UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 6-K
REPORT OF FOREIGN PRIVATE ISSUER
PURSUANT TO RULE 13a-16 OR 15d-16
UNDER THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the month of August 2023
Commission File Number: 001-41562
NewAmsterdam Pharma Company N.V.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Gooimeer 2-35
1411 DC Naarden
The Netherlands
(Address of principal executive office)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant files or will file annual reports under cover of Form 20-F or Form 40-F:
Form 20-F ☒ Form 40-F ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is submitting the Form 6-K in paper as permitted by Regulation S-T Rule 101(b)(1): ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is submitting the Form 6-K in paper as permitted by Regulation S-T Rule 101(b)(7): ☐
On August 27, 2023, representatives of NewAmsterdam Pharma Company N.V. (the “Company”) gave a presentation titled “New Insights on CETP Inhibition from Genetic Research and Clinical Trials” at the European Society of Cardiology’s 2023 Congress. A copy of the presentation is furnished as Exhibit 99.1 to this Report on Form 6-K.
SIGNATURE
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| NewAmsterdam Pharma Company N.V. | ||||||
| August 28, 2023 | By: | /s/ Michael Davidson |
||||
| Name: Michael Davidson Title: Chief Executive Officer |
||||||

Exhibit 99.1 New Insights on CETP Inhibition from Genetic Research and Clinical Trials John J.P. Kastelein, MD PhD FESC Emeritus Professor of Medicine Department of Vascular Medicine Academic Medical Center (AMC) of the University of Amsterdam 1

Disclosures • Dr Kastelein reports consultancies with 89Bio, CiVi Biotech, CSL-Behring, Draupnir Bio, Menarini Ricerce, Madrigal, North Sea Therapeutics, Novartis, Silence Therapeutics, CinCor, Scribe Therapeutics • Dr Kastelein is acting Chief Medical Officer (CMO) of Staten Biotech and Chief Science Officer (CSO) of NewAmsterdam Pharma 2

Genomic Validation of LDL-C Reduction and CETP Inhibition for CVD Reduction 3

CETP loss of function, The Ashkenazi Jewish Longevity Gene Project 4
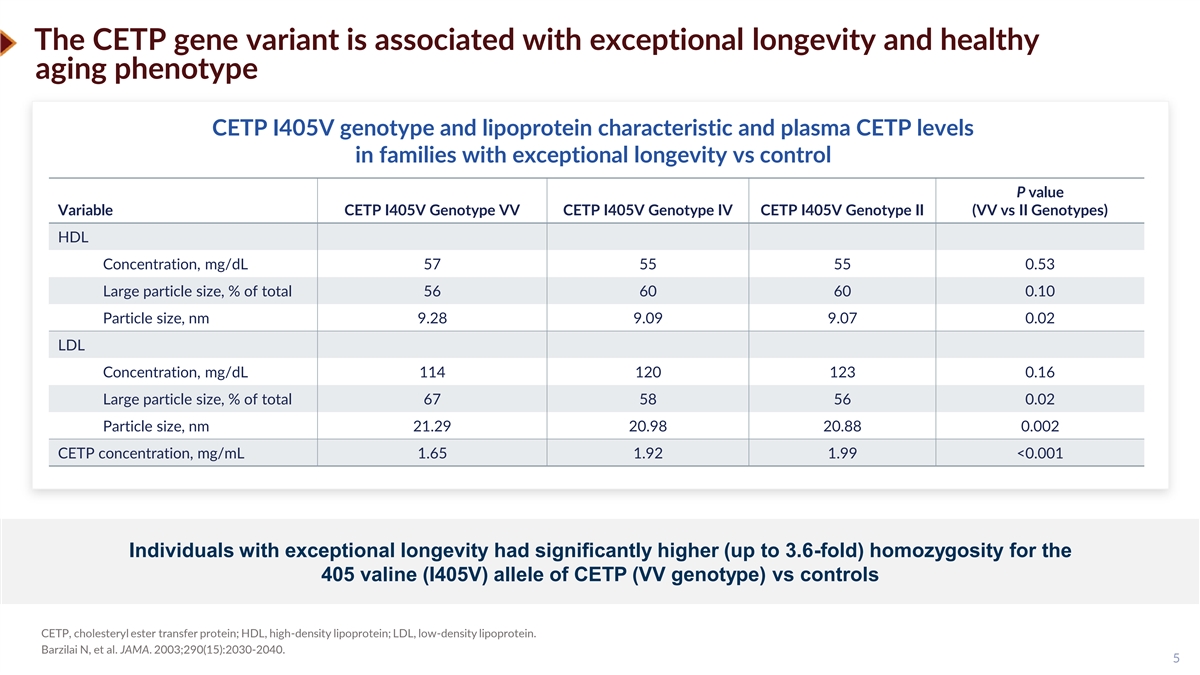
The CETP gene variant is associated with exceptional longevity and healthy aging phenotype CETP I405V genotype and lipoprotein characteristic and plasma CETP levels in families with exceptional longevity vs control P value Variable CETP I405V Genotype VV CETP I405V Genotype IV CETP I405V Genotype II (VV vs II Genotypes) HDL Concentration, mg/dL 57 55 55 0.53 Large particle size, % of total 56 60 60 0.10 Particle size, nm 9.28 9.09 9.07 0.02 LDL Concentration, mg/dL 114 120 123 0.16 Large particle size, % of total 67 58 56 0.02 Particle size, nm 21.29 20.98 20.88 0.002 CETP concentration, mg/mL 1.65 1.92 1.99 <0.001 Individuals with exceptional longevity had significantly higher (up to 3.6-fold) homozygosity for the 405 valine (I405V) allele of CETP (VV genotype) vs controls CETP, cholesteryl ester transfer protein; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein. Barzilai N, et al. JAMA. 2003;290(15):2030-2040. 5
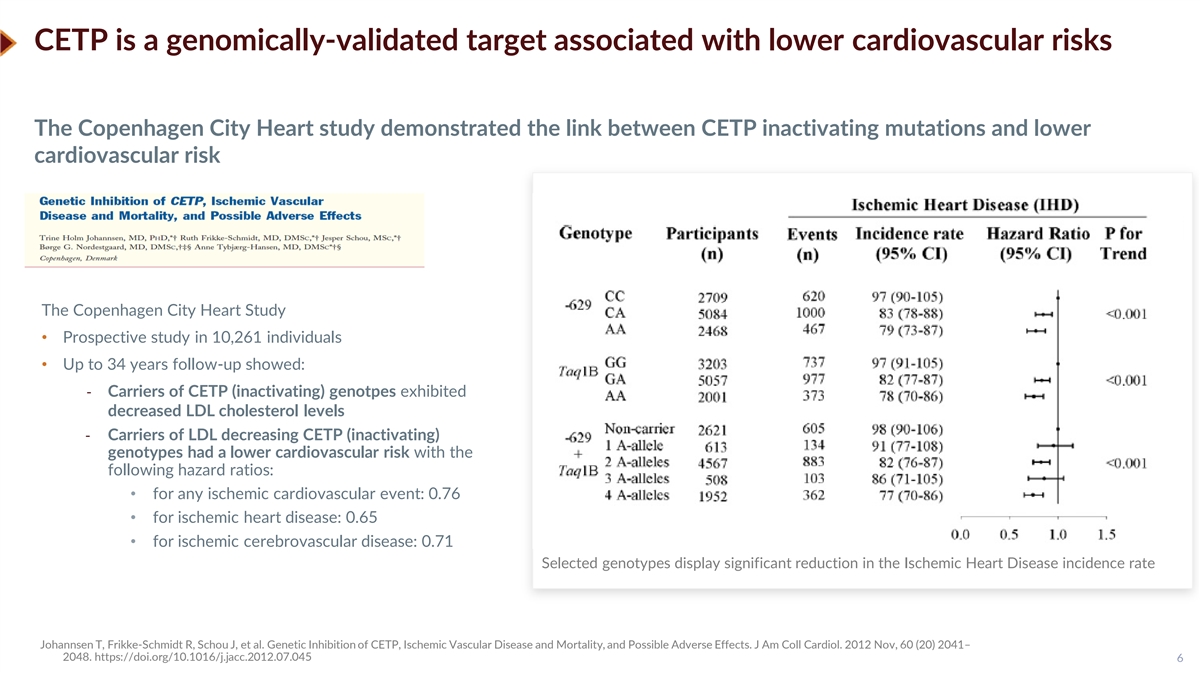
CETP is a genomically-validated target associated with lower cardiovascular risks The Copenhagen City Heart study demonstrated the link between CETP inactivating mutations and lower cardiovascular risk The Copenhagen City Heart Study • Prospective study in 10,261 individuals • Up to 34 years follow-up showed: - Carriers of CETP (inactivating) genotpes exhibited decreased LDL cholesterol levels - Carriers of LDL decreasing CETP (inactivating) genotypes had a lower cardiovascular risk with the following hazard ratios: • for any ischemic cardiovascular event: 0.76 • for ischemic heart disease: 0.65 • for ischemic cerebrovascular disease: 0.71 Selected genotypes display significant reduction in the Ischemic Heart Disease incidence rate Johannsen T, Frikke-Schmidt R, Schou J, et al. Genetic Inhibition of CETP, Ischemic Vascular Disease and Mortality, and Possible Adverse Effects. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Nov, 60 (20) 2041– 2048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2012.07.045 6
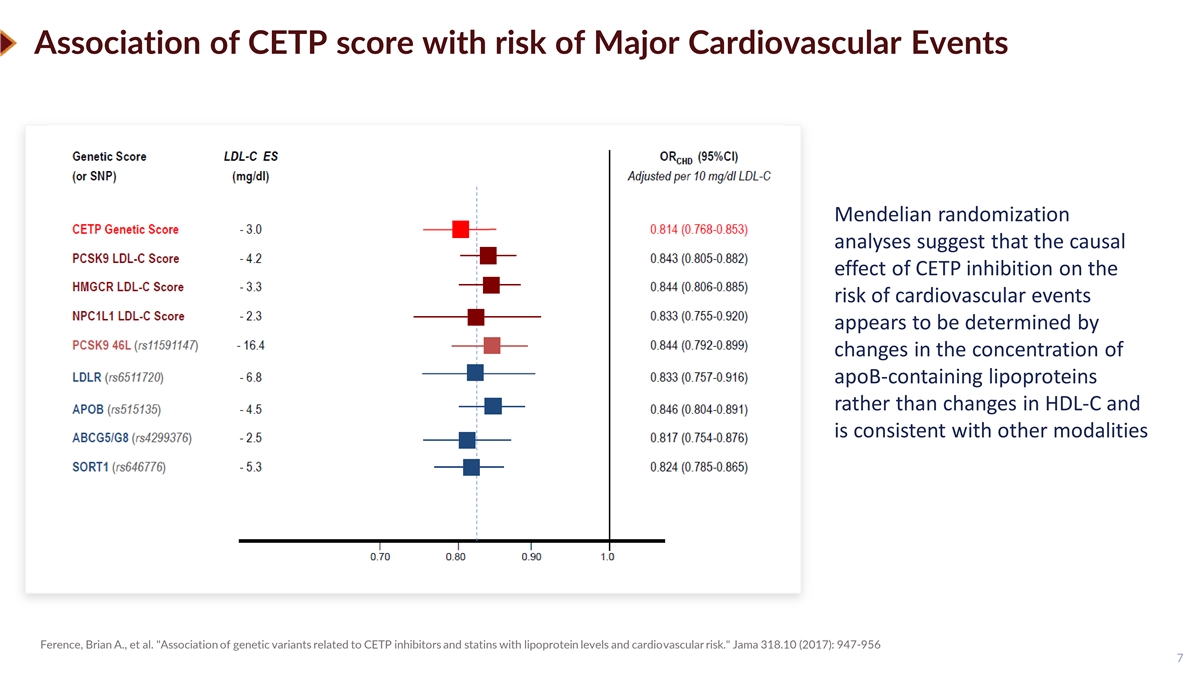
Association of CETP score with risk of Major Cardiovascular Events Mendelian randomization analyses suggest that the causal effect of CETP inhibition on the risk of cardiovascular events appears to be determined by changes in the concentration of apoB-containing lipoproteins rather than changes in HDL-C and is consistent with other modalities Ference, Brian A., et al. Association of genetic variants related to CETP inhibitors and statins with lipoprotein levels and cardiovascular risk. Jama 318.10 (2017): 947-956 7
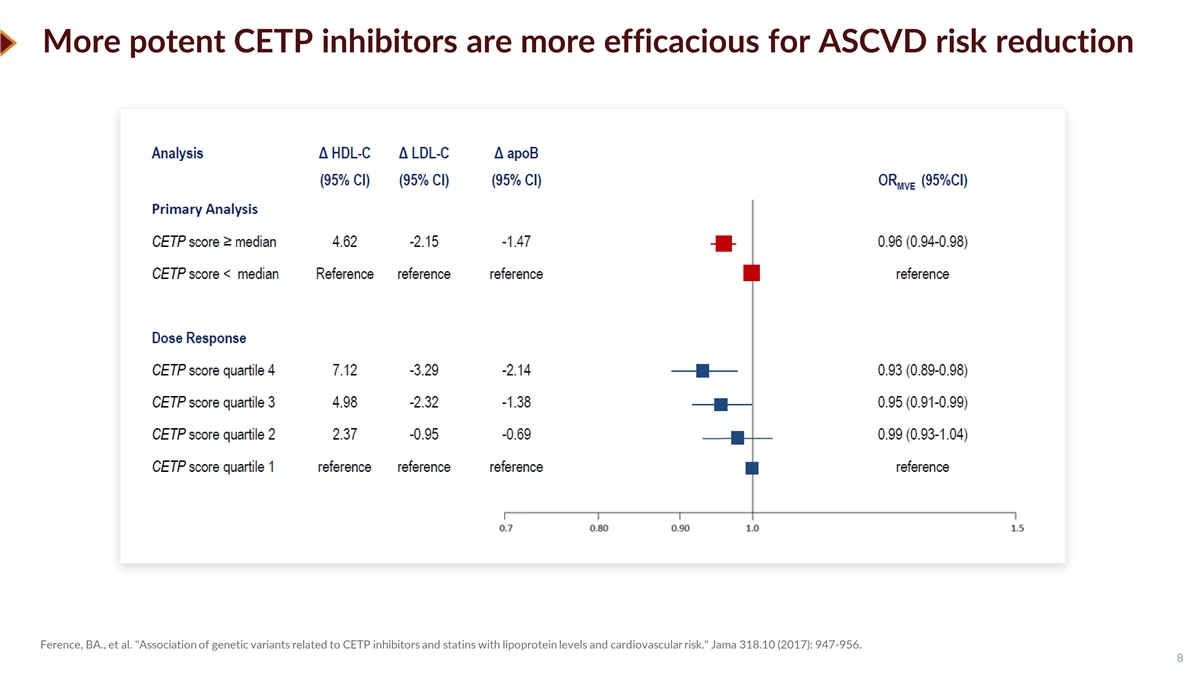
More potent CETP inhibitors are more efficacious for ASCVD risk reduction Odds Ratio Ference, BA., et al. Association of genetic variants related to CETP inhibitors and statins with lipoprotein levels and cardiovascular risk. Jama 318.10 (2017): 947-956. 8

Is there evidence for an additive effect between CETP inhibition and other mechanisms?
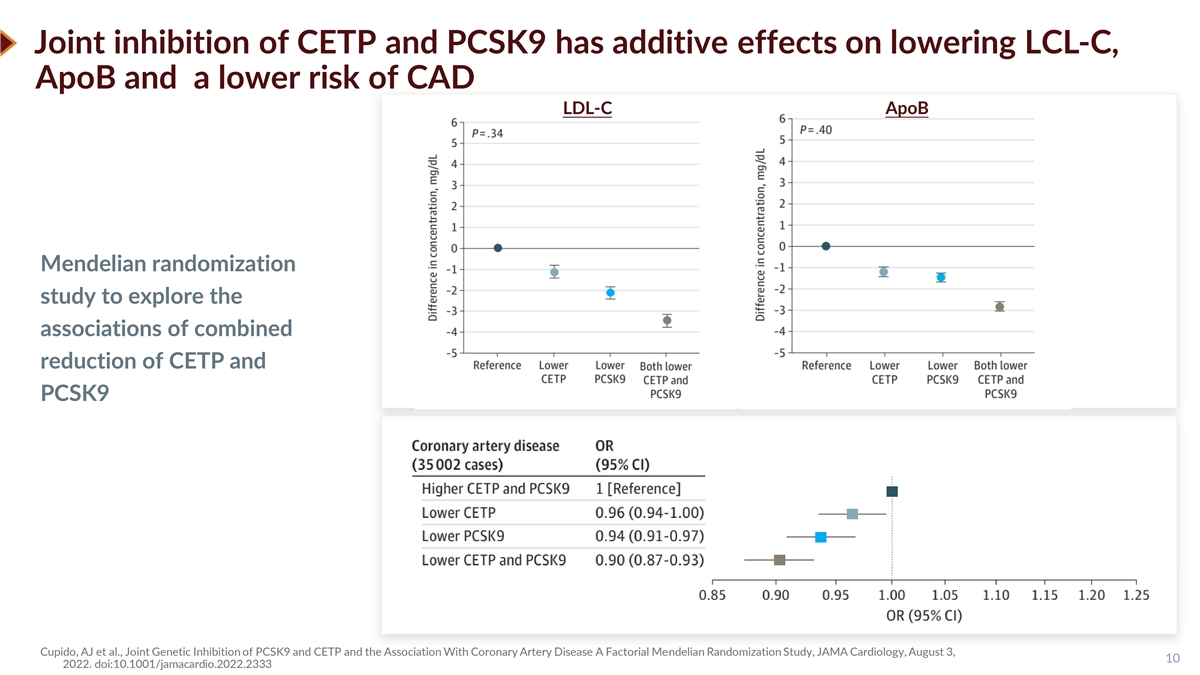
Joint inhibition of CETP and PCSK9 has additive effects on lowering LCL-C, ApoB and a lower risk of CAD LDL-C ApoB Mendelian randomization study to explore the associations of combined reduction of CETP and PCSK9 Cupido, AJ et al., Joint Genetic Inhibition of PCSK9 and CETP and the Association With Coronary Artery Disease A Factorial Mendelian Randomization Study, JAMA Cardiology, August 3, 10 2022. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2022.2333

Novel Mendelian Randomization Data
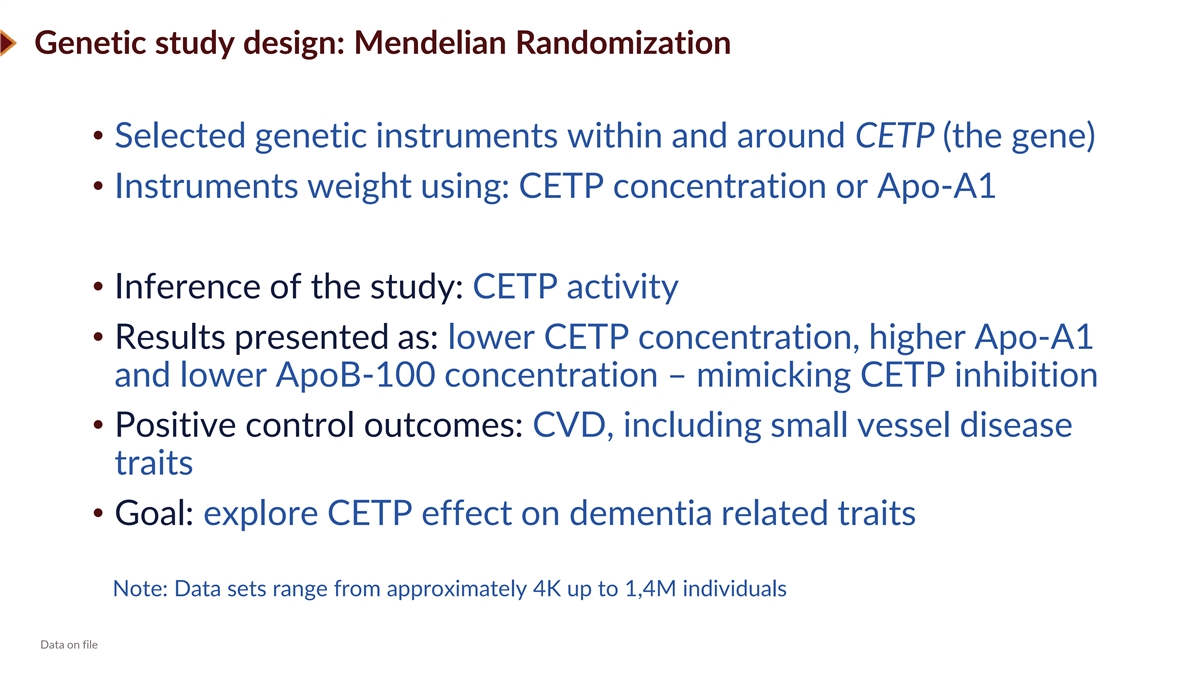
Genetic study design: Mendelian Randomization • Selected genetic instruments within and around CETP (the gene) • Instruments weight using: CETP concentration or Apo-A1 • Inference of the study: CETP activity • Results presented as: lower CETP concentration, higher Apo-A1 and lower ApoB-100 concentration – mimicking CETP inhibition • Positive control outcomes: CVD, including small vessel disease traits • Goal: explore CETP effect on dementia related traits Note: Data sets range from approximately 4K up to 1,4M individuals Data on file
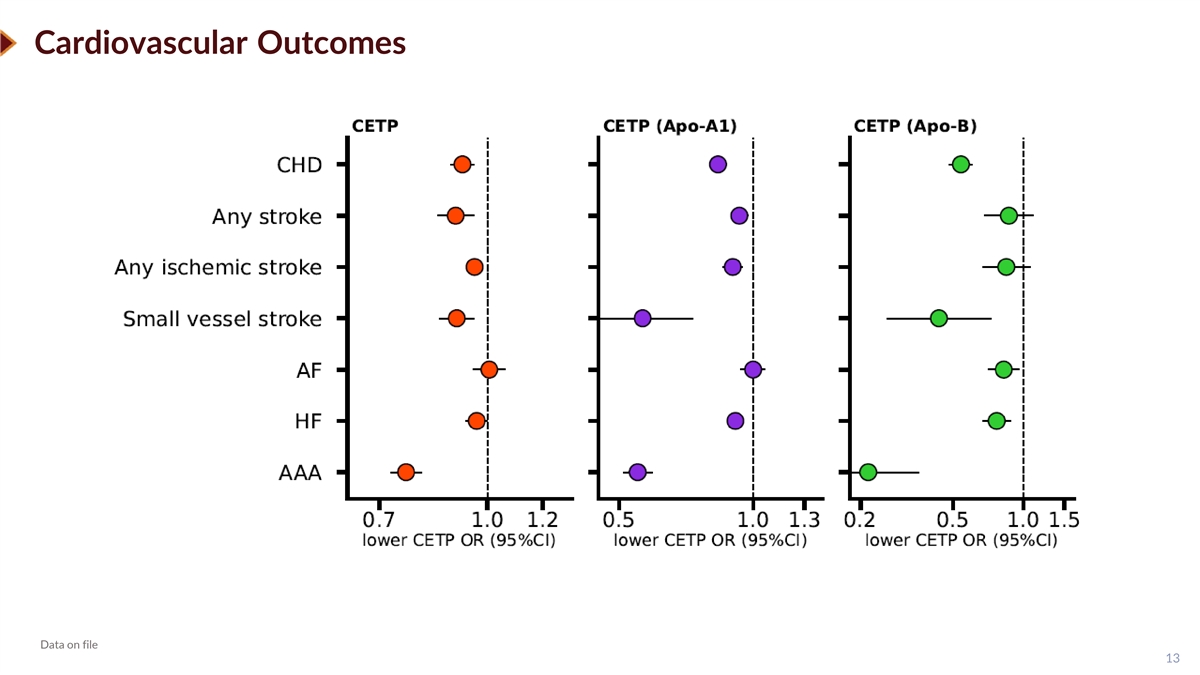
Cardiovascular Outcomes Data on file 13
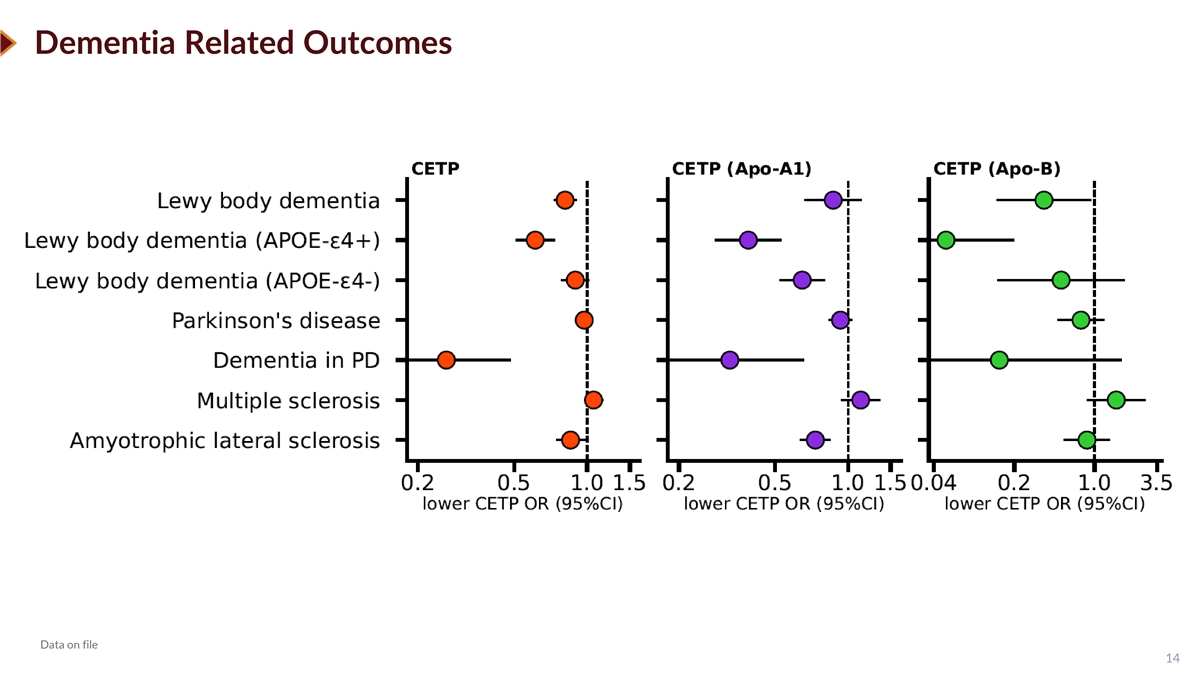
Dementia Related Outcomes Data on file 14

New Insights on CETP Inhibition from Clinical Trials 15

Torcetrapib was a one off 16

Dalcetrapib did not move the needle on LDL-C 17

Evacetrapib 's CVOT was underpowered and too short 18
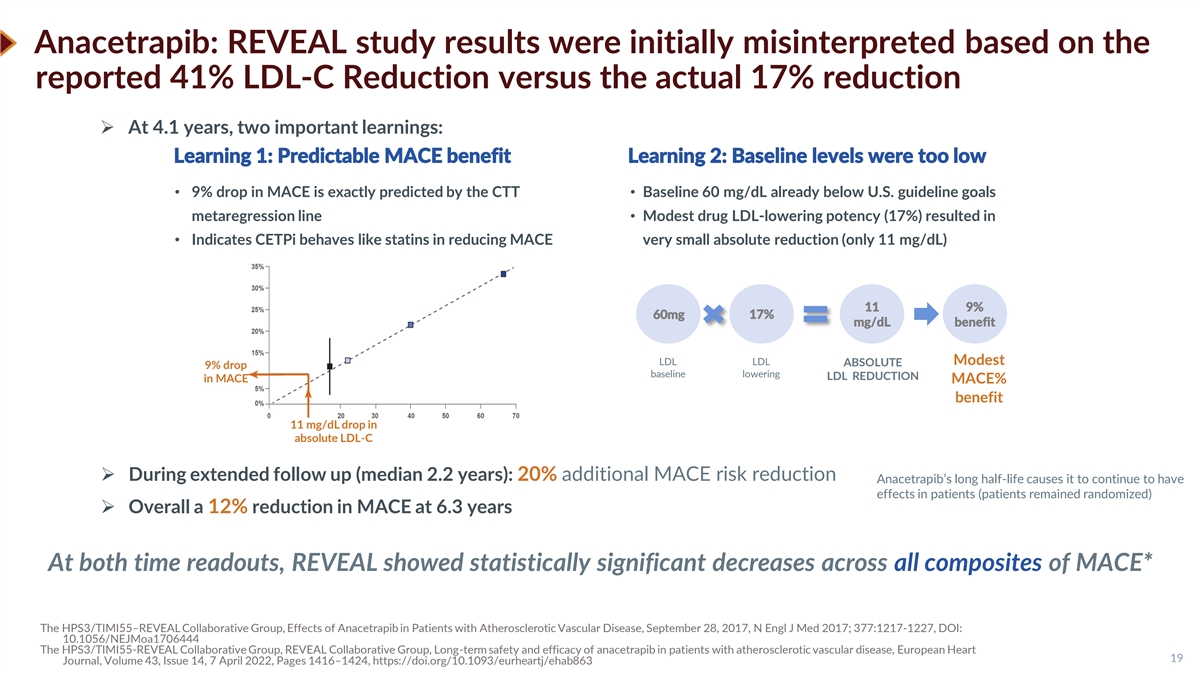
Anacetrapib: REVEAL study results were initially misinterpreted based on the reported 41% LDL-C Reduction versus the actual 17% reduction ➢ At 4.1 years, two important learnings: Learning 1: Predictable MACE benefit Learning 2: Baseline levels were too low • 9% drop in MACE is exactly predicted by the CTT • Baseline 60 mg/dL already below U.S. guideline goals metaregression line • Modest drug LDL-lowering potency (17%) resulted in • Indicates CETPi behaves like statins in reducing MACE very small absolute reduction (only 11 mg/dL) 11 9% 60mg 17% mg/dL benefit LDL LDL Modest ABSOLUTE 9% drop baseline lowering LDL REDUCTION in MACE MACE% benefit 11 mg/dL drop in absolute LDL-C ➢ During extended follow up (median 2.2 years): 20% additional MACE risk reduction Anacetrapib’s long half-life causes it to continue to have effects in patients (patients remained randomized) ➢ Overall a 12% reduction in MACE at 6.3 years At both time readouts, REVEAL showed statistically significant decreases across all composites of MACE* The HPS3/TIMI55–REVEAL Collaborative Group, Effects of Anacetrapib in Patients with Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease, September 28, 2017, N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1217-1227, DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1706444 The HPS3/TIMI55-REVEAL Collaborative Group, REVEAL Collaborative Group, Long-term safety and efficacy of anacetrapib in patients with atherosclerotic vascular disease, European Heart 19 Journal, Volume 43, Issue 14, 7 April 2022, Pages 1416–1424, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab863
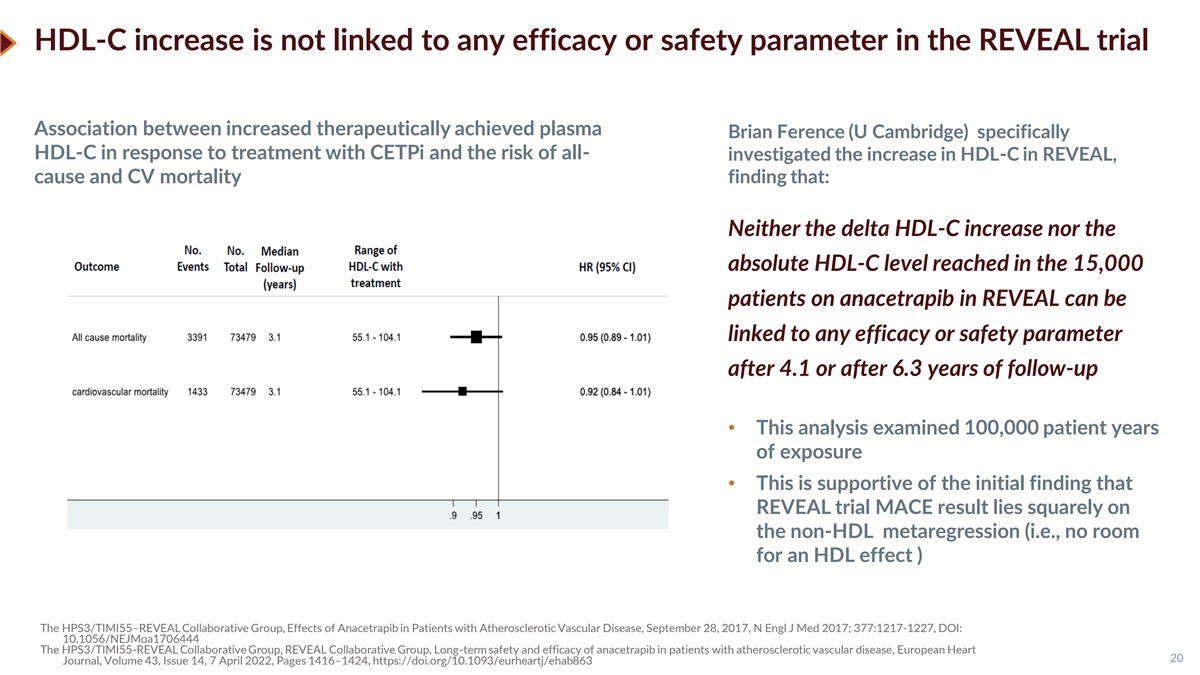
HDL-C increase is not linked to any efficacy or safety parameter in the REVEAL trial Association between increased therapeutically achieved plasma Brian Ference (U Cambridge) specifically HDL-C in response to treatment with CETPi and the risk of all- investigated the increase in HDL-C in REVEAL, cause and CV mortality finding that: Neither the delta HDL-C increase nor the absolute HDL-C level reached in the 15,000 patients on anacetrapib in REVEAL can be linked to any efficacy or safety parameter after 4.1 or after 6.3 years of follow-up • This analysis examined 100,000 patient years of exposure • This is supportive of the initial finding that REVEAL trial MACE result lies squarely on the non-HDL metaregression (i.e., no room for an HDL effect ) The HPS3/TIMI55–REVEAL Collaborative Group, Effects of Anacetrapib in Patients with Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease, September 28, 2017, N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1217-1227, DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1706444 The HPS3/TIMI55-REVEAL Collaborative Group, REVEAL Collaborative Group, Long-term safety and efficacy of anacetrapib in patients with atherosclerotic vascular disease, European Heart 20 Journal, Volume 43, Issue 14, 7 April 2022, Pages 1416–1424, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab863

Conclusions • There is overwhelming genomic evidence that demonstrate reduced cardiovascular risk in individuals with naturally lower CETP activity • The cardiovascular benefit of lower CETP activity is linked to lower LDL-C / ApoB, not higher HDL-C, and seems to be independent and additive to other biological pathways that lower LDL-C / ApoB • In addition to confirming a cardiovascular benefit, new large scale mendelian randomization data suggest that lower CETP activity may have benefit in neuro-degenerative diseases • We have seen a decrease in select biomarkers linked to AD in a soon to be announced study • There is plausible rationale why the first 3 CETP inhibitors did not demonstrate a benefit in reducing MACE th • The 4 CETP inhibitor, anacetrapib, demonstrated a significant 9% reduction in MACE at 4.1 years and an additional significant 20% reduction in the 2.2 year follow up, in line with expectations based on its modest LDL-C lowering • Genomic evidence and the results of REVEAL support the further investigation of the CETP inhibitor class 21