrument that does not qualify for hedge accounting are recognized immediately in profit or loss and are included in Financial income or Financial loss line.
Derivatives are classified as “held for trading” for accounting purposes and are accounted for at fair value through profit or loss. They are presented as current assets or liabilities to the extent they are expected to be settled within 12 months after the end of the reporting period.
Derivative financial instruments as of December 31, 2023 are classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy.
F-35
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
V Segment information
Operating segments are reported in a manner consistent with the internal reporting provided to the Chief Operating Decision Maker (“CODM”), which is the Group’s Board of Directors. The CODM is responsible for allocating resources and assessing performance of the operating segments. The operating segments are described in Note 4.
For management purposes, the Company analyzes its business based on strategic business units providing airport and non-airport services to clients in the different countries where business units are located. Assets, liabilities and results from holding companies are included as Unallocated.
W Application of IAS 29 in financial reporting of Argentine subsidiaries and associates
IAS 29 “Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary Economies” requires that the financial statements of entities whose functional currency is that of a hyperinflationary economy to be adjusted for the effects of changes in a suitable general price index and to be expressed in terms of the current unit of measurement at the closing date of the reporting period, regardless of whether they are based on the historical cost method or the current cost method. Accordingly, the inflation produced from the date of acquisition or from the revaluation date, as applicable, must be computed in the non-monetary items.
In order to conclude whether an economy is categorized as hyperinflationary in the terms of IAS 29, the standard details a series of factors to be considered, including the existence of a cumulative inflation rate in three years that approximates or exceeds 100%. Considering that the inflation in Argentina has exceeded the 100% three-year cumulative inflation rate in July 2018, and that the rest of the indicators do not contradict the conclusion that Argentina should be considered a hyperinflationary economy for accounting purposes, the Group understands that there is sufficient evidence to conclude that Argentina is a hyperinflationary economy under the terms of IAS 29 as from July 1, 2018, and, accordingly, it has applied IAS 29 as from that date in the financial reporting of its subsidiaries and associates with the Argentine peso as functional currency.
The inflation adjustment was calculated by means of conversion factor derived from the Argentine price indexes published by the National Institute of Statistics (“INDEC”).
The Government Board of the Argentine Federation of Professional Councils of Economic Sciences (FACPCE) issued Resolution JG 539/18, which prescribes the indices to be used by entities with a functional currency of the Argentine peso for the application of the restatement procedures. These indices are largely based on the Wholesale Price Index for periods up to December 31, 2016 and the Retail Price Index thereafter.
The price index as of December 31, 2023, was 3,533.19 (1,134.59 and 582.46 as of December 31, 2022 and 2021 respectively) and the conversion factor derived from the indexes for the year ended December 31, 2023, was 3.11 (1.95 and 1.51 as of December 31, 2022 and 2021 respectively).
F-36
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
W Application of IAS 29 in financial reporting of Argentine subsidiaries and associates (Cont.)
The main procedures for the above-mentioned adjustment are as follows:
● Monetary assets and liabilities which are carried at current amounts at the balance sheet date are not restated because they are already expressed in terms of the monetary unit current at the balance sheet date.
● Non-monetary assets and liabilities which are not carried at current amounts at the balance sheet date, and components of shareholders’ equity are adjusted by applying the relevant conversion factors at the date of the transactions.
● All items in the statement of income are restated by applying the relevant conversion factors.
● The effect of inflation on the Company’s net monetary position is included in Inflation adjustment in the Consolidated Statement of Income. Exchange rate gains and losses derived from the net monetary position are presented in real (inflation-adjusted) terms.
● The ongoing application of the re-translation of comparative amounts to closing exchanges rates under IAS 21 and the hyperinflation adjustments required by IAS 29 will lead to a difference in addition to the difference arising on the adoption of hyperinflation accounting. This is because the rate at which the hyperinflationary currency depreciates against a stable currency is rarely equal to the rate of inflation. The inflation adjustment and the translation of the current period is included in Currency translation adjustment in Other comprehensive income / (loss) for the year line.
X Critical accounting estimates and judgments
Critical accounting estimates are those that require management to make significant judgments and estimates about matters that are inherently uncertain. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and other assumptions that it believes are reasonable. Actual results could differ from estimates used in employing the critical accounting policies and these could have a material impact on the Group’s results of operations.
The Group’s critical accounting estimates are discussed below.
(a) |
Impairment testing |
At the date of each statement of financial position, the Group reviews the carrying amounts of its property, plant and equipment and intangible assets with finite useful lives to determine whether there is any indication that those assets have suffered an impairment loss. If any such indication exists, the recoverable amount of the asset is estimated in order to determine the extent, if any, of the impairment loss. Assets that have an indefinite useful life or assets not ready to use are not subject to amortization and are tested annually for impairment.
For the purposes of assessing impairment, assets are grouped at the lowest levels for which there are largely independent cash inflows (cash-generating units or CGUs). As mentioned in Note 12, the Company performed impairment tests for those assets with impairment indicators based on the discounted cash flow model covering the remaining concessions periods (value in use), considering significant assumptions that required management judgment related to passenger growth rates and discount rate, combined with historical information. An impairment loss, if applicable, is recognized for the amount by which the asset’s carrying amount exceeds its recoverable amount. The recoverable amount is the higher of an asset’s fair value less costs of disposal and value in use. Prior impairments of non-financial assets (other than goodwill) are reviewed for possible reversal at each reporting date. A previously recognized impairment loss of non-financial assets (other than goodwill) is reversed if, in a subsequent period, the amount of the impairment loss decreases and the decrease can be related objectively to an event occurring after the impairment was recognized, the reversal of the previously recognized impairment loss is recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Income.
F-37
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
2 Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Cont.)
X Critical accounting estimates and judgments (Cont.)
(b) |
Income taxes |
The Group is subject to income taxes in numerous jurisdictions. Significant judgment is required in determining the worldwide provision for income taxes. There are many transactions and calculations for which the ultimate tax determination is uncertain. The Group recognizes liabilities for anticipated tax audit issues based on estimates of whether additional taxes will be due. Where the final tax outcome of these matters is different from the amounts that were initially recorded, such differences will impact the current and deferred income tax assets and liabilities in the period in which such determination is made.
Deferred tax is recognized, using the liability method, on temporary differences arising between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their carrying amounts in the Consolidated Financial Statements. However, deferred tax liabilities are not recognized if they arise from the initial recognition of goodwill. Deferred income tax is determined using tax rates (and laws) that have been enacted or substantially enacted by the balance sheet date and are expected to apply when the related deferred income tax asset is realized or the deferred income tax liability is settled.
Deferred tax assets are reviewed at each reporting date and reduced to the extent that it is no longer probable that sufficient taxable income will be available to allow all or part of the asset to be settled. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are not discounted. In assessing the recoverability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is probable that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income and tax planning strategies in making this assessment.
(c) |
Concession - application of IFRIC 12 |
The Group has carried out a comprehensive implementation of the standards applicable to the accounting treatment of their concession and has determined that, among others, IFRIC 12 is applicable. The Group treats their investments related to improvements and upgrades to be performed in connection with the concession obligation under the intangible asset model established by IFRIC 12, as all investments required by the concession obligation, regardless of their nature, directly increase the maximum tariff per traffic unit. Accordingly, all amounts invested under the concession obligation have a direct correlation to the amount of fees the Group will be able to charge each passenger or cargo service provider, and thus, a direct correlation to the amount of revenues the Group will be able to generate. As a result, the Group defines all expenditures associated with investments required by the concession obligation as revenue generating activities given that they ultimately provide future benefits, whereby subsequent improvements and upgrades made to the concession are recognized as intangible assets based on the principles of IFRIC 12. Additionally, compliance with the committed investments per the Master Development Programs is mandatory, as well as the fulfillment of the maximum tariff and therefore, in case of a failure to meet any one of these obligations, the Group could be subject to sanctions and the concessions could be revoked.
F-38
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
3 Financial Risk Management
The Group’s operations expose it to a variety of risks, mainly related to market risks (including the effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates and interest rates), credit risk and liquidity risk. The Group manages its financial risk exposure independently at each operating subsidiary, however, decisions are discussed by the Board of Directors (“BOD”) members.
The most significant financial risks to which the Group is exposed are detailed below.
AFinancial Risk Factors
(i) |
Market risk |
a) |
Foreign exchange risk |
The Group operates in a number of countries throughout the world and consequently is exposed to foreign exchange rate risk. In addition, the Group has certain investments in foreign operations, whose net assets are exposed to foreign currency translation risk.
In order to manage foreign exchange risk, the Group has a strategy based on minimizing net positions of assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies together with the use of derivative financial instruments.
During last years the Argentine monetary authority imposed certain exchange rate restrictions, which also affect the value of foreign currency in alternative markets for certain restricted exchange rate transactions in the official market. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, these measures have remained in force restricting the access to the foreign exchange market in order to contain the demand for U.S. dollars include the requirement to obtain prior authorization from the Central Bank of Argentina for certain transactions in the Mercado Único y Libre de Cambios (“MULC”).
Considering this situation, the Company continues to assess the evolution of the above-mentioned variables and any other factors in its Argentine subsidiaries in order to identify the unforeseen potential effects that could alter its business and performance.
The value of the Group’s financial assets and liabilities is subject to changes arising out of the variation of foreign currency exchange rates. A significant majority of the Group’s business activities is conducted in the respective functional currencies of the subsidiaries. However, the Group transacts in currencies other than the respective functional currencies of the subsidiaries. There are material monetary balances held by the Group companies at each period-end that are denominated in other currencies (non-functional currency). The following table provides a breakdown of the Group’s main monetary net assets and liabilities which impact the Group’s profit and loss:
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
As of December 31, |
Currency Exposure / Functional currency |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
U.S. Dollar / Argentine Peso |
|
(484,709) |
|
(587,955) |
U.S. Dollar / Armenian Dram |
|
47,842 |
|
14,847 |
Euro / Armenian Dram |
|
347 |
|
4,637 |
Euro / Argentine Peso |
|
(2,831) |
|
(1,151) |
F-39
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
3 Financial Risk Management (Cont.)
A. |
Financial Risk Factors (Cont.) |
(i)Market risk (Cont.)
a)Foreign exchange risk (Cont.)
The relevant exposures correspond to:
◾ U.S. Dollar / Argentine Peso
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022 consisting primarily of U.S. dollar -denominated net monetary assets and liabilities at certain Argentine subsidiaries which functional currency is the Argentine Peso. A change of 10% in the ARS/ USD exchange rate in real (inflation-adjusted) terms would have generated a pre-tax gain / loss of USD 48,470 as of December 31, 2023 (USD 17,639 as of December 31, 2022 considering a change in 3% in the ARS/ USD exchange rate).
◾ U.S. Dollar / Armenian Dram
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022 consisting primarily of U.S. dollar -denominated net monetary assets and liabilities at the Armenian subsidiaries which functional currency is the Armenian Dram. A change of 1% in the Dram/ USD exchange rate would have generated a pre-tax gain / loss of USD 478.4 as of December 31, 2023 (USD 148.5 as of December 31, 2022).
◾ Euro / Armenian Dram
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022 consisting primarily of Euro-denominated net monetary assets and liabilities at the Armenian subsidiaries which functional currency is the Armenian Dram. A change of 1% in the Dram / Euro exchange rate would have generated a pre-tax loss / gain of USD 3.5 as of December 31, 2023 (USD 46.4 as of December 31, 2022).
◾ Euro / Argentine Peso
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022 consisting primarily of Euro-denominated net monetary assets and liabilities at certain Argentinian subsidiaries which functional currency is the Argentine Peso. A change of 10% in the Euro / ARS exchange rate in real (inflation-adjusted) terms would have generated a pre-tax gain / loss of USD 283.1 as of December 31, 2023 (USD 34.5 as of December 31, 2022 considering a change in 3% in the Euro / ARS exchange rate).
b) |
Interest rate risk |
The Group’s interest rate risk principally arises from long-term borrowings (Note 22). Borrowings issued at variable rates expose the Group to the risk that the actual cash flows differ from those expected. Borrowings issued at fixed rates expose the Group to the risk that the fair values of these differ from those expected. The Group manages this risk by maintaining an appropriate mix between fixed and floating rate interest bearing liabilities.
These activities are evaluated regularly to determine that the Group is not exposed to interest rate movements that could adversely impact its ability to meet its financial obligations and to comply with its borrowing covenants.
The following table shows a breakdown of the Group’s fixed-rate and floating-rate borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
|
|
At December 31, |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Fixed rate (*) |
|
990,251 |
|
1,075,778 |
Variable rate |
|
342,986 |
|
389,659 |
|
|
1,333,237 |
|
1,465,437 |
(*) As of December 31, 2023 includes USD 125.5 million of short-term borrowings (USD 103.5 million as of December 2022) and USD 864.8 million of long-term borrowings (USD 972.3 million as of December 31, 2022).
F-40
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
3 Financial Risk Management (Cont.)
| A. | Financial Risk Factors (Cont.) |
(i) |
Market risk (Cont.) |
(b) |
Interest rate risk (Cont.) |
The Group estimates that, other factors being constant, a 10% increase in floating rates at year-end would increase loss before income tax for the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, USD 2,695 and USD 4,083 respectively. A 10% decrease in the floating interest rate would have an equal and opposite effect on the Consolidated Statement of Income.
This sensitivity analysis provides only a limited, point-in-time view of this market risk sensitivity of certain of the Group’s financial instruments. The actual impact of rate changes on the Group’s financial instruments may differ significantly from the impact shown in the sensitivity analysis.
(ii) |
Credit risk |
The financial instruments that could be subject to concentration of credit risk consist of cash, cash equivalents, trade receivables and short-term investments.
The Group mainly places its cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments in several entities with low credit risk, reducing in this way the credit exposure to only one entity. The Group has not experienced significant losses from those assets.
Each subsidiary is responsible for managing and analyzing credit risk of its trade receivable, for each of their new customers before standard payment and delivery terms and conditions are offered. There is no significant concentration of credit risk from customers.
The Group credit policies with customers are designed to identify customers with acceptable credit history. The Group recognized provision for loss allowance to cover impairment for potential credit losses. The credit quality of the financial assets that are not yet due and not impaired can be assessed based on the credit qualification (“rating”) granted by entities external to the Group or through the historical uncollectible rates.
F-41
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
3 Financial Risk Management (Cont.)
A Financial Risk Factors (Cont.)
(ii) |
Credit risk (Cont.) |
Trade receivables and contract assets
The Group applies the IFRS 9 simplified approach to measuring expected credit losses (“ECL”) for all trade receivables and contract assets.
To measure the expected credit losses, trade receivables and contract assets have been grouped based on shared credit risk characteristics and the days past due. The contract assets relate to unbilled work in progress and have substantially the same risk characteristics as the trade receivables for the same types of contracts. The Group has therefore concluded that the expected loss rates for trade receivables are a reasonable approximation of the loss rates for the contract assets.
The policy implemented by the Group consists in performing a case by case analysis, identifying those receivables and contract assets with no reasonable expectation of recovery or with particular situations, that are impaired according to each circumstances. For all other receivables and contract assets, the expected loss rate consists in stratifying trade receivables and contract assets into categories based on overdue days. The expected loss rates are based on the payment profiles of sales over a period of 36 months before 31 December 2023 or 1 January 2023 respectively and the corresponding historical credit losses experienced within this period. The historical loss rates are adjusted to reflect historical experience of losses on trade receivables, current and forward-looking information on macroeconomic factors affecting the ability of the customers to settle the receivables. To measure the expected credit losses, trade receivables and contract assets have been grouped based on shared credit risk characteristics and the days past due.
The provision for loss allowance as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 was determined as follows for both trade receivables and contract assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Past due |
|
||||||||
|
|
Trade |
|
|
|
|
|
30‑60 |
|
60‑90 |
|
90‑180 |
|
> 180 |
|
|
|
Receivables |
|
Not due |
|
0‑30 days |
|
days |
|
days |
|
days |
|
days |
|
At December 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trade receivables – gross carrying amount |
|
148,329 |
|
86,066 |
|
23,685 |
|
9,783 |
|
2,274 |
|
4,617 |
|
21,904 |
|
Contract assets – gross carrying amount |
|
1,488 |
|
1,488 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
Expected loss rate (*) |
|
|
|
2% |
|
1% |
|
5% |
|
13% |
|
25% |
|
86% |
|
Provision for loss allowance |
|
(22,368) |
|
(1,466) |
|
(230) |
|
(449) |
|
(298) |
|
(1,150) |
|
(18,775) |
|
Net value |
|
127,449 |
|
86,088 |
|
23,455 |
|
9,334 |
|
1,976 |
|
3,467 |
|
3,129 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Past due |
|
||||||||
|
|
Trade |
|
|
|
|
|
30‑60 |
|
60‑90 |
|
90‑180 |
|
> 180 |
|
|
|
Receivables |
|
Not due |
|
0‑30 days |
|
days |
|
days |
|
days |
|
days |
|
At December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trade receivables - gross carrying amount |
|
140,335 |
|
75,105 |
|
20,644 |
|
5,420 |
|
4,426 |
|
5,815 |
|
28,925 |
|
Contract assets – gross carrying amount |
|
2,053 |
|
2,053 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
Expected loss rate (*) |
|
|
|
0% |
|
4% |
|
17% |
|
15% |
|
29% |
|
88% |
|
Provision for loss allowance |
|
(29,718) |
|
(152) |
|
(845) |
|
(945) |
|
(672) |
|
(1,660) |
|
(25,444) |
|
Net value |
|
112,670 |
|
77,006 |
|
19,799 |
|
4,475 |
|
3,754 |
|
4,155 |
|
3,481 |
|
(*) Average expected loss rate. As of December 2023 and 2022, includes effect of the impact of the provisions risen from the case by case analysis. Additionally, as of December 2022 includes effect of Argentine customer situation as described in Note 26.a.
F-42
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
3 Financial Risk Management (Cont.)
A Financial Risk Factors (Cont.)
(ii) |
Credit risk (Cont.) |
Trade receivables and contract assets (Cont.)
Trade receivables are written off where there is no reasonable expectation of recovery. Indicators that there is no reasonable expectation of recovery include, amongst others, the failure of a debtor to engage in a repayment plan with the Group, and a failure to make contractual payments for a significant period when past due.
The closing loss allowances for trade receivables and contract assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 reconcile to the opening loss allowances as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
Balance at January 1, |
|
(29,718) |
|
(60,510) |
|
Disposal of subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
310 |
|
Bad debts of the year |
|
(4,735) |
|
(13,432) |
|
Recoveries |
|
3,331 |
|
17,931 |
|
Write off |
|
2,717 |
|
3,684 |
|
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
6,037 |
|
22,299 |
|
Balance at December 31, |
|
(22,368) |
|
(29,718) |
|
During the year, the following gains/(losses) were recognized in profit or loss in relation to impaired financial assets (see Note 7):
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Impairment losses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- movement in provision for impairment |
|
(4,985) |
|
(13,443) |
|
(14,727) |
- recovery of previous impairment losses |
|
3,439 |
|
18,203 |
|
8,311 |
Net impairment losses on financial assets |
|
(1,546) |
|
4,760 |
|
(6,416) |
(iii) |
Liquidity risk |
The Group is exposed to liquidity risks, including risks associated with refinancing borrowings as they mature, the risk that borrowing facilities are not available to meet cash requirements, and the risk that financial assets cannot readily be converted to cash without loss of value. Failure to manage liquidity risks could have a material impact on the Group’s cash flow and statement of financial position. Prudent liquidity risk management implies maintaining sufficient cash, the availability of funding through an adequate amount of committed credit facilities and the ability to close out market positions. Due to the dynamic nature of the underlying businesses, the Group aims to maintain flexibility in funding its existing and prospective debt requirements by maintaining diversified funding sources with adequate committed funding lines from high quality lenders.
The Group monitors its current and projected financial position using several key internally generated reports such as cash flow and debt maturity. The Group also undertakes sensitivity analysis to assess the impact of proposed transactions, movements in interest rates on the key profitability, liquidity and balance sheet ratios.
The Group’s debt positions are continually reviewed to meet current and expected debt requirements. The Group maintains a balance between longer-term and shorter-term financings. Short-term financing is principally raised through bank facilities and overdraft positions. Medium- to longer-term financing comprises public and private bond issues, including private placements. Financing risk is spread by using different types of debt. The maturity profile is managed, by spreading the repayment dates and extending facilities.
F-43
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
3 Financial Risk Management (Cont.)
A Financial Risk Factors (Cont.)
(iii) |
Liquidity risk (Cont.) |
Liquid financial assets as a whole (comprising cash and cash equivalents) were 10.44% of total assets at the end of 2023 compared to 10.04% at the end of 2022. The Group has a conservative approach to the management of its liquidity, which consists mainly in cash at banks and cash equivalents.
(iv) |
Capital Management |
The capital structure of the Group consists of shareholders’ equity and short-term to long-term net borrowings. The type and maturity of the Group’s borrowings are analyzed further in Note 22. The Group’s equity is analyzed into its various components in the Consolidated Statement of Changes in Equity.
Capital is managed so as to promote the long-term success of the business and to maintain sustainable returns for shareholders.
The objectives of the Group for capital management are to safeguard its capacity to continue doing business and be able to provide yield to owners as well as benefits to holders of instruments of shareholder’s equity and maintain an optimum capital structure to reduce cost of capital.
|
|
At December 31, |
|
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
Borrowings |
|
1,333,237 |
|
1,465,437 |
|
Less: Cash and cash equivalents |
|
(369,848) |
|
(385,265) |
|
Net debt |
|
963,389 |
|
1,080,172 |
|
Equity |
|
803,909 |
|
862,369 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net debt to equity ratio |
|
120% |
|
125% |
|
(v) |
Argentina economical context |
CAAP’s Argentine subsidiaries are operating in an economic context in which main variables have a strong volatility as consequence of political and economic uncertainties, both in national and international environments.
On December 10, 2023, a new government took office with the aim to boost a deregulation of the Argentine economy and a reduction of the fiscal deficit mainly through cutting spending, including the gradual release of the current foreign exchange market restrictions, aiming to remove them once the macroeconomic conditions are in place to do so. On December 13, 2023, the Argentine peso experienced a sharp drop with an ARS/USD rate devalued by more than 300% at year-end while annual inflation reached 211% in 2023. Moreover, on December 13, 2023, the Central Bank of Argentina (“BCRA”) informed that entities are able to access the Mercado Único y Libre de Cambios (“MULC”) without prior approval to pay outstanding debts related to imports of goods or services with customs registration from December 13, 2023.
Among its first measures, the new government published Decree N° 70/2023 - Foundations for the Reconstruction of the Argentine Economy, which, in addition to declaring a public emergency in several areas until 31 December 2025, repeals and/or amends numerous laws of previous Government intervention in the economy, with the aim of opening up trade, services and industry, and eliminate undue restrictions. Even though the Decree must be addressed and ratified by at least one of the chambers of the Congreso de la Nación of Argentine, its provisions are partially effective as of December 29, 2023, while other provisions have been suspended following, judicial actions.
F-44
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
3 Financial Risk Management (Cont.)
A Financial Risk Factors (Cont.)
(v) |
Argentina economical context (Cont.) |
As of December 31, 2023 the main measures taken by the new government that affect the Group’s business and are already in effect are:
| ● | Restrictions on access to the official exchange market are maintained. |
| ● | Taxes over transactions that involves the purchase of foreign currencies for the payment of certain imports are maintained. |
| ● | Subject to certain requirements, the BCRA offers entities that hold debt for imports performed prior to December 13, 2023, the possibility of subscribing to dollar-denominated notes (“BOPREAL”). These notes, which are issued in three series with maturity on October 31, 2027 for Series 1, June 30, 2025 for Series 2 and March 31, 2026 for Series 3, are to be subscribed in Argentine pesos at the reference exchange rate published by the BCRA according to Communiqué “A” 3500 of the day before the subscription date. For those who subscribe the notes in primary issuance, it allows them to cancel import debts, through the sale of the notes in the secondary market with settlement in foreign currency abroad without affecting the access to the MULC or through the delivery in kind of the notes to suppliers abroad. Additionally, having subscribed the BOPREAL allows the access to the official foreign exchange market as from February 1, 2024, to pay commercial debts related to the import of goods and services prior to December 13, 2023, for a total amount equivalent to 5% of the Series 1 subscribed amount. Subsequent to December 31, 2023, AA2000 subscribed to BOPREAL’s Series 1 and Series 2, see Note 34. |
Considering this situation, the Company continues to assess the evolution of the above-mentioned variables and any other factors, in order to define its course of action and identify the unforeseen potential effects that could alter its business and performance.
B Financial instruments by category
|
|
Assets at fair value |
|
Assets at amortized |
|
|
December 31, 2023 |
|
through profit and loss |
|
cost |
|
Total |
Financial assets as per the statement of financial position |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trade receivables |
|
— |
|
127,449 |
|
127,449 |
Other receivables |
|
— |
|
154,583 |
|
154,583 |
Other financial assets (*) |
|
10,863 |
|
144,232 |
|
155,095 |
Derivative financial assets |
|
69 |
|
— |
|
69 |
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
— |
|
369,848 |
|
369,848 |
Total |
|
10,932 |
|
796,112 |
|
807,044 |
|
|
Liabilities at fair value |
|
Liabilities at |
|
|
|
|
through profit and loss |
|
amortized cost |
|
Total |
Financial liabilities as per the statement of financial position |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Borrowings |
|
— |
|
1,333,237 |
|
1,333,237 |
Leases liabilities |
|
— |
|
13,981 |
|
13,981 |
Derivative financial liabilities |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Trade payables and other liabilities |
|
— |
|
1,062,621 |
|
1,062,621 |
Total |
|
— |
|
2,409,839 |
|
2,409,839 |
F-45
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
3 Financial Risk Management (Cont.)
B Financial instruments by category (Cont.)
|
|
Assets at fair value |
|
Assets at amortized |
|
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
through profit and loss |
|
cost |
|
Total |
Financial assets as per the statement of financial position |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trade receivables |
|
— |
|
110,617 |
|
110,617 |
Other receivables |
|
— |
|
107,708 |
|
107,708 |
Other financial assets (*) |
|
15,952 |
|
57,669 |
|
73,621 |
Derivative financial assets |
|
67 |
|
— |
|
67 |
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
— |
|
385,265 |
|
385,265 |
Total |
|
16,019 |
|
661,259 |
|
677,278 |
|
|
Liabilities at fair value |
|
Liabilities at |
|
|
|
|
through profit and loss |
|
amortized cost |
|
Total |
Financial liabilities as per the statement of financial position |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Borrowings |
|
— |
|
1,465,437 |
|
1,465,437 |
Leases liabilities |
|
— |
|
8,809 |
|
8,809 |
Derivative financial liabilities |
|
51 |
|
— |
|
51 |
Trade payables and other liabilities |
|
— |
|
1,100,603 |
|
1,100,603 |
Total |
|
51 |
|
2,574,849 |
|
2,574,900 |
(*) Other financial assets measured at fair value are Level 1 hierarchy. The book value of these assets represents its fair value.
C Fair value hierarchy
IFRS 13 requires for financial instruments that are measured in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position at fair value, a disclosure of fair value measurements by level according to the following fair value measurement hierarchy:
Level 1- Quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2- Inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (that is, as prices) or indirectly (that is, derived from prices).
Level 3- Inputs for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (that is, unobservable inputs).
There were no transfers between Level 1 and Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy and there were no transfers from Level 1 and Level 2 to Level 3.
The fair value of financial instruments traded in active markets is based on quoted market prices at the reporting date. A market is regarded as active if quoted prices are readily and regularly available from an exchange, dealer, broker, industry group, pricing service, or regulatory agency, and those prices represent actual and regularly occurring market transactions on an arm’s length basis. These instruments are included in Level 1 and comprise primarily government securities, mutual funds and corporate bonds.
F-46
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
3 Financial Risk Management (Cont.)
D Fair value estimation
The estimated fair value of a financial instrument is the amount at which the instrument could be exchanged in a current transaction between willing parties, other than in a forced or liquidation sale.
4 Segment information
Operating segments are components of an enterprise where separate financial information is available that is evaluated regularly by the Chief Operating Decision Maker (“CODM”), or decision-making group, in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The Group’s chief operating decision maker is its Board of Directors. The Group’s operating segments are managed separately because each operating segment represents a strategic business unit providing airport and non-airport services (“others”) to clients in different countries. The Group’s reportable operating segments are the six countries in which the Group currently operates, which are Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay, Armenia, Ecuador and Italy.
Within each reportable segment, the Group develops and operates airport concessions (“Airports”) and provides other services not directly related to airport concessions.
Assets, liabilities and results of sub-holding and/or holding companies are not allocated and are reported within the “Unallocated” column. This column also includes head office and group services.
The elimination of any intersegment revenues and other significant intercompany operations are included in the “Intrasegment Adjustments” column.
The performance of each reportable segment is measured by its adjusted EBITDA, defined, with respect to each segment, as net income before financial income, financial loss, inflation adjustment, income tax expense, depreciation and amortization for such segment (“Adjusted EBITDA”). The Adjusted EBITDA does not exclude the amortization of the intangible asset related to the fixed fee payable to the corresponding governments for the operation of the airport concessions.
In addition, the CODM considers each reportable segment’s Adjusted EBITDA before Construction Services margin as a relevant performance measure.
Adjusted EBITDA excluding Construction Services is defined, with respect to each segment, as net income before construction services revenue, financial income, construction services cost, financial loss, inflation adjustment, income tax expense, depreciation and amortization for such segment. The Adjusted EBITDA excluding construction services revenue and construction services cost (which are based on the principles of IFRIC 12) does not exclude the amortization of the intangible asset related to the fixed fee payable to the corresponding governments for the operation of airport concessions.
F-47
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
4 Segment information (Cont.)
Geographical information
|
|
Argentina |
|
|
Brazil |
|
|
Uruguay |
|
|
Armenia |
|
|
Ecuador |
|
|
Italy |
|
|
Intrasegment |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Airports |
|
Others |
|
|
Airports |
|
Others |
|
|
Airports |
|
Others |
|
|
Airports |
|
|
Airports |
|
|
Airports |
|
|
adjustments |
|
Unallocated |
|
Total |
Year ended December 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical revenue (*) |
|
296,393 |
|
— |
|
|
45,656 |
|
— |
|
|
65,428 |
|
— |
|
|
88,519 |
|
|
78,336 |
|
|
70,121 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
644,453 |
Non-aeronautical revenue (*) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
251,155 |
|
119 |
|
|
64,838 |
|
— |
|
|
45,292 |
|
22,785 |
|
|
160,355 |
|
|
26,871 |
|
|
39,908 |
|
|
(11,598) |
|
3,926 |
|
603,651 |
Construction service revenue |
|
93,014 |
|
— |
|
|
151 |
|
— |
|
|
31,705 |
|
— |
|
|
3,630 |
|
|
21 |
|
|
16,201 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
144,722 |
Other revenue |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
20 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
7,192 |
|
|
(3,997) |
|
3,997 |
|
7,212 |
Cost of services |
|
(420,216) |
|
(40) |
|
|
(79,304) |
|
— |
|
|
(86,227) |
|
(17,818) |
|
|
(156,482) |
|
|
(62,285) |
|
|
(91,639) |
|
|
11,266 |
|
(11,932) |
|
(914,677) |
Gross profit / (loss) |
|
220,346 |
|
79 |
|
|
31,341 |
|
— |
|
|
56,218 |
|
4,967 |
|
|
96,022 |
|
|
42,943 |
|
|
41,783 |
|
|
(4,329) |
|
(4,009) |
|
485,361 |
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
(54,907) |
|
(80) |
|
|
(10,996) |
|
(68) |
|
|
(16,305) |
|
(2,611) |
|
|
(15,320) |
|
|
(17,827) |
|
|
(13,149) |
|
|
4,329 |
|
(11,735) |
|
(138,669) |
Impairment reversal / (loss) of non-financial assets (**) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
103,764 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(926) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
102,838 |
Other operating income (**) |
|
13,425 |
|
1 |
|
|
82,793 |
|
— |
|
|
58 |
|
2 |
|
|
361 |
|
|
240 |
|
|
710 |
|
|
— |
|
2,970 |
|
100,560 |
Other operating expenses |
|
(7,344) |
|
— |
|
|
(542) |
|
— |
|
|
(443) |
|
(63) |
|
|
(1,021) |
|
|
(38) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
(2) |
|
(9,453) |
Operating income / (loss) |
|
171,520 |
|
— |
|
|
206,360 |
|
(68) |
|
|
39,528 |
|
2,295 |
|
|
80,042 |
|
|
25,318 |
|
|
28,418 |
|
|
— |
|
(12,776) |
|
540,637 |
Share of income / (loss) in associates |
|
(5) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
14 |
|
|
— |
|
7,099 |
|
7,108 |
Amortization and depreciation |
|
60,534 |
|
— |
|
|
12,035 |
|
— |
|
|
6,906 |
|
1,248 |
|
|
19,638 |
|
|
6,688 |
|
|
10,695 |
|
|
— |
|
12,238 |
|
129,982 |
Adjusted Ebitda |
|
232,049 |
|
— |
|
|
218,395 |
|
(68) |
|
|
46,434 |
|
3,543 |
|
|
99,680 |
|
|
32,006 |
|
|
39,127 |
|
|
— |
|
6,561 |
|
677,727 |
Construction services revenue |
|
(93,014) |
|
— |
|
|
(151) |
|
— |
|
|
(31,705) |
|
— |
|
|
(3,630) |
|
|
(21) |
|
|
(16,201) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
(144,722) |
Construction services cost |
|
92,898 |
|
— |
|
|
151 |
|
— |
|
|
31,705 |
|
— |
|
|
3,524 |
|
|
21 |
|
|
9,972 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
138,271 |
Adjusted Ebitda excluding Construction Services |
|
231,933 |
|
— |
|
|
218,395 |
|
(68) |
|
|
46,434 |
|
3,543 |
|
|
99,574 |
|
|
32,006 |
|
|
32,898 |
|
|
— |
|
6,561 |
|
671,276 |
Construction services revenue |
|
93,014 |
|
— |
|
|
151 |
|
— |
|
|
31,705 |
|
— |
|
|
3,630 |
|
|
21 |
|
|
16,201 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
144,722 |
Construction services cost |
|
(92,898) |
|
— |
|
|
(151) |
|
— |
|
|
(31,705) |
|
— |
|
|
(3,524) |
|
|
(21) |
|
|
(9,972) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
(138,271) |
Adjusted Ebitda |
|
232,049 |
|
— |
|
|
218,395 |
|
(68) |
|
|
46,434 |
|
3,543 |
|
|
99,680 |
|
|
32,006 |
|
|
39,127 |
|
|
— |
|
6,561 |
|
677,727 |
Financial income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101,598 |
Financial loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(406,570) |
Inflation adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(40,547) |
Amortization and depreciation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(129,982) |
Income before income tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
202,226 |
Income tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24,241 |
Net income from continuing operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
226,467 |
Loss from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
Net income for the year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
226,467 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets |
|
183,773 |
|
22 |
|
|
188,160 |
|
— |
|
|
45,101 |
|
4,770 |
|
|
91,159 |
|
|
59,737 |
|
|
68,197 |
|
|
(85,454) |
|
194,445 |
|
749,910 |
Non-current assets |
|
1,170,372 |
|
20 |
|
|
667,193 |
|
— |
|
|
188,336 |
|
9,193 |
|
|
154,754 |
|
|
53,782 |
|
|
267,568 |
|
|
(768) |
|
281,616 |
|
2,792,066 |
Capital Expenditure |
|
93,326 |
|
— |
|
|
1,727 |
|
— |
|
|
36,605 |
|
2,120 |
|
|
7,073 |
|
|
3,267 |
|
|
17,504 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
161,622 |
Current liabilities |
|
127,070 |
|
9 |
|
|
221,843 |
|
— |
|
|
25,549 |
|
4,419 |
|
|
34,076 |
|
|
54,106 |
|
|
139,248 |
|
|
(85,454) |
|
165,062 |
|
685,928 |
Non-current liabilities |
|
673,245 |
|
— |
|
|
907,835 |
|
— |
|
|
60,264 |
|
1,809 |
|
|
— |
|
|
7,329 |
|
|
78,834 |
|
|
(768) |
|
323,591 |
|
2,052,139 |
(*) Mainly includes revenues recognized over time, see Note 5.
(**) The Brazilian segment includes the impact of the compensation received regarding the Natal airport, see Note 1.2.1.
F-48
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
4 Segment information (Cont.)
Geographical information (Cont.)
|
|
Argentina |
|
|
Brazil |
|
|
Uruguay |
|
|
Armenia |
|
|
Ecuador |
|
|
Italy |
|
|
Intrasegment |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Airports |
|
Others |
|
|
Airports |
|
Others |
|
|
Airports |
|
Others |
|
|
Airports |
|
|
Airports |
|
|
Airports |
|
|
adjustments |
|
Unallocated |
|
Total |
Year ended December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical revenue (*) |
|
330,288 |
|
— |
|
|
36,610 |
|
— |
|
|
43,450 |
|
— |
|
|
60,662 |
|
|
68,370 |
|
|
70,371 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
609,751 |
Non-aeronautical revenue (*) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
308,114 |
|
232 |
|
|
52,700 |
|
— |
|
|
36,289 |
|
19,882 |
|
|
145,059 |
|
|
25,060 |
|
|
32,449 |
|
|
(10,652) |
|
3,412 |
|
612,545 |
Construction service revenue |
|
124,210 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
13,169 |
|
— |
|
|
1,819 |
|
|
2,769 |
|
|
7,829 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
149,796 |
Other revenue |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
13 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
6,558 |
|
|
(1,737) |
|
1,737 |
|
6,571 |
Cost of services |
|
(526,774) |
|
(75) |
|
|
(71,095) |
|
— |
|
|
(53,459) |
|
(14,560) |
|
|
(142,705) |
|
|
(57,584) |
|
|
(94,575) |
|
|
9,477 |
|
(11,628) |
|
(962,978) |
Gross profit / (loss) |
|
235,838 |
|
157 |
|
|
18,215 |
|
— |
|
|
39,462 |
|
5,322 |
|
|
64,835 |
|
|
38,615 |
|
|
22,632 |
|
|
(2,912) |
|
(6,479) |
|
415,685 |
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
(55,947) |
|
(145) |
|
|
(13,012) |
|
(172) |
|
|
(14,599) |
|
(1,910) |
|
|
(13,019) |
|
|
(16,067) |
|
|
(17,013) |
|
|
2,912 |
|
(12,383) |
|
(141,355) |
Impairment loss of non-financial assets |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(111) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
(111) |
Other operating income |
|
15,857 |
|
2 |
|
|
16,254 |
|
— |
|
|
159 |
|
— |
|
|
175 |
|
|
91 |
|
|
4,796 |
|
|
— |
|
6 |
|
37,340 |
Other operating expenses |
|
(5,232) |
|
— |
|
|
(424) |
|
— |
|
|
(429) |
|
(49) |
|
|
(769) |
|
|
(77) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
(4) |
|
(6,984) |
Operating income / (loss) |
|
190,516 |
|
14 |
|
|
21,033 |
|
(172) |
|
|
24,593 |
|
3,363 |
|
|
51,222 |
|
|
22,562 |
|
|
10,304 |
|
|
— |
|
(18,860) |
|
304,575 |
Share of income / (loss) in associates |
|
(24) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(257) |
|
|
— |
|
(689) |
|
(970) |
Amortization and depreciation |
|
87,363 |
|
— |
|
|
11,228 |
|
— |
|
|
6,101 |
|
1,280 |
|
|
17,650 |
|
|
6,434 |
|
|
11,122 |
|
|
— |
|
11,953 |
|
153,131 |
Adjusted Ebitda |
|
277,855 |
|
14 |
|
|
32,261 |
|
(172) |
|
|
30,694 |
|
4,643 |
|
|
68,872 |
|
|
28,996 |
|
|
21,169 |
|
|
— |
|
(7,596) |
|
456,736 |
Construction services revenue |
|
(124,210) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
(13,169) |
|
— |
|
|
(1,819) |
|
|
(2,769) |
|
|
(7,829) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
(149,796) |
Construction services cost |
|
124,018 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
13,169 |
|
— |
|
|
1,766 |
|
|
2,769 |
|
|
6,133 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
147,855 |
Adjusted Ebitda excluding Construction Services |
|
277,663 |
|
14 |
|
|
32,261 |
|
(172) |
|
|
30,694 |
|
4,643 |
|
|
68,819 |
|
|
28,996 |
|
|
19,473 |
|
|
— |
|
(7,596) |
|
454,795 |
Construction services revenue |
|
124,210 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
13,169 |
|
— |
|
|
1,819 |
|
|
2,769 |
|
|
7,829 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
149,796 |
Construction services cost |
|
(124,018) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
(13,169) |
|
— |
|
|
(1,766) |
|
|
(2,769) |
|
|
(6,133) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
(147,855) |
Adjusted Ebitda |
|
277,855 |
|
14 |
|
|
32,261 |
|
(172) |
|
|
30,694 |
|
4,643 |
|
|
68,872 |
|
|
28,996 |
|
|
21,169 |
|
|
— |
|
(7,596) |
|
456,736 |
Financial income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
63,859 |
Financial loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(196,405) |
Inflation adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19,459 |
Amortization and depreciation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(153,131) |
Income before income tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
190,518 |
Income tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(24,883) |
Net income for the year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
165,635 |
Loss from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
Net income for the year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
165,635 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets |
|
213,964 |
|
74 |
|
|
100,810 |
|
43 |
|
|
33,998 |
|
4,887 |
|
|
64,762 |
|
|
53,752 |
|
|
89,098 |
|
|
(60,562) |
|
146,642 |
|
647,468 |
Non-current assets |
|
1,600,511 |
|
30 |
|
|
675,108 |
|
— |
|
|
158,248 |
|
8,240 |
|
|
169,030 |
|
|
56,025 |
|
|
255,354 |
|
|
(768) |
|
266,541 |
|
3,188,320 |
Capital Expenditure |
|
124,214 |
|
— |
|
|
1,953 |
|
— |
|
|
19,958 |
|
1,375 |
|
|
5,788 |
|
|
1,842 |
|
|
9,742 |
|
|
— |
|
2 |
|
164,874 |
Current liabilities |
|
226,136 |
|
35 |
|
|
211,308 |
|
— |
|
|
19,258 |
|
3,131 |
|
|
22,110 |
|
|
47,447 |
|
|
137,057 |
|
|
(60,562) |
|
70,399 |
|
676,319 |
Non-current liabilities |
|
797,628 |
|
— |
|
|
927,932 |
|
— |
|
|
56,797 |
|
1,986 |
|
|
16,949 |
|
|
13,536 |
|
|
99,928 |
|
|
(768) |
|
383,112 |
|
2,297,100 |
(*) Mainly includes revenues recognized over time, see Note 5.
F-49
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
4 Segment information (Cont.)
Geographical information (Cont.)
|
|
Argentina |
|
|
Brazil |
|
|
Uruguay |
|
|
Armenia |
|
|
Ecuador |
|
|
Italy |
|
|
Intrasegment |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Airports |
|
Others |
|
|
Airports |
|
Others |
|
|
Airports |
|
Others |
|
|
Airports |
|
|
Airports |
|
|
Airports |
|
|
adjustments |
|
Unallocated |
|
Total |
Year ended December 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical revenue (*) |
|
94,881 |
|
— |
|
|
24,121 |
|
— |
|
|
14,564 |
|
— |
|
|
45,312 |
|
|
46,456 |
|
|
37,475 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
262,809 |
Non-aeronautical revenue (*) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
214,573 |
|
202 |
|
|
34,329 |
|
— |
|
|
20,200 |
|
18,031 |
|
|
46,503 |
|
|
17,948 |
|
|
17,082 |
|
|
(9,037) |
|
2,256 |
|
362,087 |
Construction service revenue |
|
53,501 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
5,280 |
|
— |
|
|
6,559 |
|
|
752 |
|
|
13,668 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
79,760 |
Other revenue |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
14 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
2,243 |
|
|
(806) |
|
806 |
|
2,257 |
Cost of services |
|
(326,974) |
|
(68) |
|
|
(59,198) |
|
— |
|
|
(35,903) |
|
(11,635) |
|
|
(56,791) |
|
|
(44,371) |
|
|
(83,149) |
|
|
7,850 |
|
(12,142) |
|
(622,381) |
Gross profit / (loss) |
|
35,981 |
|
134 |
|
|
(748) |
|
— |
|
|
4,155 |
|
6,396 |
|
|
41,583 |
|
|
20,785 |
|
|
(12,681) |
|
|
(1,993) |
|
(9,080) |
|
84,532 |
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
(38,338) |
|
(145) |
|
|
(8,228) |
|
(143) |
|
|
(7,674) |
|
(1,362) |
|
|
(11,173) |
|
|
(11,703) |
|
|
(13,053) |
|
|
1,993 |
|
(12,236) |
|
(102,062) |
Impairment loss of non-financial assets |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(371) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
(371) |
Other operating income |
|
8,109 |
|
2 |
|
|
20,285 |
|
— |
|
|
152 |
|
56 |
|
|
168 |
|
|
82 |
|
|
13,923 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
42,777 |
Other operating expenses |
|
(14,925) |
|
(8) |
|
|
(2,191) |
|
— |
|
|
(119) |
|
(66) |
|
|
(703) |
|
|
(13) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
(391) |
|
(18,416) |
Operating (loss) / income |
|
(9,173) |
|
(17) |
|
|
9,118 |
|
(143) |
|
|
(3,486) |
|
5,024 |
|
|
29,875 |
|
|
9,151 |
|
|
(12,182) |
|
|
— |
|
(21,707) |
|
6,460 |
Share of income / (loss) in associates |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
- |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
91 |
|
|
— |
|
(720) |
|
(629) |
Amortization and depreciation |
|
74,743 |
|
— |
|
|
9,999 |
|
— |
|
|
11,112 |
|
1,056 |
|
|
14,411 |
|
|
7,000 |
|
|
12,290 |
|
|
— |
|
12,890 |
|
143,501 |
Adjusted Ebitda |
|
65,570 |
|
(17) |
|
|
19,117 |
|
(143) |
|
|
7,626 |
|
6,080 |
|
|
44,286 |
|
|
16,151 |
|
|
199 |
|
|
— |
|
(9,537) |
|
149,332 |
Construction services revenue |
|
(53,501) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
(5,280) |
|
— |
|
|
(6,559) |
|
|
(752) |
|
|
(13,668) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
(79,760) |
Construction services cost |
|
53,378 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
5,280 |
|
— |
|
|
6,368 |
|
|
752 |
|
|
11,675 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
77,453 |
Adjusted Ebitda excluding Construction Services |
|
65,447 |
|
(17) |
|
|
19,117 |
|
(143) |
|
|
7,626 |
|
6,080 |
|
|
44,095 |
|
|
16,151 |
|
|
(1,794) |
|
|
— |
|
(9,537) |
|
147,025 |
Construction services revenue |
|
53,501 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
5,280 |
|
— |
|
|
6,559 |
|
|
752 |
|
|
13,668 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
79,760 |
Construction services cost |
|
(53,378) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
(5,280) |
|
— |
|
|
(6,368) |
|
|
(752) |
|
|
(11,675) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
(77,453) |
Adjusted Ebitda |
|
65,570 |
|
(17) |
|
|
19,117 |
|
(143) |
|
|
7,626 |
|
6,080 |
|
|
44,286 |
|
|
16,151 |
|
|
199 |
|
|
— |
|
(9,537) |
|
149,332 |
Financial income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28,080 |
Financial loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(131,271) |
Inflation adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,691 |
Amortization and depreciation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(143,501) |
Loss before income tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(90,669) |
Income tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(69,111) |
Net loss from continuing operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(159,780) |
Loss from discontinued operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(21,196) |
Net loss for the year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(180,976) |
(*) Mainly includes revenues recognized over time, see Note 5.
5 Revenue
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Aeronautical revenue |
|
644,453 |
|
609,751 |
|
262,809 |
Non aeronautical revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commercial revenue |
|
603,651 |
|
612,545 |
|
362,087 |
Construction service revenue |
|
144,722 |
|
149,796 |
|
79,760 |
Other revenue |
|
7,212 |
|
6,571 |
|
2,257 |
Revenue |
|
1,400,038 |
|
1,378,663 |
|
706,913 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Timing of revenue recognition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Over time |
|
1,039,699 |
|
1,035,506 |
|
560,834 |
At a point in time |
|
119,730 |
|
114,826 |
|
28,126 |
Revenues accounted for under IFRS 16 |
|
240,609 |
|
228,331 |
|
117,953 |
Revenue |
|
1,400,038 |
|
1,378,663 |
|
706,913 |
F-50
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
6 Cost of services
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Salaries and social security contributions (*) |
|
(185,920) |
|
(205,891) |
|
(141,011) |
Concession fees (**) |
|
(156,245) |
|
(158,508) |
|
(94,535) |
Construction services cost |
|
(138,271) |
|
(147,855) |
|
(77,453) |
Amortization and depreciation (***) |
|
(123,679) |
|
(145,794) |
|
(135,125) |
Cost of fuel |
|
(113,067) |
|
(107,170) |
|
(24,884) |
Maintenance expenses |
|
(105,619) |
|
(107,474) |
|
(83,905) |
Services and fees |
|
(56,642) |
|
(56,834) |
|
(44,832) |
Office expenses |
|
(9,744) |
|
(10,753) |
|
(5,208) |
Provision for maintenance costs |
|
(4,364) |
|
(3,450) |
|
(4,706) |
Taxes |
|
(2,355) |
|
(3,502) |
|
(2,932) |
Others |
|
(18,771) |
|
(15,747) |
|
(7,790) |
|
|
(914,677) |
|
(962,978) |
|
(622,381) |
(*) At the year-end, the number of employees was 6.1 thousand in 2023, 6.1 thousand in 2022 and 5.8 thousand in 2021.
(**) Includes depreciation for fixed concession assets fee, as shown in Note 12, of USD 20,715 for the year ended December 31, 2023 (USD 18,764 and USD 16,502 for the year ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 respectively).
(***) Includes depreciation of leases of USD 2,464 for the year ended December 31, 2023 (USD 3,676 and USD 3,185 for the year ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 respectively).
7 Selling, general and administrative expenses
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Services and fees |
|
(39,691) |
|
(44,836) |
|
(30,897) |
Taxes (*) |
|
(37,013) |
|
(45,250) |
|
(24,756) |
Salaries and social security contributions |
|
(33,038) |
|
(32,310) |
|
(21,172) |
Amortization and depreciation (**) |
|
(6,303) |
|
(7,337) |
|
(8,376) |
Office expenses |
|
(4,870) |
|
(3,685) |
|
(1,475) |
Insurance |
|
(2,810) |
|
(2,359) |
|
(2,145) |
Maintenance expenses |
|
(2,130) |
|
(1,892) |
|
(908) |
Advertising |
|
(1,547) |
|
(1,652) |
|
(912) |
Bad debts |
|
(4,985) |
|
(13,443) |
|
(14,727) |
Bad debts recovery (***) |
|
3,439 |
|
18,203 |
|
8,311 |
Other |
|
(9,721) |
|
(6,794) |
|
(5,005) |
|
|
(138,669) |
|
(141,355) |
|
(102,062) |
(*) Mainly included taxes over bank transactions and tax on revenue not included in the line item “Income tax”.
(**) Includes depreciation of leases of USD 739 for the year ended December 31, 2023 (USD 901 and USD 969 for the year ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 respectively).
(***) During 2022 mainly includes recoveries in Argentina, as detailed in Note 26.a.
F-51
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
8 Other operating income
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Government grants (1) |
|
13,313 |
|
15,621 |
|
7,599 |
Government subsidies per Covid-19 context (2) |
|
21,511 |
|
14,133 |
|
33,366 |
Compensation for concession (3) |
|
62,677 |
|
— |
|
— |
Other |
|
3,059 |
|
7,586 |
|
1,812 |
|
|
100,560 |
|
37,340 |
|
42,777 |
(1) Correspond to grants for the development of airport infrastructure. As consideration for having granted the concession of the Group A of the National Airport System of Argentina, AA2000 assigns to the Government 15% of the total revenues of the concession, 2.5% of such revenues are destined to fund the investment commitments of AA2000 corresponding to the investment plan under the concession agreement by means of a trust in which AA2000 is the settlor; Banco de la Nación Argentina, the trustee; and the beneficiaries are AA2000 and constructors of the airports’ works. The funds in the trust are used to settle the accounts payable to suppliers of the infrastructure being built in the Argentine Airport System. As per IAS 20, the benefit received by AA2000 qualifies as a grant related to income on a monthly basis that it is recognized at fair value since there is a reasonable assurance that such benefit will be received.
(2) Mainly corresponds to the following government subsidies to support airports in the context of Covid-19 pandemic for the year ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021:
| ◾ | Re-equilibrium of concession agreements due to force majeure or fortuitous case events in Brazilian airports for a total amount of USD 17,785, USD 13,639 and USD 25,473 net of tax in 2023, 2022 and 2021 respectively. |
Due to the impact generated by the pandemic, the Brazilian subsidiaries filed a claim for economic-financial re-equilibrium of its concession contracts. This was possible due to the Brazilian Government recognition that the Covid-19 pandemic is a case of “force majeure” or “fortuitous event” concluding that the loss from the impact of the pandemic is not part of the risks assumed by the private sector and must be compensated by the Federal Government. In view of this, the Brazilian ANAC defined for the calculation of this re-equilibrium the compensation according to the companies’ projected operational result in the scenario without pandemic.
The compensatory amounts for the years 2023, 2022 and 2021 with respect of Brasilia airport were estimated at USD 15,264, USD 11,754 and USD 22,636 net of tax respectively, and the measure of this reconstitution is through the offset of the concession fee payable, see amount compensated in Note 23.
The compensatory amounts for the years 2023, 2022 and 2021 for Natal airport were estimated at USD 2,521, USD 1,885 and USD 2,837 net of tax respectively, which was received through the offset of the monthly contribution and the readjustment of aeronautical tariffs until December 31, 2023, date on which the pending amount was included in the indemnification received from the Brazilian Government as part of the re-bidding process (Note 1.2.1).
During 2023, the final compensatory amount for the year 2022 for the Brasilia and Natal airports was determined, resulting, net of tax, in an increase of USD 3,550 and USD 176, respectively compared to the amount that had initially been estimated and recognized as an Other operating income as of December 31, 2022.
During 2022, the final compensatory amounts for the year 2021 were determined, resulting, net of tax, in an increase of USD 1,046 related to Brasilia airport and a reversal of USD 190 related to the Natal Airport compared to the amounts that had initially been estimated and recognized as Other operating income as of December 31, 2021.
During 2021, the final compensatory amounts for the year 2020 was determined, resulting in a total reversal of USD 3,450 (USD 3,074 and USD 376 related to Brasilia and Natal airports respectively) compared to the amount that had initially been estimated and recognized as of December 31, 2020.
F-52
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
8 Other operating income (Cont.)
◾ On July 26, 2021 the European Commission approved, under the terms of the European Union law, an Italian grant of EUR 800 million to compensate airports and handling operators for losses caused by travel restrictions that Italy and other countries implemented in order to contain Covid-19 infections. As of December 31, 2021, the amount referring to this compensation to TA has been determined and recognized as an Other operating income of approximately EUR 9.5 million (equivalent to USD 10,900).
In June 2022, the final amount referring to the compensation granted to TA in 2021 was determined, resulting in a reversal of approximately EUR 339 thousand (equivalent to USD 362).
There are no unfulfilled conditions or other contingencies attaching to these grants.
(3) Corresponds to the indemnification regarding the concession of the Natal Airport as detailed in Note 1.2.1 for a total amount of USD 62.7 that comprises a net gain for the compensation of the assets offset by liabilities of the concession.
9 Financial results, net
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Interest income |
|
52,680 |
|
43,919 |
|
17,639 |
Foreign exchange income |
|
39,772 |
|
10,658 |
|
1,144 |
Other financial income (1) |
|
9,146 |
|
9,282 |
|
9,297 |
Financial income |
|
101,598 |
|
63,859 |
|
28,080 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense |
|
(95,185) |
|
(164,288) |
|
(125,533) |
Foreign exchange (loss) / income |
|
(203,798) |
|
79,945 |
|
112,465 |
Changes in liability for concessions (2) |
|
(98,480) |
|
(101,488) |
|
(109,103) |
Other financial loss (3) |
|
(9,107) |
|
(10,574) |
|
(9,100) |
Financial loss |
|
(406,570) |
|
(196,405) |
|
(131,271) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inflation adjustment |
|
(40,547) |
|
19,459 |
|
6,691 |
Inflation adjustment |
|
(40,547) |
|
19,459 |
|
6,691 |
Financial results, net |
|
(345,519) |
|
(113,087) |
|
(96,500) |
(1) Mainly includes gains from other financial assets for a total amount of USD 5,021 for the year ended December 31, 2023 (USD 5,695 and USD 4,990 for the year ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively).
(2) Corresponds mainly to changes in the liabilities of Brazilian concessions due to passage of time and changes in the Brazilian IPCA.
(3) Includes leases financial cost, see Note 14(ii).
10 Share of results in associates
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Share of income / (loss) in associates (Note 15) |
|
7,108 |
|
(970) |
|
(629) |
|
|
7,108 |
|
(970) |
|
(629) |
F-53
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
11 Income tax
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Current income tax |
|
(38,456) |
|
(20,468) |
|
(19,084) |
Deferred income tax |
|
62,697 |
|
(4,415) |
|
(50,027) |
|
|
24,241 |
|
(24,883) |
|
(69,111) |
The income tax expense differs from the theoretical amount that would arise using the tax rate in each country as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Income / (loss) from continuing operations before income tax |
|
202,226 |
|
190,518 |
|
(90,669) |
Loss from discontinued operations before income tax |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(21,196) |
Income / (loss) for the year before income tax |
|
202,226 |
|
190,518 |
|
(111,865) |
Tax calculated at the tax rate in each country |
|
(59,160) |
|
(57,275) |
|
37,397 |
Adjustments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-taxable income(7) |
|
57,519 |
|
17,624 |
|
19,630 |
Expenses related to non-taxable income |
|
(8,871) |
|
(19,005) |
|
(21,967) |
Non-deductible expenses |
|
(3,581) |
|
(14,402) |
|
(4,836) |
Effect of tax inflation adjustment (1) |
|
(114,289) |
|
(123,956) |
|
(74,042) |
Effect of inflation adjustment |
|
(53,895) |
|
10,253 |
|
(29,038) |
Effect of asset revaluation for tax purposes (2) |
|
119,483 |
|
141,030 |
|
79,667 |
Inflation adjustment for tax purposes of tax losses (3) |
|
81,273 |
|
57,322 |
|
— |
Unrecognized deferred taxes (4) |
|
(11,427) |
|
(43,861) |
|
(48,344) |
Income tax rate change (5) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(17,444) |
Investment project exonerations (6) |
|
12,552 |
|
6,095 |
|
— |
Other |
|
4,637 |
|
1,292 |
|
(10,134) |
Income tax |
|
24,241 |
|
(24,883) |
|
(69,111) |
(1)In order to determine the net taxable income of CAAP’s Argentine subsidiaries at the end of each year, the tax inflation adjustment determined in accordance with articles No. 95 to No. 98 of the income tax law has been incorporated into the tax results for a total amount of USD 114,289 as of December 31, 2023 (USD 123,956 and USD 74,042 as of December 31, 2022 and 2021 respectively), due to the fact that as of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 the accumulated price index variation for the last 36 months has already exceeded 100%. Likewise, the income tax law allowed the deferral of the charge generated until 2020 by the tax inflation adjustment in six consecutive years. For 2023 the tax inflation adjustment is applicable as the accumulated inflation of the last three years is greater than 100%, and the adjustment resulting from this procedure was recognized as a current tax of the year. As consequence, as of December 31, 2023, USD 114,289 (USD 123,956 and USD 74,042 as of December 31, 2022 and 2021 respectively) was recognized as a reduction of current tax losses in deferred tax.
(2)Corresponds to the asset revaluation for tax purpose included in Law No. 27.430 of Argentina. As of March 29, 2019, AA2000 start exercising the option of the asset revaluation for tax purpose.
(3)On May 23, 2022, AA2000 filed tax returns for year 2021, reporting tax losses from previous years in accordance with the mechanism provided by the tax laws in Argentina. As of December 31, 2023, the taxable base of the historical tax carryforward losses (excluding the result of the current fiscal year) amounts to ARS 38,585 million, equivalent to USD 47.7 million, (ARS 15,066 million, equivalent to USD 85.0 million, as of December 31, 2022) and adjusted by inflation to ARS 255,660 million, equivalent to USD 316.2 million, (ARS 44,411 million, equivalent to USD 250.7 million, as of December 31, 2022). AA2000 also made a filing before AFIP, under tax secrecy protection provided by law, in order to preserve its rights in a transparency framework. AA2000’s management, with the assistance of its legal and tax advisors, believe that the arguments raised before AFIP are closely related to those considered by the court in similar procedures, and therefore, it has solid arguments to support the applied criteria.
F-54
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
11 Income tax (Cont.)
(4)Mainly temporary differences for which no deferred income tax has been recognized from Brazilian concessions. Additionally, as of December 31, 2022, deferred tax assets on tax loss carry forwards from Brazilian concessions for a total amount of USD 14.8 million were unrecognized because there was not sufficient evidence that there would be enough future taxable profits to use such tax losses.
(5)In June 2021, Law 27,630 was issued in Argentina, which sets gradual percentages over net income for the determination of the income tax. Both current income tax and deferred income tax of Argentinean companies were calculated considering these new percentages.
(6)On November 9, 2022, PDS was granted by Government of Uruguay tax exemptions related to investments to be made in connection with the development and expansion of new airports (Note 26.b) and the rest of the capex program of PDS managed by CAAP until the expiry of the concession in 2053. The exemptions include VAT and customs duties otherwise applied to construction costs as well as exemptions of income tax for a 25 years period, starting in 2022.
(7)As of December 31, 2023 includes USD 35.3 million related to the reversal of the impairment of intangible assets of ICASGA (see Note 12).
OECD Pillar Two model rules
The group is within the scope of the OECD Pillar Two model rules (the Global Anti-Base Erosion Proposal, or ‘GloBE’ rules). The Pillar Two legislation implementing the GloBE rules was enacted in 2023 notably in Luxembourg, the jurisdiction of the Company, and in certain other jurisdictions where it operates. The Pillar Two legislation will come into effect as from fiscal years starting on or after 31 December 2023, hence the group has no related current tax exposure since Pillar Two was not effective at the reporting date. The Group applies the exception to recognizing and disclosing information about deferred tax assets and liabilities related to Pillar Two income taxes, as provided in the amendments to IAS 12 issued in May 2023.
The group is in the process of assessing its exposure to the Pillar Two legislation for when it comes into effect. Due to the complexities in applying the legislation and performing GloBE computations and related filings, the quantitative impact of the enacted legislation is not yet reasonably estimable at this stage. However, with the information currently available, and in light of the assessment carried out so far, the Company does not expect a material impact of the Pillar Two legislation to the consolidated financial statements. This is based on the fact that the entity liable for any resulting GloBE top-up tax to be paid, when and if the case, is the ultimate parent entity of the multinational group the Company belongs to, rather than the Company itself.
In addition, for the first three years of operation, transitional exemptions (i.e. the so-called transitional safe harbours) operate on a jurisdiction-by-jurisdiction basis to remove the need to prepare full calculations, while the top-up tax due in respect of a given jurisdiction is deemed to be zero, should one of the three foreseen tests be met. The Company has analyzed these exemptions and concluded that only one jurisdiction may be failing to meet the exemptions, but no material GloBE top-up tax is expected to arise.
F-55
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
12 Intangible assets, net
|
|
|
|
|
|
Patent, intellectual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
property rights and |
|
|
|
|
Concession Assets |
|
Goodwill |
|
others |
|
Total |
Cost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balances at January 1, 2023 |
|
4,749,233 |
|
9,003 |
|
22,658 |
|
4,780,894 |
Acquisitions |
|
150,616 |
|
— |
|
1,221 |
|
151,837 |
Impairment reversal (***) |
|
102,838 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
102,838 |
Disposals (**) |
|
(139,218) |
|
— |
|
(88) |
|
(139,306) |
Other |
|
236 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
236 |
Transfer |
|
(2,000) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(2,000) |
Transfer from property plant and equipment |
|
1,156 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1,156 |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
(709,433) |
|
290 |
|
870 |
|
(708,273) |
Balances at December 31, 2023 |
|
4,153,428 |
|
9,293 |
|
24,661 |
|
4,187,382 |
Balances at January 1, 2022 |
|
4,243,258 |
|
9,543 |
|
22,812 |
|
4,275,613 |
Disposal of subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(95) |
|
(95) |
Acquisitions |
|
155,051 |
|
— |
|
732 |
|
155,783 |
Impairment |
|
(111) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(111) |
Disposals |
|
(549) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(549) |
Other (Note 23) |
|
570 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
570 |
Transfers |
|
(55) |
|
— |
|
55 |
|
— |
Transfer of concession assets to the grantor (*) |
|
(7,956) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(7,956) |
Transfer to property plant and equipment |
|
(2) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(2) |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
359,027 |
|
(540) |
|
(846) |
|
357,641 |
Balances at December 31, 2022 |
|
4,749,233 |
|
9,003 |
|
22,658 |
|
4,780,894 |
Depreciation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated at January 1, 2023 |
|
1,800,871 |
|
— |
|
20,021 |
|
1,820,892 |
Depreciation of the year |
|
138,620 |
|
— |
|
650 |
|
139,270 |
Disposals (**) |
|
(13,554) |
|
— |
|
(17) |
|
(13,571) |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
(280,924) |
|
— |
|
750 |
|
(280,174) |
Accumulated at December 31, 2023 |
|
1,645,013 |
|
— |
|
21,404 |
|
1,666,417 |
Accumulated at January 1, 2022 |
|
1,512,731 |
|
— |
|
19,911 |
|
1,532,642 |
Disposal of subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(61) |
|
(61) |
Depreciation of the year |
|
157,522 |
|
— |
|
1,141 |
|
158,663 |
Disposals |
|
(51) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(51) |
Transfers |
|
(4) |
|
— |
|
4 |
|
— |
Transfer of concession assets to the grantor (*) |
|
(1,504) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(1,504) |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
132,177 |
|
— |
|
(974) |
|
131,203 |
Accumulated at December 31, 2022 |
|
1,800,871 |
|
— |
|
20,021 |
|
1,820,892 |
Net balances at December 31, 2023 |
|
2,508,415 |
|
9,293 |
|
3,257 |
|
2,520,965 |
Net balances at December 31, 2022 |
|
2,948,362 |
|
9,003 |
|
2,637 |
|
2,960,002 |
(*) On March 1, 2022, the operations of the Aeronautical and Air Traffic Telecommunications Service Provider Station and the Airport Control Tower of ICASGA were transferred to the Airspace Control Department, representing a net value of R$ 33.7 million (equivalent to approximately USD 7.1 million). The compensation regarding to these assets was received in December 2023 as part of the compensation related to the re-bidding process of the Natal airport, see Note 1.2.1.
(**) Mainly includes the disposal of the intangible assets regarding ICASGA’s concession, see Note 1.2.1.
(***) Mainly includes a reversal of impairment of intangible assets recognized in previous periods due to the compensation received by ICASGA as part of the re-bidding process detailed in Note 1.2.1, for an amount of USD 103.8 million.
F-56
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
12 Intangible assets, net (Cont.)
Due to the increase of traffic witnessed during 2023 across all countries, the Group has not identified impairment indicators except in the Brazilian segment due to the losses from its operations.
Therefore, the Group performed the impairment test of the Brazilian CGU (including concession assets with a carrying value of USD 688.7 million as of December 31, 2023) based on the discounted cash flow model covering the remaining concession period (value in use), considering significant assumptions that required management judgment related to passenger growth rates and discount rate, combined with historical information.
For the purpose of impairment testing, goodwill acquired in a business combination is allocated to each of the CGUs of a subsidiary or group of subsidiaries that are expected to benefit from such business combination. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the recoverable amount of aforementioned CGU’s exceed their respective carrying amount.
13 Property, plant and equipment, net
|
|
Land, |
|
Plant and |
|
Vehicles, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
building and |
|
production |
|
furniture and |
|
Works in |
|
|
|
|
|
|
improvements |
|
Equipment |
|
fixtures |
|
progress |
|
Others |
|
Total |
Cost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balances at January 1, 2023 |
|
56,644 |
|
51,920 |
|
68,597 |
|
1,055 |
|
22,521 |
|
200,737 |
Acquisitions |
|
40 |
|
2,209 |
|
5,405 |
|
1,556 |
|
575 |
|
9,785 |
Disposals |
|
— |
|
(38) |
|
(469) |
|
— |
|
(387) |
|
(894) |
Transfers |
|
1,886 |
|
57 |
|
— |
|
(1,981) |
|
38 |
|
— |
Transfers to intangible |
|
— |
|
(1,002) |
|
— |
|
(154) |
|
— |
|
(1,156) |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
791 |
|
1,083 |
|
(3,148) |
|
6 |
|
784 |
|
(484) |
Balances at December 31, 2023 |
|
59,361 |
|
54,229 |
|
70,385 |
|
482 |
|
23,531 |
|
207,988 |
Balances at January 1, 2022 |
|
56,939 |
|
64,330 |
|
51,901 |
|
1,177 |
|
24,186 |
|
198,533 |
Disposal of subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
(11,705) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(481) |
|
(12,186) |
Acquisitions |
|
175 |
|
2,036 |
|
9,063 |
|
870 |
|
347 |
|
12,491 |
Disposals |
|
(1) |
|
(153) |
|
(37) |
|
— |
|
(169) |
|
(360) |
Transfers |
|
762 |
|
159 |
|
(14) |
|
(930) |
|
23 |
|
— |
Transfers from intangible |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2 |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
(1,231) |
|
(2,749) |
|
7,684 |
|
(62) |
|
(1,385) |
|
2,257 |
Balances at December 31, 2022 |
|
56,644 |
|
51,920 |
|
68,597 |
|
1,055 |
|
22,521 |
|
200,737 |
Accumulated at January 1, 2023 |
|
15,324 |
|
38,163 |
|
52,491 |
|
— |
|
20,017 |
|
125,995 |
Depreciation of the year |
|
1,134 |
|
2,890 |
|
4,152 |
|
— |
|
944 |
|
9,120 |
Disposals |
|
— |
|
(36) |
|
(388) |
|
— |
|
(378) |
|
(802) |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
(116) |
|
850 |
|
(2,681) |
|
— |
|
703 |
|
(1,244) |
Accumulated at December 31, 2023 |
|
16,342 |
|
41,867 |
|
53,574 |
|
— |
|
21,286 |
|
133,069 |
Accumulated at January 1, 2022 |
|
14,140 |
|
48,135 |
|
40,230 |
|
— |
|
20,548 |
|
123,053 |
Disposal of subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
(10,918) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(446) |
|
(11,364) |
Depreciation of the year |
|
1,101 |
|
3,256 |
|
3,758 |
|
— |
|
1,125 |
|
9,240 |
Disposals |
|
— |
|
(121) |
|
(37) |
|
— |
|
(45) |
|
(203) |
Transfers |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
(15) |
|
— |
|
13 |
|
— |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
83 |
|
(2,191) |
|
8,555 |
|
— |
|
(1,178) |
|
5,269 |
Accumulated at December 31, 2022 |
|
15,324 |
|
38,163 |
|
52,491 |
|
— |
|
20,017 |
|
125,995 |
Net balances at December 31, 2023 |
|
43,019 |
|
12,362 |
|
16,811 |
|
482 |
|
2,245 |
|
74,919 |
Net balances at December 31, 2022 |
|
41,320 |
|
13,757 |
|
16,106 |
|
1,055 |
|
2,504 |
|
74,742 |
F-57
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
14 Leases
(i) |
Amounts recognized in Consolidated Financial Position: |
The Consolidated Statement of Financial Position shows the following amounts relating to leases:
|
|
For the year ended December 31, |
||
Right-of-use assets |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Land, building and improvements |
|
7,655 |
|
6,757 |
Plant and production equipment |
|
2,246 |
|
2,031 |
Vehicles, furniture and fixtures |
|
592 |
|
404 |
|
|
10,493 |
|
9,192 |
|
|
|
|
|
Lease liabilities |
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
3,687 |
|
3,278 |
Non-current |
|
10,294 |
|
5,531 |
|
|
13,981 |
|
8,809 |
The evolution of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities during 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
Right-of-use assets |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Balances at the beginning of the year |
|
9,192 |
|
12,902 |
Additions |
|
5,217 |
|
465 |
Contract modifications |
|
(49) |
|
(103) |
Depreciation of the year |
|
(3,203) |
|
(4,577) |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
(664) |
|
505 |
Balances at the end of the year |
|
10,493 |
|
9,192 |
Lease liabilities |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Balances at the beginning of the year |
|
8,809 |
|
12,249 |
New contracts |
|
5,336 |
|
482 |
Lease payments |
|
(3,118) |
|
(4,307) |
Contract modifications |
|
(49) |
|
(103) |
Leases financial cost |
|
446 |
|
605 |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
2,557 |
|
(117) |
Balances at the end of the year |
|
13,981 |
|
8,809 |
The maturity of lease liabilities is as follows:
|
|
1 year or less |
|
1 to 2 years |
|
2 to 5 years |
|
Over 5 years |
|
Total |
At December 31, 2023 |
|
3,822 |
|
3,883 |
|
4,879 |
|
4,052 |
|
16,636 |
At December 31, 2022 |
|
3,576 |
|
1,022 |
|
2,192 |
|
3,890 |
|
10,680 |
The amounts disclosed in the table are the contracted undiscounted cash flows.
F-58
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
14 Leases (Cont.)
(ii) |
Amounts recognized in Consolidated Statement of Income: |
The Consolidated Statement of Income shows the following amounts relating to leases:
|
|
For the year ended December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Depreciation charge of right-of-use assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Land, building and improvements |
|
(2,730) |
|
(3,966) |
|
(3,514) |
Plant and production equipment |
|
(198) |
|
(179) |
|
(160) |
Vehicles, furniture and fixtures |
|
(275) |
|
(432) |
|
(480) |
|
|
(3,203) |
|
(4,577) |
|
(4,154) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financial expenses (Leases financial cost) |
|
(446) |
|
(605) |
|
(737) |
Expense relating to short-term leases (included in cost of services and selling, general and administrative expenses) |
|
(865) |
|
(412) |
|
(827) |
Expense relating to leases of low-value assets that are not shown above as short-term leases (included in cost of services and selling, general and administrative expenses) |
|
(326) |
|
(300) |
|
(299) |
Expense relating to variable lease payments not included in lease liabilities (included in cost of services) |
|
(1,855) |
|
(1,330) |
|
(467) |
(iii) |
Variable lease payments |
Some security equipment leases contain variable payment terms that are linked to passenger traffic. Variable lease payments that depend on passengers are recognized in profit or loss in the period in which the condition that triggers those payments occurs. A 10% increase in passenger traffic across airports in the Group with such variable lease contracts would increase total lease payments by approximately USD 185.5 as of December 31, 2023 (USD 133.0 and 67.1 as of December 31, 2022 and 2021 respectively).
(iv) |
The Group as a lessor |
As indicated in Note 2.P, leases and sub-concession of spaces are classified as operating leases. These revenues mainly refer to sub-concessions of commercial spaces (duty free shops, food and beverage services, retail stores) and advertising spaces, among others. Lease payments for some contracts include a minimum agreed upon amount and other variable lease payments by applying a percentage on lessors’ revenues, both of which are set forth in the lease agreements. Where considered necessary to reduce credit risk, the Group may obtain guarantees for the term of the lease.
Commercial revenues corresponding to variable income from lease or sub-concession of spaces that do not depend on an index or rate, for example determined on the basis of lessee’s sales or passenger traffic, correspond, as December 31, 2023, to a 42% of total revenues of leases and sub-concession of spaces (48% and 39% as of December 31, 2022 and 2021 respectively).
F-59
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
14 Leases (Cont.)
(iv) |
The group as a lessor (Cont.) |
Minimum lease payments receivable on leases and sub-concession of spaces with third parties at its airports facilities are as follows:
|
|
At December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Within 1 year |
|
109,314 |
|
99,142 |
|
77,387 |
Between 1 and 5 years |
|
266,875 |
|
241,115 |
|
175,409 |
Later than 5 years |
|
160,059 |
|
136,344 |
|
42,082 |
Total |
|
536,248 |
|
476,601 |
|
294,878 |
15 Investments in associates
|
|
For the year ended December 31, |
|
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
Balances at the beginning of the year |
|
1,911 |
|
2,355 |
|
Share of income/(loss) in associates (Note 10) |
|
7,108 |
|
(970) |
|
Contributions |
|
84 |
|
260 |
|
Acquisitions (1) |
|
3,384 |
|
— |
|
Others |
|
(425) |
|
223 |
|
Translation differences |
|
(70) |
|
43 |
|
Balances at the end of the year |
|
11,992 |
|
1,911 |
|
(1) Consist of the consideration for the acquisition of Navinten S.A. (Note 28)
F-60
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
15 Investments in associates (Cont)
Breakdown of the share of income/(loss) in associates is as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Sociedad Aeroportuaria Kuntur Wasi S.A. |
|
(84) |
|
(260) |
|
(741) |
Navinten S.A. (**) |
|
7,292 |
|
— |
|
— |
Others |
|
(100) |
|
(710) |
|
112 |
|
|
7,108 |
|
(970) |
|
(629) |
Main Associates are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investment in associates |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Percentage of |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
ownership at |
|
For the year ended |
||||
|
|
|
|
Country of |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
||||
Company |
|
Main activity |
|
incorporation |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Aeropuertos Ecológicos de Galápagos S.A. (*) |
|
Airport Operation |
|
Ecuador |
|
99.90 |
% |
99.90 |
% |
1,000 |
|
1,000 |
Navinten S.A. (**) |
|
Duty free operation |
|
Uruguay |
|
49.00 |
% |
— |
|
10,264 |
|
— |
Sociedad Aeroportuaria Kuntur Wasi S.A. (***) |
|
Airport Operation |
|
Perú |
|
47.90 |
% |
47.90 |
% |
— |
|
— |
Others |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
728 |
|
911 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11,992 |
|
1,911 |
(*) Under the terms of the Galapagos Concession Agreement, the net income generated by the Company must be transferred entirely to the Dirección General de Aviación Civil (“DGAC”), however, the Group maintains the operational management of such company and therefore has significant influence.
(**) See Note 28 regarding the acquisition of Navinten S.A.
(***) On July 13, 2017, the Government of Peru notified the unilateral decision to rescind the concession agreement for the Nuevo Aeropuerto International de Chinchero; therefore, since then the investment has been maintained in zero.
F-61
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
16 Deferred income tax
Deferred income taxes are calculated in full on temporary differences under the liability method using the tax rate enacted in each country that are expected to apply in the period the temporary difference will reverse. The tax rate per country is the following: Uruguay: 25%, Argentina: 35%, Italy: 29%, Armenia: 18%, Brazil: 34%, Ecuador: 25%, Spain: 25%, Luxembourg: 25%.
The evolution of deferred tax assets and liabilities during the years 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
Deferred tax liabilities
|
|
Property, plant |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
and equipment and |
|
Tax inflation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intangibles Assets |
|
adjustment |
|
Other liabilities |
|
Total |
Balances at January 1, 2023 |
|
304,726 |
|
13,449 |
|
7,106 |
|
325,281 |
Increase/ (decrease) of deferred tax liabilities for the year |
|
37,230 |
|
1,822 |
|
8,943 |
|
47,995 |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
(54,458) |
|
(4,344) |
|
133 |
|
(58,669) |
Balances at December 31, 2023 |
|
287,498 |
|
10,927 |
|
16,182 |
|
314,607 |
Balances at January 1, 2022 |
|
279,478 |
|
32,322 |
|
8,085 |
|
319,885 |
Increase/(decrease) of deferred tax liabilities for the year |
|
19,214 |
|
(5,295) |
|
76 |
|
13,995 |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
6,034 |
|
(13,578) |
|
(1,055) |
|
(8,599) |
Balances at December 31, 2022 |
|
304,726 |
|
13,449 |
|
7,106 |
|
325,281 |
Deferred tax assets
|
|
|
|
Tax loss |
|
Property, plant and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provisions and |
|
carry |
|
equipment and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
allowances |
|
forwards |
|
Intangibles Assets |
|
Other |
|
Total |
Balances at January 1, 2023 |
|
26,266 |
|
112,775 |
|
989 |
|
7,675 |
|
147,705 |
(Decrease) / increase of deferred tax assets for the year |
|
1,786 |
|
105,839 |
|
(164) |
|
3,231 |
|
110,692 |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
(4,245) |
|
(13,238) |
|
(12) |
|
(898) |
|
(18,393) |
Balances at December 31, 2023 |
|
23,807 |
|
205,376 |
|
813 |
|
10,008 |
|
240,004 |
Balances at January 1, 2022 |
|
34,073 |
|
113,304 |
|
932 |
|
13,022 |
|
161,331 |
Disposal of subsidiaries |
|
(343) |
|
(2,198) |
|
— |
|
16 |
|
(2,525) |
(Decrease) / increase of deferred tax assets for the year |
|
(410) |
|
12,580 |
|
(108) |
|
(2,482) |
|
9,580 |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
(7,054) |
|
(10,911) |
|
165 |
|
(2,881) |
|
(20,681) |
Balances at December 31, 2022 |
|
26,266 |
|
112,775 |
|
989 |
|
7,675 |
|
147,705 |
F-62
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
16 Deferred income tax (Cont.)
The Group does not recognize deferred tax assets for unused tax loss carryforward or unused tax credit if it is not probable that there will be sufficient future taxable profit against which the loss carryforward or credit can be utilized.
At December 31, 2023 an amount of USD 224.5 million (USD 210.0 million at December 31, 2022) has not been recognized within deferred tax assets because there is not sufficient evidence that there will be enough taxable profit available to allow the benefit of part or all of that deferred tax asset to be utilized. Unused tax loss carryforwards do not expire although there are certain deduction limits.
At December 31, 2023, USD 62.3 (USD 61.8 million at December 31, 2022) of the deferred tax asset relates to tax losses carryforward that do not expire, while the remaining USD 143.1 million (USD 51.0 million at December 31, 2022) expire as follows:
|
|
For the year ended December 31, |
||
Expiration date |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
December 31, 2025 |
|
73,344 |
|
50,161 |
December 31, 2026 |
|
1,095 |
|
837 |
December 31, 2027 |
|
38,320 |
|
16 |
December 31, 2028 |
|
30,384 |
|
— |
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are offset when (1) there is a legally enforceable right to set-off current tax assets against current tax liabilities and (2) when the deferred income taxes relate to the same fiscal authority on either the same taxable entity or different taxable entities where there is an intention to settle the balances on a net basis. The following amounts, determined after appropriate set-off, are shown in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Deferred tax assets |
|
62,712 |
|
54,882 |
Deferred tax liabilities |
|
(137,315) |
|
(232,458) |
F-63
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
17 Other receivables
|
|
At December 31, |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Non-Current |
|
|
|
|
Tax credits |
|
9,623 |
|
10,992 |
Trust funds (1) |
|
22,627 |
|
54,782 |
Prepaid expenses |
|
192 |
|
792 |
Other |
|
10,198 |
|
12,199 |
|
|
42,640 |
|
78,765 |
Current |
|
|
|
|
Tax credits |
|
13,646 |
|
10,925 |
Guarantee deposit (4) |
|
35,809 |
|
9,605 |
Receivables from related parties (Note 27) |
|
9,315 |
|
10,140 |
Prepaid expenses |
|
4,662 |
|
4,849 |
Compensation receivable (5) |
|
66,612 |
|
— |
Government grants to receive (2) |
|
459 |
|
7,193 |
Other (3) |
|
15,046 |
|
15,088 |
|
|
145,549 |
|
57,800 |
(1) Funds are held by a trust, on which the Company does not have the power to direct the relevant activities of the trustee company and is not exposed, or have rights, to variable returns, as such does not consolidate the trustee company.
(2) As of December 31, 2023 and 2022 included grants to be received by TA and ICASGA (Note 8).
(3) Mainly includes receivable for the additional Municipal tax on passenger boarding fees of TA for a total amount of USD 7,595 as of December 31,2023 (USD 5,188 as of December 31,2022).
(4) Mainly includes the indemnification that ICAGSA received in cash from the Brazilian Government amounting the equivalent to USD 41.3 million (see Note 1.2.1). ICASGA was required to maintain the amount collected in a guarantee deposit account of BNDES. The cash cannot be withdrawn or used by ICASGA until the borrowings with BNDES are paid-off from that bank account, which occurred in January 2024 (see note 34). As a result, ICASGA borrowings with BNDES (USD 15.6 million as of December 31, 2023) have been presented net of the cash in guarantee deposits, as the requirements under IFRS were met.
(5) As of December 31, 2023 included the compensation receivable related to the Natal airport as detailed in Note 1.2.1.
The fair value of financial assets within current other receivables approximates to its carrying amount. The fair value of financial assets within non-current receivables amounts to approximately USD 24.4 million at December 31, 2023 (USD 58.8 million as of December 31, 2022). The fair value of these financial assets was calculated using a discounted cash flow (Level 3).
18 Inventories
|
|
At December 31, |
||
Non- Current |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Supplies |
|
318 |
|
254 |
|
|
318 |
|
254 |
Current |
|
|
|
|
Supplies |
|
4,881 |
|
4,844 |
Oil and byproducts |
|
11,263 |
|
10,917 |
Others |
|
4 |
|
4 |
|
|
16,148 |
|
15,765 |
F-64
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
19 Trade receivables
|
|
At December 31, |
||
Non-Current |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Accounts receivable |
|
4,581 |
|
4,683 |
Trade receivables from related parties (Note 27) |
|
741 |
|
1,431 |
Loss allowance (see Note 3A(ii)) |
|
(4,433) |
|
(4,533) |
|
|
889 |
|
1,581 |
Current |
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable |
|
138,586 |
|
129,168 |
Trade receivables from related parties (Note 27) |
|
4,421 |
|
5,053 |
Contract assets |
|
1,488 |
|
2,053 |
Loss allowance (see Note 3A(ii)) |
|
(17,935) |
|
(25,185) |
|
|
126,560 |
|
111,089 |
Fair value of trade receivables approximates to the net book value.
F-65
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
20 Other financial assets
|
|
At December 31, |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Non-current |
|
|
|
|
Other financial assets at fair value through profit or loss |
|
|
|
|
Equity investments (*) |
|
3,690 |
|
3,160 |
Other |
|
2,289 |
|
— |
|
|
5,979 |
|
3,160 |
Other financial assets at amortized cost |
|
|
|
|
Related parties (Note 27) |
|
6,545 |
|
2,954 |
Corporate Bonds |
|
53,735 |
|
— |
Other (**) |
|
810 |
|
810 |
|
|
61,090 |
|
3,764 |
|
|
67,069 |
|
6,924 |
Current |
|
|
|
|
Other financial assets at fair value through profit or loss |
|
|
|
|
Corporate Bonds |
|
729 |
|
7,913 |
Mutual funds |
|
3,515 |
|
4,458 |
Government securities |
|
434 |
|
313 |
Other |
|
206 |
|
108 |
|
|
4,884 |
|
12,792 |
Other financial assets at amortized cost |
|
|
|
|
Corporate Bonds |
|
4,959 |
|
— |
Related parties (Note 27) |
|
24,890 |
|
— |
Time Deposits |
|
43,159 |
|
39,078 |
Treasury bills |
|
9,658 |
|
1,956 |
Other (**) |
|
476 |
|
12,871 |
|
|
83,142 |
|
53,905 |
|
|
88,026 |
|
66,697 |
(*) As of December 31, 2023 and 2022 includes equity investments where the Group holds a minor equity interest and does not exert significant influence, mainly TA’s purchase of an 8.16% stake in Firenze Parcheggi S.p.A., a company that manages public parking lots in Florence.
(**) As of December 31, 2022 mainly included restricted cash in the interest payment account established, and maintained until November 29, 2023, to perform payments related to fees, expenses and interests of the Senior Secured Guaranteed Notes due 2034 of ACI Airport Sudamérica S.A.U. (see Note 22).
Fair value of other financial assets approximate book value.
F-66
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
21 Cash and cash equivalents
|
|
At December 31, |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Cash to be deposited |
|
657 |
|
568 |
Cash at banks |
|
192,381 |
|
255,743 |
Time deposits |
|
16,729 |
|
12,474 |
Other cash equivalents (1) |
|
160,081 |
|
116,480 |
|
|
369,848 |
|
385,265 |
(1) Mainly includes bank deposit certificates with immediate liquidity, treasury bills and highly liquid investments in mutual funds.
The Group considers that its cash and cash equivalents have low credit risk based, mainly, on the external credit ratings of the counterparties.
As of December 31, 2023, cash and cash equivalents includes restricted cash on deposit as collateral for a total amount of USD 5,864 (USD 4,843 as of December 31, 2022).
22 Borrowings
|
|
At December 31, |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Non-current |
|
|
|
|
Bank and financial borrowings (**) |
|
278,147 |
|
353,740 |
Notes (*) |
|
855,402 |
|
933,681 |
|
|
1,133,549 |
|
1,287,421 |
Current |
|
|
|
|
Bank and financial borrowings (**) |
|
114,092 |
|
125,164 |
Notes (*) |
|
85,535 |
|
52,852 |
Bank overdrafts |
|
61 |
|
— |
|
|
199,688 |
|
178,016 |
Total Borrowings |
|
1,333,237 |
|
1,465,437 |
Changes in borrowings during the years are as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Balances at the beginning of the year |
|
1,465,437 |
|
1,439,603 |
Loans obtained |
|
87,846 |
|
371,951 |
Loans repaid |
|
(200,475) |
|
(328,775) |
Interest paid |
|
(83,791) |
|
(111,387) |
Accrued interest for the year |
|
90,928 |
|
115,093 |
Offsetting of financial assets (Note 17) |
|
(15,224) |
|
— |
Debt renegotiation expenses capitalization |
|
(110) |
|
(2,011) |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
(11,374) |
|
(19,037) |
Balances at the end of the year |
|
1,333,237 |
|
1,465,437 |
F-67
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
22 Borrowings (Cont.)
The maturity of borrowings is as follows:
|
|
1 year or less |
|
1 to 2 years |
|
2 to 5 years |
|
Over 5 years |
|
Total |
At December 31, 2023 (1) |
|
294,299 |
|
239,443 |
|
569,488 |
|
711,815 |
|
1,815,045 |
At December 31, 2022 (1) |
|
278,427 |
|
252,961 |
|
622,876 |
|
895,887 |
|
2,050,151 |
(1) The amounts disclosed in the table are undiscounted cash flows of principal and estimated interest. Variable interest rate cash flows have been estimated using variable interest rates applicable at the end of the reporting period.
|
|
At December 31, |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Fair value of borrowings (2) |
|
1,328,357 |
|
1,423,983 |
|
|
1,328,357 |
|
1,423,983 |
(2) Valuation at quotation prices not adjusted in active markets for identical liabilities included Fair Value Level 2 under IFRS 13 hierarchy. There are no financial liabilities measured at fair value.
(*) Notes include the following as of December 31, 2023:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Company |
|
Note |
|
Issuance |
|
Currency |
|
Nominal value (in |
|
Maturity |
|
Interest rate |
|
Outstanding |
ACI |
|
Senior secured guarantee notes |
|
November 2021 |
|
USD |
|
246.2 |
|
November 2034 |
|
Fixed 6.875% |
|
235.9 |
|
|
Senior secured guarantee notes |
|
May 2015, May 2020 (1) |
|
USD |
|
14.6 |
|
November 2032 |
|
Fixed 6.875% |
|
11.4 |
CAI |
|
Secured notes |
|
January 2020 |
|
EUR |
|
71.8 |
|
December 2024 |
|
Fixed 4.556% |
|
67.7 |
|
|
Senior secured guarantee notes |
|
February 2017, May 2020 (1) |
|
USD |
|
212.3 |
|
February 2027 |
|
Fixed 6.875% |
|
67.8 |
|
|
|
|
October 2021 |
|
USD |
|
208.9 |
|
August 2031 |
|
Fixed 8.500% |
|
208.6 |
AA2000 |
|
Class 1 Series 2021 Notes |
|
November 2021 |
|
USD |
|
64.0 |
|
August 2031 |
|
Fixed 8.500% |
|
61.2 |
|
|
Class 4 Notes |
|
November 2021 |
|
USD |
|
62.0 |
|
November 2028 |
|
Fixed 9.500% |
|
60.7 |
|
|
Class 5 Notes |
|
February 2022 |
|
USD (2) |
|
138.0 |
|
February 2032 |
|
Fixed 5.500% |
|
138.3 |
|
|
Class 6 Notes |
|
February 2022 |
|
USD (2) |
|
36.0 |
|
February 2025 |
|
Fixed 2.000% |
|
34.4 |
|
|
Class 9 Notes |
|
August 2022 |
|
USD (2) |
|
30.0 |
|
August 2026 |
|
Fixed 0.000% |
|
30.0 |
|
|
|
|
July-2023 |
|
USD (2) |
|
2.7 |
|
Aug-2026 |
|
Fixed 0.000% |
|
0.4 |
|
|
Class 10 Notes |
|
July-2023 |
|
USD (2) |
|
25.0 |
|
July-2025 |
|
Fixed 0.000% |
|
24.5 |
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
940.9 |
(1) |
A partial exchange of the notes initially issued was performed during 2020 and 2021, which is detailed below |
(2) |
These notes are dollar-linked, denominated in U.S. dollars but issued and payable in Argentine pesos |
F-68
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
22 Borrowings (Cont.)
(*) Notes include the following as of December 31, 2022:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Company |
|
Note |
|
Issuance |
|
Currency |
|
Nominal value (in |
|
Maturity |
|
Interest rate |
|
Outstanding |
ACI |
|
Senior secured guarantee notes |
|
November 2021 |
|
USD |
|
246.2 |
|
November 2034 |
|
Fixed 6.875% |
|
234.6 |
|
|
Senior secured guarantee notes |
|
May 2015, May 2020 (1) |
|
USD |
|
14.6 |
|
November 2032 |
|
Fixed 6.875% |
|
12.5 |
CAI |
|
Secured notes |
|
January 2020 |
|
EUR |
|
71.8 |
|
December 2024 |
|
Fixed 4.556% |
|
64.9 |
|
|
Senior secured guarantee notes |
|
February 2017, May 2020 (1) |
|
USD |
|
212.3 |
|
February 2027 |
|
Fixed 6.875% |
|
91.1 |
|
|
|
|
October 2021 |
|
USD |
|
208.9 |
|
August 2031 |
|
Fixed 8.500% |
|
208.1 |
|
|
Class 3 Notes |
|
September 2021 |
|
USD (2) |
|
30.5 |
|
September 2023 |
|
Fixed 4.000% |
|
30.5 |
|
|
Class 1 Series 2021 Notes |
|
November 2021 |
|
USD |
|
64.0 |
|
August 2031 |
|
Fixed 8.500% |
|
60.6 |
AA2000 |
|
Class 4 Notes |
|
November 2021 |
|
USD |
|
62.0 |
|
November 2028 |
|
Fixed 9.500% |
|
60.2 |
|
|
Class 5 Notes |
|
February 2022 |
|
USD (2) |
|
138.0 |
|
February 2032 |
|
Fixed 5.500% |
|
138.3 |
|
|
Class 6 Notes |
|
February 2022 |
|
USD (2) |
|
36.0 |
|
February 2025 |
|
Fixed 2.000% |
|
35.9 |
|
|
Class 7 Notes |
|
July 2022 |
|
USD (2) |
|
20.0 |
|
July 2025 |
|
Fixed 0.000% |
|
19.9 |
|
|
Class 9 Notes |
|
August 2022 |
|
USD (2) |
|
30.0 |
|
August 2026 |
|
Fixed 0.000% |
|
29.9 |
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
986.5 |
F-69
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
22 Borrowings (Cont.)
| ● | ACI Senior Secured Guarantee Notes (“ACI Existing Notes”) are guaranteed and have a security package that includes the pledge of the shares in PDS and Cerealsur S.A., and certain accounts of Cerealsur S.A. and ACI. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, they were secured by a debt service reserve account of ACI and the funds contained therein. These notes are fully and unconditionally guaranteed by Cerealsur S.A.and PDS. |
On May 26, 2020, ACI issued USD 180.9 million aggregate principal amount of 6.875% Cash/7.875% PIK Senior Secured Guaranteed Notes due 2032 to repurchase and exchange 93.6% of the total original principal amount of the ACI Existing Notes obtaining consents to certain proposed amendments to the indenture governing the ACI Existing Notes and certain waivers. The main covenants and guarantees remain unchanged except for the incorporation of ACI’s shares pledge.
On November 12, 2021, ACI issued USD 246.2 million aggregate principal amount of 6.875% Senior Secured Guaranteed Notes due 2034 (the “New Notes”) consolidating the repurchase and exchange of 40.62% of the total original principal amount of the Series 2015 Notes, 96.43% of the total original amount of the Series 2020 Notes and a new money offering of USD 52.9 in a private transaction under the same terms as the New Notes. The main guarantees remain unchanged while the covenants over ACI Existing Notes were eliminated; an Interest payment account was funded with a portion of the proceeds of the issuance of the New Notes to cancel interest payments until November 29, 2023, amounting as of December 31, 2022, USD 12.9 million and a stand by letter was issued by Goldman Sachs Bank for USD 8.5 million which remains in force as of December 31, 2023.
| ● | The Italian Notes are secured by an economic first ranking pledge in respect of all the shares representing 100% of the share capital of CAI, 100% of the share capital of Dicasa Spain S.A.U. and the shares representing CAI’s holding in TA. |
The main covenants are limitations to take on additional indebtedness, make payments of dividends and other payments that are specifically restricted, selling assets as well as requiring compliance with certain financial ratios. As of December 31, 2023, it has been in compliance with the covenants.
| ● | The Senior guarantee notes of AA2000 (“AA2000 Existing Notes”) are secured by a collateral assignment of fiduciary rights of certain revenue of AA2000. |
The main covenants require compliance with certain financial ratios as well as restriction to incur additional debt and limitations on the payments of dividends if any default, whether declared or not, has occurred. As of December 31, 2023 AA2000 is in compliance with said covenants.
On May 20, 2020 AA2000 issued USD 306 million aggregate principal amount of 6.875% Cash/9.375% PIK Class I Series 2020 Additional Senior Secured Notes due 2027 (the “Series 2020 Additional Notes”) in exchange of 86.73% of the total original principal amount of AA2000 Existing Notes. The collateral assignment of revenue under AA2000 Existing Notes was extended to the Series 2020 Additional Notes in equal terms.Accrued interest are capitalized quarterly. The main covenants and guarantees remain unchanged.
On October 28, 2021, AA2000 issued USD 208.9 million aggregate principal amount of 8.5% Class I Series 2021 Additional Senior Secured Notes due 2031 (the “Series 2021 Notes”) to repurchase and exchange 24.61% of the total original principal amount of the Series 2017 Notes and 66.83% of the original principal amount of Series 2020 Additional Notes. Additionally, on November 4, 2021, AA2000 issued USD 64 million of Series 2021 Notes related to a new fund raising. The main covenants and guarantees remain unchanged.
F-70
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
22 Borrowings (Cont.)
The Series 2021 Notes and the Existing Notes not exchanged are secured by the collateral currently securing the Existing Notes on a pro rata and pari passu basis. In addition, to secure its obligations under the Series 2021 Notes, AA2000, together with the relevant parties thereto, amended the cargo trust agreement dated August 9, 2019, entered into by AA2000 and the trustee (as amended, the “Cargo Trust”) in order to include holders of Series 2021 Notes as beneficiaries therein, granting them a security interest which is subordinated to (i) the rights of creditors under certain existing loans of AA2000, and (ii) any debt permitted to be incurred to finance or refinance any capital expenditures made or to be made pursuant to the concession agreement entered into by AA2000 with the Argentine National Government (as amended form time to time, the “Concession Agreement”) for the operation of the airports in Argentina.
Once the Existing Notes not exchanged in the Exchange Offer mature or are cancelled in full, AA2000 is required to amend and restate the Cargo Trust and the current trust related to the tariffs dated January 19, 2017, entered into by AA2000 and the trustee thereto (the “Tariffs Trust”), so that the Series 2021 Notes become secured under the Cargo Trust on a pro rata and pari passu basis with the existing beneficiaries of the Cargo Trust, and these beneficiaries in turn become secured under the Tariffs Trust on a pro rata and pari passu basis with the Series 2021 Notes. In accordance with the Concession Agreement, the collateral assignment of revenue must be authorized by ORSNA. ORSNA approved, on October 15 2021, the amendment of the Tariffs Trust and of the Cargo Trust to include the Series 2021 Notes as beneficiaries thereto (including their future amendment and restatement, once the Existing Notes are cancelled in full). Furthermore, AA2000 received the approval from the Central Bank of Argentina to establish a non-interest bearing U.S. dollar trust account in the United States to secure the Series 2021.
On November 4, 2021, AA2000 additionally issued USD 62 million aggregate principal amount of Class 4 Senior Secured Notes related to a new money offering. These Senior Secured Notes are secured by a first priority lien on the Cargo Trust on a pari passu basis with certain commercial bank lenders to AA2000 and a second priority lien with new debt incurred by AA2000 to fund infrastructure works for a total amount of up to USD 235 million.
On February 21, 2022, AA2000 issued USD 174 million of dollar-linked notes, in the local market, in two tranches:
| ● | USD 138 million of Class 5 Notes, with a five-year grace period and quarterly amortization, starting May 2027. AA2000 is using these proceeds to fund infrastructure works in the Group “A” airports, within the National Airports System; |
| ● | USD 36 million of Class 6 Notes. |
In June 2022, AA2000 repurchased USD 2 million of dollar-linked notes issued in August 2020. In August 2022, USD 25.4 million of these notes were exchanged for dollar-linked Class 9 Notes, while at the maturity date, in August 2022, AA2000 repaid the remaining USD 12.6 million.
On July 8, 2022, AA2000 issued USD 20 million of dollar-linked Class 7 Notes in the local market. In December 2023, the notes were early redeemed.
On August 19, 2022, AA2000 issued USD 30 million of dollar-linked Class 9 Notes in the local market, repayable in three installments of USD 10 million each, in February, May and August 2026. The integration of the nominal value amounted to USD 25.4 million through the exchange of Class 2 Notes while the remaining USD 4.6 million were integrated in ARS.
In July, 2023, AA2000 issued additional Class 9 Dollar - linked Notes, for a total amount of USD 2.7 million. The main covenants and guarantees remain unchanged. Furthermore, AA2000 issued USD 25.0 million aggregate principal amount of Class 10 Dollar - linked Notes to repurchase and exchange 90.7% of the total original principal amount of the Series 3 Notes.
F-71
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
22 Borrowings (Cont.)
(**) As of December 31, 2023, significant bank and financial borrowings include the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(In millions |
|
|
||
Company |
|
Lender |
|
Currency |
|
Maturity |
|
Interest Rate |
|
of USD) |
|
Capitalization(2) |
||
|
|
BNDES |
|
R$ |
|
Sept-2032 |
|
Variable |
|
TJLP(1) plus spread |
|
6.6 |
|
|
ICASGA |
|
BNDES |
|
R$ |
|
June-2032 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R. plus spread plus IPCA |
|
1.8 |
|
|
|
|
BNDES |
|
R$ |
|
Sept-2032 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R. plus spread plus IPCA |
|
4.9 |
|
A |
|
|
BNDES |
|
R$ |
|
July -2032 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R. plus spread plus IPCA |
|
2.3 |
|
|
ICAB |
|
BNDES |
|
R$ |
|
Dec-2033 |
|
Variable |
|
TJLP(1) plus spread |
|
213.9 |
|
A |
|
|
Banco Guayaquil SA |
|
USD |
|
Feb-2026 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R.E.(3) plus spread |
|
4.2 |
|
D |
TAGSA |
|
Banco Guayaquil SA |
|
USD |
|
Dec-2025 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R.E.(3) plus spread |
|
1.4 |
|
D |
|
|
Banco Bolivariano CA |
|
USD |
|
Dec-2025 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R.E.(3) plus spread |
|
3.6 |
|
D |
|
|
Banco Bolivariano CA |
|
USD |
|
Nov-2024 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R.E.(3) plus spread |
|
1.8 |
|
D |
|
|
Scotiabank Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
Oct-2024 |
|
Fixed |
|
4.30% |
|
0.4 |
|
D |
TCU |
|
Scotiabank Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
Feb-2026 |
|
Fixed |
|
4.30% |
|
0.6 |
|
D |
|
|
Santander Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
Nov-2027 |
|
Fixed |
|
5.37% |
|
1.0 |
|
D |
|
|
Santander Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
Jan-2028 |
|
Fixed |
|
5.37% |
|
1.0 |
|
D |
|
|
Banco de Innovación de Infraestructuras y Desarrollo |
|
EUR |
|
Sept-2027 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 6 month plus spread |
|
13.0 |
|
D |
|
|
Unicredit |
|
EUR |
|
Mar-2024 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 3 month plus spread |
|
9.4 |
|
D |
TA |
|
ISP-SACE |
|
EUR |
|
Sept-2026 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 3 month plus spread |
|
60.5 |
|
D |
|
|
BPM |
|
EUR |
|
June-2024 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 3 month plus spread |
|
0.1 |
|
D |
|
|
BPM |
|
EUR |
|
Feb-2024 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 3 month plus spread |
|
4.0 |
|
D |
|
|
MPS Servicio capital |
|
EUR |
|
Mar-2024 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 6 month plus spread |
|
12.3 |
|
D |
|
|
Banca Intesa San Paolo |
|
EUR |
|
Jan-2024 |
|
Fixed |
|
6.10% |
|
12.2 |
|
D |
AIA |
|
Ameriabank C.J.S.C. |
|
EUR |
|
Dec-2024 |
|
Fixed |
|
6.00% |
|
13.2 |
|
B |
|
|
Banco de la Provincia de Buenos Aires |
|
USD |
|
July-2024 |
|
Fixed |
|
7.00% |
|
0.3 |
|
D |
AA2000 |
|
Onshore renegotiation - ICBC |
|
USD |
|
Nov-2024 |
|
Fixed |
|
8.50% |
|
9.0 |
|
A |
|
|
ICBC Dubai |
|
USD |
|
Oct-2025 |
|
Variable |
|
SOFR plus spread |
|
10.2 |
|
B |
|
|
ICBC |
|
USD |
|
Jan-2024 |
|
Fixed |
|
15.50% |
|
0.5 |
|
D |
|
|
ICBC |
|
USD |
|
Dec-2024 |
|
Fixed |
|
15.50% |
|
0.1 |
|
D |
CAISA |
|
Santander Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
Apr-2027 |
|
Fixed |
|
5.10% |
|
5.5 |
|
B |
|
|
Banco Itaú |
|
USD |
|
Apr-2027 |
|
Fixed |
|
3.80% |
|
5.5 |
|
|
PDS |
|
Banco de la República Oriental del Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
Mar-2028 |
|
Variable |
|
6.14% |
|
8.5 |
|
C |
Total (***) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
407.8 |
|
|
(***) The total outstanding amount includes the financial debt of ICASGA with BNDES which, as disclosed in Note 17, is shown in the Consolidated statement of financial position offset of guarantee deposits. Therefore, the net amount of Bank and financial borrowings amounts to USD 392.2 million.
F-72
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
22Borrowings (Cont.)
(**) As of December 31, 2022, significant bank and financial borrowings include the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(In millions |
|
|
||
Company |
|
Lender |
|
Currency |
|
Maturity |
|
Interest Rate |
|
of USD) |
|
Capitalization(2) |
||
|
|
BNDES |
|
R$ |
|
September 2032 |
|
Variable |
|
TJLP(1) plus spread |
|
6.4 |
|
|
ICASGA/AGIB |
|
BNDES |
|
R$ |
|
June 2032 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R. plus spread plus IPCA |
|
1.8 |
|
A |
|
|
BNDES |
|
R$ |
|
September 2032 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R. plus spread plus IPCA |
|
5.5 |
|
|
|
|
BNDES |
|
R$ |
|
July 2032 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R. plus spread plus IPCA |
|
1.7 |
|
|
ICAB |
|
BNDES |
|
R$ |
|
December 2033 |
|
Variable |
|
TJLP(1) plus spread |
|
208.3 |
|
A |
|
|
Votorantim |
|
R$ |
|
March 2023 |
|
Variable |
|
CDI plus spread |
|
0.8 |
|
C |
|
|
Banco Guayaquil SA |
|
USD |
|
February 2026 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R.E.(3) plus spread |
|
5.9 |
|
D |
|
|
Banco Guayaquil SA |
|
USD |
|
December 2025 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R.E.(3) plus spread |
|
2.1 |
|
D |
TAGSA |
|
Banco Bolivariano CA |
|
USD |
|
December 2025 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R.E.(3) plus spread |
|
5.4 |
|
D |
|
|
Banco Bolivariano CA |
|
USD |
|
November 2024 |
|
Variable |
|
T.R.E.(3) plus spread |
|
3.6 |
|
D |
|
|
Santander Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
April 2023 |
|
Fixed |
|
4.40% |
|
0.2 |
|
D |
TCU |
|
Scotiabank Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
October 2024 |
|
Fixed |
|
4.30% |
|
1.0 |
|
D |
|
|
Scotiabank Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
February 2026 |
|
Fixed |
|
4.30% |
|
0.8 |
|
D |
|
|
Santander Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
November 2027 |
|
Fixed |
|
5.37% |
|
1.0 |
|
D |
|
|
Banco de Innovación de Infraestructuras y Desarrollo |
|
EUR |
|
September 2027 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 6 month plus spread |
|
15.5 |
|
D |
|
|
BPM |
|
EUR |
|
December 2023 |
|
Fixed |
|
1.65% |
|
0.1 |
|
D |
|
|
Unicredit |
|
EUR |
|
March 2023 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 3 month plus spread |
|
10.1 |
|
D |
|
|
BNL |
|
EUR |
|
May 2023 |
|
Fixed |
|
3.76% |
|
5.4 |
|
D |
TA |
|
ISP-SACE |
|
EUR |
|
September 2026 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 3 month plus spread |
|
85.1 |
|
D |
|
|
BPM |
|
EUR |
|
June 2023 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 3 month plus spread |
|
0.1 |
|
D |
|
|
BPM |
|
EUR |
|
June 2024 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 3 month plus spread |
|
0.2 |
|
D |
|
|
BPM |
|
EUR |
|
January 2023 |
|
Variable |
|
Euribor 3 month plus spread |
|
3.8 |
|
D |
|
|
MPS Servicio capital |
|
EUR |
|
March 2023 |
|
Fixed |
|
1.86% |
|
11.8 |
|
D |
|
|
Banca Intesa San Paolo |
|
EUR |
|
March 2023 |
|
Fixed |
|
1.60% |
|
11.9 |
|
D |
AIA |
|
Ameriabank C.J.S.C. |
|
EUR |
|
December 2025 |
|
Fixed |
|
6.00% |
|
21.1 |
|
B |
ANSA |
|
Banco Macro (4) |
|
ARS |
|
November 2024 |
|
Variable |
|
BADLAR plus spread |
|
1.2 |
|
A |
|
|
Banco de la Provincia de Buenos Aires |
|
USD |
|
July 2024 |
|
Fixed |
|
7.00% |
|
0.8 |
|
D |
AA2000 |
|
Onshore renegotiation |
|
ARS |
|
November 2024 |
|
Variable |
|
BADCOR plus spread |
|
8.0 |
|
A |
|
|
Onshore renegotiation - ICBC |
|
USD |
|
November 2024 |
|
Fixed |
|
8.50% |
|
17.8 |
|
A |
|
|
Citibank N.A. (5) |
|
USD |
|
February 2023 |
|
Variable |
|
SOFR plus spread |
|
2.4 |
|
A |
|
|
Offshore renegotiation |
|
ARS |
|
November 2024 |
|
Variable |
|
BADCOR plus spread |
|
1.6 |
|
A |
|
|
ICBC Dubai |
|
USD |
|
October 2025 |
|
Variable |
|
SOFR plus spread |
|
10.2 |
|
B |
|
|
Banco Ciudad |
|
USD |
|
November 2023 |
|
Fixed |
|
6.00% |
|
3.5 |
|
B |
CAISA |
|
Santander Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
April 2027 |
|
Fixed |
|
5.10% |
|
6.9 |
|
|
|
|
Banco Itaú |
|
USD |
|
April 2027 |
|
Fixed |
|
3.80% |
|
6.9 |
|
B |
PDS |
|
Banco de la República Oriental del Uruguay |
|
USD |
|
March 2028 |
|
Variable |
|
7.03% |
|
10.0 |
|
C |
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
478.9 |
|
|
(1) TJLP - Taxa de Juros de Longo Prazo (Brazilian Long term interest rate).
IPCA: corresponds to the Brazilian Consumer Price index.
(2) A - Secured/guaranteed
B – Secured/unguaranteed
C – Unsecured/guaranteed
D - Unsecured/unguaranteed
ARS - Argentine Pesos.
R$ - Brazilian Reales.
(3) T.R.E - Tasa Referencial Ecuador (Ecuadorian reference interest rate).
(4) The loan was prepaid during 2023.
(5) Comprises loans with Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (Argentina) S.A., Banco Galicia and Buenos Aires S.A.U., Banco Santander Río S.A. (“the onshore credit facility”) and Citibank N.A. (“the offshore credit facility”).
F-73
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
22 Borrowings (Cont.)
- |
The Credit Facility Agreement between ICASGA and the Banco Nacional do Desenvolvimento Econômico e Social (“BNDES”) is secured by the pledge of the shares of ICASGA, together with any dividends and distributions in connection therewith, as well as the fiduciary assignment of rights arising under the Natal Airport concession agreement and certain letters of guarantees issued by indirect shareholders and affiliates of ICASGA. It also establishes a required pre-authorization by BNDES on payments of ICASGA dividends if exceeding 25% of net profits. |
The Credit Facility Agreement between ICAB and BNDES is secured by the pledge of ICAB and Inframérica Participaçoes S.A. shares, the fiduciary assignment of rights arising under the Brasilia airport concession agreement and letters of guarantee issued by indirect shareholders and affiliates of ICAB. It also establishes under certain circumstances a required pre-authorization by BNDES on payments of ICAB dividends if exceeding 25% of net profits and compliance of certain financial ratios.
During 2017 and 2018 ICAB and ICASGA entered into amendments and extension agreements with BNDES in which ACI Airports S.à r.l. and CAAP agreed not to create any encumbrances on their shares in Inframérica, and not to sell, acquire, merge or spin-off assets or undertake any other action that results or that may result in a change in the current corporate structure of Inframérica or any change of control in Inframérica, without the prior consent of BNDES. ACI Airports S.à r.l. has agreed not to undertake any change of control in CAAP without the prior consent of BNDES. In addition, ACI Airports S.à r.l. has agreed to maintain a minimum credit rating (the “Minimum Rating”) or a stand-alone rating (without including the sovereign rating) of at least B-/B3, being in compliance as of December 31,2023.
As of June 30, 2023, ICAB did not meet one of the obligations set forth in the financing agreement with BNDES, regarding the payment of the variable concession fee. On August 15, 2023, ICAB issued a formal letter to the Brazilian ANAC, informing that payment of the variable concession fee was made through the application of Covid - 19 re - equilibrium credits (see Note 8). With the netting of the debt with the existing credits, ICAB complies with its obligations under BNDES agreement and, therefore, since then has been in compliance with the obligation.
As mentioned in Note 1.2.1, on December 31, 2023, ICASGA was absorbed by ACIB, therefore the financial debts of ICASGA were transferred to ACIB.
F-74
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
22 Borrowings (Cont.)
- |
In December 2022, AIA entered into a new loan agreement with Ameriabank C.J.S.C. for up to EUR 40 million of which EUR 20 million were disbursed in December 2022, while the remaining EUR 20 million were disbursed in April, 2023. In December 2023 AIA prepaid EUR 20 million, which has shortened the loan repayment date up to December 23, 2024. This agreement provides restrictions regarding payments, taking on additional indebtedness, disposal of assets and transactions with affiliates, and the maintenance of certain financial ratios. According to this agreement, these ratios must be met as of June 30 and December 31 of each year the loan is outstanding, and are met as of December 31, 2023. |
As of December 31, 2023, AIA pledged to the security agent cash held in bank accounts for USD 59,072 (USD 38,511 as of December 31, 2022). Additionally, the loan is secured by the pledge of shares of the Company and certain collection rights.
- |
TA, pursuant to the loan agreement with Banco de Innovación de Infraestructuras y Desarrollo/ MPS Servicio capital is required to comply with certain financial ratios, which have been met as of December 31, 2023. |
On November 6, 2020, EUR 85 million of proceeds were disbursed to TA under a loan signed with a pool of leading financial institutions comprising Intesa Sanpaolo and BNL-BNP Paribas. The loan is 90% backed by SACE guarantees pursuant to the provisions of Decree-Law No. 23/2020 within the framework of the programme “Garanzia Italia”, an Italian guarantee scheme intended to support Italian companies affected by the Covid-19 crisis. The loan has a term of six years, with a two-year grace period and TA is required to comply with certain financial covenants and restrictions, which have been met as of December 31, 2023.
- |
ANSA loan with Banco Macro was secured with a guarantee letter of Corporación América S.A. In addition, ANSA entered into an assignment of collection rights agreement in favor of Banco Macro. The loan was prepaid in November 2023 and the guarantees released. |
- |
On August 9, 2019, AA2000 entered into two credit facility agreements: (a) the onshore credit facility agreement, by and among AA2000, as borrower, Banco Galicia and Buenos Aires S.A.U., Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (Argentina) S.A. (“ICBC”) and Banco Santander Río S.A., as lenders (collectively, the “Lenders”), Citibank N.A. (“Citibank”), as administrative agent and Citibank Argentina, as local collateral agent, local disbursement agent and local paying agent, for an aggregate principal amount of USD 85 million and (b) the offshore credit facility agreement, by and among AA2000, as borrower, Citibank acting through its international banking facility, as lender, Citibank N.A., as administrative agent and Citibank Argentina as local collateral agent and local custodian agent for an aggregate principal amount of USD 35 million (collectively, the “2019 Credit Facilities”). |
To secure its obligations under the two credit facility agreements, pursuant to the Argentine Collateral Trust Agreement dated August 9, 2019 (under Argentine law), AA2000 transferred and assigned to the collateral trustee, acting on behalf of the Trust, for the benefit of the Lenders, acting as the beneficiaries, all: (a) rights, title and interest in, to and under each payment of the cargo airport charges payable by the user of such services in connection with all proceeds derived from export and import services carried out by Terminal de Cargas Argentina (a business unit of AA2000); and (b) any residual amount that AA2000 could be entitled to receive pursuant to article 11.4 of the collateral trust agreement dated January 17, 2017, entered into AA2000 and Citibank, in respect of the rights to receive payment in the event of a termination, expropriation or redemption of the concession agreement entered by and between the National Government and AA2000 on February 9, 1998 and approved by Decree No. 163/1998; including the right to receive and withhold all the payments pursuant to them and any other produced by them, assigned in trust to secure the Existing Notes issued by AA2000.
F-75
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
22 Borrowings (Cont.)
During 2020 and 2021, AA2000 entered into framework amendments (“Framework Agreement”) and extension agreements with the financial institutions with respect to the above loans, including the extension of the final maturity. Additionally, under the Framework Agreement, AA2000 signed bilateral contracts with each of the financial institutions and signed an amendment to the aforementioned agreement where the obligation to comply with certain ratios foreseen in the 2019 Credit Facilities has been waived.
On November 18, 2021, AA2000 agreed with the Lenders the granting of a bimonetary loan in order to prepay the loans from the Framework Agreement. The loans are secured by the Argentine Collateral Trust Agreement. Disbursements were made in November and December 2021, both in USD (Onshore renegotiation – ICBC) and in ARS (Offshore renegotiation) for USD 10 million and ARS 3,944 million (equivalent to USD 22.3 million) respectively. During 2022 disbursements under the bimonetary loan were granted and used to offset the installments of the Framework Agreement for ARS 3,682.0 million (equivalent to USD 20.8 million) and for USD 7.8 million. Additionally, prepayments of the bimonetary loans in ARS were made during 2022 for ARS 6,085.0 million (equivalent to USD 34.3 million).
In March 2023, AA2000 obtained a bank overdraft from Citibank N.A. and prepaid the bimonetary loan in ARS, for ARS 1,350.5 million (equivalent to USD 1.7 million). The outstanding balance is to be repaid in installments to be made until March 2024.
On July 29, 2022, AA2000 obtained a loan from Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Dubai branch, for a total amount of USD 10 million. The loan will be repaid in three installments to be made in April, July and October 2025. The loan is secured by a first priority lien on the income generated in the cargo terminal on a pari passu basis with certain commercial bank lenders to AA2000 and the Class 4 Notes, and a second priority lien on the international and regional air station usage fees and concession compensation rights.
- |
CAISA pursuant to the credit facilities with Banco Santander S.A. and Banco Itaú Uruguay S.A. is required to comply with certain financial ratios as well as certain restrictions. Assignment of certain revenues has been given to secure the aforementioned credit facilities. |
- |
On April 16, 2021, PDS obtained a loan of USD 10 million with Banco de la República Oriental del Uruguay (BROU) accruing interest at a variable rate set by BROU. This loan is repayable in 60 monthly installments starting on April 2023 and is secured by a guarantee issued by CAAP, and by a stand by letter issued by Morgan Stanley Private Bank, National Association for USD 1.5 million guaranteed by Corporación America Sudamericana S.A. |
As of December 31, 2023, the Company and its subsidiaries met the financial covenants under outstanding financings.
F-76
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
23 Other liabilities
|
|
At December 31, |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Non-current |
|
|
|
|
Concession fee payable (1) |
|
690,319 |
|
700,395 |
Advances from customers |
|
13,368 |
|
13,910 |
Provisions for legal claims (4) |
|
8,979 |
|
9,712 |
Provision for maintenance costs (2) |
|
21,364 |
|
19,079 |
Other taxes payable |
|
199 |
|
508 |
Employee benefit obligation (3) |
|
4,382 |
|
4,376 |
Salary payable |
|
291 |
|
286 |
Other liabilities with related parties (Note 27) |
|
15,275 |
|
1,382 |
Other payables |
|
14,187 |
|
18,735 |
|
|
768,364 |
|
768,383 |
Current |
|
|
|
|
Concession fee payable (1) |
|
223,051 |
|
228,614 |
Other taxes payable |
|
18,921 |
|
17,288 |
Salary payable |
|
41,656 |
|
46,061 |
Other liabilities with related parties (Note 27) |
|
2,689 |
|
1,121 |
Advances from customers |
|
5,647 |
|
5,098 |
Provision for maintenance cost (2) |
|
5,678 |
|
3,835 |
Expenses provisions |
|
6,203 |
|
2,413 |
Provisions for legal claims (4) |
|
5,286 |
|
3,424 |
Other payables (*) |
|
36,733 |
|
49,224 |
|
|
345,864 |
|
357,078 |
(*) As of December 31, 2023, includes deferred income for a total amount of USD 21,060 (USD 15,395 as of December 31, 2022).
Maturity of the other liabilities is as follows:
|
|
1 year or less |
|
1 - 2 years |
|
2 - 5 years |
|
Over 5 years |
|
Total |
At December 31, 2023 (**) |
|
345,864 |
|
96,071 |
|
279,683 |
|
1,266,124 |
|
1,987,742 |
At December 31, 2022 (**) |
|
357,078 |
|
88,255 |
|
263,318 |
|
1,549,369 |
|
2,258,020 |
(**) The amounts disclosed in the table are undiscounted cash flows
The fair value of financial liabilities within current and non-current other liabilities approximates to its carrying amount.
F-77
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
23 Other liabilities (Cont.)
(1) The most significant amounts included in the concession fee payable result from the concession agreement between the Brazilian ANAC and ICAB as of December 2023 and between the Brazilian ANAC – ICAB and ICASGA as of December 2022. The Brazilian concession agreement establishes the payment of a fixed and variable concession fee.
a) |
Fixed concession fee |
The Brasilia Airport concession agreement established a fixed concession fee of R$ 4,501,132 thousand, payable in 25 equal annual installments since inception of the concession period. The concession fee is adjusted for inflation annually based on the changes in the Brazilian IPCA. The Natal Airport concession agreement established an annual fixed concession fee of R$ 6,800 thousand, payable as from the 37th month of the inception of the concession, and adjusted periodically by the Selic rate. The Group initially recognized the present value of fixed concession fee against a concession asset in intangible assets. The liability is presented as current and non-current concession fee payable within other liabilities. Due to the re-bidding process of the Natal Airport (Note 1.2.1), as of December 31, 2023 ICASGA extinguished all the concession fees obligations.
This fixed concession fee is divided in two parts:
(a) |
Right of use if the airport operates at the existing operating capacity at the beginning of the concession, and |
(b) |
the second portion relates to the Group estimation of the value of the right of use after completion of the infrastructure works that increase capacity of the airport. |
Changes in the liability related to the increase capacity of the airport or contract modifications are accounted for against the “Concession asset”. Changes in the liabilities due to passage of time and inflation adjustment are recognized against profit or loss of the year.
b) |
Variable concession fee |
The concession agreement for the Brasilia Airport requires payment of an annual fee of 2% of aeronautical and commercial revenues with a cap annually established by the Brazilian ANAC. After that limit, concession fee is calculated at 4.5%.
Changes in the year for fixed and variable concession fee payable are as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Balances at the beginning of the year |
|
929,009 |
|
825,034 |
Financial result (*) |
|
100,237 |
|
112,345 |
Concession fees |
|
135,530 |
|
139,744 |
Payments (**) |
|
(199,618) |
|
(157,898) |
Re-equilibrium compensation (***) |
|
(22,946) |
|
(15,434) |
Other (****) |
|
(75,475) |
|
570 |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
46,633 |
|
24,648 |
Balances at the end of the year |
|
913,370 |
|
929,009 |
(*) Mainly includes changes in the liabilities of Brazilian concessions due to passage of time and inflation adjustment shown in Note 9.
(**) As of December 31, 2023, includes USD 19,156 that were deducted from the indemnification received by ICASGA due to de re-bidding process described in Note 1.2.1. As of December 31, 2022 included USD 24,126 concession fee payable that were offset against credits of AA2000.
(***) Mainly includes compensation with the re-equilibrium granted to ICAB detailed in Note 8.
F-78
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
23 Other liabilities (Cont.)
b)Variable concession fee (Cont.)
(****) Mainly includes the extinguishment of future concession fee obligations of ICASGA due to the re-bidding process detailed in Note 1.2.1 for the equivalent to USD 74,640.
On October 23, 2020, the Ministério da Infraestrutura of Brazil issued an order (Portaria No. 157) that allow companies to re-schedule at least 50% of their 2020 concession fee payment. On November 2, 2020, ICAB re-scheduled 50% of its fixed concession fees payment of 2020, in accordance with the provisions of the aforementioned order, to the six final years of the concession. The Government order (Portaria No. 157) determined that re-scheduling the payments of the concession fee must not exceed, for each financial year, 75% above the original value and 50% above the original value for the last five years of the concession. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, a 50% of the fixed concession fee to be paid in 2021 by ICAB was pending as a re-scheduling of such fee was requested. Even though, the Brazilian Ministry of Infrastructure had granted its approval, the Brazilian ANAC denied ICAB’s request, and initiated administrative proceedings with a view to declaring ICAB in default of its payment obligations. Therefore, ICAB initiated a judicial procedure and, on February 2, 2022, a writ of mandamus was granted by a Federal judge suspending any act or enforceability in connection with the unpaid portion of the concession fee due to the Brazilian ANAC. The Brazilian ANAC appealed, but in April 2022, the court of justice provisionally maintained the first instance judgment favorable to ICAB. In November 2023, the case was decided and the first instance ruling in favor of ICAB was confirmed, granting ICAB the right to reschedule the 50% of 2021’ fixed concession fee. The Brazilian ANAC appealed the ruling and the court of justice has not issued its decision as of December 31, 2023.
Regarding the 2022 concession fee a partial payment of R$ 81.6 million (equivalent to USD 15 million) was made through the application of re-equilibrium credits. To pay the remaining amount ICAB presented on November 21, 2022 to the Ministry of Infrastructure, an offer of court payment orders, which is still in process of analysis. In December 2022, the Ministry issued an official letter confirming that, during the time it takes to issue a final opinion, ICAB is in compliance with its obligations.
On December 17, 2020 AA2000 reached an agreement with ORSNA in relation with past due payments of concession fees and development trusts suspended during 2020, for approximately USD 38 million to be paid in installments between October 2021 and September 2022. On September 2, 2021, AA2000 and ORSNA agreed to postpone the past due payments which were paid in installments that concluded on November 2023.
(2) Changes in the year of the Provision for maintenance costs is as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Balances at the beginning of the year |
|
22,914 |
|
21,671 |
Accrual of the year |
|
5,349 |
|
4,118 |
Use of the provision |
|
(2,127) |
|
(1,652) |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
906 |
|
(1,223) |
Balances at the end of the year |
|
27,042 |
|
22,914 |
(3) TAGSA and Toscana have post-employment benefits which are defined benefit obligations. The amount of termination benefit has been calculated using the “Projected Unit Credit Method”, making actuarial valuations at the end of the year.
The assumptions used for the purposes of valuation of TA long term benefits at December 31, 2023 and 2022 are:
- Annual discount rate: 3.17% (3.77% in 2022).
- Annual inflation rate: 2.0% (5.9% for the year 2023, 2.3% for the year 2024 and 2% from 2025 in 2022).
- Annual employee termination benefit increase rate: 3% (5.9% for the year 2023, 3.2% for the year 2024 and 3% from 2025 in 2022).
F-79
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
23 Other liabilities (Cont.)
The iBoxx Eurozone Corporate AA 10+ index has been selected as the discount rate to be used, as the term of 10 or more years is comparable to the average remaining period of service of the personnel subject to the long term benefit.
The sensibility in relation with the provision of Toscana for a total amount of USD 2.4 million is as follows:
Assumption |
|
Annual discount rate |
|
Annual rate of inflation |
|
Annual turnover rate |
||||||
Variation rates |
|
0.5% |
|
(0.5)% |
|
0.25% |
|
(0.25)% |
|
2.5% |
|
(2.5)% |
Provision for salary payable |
|
2,327 |
|
2,526 |
|
2,452 |
|
2,395 |
|
2,429 |
|
2,418 |
The assumptions used for the valuation of TAGSA at December 31, 2023 and 2022 are:
- Annual discount rate: 5.77% (5.96% in 2022).
- Annual turnover rate: 15.52% (14.98% in 2022).
- Annual employee termination benefit (in years): 6.84 (7.06 in 2022).
- Annual employee mortality and disability rate: TM IESS 2002 (TM IESS 2002 in 2022). (*)
- Annual employee future wage increase: 1.33% (1.29% in 2022).
(*) |
Mortality Table “Instituto Ecuatoriano de Seguridad Social” |
The sensibility in relation with the prevision of TAGSA for a total amount of USD 2.0 million is as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Annual employee future |
|
|
|
|
||
Assumption |
|
Annual discount rate |
|
wage increase |
|
Annual turnover rate |
||||||
Variation rates |
|
0.5% |
|
(0.5)% |
|
0.5% |
|
(0.5)% |
|
0.5% |
|
(0.5)% |
Provision for salary payable |
|
1,880 |
|
2,040 |
|
2,042 |
|
1,878 |
|
1,951 |
|
1,965 |
Changes of the provision in the year is as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Balances at the beginning of the year |
|
4,376 |
|
7,990 |
Disposal of subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
(2,084) |
Actuarial gain/loss (in other comprehensive income) |
|
(32) |
|
(1,016) |
Service Cost |
|
367 |
|
450 |
Amounts paid in the year |
|
(418) |
|
(585) |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
89 |
|
(379) |
At the end of the year |
|
4,382 |
|
4,376 |
The amounts shown in the Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income for USD 4 in 2023 (USD 859 in 2022) correspond to the actuarial (loss)/income of USD (8) (USD 1,016 in 2022), net of taxes of USD 12 (USD 157 in 2022).
F-80
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
23 Other liabilities (Cont.)
(4) Changes in the year of the provision for legal claims is as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Balances at the beginning of the year |
|
13,136 |
|
11,846 |
Disposal of subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
(1,177) |
Accrual of the year |
|
4,469 |
|
5,674 |
Use of the provision |
|
(1,911) |
|
(2,319) |
Translation differences and inflation adjustment |
|
(1,429) |
|
(888) |
Balances at the end of the year |
|
14,265 |
|
13,136 |
24 Trade payables
|
|
At December 31, |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Non-current |
|
|
|
|
Trade payable with suppliers |
|
2,617 |
|
3,307 |
|
|
2,617 |
|
3,307 |
Current |
|
|
|
|
Trade payables with suppliers |
|
107,502 |
|
118,349 |
Trade payables with related parties (Note 27) |
|
5,266 |
|
5,753 |
|
|
112,768 |
|
124,102 |
Fair value of trade payables does not materially differ from the net book value.
25 Equity
a) Share capital and treasury shares
As of December 2023, 2022 and 2021, Share capital amounted to USD 163,223.
The movements of treasury shares for the year is as follows:
On March 12, 2021, 590,000 shares (equivalent to USD 1,800), already assigned and fully vested as of December 31, 2020, were delivered to the eligible executives and key employees (Note 30).
In December 2021, additional 250,000 shares (equivalent to USD 1,440) were assigned to employees. In December 2023, 2022 and 2021, 50,000, 62,500 and 125,000 of those shares (equivalent to USD 288, USD 360 and USD 720 respectively) assigned during 2021 and fully vested, were delivered to the eligible executives and key employees, while the remaining 12,500 shares have been forfeited during 2022 (Note 30).
In April 2022, USD 500 (equivalent to 89,767 shares) were assigned to employees to be delivered in shares. In May 2022 and April 2023, 26,930 shares were delivered in each installment (equivalent to USD 150 each) while the remaining shares will vest in an installment in May 2024 (Note 30).
F-81
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
25 Equity (Cont.)
a) Share capital and treasury shares (Cont.)
In December 2022, USD 314 (equivalent to 56,348 shares) were assigned to employees to be delivered in shares. In January and April 2023, 16,904 shares were delivered in each installment (equivalent to USD 94 each) while the remaining shares will vest in an additional installment in May 2024 (Note 30).
In April 2023, USD 739 (equivalent to 77,938 shares) were assigned to employees of which 23,381 shares (equivalent to USD 221.7) were delivered to the eligible executives and key employees, while the remaining shares will vest in installments in May 2024 and May 2025.
In November 2023, USD 340 (equivalent to 35,910 shares) were assigned to employees of which 10,773 shares (equivalent to USD 102.1) were delivered to the eligible executives and key employees, while the remaining shares will vest in installments in May 2024 and May 2025.
As of December 31,2023 and 2022, the remaining new shares are held in treasury until their allocation to executives and key employees in accordance with the Management Compensation Plan.
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
||||
Treasury shares |
|
Shares |
|
USD |
|
Shares |
|
USD |
At January 1 |
|
2,396,015 |
|
4,600 |
|
2,485,445 |
|
4,772 |
Transfer of treasury shares to executives and key employees |
|
(144,892) |
|
(278) |
|
(89,430) |
|
(172) |
At December 31 |
|
2,251,123 |
|
4,322 |
|
2,396,015 |
|
4,600 |
b) Share premium
As of December 2023, 2022 and 2021, Share premium amounted to USD 183,430.
c) Other reserves
The movements of Other Reserves of the owners of the Company is as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
At the beginning of the year |
|
(1,314,025) |
|
(1,321,211) |
|
(1,321,142) |
Change in participations (*) |
|
12 |
|
6,682 |
|
1,433 |
Share-based compensation reserve (Note 30) |
|
1,055 |
|
667 |
|
1,020 |
Execution of share-based compensation reserve |
|
(949) |
|
(510) |
|
(2,520) |
Remeasurement of defined benefit obligations net for income tax |
|
19 |
|
347 |
|
(2) |
|
|
(1,313,888) |
|
(1,314,025) |
|
(1,321,211) |
(*) This consists mainly in change in participations in Corporación América S.A., see Note 25 e).
F-82
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
25 Equity (Cont.)
d) Other comprehensive income / (loss)
The movements of the reserve of other comprehensive income / (loss) for the year of the owners of the parent is as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transfer from |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remeasurement |
|
Share of other |
|
Income |
|
shareholders |
|
|
|
|
Currency |
|
of defined |
|
comprehensive |
|
Tax |
|
equity – currency |
|
|
|
|
translation |
|
benefit |
|
loss from |
|
effect |
|
translation |
|
|
|
|
adjustments |
|
obligations (*) |
|
associates |
|
(*) |
|
differences |
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balances at January 1, 2023 |
|
(273,378) |
|
520 |
|
(41,169) |
|
(122) |
|
63,402 |
|
(250,747) |
Other comprehensive income/(loss) for the year |
|
(231,637) |
|
12 |
|
(70) |
|
7 |
|
— |
|
(231,688) |
For the year ended December 31, 2023 |
|
(505,015) |
|
532 |
|
(41,239) |
|
(115) |
|
63,402 |
|
(482,435) |
Balances at January 1, 2022 |
|
(343,837) |
|
120 |
|
(41,212) |
|
(69) |
|
63,402 |
|
(321,596) |
Other comprehensive income/(loss) for the year |
|
70,459 |
|
400 |
|
43 |
|
(53) |
|
— |
|
70,849 |
For the year ended December 31, 2022 |
|
(273,378) |
|
520 |
|
(41,169) |
|
(122) |
|
63,402 |
|
(250,747) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balances at January 1, 2021 |
|
(439,407) |
|
92 |
|
(41,267) |
|
(39) |
|
63,402 |
|
(417,219) |
Other comprehensive income/(loss) for the year |
|
95,570 |
|
28 |
|
55 |
|
(30) |
|
— |
|
95,623 |
For the year ended December 31, 2021 |
|
(343,837) |
|
120 |
|
(41,212) |
|
(69) |
|
63,402 |
|
(321,596) |
(*) Income tax relating to OCI amounts to Remeasurement of defined benefit obligations. The movement was recognized as other comprehensive income / (loss) of other reserves.
F-83
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
25 Equity (Cont.)
e) Non – controlling interest
The movements of the non- controlling interest for the year is as follows:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
At the beginning of the year |
|
146,274 |
|
303,877 |
|
315,876 |
Shareholder contributions (1) |
|
9,424 |
|
24,170 |
|
11,475 |
Loss for the year |
|
(13,039) |
|
(2,531) |
|
(63,221) |
Redemption of preferred shares (f) |
|
— |
|
(182,336) |
|
— |
Other comprehensive (loss) / income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Currency translation |
|
(50,047) |
|
20,646 |
|
43,071 |
Remeasurement of defined benefit obligations |
|
(20) |
|
616 |
|
69 |
Reserve for income tax |
|
5 |
|
(104) |
|
(41) |
|
|
(50,062) |
|
21,158 |
|
43,099 |
Changes in non-controlling interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in the participations –acquisitions (2) |
|
(12) |
|
(6,682) |
|
(991) |
Dividends paid |
|
(13,656) |
|
(11,382) |
|
(2,361) |
|
|
(13,668) |
|
(18,064) |
|
(3,352) |
Non-controlling interest at the end of the year |
|
78,929 |
|
146,274 |
|
303,877 |
(1) Corresponds mainly to contributions made by the non-controlling interest in ICAB.
(2) In 2022 and 2021, corresponds mainly to contributions of Cedicor S.A. in Corporación América S.A. capitalized on December 1, 2022 and December 16, 2021, increasing its participation from 96.18% to 97.22% in 2022 and from 95.80% to 96.18% in 2021.
f) Redemption of preferred shares
On March 10, 2022, an extraordinary general meeting of AA2000 approved the redemption of the preferred shares, the reduction of the capital stock and the amendment of Article 2.01 of AA2000’s bylaws. The total redemption value amounted ARS 17,225,719,240 (equivalent to approximately USD 155.2 million), which adjusted by inflation as of December 31, 2022 amounts to ARS 32,302,581,376 (equivalent to approximately USD 182.3 million).
As of December 31, 2022, the preferred shares were fully settled in cash by AA2000. The payments adjusted by inflation since the date of each disbursement amounts to ARS 30,476,665,719 (equivalent to approximately USD 172.0 million).
F-84
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits
a. Contingencies
CAAP and its subsidiaries are, from time to time, subject to various claims, lawsuits and other legal proceedings, including customer claims, in which third parties are seeking payment for alleged damages, reimbursement for losses or indemnity. Some of these claims, lawsuits and other legal proceedings are subject to substantial uncertainties. Accordingly, the potential liability with respect to such claims, lawsuits and other legal proceedings cannot be estimated with certainty. Management, with the assistance of legal counsel, periodically reviews the status of each significant matter and assesses potential financial exposure. If a potential loss from a claim, lawsuit or proceeding is considered probable and the amount can be reasonably estimated, a provision is recorded. Accruals for loss contingencies reflect a reasonable estimate of the losses to be incurred based on information available to management as of the date of preparation of the Financial Statements, and take into consideration the Group’s litigation and settlement strategies.
The Company believes that the aggregate provisions recorded for losses in these Consolidated Financial Statements, are adequate based upon currently available information.
AA2000 Environmental proceedings
Pursuant to the Final Memorandum of Agreement entered into with the Argentine Government, dated April 3, 2007, AA2000 is required to assess and remediate environmental damage at their airports in Argentina.
In August 2005, a civil action was brought by Asociación de Superficiarios de la Patagonia, a non-governmental organization, against Shell Oil Company for alleged environmental damages caused by an oil spill at Ezeiza Airport and, in September 2006, AA2000 was called to intervene as a third party at the request of the plaintiff. The lawsuit alleges that AA2000 is jointly liable with Shell due to the fact that AA2000 manages the real property at which the environmental damages occurred. AA2000 has asserted that Shell is solely responsible for any damages. As of the date of these Consolidated Financial Statements, Shell Oil Company and the ORSNA are currently jointly working in the damage remediation activities.
In August 2011, Asociación de Superficiarios de la Patagonia (“ASSUPA”) brought a civil action against AA2000 in an Argentine administrative federal court in the City of Buenos Aires (Justicia Federal en lo Contencioso Administrativo de la Capital Federal), under the General Environmental Law No. 25,675, requesting compensation for environmental damage caused in all airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
A “General Remediation Agreement” was entered into with ASSUPA, under which the execution of airport-specific improvement and renovation works was agreed. It was also agreed that these remediation works will be funded out of the Trust Fund for Funding Infrastructure Works in airports under the AA2000 Concession Agreement (2.5%).
In connection with the civil action filed by ASSUPA, on April 15, 2021, a specific agreement covering the improvement and renovation works at Ezeiza airport was signed.
The agreements subscribed with ASSUPA were submitted to ORSNA and were also approved by the Court hearing the civil action filed by ASSUPA on August 30, 2021.
In addition, an agreement covering the fees of ASSUPA’s legal counsel and technical experts has also been signed. The monetary amount of this agreement was recognized as of September 30, 2021 and was included in Other operating expenses line.
The amounts to be paid in connection with the remediation works will be considered investments under the AA2000 Concession Agreement.
F-85
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
a. Contingencies (Cont.)
ANSA civil proceedings
On October 26, 2018, Aeropuertos del Neuquén S.A. (“ANSA”) was served with a complaint from a supplier alleging ANSA’s breach of contract for the financing of the construction of a hangar at the airport of Neuquén.
On July 7, 2022, the first instance judgment rejected the claim and imposed the payment of the Court costs to the plaintiff who appealed.
On December 13, 2023, the Court of Appeals partially upheld the plaintiff’s appeal on the merits and reversed the first instance ruling, ordering ANSA to pay the sum of USD 0.6 million plus USD 0.3 million in interest (set as of December 29, 2023, at an annually rate of 8%). The legal costs of both instances were put on the charges of ANSA and amount, in total, to 53.3% of the amount of the judgment. Those costs include the plaintiff’s counsel’s fees.
This ruling was appealed before the Supreme Court of Neuquen by ANSA (both on the merits and the legal costs) and by plaintiff’s counsel (with respect of on the amount of legal fees allocated).
Both extraordinary appeals are pending.
The filing of the appeal does not prevent the beneficiaries of the sentence from requesting provisional seizures against ANSA to ensure the collection of their fees if the judgement were confirmed. These seizures cannot be executed until the provincial extraordinary appeal is resolved and the execution will proceed only if the appeal is dismissed. If seizures are requested, it will be required to replace them by insurance policies. The counsel’s fees should be covered by the insurance policy previously filed in the proceedings.
ANSA also received a claim from a supplier of USD 0.5 million regarding a breach of contract. Within the framework of the lawsuit, the court ordered an attachment order on ANSA’s bank accounts in the amount of USD 0.3 million, which was replaced by an insurance offered by ANSA in the amount of USD 0.5 million. A hearing was held on July 14, 2022, and the evidence offered by both parties is currently being reviewed.
As of December 31, 2023, provisions in the amount of USD 0.9 million regarding ANSA’s legal proceedings have been recorded.
AA2000 civil proceedings - Conflict with Aerolíneas Argentinas (“ARSA”)
This airline is currently AA2000’s main customer and recorded an outstanding debt with AA2000. The singularity of ARSA lies in its status as state-owned company, since it is owned by the Argentinian State, which is in turn the grantor of AA2000 Concession Agreement.
Claims have been made before ORSNA as well as formal presentations before the Ministry of Transportation, requesting mechanisms to resolve the situation through different alternatives such as payment plans, compensation and agreements. Considering this situation and in accordance with IFRS 15, as from October 1, 2019, only revenue from passenger fees related to ARSA was being recognized.
On February 2, 2021, ARSA sent a document to AA2000, which contained a proposal of debt acknowledgment for the amounts owed until March 31, 2020 (ARS 120.6 million and USD 36.5 million).
On July 21, 2021, AA2000 sent a proposal to the ORSNA in order to apply this credit against debts held by Fideicomiso de Fortalecimiento del Sistema Nacional de Aeropuertos.Both parties agreed the form of application of the assigned credits, which will become effective upon endorsement by the Ministry of Transportation.
F-86
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
a. Contingencies (Cont.)
AA2000 civil proceedings - Conflict with Aerolíneas Argentinas (“ARSA”) (Cont.)
On April 5, 2022, the Ministry of Transportation initiated the planned intervention. On June 14, 2022, the ORSNA notified AA2000 that the Ministry of Transportation has completed its intervention, and approved the assignment in the terms described. Consequently, revenues, bad debt recovery, foreign exchange income and interest income for total amounts of approximately USD 4.8, 10.1, 13.0 and 4.8 million respectively, were recognized.
In 2023, ARSA made several payments in cash for a total amount of approximately USD 27.5 million, including both outstanding past due debt and current amounts. As at December 31, 2023, the remaining amount owed by ARSA to AA2000 equals USD 2.4 million.
Brazil legal proceedings
Civil Proceedings
Inframérica Participações S.A. identified three payments totaling R$ 858 thousand made during 2014 by ICAB, when Infravix Participações S.A. was still an indirect shareholder of the Inframérica, to individuals or entities for which Inframérica was unable to clearly identify a proper purpose. On September 14, 2019, Receita Federal imposed Inframérica to pay the amount of R$1.3 million in late taxes, claiming that these alleged payments were allegedly without cause or did not identify a beneficiary. ICAB is contesting the fine through an administrative procedure. The outcome of this procedure is still uncertain. Neither ICAB nor ICASGA have been notified of any investigation against them.
If these payments are ultimately found to have been improper, additional fines and sanctions may be applied, as well as other penalties.
Tax Proceedings
On November 1, 2017, ICASGA initiated a lawsuit before the Municipality of São Gonçalo do Amarante to dispute the legality of the Property and Urban Territorial Tax (“IPTU”) collected by the City of São Gonçalo do Amarante.
On January 18, 2018, the judge granted a provisional decision by suspending the tax collection, and on August 27, 2019, a further ruling found the collection as unfounded. The Municipality appealed and obtained a provisional decision, which allowed for the collection of such tax up to the amount of approximately R$ 17 million. On December 11, 2019, ICASGA appealed said provisional decision which was granted on May 27, 2020 and, consequently, the tax collection was suspended. The Municipality appealed again before the Brazilian Supreme Court and, on June 16, 2020, such appeal was denied. The tax collection remains suspended until trial by the State Court is completed.
On November 17, 2020, the State Court made its final decision dismissing the collection of IPTU which was appealed by the Municipality before the Brazilian Supreme Court. On August 1, 2023, a first decision was granted, in favor of the City. The Minister decided to revoke the State Court’s last decision and ruled that the State Court had to analyze the lawsuit again. ICASGA submitted an appeal before the Supreme Court, asking this monocratic decision adopted in August to be reviewed by the other Ministers which was granted on September 29, 2023. The Supreme Court partially changed its decision, and decided to keep IPTU immunity as a rule, but to allow the Municipality to collect this tax only over the areas occupied by third parties who exploit activities unrelated to the airport public service.
After the Supreme Court’s decision, in December 2023 the Municipality rectified the value of the tax demanded from R$ 80 million (equivalent to USD 16.5 million), to R$ 8 million (equivalent to USD 1.7 million), which is the total value of IPTU for all the concession years. ICASGA filled an administrative appeal, since still consider that the amount is not correct and should not be charged over ICASGA.
F-87
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
a. Contingencies (Cont.)
Brazil legal proceedings (Cont.)
In September 2014, ICAB initiated a lawsuit that dispute the legality of the IPTU collected by the Federal District. In October 2014, the judge granted a provisional decision by suspending the tax collection, and in April 2015, a further ruling found the collection as unfounded.
In June 2022, the Brazilian Supreme Court confirmed the decision of the Federal District Court excluding ICAB’s responsibility for the payment of IPTU and restricting this tax to the areas occupied by third parties who pursue activities unrelated to the airport. This lawsuit is now concluded.
The Federal District initiated a new lawsuit, demanding the payment of R$ 5.0 million (equivalent to USD 1.0 million) on pending IPTU. On January 21, 2020, ICAB was notified about this new proceeding and on March of 2020, ICAB filed a response arguing in the same rights as those raised in the prior proceeding. In September 2022, the Federal District, again, sued ICAB, claiming the payment of R$ 1.2 million (equivalent to USD 0.2 million) of IPTU. ICAB answered the complaint under the same rights raised on prior lawsuits. As of December 31, 2023, none of this claims have been ruled by the court of first instance.
ACI do Brasil shall replace ICASGA in all legal proceedings as consequence of the absorption of ICASGA by ACI do Brasil, effective as from December 31, 2023.
Ecuadorian Proceedings
Tax Proceedings
The Ecuadorian tax authority (Servicio de Rentas Internas del Ecuador, “SRI”) determined that TAGSA has to pay roughly USD 3.3 million in connection with differences established by the SRI for the 2017 withholding tax determination. The request for a nullity resolution against this determination was submitted by TAGSA on April 27, 2021, which was rejected on November 8, 2021, by the SRI. TAGSA exhausted the administrative instance, since the outcome was not positive and submitted a judicial claim on January 31, 2022, for an amount of USD 4.5 million. On July 13 and September 6, 2022, took place two hearings, and on October 18 a rule was issued in favor of TAGSA. On December 12, 2022, the SRI submitted a cassation complaint against the ruling, which was accepted by the National Court on July 6, 2023. On July 14, 2023 TAGSA submitted its response and now the parties are waiting for the Court to schedule the hearing. As of December 31, 2023, guarantees, amounting USD 0.5 million have been constituted by TAGSA in favour of SRI.
Italian proceedings
TA entered into two preliminary sales contracts with Nuove Iniziative Toscane (“NIT”) in 2018 with the commitment to purchase, from NIT itself, land and buildings located in the “Piana di Castello” near the Municipality of Florence. For the first contract, the expected price was equal to EUR 75 million, of which EUR 3 million were paid as a deposit at the time of the execution, while for the second the expected price was equal to EUR 90 thousand, of which EUR 9 thousand were already paid.
On September 10, 2021, NIT filed a claim before the Civil Court of Milan - claiming the fulfillment of the conditions precedent to obtain the issuance of a constitutive sentence pursuant to art. 2932 of the Italian Civil Code, - condemning TA to pay the relative price (net of the deposits already paid, therefore EUR 72 million for the first contract and EUR 81 thousand for the second contract). NIT also requests TA to pay for the compensation of the damages suffered, as well as any further pecuniary damage.
F-88
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
a. Contingencies (Cont.)
Italian proceedings (Cont.)
On January 20, 2022, TA answered the claim by rejecting, as inadmissible and unfounded, all the requests made by NIT; taking into consideration the non-occurrence of the conditions precedent, and consequently condemn NIT to immediately return the sums already paid by TA.The next court hearing was postponed to September, 2023. However, such hearing did not take place since the parties proceeded to submit their closing arguments in writing.
The parties submitted their final briefs in December 2023, and it is expected that the resolution is issued during 2024.
Peruvian proceedings
On July 13, 2017, the Government of Peru notified the unilateral decision to rescind the concession agreement for the Nuevo Aeropuerto Internacional de Chinchero.
On June 21, 2018, an arbitration procedure request was submitted by Kuntur Wasi to the competent authority ICSID (known as CIADI in Spanish). On the same date, Corporación América S.A. also submitted to CIADI a request for the arbitration procedure under the Bilateral investment treaty framework. Both procedures before CIADI shall be carried out in a single docket.
On August 10, 2023, Kuntur Wasi received notification from the CIADI Arbitral Court regarding a favorable resolution concerning the arbitration procedure due to unreasonably and arbitrary unilateral termination of the Concession Agreement by the Peruvian Ministry of Transports and Communications. While the Arbitral Court has already determined the final award for damages and losses, and on February 28, 2024 both parties submitted further information that was required to calculate the business profit based on the invested amounts as well as the recognition of interests on the related amounts.
F-89
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
a. Contingencies (Cont.)
Following advice taken from local counsel and unless otherwise mentioned, no provision has been recognized at December 31, 2023 in relation to the above proceedings.
b. Commitments
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of |
|
Concession Start |
|
Concession |
|
|
Country |
|
Concession |
|
Airports |
|
Date |
|
End Date |
|
Extension Details |
Argentina |
|
AA2000 |
|
35 |
|
1998 |
|
2038 |
|
|
|
|
ANSA |
|
1 |
|
2001 |
|
20261 |
|
|
|
|
BBL |
|
1 |
|
2008 |
|
2033 |
|
10 years |
Italy |
|
TA (SAT) |
|
1 |
|
2006 (2014) |
|
2048 |
|
|
|
|
TA (ADF) |
|
1 |
|
2003 (2014) |
|
2045 |
|
|
Brazil2 |
|
ICAB |
|
1 |
|
2012 |
|
2037 |
|
5 years |
Uruguay |
|
PDS |
|
7 |
|
2003 |
|
20533 |
|
|
|
|
CAISA |
|
1 |
|
1993 (2008) (2019) |
|
2033 |
|
|
Ecuador |
|
TAGSA |
|
1 |
|
2004 |
|
20314 |
|
|
|
|
ECOGAL |
|
1 |
|
2011 |
|
2026 |
|
|
Armenia |
|
AIA |
|
2 |
|
2002 |
|
2032 |
|
Option to renew every 5 years |
Total |
|
|
|
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
In 2021, the Group obtained a five-years extension. |
2. |
Due to the re-bidding process detailed in Note 1.2.1, ICASGA concession has been handed over to a new concessionary. |
3. |
In 2021, the Group obtained a twenty-year extension and the concession of six new regional airports, of which PDS is taking control between 2022 and 2025. |
4. |
In 2021, the Group obtained a two-years extension. |
F-90
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Argentine Concession Agreement
In February 1998 AA2000 was awarded the concession agreement for the use, operation and management of 33 airports in Argentina (the “Group A” airports). The concession agreement was subsequently amended and supplemented by the memorandum of agreement it entered into with the Argentine National Government on April 3, 2007 (the “Memorandum of Agreement”). References to the concession agreement amended and supplemented by the Memorandum of Agreement are carried out as the “Argentine Concession Agreement”.
Likewise, and in order to be able to continue with the policies related to the expansion of the aviation market, AA2000 was awarded the concessions for the operation of the El Palomar Airport and Termas de Rio Hondo Airports, which were brought under the AA2000 Concession Agreement pursuant to Decree No. 1107/2017 and Resolution of ORSNA No. 27/2021 respectively.
The Argentine Concession Agreement was granted for an initial period of 30 years through February 13, 2028 and an additional extension period of up to 10 years.
In December 2020, the Argentine Government extended the term of the AA2000 Concession Agreement until February 2038.
Obligations assumed by AA2000 as Concessionaire
Under the terms of the Concession Agreement, AA2000 is responsible for several functions in connection with the airports, among others; operating airport services and facilities in a reliable manner, implementing the master plans approved by the ORSNA, investing in airport infrastructure in accordance with the applicable investment plan, the maintenance of airports under the concession agreement.
Pursuant to the Technical Conditions of the Extension approved by Decree No. 1009/2020, other several financial commitments were imposed to AA2000 including the availability of funds to make direct investments.
The Financial Projection of Income and Expenses attached to the Technical Conditions of the Extension include the detail of the estimated dates in which the required commitments and capital expenditures would be performed.
The Argentine Concession Agreement requires AA2000 to formulate a master plan for each of its airports. Each master plan establishes the investment commitments to be received by each airport during the term of the Argentine Concession Agreement, taking into account the expected demand of aeronautical and commercial services. AA2000 has executed the capital expenditures committed under the investment plan submitted for the period 2006-2028. In order to strengthen the airport system, new investments commitments were established, listed in the Technical Conditions for the Extension, for the periods 2021, 2022-2023; 2024-2027 and 2028-2038.
AA2000’s capital expenditures under the Technical Conditions of the Extension equals the aggregate amount of approximately USD 500 million plus VAT, to be executed in two phases: (i) phase 1, approximately USD 336 million plus VAT to be executed preferably within 2022 and 2023, and (ii) phase 2, annual investments of approximately USD 41 million plus VAT between 2024 and 2027, for a total of approximately USD 164 million plus VAT. Investments between 2028 and 2038 will be further determined based on the operational needs of the airport system and will take into consideration the economic equilibrium of the concession.
As of December 31, 2023, works amounting to USD 262.1 million (VAT included) have been initiated, of which USD 190.3 million (VAT included) have been executed. Considering the amount utilized for the redemption of preferred shares in 2022, totaling USD 174.2 million, the total amount committed equals USD 436.3 million (VAT included), thus exceeding the commitment amount of phase 1, with execution totaling USD 364.5 million (VAT included).
F-91
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Argentine Concession Agreement (Cont.)
Obligations assumed by AA2000 as Concessionaire (Cont.)
On July 28, 2023, ORSNA issued Resolution N° 56-23, in which it laid down the conditions related to the Review of the Financial Projection of Income and Expenses (in Spanish, PFIE) for the concession period of 2019-2023. Among other decisions, it was determined that the revision of the financial and economic equation of the concession agreement, will be finalized upon reaching the international passenger traffic level of 2019. AA2000 challenged Resolution N° 56-23. On November 27, 2023 both, ORSNA and AA2000, agreed: (i) to suspend the current procedural deadlines until June 30, 2024, (ii) that AA2000 must produce at its own cost and expense a passenger traffic projection study; (iii) to postpone until May 30, 2024 the ordinary annual review of the PFIE of the concession, covering periods until December 31, 2023. As of December 31, 2023, AA2000 has fulfilled the commitments assumed under the referred agreement.
Pursuant to the terms of the Argentine Concession Agreement, the Argentine National Government will have the right to buyout the concession at any time as from February 13, 2018. If such right is exercised, the Argentine National Government is required to indemnify AA2000 and assume in full any debts incurred by AA2000 to acquire goods or services for purposes of providing airport services, except for debts incurred in connection with the investment plan for which AA2000 would be compensated as part of the payment made to AA2000 by the Argentine Government.
Additionally, the Argentine Concession Agreement defines some additional conditions upon which either the Argentine National Government or AA2000 could demand the termination of the agreement. Termination of the AA2000 Concession Agreement would constitute a default under the Senior secured guarantee notes due 2027, the Class 1 Series 2021 Notes due 2031, the Onshore renegotiation and the ICBC Dubai Loan.
Concession fees
Under the terms of the Argentine Concession Agreement, AA2000 is required to, on a monthly basis, allocate an amount equal to 15% of revenues (in Argentine pesos) to the Specific Allocation of Revenue, as follows:
- 11.25% of total revenue to a trust for the development of the Argentine National Airport System to fund capital expenditures for the Argentine National Airport System. Of such funds, a 30% will be previously deducted for deposit in an account to the order of the National Administration of Social Security of Argentina. The ORSNA will determine which construction projects within the Argentine National Airport System shall be implemented with such funds, whether at airports operated by AA2000 or not. AA2000 may file proposals with the ORSNA, which, together with the ORSNA’s proposals, shall be communicated to the Secretary of Transportation, which shall decide the application of the trust funds.
- 1.25% of total revenue to a fund to study, control and regulate the Argentine Concession, which shall be administered and managed by the ORSNA.
- 2.5% of total revenue to a trust for investment commitments for the “Group A” airports of the Argentine National Airport System. (Those operated by AA2000).
AA2000 may cancel the obligations to provide amounts of money to the trust through the assignment of credits whose cause and/or title are the result of the provision of aeronautical and/or airport services performed within the framework of the concession, with the previous intervention of The Secretary of Transportation and the authorization of the ORSNA.
F-92
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Argentine Concession Agreement (Cont.)
Guarantees
In order to guarantee performance of the works, AA2000 has contracted a surety bond to comply with the investment plan guarantee required by the ORSNA’s Resolution No. 60/2021 amounting as of December 31, 2023, USD 130 million. Additionally, AA2000 sets up a guarantee for concession contract fulfillment for the total amount is for ARS 6,499.2 million (approximately USD 8.0 million) which is renewed on an annual basis.
Insurance
In addition, AA2000 is required to maintain a civil liability insurance policy covering personal and property damages, loss or injury in an amount of at least ARS 300 million (approximately USD 0.4 million). AA2000 has taken out insurance policy for an amount of USD 300 million covering liabilities that may arise under civil law in connection with the management and development of work in the airports. Additionally maintains insurances regarding operational and construction risk for USD 3.184 million and USD 40 million respectively.
Other information regarding AA2000 as Concessionaire
As a result of the renegotiation of the concession contract, in 2006 AA2000 delivered to the Argentine Government 496,161,413 preferred shares which were convertible into common shares of AA2000. Such preferred shares had a nominal value of ARS 1 each and had no voting rights. Such shares were redeemable by AA2000 at any time at nominal value plus accrued interest. Beginning in 2020, the Argentine Government had the option to convert all of the preferred shares into common shares of AA2000, up to a maximum amount of 12.5% per year of the total amount of the initial preferred shares issued to the Argentine Government, to the extent AA2000 had not previously redeemed such annual percentage for the respective year. In addition, according to the agreement for AA2000 Concession extension, AA2000 had the option to redeem the preferred shares during 2022, which was exercised, see Note 25.f.
In addition to the airports operated under the AA2000 Concession Agreement, the Group also operates the Neuquén Airport and the Bahía Blanca Airport.
The Neuquén Airport and the Bahía Blanca Airport are not material to CAAP’s business.
Uruguayan Concession Agreements
Carrasco International Airport and New Airports
PDS signed with the Uruguayan Government a concession agreement which granted from year 2003 to 2023 the management, exploitation, construction, maintenance and operation of Carrasco International Airport “Gral. Cesáreo L. Berisso”. A first amendment to the contract dated September 2, 2014 extended the concession until November 20, 2033. As of November 8, 2021, a second amendment to the concession agreement was made, modifying among other things, (i) extending the term of the agreement until November 20, 2053, (ii) incorporating into the concession six additional new airports located in Rivera, Salto, Carmelo, Durazno, Melo, Paysandú,(“New Airports”) and (iii) requiring PDS to make capital expenditures in connection with the development of the New Airports of USD 67 million in the aggregate between 2022 and 2028 in accordance with the following investment schedule, which may be adjusted as a result of force majeure events and certain other particular circumstances: USD 13 million during 2022, USD 32 million during 2023, USD 18 million during 2024; and USD 4 million during 2028.
F-93
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Uruguayan Concession Agreements (Cont.)
Carrasco International Airport and New Airports (Cont.)
Except with respect to the Durazno International Airport in which operations will not start before January 1, 2025, the operation of the New Airports by PDS under the amended concession agreement started progressively once certain conditions were met, including without limitation, the issuance of certain environmental permits. On January 11, April 22, July 22, October 20, 2022 and February 8, 2023, the International Airport of Carmelo “Balneario Zargazazú”, the International Airport of Rivera “Pte. Gral Oscar D. Gestido”, the International Airport of Salto “Nueva Hespérides”, the International Airport of Melo and the International Airport of Paysandú “Brig. Gral. Tydeo Larre Borges” were taken over by PDS, respectively.
The terms and conditions under the amended concession agreement are substantially the same as those currently in place for the Carrasco Airport except for, within others, the operation of the new airports, the terms of the concession, insurance, guarantees and early termination of the agreement.
Obligations assumed by PDS as Concessionaire
Under the terms of the Concession Agreement, PDS is responsible for several functions in connection with the airports, among others; operating airport services and facilities in a reliable manner, make investments and maintenance as described in the technical attachments to the concession agreement, maintain the guarantees and insurance policies valid and current, pay the annual concession fee.
During the next five years, PDS is committed to make additional capital expenditures in the amount of USD 41.5 million including the investments committed in respect of the New Airports.
Upon execution of the amended concession agreement, the Uruguayan Ministry of Defense will still have the right, with prior authorization from the Uruguayan executive power, to terminate the concession agreement prior to the scheduled termination date due to reasons based on “public interest”. In this case, an indemnification amount shall be paid the amount of which depends on whether the termination relates to one or more of the New Airports or to the Carrasco International Airport, in accordance with the following; the early termination may be done either: (i) with respect to the Carrasco Airport and the New Airports (“Full Termination”), or (ii) with respect to one or more of the New Airports only (“Partial Termination”).
F-94
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Uruguayan Concession Agreements (Cont.)
Carrasco International Airport and New Airports (Cont.)
Obligations assumed by PDS as Concessionaire (Cont.)
Additionally, the concession agreement may be terminated by the Defense Ministry (with prior approval of the executive power) upon repeated and material breaches of the concession agreement by PDS. In the event of force majeure (e.g., the destruction severe damage that prevents the airport’s operations), the Defense Ministry will be entitled to terminate the concession agreement without paying the termination payment to PDS and collect all of the indemnification payments under all of the airport’s insurance policies. Alternatively, the Defense Ministry could request PDS to re-build the airport if the reconstruction of the airport does not alter the terms of the concession agreement.
The concession agreement may be also terminated by mutual agreement (with prior approval of the Uruguayan executive power). No termination fee is payable by any party in this circumstance.
Concession fees
Pursuant to the concession agreement, PDS is required to pay to the Uruguayan Government an annual fee, which will be the higher of: a) USD 5,789; or b) the amount resulting from multiplying the work units (per passenger or per each 100 kilograms of cargo or mailing) by USD 0.00532, plus applicable cargo fees. The aforementioned 2014 amendment established additional fees based on the number of passengers that use the Carrasco Airport and as long as the number of passengers exceed 1.5 million passengers per year. These additional fees are calculated by multiplying the number of passengers by a fix coefficient, depending on the volume of passengers.
Guarantees
Based on the above, PDS is required to provide the following guarantees: a guarantee securing the completion of the construction work of the new terminal for a total amount as of December 31, 2023 of USD 4.7 and a performance guarantee for USD 7.6 million that will be returned to PDS six months after the expiration of the concession agreement. Guarantees securing the completion of each group of construction works related to the New Airports, to be determined under the Investment Program and for the amounts set forth under the Investment Schedule. The guarantees are set as an amount equal to 5% of each group of construction work to be performed.
Insurance
PDS must contract civil liability insurance against damages, losses or injuries that could be caused to persons or property in relation to the performance under the concession agreement, with itself and the Uruguayan Ministry of Defense as loss payees, to cover all risks until termination or expiration of the concession. The minimum coverage amount is USD 250 million. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the coverage amount was USD 300 million.
F-95
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Uruguayan Concession Agreements (Cont.)
Punta del Este Airport
CAISA signed with the Uruguayan Government a concession agreement which grants until the year 2019 for the reconstruction, maintenance and partial operation of the services of International Airport C/C Carlos A. Curbelo (Laguna del Sauce) – Punta del Este.
As of June 28, 2019, the concession agreement between CAISA and the Ministry of Defense was amended extending its term to March 31, 2033.
Terms of the Punta del Este Concession Agreement extension include a minimum annual concession fee of USD 500 and incremental capital expenditures of approximately USD 35 million, including the construction of a new general aviation terminal building, remodeling of boarding areas and a new VIP lounge, together with implementation of technology and innovation to improve the passenger experience. In June 2023, the minimum annual concession fee was increased from USD 577 up to USD 611 aligned with an increase in tariffs.
During the next five years and upon execution of the amendment, CAISA expects to incur additional capital expenditures in the amount of USD 5.0 million, all required by contract.
Based on the above, CAISA was required to provide the following guarantees: a guarantee securing the completion of the construction works and a guarantee for concession contract fulfillment for USD 1.6 million and USD 4.2 million (secured by TCU S.A.) respectively.
Additionally, CAISA must contract civil liability insurance against damages, losses or injuries that could be caused to persons or property in relation to the performance under the concession agreement. The amount covered as of December 31, 2023 is approximately USD 340 million.
Ecuadorian Concession Agreement
TAGSA
TAGSA has a concession agreement which granted until July 27, 2029 the development, operation and maintenance of Guayaquil airport, José Joaquin de Olmedo (“JJO”). On July 20, 2021 TAGSA, AAG and the Municipality of Guayaquil entered into an amendment of the agreement resolving to extend the concession of the Guayaquil airport for additional two years, i.e. until July 27, 2031.
Obligations assumed by TAGSA as Concessionaire
Under the terms of the Concession Agreement, TAGSA is responsible for several functions in connection with the airport, among others; operate and manage the airport, make investments and maintenance specified in the Concession Agreement and expansion of the national terminal, pay the annual concession fee, provide other non-aeronautic services.
On July 6, 2018, TAGSA amended the concession agreement (the “Guayaquil Concession Agreement”) which established new additional works for an amount of USD 32.2 million to be completed by TAGSA prior to the end of the concession’s term. As of December 31, 2023, USD 4.9 million remain pending.
The concession agreement may be terminated prior to the scheduled termination date upon the breach by TAGSA and/or by AAG of its obligations stipulated in the concession agreement or any amendment as well as due to mutual agreement of the parties.
F-96
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Ecuadorian Concession Agreement (Cont.)
Concession fees
TAGSA was required to pay the annual concession amount to a trust, which amounts to 55.25% of gross revenues from tariffs and charges, and certain other commercial revenues from the operation of JJO to the Trust Fund for Development of the New Airport of Guayaquil, plus a fixed amount of USD 1.5 million per year for administrative services. The Guayaquil Concession Agreement included an increase of USD 524.6 (for the six-month period from August 2019 to January 2020) on a one-time basis; thereafter the amount and calculation applied in the previous period will be maintained. Due to COVID-19 pandemic, on July 20, 2021 a reduction of the annual concession fee to be paid in 2021 from 55.25% to 53.66% was agreed. In addition, from 2022 and until the economic and financial equilibrium is met, the concession fee to be paid will be 50.25%.
Guarantees
TAGSA is required to maintain a performance bond as security for the timely fulfillment of the obligations under the concession agreement of USD 3.0 million for the rest of the concession. In addition, TAGSA is required to maintain a performance bond for the payments to the Trust for the development of the new Guayaquil Airport that corresponds to an amount of 20% of the amount that is required to be paid by TAGSA to the Trust minus the amount of the performance bond of Guayaquil Concession Agreement. The current amount of the performance bond is USD 6.4 million.
Insurance
In addition, TAGSA is required to maintain a civil liability insurance policy covering personal and property damages, loss or injury. TAGSA has taken out an insurance policy for an amount of approximately USD 570.6 million covering liabilities that may arise under civil law in connection with the management and development of work in the airports.
ECOGAL
ECOGAL has a concession agreement, which granted until 2026 the development, operation and maintenance of Seymour Airport in Galapagos Island.
ECOGAL is required to deliver a performance bond of USD 700 to the Dirección General de Aviación Civil de Ecuador (“DGAC”), which should be in place during the term of the Galapagos Concession Agreement. This bond is renewed annually.
F-97
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Brazilian Concession Agreement
ICAB signed with the Brazilian ANAC a concession agreement which grants the construction, operation and maintenance of the airport of Brasilia for a period of 25 years from 2012. They can be extended for another five years if necessary to reestablish economic equilibrium.
Obligations assumed by ICAB as Concessionaire
Under the terms of the Concession Agreements, ICAB is responsible for several functions in connection with the airports, among others; provide adequate services to passengers and users of the airports, provide proper services, presenting the Brazilian ANAC with an Infrastructure Management Plan and Services Quality plan every five years making any necessary investments to expand airport operations to sustain the required service levels. During the next five years, ICAB expects to incur additional mandatory investments in the amount of USD 9.4 million with respect to the Brasilia Airport.
The Brazilian Concession Agreement will be deemed terminated prior to the scheduled termination date upon any of the following events;
- |
the expropriation of the concession by the Brazilian ANAC for reasons of public interest; |
- |
forfeiture declaration by the Brazilian ANAC as a result of the breach of material contractual obligations by ICAB pursuant to Article 38 of the Brazilian Concessions Law; |
- |
termination by a judicial order resulting from an action filed by ICAB based upon the breach of the Brazilian ANAC obligations; |
- |
the annulment of the Brazilian Concession Agreements by a judicial or administrative order based on the discovery of illegalities or irregularities in the tender documents, in the bid process or in the Brazilian Concession Agreement; or |
- |
bankruptcy or liquidation of ICAB, as the case may be. |
If the Brazilian Concession Agreement is terminated in connection with a forfeiture declaration issued by the Brazilian ANAC, then the amount of the indemnification payment will be limited to the non-amortized amount of assets reverted to the Brazilian Government less the amount of (i) any applicable losses; (ii) fines; and (iii) insurance payments received by ICAB, in each case, in connection with the events and circumstances that resulted in the forfeiture declaration.
Concession fees
Grant payment obligations arising from this concession agreement are described in Note 23.
Guarantees
Under the Brazilian Concession Agreement, the Brazilian concessionaires are required to provide certain performance bonds for some events. Main performance bonds relates to Phase I-B and Phase II events. The current amount of Phase II is R$ 258.3 million (equivalent to USD 53.4 million) in ICAB. The performance bond in ICAB is granted by a guarantee letter of CAAP signed with BMG insurance company, which became in force on December 2021.
F-98
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Armenian Concession Agreement
AIA CJSC has been awarded a concession agreement, which grants until year 2032 the exclusive rights of exploitation, administration, maintenance and operation of Yerevan airport, Zvartnots. At the end of the concession period, the Company has the option to indefinitely extend the term of the concession agreement for additional periods of five years. The Armenian Concession Agreement does not require AIA to pay any fee or other consideration of any kind whatsoever for the rights granted to it under the Armenian Concession Agreement.Within the scope of the Armenian Concession Agreement the Company planned to build a new terminal in three phases. The first two phases are completed, which mainly included the construction of a new terminal for arrivals and departures.
Obligations assumed by AIA as Concessionaire
Under the terms of the Concession Agreement, AIA is responsible for several functions in connection with the airports, among others; operate and manage the airports, comply with the master plan, provide the Armenian Government with an annual report (and such other reports as the Armenian Government may reasonably request) on the development of the management, exploitation and operation of the airport.
Every five years during the term of the concession, the Company is required to submit a Master Plan to the Government of the Republic of Armenia, which describes the works to be executed in that five-year period, including the corresponding preliminary estimates and also sets forth the guidelines for the works and operations related to improvement and maintenance of the Airport during the remaining part of the term, as well as the description of actual works. The Master Plan will be updated every five years and extended to cover the 30-year term of the Armenian Concession Agreement.
During the next five years, AIA expects to incur USD 70 million in capital expenditures in Zvartnots Airport and Shirak Airport in accordance with the master plan to be approved by the Armenian Government as presented by AIA’s management. Some of these investments are conditioned upon reaching certain passenger level thresholds.
The Armenian Concession Agreement may be terminated prior to the scheduled termination date upon the occurrence of any of the following events:
-concession manager’s breach of certain obligations;
-bankruptcy of the concession manager;
-administrative discretionary act;
-the Armenian Government’s breach of any of its obligations; and
-force majeure events.
Italian Concession Agreement
TA has the concession of the airports of Pisa and Florence.
The concession for Pisa Airport (“Pisa Concession”) was approved on December 7, 2006, with the Inter-Ministerial Decree issued by the Ministry of Transportation, the Ministry of the Economy and the Ministry of Defense. The Concession Agreement initially expired on December 7, 2046.
F-99
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Italian Concession Agreement (Cont.)
The Florence Concession was approved on March 11, 2003, with the Inter-Ministerial Decree issued by the Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport and the Ministry of the Economy and Finance. In order to meet the urgent need to implement the relevant legal framework, the abovementioned Inter-Ministerial Decree provided the extension of the duration of the concession to 40 years. The Concession Agreement initially was due to expire on February 10, 2043.
In view of the drop in traffic at Italian airports deriving from the Covid-19 virus outbreak and in order to contain the consequent economic effects, the term of all the current concessions for the management and development of airport activities was extended by two additional years under Law No. 77 of July 17, 2020, which amends Article 202 paragraph 1-bis of Decree-Law No. 34 of May 19, 2020, extending Pisa and Florence concessions until 2048 and 2045, respectively.
Obligations assumed by TA as Concessionaire
Under the terms of the Concession Agreements, TA is responsible for several functions in connection with the airports, among others; organize and manage the airport business, pay the annual concession fee, guarantee the suitability of the standards of offered services.
Pursuant the terms of the Italian Concession Agreements, TA is required to present a long-term master plan for each individual airport. The master plan projections (including traffic, operating expenses, investment commitments, etc.) are used by ENAC (Italian regulatory authority) to determine airport tariffs, and are revised every four years. Once approved by ENAC, the investment commitments in the master plan become binding obligations under the terms of the respective Concession.
On November 3, 2015, TA received the technical approval by ENAC of its 2014-2029 master plan for Florence Airport, and on December 28, 2017, the Ministry of Environment, after conducting an environmental impact assessment (Valutazione di Impatto Ambientale), approved such master plan. However, on May 27, 2019, upon request of the Environmental Association (Associazione VAS Vita Ambiente) and other authorities, such approval was repealed through judgment No. 793.
On July 25, 2019, TA, jointly with the Ministry of Environment, ENAC and other authorities, appealed such judgement and on February 14, 2020, TA was notified by the Council of State the need to undertake a new environmental procedure regarding the master plan. In the meantime, the legal framework was changing by the Italian Government and the public debate procedure was introduced as mandatory in case of new runway and new passenger Terminal. Therefore, during 2022 a project review of the master plan was performed and a new master plan 2035 was defined. On October 2022, TA started the public debate process. Once finished (in 2024), the master plan 2035 will be subjected to the environmental impact and strategic assessment procedure at the Environmental Ministry.
In relation with Pisa Airport, on October 24, 2017, ENAC approved and signed 2015-2028 master plan.
Both, Pisa and Florence Concession Agreements provides that, in the event needs of public interest arise, TA may request that the concessions be revoked, at which time TA will assume the burden of making all compensatory payments to be determined with the relevant third parties and after consulting ENAC.
The concessions granted may be forfeited before its expiration date upon the occurrence of specified events of default. If any of the concessions is revoked before its expiration, whether through a forfeiture or termination due to an event of default, ENAC shall regain the rights over the assets which were assigned to TA.
F-100
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Italian Concession Agreement (Cont.)
Concession fees
As consideration for both airport concessions granted by ENAC, TA is required to pay annual fees to be determined pursuant to Law No. 662/1996, which states that the relevant fees shall be the subject of the joint determination of the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport. The fees are established by Inter-Managerial Decree (decreto interdirigenziale) dated June 30, 2003, which provides the adoption of a work load unit criteria, where each unit corresponds to one passenger or 100 kg of goods or post.
Concession fee payments are to be made in two separate installments, the first one to be made each July 31 and the second one each January 31 of each year during the concession agreement. The following year, each payment shall be equivalent to 50% of the annual concession fee payments. The value of the minimum concession fee is adjusted on an annual basis according to inflation.
Guarantees
Suretyships provided to third parties on behalf of TA (EUR 10.4 million as of December 31, 2023 and EUR 10.6 million as of December 31, 2022, equivalent to USD 11.5 million and USD 11.3 million respectively) mainly refer to performance bonds with ENAC as beneficiary, in order to guarantee full and exact fulfillment of the obligations of the concessionaire under the concession agreements; of the Municipalities of Pisa and Florence to ensure compliance with municipal regulations in the execution of works for the expansion of the airports infrastructure by TA and other items.
Insurance
Under the Pisa and Florence Concession Agreement, TA shall procure an insurance policy, for an amount to be determined in agreement with ENAC, in order to cover a series of risks related to the assets used either directly or indirectly in the airport management business (e.g., fires, aircraft crashes, damages due to transported goods, machinery or natural events). TA has taken out insurance policy for an amount of about EUR 868 million covering property damages, business interruptions and airport liabilities.
F-101
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
b. Commitments (Cont.)
Italian Concession Agreement (Cont.)
Acquisition of Cemes Aeroporti S.r.l. and formation of Toscana Aeroporti Costruzioni S.r.l.
On January 26, 2021, TA signed an agreement to acquire a 51% stake in Cemes Aeroporti S.r.l., a recently-formed company operating in the construction sector, which has concurrently changed its corporate name to Toscana Aeroporti Costruzioni S.r.l. (“TAC”). This transaction was accounted for using the acquisition method since the Group acquired control over TAC, which was therefore fully consolidated from the date on which control was exercised. This acquisition was made with a view to facilitating the necessary works for the planned infrastructural development at the Florence and Pisa airports committed to by TA.
The consideration for the transaction amounts to EUR 4.5 million, payable in five annual installments until December 31, 2025. In addition, the agreement between the parties envisages a call option exercisable by TA during the period between January 1, 2024 and July 1, 2024, to acquire a further 19% stake in TAC for a pre-set consideration of EUR 2.2 million. The transaction does not entail any assumption of debt or assignment of receivables.
Net identifiable assets arising from the acquisition amounted to EUR 1 million, including cash and cash equivalents for a total amount of EUR 8 thousands (approximately USD 10). TA has elected to recognize non-controlling interests in the acquired entity at the non-controlling interest’s proportionate share of the acquired entity’s net identifiable assets at the time of the acquisition.
The fair value of the consideration reflects the net present value of the consideration to be paid in installments for the purchase. Goodwill for an amount of EUR 3.7 million (approximately USD 4.5 million) was recognized. This goodwill is not tax deductible.
CAAP - Preferred bidder to operate Abuja and Kano airports in Nigeria
In October 2022, a consortium formed by CAAP, Mota - Engil, Engenharia e Construção África S.A., and Mota - Engil Nigeria Limited (the “Consortium”), of which the Company holds a 51% stake, has been declared by the Federal Government of Nigeria as preferred bidder for the Abuja and Kano airports and cargo terminals concessions. A preferred bidder’s bank guarantee has been issued for USD 1.8 and USD 0.4 million related to the Abuja and Kano airports respectively, expiring on May 22, 2024. These guarantees have been counter guaranteed by CAAP for 51% of the total amount. The Consortium, the Federal Ministry of Aviation and the Federal Airports Authority of Nigeria are currently revising and negotiating the final terms and conditions of the concession agreements.
In May 2023, the structure under the Consortium was created in Nigeria, with Corporacion Africa Airports Nigeria Limited as a holding company and Kano Airport Concession Company Limited and Abuja Airport Concession Company Limited as operating companies related to the Kano and Abuja airports and cargo terminal concessions respectively. As of December 31, 2023, CAAP holds indirectly a 51% of ownership of Corporacion Africa Airports Nigeria Limited, which is in turn 100% owner of Kano Airport Concession Company Limited and Abuja Airport Concession Company Limited. The companies remain without operation until the concession agreements are executed.
Other commitments
As of December 31, 2023, TAC holds guarantees related to construction works for an amount of EUR 0.9 million (approximately USD 1.0 million).
As of December 31, 2023, CAAP guarantees an energy supply contract signed by ICASGA, covering the purchase of electric power for R$ 0.9 million (equivalent to approximately USD 186) and an energy supply contract signed by ICAB covering the purchase of electric power for R$ 1.8 million (equivalent to approximately USD 372).
F-102
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
26 Contingencies, commitments and restrictions on the distribution of profits (Cont.)
c. Restrictions to the distribution of profits and payment of dividends
As of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, equity as defined under Luxembourg laws and regulations (“Lux GAAP”) consisted of:
|
|
At December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Share capital |
|
163,223 |
|
163,223 |
|
163,223 |
Share premium |
|
183,430 |
|
183,430 |
|
183,430 |
Reserve for own shares |
|
4,322 |
|
4,600 |
|
4,772 |
Legal reserve |
|
3,676 |
|
1,081 |
|
1,081 |
Free distributable reserves |
|
378,910 |
|
378,910 |
|
378,910 |
Non-distributable reserves |
|
1,353,706 |
|
1,353,428 |
|
1,353,255 |
Retained earnings |
|
37,890 |
|
(34,372) |
|
(86,279) |
Total equity in accordance with Luxembourg law |
|
2,125,157 |
|
2,050,300 |
|
1,998,392 |
At least 5% of the Company’s net income per year, as calculated in accordance with Luxembourg law and regulations, must be allocated to the creation of a legal reserve equivalent to 10% of the Company’s share capital. Dividends may not be paid out of the legal reserve. The Company may pay dividends to the extent, among other conditions, that it has distributable retained earnings calculated in accordance with Luxembourg laws and regulations.
27 Related party balances and transactions
Corporación América Airports S.A. is controlled by ACI Airports S.à r.l., which is controlled by Corporación América International S.à r.l. (previously denominated America Corporation International S.à r.l.), both of which are Luxembourg based companies.
Corporación América International S.à r.l. is controlled by Southern Cone Foundation (CAAP’s ultimate parent company), a foundation created under the laws of Liechtenstein, having its corporate domicile in Vaduz. The foundation’s purpose is to manage its assets through the decisions adopted by its independent board of directors. The potential beneficiaries of this foundation are members of the Eurnekian family and religious, charitable and educational institutions. Interests in subsidiaries are set out in Note 2.B.
Transactions and balances with “Associates” are those carried out with entities over which CAAP exerts significant influence in accordance with IFRS, but does not have control. Transactions and balances with related parties, which are not associates and are not consolidated are disclosed as “Other related parties”. The Group receives services from related parties, such as internal audit, management control, financial assistance, technology outsourcing services and construction services.
F-103
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
27 Related party balances and transactions (Cont.)
Summary of balances with related parties are:
|
|
At December 31, |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Year-end balances |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) Arising from sales / purchases of goods / other |
|
|
|
|
Trade receivables with associates |
|
4,200 |
|
4,174 |
Trade receivables with other related parties |
|
962 |
|
2,310 |
Other receivables with associates |
|
58 |
|
445 |
Other receivables with other related parties |
|
9,257 |
|
9,695 |
Other financial assets with associates |
|
3,108 |
|
2,954 |
Other financial assets with other related parties(*) |
|
28,327 |
|
— |
Trade payables to associates |
|
(2,765) |
|
(2,714) |
Trade payables to other related parties |
|
(2,501) |
|
(3,039) |
|
|
40,646 |
|
13,825 |
(b) Other liabilities |
|
|
|
|
Other liabilities to associates(**) |
|
(15,539) |
|
— |
Other liabilities to other related parties |
|
(2,425) |
|
(2,503) |
|
|
(17,964) |
|
(2,503) |
(c) Other balances |
|
|
|
|
Cash at banks in other related parties |
|
23,249 |
|
4,652 |
|
|
23,249 |
|
4,652 |
(*) Mainly includes loans and time deposits to other related parties amounting to USD 14.8 and USD 10.1 respectively. The loan accrues interests at a fixed annual rate of 4.5%, maturing in June 2024, while the time deposits accrues interests at a fixed annual rate of 4.0%, maturing in July 2024.
(**) Includes deferred income from associates.
|
|
For the year ended December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Transactions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aeronautical/Commercial revenue |
|
14,267 |
|
9,957 |
|
6,263 |
Fees |
|
(10,300) |
|
(7,266) |
|
(6,795) |
Interest accruals |
|
660 |
|
1,240 |
|
695 |
Acquisition of goods and services |
|
(22,955) |
|
(22,278) |
|
(10,743) |
Others |
|
(4,198) |
|
(4,367) |
|
(4,201) |
The Group leases buildings to other related parties, which are recognized under the scope of IFRS 16 and accounted in Lease liabilities line for an amount of USD 6,973 as of December 31, 2023 (USD 2,201 as of December 31, 2022). Additionally, the Group has variable equipment leases with other related parties that are excluded from the lease liability according to IFRS 16. Transactions related to those leases are included in Acquisition of goods and services line for an amount of USD 5,433 (USD 6,122 as of December 31, 2022).
Remuneration accrued related to the Group’s key staff amounted to approximately 1.9% of total remunerations at December 31, 2023, 2.2% accrued at December 31, 2022 and 2.7% accrued at December 31, 2021.
F-104
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
28 Business combinations, other acquisitions and investments
In December 2023, after a series of purchase and sale operations, CAAP became holder of 49% of the share capital of Navinten S.A. (“Navinten”), a non-listed company based in Uruguay that operates duty-free shops at Uruguayan airports. The acquisition increases the Group’s market share in the commercial business linked to the airports of said country.
The consideration for the transaction amounts to USD 3.4 million payable through a promissory note issued by CAAP and the fair value of the net assets acquired amounted to USD 4.1 million, resulting in a net gain shown in Share of income/ (loss) in associates in the Consolidated Statement of Income of USD 0.7 million. The result in associates that related to Navinten is USD 7.3 million and is included also in Share of income/ (loss) in associates (Note 15).
Subject to meeting certain performance metrics between 2024 and 2027, CAAP has the right to receive a single-lump sum of USD 5.5 million, adjustable and payable according to certain parameters. This earn-out, if applicable, shall be payable within the first three months of calendar year 2028.
In addition, a call option agreement was signed, which gives CAAP the exclusive and irrevocable right, but not obligation, to purchase the remaining 51% of Navinten’s share capital. The purchase option may be exercised from November 20, 2027 to November 20, 2038 at a purchase price equal to 51% of the difference between Navinten’s current assets and current liabilities on the date of exercise of the option.
F-105
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
29 Cash flow disclosures
|
|
At December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Changes in working capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other receivables and credits |
|
(32,429) |
|
(55,064) |
|
(4,503) |
Inventories |
|
(1,551) |
|
(3,566) |
|
(2,767) |
Other liabilities |
|
(19,323) |
|
989 |
|
(4,985) |
|
|
(53,303) |
|
(57,641) |
|
(12,255) |
The most significant non-cash transactions are detailed below:
|
|
For the year ended December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Intangible assets acquisition with an increase in Other liabilities / Borrowings / Lease liabilities |
|
(1,180) |
|
(111) |
|
(13) |
Property, plant and equipment with an increase in Other liabilities |
|
(124) |
|
— |
|
— |
Right-of-use asset initial recognition with an increase in Lease liabilities (Note 14) |
|
(5,217) |
|
(465) |
|
(2,407) |
Concession fees paid with credit of financial re-equilibrium (Note 23) |
|
(22,946) |
|
(15,434) |
|
(25,473) |
Constitution/of Interest Payment Account |
|
— |
|
— |
|
29,960 |
Other taxes paid with financial re-equilibrium |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(2,438) |
Compensation of trade receivables |
|
— |
|
27,844 |
|
— |
Application of credits compensated with concession fees |
|
(19,156) |
|
(24,126) |
|
— |
Application of credits compensated with other liabilities |
|
— |
|
(3,717) |
|
— |
Income tax paid with tax certificates |
|
(2,339) |
|
(971) |
|
— |
Purchase of Navinten shares (Note 28) |
|
(3,384) |
|
— |
|
— |
Sale of Navinten shares (Note 28) |
|
3,384 |
|
— |
|
— |
ICASGA’s compensation received through a guarantee deposit (Note 17) |
|
(41,262) |
|
— |
|
— |
Release of concession fee payable due to ICAGSA’s re-bidding process (Note 23) |
|
(74,640) |
|
— |
|
— |
Compensation of ICASGA’s re-equilibriums |
|
5,309 |
|
— |
|
— |
Compensation of ICASGA’s monthly contribution |
|
(3,767) |
|
— |
|
— |
ICASGA’s compensation to be collected (Note 17) |
|
(66,612) |
|
— |
|
— |
F-106
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
29 Cash flow disclosures (Cont).
Reconciliation of debt:
According to the IAS 7, the movements in the debt of the year that impact on the cash flow as part of the financing activities are detailed below:
|
|
Bank and financial |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
borrowings |
|
Notes |
|
Bank overdrafts |
|
Total |
Values at the beginning of the year |
|
478,904 |
|
986,533 |
|
— |
|
1,465,437 |
Proceeds from borrowings |
|
81,900 |
|
1,682 |
|
4,264 |
|
87,846 |
Loans and interest paid |
|
(202,341) |
|
(78,455) |
|
(3,470) |
|
(284,266) |
Debt renegotiation expenses |
|
— |
|
(110) |
|
— |
|
(110) |
Effects of exchange rate changes and inflation adjustment |
|
11,219 |
|
(20,452) |
|
(2,141) |
|
(11,374) |
Other non-cash movements * |
|
22,557 |
|
51,739 |
|
1,408 |
|
75,704 |
Balances as of December 31, 2023 |
|
392,239 |
|
940,937 |
|
61 |
|
1,333,237 |
|
|
Bank and financial |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
borrowings |
|
Notes |
|
Banks overdrafts |
|
Total |
Values at the beginning of the year |
|
612,269 |
|
827,334 |
|
— |
|
1,439,603 |
Proceeds from borrowings |
|
143,388 |
|
210,762 |
|
17,801 |
|
371,951 |
Loans and interest paid |
|
(321,435) |
|
(101,757) |
|
(16,970) |
|
(440,162) |
Debt renegotiation expenses |
|
(1,282) |
|
(729) |
|
— |
|
(2,011) |
Effects of exchange rate changes and inflation adjustment |
|
(7,518) |
|
(10,504) |
|
(1,015) |
|
(19,037) |
Other non-cash movements * |
|
53,482 |
|
61,427 |
|
184 |
|
115,093 |
Balances as of December 31, 2022 |
|
478,904 |
|
986,533 |
|
— |
|
1,465,437 |
|
|
Bank and financial |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
borrowings |
|
Notes |
|
Banks overdrafts |
|
Total |
Values at the beginning of the year |
|
664,337 |
|
680,480 |
|
— |
|
1,344,817 |
Proceeds from borrowings |
|
185,465 |
|
181,079 |
|
— |
|
366,544 |
Loans and interest paid |
|
(258,615) |
|
(94,332) |
|
— |
|
(352,947) |
Debt renegotiation expenses |
|
(2,204) |
|
(18,235) |
|
— |
|
(20,439) |
Effects of exchange rate changes and inflation adjustment |
|
(38,450) |
|
(4,592) |
|
— |
|
(43,042) |
Other non-cash movements * |
|
61,736 |
|
82,934 |
|
— |
|
144,670 |
Balances as of December 31, 2021 |
|
612,269 |
|
827,334 |
|
— |
|
1,439,603 |
* This line mainly includes interest accrued.
F-107
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
30 Share-based payments
Management share compensation plan
On August 20, 2020, the Company approved a management share compensation plan for a period beginning on such date and ending on December 31, 2025, extendable thereafter upon approval of the Board of Directors.
The purpose of the plan is to permit executives and key employees of either the Company or any of its subsidiaries or its affiliates acting as employers (together the “Company Group”) who are eligible to receive an annual incentive compensation consisting either of (i) a certain number of shares in the share capital of the Company or of (ii) contractual rights to receive, at a certain point in time, a certain number of shares, thereby encouraging the employees to focus on the long term growth and its contribution to the success of the Company Group.
The operation of the plan is supervised by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors.
The Committee will determine, in its sole discretion, whether shares will be issued and allocated or rights will be granted to executives and key employees.
Shares earmarked for the plan are held in treasury until they are allocated to executives and key employees in accordance with the Management Compensation Plan by the Compensation Committee.
Under the plan, executives and key employees are granted shares which only vest if certain performance standards are met and are recognized as part of employee benefit costs in the period the shares are granted, being recorded in Salaries and social security contributions or Services and fees and as an increase in Other reserves in equity as services provided were received as consideration for the Company’s own equity instruments.
The value of shares granted is recognized on the grant date (grant date fair value) based on the closing share price at which the Company’s shares are traded on the NYSE.
As detailed in Note 25.a, as of December 31, 2023, certain awards in shares were approved under the terms of the Management share compensation plan and most of those shares have been already allocated to eligible employees.
Set out below are summaries of shares granted under the plan for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
price per share |
|
2023 |
|
price per share |
|
2022 |
As at January 1, |
|
5.62 |
|
169,185 |
|
5.76 |
|
125,000 |
Granted during the year |
|
9.48 |
|
113,848 |
|
5.57 |
|
146,115 |
Forfeited during the year |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(5.80) |
|
(12,500) |
Exercised during the year |
|
(6.55) |
|
(144,892) |
|
(5.70) |
|
(89,430) |
As at December 31, |
|
7.83 |
|
138,141 |
|
5.62 |
|
169,185 |
F-108
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
30 Share-based payments (Cont.)
Management share compensation plan (Cont.)
Additionally, below are summaries the amounts in U.S. dollars of shares granted and accrued under each plan for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021:
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
||||||
Assignment date |
|
Granted |
|
Accrued |
|
Granted |
|
Accrued |
|
Granted |
|
Accrued |
December 2021 (*) |
|
— |
|
96 |
|
— |
|
252 |
|
1,440 |
|
1,020 |
April 2022 |
|
— |
|
150 |
|
500 |
|
317 |
|
— |
|
— |
December 2022 |
|
— |
|
184 |
|
314 |
|
98 |
|
— |
|
— |
April 2023 |
|
739 |
|
474 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
November 2023 |
|
340 |
|
151 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
As at December 31, |
|
1,079 |
|
1,055 |
|
814 |
|
667 |
|
1,440 |
|
1,020 |
(*) Includes shares forfeited during 2022 for USD 72.
31 Discontinued operations
In December 2021, the Group sold the participation in Aeropuertos Andinos del Perú S.A. (“AAP”). CAAP’s decision to no longer operate in Peru is part of a long-term strategic plan that seeks to concentrate efforts and resources towards core and relevant assets in jurisdictions with long-term meaningful growth opportunities.
AAP was not previously classified as an asset held for sale or as a discontinued operation. The comparative Consolidated Statement of Income, Statement of Comprehensive Income and Statement of Cash Flow has been re-presented to show the discontinued operation separately from continuing operations.
For the sale of the shares in the associate, the company received USD 5 thousand, while it has committed to make a one-time payment to the buyer for assumed liabilities and future CAPEX commitments of AAP amounting to USD 17.2 million, of which USD 2.5 were paid in 2021 while the remaining USD 14.7 million were paid in four installments between January and December 2022.
As of December 31, 2021, the operation resulted in a reversal of currency translation adjustment loss of USD 0.9 million and a loss of USD 21.2 million which are shown in the statement of comprehensive income and in the statement of income respectively, as well as in a decrease of the Investments in associates of USD 3.1 million.
In this operation, it was also agreed that the guarantees, which CAAP had issued in favor of AAP, remained in force until December 2022, when the last payment owed by CAAP was disbursed and the guarantees released.
F-109
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
32 Earnings per share
a) Basic earnings per share
Basic earnings per share is calculated by dividing the profit or loss attributable to equity holders of the Group by the weighted average number of shares outstanding each year.
The following table shows the net income and the number of shares that have been used for the calculation of the basic earnings per share total:
|
|
At December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Income / (loss) attributable to equity holders of the Group |
|
239,506 |
|
168,166 |
|
(117,755) |
Weighted average number of shares (thousands) (Note 32. c) |
|
160,891 |
|
160,755 |
|
160,500 |
Basic earnings per share of the year |
|
1.49 |
|
1.05 |
|
(0.73) |
|
|
At December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
From continuing operations attributable to the ordinary equity holders of the Group |
|
1.49 |
|
1.05 |
|
(0.60) |
From discontinued operations |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(0.13) |
Total basic earnings per share attributable to the ordinary equity holders of the Group |
|
1.49 |
|
1.05 |
|
(0.73) |
F-110
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
32 Earnings per share (Cont.)
b) Diluted earnings per share
Diluted earnings per share is calculated by dividing the profit or loss attributable to ordinary equity holders of the Group by the weighted average number of ordinary shares outstanding during each year plus the weighted average number of ordinary shares that would be issued on conversion of all the dilutive potential ordinary shares into ordinary shares.
The following tables shows the net income and the number of shares that have been used for the calculation of the diluted earnings per share total:
|
|
At December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Income / (loss) attributable to equity holders of the Group |
|
239,506 |
|
168,166 |
|
(117,755) |
Weighted average number of shares and potential ordinary shares (thousands) (Note 32.c) |
|
161,058 |
|
160,795 |
|
160,500 |
Diluted earnings per share of the year |
|
1.49 |
|
1.05 |
|
(0.73) |
|
|
At December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
From continuing operations attributable to the ordinary equity holders of the Group |
|
1.49 |
|
1.05 |
|
(0.60) |
From discontinued operations |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(0.13) |
Total diluted earnings per share attributable to the ordinary equity holders of the Group |
|
1.49 |
|
1.05 |
|
(0.73) |
c) Weighted average number of shares used as the denominator
|
|
At December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Weighted average number of shares outstanding |
|
163,223 |
|
163,223 |
|
163,223 |
Weighted average number of treasury shares |
|
(2,332) |
|
(2,468) |
|
(2,723) |
Weighted average number of ordinary shares used as the denominator in calculating basic earnings per share |
|
160,891 |
|
160,755 |
|
160,500 |
Adjustments for calculation of diluted earnings per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity settled share based payment (1) |
|
167 |
|
40 |
|
— |
Weighted average number of ordinary shares and potential ordinary shares used as the denominator in calculating diluted earnings per share |
|
161,058 |
|
160,795 |
|
160,500 |
(1) Rights to equity settled share based payment granted to executives and key employees in accordance with the Management Compensation Plan by the Compensation Committee (Note 30) are included in the calculation of diluted earnings per share, assuming all outstanding rights will vest. The rights are not included in the determination of basic earnings per share.
F-111
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
33 Restricted Net Assets
The Company’s ability to pay dividends is primarily dependent on the Company receiving distributions of funds from its subsidiaries. According to the information provided by the Company’s subsidiaries, as a result of the financing conditions their ability to transfer a portion of their net assets to the Company either in the form of dividends, loans or advances are restricted as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Even though the Company currently does not require any dividends, loans or advances from its subsidiaries for working capital and other funding purposes, the Company may in the future require additional cash resources from them due to changes in business conditions, to fund future acquisitions and development or merely to declare and pay dividends or distributions to the Company’s shareholders.
The Company performed a test on the restricted net assets of its consolidated subsidiaries (the “restricted net assets”) in accordance with Securities and Exchange Commission Regulation S-X Rule 4-08 (e) (3), “General Notes to Financial Statements” and concluded that it was applicable for the Company to disclose its condensed financial information for the parent Company only. See Note 35.
34 Subsequent events
Compensation from the Re-bidding process of the Natal Airport
On January 5, 2024, the outstanding compensation that amounted to R$ 323.4 million (equivalent to USD 66.8 million) was collected by ACIB.
Additionally, on January 15, 2024, the outstanding financial debt owing to BNDES for a total amount of R$ 75.9 million (equivalent to USD 15.7 million) was prepaid, after which the related guarantees were released.
AA2000 - Indebtedness
In January and February 2024, AA2000 subscribed for USD 1.1 million and USD 0.6 million of Series 1 and Series 2 BOPREAL’s notes respectively.
As of the date of issuance of these Consolidated Financial Statements AA2000 has sold the Series 1 notes applying the proceeds to the payment of import debts.
Additionally, in March 2024, AA2000 repurchased dollar-linked Class 6, Class 9 and Class 10 Notes for USD 4.7 million, USD 1.6 million and USD 4.5 million respectively.
There are no other subsequent events that could significantly affect the Company’s financial position as of December 31, 2023.
35 Condensed Financial Information of the Company
The condensed financial information of the Company has been prepared in accordance with SEC Regulation S-X Rule 5-04 and Rule 12-04, using the same accounting policies as set out in the Group’s Consolidated Financial Statements. The results of operations reflected in the financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS differ from those reflected in the statutory financial statements of the Company prepared in accordance with Lux GAAP (see Note 26.c).
Certain information and footnote disclosures generally included in financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS have been condensed or omitted. The footnote disclosures contain supplemental information relating to the operations of the Company, as such, these statements are not the general-purpose financial statements of the reporting entity and should be read in conjunction with the notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements of the Group.
F-112
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
35 Condensed Financial Information of the Company (Cont.)
For the purpose of presenting parent only financial information, the Company records its investments in subsidiaries under the equity method of accounting. Such investments are presented on the separate condensed balance sheets of the Company as Investments in subsidiaries and the income/loss of the subsidiaries are presented as Share of (loss) / income in subsidiaries and associates. Certain information and footnote disclosures generally included in the Consolidated Financial Statements prepared in accordance with IFRS have been condensed and omitted.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company did not have significant capital commitments and other significant commitments, or guarantees, except for those that have been separately disclosed in the Consolidated Financial Statements, mainly included in Note 22 and 26.b.
CONDENSED STATEMENT OF INCOME
|
|
For the year ended |
|
For the year ended |
|
For the year ended |
|
|
December 31, 2023 |
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
December 31, 2021 |
Continuing operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
(7,728) |
|
(7,342) |
|
(5,697) |
Other operating income |
|
2,972 |
|
6 |
|
— |
Other operating expense |
|
(1) |
|
(5) |
|
— |
Operating loss |
|
(4,757) |
|
(7,341) |
|
(5,697) |
Share of income / (loss) in subsidiaries and associates |
|
247,585 |
|
182,050 |
|
(88,022) |
Income / (loss) before financial results and income tax |
|
242,828 |
|
174,709 |
|
(93,719) |
Financial income |
|
1,905 |
|
1,874 |
|
53 |
Financial loss |
|
(586) |
|
(429) |
|
(431) |
Income / (loss) before income tax from continuing operations |
|
244,147 |
|
176,154 |
|
(94,097) |
Income tax |
|
(4,629) |
|
(1,307) |
|
(1,028) |
Income / (loss) for the year from continuing operations |
|
239,518 |
|
174,847 |
|
(95,125) |
Loss from discontinued operations |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(21,196) |
Income / (loss) for the year |
|
239,518 |
|
174,847 |
|
(116,321) |
CONDENSED STATEMENT OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
|
|
For the year ended |
|
For the year ended |
|
For the year ended |
|
|
December |
|
December |
|
December |
|
|
31, 2023 |
|
31, 2022 |
|
31, 2021 |
Income / (loss) for the year |
|
239,518 |
|
174,847 |
|
(116,321) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Items that may be reclassified to profit or loss: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share of other comprehensive (loss) / income from subsidiaries and associates from continuing operations |
|
(231,688) |
|
70,849 |
|
94,703 |
Other comprehensive (loss) / income for the year, net of income tax from continuing operations |
|
(231,688) |
|
70,849 |
|
94,703 |
Currency translation adjustment from discontinued operations |
|
— |
|
— |
|
920 |
Other comprehensive income / (loss) of discontinued operations for the year, net of income tax |
|
— |
|
— |
|
920 |
Total comprehensive income / (loss) for the year |
|
7,830 |
|
245,696 |
|
(20,698) |
F-113
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
35 Condensed Financial Information of the Company (Cont.)
CONDENSED STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION
|
|
At December |
|
At December |
|
|
31, 2023 |
|
31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
Non-current assets |
|
|
|
|
Property, plant and equipment, net |
|
12 |
|
15 |
Right-of-use asset |
|
270 |
|
56 |
Investments in subsidiaries |
|
746,199 |
|
738,851 |
Investments in associates |
|
10,264 |
|
— |
Other financial assets at amortized cost |
|
3,920 |
|
— |
Current assets |
|
|
|
|
Other financial assets at fair value through profit or loss |
|
2,200 |
|
— |
Other financial assets at amortized cost |
|
31 |
|
— |
Other receivables |
|
202 |
|
133 |
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
1,325 |
|
1,220 |
Total assets |
|
764,423 |
|
740,275 |
|
|
|
|
|
EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
Share capital |
|
163,223 |
|
163,223 |
Share premium |
|
183,430 |
|
183,430 |
Treasury shares |
|
(4,322) |
|
(4,600) |
Free distributable reserve |
|
378,910 |
|
378,910 |
Non-distributable reserve |
|
1,358,028 |
|
1,358,028 |
Currency translation adjustment |
|
(482,852) |
|
(251,145) |
Legal reserves |
|
3,676 |
|
1,081 |
Other reserves |
|
(1,343,094) |
|
(1,343,219) |
Retained earnings |
|
467,981 |
|
230,387 |
Equity |
|
724,980 |
|
716,095 |
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
Non-current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
Deferred tax liabilities |
|
3,648 |
|
1,230 |
Lease liabilities |
|
229 |
|
17 |
Current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
Borrowings |
|
33,413 |
|
20,354 |
Other liabilities |
|
1,773 |
|
2,024 |
Lease liabilities |
|
49 |
|
36 |
Trade payables |
|
331 |
|
519 |
Total liabilities |
|
39,443 |
|
24,180 |
Total equity and liabilities |
|
764,423 |
|
740,275 |
F-114
Corporación América Airports S.A. Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the
years ended on December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
(Amounts in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data or as otherwise indicated)
35 Condensed Financial Information of the Company (Cont.)
CONDENSED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
|
|
For the year ended |
|
For the year ended |
|
For the year ended |
Cash flows from operating activities |
|
December 31, 2023 |
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
December 31, 2021 |
Income / (loss) for the year from continuing operations |
|
239,518 |
|
174,847 |
|
(95,125) |
Adjustments for: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization and depreciation |
|
40 |
|
57 |
|
50 |
Deferred income tax |
|
2,418 |
|
202 |
|
1,028 |
Income tax accrued |
|
2,211 |
|
1,105 |
|
— |
Share of income / (loss) in subsidiaries and associates |
|
(247,585) |
|
(182,050) |
|
88,022 |
Interest expense |
|
559 |
|
426 |
|
426 |
Net foreign exchange |
|
(471) |
|
(1,874) |
|
(51) |
Other financial results, net |
|
8 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
Share base compensation |
|
420 |
|
317 |
|
— |
Financial results, net |
|
(153) |
|
— |
|
— |
Changes in working capital |
|
(2,919) |
|
760 |
|
721 |
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
(5,954) |
|
(6,207) |
|
(4,925) |
Net cash used in discontinued activities |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Cash contribution in subsidiaries and associates |
|
(58,987) |
|
(36,417) |
|
(4,544) |
Disposals of other financial assets |
|
760 |
|
— |
|
— |
Dividends and refund of cash contributions from subsidiaries |
|
64,344 |
|
57,000 |
|
11,494 |
Net cash provided by investing activities |
|
6,117 |
|
20,583 |
|
6,950 |
Net cash used in discontinued investing activities |
|
— |
|
(14,700) |
|
(2,495) |
Principal elements of lease payments |
|
(44) |
|
(53) |
|
(51) |
Net cash (used in) by financing activities |
|
(44) |
|
(53) |
|
(51) |
Net cash used in discontinued operations from financing activities |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increase in cash and cash equivalents |
|
119 |
|
14,323 |
|
1,974 |
Decrease in cash and cash equivalents from discontinued operations |
|
— |
|
(14,700) |
|
(2,495) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
At the beginning of the year |
|
1,220 |
|
1,614 |
|
2,166 |
Effect of exchange rate changes in cash and cash equivalents |
|
(14) |
|
(17) |
|
(31) |
Increase / (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
|
119 |
|
(377) |
|
(521) |
At the end of the year |
|
1,325 |
|
1,220 |
|
1,614 |
F-115
Exhibit 2.2
DESCRIPTION OF SHARE CAPITAL
We are a public limited liability company (société anonyme) incorporated in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The following is a summary of the material terms of our common shares, par value U.S.$1.00 nominal value per share (the “Common Shares”), which are the only type and class of securities of the Company that are registered under Section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”), as amended.
Type and Class of Securities
Our authorized share capital consists of 225,000,000 Common Shares with a nominal value of U.S.$ 1.00 per share. We have163,222,707 Common Shares issued and outstanding of which 2,251,123 are held as treasury shares as of the date of this report. All of our issued and outstanding Common Shares are fully paid and the board of directors may not call on or compel our shareholders to contribute additional amounts to the Company. Our Common Shares are listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol “CAAP” and may be freely transferred under our amended articles of association, subject to applicable law.
Common Shares
Common Shares are issued in registered form only and no certificates will be issued. The Company is entitled to treat the registered holder of any share as the absolute owner thereof and is not bound to recognize any equitable claim or other claim or interest in such share on the part of any other person.
Issuance of Common Shares
Our shareholders have renewed the initial authorization granted to the board of directors to issue Common Shares up to the maximum amount of the authorized unissued share capital of the Company for a period of five years from the date of the deed renewing such authorization, which period may be further renewed, to such persons, and on such terms and for such consideration as the board of directors may determine.
Pre-emptive Rights
In the event of any capital increase whether in cash or in kind, the holders of our Common Shares shall have pre-emptive rights to subscribe for additional common shares proportionally to their existing equity in our share capital, except as noted below. The exercise period for such pre-emptive rights is determined by the board of directors but must be at least 14 days from the date of the publication of the offering in the Luxembourg Official Gazette (Recueil électronique des sociétés et associations) and a journal published in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. If holders of Common Shares do not elect to exercise their pre-emptive rights, the other holders of pre-emptive rights shall benefit from secondary pre-emptive subscription rights for unsubscribed shares; provided, however, that the general meeting (or the board of directors, as authorized from time to time by the general meeting) may limit or withdraw such pre-emptive subscription rights in accordance with applicable law and our articles of association. The board of directors is also authorized for a period of five years commencing on May 23, 2023, to cancel or limit the pre-emptive rights of the shareholders in accordance with our articles of association and in connection with the issuance of shares (i) for payment in cash or in kind, or (ii) in connection with a conversion of profits and reserves (including share premium and capital surplus).
Meetings of Shareholders
The board of directors shall convene at least one general shareholders meeting each calendar year (the “annual general meeting”) for the purpose of, among other things, approving the annual accounts, deciding on the allocation of the annual profit, if any, and as the case may be, electing or renewing the mandates of directors. Under Luxembourg law, the annual general meeting must be held within six months of the end of the fiscal year. A general meeting can be adjourned at the request of one or more shareholders representing at least 10.0% of the issued share capital.
The board of directors may convene any general meeting whenever in its judgment such a meeting is necessary. The board of directors must convene a general meeting within a period of one month upon notice,
which notice must set forth certain information specified in the articles of association, to the Company from shareholders holding at least the 10.0% threshold on the date of such notice. In addition, one or more shareholders who together hold at least 10.0% of the issued share capital on the date of the notice to the Company, which notice must set forth certain information specified in the articles of association, may require that the Company include on the agenda of such general meeting one or more additional items. At least eight days’ notice to shareholders is required for a general meeting. No business may be transacted at a general meeting, other than business that is properly brought before the general meeting in accordance with our articles of association.
Voting Rights
Holders of our Common Shares are entitled to one vote per share on all matters submitted to a vote of holders of Common Shares. Luxembourg law does not provide for cumulative voting in the election of directors. Voting of shareholders at a general meeting may be in person, by proxy or by voting bulletin. Our articles of association specify how the Company shall determine the shareholders of record entitled to notice of or to vote at any meeting of shareholders or any adjournment thereof.
Amendments to the Articles of Association
Except where our articles of association authorize the board of directors to approve an increase in share capital, approve a redemption and subsequent cancellation of shares and change the address of its registered office and subsequently record such change in the presence of a Luxembourg notary, our articles of association require a special resolution approved at an extraordinary general shareholders´ meeting to amend the articles of association. The agenda of the extraordinary general shareholders´ meeting must indicate the proposed amendments to the articles of association. Any resolutions to amend the articles of association must be taken before a Luxembourg notary and such amendments must be published in accordance with Luxembourg law. Resolutions to amend the articles of association may only be passed in a general meeting where at least one half of the share capital is represented, and the agenda indicates the proposed amendments to the articles of association, and the text of those which pertain to the purpose or the form of the Company. If the required quorum is not obtained, a second general meeting may be convened by an announcement filed with the Luxembourg Trade and Companies Register and published in the Luxembourg Official Gazette (Recueil Électronique des Sociétés et Associations) and in a Luxembourg newspaper at least 15 days before the relevant meeting which shall deliberate validly regardless of the proportion of the capital represented. The applicable majority for both meetings shall be 66.67% of all votes validly cast.
Variation of Share Rights
Under Luxembourg law, where a resolution of an extraordinary general shareholders meeting will change the rights of our Common Shares or any other outstanding class of shares, the resolution must, in order to be valid, fulfill the quorum and voting requirements for an extraordinary general meeting with respect to each such class.
Permitted Transfers of Common Shares
The Common Shares are freely transferable subject to compliance with transfer formalities under applicable law.
Dividend Rights
Under Luxembourg law, dividends may only be declared from the freely available distributable reserves of the Company. Interim dividends may be declared by the board of directors, subject to certain mandatory legal requirements as detailed in the articles of association. The general shareholders meeting would in the normal course be asked to declare as final the interim dividends paid during the year. The shareholders may declare dividends at a general meeting.
Dividends may be paid in U.S. dollars, Euro or any other currency chosen by the board of directors or the general meeting and dividends may be paid at such places and times as may be determined by the board of directors within the limits of any decision made at the general shareholders meeting. Dividends may also be paid in kind in assets of any nature, and the valuation of those assets shall be established by the board of directors according to valuation methods determined in its discretion.
Distributions on winding up of the Company
The Company may be dissolved, at any time, by a resolution of the general meeting adopted in the manner required for amendment of the articles of association. In the event of dissolution of the Company, the liquidation shall be carried out by one or more liquidators (who may be physical persons or legal entities) appointed by the general meeting which authorized such liquidation. The general meeting shall also determine the powers and the remuneration of the liquidator(s). Under the liquidation of the Company, the surplus assets of the Company available for distribution among shareholders shall be distributed in accordance with the rules on distributions set forth in our articles of association, by way of advance payments or after payment (or provisions, as the case may be) of the Company’s liabilities.
Registration Rights and Indemnification Agreement
We entered into a registration rights and indemnification agreement with the Majority Shareholder. This agreement grants the Majority Shareholder the right to demand up to five registrations for the sale of our Common Shares. Additionally, the agreement provides the Majority Shareholder and its affiliate transferees customary “piggyback” registration rights. The registration rights and indemnification agreement also provide that we will pay certain expenses relating to such registrations and indemnify such holders of registrable securities against certain liabilities, which may arise under the Securities Act.
Board of Directors
Our articles of association provide that our business is to be managed and conducted by or under the direction of our board of directors. In managing the business of the Company, the board of directors is vested with the broadest powers to perform or cause to be performed any actions necessary or useful in connection with the purpose of the Company. All powers not expressly reserved by the Luxembourg Companies law or by the articles of association to the general shareholders meeting shall fall within the authority of the board of directors.
Our board of directors is composed of up to nine directors, appointed by the general shareholders meeting. The members of the board of directors shall be elected for a term not exceeding six years and shall be eligible to stand for re-election. A director may be removed with or without cause and/or replaced, at any time, by a resolution adopted at the general shareholders meeting. The general shareholders meeting shall also determine the number of directors, the remuneration and their term of office. In the event of any director vacancy, the remaining directors may elect at a meeting of the board of directors, by majority vote, to fill such vacancy or vacancies, as the case may be, until the following general shareholders meeting.
Executive Committee
The management of the Company is delegated to an executive committee (comité de direction) consisting of a maximum of five members including, inter alia, a Chief Executive Officer, a Chief Financial Officer, a Head of Legal and Compliance and other members of the senior management designated from time to time by the board of directors. The executive committee has the broadest powers possible under Luxembourg law and remains under the supervision and control of the board of directors.
Mergers and de-mergers
A merger by absorption whereby a Luxembourg company, after its dissolution without liquidation, transfers to the absorbing company all of its assets and liabilities in exchange for the issuance to the shareholders of the company being acquired of shares in the acquiring company, or a merger effected by transfer of assets to a newly incorporated company, must, in principle, subject to certain exceptions, be approved by a special resolution of shareholders of the Luxembourg company to be held before a notary. Similarly, a de-merger of a Luxembourg company is, in principle, subject to certain exceptions subject to the approval by a special resolution of shareholders.
Shareholder Suits and Information Rights
Class actions and derivative actions are generally not available to shareholders under Luxembourg law. Minority shareholders holding securities entitled to vote at the general meeting that resolved on the granting of discharge to the directors and holding at least 10.0% of the voting rights of the Company may bring an action against the directors on behalf of the Company.
Minority shareholders holding at least 10.0% of the voting rights of the Company may also ask the directors questions in writing concerning acts of management of the Company or one of its subsidiaries, and if the Company fails to answer these questions within one month, these shareholders may apply to the Luxembourg courts to appoint one or more experts instructed to submit a report on these acts of management. Furthermore, consideration would be given by a Luxembourg court in summary proceedings to acts that are alleged to constitute an abuse of majority rights against the minority shareholders.
Indemnification of Directors and Officers
Our articles of association provide that we will, to the extent permitted by law, indemnify our directors and officers against liability and expenses reasonably incurred or paid by them in connection with claims, actions, suits or proceedings in which they become involved as a party or otherwise by virtue of performing or having performed as a director or officer, and against amounts paid or incurred by them in the settlement of such claims, actions, suits or proceedings, if such person acted in good faith and in a manner the person reasonably believed to be in, and not opposed to, the best interests of the Company, and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe the person’s conduct was unlawful. The indemnification extends, among other things, to legal fees, costs and amounts paid in the context of a settlement. We have entered enter into separate indemnification agreements with our directors and executive officers. Except for proceedings to enforce rights to indemnification or advancement of expenses, we shall not be obligated to indemnify any such officer or director in connection with a proceeding initiated by such person when such proceeding (or part thereof) was consented to by the board of directors.
Our articles of association provide that we may purchase and maintain insurance or furnish similar protection or make other arrangements, including, but not limited to, providing a trust fund, letter of credit or surety bond on behalf of our directors or officers against any liability asserted against them in their capacity as a director or officer.
Access to Books and Records and Dissemination of Information
The register of shareholders of the Company is available for inspection, at the Company’s registered office, by shareholders.
Each year, the shareholders have the right to inspect, at the Company’s registered office, for at least eight calendar days prior to the annual general meeting, among other things, (i) the annual accounts, as well as the list of directors and of the approved statutory auditors (réviseur(s) d’entreprises agréé(s)),, (ii) the report of the approved statutory auditors and (iii) in case of amendments to our articles of association, the text of the proposed amendments and the draft of the resulting consolidated articles of association. Each shareholder is entitled to obtain these free of charge, upon request. Under Luxembourg law, it is generally accepted that a shareholder has the right to receive responses to questions concerning items on the agenda for a general meeting of shareholders, if such responses are necessary or useful for a shareholder to make an informed decision concerning such agenda item, unless a response to such questions could be detrimental to our interests.
Registrar and Transfer Agent
We have appointed Equinity Trust Company, LLC (formerly known as American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC.) as our U.S. registrar and transfer agent.
Repurchase of Common Shares
Pursuant to our articles of association, our board of directors may redeem our Common Shares in accordance with Luxembourg law on such terms and in such manner as may be authorized by the general meeting of shareholders in an ordinary resolution, subject to the rules of any stock exchange on which our Common Shares are traded.
Reduction of Share Capital
The share capital of the Company may be reduced by a resolution adopted by the general meeting of shareholders in the manner required for the amendment of the articles of association.
Non-Distributable Reserve
Our articles of association provide for the creation of a non-distributable reserve. We recorded this non-distributable reserve in the amount of U.S.$ 1,353.7 million. The non-distributable reserve may be reduced by a resolution adopted by the general meeting of shareholders in the manner required for in the amendment of the articles of association.
Annual Accounts
The board of directors shall draw up the annual accounts of the Company that shall be submitted to the approval of the shareholders at the annual general meeting. Except in some cases provided for by Luxembourg law, our board of directors must also annually prepare management reports on the annual accounts and consolidated accounts. The annual accounts and consolidated accounts are audited by an approved statutory auditor (réviseur d’entreprises agréé).
The annual accounts and the consolidated accounts, after approval by the annual general meeting of shareholders, will be filed with the Luxembourg Trade and Companies Register).
Exhibit 8.1
List of Subsidiaries and Associates
|
●
America International Airports, LLC
|
USA |
|
●
Yokelet S.L.U.
|
Spain |
|
●
ACI Airports Italia S.A.
|
Spain |
|
●
ACI Airport Sudamérica S.A.
|
Spain |
|
●
ACI do Brasil S.A.
|
Brazil |
|
●
Inframérica Participaçoes S.A.
|
Brazil |
|
●
Armenia International Airports C.J.S.C.
|
Armenia |
|
●
Cedicor S.A.
|
Uruguay |
|
●
Abafor S.A.
|
Uruguay |
|
●
Cerealsur S.A.
|
Uruguay |
|
●
CAAirports International Services S.A.
|
Uruguay |
|
●
Dicasa Spain S.A.
|
Spain |
|
●
Corporación Aeroportuaria S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Inframerica Concessionária do Aeroporto de Brasilia S.A.
|
Brazil |
|
●
Terminal de Cargas Uruguay S.A.
|
Uruguay |
|
●
Corporación América S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Consorcio Aeropuertos Internacionales S.P.A.
|
Uruguay |
|
●
Puerta del Sur S.A.
|
Uruguay |
|
●
Corporación América Italia S.P.A.
|
Italy |
|
●
Terminal Aeroportuaria de Guayaquil S.A.
|
Ecuador |
|
●
Aeropuerto Ecológico de Galápagos S.A.
|
Ecuador |
|
●
Cedicor Sucursal Ecuador S.A.
|
Ecuador |
|
●
Corporación América Sudamericana S.A.
|
Panama |
|
●
Toscana Aeroporti S.p.A.
|
Italy |
|
●
Alatoscana Spa
|
Italy |
|
●
Jet Fuel Co. S..R.L
|
Italy |
|
●
Parcheggi Peretola S.R.L.
|
Italy |
|
●
Toscana Aeroporti Engineering S.R.L.
|
Italy |
|
●
Toscana Aeroporti Handling S.R.L.
|
Italy |
|
●
A.C.Quasarda S.c.a.r.l
Toscana Aeroporti Costruzioni S.r.l |
Italy Italy |
|
●
Corporación América Sudamérica Suc. Ecuador
|
Ecuador |
|
●
Aerocombustibles Argentinos S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Aeropuerto de Bahía Blanca S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Aeropuerto del Neuquén S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Aeropuertos Argentina 2000 S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Enarsa Aeropuertos S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Paoletti américa S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Texelrio S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Servicios y Tecnología Aeroportuaria S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Cargo & Logistics S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Villalonga Furlong S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Caminos del Paraná S.A.
|
Argentina |
|
●
Corporandino S.A.
|
Perú |
|
●
Sociedad Aeroportuaria Kuntur Wasi.S.A.
|
Perú |
|
●
Anabe ITG, S.L.
|
Spain |
|
●
Sinatus S.A.
|
Uruguay |
|
●
Corporacion Africa Airports Nigeria Limited
|
Nigeria |
|
●
Abuja Airport Concession Company Limited
|
Nigeria |
|
●
Kano Airport Concession Company Limited
|
Nigeria |
|
●
Barnsley ITG, S.L.U
|
Spain |
|
●
Aeroasist Handling SAU
|
Argentina |
|
●
Navinten S.A.
|
Uruguay |
Exhibit 11.1

Insider Trading
Prevention Policy
APPROVED |
REVIEWED |
AUTHORIZED |
|
|
|
Compliance |
Legal Audit Committee |
Board of Directors |
 |
Code: |
LX-GO-0045e |
Policy |
Version |
2 |
Manual |
|
Effective |
MAR/23/2022 |
Procedure |
|
|
|
WI/Practice/Table |
|
Insider Trading Prevention Policy | |||
Change Records
Date |
Version |
Change description |
AUG/22/2018 |
1 |
Policy issuance. |
MAR/23/2022 |
2 |
Policy update. |
2
Important Note: |
This document could be obsolete. The effective version is published in the Normative System. |
 |
Code: |
LX-GO-0045e |
Policy |
Version |
2 |
Manual |
|
Effective |
MAR/23/2022 |
Procedure |
|
|
|
WI/Practice/Table |
|
Insider Trading Prevention Policy | |||
1. |
Purpose |
The Board of Directors of Corporación América Airports (“CAAP” or the “Company”) establishes this policy regarding non‐public information obtained through involvement with CAAP, its subsidiaries and controlled affiliates (together with CAAP, the “Companies”) and the trading of Securities (as defined below) based on such non‐public information.
The purpose of this policy is to establish guidelines that will assist the members of the Board of Directors, members of committees, Senior Management, employees, interns and trainees (“the Colleagues”) and anyone who by his job, profession or function has access to said information, to comply with their obligations under the securities & exchange laws and regulations of the Company’s jurisdiction and the jurisdictions in which Companies’ Securities are traded.
This policy and the obligations imposed hereunder do not in any way limit the restrictions and obligations imposed by applicable laws and regulations. Colleagues should be informed of the rules imposed by applicable laws and regulations governing the trading of Securities prior to engaging in any transaction involving Securities.
Additionally, this policy imposes on certain individuals certain special prohibitions and/or notice obligations.
2. |
Scope |
This policy is applicable to CAAP, its subsidiaries and controlled affiliates, to the Colleagues, and to whom by his job, profession or function has access to material, non‐ public information.
3. |
Responsibilities |
The Board of Directors and the Audit Committee are the highest‐level decision‐making bodies regarding the implementation of this policy, including the authorization for any changes hereof.
The Management is responsible for accomplishing and promoting compliance with this policy.
Additionally, with the assistance of the Compliance and Legal Department, they will adopt the necessary measures to ensure that all the Colleagues are trained to comply with this policy.
The Compliance Department will resolve issues of interpretation of this Policy that cannot be satisfactorily addressed through normal supervisory channels. For that purpose, they have direct access to the Board of Directors and/or the Audit Committee.
3
Important Note: |
This document could be obsolete. The effective version is published in the Normative System. |
 |
Code: |
LX-GO-0045e |
Policy |
Version |
2 |
Manual |
|
Effective |
MAR/23/2022 |
Procedure |
|
|
|
WI/Practice/Table |
|
Insider Trading Prevention Policy | |||
4. |
Related Documents |
· |
Corporate Governance Code. |
· |
Code of Conduct. |
· |
Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers. |
· |
Integrity Line Policy. |
· |
Blackout Period Calendar. |
· |
Disclosure Policy. |
· |
Related‐Party Transactions Policy. |
· |
Conflict of Interest Prevention Policy. |
· |
Gifts, Entertainment and Donations Policy. |
· |
Anti‐bribery and anti‐corruption Policy. |
· |
Third Parties Policy. |
· |
Joint Venture Due Diligence Work Instruction. |
· |
Merger & Acquisition Due Diligence Work Instruction. |
5. |
Definitions |
· |
“Companies’ Securities” are any Securities issued by any of the Companies or based on or relating to a Security issued by any of the Companies. |
· |
“Family member” includes –but is not limited to‐ a Colleague´s spouse or domestic partner, children, parents; daughters, sons; siblings; brothers, sisters and parents in law, and anyone else regularly living in his/her household. Colleagues are responsible for the compliance with this policy by their family members. It should be noted, however, that although certain relatives may not be considered family members for purposes of the trading restrictions imposed by this policy, under no circumstances can material, non‐public information be disclosed to them or to any other person. If any such disclosure is made, the trading of Securities by any of these persons may give rise to liability on the part of the disclosing person. |
· |
“Material information” is any information that a reasonable investor would be expected to take into account in making a decision to purchase, keep or sell Securities. Examples of information frequently considered material include the following: projections of future earnings or losses; unreleased annual, quarterly or monthly financial results; news of a pending or proposed joint venture, merger or acquisition; news of a significant purchase or sale of assets; changes in the composition of the board of directors or senior management; news concerning material agreements, development of new products, cancellation of existing products, or development of new markets; and developments concerning material litigation. Both good and bad news may be material. |
4
Important Note: |
This document could be obsolete. The effective version is published in the Normative System. |
 |
Code: |
LX-GO-0045e |
Policy |
Version |
2 |
Manual |
|
Effective |
MAR/23/2022 |
Procedure |
|
|
|
WI/Practice/Table |
|
Insider Trading Prevention Policy | |||
· |
“Non‐public information” is any information that is not generally available to the public. To allow for the orderly dissemination of information, information is not considered generally available to the public for purposes of this statement of policy and procedures until the second business day after it has been first publicly released by means of the worldwide distribution of press releases or the filing of reports with the applicable securities authorities. |
· |
“Other Entities” are any entities with which any of the Companies has a business relationship, is undertaking, negotiating or analyzing a transaction, or any entity in which any of the Companies owns a significant equity interest (whether or not they control such entity). These entities include, without limitation, actual or potential customers, suppliers and partners, and targets to an acquisition, merger, integration, joint venture or investment. |
· |
“Other Entities’ Securities” are any Securities issued by any Other Entity or based on or relating to a Security issued by any Other Entity. |
· |
“Securities” are any of the following: |
a. |
publicly traded debt and equity securities; |
b. |
derivative financial instruments and covered warrants or warrants which have the securities referred to in subparagraph a as the underlying instrument, including transactions where the exercise thereof involves the payment of a cash differential; |
c. |
certificates of interest or participation in funds, trusts or similar collective investment structures which hold any of the securities referred to in subparagraphs a. or b.; |
d. |
securities (whether publicly traded or not) that afford the right to subscribe for, buy or sell any of the securities referred to in subparagraphs a. to c.; and |
e. |
any other instrument admitted for trading in a regulated market or over the counter. |
· |
“CAAP’s Securities” are any Securities issued by CAAP or based on or relating to a Security issued by CAAP. |
6. |
Description |
6.1. |
General Statements about Non‐Public Information |
1. |
All non‐public information concerning the Companies and their affairs is and remains the property of the Companies. |
2. |
A Colleague coming across such information acquires no interests or right in the information, and merely holds it as consequence of his position or employment. |
5
Important Note: |
This document could be obsolete. The effective version is published in the Normative System. |
 |
Code: |
LX-GO-0045e |
Policy |
Version |
2 |
Manual |
|
Effective |
MAR/23/2022 |
Procedure |
|
|
|
WI/Practice/Table |
|
Insider Trading Prevention Policy | |||
6.2. |
Statement of principles |
1. |
If a Colleague has material, non‐public information (also known as “inside information”) relating to any of the Companies, neither that person nor any family member of such person may (i) directly or indirectly purchase or sell Companies’ Securities, (ii) engage in any action to take advantage of such information, or (iii) pass on that information to others. |
2. |
Similarly, if in the course of the Companies’ business a Colleague obtains material, non‐public information relating to any Other Entity, neither that person nor any family member of such person may (i) directly or indirectly purchase or sell such Other Entity’s Securities, (ii) engage in any action to take advantage of such information, or (iii) pass on to others that information. |
3. |
These prohibitions apply even if there is an independent, valid reason for effectuating a transaction. |
6.3. |
Restrictions |
6.3.1 |
Trading |
A)General Restriction. The Colleagues (and their family members) with knowledge of material, non‐public information that belongs to the Companies or to Other Entities, must refrain from buying or selling, directly or indirectly, Securities of the Companies or of Other Entities, according to the case.
B)Blackout Period. (a) Members of The Board of Directors, (b) The Chief Executive Officer, (c) the Chief Financial Officer, (d) the Company’s senior managers, (e) all employees who primarily report, directly or indirectly, to the Chief Financial Officer or the Investors Relation Manager, (f) any colleagues of any of the Companies who are entrusted with any task or responsibility concerning the collection or preparation of information for financial reporting purposes or that have regular access to such information, (g) any other person designated by the Chief Financial Officer or the Chief Compliance Officer, and (h) the family members of the persons listed in (a) to (g) may not directly or indirectly purchase or sell Companies’ Securities during the period which commences on the fifteenth calendar day of the third month of each fiscal quarter and terminates at the close of trading on the second business day following public release of quarterly or annual earnings releases. The blackout period shall commence on the referred date even though some of the markets in which the Companies’ Securities trade are not open for trading.
C)Trading Restrictions. Trading directly or indirectly in Companies’ Securities or, as applicable, Other Entities’ Securities by the Colleagues (and their family members), as appropriate, is also prohibited whenever the CFO or the Investors Relation Manager or The Chief Compliance Officer, issues an announcement of a “Trading Restriction” regarding Companies’ Securities or Other Entities’ Securities, as applicable, and such prohibition shall continue until an announcement is
6
Important Note: |
This document could be obsolete. The effective version is published in the Normative System. |
 |
Code: |
LX-GO-0045e |
Policy |
Version |
2 |
Manual |
|
Effective |
MAR/23/2022 |
Procedure |
|
|
|
WI/Practice/Table |
|
Insider Trading Prevention Policy | |||
issued ending the Trading Restriction. A Trading Restriction prohibits trading even if normally permitted. A Trading Restriction will generally be imposed when, among other things, any of the Companies are involved in material negotiations that the parties do not wish to disclose at such time. The existence of a Trading Restriction itself will generally constitute material, non‐public information and thus its existence should not be disclosed to any other person (except as strictly necessary to ensure compliance with the Trading Restriction).
D)In order to comply with the restrictions stated in “C)”, those Colleagues who participate in the analysis or negotiation of a transaction, project, or event that could have a material impact on the value of the Companies’ Securities or, if applicable, on the value of Other Entities’ Securities, must notify their situation to Compliance Department (through the email insidertrading@caairports.com), who will determine whether it is necessary for the concerned Colleague(s) to sign a letter undertaking not to directly or indirectly purchase or sell Companies’ Securities or Other Entities’ Securities for themselves or on behalf of third parties, until the close of the second business day following public release containing the communication of the aforementioned transaction or event, or at the time the Company decided to cancel such negotiation, event or project. The managers and directors leading the negotiation of the relevant transaction or event are responsible for ensuring that their colleagues are aware of the requirement established in this paragraph.
6.3.2 |
Tipping |
The Colleagues of the Companies and anyone who by his job, profession or function has access to material, non‐public information of the Companies, must abstain from directly or indirectly disclosing said information to third parties that are subject to (a) a legal prohibition to trade in Securities while in the possession of material, non‐public information, or (b) a confidentiality agreement, or professional standard of conduct, with the relevant Companies prohibiting the use of material, non‐public information for any purposes other than those for which such information has been disclosed. Even when the above conditions are met, material, non‐public information should only be disclosed on a need‐to‐know basis.
6.4. |
Consequences of Failure to Comply with this Policy |
Buying or selling Securities on the basis of material, non‐public information, or passing that information on to another party who buys or sells, may subject the individual to disgorgement of illegal profits as well as severe civil and criminal liability under the securities laws and regulations of the Companies jurisdictions of organization or the jurisdictions in which the Securities are traded. In certain jurisdictions, civil penalties may amount to ten times the profit realized, or loss avoided, and criminal penalties may include imprisonment. In addition, CAAP may be exposed to economic and reputational damages.
7
Important Note: |
This document could be obsolete. The effective version is published in the Normative System. |
 |
Code: |
LX-GO-0045e |
Policy |
Version |
2 |
Manual |
|
Effective |
MAR/23/2022 |
Procedure |
|
|
|
WI/Practice/Table |
|
Insider Trading Prevention Policy | |||
The Companies’ Securities are traded in different markets, each subject to its own laws and regulations. Accordingly, certain trading transactions undertaken while in possession of material, non‐public information that are permitted in one market, may still give rise to liability in another market. As a result, Colleagues of the Companies and anyone who by his job, profession or function has access to said information should take care to comply with this policy regardless of exceptions or safe harbors that may be applicable in a particular market.
In addition, the Colleagues of the Companies and anyone who by his job, profession or function has access to material, non‐public information, willfully or knowingly violates this policy may be subject to disciplinary measures. In the event that a violation is committed by members of the Board of Directors or any other governing or surveillance bodies of the Companies, the members of the Board of Directors shall have the power to propose to the following shareholders meeting the revocation, with cause, of the appointment of the breaching director or member of other governing or surveillance body. Violations committed by persons contractually related to the Companies may result in termination of the respective agreements.
The Companies reserve the right to, take all available action, including legal action, depending on the seriousness of the case.
6.5 Trading Prior communication
The members of the Board of Directors, the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and the Company’s first‐ line Management must communicate the operations of direct or indirect purchase or sale of Companies’ Securities, to the mail insidertrading@caaiports.com, at least in the session immediately prior to the one in which they expect to order the operation.
The Investor Relations Department will verify if the period in which the trading operation reported by the colleague is contemporaneous to some restriction.
According to the information checked with the IR Department, the Chief Compliance Officer will determine that the operation does not violate the restrictions established in this policy and will respond no later than the business day following the receipt of said communication.
The restricted persons shall not order the operations until they receive the prior confirmation from insidertrading@caaiports.com
Likewise, if deemed necessary, the Compliance Department may request periodic confirmations from the aforementioned persons regarding the Company’s securities that are in their possession, in order to carry out further controls regarding the compliance with the policy.
8
Important Note: |
This document could be obsolete. The effective version is published in the Normative System. |
 |
Code: |
LX-GO-0045e |
Policy |
Version |
2 |
Manual |
|
Effective |
MAR/23/2022 |
Procedure |
|
|
|
WI/Practice/Table |
|
Insider Trading Prevention Policy | |||
Statement of Commitment
I declare that I have read and understood the Company’s Insider Trading Prevention Policy. I agree to fully comply with this Policy and policies connected therewith in all my activities related to the Company and / or when I am representing it. I understand that it is my responsibility to respect the policies, practices and guidelines established and mentioned in the Code of Conduct and I accept that this Statement of Commitment constitutes an expression of my free consent to observe this Policy.
Full Name: |
|
|
|
|
|
Personnel File Number: |
|
|
|
|
|
Department: |
|
|
|
|
|
Place / Date: |
|
|
|
|
|
Signature: |
|
|
|
9
Important Note: |
This document could be obsolete. The effective version is published in the Normative System. |
Exhibit 12.1
CERTIFICATION
I, Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this annual report on Form 20-F of Corporación América Airports S.A.;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the company as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The company’s other certifying officer and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) for the company and have:
(a) |
Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the company, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; |
(b) |
Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles; |
(c) |
Evaluated the effectiveness of the company’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and |
(d) |
Disclosed in this report any change in the company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by the annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the company’s internal control over financial reporting; and |
5. The company’s other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the company’s auditors and the audit committee of the company’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a)All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the company’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b)Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the company’s internal control over financial reporting.
By: |
/s/ Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
Name: |
Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
Title: |
Chief Executive Officer |
|
Dated: |
March 28, 2024 |
|
Exhibit 12.2
CERTIFICATION
I, Jorge Arruda Filho, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this annual report on Form 20-F of Corporación América Airports S.A.;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the company as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The company’s other certifying officer and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) for the company and have:
(a) |
Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the company, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; |
(b) |
Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles; |
(c) |
Evaluated the effectiveness of the company’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and |
(d) |
Disclosed in this report any change in the company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by the annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect the company’s internal control over financial reporting; and |
5. The company’s other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the company’s auditors and the audit committee of the company’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) |
All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the company’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and |
(b) |
Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the company’s internal control over financial reporting. |
By: |
/s/ Jorge Arruda Filho |
|
Name: |
Jorge Arruda Filho |
|
Title: |
Chief Financial Officer |
|
Dated: |
March 28, 2024 |
|
Exhibit 13.1
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE U.S. SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of Corporación América Airports S.A. (the “Company”) on Form 20-F for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, as filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian, Chief Executive Officer, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. section 1350, as adopted pursuant to section 906 of the U.S. Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to the best of my knowledge:
(i) |
the Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and |
(ii) |
the information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company. |
/s/ Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
|
Name: |
Martín Francisco Antranik Eurnekian |
|
Title: |
Chief Executive Officer |
|
Date: |
March 28, 2024 |
|
Exhibit 13.2
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE U.S. SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual Report of Corporación America Airports S.A. (the “Company”) on Form 20-F for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, as filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Jorge Arruda Filho, Chief Financial Officer, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. section 1350, as adopted pursuant to section 906 of the U.S. Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to the best of my knowledge:
(i) |
the Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and |
(ii) |
the information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company. |
/s/ Jorge Arruda Filho |
|
|
Name: |
Jorge Arruda Filho |
|
Title: |
Chief Financial Officer |
|
Date: |
March 28, 2024 |
|
Exhibit 23
CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
We hereby consent to the incorporation by reference in the Registration Statements on Form F-3 (No. 333-274239) and Form S-8 (No. 333-248633) of Corporación América Airports S.A. of our report dated March 20, 2024 relating to the financial statements and the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, which appears in this Form 20-F.
/s/ PRICE WATERHOUSE & CO. S.R.L. |
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Juan Manuel Gallego Tinto |
|
Buenos Aires, Argentina |
|
March 28, 2024 |
|
Exhibit 97

DODD-FRANK CLAWBACK POLICY1
The Board of Directors (the “Board”) of Corporación América Airports S.A. (the “Company”) has adopted this Dodd-Frank Clawback Policy (this “Policy”) in accordance with the applicable provisions of The New York Stock Exchange Listed Company Manual (the “Clawback Rules”), promulgated pursuant to the final rules adopted by the Securities and Exchange Commission enacting the clawback standards under Section 954 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. The Compensation Committee (the “Committee”) is designated to administer this Policy. Capitalized terms not otherwise defined in this Policy have the meanings given to them under the Clawback Rules.
Recovery of Erroneously Awarded Incentive Compensation. The Company shall comply with the Clawback Rules and reasonably promptly recover Erroneously Awarded Compensation Received by current or former Executive Officers of the Company (“Covered Individuals”) as required by the Clawback Rules. The Committee or a majority of the independent directors serving on the board of directors, as applicable, may determine to not recover Erroneously Awarded Compensation pursuant to this Policy in circumstances where non-enforcement is expressly permitted by the Clawback Rules, including where recovery would violate applicable home country laws in effect before November 28, 2022.
Covered Individuals. Senior members of the management team of the Company and/or its subsidiaries, CEOs and key executives reporting to the corresponding CEO with significant impact on the bottom line and/or future growth of the Company and/or its subsidiaries, as determined by the Committee.
Covered Compensation. This Policy applies to the Incentive-based Compensation received by a Covered Individual: (1) after such Covered Individual began service as an Executive Officer; (2) who served as an Executive Officer at any time during the performance period for that Incentive- based Compensation; (3) while the Company has a class of securities listed on a national securities exchange or a national securities association; and (4) during the three completed fiscal years immediately preceding the date that the Company is required to prepare an accounting restatement as described above (or during any transition period, that results from a change in the Company’s fiscal year, within or immediately following those three completed fiscal years, as determined in accordance with the Clawback Rules).
The amount of Incentive-based Compensation subject to this Policy is the Erroneously Awarded Compensation, which is the amount of Incentive-based Compensation Received by a Covered Individual that exceeds the amount of Incentive-based Compensation that otherwise would have been Received by the Covered Individual had it been determined based on the restated amount (or otherwise determined in accordance with the Clawback Rules), and will be computed without regard to any taxes paid by the Covered Individual (or withheld from the Incentive-based Compensation). The Committee shall make all determinations regarding the amount of Erroneously Awarded Compensation.
Method of Recovery. The Committee shall determine, in its sole discretion, the manner in which any Erroneously Awarded Compensation shall be recovered. Methods of recovery may include, but are not limited to: (1) seeking direct repayment from the Covered Individual; (2) reducing (subject to applicable law and the terms and conditions of the applicable plan, program or arrangement pursuant to which the incentive-based compensation was paid) the amount that would otherwise be payable to the Covered Individual under any compensation, bonus, incentive, equity and other benefit plan, agreement, policy or arrangement maintained by the Company or any of its affiliates; (3) cancelling any award (whether cash- or equity-based) or portion thereof previously granted to the Covered Individual; or (4) any combination of the foregoing.
No-Fault Basis. This Policy applies on a no-fault basis, and Covered Individuals will be subject to recovery under this Policy without regard to their personal culpability.
Other Company Arrangements. This Policy shall be in addition to, and not in lieu of, any other clawback, recovery or recoupment policy maintained by the Company from time to time, as well as any clawback, recovery or recoupment provision in any of the Company’s plans, awards or individual agreements (including the clawback, recovery and recoupment provisions in the Company’s equity award agreements) (collectively, “Other Company Arrangement”) and any other rights or remedies available to the Company, including termination of employment; provided, however, that there is no intention to, nor shall there be, any duplicative recoupment of the same compensation under more than one policy, plan, award or agreement. In addition, no Other Company Arrangement shall serve to restrict the scope or the recoverability of Erroneously Awarded Compensation under this Policy or in any way limit recovery in compliance with the Clawback Rules.
No Indemnification. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary set forth in any policy, arrangement, bylaws, charter, certificate of incorporation or plan of the Company or any individual agreement between a Covered Individual and the Company or any of its affiliates, no Covered Individual shall be entitled to indemnification from the Company or any of its affiliates for the amount that is or may be recovered by the Company pursuant to this Policy; provided, however, that to the extent expense advancement or reimbursement is available to a Covered Individual, this Policy shall not serve to prohibit such advancement or reimbursement.
Administration; Interpretation. The Committee shall interpret and construe this Policy consistent with the Clawback Rules and applicable laws and regulation and shall make all determinations necessary, appropriate or advisable for the administration of this Policy. Any determinations made by the Committee shall be final, binding and conclusive on all affected individuals. As required by the Clawback Rules, the Company shall provide public disclosures related to this Policy and any applicable recoveries of Erroneously Awarded Compensation. To the extent this Policy conflicts or is inconsistent with the Clawback Rules, the Clawback Rules shall govern. In no event is this Policy intended to be broader than, or require recoupment in addition to, that required pursuant to the Clawback Rules.
2
Amendment or Termination of this Policy. The Board reserves the right to amend this Policy at any time and for any reason, subject to applicable law and the Clawback Rules. To the extent that the Clawback Rules cease to be in force or cease to apply to the Company, this Policy shall also cease to be in force.
3
COVERED INDIVIDUAL ACKNOWLEDGMENT
I, [INSERT NAME], acknowledge that I have received a copy of the Policy and the Clawback Rules, and that I have read and understood the Policy and the Clawback Rules. I further understand that the Policy applies to my Incentive-Based Compensation, as defined in the Clawback Rules, and that I agree to take all actions necessary to assist the Company in complying with the Policy and the Clawback Rules.
|
COVERED INDIVIDUAL |
|
|
|
|
|
Name: |
|
|
|
Date: |