
Corporate Presentation December 4, 2025 Exhibit 99.2

This presentation and any accompanying oral commentary have been prepared by MapLight Therapeutics, Inc. (“MapLight”, “we,” “us,” “our,” the “Company”, or similar terms) for informational purposes only and not for any other purpose. This presentation contains trademarks, service marks, trade names and copyrights of MapLight and other companies which are the property of their respective owners. This presentation discusses product candidates that are under pre-clinical and clinical study, and which have not yet been approved for marketing by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. No representation is made as to the safety or efficacy of these product candidates for the uses for which they are being studied. Statements contained in this presentation and the accompanying oral commentary, other than statements of historical facts, may be forward-looking statements, including, but not limited to: statements about our expectations regarding the potential benefits, efficacy and safety of our product candidates and platform; our expectations with regard to the design and results of our research and development programs, preclinical studies, and clinical trials; our preclinical, clinical, and regulatory development plans for our product candidates; our expectations with regard to our ability to discover, develop, license, or acquire additional product candidates and advance such product candidates into, and successfully complete, preclinical studies and clinical trials; the potential patient populations for our product candidates and any future product candidates; and our business strategy. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “expects,” “plans,” “anticipates,” “could,” “intends,” “targets,” “projects,” “contemplates,” “believes,” “estimates,” “predicts,” “potential” or “continue” or the negative of these terms or other similar expressions. These statements involve substantial known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our actual results, timing of results, levels of activity, performance, or achievements to be materially different from the information expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. These statements involve risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those reflected in such statements. Risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially include risks and uncertainties that are described in the “Risk Factors” section of our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) on December 4, 2025 and other filings we make with the SEC from time to time. These documents are available under the “SEC Filings” page of the “Investors” section of our website at www.maplightrx.com. New risks emerge from time to time. It is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially and adversely from those anticipated or implied in the forward-looking statements. We may not actually achieve the plans, intentions, or expectations disclosed in our forward-looking statements, and you should not place undue reliance on our forward-looking statements. Actual results or events could differ materially from the plans, intentions and expectations disclosed in the forward-looking statements we make. The forward-looking statements in this presentation represent our views as of the date of this presentation. We anticipate that subsequent events and developments will cause our views to change. However, while we may elect to update these forward-looking statements at some point in the future, we have no current intention of doing so except to the extent required by applicable law. Except as required by law, neither we nor any other person assumes responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of the forward-looking statements in this presentation and the accompanying oral commentary. You should, therefore, not rely on these forward-looking statements as representing our views as of any date subsequent to the date of this presentation. This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and by us relating to market size and other data about our industry. These data involve a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates. In addition, projections, assumptions and estimates of the future performance of the markets in which we operate are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk. Safe Harbor and Forward-Looking Statements

Innovation-Driven Company Globally Recognized Scientific Founders Established in 2018 to >100 Employees Broad & Diversified Product Pipeline Differentiated M1/M4 Muscarinic Agonist Multiple Product Candidates + Discovery Platform Strong Financial Position ~$497M in Pro Forma Cash (as of 9/30)(1) Cash Runway Through 2027 Chris Kroeger, MD CEO and Founder Vish Setia Chief Financial Officer Erin Foff, MD, PhD Chief Medical Officer 3 Corporate Snapshot James Lillie, PhD Chief Scientific Officer Anatol Kreitzer, PhD Chief Discovery Officer Kristopher Hanson General Counsel Jonathan GillisChief Administrative & Accounting Officer Pro forma cash based on cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments balance of ~$227.2M (as of September 30, 2025) and net proceeds from IPO (including exercise of overallotment option) and concurrent private placement of ~$269.8M after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions, placement agent fees and offering expenses.

Employ Medicinal Chemistry, Pharmacokinetics and Formulation Expertise to Optimize Drug Properties Our Rational Drug Discovery Approach Seeks to Address the Lack of Neural Circuit-Specific Pharmacotherapies Explore Causal Link Between Neural Circuit Activity and Disease Symptoms Identify Potential Druggable Targets Within These Disease-Relevant Neural Circuits Validate Expression, Selectivity and Location of Potential Targets in Brain Tissue

Our Pipeline of Product Candidates GPR = G-protein-coupled receptor. PAC = peripherally acting anti-cholinergic. PAM = positive allosteric modulator. Leveraging Our Versatile Circuit-Based Discovery Platform for Ongoing Pipeline Expansion Program Circuit Indications Preclinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Anticipated Milestones ML-007C-MA M1/M4 agonist co-formulated with PAC Direct and Indirect Pathways Schizophrenia Topline results in 2H 2026 Alzheimer’s Disease Psychosis Topline results in 2H 2027 ML-004 5-HT1B/1D agonist Dorsal Raphe to Nucleus Accumbens Autism Spectrum Disorder Sociability/Irritability Topline results in 2H 2026 ML-021 M4 antagonist Direct Pathway Parkinson’s Disease IND-enabling studies complete in 2H 2026 ML-009 GPR52 PAM Indirect Pathway Hyperactivity/Impulsivity Preclinical candidate nominated ZEPHYR VISTA IRIS Potential in other indications being explored

ML-007C-MA Lead Asset in Development for Schizophrenia and ADP

Muscarinic Receptor Agonism is the First Novel MoA Approved for Treatment of Schizophrenia in Decades AE = adverse events; AD = Alzheimer’s disease; ADP = Alzheimer’s disease psychosis. Represents 2022 TRx estimates as per Symphony Health. Ringeisen H, et al. Mental and Substance Use Disorders Prevalence Study: Findings report. RTI International; 2023. Ismail et al, Nat Rev Neurol. PMC March 2022. Ropacki SA et al, Am. J. Psychiatry 162 (2005). Represents global sales estimates based on third-party market research sources, accessed November 2025. Sub-Optimal Current Standard of Care Primarily rely on D2 dopamine receptor blockade Primarily treat positive symptoms Boxed warning and risk of serious motor and metabolic AEs 64 million antipsychotics Rx in US (1) Suboptimal outcomes and low compliance rates Multiple drugs achieved >$5B peak sales, with notable uptake for late entrants with modest differentiation Modulate ACh without direct D2 dopamine receptor blockade Efficacy across positive and negative symptoms No boxed warning or existing antipsychotics’ class warnings & precautions Schizophrenia and ADP affect 5M+ people in the US (2)(3) Potential for treatment of psychosis, cognitive and motor symptoms in multiple other conditions Emergence of Novel Muscarinic Class Global Sales for Antipsychotics and Muscarinic Class Projected to Exceed $20B by 2032 (4)
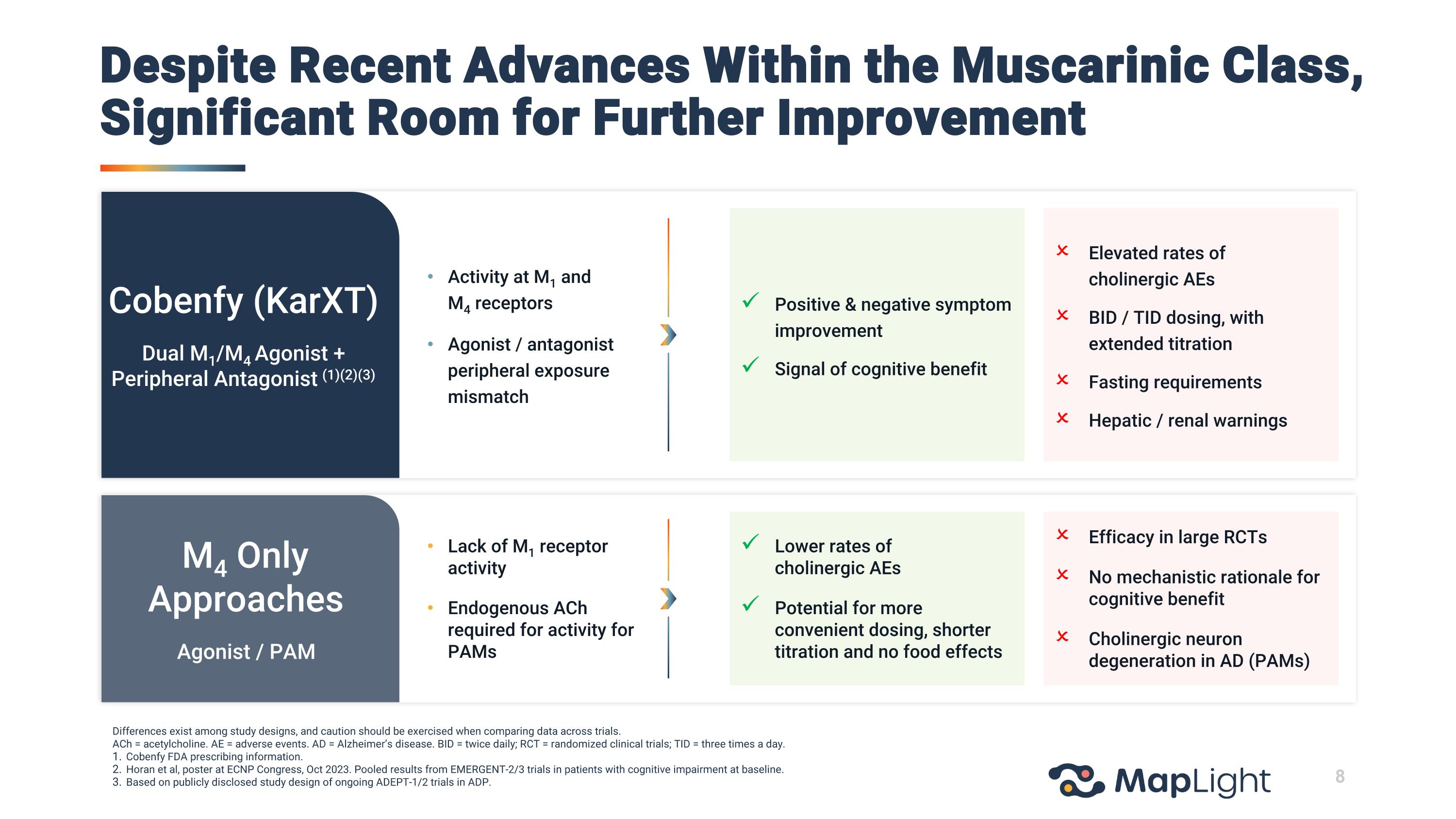
Activity at M1 andM4 receptors Agonist / antagonistperipheral exposure mismatch Lack of M1 receptor activity Endogenous ACh required for activity for PAMs Positive & negative symptom improvement Signal of cognitive benefit Elevated rates of cholinergic AEs BID / TID dosing, with extended titration Fasting requirements Hepatic / renal warnings Lower rates of cholinergic AEs Potential for more convenient dosing, shorter titration and no food effects Efficacy in large RCTs No mechanistic rationale for cognitive benefit Cholinergic neuron degeneration in AD (PAMs) M4 Only Approaches Agonist / PAM Cobenfy (KarXT) Dual M1/M4 Agonist + Peripheral Antagonist (1)(2)(3) Differences exist among study designs, and caution should be exercised when comparing data across trials. ACh = acetylcholine. AE = adverse events. AD = Alzheimer’s disease. BID = twice daily; RCT = randomized clinical trials; TID = three times a day. Cobenfy FDA prescribing information. Horan et al, poster at ECNP Congress, Oct 2023. Pooled results from EMERGENT-2/3 trials in patients with cognitive impairment at baseline. Based on publicly disclosed study design of ongoing ADEPT-1/2 trials in ADP. Despite Recent Advances Within the Muscarinic Class, Significant Room for Further Improvement

Safety and Tolerability Improved Ease of Use Improvement Across Key Symptom Domains Broad IP Portfolio Expected to Provide Coverage Into 2040s (2) ML-007C-MA Novel M1/M4 Agonist + Fesoterodine(1) 9 ML-007C-MA: Our Novel M1/M4 Muscarinic Agonist Potential Areas of Differentiation Strong Activation of Both M1 & M4 Receptors Synchronized Agonist / Antagonist Exposure Rational and Deliberate Clinical Strategy Fesoterodine is indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder in adult patients with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency. Intellectual property portfolio coverage based on latest-to-expire issued patents and provisional applications covering composition of matter for ML-007, treatment and method of use. Significant Need for a Safer and More Convenient Treatment Option With Robust M1/M4 Activation
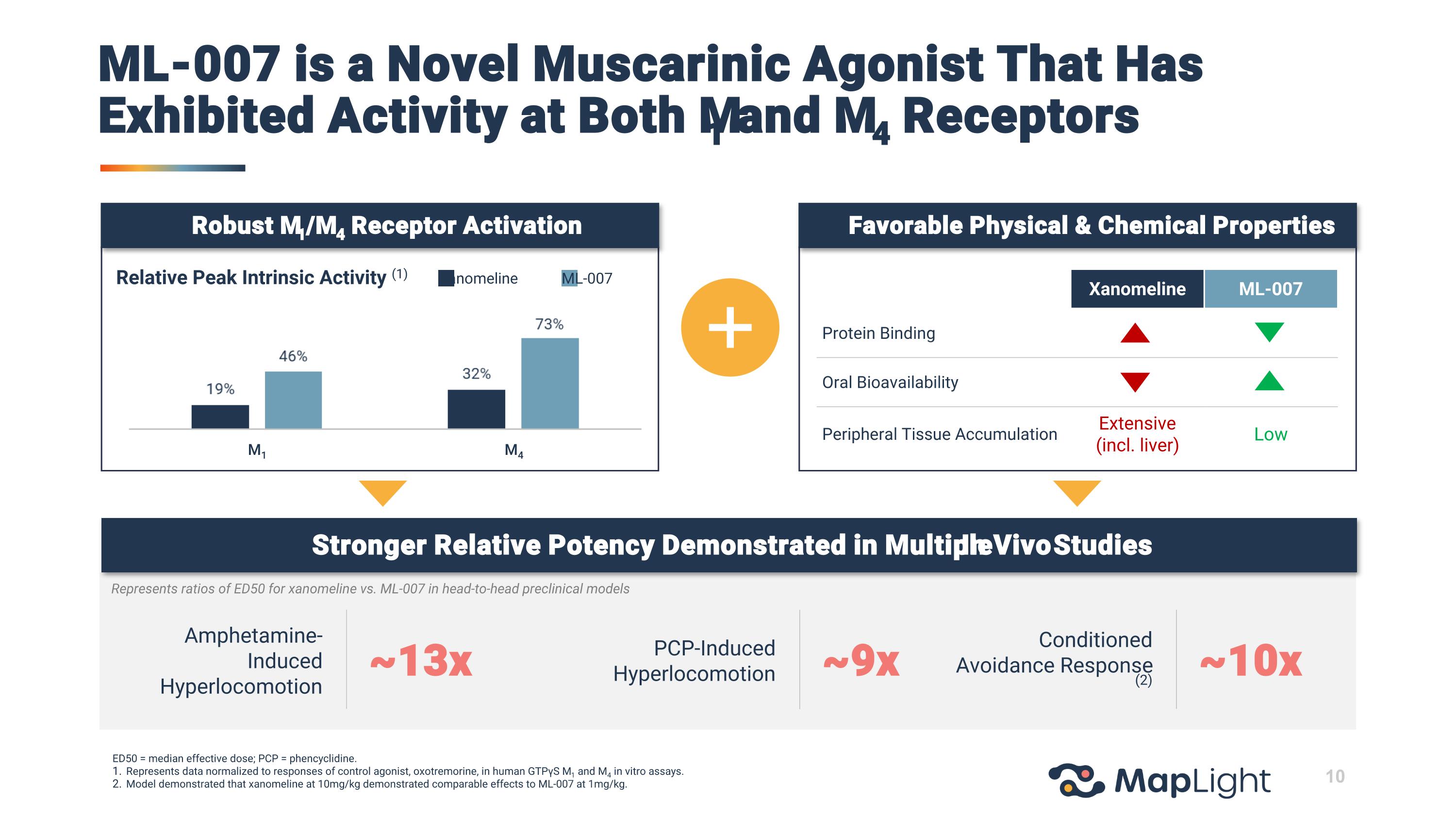
Amphetamine-Induced Hyperlocomotion PCP-Induced Hyperlocomotion Conditioned Avoidance Response (2) ~13x ~9x ~10x Xanomeline ML-007 Relative Peak Intrinsic Activity (1) Xanomeline ML-007 Protein Binding Oral Bioavailability Peripheral Tissue Accumulation Extensive (incl. liver) Low Stronger Relative Potency Demonstrated in Multiple In Vivo Studies Represents ratios of ED50 for xanomeline vs. ML-007 in head-to-head preclinical models ED50 = median effective dose; PCP = phencyclidine. Represents data normalized to responses of control agonist, oxotremorine, in human GTPγS M1 and M4 in vitro assays. Model demonstrated that xanomeline at 10mg/kg demonstrated comparable effects to ML-007 at 1mg/kg. Favorable Physical & Chemical Properties Robust M1/M4 Receptor Activation M1 M4 ML-007 is a Novel Muscarinic Agonist That Has Exhibited Activity at Both M1 and M4 Receptors

210/3 mg BID Dose (2) 330/6 mg QD Dose (2) ML-007 PAC Ratio Dose notation refers to the co-formulated combination of ML‑007 and PAC. For example, 210/3 mg indicates 210 mg of ML‑007 and 3 mg of peripherally acting anti-cholinergic (PAC) . BID = twice daily; CV = coefficient of variation; QD = once daily. Data points show geometric mean observed data from individual study; lines represent model-simulated values. Observations after 7 days of maintenance dosing. PAC concentration of active metabolite 5-HMT. Calculated using last maintenance Day 7 dose data. Low Variability Observed at Target Doses – CV of ~30% (3) Steady State Plasma Concentrations From Study 013 (1) Close Matching of Plasma Exposures for ML-007 & PAC to Offset Peripheral Cholinergic Activity ML-007 or PAC Plasma Concentration (ng/mL) ML-007C-MA Concentration Ratio ML-007 or PAC Plasma Concentration (ng/mL) ML-007C-MA Concentration Ratio
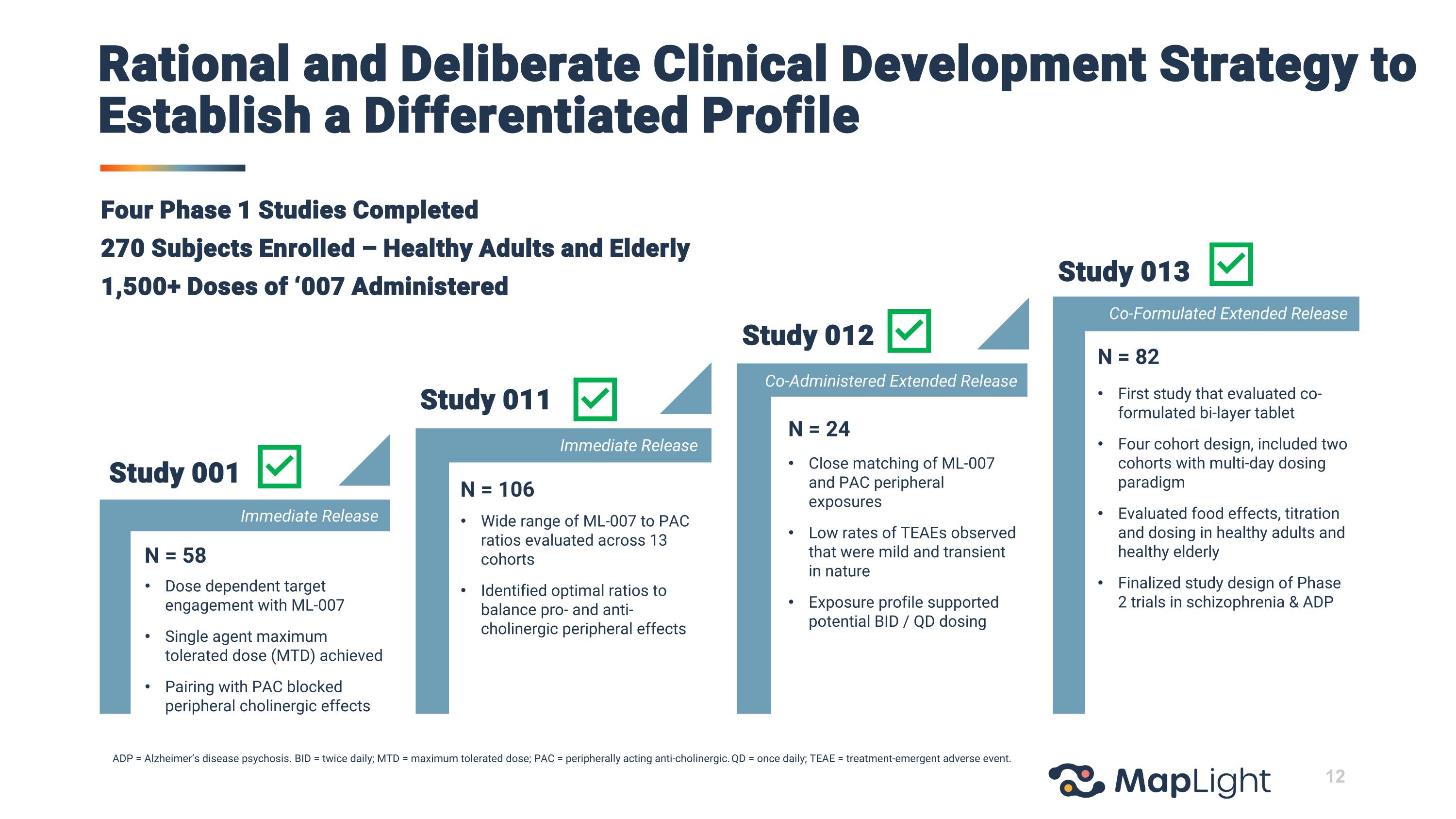
Four Phase 1 Studies Completed 270 Subjects Enrolled – Healthy Adults and Elderly 1,500+ Doses of ‘007 Administered ADP = Alzheimer’s disease psychosis. BID = twice daily; MTD = maximum tolerated dose; PAC = peripherally acting anti-cholinergic. QD = once daily; TEAE = treatment-emergent adverse event. N = 58 Dose dependent target engagement with ML-007 Single agent maximum tolerated dose (MTD) achieved Pairing with PAC blocked peripheral cholinergic effects N = 106 Wide range of ML-007 to PAC ratios evaluated across 13 cohorts Identified optimal ratios to balance pro- and anti-cholinergic peripheral effects N = 24 Close matching of ML-007 and PAC peripheral exposures Low rates of TEAEs observed that were mild and transient in nature Exposure profile supported potential BID / QD dosing N = 82 First study that evaluated co-formulated bi-layer tablet Four cohort design, included two cohorts with multi-day dosing paradigm Evaluated food effects, titration and dosing in healthy adults and healthy elderly Finalized study design of Phase 2 trials in schizophrenia & ADP Co-Administered Extended Release Co-Formulated Extended Release Immediate Release Immediate Release Study 001 Study 011 Study 012 Study 013 Rational and Deliberate Clinical Development Strategy to Establish a Differentiated Profile

ML-007C-MA Key Areas of Potential Differentiation

Safety and Tolerability KarXT: Elevated Rates of Pro and Anticholinergic AEs TEAEs reported in 67-89% of subjects in Phase 1 healthy volunteer trial at doses similar to the clinically efficacious doses, with moderate TEAEs in 17-33% of subjects (1) Phase 2 and 3 trials in schizophrenia patients reported similar rates and types of AEs (2) 52-week OLE studies in schizophrenia reported discontinuation rates of ~47-77% (3) Early real-world evidence suggest tolerability challenges (e.g., lower doses, longer titrations, incidence of nausea / vomiting) (4) ML-007C-MA: Precision Matching of Agonist / Antagonist Synchronizing peripheral exposures of components designed to offer improved tolerability Rational and deliberate clinical development approach to identify optimal ratios of components Favorable safety / tolerability profile observed in healthy adults and elderly subjects to date Differences exist among study designs, and caution should be exercised when comparing data across trials. ADP = Alzheimer’s disease psychosis; AE = adverse event; OLE = open label extension; TEAE = treatment-emergent adverse event; TID = three times a day. Brannan et al, poster at ASCP 2019. Phase 1 trial with multiple ascending doses in healthy volunteers. AE rates shown across cohorts. Brannan et al, posters at NEI Congress, Nov 2023. Pooled results from EMERGENT trials. Based on FDA NDA Review for Cobenfy. Represents interim data submitted as part of 120-day update. Kutz et al, poster at Psych Congress 2025. Areas of Potential Differentiation
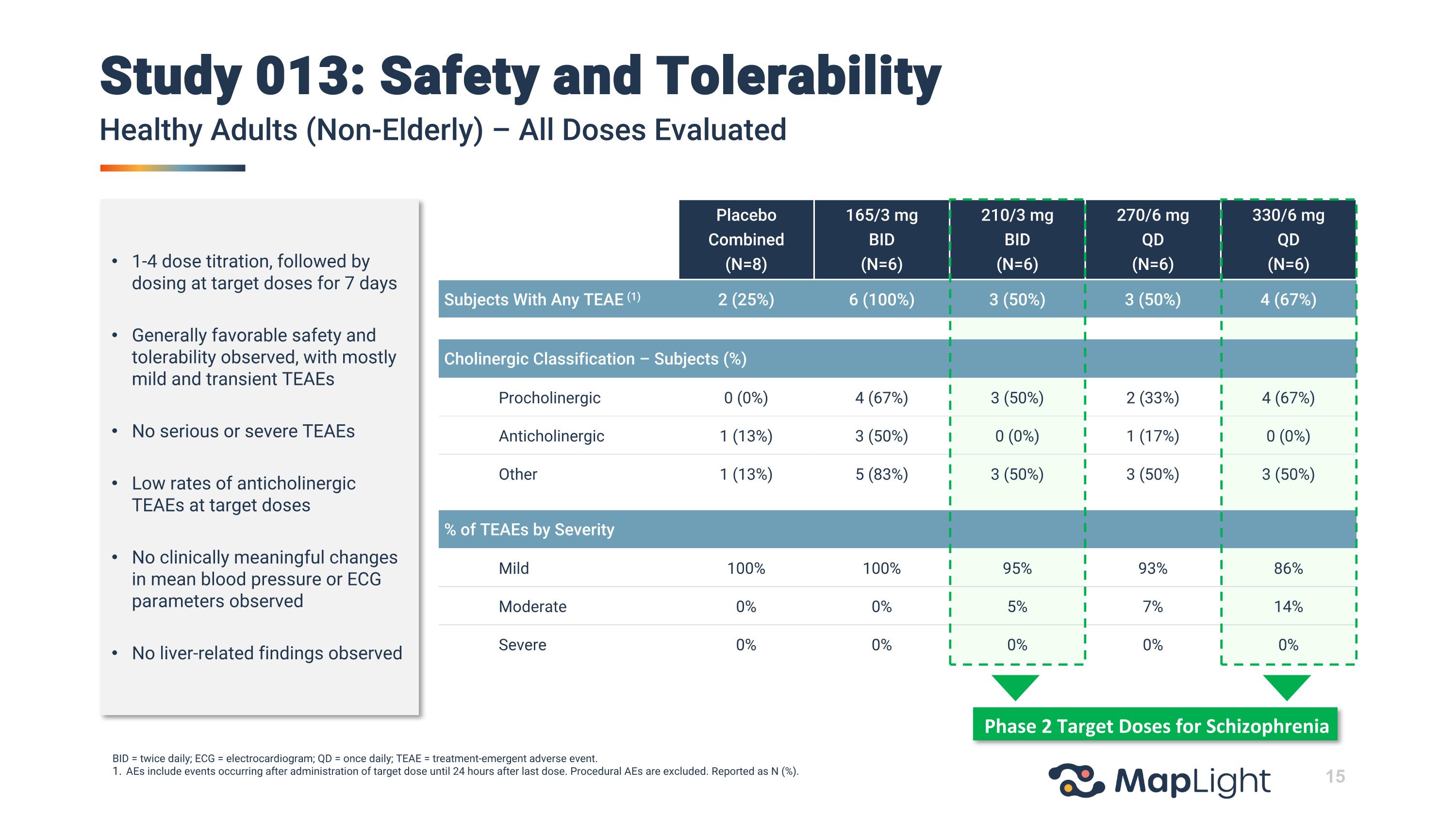
Placebo Combined (N=8) 165/3 mg BID (N=6) 210/3 mg BID (N=6) 270/6 mg QD (N=6) 330/6 mg QD (N=6) Subjects With Any TEAE (1) 2 (25%) 6 (100%) 3 (50%) 3 (50%) 4 (67%) Cholinergic Classification – Subjects (%) Procholinergic 0 (0%) 4 (67%) 3 (50%) 2 (33%) 4 (67%) Anticholinergic 1 (13%) 3 (50%) 0 (0%) 1 (17%) 0 (0%) Other 1 (13%) 5 (83%) 3 (50%) 3 (50%) 3 (50%) % of TEAEs by Severity Mild 100% 100% 95% 93% 86% Moderate 0% 0% 5% 7% 14% Severe 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Study 013: Safety and TolerabilityHealthy Adults (Non-Elderly) – All Doses Evaluated BID = twice daily; ECG = electrocardiogram; QD = once daily; TEAE = treatment-emergent adverse event. AEs include events occurring after administration of target dose until 24 hours after last dose. Procedural AEs are excluded. Reported as N (%). Phase 2 Target Doses for Schizophrenia 1-4 dose titration, followed by dosing at target doses for 7 days Generally favorable safety and tolerability observed, with mostly mild and transient TEAEs No serious or severe TEAEs Low rates of anticholinergic TEAEs at target doses No clinically meaningful changes in mean blood pressure or ECG parameters observed No liver-related findings observed
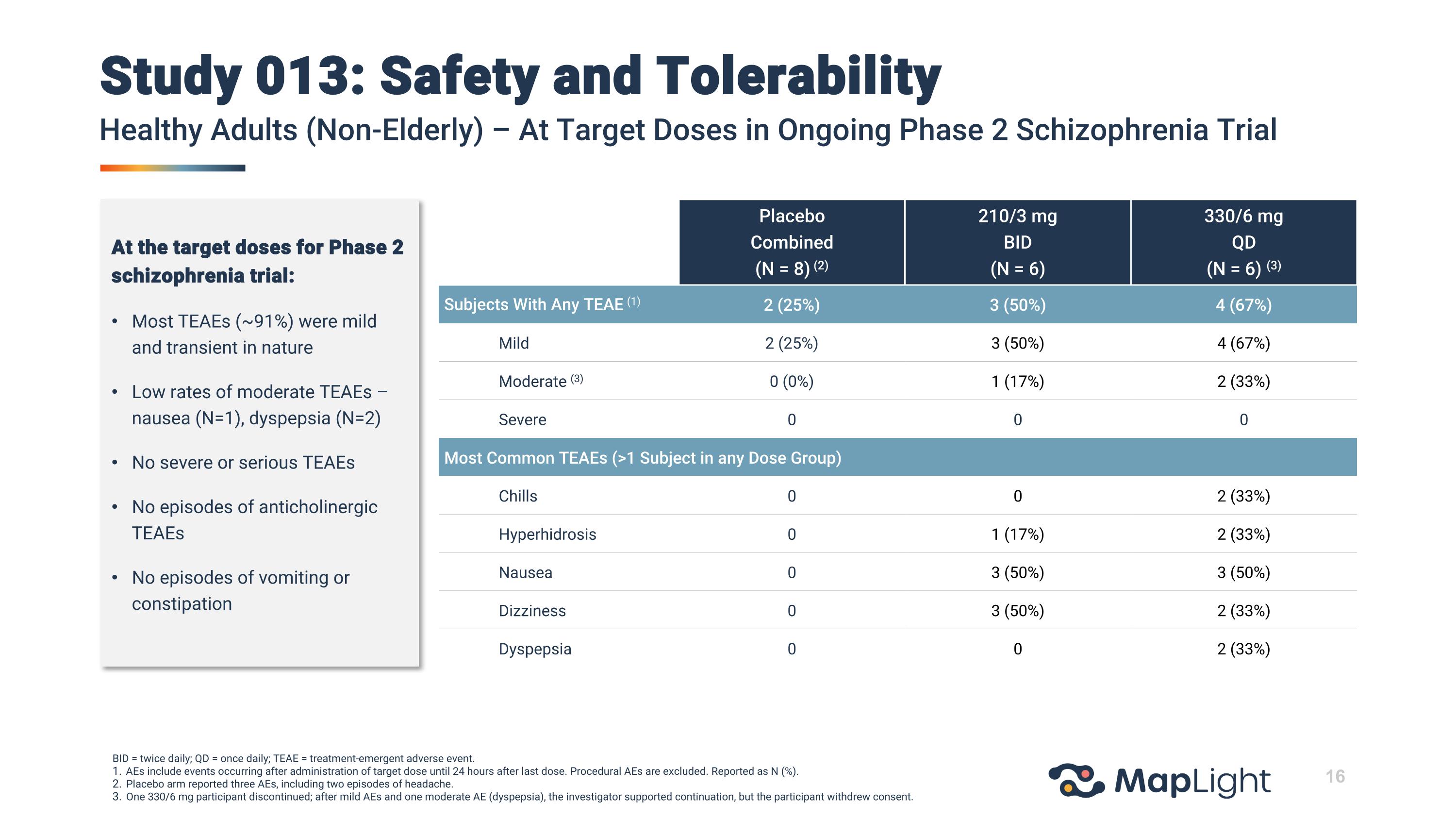
Study 013: Safety and TolerabilityHealthy Adults (Non-Elderly) – At Target Doses in Ongoing Phase 2 Schizophrenia Trial BID = twice daily; QD = once daily; TEAE = treatment-emergent adverse event. AEs include events occurring after administration of target dose until 24 hours after last dose. Procedural AEs are excluded. Reported as N (%). Placebo arm reported three AEs, including two episodes of headache. One 330/6 mg participant discontinued; after mild AEs and one moderate AE (dyspepsia), the investigator supported continuation, but the participant withdrew consent. Placebo Combined (N = 8) (2) 210/3 mg BID (N = 6) 330/6 mg QD (N = 6) (3) Subjects With Any TEAE (1) 2 (25%) 3 (50%) 4 (67%) Mild 2 (25%) 3 (50%) 4 (67%) Moderate (3) 0 (0%) 1 (17%) 2 (33%) Severe 0 0 0 Most Common TEAEs (>1 Subject in any Dose Group) Chills 0 0 2 (33%) Hyperhidrosis 0 1 (17%) 2 (33%) Nausea 0 3 (50%) 3 (50%) Dizziness 0 3 (50%) 2 (33%) Dyspepsia 0 0 2 (33%) At the target doses for Phase 2 schizophrenia trial: Most TEAEs (~91%) were mild and transient in nature Low rates of moderate TEAEs –nausea (N=1), dyspepsia (N=2) No severe or serious TEAEs No episodes of anticholinergic TEAEs No episodes of vomiting or constipation
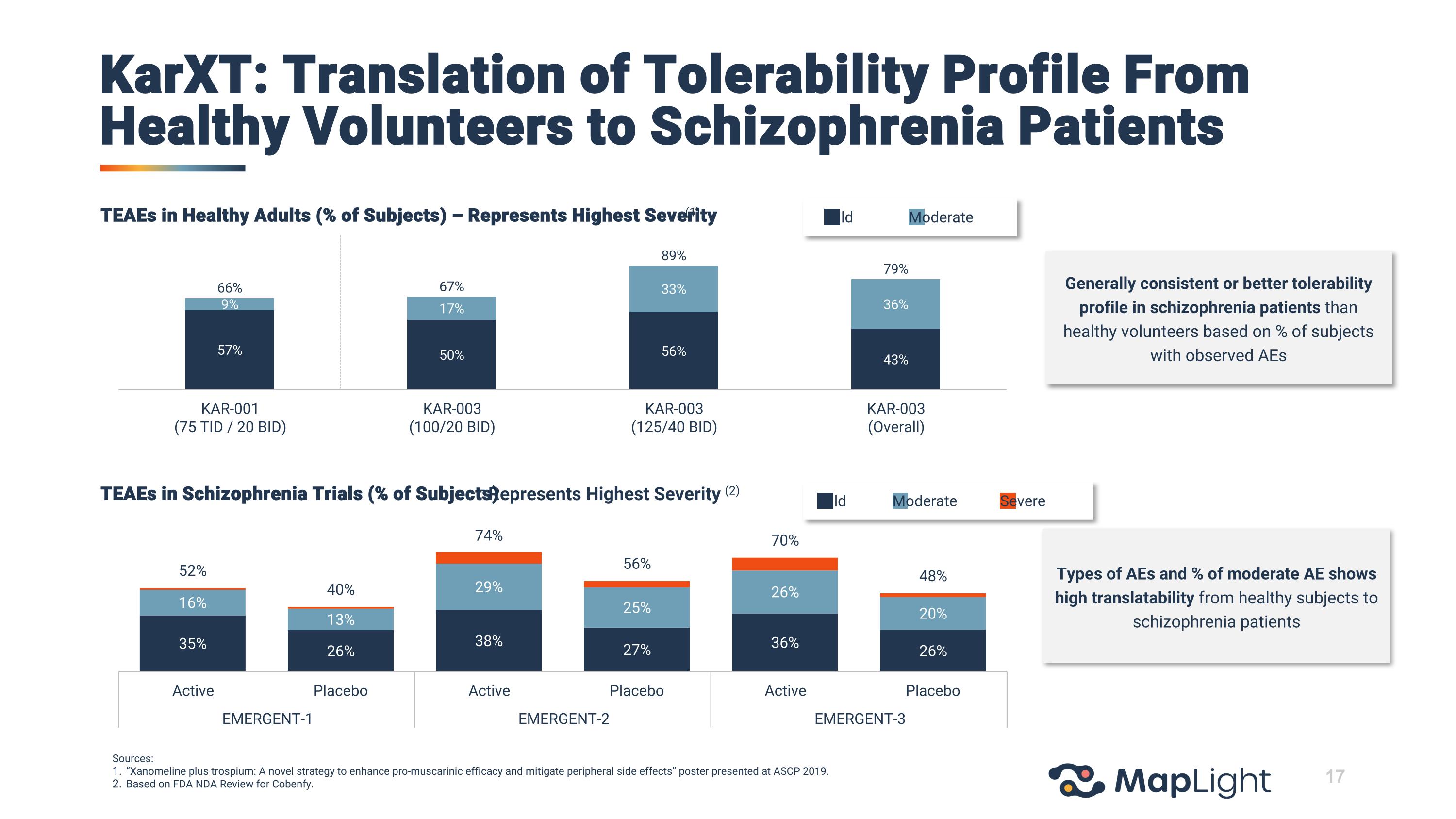
KarXT: Translation of Tolerability Profile From Healthy Volunteers to Schizophrenia Patients Types of AEs and % of moderate AE shows high translatability from healthy subjects to schizophrenia patients TEAEs in Schizophrenia Trials (% of Subjects) – Represents Highest Severity (2) TEAEs in Healthy Adults (% of Subjects) – Represents Highest Severity (1) Sources: “Xanomeline plus trospium: A novel strategy to enhance pro-muscarinic efficacy and mitigate peripheral side effects” poster presented at ASCP 2019. Based on FDA NDA Review for Cobenfy. Mild Moderate Mild Moderate Severe Generally consistent or better tolerability profile in schizophrenia patients than healthy volunteers based on % of subjects with observed AEs 17

Study 013: Safety and TolerabilityHealthy Elderly – All Doses Evaluated Placebo Combined (N=7) (2) 165/3 mg BID (with 2d titration) (N=6) 210/3 mg BID (with 2-7d titration) (N=11) (3) 330/6 mg QD(with 7d titration) (N=6) (4) Subjects with Any TEAE (1) 5 (71%) 4 (67%) 8 (73%) 6 (100%) Cholinergic Classification – Subjects (%) Procholinergic 1 (14%) 2 (33%) 6 (55%) 6 (100%) Anticholinergic 1 (14%) 1 (17%) 4 (36%) 0 Other 3 (43%) 3 (50%) 8 (73%) 6 (100%) % of TEAEs by Severity Mild 100% 100% 93% 72% Moderate (3) 0% 0% 7% 28% Severe 0% 0% 0% 0% Phase 2 Target Dose for ADP ADP = Alzheimer’s disease psychosis; BID = twice daily; ECG = electrocardiogram; QD = once daily; TEAE = treatment-emergent adverse event. AEs include events occurring after administration of target dose until 24 hours after last dose. Procedural AEs are excluded. Reported as N (%). One participant (placebo) discontinued from the study due to an AE during titration; one participant (placebo) had an AE during maintenance dosing that led to study drug withdrawal. Two participants had their dose reduced to 165/3 mg BID after experiencing AEs; one additional participant was discontinued from the study for non-compliance with clinic rules. Four participants had AEs that led to withdrawal of study drug and one additional participant had their dose reduced to 270/6 mg QD due to AEs. 2-7 day titration period, followed by dosing at target doses for 7 days Generally favorable safety and tolerability with BID dosing, with mostly mild and transient TEAEs Highest dose given QD was not well tolerated – potential to explore lower QD doses Low rates of anticholinergic TEAEs No clinically meaningful changes in mean blood pressure or ECG parameters observed No liver-related findings observed
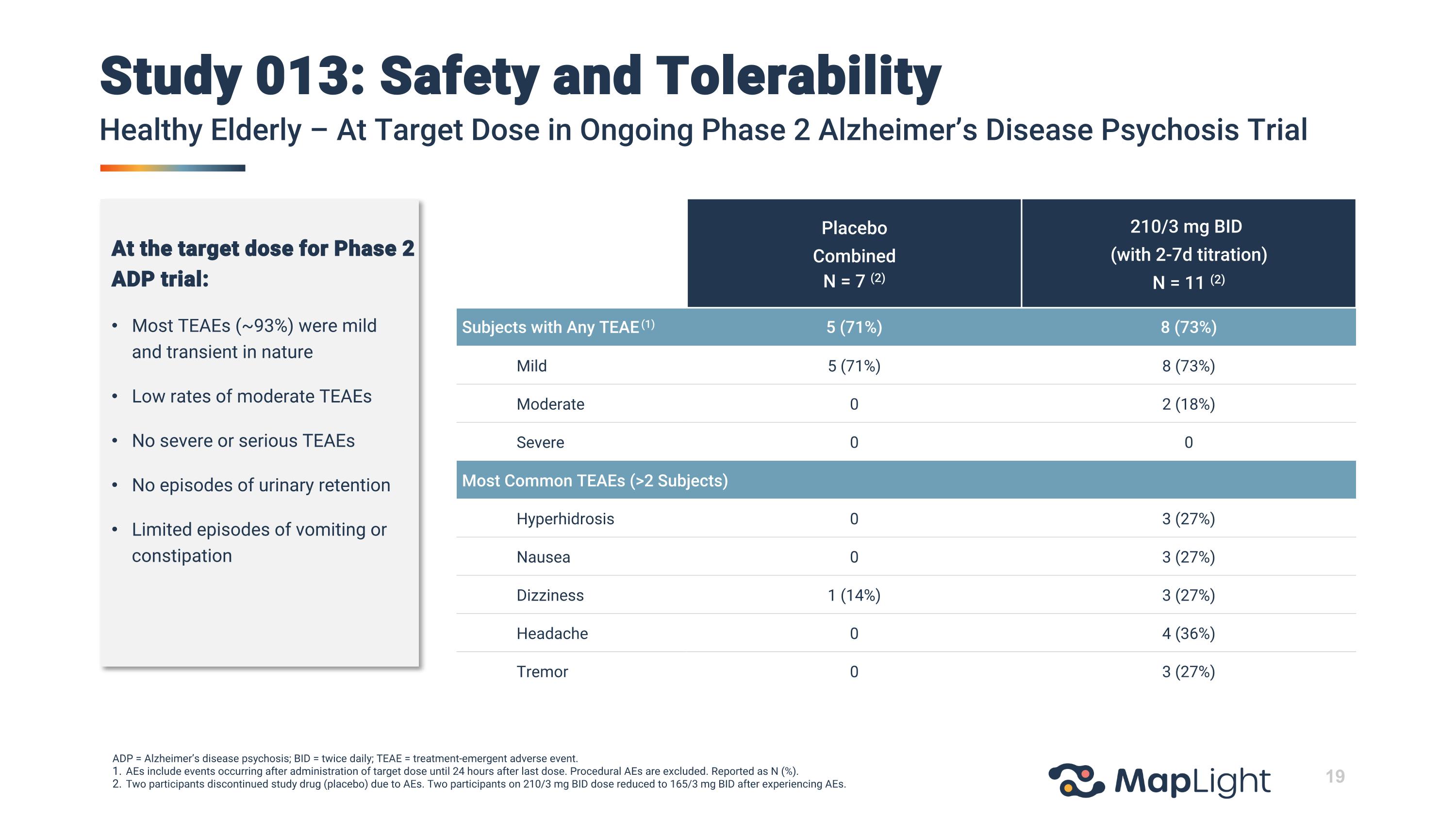
Study 013: Safety and TolerabilityHealthy Elderly – At Target Dose in Ongoing Phase 2 Alzheimer’s Disease Psychosis Trial ADP = Alzheimer’s disease psychosis; BID = twice daily; TEAE = treatment-emergent adverse event. AEs include events occurring after administration of target dose until 24 hours after last dose. Procedural AEs are excluded. Reported as N (%). Two participants discontinued study drug (placebo) due to AEs. Two participants on 210/3 mg BID dose reduced to 165/3 mg BID after experiencing AEs. Placebo CombinedN = 7 (2) 210/3 mg BID (with 2-7d titration) N = 11 (2) Subjects with Any TEAE (1) 5 (71%) 8 (73%) Mild 5 (71%) 8 (73%) Moderate 0 2 (18%) Severe 0 0 Most Common TEAEs (>2 Subjects) Hyperhidrosis 0 3 (27%) Nausea 0 3 (27%) Dizziness 1 (14%) 3 (27%) Headache 0 4 (36%) Tremor 0 3 (27%) At the target dose for Phase 2 ADP trial: Most TEAEs (~93%) were mild and transient in nature Low rates of moderate TEAEs No severe or serious TEAEs No episodes of urinary retention Limited episodes of vomiting or constipation
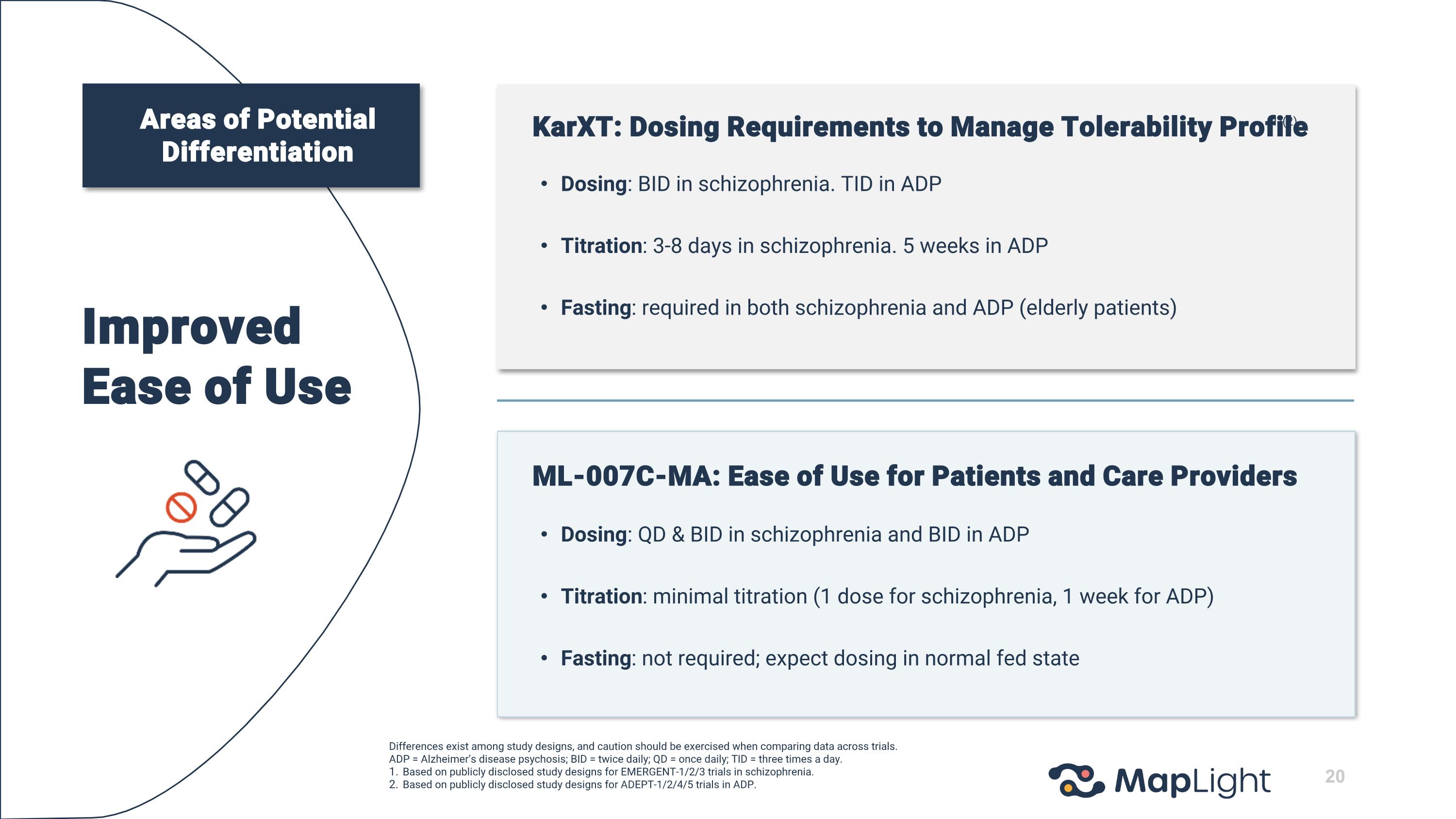
Improved Ease of Use KarXT: Dosing Requirements to Manage Tolerability Profile (1)(2) Dosing: BID in schizophrenia. TID in ADP Titration: 3-8 days in schizophrenia. 5 weeks in ADP Fasting: required in both schizophrenia and ADP (elderly patients) ML-007C-MA: Ease of Use for Patients and Care Providers Dosing: QD & BID in schizophrenia and BID in ADP Titration: minimal titration (1 dose for schizophrenia, 1 week for ADP) Fasting: not required; expect dosing in normal fed state Differences exist among study designs, and caution should be exercised when comparing data across trials. ADP = Alzheimer’s disease psychosis; BID = twice daily; QD = once daily; TID = three times a day. Based on publicly disclosed study designs for EMERGENT-1/2/3 trials in schizophrenia. Based on publicly disclosed study designs for ADEPT-1/2/4/5 trials in ADP. Areas of Potential Differentiation
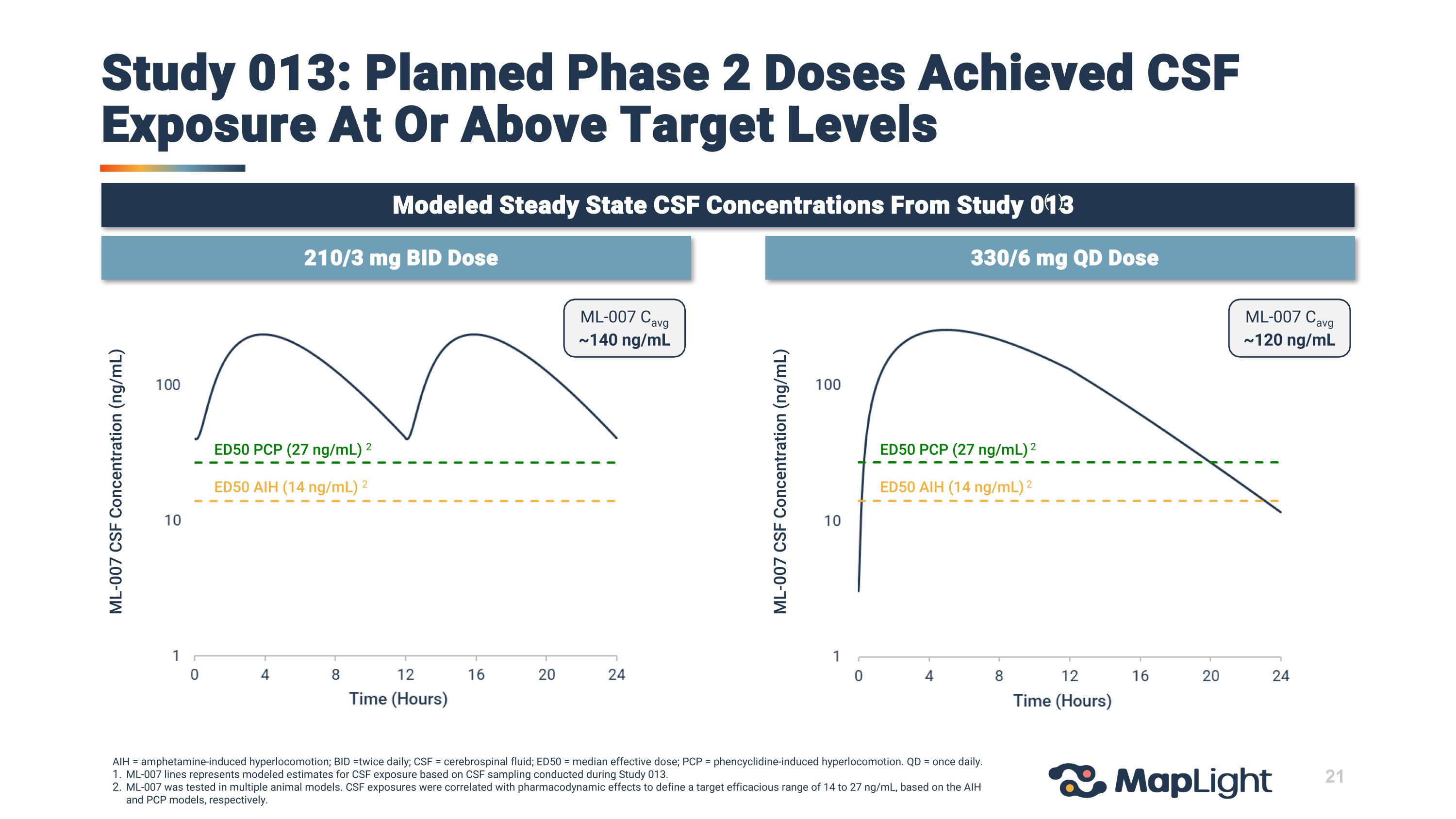
21 Study 013: Planned Phase 2 Doses Achieved CSF Exposure At Or Above Target Levels AIH = amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion; BID =twice daily; CSF = cerebrospinal fluid; ED50 = median effective dose; PCP = phencyclidine-induced hyperlocomotion. QD = once daily. ML-007 lines represents modeled estimates for CSF exposure based on CSF sampling conducted during Study 013. ML-007 was tested in multiple animal models. CSF exposures were correlated with pharmacodynamic effects to define a target efficacious range of 14 to 27 ng/mL, based on the AIH and PCP models, respectively. 210/3 mg BID Dose 330/6 mg QD Dose Modeled Steady State CSF Concentrations From Study 013 (1) ML-007 CSF Concentration (ng/mL) ML-007 CSF Concentration (ng/mL) ML-007 Cavg ~120 ng/mL ML-007 Cavg ~140 ng/mL ED50 PCP (27 ng/mL) 2 ED50 AIH (14 ng/mL) 2 ED50 PCP (27 ng/mL) 2 ED50 AIH (14 ng/mL) 2
Improvement Across Key Symptom Domains KarXT: Cognitive Benefit Trend in Exploratory Analyses (1) Xanomeline showed clinically meaningful cognitive benefit in Phase 2 AD trial (2) ML-007C-MA: Potential Improvement Across Symptom Domains ML-007 has demonstrated robust M1/M4 activity (vs. xanomeline) in vitro and in vivo Both M1 and M4 receptors play significant roles in reduction of positive and negative symptoms in preclinical models of schizophrenia ML-007’s pro-cognitive potential demonstrated in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease Differences exist among study designs, and caution should be exercised when comparing data across trials. ACh = acetylcholine; AD = Alzheimer’s disease; ADP = Alzheimer’s disease psychosis; PAM = positive allosteric modulator. Horan et al, poster at ECNP Congress, Oct 2023. Pooled results from EMERGENT-2/3 trials in patients with cognitive impairment at baseline. Veroff AE et al, PubMed 9876958, Dec 1998. Woolf NJ. et al, Neurobiology Learn Mem, Nov 1996 M4 Specific Approaches: No Mechanistic Rationale for Cognitive Benefit Lack of M1 activity may impact broader efficacy as reported in recent competitor updates PAM approach requires endogenous ACh – reduced in neurodegenerative diseases like ADP (3) Areas of Potential Differentiation
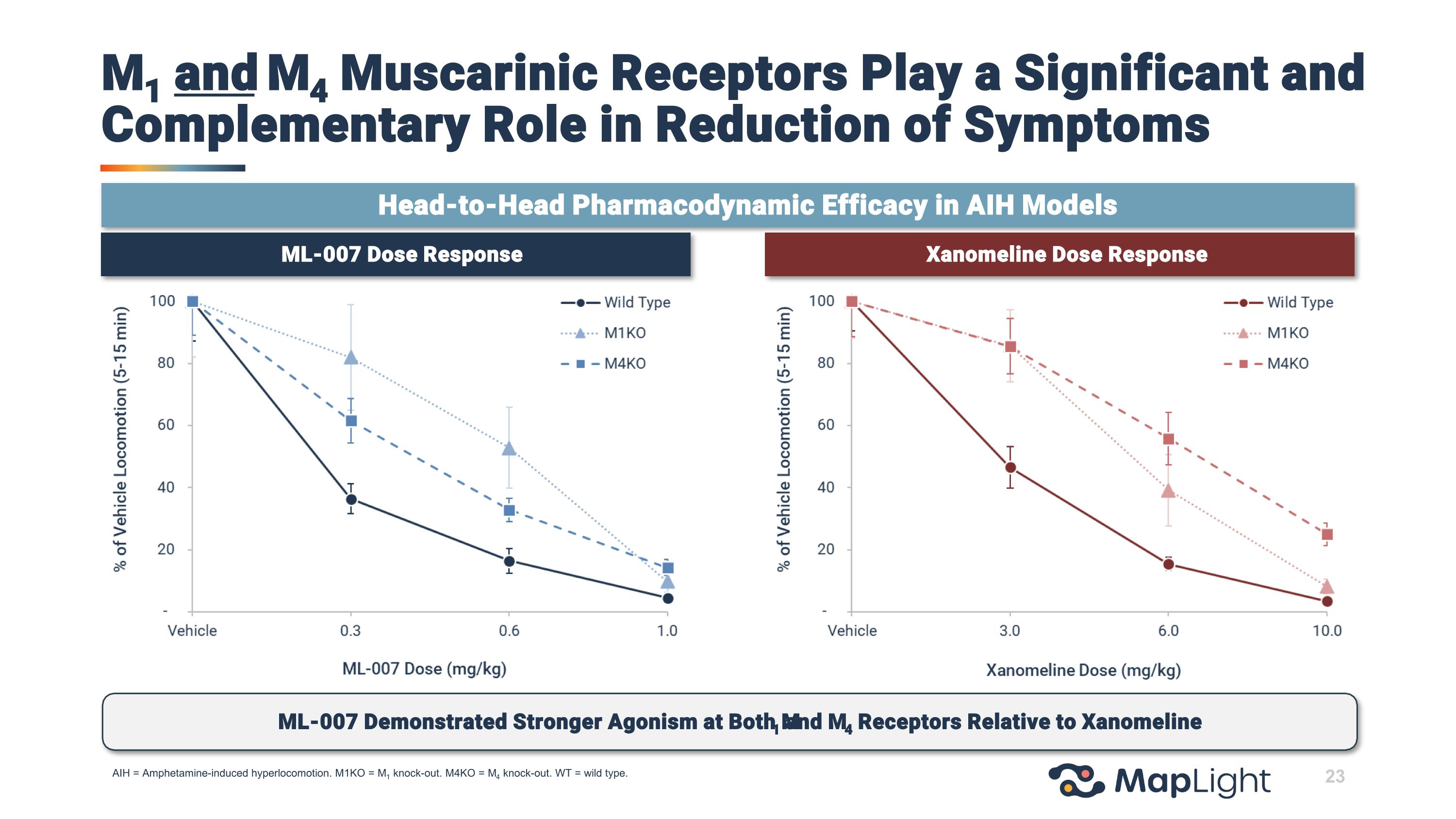
23 ML-007 Dose Response Xanomeline Dose Response AIH = Amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion. M1KO = M1 knock-out. M4KO = M4 knock-out. WT = wild type. M1 and M4 Muscarinic Receptors Play a Significant and Complementary Role in Reduction of Symptoms ML-007 Demonstrated Stronger Agonism at Both M1 and M4 Receptors Relative to Xanomeline Head-to-Head Pharmacodynamic Efficacy in AIH Models
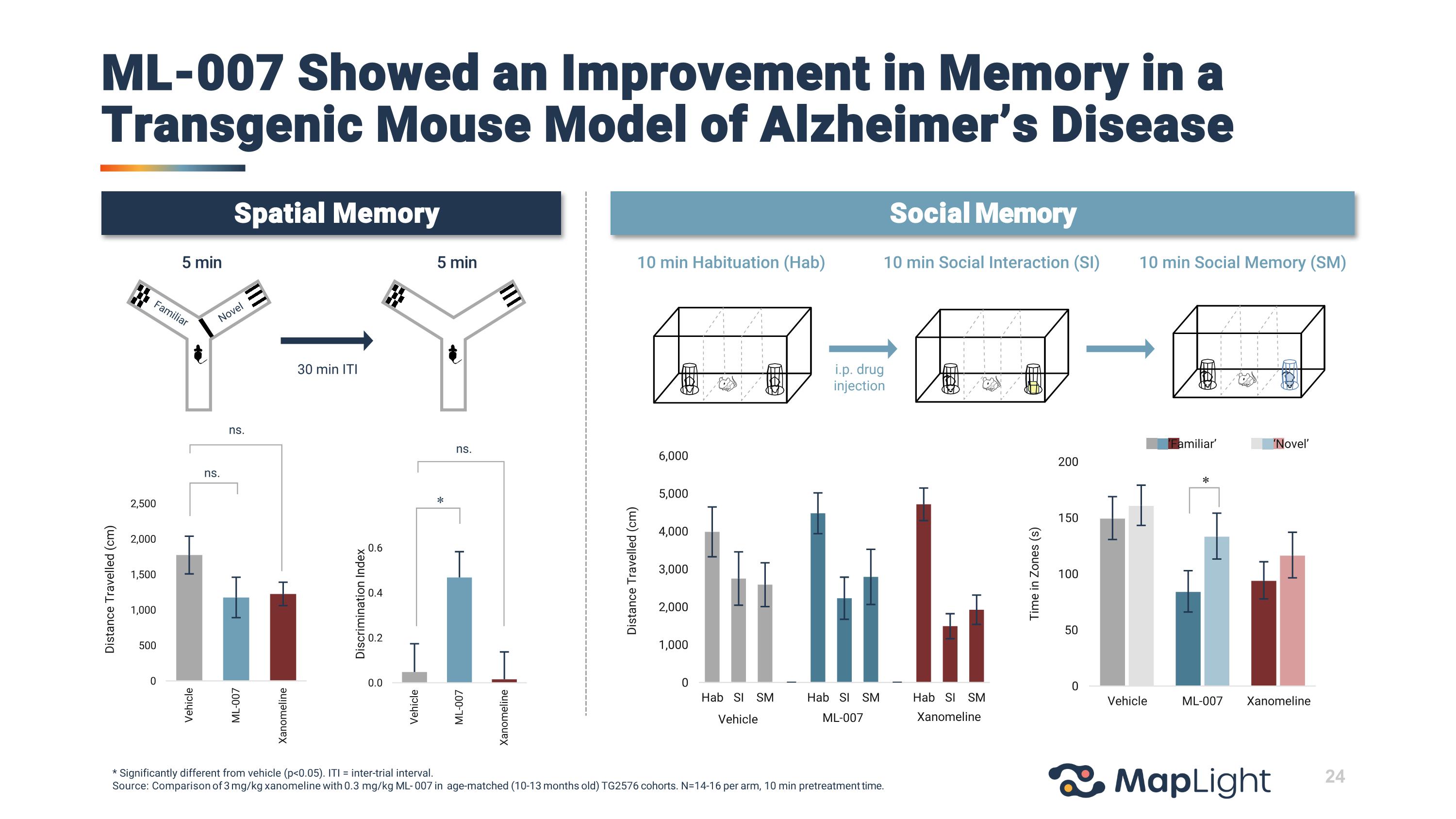
ns. ns. ns. * Vehicle ML-007 Xanomeline * ‘Familiar’ ‘Novel’ 24 Spatial Memory Social Memory * Significantly different from vehicle (p<0.05). ITI = inter-trial interval. Source: Comparison of 3 mg/kg xanomeline with 0.3 mg/kg ML- 007 in age-matched (10-13 months old) TG2576 cohorts. N=14-16 per arm, 10 min pretreatment time. ML-007 Showed an Improvement in Memory in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease 5 min 5 min 30 min ITI Familiar Novel 10 min Habituation (Hab) i.p. drug injection 10 min Social Memory (SM) 10 min Social Interaction (SI) i.p. drug injection

ML-007C-MA Clinical Development

26 Establish Efficacy / Safety in Key Indications Explore and Pursue Additional Indications Parallel development plans in schizophrenia and ADP Phase 2 studies designed to be adequate and well controlled Data-driven clinical design and execution strategy designed to mitigate placebo response Prioritization of key registration-enabling activities Broad potential in multiple indications, including: Cognition in Alzheimer’s disease Psychoses in other neurodegenerative conditions Bipolar disorder Dyskinesias Autism spectrum disorder Our Development Strategy for ML-007C-MA

27 Trial Type Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial Location US only, multicenter (25 sites) Global, multicenter (100 sites) Participants Hospitalized adult patients with schizophrenia Sample size = 300 Subjects with psychosis associated with Alzheimer’s disease Sample size = 300 Primary Endpoint Change in PANSS score at 5 weeks vs. baseline Change in NPI-C H+D scores at 7 weeks vs. baseline Treatment Groups 1:1:1 randomization: placebo, 210/3mg BID and 330/6mg QD Option to drop down: 165/3mg BID or 270/6mg QD 1:1 randomization: placebo and 210/3 mg BID Option to drop down: 105/1.5mg BID Topline Results Expected in second half of 2026 Expected in second half of 2027 Phase 2 in Schizophrenia Phase 2 in ADP Design of Ongoing Phase 2 Studies ADP = Alzheimer’s disease psychosis; BID = twice daily; QD = once daily; PANSS = Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; NPI-C H+D = Neuropsychiatric Inventory Clinician, Hallucinations and Delusions.

Strategies to Mitigate Placebo Response in Ongoing Phase 2 Schizophrenia Study Limited number of sites (25) Single geography - US only Extensive vetting of sites using: Quality metrics for raters in recent acute schizophrenia studies Recent enrollment in positive acute schizophrenia studies 1:1 interviews with PIs Input from external consultants Individual site enrollment gated based on data quality from initial participants Limited number of participants (N=300) Single study with conservative enrollment metrics to avoid pushing enrollment too fast Participants required to complete a 3-step robust eligibility review process Duplicate patient exclusion process Target population must have moderate-to-severe symptoms at screening and baseline Excludes participants with >20% improvement from screening to baseline In-sourced site relationship and data quality oversight responsibilities with in-house CRA / monitoring program Robust quality monitoring during study conduct (independent central review, regular cadence of blinded data analytics) Placebo response training to all participant facing site staff Expectancy bias education to participants CRO selected based on track record in recent schizophrenia studies 28 PI = Principal investigator. Similar Strategies Employed in the Ongoing Phase 2 VISTA Study for ADP Study Conduct Site Selection Enrollment

ML-004 Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
30 Core symptoms: Impaired social communication Restricted, repetitive thoughts and behaviors Comorbid neurobehavioral symptoms include: Irritability and aggression (in 25% of ASD patients) Hyperactivity, mood lability Affects ~1.8M children & adolescents and >5M adults in US No FDA approved treatments for core symptoms of ASD Only widely accepted intervention is long-term behavioral therapy (30-40 hours / week) Off label usage of ADHD medications, SSRIs, SNRIs, and supplements Two atypical antipsychotics approved for ASD-associated irritability Risk of serious side effects Ineffective in treating core social features Dysregulated serotonin signaling implicated in ASD pathology ML-004 – novel IR/ER oral formulation of zolmitriptan (5-HT1B/1D agonist) Zolmitriptan approved for acute treatment of migraines Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics evaluated in Phase 1 trials Ongoing Phase 2 trial to evaluate efficacy and safety in ASD patients ASD Overview Unmet Medical Need ML-004 Potential ML-004: Potential Treatment of Social Communication Deficits and Irritability in ASD Patients ASD = autism spectrum disorder; ADHD = attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; SSRI = selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; SNRI = serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. Source: US CDC prevalence estimates.

Multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Randomized approximately 160 subjects with ASD Adolescent (age 12-17) and adult (age 18-45) Flexible dosing paradigm, with target maintenance dose of 48mg and 72mg Primary Endpoint: ABI, Social Communication Domain Score Change vs. baseline assessed after 12 weeks of maintenance dosing Secondary Endpoint: Change in ABC-I score vs. baseline for patients with moderate or greater irritability score at baseline Other secondary and exploratory endpoints Patients eligible to participate in 52-week OLE trial following completion of Phase 2 trial 31 ABI - Autism Behavior Inventory, ABC-I - Aberrant Behavior Checklist-Irritability; ASD = autism spectrum disorder. OLE = open label extension. ML-004: Ongoing Global Phase 2 Trial in ASD

Potential for a well tolerated and convenient option without sacrificing strong M1/M4 activation Broad development strategy, including parallel advancement in schizophrenia and ADP Versatile and reproducible discovery platform leveraging our deep understanding of circuit biology Extensive medicinal chemistry and formulation expertise ML-004 in Phase 2 trial for treatment of sociability and / or irritability symptoms of ASD Expect to continue advancing early-stage pipeline Seasoned team with experience in drug development and commercialization Strong financial position with cash runway through key milestones Differentiated M1/M4 Muscarinic Agonist Broad and Diversified Product Pipeline 32 Circuit-Specific Discovery Strategy Established Track Record of Execution Corporate Summary































