UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 6-K
Report of Foreign Private Issuer
Pursuant to Rule 13a-16 or 15d-16
of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934
For the month of September 2025
Commission File Number: 001-37643
PURPLE BIOTECH LTD.
(Translation of registrant’s name into English)
4 Oppenheimer Street, Science Park, Rehovot 7670104, Israel
(Address of principal executive offices)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant files or will file annual reports under cover Form 20-F or Form 40-F.
Form 20-F ☒ Form 40-F ☐
Purple Biotech
On September 15, 2025, Purple Biotech Ltd. (the “Company” or the “Registrant”) issued an updated Company presentation, “Purple Biotech Corporate presentation September 2025”, which is attached hereto as Exhibit 99.1.
| Exhibit | ||
| 99.1 | Purple Biotech Corporate presentation September 2025 |
Incorporation by Reference
This Report on Form 6-K, including all exhibits attached hereto, is hereby incorporated by reference into each of the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on May 20, 2016 (Registration file number 333-211478), the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 6, 2017 (Registration file number 333-218538), the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form F-3, as amended, originally filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on July 16, 2018 (Registration file number 333-226195), the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on March 28, 2019 (Registration file number 333-230584), the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form F-3 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 16, 2019 (Registration file number 333-233795), the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form F-1 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 27, 2019 (Registration file number 333-235729), the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form F-3 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on May 13, 2020 (Registration file number 333-238229), the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on May 18, 2020 (Registration file number 333-238481), each of the Registrant’s Registration Statements on Form F-3 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on July 10, 2020 (Registration file numbers 333-239807 and 333-233793), the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 4, 2022 (Registration file number 333-264107) and the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form F-3 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on March 23, 2023 (Registration file number 333-270769), the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form F-3, as amended, originally filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 8, 2022 (Registration file number 333-268710), the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form F-1, as amended, originally filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 30, 2023 (Registration file number 333-275216) and the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form F-1, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on July 22, 2024 (Registration file number 333-280947), to be a part thereof from the date on which this report is submitted, to the extent not superseded by documents or reports subsequently filed or furnished.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| September 15, 2025 | PURPLE BIOTECH LTD. | |
| By: | /s/ Gil Efron | |
| Gil Efron | ||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||
Exhibit 99.1


NASDAQ/TASE: PPBT September 2025 CORPORATE PRESENTATION 2 Forward - looking Statements and Safe Harbor Certain statements in this presentation that are forward - looking and not statements of historical fact are forward - looking statements within the meaning of the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 . Such forward - looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements that are not statements of historical fact, and may be identified by words such as “believe”, “expect”, “intend”, “plan”, “may”, “should”, “could”, “might”, “seek”, “target”, “will”, “project”, “forecast”, “continue” or “anticipate” or their negatives or variations of these words or other comparable words or by the fact that these statements do not relate strictly to historical matters . You should not place undue reliance on these forward - looking statements, which are not guarantees of future performance . Forward - looking statements reflect our current views, expectations, beliefs or intentions with respect to future events, and are subject to a number of assumptions, involve known and unknown risks, many of which are beyond our control, as well as uncertainties and other factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be significantly different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward - looking statements . Important factors that could cause or contribute to such differences include, among others, risks relating to : the plans, strategies and objectives of management for future operations ; product development for NT 219 , CM 24 and IM 1240 ; the process by which such early stage therapeutic candidates could potentially lead to an approved drug product is long and subject to highly significant risks, particularly with respect to a joint development collaboration ; the fact that drug development and commercialization involves a lengthy and expensive process with uncertain outcomes ; our ability to successfully develop and commercialize our pharmaceutical products ; the expense, length, progress and results of any clinical trials ; the impact of any changes in regulation and legislation that could affect the pharmaceutical industry ; the difficulty in receiving the regulatory approvals necessary in order to commercialize our products ; the difficulty of predicting actions of the U . S . Food and Drug Administration or any other applicable regulator of pharmaceutical products ; the regulatory environment and changes in the health policies and regimes in the countries in which we operate ; the uncertainty surrounding the actual market reception to our pharmaceutical products once cleared for marketing in a particular market ; the introduction of competing products ; patents obtained by competitors ; dependence on the effectiveness of our patents and other protections for innovative products ; our ability to obtain, maintain and defend issued patents ; the commencement of any patent interference or infringement action against our patents, and our ability to prevail, obtain a favorable decision or recover damages in any such action ; and the exposure to litigation, including patent litigation, and/or regulatory actions ; the impact of the economic, public health, political and security situation in Israel, the U . S . and other countries in which we may operate or obtain approvals for our products or our business, and other factors that are discussed in our Annual Report on Form 20 - F for the year ended December 31 , 2024 and in our other filings with the U . S . Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), including our cautionary discussion of risks and uncertainties under “Risk Factors” in our Registration Statements and Annual Reports . These are factors that we believe could cause our actual results to differ materially from expected results . Other factors besides those we have listed could also adversely affect us . Any forward - looking statement in this press release speaks only as of the date which it is made . We disclaim any intention or obligation to publicly update or revise any forward - looking statement or other information contained herein, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by applicable law . You are advised, however, to consult any additional disclosures we make in our reports to the SEC, which are available on the SEC’s website, https : //www . sec . gov . The trademarks, tradenames, service marks and logos included herein are the property of the owners thereof and are used for reference purposes only .

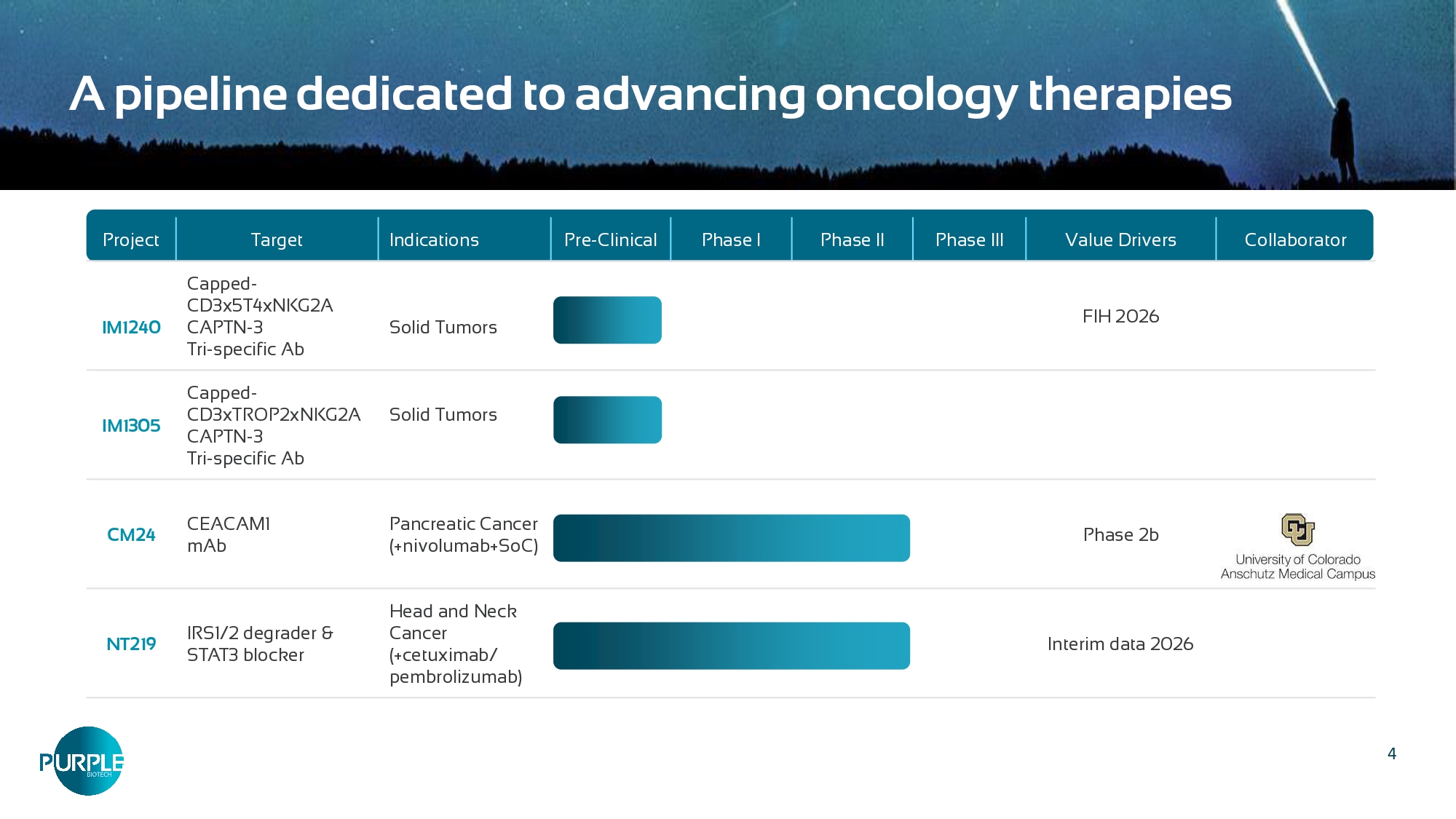
Such use should not be construed as an endorsement of the products or services of the Company 3 Purple Biotech develops promising first - in - class drug candidates to treat cancers with high unmet medical need Next generation tri - specific antibody platform • CAPTN - 3: Conditionally activated T - cell engager (TCE) enhanced by NK cell engager arm and a Tumor Associated Antigen engager Partnership and investment opportunities: Two Phase 2 first - in - class drugs • CM24, aCEACAM1 antibody: Unlocking personalized immunotherapy through biomarker - guided patient targeting; positive randomized Phase 2a results • NT219, IRS1/2 degrader and STAT3 blocker : Sensitizing the tumor & tumor microenvironment; Safety and anti - tumor activity demonstrated in Phase 1 Cash balance $10.5M*, cash runway into 1H 2027 *As of September 10, 2025 4 Collaborator Value Drivers Phase III Phase II Phase I Pre - Clinical Indications Target Project FIH 2026 Solid Tumors Capped - CD3x5T4xNKG2A CAPTN - 3 Tri - specific Ab IM1240 Solid Tumors Capped - CD3xTROP2xNKG2A CAPTN - 3 Tri - specific Ab IM1305 Phase 2b Pancreatic Cancer (+nivolumab+SoC) CEACAM1 mAb CM24 Interim data 2026 Head and Neck Cancer (+cetuximab/ pembrolizumab) IRS1/2 degrader & STAT3 blocker NT219 A pipeline dedicated to advancing oncology therapies

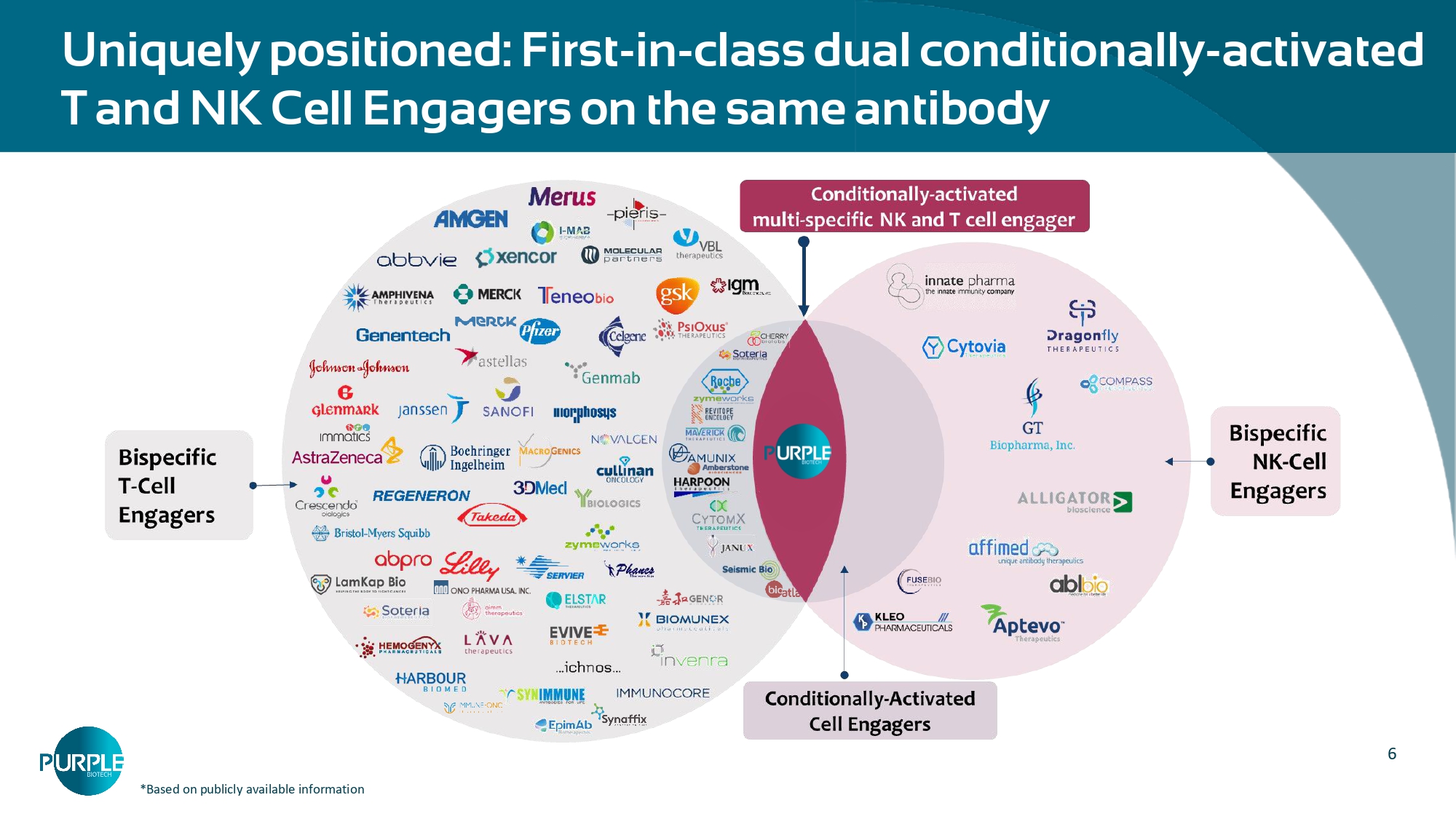
CAPTN - 3: Conditionally - Activated Tri - Specific Antibody Platform 6 Uniquely positioned: First - in - class dual conditionally - activated T and NK Cell Engagers on the same antibody *Based on publicly available information
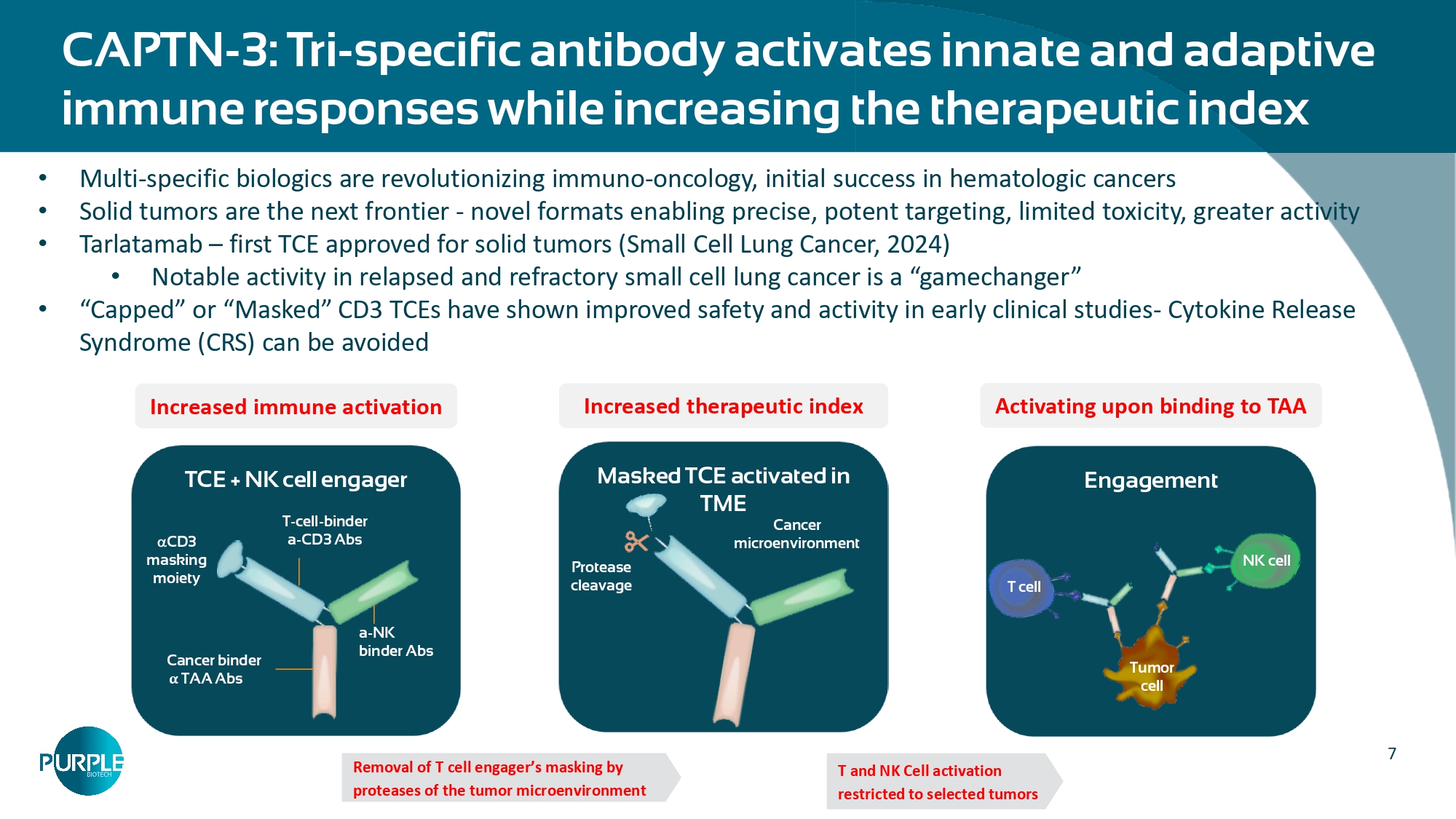
7 CAPTN - 3: Tri - specific antibody activates innate and adaptive immune responses while increasing the therapeutic index Engagement TCE + NK cell engager Cancer binder α TAA Abs a - NK binder Abs T - cell - binder a - CD3 Abs CD3 masking moiety Tumor cell NK cell Masked TCE activated in TME Cancer microenvironment Protease cleavage Removal of T cell engager’s masking by proteases of the tumor microenvironment T and NK Cell activation restricted to selected tumors T cell • Multi - specific biologics are revolutionizing immuno - oncology, initial success in hematologic cancers • Solid tumors are the next frontier - novel formats enabling precise, potent targeting, limited toxicity, greater activity • Tarlatamab – first TCE approved for solid tumors (Small Cell Lung Cancer, 2024) • Notable activity in relapsed and refractory small cell lung cancer is a “gamechanger” • “Capped” or “Masked” CD3 TCEs have shown improved safety and activity in early clinical studies - Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) can be avoided Increased immune activation Increased therapeutic index Activating upon binding to TAA 8 Plug & Play Tri - specific Scaffold differentiated by Capped TCE + with an NK Cell Activating Arm ▪ NKG2A ▪ NK2D ▪ Other NK cell engagers NK engager Cap - HSA CD3 TAA ▪ α 5T4 ▪ α TROP2 ▪ α EGFR ▪ Other Multiple opportunities for development and partnering • Modular architecture allows integration of multiple TAAs or NK - activating arms, enabling a robust pipeline of novel drug candidates.
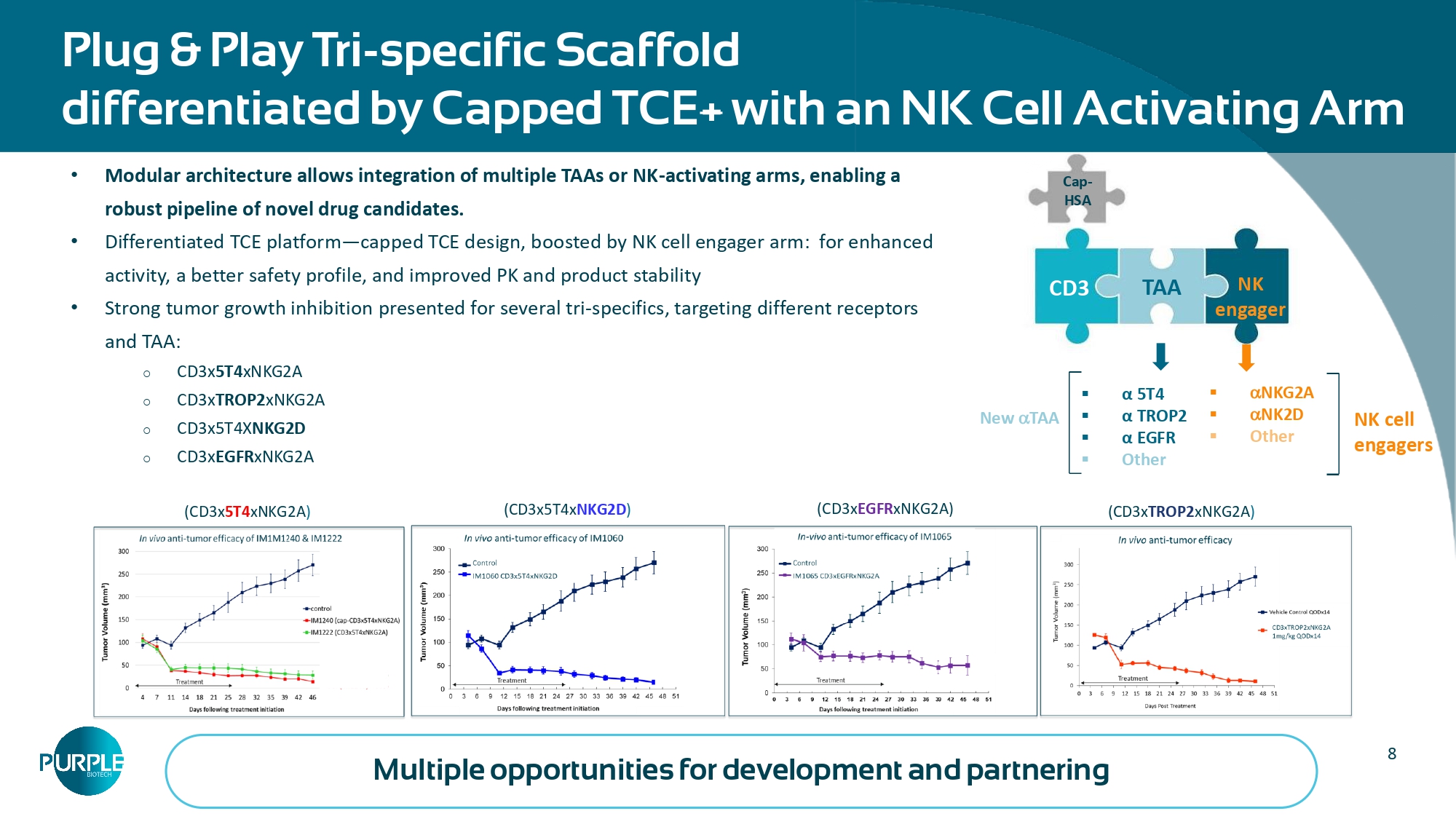
• Differentiated TCE platform — capped TCE design, boosted by NK cell engager arm: for enhanced activity, a better safety profile, and improved PK and product stability • Strong tumor growth inhibition presented for several tri - specifics, targeting different receptors and TAA: o CD3x 5T4 xNKG2A o CD3x TROP2 xNKG2A o CD3x5T4X NKG2D o CD3x EGFR xNKG2A (CD3x 5T4 xNKG2A ) (CD3x5T4x NKG2D ) (CD3x EGFR xNKG2A) New TAA (CD3x TROP2 xNKG2A )
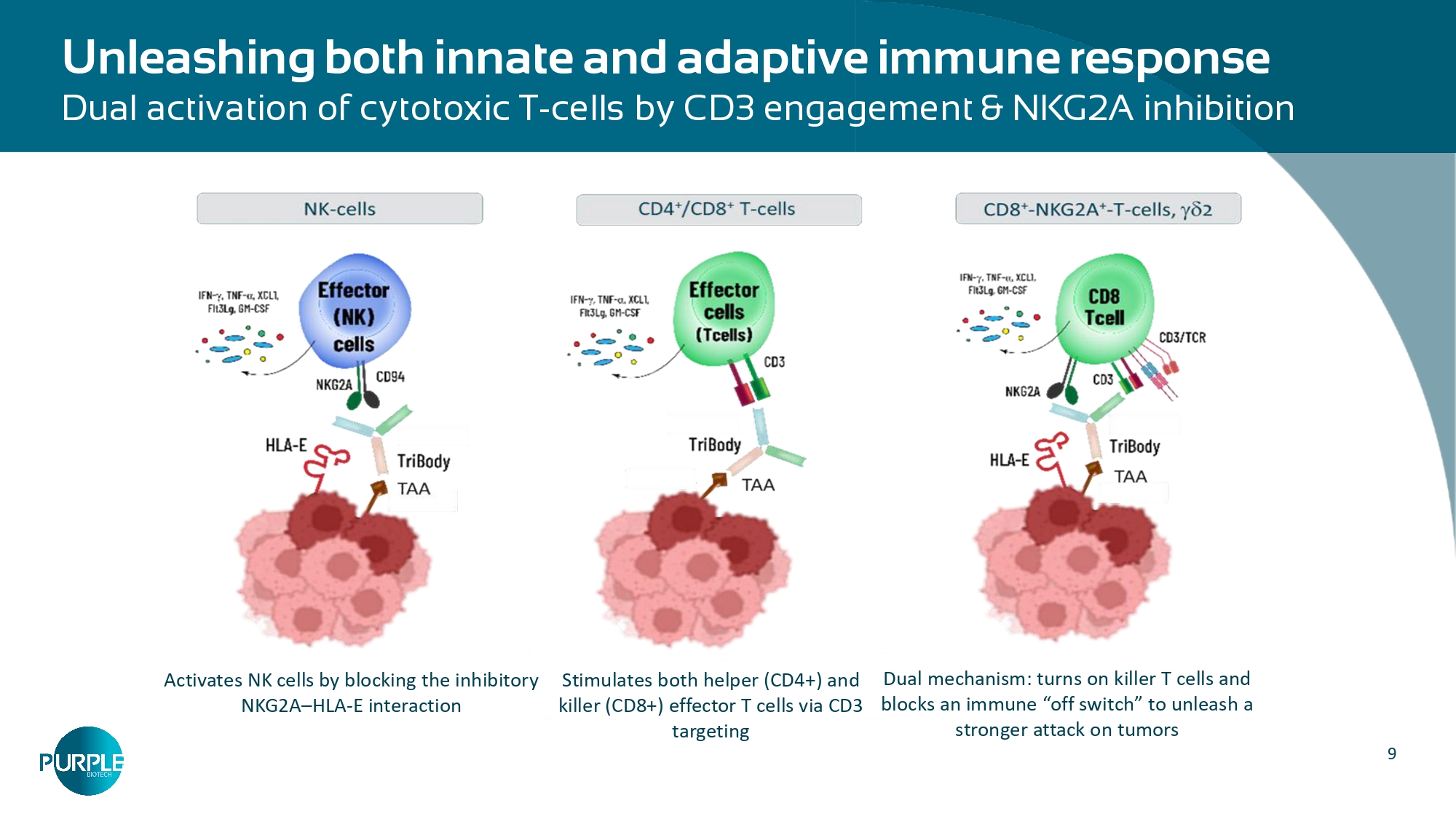
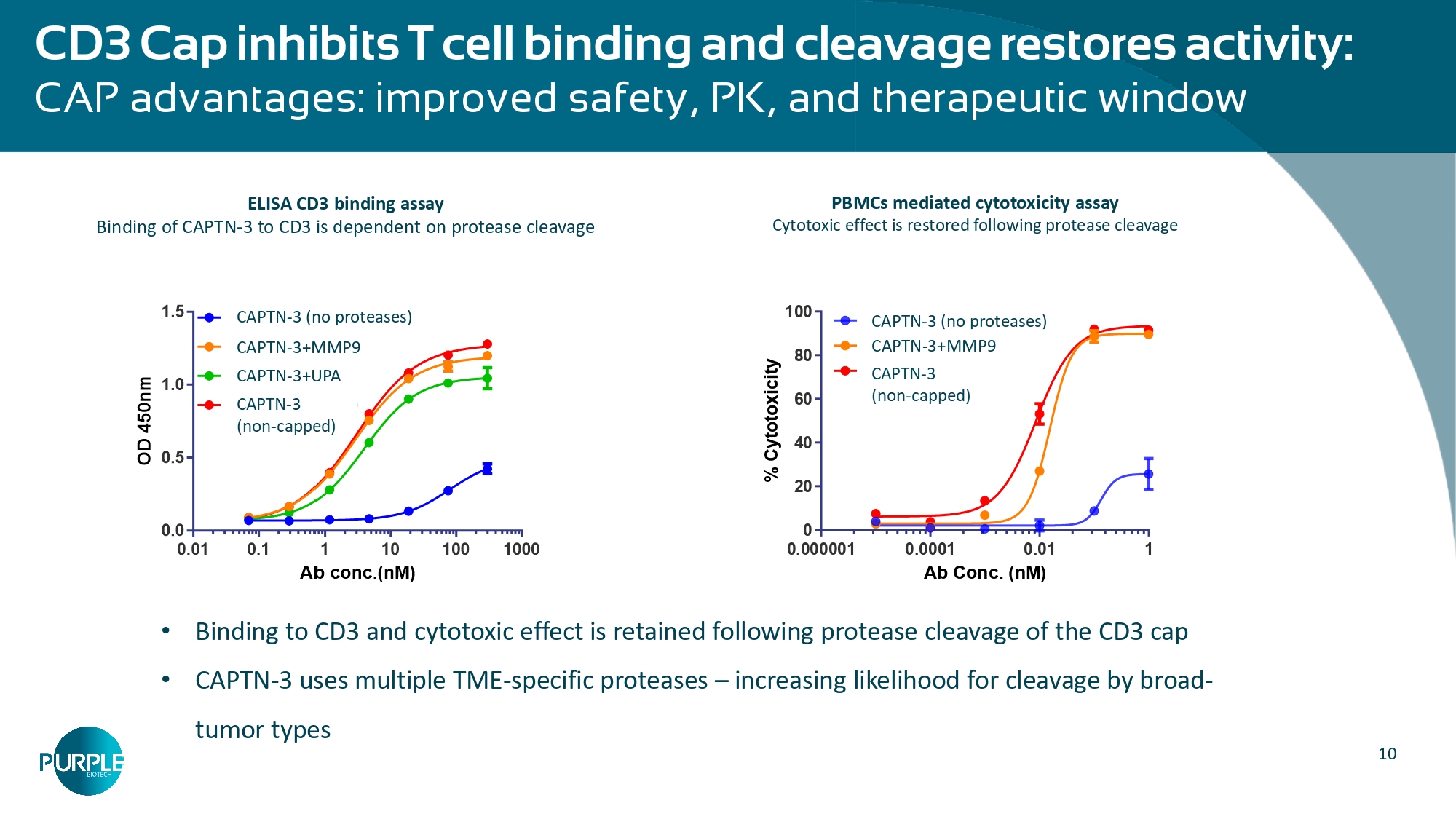
9 Unleashing both innate and adaptive immune response Dual activation of cytotoxic T - cells by CD3 engagement & NKG2A inhibition Stimulates both helper (CD4+) and killer (CD8+) effector T cells via CD3 targeting Dual mechanism: turns on killer T cells and blocks an immune “off switch” to unleash a stronger attack on tumors Activates NK cells by blocking the inhibitory NKG2A – HLA - E interaction 10 • Binding to CD3 and cytotoxic effect is retained following protease cleavage of the CD3 cap • CAPTN - 3 uses multiple TME - specific proteases – increasing likelihood for cleavage by broad - tumor types CD3 Cap inhibits T cell binding and cleavage restores activity: CAP advantages: improved safety, PK, and therapeutic window PBMCs mediated cytotoxicity assay Cytotoxic effect is restored following protease cleavage ELISA CD3 binding assay Binding of CAPTN - 3 to CD3 is dependent on protease cleavage (no proteases) CAPTN - 3 (no proteases) CAPTN - 3+MMP9 CAPTN - 3+UPA % Cytotoxicity 0.000001 0.0001 0.01 Ab Conc.
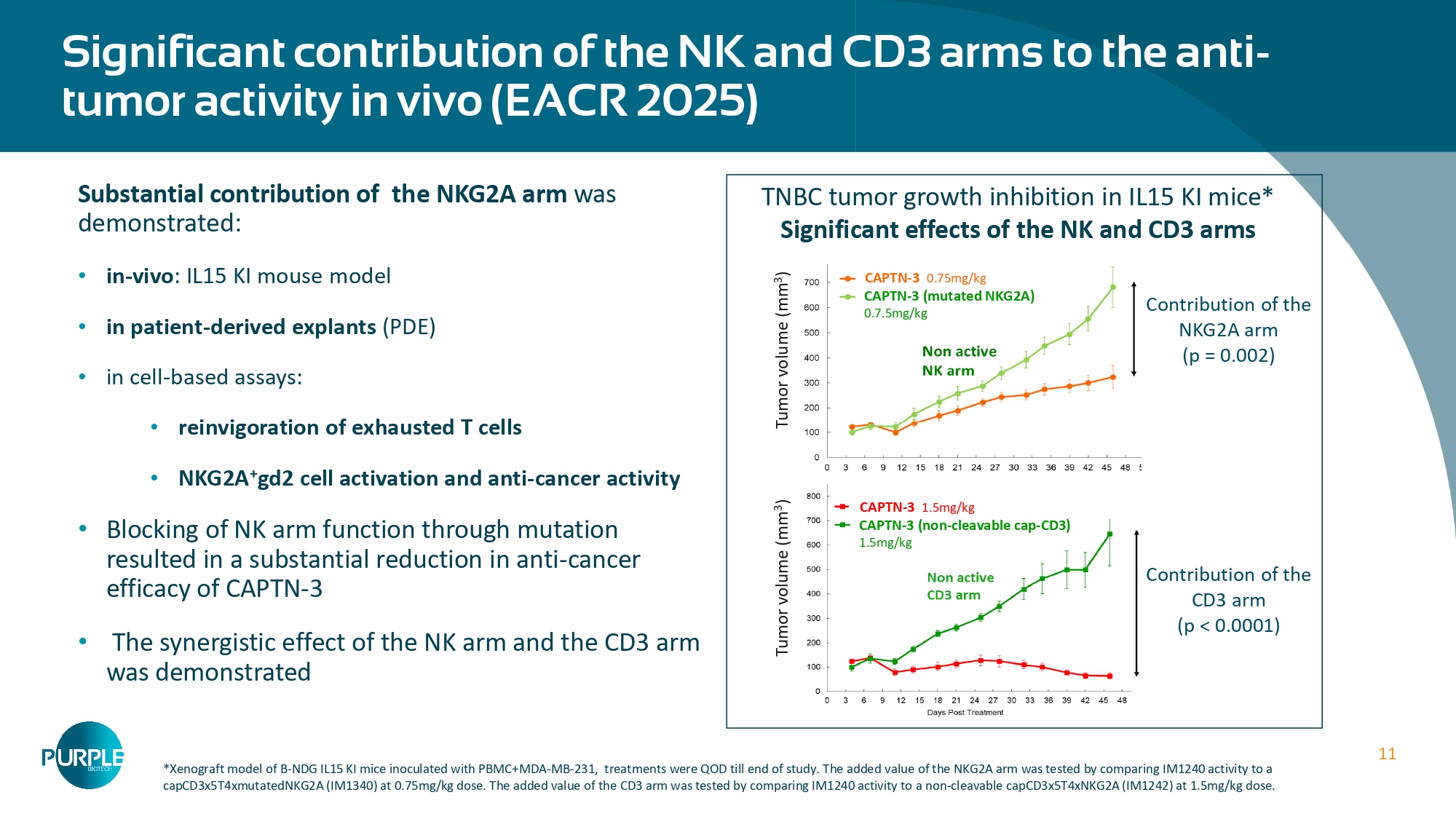
(nM) 1 60 40 20 0 80 100 ProTribody + MMP9 ProTribody (no proteases) CAPTN - 3 (no proteases) CAPTN - 3+MMP9 TriBody 11 Substantial contribution of the NKG2A arm was demonstrated: • in - vivo : IL15 KI mouse model • in patient - derived explants (PDE) • in cell - based assays: • reinvigoration of exhausted T cells • NKG2A + gd2 cell activation and anti - cancer activity • Blocking of NK arm function through mutation resulted in a substantial reduction in anti - cancer efficacy of CAPTN - 3 • The synergistic effect of the NK arm and the CD3 arm was demonstrated Significant contribution of the NK and CD3 arms to the anti - tumor activity in vivo (EACR 2025) TNBC tumor growth inhibition in IL15 KI mice* Significant effects of the NK and CD3 arms Contribution of the NKG2A arm (p = 0.002) Contribution of the CD3 arm (p < 0.0001) Tumor volume (mm 3 ) Tumor volume (mm 3 ) CAPTN - 3 1.5mg/kg CAPTN - 3 (non - cleavable cap - CD3) 1.5mg/kg CAPTN - 3 0.75mg/kg CAPTN - 3 (mutated NKG2A) 0.7.5mg/kg *Xenograft model of B - NDG IL15 KI mice inoculated with PBMC+MDA - MB - 231, treatments were QOD till end of study. The added value of the NKG2A arm was tested by comparing IM1240 activity to a capCD3x5T4xmutatedNKG2A (IM1340) at 0.75mg/kg dose. The added value of the CD3 arm was tested by comparing IM1240 activity to a non - cleavable capCD3x5T4xNKG2A (IM1242) at 1.5mg/kg dose.
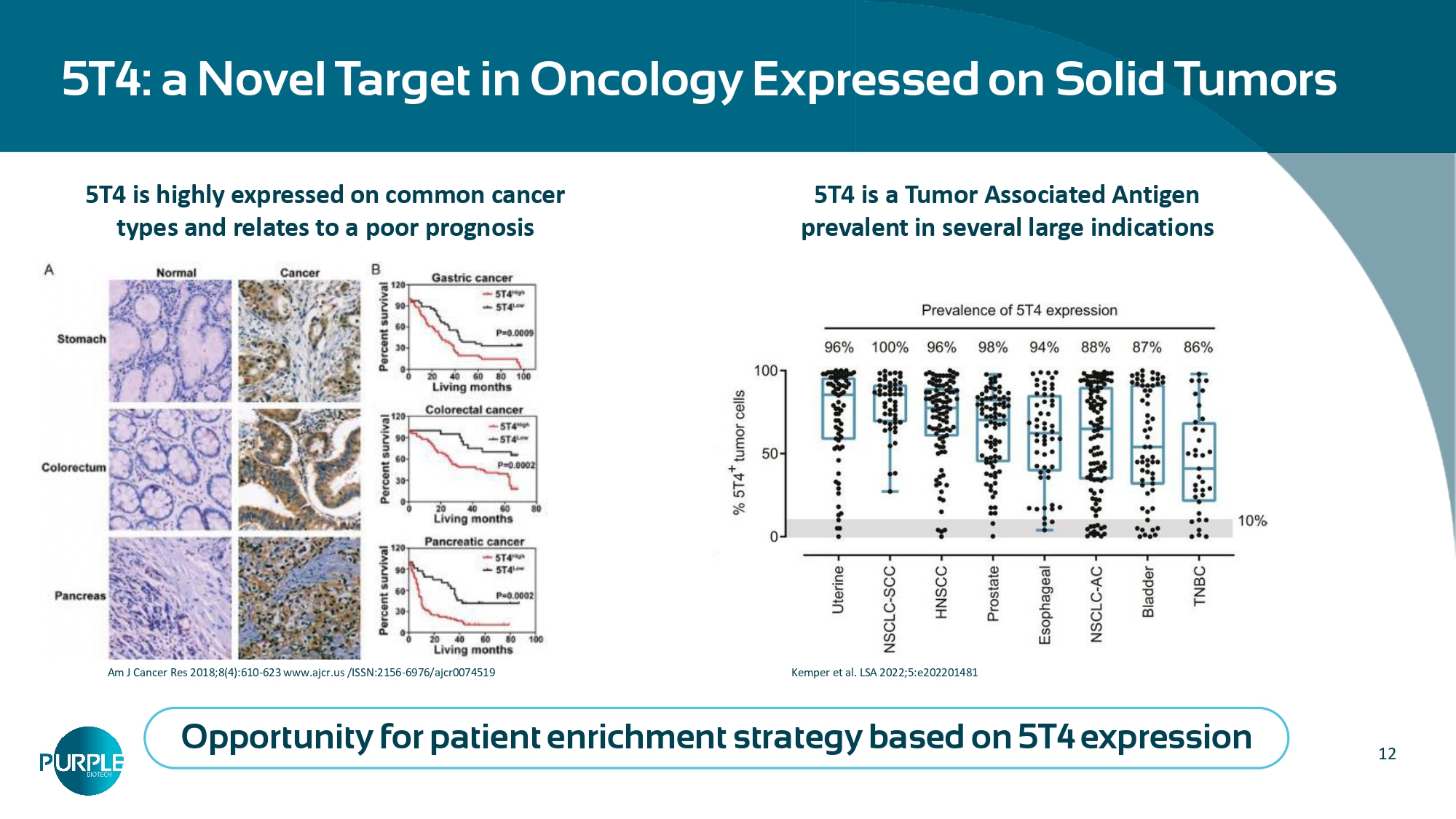
12 5T4: a Novel Target in Oncology Expressed on Solid Tumors 5T4 is highly expressed on common cancer types and relates to a poor prognosis Am J Cancer Res 2018;8(4):610 - 623 www.ajcr.us /ISSN:2156 - 6976/ajcr0074519 5T4 is a Tumor Associated Antigen prevalent in several large indications Opportunity for patient enrichment strategy based on 5T4 expression Kemper et al. LSA 2022;5:e202201481 *TNBC MDA - MB - 231 cells were s.c.
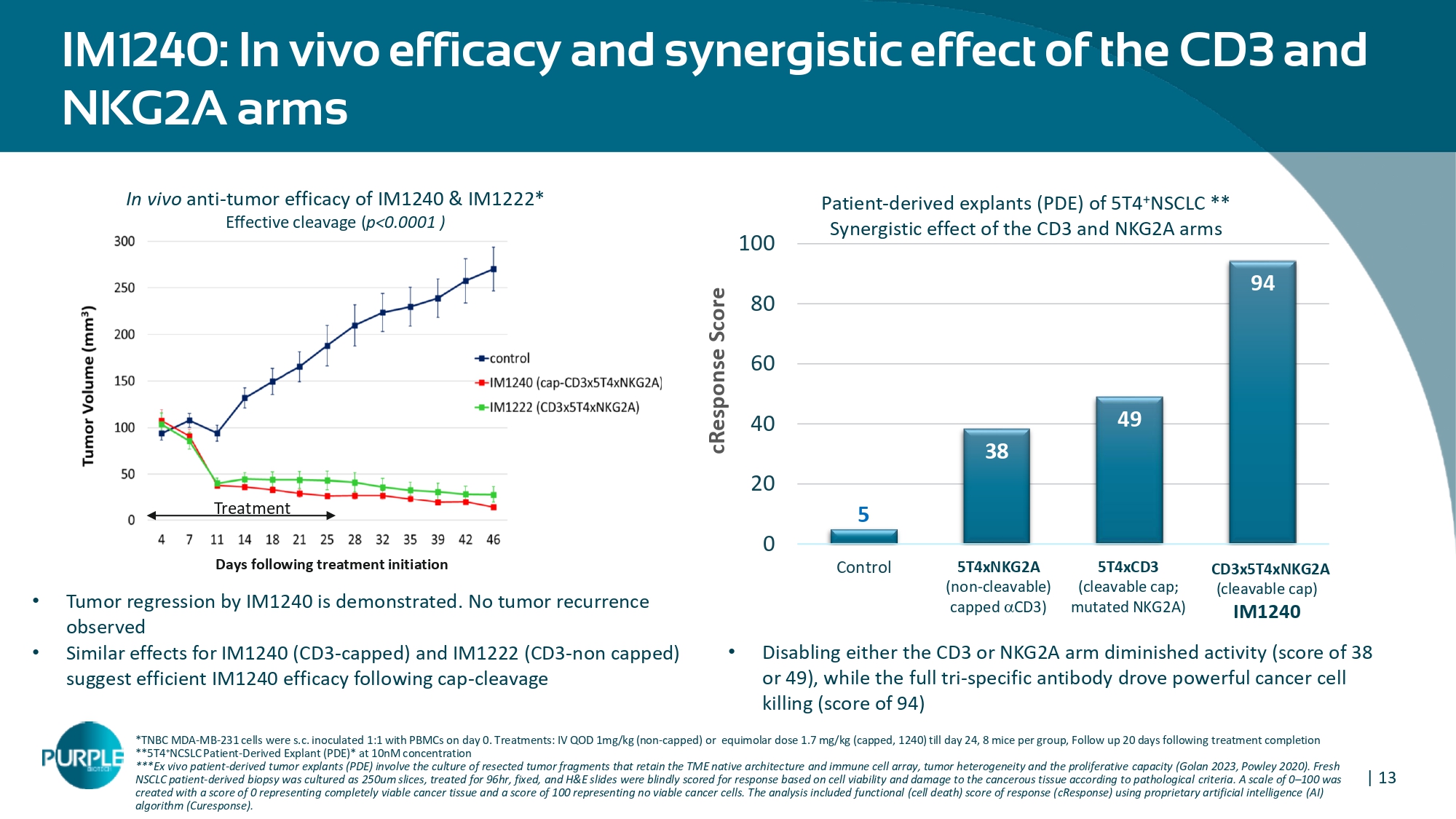
inoculated 1:1 with PBMCs on day 0. Treatments: IV QOD 1mg/kg (non - capped) or equimolar dose 1.7 mg/kg (capped, 1240) till day 24, 8 mice per group, Follow up 20 days following treatment completion **5T4 + NCSLC Patient - Derived Explant (PDE)* at 10nM concentration ***Ex vivo patient - derived tumor explants (PDE) involve the culture of resected tumor fragments that retain the TME native architecture and immune cell array, tumor heterogeneity and the proliferative capacity (Golan 2023, Powley 2020). Fresh NSCLC patient - derived biopsy was cultured as 250um slices, treated for 96hr, fixed, and H&E slides were blindly scored for response based on cell viability and damage to the cancerous tissue according to pathological criteria. A scale of 0 – 100 was | 13 created with a score of 0 representing completely viable cancer tissue and a score of 100 representing no viable cancer cells. The analysis included functional (cell death) score of response (cResponse) using proprietary artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm (Curesponse). 5 38 49 94 0 20 40 60 80 100 Control IM1242 IM1340 IM1240 cResponse Score CD3x5T4xNKG2A (cleavable cap) IM1240 5T4xNKG2A (non - cleavable) capped CD3) 5T4xCD3 (cleavable cap; mutated NKG2A) Patient - derived explants (PDE) of 5T4 + NSCLC ** Synergistic effect of the CD3 and NKG2A arms IM1240: In vivo efficacy and synergistic effect of the CD3 and NKG2A arms Days following treatment initiation Treatment In vivo anti - tumor efficacy of IM1240 & IM1222* Effective cleavage ( p<0.0001 ) • Tumor regression by IM1240 is demonstrated. No tumor recurrence observed • Similar effects for IM1240 (CD3 - capped) and IM1222 (CD3 - non capped) suggest efficient IM1240 efficacy following cap - cleavage • Disabling either the CD3 or NKG2A arm diminished activity (score of 38 or 49), while the full tri - specific antibody drove powerful cancer cell killing (score of 94)
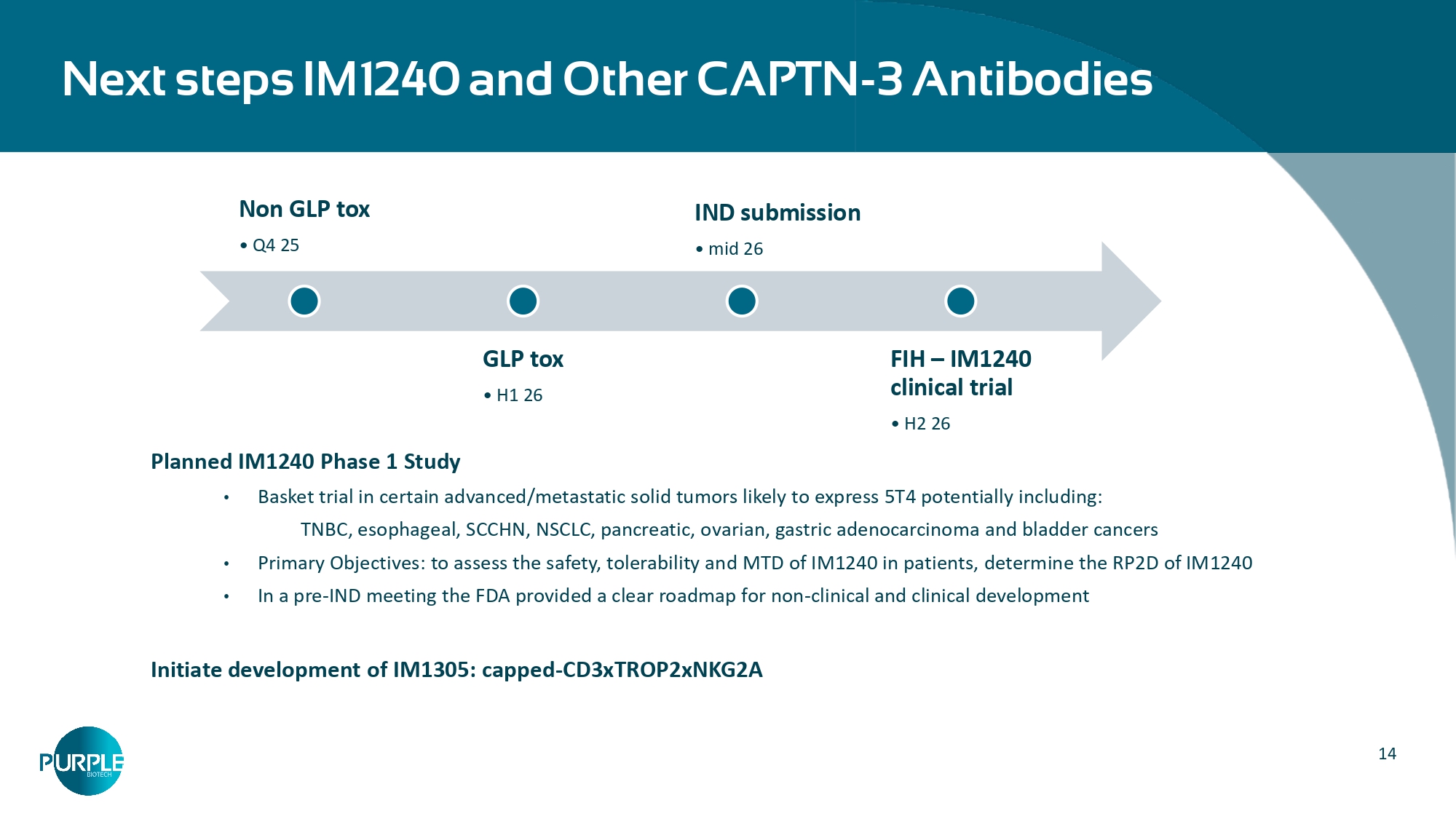
14 Next steps IM1240 and Other CAPTN - 3 Antibodies Non GLP tox • Q4 25 GLP tox • H1 26 IND submission • mid 26 FIH – IM1240 clinical trial • H2 26 Planned IM1240 Phase 1 Study • Basket trial in certain advanced/metastatic solid tumors likely to express 5T4 potentially including: TNBC, esophageal, SCCHN, NSCLC, pancreatic, ovarian, gastric adenocarcinoma and bladder cancers • Primary Objectives: to assess the safety, tolerability and MTD of IM1240 in patients, determine the RP2D of IM1240 • In a pre - IND meeting the FDA provided a clear roadmap for non - clinical and clinical development Initiate development of IM1305: capped - CD3xTROP2xNKG2A CM24: an α - CEACAM1* mAb Significant opportunity in multiple large indications with unmet medical need Clinical POC achieved in PDAC *Carcinoembryonic Antigen Cell Adhesion Molecule

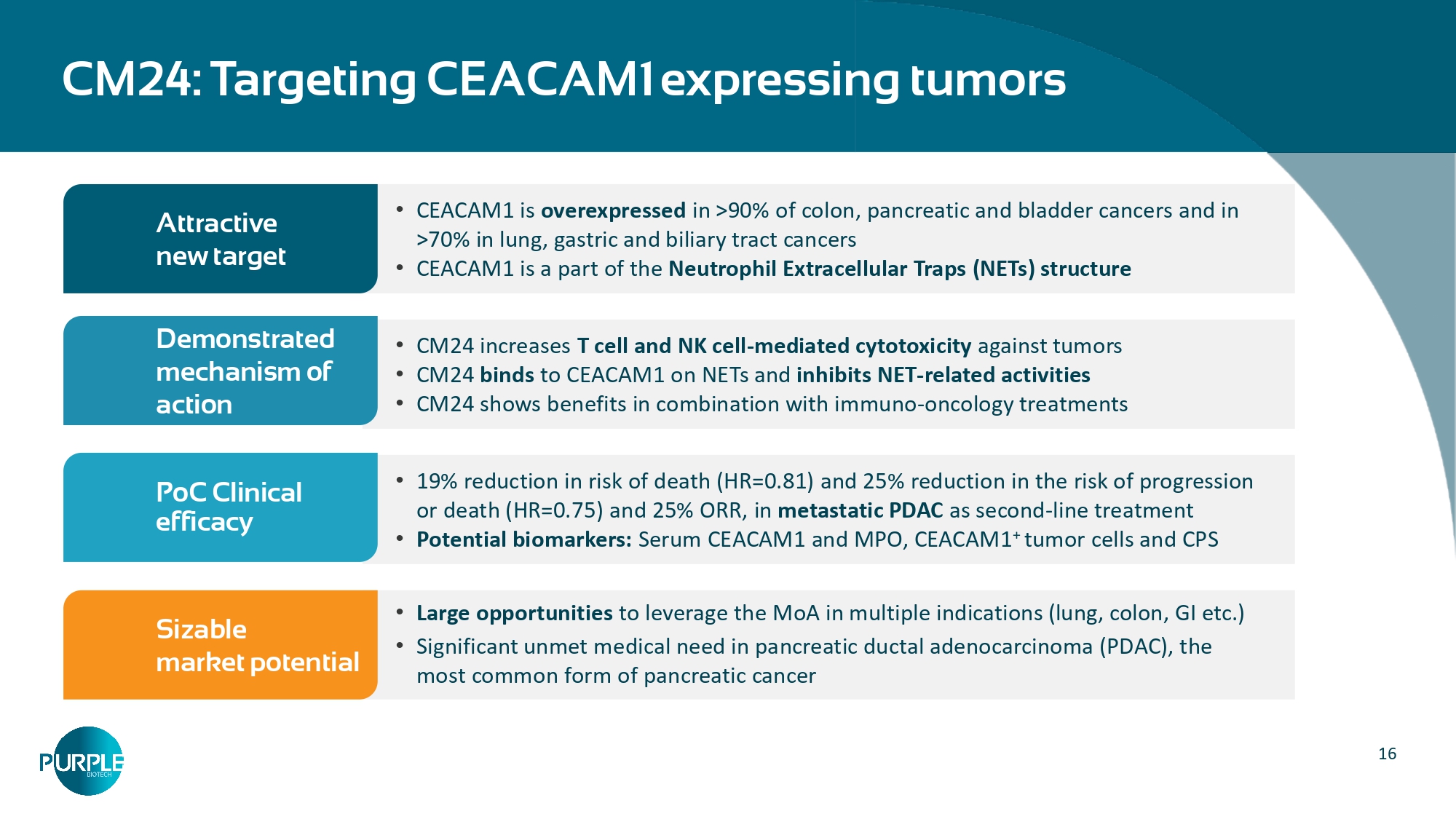
16 CM24: Targeting CEACAM1 expressing tumors • CEACAM1 is overexpressed in >90% of colon, pancreatic and bladder cancers and in >70% in lung, gastric and biliary tract cancers • CEACAM1 is a part of the Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) structure Attractive new target • CM24 increases T cell and NK cell - mediated cytotoxicity against tumors • CM24 binds to CEACAM1 on NETs and inhibits NET - related activities • CM24 shows benefits in combination with immuno - oncology treatments Demonstrated mechanism of action • 19% reduction in risk of death (HR=0.81) and 25% reduction in the risk of progression or death (HR=0.75) and 25% ORR, in metastatic PDAC as second - line treatment • Potential biomarkers: Serum CEACAM1 and MPO, CEACAM1 + tumor cells and CPS PoC Clinical efficacy • Large opportunities to leverage the MoA in multiple indications (lung, colon, GI etc.) • Significant unmet medical need in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), the most common form of pancreatic cancer Sizable market potential 17 CM24: Immune modulation of CEACAM1 expressing TMEs Markel et al, J Immunol 2002, 2006; Immunology, 2008; Cancer Immunol Immunother 2010; Ortenberg et al, Mol Cancer Ther 2012; Zhou, 2009; Li, 2013; Huang, 2015; Acharya N, et al.
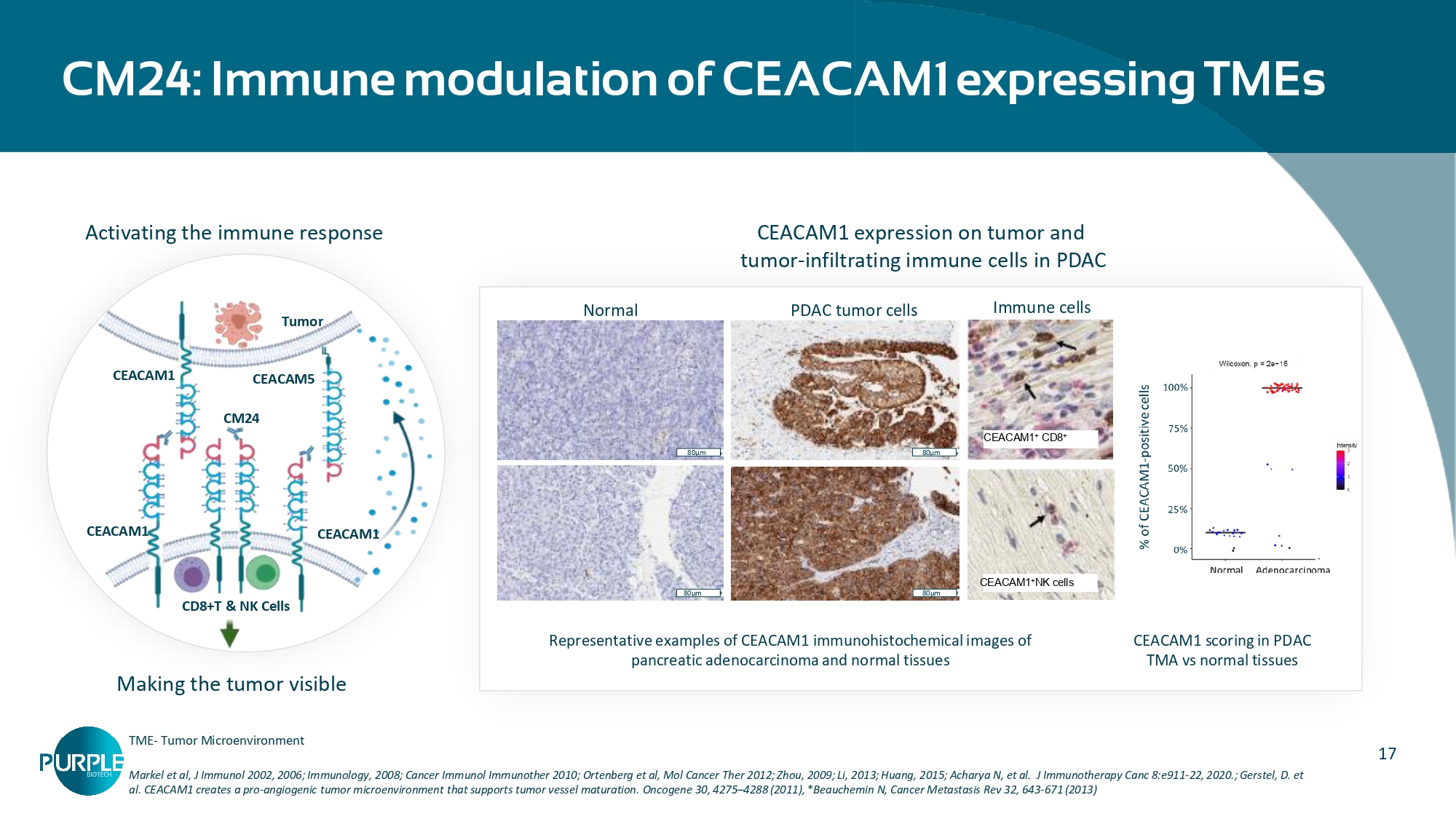
J Immunotherapy Canc 8:e911 - 22, 2020.; Gerstel, D. et al. CEACAM1 creates a pro - angiogenic tumor microenvironment that supports tumor vessel maturation. Oncogene 30, 4275 – 4288 (2011), * Beauchemin N, Cancer Metastasis Rev 32, 643 - 671 (2013) CEACAM1 expression on tumor and tumor - infiltrating immune cells in PDAC CEACAM1 scoring in PDAC TMA vs normal tissues Representative examples of CEACAM1 immunohistochemical images of pancreatic adenocarcinoma and normal tissues PDAC tumor cells Normal 80µm 80µm 80µm 80µm CEACAM1 + CD8 + CEACAM1 + NK cells Immune cells Tumor CD8+T & NK Cells CEACAM1 CEACAM1 CEACAM1 CEACAM5 CM24 Activating the immune response Making the tumor visible TME - Tumor Microenvironment 18 CM24 CCAM1 CM24 CCAM1 CM24 CM24 blocks NET - related activities by CEACAM1 inhibition (adapted from ‘Chen, Q et al.
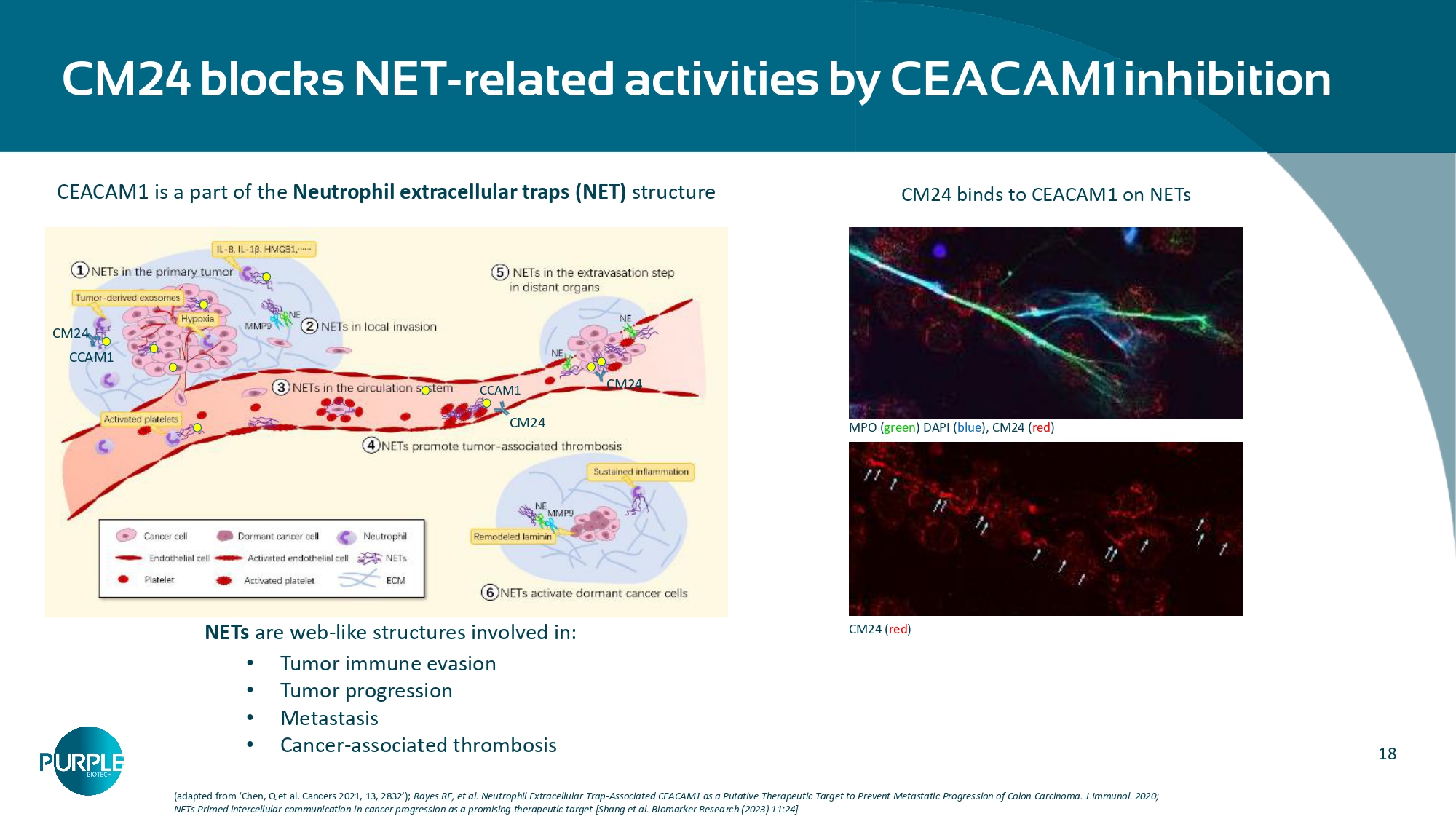
Cancers 2021, 13, 2832’); Rayes RF, et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Trap - Associated CEACAM1 as a Putative Therapeutic Target to Prevent Metastatic Progression of Colon Carcinoma. J Immunol. 2020; NETs Primed intercellular communication in cancer progression as a promising therapeutic target [Shang et al. Biomarker Research (2023) 11:24] CEACAM1 is a part of the Neutrophil extracellular traps (NET) structure MPO ( green ) DAPI ( blue ), CM24 ( red ) CM24 ( red ) CM24 binds to CEACAM1 on NETs NETs are web - like structures involved in: • Tumor immune evasion • Tumor progression • Metastasis • Cancer - associated thrombosis 19 Large market opportunity based on CEACAM1 expression in PDAC 1.https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html , 2.
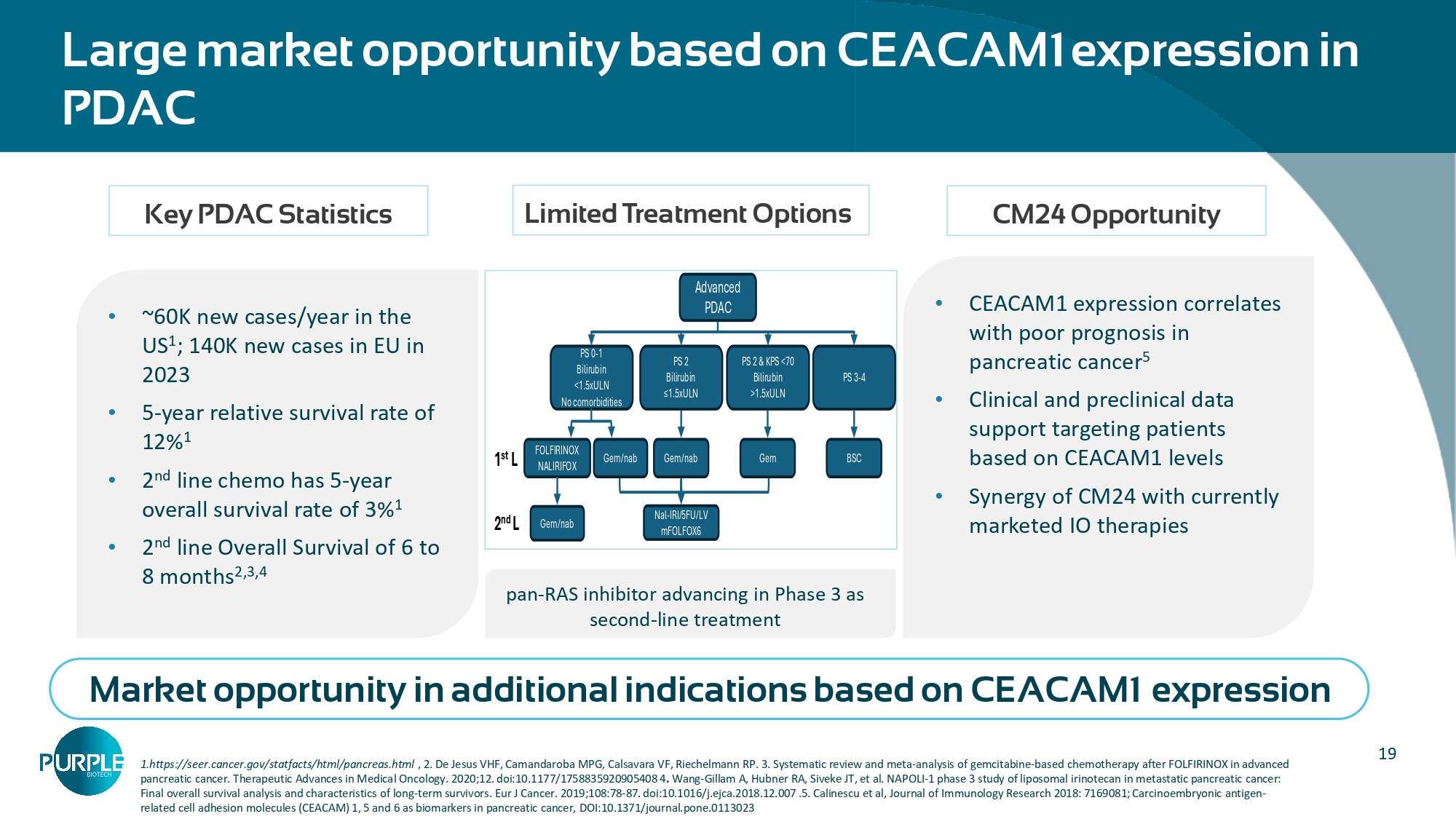
De Jesus VHF, Camandaroba MPG, Calsavara VF, Riechelmann RP. 3. Systematic review and meta - analysis of gemcitabine - based chemotherapy after FOLFIRINOX in advanced pancreatic cancer. Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology. 2020;12. doi:10.1177/1758835920905408 4 . Wang - Gillam A, Hubner RA, Siveke JT, et al. NAPOLI - 1 phase 3 study of liposomal irinotecan in metastatic pancreatic cancer: Final overall survival analysis and characteristics of long - term survivors. Eur J Cancer. 2019;108:78 - 87. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2018.12.007 .5. Calinescu et al, Journal of Immunology Research 2018: 7169081; Carcinoembryonic antigen - related cell adhesion molecules (CEACAM) 1, 5 and 6 as biomarkers in pancreatic cancer, DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0113023 • ~60K new cases/year in the US 1 ; 140K new cases in EU in 2023 • 5 - year relative survival rate of 12% 1 • 2 nd line chemo has 5 - year overall survival rate of 3% 1 • 2 nd line Overall Survival of 6 to 8 months 2,3,4 • CEACAM1 expression correlates with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer 5 • Clinical and preclinical data support targeting patients based on CEACAM1 levels • Synergy of CM24 with currently marketed IO therapies Key PDAC Statistics Limited Treatment Options CM24 Opportunity Market opportunity in additional indications based on CEACAM1 expression pan - RAS inhibitor advancing in Phase 3 as second - line treatment Advanced PDAC PS 0 - 1 Bilirubin <1.5xULN No comorbidities PS 2 Bilirubin ≤1.5xULN PS 2 C KPS <70 Bilirubin >1.5xULN PS 3 - 4 FOLFIRINOX NALIRIFOX Nal - IRI/5FU/LV mFOLFOX6 Gem/nab Gem/nab Gem BSC Gem/nab 1 st L 2 nd L 20 A randomized Bayesian study of CM24 in combination with nivolumab plus SoC chemotherapy in 2 nd line PDAC patients* Primary endpoint : OS Secondary endpoints: PFS, ORR, DCR OS rate @ 6 & 12 months, PFS rate @ 3 & 6 months Completed Randomized Phase 2 Combination Study (NCT04731467) Experimental arm CM24 + nivolumab & Nal - IRI/5FU/LV n=16 Control arm Nal - IRI/5FU/LV n=15 PDAC patients progressing on or after 1 st line standard of care chemotherapy Randomized n=31 1:1 *The other part of the study with gemcitabine/nab - paclitaxel regimen (n=32) was affected by informative censoring hence non interpretable Safety - well tolerated Exploratory biomarkers : Serum & tumor CEACAM1, NET marker (Myeloperoxidase - MPO), PDL1 Demographics and patient characteristics (ITT)

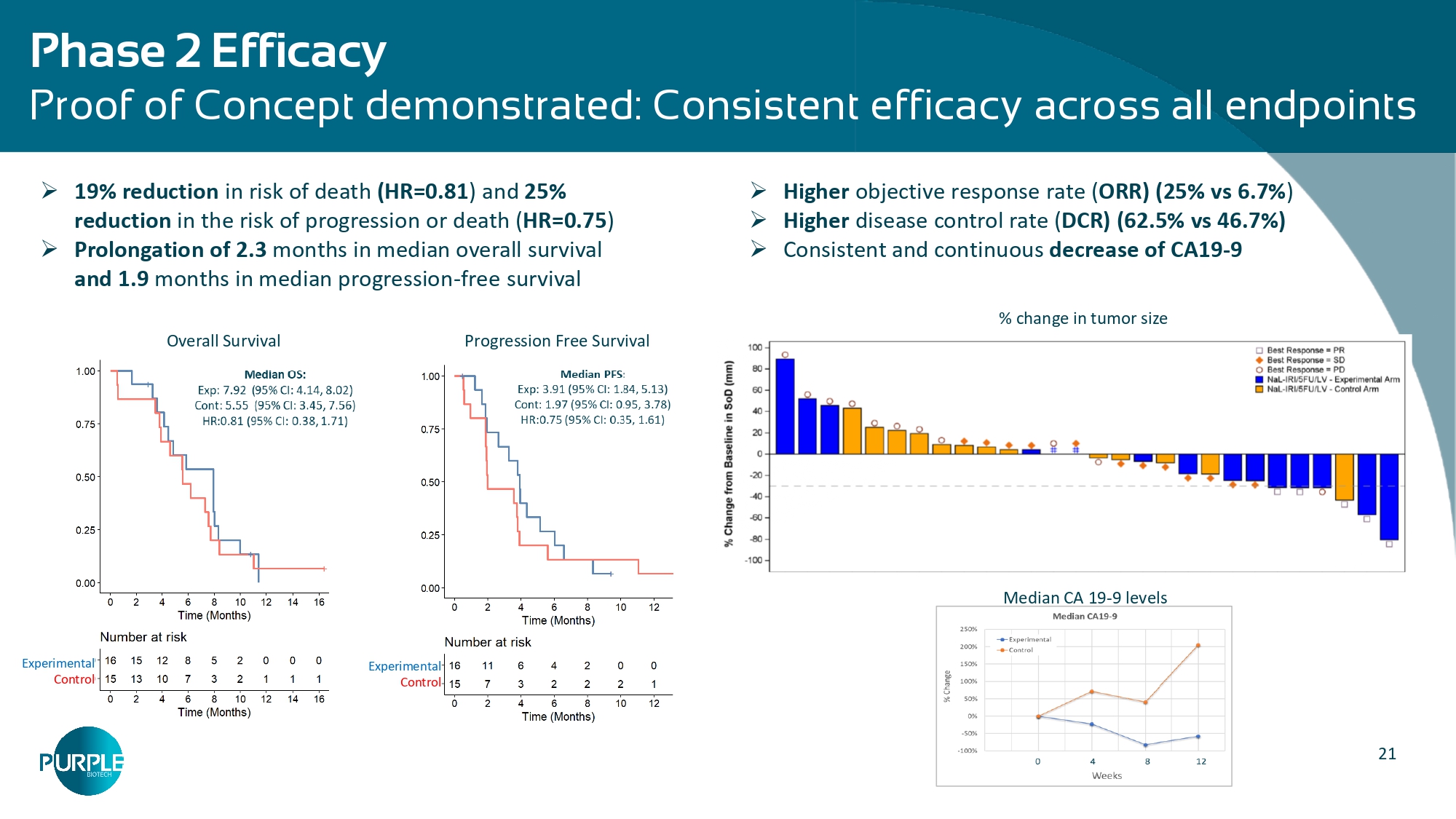
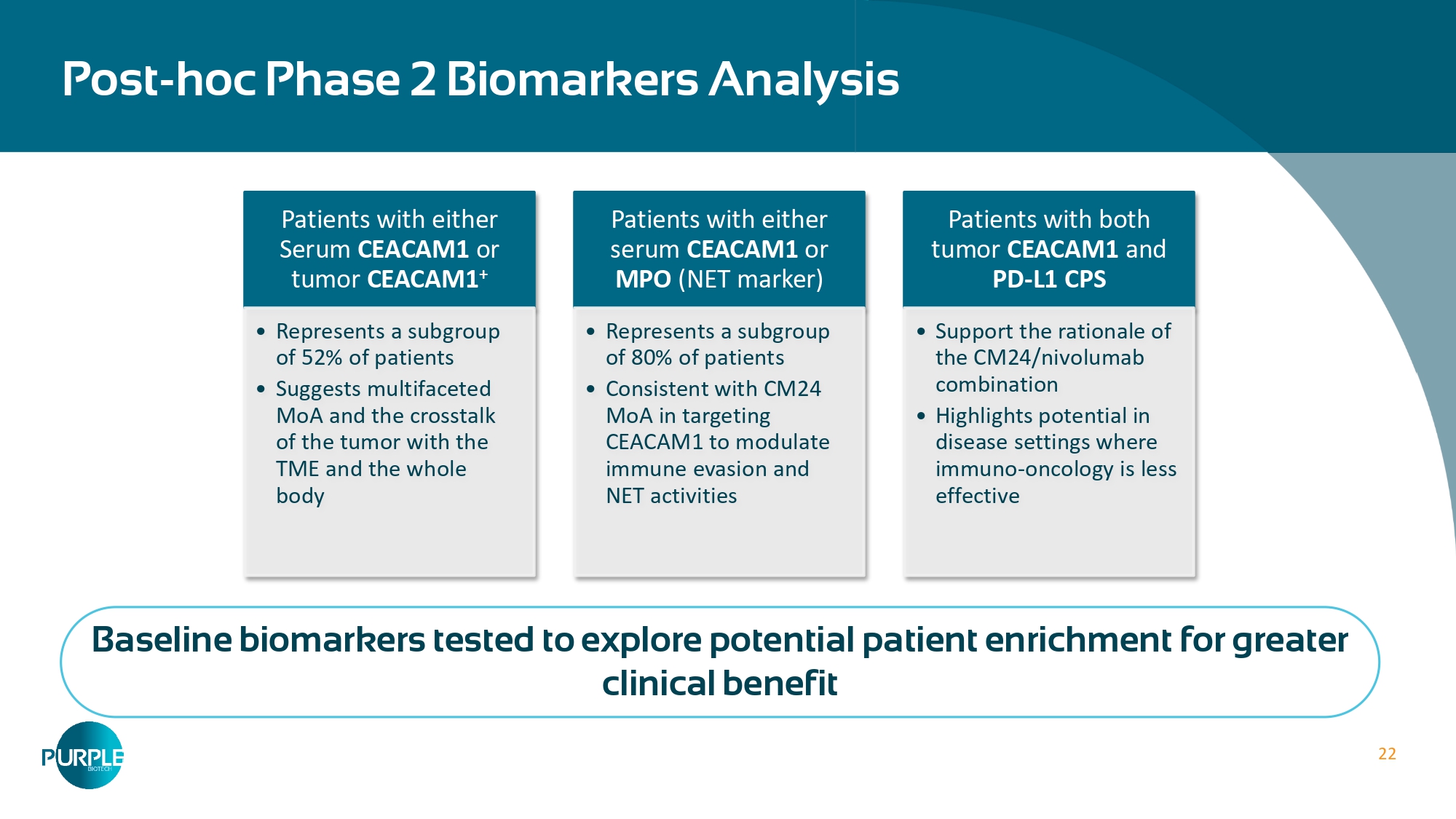
21 Phase 2 Efficacy Proof of Concept demonstrated: Consistent efficacy across all endpoints » Higher objective response rate ( ORR) (25% vs 6.7% ) » Higher disease control rate ( DCR) (62.5% vs 46.7%) » Consistent and continuous decrease of CA19 - 9 Median CA 19 - 9 levels % change in tumor size » 19% reduction in risk of death (HR=0.81 ) and 25% reduction in the risk of progression or death ( HR=0.75 ) » Prolongation of 2.3 months in median overall survival and 1.9 months in median progression - free survival Overall Survival Progression Free Survival Experimental Control Experimental Control 22 Post - hoc Phase 2 Biomarkers Analysis Patients with either Serum CEACAM 1 or tumor CEACAM 1 + • Represents a subgroup of 52% of patients • Suggests multifaceted MoA and the crosstalk of the tumor with the TME and the whole body Patients with either serum CEACAM 1 or MPO (NET marker) • Represents a subgroup of 80% of patients • Consistent with CM24 MoA in targeting CEACAM1 to modulate immune evasion and NET activities Patients with both tumor CEACAM1 and PD - L1 CPS • Support the rationale of the CM24/nivolumab combination • Highlights potential in disease settings where immuno - oncology is less effective Baseline biomarkers tested to explore potential patient enrichment for greater clinical benefit
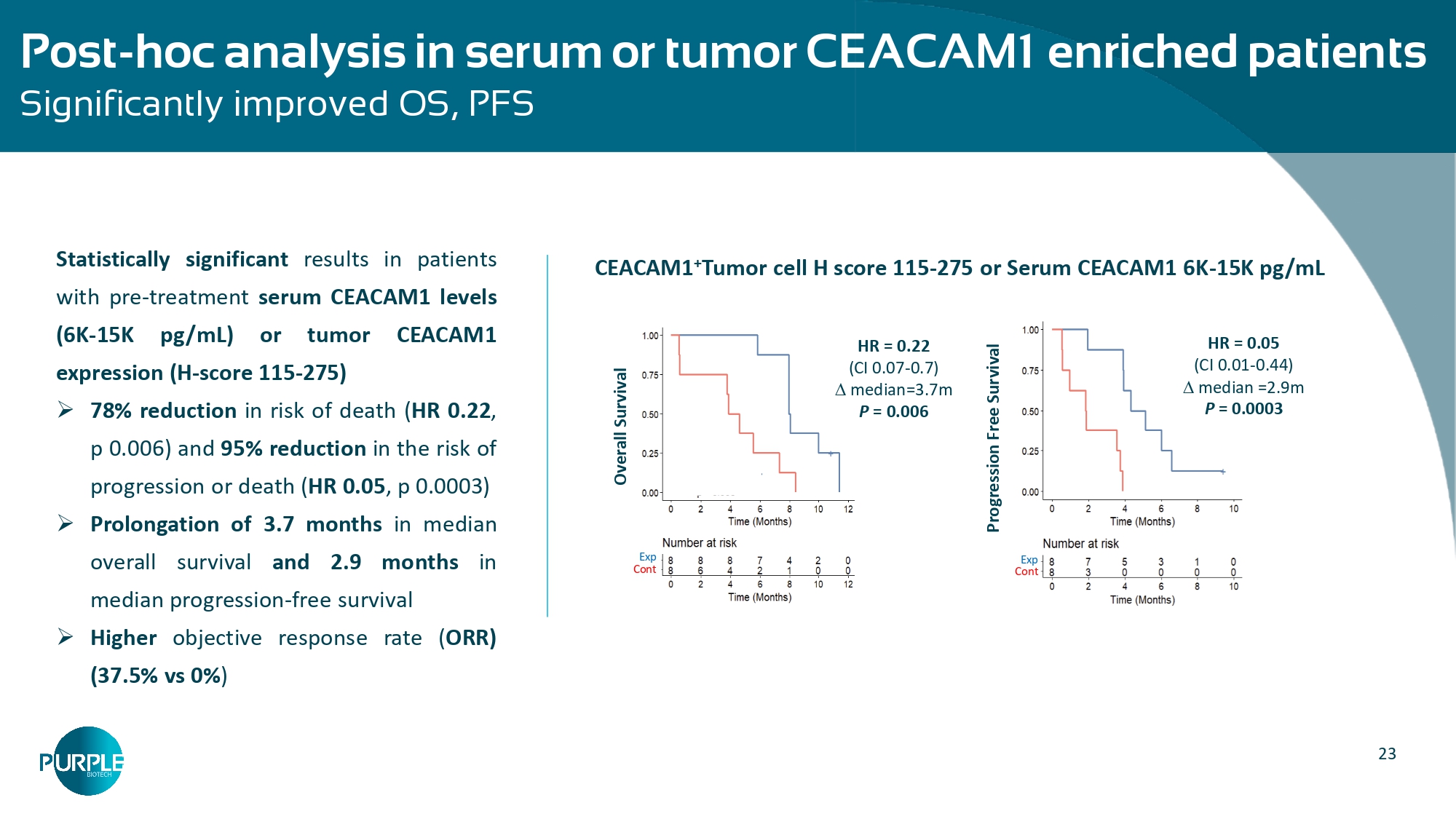
23 Post - hoc analysis in serum or tumor CEACAM1 enriched patients Significantly improved OS, PFS Statistically significant results in patients with pre - treatment serum CEACAM 1 levels ( 6 K - 15 K pg/mL) or tumor CEACAM 1 expression (H - score 115 - 275 ) » 78 % reduction in risk of death ( HR 0 . 22 , p 0 . 006 ) and 95 % reduction in the risk of progression or death ( HR 0 . 05 , p 0 . 0003 ) » Prolongation of 3 .
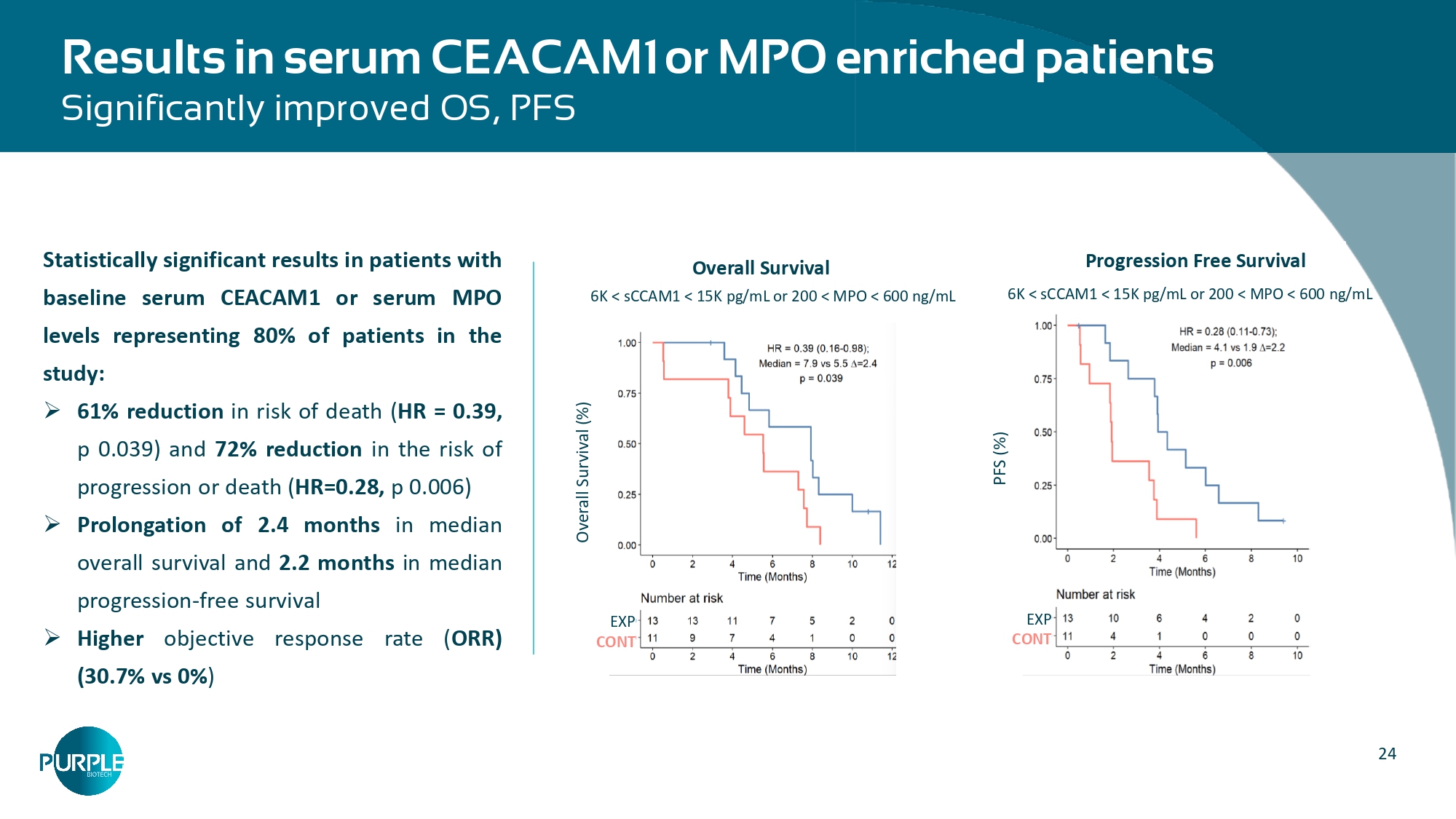
7 months in median overall survival and 2.9 months in median progression - free survival » Higher objective response rate ( ORR) (37.5% vs 0% ) CEACAM1 + Tumor cell H score 115 - 275 or Serum CEACAM1 6K - 15K pg/mL Overall Survival HR = 0.22 (CI 0.07 - 0.7) median=3.7m P = 0.006 Exp Cont Progression Free Survival HR = 0.05 (CI 0.01 - 0.44) median =2.9m P = 0.0003 Exp Cont 24 Results in serum CEACAM1 or MPO enriched patients Significantly improved OS, PFS PFS (%) EXP CONT Progression Free Survival 6K < sCCAM1 < 15K pg/mL or 200 < MPO < 600 ng/mL Overall Survival (%) EXP CONT Overall Survival 6K < sCCAM1 < 15K pg/mL or 200 < MPO < 600 ng/mL Statistically significant results in patients with baseline serum CEACAM 1 or serum MPO levels representing 80 % of patients in the study : » 61 % reduction in risk of death ( HR = 0 . 39 , p 0 . 039 ) and 72 % reduction in the risk of progression or death ( HR= 0 . 28 , p 0 . 006 ) » Prolongation of 2 . 4 months in median overall survival and 2 . 2 months in median progression - free survival » Higher objective response rate ( ORR) (30.7% vs 0% )
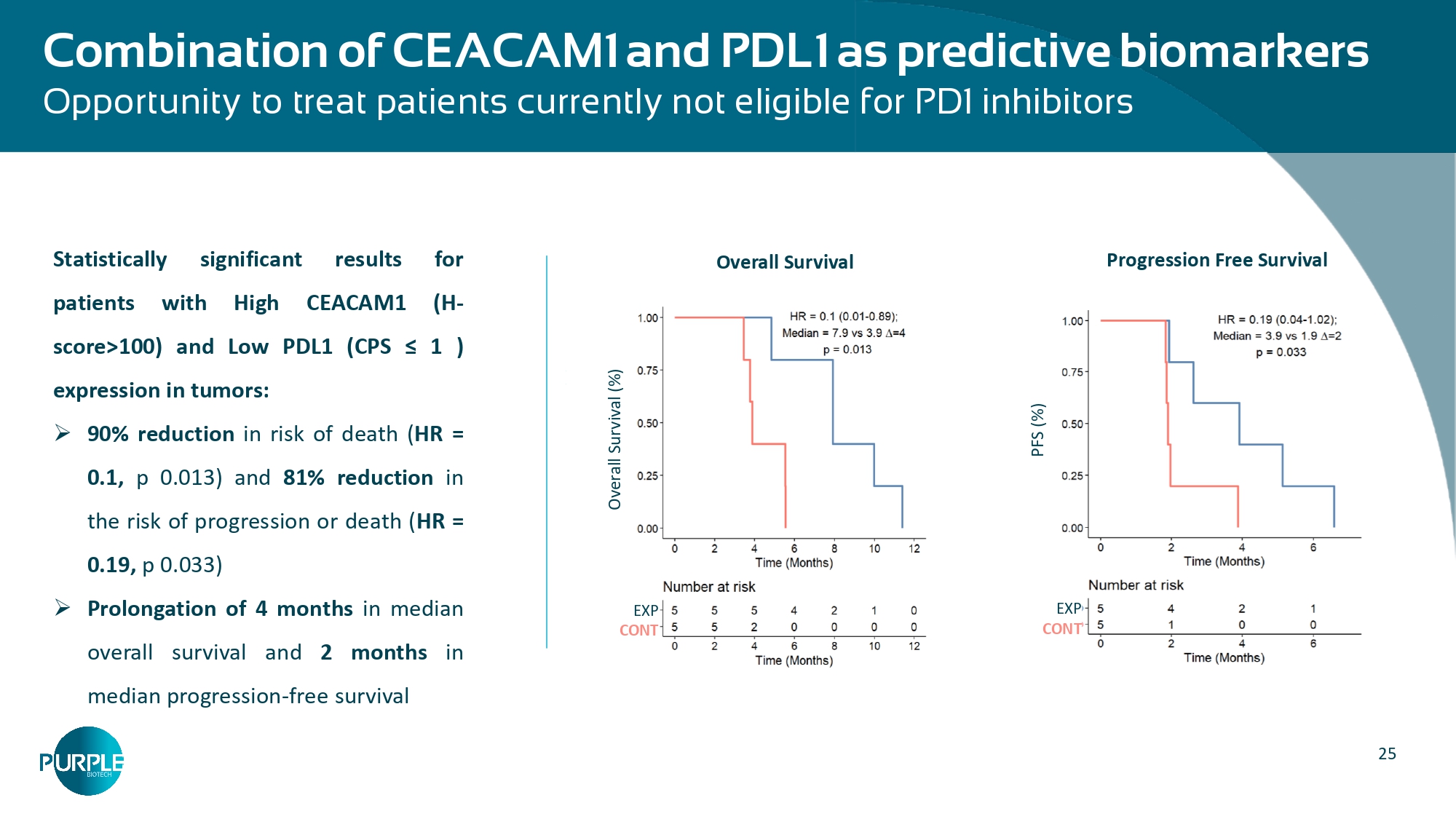
25 Combination of CEACAM1 and PDL1 as predictive biomarkers Opportunity to treat patients currently not eligible for PD1 inhibitors PFS (%) EXP CONT Overall Survival (%) EXP CONT Progression Free Survival Overall Survival Statistically significant patients with High results for CEACAM1 (H - score>100) and Low PDL1 (CPS ≤ 1 ) expression in tumors: » 90 % reduction in risk of death ( HR = 0 . 1 , p 0 . 013 ) and 81 % reduction in the risk of progression or death ( HR = 0 . 19 , p 0 .
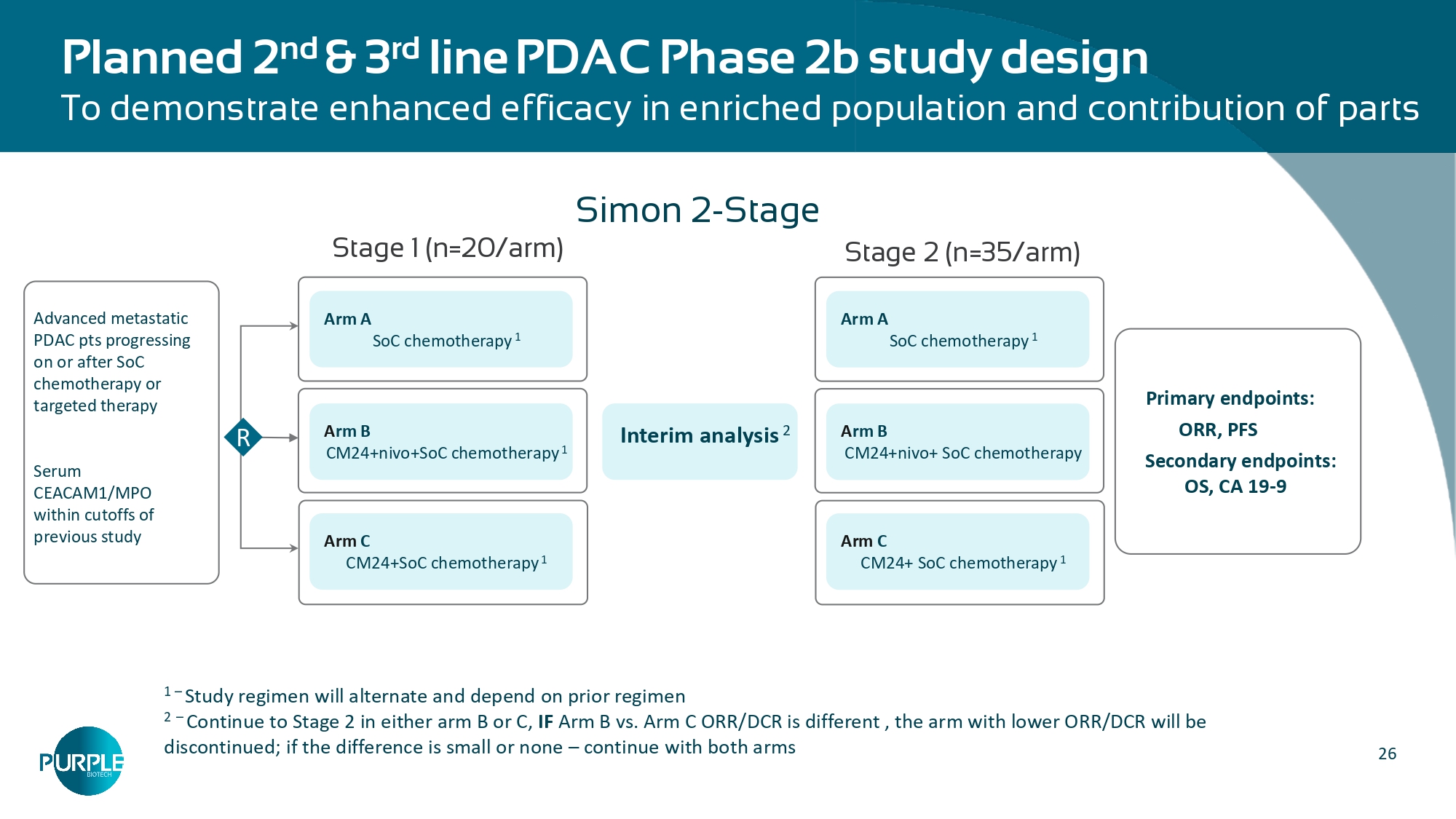
033 ) » Prolongation of 4 months in median overall survival and 2 months in median progression - free survival 26 Planned 2 nd & 3 rd line PDAC Phase 2b study design To demonstrate enhanced efficacy in enriched population and contribution of parts Advanced metastatic PDAC pts progressing on or after SoC chemotherapy or targeted therapy Serum CEACAM1/MPO within cutoffs of previous study Arm A SoC chemotherapy 1 Arm C CM24+SoC chemotherapy 1 Primary endpoints: ORR, PFS Secondary endpoints: OS, CA 19 - 9 R A rm B CM24+nivo+SoC chemotherapy 1 Arm A SoC chemotherapy 1 Arm C CM24+ SoC chemotherapy 1 A rm B CM24+nivo+ SoC chemotherapy Stage 1 (n=20/arm) Stage 2 (n=35/arm) 1 – Study regimen will alternate and depend on prior regimen 2 – Continue to Stage 2 in either arm B or C, IF Arm B vs. Arm C ORR/DCR is different , the arm with lower ORR/DCR will be discontinued; if the difference is small or none – continue with both arms Simon 2 - Stage Interim analysis 2 NT219: Small Molecule Degrader of IRS 1/2 and Blocker of STAT3 Recurrent/Metastatic Head & Neck Cancer (R/M SCCHN)

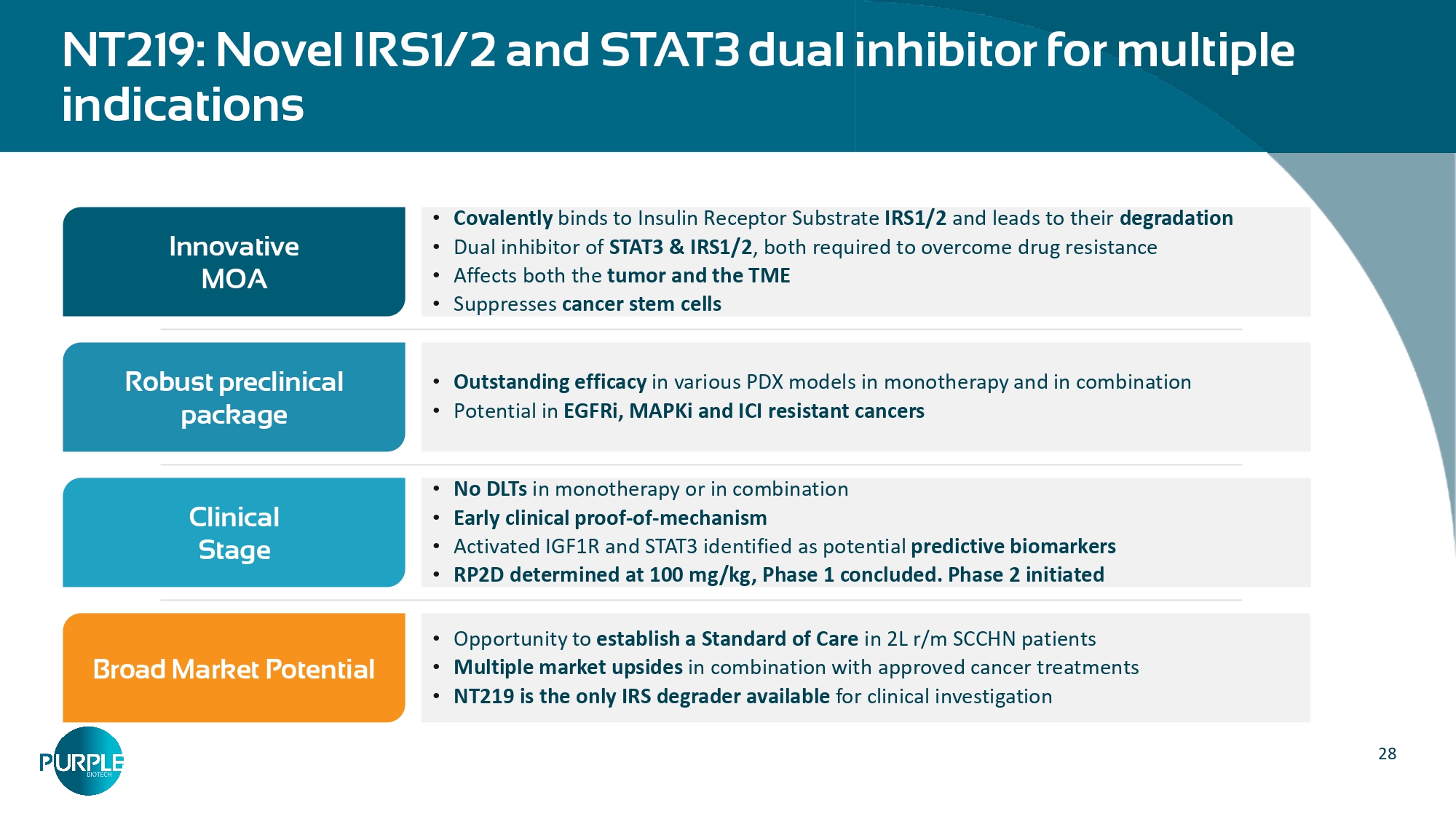
28 NT219: Novel IRS1/2 and STAT3 dual inhibitor for multiple indications • Covalently binds to Insulin Receptor Substrate IRS1/2 and leads to their degradation • Dual inhibitor of STAT3 & IRS1/2 , both required to overcome drug resistance • Affects both the tumor and the TME • Suppresses cancer stem cells Innovative MOA • Outstanding efficacy in various PDX models in monotherapy and in combination • Potential in EGFRi, MAPKi and ICI resistant cancers Robust preclinical package • No DLTs in monotherapy or in combination • Early clinical proof - of - mechanism • Activated IGF1R and STAT3 identified as potential predictive biomarkers • RP2D determined at 100 mg/kg, Phase 1 concluded.
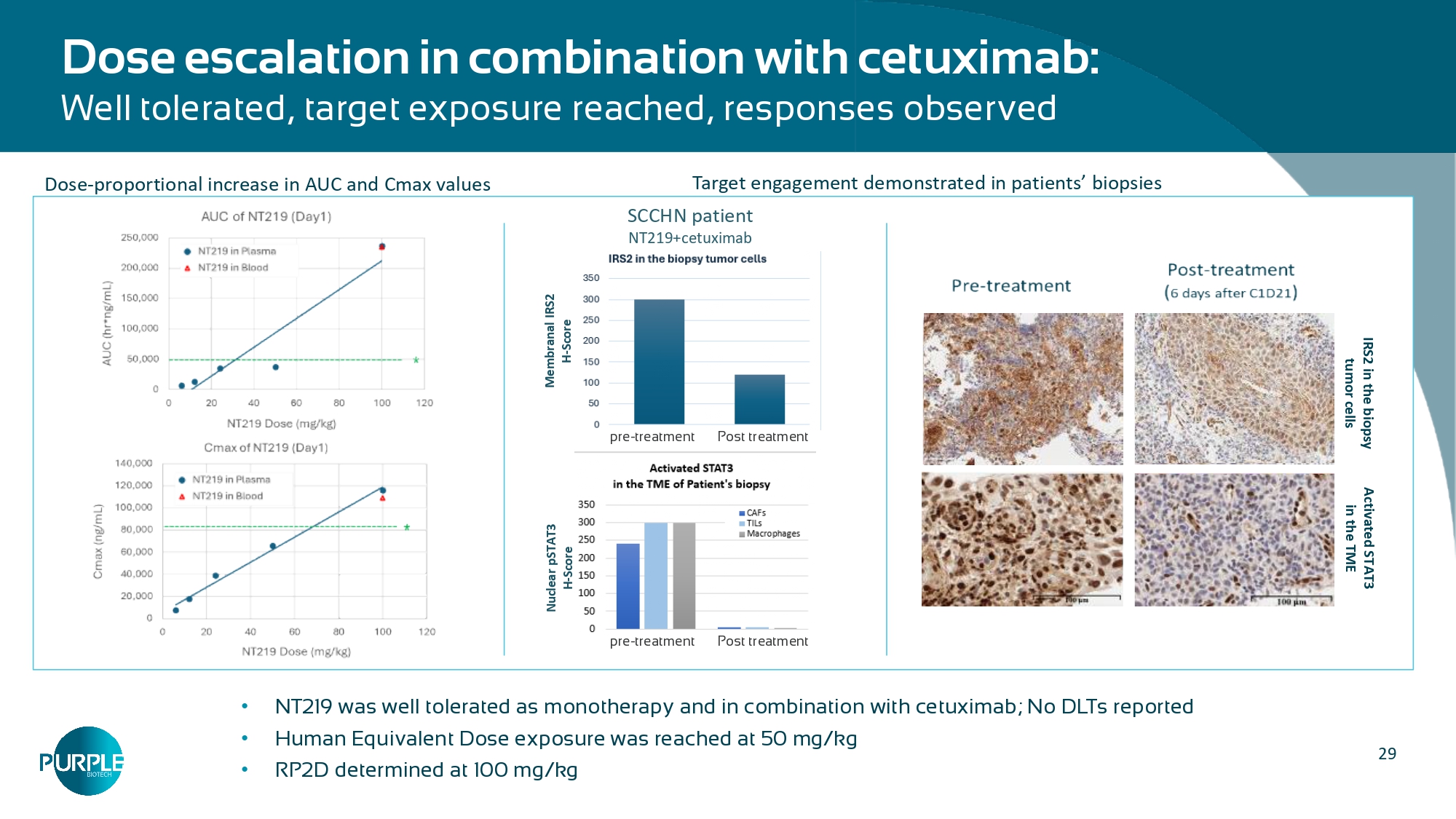
Phase 2 initiated Clinical Stage • Opportunity to establish a Standard of Care in 2L r/m SCCHN patients • Multiple market upsides in combination with approved cancer treatments • NT219 is the only IRS degrader available for clinical investigation Broad Market Potential 29 Dose escalation in combination with cetuximab: Well tolerated, target exposure reached, responses observed • NT219 was well tolerated as monotherapy and in combination with cetuximab; No DLTs reported • Human Equivalent Dose exposure was reached at 50 mg/kg • RP2D determined at 100 mg/kg IRS2 in the biopsy tumor cells Activated STAT3 in the TME Nuclear pSTAT3 H - Score Membranal IRS2 H - Score SCCHN patient NT219+cetuximab pre - treatment Post treatment pre - treatment Post treatment Target engagement demonstrated in patients’ biopsies Dose - proportional increase in AUC and Cmax values 30 Monotherapy efficacy: • 20 evaluable patients (all doses): 2 PR (confirmed - GEJ, unconfirmed - PDAC), 5 SD Efficacy overview of combination arm in SCCHN patients: • 16 evaluable patients (all doses 6, 12, 24, 50, 100 mg/kg) • Median follow - up of 9.4 months (95% CI: 3.4 - 10.0) • Out of 8 treated with active doses (50 and 100 mg/kg): • 2 confirmed PRs; 3 SD • ORR:25%, DCR: 62.5% Biomarker analysis at 50mg/kg dose of NT219 with cetuximab : • Significant differences in the activated pIGF1R and pSTAT3 were revealed in the 2 responders (PR) compared to the 2 non - responders (PD), verified in the 100mg/kg cohort.
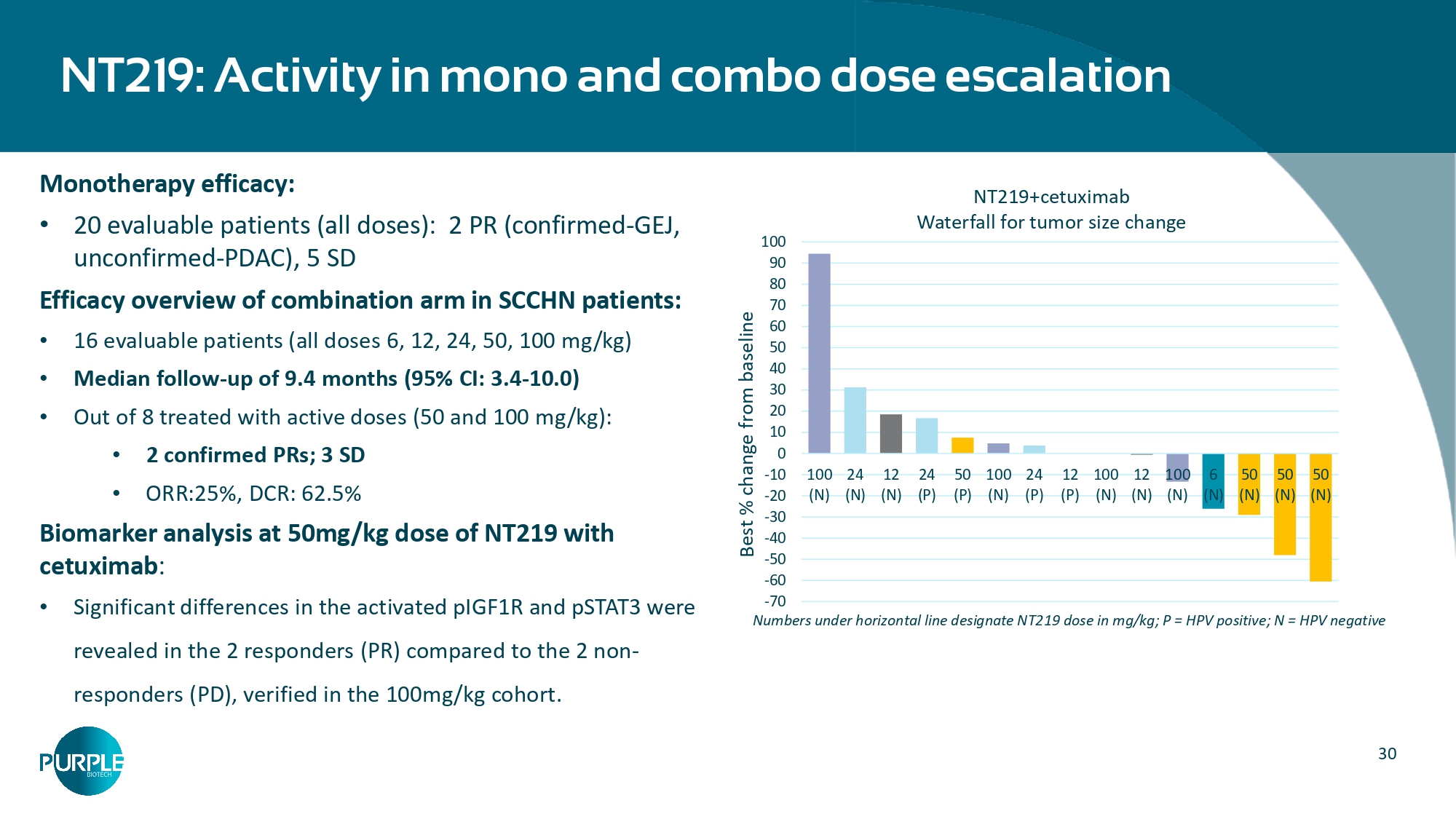
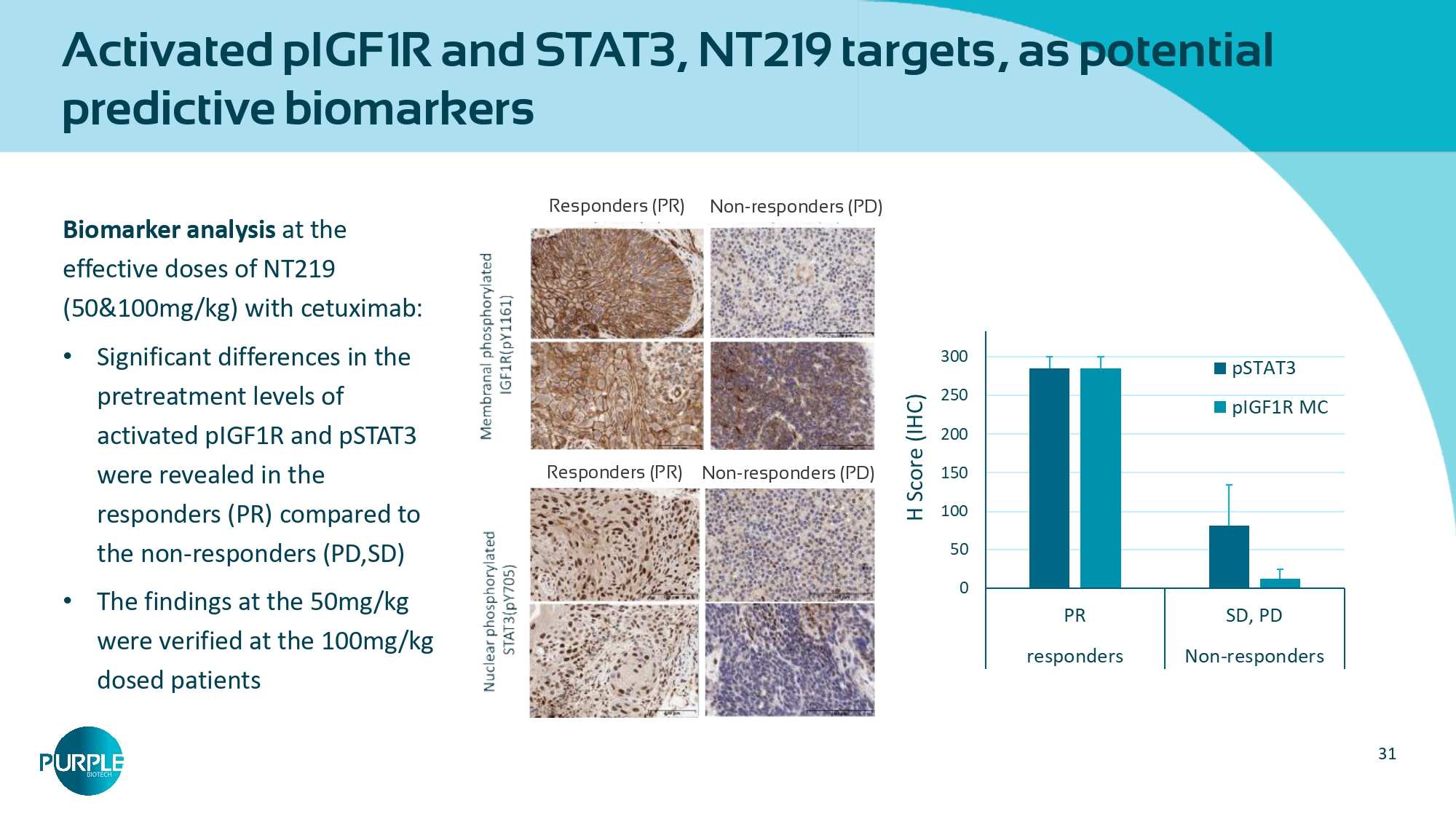
NT219: Activity in mono and combo dose escalation Numbers under horizontal line designate NT219 dose in mg/kg; P = HPV positive; N = HPV negative (N) (N) (N) (P) (P) (N) (P) (P) (N) (N) (N) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 - 10 100 24 12 24 50 100 24 12 100 12 100 6 50 50 50 - 20 (N) (N) (N) (N) - 30 - 40 - 50 - 60 - 70 Best % change from baseline NT219+cetuximab Waterfall for tumor size change 31 Activated pIGF1R and STAT3, NT219 targets, as potential predictive biomarkers Biomarker analysis at the effective doses of NT219 (50&100mg/kg) with cetuximab: • Significant differences in the pretreatment levels of activated pIGF1R and pSTAT3 were revealed in the responders (PR) compared to the non - responders (PD,SD) • The findings at the 50mg/kg were verified at the 100mg/kg dosed patients Responders (PR) Non - responders (PD) Responders (PR) Non - responders (PD)
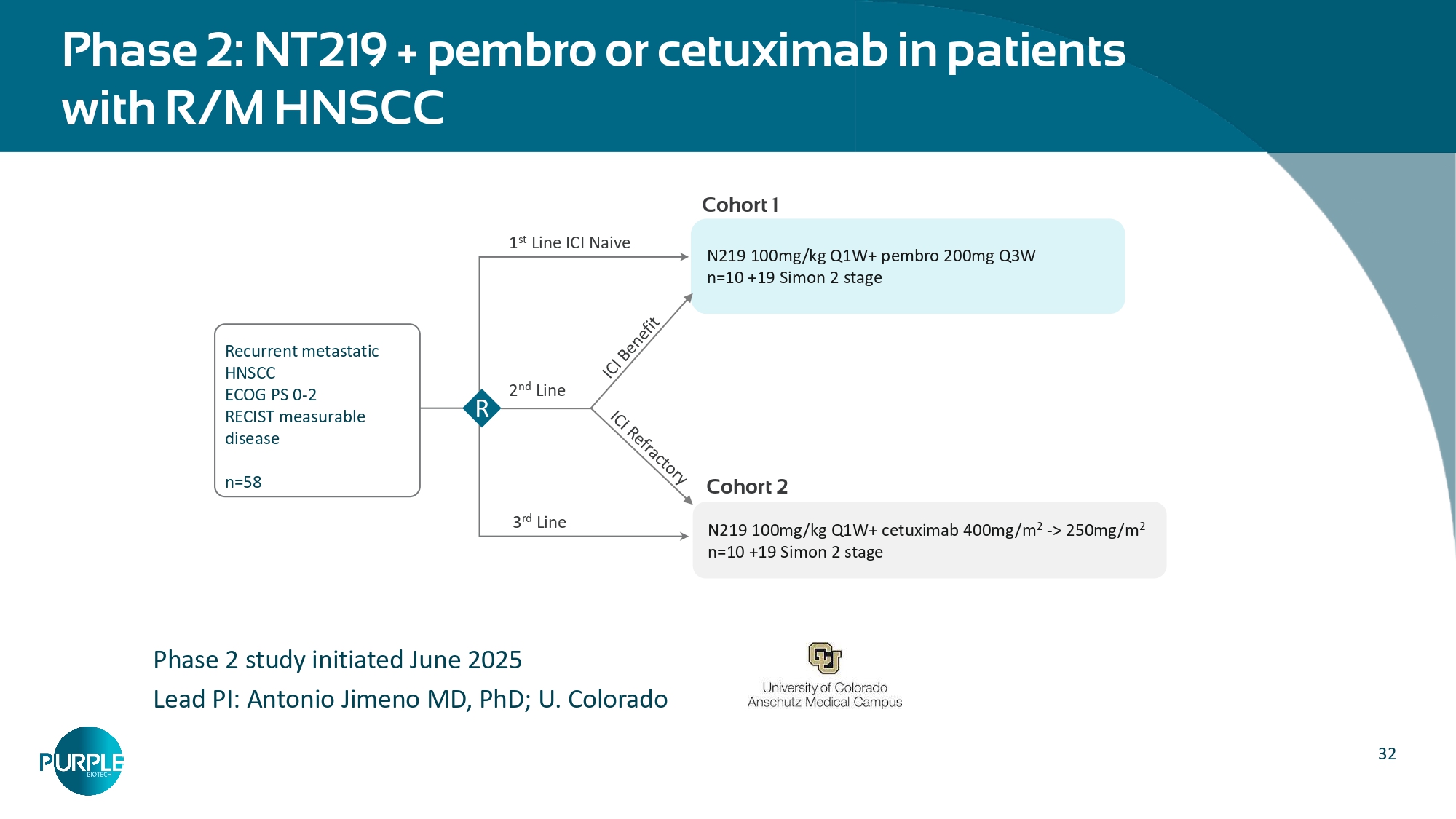
32 Phase 2: NT219 + pembro or cetuximab in patients with R/M HNSCC Phase 2 study initiated June 2025 Lead PI: Antonio Jimeno MD, PhD; U.

Colorado Recurrent metastatic HNSCC ECOG PS 0 - 2 RECIST measurable disease n=58 N219 100mg/kg Q1W+ pembro 200mg Q3W n=10 +19 Simon 2 stage N219 100mg/kg Q1W+ cetuximab 400mg/m 2 - > 250mg/m 2 n=10 +19 Simon 2 stage R 1 st Line ICI Naive 2 nd Line 3 rd Line Cohort 1 Cohort 2 33 Purple Biotech develops promising first - in - class drug candidates to treat cancers with high unmet medical need Next generation tri - specific antibody platform • CAPTN - 3: Conditionally activated T - cell engager (TCE) enhanced by NK cell engager arm and a Tumor Associated Antigen engager Partnership and investment opportunities: Two Phase 2 first - in - class drugs • CM24, aCEACAM1 antibody: Unlocking personalized immunotherapy through biomarker - guided patient targeting; positive randomized Phase 2a results • NT219, IRS1/2 degrader and STAT3 blocker : Sensitizing the tumor & tumor microenvironment; Safety and anti - tumor activity demonstrated in Phase 1 Cash balance $10.5M*, cash runway into 1H 2027 *As of September 10, 2025 34 Leadership Team Michael Schickler, PhD Head of Clinical and Regulatory Affairs Formerly at Hoffmann - La Roche, CEO at CureTech Hadas Reuveni, PhD VP Research & Development Formerly at Keryx (NASDAQ:KERX) Gil Efron Chief Executive Officer Former Deputy CEO & CFO at Kamada (NASDAQ:KMDA) Eric K. Rowinsky, MD Chairman of the Board Former CMO at ImClone, Stemline, Board member at Biogen Inc. Shai Lankry Chief Financial Officer Former CFO at Gamida Cell Ltd. (NASDAQ:GMDA)


35 Contact Us: ir@purple - biotech.com THANK YOU Appendix A | CAPTN - 3


Appendix B | CM24
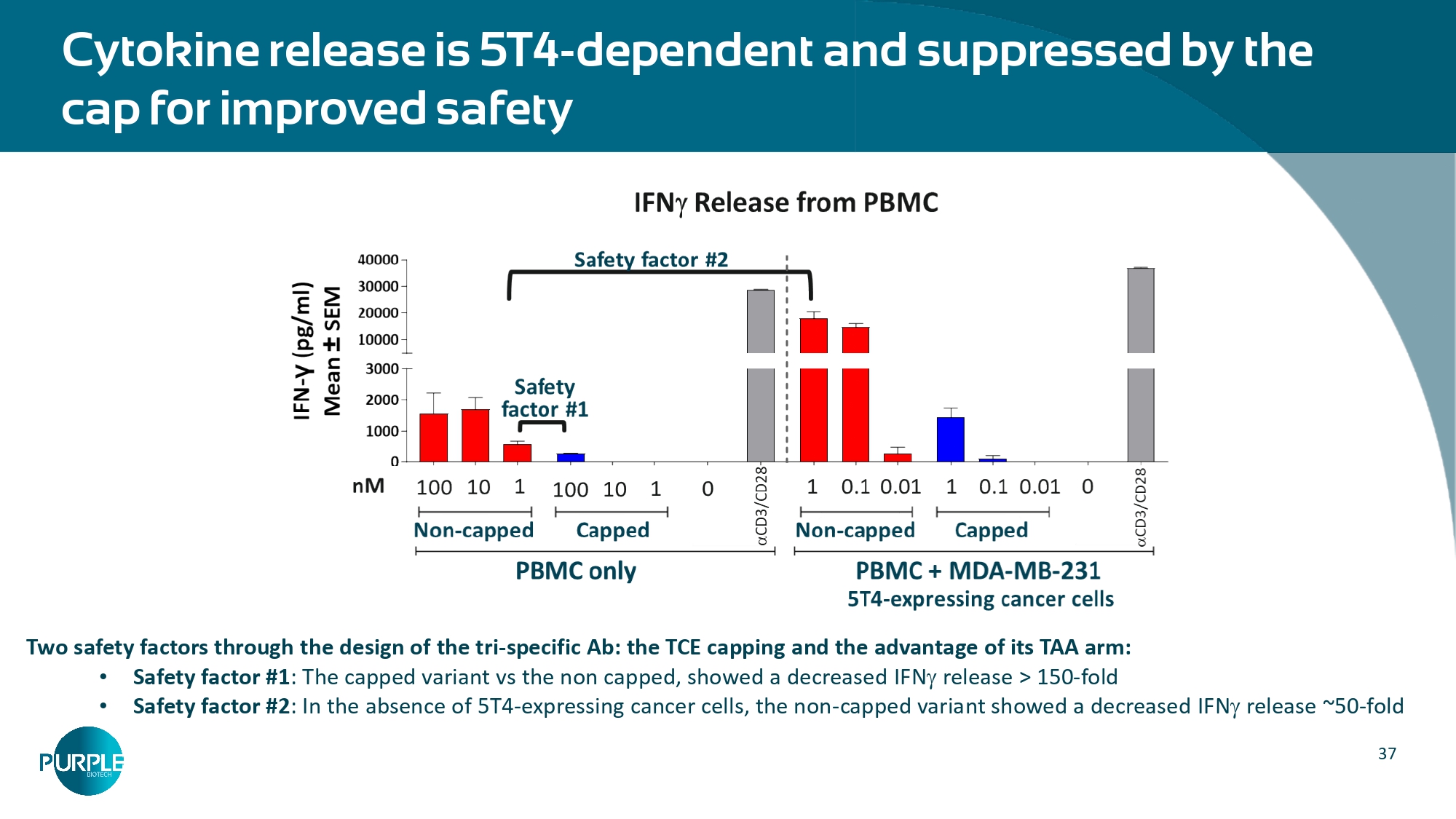
Two safety factors through the design of the tri - specific Ab: the TCE capping and the advantage of its TAA arm: • Safety factor #1 : The capped variant vs the non capped, showed a decreased IFN release > 150 - fold • Safety factor #2 : In the absence of 5T4 - expressing cancer cells, the non - capped variant showed a decreased IFN release ~50 - fold 37 Cytokine release is 5T4 - dependent and suppressed by the cap for improved safety 39 Confidential CEACAM1 Plays a Key Role in Cancer Biology 01 | ADHESION Horst, 2011 “ CEACAM1 creates a pro - angiogenic tumor microenvironment that supports tumor vessel maturation ” “ Neutrophil extracellular trap - associated CEACAM1 as a putative therapeutic target to prevent metastatic progression of colon carcinoma ” Ferri, 2020 Tsuzuki, 2020 Tsang, 2020 Blumberg, 2015 “C EACAM1 regulates TIM - 3 - mediated tolerance and exhaustion ” “ CEACAM1 regulates Fas - mediated apoptosis in Jurkat T - cells via its interaction with β - catenin ” Shively, 2013 02 | IMMUNE CELLS/ IMMUNE EXCLUSION 03 | IMMUNO - ONCOLOGY “ Immune-checkpoint molecules on regulatory T-cells as a potential therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell cancers” “[Blockade] enhances natural killer cell cytotoxicity against tumor cells through blockade of the inhibitory CEACAM1 / CEACAM5 immune checkpoint pathway ”
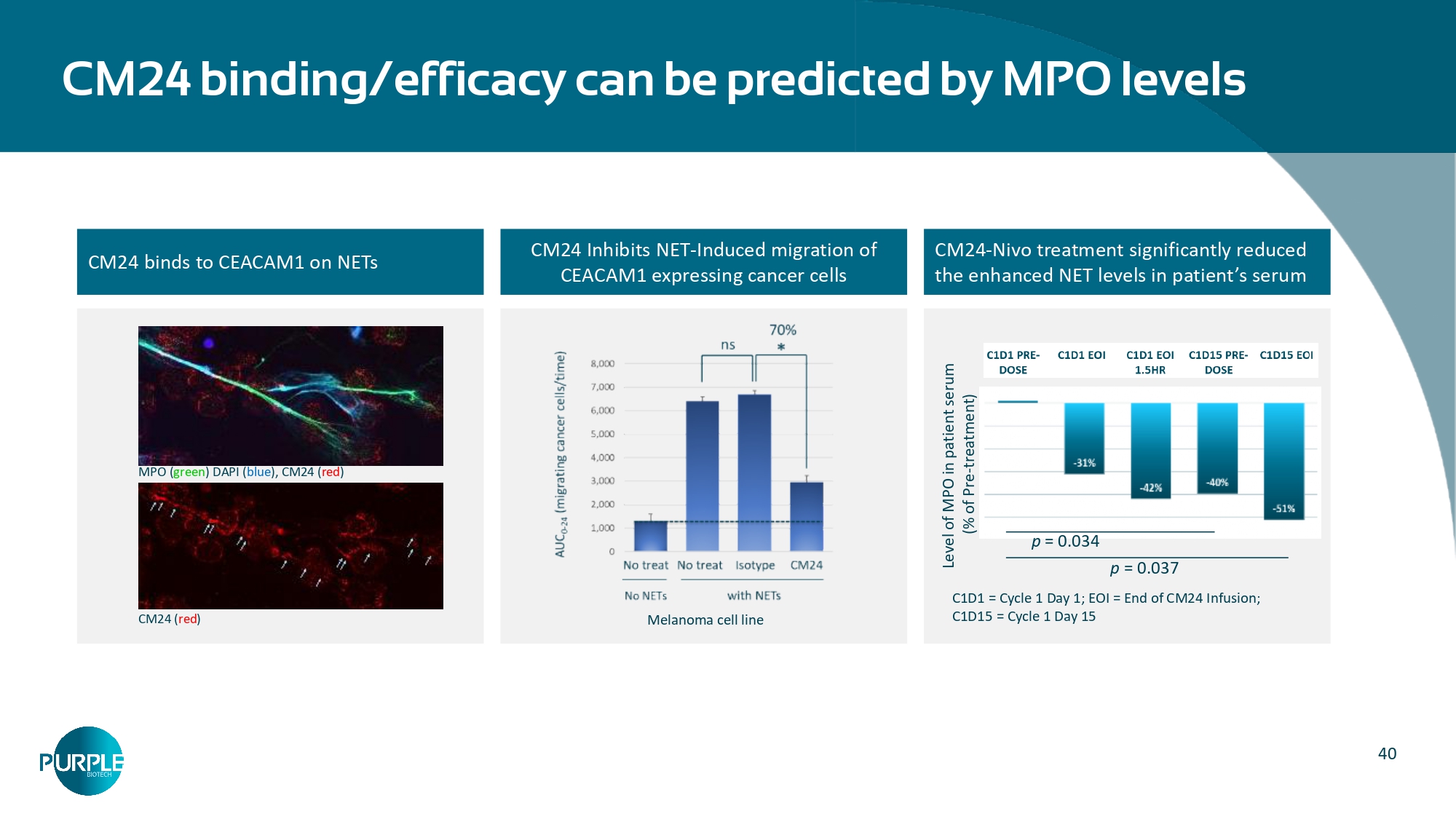
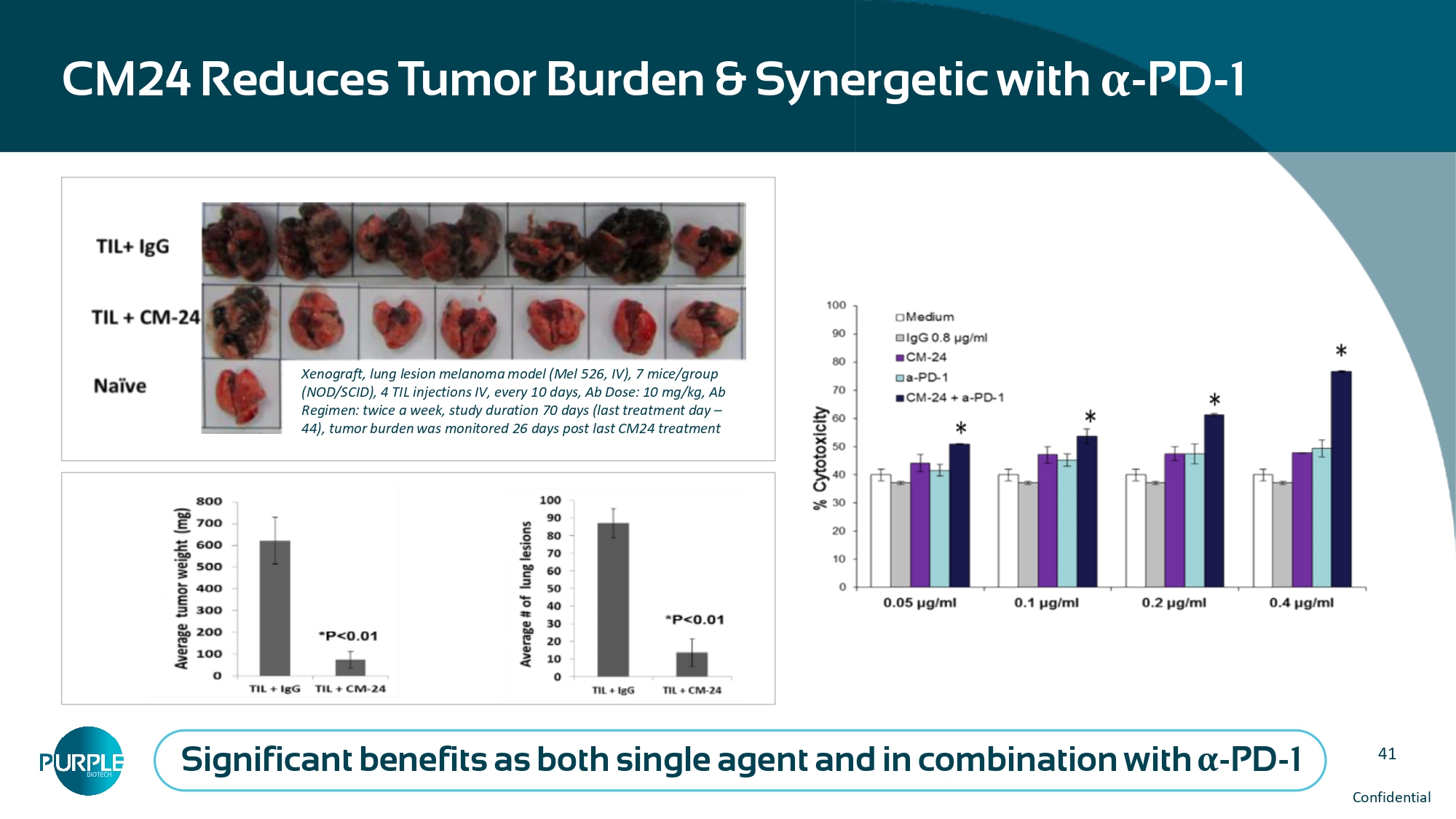
40 CM24 binds to CEACAM1 on NETs CM24 Inhibits NET - Induced migration of CEACAM1 expressing cancer cells CM24 - Nivo treatment significantly reduced the enhanced NET levels in patient’s serum CM24 binding/efficacy can be predicted by MPO levels MPO ( green ) DAPI ( blue ), CM24 ( red ) CM24 ( red ) Level of MPO in patient serum (% of Pre - treatment) p = 0.034 p = 0.037 C1D1 = Cycle 1 Day 1; EOI = End of CM24 Infusion; C1D15 = Cycle 1 Day 15 Melanoma cell line 41 Confidential CM24 Reduces Tumor Burden & Synergetic with α - PD - 1 Xenograft, lung lesion melanoma model (Mel 526, IV), 7 mice/group (NOD/SCID), 4 TIL injections IV, every 10 days, Ab Dose: 10 mg/kg, Ab Regimen: twice a week, study duration 70 days (last treatment day – 44), tumor burden was monitored 26 days post last CM24 treatment Significant benefits as both single agent and in combination with α - PD - 1
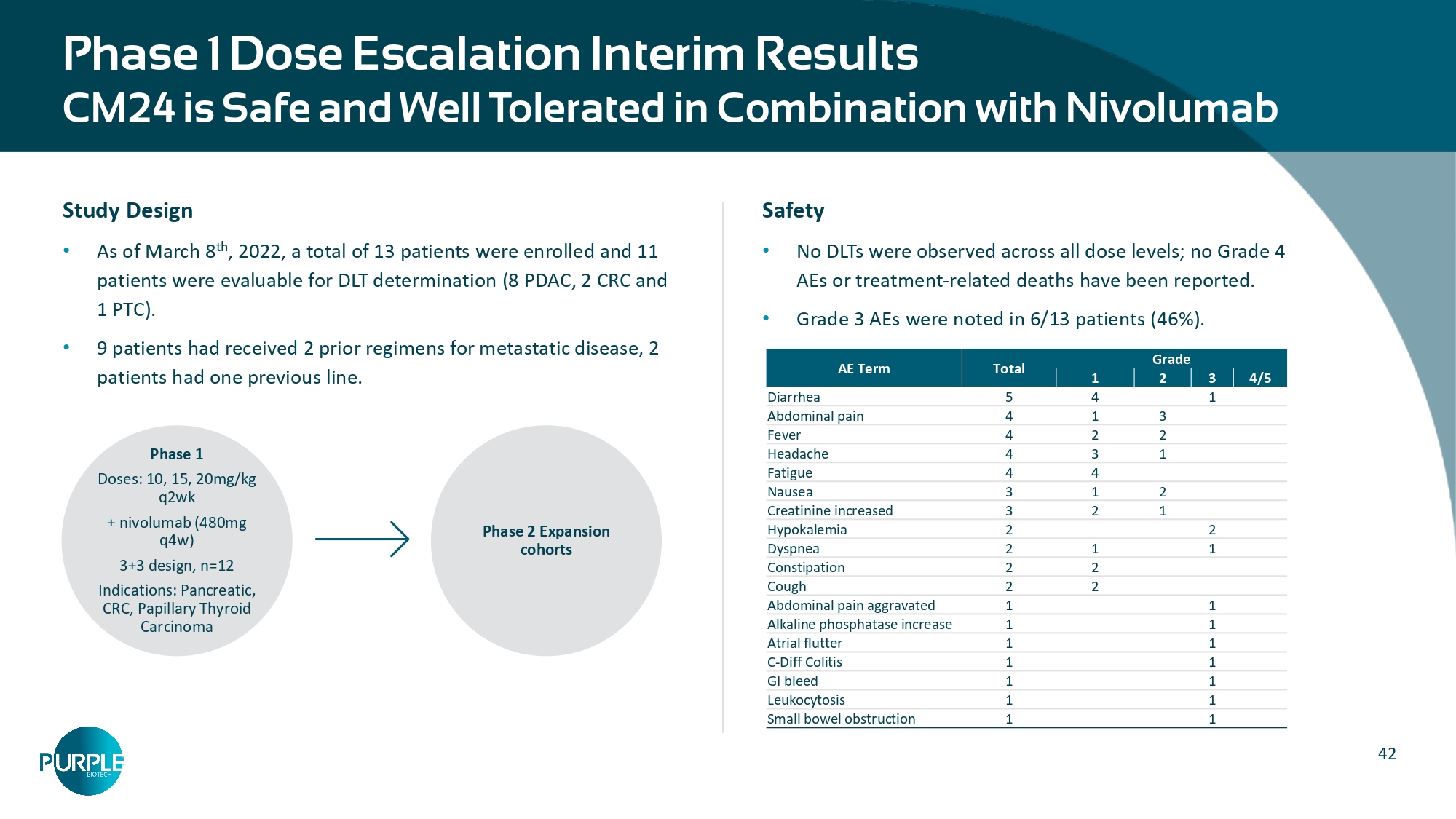
42 Phase 1 Dose Escalation Interim Results CM24 is Safe and Well Tolerated in Combination with Nivolumab Total Grade AE Term 4/5 3 2 1 1 4 5 Diarrhea 3 1 4 Abdominal pain 2 2 4 Fever 1 3 4 Headache 4 4 Fatigue 2 1 3 Nausea 1 2 3 Creatinine increased 2 2 Hypokalemia 1 1 2 Dyspnea 2 2 Constipation 2 2 Cough 1 1 Abdominal pain aggravated 1 1 Alkaline phosphatase increase 1 1 Atrial flutter 1 1 C - Diff Colitis 1 1 GI bleed 1 1 Leukocytosis 1 1 Small bowel obstruction Study Design • As of March 8 th , 2022, a total of 13 patients were enrolled and 11 patients were evaluable for DLT determination (8 PDAC, 2 CRC and 1 PTC). • 9 patients had received 2 prior regimens for metastatic disease, 2 patients had one previous line. Phase 1 Doses: 10, 15, 20mg/kg q2wk + nivolumab (480mg q4w) 3+3 design, n=12 Indications: Pancreatic, CRC, Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Phase 2 Expansion cohorts Safety • No DLTs were observed across all dose levels; no Grade 4 AEs or treatment - related deaths have been reported. • Grade 3 AEs were noted in 6/13 patients (46%).

43 Confidential CM24 Phase 1 Combination Study (NCT04731467) Demographics In the Phase 1 part, patients with indicated refractory cancers were administered CM24 at 10, 15, and 20mg/kg q2w and nivolumab 480mg q4w. • The primary objective of this part was to evaluate safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and determine the RP2D • Safety was assessed according to CTCAE v5 and preliminary anti - tumor activity was assessed by the investigators according to RECISTv1.1 using CT/MRI • CM24 and CEACAM1 measurements in serum, biopsy specimens, and TILs, as well as tumor and TILs PD - L1 levels are being determined As of March 8th, 2022, a total of 13 patients were enrolled and 11 patients were evaluable for dose - limiting toxicity (DLT) determination (8 PDAC, 2 CRC and 1 PTC) • 9 patients had received 2 prior regimens for metastatic disease and 2 patients had one previous line. Demographics of patients treated with CM24 (10, 15, 20mg/kg) in combination with nivolumab (480mg) Prior Lines of Therapy, n (%) 65 (49 - 76) Median age, years (range) 2 (18%) 1 Sex, n (%) 9 (82%) 2 5 (45%) Male Diagnosis , n (%) 6 (55%) Female 8 (73%) Pancreatic cancer Ethnicity, n (%) 1 (9%) Papillary Thyroid cancer 10 (91%) Not Hispanic or Latino 2 (18%) Colorectal cancer 1 (9%) Hispanic or Latino 23 (11 - 73) Median Time from Initial Diagnosis months (range) Race, n (%) ECOG, n (%) 10 (91%) White 7 (64%) 0 1 (9%) Black or African American 4 (36%) 1 44 Confidential Confirmed Partial Response in a 3L PDAC Patient Patient Profile • 65 y/o female, pancreatic cancer • 2 prior lines of treatments: FOLFIRINOX and gemcitabine/nab - paclitaxel • Post Whipple Procedure • Patient had a germline NF1 VUS, with MSI - S and PDL - 1 IHC 2+ and 5% staining • Confirmed Partial Response: after initial treatment, the patient had a Partial Response of 40%, with a definite reduction of the para - tracheal adenopathy and liver lesions and 58% reduction in CA19 - 9 levels • Under treatment for 6 months, still under monitoring.
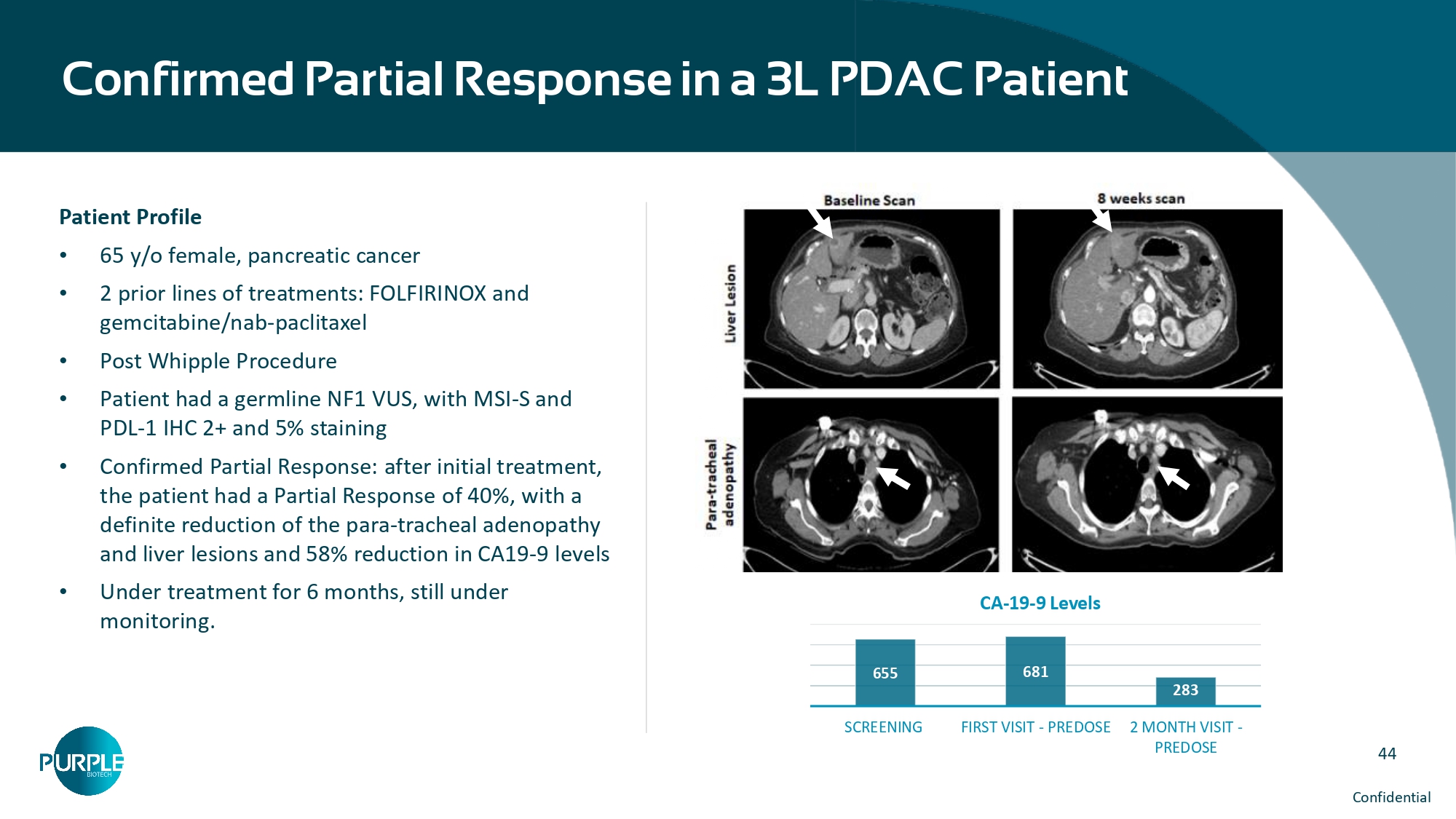
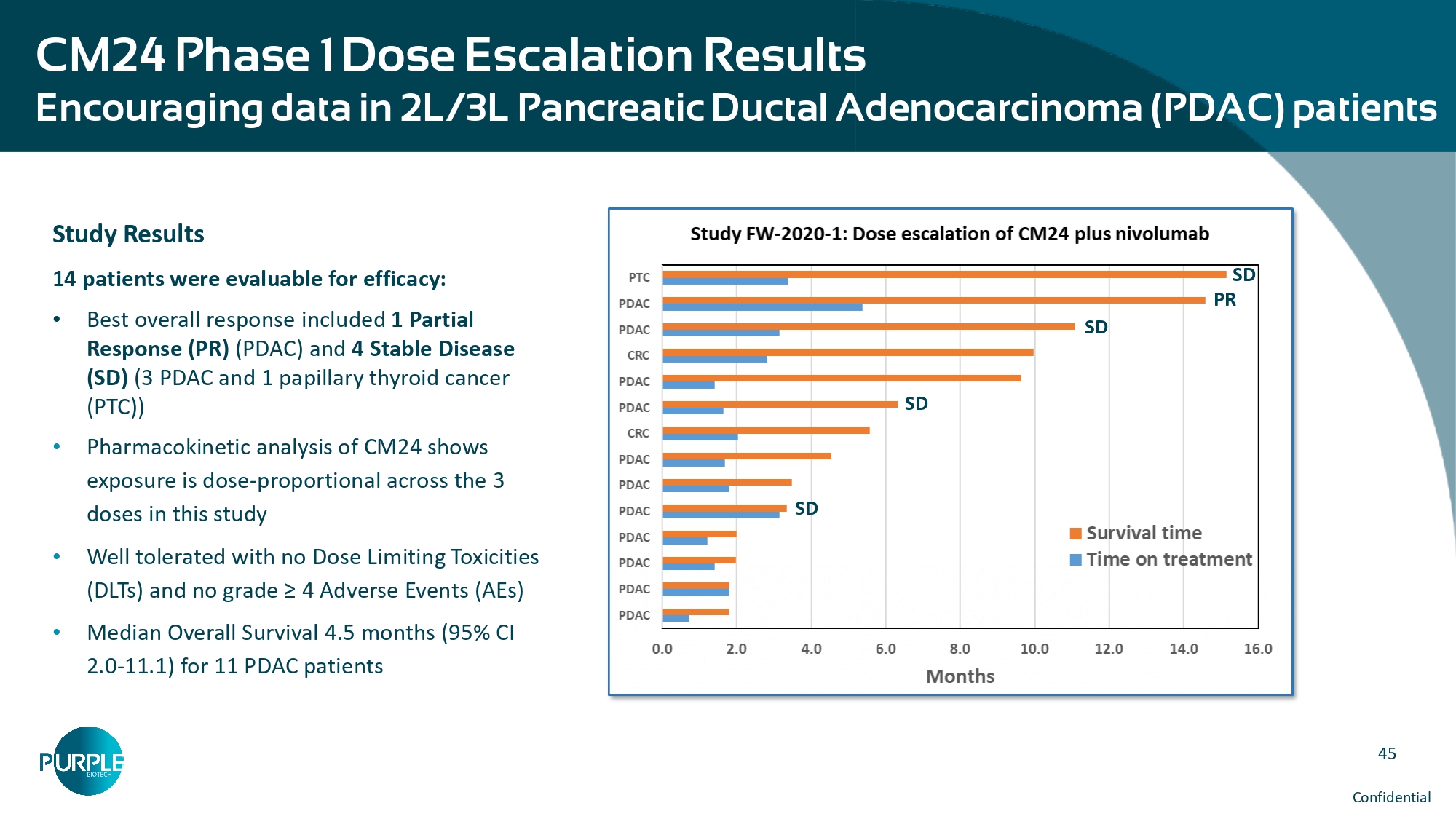
655 681 283 SCREENING FIRST VISIT - PREDOSE 2 MONTH VISIT - PREDOSE CA - 19 - 9 Levels 45 Confidential CM24 Phase 1 Dose Escalation Results Encouraging data in 2L/3L Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients Study Results 14 patients were evaluable for efficacy: • Best overall response included 1 Partial Response (PR) (PDAC) and 4 Stable Disease (SD) (3 PDAC and 1 papillary thyroid cancer (PTC)) • Pharmacokinetic analysis of CM24 shows exposure is dose - proportional across the 3 doses in this study • Well tolerated with no Dose Limiting Toxicities (DLTs) and no grade ≥ 4 Adverse Events (AEs) • Median Overall Survival 4.5 months (95% CI 2.0 - 11.1) for 11 PDAC patients SD SD PR SD SD | 47 NT219 targets 2 critical signalling pathways simultaneously leading IRS1/2 to degradation and blocking STAT3 IRS1/2 • Promotes a tumor - protective microenvironment • Overexpressed in multiple tumor types • Activated as a feedback response to anti - cancer therapies • Regulates major survival pathways STAT3 • Well - established transcription factor associated with the tumorigenic phenotype • Hyperactivated in many cancers • Promotes proliferation, survival, angiogenesis and metastasis • Critical player in tumor immune evasion Hadas Reuveni et al.

Appendix C | NT219
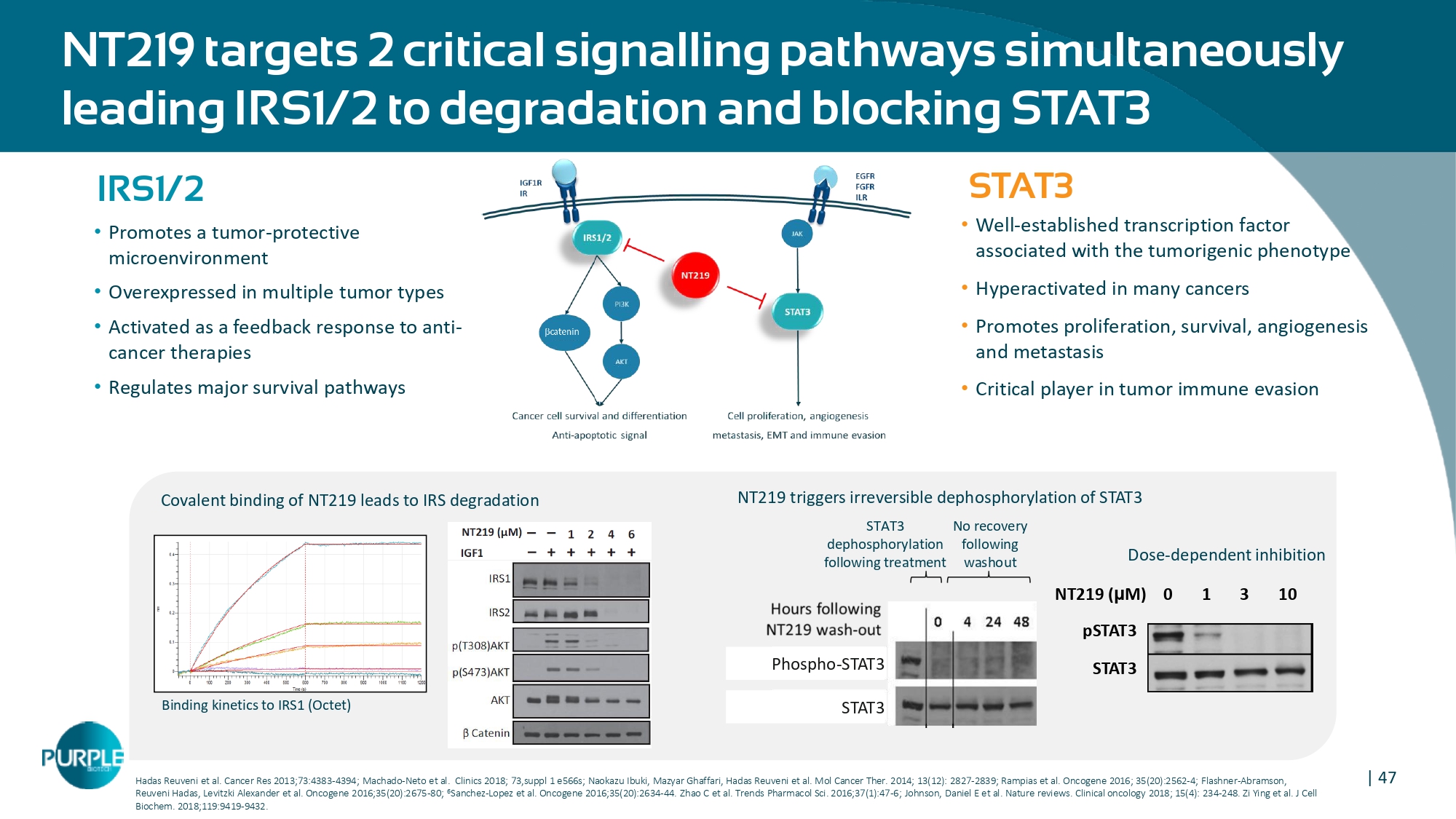
Cancer Res 2013;73:4383 - 4394; Machado - Neto et al. Clinics 2018; 73,suppl 1 e566s; Naokazu Ibuki, Mazyar Ghaffari, Hadas Reuveni et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014; 13(12): 2827 - 2839; Rampias et al. Oncogene 2016; 35(20):2562 - 4; Flashner - Abramson, Reuveni Hadas, Levitzki Alexander et al. Oncogene 2016;35(20):2675 - 80; 6 Sanchez - Lopez et al. Oncogene 2016;35(20):2634 - 44. Zhao C et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016;37(1):47 - 6; Johnson, Daniel E et al. Nature reviews. Clinical oncology 2018; 15(4): 234 - 248. Zi Ying et al. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:9419 - 9432. Binding kinetics to IRS1 (Octet) STAT3 Dose - dependent inhibition NT219 ( μ M) 0 1 3 10 pSTAT3 NT219 triggers irreversible dephosphorylation of STAT3 STAT3 No recovery dephosphorylation following following treatment washout Phospho - STAT3 STAT3 Covalent binding of NT219 leads to IRS degradation 48 Novel MOA: IRS Degradation By NT219 Blocking IGF1R - AKT Pathway 1 Binding to IRS 1 1 Reuveni et al.
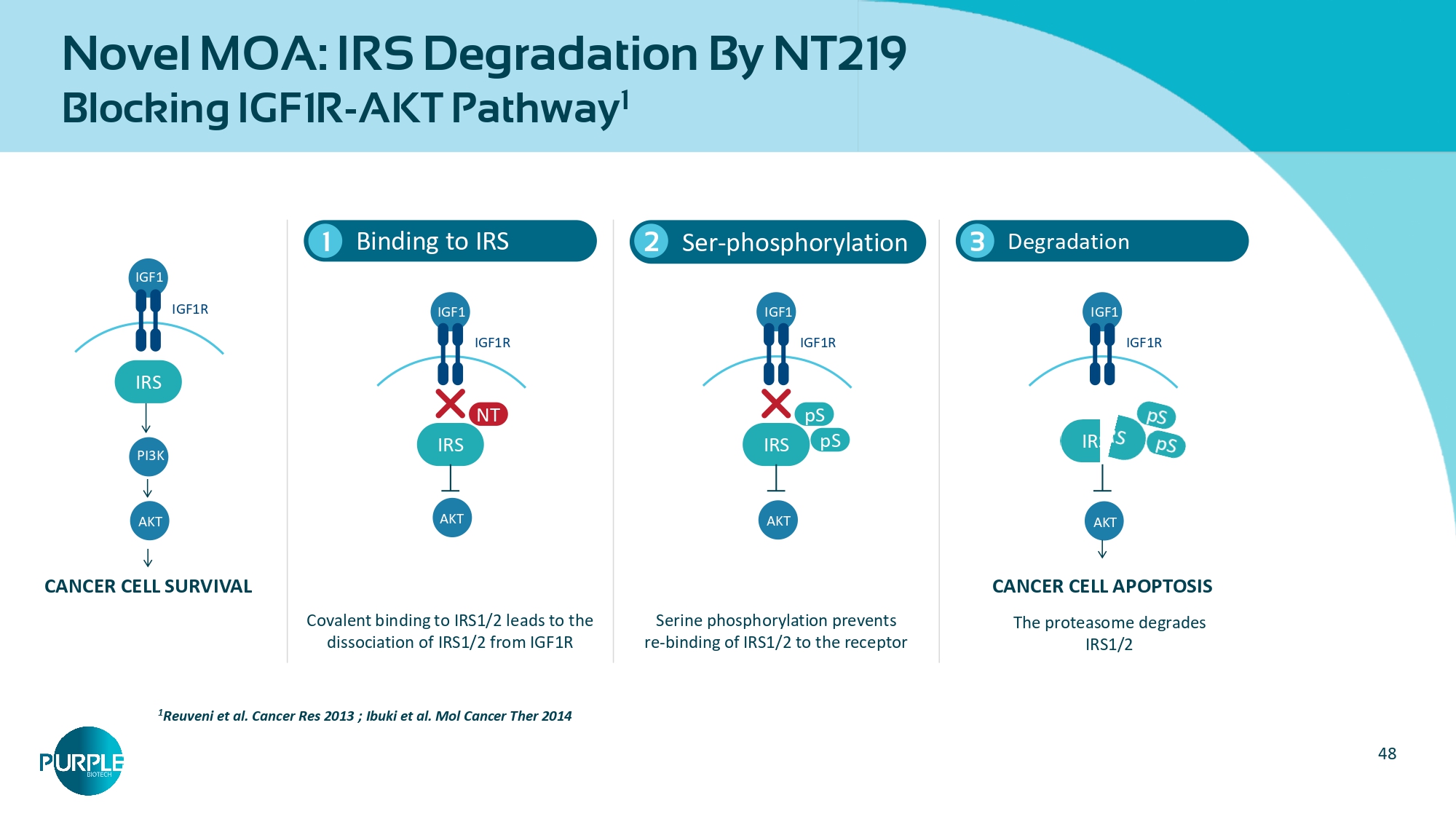
Cancer Res 2013 ; Ibuki et al.
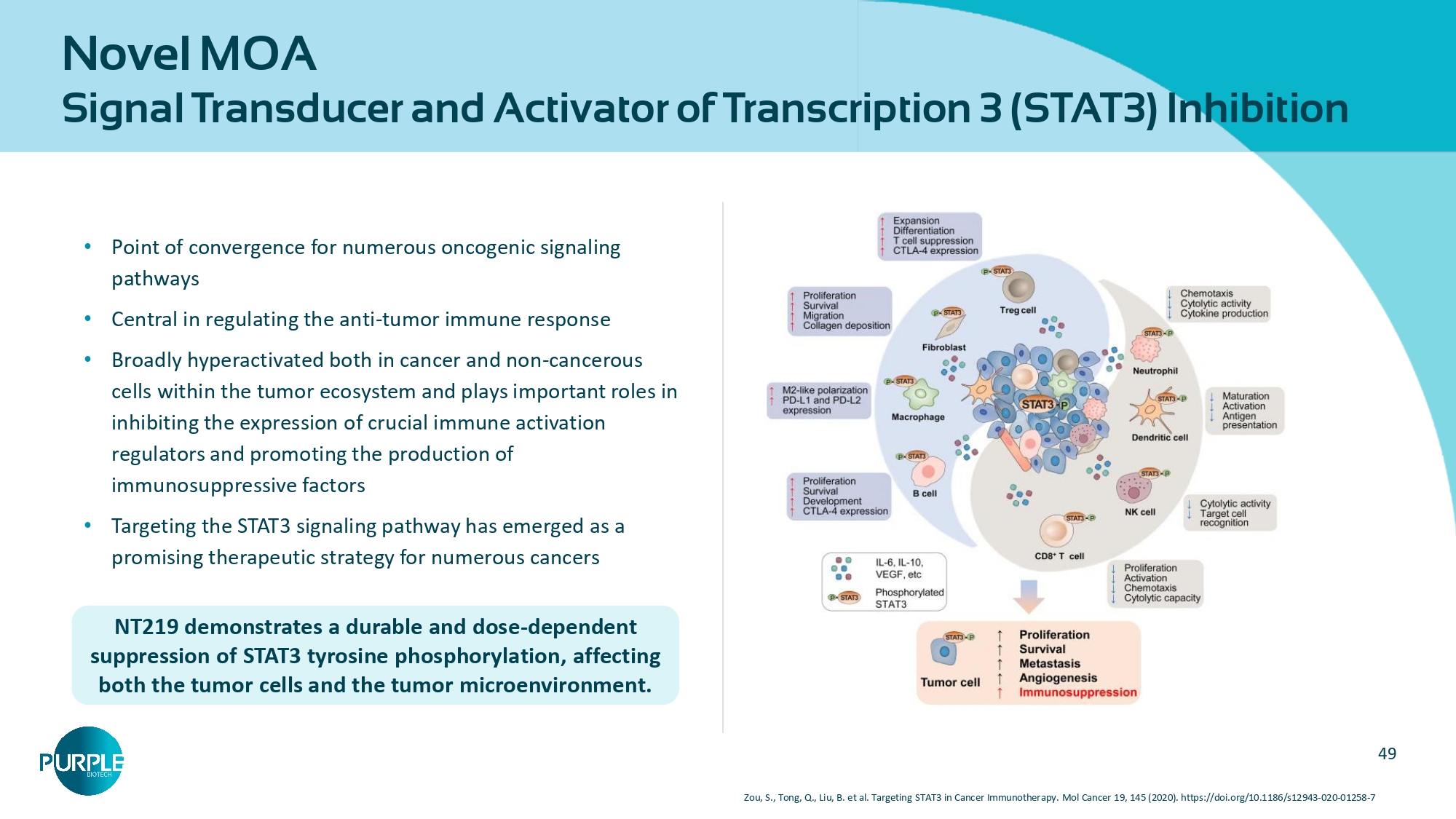
Mol Cancer Ther 2014 2 Ser - phosphorylation Degradation 3 Covalent binding to IRS1/2 leads to the dissociation of IRS1/2 from IGF1R Serine phosphorylation prevents re - binding of IRS1/2 to the receptor CANCER CELL SURVIVAL CANCER CELL APOPTOSIS The proteasome degrades IRS1/2 IGF1 IGF1R IRS AKT PI3K IGF1 IGF1R IRS NT AKT IGF1 IGF1R IRS pS pS AKT IGF1 IGF1R AKT 49 Novel MOA Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Inhibition • Point of convergence for numerous oncogenic signaling pathways • Central in regulating the anti - tumor immune response • Broadly hyperactivated both in cancer and non - cancerous cells within the tumor ecosystem and plays important roles in inhibiting the expression of crucial immune activation regulators and promoting the production of immunosuppressive factors • Targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for numerous cancers NT219 demonstrates a durable and dose - dependent suppression of STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation, affecting both the tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment. Zou, S., Tong, Q., Liu, B. et al. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol Cancer 19, 145 (2020).
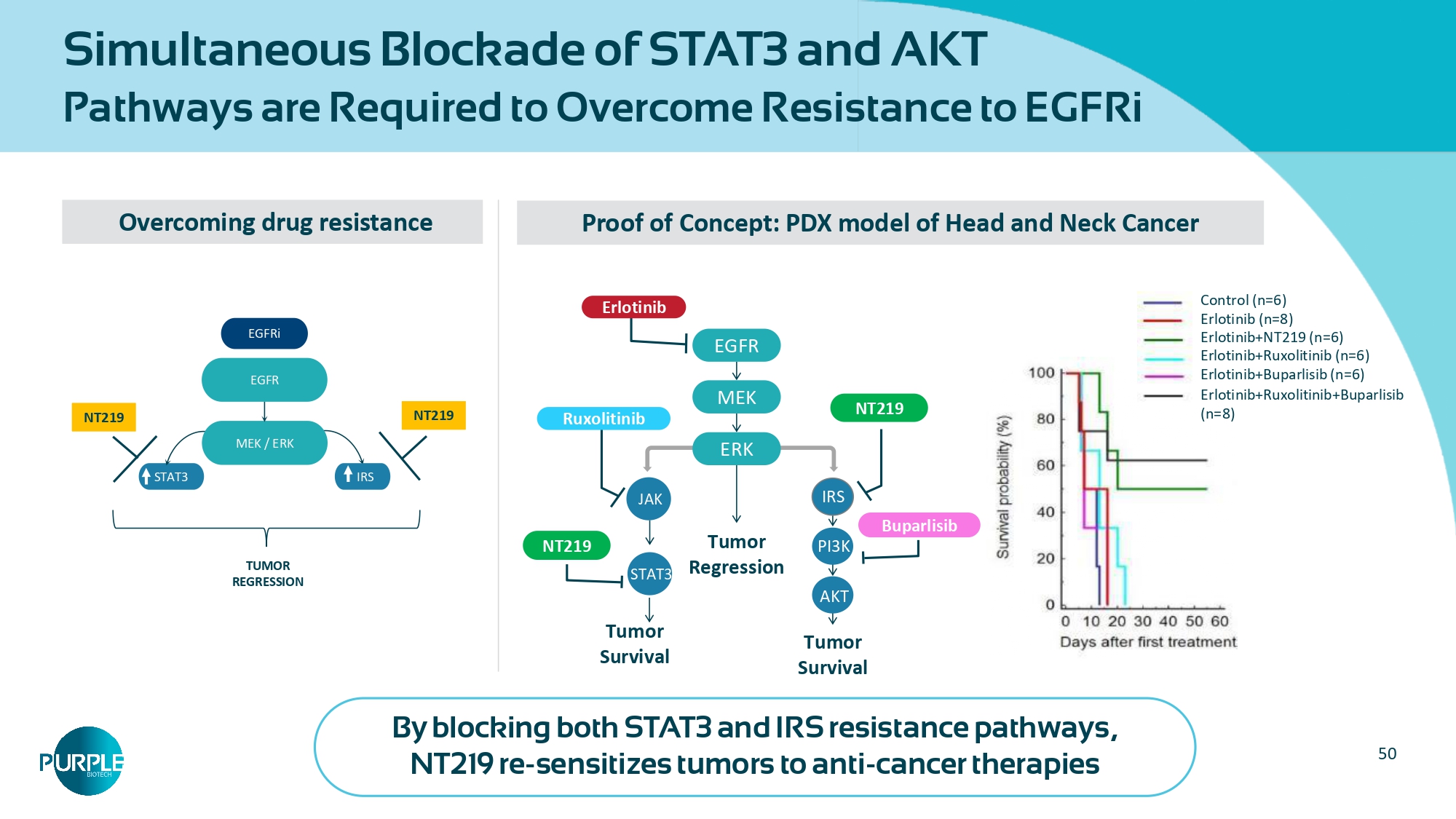
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943 - 020 - 01258 - 7 50 Simultaneous Blockade of STAT3 and AKT Pathways are Required to Overcome Resistance to EGFRi Overcoming drug resistance NT219 NT219 STAT3 IRS EGFR EGFRi MEK / ERK TUMOR REGRESSION Proof of Concept: PDX model of Head and Neck Cancer Control (n=6) Erlotinib (n=8) Erlotinib+NT219 (n=6) Erlotinib+Ruxolitinib (n=6) Erlotinib+Buparlisib (n=6) Erlotinib+Ruxolitinib+Buparlisib (n=8) STAT3 IRS EGFR MEK Tumor Regression ERK PI3K AKT Tumor Survival Tumor Survival Buparlisib Ruxolitinib Erlotinib NT219 NT219 JAK By blocking both STAT3 and IRS resistance pathways, NT219 re - sensitizes tumors to anti - cancer therapies 51 NT219 re - sensitizes PD1 - refractory models and restores sensitivity to EGFRi 6 8 20 22 0 500 1000 1500 2000 Tumor volume (mm 3 ) 10 12 14 16 18 Days following tumor challenge Control (n=10) α - PD - 1 (n=10) NT219 (n=10) NT219+α - PD - 1 (n=10) * Collaboration with Prof.
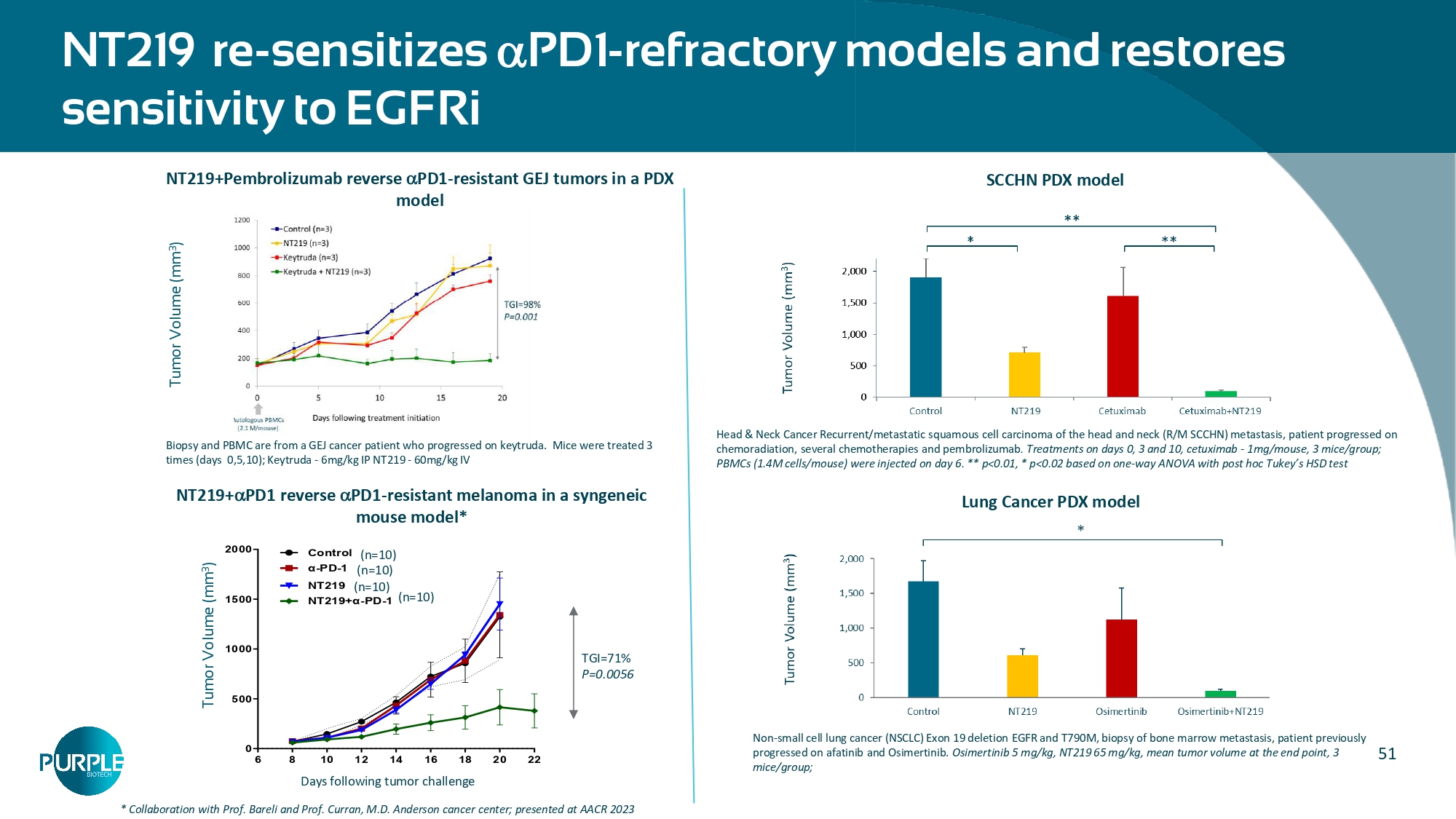
Bareli and Prof. Curran, M.D. Anderson cancer center; presented at AACR 2023 NT219+ PD1 reverse PD1 - resistant melanoma in a syngeneic mouse model* Tumor Volume (mm 3 ) Tumor Volume (mm 3 ) Biopsy and PBMC are from a GEJ cancer patient who progressed on keytruda. Mice were treated 3 times (days 0,5,10); Keytruda - 6mg/kg IP NT219 - 60mg/kg IV TGI=71% P=0.0056 NT219+Pembrolizumab reverse PD1 - resistant GEJ tumors in a PDX SCCHN PDX model model Head & Neck Cancer Recurrent/metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (R/M SCCHN) metastasis, patient progressed on chemoradiation, several chemotherapies and pembrolizumab . Treatments on days 0, 3 and 10, cetuximab - 1mg/mouse, 3 mice/group; PBMCs (1.4M cells/mouse) were injected on day 6. ** p<0.01, * p<0.02 based on one - way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s HSD test Lung Cancer PDX model Non - small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Exon 19 deletion EGFR and T790M, biopsy of bone marrow metastasis, patient previously progressed on afatinib and Osimertinib.
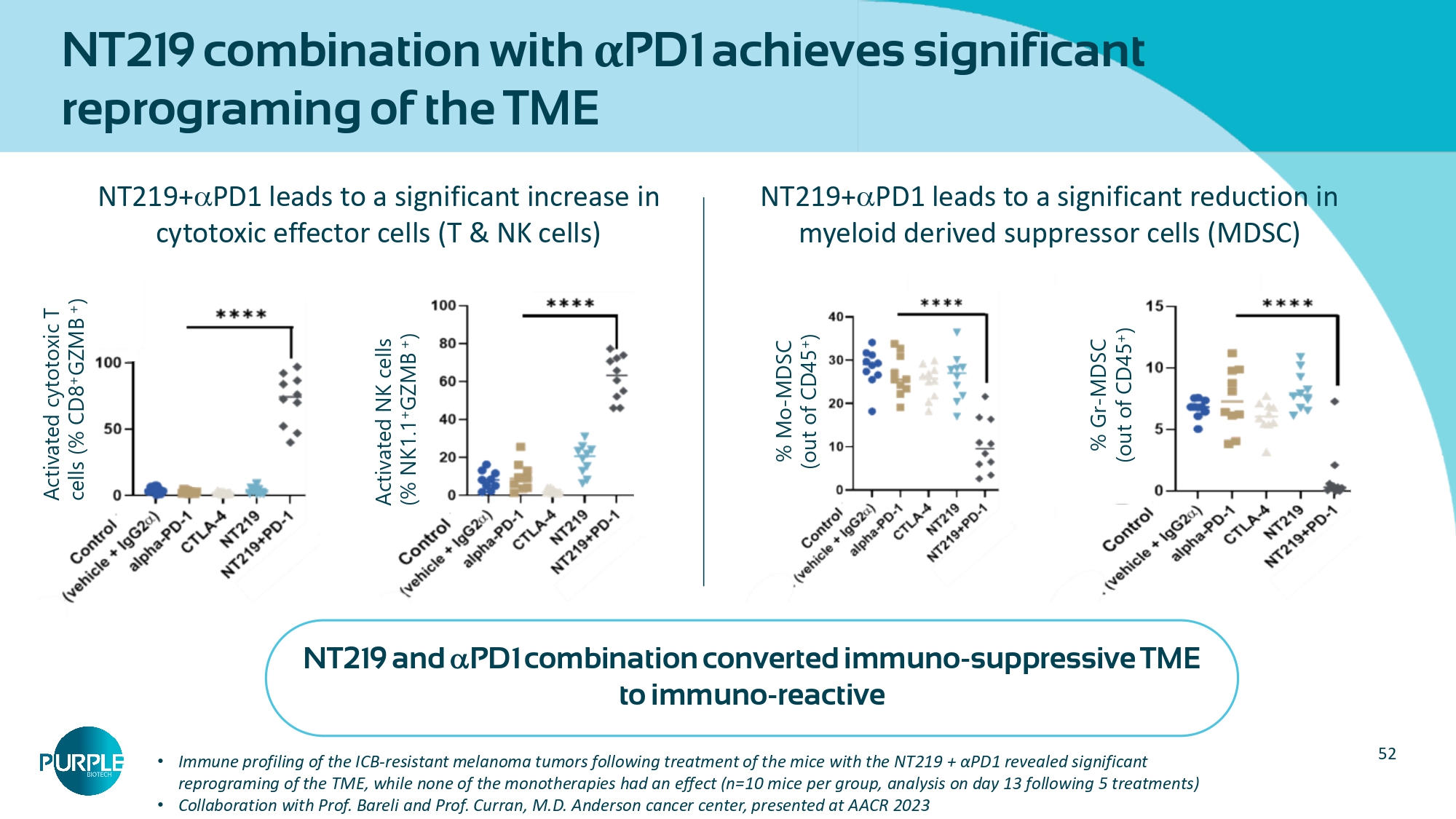
Osimertinib 5 mg/kg, NT219 65 mg/kg, mean tumor volume at the end point, 3 mice/group; 52 NT219 combination with α PD1 achieves significant reprograming of the TME NT219 and PD1 combination converted immuno - suppressive TME to immuno - reactive • Immune profiling of the ICB - resistant melanoma tumors following treatment of the mice with the NT219 + αPD1 revealed significant reprograming of the TME, while none of the monotherapies had an effect (n=10 mice per group, analysis on day 13 following 5 treatments) • Collaboration with Prof. Bareli and Prof. Curran, M.D. Anderson cancer center, presented at AACR 2023 Activated cytotoxic T cells (% CD8 + GZMB + ) Activated NK cells (% NK1.1 + GZMB + ) NT219+ PD1 leads to a significant increase in cytotoxic effector cells (T & NK cells) NT219+ PD1 leads to a significant reduction in myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSC) % Mo - MDSC (out of CD45 + ) % Gr - MDSC (out of CD45 + )
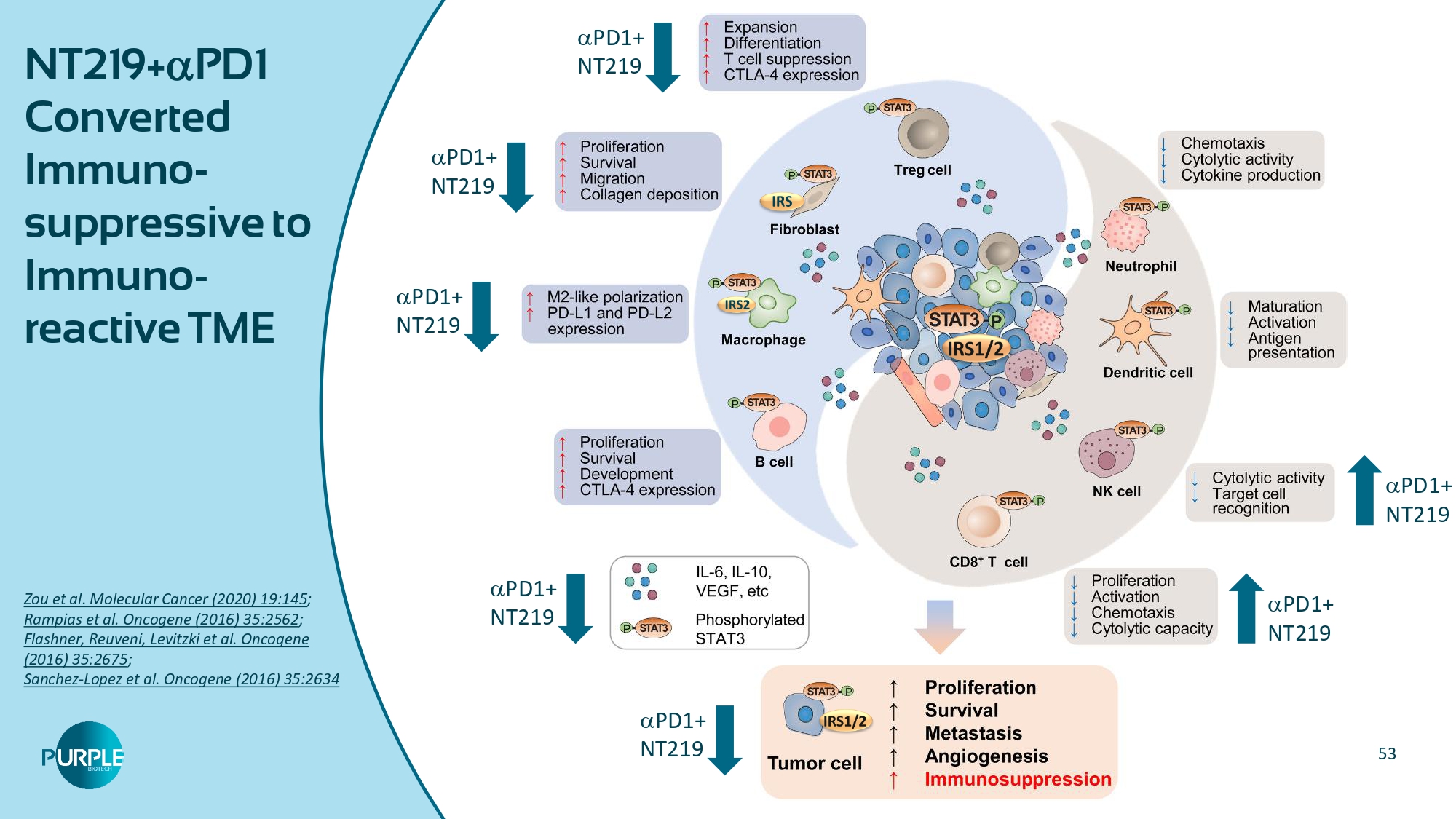
53 NT219+ PD1 Converted Immuno - suppressive to Immuno - reactive TME Zou et al. Molecular Cancer (2020) 19:145 ; Rampias et al. Oncogene (2016) 35:2562 ; Flashner, Reuveni, Levitzki et al. Oncogene (2016) 35:2675 ; Sanchez - Lopez et al. Oncogene (2016) 35:2634 PD1+ NT219 PD1+ NT219 PD1+ NT219 PD1+ NT219 PD1+ NT219 PD1+ NT219 PD1+ NT219 54 Selected Publications Michael Karin Alexander Levitzki Menashe Bar - Eli Michael Cox

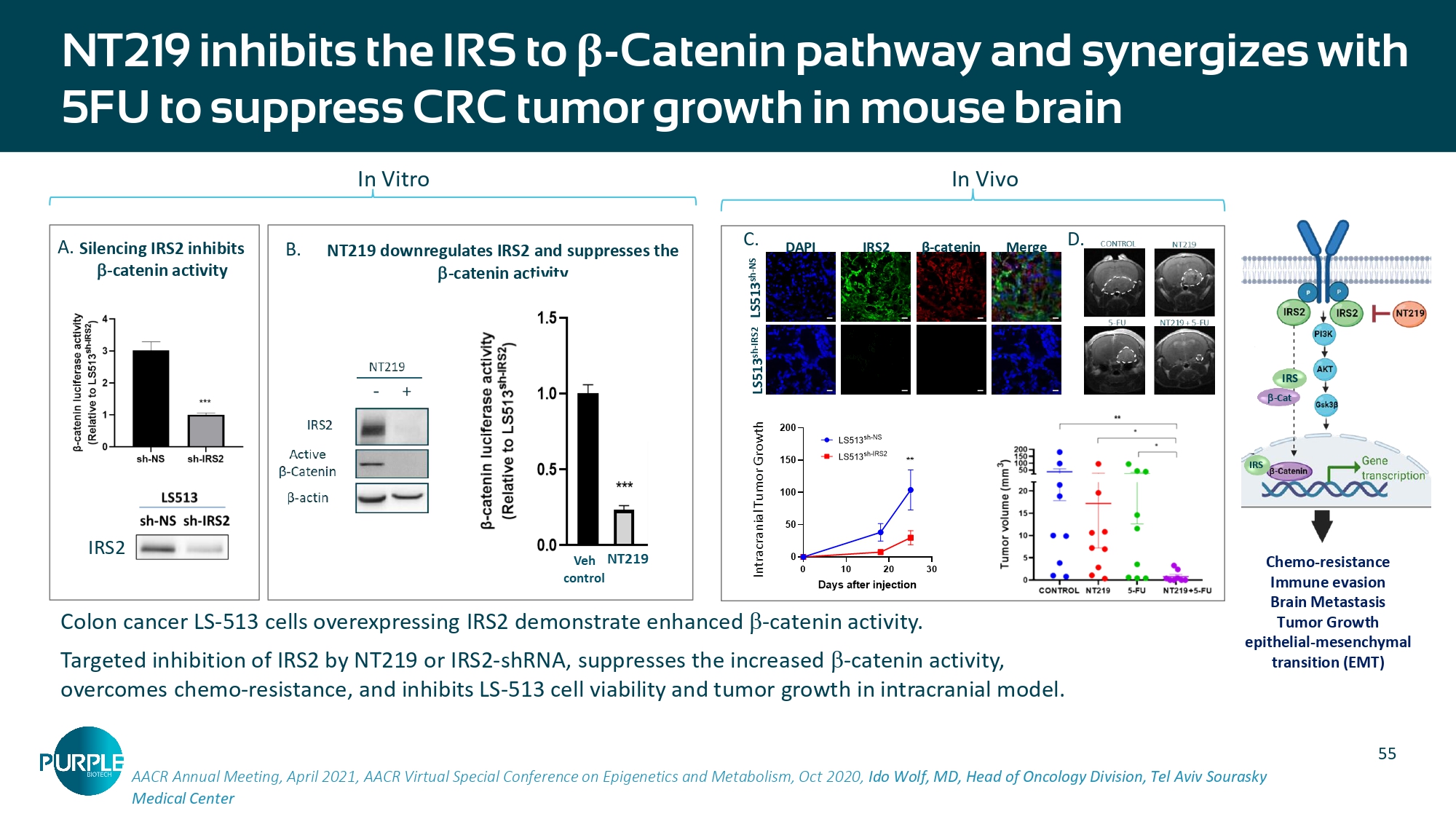
55 AACR Annual Meeting, April 2021, AACR Virtual Special Conference on Epigenetics and Metabolism, Oct 2020, Ido Wolf, MD, Head of Oncology Division, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center Colon cancer LS - 513 cells overexpressing IRS2 demonstrate enhanced - catenin activity. Targeted inhibition of IRS2 by NT219 or IRS2 - shRNA, suppresses the increased - catenin activity, overcomes chemo - resistance, and inhibits LS - 513 cell viability and tumor growth in intracranial model. NT219 inhibits the IRS to β - Catenin pathway and synergizes with 5FU to suppress CRC tumor growth in mouse brain Chemo - resistance Immune evasion Brain Metastasis Tumor Growth epithelial - mesenchymal transition (EMT) IRS - Cat IRS IRS2 NT219 downregulates IRS2 and suppresses the - catenin activity In Vitro In Vivo LS513 sh - NS LS513 sh - IRS2 1 0 μ m 1 0 μ m 1 0 μ m 1 0 μ m 1 1 1 1 A. Silencing IRS2 inhibits - catenin activity B. C. DAPI IRS2 β - catenin Merge D.
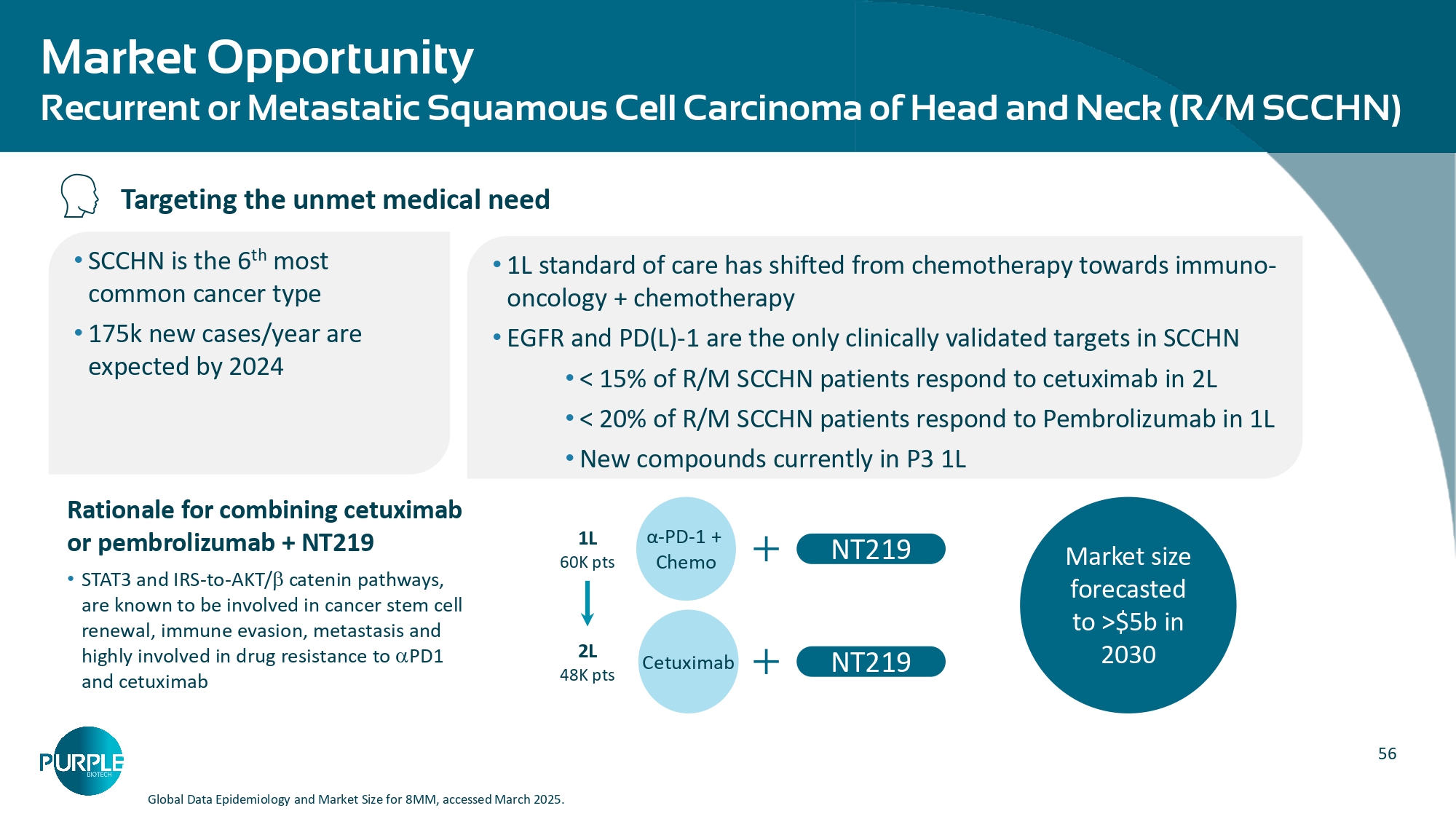
56 Market size forecasted to >$5b in 2030 Market Opportunity Recurrent or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Head and Neck (R/M SCCHN) Global Data Epidemiology and Market Size for 8MM, accessed March 2025. Rationale for combining cetuximab or pembrolizumab + NT219 • STAT3 and IRS - to - AKT/ catenin pathways, are known to be involved in cancer stem cell renewal, immune evasion, metastasis and highly involved in drug resistance to PD1 and cetuximab • SCCHN is the 6 th most common cancer type • 175k new cases/year are expected by 2024 • 1L standard of care has shifted from chemotherapy towards immuno - oncology + chemotherapy • EGFR and PD(L) - 1 are the only clinically validated targets in SCCHN • < 15% of R/M SCCHN patients respond to cetuximab in 2L • < 20% of R/M SCCHN patients respond to Pembrolizumab in 1L • New compounds currently in P3 1L Targeting the unmet medical need α - PD - 1 + Chemo 1L 60K pts NT219 Cetuximab 2L 48K pts NT219