FY0001743102falseJan. 31, 2018Jan. 31, 2018Feb. 28, 2018Jun. 30, 2018Jul. 31, 2019Sep. 30, 2019Apr. 30, 2020Nov. 30, 2024Aug. 31, 2021Jun. 30, 2015Jul. 31, 2019Jan. 31, 2021Jan. 31, 2022http://fasb.org/us-gaap/2024#UsefulLifeShorterOfTermOfLeaseOrAssetUtilityMemberoneonehttp://fasb.org/srt/2024#ChiefExecutiveOfficerMemberJuly 1, 2023August 31, 2023January 1 2024January 31, 2024August 1 2024September 30, 20240001743102us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-12-310001743102us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:AccountsReceivableAndContractAssetsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:O2023Q3DividendsMember2023-07-012023-07-310001743102jfin:TwoThousandNineteenIncentivePlanMember2021-08-012021-08-310001743102us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:StateAdministrationOfTaxationChinaMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedToRelatedPartiesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:LoansToRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:SubsidiaryShareholderMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiCaiyinAssetManagementCoLtdMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:EmployeeIncentivePlanMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiayinFinanceTechnologyCoLtdMember2016-09-300001743102country:ID2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:TransferredAtPointInTimeMemberjfin:LoanFacilitationServicesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiCaiyinMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:TransferredAtPointInTimeMemberjfin:OtherRevenueInvestorReferralMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:JiayinShukeInformationTechnologyCoLtdMemberus-gaap:StateAdministrationOfTaxationChinaMembersrt:MaximumMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:KeenBestMember2020-09-292020-09-2900017431022021-12-310001743102jfin:OtherRevenueOthersMemberjfin:TransferredAtAPointInTimeOrOverTimeMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:ReleasingOfGuaranteeLiabilitiesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:AguilaInformationSAPIDeCVMember2021-06-012021-06-300001743102jfin:OfficeEquipmentFurnitureMembersrt:MaximumMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassBMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-01-012022-12-3100017431022022-12-3100017431022023-11-012023-11-300001743102us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:JiayinHoldingsLimitedMembersrt:SubsidiariesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:VehiclesMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:PtRumahInovasiJetMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:OptionMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310001743102jfin:GeerongYunkeInformationTechnologyCoLtdMemberus-gaap:StateAdministrationOfTaxationChinaMembersrt:MaximumMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:EquipmentMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:ExclusiveConsultationAndServiceAgreementMemberjfin:ShanghaiKunjiaTechnologyCoLtdMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiJiayinFinanceServicesCoLtdMember2022-04-300001743102us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:O2024Q1DividendsMember2024-01-310001743102us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-12-310001743102us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiCaiyinMember2021-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiKunjiaTechnologyCoLtdMembersrt:SubsidiariesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:GeerongYunkeInformationTechnologyCoLtdMembersrt:SubsidiariesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:EquipmentMembersrt:MaximumMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2020-01-012020-12-310001743102jfin:PtRumahInovasiJetMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:AguilaInformationSAPIDeCVMember2021-12-310001743102jfin:LoansToRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:KeenBestMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2021-12-310001743102jfin:KeenBestMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiCaiyinAssetManagementCoLtdMember2023-01-012023-12-3100017431022024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedByRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiayinZhuoyueWealthManagementCoLtdMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102country:NG2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:OptionMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:AccountingStandardUpdate201409Member2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102srt:ParentCompanyMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:KeenBestMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryShanghaiJiayinTechnologyCoLtdMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:LoansToRelatedPartiesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiCaiyinMember2022-12-310001743102jfin:EmprendeConmoviSADeCVSofomEnrMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedByRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiayinZhuoyueWealthManagementCoLtdMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:ReleasingOfGuaranteeLiabilitiesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:SunshinewoodsHoldingsLimitedMemberjfin:LoansFromRelatedPartiesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:TransferredAtPointInTimeMemberjfin:OtherRevenueInvestorReferralMember2022-01-012022-12-3100017431022023-12-310001743102us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassBMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2023-12-310001743102srt:MaximumMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:VehiclesMembersrt:MinimumMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:OtherRevenueOthersMemberjfin:TransferredAtAPointInTimeOrOverTimeMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:JiayinShukeInformationTechnologyCoLtdMemberus-gaap:StateAdministrationOfTaxationChinaMembersrt:MinimumMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-12-310001743102jfin:SunshinewoodsHoldingsLimitedMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102country:ID2024-01-012024-12-310001743102srt:ParentCompanyMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:GayangHongKongCompanyLimitedMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:JiayinShukeInformationTechnologyCoLtdMemberus-gaap:StateAdministrationOfTaxationChinaMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-12-310001743102country:SG2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:ExpiringBetweenTwentyTwentySixToTwentyTwentyNineMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedByRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiayinFinanceServicesCoLtdMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassBMember2022-12-310001743102jfin:AguilaInformationSAPIDeCVMember2022-12-310001743102country:ID2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:ReleasingOfGuaranteeLiabilitiesMemberus-gaap:TransferredOverTimeMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:AccountingStandardsUpdate202307Member2024-12-310001743102jfin:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheFourMemberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiayinFinanceTechnologyCoLtdMember2016-09-012016-09-300001743102us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102srt:ParentCompanyMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310001743102jfin:LoansToRelatedPartiesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:ShenzhenRongxinbaoMemberjfin:ShanghaiCaiyinMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:LoansFromRelatedPartiesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102dei:BusinessContactMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:GuaranteeArrangementMember2024-12-3100017431022023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:VehiclesMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiCaiyinMember2021-01-012021-12-310001743102us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:OfficeEquipmentFurnitureMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:AguilaInformationSAPIDeCVMember2021-01-012021-12-310001743102jfin:O2023Q3DividendsMember2023-07-310001743102us-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2025-02-280001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedByRelatedPartiesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102srt:ParentCompanyMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:CustomerAMemberus-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMemberjfin:AccountsReceivableAndContractAssetsMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:LoansToRelatedPartiesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:LoansToRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:AguilaInformationSAPIDeCVMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedToRelatedPartiesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:AguilaInformationMember2021-01-050001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedToRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:AguilaInformationSAPIDeCVMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:AguilaInformationSAPIDeCVMember2021-01-052021-01-050001743102srt:ParentCompanyMember2021-12-310001743102us-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2025-03-272025-03-270001743102us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:FujianZhuoqunMemberjfin:ShanghaiCaiyinMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedByRelatedPartiesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:ReleasingOfGuaranteeLiabilitiesMemberus-gaap:TransferredOverTimeMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheTwoMemberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiayinFinanceTechnologyCoLtdMember2016-09-012016-09-300001743102us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102country:HK2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2024-12-310001743102country:CN2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:KeenBestMember2020-12-310001743102srt:ParentCompanyMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:OfficeEquipmentFurnitureMembersrt:MinimumMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2022-12-310001743102us-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:NetAssetsGeographicAreaMembercountry:CN2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiJirongzhichengEnterpriseDevelopmentCoLtdMembersrt:SubsidiariesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:O2024Q3DividendsMember2024-08-310001743102us-gaap:TransferredAtPointInTimeMemberjfin:OtherRevenueInvestorReferralMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:CommercialPropertyPurchaseAgreementMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiCaiyinMember2019-08-310001743102jfin:AdsMember2019-05-102019-05-100001743102srt:MinimumMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiayinFinanceTechnologyCoLtdMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheThreeMember2016-09-012016-09-300001743102us-gaap:VehiclesMembersrt:MaximumMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiCaiyinMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:ShenzhenRongxinbaoMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiChuangzhenSoftwareCoLtdMember2021-01-012021-12-310001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedByRelatedPartiesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:AccountsReceivableAndContractAssetsMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2022-12-310001743102jfin:KeenBestMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102country:ID2021-01-012021-12-310001743102jfin:FortunifyInternationalHoldingsPteLtdMember2024-08-310001743102us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:FacilitationAndServicingMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:ReleasingOfGuaranteeLiabilitiesMemberus-gaap:TransferredOverTimeMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2019-05-102019-05-100001743102jfin:LoansToRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiajieAssetsManagementCoLtdMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2019-05-100001743102jfin:SubsidiaryShareholderMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:DreamGloryLPMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:FacilitationAndServicingMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:OptionMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:FacilitationAndServicingMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryShanghaiJiajieInternetInformationServicesCoLtdMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:CommercialPropertyPurchaseAgreementMember2024-12-172024-12-170001743102jfin:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryJiayinShukeInformationTechnologyCoLtdMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:JiayinSoutheastAsiaHoldingsLimitedMembersrt:SubsidiariesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonStockMember2019-05-102019-05-100001743102jfin:ShanghaiJiayinFinanceServicesCoLtdMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:StateAdministrationOfTaxationChinaMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102currency:CNY2024-12-310001743102jfin:EmprendeConmoviSADeCVSofomEnrMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassBMember2021-12-310001743102us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiKunjiaTechnologyCoLtdMemberjfin:ExclusivePurchaseAgreementmemberMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:NewDreamCapitalHoldingsLimitedMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiChuangzhenSoftwareCoLtdMembersrt:SubsidiariesMember2024-01-012024-12-3100017431022019-05-102019-05-100001743102us-gaap:TransferredAtPointInTimeMemberjfin:LoanFacilitationServicesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:GeerongYunkeInformationTechnologyCoLtdMemberus-gaap:StateAdministrationOfTaxationChinaMembersrt:MinimumMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:FujianZhuoqunMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedToRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:JiayinTechnologyServiceShanghaiCoLtdMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:EquityPledgeAgreementMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedByRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiayinZhuoyueWealthManagementCoLtdMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:EquipmentMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2019-05-100001743102us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiCaiyinAssetManagementCoLtdMember2021-01-012021-12-3100017431022024-12-310001743102us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:SecurityDepositsMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2021-12-310001743102us-gaap:EquipmentMembersrt:MinimumMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiChuangzhenSoftwareCoLtdMember2020-01-012020-12-310001743102us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2024-01-012024-12-3100017431022022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:ShenzhenRongxinbaoMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:NetAssetsGeographicAreaMembercountry:CN2024-01-012024-12-3100017431022024-08-310001743102jfin:GeerongYunkeInformationTechnologyCoLtdMemberus-gaap:StateAdministrationOfTaxationChinaMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:LoansToRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:GayangHongKongCompanyLimitedMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:TransferredAtPointInTimeMemberjfin:LoanFacilitationServicesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2019-05-102019-05-100001743102jfin:CommercialPropertyPurchaseAgreementMember2024-12-170001743102us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2023-12-310001743102us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:GayangHongKongCompanyLimitedMember2022-12-310001743102jfin:OfficeEquipmentFurnitureMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:SecurityDepositsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:OtherRevenueOthersMemberjfin:TransferredAtAPointInTimeOrOverTimeMember2022-01-012022-12-3100017431022019-05-100001743102jfin:ShanghaiJiayinZhuoyueWealthManagementCoLtdMember2023-12-310001743102srt:ParentCompanyMember2022-12-310001743102us-gaap:StateAdministrationOfTaxationChinaMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:LoansToRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:SubsidiaryShareholderMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:AguilaInformationSAPIDeCVMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryGuangxiChuangzhenInformationTechnologyCoLtdMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2023-12-310001743102jfin:JiayinTechnologyServiceShanghaiCoLtdMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:O2024Q3DividendsMember2024-08-012024-08-310001743102jfin:GayangHongKongCompanyLimitedMember2021-12-310001743102us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:FortunifyInternationalHoldingsPteLtdMember2024-08-012024-08-310001743102us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiCaiyinAssetManagementCoLtdMember2020-01-012020-12-310001743102us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:GeerongYunShanghaiTechnologyDevelopmentCoLtdMembersrt:SubsidiariesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102jfin:ServicesProvidedByRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiayinFinanceServicesCoLtdMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102jfin:LoansToRelatedPartiesMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiajieAssetsManagementCoLtdMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102currency:CNY2023-12-310001743102jfin:O2024Q1DividendsMember2024-01-012024-01-310001743102us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2023-01-012023-12-310001743102srt:SubsidiariesMemberjfin:GeerongHKLimitedMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:ReleasingOfGuaranteeLiabilitiesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102jfin:ShanghaiJiayinZhuoyueWealthManagementCoLtdMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2024-12-310001743102jfin:HainanYinkeFinancingGuaranteeCoLtdMembersrt:SubsidiariesMember2024-01-012024-12-310001743102us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-01-012022-12-310001743102us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2024-12-310001743102us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheOneMemberjfin:ShanghaiJiayinFinanceTechnologyCoLtdMember2016-09-012016-09-300001743102us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-12-31iso4217:CNYxbrli:sharesxbrli:purejfin:Segmentjfin:ConvertibleNotesxbrli:sharesiso4217:CNYjfin:Loansjfin:Voteiso4217:USD
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 20-F
(Mark One)
|
|
☐ |
REGISTRATION STATEMENT PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OR 12(g) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
OR
|
|
☒ |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
OR
|
|
☐ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
OR
|
|
☐ |
SHELL COMPANY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Date of event requiring this shell company report
Commission file number: 001-38806
Jiayin Group Inc.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
N/A
(Translation of Registrant’s name into English)
Cayman Islands
(Jurisdiction of incorporation or organization)
18th Floor, Building No. 1, Youyou Century Plaza,
428 South Yanggao Road, Pudong
New Area, Shanghai 200122
People’s Republic of China
(Address of principal executive offices)
Chunlin Fan, Chief Financial Officer
Tel: 86 21-6190-6826
E-mail: fanchunlin@jiayinfintech.cn
18th Floor, Building No. 1, Youyou Century Plaza,
428 South Yanggao Road, Pudong
New Area, Shanghai 200122
People’s Republic of China
(Name, Telephone, E-mail and/or Facsimile number and Address of Company Contact Person)
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
|
|
|
Title of each class
|
Trading
Symbol(s)
|
Name of each exchange on
which registered
|
|
American Depositary Shares, each representing
four Class A ordinary shares, par value US$0.000000005 per share
|
JFIN |
The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC |
Class A ordinary shares, par value US$0.000000005 per share* |
|
The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC |
* Not for trading, but only in connection with the listing on The Nasdaq Stock Market of American depositary shares.
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
(Title of Class)
Securities for which there is a reporting obligation pursuant to Section 15(d) of the Act:
None
(Title of Class)
Indicate the number of outstanding shares of each of the Issuer’s classes of capital or common stock as of the close of the period covered by the annual report.
There were 213,478,184 ordinary shares outstanding, consisting of 105,478,184 Class A ordinary shares and 108,000,000 Class B ordinary shares, par value US$0.000000005 per share, as of December 31, 2024.
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
If this report is an annual or transition report, indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or an emerging growth company. See definition of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
|
|
|
|
Large accelerated filer |
☐ |
Accelerated filer |
☒ |
Non-accelerated filer |
☐ |
Emerging growth company |
☐ |
If an emerging growth company that prepares its financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards † provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
† The term “new or revised financial accounting standard” refers to any update issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board to its Accounting Standards Codification after April 5, 2012.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark which basis of accounting the registrant has used to prepare the financial statements included in this filing:
|
|
|
U.S. GAAP ☒ |
International Financial Reporting Standards as issued
by the International Accounting Standards Board ☐
|
Other ☐ |
If “Other” has been checked in response to the previous question, indicate by check mark which financial statement item the registrant has elected to follow. Item 17 ☐ Item 18 ☐
If this is an annual report, indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
(APPLICABLE ONLY TO ISSUERS INVOLVED IN BANKRUPTCY PROCEEDINGS DURING THE PAST FIVE YEARS)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed all documents and reports required to be filed by Sections 12, 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 subsequent to the distribution of securities under a plan confirmed by a court. Yes ☐ No ☐
INTRODUCTION
Unless otherwise indicated or the context otherwise requires in this annual report on Form 20-F:
•
“ADSs” refers to our American depositary shares, each of which represents four Class A ordinary shares;
•
“China” or the “PRC” refers to the People’s Republic of China, including, for the purposes of this annual report only, Hong Kong and Macau, unless referencing specific laws and regulations adopted by the People’s Republic of China and other legal and tax matters applicable only to mainland China; “PRC subsidiaries” and “PRC entities” refer to entities established in accordance with laws and regulations of mainland China;
•
“consolidated VIE” refers to Shanghai Jiayin Technology Co., Ltd. (“Jiayin Technology”, formerly known as Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd.);
•
“institutional funding partners” refers to the institutions that fund the loans that we and the VIE Group facilitate;
•
“loan facilitation volume” refers to the total amount of loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform during a certain period;
•
“M3+ Delinquency Rate by Vintage” refers to the total amount of principal for all loans in a vintage for which any repayment was more than 90 days past due as of a particular date, less the total amount of past due principal recovered for such loans, and divided by the total amount of principal for all loans in such vintage. M3+ Delinquency Rate by Vintage for quarter vintage is calculated as the weighted average of M3+ Delinquency Rate by Vintage for each month in such quarter by loan facilitation volume;
•
“online investors” refers to the investors that we and the VIE Group refer to third-party financial service providers under the investor referral services to purchase the investment products they offer on our Youdao wealth platform;
•
number of “borrowers” for a certain period refers to the total number of borrowers whose loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform were funded during such period;
•
“Parent” refers to Jiayin Group Inc., a Cayman Islands holding company;
•
“registered users” refer to individuals who have registered on our and the VIE Group’s platform;
•
“repeat borrowers” during a certain period refers to borrowers who borrowed in such period and have borrowed at least twice since such borrowers’ registration with us until the end of such period;
•
“ordinary shares” refers to our Class A and Class B ordinary shares, par value US$0.000000005 per share;
•
“RMB” and “Renminbi” refer to the legal currency of China;
•
“US$,” “U.S. dollars,” “$,” and “dollars” refer to the legal currency of the United States;
•
“vintage” refers to loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform during a certain period;
•
“we,” “us,” “our company,” “the Company” and “our” refer to the Parent and its subsidiaries; and
•
“VIE Group” refers to Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries.
Our reporting currency is the Renminbi because our business is mainly conducted in China and all of our revenues are denominated in Renminbi. This annual report contains translations of Renminbi amounts into U.S. dollars at specific rates solely for the convenience of the reader. The conversion of Renminbi into U.S. dollars in this annual report is based on the rate certified for customs purposes by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. Unless otherwise noted, all translations from Renminbi to U.S. dollars and from U.S. dollars to Renminbi in this annual report were made at RMB 7.2993 to US$1.00, the noon buying rate on December 31, 2024 set forth in the H.10 statistical release of the U.S. Federal Reserve Board. We make no representation that any Renminbi or U.S. dollar amounts could have been, or could be, converted into U.S. dollars or Renminbi, as the case may be, at any particular rate, the rates stated below, or at all. The PRC government imposes control over its foreign currency reserves in part through direct regulation of the conversion of Renminbi into foreign exchange and through restrictions on foreign trade.
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This annual report on Form 20-F contains forward-looking statements that reflect our current expectations and views of future events. Known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors, including those listed under “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors”, may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from those expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. These statements are made under the “safe harbor” provisions of the U.S. Private Securities Litigations Reform Act of 1995.
You can identify some of these forward-looking statements by words or phrases such as “may,” “will,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “aim,” “estimate,” “intend,” “plan,” “believe,” “is/are likely to,” “potential,” “continue” or other similar expressions. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events that we believe may affect our financial condition, results of operations, business strategy and financial needs. These forward-looking statements include statements relating to:
•
our mission and strategies;
•
our future business development, financial condition and results of operations;
•
the expected growth of the online consumer finance market in China;
•
our expectations regarding demand for and market acceptance of our products and services;
•
our expectations regarding our relationships with borrowers and institutional funding partners;
•
competition in our industry;
•
general economic and business condition in China and elsewhere; and
•
relevant government policies and regulations relating to our industry;
These forward-looking statements involve various risks and uncertainties. Although we believe that our expectations expressed in these forward-looking statements are reasonable, our expectations may later be found to be incorrect. Our actual results could be materially different from our expectations. You should thoroughly read this annual report and the documents that we refer to with the understanding that our actual future results may be materially different from and worse than what we expect. In addition, the rapidly changing nature of the online consumer finance industry results in significant uncertainties for any projections or estimates relating to the growth prospects or future condition of our market. Furthermore, if any one or more of the assumptions underlying the market data are later found to be incorrect, actual results may differ from the projections based on these assumptions. You should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. We qualify all of our forward-looking statements by these cautionary statements.
The forward-looking statements made in this annual report relate only to events or information as of the date on which the statements are made in this annual report. Except as required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or revise publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, after the date on which the statements are made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events.
PART I
Jiayin Group Inc. is a Cayman Islands holding company primarily operating in China through (i) its PRC subsidiaries, including Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd., or Shanghai Kunjia, and Shanghai Chuangzhen Technology Co., Ltd., or Chuangzhen Technology, and its subsidiaries in which we hold equity ownership interests, and (ii) contractual arrangements among (x) Shanghai Kunjia, (y) the consolidated variable interest entity, or the consolidated VIE, namely, Shanghai Jiayin Technology Co., Ltd., or Jiayin Technology, a limited liability company established under PRC law, and (z) the shareholders of the consolidated VIE. Jiayin Group Inc. does not hold any equity interest in the consolidated VIE. Investors in the ADSs thus are not purchasing, and may never hold, equity interests in the consolidated VIE. PRC laws, regulations, and rules restrict and impose conditions on direct foreign investment in China-based companies that engage in certain types of business, and we therefore operate these businesses in China through the VIE structure which provides investors with exposure to foreign investment in the Chinese operating companies. For a summary of these contractual arrangements, see “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure.” As used in this annual report, “we,” “us” or “our” refers to Jiayin Group Inc. and its subsidiaries.
Our corporate structure is subject to risks relating to our contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology and its shareholders. These contractual arrangements have not been tested in a court of law. If the PRC government finds these contractual arrangements non-compliant with the restrictions on direct foreign investment in the relevant industries, or if the relevant PRC laws, regulations, and rules or the interpretation thereof change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our beneficial interest in the consolidated VIE or forfeit our rights under the contractual arrangements. If we are unable to claim our right to control the assets of the consolidated VIE, the ADSs may decline in value or become worthless. In addition, changes in China’s economic, political or social conditions, or government policies may cause our and the consolidated VIE’s underlying operations in China to become prohibitive, which could materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business, financial condition, and results of operations. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure.”
We face various legal and operational risks and uncertainties relating to doing business in China. We operate our business primarily in China, and are subject to complex and evolving PRC laws and regulations. The recent statements and regulatory actions by China’s government, such as those related to the use of data security, anti-monopoly concerns, and the regulatory approvals on overseas listings, may impact our ability to conduct the business, accept foreign investments and/or list on a U.S. or other foreign exchange. The interpretation and enforcement of PRC laws and regulations could limit the legal protection available to you and us, hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer the ADSs, result in a material adverse effect on our business operations, and damage our reputation, which might further cause the ADSs to significantly decline in value or become worthless. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China.”
On December 16, 2021, the PCAOB issued a report notifying the Commission of its determinations that they are unable to inspect or investigate completely PCAOB-registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and in Hong Kong. The report sets forth lists identifying the registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong, respectively, that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely. On December 15, 2022, the PCAOB announced that it was able to conduct inspections and investigations completely of PCAOB-registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong in 2022. The PCAOB vacated its previous determinations issued in December 2021 accordingly. We do not expect to be identified as a “Commission-Identified Issuer” under the HFCAA for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024 after we file our annual report on Form 20-F for such fiscal year. However, whether the PCAOB will continue to conduct inspections and investigations completely to its satisfaction of PCAOB-registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong is subject to uncertainty and depends on a number of factors out of our and our auditor’s control, including positions taken by authorities of the PRC. The PCAOB is required under the HFCAA to make its determination on an annual basis with regards to its ability to inspect and investigate completely accounting firms based in the mainland China and Hong Kong. The possibility of being a “Commission-Identified Issuer” and risk of delisting could continue to adversely affect the trading price of our securities. Should the PCAOB again encounter impediments to inspections and investigations in mainland China or Hong Kong as a result of positions taken by any authority in either jurisdiction, the PCAOB will make determinations under the HFCAA as and when appropriate.
In addition, on December 29, 2022, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023 was signed into law, which, among others, amended the HFCAA to reduce the number of consecutive years an issuer can be identified as a Commission-Identified Issuer before the SEC must impose an initial trading prohibition on the issuer’s securities from three years to two. Therefore, once an issuer is identified as a Commission-Identified Issuer for two consecutive years, the SEC is required under the HFCAA to prohibit the trading of the issuer’s securities on a national securities exchange and in the over-the-counter market. For more details, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry—Trading in our securities may be prohibited under the Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act or the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act, if it is later determined that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely our auditor, and as a result, U.S. national securities exchanges, such as Nasdaq, may determine to delist our securities.”
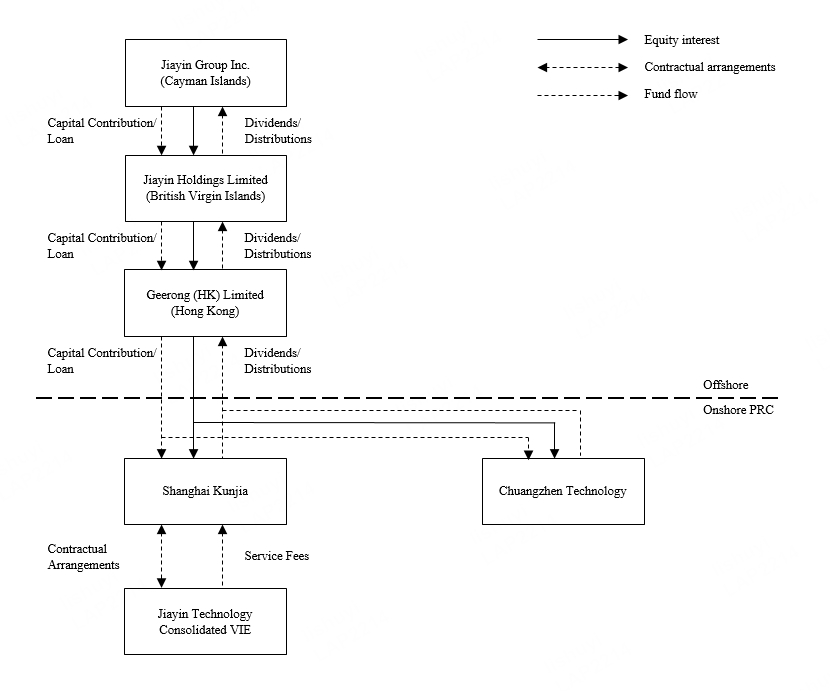
Fund Flows Between Jiayin Group Inc., Its Subsidiaries and the Consolidated VIE
Under PRC law, we may provide funding to our PRC subsidiaries only through capital contributions or loans, and to the consolidated VIE only through loans, subject to the satisfaction of applicable government registration and approval requirements. We rely on dividends and other distributions from our PRC subsidiaries to satisfy part of our liquidity requirement. Under the contractual arrangements among Shanghai Kunjia, the consolidated VIE, and the shareholders of the consolidated VIE, Shanghai Kunjia is entitled to substantially all of the economic benefits of the consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries in the form of service fees. For risks relating to the fund flows of our China operations, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—PRC regulation of loans to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore holding companies and governmental administration of currency conversion may delay or prevent us from using the proceeds of further offerings to make loans to or make additional capital contributions to our PRC subsidiaries, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand our business” and “—We rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our PRC subsidiaries to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have, and any limitation on the ability of our PRC subsidiaries to make payments to us could have a material adverse effect on our ability to conduct our business.”
Transfer of funds between any entities in our consolidated group is subject to our cash management policy that outlines appropriate internal control procedures on the handling, depositing, receiving, transferring, safeguarding, and documentation and recording of cash assets. The finance department at the Jiayin Group Inc. level with authorized persons at each entity has the centralized responsibility for undertaking cash handling activity. Based on the amount of a fund transfer and the nature of the use of funds, requisite internal approval must be obtained prior to each fund transfer: all transactions require, at a minimum, the approval of the financial controller; for certain transactions with large amounts, approval of our vice president of finance, and in some instances, approval of both our vice president of finance and chief executive officer, is also required.
Assets Transfer Occurred Between the Parent, Its Subsidiaries and the Consolidated VIE
Under the Contractual Arrangements, Shanghai Kunjia provides services to the consolidated VIE and is entitled to receive service fees from the consolidated VIE in exchange. The Contractual Arrangements provide that for any fiscal quarter where the consolidated VIE records pre-tax profit, the consolidated VIE shall pay to Shanghai Kunjia a service fee at an amount equivalent to its pre-tax profit excluding service fees under U.S. GAAP after making up the accumulated losses under U.S. GAAP from prior years, subject to compliance with applicable PRC laws. Notwithstanding the foregoing, pursuant to the Contractual Arrangements, Shanghai Kunjia is entitled to adjust the service fee based on the operating status and needs for business development of the consolidated VIE, and by considering among other things, the complexity of the services, the actual costs that may be incurred to provide the services, as well as the value and comparable price on the market of such services.
For the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, the consolidated VIE was in an accumulated deficit position. The consolidated VIE had accumulated deficits of RMB965 million, RMB636 million and RMB614 million (US$84 million) as of December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. In light of that, Shanghai Kunjia did not charge the consolidated VIE for any service fees, and consequently, the consolidated VIE had not paid any service fees to Shanghai Kunjia as of December 31, 2024. Shanghai Kunjia intends to charge the consolidated VIE for service fees after the pre-tax profit under U.S. GAAP of the consolidated VIE exceeds its accumulated losses under U.S. GAAP, pursuant to the Contractual Arrangements. For the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, the Parent company received the cash dividends from its PRC subsidiaries of nil, RMB157.7 and RMB303.7 million (US$41.6 million), respectively.
We provide loans to some of our overseas subsidiaries to support their business growth. We provided loans of RMB20.9 million, RMB5.6 million and nil to our overseas subsidiaries in Nigeria to extend small credit loan business to individual borrowers in 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. As of the date of this annual report, we have disposed of our subsidiaries in Nigeria. In 2022, 2023 and 2024, we did not make any capital contribution or provide any loan to our PRC subsidiaries or the consolidated VIE.
Neither the subsidiaries of the Parent nor the consolidated VIE is obligated to make dividends or distributions to the Parent under the Contractual Arrangements. As of the date of this annual report, dividends of RMB461.4 million (US$63.2 million) have been made to the Parent by the Parent’s subsidiaries.
Dividends or Distributions on Our ADSs or Class A Ordinary Shares Made to the U.S. Investors and Their Tax Consequences
Jiayin Technology paid a cash dividend of RMB400 million to its shareholders in March 2018 before entering into the Contractual Arrangements. The dividend was distributed to facilitate the delisting of Jiayin Technology from the National Equities Exchange and Quotations Co., Ltd., or the NEEQ, and to fund the settlement of related party balances.
On March 28, 2023, our board of directors, or the Board, approved and adopted a dividend policy, under which we and the VIE Group may choose to declare and distribute cash dividend twice each fiscal year, starting from 2023, at an aggregate amount of no less than 15% of the net income after tax of we and the VIE Group in the previous fiscal year on a consolidated basis. On July 10, 2023, our board of directors approved the payment of a cash dividend of US$0.10 per ordinary share, or US$0.40 per ADS ("July 2023 Dividend"). The aggregate amount of cash distributed for the July 2023 Dividend was approximately US$21.5 million. On January 8, 2024, our board of directors approved the payment of a cash dividend of US$0.10 per ordinary share, or US$0.40 per ADS ("January 2024 Dividend"). The aggregate amount of cash distributed for the January 2024 Dividend was US$21.2 million. On August 16, 2024, our board of directors approved the payment of a cash dividend of US$0.125 per ordinary share, or US$0.50 per ADS ("August 2024 Dividend"). The aggregate amount of cash distributed for the August 2024 Dividend was US$26.6 million. On November 19, 2024, our board of directors approved and adopted an amended dividend policy (the “Amended Dividend Policy”) to replace the prior dividend policy in its entirety, with immediate effect. Under the Amended Dividend Policy, we may choose to declare and distribute a cash dividend once each fiscal year, starting from 2025, at an aggregate amount of no less than 15% of our net income after tax in the previous fiscal year. On March 27, 2025, in order to provide investors with higher returns, our board of directors approved and adopted a further adjustment to the Amended Dividend Policy to increase the annual dividend amount such that we may choose to declare and distribute a cash dividend once each fiscal year, starting from 2025, at an aggregate amount of around 30% of our net income after tax in the previous fiscal year. The determination to make dividend distributions in any particular fiscal year will be made at the discretion of our board of directors based upon factors such as our results of operations, cash flow, general financial condition, capital requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant. For more details, see “Item 8. Financial Information—A. Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information—Dividend Policy.”
In addition, subject to the passive foreign investment company rules discussed in detail under “Item 10. Additional Information—E. Taxation—Passive Foreign Investment Company”, the gross amount of any distribution that we make to investors with respect to our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares (including any amounts withheld to reflect PRC or other withholding taxes) will be taxable as a dividend, to the extent paid out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under United States federal income tax principles. Furthermore, if we are considered a PRC tax resident enterprise for tax purposes, any dividends we pay to our overseas shareholders may be regarded as China-sourced income and as a result may be subject to PRC withholding tax. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—If we are classified as a PRC resident enterprise for PRC income tax purposes, such classification could result in unfavorable tax consequences to us and our non-PRC shareholders or ADS holders.” For further discussion on PRC and United States federal income tax considerations of an investment in the ADSs, see “Item 10. Additional Information—E. Taxation.”
Restrictions on Foreign Exchange and the Ability to Transfer Cash between Entities, Across Borders and to U.S. Investors
Our cash dividends, if any, will be paid in U.S. dollars. The PRC government imposes controls on the convertibility of Renminbi into foreign currencies and, in certain cases, the remittance of currency out of mainland China. The majority of our income is received in Renminbi and shortages in foreign currencies may restrict our ability to pay dividends or other payments, or otherwise satisfy our foreign currency denominated obligations, if any. Under existing PRC foreign exchange regulations, payments of current account items, including profit distributions, interest payments and expenditures from trade-related transactions, can be made in foreign currencies without prior approval from SAFE as long as certain procedural requirements are met. Approval from appropriate government authorities is required if Renminbi is converted into foreign currency and remitted out of mainland China to pay capital expenses such as the repayment of loans denominated in foreign currencies. The PRC government may at its discretion, impose restrictions on access to foreign currencies for current account transactions and if this occurs in the future, we may not be able to pay dividends in foreign currencies to our shareholders.
Relevant PRC laws and regulations permit the PRC companies to pay dividends only out of their retained earnings, if any, as determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. Additionally, our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE can only distribute dividends upon approval of the shareholders after they have met the PRC requirements for appropriation to the statutory reserves. As a result of these and other restrictions under the PRC laws and regulations, our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE are restricted to transfer a portion of their net assets to us either in the form of dividends, loans or advances. Even though we currently do not require any such dividends, loans or advances from our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE for working capital and other funding purposes, we may in the future require additional cash resources from our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE due to changes in business conditions, to fund future acquisitions and developments, or merely declare and pay dividends to or distributions to our shareholders.
For our Hong Kong subsidiary, Geerong (HK) Limited, there are no restrictions or limitations on its ability to transfer cash out of Hong Kong under the laws and regulations of Hong Kong that are in place as of the date of this annual report. However, if Geerong (HK) Limited is not able to transfer cash out of Hong Kong, we will not be able to fund operations in other regions or have it available to distribute to our investors.
As of the date of this annual report, we have not had difficulties in transferring cash between any entities in our consolidated group whether in the form of dividends or payments of intercompany obligations.
For a diagram illustrating the typical fund flow among Jiayin Group Inc., our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE, see “Item 3. Key Information—Restrictions on Foreign Exchange and the Ability to Transfer Cash between Entities, Across Borders and to U.S. Investors.”
For a condensed consolidating schedule depicting the financial position, cash flow and results of operations for the Parent, the consolidated VIE, and any eliminating adjustments separately, see “Item 3. Key Information—Condensed Consolidation Schedule.”
ITEM 1. IDENTITY OF DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND ADVISERS
Not applicable.
ITEM 2. OFFER STATISTICS AND EXPECTED TIMETABLE
Not applicable.
ITEM 3. KEY INFORMATION
The Consolidated VIE and China Operations
Jiayin Group Inc. is a Cayman Islands holding company primarily operating in China through (i) its PRC subsidiaries, including Shanghai Kunjia and Chuangzhen Technology and its subsidiaries, in which we hold equity ownership interests, and (ii) contractual arrangements among (x) Shanghai Kunjia, (y) the consolidated VIE, namely, Jiayin Technology, and (z) the shareholders of the consolidated VIE. We do not own any equity interest in Jiayin Technology. Investors in the ADSs thus are not purchasing, and may never hold, equity interests in the Jiayin Technology. PRC laws, regulations, and rules restrict and impose conditions on direct foreign investment in China-based companies that engage in certain types of business, and we therefore operate these businesses in China through the VIE structure which provides investors with exposure to foreign investment in the Chinese operating companies.
We have determined that we control Jiayin Technology for financial reporting purpose in accordance with the contractual arrangements. In June 2018, Shanghai Kunjia entered into a series of contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology and its shareholders, allowing us to exercise effective control over Jiayin Technology. These agreements or their forms include:(i) an exclusive consultation and service agreement, which enables us to receive substantially all of the economic benefits of Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries, (ii) powers of attorney and an equity pledge agreement, which provide us with effective control over Jiayin Technology, and (iii) an exclusive call option agreement, which provides us with the option to purchase all of the equity interests in Jiayin Technology. For more details of these contractual arrangements, see “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure—Contractual Arrangements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the Shareholders of Jiayin Technology.”
However, control through these contractual arrangements may be less effective than direct ownership, and we could face heightened risks and costs in enforcing these contractual arrangements, because it remains to be observed regarding the interpretation and application of current and future PRC laws, regulations, and rules relating to these contractual arrangements, and these contractual arrangements have not been tested in a court of law. If the PRC government finds such agreements non-compliant with relevant PRC laws, regulations, and rules, or if these laws, regulations, and rules or the interpretation thereof change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our beneficial interest in Jiayin Technology or forfeit our rights under the contractual arrangements. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure—The interpretation and implementation of the Foreign Investment Law of the PRC may impact the viability of our current corporate structure, corporate governance and business operations,” “—If the PRC government deems that the Contractual Arrangements in relation to Jiayin Technology do not comply with PRC regulatory restrictions on foreign investment in the relevant industries, or if these regulations or the interpretation of existing regulations change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our beneficial interest in those operations,” and “—We rely on Contractual Arrangements with Jiayin Technology and shareholders of Jiayin Technology for certain business operations, which may not be as effective as direct ownership in providing operational control, and these contractual arrangements have not been tested in a court of law.”
The following diagram illustrates the corporate structure of us and the consolidated VIE, including the names, places of incorporation and the proportion of ownership interests in our and the consolidated VIE’s significant subsidiaries and consolidated affiliated entities and their subsidiaries as of the date of this annual report:

(1)
Jiayin Southeast Asia Holdings Limited was established in February 2018 to develop and operate our overseas business.
(2)
Jiayin Technology is owned as to 58% by Mr. Dinggui Yan, our founder, director and chief executive officer, 27% by Shanghai Jinmushuihuotu Investment Center (Limited Partnership), or Jinmushuihuotu Investment, 12% by Mr. Guanglin Zhang, and 3% by Mr. Yuanle Wu, who both are employees of our company. Jinmushuihuotu Investment is established in connection with the share incentive plan of Jiayin Technology. See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—B. Compensation—Share Incentive Plans—2019 Share Incentive Plan.” The general partner of Jinmushuihuotu Investment is Shanghai Jinmushuihuotu Marketing and Planning Co., Ltd., or Jinmushuihuotu Marketing, which is controlled by Mr. Dinggui Yan.
(3)
Jiayin Technology entered into Contractual Arrangements with Shanghai Kunjia. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure—Contractual Arrangements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the shareholders of Jiayin Technology.”
(4)
Jiangxi Yunkaijianming Technology Co., Ltd. (“Jiangxi Yunkaijianming”, formerly known as “Geerong Yun (Shanghai) Technology Development Co., Ltd.) became our wholly-owned subsidiary after the business combination in September 2019.
(5)
Shanghai Jiajie Internet Information Services Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Jiajie”, formerly known as Shanghai Jiajie Internet Finance Information Services Co., Ltd.”) became our wholly-owned subsidiary after the business combination in July 2019.
(6)
Shanghai Chuangzhen Software Co., Ltd. (“Chuangzhen Software”) was established in April 2020.
(7)
Jiayin Shuke Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Jiayin Shuke”) was established in January 2021.
(8)
Hainan Yinke Financing Guarantee Co., Ltd. (“Hainan Yinke”) was established in August 2021.
(9)
Guangxi Chuangzhen Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Guangxi Chuangzhen”) was established in January 2022.
(10)
Shanghai Jirongzhicheng Enterprise Development Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Jirongzhicheng”) was established in November 2024.
Fund Flows Between Jiayin Group Inc., Its Subsidiaries and the Consolidated VIE
Under PRC law, we may provide funding to our PRC subsidiaries only through capital contributions or loans, and to the consolidated VIE only through loans, subject to the satisfaction of applicable government registration and approval requirements. We rely on dividends and other distributions from our PRC subsidiaries to satisfy part of our liquidity requirement. Under the contractual arrangements among Shanghai Kunjia, the consolidated VIE, and the shareholders of the consolidated VIE, Shanghai Kunjia is entitled to substantially all of the economic benefits of the consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries in the form of service fees.
For risks relating to the fund flows of our China operations, you should carefully consider the risks described under “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China” including, but not limited to, the following:
•
PRC regulation of loans to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore holding companies and governmental administration of currency conversion may delay or prevent us from using the proceeds of further offerings to make loans to or make additional capital contributions to our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand our business;
•
We rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our PRC subsidiaries to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have, and any limitation on the ability of our PRC subsidiaries to make payments to us could have a material adverse effect on our ability to conduct our business; and
•
Governmental administration of conversion and remittance of foreign currency may limit our ability to transfer cash out of China to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have, and may affect the value of your investment.
For a condensed consolidating schedule depicting the financial position, cash flow and results of operations for the Parent, the consolidated VIE, and any eliminating adjustments separately, see “Item 3. Key Information—Condensed Consolidation Schedule”.
Transfer of funds between any entities in our consolidated group is subject to our cash management policy that outlines appropriate internal control procedures on the handling, depositing, receiving, transferring, safeguarding, and documentation and recording of cash assets. The finance department at the Jiayin Group Inc. level with authorized persons at each entity has the centralized responsibility for undertaking cash handling activity. Based on the amount of a fund transfer and the nature of the use of funds, requisite internal approval must be obtained prior to each fund transfer: all transactions require, at a minimum, the approval of the financial controller; for certain transactions with large amounts, approval of our vice president of finance, and in some instances, approval of both our vice president of finance and chief executive officer, is also required.
Assets Transfer Occurred Between the Parent, Its Subsidiaries and the Consolidated VIE
Under the Contractual Arrangements, Shanghai Kunjia provides services to the consolidated VIE and is entitled to receive service fees from the consolidated VIE in exchange. The Contractual Arrangements provide that for any fiscal quarter where the consolidated VIE records pre-tax profit, the consolidated VIE shall pay to Shanghai Kunjia a service fee at an amount equivalent to its pre-tax profit excluding service fees under U.S. GAAP after making up the accumulated losses under U.S. GAAP from prior years, subject to compliance with applicable PRC laws. Notwithstanding the foregoing, pursuant to the Contractual Arrangements, Shanghai Kunjia is entitled to adjust the service fee based on the operating status and needs for business development of the consolidated VIE, and by considering among other things, the complexity of the services, the actual costs that may be incurred to provide the services, as well as the value and comparable price on the market of such services.
For the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, the consolidated VIE was in an accumulated deficit position. The consolidated VIE had accumulated deficits of RMB965 million, RMB636 million and RMB614 million (US$84 million) as of December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. In light of that, Shanghai Kunjia did not charge the consolidated VIE for any service fees, and consequently, the consolidated VIE had not paid any service fees to Shanghai Kunjia as of December 31, 2024. Shanghai Kunjia intends to charge the consolidated VIE for service fees after the pre-tax profit under U.S. GAAP of the consolidated VIE exceeds its accumulated losses under U.S. GAAP, pursuant to the Contractual Arrangements. For the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, the Parent company received the cash dividends from its PRC subsidiaries of nil, RMB157.7 and RMB303.7 million (US$41.6 million), respectively.
We provide loans to some of our overseas subsidiaries to support their business growth. We provided loans of RMB20.9 million, RMB5.6 million and nil to our overseas subsidiaries in Nigeria to extend small credit loan business to individual borrowers in 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. As of the date of this annual report, we have disposed of our subsidiaries in Nigeria. In 2022, 2023 and 2024, we did not make any capital contribution or provide any loan to our PRC subsidiaries or the consolidated VIE.
Neither the subsidiaries of the Parent nor the consolidated VIE is obligated to make dividends or distributions to the Parent under the Contractual Arrangements. As of the date of this annual report, dividends of RMB461.4 million (US$63.2 million) have been made to the Parent by the Parent’s subsidiaries.
Dividends or Distributions on Our ADSs or Class A Ordinary Shares Made to the U.S. Investors and Their Tax Consequences
Jiayin Technology paid a cash dividend of RMB400 million to its shareholders in March 2018 before entering into the Contractual Arrangements. The dividend was distributed to facilitate the delisting of Jiayin Technology from the National Equities Exchange and Quotations Co., Ltd., or the NEEQ, and to fund the settlement of related party balances.
On March 28, 2023, our Board approved and adopted a dividend policy, under which the Company may choose to declare and distribute cash dividend twice each fiscal year, starting from 2023, at an aggregate amount of no less than 15% of the net income after tax of the Company in the previous fiscal year on a consolidated basis. On November 19, 2024, our board of directors approved and adopted an amended dividend policy (the “Amended Dividend Policy”) to replace the prior dividend policy in its entirety, with immediate effect. Under the Amended Dividend Policy, we may choose to declare and distribute a cash dividend once each fiscal year, starting from 2025, at an aggregate amount of no less than 15% of our net income after tax in the previous fiscal year. On March 27, 2025, in order to provide investors with higher returns, our board of directors approved and adopted a further adjustment to the Amended Dividend Policy to increase the annual dividend amount such that we may choose to declare and distribute a cash dividend once each fiscal year, starting from 2025, at an aggregate amount of around 30% of our net income after tax in the previous fiscal year. The determination to make dividend distributions in any particular fiscal year will be made at the discretion of our board of directors based upon factors such as our results of operations, cash flow, general financial condition, capital requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant. For more details, see “Item 8. Financial Information—A. Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information—Dividend Policy.”
In addition, subject to the passive foreign investment company rules discussed in detail under “Item 10. Additional Information—E. Taxation—Passive Foreign Investment Company”, the gross amount of any distribution that we make to investors with respect to our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares (including any amounts withheld to reflect PRC or other withholding taxes) will be taxable as a dividend, to the extent paid out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under United States federal income tax principles. Furthermore, if we are considered a PRC tax resident enterprise for tax purposes, any dividends we pay to our overseas shareholders may be regarded as China-sourced income and as a result may be subject to PRC withholding tax. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—If we are classified as a PRC resident enterprise for PRC income tax purposes, such classification could result in unfavorable tax consequences to us and our non-PRC shareholders or ADS holders.” For further discussion on PRC and United States federal income tax considerations of an investment in the ADSs, see “Item 10—Additional Information—E. Taxation.”
Restrictions on Foreign Exchange and the Ability to Transfer Cash between Entities, Across Borders and to U.S. Investors
Our cash dividends, if any, will be paid in U.S. dollars. The PRC government imposes administrative measures on the convertibility of Renminbi into foreign currencies and, in certain cases, the remittance of currency out of mainland China. The majority of our income is received in Renminbi and shortages in foreign currencies may restrict our ability to pay dividends or other payments, or otherwise satisfy our foreign currency denominated obligations, if any. Under existing PRC foreign exchange regulations, payments of current account items, including profit distributions, interest payments and expenditures from trade-related transactions, can be made in foreign currencies without prior approval from SAFE as long as certain procedural requirements are met. Approval from appropriate government authorities is required if Renminbi is converted into foreign currency and remitted out of mainland China to pay capital expenses such as the repayment of loans denominated in foreign currencies. The PRC government may, impose administrative measures on access to foreign currencies for current account transactions and if this occurs in the future, we may not be able to pay dividends in foreign currencies to our shareholders.
Relevant PRC laws and regulations permit the PRC companies, such as our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE, to pay dividends only out of their retained earnings, if any, as determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations.
Each of our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE that is in retained earnings position as of the end of each year is required to set aside 10% of its after-tax profits each year, if any, to fund certain statutory reserve funds until such reserve funds reach 50% of its registered capital. The aforementioned registered capital refers to the total amount of share capital of all issued shares or the total amount of capital contribution subscribed by all shareholders, as registered with the registration authority. Furthermore, each of our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE may allocate a portion of its after-tax profits based on PRC accounting standards to a discretionary surplus fund at their discretion. The statutory reserve funds and the discretionary surplus funds are not distributable as cash dividends. After our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE have generated retained earnings and met the requirements for appropriation to the statutory reserves and until such reserves reach 50% of its registered capital, respectively, our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE can distribute dividends upon approval of the shareholders. As a result of these and other restrictions under the PRC laws and regulations, our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE are restricted to transfer a portion of their net assets to us either in the form of dividends, loans or advances. Even though we currently do not require any such dividends, loans or advances from our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE for working capital and other funding purposes, we may in the future require additional cash resources from our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE due to changes in business conditions, to fund future acquisitions and developments, or merely declare and pay dividends to or distributions to our shareholders.
For our Hong Kong subsidiary, Geerong (HK) Limited, there are no restrictions or limitations on its ability to transfer cash out of Hong Kong under the laws and regulations of Hong Kong that are in place as of the date of this annual report. However, if Geerong (HK) Limited is not able to transfer cash out of Hong Kong, we will not be able to fund operations in other regions or have it available to distribute to our investors.
As of the date of this annual report, we have not had difficulties in transferring cash between any entities in our consolidated group whether in the form of dividends or payments of intercompany obligations.
The following diagram illustrates the typical fund flow among Jiayin Group Inc., our PRC subsidiaries, and the consolidated VIE.
Condensed Consolidation Schedule
The following tables set forth the summary consolidated balance sheets data as of December 31, 2023 and 2024 of (i) the Parent, (ii) the WFOE, (iii) the other subsidiaries of the Parent inside and outside mainland China, separately, and (iv) the VIE Group, and the summary of the consolidated statement of income and cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2023 and 2024 Our and the VIE Group’s consolidated financial statements are prepared and presented in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, or U.S. GAAP except that the equity method has been used to account for investments in subsidiaries and VIE. Our and the VIE Group’s historical results are not necessarily indicative of results expected for future periods. You should read this information together with our and the VIE Group’s consolidated financial statements and the related notes and “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects” included elsewhere in this annual report.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, 2024 |
|
|
|
Parent |
|
|
Consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries |
|
|
Shanghai Kunjia
(WFOE) |
|
|
Other subsidiaries inside
mainland China |
|
|
Subsidiaries outside
mainland China |
|
|
Eliminations |
|
|
Consolidated
total |
|
|
|
(RMB in thousands) |
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
298 |
|
|
|
5,439 |
|
|
|
114 |
|
|
|
530,424 |
|
|
|
4,248 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
540,523 |
|
Accounts receivable
and contract assets,
net |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
54,404 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,932,351 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,986,755 |
|
Long-term
investments, net |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
162,267 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
162,267 |
|
Investment in
subsidiaries and
VIEs and VIEs'
subsidiaries |
|
|
3,101,038 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
69,201 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,244,525 |
|
|
|
(6,414,764 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Intercompany
balances* |
|
|
79,697 |
|
|
|
228,195 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(73,550 |
) |
|
|
(234,342 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Other assets |
|
|
2,506 |
|
|
|
80,057 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,614,799 |
|
|
|
22,986 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,720,348 |
|
Total assets |
|
|
3,183,539 |
|
|
|
368,095 |
|
|
|
69,315 |
|
|
|
5,004,024 |
|
|
|
3,199,684 |
|
|
|
(6,414,764 |
) |
|
|
5,409,893 |
|
Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tax payables |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
25,935 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
658,447 |
|
|
|
2,652 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
687,034 |
|
Other liabilities |
|
|
54,266 |
|
|
|
272,959 |
|
|
|
89 |
|
|
|
1,170,278 |
|
|
|
97,653 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,595,245 |
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
54,266 |
|
|
|
298,894 |
|
|
|
89 |
|
|
|
1,828,725 |
|
|
|
100,305 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,282,279 |
|
Total net assets |
|
|
3,129,273 |
|
|
|
69,201 |
|
|
|
69,226 |
|
|
|
3,175,299 |
|
|
|
3,099,379 |
|
|
|
(6,414,764 |
) |
|
|
3,127,614 |
|
* Intercompany balances resulted from regular transactions in the business operations of the entities, and no service fees were charged by Shanghai Kunjia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
Parent |
|
|
Consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries |
|
|
Shanghai Kunjia
(WFOE) |
|
|
Other subsidiaries inside
mainland China |
|
|
Subsidiaries outside
mainland China |
|
|
Eliminations |
|
|
Consolidated
total |
|
|
|
(RMB in thousands) |
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
804 |
|
|
|
81,384 |
|
|
|
1,682 |
|
|
|
275,054 |
|
|
|
11,269 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
370,193 |
|
Accounts receivable
and contract assets,
net |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
97,187 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,006,358 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,103,545 |
|
Long-term
investments, net |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
101,481 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
101,481 |
|
Investment in
subsidiaries and
VIEs and VIEs'
subsidiaries |
|
|
2,269,730 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
12,913 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,256,571 |
|
|
|
(4,539,214 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Intercompany
balances* |
|
|
134,255 |
|
|
|
62,917 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
6,225 |
|
|
|
(203,397 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Other assets |
|
|
2,627 |
|
|
|
74,280 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,795,297 |
|
|
|
197,343 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,069,547 |
|
Total assets |
|
|
2,407,416 |
|
|
|
315,768 |
|
|
|
14,595 |
|
|
|
5,082,934 |
|
|
|
2,363,267 |
|
|
|
(4,539,214 |
) |
|
|
5,644,766 |
|
Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tax payables |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
24,249 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
519,951 |
|
|
|
24,618 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
568,819 |
|
Other liabilities |
|
|
25,275 |
|
|
|
278,606 |
|
|
|
1,650 |
|
|
|
2,319,356 |
|
|
|
70,599 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,695,486 |
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
25,275 |
|
|
|
302,855 |
|
|
|
1,651 |
|
|
|
2,839,307 |
|
|
|
95,217 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,264,305 |
|
Total net assets |
|
|
2,382,141 |
|
|
|
12,913 |
|
|
|
12,944 |
|
|
|
2,243,627 |
|
|
|
2,268,050 |
|
|
|
(4,539,214 |
) |
|
|
2,380,461 |
|
* Intercompany balances resulted from regular transactions in the business operations of the entities, and no service fees were charged by Shanghai Kunjia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the year ended December 31, 2024 |
|
|
|
Parent |
|
|
Consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries |
|
|
Shanghai Kunjia
(WFOE) |
|
|
Other subsidiaries inside
mainland China |
|
|
Subsidiaries outside
mainland China |
|
|
Eliminations |
|
|
Consolidated
total |
|
|
|
(RMB in thousands) |
|
Net revenue |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,621,778 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,827,136 |
|
|
|
39,696 |
|
|
|
(1,687,578 |
) |
|
|
5,801,032 |
|
Total operating costs and
expenses |
|
|
(3,736 |
) |
|
|
(1,608,346 |
) |
|
|
(26 |
) |
|
|
(4,588,087 |
) |
|
|
(40,400 |
) |
|
|
1,687,578 |
|
|
|
(4,553,017 |
) |
(Loss)/Income from operations |
|
|
(3,736 |
) |
|
|
13,432 |
|
|
|
(26 |
) |
|
|
1,239,049 |
|
|
|
(704 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,248,015 |
|
Equity in earnings of subsidiaries
and VIEs and VIEs' subsidiaries |
|
|
1,060,219 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
22,309 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,095,954 |
|
|
|
(2,178,482 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Net income |
|
|
1,056,478 |
|
|
|
22,309 |
|
|
|
22,302 |
|
|
|
1,073,652 |
|
|
|
1,229,209 |
|
|
|
(2,347,482 |
) |
|
|
1,056,468 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the year ended December 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
Parent |
|
|
Consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries |
|
|
Shanghai Kunjia
(WFOE) |
|
|
Other subsidiaries inside
mainland China |
|
|
Subsidiaries outside
mainland China |
|
|
Eliminations |
|
|
Consolidated
total |
|
|
|
(RMB in thousands) |
|
|
Net revenue |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,670,688 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,720,863 |
|
|
|
96,483 |
|
|
|
(1,021,161 |
) |
|
|
5,466,873 |
|
Total operating costs and
expenses |
|
|
(4,546 |
) |
|
|
(1,614,045 |
) |
|
|
(45 |
) |
|
|
(3,444,526 |
) |
|
|
(92,402 |
) |
|
|
1,021,161 |
|
|
|
(4,134,403 |
) |
(Loss)/Income from operations |
|
|
(4,546 |
) |
|
|
56,643 |
|
|
|
(45 |
) |
|
|
1,276,337 |
|
|
|
4,081 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,332,470 |
|
Equity in earnings of subsidiaries
and VIEs and VIEs' subsidiaries |
|
|
1,720,465 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
328,844 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,469,714 |
|
|
|
(3,519,023 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Net income |
|
|
1,297,619 |
|
|
|
328,844 |
|
|
|
328,866 |
|
|
|
1,140,848 |
|
|
|
1,720,422 |
|
|
|
(3,519,023 |
) |
|
|
1,297,576 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the year ended December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
Parent |
|
|
Consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries |
|
|
Shanghai Kunjia
(WFOE) |
|
|
Other subsidiaries inside
mainland China |
|
|
Subsidiaries outside
mainland China |
|
|
Eliminations |
|
|
Consolidated
total |
|
|
|
(RMB in thousands) |
|
|
Net revenue |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
972,029 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,979,683 |
|
|
|
44,100 |
|
|
|
(724,398 |
) |
|
|
3,271,414 |
|
Total operating costs and expenses |
|
|
(6,494 |
) |
|
|
(919,825 |
) |
|
|
(45 |
) |
|
|
(1,798,121 |
) |
|
|
(89,308 |
) |
|
|
724,398 |
|
|
|
(2,089,395 |
) |
(Loss)/Income from operations |
|
|
(6,494 |
) |
|
|
52,204 |
|
|
|
(45 |
) |
|
|
1,181,562 |
|
|
|
(45,208 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,182,019 |
|
Equity in earnings of subsidiaries
and VIEs and VIEs' subsidiaries |
|
|
1,199,673 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
164,741 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,165,074 |
|
|
|
(2,529,488 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Net income |
|
|
1,179,658 |
|
|
|
164,741 |
|
|
|
164,722 |
|
|
|
1,000,352 |
|
|
|
1,200,247 |
|
|
|
(2,529,488 |
) |
|
|
1,180,232 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the year ended December 31, 2024 |
|
|
|
Parent |
|
|
Consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries |
|
|
Shanghai Kunjia
(WFOE) |
|
|
Other subsidiaries inside
mainland China |
|
|
Subsidiaries outside
mainland China |
|
|
Eliminations |
|
|
Consolidated
total |
|
|
|
(RMB in thousands) |
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in)
operating activities |
|
|
300,515 |
|
|
|
(169,333 |
) |
|
|
(7 |
) |
|
|
1,624,602 |
|
|
|
(27,553 |
) |
|
|
(302,736 |
) |
|
|
1,425,488 |
|
Net cash (used in) provided by
investing activities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(61,774 |
) |
|
|
(1,561 |
) |
|
|
(943,632 |
) |
|
|
304,398 |
|
|
|
(80,951 |
) |
|
|
(783,520 |
) |
Net cash (used in) provided by
financing activities |
|
|
(301,006 |
) |
|
|
152,727 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(288,500 |
) |
|
|
(279,595 |
) |
|
|
383,687 |
|
|
|
(332,687 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the year ended December 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
Parent |
|
|
Consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries |
|
|
Shanghai Kunjia
(WFOE) |
|
|
Other subsidiaries inside
mainland China |
|
|
Subsidiaries outside
mainland China |
|
|
Eliminations |
|
|
Consolidated
total |
|
|
|
(RMB in thousands) |
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in)
operating activities |
|
|
144,310 |
|
|
|
139,602 |
|
|
|
291 |
|
|
|
327,764 |
|
|
|
(64,707 |
) |
|
|
(157,672 |
) |
|
|
389,588 |
|
Net cash (used in) provided by
investing activities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(74,100 |
) |
|
|
(38,081 |
) |
|
|
(49,526 |
) |
|
|
223,695 |
|
|
|
(167,838 |
) |
|
|
(105,850 |
) |
Net cash (used in) provided by
financing activities |
|
|
(155,400 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
38,081 |
|
|
|
(244,000 |
) |
|
|
(157,672 |
) |
|
|
325,510 |
|
|
|
(193,481 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the year ended December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
Parent |
|
|
Consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries |
|
|
Shanghai Kunjia
(WFOE) |
|
|
Other subsidiaries inside
mainland China |
|
|
Subsidiaries outside
mainland China |
|
|
Eliminations |
|
|
Consolidated
total |
|
|
|
(RMB in thousands) |
|
|
Net cash (used in) provided by
operating activities |
|
|
(21,917 |
) |
|
|
8,807 |
|
|
|
15,020 |
|
|
|
146,876 |
|
|
|
(15,194 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
133,592 |
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(7,265 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(9,466 |
) |
|
|
(6,218 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(22,949 |
) |
Net cash provided by (used in)
financing activities |
|
|
8,783 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(21,349 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(12,566 |
) |
Approvals Required from the PRC Authorities for Offering Securities to Foreign Investors
We are required to complete filing or fulfill other requirements of the China Securities Regulatory Commission, or the CSRC within three business days after the closing of our future offerings, according to the Trial Administrative Measures (as defined below). We do not believe we are required to obtain any approvals from the CAC or other PRC government authorities under PRC law in connection with a future offering of our securities to foreign investors.
Approval Required from the China Securities Regulatory Commission
On February 17, 2023, the CSRC promulgated the Trial Administrative Measures of Overseas Securities Offering and Listing by Domestic Enterprises, or the Trial Administrative Measures, and five supporting guidelines, which became effective on March 31, 2023. According to the Trial Administrative Measures, we are required to complete the filing procedures with the CSRC for any future follow-on offerings within three business days after the closing of the offering.
On February 24, 2023, the CSRC and other relevant government authorities published the Provisions on Strengthening Confidentiality and Archives Management of Overseas Securities Offering and Listing by Domestic Enterprises, or the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management, which became effective on March 31, 2023. According to the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management, PRC domestic enterprises that seek to offer and list securities in overseas markets shall establish confidentiality and archives management system. The PRC domestic enterprises shall obtain approval from the competent authority and file with the confidential administration department at the same level when providing or publicly disclosing documents and materials related to state secrets or secrets of the governmental authorities to the underwriters or other agencies or the offshore regulatory authorities, and shall complete corresponding procedures when providing or publicly disclosing documents and materials which may adversely influence national security and the public interest. The PRC domestic enterprises shall provide written statements on the implementation on the aforementioned rules to the underwriter and other agencies. Nevertheless, the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management do not provide a clear scope of materials that, if divulged, will jeopardize national security or public interest, and the PRC government authorities may have certain discretion in the interpretation and enforcement of the applicable laws. Given the uncertainties surrounding the interpretation of the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management, we cannot assure you that we will not be required to obtain any approval from or complete filing procedures with the competent authorities for our future offerings.
As advised by our PRC legal counsel, King & Wood Mallesons, the Trial Administrative Measures and the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management may subject us to additional compliance requirement in the future for a future securities offering, including completion of filing procedures and obtaining required approval. We cannot assure you that we will be able to get the clearance of filing procedures or obtain the required approval on a timely basis, or at all. Any failure of us to fully comply with new regulatory requirements may significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer our securities, cause significant disruption to our business operations, and severely damage our reputation, which would materially and adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations and cause our ADSs to significantly decline in value or become worthless, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure—The approval, filing or other requirements of the CSRC, the CAC or other PRC government authorities may be required under PRC law in connection with a future offering of our securities to foreign investors.”
Approval from the Cyberspace Administration of China or Other PRC Government Authorities
With respect to the Cyberspace Administration of China, or the CAC, as advised by our PRC legal counsel, we believe that there is a relatively low likelihood that we and the consolidated VIE will be subject to the cybersecurity review by the CAC for a future offering of our securities to foreign investors, given that: (i) neither we nor the consolidated VIE has been recognized as critical information infrastructure operators. The aforementioned critical information infrastructure refers to important network infrastructure and information system in public telecommunications, information services, energy sources, transportation and other critical industries and domains, in which any destruction or data leakage will have severe impact on national security, the nation’s welfare, people’s living and public interests; (ii) data processed in our and the consolidated VIE’s business do not have impact or potential impact on national security; and (iii) it is still uncertain whether the Cybersecurity Review Measures (as defined below) will be applicable to a future offering conducted by China-based companies listed overseas. For further discussion on the risks relating to the oversight of the CAC, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure—It is unclear whether we and the consolidated VIE will be subject to the oversight of the CAC and how such oversight may impact us. Our and the consolidated VIE’s business could be interrupted or we and the consolidated VIE could be subject to liabilities which may materially and adversely affect the results of our and the consolidated VIE’s operation and the value of your investment.”
As advised by our PRC legal counsel, we believe that approvals or permissions from the CSRC are not required for the operations of the consolidated VIE and our other subsidiaries, and that there is a relatively low likelihood that the operations of the consolidated VIE and our other subsidiaries will be subject to the cybersecurity review by the CAC, given that: (i) neither the consolidated VIE nor any of our other subsidiaries has been recognized as critical information infrastructure operators; and (ii) data processed in the consolidated VIE and our other subsidiaries’ business do not have impact or potential impact on national security. Furthermore, our and the VIE Group’s online platform, operated by Geerong Yunke Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Geerong Yunke”) and Shanghai Yixin Internet Technology Co., Ltd.(“Shanghai Yixin”) may be deemed to be providing commercial Internet information services, which would require the aforementioned companies to obtain certain value-added telecommunications business license. We cannot assure you that we can obtain these licenses in a timely manner, or at all.
Any failure to obtain the relevant approvals or licenses may subject us to sanctions, including rectification orders and warnings, fines, confiscation of illegal gains, and, in case of significant infringement, orders to close our online platform, which may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations. For further discussion on the risks relating to the regulatory oversight of the online platform, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—We and the VIE Group may be adversely affected by the complexity and changes in PRC regulation of Internet-related businesses and companies, and any lack of requisite approvals, licenses or permits applicable to our and the VIE Group’s business may have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.”
Except as otherwise disclosed in the foregoing, we do not believe we are required to obtain any approvals from the CAC or other PRC government authorities under PRC law in connection with a future offering of our securities to foreign investors as of the date of this annual report.
If we inadvertently conclude any prior approval is not required and the CSRC, the CAC or other relevant PRC regulatory agencies subsequently determine that prior approval is required for any of our future offerings of securities overseas or to maintain the listing status of our ADSs, we cannot guarantee that we will be able to obtain such approval in a timely manner, or at all, or to maintain such approval once we receive it. The CSRC, the CAC or other PRC regulatory agencies also may take actions requiring us, or making it advisable for us, not to proceed with such offering or maintain the listing status of our ADSs. If we proceed with any of such offering or maintain the listing status of our ADSs without obtaining these regulatory agencies’ approval to the extent it is required, or if we are unable to comply with any new approval requirements which might be adopted for future offerings, we may face regulatory actions or other sanctions from these regulatory agencies. For example, regulatory agencies may impose fines and penalties on our operations in China, limit our ability to pay dividends outside of China, limit our operating privileges in China, delay or restrict the repatriation of the proceeds from offering of securities overseas into China or take other actions that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects, as well as the trading price of the ADSs.
Furthermore, if we are required to obtain any other approvals from or complete filings and/or other regulatory procedures with the CSRC, the CAC or other PRC regulatory agencies as a result of change in applicable laws, regulations or interpretations for any future offering or the listing of the ADSs, we cannot assure you that we can obtain the required approval or complete the required filings and/or other regulatory procedures in a timely manner, or at all. Any failure to obtain such approval or complete such filings and/or other regulatory procedures may subject us to regulatory actions or other sanctions taken by the relevant government authorities, which may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Risks Relating to the Consolidated VIE and China Operations
Investing in the ADSs involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the risks described under “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors” and other information contained in this annual report on Form 20-F, before you decide whether to purchase the ADSs. In particular, we are subject to risks and uncertainties relating to our corporate structure and doing business in China, including, but not limited to, the following:
•
Jiayin Group Inc. is a Cayman Islands holding company primarily operating in China through its subsidiaries and contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology. Investors in the ADSs thus are not purchasing, and may never hold, equity interests in the consolidated VIE. The interpretation and application of current and future PRC laws, regulations, and rules relating to such agreements that establish the VIE structure for the majority of our and the consolidated VIE’s operations in China, including potential future actions by the PRC government remains to be observed, which could affect the enforceability of our contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology and, consequently, significantly affect the financial condition and results of operations of Jiayin Group Inc. If the PRC government finds such agreements non-compliant with relevant PRC laws, regulations, and rules, or if these laws, regulations, and rules or the interpretation thereof change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our beneficial interest in Jiayin Technology or forfeit our rights under the contractual arrangements;
•
The PRC government has authority to exert influence on the China operations of an offshore holding company, such as us. Changes in China’s economic, political or social conditions, or government policies may cause our and the consolidated VIE’s underlying operations in China to become prohibitive, which could materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business, financial condition, and results of operations;
•
We and the consolidated VIE are subject to extensive and evolving legal development, non-compliance with which, or changes in which, may materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business and prospects, and may result in a material change in our and the consolidated VIE’s operations and/or the value of our ADSs or could significantly limit or completely hinder our and the consolidated VIE’s ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of our securities to significantly decline or be worthless;
•
It is unclear whether we and the consolidated VIE will be subject to the oversight of the CAC and how such oversight may impact us. Our and the consolidated VIE’s business could be interrupted or we and the consolidated VIE could be subject to liabilities which may materially and adversely affect the results of our and the consolidated VIE’s operation and the value of your investment;
•
The PRC government’s oversight over our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations could result in a material adverse change in our and the consolidated VIE’s operations and the value of our ADSs;
•
The approval, filing or other requirements of the CSRC, the CAC or other PRC government authorities may be required under PRC law in connection with our future offering;
•
The interpretation and implementation of the Foreign Investment Law of the PRC may impact the viability of our current corporate structure, corporate governance and business operations;
•
If the PRC government deems that the Contractual Arrangements in relation to Jiayin Technology do not comply with PRC regulatory restrictions on foreign investment in the relevant industries, or if these regulations or the interpretation of existing regulations change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our beneficial interest in those operations;
•
We rely on Contractual Arrangements with Jiayin Technology and shareholders of Jiayin Technology for certain business operations, which may not be as effective as direct ownership in providing operational control, and these contractual arrangements have not been tested in a court of law;
•
Any failure by Jiayin Technology or shareholders of Jiayin Technology to perform their obligations under our Contractual Arrangements with them would have a material adverse effect on our business;
•
The shareholders of the consolidated VIE may have potential conflicts of interest with us, which may materially and adversely affect our business and financial condition;
•
Contractual Arrangements in relation to the consolidated VIE may be subject to scrutiny by the PRC tax authorities and they may determine that we or consolidated VIE owe additional taxes, which could negatively affect our financial condition and the value of your investment;
•
We may lose the ability to use and enjoy assets held by the VIE Group that are material to the operation of our business if the entities within the VIE Group declare bankruptcy or become subject to a dissolution or liquidation proceeding;
•
Changes in China’s economic, political or social conditions or government policies could have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations;
•
A downturn in the global economy could reduce the demand for consumer loans and investments, which could materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business and financial condition;
•
The interpretation and enforcement of PRC laws and regulations could limit the legal protections available to you and us, significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer our ADSs, cause significant disruption to our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations, and severely damage our and the consolidated VIE’s reputation, which would materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s financial condition and results of operations and cause our ADSs to significantly decline in value or become worthless;
•
We and the VIE Group may be adversely affected by the complexity and changes in PRC regulation of Internet-related businesses and companies, and any lack of requisite approvals, licenses or permits applicable to our and the VIE Group’s business may have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations;
•
We primarily rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our PRC subsidiaries to fund the cash and financing requirements we may have, and any limitation on the ability of our PRC subsidiaries to make payments to us could have a material adverse effect on our ability to conduct our business;
•
PRC regulation of loans to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore holding companies and governmental administration of currency conversion may delay or prevent us from using the proceeds of further offerings to make loans to or make additional capital contributions to our PRC subsidiaries, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand our business;
•
Fluctuations in exchange rates could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and the price of our ADSs;
•
Governmental administration of conversion and remittance of foreign currency may limit our ability to transfer cash out of China to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have, and may affect the value of your investment; Failure to make adequate contributions to various employee benefit plans and withhold individual income tax on employees’ salaries as required by PRC regulations may subject us to penalties;
•
The M&A Rules and certain other PRC regulations establish complex procedures for some acquisitions of Chinese companies by foreign investors, which could make it more difficult for us to pursue growth through acquisitions in China;
•
PRC regulations relating to offshore investment activities by PRC residents may limit our PRC subsidiaries’ ability to increase their registered capital or distribute profits to us or otherwise expose us or our PRC resident beneficial owners to liability and penalties under PRC law;
•
Any failure to comply with PRC regulations regarding the registration requirements for employee share incentive plans may subject the PRC plan participants or us to fines and other legal or administrative sanctions;
•
If we are classified as a PRC resident enterprise for PRC income tax purposes, such classification could result in unfavorable tax consequences to us and our non-PRC shareholders or ADS holders;
•
We may not be able to obtain certain benefits under relevant tax treaty on dividends paid by our PRC subsidiaries to us through our Hong Kong subsidiary; and
•
We face uncertainty with respect to indirect transfers of equity interests in PRC resident enterprises by their non-PRC holding companies.
For further details on the regulatory, liquidity and enforcement risks relating to our corporate structure and the fact that we conduct substantially all of our operations in China, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure” and “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China.”
Risks Related to PCAOB Inspections
On December 16, 2021, the PCAOB issued a report notifying the Commission of its determinations that they are unable to inspect or investigate completely PCAOB-registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and in Hong Kong. The report sets forth lists identifying the registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong, respectively, that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely. Our and the VIE Group’s financial statements as of December 31, 2022 and for the year ended December 31, 2022 contained in this annual report have been audited by Marcum Asia CPAs LLP, or Marcum Asia, an independent registered public accounting firm that is headquartered in Manhattan, New York, and has been inspected by the PCAOB on a regular basis. As of the date hereof, Marcum Asia is not included in the list of PCAOB identified firms in the PCAOB Determination Report issued on December 16, 2021. On December 15, 2022, the PCAOB announced that it was able to conduct inspections and investigations completely of PCAOB-registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong in 2022. The PCAOB vacated its previous determinations issued in December 2021 accordingly. On December 18, 2023, we dismissed Marcum Asia and appointed Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Certified Public Accountants LLP, or Deloitte, which is located in mainland China, as our independent registered public accounting firm, to issue our audit report for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2023 and 2024. We do not expect to be identified as a “Commission-Identified Issuer” under the HFCAA for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024 after we file our annual report on Form 20-F for such fiscal year. However, whether the PCAOB will continue to conduct inspections and investigations completely to its satisfaction of PCAOB-registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong is subject to uncertainty and depends on a number of factors out of our and our auditor’s control, including positions taken by authorities of the PRC. The PCAOB is required under the HFCAA to make its determination on an annual basis with regards to its ability to inspect and investigate completely accounting firms based in the mainland China and Hong Kong. The possibility of being a “Commission-Identified Issuer” and risk of delisting could continue to adversely affect the trading price of our securities. Should the PCAOB again encounter impediments to inspections and investigations in mainland China or Hong Kong as a result of positions taken by any authority in either jurisdiction, the PCAOB will make determinations under the HFCAA as and when appropriate.
In addition, on December 29, 2022, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023 was signed into law, which, among others, amended the HFCAA to reduce the number of consecutive years an issuer can be identified as a Commission-Identified Issuer before the SEC must impose an initial trading prohibition on the issuer’s securities from three years to two. Therefore, once an issuer is identified as a Commission-Identified Issuer for two consecutive years, the SEC is required under the HFCAA to prohibit the trading of the issuer’s securities on a national securities exchange and in the over-the-counter market. For more details, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry—Trading in our securities may be prohibited under the Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act or the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act, if it is later determined that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely our auditor, and as a result, U.S. national securities exchanges, such as Nasdaq, may determine to delist our securities.”
Enforceability of Civil Liability
We are an exempted company limited by shares incorporated under the laws of the Cayman Islands. We conduct substantially all of our operations in China and substantially all of our assets are located in China. In addition, a majority of our directors and executive officers reside within China, and most of the assets of these persons are located within China. None of our directors and executive officers resides in Hong Kong, and their assets are primarily located outside Hong Kong. As a result, it may be difficult or impossible for you to effect service of process within the United States upon these individuals, or to bring an action against us or against these individuals in the United States in the event that you believe your rights have been infringed under the U.S. federal securities laws or otherwise. Even if you are successful in bringing an action of this kind, the laws of the Cayman Islands and of the PRC may render you unable to enforce a judgment against our assets or the assets of our directors and officers.
There is no statutory enforcement in the Cayman Islands of judgments obtained in the federal or state courts of the United States (and the Cayman Islands are not a party to any treaties for the reciprocal enforcement or recognition of such judgments), however, the courts of the Cayman Islands will, at common law, recognize and enforce a foreign money judgment of a foreign court of competent jurisdiction without any re-examination of the merits of the underlying dispute based on the principle that a judgment of a competent foreign court imposes upon the judgment debtor an obligation to pay the liquidated sum for which such judgment has been given, provided such judgment (a) is given by a foreign court of competent jurisdiction, (b) imposes on the judgment debtor a liability to pay a liquidated sum for which the judgment has been given, (c) is final, (d) is not in respect of taxes, a fine or a penalty, (e) is not inconsistent with a Cayman Islands judgment in respect of the same matter, and (f) is not impeachable on the grounds of fraud and was not obtained in a manner and is not of a kind the enforcement of which is contrary to natural justice or the public policy of the Cayman Islands. However, the Cayman Islands courts are unlikely to enforce a judgment obtained from the U.S. courts under civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities law if such judgment is determined by the courts of the Cayman Islands to give rise to obligations to make payments that are penal or punitive in nature. Because such a determination has not yet been made by a court of the Cayman Islands, it is uncertain whether such civil liability judgments from U.S. courts would be enforceable in the Cayman Islands. A Cayman Islands court may stay enforcement proceedings if concurrent proceedings are being brought elsewhere.
The recognition and enforcement of foreign judgments are provided for under the PRC Civil Procedures Law. PRC courts may recognize and enforce foreign judgments in accordance with the requirements of the PRC Civil Procedures Law based either on treaties between China and the country where the judgment is made or on principles of reciprocity between jurisdictions. China does not have any treaties or other forms of reciprocity with the United States that provide for the reciprocal recognition and enforcement of foreign judgments. In addition, according to the PRC Civil Procedures Law, the PRC courts will not enforce a foreign judgment against us or our director and officers if they decide that the judgment violates the basic principles of PRC laws or national sovereignty, security or public interest. As a result, it is uncertain whether and on what basis a PRC court would enforce a judgment rendered by a court in the United States.
There is uncertainty as to whether the courts of Hong Kong would (i) recognize or enforce judgments of United States courts obtained against us or our directors or officers predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the securities laws of the United States or any state in the United States or (ii) entertain original actions brought in Hong Kong against us or our directors or officers predicated upon the securities laws of the United States or any state in the United States.
A judgment of a court in the United States predicated upon U.S. federal or state securities laws may be enforced in Hong Kong at common law by bringing an action in a Hong Kong court on that judgment for the amount due thereunder, and then seeking summary judgment on the strength of the foreign judgment, provided that the foreign judgment, among other things, is (i) for a debt or a definite sum of money (not being taxes or similar charges to a foreign government taxing authority or a fine or other penalty) and (ii) final and conclusive on the merits of the claim, but not otherwise. Such a judgment may not, in any event, be so enforced in Hong Kong if (a) it was obtained by fraud; (b) the proceedings in which the judgment was obtained were opposed to natural justice; (c) its enforcement or recognition would be contrary to the public policy of Hong Kong; (d) the court of the United States was not jurisdictionally competent; or (e) the judgment was in conflict with a prior Hong Kong judgment.
Hong Kong has no arrangement for the reciprocal enforcement of judgments with the United States. As a result, there is uncertainty as to the enforceability in Hong Kong, in original actions or in actions for enforcement, of judgments of United States courts of civil liabilities predicated solely upon the federal securities laws of the United States or the securities laws of any State or territory within the United States.
B.
Capitalization and Indebtedness
Not applicable.
C.
Reasons for the Offer and Use of Proceeds
Not applicable.
Summary of Risk Factors
Set forth below is only a summary of the principal risks associated with an investment in our shares. See below under this “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors” for a detailed discussion of the numerous risks and uncertainties to which our Company and the VIE Group are subject to.
•
We and the VIE Group operate in China’s online consumer finance marketplace, an evolving industry, which makes it difficult to evaluate our and the VIE Group’s future prospects.
•
The laws and regulations governing online consumer finance industry in China are evolving and subject to changes, which may limit the growth of our and the VIE Group’s business. If we and the VIE Group fail to comply with existing and future applicable laws, regulations or requirements of local regulatory authorities, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial conditions and results of operations would be materially and adversely affected.
•
Jiayin Group Inc. is a Cayman Islands holding company primarily operating in China through its subsidiaries and contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology. Investors in the ADSs thus are not purchasing, and may never hold, equity interests in the consolidated VIE. The interpretation and application of current and future PRC laws, regulations, and rules relating to such agreements that establish the VIE structure for the majority of our and the consolidated VIE’s operations in China, including potential future actions by the PRC government remains to be observed, which could affect the enforceability of our contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology and, consequently, significantly affect the financial condition and results of operations of Jiayin Group Inc. If the PRC government finds such agreements non-compliant with relevant PRC laws, regulations, and rules, or if these laws, regulations, and rules or the interpretation thereof change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our beneficial interest in Jiayin Technology or forfeit our rights under the contractual arrangements.
•
If our and the VIE Group’s practice is deemed to violate any PRC laws and regulations, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations would be materially and adversely affected.
•
Our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with institutional funding partners may expose us to regulatory requirements and we and the VIE Group may be required to obtain additional government approval or license due to our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with institutional funding partners.
•
Because we conduct businesses in many countries and intend to continue to expand in international markets, we are subject to legal, reputational and operational risks, as well as a broad array of local legal and regulatory requirements that could adversely affect our operations.
•
If we and the VIE Group are unable to maintain and increase the number of our and the VIE Group’s borrowers or the volume of loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform, our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations will be adversely affected.
•
If we and the VIE Group are unable to secure funding from institutional funding partners on terms acceptable to us, or at all, our and the VIE Group’s reputation, results of operations and financial condition may be materially and adversely affected.
•
If we and the VIE Group are unable to provide a high-quality user experience, our and the VIE Group’s business and reputation may be materially and adversely affected.
•
Any negative publicity with respect to us, the online consumer finance industry in general and our third-party partners may materially and adversely affect our business and results of operations.
•
We and the VIE Group are subject to credit cycles and the risk of deterioration of credit profiles of borrowers.
•
Broader macro, political and socio-economic factors and regulatory environment in China affecting market conditions can materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business and operating results.
•
Credit and other information that we and the VIE Group receive from prospective borrowers and third parties about a borrower may be inaccurate or may not accurately reflect the borrower’s creditworthiness, which may compromise the accuracy of our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment.
•
We and the VIE Group rely on our and the VIE Group’s proprietary credit assessment model in assessing the creditworthiness of our and the VIE Group’s borrowers and the risks associated with loans. If our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment model is flawed or ineffective, or if we and the VIE Group otherwise fail or are perceived to fail to manage the default risks of loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform, our and the VIE Group’s reputation and market share would be materially and adversely affected, which would severely impact our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
•
We and the VIE Group have obligations to verify information relating to borrowers and detecting fraud. If we and the VIE Group fail to perform such obligations to meet the requirements of relevant laws and regulations, we and the VIE Group may be subject to liabilities. Our and the VIE Group’s reputation may be harmed if information supplied by borrowers is inaccurate, misleading or incomplete.
•
We and the VIE Group do not impose restrictions on borrowers’ use of loans facilitated by our and the VIE Group’s platform or prohibit our and the VIE Group’s borrowers from incurring other debt or impose financial covenants on borrowers during the term of the loan, which will increase the risk of non-payment on our and the VIE Group’s loans.
•
Fraudulent activities on our and the VIE Group’s platform could negatively impact our and the VIE Group’s operating results, brand and reputation and cause the use of our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services to decrease.
•
Our and the VIE Group’s risk management system comprising our and the VIE Group’s policy framework, credit assessment and fraud detection technology and modules may not be adequate, which may adversely affect the reliability of our and the VIE Group’s platform, and in turn damage our and the VIE Group’s reputation, business and results of operations.
•
Trading in our securities may be prohibited under the Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act or the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act, if it is later determined that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely our auditor, and as a result, U.S. national securities exchanges, such as Nasdaq, may determine to delist our securities.
•
The PRC government has authority to exert influence on the China operations of an offshore holding company, such as us. Changes in China’s economic, political or social conditions, or government policies may cause our and the consolidated VIE’s underlying operations in China to become prohibitive, which could materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
•
We and the consolidated VIE are subject to extensive and evolving legal development, non-compliance with which, or changes in which, may materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business and prospects, and may result in a material change in our and the consolidated VIE’s operations and/or the value of our ADSs or could significantly limit or completely hinder our and the consolidated VIE’s ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of our securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
•
It is unclear whether we and the consolidated VIE will be subject to the oversight of the CAC and how such oversight may impact us. Our and the consolidated VIE’s business could be interrupted or we and the consolidated VIE could be subject to liabilities which may materially and adversely affect the results of our and the consolidated VIE’s operation and the value of your investment.
•
The PRC government’s oversight over our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations could result in a material adverse change in our and the consolidated VIE’s operations and the value of our ADSs.
•
The approval, filing or other requirements of the CSRC, the CAC or other PRC government authorities may be required under PRC law in connection with a future offering of our securities to foreign investors.
•
If the PRC government deems that the Contractual Arrangements in relation to Jiayin Technology do not comply with PRC regulatory restrictions on foreign investment in the relevant industries, or if these regulations or the interpretation of existing regulations change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our beneficial interest in those operations.
•
We rely on Contractual Arrangements with Jiayin Technology and shareholders of Jiayin Technology for certain business operations, which may not be as effective as direct ownership in providing operational control, and these contractual arrangements have not been tested in a court of law.
•
Changes in China’s economic, political or social conditions or government policies could have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
•
PRC regulation of loans to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore holding companies and governmental administration of currency conversion may delay or prevent us from using the proceeds of further offerings to make loans to or make additional capital contributions to our PRC subsidiaries, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand our business.
•
The interpretation and enforcement of PRC laws and regulations could limit the legal protections available to you and us, significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer our ADSs, cause significant disruption to our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations, and severely damage our and the consolidated VIE’s reputation, which would materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s financial condition and results of operations and cause our ADSs to significantly decline in value or become worthless.
•
We cannot guarantee that any share repurchase plan will be fully consummated or that any share repurchase plan will enhance long-term shareholder value, and share repurchases could increase the volatility of the trading price of the ADSs and could diminish our cash reserves.
•
Our dual-class share structure will limit your ability to influence corporate matters and could discourage others from pursuing any change of control transactions that holders of our Class A ordinary shares and ADSs may view as beneficial.
Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry
We and the VIE Group operate in China’s online consumer finance marketplace, an evolving industry, which makes it difficult to evaluate our and the VIE Group’s future prospects.
The regulatory framework for China’s online consumer finance industry is evolving. It is possible that the PRC laws and regulations may change in ways that do not favor our and the VIE Group’s development. If that happens, there may not be adequate loans facilitated on our and the VIE Group’s platform, and our and the VIE Group’s current business model may be negatively affected. Attracting and retaining borrowers and institutional funding partners is critical to increase the volume of loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform. In addition, our and the VIE Group’s business has grown substantially in recent years, but our and the VIE Group’s past growth rates may not be indicative of our and the VIE Group’s future growth.
You should consider our and the VIE Group’s business and prospects in light of the risks and challenges we and the VIE Group encounter or may encounter in this developing and rapidly evolving industry. These risks and challenges include our and the VIE Group’s ability to, among other things:
•
maintain the security of our and the VIE Group’s platform and the confidentiality of the information provided and utilized across our and the VIE Group’s platform;
•
navigate an evolving regulatory environment;
•
expand the base of borrowers and institutional funding partners served on our and the VIE Group’s platform;
•
maintain our and the VIE Group’s credit standards;
•
enhance our and the VIE Group’s risk management capabilities;
•
improve our and the VIE Group’s operational efficiency;
•
continue to scale our and the VIE Group’s technology infrastructure to support the growth of our and the VIE Group’s platform and higher transaction volume;
•
operate without being adversely affected by the negative publicity about the industry in general and our and the VIE Group’s company in particular;
•
cultivate a vibrant consumer finance ecosystem;
•
attract, retain and motivate talented employees; and defend ourselves in litigation, and against regulatory, intellectual property, privacy or other claims.
If the market for our and the VIE Group’s platform does not develop as we and the VIE Group expect, if we and the VIE Group fail to educate potential users and funding sources about the value of our and the VIE Group’s platform and services, or if we and the VIE Group fail to address the needs of our and the VIE Group’s target customers, our and the VIE Group’s reputation, business and results of operations will be materially and adversely affected.
The laws and regulations governing online consumer finance industry in China are evolving and subject to changes, which may limit the growth of our and the VIE Group’s business. If we and the VIE Group fail to comply with existing and future applicable laws, regulations or requirements of local regulatory authorities, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial conditions and results of operations would be materially and adversely affected.
The laws and regulations governing online consumer finance industry in China are evolving. Before any industry-specific regulations were introduced in mid-2015, the PRC government relied on general and basic laws and regulations for governing the online consumer finance industry, including the Civil Code of the PRC and related judicial interpretations promulgated by the Supreme People’s Court. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—Regulation—Regulations Relating to Online Consumer Finance Services.”
In July 2015, the People’s Bank of China, or the PBOC, together with nine other PRC regulatory agencies jointly issued a series of policy measures applicable to the online finance industry titled the Guidelines on Promoting the Healthy Development of Online Finance Industry, or the Guidelines. The Guidelines formally introduced for the first time the regulatory framework and basic principles governing the online finance industry. Following the core principles of the Guidelines, a series of additional restrictions and affirmative obligations were imposed on online lending information intermediaries by (i) the Circular on Regulating and Rectifying of “Cash Loan” Services in December 2017, or the Circular 141, (ii) the Interim Measures for the Administration of Online Loans by Commercial Banks issued in July 2020, or the Commercial Banks Online Lending Measures, (iii) the Notice on Further Regulating Commercial Banks Online Lending issued in February 2021, or the Circular 24, (iv) the Notice on Further Strengthening the Regulation and Management Work of Internet Consumer Loan for College Students in February 2021, or the Notice on Internet Consumer Loan for College Students, and (v) the Announcement No. 3 issued by the PBOC on March 2021.
The laws, regulations, rules and governmental policies are expected to continue to evolve in our and the VIE Group’s industry. The growth in popularity of online consumer finance in China increases the likelihood for the government authorities to further regulate our and the VIE Group’s industry. For instance, business failures of, or accusations of fraud and unfair dealing against, certain companies in the online consumer finance industry in China have surfaced in recent years, creating a negative public perception of online consumer finance market players. In an effort to manage risks and maintain market integrity, PRC regulatory authorities have issued various guidelines and policies that impose stricter requirements on online consumer finance platforms. Certain of these policies impose limits on the growth of the online consumer finance industry and market. Considering the regulatory environment on online lending intermediaries, we and the VIE Group ceased to offer new loans for online individual investors’ subscription since April 2020 and transitioned to a full institutional funding partner model. In November 2020, the outstanding loan balance of our and the VIE Group’s legacy P2P lending business was reduced to zero.
We and the VIE Group are unable to predict with certainty the impact, if any, that future legislation, judicial interpretations or regulations relating to the online consumer finance industry, or the status and scrutiny of implementation thereof will have on our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations. Future changes to the PRC law and regulation may require us to change our business model or limit the growth of our and the VIE Group’s business. To the extent that we and the VIE Group are not able to fully comply with any applicable laws or regulations, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations may be materially and adversely affected.
If our and the VIE Group’s practice is deemed to violate any PRC laws and regulations, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations would be materially and adversely affected.
The PRC regulatory regime with respect to the online consumer finance industry is evolving, which result in difficulties in determining whether our and the VIE Group’s existing practices may be interpreted to violate any applicable laws and regulations.
To comply with existing laws, regulations, rules and governmental policies relating to the online consumer finance industry, we and the VIE Group have implemented various policies and procedures to conduct our and the VIE Group’s business and operations. However, we and the VIE Group cannot be certain that our and the VIE Group’s existing practices would not be deemed to be in violation of any existing or future laws, rules and regulations that are applicable to our and the VIE Group’s business.
Circular 141 requires banking financial institutions that participate in the “cash loan” business to ensure that no third parties will charge borrowers any interest or fees from borrowers and they themselves will not accept any credit enhancement services or other similar services from third parties without qualification to provide guarantee. Since the third quarter of 2019, we and the VIE Group have proactively made an adjustment to our and the VIE Group’s cooperation model with institutional funding partners through Geerong Yunke and Jiangxi Yunkaijianming. To comply with Circular 141, we and the VIE Group cooperate with certain institutional funding partners such as commercial banks, trusts, consumer finance companies and microcredit companies by having them charge fees directly from borrowers and pay service fees to us. However, due to the fact that the laws and regulations are rapidly evolving, we and the VIE Group cannot assure you that our and the VIE Group’s business model will be in full compliance with existing and future laws and regulations.
Moreover, Circular 141 prohibits banking financial institutions from outsourcing core businesses, such as credit examination and risk control. Currently, loans facilitated by Geerong Yunke and Jiangxi Yunkaijianming are directly funded to the borrowers. We and the VIE Group refer to such institutional funding partners borrowers from qualified credit applicants, and only provide initial screening and technical services. They will then review the applications and conduct risk controls themselves. However, we and the VIE Group cannot rule out the possibility that government authorities could consider our and the VIE Group’s services to be in violation of Circular 141. If any of our and the VIE Group’s services are deemed to be in violation of Circular 141, we and the VIE Group could face penalties, including but not limited to suspensions of operation, orders to rectify and condemnation. If this is the case, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
In addition, on October 9, 2019, CBIRC, together with eight other PRC regulatory agencies jointly issued the Notice on Printing and Distributing the Supplementary Provisions on the Supervision and Management of Financing Guarantee Companies (the “CBIRC Circular 37”), which explicitly provides that institutions providing customer promotion, credit assessment and other services for various lending institutions shall not provide financing guarantee services without approval. For the loans facilitated between borrowers and institutional funding partners, we and the VIE group have engaged third-party licensed financing guarantee companies (the “Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers”) to provide financing guarantees to our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners. If any borrower defaults, the Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers are obligated to repay the overdue amount and interest to the corresponding institutional funding partner. The Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers also demand counter-guarantees by another credit enhancement company in some contracts cases. Under certain circumstances, we and the VIE Group also provide additional commitment to certain institutional funding partners or the Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers. To better manage the associated risks, we and the VIE Group in turn obtain a back-to-back guarantee from another third-party company.
Despite our and the VIE Group’s efforts to reduce regulatory risks, we and the VIE group cannot assure you that the relevant government authorities would not interpret the commitments we and the VIE Group provided to our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners or the Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers as an operation of financing guarantee business without approval. If relevant government authorities take the view that the commitments we and the VIE Group provided to our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners or the Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers is a provision of financing guarantee business without approval, we and the VIE Group would be subject to licensing requirements, fines and other administrative penalties. As a result, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition, and results of operations could be adversely affected.
To further reduce the regulatory risks, apart from licensed third-party financing guarantee companies, starting January 2022, we and the VIE Group established our and the VIE Group’s own licensed financing guarantee companies to provide additional commitment to certain institutional funding partners or the Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers, or provide financing guarantee services directly to our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners for the loans funded by them. According to the regulations on financial guarantee, the maximum amount of outstanding guarantee liabilities of a licensed financing guarantee company may not exceed ten times of its net assets. As a result, the maximum amount of outstanding guarantee liabilities that can be provided by our and the VIE Group’s own licensed guarantee companies cannot meet the needs of all of our institutional funding partners.
Furthermore, it is reported that, in July 2021, the Credit Bureau of the PBOC issued a notice to the online platform operators, requiring online platforms to achieve full “disconnection” of personal information from financial institutions. Online platform operators which provide online loan facilitating services, shall not provide information submitted by individuals, information generated within the online platform or information obtained from external sources directly to financial institutions in the name of application information, identity information, basic information, personal profile scoring information, etc. During our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with certain institutional funding partners since the third quarter of 2019, we and the VIE Group provide the personal information of individual borrowers after initial screening to our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners. To ensure compliance, we have involved two licensed credit reporting institutions and have substantially completed our business adjustments with respect to disconnecting direct connection for credit reporting as of the date of this annual report. In particular, we have entered into collaboration agreements with two licensed credit reporting institutions to ensure the flow of personal information complies with the requirements of Measures for the Administration of the Credit Reporting and the notice of the Credit Bureau of the PBOC.
In addition, we and the VIE Group cannot assure you that the business operations of our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners currently are, or will continue to be, in compliance with the relevant PRC laws and regulations. Failure of our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners to comply with the relevant PRC laws and regulations may materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects. For example, the Implementation Measures of the PBOC for Protecting Rights and Interests of Financial Consumers provide that banks and payment institutions shall follow the principles of voluntariness, equality, fairness and good faith, and protect the legitimate rights and interests of consumers of financial products and services when providing financial products or services to consumers. The aforementioned Measures also specify various requirements on banks and payment institutions to protect consumers’ financial information, including requirements on the collection, disclosure, notification, use, management, storage and confidentiality of such information. In the event our and the VIE Group’s funding partners violate the provisions in the measures, they could become subject to penalties, including warnings, fines, suspension of business and revocation of required licenses, and as a result, we and the VIE Group may need to modify our and the VIE Group’s business practices and our and the VIE Group’s business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects would be materially and adversely affected.
As of the date of this annual report, we and the VIE Group have not been subject to any material fines or other penalties under any PRC laws or regulations, including those governing the online consumer finance industry and financing guarantee services in China. If our and the VIE Group’s practice is deemed to violate any laws, regulations and rules, we and the VIE Group may face, among others, regulatory warning, corrective order, condemnation, fines and criminal liability. If such situations occur, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects would be materially and adversely affected.
Our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with institutional funding partners may expose us to regulatory requirements and we and the VIE Group may be required to obtain additional government approval or license due to our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with institutional funding partners.
We and the VIE Group have expanded our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partner base and the volume of loans funded by our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners in 2020 and since April 2020, we and the VIE Group collaborate exclusively with institutional funding partners to fund our and the VIE Group’s loans. Our and the VIE Group’s collaboration with institutional funding partners has exposed us to and may continue to expose us to additional regulatory requirements faced by such institutional funding partners. For example, Circular 141 provides a series of guidance on the cash loan business of financial institutions. In July 2020, the CBIRC issued the Commercial Banks Online Lending Measures to provide detailed rules on online loans provided by commercial banks. Further, on February 19, 2021, the CBIRC further issued the Notice of Further Regulating Online Loan Business of Commercial Banks, also known as Circular 24, which provides that the commercial banks shall independently carry out the risk management of online loans and are forbidden from outsourcing the material procedures of loan management. Circular 24 will also apply by analogy to branches of foreign banks, trusts, consumer finance companies and auto finance companies. To comply with such guidance, our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners, such as commercial banks, trusts, consumer finance companies and microcredit companies, may need to change their cooperation model with their business partners, including us, which may adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business. In addition, we and the VIE Group cannot assure you that the business operations of our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners currently are or will be in compliance with the relevant PRC laws and regulations, and in the event that our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners do not operate their businesses in accordance with the relevant PRC laws and regulations, they will be exposed to various regulatory risks and therefore, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and prospects would be materially and adversely affected.
In addition, CBIRC Circular 37 explicitly provides that institutions providing customer promotion, credit assessment and other services for various lending institutions shall not provide financing guarantee services without approval. For the loans facilitated between borrowers and institutional funding partners, we and the VIE Group have engaged the Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers to provide financing guarantees to our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners. If any borrower defaults, the Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers are obligated to repay the overdue amount and interest to the corresponding institutional funding partner. The Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers also demand counter-guarantees by another credit enhancement company in some contracts cases. Under certain circumstances, we and the VIE Group also provide additional commitment to certain institutional funding partners or the Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers. To better manage the associated risks, we and the VIE Group in turn obtain a back-to-back guarantee from another third-party company. Despite our and the VIE Group’s efforts to reduce regulatory risks, we and the VIE Group cannot assure you that the relevant government authorities would not interpret the commitments we and the VIE Group provided to our institutional funding partners or the Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers as an operation of financing guarantee business without approval. If relevant government authorities take the view that the commitments we provided to our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners or the Licensed Credit Enhancement Providers is a provision of financing guarantee business without approval, we and the VIE Group would be subject to licensing requirements, fines and other administrative penalties. As a result, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition, and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Because we conduct businesses in many countries and intend to continue to expand in international markets, we are subject to legal, reputational and operational risks, as well as a broad array of local legal and regulatory requirements that could adversely affect our operations.
While we operate our businesses with a focus on the China market, we have been exploring opportunities in other developing countries with a significant size of low- to mid- income population in recent years and intend to continue to expand our businesses in international markets. For example, we established our Indonesia office in 2019 to supervise our rapid development in Southeast Asia and we increased our investments in Indonesia in recent years to explore more business opportunities in local markets.
Operating a multinational business creates difficulties associated with staffing, managing our global operations, as well as complying with local legal and regulatory requirements. Our existing operations in international markets may not succeed eventually, and may expose us to increased risks associated with different market dynamics and competition in the international markets. We are subject to a variety of local laws and regulations that involve matters central to our business, including, among others, financial services, data privacy and security, competition, consumer protection and taxation. These laws can be particularly restrictive in certain jurisdictions, as they constantly evolve and remain subject to change. In addition, the application and interpretation of these laws and regulations, which are subject to change, could result in government inquiries, claims, disputes, changes to our business practices, increased cost of operations and declines in user growth, retention or engagement, any of which could seriously harm our business.
Furthermore, we expect our operations to continue to expand in many jurisdictions. Some of these jurisdictions have undergone significant political, economic and social change in recent years and the risk of new, unforeseen changes in these jurisdictions remains greater than in the U.S. or other more developed countries. Although we have engaged experienced staffs and consultants in jurisdictions in which we deem appropriate, we cannot assure you that we will continue to be found to be operating in compliance with all applicable laws or regulations which we may be subject to. We may also be subject to increased reputational risk, or be scrutinized for compliance with labor, social security or tax requirements in connection with certain of our employment practices in different jurisdictions. In addition, we cannot assure you that laws and regulations applicable to us will not be modified or interpreted in ways that could adversely affect our business. Our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected if we cannot effectively manage our business to address the market demands and complexities of operating a multinational business.
If we and the VIE Group are unable to maintain and increase the number of our and the VIE Group’s borrowers or the volume of loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform, our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations will be adversely affected.
The total loan facilitation volume facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform was RMB55.5 billion in 2022, RMB88.1 billion in 2023 and RMB100.8 billion (US$13.8 billion) in 2024, respectively. To maintain the high growth momentum of our and the VIE Group’s platform, we and the VIE Group must continuously increase the volume of loans by retaining current participants and attracting more users whose financing needs can be met on our and the VIE Group’s platform. If there are insufficient institutional funding sources, borrowers may not be able to obtain capital through our and the VIE Group’s platform and may turn to other sources for their borrowing needs. If we and the VIE Group are unable to attract qualified borrowers and sufficient institutional funding, or if borrowers do not continue to participate in our and the VIE Group’s platform at the current rates due to any changes or other business or regulatory reasons, we and the VIE Group may be required to modify the way we and the VIE Group conduct our and the VIE Group’s business to ensure compliance with existing or new PRC laws and regulations, we and the VIE Group might not be able to increase our and the VIE Group’s loan transaction volume and revenues as we and the VIE Group expect, and our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations may be adversely affected.
If we and the VIE Group are unable to secure funding from institutional funding partners on terms acceptable to us, or at all, our and the VIE Group’s reputation, results of operations and financial condition may be materially and adversely affected.
We and the VIE Group collaborate with institutional funding partners to fund certain loans we and the VIE Group facilitate. Our and the VIE Group’s current institutional funding partners include commercial banks, trusts, consumer finance companies and microcredit companies. The growth and success of our and the VIE Group’s future operations depend on the availability of adequate funding, at a commercially reasonable cost, to meet borrower demand for loans facilitated on our and the VIE Group’s platform.
The availability of funding from institutional funding partners depends on many factors, some of which are out of our and the VIE Group’s control. Some of our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners have limited operating history, and there can be no assurance that we and the VIE Group will be able to rely on their funding in the future. Our and the VIE Group’s ability to cooperate with new institutional funding partners may be subject to regulatory or other limitations. In addition, regardless of our and the VIE Group’s risk management efforts, loans facilitated by us may nevertheless be considered riskier and have a higher delinquency rate than loans provided by traditional financial institutions.
If the funding partners’ risk appetite changes due to changes in economic conditions, regulatory regime, any unexpected shortage of funds, availability of licensed third party credit enhancement service providers or other reasons, funding partners may choose to offer different investment terms, which are not acceptable to us, or choose to not invest in loans facilitated on our and the VIE Group’s platforms. In the event there is a sudden or unexpected shortage of funds from our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners, or if our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners have determined not to continue to collaborate with us, we and the VIE Group may not be able to maintain necessary levels of funding without incurring high costs of capital, or at all. If adequate funds are not available to meet borrowers’ demand for loans when they arise, our and the VIE Group’s platforms may not be able to fulfill all loan requests and the volume of loans facilitated on our and the VIE Group’s platforms may be significantly impacted. If the volume of loans facilitated on our and the VIE Group’s platforms are unable to fulfill all loan requests of potential borrowers on a timely basis, we and the VIE Group may experience a loss of market share or slower than expected growth, in which case our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected. While we and the VIE Group have managed to diversify our and the VIE Group’s funding sources, there can be no assurance that our and the VIE Group’s funding sources will remain or become increasingly diversified in the future. If we and the VIE Group become dependent on a small number of institutional funding partners and any such institutional funding partner determines not to collaborate with us or limits the funding that is available, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flow may be materially and adversely affected.
Our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners typically agree to provide funding to our and the VIE Group’s users who meet their predetermined criteria, subject to their approval process. In addition, while our and the VIE Group’s users’ loan requests are usually approved if they fall within the parameters set and agreed upon by us and our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners, they may implement additional requirements in their approval process outside of our and the VIE Group’s monitor and control. Thus, there is no assurance that our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners could provide reliable, sustainable and adequate funding to support the required liquidity as they could decline to fund user loans facilitated on our and the VIE Group’s platform. In addition, if PRC laws and regulations impose more restrictions on cooperation with institutional funding partners, these institutional funding partners will become more selective in choosing cooperation partners, which may drive up the funding costs and the competition among loan facilitation platforms to cooperate with a limited number of institutional funding partners as well as other non-institutional funding sources. Any of the above may materially increase our and the VIE Group’s funding costs, which may adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s results of operations and profitability. Furthermore, if PRC laws and regulations are issued that prohibit our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners, our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with our and the VIE Group’s funding partners may have to be terminated or suspended, which may materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we and the VIE Group are unable to provide a high-quality user experience, our and the VIE Group’s business and reputation may be materially and adversely affected.
The success of our and the VIE Group’s business largely depends on our and the VIE Group’s ability to provide high-quality user experience, which in turn depends on a variety of factors. These factors include our and the VIE Group’s ability to continue to offer loan facilitation services at competitive amount of financing interest and service fees and adequate credit limits, reliable and user-friendly website interface and mobile apps for users to browse, apply for credit, and further improve our and the VIE Group’s online transaction process. If users are not satisfied with our and the VIE Group’s services, or our and the VIE Group’s system is severely interrupted or otherwise fail to meet the borrowers’ requests, our and the VIE Group’s reputation and borrower loyalty could be adversely affected.
In addition, if our and the VIE Group’s user service representatives fail to provide satisfactory service, or if waiting time for our and the VIE Group’s user service hotline is too long due to the high volume of inquiries from users at peak times, our and the VIE Group’s brands and borrower loyalty may be adversely affected. In addition, any negative publicity or poor feedback regarding our and the VIE Group’s borrower service may harm our and the VIE Group’s brands and reputation and in turn cause us to lose borrowers and market share. As a result, if we and the VIE Group are unable to continue to maintain or enhance our and the VIE Group’s borrower experience and provide a high-quality borrower service, we and the VIE Group may not be able to retain borrowers or attract prospective borrowers, which could have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
Furthermore, our and the VIE Group’s platform features a high proportion of repeat borrowers. Out of the total loan volume facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform in 2022, 2023 and 2024, 71.6%, 75.0% and 74.2%, respectively, was attributable to repeat borrowers who had successfully borrowed on our and the VIE Group’s platform before. The loan size of repeat borrowing of repeat borrowers tends to be larger than that of first time borrowing. Repeat borrowing also generally contributes to a higher overall credit quality of borrowers on our and the VIE Group’s platform as we and the VIE Group only permit borrowers with positive repayment histories to become repeat borrowers. If we and the VIE Group are unable to maintain a high-quality user experience in the future, the numbers of our and the VIE Group’s repeat borrowing rate and repeat borrowers on our and the VIE Group’s platform will decrease. As a result, the credit quality, amount of transaction and service fees and overall profitability of our and the VIE Group’s platform may be adversely affected.
Any negative publicity with respect to us, the online consumer finance industry in general and our third-party partners may materially and adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Reputation of our brand is critical to our business and competitiveness. Factors that are vital to our reputation include but are not limited to our ability to:
•
maintain the quality and reliability of our and the VIE Group’s platform;
•
provide borrowers and institutional funding partners with a superior experience in our and the VIE Group’s platform;
•
enhance and improve our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment;
•
effectively manage and resolve complaints from borrowers and institutional funding partners; and
•
effectively protect personal information and privacy of borrowers and institutional funding partners.
Any malicious or negative allegation made by the media or other parties about the foregoing or other aspects of our company, including but not limited to our management, business, compliance with law, financial condition or prospects, whether with merit or not, could severely compromise our reputation and harm our business and operating results.
As the China online consumer finance industry is evolving, negative publicity about this industry may arise from time to time. Negative publicity about China’s online consumer finance industry in general may also have a negative impact on our reputation, regardless of whether we have engaged in any inappropriate activities. The PRC government has recently instituted specific rules to develop a more transparent regulatory environment for the online consumer finance industry. Any players in China’s online consumer finance industry who are not in compliance with these regulations may adversely impact the reputation of the industry as a whole. Furthermore, any negative development in, or negative perception of, the online consumer finance industry as a whole, even if factually incorrect or based on isolated incidents, could compromise our image, undermine the trust and credibility we have established and impose a negative impact on our ability to attract new funding partners and borrowers. Negative developments in the online consumer finance industry, such as widespread borrower defaults, fraudulent behavior and/or the closure of other online consumer finance platforms, may also lead to tightened regulatory scrutiny of the sector and limit the scope of permissible business activities that may be conducted by online consumer finance platforms like us. For instance, there were a number of reports of business failures of, or accusations of fraud and unfair dealing against, certain companies in the online consumer finance industry in China. Although the market exits of these companies may result in more healthy and stable development of the overall online consumer finance industry, to the extent borrowers or funding partners associate our company with these companies, they may be less willing to initiate transactions on our platform. Our business, financial condition and results of operations were adversely affected by such unfavorable market developments. See “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects.”
In addition, negative publicity about our partners, service providers or other counterparties, such as negative publicity about their loan collection practices and any failure by them to adequately protect the information of our funding partners and borrowers, to comply with applicable laws and regulations or to otherwise meet required quality and service standards could harm our reputation. If any of the foregoing takes place, our business and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
Changes in PRC regulations relating to interest rates for marketplace and microcredit lending could have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business.
According to the relevant PRC laws and regulations, in the context of lending activities between individuals, entities or other organizations that are not licensed financial institutions, if the interest rate of a loan exceeds 36% per annum, the exceeding part of the interest rate is invalid and void; if the interest rate of a loan exceeds 24% per annum but is no more than 36% per annum, the exceeding part will be treated as natural obligation—valid but not enforceable in the PRC judicial system, while the enforceability of the 24% per annum part will not be affected. In addition, on August 4, 2017, the Supreme People’s Court promulgated the Circular of Several Suggestions on Further Strengthening the Judicial Practice Regarding Financial Cases, which provides, among others, that (i) the claim of a borrower under a financial loan agreement to adjust or cut down the part of interest exceeding 24% per annum on the basis that the aggregate amount of interest, compound interest, default interest, liquidated damages and other fees collectively claimed by the lender is overly high shall be supported by the PRC courts; and (ii) in the context of online finance disputes, if the online loan facilitation platforms and the lender circumvent the upper limit of the judicially protected interest rate by charging intermediary fee, it shall be ruled as invalid. In addition, under Circular 141, the overall borrowing costs charged to borrowers should be calculated by loan interest together with all relevant fees and presented in an annualized form.
On July 20, 2020, the Supreme People’s Court and the National Development and Reform Commission jointly released the Opinions on Providing Judicial Services and Safeguards for Accelerating the Improvement of the Socialist Market Economic System for the New Era. This document states that if the interest and fees, including interest, compound interest, penalty interest, liquidated damages and other fees, claimed by one party to the loan contract exceed the upper limit under judicial protection, the claim will not be supported by the court, and if the parties to the loan disguise the financing cost in an attempt to circumvent the upper limit, the rights and obligations of all parties to the loan will be determined by the actual loan relationship.
On September 1, 2015, the Provisions of the Supreme People’s Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Law in the Trial of Private Lending Cases came into effect and was then amended on August 20, 2020 and January 1, 2021. Under these amendments, if the service fees or other fees that we and the VIE Group charge are deemed to be loan interest or fees related to loans (inclusive of any default rate and default penalty and any other fee), then in the event that the sum of the annualized interest that lenders charge and fees we and the VIE Group and our and the VIE Group’s business partners charge exceed four times the one-year Loan Prime Rate at the time of the establishment of the agreement, the borrower may refuse to pay the portion that exceeds the limit. In that case, PRC courts will not uphold our and the VIE Group’s request to demand the payment of fees that exceed the limit from the borrower. The aforementioned one-year Loan Prime Rate refers to the one-year loan market quoted interest rate issued by the National Bank Interbank Funding Center. The one-year Loan Prime Rate issued by the National Bank Interbank Funding Center on April 21, 2025 was 3.1%, and we and the VIE Group cannot assure you that the one-year Loan Prime Rate or the upper limit on interest and fee rates will not decrease in the future. As to the cases accepted by PRC courts of first instance on or after August 20, 2020 and in which the loan contracts were established before August 20, 2020, if the lender requests that the court apply the previous limits of 24% and 36% for calculating the loan interest accrued from the establishment of the loan contracts up to August 19, 2020, such request will be supported by the court, but the loan interest accrued from August 20, 2020 to the date of the loan repayment shall be calculated by applying the new limit of four times the one-year Loan Prime Rate at the time of the filing of the lawsuit.
On December 29, 2020, the Supreme People’s Court also issued the Reply Regarding the Scope of Application of the New Private Lending Judicial Interpretation, which provides that the two amendments are not applicable to disputes arising from the relevant financial business of microcredit companies, financing guarantee companies, and five other types of local financial organizations which are regulated by local financial authorities. However, it remains to be further observed in the interpretation and implementation of the two amendments, including their applicability in practice, the basis of the formula used to calculate the interest limit, and the scope of inclusion of related fees, as well as inconsistencies between the standard and the level of enforcement by different PRC courts. If we and the VIE Group are unable to comply with such regulatory requirements, supervision or guidance or are deemed to be charging above the maximum interest rates permitted by the relevant laws, regulations, policies or guidance, we and the VIE Group could be subject to orders of suspension, cessation or rectification, cancellation of qualifications, or other penalties, and our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition, results of operations and our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with business partners could be materially and adversely affected as a result.
To further clarify the way of calculating “total annual interest rate,” the PBOC issued the Announcement No. 3 on March 2021, which confirms that the annualized rate of a loan should be calculated as the annualized ratio of total costs (to borrower) to outstanding principal amount. The costs include interest and other fees and charges directly related to the loan. The amount of principal should be specified in the loan contract or other loan certificates. If the loan is repaid in installments, the outstanding principal amount should be the balance after each repayment. The calculation of the annualized interest rate may be based on compound interest or simple interest. The calculation based on compound interest is equivalent to that of the internal rate of return, and the simple-interest approach should be specified as such.
Consequently, PRC courts will not uphold our and the VIE Group’s request to demand the payment of fees that exceed the limit from the borrower. If the borrower has already paid the fees that exceed the limit, the borrower may request that our own licensed financing guarantee companies which directly provide financing guarantee services to the institutional funding partners refund the portion exceeding the limit and the PRC courts may uphold such requests. To ensure compliance with the caps, our and the VIE Group’s own licensed financing guarantee companies may need to reduce the fees they charge to our and the VIE Group’s borrowers, subject to further negotiation with them. Institutional funding partners may further lower the annual percentage rate of charge of their loans from time to time if the cap of aggregated borrowing costs charged by licensed financial institutions is further lowered by any newly adopted, or by the application of any existing, laws, regulations or ruling. If our and the VIE Group’s funding partners or us are unable to comply with such regulatory requirements, supervision or guidance or are deemed to be charging above the limits permitted by the relevant laws and regulations, our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition, results of operations and our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with our and the VIE Group’s funding partners could be materially and adversely affected.
We and the VIE Group are subject to credit cycles and the risk of deterioration of credit profiles of borrowers.
Our and the VIE Group’s business is subject to credit cycle, which is in turn associated with the volatility of general economy. If economic conditions deteriorate, we and the VIE Group may face increased risk of default or delinquency of borrowers, which will result in lower returns or even losses. In the event that the creditworthiness of our and the VIE Group’s borrowers deteriorates or we and the VIE Group cannot track the deterioration of their creditworthiness, the criteria we and the VIE Group use for the analysis of borrower credit profiles may be rendered inaccurate, and our and the VIE Group’s risk management system may be subsequently rendered ineffective. This in turn may lead to higher default rates and adverse impact on our and the VIE Group’s reputation, business, results of operations and financial positions.
Broader macro, political and socio-economic factors and regulatory environment in China affecting market conditions can materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business and operating results.
General economic, macro, political and socio-economic factors beyond our and the VIE Group’s control and regulatory environment in China may deter borrowers’ interest in seeking loans through our and the VIE Group’s platform, and similarly, funding partners’ willingness to lend. Such factors include the general interest rate, unemployment rates, residential home values and availability of other investment opportunities. If any of these risk factors should materialize, the volume of loans facilitated on our and the VIE Group’s platform will necessarily decline, and our and the VIE Group’s revenues and operating results may be adversely affected. For instance, from the second quarter of 2019, the loan facilitation volume on our and the VIE Group’s platform decreased due to regulatory requirements that an online lending intermediary to reduce the number of individual investors, business volume and number of borrowers. In view of the changing regulatory environment, we and the VIE Group have stopped funding our and the VIE Group’s loans with individual investors in April 2020, which negatively affected our and the VIE Group’s business and financial performance in 2020.
Economic conditions in China are subject to domestic economic and political policies, and are also sensitive to global economic conditions, regional instability and tension, as well as the relationship among China and other countries. While the economy in China has grown significantly over the past decades, growth has been uneven, both geographically and among various sectors of the economy. The global macroeconomic environment is also facing challenges. Unrest, terrorist threats and the potential for war in the Middle East and elsewhere may increase market volatility across the globe. The conflict in Ukraine and the imposition of broad economic sanctions on Russia could raise energy prices and disrupt global markets. There have also been concerns about the relationship between China and other countries, including the surrounding Asian countries, which may result in or intensify potential conflicts in relation to territorial disputes. In addition, there is significant uncertainty about the future relationship between the United States and China with respect to trade policies, treaties, government regulations and tariffs. Any severe or prolonged slowdown in the global or Chinese economy may further adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
We and the VIE Group cannot guarantee that economic conditions will remain favorable for our and the VIE Group’s business or industry and that demand and supply for consumer loans such as those we and the VIE Group primarily facilitate over our and the VIE Group’s platform will continue to be met at current levels. If demand or supply reduces, or if the default rate increases, our and the VIE Group’s growth and revenue will be negatively impacted.
Credit and other information that we and the VIE Group receive from prospective borrowers and third parties about a borrower may be inaccurate or may not accurately reflect the borrower’s creditworthiness, which may compromise the accuracy of our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment.
For the purpose of credit assessment, we and the VIE Group obtain from prospective borrowers and third parties certain information of the prospective borrowers, which may not be complete, accurate or reliable. The third parties whom we and the VIE Group collaborate with include industry anti-fraud service providers, Internet or wireless service providers, online shopping websites and payment service providers. A credit score assigned to a borrower may not reflect that particular borrower’s actual creditworthiness because the credit score may be based on outdated, incomplete or inaccurate borrower information. Additionally, once we and the VIE Group have obtained a borrower’s information, the borrower may subsequently (i) become delinquent in the payment of an outstanding obligation; (ii) default on a pre-existing debt obligation; (iii) take on additional debt; or (iv) sustain other adverse financial events, making the information we and the VIE Group have previously obtained inaccurate. We and the VIE Group currently cannot determine whether borrowers have outstanding loans through other online consumer finance platforms at the time they obtain a loan from us. This creates the risk that a borrower may borrow money through our and the VIE Group’s platform in order to pay off loans on other online consumer finance platforms and vice versa. If a borrower incurs additional debt before fully repaying any loan such borrower takes out on our and the VIE Group’s platform, the additional debt may impair the ability of that borrower to make payments on his or her loan and the funding partner’s ability to receive returns associated with such loan. In addition, the additional debt may adversely affect the borrower’s creditworthiness generally, and could result in the financial distress or insolvency of the borrower. To the extent that a borrower has or incurs other indebtedness and cannot repay all of his or her indebtedness, the obligations under the loans will rank pari passu to each other and the borrower may choose to make payments to other creditors rather than to funding partners on our and the VIE Group’s platform.
The additional debt may adversely affect the borrower’s creditworthiness generally, and could result in the financial distress or insolvency of the borrower, impairing the borrower’s ability to repay the loan and the funding partner’s ability to receive investment returns associated with such loan. In addition, if a borrower incurs debt on other online loan facilitation platforms in order to repay our and the VIE Group’s loans, the borrower’s ability to repay such loans is limited by the availability of funding sources subject to factors beyond the borrower’s control, which may adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s results of operations. Such inaccurate or incomplete borrower information could compromise the accuracy of our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment and adversely affect the effectiveness of our and the VIE Group’s risk management, which could in turn harm our and the VIE Group’s reputation, and as a result our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
We and the VIE Group rely on our and the VIE Group’s proprietary credit assessment model in assessing the creditworthiness of our and the VIE Group’s borrowers and the risks associated with loans. If our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment model is flawed or ineffective, or if we and the VIE Group otherwise fail or are perceived to fail to manage the default risks of loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform, our and the VIE Group’s reputation and market share would be materially and adversely affected, which would severely impact our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
Our and the VIE Group’s ability to attract funding partners and borrowers to, and build trust in, our and the VIE Group’s platform is significantly dependent on our and the VIE Group’s ability to effectively evaluate borrowers’ credit profiles and likelihood of default. To conduct this evaluation, we and the VIE Group utilize our and the VIE Group’s proprietary and open credit assessment model, which is built based on data collected through various channels and strengthened by our and the VIE Group’s sophisticated artificial intelligence and advanced machine learning techniques. Our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment model conducts in-depth anti-fraud and delinquency history analysis of the borrowers, assigns the borrowers a credit score based on their risk profile. However, our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment model may not effectively assess the credit risk of the borrower or predict future delinquency rate and loan losses. If we and the VIE Group are unable to effectively classify borrowers into the relative risk categories, We and the VIE Group may be unable to effectively manage the default risks of loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform, which may adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s ability to accurately account for risks related to such loans. Although the institutional funding partners on our and the VIE Group’s platform have their own risk management systems and our and the VIE Group’s main business is to connect them with borrowers, we and the VIE Group may still be subject to liabilities because of borrowers’ defaults.
In addition, if a borrower’s financial condition worsens after his or her loan application is approved, we and the VIE Group may not be able to take measures to prevent default on the part of the borrower and thereby maintain a reasonably low default rate for loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform. Our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment model may not be able to timely and accurately adjust down the credit rating assigned to a borrower if such borrower’s creditworthiness deteriorates. In addition, certain line items on our and the VIE Group’s financial statements, including allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets, loans receivable and others, are and were recorded based on the default rate that we and the VIE Group estimate. Since our and the VIE Group’s estimate of the risks might be inaccurate, our and the VIE Group’s consolidated financial statements may be materially misstated.
While we and the VIE Group continuously refine the algorithms, data processing and machine learning used by our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment model to reduce the likelihood of misclassifying borrower, our and the VIE Group’s approval process could be negatively affected if any of these decision-making and scoring systems contain programming or other errors, are ineffective or the data provided by borrowers or third parties are incorrect or stale. If any of the foregoing were to occur in the future, borrowers may reduce the use of our and the VIE Group’s platform for financing, and our and the VIE Group’s reputation and market share would be materially and adversely affected, which would severely impact our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
We and the VIE Group have obligations to verify information relating to borrowers and detecting fraud. If we and the VIE Group fail to perform such obligations to meet the requirements of relevant laws and regulations, we and the VIE Group may be subject to liabilities. Our and the VIE Group’s reputation may be harmed if information supplied by borrowers is inaccurate, misleading or incomplete.
Our and the VIE Group’s business of connecting funding partners and borrowers constitutes an intermediary service, and our and the VIE Group’s contracts with funding partners and/or borrowers are intermediation contracts under the Civil Code. Under the Civil Code, an intermediary that intentionally conceals any material information or provides false information in connection with the conclusion of an intermediation contract which results in harm to the client’s interests may not claim any service fee for its intermediary services, and is liable for any damage incurred by the client. Therefore, if we and the VIE Group fail to provide material information to funding partners and are found to be at fault for our and the VIE Group’s failure or deemed failure to exercise proper care to conduct adequate information verification or supervision, we and the VIE Group could be subject to liabilities as an intermediary under the Civil Code. Furthermore, if we and the VIE Group fail to complete our and the VIE Group’s obligations under the agreements with institutional funding partners and borrowers, we and the VIE Group could also be held liable for damages caused to borrowers or institutional funding partners pursuant to the Civil Code.
We and the VIE Group leverage a large database of fraudulent account information and sophisticated rule-based detection technology to detect fraudulent behaviors. We and the VIE Group update our and the VIE Group’s database on a daily basis based on new data collected and fraudulent behavior detected during the ordinary course of our and the VIE Group’s business operations. Although we and the VIE Group believe that as an online loan facilitation platform, we and the VIE Group should not bear the credit risk for funding partners as long as we and the VIE Group take reasonable measures to detect fraudulent behavior, we and the VIE Group cannot assure you that we and the VIE Group would not be subject to liability if we and the VIE Group fail to detect any fraudulent behavior. Any such liability could materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s results of operations and financial condition.
We and the VIE Group do not impose restrictions on borrowers’ use of loans facilitated by our and the VIE Group’s platform or prohibit our and the VIE Group’s borrowers from incurring other debt or impose financial covenants on borrowers during the term of the loan, which will increase the risk of non-payment on our and the VIE Group’s loans.
We and the VIE Group are faced with the risk that borrowers borrow money by using loan facilitation services provided by us and the VIE Group to pay off loans on other online consumer finance platforms. Subject to credit assessment result, borrowers may take out new loans on our and the VIE Group’s platform to pay off their other existing loans facilitated by others. We and the VIE Group also do not prohibit our and the VIE Group’s borrowers from incurring additional indebtedness, which may impair the borrower’s ability to observe his or her payment obligations under loan facilitation services on our and the VIE Group’s platform and therefore adversely affect the relevant funding partner’s returns. Although we and the VIE Group take certain measures to monitor our and the VIE Group’s borrowers’ credit records and indebtedness, we and the VIE Group may not be able to effectively prevent the occurrence of such behavior given the practical difficulty in tracking and controlling the usage of borrowed funds and the financial activities of our and the VIE Group’s borrowers.
If a borrower becomes insolvent or otherwise run into financial distress, any unsecured loan (including those obtained through our and the VIE Group’s platform) will rank pari passu to each other and the borrower may cherry-pick among his or her creditors and our and the VIE Group’s funding partners may suffer losses. For secured loans, the ability of other secured lenders to exercise remedies against the assets of the borrower may impair the borrower’s ability to repay the loan to our and the VIE Group’s funding partners. Funding partners may lose their confidence in us and our and the VIE Group’s reputation and business may be adversely affected.
Fraudulent activities on our and the VIE Group’s platform could negatively impact our and the VIE Group’s operating results, brand and reputation and cause the use of our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services to decrease.
We and the VIE Group are subject to the risk of fraudulent activities both on our and the VIE Group’s platform, which may be associated with borrowers, funding partners and third parties handling the information of borrowers and funding partners. Our and the VIE Group’s resources, technologies and fraud detection tools may be insufficient to accurately detect and prevent fraud. Significant increases in fraudulent activities could negatively impact our and the VIE Group’s brand and reputation, result in losses suffered by the funding partners, reduce the volume of loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform and lead us to take additional steps to reduce fraud risk, which could increase our and the VIE Group’s costs and expenses. High profile fraudulent activities could even lead to regulatory intervention and litigation, and may divert our and the VIE Group’s management’s attention and cause us to incur additional expenses and costs. If any of the foregoing were to occur, our and the VIE Group’s results of operations and financial condition could be materially and adversely affected.
Our and the VIE Group’s risk management system comprising our and the VIE Group’s policy framework, credit assessment and fraud detection technology and modules may not be adequate, which may adversely affect the reliability of our and the VIE Group’s platform, and in turn damage our and the VIE Group’s reputation, business and results of operations.
The success of our and the VIE Group’s online platform relies heavily on our and the VIE Group’s ability to detect, assess and control credit risk, and therefore to prevent fraud. Despite the measures we and the VIE Group take to assess and manage risk, the information and data we and the VIE Group utilize may not be sufficient to allow us to adequately capture a borrower applicant’s credit risk. Such information and data include, among others, demographic information, credit history with us and with other financial institutions, and blacklists maintained by other forums and organizations. We and the VIE Group constantly update and optimize our and the VIE Group’s risk management system, but the system may have loopholes or defects which may prevent us from effectively identifying risks, or the data provided may be inaccurate or stale or insufficient, such that we and the VIE Group may misjudge the risk and misalign the risk profile. The information may also not be sufficient for prediction of future non-payment. Such risks and errors may erode funding partner confidence in our and the VIE Group’s platform and therefore harm our and the VIE Group’s reputation and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
Interim period results can vary significantly due to a host of variables and therefore interim period results of our and the VIE Group’s performance may not accurately indicate future performance.
Our and the VIE Group’s interim period results of operations, including operating revenue, expenses, the number of loans and other key performance indicators, may fluctuate significantly such that comparisons of our and the VIE Group’s operating results period-on-period may not be meaningful. Results of any interim period cannot fully indicate future performance. Fluctuations may be due to any number of variables, including some beyond our and the VIE Group’s control, such as:
•
our and the VIE Group’s ability to grow our and the VIE Group’s users base by attracting new and retaining repeat borrowers;
•
the volume and quality of the loans we and the VIE Group facilitated and the acquisition of funding partners and borrowers;
•
the level of operating expenses in the acquisition of funding partners and borrowers, the growth and maintenance of our and the VIE Group’s business, operations and infrastructure and the timing;
•
disruptions to the telecommunications network or security breaches;
•
general macroeconomic and socio-political factors affecting the market and industry, particularly with respect to interest rates, consumer spending and levels of disposable income;
•
seasonality of our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services;
•
our and the VIE Group’s strategy with a focus on long-term growth instead of immediate profitability; and
•
The incurring of expenses related to acquisitions activities of businesses or technologies and potential future charges for impairment of goodwill, if any.
Fluctuations in our and the VIE Group’s interim period results may affect the price of our ADSs in an adverse manner.
Our and the VIE Group’s failure to compete effectively could adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s results of operations and market share.
The online consumer finance market is an evolving industry in China. We and the VIE Group face competition from other online consumer finance platforms, online platforms that engage in online loan facilitation and traditional financial institutions. We and the VIE Group compete with other online platforms that engage in online lending businesses for borrowers. We and the VIE Group also compete with traditional financial institutions, including credit card issuers, online consumer finance business units in commercial banks and other online consumer finance companies.
Our and the VIE Group’s competitors operate with different business models, have different cost structures or participate selectively in different market segments. They may ultimately prove more successful or more adaptable to new regulatory, technological and other developments. Some of our and the VIE Group’s current and potential competitors have significantly more financial, technical, marketing and other resources than we and the VIE Group do and may be able to devote greater resources to the development, promotion, sale and support of their platforms. Our and the VIE Group’s competitors may also have more extensive borrower or funding partner bases, greater brand recognition and brand loyalty and broader partner relationships than us. Additionally, a current or potential competitor may acquire one or more of our and the VIE Group’s existing competitors or form a strategic alliance with one or more of our and the VIE Group’s competitors. Any of the foregoing could adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business, results of operations, financial condition and future growth.
In addition, our and the VIE Group’s competitors may be better at developing new products, or responding faster to new technologies. When new competitors seek to enter our and the VIE Group’s target market, or when existing market participants seek to increase their market share, they sometimes undercut the pricing and/or terms prevalent in that market, which could adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s market share or ability to exploit new market opportunities. Also, since the online consumer finance industry in China is evolving, potential funding partners and borrowers may not fully understand how our and the VIE Group’s platform works and may not be able to fully appreciate the additional customer protections and features that we and the VIE Group have invested in and adopted on our and the VIE Group’s platform as compared to others. Our and the VIE Group’s pricing and terms could deteriorate if we and the VIE Group fail to act to meet these competitive challenges. Furthermore, to the extent that our and the VIE Group’s competitors are able to offer more attractive terms to our and the VIE Group’s business partners, such business partners may choose to terminate their relationships with us. If we and the VIE Group are unable to compete with such companies and meet the need for innovation in our and the VIE Group’s industry, the demand for our and the VIE Group’s platform could stagnate or substantially decline, we and the VIE Group could experience reduced revenues and our and the VIE Group’s platform could fail to achieve or maintain more widespread market acceptance, any of which could harm our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
If we and the VIE Group fail to promote and maintain our and the VIE Group’s brand in a cost-efficient way, our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations may be harmed.
We and the VIE Group believe that developing and maintaining awareness of our and the VIE Group’s brand effectively is critical to attracting new and retaining existing funding partners and borrowers to our and the VIE Group’s platform. This depends largely on the effectiveness of our and the VIE Group’s marketing efforts and the success of the channels we and the VIE Group use to promote our and the VIE Group’s platform. If any of our and the VIE Group’s current marketing channels become less effective, if we and the VIE Group are unable to continue to use any of these channels, or if the cost of using these channels were to significantly increase or if we and the VIE Group are not successful in generating new channels, we and the VIE Group may not be able to attract new funding partners and borrowers in a cost-effective manner or convert potential funding partners and borrowers into active funding partners and borrowers on our and the VIE Group’s platform.
We and the VIE Group have incurred expenses on a variety of brand promotion and borrower and online investor acquisition efforts designed to enhance our and the VIE Group’s brand recognition and increase the number of borrowers and online investors on our and the VIE Group’s platform. The costs of any such branding and marketing activities are likely to be considerable. These efforts may not result in increased revenues in the immediate future or at all and, even if they do, any increases in revenues may not offset the expenses incurred. If we and the VIE Group fail to successfully promote and maintain our and the VIE Group’s brand and increase revenues while incurring substantial expenses, our and the VIE Group’s results of operations and financial condition would be adversely affected, which may impair our and the VIE Group’s ability to grow our and the VIE Group’s business.
We and the VIE Group operate in a market where the credit infrastructure is still developing.
China’s credit infrastructure is still developing. The nationwide financial basic credit reporting system operated by the Credit Reference Center, which was established by the People’s Bank of China in 2006, only records limited credit information, such as tax payments, civil lawsuits, foreclosure and bankruptcy. Moreover, this credit database is accessible to data owners themselves and data users who have obtained written authorization from the data owners. In 2015, the People’s Bank of China announced that it would open the credit reporting market to private sectors with a view to spurring competition and innovation, but it may be a long-term process to establish a widely- applicable, reliable and sophisticated credit infrastructure in the market we and the VIE Group operate.
Our and the VIE Group’s fee rates may decline in the future.
We and the VIE Group generate a substantial majority of our and the VIE Group’s total revenues from service fees we and the VIE Group receive from our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners and guarantors. These fee rates may be affected by the loan volume and quality we and the VIE Group facilitated, the macroeconomic factors as well as the competition in the online consumer finance industry. We and the VIE Group may be unable to offer attractive service fee rates while driving the growth and profitability of our and the VIE Group’s business. Furthermore, our and the VIE Group’s competitors may lower their fee rates in an effort to lure funding partners away from us. If we and the VIE Group reduce our and the VIE Group’s fee rates in order to compete more effectively, the profitability of our and the VIE Group’s business could be adversely affected. If we and the VIE Group do not reduce our and the VIE Group’s fee rates, funding partners may leave our and the VIE Group’s platform, and the total service fees we and the VIE Group receive may decline. Any material decline in our and the VIE Group’s fee rates or the fees we and the VIE Group receive could have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our business depends on the continued efforts of our senior management. If one or more of our key executives were unable or unwilling to continue in their present positions, our business may be severely disrupted.
Our business operations depend on the continued services of our senior management, particularly the executive officers named in this annual report. While we have provided different incentives to our management, we cannot assure you that we can continue to retain their services. There have been departures of our senior management members in the past and we cannot assure you that our existing senior management members will not terminate their employment with us in the future. If one or more of our key executives were unable or unwilling to continue in their present positions, we may not be able to replace them easily or at all, our future growth may be constrained, our business may be severely disrupted and our financial condition and results of operations may be materially and adversely affected, and we may incur additional expenses to recruit, train and retain qualified personnel. In addition, although we have entered into confidentiality and non-competition agreements with our management, there is no assurance that any member of our management team will not join our competitors or form a competing business. If any dispute arises between our current or former officers and us, we may have to incur substantial costs and expenses in order to enforce such agreements in China or we may be unable to enforce them at all.
We face risks related to natural disasters, health epidemics and other outbreaks, which could significantly disrupt our operations.
We are vulnerable to natural disasters and other calamities. Fire, floods, typhoons, earthquakes, power loss, telecommunications failures, break-ins, war, riots, terrorist attacks or similar events may give rise to server interruptions, breakdowns, system failures, technology platform failures or Internet failures, which could cause the loss or corruption of data or malfunctions of software or hardware as well as adversely affect our ability to provide products and services on our platform.
Our business could also be adversely affected by the effects of coronavirus (including COVID-19), Ebola virus disease, Zika virus disease, H1N1 flu, H7N9 flu, avian flu, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, or SARS, or other epidemics. Our business operations could be disrupted if any of our employees is suspected of having coronavirus, Ebola virus disease, Zika virus disease, H1N1 flu, H7N9 flu, avian flu, SARS or other epidemic, since it could require our employees to be quarantined and/or our offices to be disinfected.
Our headquarters are located in Shanghai, where most of our directors and management and a large majority of our employees currently reside. In addition, most of our system hardware and back-up systems are hosted in leased facilities located in Shanghai. Consequently, if any of the abovementioned natural disasters, health epidemics or other outbreaks were to occur in Shanghai or other locations where we operate in, our operation may experience material disruptions, such as temporary closure of our offices and suspension of services, which may materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our business operation could also be disrupted if any of our employees are suspected of having contracted any contagious disease or condition, since it could require our employees to be quarantined or our offices to be closed down and disinfected. All of these would have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition in the near terms. Additionally, if the outbreak persists or escalates, we may be subject to further negative impact on our business operations and financial condition. Our operation could also be severely disrupted if our users or business partners were affected by such natural disasters or health epidemics.
Misconduct, errors and failure to function by our and the VIE Group’s employees and third-party service providers could harm our and the VIE Group’s business and reputation.
We and the VIE Group are exposed to many types of operational risks, including the risk of misconduct and errors by our and the VIE Group’s employees and third-party service providers. Our and the VIE Group’s business depends on our and the VIE Group’s employees and third-party service providers to interact with potential funding partners and borrowers, process large numbers of transactions and support the loan collection process, all of which involve the use and disclosure of personal information. We and the VIE Group could be materially adversely affected if transactions were redirected, misappropriated or otherwise improperly executed, if personal information was disclosed to unintended recipients or if an operational breakdown or failure in the processing of transactions occurred, whether as a result of human error, purposeful sabotage or fraudulent manipulation of our and the VIE Group’s operations or systems. In addition, the manner in which we and the VIE Group store and use certain personal information and interact with funding partners and borrowers through our and the VIE Group’s platform is governed by various PRC laws. It is not always possible to identify and deter misconduct or errors by employees or third-party service providers, and the precautions we and the VIE Group take to detect and prevent this activity may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses. If any of our and the VIE Group’s employees or third-party service providers take, convert or misuse funds, documents or data or fail to follow protocol when interacting with funding partners and borrowers, we and the VIE Group could be liable for damages and be subject to regulatory actions and penalties. We and the VIE Group could also be perceived to have facilitated or participated in the illegal misappropriation of funds, documents or data, or the failure to follow protocol, and therefore be subject to civil or criminal liability. In addition to our and the VIE Group’s own collecting team, we and the VIE Group also use certain third-party service providers for loan collection services. Aggressive practices or misconduct by any of our and the VIE Group’s third-party service providers in the course of collecting loans could damage our and the VIE Group’s reputation.
Cyber-attacks, computer viruses, physical or electronic break-ins or similar disruptions of us and the VIE Group or of a third-party, including events beyond our and the VIE Group’s control, could result in disclosure or misuse of confidential information and misappropriation of funds of our and the VIE Group’s funding partners and borrowers, subject us to liabilities, reduce the attractiveness of our and the VIE Group’s platform and cause reputational harm and adversely impact our and the VIE Group’s results of operations and financial condition.
Our and the VIE Group’s platform collects, stores and processes certain personal and other sensitive data from our and the VIE Group’s funding partners and borrowers. The massive data that we and the VIE Group have processed and stored makes us or third-party service providers who host our and the VIE Group’s servers a target and potentially vulnerable to cyber-attacks, computer viruses, physical or electronic break-ins or similar disruptions.
While we and the VIE Group have taken steps to protect the confidential information that we and the VIE Group have access to, our and the VIE Group’s security measures could be breached. Because techniques used to sabotage or obtain unauthorized access to systems change frequently and generally are not recognized until they are launched against a target, we and the VIE Group may be unable to anticipate these techniques or to implement adequate preventative measures. Any accidental or willful security breaches or other unauthorized access to our and the VIE Group’s platform could cause confidential borrower and funding partner information to be stolen and used for criminal purposes. As personally identifiable and other confidential information is increasingly subject to legislation and regulations in numerous domestic and international jurisdictions, any inability to protect confidential information of our and the VIE Group’s funding partners and borrowers could result in additional cost and liability for us, damage our and the VIE Group’s reputation, inhibit the use of our and the VIE Group’s platform and harm our and the VIE Group’s business.
We and the VIE Group also face indirect technology, cybersecurity and operational risks relating to the third parties whom we and the VIE Group work with to facilitate or enable our and the VIE Group’s business activities, including, among others, third-party online payment service providers who manage accounts for certain borrower and funding partner funds and external cloud service provider. As a result of increasing consolidation and interdependence of technology systems, a technology failure, cyber-attack or other information or security breach that significantly compromises the systems of one entity could have a material impact on its counterparties. Any cyber-attack, computer viruses, physical or electronic break-ins or similar disruptions of such third-party payment service providers could, among other things, adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s ability to serve our and the VIE Group’s users, and could even result in misappropriation of funds of our and the VIE Group’s funding partners and borrowers. If that were to occur, both we and the VIE Group and third-party payment service providers could be held liable to funding partners and borrowers who suffer losses from the misappropriation.
Security breaches or unauthorized access to confidential information could also expose us to liability related to the loss of the information, time-consuming and expensive litigation and negative publicity. If security measures are breached because of third-party action, employee error, malfeasance or otherwise, or if design flaws in our and the VIE Group’s technology infrastructure are exposed and exploited, our and the VIE Group’s relationships with funding partners and borrowers could be severely damaged, we and the VIE Group could incur significant liability and our and the VIE Group’s business and operations could be adversely affected.
If we and the VIE Group are unable to protect the confidential information of our and the VIE Group’s users and adapt to the relevant regulatory framework regarding protection of such information, our and the VIE Group’s business and operations may be adversely affected.
The PRC government authorities have enacted a series of laws and regulations on the protection of personal information, under which Internet service providers and other network operators are required to comply with the principles of legality, justification and necessity, to clearly indicate the purposes, methods and scope of any information collection and usage, and to obtain the consent of users, as well as to establish a user information protection system with appropriate remedial measures. We and the VIE Group have obtained written consent from our and the VIE Group’s users to use their personal information within the scope of authorization and we and the VIE Group have taken technical measures to ensure the security of such personal information and to prevent any loss or divergence of personal information from. However, it remains to be observed as to the interpretation and application of such laws. If such laws or regulations are to be interpreted and applied in a manner inconsistent with our and the VIE Group’s current policies and practices, changes to the features of our and the VIE Group’s system may be required and additional costs may be incurred. We and the VIE Group cannot assure you that our and the VIE Group’s existing user information protection system and technical measures will be considered sufficient under applicable laws and regulations. If we and the VIE Group are unable to address any information protection concerns, or to comply with the then applicable laws and regulations, we and the VIE Group may incur additional costs and liability and our and the VIE Group’s reputation, business and operations might be adversely affected. See ‘‘Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—Regulation—Regulations Relating to Internet Companies—Regulations on Privacy Protection’’ for more details.
On June 1, 2017, the Cyber Security Law of the PRC became effective. The law requires network products and services providers as we and the VIE Group are, among other things, to strictly preserve the secrecy of user information they collect and to store within mainland China data that is gathered or produced by such network products and services provider in the country. If we and the VIE Group are deemed to have violated the law, potential penalties include, depending on the nature of violation, forced shut down of our and the VIE Group’s websites, revocation of business licenses, freezing of assets, and fines imposed on the company ranging from approximately RMB10,000 to RMB1 million or management personnel ranging from approximately RMB5,000 to RMB1 million.
If we and the VIE Group are found to have violated the Cyber Security Law of the PRC in a government enforcement action, we and the VIE Group may face severe penalties that may result in monetary losses, losses of access to assets essential for daily operation of our and the VIE Group’s business or for the continuance of service provision, and temporary or total disruption of our and the VIE Group’s business for an extended period of time. In addition, the finding of a violation of the Cyber Security Law of the PRC, even if later repealed, may cause damages to our and the VIE Group’s reputation and our and the VIE Group’s brand name, causing users to lose confidence in our and the VIE Group’s service and to refrain from choosing or continuing to use our and the VIE Group’s products and services.
All of these consequences may have a material adverse impact on our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
Furthermore, the stringent reporting obligation imposed by the Cyber Security Law of the PRC itself, without a finding of violation, may have a material adverse impact on our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations. As we and the VIE Group are obligated by the law to inform our and the VIE Group’s users of any security flaw or vulnerability as they are discovered, users may become wary of the existence or frequency of such reports and lose confidence in the security of our and the VIE Group’s system, and thus may be discouraged from choosing or continuing to use our and the VIE Group’s services, even if the security flaws or vulnerabilities are readily fixable and can be easily overcome.
In addition, the Personal Information Security Specification came into force in May 2018, and the final amended version of it came into force on October 1, 2020. Although the Personal Information Security Specification is not yet a mandatory regulation, it nonetheless has a key implementing role under China’s Cyber Security Law with respect to protecting personal information in China. Furthermore, it is likely that the Personal Information Security Specification will be relied on by Chinese government agencies as a standard to determine whether businesses have abided by China’s data protection rules. Meanwhile, under the Personal Information Security Specification, the data controller must provide the purpose of collecting and using personal information, as well as the business functions of such purpose, and the Personal Information Security Specification requires the data controller to distinguish its core function from additional functions to ensure the data controller will only collect personal information as needed.
In addition, on June 10, 2021, the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress, or the SCNPC, promulgated the PRC Data Security Law, which took effect in September 2021. The Data Security Law provides for a security review procedure for the data activities that may affect national security. On August 20, 2021, the SCNPC issued the Personal Information Protection Law, effective since November 1, 2021, which reiterates the circumstances under which a personal information processor could process personal information and the requirements for such circumstances. The Personal Information Protection Law clarifies the scope of application, the definition of personal information and sensitive personal information, the legal basis of personal information processing and the basic requirements of notice and consent. On December 28, 2021, the CAC published the Measures for Cybersecurity Review, which took effect on January 15, 2022 and further restates and expands the applicable scope of the cybersecurity review. Pursuant to the draft measures, critical information infrastructure operators that intend to purchase internet products and services and online platform operators engaging in data processing activities that affect or may affect national security must be subject to the cybersecurity review. On September 30, 2024, the State Council released the Network Data Regulation, which came into force on January 1, 2025. The Network Data Regulation is not only the first at the administrative regulation level specifically for network data security, but it also serves as a comprehensive implementing regulation for the compliance requirements set out by the Cyber Security Law, the Data Security Law, and Personal Information Protection Law.
The relevant regulatory authorities in China continue to monitor websites and apps in relation to the protection of personal data, privacy and information security, and may impose additional requirements from time to time. We and the VIE Group believe that we and the VIE Group have conformed our and the VIE Group’s practices in line with current requirements. However, we and the VIE Group cannot assure that our and the VIE Group’s existing user information protection system and technical measures will be considered sufficient under all applicable laws and regulations. There are uncertainties as to the interpretation and application of laws in one jurisdiction which may be interpreted and applied in a manner inconsistent to another jurisdiction and may conflict with our and the VIE Group’s current policies and practices or require changes to the features of our and the VIE Group’s system. If we and the VIE Group are unable to address any information protection concerns, any compromise of security that results unauthorized disclosure or transfer of personal data, or to comply with the then applicable laws and regulations, we and the VIE Group may incur additional costs and liability and result in governmental enforcement actions, litigation, fines and penalties or adverse publicity and could cause our and the VIE Group’s users to lose trust in us, which could have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
The trend of tightening regulations on protection of data security also appear in other jurisdictions. For example, in May 2018, a new data protection regime, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation became applicable; the General Data Protection Regulation can apply to the processing of personal data by companies outside of the European Union, including where the processing of personal data relates to the offering of goods and services to, or monitoring the behavior of, individuals in the European Union. The General Data Protection Regulation and data protection laws in other jurisdictions may apply to our and the VIE Group’s processing of personal data in the future. The application of these laws to our and the VIE Group’s business would impose on us more stringent compliance requirements with more significant penalties for non-compliance than PRC data protection laws and regulations, and our and the VIE Group’s compliance with such requirements could require significant resources and result in substantial costs, which may materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We and the VIE Group collect, process and store personal information concerning our and the VIE Group’s borrowers, as well as personal information pertaining to our and the VIE Group’s business partners and employees. Compliance with applicable personal information and information security laws and regulations is a rigorous and time-intensive process. As global information protection laws and regulations increase in number and complexity, we and the VIE Group cannot assure you that our and the VIE Group’s information protection systems will be considered sufficient under all applicable laws and regulations. Furthermore, we and the VIE Group cannot assure you that the information we and the VIE Group receive from our and the VIE Group’s third-party data partners are obtained and transmitted to us in full compliance with relevant laws and regulations. Moreover, there could be new laws, regulations or industry standards that require us to change our and the VIE Group’s business practices and privacy policies, and we and the VIE Group may also be required to put in place additional mechanisms ensuring compliance with new information protection laws, all of which may increase our and the VIE Group’s costs and materially harm our and the VIE Group’s business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations. Any failure or perceived failure by us to comply with applicable laws and regulations could result in reputational damage or proceedings or actions against us by governmental entities, individuals or others. These proceedings or actions could subject us to significant civil or criminal penalties and negative publicity, result in the delayed or halted processing of personal information that we and the VIE Group need to undertake to carry on our and the VIE Group’s business, as well as the forced transfer or confiscation of certain personal information.
Any failure by our and the VIE Group’s third-party service providers or institutional funding partners to comply with applicable anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing laws and regulations could damage our and the VIE Group’s reputation.
Currently, we and the VIE Group rely on our and the VIE Group’s third-party service providers, in particular payment companies that handle the transfer of funds between borrowers and lenders, to have their own appropriate anti-money laundering policies and procedures. For institutional funding partners, they generally transfer the funds to borrowers directly. The payment companies and our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners are subject to anti-money laundering obligations under applicable anti-money laundering laws and regulations and are regulated in that respect by the People’s Bank of China. If any of our and the VIE Group’s third-party service providers or institutional funding partners fails to comply with applicable anti-money laundering laws and regulations, our and the VIE Group’s reputation could suffer and we and the VIE Group could become subject to regulatory intervention, which could have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, our and the VIE Group’s platform is subject to anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing in PRC and other jurisdictions where we and the VIE Group operate. While we and the VIE Group are in the process of formulating policies and procedures, including internal controls and “know-your-customer” procedures, aimed at preventing money laundering and terrorism financing, we and the VIE Group cannot assure you that we and the VIE Group will be able to establish and maintain effective anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing policies and procedures to protect our and the VIE Group’s platform from being exploited for money laundering or terrorism financing purposes or that such policies and procedures, if adopted, will be deemed to be in compliance with applicable anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing laws and regulations.
We and the VIE Group have not been subject to fines or other penalties, or suffered business or other reputational harm, as a result of actual or alleged money laundering or terrorist financing activities in the past. However, our and the VIE Group’s policies and procedures may not be completely effective in preventing other parties from using us, any of our and the VIE Group’s users or third-party partners as a conduit for money laundering (including illegal cash operations), terrorist financing or sanctioned activities without our and the VIE Group’s knowledge. If we and the VIE Group were to be associated with money laundering (including illegal cash operations), terrorist financing or sanctioned activities, our and the VIE Group’s reputation could suffer and we and the VIE Group could become subject to regulatory fines, sanctions, or legal enforcement, including being added to any “blacklists” that would prohibit certain parties from engaging in transactions with us, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s financial condition and results of operations. In addition, the laws and regulations on anti-money laundering and anti-terrorist financing might be tightened in the future, which may impose more obligations on us and our and the VIE Group’s users and third-party partners. Even if we, our and the VIE Group’s users and business partners comply with the applicable domestic and overseas anti-money laundering laws and regulations, we and the VIE Group may not be able to fully eliminate money laundering and other illegal or improper activities in light of the complexity and the secrecy of these activities.
If we fail to implement and maintain an effective system of internal controls over financial reporting, we may be unable to accurately report our results of operations, meet our reporting obligations or prevent fraud.
We are a public company in the United State subject to reporting obligations under the U.S. securities laws. Among other things, the Securities and Exchange Commission, or the SEC, as required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, or Section 404, adopted rules requiring every public company, including us, to include a management report on the company’s internal control over financial reporting in its annual report, which contains management’s assessment of the effectiveness of the company’s internal control over financial reporting. We are required to include such report in our annual report on Form 20-F starting from the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020. In addition, as we ceased to be an “emerging growth company” for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2024, such term is defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (as amended by the Fixing America’s Surface Transportation Act of 2015), or the JOBS Act, our independent registered public accounting firm is required to attest to and report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting.
Our management and our independent registered public accounting firm, which has issued an attestation report, have concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2024. See “Item 15. Controls and Procedures”.
However, in the future we may determine that we have material weaknesses, or our independent registered public accounting firm may disagree with our management assessment of the effectiveness of our internal controls. Our failure to correct the material weaknesses and control deficiencies or our failure to discover and address any other material weaknesses or control deficiencies could result in inaccuracies in our financial statements and could also impair our ability to comply with applicable financial reporting requirements and related regulatory filings on a timely basis. As a result, our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects, as well as the trading price of our ADSs, may be materially and adversely affected. Moreover, ineffective internal control over financial reporting significantly hinders our ability to prevent fraud.
Our recent purchase of certain commercial property has placed and may continue to place constraints on our cash position and liquidity, and any future decline in value of such property could materially and adversely affect our results of operation.
On December 17, 2024, we entered into a definitive agreement to purchase certain commercial property located in Shanghai, China (the “Commercial Property”) of approximately 43,500 square meters for total cash consideration of approximately RMB1.35 billion (US$184.9 million). In March 2025, we paid all consideration for, and obtained title to, the Commercial Property. The Commercial Property will primarily be used as our new headquarters to meet the demand arising from the continuing growth of our businesses. As we paid the purchase price using cash on hand, the purchase of the Commercial Property has and may continue to place constraints on our cash and liquidity, which may limit our ability to deploy capital for other strategic initiatives to drive our business growth. If the Commercial Property does not generate expected financial or strategic benefits over time, the return on our investment may be lower than anticipated, which could negatively impact shareholder value.
In addition, the Commercial Property may decline in value and accordingly may be subject to significant impairment losses. We evaluate the Commercial Property for impairment on a periodic basis based on events and changes in circumstances that may impact the carrying amounts of such property. If we determine that the fair value of the Commercial Property is less than its carrying value, we may need to adjust the value of such property and recognize an impairment loss, in which case our results of operation may be materially and adversely affected.
Borrower growth and activity on mobile devices depend upon effective use of mobile operating system, networks and standards, which we and the VIE Group do not control.
Our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services are mostly offered through mobile apps. As new mobile devices and platforms are released, it is difficult to predict the problems we and the VIE Group may encounter in developing applications for these new devices and platforms, and we and the VIE Group may need to devote significant resources to the development, support and maintenance of such applications. In addition, our and the VIE Group’s future growth and our and the VIE Group’s results of operations could suffer if we and the VIE Group experience difficulties in the future in integrating our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services into mobile devices or if problems arise with our and the VIE Group’s relationships with providers of mobile operating systems or mobile app stores, or if we and the VIE Group face increased costs to distribute or have users utilize our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services on mobile devices. We and the VIE Group are further dependent on the interoperability of providing our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services on popular mobile operating systems that we and the VIE Group do not control, such as iOS and Android, and any changes in such systems that degrade the accessibility of our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services or give preferential treatment to competing products could adversely affect the usability of our and the VIE Group’s services on mobile devices. In the event that it is more difficult for our and the VIE Group’s users to access and utilize our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services on their mobile devices, or if our and the VIE Group’s users choose not to access or utilize our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services on their mobile devices or to use mobile operating systems that do not offer access to our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation services, our and the VIE Group’s user growth could be harmed and our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and operating results may be adversely affected.
Our and the VIE Group’s operations depend on the performance of the Internet infrastructure and telecommunications networks in China.
Almost all access to the Internet in China is maintained through state-owned telecommunication operators under the administrative control and regulatory supervision of the MIIT. We and the VIE Group primarily rely on a limited number of telecommunication service providers to provide us with data communications capacity through local telecommunications lines and Internet data centers to host our and the VIE Group’s servers.
We and the VIE Group have limited access to alternative networks or services in the event of disruptions, failures or other problems with China’s Internet infrastructure or the fixed telecommunications networks provided by telecommunication service providers. With the expansion of our and the VIE Group’s business, we and the VIE Group may be required to upgrade our and the VIE Group’s technology and infrastructure to keep up with the increasing traffic on our and the VIE Group’s platform. We and the VIE Group cannot assure you that the Internet infrastructure and the fixed telecommunications networks in China will be able to support the demands associated with the continued growth in Internet usage.
In addition, we and the VIE Group have no control over the costs of the services provided by telecommunication service providers. If the prices we and the VIE Group pay for telecommunications and Internet services rise significantly, our and the VIE Group’s results of operations may be adversely affected. Furthermore, if Internet access fees or other charges to Internet users increase, our and the VIE Group’s user traffic may decline and our and the VIE Group’s business may be harmed.
Our and the VIE Group’s platform and internal systems rely on software that is highly technical, and if it contains undetected errors, our and the VIE Group’s business could be adversely affected.
Our and the VIE Group’s platform and internal systems rely on software that is highly technical and complex. In addition, our and the VIE Group’s platform and internal systems depend on the ability of such software to store, retrieve, process and manage immense amounts of data. In particular, we and the VIE Group used to open credit assessment platforms to these expert consultants, where they have access to a limited amount of desensitized, grouped and tagged borrower data, based on which they used such data to develop their own credit assessment models. The software on which we and the VIE Group rely may have contained, and may now or in the future contain, undetected errors or bugs. Some errors may only be discovered after the code has been released for external or internal use. Errors or other design defects within the software on which we and the VIE Group rely may result in a negative experience for funding partners and borrowers using our and the VIE Group’s platform, delay introductions of new features or enhancements, result in errors or compromise our and the VIE Group’s ability to protect borrower or funding partner data or our and the VIE Group’s intellectual property. Any errors, bugs or defects discovered in the software on which we and the VIE Group rely could result in harm to our and the VIE Group’s reputation, loss of borrowers or funding partners or liability for damages, any of which could adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
We may not be able to prevent others from unauthorized use of our intellectual property, which could harm our business and competitive position.
We regard our trademarks, domain names, know-how, proprietary technologies and similar intellectual property as critical to our success, and we rely on a combination of intellectual property laws and contractual arrangements, including confidentiality, invention assignment and non-compete agreements with our employees and others to protect our proprietary rights. See also “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview— Intellectual Property.” Despite these measures, any of our intellectual property rights could be challenged, invalidated, circumvented or misappropriated, or such intellectual property may not be sufficient to provide us with competitive advantages. In addition, because of the rapid pace of technological change in our industry, parts of our business rely on technologies developed or licensed by third parties, and we may not be able to obtain or continue to obtain licenses and technologies from these third parties on reasonable terms, or at all.
It is often difficult to maintain and enforce intellectual property rights. Confidentiality, invention assignment and non-compete agreements may be breached by counterparties, and there may not be adequate remedies available to us for any such breach. Accordingly, we may not be able to effectively protect our intellectual property rights or to enforce our contractual rights. Preventing any unauthorized use of our intellectual property is difficult and costly and the steps we take may be inadequate to prevent the misappropriation of our intellectual property. In the event that we resort to litigation to enforce our intellectual property rights, such litigation could result in substantial costs and a diversion of our managerial and financial resources. We can provide no assurance that we will prevail in such litigation. In addition, our trade secrets may be leaked or otherwise become available to, or be independently discovered by, our competitors. To the extent that our employees or consultants use intellectual property owned by others in their work for us, disputes may arise as to the rights in related know-how and inventions. Any failure in protecting or enforcing our intellectual property rights could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may be subject to intellectual property infringement claims, which may be expensive to defend and may disrupt our business and operations.
We cannot be certain that our operations or any aspects of our business do not or will not infringe upon or otherwise violate trademarks, patents, copyrights, know-how or other intellectual property rights held by third parties. We may be from time to time in the future subject to legal proceedings and claims relating to the intellectual property rights of others. In addition, there may be third-party trademarks, patents, copyrights, know-how or other intellectual property rights that are infringed by our products, services or other aspects of our business without our awareness.
Holders of such intellectual property rights may seek to enforce such intellectual property rights against us in China, the United States or other jurisdictions. If any third-party infringement claims are brought against us, we may be forced to divert management’s time and other resources from our business and operations to defend against these claims, regardless of their merits. As the date of this annual report, the applications for certain trademarks filed by us are still pending. If we are unable to complete these registrations, we may not be able to prohibit unauthorized use or prevent other infringements of these trademarks. In addition, certain of the trademarks we use for the daily operation or promotion of our business have already been registered by independent third parties outside of our control, and such trademarks are currently subject to administrative or legal proceedings. In the event that these administrative and legal proceedings are resolved adversely to us, we may be prohibited from using such trademarks and subject to fines and other legal or administrative sanctions, and our business, financial condition and results of operations may be materially and adversely affected.
Additionally, the application and interpretation of China’s intellectual property right laws and the procedures and standards for granting trademarks, patents, copyrights, know-how or other intellectual property rights in China are still evolving, and we cannot assure you that PRC courts or regulatory authorities would agree with our analysis. If we were found to have violated the intellectual property rights of others, we may be subject to liability for our infringement activities or may be prohibited from using such intellectual property, and we may incur licensing fees or be forced to develop alternatives of our own. As a result, our business and results of operations may be materially and adversely affected.
We and the VIE Group may be held liable for information or content displayed on, retrieved from or linked to our and the VIE Group’s mobile applications, which may materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business and operating results.
In addition to our and the VIE Group’s website, we and the VIE Group also offer online consumer finance products through our and the VIE Group’s mobile applications, which are regulated by the Administrative Provisions on Mobile Internet Applications Information Services, or the APP Provisions, promulgated by the CAC, on June 28, 2016 and amended on June 14, 2022. According to the APP Provisions, the providers of mobile applications shall not create, copy, publish or distribute information and content that is prohibited by laws and regulations. We and the VIE Group have implemented internal control procedures screening the information and content on our and the VIE Group’s mobile applications to ensure their compliance with the APP Provisions. However, we and the VIE Group cannot assure that all the information or content displayed on, retrieved from or linked to our and the VIE Group’s mobile applications complies with the requirements of the APP Provisions at all times. If our and the VIE Group’s mobile applications were found to be violating the APP Provisions, we and the VIE Group may be subject to administrative penalties, including warning, service suspension or removal of our and the VIE Group’s mobile applications from the relevant mobile application store, which may materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business and operating results.
We may from time to time be subject to claims, controversies, lawsuits and legal proceedings, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and reputation.
We may from time to time become subject to or involved in various claims, controversies, lawsuits, and legal proceedings. Claims, lawsuits, and litigations are subject to inherent uncertainties, and we are uncertain whether the foregoing claim would develop into a lawsuit. Lawsuits and litigations may cause us to incur defense costs, utilize a significant portion of our resources and divert management’s attention from our day-to-day operations, any of which could harm our business. Any settlements or judgments against us could have a material adverse impact on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. In addition, negative publicity regarding claims or judgments made against us may damage our reputation and may result in a material adverse impact on us.
In the past, shareholders of public companies have often brought securities class action suits against those companies following periods of instability in the market price of their securities. For example, on September 11, 2020, a securities class action complaint was filed against us and our officers and directors in the Supreme Court of the State of New York, County of New York. An amended complaint was filed on February 1, 2021, which added as defendants the underwriters for our initial public offering. The plaintiff asserted claims under Sections 11 and 15 of the Securities Act of 1933 based on purported misstatements and omissions in Form F-1 registration statement for our initial public offering. The plaintiff brought his claims individually and on behalf of all other persons who acquired our American Depositary Shares pursuant and/or traceable to our initial public offering, and seeks compensatory damages, rescission, injunctive relief, and costs and expenses, including attorneys’ fees and expert fees in unidentified amounts. On August 15, 2022, the Court entered an order of preliminary approval of a settlement in the Action. The Court has approved the settlement and the case has been dismissed. Under the terms of the settlement, we paid an aggregate of US$2.0 million in 2022 as a full and final settlement to resolve all claims that arise out of or relate to the subject matter of the class action as to all parties involved in the action.
The class action suit that we are aware of and if we were involved in a class action suit in the future, it could divert a significant amount of our management’s attention and other resources from our business and operations and require us to incur significant expenses to defend the suit, which could harm our results of operations. Any such class action suit, whether or not successful, could harm our reputation and restrict our ability to raise capital in the future.
In addition, if a claim is successfully made against us, we may be required to pay significant damages, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
From time to time we may evaluate and potentially consummate strategic investments or acquisitions, which could require significant management attention, disrupt our business and adversely affect our financial results.
We may evaluate and consider strategic investments, combinations, acquisitions or alliances to further increase the value of our platform and better match funding partners and borrowers. These transactions could be material to our financial condition and results of operations if consummated. If we are able to identify an appropriate business opportunity, we may not be able to successfully consummate the transaction and, even if we do consummate such a transaction, we may be unable to obtain the benefits or avoid the difficulties and risks of such transaction.
Strategic investments or acquisitions will involve risks commonly encountered in business relationships, including:
•
difficulties in assimilating and integrating the operations, personnel, systems, data, technologies, rights, platforms, products and services of the acquired business;
•
inability of the acquired technologies, products or businesses to achieve expected levels of revenue, profitability, productivity or other benefits;
•
difficulties in retaining, training, motivating and integrating key personnel;
•
diversion of management’s time and resources from our daily operations;
•
difficulties in maintaining uniform standards, controls, procedures and policies within the combined organizations;
•
difficulties in retaining relationships with our funding partners and borrowers, employees and suppliers of the acquired business;
•
risks of entering markets in which we have limited or no prior experience;
•
regulatory risks, including remaining in good standing with existing regulatory bodies or receiving any necessary pre-closing or post-closing approvals, as well as being subject to new regulators with oversight over an acquired business;
•
assumption of contractual obligations that contain terms that are not beneficial to us, require us to license or waive intellectual property rights or increase our risk for liability;
•
failure to successfully further develop the acquired technology;
•
liability for activities of the acquired business before the acquisition, including intellectual property infringement claims, violations of laws, commercial disputes, tax liabilities and other known and unknown liabilities;
•
potential disruptions to our ongoing businesses; and
•
unexpected costs and unknown risks and liabilities associated with strategic investments or acquisitions.
We have made certain investments and acquisitions during past years. However, our investments and acquisitions may not be successful, may not benefit our business strategy, may not generate sufficient revenues to offset the associated acquisition costs or may not otherwise result in the intended benefits. In addition, we cannot assure you that any future investment in or acquisition of new businesses or technology will lead to the successful development of new or enhanced loan facilitation services provided by our and the VIE Group’s platform or that any new or enhanced loan facilitation services, if developed, will achieve market acceptance or prove to be profitable.
Competition for employees is intense, and we may not be able to attract and retain the qualified and skilled employees needed to support our business.
We believe our success depends on the efforts and talent of our employees, including risk management, software engineering, financial and marketing personnel. Our future success depends on our continued ability to attract, develop, motivate and retain qualified and skilled employees. Competition for highly skilled technical, risk management and financial personnel is extremely intense. We may not be able to hire and retain these personnel at compensation levels consistent with our existing compensation and salary structure. Some of the companies with which we compete for experienced employees have greater resources than we have and may be able to offer more attractive terms of employment.
In addition, we invest significant time and expenses in training our employees, which increases their value to competitors who may seek to recruit them. If we fail to retain our employees, we could incur significant expenses in hiring and training new employees, and the quality of our services and our ability to match funding partners and borrowers could diminish, resulting in a material adverse effect to our business.
Increases in labor costs in the PRC may adversely affect our business and results of operations.
The economy in China has experienced increases in inflation and labor costs in recent years. As a result, average wages in the PRC are expected to continue to increase. In addition, we are required by PRC laws and regulations to pay various statutory employee benefits, including pension, housing fund, medical insurance, work-related injury insurance, unemployment insurance and maternity insurance to designated government agencies for the benefit of our employees. We expect that our labor costs, including wages and employee benefits, will continue to increase. Unless we are able to control our labor costs or pass on these increased labor costs to our users by increasing the fees of our services, our financial condition and results of operations may be adversely affected.
Loss of or failure to maintain relationships with our and the VIE Group’s business partners may adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
We and the VIE Group currently work with a number of business partners in various aspects of our and the VIE Group’s business. Pursuing, establishing and maintaining relationships with business partners require significant time and resources as does integrating third-party data and services with our and the VIE Group’s system. Our and the VIE Group’s current agreements with business partners generally do not prohibit them from working with our and the VIE Group’s competitors or from offering competing services. Our and the VIE Group’s competitors may be more effective in providing incentives to our and the VIE Group’s business partners to favor their products or services, which may in turn reduce the volume of loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform. Certain types of business partners may devote more resources to support their own competing businesses. In addition, these business partners may not perform as expected under our and the VIE Group’s agreements with them, and we and the VIE Group may have disagreements or disputes with them, which could adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s brand and reputation. If we and the VIE Group cannot successfully enter into and maintain effective relationships with business partners, our and the VIE Group’s business will be harmed.
We and the VIE Group do not have any business insurance coverage.
Insurance companies in China currently do not offer as extensive an array of insurance products as insurance companies in more developed economies. Currently, we and the VIE Group do not have any business liability or disruption insurance to cover our and the VIE Group’s operations. We and the VIE Group have determined that the costs of insuring for these risks and the difficulties associated with acquiring such insurance on commercially reasonable terms make it impractical for us to have such insurance. Any uninsured business disruptions may result in our and the VIE Group’s incurring substantial costs and the diversion of resources, which could have an adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s results of operations and financial condition.
We and the VIE Group may not be able to obtain additional capital on favorable terms or at all.
We and the VIE Group believe our and the VIE Group’s cash and cash equivalents on hand will be sufficient to meet our and the VIE Group’s current and anticipated needs for general corporate purposes. However, we and the VIE Group need to make continued investments in facilities, hardware, software, technological systems and to retain talents to remain competitive. Due to the unpredictable nature of the capital markets and our and the VIE Group’s industry, we and the VIE Group cannot assure you that we and the VIE Group will be able to raise additional capital on terms favorable to us, or at all, if and when required, especially if we and the VIE Group experience disappointing operating results. If adequate capital is not available to us as required, our and the VIE Group’s ability to fund our and the VIE Group’s operations, take advantage of unanticipated opportunities, develop or enhance our and the VIE Group’s infrastructure or respond to competitive pressures could be significantly limited, which would adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations. If we and the VIE Group do raise additional funds through the issuance of equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership interests of our and the VIE Group’s shareholders could be significantly diluted. These newly issued securities may have rights, preferences or privileges senior to those of existing shareholders.
Some aspects of our and the VIE Group’s digital operations include open source software, and any failure to comply with the terms of one or more of these open source licenses could negatively affect our and the VIE Group’s business.
Some aspects of our and the VIE Group’s digital operations include software covered by open source licenses. The terms of various open source licenses have not been interpreted by PRC courts, and there is a risk that such licenses could be construed in a manner that imposes unanticipated conditions or restrictions on our and the VIE Group’s online and mobile-based channels.
If portions of our and the VIE Group’s proprietary software are determined to be subject to an open source license, we and the VIE Group could be required to publicly release the affected portions of our and the VIE Group’s source code, re-engineer all or a portion of our and the VIE Group’s technologies if required so by the license, or otherwise be limited in the licensing of our and the VIE Group’s technologies, each of which could reduce or eliminate the value of our and the VIE Group’s technologies and loan facilitation services. In addition to risks related to license requirements, usage of open source software can lead to greater risks than use of third-party commercial software, as open source licensors generally do not provide warranties or controls on the origin of the software. Many of the risks associated with use of open source software cannot be eliminated, and could adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business.
Trading in our securities may be prohibited under the Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act or the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act, if it is later determined that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely our auditor, and as a result, U.S. national securities exchanges, such as Nasdaq, may determine to delist our securities.
On December 18, 2020, the former U.S. president signed into law the Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act, or the HFCAA. In essence, the HFCAA requires the SEC to prohibit foreign companies from listing securities on U.S. securities exchanges if a company retains a foreign accounting firm that cannot be inspected by the PCAOB for three consecutive years, beginning in 2021. On March 24, 2021, the SEC adopted interim final rules relating to the implementation of certain disclosure and documentation requirements of the HFCAA. On December 2, 2021, the SEC adopted amendments to finalize rules implementing the submission and disclosure requirements in the HFCAA which will go into effect 30 days after publication in the Federal Registrar. The SEC may propose additional rules or guidance that could impact us if our auditor is not subject to PCAOB inspection.
On December 29, 2022, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2023 was signed into law, which, among others, amended the HFCAA to reduce the number of consecutive years an issuer can be identified as a Commission-Identified Issuer before the SEC must impose an initial trading prohibition on the issuer’s securities from three years to two. Therefore, once an issuer is identified as a Commission-Identified Issuer for two consecutive years, the SEC is required under the HFCAA to prohibit the trading of the issuer’s securities on a national securities exchange and in the over-the-counter market.
On September 22, 2021, the PCAOB adopted a new rule related to its responsibilities under the HFCAA, which provides a framework for the PCAOB to use when determining, as contemplated under the HFCAA, whether it is unable to inspect or investigate completely registered public accounting firms located in a foreign jurisdiction because of a position taken by one or more authorities in that jurisdiction. The new rule became effective on November 4, 2021.
On December 16, 2021, the PCAOB issued a report notifying the Commission of its determinations (the “PCAOB Determinations”) that they are unable to inspect or investigate completely PCAOB-registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and in Hong Kong. The report sets forth lists identifying the registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong, respectively, that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely.
On August 26, 2022, the PCAOB signed a Statement of Protocol with the CSRC and Ministry of Finance, taking the first step toward opening access for the PCAOB to inspect and investigate registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong completely, consistent with U.S. law.
On December 15, 2022, the PCAOB announced that it was able to conduct inspections and investigations completely of PCAOB-registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong in 2022. The PCAOB vacated its previous determinations issued in December 2021 accordingly.
On December 18, 2023, we dismissed Marcum Asia CPAs LLP, a firm registered with the PCAOB and headquartered in New York, the United States, and appointed Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Certified Public Accountants LLP, or Deloitte, which is located in mainland China, as our independent registered public accounting firm. We do not expect to be identified as a “Commission-Identified Issuer” under the HFCAA for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024 after we file our annual report on Form 20-F for such fiscal year. However, whether the PCAOB will continue to conduct inspections and investigations completely to its satisfaction of PCAOB-registered public accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong is subject to uncertainty and depends on a number of factors out of our and our auditor’s control, including positions taken by authorities of the PRC. The PCAOB is expected to continue to demand complete access to inspections and investigations against accounting firms headquartered in mainland China and Hong Kong in the future. The PCAOB is required under the HFCAA to make its determination on an annual basis with regards to its ability to inspect and investigate completely accounting firms based in the mainland China and Hong Kong. The possibility of being a “Commission-Identified Issuer” and risk of delisting could continue to adversely affect the trading price of our securities. Should the PCAOB again encounter impediments to inspections and investigations in mainland China or Hong Kong as a result of positions taken by any authority in either jurisdiction, the PCAOB will make determinations under the HFCAA as and when appropriate.
Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure
Jiayin Group Inc. is a Cayman Islands holding company primarily operating in China through its subsidiaries and contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology. Investors in the ADSs thus are not purchasing, and may never hold, equity interests in the consolidated VIE. The interpretation and application of current and future PRC laws, regulations, and rules relating to such agreements that establish the VIE structure for the majority of our and the consolidated VIE’s operations in China, including potential future actions by the PRC government remains to be observed, which could affect the enforceability of our contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology and, consequently, significantly affect the financial condition and results of operations of Jiayin Group Inc. If the PRC government finds such agreements non-compliant with relevant PRC laws, regulations, and rules, or if these laws, regulations, and rules or the interpretation thereof change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our beneficial interest in Jiayin Technology or forfeit our rights under the contractual arrangements.
We are an exempted company incorporated under the laws of the Cayman Islands, and Shanghai Kunjia, our indirectly wholly-owned PRC subsidiary, is considered a foreign-invested enterprise. However, PRC laws and regulations place certain restrictions and conditions on foreign ownership of certain areas of businesses. To comply with PRC laws and regulations, we conduct our business activities through the consolidated VIE in China. As such, Shanghai Kunjia entered into the Contractual Arrangements with Jiayin Technology and the shareholders of Jiayin Technology, among others, pursuant to which, we are able to:(i) exercise effective control over Jiayin Technology; (ii) receive substantially all of the economic benefits of Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries; (iii) have an exclusive call option to purchase all or part of the equity interests in and/or assets of Jiayin Technology when and to the extent permitted by laws; (iv) have an exclusive option to purchase, or designate one or more persons to purchase from Jiayin Technology all or any part of its assets at any time and from time to time in our absolute direction to the extent permitted by PRC laws; (v) appoint us or our designated person to exercise all shareholder rights in Jiayin Technology; and (vi) have all of the equity interests in Jiayin Technology pledged to us as a continuing first priority security interest for performance of the Contractual Arrangements. The Contractual Arrangements allow the results of operation and assets and liabilities of Jiayin Technology to be consolidated into our results of operations and assets and liabilities under U.S. GAAP as if it was our wholly-owned subsidiary.
If the Contractual Arrangements that establish the structure for operating our and the consolidated VIE’s business in the PRC are found to be in violation of any existing or any PRC laws or regulations in the future, or the PRC government finds that we, or the consolidated VIE fails to obtain or maintain any of the required permits or approvals, the relevant PRC regulatory authorities, including the MIIT, MOFCOM and SAT, would have discretion in dealing with such violations, including:
•
revoking the business and operating licenses;
•
discontinuing or restricting the operations;
•
imposing fines or confiscating any of the income from us and the consolidated VIE that they deem to have been obtained through illegal operations;
•
requiring us to restructure our and the consolidated VIE’s operations in such a way as to compel us to establish new entities, re-apply for the necessary licenses or relocate our and the consolidated VIE’s business, staff and assets;
•
imposing additional conditions or requirements with which we and the consolidated VIE may not be able to comply;
•
restricting or prohibiting the use of proceeds from the initial public offering or other financing activities to finance our and the consolidated VIE’s business and operations in the PRC; or
•
taking other regulatory or enforcement actions that could be harmful to our and the consolidated VIE’s business.
Any of these actions could cause significant disruption or result in a material change to our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations, and may materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, it is unclear what impact the PRC government actions would have on us and on our ability to consolidate the financial results of Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries in our consolidated financial statements, if the PRC governmental authorities find the consolidated VIE’s legal structure and Contractual Arrangements to be in violation of PRC laws, rules and regulations. If any of these penalties results in our inability to direct the activities of Jiayin Technology or its subsidiaries that most significantly impact its economic performance and/or our failure to receive the economic benefits from Jiayin Technology or its subsidiaries, we may not be able to consolidate Jiayin Technology and/or its subsidiaries into our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP. If we are unable to claim our right to control the assets of the consolidated VIE, the ADSs may decline in value or become worthless.
The PRC government has authority to exert influence on the China operations of an offshore holding company, such as us. Changes in China’s economic, political or social conditions, or government policies may cause our and the consolidated VIE’s underlying operations in China to become prohibitive, which could materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Substantially all of our and the consolidated VIE’s operations are located in China and as a result, the continuation of the underlying operations in China is vital to our and the consolidated VIE’s success. The PRC government has authority to exert influence on the China operations of an offshore holding company, such as us. Despite economic reforms and measures implemented by the PRC government, the PRC government continues to play a significant role in regulating industrial development, allocation of natural and other resources, production, pricing and management of currency.
Our and the consolidated VIE’s ability to successfully conduct and expand business operations in the PRC depends on a number of factors, including macro-economic and other market conditions. Demand for our and the consolidated VIE’s services and our and the consolidated VIE’s business, financial condition and results of operations may be materially and adversely affected by the following factors:
•
political instability or changes in social conditions of the PRC;
•
changes in laws, regulations, and administrative directives or the interpretation thereof;
•
measures which may be introduced to control inflation or deflation; and
•
changes in the rate or method of taxation.
These factors are affected by a number of variables which are beyond our and the consolidated VIE’s control. In the event that our or the consolidated VIE’s underlying operations in China become prohibitive, we and the consolidated VIE may not be able to relocate and/or reproduce operating activities elsewhere, which could cause significant business disruptions and materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We and the consolidated VIE are subject to extensive and evolving legal development, non-compliance with which, or changes in which, may materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business and prospects, and may result in a material change in our and the consolidated VIE’s operations and/or the value of our ADSs or could significantly limit or completely hinder our and the consolidated VIE’s ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of our securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
PRC companies are subject to various PRC laws, regulations and government policies and the relevant laws, regulations and policies continue to evolve. The recent statements and regulatory actions by China’s government, such as those related to the use of data security, anti-monopoly concerns, and the regulatory approvals on overseas listings, may impact our ability to conduct the business, accept foreign investments and/or list on a U.S. or other foreign exchange. In addition, the PRC government may adopt new measures that may affect our and the consolidated VIE’s operations, or may exert more oversight and influence on offerings conducted outside of China and foreign investment in China-based companies, and we and the consolidated VIE may be subject to challenges brought by these new laws, regulations and policies. However, since the PRC legal system continues to rapidly evolve, the interpretations of many laws, regulations and rules may change. Furthermore, as we and the consolidated VIE may be subject to additional, yet undetermined, laws and regulations, compliance may require us to obtain additional permits and licenses, complete or update registrations with relevant regulatory authorities, adjust our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations, as well as allocate additional resources to monitor developments in the relevant regulatory environment. However, under the stringent regulatory environment, it may take much more time for the relevant regulatory authorities to approve new applications for permits and licenses, and complete or update registrations and we cannot assure you that we and the consolidated VIE will be able to comply with these laws and regulations in a timely manner or at all. The failure to comply with these laws and regulations may delay, or possibly prevent, us to conduct business, accept foreign investments, or listing overseas.
The occurrence of any of these events may materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business and prospects and may result in a material change in our and the consolidated VIE’s operations and/or the value of our ADSs or could significantly limit or completely hinder our and the consolidated VIE’s ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors. In addition, if any of changes causes us unable to direct the activities of the consolidated VIE or lose the right to receive their economic benefits, we may not be able to consolidate the VIE into our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, which could cause the value of our ADSs to significantly decline or become worthless.
It is unclear whether we and the consolidated VIE will be subject to the oversight of the CAC and how such oversight may impact us. Our and the consolidated VIE’s business could be interrupted or we and the consolidated VIE could be subject to liabilities which may materially and adversely affect the results of our and the consolidated VIE’s operation and the value of your investment.
On December 28, 2021, the CAC, NDRC, MIIT, the MPS, the Ministry of National Security, the MOF, the MOFCOM, the PBOC, the National Radio and Television Administration, the CSRC, the National Administration of State Secrets Protection and the State Cryptography Administration jointly released the Measures for Cybersecurity Review, or the Cybersecurity Review Measures, which took effect on February 15, 2022. According to the Cybersecurity Review Measures, (i) critical information infrastructure operators that intend to purchase internet products and services and (ii) online platform operators engaging in data processing activities that affect or may affect national security must be subject to the cybersecurity review. According to the Regulations for Safe Protection of Critical Information Infrastructure, or the Safe Protection Regulations, which took effect on September 1, 2021, critical information infrastructure refers to important network infrastructure and information system in public telecommunications, information services, energy sources, transportation and other critical industries and domains, in which any destruction or data leakage will have severe impact on national security, the nation’s welfare, people’s living and public interests. As of the date hereof, neither we nor the consolidated VIE has received any notice from government authorities identifying us or the consolidated VIE as a critical information infrastructure operator. If we and the consolidated VIE are identified as an infrastructure operator in the future, we and the consolidated VIE must be subject to cybersecurity review.
Furthermore, online platform operators applying for listing on a foreign exchange must go through cybersecurity review if it possesses personal information of more than one million users, according to the Cybersecurity Review Measures. The review focuses on several factors, including, among others, (i) the risk of theft, leakage, corruption, illegal use or export of any core or important data, or a large amount of personal information, and (ii) the risk of any critical information infrastructure, core or important data, or a large amount of personal information being affected, controlled or maliciously exploited by a foreign government after a company is listed overseas. Nevertheless, it is still uncertain whether the Cybersecurity Review Measures will be applicable to a future offering conducted by China-based companies listed overseas. As of the date hereof, neither we nor the consolidated VIE has received any notice from government authorities requiring us to going through cybersecurity review by the CAC.
In light of the foregoing, as advised by our PRC legal counsel, we believe that there is a relatively low likelihood that we and the consolidated VIE will be subject to the cybersecurity review by the CAC for a future offering of our securities to foreign investors, given that: (i) neither we nor the consolidated VIE has been recognized as critical information infrastructure operators; (ii) data processed in our and the consolidated VIE’s business do not have impact or potential impact on national security; and (iii) it is still uncertain whether the Cybersecurity Review Measures will be applicable to a future offering conducted by China-based companies listed overseas. However, it remains to be observed as to how the Cybersecurity Review Measures will be interpreted and whether the PRC regulatory agencies, including the CAC, may adopt new laws, regulations, rules, or detailed implementation and interpretation related to the Cybersecurity Review Measures. If any such new laws, regulations, rules, or implementation and interpretation comes into effect, we and the consolidated VIE will take all reasonable measures and actions to comply and to minimize the adverse effect of such laws on us.
We cannot assure you that PRC regulatory agencies, including the CAC, would take the same view as we and our PRC legal counsel do, and there is no assurance that we and the consolidated VIE can fully or timely comply with such laws. In addition, we and/or the consolidated VIE may be required to go through cybersecurity review by the CAC as a result of change in applicable laws, regulations or interpretations. In the event that we and the consolidated VIE are subject to any mandatory cybersecurity review and other specific actions required by the CAC, we and the consolidated VIE face uncertainty as to whether any clearance or other required actions can be timely completed, or at all. Given such uncertainty, we and the consolidated VIE may be further required to suspend our and the consolidated VIE’s relevant business, shut down our and the consolidated VIE’s website, or face other penalties, which could materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business, financial condition, and results of operations, and/or the value of our ADSs or could significantly limit or completely hinder our and the consolidated VIE’s ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors. In addition, if any of these events causes us unable to direct the activities of the consolidated VIE or lose the right to receive their economic benefits, we may not be able to consolidate the VIE into our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, which could cause the value of our ADSs to significantly decline or become worthless.
On September 30, 2024, the State Council released the Regulations on the Management of Network Data Security, also known as the Network Data Regulation, which came into force on January 1, 2025. The Network Data Regulation is not only the first at the administrative regulation level specifically for network data security, but it also serves as a comprehensive implementing regulation for the compliance requirements set out by the Cyber Security Law, Data Security Law, and Personal Information Protection Law. The Network Data Regulation introduces several key obligations, including requiring network data handlers to specify the purpose and method of personal information processing, as well as the types of personal information involved, before any personal information is handled. It also clarifies definitions for important data, outlines the obligations of those handling important data, establishes broader contractual requirements for data sharing between data handlers, and introduces a new exemption for regulatory obligations regarding cross-border data transfers.
As the Network Data Regulation is relatively new, it remains to be seen how this regulation will be interpreted and implemented, and to what extent it will affect our operations.
We cannot assure you that we will be able to comply with new regulatory requirements relating to our future overseas capital raising activities, and may be subject to more stringent requirements with respect to matters including data privacy and cross-border investigation and enforcement of legal claims. In the event that we and the consolidated VIE are subject to any mandatory cybersecurity review and other specific actions required by the CAC, we and the consolidated VIE face uncertainty as to whether any clearance or other required actions can be timely completed, or at all. Given such uncertainty, we and the consolidated VIE may be further required to suspend our and the consolidated VIE’s relevant business, shut down our and the consolidated VIE’s website, or face other penalties, which could materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business, financial condition, and results of operations, and/or the value of our ADSs or could significantly limit or completely hinder our and the consolidated VIE’s ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors. In addition, if any of these events causes us unable to direct the activities of the consolidated VIE or lose the right to receive their economic benefits, we may not be able to consolidate the VIE into our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, which could cause the value of our ADSs to significantly decline or become worthless.
The PRC government’s oversight over our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations could result in a material adverse change in our and the consolidated VIE’s operations and the value of our ADSs.
We conduct our business in China primarily through our PRC subsidiaries, including Shanghai Kunjia and Chuangzhen Technology and its subsidiaries in which we hold equity ownership interests, and the contractual arrangements with the consolidated VIE. Our and the consolidated VIE’s operations in China are governed by PRC laws and regulations. The PRC government has oversight over the conduct of our and the consolidated VIE’s business, and it regulates and may influence our and the consolidated VIE’s operations, which could result in a material adverse change in our and the consolidated VIE’s operation and/or the value of our ADSs. Also, the PRC government has exerted oversight over offerings that are conducted overseas and/or foreign investment in China-based issuers like us in recent years, which could significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of such securities to significantly decline or be worthless. In addition, implementation of industry-wide regulations directly targeting our and the consolidated VIE’s operations could cause the value of our securities to significantly decline.
The approval, filing or other requirements of the CSRC, the CAC or other PRC government authorities may be required under PRC law in connection with a future offering of our securities to foreign investors.
We are required to complete filing or fulfill other requirements of the CSRC within three business days after the closing of our future offerings, according to the Trial Administrative Measures. We do not believe we are required to obtain any approvals from the CAC or other PRC government authorities under PRC law in connection with a future offering of our securities to foreign investors as of the date of this annual report.
On February 17, 2023, the CSRC promulgated the Trial Administrative Measures and five supporting guidelines, which became effective on March 31, 2023. The Trial Administrative Measures lay out filing procedures for PRC domestic enterprises to file their initial public offerings and follow-on overseas offerings with the CSRC. PRC domestic enterprises are required to file follow-on offerings with the CSRC within three business days after the closing of such offerings.
According to the Trial Administrative Measures, an overseas offering and listing is prohibited under any of the following circumstances: (i) if the intended securities offering and listing is specifically prohibited by laws, regulations or relevant national provisions; (ii) if the intended securities offering and listing may constitute a threat to or endangers national security as reviewed and determined by competent authorities under the State Council in accordance with law; (iii) if, in the past three years, the PRC domestic enterprise or its controlling shareholders or actual controllers have committed corruption, bribery, embezzlement, misappropriation of property, or other criminal offenses disruptive to the order of the socialist market economy; (iv) if the PRC domestic enterprise is currently under judicial investigation for suspicion of criminal offenses, or is under investigation for suspicion of material violations of law; and (v) if there are material ownership disputes over the equity held by the controlling shareholder or held by the shareholder controlled by the controlling shareholder or actual controller.
As a result, we are required to complete the filing procedures with the CSRC for any future follow-on offerings within three business days after the closing of the offering.
On February 24, 2023, the CSRC and other relevant government authorities published the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management. According to the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management, PRC domestic enterprises that seek to offer and list securities in overseas markets shall establish confidentiality and archives management system.
The PRC domestic enterprises shall obtain approval from the competent authority and file with the confidential administration department at the same level when providing or publicly disclosing documents and materials related to state secrets or secrets of the governmental authorities to the underwriters or other agencies or the offshore regulatory authorities, and shall complete corresponding procedures when providing or publicly disclosing documents and materials which may adversely influence national security and the public interest. The PRC domestic enterprises shall provide written statements on the implementation on the aforementioned rules to the underwriter and other agencies. Nevertheless, the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management do not provide a clear scope of materials that, if divulged, will jeopardize national security or public interest, and the PRC government authorities may have certain discretion in the interpretation and enforcement of the applicable laws. Given it remains to be observed surrounding the interpretation of the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management, we cannot assure you that we will not be required to obtain any approval from or complete filing procedures with the competent authorities for our future offerings.
The Trial Administrative Measures and the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management, as advised by our PRC legal counsel, may subject us to additional compliance requirement in the future for a future securities offering, including completion of filing procedures and obtaining required approval. We cannot assure you that we will be able to get the clearance of filing procedures or obtain the required approval on a timely basis, or at all. Any failure of us to fully comply with new regulatory requirements may significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer our securities, cause significant disruption to our business operations, and severely damage our reputation, which would materially and adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations and cause our ADSs to significantly decline in value or become worthless.
With respect to the Cyberspace Administration of China, or the CAC, as advised by our PRC legal counsel, we believe that there is a relatively low likelihood that we and the consolidated VIE will be subject to the cybersecurity review by the CAC for a future offering of our securities to foreign investors, given that: (i) neither we nor the consolidated VIE has been recognized as critical information infrastructure operators; (ii) data processed in our and the consolidated VIE’s business do not have impact or potential impact on national security; and (iii) it is still uncertain whether the Cybersecurity Review Measures will be applicable to a future offering conducted by China-based companies listed overseas. For further discussion on the risks relating to the oversight of the CAC, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure——It is unclear whether we and the consolidated VIE will be subject to the oversight of the CAC and how such oversight may impact us. Our and the consolidated VIE’s business could be interrupted or we and the consolidated VIE could be subject to liabilities which may materially and adversely affect the results of our and the consolidated VIE’s operation and the value of your investment.”
As advised by our PRC legal counsel, we believe that approvals or permissions from the CSRC are not required for the operations of the consolidated VIE and our other subsidiaries, and that there is a relatively low likelihood that the operations of the consolidated VIE and our other subsidiaries will be subject to the cybersecurity review by the CAC, given that: (i) neither the consolidated VIE nor any of our other subsidiaries has been recognized as critical information infrastructure operators; and (ii) data processed in the consolidated VIE and our other subsidiaries’ business do not have impact or potential impact on national security. Furthermore, our and the VIE Group’s online platform, operated by Geerong Yunke and Shanghai Yixin may be deemed to be providing commercial Internet information services, which would require the aforementioned companies to obtain certain value-added telecommunications business license. We cannot assure you that we can obtain these licenses in a timely manner, or at all. Any failure to obtain the relevant approvals or licenses may subject us to sanctions, including rectification orders and warnings, fines, confiscation of illegal gains, and, in case of significant infringement, orders to close our online platform, which may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations. For further discussion on the risks relating to the regulatory oversight of the online platform, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—We and the VIE Group may be adversely affected by the complexity and changes in PRC regulation of Internet-related businesses and companies, and any lack of requisite approvals, licenses or permits applicable to our and the VIE Group’s business may have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.”
Except as otherwise disclosed in the foregoing, we do not believe we are required to obtain any approvals from the CAC or other PRC government authorities under PRC law in connection with a future offering of our securities to foreign investors as of the date of the annual report.
If we inadvertently conclude any prior approval is not required and the CSRC, the CAC or other relevant PRC regulatory agencies subsequently determine that prior approval is required for any of our future offerings of securities overseas or to maintain the listing status of our ADSs, we cannot guarantee that we will be able to obtain such approval in a timely manner, or at all, or to maintain such approval once we receive it. The CSRC, the CAC or other PRC regulatory agencies also may take actions requiring us, or making it advisable for us, not to proceed with such offering or maintain the listing status of our ADSs. If we proceed with any of such offering or maintain the listing status of our ADSs without obtaining these regulatory agencies’ approval to the extent it is required, or if we are unable to comply with any new approval requirements which might be adopted for future offerings, we may face regulatory actions or other sanctions from these regulatory agencies. For example, regulatory agencies may impose fines and penalties on our operations in China, limit our ability to pay dividends outside of China, limit our operating privileges in China, delay or restrict the repatriation of the proceeds from offering of securities overseas into China or take other actions that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects, as well as the trading price of the ADSs.
Furthermore, if we are required to obtain any other approvals from or complete filings and/or other regulatory procedures with the CSRC, the CAC or other PRC regulatory agencies as a result of change in applicable laws, regulations or interpretations for any future offering or the listing of the ADSs, we cannot assure you that we can obtain the required approval or complete the required filings and/or other regulatory procedures in a timely manner, or at all. Any failure to obtain such approval or complete such filings and/or other regulatory procedures may subject us to regulatory actions or other sanctions taken by the relevant government authorities, which may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
The interpretation and implementation of the Foreign Investment Law of the PRC may impact the viability of our current corporate structure, corporate governance and business operations.
On March 15, 2019, the National People’s Congress adopted the Foreign Investment Law of the PRC, which became effective on January 1, 2020 and replaced three existing laws regulating foreign investment in China, namely, the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Wholly Foreign-owned Enterprises, the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Sino-Foreign Equity Joint Ventures, the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Sino-Foreign Cooperative Joint Ventures, together with their implementation rules and ancillary regulations. The Foreign Investment Law of the PRC embodies an expected PRC regulatory trend to rationalize its foreign investment regulatory regime in line with prevailing international practice and the legislative efforts to unify the corporate legal requirements for both foreign and domestic investments. However, uncertainties still exist in relation to its interpretation and implementation. For example, the Foreign Investment Law of the PRC adds a catch-all clause to the definition of “foreign investment” so that foreign investment, by its definition, includes “investments made by foreign investors in China through other means defined by other laws or administrative regulations or provisions promulgated by the State Council” without further elaboration on the meaning of “other means”. It leaves leeway for the future legislations promulgated by the State Council to provide for contractual arrangements as a form of foreign investment. On December 26, 2019, the State Council promulgated the Implementation Regulations on the Foreign Investment Law of the PRC, or the Implementation Regulations, which came into effect on January 1, 2020. However, the Implementation Regulations on the Foreign Investment Law still remains silent on whether contractual arrangements should be deemed as a form of foreign investment. It is therefore uncertain whether our corporate structure will be seen as violating the foreign investment rules as we are currently leveraging the contractual arrangement to operate certain businesses in which foreign investors are prohibited from or restricted from investing. Furthermore, if future legislations prescribed by the State Council mandate further actions to be taken by companies with respect to existing contractual arrangement, we may face substantial uncertainties as to whether we can complete such actions in a timely manner, or at all. If we fail to take appropriate and timely measures to comply with any of these or similar regulatory compliance requirements, our current corporate structure, corporate governance and business operations could be materially and adversely affected.
If the PRC government deems that the Contractual Arrangements in relation to Jiayin Technology do not comply with PRC regulatory restrictions on foreign investment in the relevant industries, or if these regulations or the interpretation of existing regulations change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our beneficial interest in those operations.
Foreign investors are generally not allowed to own more than 50% of the equity interests in a value-added telecommunication service provider (except e-commerce, domestic multi-party communication, storage and forwarding and call center) in accordance with the Special Administrative Measures for Access of Foreign Investment (Negative List) (2024 Version).
We are a Cayman Islands exempted company and our subsidiaries in the PRC, or PRC subsidiaries, are considered foreign invested enterprises. However, PRC laws and regulations place certain restrictions and conditions on foreign ownership of certain areas of businesses. To comply with PRC laws and regulations, we hold a value-added telecommunications license through our subsidiary, Shanghai Yixin Network Technology Co., Ltd. Due to PRC legal restrictions on foreign ownership and investment in, among other areas, value-added telecommunications services, we set up a series of Contractual Arrangements entered into among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the shareholders of Jiayin Technology to conduct our operations in China. For a detailed description of these Contractual Arrangements, see “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure—Contractual Arrangements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the Shareholders of Jiayin Technology.” As a result of these Contractual Arrangements, we exert control over Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries and consolidate their operating results in our financial statements under U.S. GAAP.
In the opinion of our PRC legal counsel, King & Wood Mallesons, the ownership structure of Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries is not in violation of existing PRC laws, regulations and rules currently in effect; and each of the VIE contractual agreements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the shareholders of Jiayin Technology is valid, binding and enforceable upon each party to such agreements in accordance with their terms and applicable PRC laws and regulations currently in effect.
As of and for the year ended December 31, 2024 and till the date of this annual report, the Company is not aware of any notice from the PRC government that the PRC government holds the opinion that the ownership structure of Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries is illegal, or any of the VIE contractual agreements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the shareholders of Jiayin Technology governed by PRC laws are illegal. However, King & Wood Mallesons has also advised us that there are substantial uncertainties regarding the interpretation and application of PRC laws, rules and regulations and there can be no assurance that the PRC government will take a view that is consistent with the opinion of our PRC legal counsel, King & Wood Mallesons, in the future.
It is uncertain whether any new PRC laws, regulations or rules relating to the “variable interest entity” structure, or the VIE structure, will be adopted or if adopted, what they would provide. If the ownership structure, Contractual Arrangements and business of our company, our subsidiaries, Jiayin Technology or its subsidiaries are found to be in violation of any existing or future PRC laws or regulations, or we fail to obtain or maintain any of the required permits or approvals, the relevant governmental authorities would have discretion in dealing with such violation, including levying fines, confiscating our income or the income of Jiayin Technology or its subsidiaries, revoking the business licenses or operating licenses of Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology or its subsidiaries, shutting down our servers or blocking our online platform, discontinuing or placing restrictions or onerous conditions on our operations, requiring us to undergo a costly and disruptive restructuring, restricting or prohibiting our use of proceeds from our initial public offering to finance our business and operations in China, and taking other regulatory or enforcement actions that could be harmful to our business. Any of these actions could cause significant disruption to our business operations and severely damage our reputation, which would in turn materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. If any of these occurrences results in our inability to direct the activities of Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries, and/or our failure to receive economic benefits from Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries, we may not be able to consolidate their results into our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
We rely on Contractual Arrangements with Jiayin Technology and shareholders of Jiayin Technology for certain business operations, which may not be as effective as direct ownership in providing operational control, and these contractual arrangements have not been tested in a court of law.
We have relied and expect to continue to rely on Contractual Arrangements with the consolidated VIE, Jiayin Technology and the shareholders of Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries, to operate our online consumer finance platform business, including, among others, the operation of www.niwodai.com and our apps, as well as certain other complementary businesses.
For a description of these Contractual Arrangements, see “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure—Contractual Arrangements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the Shareholders of Jiayin Technology.” These Contractual Arrangements may not be as effective as direct ownership in providing us with control over the consolidated VIE, and these contractual arrangements have not been tested in a court of law. For example, Jiayin Technology, or shareholders of Jiayin Technology may fail to fulfill their contractual obligations with us, such as failure to maintain our website and use the domain names and trademarks in a manner as stipulated in the Contractual Arrangements, or taking other actions that are detrimental to our interests.
If we had direct ownership of the consolidated VIE, we would be able to exercise our rights as a shareholder to effect changes in the board of directors of consolidated VIE, which in turn could implement changes, subject to any applicable fiduciary obligations, at the management and operational level. However, under the current Contractual Arrangements, we rely on the performance by Jiayin Technology, shareholders of Jiayin Technology of their obligations under the Contractual Arrangements to exercise control over the consolidated VIE. The consolidated VIE and its shareholders may not act in the best interests of our company or may not perform their obligations under these contracts. Such risks exist throughout the period in which we intend to operate our business through the Contractual Arrangements with Jiayin Technology and shareholders of Jiayin Technology. If any of Jiayin Technology and shareholders of Jiayin Technology is uncooperative or any dispute relating to these contracts remains unresolved, we will have to enforce our rights under these contracts through the operations of PRC laws and arbitration, litigation and other legal proceedings, the outcome of which will be subject to uncertainties. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure—Any failure by Jiayin Technology or shareholders of Jiayin Technology to perform their obligations under our Contractual Arrangements with them would have a material adverse effect on our business.” Therefore, our Contractual Arrangements with Jiayin Technology and shareholders of Jiayin Technology may not be as effective in ensuring our control over the relevant portion of our business operations as direct ownership would be.
Any failure by Jiayin Technology or shareholders of Jiayin Technology to perform their obligations under our Contractual Arrangements with them would have a material adverse effect on our business.
We have entered into a series of Contractual Arrangements with Jiayin Technology, the consolidated VIE and the shareholders of Jiayin Technology. For a description of these Contractual Arrangements, see “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure.” If the consolidated VIE or the shareholders of Jiayin Technology fail to perform their respective obligations under the Contractual Arrangements, we may incur substantial costs and expend additional resources to enforce such arrangements.
We may also have to rely on legal remedies under PRC laws, including seeking specific performance or injunctive relief, and claiming damages, which we cannot assure you that it will be effective under PRC laws. For example, if the shareholders of Jiayin Technology were to refuse to transfer their equity interests in Jiayin Technology to us or our designee when we exercise the purchase option pursuant to these Contractual Arrangements, or if they were otherwise to act in bad faith toward us, then we may have to take legal actions to compel them to perform their contractual obligations.
All the agreements under our Contractual Arrangements are governed by PRC laws and provide for the resolution of disputes through arbitration in China. Accordingly, these contracts would be interpreted in accordance with PRC laws and any disputes would be resolved in accordance with PRC legal procedures. Meanwhile, there are very few precedents and little formal guidance as to how Contractual Arrangements in the context of a variable interest entity should be interpreted or enforced under PRC laws. It may be difficult to evaluate the ultimate outcome of such arbitration should legal action become necessary. In addition, under PRC laws, rulings by arbitrators are final and parties cannot appeal arbitration results in court unless such rulings are revoked or determined unenforceable by a competent court. If the losing parties fail to carry out the arbitration awards within a prescribed time limit, the prevailing parties may only enforce the arbitration awards in PRC courts through arbitration award recognition proceedings. In the event that we are unable to enforce these Contractual Arrangements, or if we suffer significant delay or other obstacles in the process of enforcing these Contractual Arrangements, we may not be able to exert effective control over Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries, and our ability to conduct our business may be negatively affected. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—The interpretation and enforcement of PRC laws and regulations could limit the legal protections available to you and us, significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer our ADSs, cause significant disruption to our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations, and severely damage our and the consolidated VIE’s reputation, which would materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s financial condition and results of operations and cause our ADSs to significantly decline in value or become worthless.”
The shareholders of the consolidated VIE may have potential conflicts of interest with us, which may materially and adversely affect our business and financial condition.
The equity interests of the consolidated VIE are held by their respective shareholders. Their interests may differ from the interests of our company as a whole. These shareholders may breach, or cause the consolidated VIE to breach, the existing Contractual Arrangements we have with them and the consolidated VIE, which would have a material adverse effect on our ability to effectively control the consolidated VIE and subsidiaries of the consolidated VIE, and receive economic benefits from them. For example, the shareholders of Jiayin Technology may be able to cause our agreements with Jiayin Technology to be performed in a manner adverse to us by, among other things, failing to remit payments due under the Contractual Arrangements to us on a timely basis. We cannot assure you that when conflicts of interest arise, any or all of these shareholders will act in the best interests of our company or such conflicts will be resolved in our favor.
Currently, we do not have any arrangements to address potential conflicts of interest between these shareholders and our company, except that we could exercise our call option under the exclusive call option agreement with shareholders of Jiayin Technology to request them to transfer all of their equity interests in Jiayin Technology to a PRC entity or individual designated by us, to the extent permitted by PRC laws. If we cannot resolve any conflict of interest or dispute between us and the shareholders of the consolidated VIE, we would have to rely on legal proceedings, which could result in the disruption of our business and subject us to substantial uncertainty as to the outcome of any such legal proceedings.
Contractual Arrangements in relation to the consolidated VIE may be subject to scrutiny by the PRC tax authorities and they may determine that we or consolidated VIE owe additional taxes, which could negatively affect our financial condition and the value of your investment.
Under applicable PRC laws and regulations, arrangements and transactions among related parties may be subject to audit or challenge by the PRC tax authorities. The PRC enterprise income tax law requires every enterprise in China to submit its annual enterprise income tax return together with a report on transactions with its related parties to the relevant tax authorities. The tax authorities may impose reasonable adjustments on taxation if they have identified any related party transactions that are inconsistent with arm’s length principles. We may face material and adverse tax consequences if the PRC tax authorities determine that the Contractual Arrangements in relation to the consolidated VIE were not entered into on an arm’s length basis in such a way as to result in an impermissible reduction in taxes under applicable PRC laws, regulations and rules, and adjust the income of Jiayin Technology in the form of a transfer pricing adjustment. A transfer pricing adjustment could, among other things, result in a reduction of expense deductions recorded by Jiayin Technology for PRC tax purposes, which could in turn increase their tax liabilities without reducing tax expenses of Shanghai Kunjia. In addition, if Shanghai Kunjia requests the shareholders of Jiayin Technology to transfer their equity interests in Jiayin Technology at nominal or no value pursuant to these Contractual Arrangements, such transfer could be viewed as a gift and subject Shanghai Kunjia to PRC income tax.
Furthermore, the PRC tax authorities may impose late payment fees and other penalties on Jiayin Technology for the adjusted but unpaid taxes according to the applicable regulations. Our financial position could be materially and adversely affected if Jiayin Technology’s tax liabilities increase or if they are required to pay late payment fees and other penalties.
We may lose the ability to use and enjoy assets held by the VIE Group that are material to the operation of our business if the entities within the VIE Group declare bankruptcy or become subject to a dissolution or liquidation proceeding.
The VIE Group holds certain assets that are material to the operation of our business, including, among others, intellectual properties, hardware and software. Under the Contractual Arrangements, the VIE Group may not, and the shareholders of the VIE Group may not cause them to, in any manner, sell, transfer, mortgage or dispose of their assets or their legal or beneficial interests in the business without our prior consent. However, in the event the VIE Group’s shareholders breach these Contractual Arrangements and voluntarily liquidate any entity within the VIE Group, or the entities within the VIE Group declare bankruptcy and all or part of their assets become subject to liens or rights of third-party creditors, or are otherwise disposed of without our consent, we may be unable to continue some or all of our business activities, which could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. If the entities within the VIE Group undergo a voluntary or involuntary liquidation proceeding, independent third-party creditors may claim rights to some or all of these assets, thereby hindering our ability to operate our business, which could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Risks Relating to Doing Business in China
Changes in China’s economic, political or social conditions or government policies could have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
Substantially all of our and the VIE Group’s operations are located in China. Accordingly, our and the VIE Group’s business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations may be influenced to a significant degree by political, economic and social conditions in China generally and by continued economic growth in China as a whole.
The Chinese economy has experienced significant growth over the past decades since the implementation of China’s reform and opening-up policy, and the PRC government continues to play a significant role in regulating industry development by imposing industrial policies. In addition, the Chinese government has implemented in the past certain measures to speed up the economic and social growth. These measures may lead to a reduction in demand for our services and consequently have a material adverse effect on our businesses, financial condition and results of operations.
A downturn in the global economy could reduce the demand for consumer loans and investments, which could materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business and financial condition.
The global financial markets have experienced significant disruptions between 2008 and 2009, and the United States, Europe and other economies have experienced periods of recessions. The recovery from the economic downturns of 2008 and 2009 has been uneven and is facing new challenges, including the announcement of Brexit which creates additional global economic uncertainty and the slowdown of the Chinese economy since 2012. The recovery from the COIVD-19 pandemic across the globe remains uncertain. There is considerable uncertainty over the long-term effects of the expansionary monetary and fiscal policies adopted by the central banks and financial authorities of some of the world’s leading economies. Further, there have also been concerns over unrest in the Middle East, which have resulted in volatility in financial and other markets.
Moreover, there have been concerns about the economic effect of the tensions in the relationship between China and other countries, including the United States the surrounding Asian countries. In particular, political tensions between the United States and China have escalated in recent years due to, among other things, the trade war between the two countries since 2018, the COVID-19 outbreak, the PRC National People’s Congress’ passage of Hong Kong national security legislation, the imposition of U.S. sanctions on certain Chinese officials from China’s central government and the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region by the U.S. government, and the imposition of sanctions on certain individuals from the U.S. by the Chinese government, various executive orders issued by U.S. President Donald J. Trump, such as the one issued in August 2020 that prohibits certain transactions with ByteDance Ltd., Tencent Holdings Limited and the respective subsidiaries of such companies, the executive order issued in November 2020 that prohibits U.S. persons from transacting publicly traded securities of certain “Communist Chinese military companies” named in such executive order, the executive order issued in January 2021 that prohibits such transactions as are identified by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce with certain “Chinese connected software applications,” including Alipay and WeChat Pay, as well as the Rules on Counteracting Unjustified Extra-territorial Application of Foreign Legislation and Other Measures promulgated by the MOFCOM on January 9, 2021, which apply to Chinese individuals or entities that are purportedly barred by a foreign country’s law from dealing with nationals or entities of a third country.
In October 2022, the U.S. government implemented comprehensive export controls to restrict the export of advanced semiconductors and the equipment required to manufacture them to China. Starting from February 2025, the U.S. government imposed a series of tariff increases on imports from China. Following the recent announcement by President Trump on April 9, 2025, the tariffs on imports from China have been raised to 145%, and a fact sheet issued by White House on April 15, 2025 indicated that tariffs on certain goods imported from China could be as high as 245%. In response to the multiple rounds of tariff increases by the U.S. government, China also announced several rounds of retaliatory tariffs on goods imported from the U.S., raising the rate to 125%. There may be further developments in tariff policies that are currently unpredictable. Rising political tensions between China and the U.S. could reduce levels of trades, investments, technological exchanges and other economic activities between the two major economies, which would have a material adverse effect on global economic conditions and the stability of global financial markets. The measures taken by the U.S. and Chinese governments may have the effect of restricting our and the VIE Group’s ability to transact or otherwise do business with entities within or outside of China and may cause investors to lose confidence in Chinese companies and counterparties, including us. If we and the VIE Group were unable to conduct its business as it is currently conducted as a result of such regulatory or policy changes, our and the VIE Group’s business, results of operations and financial condition would be materially and adversely affected.
In October 2024, the U.S. Treasury Department issued a final rule establishing a new national security regulatory framework restricting outbound investment from the United States in certain sensitive industries and sectors in China including the Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and Macau (the “Outbound Investment Rule”). The Outbound Investment Rule, which took effect on January 2, 2025, targets investments involving any “covered foreign person” which includes persons and entities associated with countries of concern, currently only China, that engage in certain activities in three sectors: (i) semiconductor and microelectronics, (ii) quantum information technologies, and (iii) artificial intelligence systems. Depending on the activity in question, the Outbound Investment Rule imposes obligations on U.S. persons, either prohibiting, or requiring notification to the U.S. government concerning, “covered transactions,” which is defined to include, among other things, acquisitions of equity interests or provision of certain debt financing to covered foreign persons, brownfield or greenfield investment in China, or entry into a joint venture with a covered person, unless an enumerated exception applies, such as investment in publicly traded securities. We currently do not believe that we are a “covered foreign person” under the Outbound Investment Rule. However, there is no assurance that the U.S. Treasury Department will take the same view as ours. If we were to be deemed a Covered Foreign Person, our ability to raise capital would be significantly and negatively affected, which could be detrimental to our business, financial condition and prospects. In such case, the trading prices of our ADSs and/or our Class A ordinary shares may be materially and adversely affected and the value of our securities may decline significantly. It is also possible that the U.S. government may expand the sectors and technologies subject to the Outbound Investment Rule or adopt additional laws or regulations further restricting outbound investment from the U.S. to or relating to China. For example, on February 20, 2025, President Trump issued the America First Trade Policy Memorandum, which proposes possible expansion of the set of technologies of concern and a review of exceptions to the Outbound Investment Rule, possibly including changes to the existing exception for publicly trades securities. As of the date of this annual report, the proposed changes under the America First Investment Policy are not implemented, although the proposed restrictions may further deepen the uncertainties for cross-border collaborations, investments, and funding opportunities for China-based issuers including us. If our ability to raise such capital is significantly and negatively affected, it could be detrimental to our business, financial condition and prospects, and our ADSs may significantly decline in value.
Furthermore, there were media reports on deliberations within the U.S. government regarding potentially limiting or restricting China-based companies from accessing U.S. capital markets, and delisting China-based companies from U.S. national securities exchanges. In January 2021, after reversing its own delisting decision, the NYSE ultimately resolved to delist China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom in compliance with the executive order issued in November 2020, after receiving additional guidance from the U.S. Department of Treasury and its Office of Foreign Assets Control. These delistings have introduced greater confusion and uncertainty about the status and prospects of Chinese companies listed on the U.S. stock exchanges. On April 9, 2025, amid the escalation of trade war between the U.S. and China, the U.S. Secretary of the State, Scott Bessent, indicated the possibility of delisting U.S.-listed China-based issuers. If any further such deliberations were to materialize, it may have a material and adverse impact on the stock performance of China-based issuers listed in the United States such as us, and we cannot assure you that we will always be able to maintain the listing of our ADSs on a national stock exchange in the U.S., such as the Nasdaq Stock Market or the NYSE, or that you will always be allowed to trade our ADSs.
The interpretation and enforcement of PRC laws and regulations could limit the legal protections available to you and us, significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer our ADSs, cause significant disruption to our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations, and severely damage our and the consolidated VIE’s reputation, which would materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s financial condition and results of operations and cause our ADSs to significantly decline in value or become worthless.
The PRC legal system is based on written statutes and prior court decisions have limited value as precedents. Since the PRC legal system continues to rapidly evolve, the interpretations of many laws, regulations and rules may change.
In particular, PRC laws and regulations concerning the online consumer finance industry are evolving. Although we have taken measures to comply with the laws and regulations that are applicable to our business operations, including the regulatory principles raised by the CBIRC, and avoid conducting any non-compliant activities under the applicable laws and regulations, such as illegal fund-raising, forming capital pool or providing guarantee to investors, the PRC government authority may promulgate new laws and regulations regulating the online consumer finance industry in the future. We cannot assure you that our practice would not be deemed to violate any new PRC laws or regulations relating to online consumer finance. Moreover, developments in the online consumer finance industry may lead to changes in PRC laws, regulations and policies or in the interpretation and application of existing laws, regulations and policies that may limit or restrict online consumer finance platform like us, which could materially and adversely affect our business and operations.
From time to time, we may have to resort to administrative and court proceedings to enforce our legal rights. However, since PRC administrative and court authorities have certain discretion within their scope of authority in interpreting and implementing statutory and contractual terms, it may be difficult to evaluate the outcome of administrative and court proceedings and the level of legal protection we enjoy. Such uncertainties, including uncertainty over the scope and effect of our contractual, property (including intellectual property) and procedural rights, could limit the legal protections available to you and us, significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer our ADSs, cause significant disruption to our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations, and severely damage our and the consolidated VIE’s reputation, which would materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s financial condition and results of operations and cause our ADSs to significantly decline in value or become worthless.
We and the VIE Group may be adversely affected by the complexity and changes in PRC regulation of Internet-related businesses and companies, and any lack of requisite approvals, licenses or permits applicable to our and the VIE Group’s business may have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
The PRC government regulates the Internet industry, including foreign ownership of, and the licensing and permit requirements pertaining to, companies in the Internet industry. These Internet-related laws and regulations are evolving. As a result, in certain circumstances it may be difficult to determine what actions or omissions may be deemed to be in violation of applicable laws and regulations.
The evolving PRC regulatory system for the Internet industry may lead to the establishment of new regulatory agencies. For example, in May 2011, the State Council announced the establishment of a new department, the CAC (with the involvement of the State Council Information Office, the MIIT, and the Ministry of Public Security). The primary role of this new agency is to facilitate the policy-making and legislative development in this field, to direct and coordinate with the relevant departments in connection with online content administration and to deal with cross-ministry regulatory matters in relation to the Internet industry.
Our and the VIE Group’s online platform, operated by Geerong Yunke and Shanghai Yixin may be deemed to be providing commercial Internet information services, which would require the aforementioned companies to obtain certain value-added telecommunications business license. We cannot assure you that we can obtain these licenses in a timely manner, or at all. Any failure to obtain the relevant approvals or licenses may subject us to sanctions, including rectification orders and warnings, fines, confiscation of illegal gains, and, in case of significant infringement, orders to close our online platform, which may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—Regulation—Regulations Relating to Internet Companies—Regulations on Value-Added Telecommunication Services.” Furthermore, it is uncertain if Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries will be required to obtain a separate operating license with respect to our and the VIE Group’s mobile applications in addition to the value-added telecommunications business license.
We and the VIE Group cannot assure you that we and the VIE Group have obtained all the permits or licenses required for conducting our and the VIE Group’s business in China or will be able to maintain our and the VIE Group’s existing licenses or obtain new ones. If the PRC government considers that we and the VIE Group were operating without the proper approvals, licenses or permits or promulgates new laws and regulations that require additional approvals or licenses or imposes additional restrictions on the operation of any part of our and the VIE Group’s business, it has the power, among other things, to levy fines, confiscate our and the VIE Group’s net income, revoke our and the VIE Group’s business licenses, and require us to discontinue our and the VIE Group’s relevant business or impose restrictions on the affected portion of our and the VIE Group’s business.
Any of these actions by the PRC government may have a material adverse effect on our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
We rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our PRC subsidiaries to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have, and any limitation on the ability of our PRC subsidiaries to make payments to us could have a material adverse effect on our ability to conduct our business.
We are a holding company, and we rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our PRC subsidiaries for our cash and financing requirements, including the funds necessary to pay dividends and other cash distributions to our shareholders and service any debt we may incur. If our PRC subsidiaries incur debt on their own behalf in the future, the instruments governing the debt may restrict their ability to pay dividends or make other distributions to us. In addition, the PRC tax authorities may require our PRC subsidiaries to adjust its taxable income under the Contractual Arrangements it currently has in place with Jiayin Technology and its shareholders in a manner that would materially and adversely affect their ability to pay dividends and other distributions to us. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure—Contractual Arrangements in relation to the consolidated VIE may be subject to scrutiny by the PRC tax authorities and they may determine that we or consolidated VIE owe additional taxes, which could negatively affect our financial condition and the value of your investment.”
Relevant PRC laws and regulations permit the PRC companies, such as our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE, to pay dividends only out of their retained earnings, if any, as determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. Each of our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE that is in retained earnings position as of the end of each year is required to set aside 10% of its after-tax profits each year, if any, to fund certain statutory reserve funds until such reserve funds reach 50% of its registered capital. The aforementioned registered capital refers to the total amount of share capital of all issued shares or the total amount of capital contribution subscribed by all shareholders, as registered with the registration authority. Furthermore, each of our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE may allocate a portion of its after-tax profits based on PRC accounting standards to a discretionary surplus fund at their discretion. The statutory reserve funds and the discretionary surplus funds are not distributable as cash dividends. After our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE have generated retained earnings and met the requirements for appropriation to the statutory reserves and until such reserves reach 50% of its registered capital, respectively, our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE can distribute dividends upon approval of the shareholders. The foregoing restrictions on the ability of our PRC subsidiaries to make payments to us could have a material adverse effect on our ability to conduct our business.
PRC regulation of loans to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore holding companies and governmental administration of currency conversion may delay or prevent us from using the proceeds of further offerings to make loans to or make additional capital contributions to our PRC subsidiaries, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand our business.
Any funds we transfer to our PRC subsidiaries, either as a shareholder loan or as an increase in registered capital, are subject to approval by or registration with relevant governmental authorities in China. According to the relevant PRC regulations on foreign-invested enterprises in China, capital contributions to our PRC subsidiaries are subject to the requirement of registration with PRC State Administration for Market Regulation or its local counterparts, and filed with the Ministry of Commerce or its local counterparts. In addition, (a) any foreign loan procured by our PRC subsidiaries is required to be registered with SAFE, or its local branches, and (b) each of our PRC subsidiaries may not procure loans which exceed statutory limits. Any medium or long term loan to be provided by us to a VIE of our company must be recorded and registered by the National Development and Reform Committee and the SAFE or its local branches. We may not complete such recording or registrations on a timely basis, if at all, with respect to future capital contributions or foreign loans by us to our PRC subsidiaries. If we fail to complete such recording or registration, our ability to use the foreign currency we hold, including the proceeds of our further offerings, and to capitalize our PRC operations may be negatively affected, which could adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand our business.
In 2008, the SAFE promulgated the Circular on the Relevant Operating Issues Concerning the Improvement of the Administration of the Payment and Settlement of Foreign Currency Capital of Foreign-Invested Enterprises, or SAFE Circular 142, which used to regulate the conversion by foreign-invested enterprises of foreign currency into Renminbi by restricting the usage of converted Renminbi. On March 30, 2015, the SAFE promulgated the Circular on Reforming the Management Approach Regarding the Foreign Exchange Capital Settlement of Foreign-Invested Enterprises, or SAFE Circular 19. SAFE Circular 19 took effect as of June 1, 2015 and superseded SAFE Circular 142 on the same date. SAFE Circular 19 launched a nationwide reform of the administration of the settlement of the foreign exchange capitals of foreign-invested enterprises and allows foreign-invested enterprises to settle their foreign exchange capital at their discretion, but continues to prohibit foreign-invested enterprises from using the Renminbi fund converted from their foreign exchange capitals for expenditures beyond their business scopes. On June 9, 2016, the SAFE promulgated the Circular on Reforming and Standardizing the Administrative Provisions on Capital Account Foreign Exchange, or SAFE Circular 16 and was recently amended on December 4, 2023.
SAFE Circular 16 continue to prohibit foreign-invested enterprises from, among other things, using RMB fund converted from its foreign exchange capitals for expenditure beyond its business scope, investment and financing (wealth management products and structured deposits with risk rating results not higher than Level II), providing loans to non-affiliated enterprises or constructing or purchasing real estate not for self-use. On October 23, 2019, SAFE promulgated the Circular of the State Administration of Foreign Exchange on Further Promoting the Facilitation of Cross-Border Trade and Investment, which removes the restrictions on domestic equity investments by non-investment foreign-invested enterprises with their capital funds, provided that certain conditions are met. If the consolidated VIE requires financial support from us or our PRC subsidiaries in the future, and we find it necessary to use foreign currency-denominated capital to provide such financial support, our ability to fund the consolidated VIE’s operations will be subject to statutory limits and restrictions, including those described above. The applicable foreign exchange circulars and rules may limit our ability to transfer the net proceeds from any future offerings to our PRC subsidiaries and convert the net proceeds into RMB, which may adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Fluctuations in exchange rates could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and the price of our ADSs.
The value of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar and other currencies may fluctuate and is affected by, among other things, changes in political and economic conditions in China and by China’s foreign exchange policies. On July 21, 2005, the PRC government changed its decade-old policy of pegging the value of the Renminbi to the U.S. dollar, and the Renminbi appreciated more than 20% against the U.S. dollar over the following three years. Between July 2008 and June 2010, this appreciation halted and the exchange rate between the Renminbi and the U.S. dollar remained within a narrow band. Since June 2010, the Renminbi has fluctuated against the U.S. dollar, at times significantly and unpredictably. With the development of the foreign exchange market and progress towards interest rate liberalization and Renminbi internationalization, the PRC government may in the future announce further changes to the exchange rate system and we cannot assure you that the Renminbi will not appreciate or depreciate significantly in value against the U.S. dollar in the future. It is difficult to predict how market forces or PRC or U.S. government policy may impact the exchange rate between the Renminbi and the U.S. dollar in the future. Significant revaluation of the Renminbi may have a material and adverse effect on your investment. For example, to the extent that we need to convert U.S. dollars we receive from our initial public offering or future offering into Renminbi for our operations, appreciation of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar would have an adverse effect on the Renminbi amount we would receive from the conversion. Conversely, if we decide to convert our Renminbi into U.S. dollars for the purpose of making payments for dividends on our Class A ordinary shares or ADSs or for other business purposes, appreciation of the U.S. dollar against the Renminbi would have a negative effect on the U.S. dollar amount available to us.
Very limited hedging options are available in China to reduce our exposure to exchange rate fluctuations. As of the date of this annual report, we have not entered into any hedging transactions in an effort to reduce our exposure to foreign currency exchange risk. While we may decide to enter into hedging transactions in the future, the availability and effectiveness of these hedges may be limited and we may not be able to adequately hedge our exposure or at all.
Governmental administration of conversion and remittance of foreign currency may limit our ability to transfer cash out of China to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have, and may affect the value of your investment.
The PRC government imposes certain measures on the convertibility of the Renminbi into foreign currencies and, in certain cases, the remittance of foreign currency out of mainland China. We receive substantially all of our net revenues in RMB. Under our current corporate structure, our company in the Cayman Islands relies on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our PRC subsidiaries to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—We rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our PRC subsidiaries to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have, and any limitation on the ability of our PRC subsidiaries to make payments to us could have a material adverse effect on our ability to conduct our business.”
Under existing PRC foreign exchange regulations, payments of current account items, such as dividends, profit distributions and trade and service-related foreign exchange transactions, can be made in foreign currencies without prior approval from SAFE by complying with certain procedural requirements. Therefore, our PRC subsidiaries are able to pay dividends in foreign currencies to us without prior approval from SAFE, subject to the condition that the remittance of such dividends outside of the PRC complies with certain procedures under PRC foreign exchange regulation, such as the overseas investment registrations by the beneficial owners of our company who are PRC residents. In contrast, approval from or registration with appropriate government authorities is required where RMB is to be converted into foreign currency and remitted out of China to pay capital expenses such as the repayment of loans denominated in foreign currencies.
Since a significant amount of our future revenue and cash flow will be denominated in RMB, any existing and future restrictions on currency exchange may limit our ability to utilize cash generated in RMB to fund our business activities outside of the PRC or pay dividends in foreign currencies to our shareholders, including holders of the ADSs, and may limit our ability to obtain foreign currency through debt or equity financing for our onshore subsidiaries.
Failure to make adequate contributions to various employee benefit plans and withhold individual income tax on employees’ salaries as required by PRC regulations may subject us to penalties.
Companies operating in China are required to participate in various government sponsored employee benefit plans, including certain social insurance, housing provident funds and other welfare-oriented payment obligations, and contribute to the plans in amounts equal to certain percentages of salaries, including bonuses and allowances, of our employees up to a maximum amount specified by the local government from time to time at locations where we operate our businesses. The requirement of employee benefit plans has not been implemented consistently by the local governments in China given the different levels of economic development in different locations. Companies are required to make payments to the employee benefit plans for its employees in accordance with the percentages stipulated under relevant regulations and are required to withhold the amounts that are required to be contributed by employees. Companies operating in China are also required to withhold individual income tax on employees’ salaries based on the actual salary of each employee upon payment.
Prior to March 2018, we failed to make adequate employee benefit plan payments or employee individual income tax withholdings. We have recorded accruals for estimated underpaid amounts in our financial statements accordingly. As of the date of the annual report, we have not received any notification from the relevant PRC authorities alleging that we have not made adequate payments and demanding payment of the same. We also are not aware of any material employee’s complaint or demand for payment of the same, nor have we received any notification from labor arbitration tribunals or the PRC courts regarding disputes with respect to material social welfare and housing provident fund contributions as of the date of this annual report. Remitting such underpaid amounts involves conditions on the implementation level, including, for instance, varying levels of acceptance by our employees of the employee benefit plans, some of which are beyond our control. In accordance with relevant PRC laws and regulations, we may be required to settle such underpaid amounts of employee benefit payments or employee withholding individual income tax payments on our own before a stipulated deadline, which would adversely affect our liquidity status. Furthermore, we may also be subject to late fees or fines in relation to the underpaid amounts. For instance, we may be subject to a late fee of 0.05% or 0.2%, depending on the circumstances, of the amount of overdue social insurance payments per day and a fine ranging from one to three times of the overdue amount. In addition, we may be subject to a fine in relation to the overdue employee withholding payments ranging from 50% to three times of the overdue amount. If we are subject to late fees or fines in relation to the underpaid employee benefits or withhold individual income tax on employees’ salaries, our financial condition and results of operations may be adversely affected.
The M&A Rules and certain other PRC regulations establish complex procedures for some acquisitions of Chinese companies by foreign investors, which could make it more difficult for us to pursue growth through acquisitions in China.
The Regulations on Mergers and Acquisitions of Domestic Companies by Foreign Investors, or the M&A Rules, adopted by six PRC regulatory agencies in 2006 and amended in 2009, and some other regulations and rules concerning mergers and acquisitions established additional procedures and requirements that could make merger and acquisition activities by foreign investors more time consuming and complex, including requirements in some instances that the MOC be notified in advance of any change-of-control transaction in which a foreign investor takes control of a PRC domestic enterprise. Moreover, the Anti-Monopoly Law requires that the MOC shall be notified in advance of any concentration of undertaking if certain thresholds are triggered. In addition, the security review rules issued by the MOC that became effective in September 2011 specify that mergers and acquisitions by foreign investors that raise “national defense and security” concerns and mergers and acquisitions through which foreign investors may acquire de facto control over domestic enterprises that raise “national security” concerns are subject to strict review by the MOC, and the rules prohibit any activities attempting to bypass a security review, including by structuring the transaction through a proxy or contractual control arrangement. The MOC in December 2020 have established procedures and requirements that are expected to make merger and acquisition activities in China by foreign investors more time-consuming and complex. In the future, we may grow our business by acquiring complementary businesses. Complying with the requirements of the above-mentioned regulations and other relevant rules to complete such transactions could be time consuming, and any required approval processes, including obtaining approval from the MOC or its local counterparts may delay or inhibit our ability to complete such transactions, which could affect our ability to expand our business or maintain our market share.
PRC regulations relating to offshore investment activities by PRC residents may limit our PRC subsidiaries’ ability to increase their registered capital or distribute profits to us or otherwise expose us or our PRC resident beneficial owners to liability and penalties under PRC law.
The SAFE promulgated the Circular on Relevant Issues Relating to PRC Resident’s Investment and Financing and Roundtrip Investment through Special Purpose Vehicles, or SAFE Circular 37, in July 2014 that requires PRC residents or entities to register with SAFE or its local branch in connection with their establishment or control of an offshore entity established for the purpose of overseas investment or financing. In addition, such PRC residents or entities must update their SAFE registrations when the offshore special purpose vehicle undergoes material events relating to any change of basic information (including change of such PRC residents or entities, name and operation term), increases or decreases in investment amount, transfers or exchanges of shares, or mergers or divisions. According to the Circular on Further Simplifying and Improving the Administration of the Foreign Exchange Concerning Direct Investment released on February 13, 2015 by the SAFE, local banks will examine and handle foreign exchange registration for overseas direct investment, including the initial foreign exchange registration and amendment registration, under Circular 37.
If our shareholders who are PRC residents or entities do not complete their registration with the local SAFE branches, our PRC subsidiaries may be prohibited from distributing their profits and proceeds from any reduction in capital, share transfer or liquidation to us, and we may be restricted in our ability to contribute additional capital to our PRC subsidiaries. Moreover, failure to comply with the SAFE registration described above could result in liability under PRC laws for evasion of applicable foreign exchange restrictions.
As of the date of this annual report, Mr. Dinggui Yan, Mr. Guanglin Zhang and Mr. Yuanle Wu, who directly or indirectly hold shares in our Cayman Islands holding company and who are known to us as being PRC residents have completed the foreign exchange registrations in accordance with SAFE Circular 37.
However, we may not be informed of the identities of all the PRC residents or entities holding direct or indirect interest in our company, nor can we compel our beneficial owners to comply with the requirements of SAFE Circular 37. As a result, we cannot assure you that all of our shareholders or beneficial owners who are PRC residents or entities have complied with, and will in the future make or obtain any applicable registrations or approvals required by, SAFE Circular 37. Failure by such shareholders or beneficial owners to comply with SAFE Circular 37, or failure by us to amend the foreign exchange registrations of our PRC subsidiaries, could subject us to fines or legal sanctions, restrict our overseas or cross-border investment activities, limit our PRC subsidiaries’ ability to make distributions or pay dividends to us or affect our ownership structure, which could adversely affect our business and prospects.
Any failure to comply with PRC regulations regarding the registration requirements for employee share incentive plans may subject the PRC plan participants or us to fines and other legal or administrative sanctions.
Pursuant to SAFE Circular 37, PRC residents who participate in stock incentive plans in overseas non-publicly-listed companies may submit applications to SAFE or its local branches for the foreign exchange registration with respect to offshore special purpose vehicles. In the meantime, our directors, executive officers and other employees who are PRC citizens, subject to limited exceptions, and who have been granted stock options by us, may follow the Circular on Issues Concerning the Foreign Exchange Administration for Domestic Individuals Participating in Share Incentive Plan of Overseas Publicly-Listed Company, promulgated by the SAFE in 2012, or 2012 SAFE Notices. Pursuant to the 2012 SAFE Notices, PRC citizens and non-PRC citizens who reside in China for a continuous period of no less than one year who participate in any stock incentive plan of an overseas publicly listed company, subject to a few exceptions, are required to register with SAFE through a domestic qualified agent, which could be the PRC subsidiaries of such overseas listed company, and complete certain other procedures. In addition, an overseas entrusted institution must be retained to handle matters in connection with the exercise or sale of stock options and the purchase or sale of shares and interests. We and our directors, executive officers and other employees who are PRC citizens or who reside in the PRC for a continuous period of not less than one year and who have been granted stock options are subject to these regulations. Failure to complete the SAFE registrations may subject them to fines and legal sanctions, and may also limit our ability to contribute additional capital into our PRC subsidiaries and limit our PRC subsidiaries’ ability to distribute dividends to us. We also face regulatory uncertainties that could restrict our ability to adopt additional incentive plans for our directors, executive officers and employees under PRC law. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—Regulation—Regulations Relating to Foreign Exchange—Regulations on Employee Share Incentive Plans of Overseas Publicly-Listed Company.”
The State Administration of Taxation, or SAT, has issued certain circulars concerning employee stock options and restricted shares. Under these circulars, our employees working in China who exercise stock options or are granted restricted shares will be subject to PRC individual income tax. Our PRC subsidiaries have obligations to file documents related to employee stock options or restricted shares with relevant tax authorities and to withhold individual income taxes of those employees who exercise their share options. If our employees fail to pay or we fail to withhold their income taxes according to relevant laws and regulations, we may face sanctions imposed by the tax authorities or other PRC governmental authorities. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—Regulation—Regulations Relating to Foreign Exchange—Regulations on Employee Share Incentive Plans of Overseas Publicly-Listed Company.”
If we are classified as a PRC resident enterprise for PRC income tax purposes, such classification could result in unfavorable tax consequences to us and our non-PRC shareholders or ADS holders.
Under the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law and its implementation rules, an enterprise established outside of the PRC with a “de facto management body” within the PRC is considered a resident enterprise and will be subject to the enterprise income tax on its global income at the rate of 25%. The implementation rules define the term “de facto management body” as the body that exercises full and substantial control over and overall management of the business, productions, personnel, accounts and properties of an enterprise. In April 2009, the SAT issued a circular, known as SAT Circular 82, which provides certain specific criteria for determining whether the “de facto management body” of a PRC-controlled enterprise that is incorporated offshore is located in China. Although this circular only applies to offshore enterprises controlled by PRC enterprises or PRC enterprise groups, not those controlled by PRC individuals or foreigners like us, the criteria set forth in the circular may reflect the SAT’s general position on how the “de facto management body” test should be applied in determining the tax resident status of all offshore enterprises. According to SAT Circular 82, an offshore incorporated enterprise controlled by a PRC enterprise or a PRC enterprise group will be regarded as a PRC tax resident by virtue of having its “de facto management body” in China and will be subject to PRC enterprise income tax on its global income only if all of the following conditions are met: (i) the senior executives and core management departments in charge of the day-to-day operations have their presence mainly in the PRC; (ii) decisions relating to the enterprise’s financial and human resource matters are made or are subject to approval by organizations or personnel in the PRC; (iii) the enterprise’s primary assets, accounting books and records, company seals, and board and shareholder resolutions, are located or maintained in the PRC; and (iv) at least 50% of voting board members or senior executives habitually reside in the PRC.
We believe none of our entities outside of China is a PRC resident enterprise for PRC tax purposes. See “Item 10. Additional Information— E. Taxation—People’s Republic of China Tax Considerations.” However, the tax resident status of an enterprise is subject to determination by the PRC tax authorities and it remains to be observed with respect to the interpretation of the term “de facto management body.” As substantially all of our management members are based in China, it remains to be observed how the tax residency rule will apply to our case. If the PRC tax authorities determine that Jiayin Group Inc. or any of our subsidiaries outside of China is a PRC resident enterprise for PRC enterprise income tax purposes, then Jiayin Group Inc. or such subsidiary could be subject to PRC tax at a rate of 25% on its world-wide income, which could materially reduce our net income. In addition, we will also be subject to PRC enterprise income tax reporting obligations. Furthermore, if the PRC tax authorities determine that we are a PRC resident enterprise for enterprise income tax purposes, dividends we pay on, and gains realized on the sale or other disposition of, our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares may be subject to PRC tax, at a rate of 10% in the case of non-PRC enterprises or 20% in the case of non-PRC individuals (in each case, subject to the provisions of any applicable tax treaty), if deemed to be from PRC sources. It is unclear whether non-PRC shareholders of our company would be able to claim the benefits of any tax treaties between their country of tax residence and the PRC in the event that we are treated as a PRC resident enterprise. Any such tax may reduce the returns on your investment in the ADSs or Class A ordinary shares.
We may not be able to obtain certain benefits under relevant tax treaty on dividends paid by our PRC subsidiaries to us through our Hong Kong subsidiary.
We are a holding company incorporated under the laws of the Cayman Islands and as such primarily rely on dividends and other distributions on equity from our PRC subsidiaries to satisfy part of our funding requirements. Pursuant to the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law, a withholding tax rate of 10% currently applies to dividends paid by a PRC “resident enterprise” to a foreign enterprise investor, unless any such foreign investor’s jurisdiction of incorporation has a tax treaty with China that provides for preferential tax treatment. Pursuant to the Arrangement between the Mainland China and the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region for the Avoidance of Double Taxation and Tax Evasion on Income, or the Double Tax Avoidance Arrangement, and SAT Circular 81 (as defined below), such withholding tax rate may be lowered to 5% if the PRC enterprise is at least 25% held by a Hong Kong enterprise for at least 12 consecutive months prior to distribution of the dividends and is determined by the relevant PRC tax authority to have satisfied other conditions and requirements under the Double Tax Avoidance Arrangement and other applicable PRC laws. Furthermore, under the Announcement of the State Taxation Administration on Issuing the Measures for the Administration of Non-resident Taxpayers’ Enjoyment of Treaty Benefits, which became effective in January 2020, the non-resident enterprises shall determine whether they are qualified to enjoy the preferential tax treatment under the tax treaties and file the Information Reporting Form for Non-resident Taxpayers Claiming Treaty Benefits.
The non-resident enterprises shall directly apply the reduced withholding tax rate when performing tax filings and collect and retain relevant supporting documents, which will be subject to post-tax filing examinations by the relevant tax authorities. There are also other conditions for enjoying the reduced withholding tax rate according to other relevant tax rules and regulations. See “Item 10. Additional Information— E. Taxation—People’s Republic of China Tax Considerations.” We cannot assure you that our determination regarding our qualification to enjoy the preferential tax treatment will not be challenged by the relevant PRC tax authority or we will be able to complete the necessary filings with the relevant PRC tax authority and enjoy the preferential withholding tax rate of 5% under the Double Taxation Arrangement with respect to dividends to be paid by our PRC subsidiaries to Geerong (HK) Limited (“Geerong (HK)”, formerly known as “Jiayin (HK) Limited”), our Hong Kong subsidiary.
We face uncertainty with respect to indirect transfers of equity interests in PRC resident enterprises by their non-PRC holding companies.
According to the Bulletin of the SAT on Several Issues Concerning the Enterprise Income Tax on Indirect Transfers of Assets by Non-Resident Enterprises, or SAT Bulletin 7, promulgated by the SAT in February 2015, if a non-resident enterprise transfers the equity interests of a PRC resident enterprise indirectly by transfer of the equity interests of an offshore holding company (other than a purchase and sale of shares issued by a PRC resident enterprise in public securities market) without a reasonable commercial purpose, the PRC tax authorities have the power to reassess the nature of the transaction and the indirect equity transfer will be treated as a direct transfer. As a result, the gain derived from such transfer, which means the equity transfer price minus the cost of equity, will be subject to PRC withholding tax at a rate of up to 10%. Under the terms of SAT Bulletin 7, a transfer which meets all of the following circumstances shall be directly deemed as having no reasonable commercial purposes: (i) over 75% of the value of the equity interests of the offshore holding company are directly or indirectly derived from PRC taxable properties; (ii) at any time during the year before the indirect transfer, over 90% of the total properties of the offshore holding company are investments within PRC territory, or in the year before the indirect transfer, over 90% of the offshore holding company’s revenue is directly or indirectly derived from PRC territory; (iii) the function performed and risks assumed by the offshore holding company are insufficient to substantiate its corporate existence; or (iv) the foreign income tax imposed on the indirect transfer is lower than the PRC tax imposed on the direct transfer of the PRC taxable properties. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—Regulation—Regulations Relating to Tax.”
We face uncertainties as to the reporting and other implications of certain past and future transactions where PRC taxable assets are involved, such as offshore restructuring, sale of the shares in our offshore subsidiaries or investments. Our company and our non-PRC resident investors may be subject to filing obligations or taxed or subject to withholding obligations in such transactions, under SAT Bulletin 7. See “Item 10. Additional Information— E. Taxation—People’s Republic of China Tax Considerations.” For transfer of shares in our company by investors that are non-PRC resident enterprises, our PRC subsidiaries may be requested to assist in the filing under SAT Bulletin 7. As a result, we may be required to expend valuable resources to comply with SAT Bulletin 7 or to request the relevant transferors from whom we purchase taxable assets to comply with these circulars, or to establish that our company should not be taxed under these circulars, which may have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Risks Relating to our American Depositary Shares
The market price for our ADSs may be volatile.
The trading prices of our ADSs are likely to be volatile and could fluctuate widely due to factors beyond our control. This may happen because of broad market and industry factors, like the performance and fluctuation in the market prices or the underperformance or deteriorating financial results of other listed Internet or other companies based in China that have listed their securities in the United States in recent years. The securities of some of these companies have experienced significant volatility since their initial public offerings, including, in some cases, substantial price declines in their trading prices. The trading performances of other Chinese companies’ securities after their offerings, including Internet and e-commerce companies, may affect the attitudes of investors toward Chinese companies listed in the United States, which consequently may impact the trading performance of our ADSs, regardless of our actual operating performance. In addition, any negative news or perceptions about inadequate corporate governance practices or fraudulent accounting, corporate structure or other matters of other Chinese companies may also negatively affect the attitudes of investors towards Chinese companies in general, including us, regardless of whether we have conducted any inappropriate activities. In addition, securities markets may from time to time experience significant price and volume fluctuations that are not related to our operating performance, which may have a material adverse effect on the market price of our ADSs.
In addition to the above factors, the price and trading volume of our ADSs may be highly volatile due to multiple factors, including the following:
•
regulatory developments affecting us, our users, or our industry; conditions in the online consumer finance industries;
•
announcements of studies and reports relating to the quality of our service offerings or those of our competitors;
•
changes in the economic performance or market valuations of other online consumer finance market;
•
actual or anticipated fluctuations in our quarterly results of operations and changes or revisions of our expected results;
•
changes in financial estimates by securities research analysts;
•
announcements by us or our competitors of new product and service offerings, acquisitions, strategic relationships, joint ventures or capital commitments;
•
additions to or departures of our senior management;
•
detrimental negative publicity about us, our management or our industry;
•
fluctuations of exchange rates between the RMB and the U.S. dollar;
•
release or expiry of lock-up or other transfer restrictions on our outstanding shares or ADSs; and
•
sales or perceived potential sales of additional Class A ordinary shares or ADSs
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about our business, the market price for our ADSs and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our ADSs will depend in part on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about us or our business. If research analysts do not establish and maintain adequate research coverage or if one or more of the analysts who cover us downgrade our ADSs or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about our business, the market price for our ADSs would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts cease coverage of our company or fail to publish reports on us regularly, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which, in turn, could cause the market price or trading volume for our ADSs to decline.
You may need to rely primarily on price appreciation of our ADSs for return on your investment as you may not receive any dividends in any given year which is permitted under our dividend policy.
Our board of directors has discretion as to whether to distribute dividends, subject to certain restrictions under Cayman Islands law, namely that our company may only pay dividends out of profits or share premium, and provided always that in no circumstances may a dividend be paid if this would result in our company being unable to pay its debts as they fall due in the ordinary course of business. In addition, our shareholders may by ordinary resolution declare a dividend, but no dividend may exceed the amount recommended by our directors. On March 28, 2023, our board of directors approved and adopted a dividend policy to declare and distribute cash dividend twice each fiscal year, starting from 2023, at an aggregate amount of no less than 15% of the net income after tax of the Company in the previous fiscal year on a consolidated basis. On November 19, 2024, our board of directors approved and adopted an amended dividend policy (the “Amended Dividend Policy”) to replace the prior dividend policy in its entirety, with immediate effect. Under the Amended Dividend Policy, we may choose to declare and distribute a cash dividend once each fiscal year, starting from 2025, at an aggregate amount of no less than 15% of our net income after tax in the previous fiscal year. On March 27, 2025, in order to provide investors with higher returns, our board of directors approved and adopted a further adjustment to the Amended Dividend Policy to increase the annual dividend amount such that we may choose to declare and distribute a cash dividend once each fiscal year, starting from 2025, at an aggregate amount of around 30% of our net income after tax in the previous fiscal year. The determination to make dividend distributions in any particular fiscal year will be made at the discretion of our board of directors based upon factors such as our results of operations, cash flow, general financial condition, capital requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant. Even if our board of directors decides to pay dividends, the form, frequency and amount will depend upon factors such as our results of operations, cash flow, general financial condition, capital requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant. Accordingly, the return on your investment in our ADSs will likely depend primarily upon any future price appreciation of our ADSs. There is no guarantee that our ADSs will appreciate in value in the future or even maintain the price at which you purchased the ADSs. You may not realize a return on your investment in our ADSs and you may even lose your entire investment in our ADSs.
Substantial future sales or perceived potential sales of our ADSs in the public market could cause the price of our ADSs to decline.
Sales of our ADSs in the public market, or the perception that these sales could occur, could cause the market price of our ADSs to decline. The Class A ordinary shares held by our existing shareholders may be sold in the public market subject to volume and other restrictions as applicable provided in Rules 144 and 701 under the Securities Act.
Certain holders of our ordinary shares may cause us to register under the Securities Act the sale of their shares. Registration of these shares under the Securities Act would result in ADSs representing these shares becoming freely tradable without restriction under the Securities Act immediately upon the effectiveness of the registration. Sales of these registered shares in the form of ADSs in the public market could cause the price of our ADSs to decline.
We cannot guarantee that any share repurchase plan will be fully consummated or that any share repurchase plan will enhance long-term shareholder value, and share repurchases could increase the volatility of the trading price of the ADSs and could diminish our cash reserves.
On June 16, 2022, we announced that our board of directors authorized a share repurchase plan under which we may repurchase our ordinary shares in the form of ADSs with an aggregate value of US$10.0 million during the 12-month period beginning on June 13, 2022. On June 7, 2023, our board of directors approved to extend the share repurchase plan for a period of 12-months period beginning on June 13, 2023 and ending on June 12, 2024. In March 2024, our board of directors approved an adjustment to the existing share repurchase plan, pursuant to which the aggregate value of ordinary shares authorized for repurchase under the plan shall not exceed US$30 million. On June 4, 2024, our board of directors approved to further extend the share repurchase plan for another period of 12 months, commencing on June 13, 2024 and ending on June 12, 2025. Pursuant to the extended share repurchase plan, we may repurchase our ordinary shares through June 12, 2025 with an aggregate value not exceeding the remaining balance under the share repurchase plan.
As of March 31, 2025, the Company had repurchased approximately 3.8 million of its ADSs for approximately US$16.8 million under the share repurchase plan.
Our board of directors also has the discretion to authorize additional share repurchase plans in the future. The share repurchase plans do not obligate us to repurchase any specific dollar amount or to acquire any specific number of ADSs and/or shares. We cannot guarantee that any share repurchase plan will enhance long-term shareholder value. The share repurchase plans could increase the volatility of the trading price of the ADSs and may be suspended or terminated at any time. Furthermore, share repurchases could diminish our cash reserves.
The voting rights of holders of ADSs are limited by the terms of the deposit agreement, and you may not be able to exercise your right to direct the voting of the underlying Class A ordinary shares which are represented by your ADSs.
As a holder of our ADSs, you will not have any direct right to attend general meetings of our shareholders or to cast any votes at such meetings. You will only be able to exercise the voting rights which attach to the underlying Class A ordinary shares which are represented by your ADSs indirectly by giving voting instructions to the depositary in accordance with the provisions of the deposit agreement. Under the deposit agreement, you may vote only by giving voting instructions to the depositary, as the holder of the underlying Class A ordinary shares which are represented by your ADSs. Upon receipt of your voting instructions, the depositary will endeavor to vote the underlying Class A ordinary shares in accordance with your instructions in the event voting is by poll, and in accordance with instructions received from a majority of holders of ADSs who provide instructions in the event voting is by show of hands. The depositary will not join in demanding a vote by poll. You will not be able to directly exercise any right to vote with respect to the underlying Class A ordinary shares represented by your ADSs unless you withdraw such shares and become the registered holder of such shares prior to the record date for the general meeting. Under our amended and restated memorandum and articles of association, the minimum notice period required to be given by our company to our registered shareholders for convening a general meeting is seven calendar days. When a general meeting is convened, you may not receive sufficient advance notice to enable you to withdraw the underlying Class A ordinary shares which are represented by your ADSs and become the registered holder of such shares prior to the record date for the general meeting to allow you to attend the general meeting or to vote directly with respect to any specific matter or resolution which is to be considered and voted upon at the general meeting. In addition, under our amended and restated memorandum and articles of association, for the purposes of determining those shareholders who are entitled to attend and vote at any general meeting, our directors may close our register of members and/or fix in advance a record date for such meeting, and such closure of our register of members or the setting of such a record date may prevent you from withdrawing the underlying Class A ordinary shares which are represented by your ADSs and becoming the registered holder of such shares prior to the record date, so that you would not be able to attend the general meeting or to vote directly. Where any matter is to be put to a vote at a general meeting, the depositary will, if we request, and subject to the terms of the deposit agreement, endeavor to notify you of the upcoming vote and to deliver our voting materials to you. We cannot assure you that you will receive the voting materials in time to ensure that you can instruct the depositary to vote the underlying Class A ordinary shares which are represented by your ADSs. In addition, the depositary and its agents are not responsible for failing to carry out voting instructions or for their manner of carrying out your voting instructions. This means that you may not be able to exercise your right to direct the voting of the underlying Class A ordinary shares which are represented by your ADSs, and you may have no legal remedy if the underlying Class A ordinary shares are not voted as you requested.
ADS holders may not be entitled to a jury trial with respect to claims arising under the deposit agreement, which could result in less favorable outcomes to the plaintiff(s) in any such action.
The deposit agreement governing the ADSs representing our Class A ordinary shares provides that holders and beneficial owners of ADSs irrevocably waive the right to a trial by jury in any legal proceeding arising out of or relating to the deposit agreement or the ADSs, including in respect of claims under federal securities laws, against us or the depositary to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law. If this jury trial waiver provision is prohibited by applicable law, an action could nevertheless proceed under the terms of the deposit agreement with a jury trial. To our knowledge, the enforceability of a jury trial waiver under the federal securities laws has not been finally adjudicated by a federal court. However, we believe that a jury trial waiver provision is generally enforceable under the laws of the State of New York, which govern the deposit agreement, by a court of the State of New York or a federal court, which has non-exclusive jurisdiction over matters arising under the deposit agreement, applying such law. In determining whether to enforce a jury trial waiver provision, New York courts and federal courts will consider whether the visibility of the jury trial waiver provision within the agreement is sufficiently prominent such that a party has knowingly waived any right to trial by jury. We believe that this is the case with respect to the deposit agreement and the ADSs. In addition, New York courts will not enforce a jury trial waiver provision in order to bar a viable setoff or counterclaim sounding in fraud or one which is based upon a creditor’s negligence in failing to liquidate collateral upon a guarantor’s demand, or in the case of an intentional tort claim (as opposed to a contract dispute), none of which we believe are applicable in the case of the deposit agreement or the ADSs. No condition, stipulation or provision of the deposit agreement or ADSs serves as a waiver by any holder or beneficial owner of ADSs or by us or the depositary of compliance with any provision of the federal securities laws. If you or any other holder or beneficial owner of ADSs brings a claim against us or the depositary in connection with such matters, you or such other holder or beneficial owner may not be entitled to a jury trial with respect to such claims, which may have the effect of limiting and discouraging lawsuits against us and/or the depositary. If a lawsuit is brought against us and/or the depositary under the deposit agreement, it may be heard only by a judge or justice of the applicable trial court, which would be conducted according to different civil procedures and may result in different outcomes than a trial by jury would have had, including results that could be less favorable to the plaintiff(s) in any such action, depending on, among other things, the nature of the claims, the judge or justice hearing such claims, and the venue of the hearing.
Except in limited circumstances, the depositary for our ADSs will give us a discretionary proxy to vote our underlying Class A ordinary shares represented by your ADSs if you do not instruct the depositary how to vote such shares, which could adversely affect your interests.
Under the deposit agreement for our ADSs, the depositary will give us (or our nominee) a discretionary proxy to vote our Class A ordinary shares underlying your ADSs at shareholders’ meetings if you do not give voting instructions to the depositary as to how to vote the Class A ordinary shares underlying your ADSs at any particular shareholders’ meeting, unless:
•
we have failed to timely provide the depositary with our notice of meeting and related voting materials;
•
we have instructed the depositary that we do not wish a discretionary proxy to be given;
•
we have informed the depositary that there is substantial opposition as to a matter to be voted on at the meeting;
•
a matter to be voted on at the meeting may have a material adverse impact on shareholders; or
•
voting at the meeting is made on a show of hands.
The effect of this discretionary proxy is that, if you fail to give voting instructions to the depositary as to how to vote the Class A ordinary shares underlying your ADSs at any particular shareholders’ meeting, you cannot prevent our underlying Class A ordinary shares represented by your ADSs from being voted at that meeting, absent the situations described above, and it may make it more difficult for shareholders to influence our management. Holders of our ordinary shares are not subject to this discretionary proxy.
Your rights to pursue claims against the depositary as a holder of ADSs are limited by the terms of the deposit agreement and the deposit agreement may be amended or terminated without your consent.
Under the deposit agreement, any action or proceeding against or involving the depositary, arising out of or based upon the deposit agreement or the transactions contemplated thereby or by virtue of owning the ADSs may only be instituted by you in a state or federal court in the City of New York, and you, as a holder of our ADSs, will have irrevocably waived any objection which you may have to the laying of venue of any such proceeding, and irrevocably submitted to the exclusive jurisdiction of such courts in any such action or proceeding instituted by any person. Also, we may amend or terminate the deposit agreement without your consent. If you continue to hold your ADSs after an amendment to the deposit agreement, you agree to be bound by the deposit agreement as amended. See “Item 12. Description of Securities other than Equity Securities—D. American Depositary Shares.”
Your right to participate in any future rights offerings may be limited, which may cause dilution to your holdings.
We may from time to time distribute rights to our shareholders, including rights to acquire our securities. However, we cannot make such rights available to you in the United States unless we register both the rights and the securities to which the rights relate under the Securities Act or an exemption from the registration requirements is available. Under the deposit agreement, the depositary will not make rights available to you unless both the rights and the underlying securities to be distributed to ADS holders are either registered under the Securities Act or exempt from registration under the Securities Act. We are under no obligation to file a registration statement with respect to any such rights or securities or to endeavor to cause such a registration statement to be declared effective and we may not be able to establish a necessary exemption from registration under the Securities Act. Accordingly, you may be unable to participate in our rights offerings in the future and may experience dilution in your holdings.
You may not receive dividends or other distributions on our Class A ordinary shares and you may not receive any value for them if it is illegal or impractical to make them available to you.
The depositary of our ADSs has agreed to pay to you the cash dividends or other distributions it or the custodian receives on our Class A ordinary shares or other deposited securities underlying our ADSs, after deducting its fees and expenses. You will receive these distributions in proportion to the number of Class A ordinary shares your ADSs represent. However, the depositary is not responsible if it decides that it is unlawful or impractical to make a distribution available to any holders of ADSs. For example, it would be unlawful to make a distribution to a holder of ADSs if it consists of securities that require registration under the Securities Act but that are not properly registered or distributed under an applicable exemption from registration. The depositary may also determine that it is not feasible to distribute certain property through the mail. Additionally, the value of certain distributions may be less than the cost of mailing them. In these cases, the depositary may determine not to distribute such property. We have no obligation to register under U.S. securities laws any ADSs, ordinary shares, rights or other securities received through such distributions. We also have no obligation to take any other action to permit the distribution of ADSs, ordinary shares, rights or anything else to holders of ADSs. This means that you may not receive distributions we make on our Class A ordinary shares or any value for them if it is illegal or impractical for us to make them available to you. These restrictions may cause a material decline in the value of our ADSs.
You may be subject to limitations on transfer of your ADSs.
Your ADSs are transferable on the books of the depositary. However, the depositary may close its transfer books at any time or from time to time when it deems expedient in connection with the performance of its duties.
In addition, the depositary may refuse to deliver, transfer or register transfers of ADSs generally when our books or the books of the depositary are closed, or at any time if we or the depositary deems it advisable to do so because of any requirement of law or of any government or governmental body, or under any provision of the deposit agreement, or for any other reason.
Certain judgments obtained against us by our shareholders may not be enforceable.
We are an exempted company limited by shares incorporated under the laws of the Cayman Islands. We conduct substantially all of our operations in China and substantially all of our assets are located in China. In addition, a majority of our directors and executive officers reside within China, and most of the assets of these persons are located within China. None of our directors and executive officers resides in Hong Kong, and their assets are primarily located outside Hong Kong. As a result, it may be difficult or impossible for you to effect service of process within the United States upon these individuals, or to bring an action against us or against these individuals in the United States in the event that you believe your rights have been infringed under the U.S. federal securities laws or otherwise. Even if you are successful in bringing an action of this kind, the laws of the Cayman Islands and of the PRC may render you unable to enforce a judgment against our assets or the assets of our directors and officers.
There is no statutory enforcement in the Cayman Islands of judgments obtained in the federal or state courts of the United States (and the Cayman Islands are not a party to any treaties for the reciprocal enforcement or recognition of such judgments), however, the courts of the Cayman Islands will, at common law, recognize and enforce a foreign money judgment of a foreign court of competent jurisdiction without any re-examination of the merits of the underlying dispute based on the principle that a judgment of a competent foreign court imposes upon the judgment debtor an obligation to pay the liquidated sum for which such judgment has been given, provided such judgment (a) is given by a foreign court of competent jurisdiction, (b) imposes on the judgment debtor a liability to pay a liquidated sum for which the judgment has been given, (c) is final and conclusive, (d) is not in respect of taxes, a fine or a penalty, (e) is not inconsistent with a Cayman Islands judgment in respect of the same matter, and (f) is not impeachable on the grounds of fraud and was not obtained in a manner and is not of a kind the enforcement of which is contrary to natural justice or the public policy of the Cayman Islands. However, the Cayman Islands courts are unlikely to enforce a judgment obtained from the U.S. courts under civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities law if such judgment is determined by the courts of the Cayman Islands to give rise to obligations to make payments that are penal or punitive in nature.
Because such a determination has not yet been made by a court of the Cayman Islands, it is uncertain whether such civil liability judgments from U.S. courts would be enforceable in the Cayman Islands. A Cayman Islands court may stay enforcement proceedings if concurrent proceedings are being brought elsewhere.
The recognition and enforcement of foreign judgments are provided for under the PRC Civil Procedures Law. PRC courts may recognize and enforce foreign judgments in accordance with the requirements of the PRC Civil Procedures Law based either on treaties between China and the country where the judgment is made or on principles of reciprocity between jurisdictions. China does not have any treaties or other forms of reciprocity with the United States that provide for the reciprocal recognition and enforcement of foreign judgments. In addition, according to the PRC Civil Procedures Law, the PRC courts will not enforce a foreign judgment against us or our director and officers if they decide that the judgment violates the basic principles of PRC laws or national sovereignty, security or public interest. As a result, it is uncertain whether and on what basis a PRC court would enforce a judgment rendered by a court in the United States.
In addition, judgment of United States courts will not be directly enforced in Hong Kong. There are currently no treaties or other arrangements providing for reciprocal enforcement of foreign judgments between Hong Kong and the United States. There is uncertainty as to whether the courts of Hong Kong would (i) recognize or enforce judgments of United States courts obtained against us or our directors or officers predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the securities laws of the United States or any state in the United States or (ii) entertain original actions brought in Hong Kong against us or our directors or officers predicated upon the securities laws of the United States or any state in the United States. A judgment of a court in the United States predicated upon U.S. federal or state securities laws may be enforced in Hong Kong at common law by bringing an action in a Hong Kong court on that judgment for the amount due thereunder, and then seeking summary judgment on the strength of the foreign judgment, provided that the foreign judgment, among other things, is (i) for a debt or a definite sum of money (not being taxes or similar charges to a foreign government taxing authority or a fine or other penalty) and (ii) final and conclusive on the merits of the claim, but not otherwise. Such a judgment may not, in any event, be so enforced in Hong Kong if (a) it was obtained by fraud; (b) the proceedings in which the judgment was obtained were opposed to natural justice; (c) its enforcement or recognition would be contrary to the public policy of Hong Kong; (d) the court of the United States was not jurisdictionally competent; or (e) the judgment was in conflict with a prior Hong Kong judgment. Hong Kong has no arrangement for the reciprocal enforcement of judgments with the United States. As a result, there is uncertainty as to the enforceability in Hong Kong, in original actions or in actions for enforcement, of judgments of United States courts of civil liabilities predicated solely upon the federal securities laws of the United States or the securities laws of any State or territory within the United States.
You may face difficulties in protecting your interests, and your ability to protect your rights through U.S. courts may be limited, because we are incorporated under Cayman Islands law and we conduct the majority of our operations in China and all of our directors and officers reside outside the United States.
We are an exempted company incorporated under the laws of the Cayman Islands with limited liability. Our corporate affairs are governed by our memorandum and articles of association, as amended from time to time, the Companies Act (As Revised) of Cayman Islands and the common law of Cayman Islands. The rights of shareholders to take action against the directors, actions by minority shareholders and the fiduciary duties of our directors owed to us under Cayman Islands law are to a large extent governed by the common law of Cayman Islands. The common law of Cayman Islands is derived in part from comparatively limited judicial precedent in Cayman Islands as well as from the common law of England, the decisions of whose courts are of persuasive authority, but are not binding, on a court in Cayman Islands. The rights of our shareholders and the fiduciary duties of our directors under Cayman Islands law are not as clearly established as they would be under statutes or judicial precedent in some jurisdictions in the United States. In particular, Cayman Islands have a less developed body of securities laws than the United States. Some U.S. states, such as Delaware, have more fully developed and judicially interpreted bodies of corporate law than Cayman Islands. In addition, Cayman Islands companies may not have standing to initiate a shareholder derivative action in a federal court of the United States.
Shareholders of Cayman Islands exempted companies like us have no general rights under Cayman Islands law to inspect corporate records or to obtain copies of register of members of these companies (save for our memorandum and articles of association, special resolutions passed by our shareholders and our register of mortgages and charges). Under Cayman Islands law, the names of current directors can be obtained from a search conducted at the Registrar of Companies in the Cayman Islands. Our directors have discretion under our amended and restated memorandum and articles of association to determine whether or not, and under what conditions, our corporate records may be inspected by our shareholders, but are not obliged to make them available to our shareholders. This may make it more difficult for you to obtain the information needed to establish any facts necessary for a shareholder resolution or to solicit proxies from other shareholders in connection with a proxy contest.
In addition, as a company primarily operating in China, there are significant legal and other obstacles for U.S. authorities to obtaining information needed for investigations or litigations. In China, there are significant legal and other obstacles to providing information needed for regulatory investigations or litigation initiated outside China.
Although the authorities in China may establish a regulatory cooperation mechanism with the securities regulatory authorities of another country or region to implement cross-border supervision and administration, such cooperation with the securities regulatory authorities in the United States or other jurisdictions may not be efficient in the absence of mutual and practical cooperation mechanism. Similar limitations apply to the pursuit of actions against individuals, including officers, directors and individual gatekeepers, who may have engaged in fraud or other wrongdoing. Moreover, local authorities often are constrained in their ability to assist U.S. authorities and overseas investors more generally. According to Article 177 of the PRC Securities Law which became effective in March 2020, no overseas securities regulator is allowed to directly conduct investigation or evidence collection activities within the territory of the PRC, and without the consent by the Chinese securities regulatory authorities and the other competent governmental agencies, no entity or individual may provide documents or materials related to securities business to any foreign party. Accordingly, without the consent of the competent PRC securities regulators and relevant authorities, no organization or individual may provide the documents and material relating to securities business activities to overseas parties. While detailed interpretation of or implementation rules under the article have yet to be promulgated, the inability for an overseas securities regulator to directly conduct investigations or evidence collection activities within China and the potential obstacles for information provision may further increase difficulties faced by you in protecting your interests.
Furthermore, according to Article 177 of the PRC Securities Law which became effective in March 2020, no overseas securities regulator is allowed to directly conduct investigations or evidence collection activities within the PRC territory.
As a result, our public shareholders and holders of our ADSs may have more difficulty in protecting their interests through actions against us, our management, our directors or our major shareholders and limited remedies than would shareholders of a corporation incorporated in a jurisdiction in the United States.
Our dual-class share structure will limit your ability to influence corporate matters and could discourage others from pursuing any change of control transactions that holders of our Class A ordinary shares and ADSs may view as beneficial.
We have a dual-class share structure such that our ordinary shares consist of Class A ordinary shares and Class B ordinary shares with disparate voting powers. In respect of all matters subject to a shareholders’ vote, each Class A ordinary share is entitled to one vote, and each Class B ordinary share is entitled to ten votes, voting together as one class. Each Class B ordinary share is convertible into one Class A ordinary share at any time by the holder thereof. Class A ordinary shares are not convertible into Class B ordinary shares under any circumstances. As of March 31, 2025, Mr. Dinggui Yan, the beneficial owner of our Class B ordinary shares, beneficially owned approximately 91.2% of the aggregate voting power of our company. As a result, Mr. Dinggui Yan will have considerable influence over matters such as electing directors and approving material mergers, acquisitions or other business combination transactions. Upon any direct or indirect sale, transfer, assignment or disposition of Class B ordinary share by a shareholder to any person or entity which is not an affiliate of such holder, or the direct or indirect transfer or assignment of the voting power attached to such number of Class B ordinary shares through voting proxy or otherwise to any person or entity which is not an affiliate of such holder, such Class B ordinary shares shall be automatically and immediately converted into the equivalent number of Class A ordinary shares. The concentrated control associated with our dual-class share structure will limit your ability to influence corporate matters and could also discourage others from pursuing any potential merger, takeover or other change of control transactions, which could have the effect of depriving the holders of our Class A ordinary shares and the ADSs of the opportunity to sell their shares at a premium over the prevailing market price.
The dual-class structure of our ordinary shares may adversely affect the trading market for our ADSs.
S&P Dow Jones and FTSE Russell have changed their eligibility criteria for inclusion of shares of public companies on certain indices, including the S&P 500, to exclude companies with multiple classes of shares and companies whose public shareholders hold no more than 5% of total voting power from being added to such indices. In addition, several shareholder advisory firms have announced their opposition to the use of multiple class structures. As a result, the dual class structure of our ordinary shares may prevent the inclusion of our ADSs representing Class A ordinary shares in such indices and may cause shareholder advisory firms to publish negative commentary about our corporate governance practices or otherwise seek to cause us to change our capital structure. Any such exclusion from indices could result in a less active trading market for our ADSs. Any actions or publications by shareholder advisory firms critical of our corporate governance practices or capital structure could also adversely affect the value of our ADSs.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or reports about our business, or if they adversely change their recommendations regarding our ADSs, the market price for our ADSs and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our ADSs will be influenced by research or reports that industry or securities analysts publish about our business. If one or more analysts who cover us downgrade our ADSs, the market price for our ADSs would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts cease to cover us or fail to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause the market price or trading volume for our ADSs to decline.
Our memorandum and articles of association contain anti-takeover provisions that could discourage a third party from acquiring us and adversely affect the rights of holders of our ordinary shares and ADSs.
Our memorandum and articles of association contain certain provisions that could limit the ability of others to acquire control of our company, including a provision that grants authority to our board of directors to establish and issue from time to time one or more series of preferred shares without action by our shareholders and to determine, with respect to any series of preferred shares, the terms and rights of that series. These provisions could have the effect of depriving our shareholders and ADS holders of the opportunity to sell their shares or ADSs at a premium over the prevailing market price by discouraging third parties from seeking to obtain control of our company in a tender offer or similar transactions.
Certain existing shareholders have substantial influence over our company and their interests may not be aligned with the interests of our other shareholders.
As of March 31, 2025, Mr. Dinggui Yan, our founder, director and chief executive officer, beneficially owned approximately 91.2% of the total voting power of our Company. As a result, he has substantial influence over our business, including significant corporate actions such as mergers, consolidations, sales of all or substantially all of our assets, election of directors and other significant corporate actions.
Mr. Yan may take actions that are not in the best interest of us or our other shareholders. This concentration of ownership may discourage, delay or prevent a change in control of our company, which could deprive our shareholders of an opportunity to receive a premium for their shares as part of a sale of our company and may reduce the price of the ADSs. These actions may be taken even if they are opposed by our other shareholders. In addition, the significant concentration of share ownership may adversely affect the trading price of the ADSs due to investors’ perception that conflicts of interest may exist or arise. In addition, this concentrated control will limit your ability to influence corporate matters and could also discourage others from pursuing any potential merger, takeover or other change of control transactions, which could have the effect of depriving the holders of our ordinary shares and our ADSs of the opportunity to sell their shares at a premium over the prevailing market price. For more information regarding our principal shareholders and their affiliated entities, see “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—E. Share Ownership.”
We have granted, and may continue to grant, share incentive awards, which may result in increased share-based compensation expenses.
Jiayin Technology first adopted our 2016 Share Incentive Plan in September 2016, which allowed Jiayin Technology to grant share-based compensation awards to our founders, employees and officers to incentivize their performance and align their interests with ours. We account for compensation costs for all share options using a fair-value based method and recognize expenses in our consolidated statements of comprehensive income in accordance with U.S. GAAP. In February 2019, we adopted a new share incentive plan, or the 2019 Share Incentive Plan, which became effective after the completion of our initial public offering in May 2019. All outstanding options granted under the 2016 Share Incentive Plan have been cancelled or replaced with options granted under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan. As of December 31, 2024, we had granted options to purchase an aggregate of 73,938,000 Class A ordinary shares (excluding options that were forfeited, cancelled, or exercised after the relevant grant date) and restricted share units (“RSUs”) to receive an aggregate of 21,840,000 Class A ordinary shares (excluding RSUs that were forfeited, cancelled, or vested after the relevant grant date), pursuant to the 2019 Share Incentive Plan. See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—B. Compensation—Share Incentive Plans.”
We believe the granting of share incentive awards is of significant importance to our ability to attract and retain employees, and we will continue to grant share incentive awards to employees in the future. As a result, our expenses associated with share-based compensation may increase, which may have an adverse effect on our results of operations.
We are a foreign private issuer within the meaning of the rules under the Exchange Act, and as such we are exempt from certain provisions applicable to U.S. domestic public companies.
Because we qualify as a foreign private issuer under the Exchange Act, we are exempt from certain provisions of the securities rules and regulations in the United States that are applicable to U.S. domestic issuers, including:
•
the rules under the Exchange Act requiring the filing with the SEC of quarterly reports on Form 10-Q or current reports on Form 8-K;
•
the sections of the Exchange Act regulating the solicitation of proxies, consents, or authorizations in respect of a security registered under the Exchange Act; the sections of the Exchange Act requiring insiders to file public reports of their stock ownership and trading activities and liability for insiders who profit from trades made in a short period of time; and
•
the selective disclosure rules by issuers of material nonpublic information under Regulation FD.
We will be required to file an annual report on Form 20-F within four months of the end of each fiscal year. In addition, we intend to publish our results on a quarterly basis as press releases, distributed pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Nasdaq. Press releases relating to financial results and material events will also be furnished to the SEC on Form 6-K. However, the information we are required to file with or furnish to the SEC will be less extensive and less timely compared to that required to be filed with the SEC by U.S. domestic issuers. As a result, you may not be offered the same protections or information that would be made available to you if you were investing in a U.S. domestic issuer.
As an exempted company incorporated in the Cayman Islands, we are permitted to adopt certain home country practices in relation to corporate governance matters that differ significantly from the Nasdaq corporate governance listing standards; these practices may afford less protection to shareholders than they would enjoy if we complied fully with the Nasdaq Stock Market Rules. We currently follow and intent to continue to follow our home country practice in lieu of certain requirements of the Rule 5600 Series of the Nasdaq Stock Market Rules, including:
▪
have a majority of the board be independent (although all of the members of the audit committee must be independent under the Exchange Act);
▪
have an audit committee of at least three independent directors;
▪
have a nominating and corporate governance committee consisting entirely of independent directors; and
▪
hold an annual meeting of shareholders no later than one year after the end of our fiscal year.
We are a “controlled company” within the meaning of the Nasdaq Stock Market Rules and, as a result, can rely on exemptions from certain corporate governance requirements that provide protection to shareholders of other companies.
We are a “controlled company” as defined under the Nasdaq Stock Market Rules since Mr. Dinggui Yan beneficially owns more than 50% of our total voting power. For so long as we remain a controlled company under this definition, we are also permitted to elect to rely on certain exemptions from corporate governance rules. As a result, you will not have the same protection afforded to shareholders of companies that are subject to these corporate governance requirements.
If we are a passive foreign investment company, or PFIC, for United States federal income tax purposes, United States Holders of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares could be subject to adverse United States federal income tax consequences.
We will be a passive foreign investment company, or PFIC, for United States federal income tax purposes for any taxable year if, applying the applicable look-through rules, either (i) at least 75% of our gross income for such year is passive income or (ii) at least 50% of the value of our assets (generally determined based on an average of the quarterly values of the assets) during such year is attributable to assets that produce or are held for the production of passive income. Based on the market price of our ADSs, the value of our assets and the nature and composition of our income and assets, we do not believe that we were a PFIC for United States federal income tax purposes for our taxable year ended December 31, 2024. However, we believe that we were a PFIC for our taxable year ended December 31, 2023, although there can be no assurance in this regard. A separate determination must be made after the close of each taxable year as to whether we were a PFIC for that year. Moreover, the application of the PFIC rules is subject to uncertainty in several respects, and we cannot assure you that the United States Internal Revenue Service, or the IRS, will not take a contrary position to any determination we make. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that we will or will not be treated as a PFIC for any taxable year or that the IRS will not take a contrary position to any determination we make.
Changes in the value of our assets and/or the nature or composition of our income or assets may cause us to be or become a PFIC. The determination of whether we will be a PFIC for any taxable year may depend in part upon the value of our goodwill and other unbooked intangibles not reflected on our balance sheet (which may depend upon the market price of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares from time to time, which may fluctuate significantly) and also may be affected by how, and how quickly, we spend our liquid assets and the cash we generate from our operations and raise in any offering. In estimating the value of our assets and other unbooked intangibles, we have taken into account our market capitalization. Among other matters, if our market capitalization declines, we may be more likely to be a PFIC because our liquid assets and cash (which are for this purpose considered assets that produce passive income) may then represent a greater percentage of the value of our overall assets. Further, while we believe our classification methodology and valuation approach are reasonable, it is possible that the IRS may challenge our classification or valuation of our goodwill and other unbooked intangibles, which may result in our being a PFIC for one or more taxable years.
If we are a PFIC for any taxable year (as we believe we were for our taxable year ended December 31, 2023 (but not for our taxable years ended December 31, 2024)) during which a United States Holder (as defined in “Item 10. Additional Information––E. Taxation––United States Federal Income Tax Considerations”) hold our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares, certain adverse United States federal income tax consequences could apply to such United States Holder, including burdensome reporting requirements. United States Holders who have held our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares during 2023 are strongly encouraged to consult their tax advisors regarding the application of the PFIC rules and to refer to “Item 10. Additional Information— E. Taxation—Passive Foreign Investment Company—U.S. Holders During 2023.” Prospective investors who are United States Holders are strongly encouraged to consult their tax advisors regarding the potential application of the PFIC rules. See “Item 10. Additional Information— E. Taxation—Passive Foreign Investment Company”.
We incur significant costs as a result of being a public company.
As a U.S. public company, we incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we have not incurred as a private company. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as well as rules subsequently implemented by the SEC and the Nasdaq, impose various requirements on the corporate governance practices of public companies.
These rules and regulations have increased our legal and financial compliance costs and made some corporate activities more time-consuming and costly. For example, as a result of becoming a public company, we need to increase the number of independent directors and adopt policies regarding internal controls and disclosure controls and procedures. In addition, as we ceased to be an “emerging growth company” starting from the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024, we need to incur significant expenses and devote substantial management effort toward ensuring compliance with the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the other rules and regulations of the SEC that an emerging growth company is exempt from. Operating as a public company makes it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and we may be required to accept reduced policy limits and coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain the same or similar coverage. In addition, we have incurred and may continue to incur additional costs associated with our public company reporting requirements. It may also be more difficult for us to find qualified persons to serve on our board of directors or as executive officers. We are currently evaluating and monitoring developments with respect to these rules and regulations, and we cannot predict or estimate with any degree of certainty the amount of additional costs we may incur or the timing of such costs.
In the past, shareholders of a public company often brought securities class action suits against the company following periods of instability in the market price of that company’s securities. Our shareholders previously brought securities class action against us, which was subsequently settled in 2022. If we were involved in a class action suit again, it could divert a significant amount of our management’s attention and other resources from our business and operations, which could harm our results of operations and require us to incur significant expenses to defend the suit. Any such class action suit, whether or not successful, could harm our reputation and restrict our ability to raise capital in the future. In addition, if a claim is successfully made against us, we may be required to pay significant damages, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
ITEM 4. INFORMATION ON THE COMPANY
A.
History and Development of the Company
The origin of our business can be traced back to 2011. Mr. Dinggui Yan, our founder, director and chief executive officer, commenced a consumer finance platform in 2011 through several entities controlled by him in China. In June 2015, Mr. Dinggui Yan acquired Shanghai Jiayin Technology Co., Ltd., or Jiayin Technology, a shell company previously known as Furen Technology Limited and listed on the National Equities Exchange and Quotations Co., Ltd., or the NEEQ.
In September 2015, Shanghai Wuxingjia Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Wuxingjia”, formerly known as “Shanghai Niwodai Internet Services Co., Ltd.”) was established as a wholly-owned subsidiary of Jiayin Technology to develop our online consumer finance platform business. Mr. Dinggui Yan launched Shanghai Caiyin Asset Management Co., Ltd., or Shanghai Caiyin, in September 2015. We entered into a collaboration agreement with Shanghai Caiyin in 2015 to engage Shanghai Caiyin to provide post-origination loan management services and manage our individual investor assurance program for loans facilitated prior to April 28, 2018. In December 2015, Shanghai Caiyin also acquired the servicing rights and obligations of all outstanding loan contracts facilitated by Niwodai Finance, which operated our founder’s consumer finance platform at that time, as well as the obligation to continue to provide guarantee on those loans. Niwodai Finance subsequently ceased to operate the individual financing business. We launched our online individual financing platform in December 2015.
In December 2017, we incorporated Jiayin Group Inc. under the laws of the Cayman Islands as our offshore holding company, and in January 2018, we established a wholly-owned subsidiary in the British Virgin Islands, Jiayin Holdings Limited, and a wholly-owned subsidiary in Hong Kong, Geerong (HK), as our intermediate holding companies, to facilitate our initial public offering in the United States.
Jiayin Technology was delisted from NEEQ in April 2018.
In June 2018, we incorporated Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd., or Shanghai Kunjia, as a wholly-foreign owned entity in China. As a result of the restructuring in 2018, we hold equity interest in Shanghai Kunjia through our current offshore structure. At the same time, Shanghai Kunjia entered into a series of contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology and its shareholders, among which several agreements were terminated and simultaneously replaced by a series of contractual arrangements with substantially same terms in October 2018 for the purpose of registering pledges of equity interest in Jiayin Technology with the government authority. As a result of these contractual arrangements, or the Contractual Arrangements, we are the primary beneficiary of Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries for accounting purposes, and, therefore, have consolidated the financial results of Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries in our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
On May 10, 2019, our ADSs commenced trading on the NASDAQ under the symbol “JFIN”. We raised a total of approximately US$35.0 million in net proceeds from the initial public offering, after the underwriter’s full exercise of their option to purchase additional ADSs, and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions as well as other estimated offering expenses.
In September 2019, we disposed of Shanghai Caiyin, a consolidated affiliated entity. On September 16, 2019, Shanghai Wuxingjia a consolidated affiliated entity of our Company, entered into an agreement with Shenzhen Rongxinbao Non-Financial Guarantee Co., Ltd. (“Shenzhen Rongxinbao”), an independent third-party licensed financing guarantee company, and Shanghai Jiayin Finance Services Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Jiayin”), a company controlled by Mr. Dinggui Yan, the founder, director and chief executive officer of our Company, which wholly owns the equity interest of Shanghai Caiyin, pursuant to which Shanghai Jiayin agreed to transfer all of its equity interest in Shanghai Caiyin to Shenzhen Rongxinbao.
In September 2019, we conducted a business combination with Jiangxi Yunkaijianming, an innovative fintech-driven platform connecting financial institutions. Prior to the combination, Jiangxi Yunkaijianming and our Company were under the common control of Mr. Dinggui Yan, the founder, director and chief executive officer of our Company. After the combination, Jiangxi Yunkaijianming became a wholly-owned subsidiary of our Company. The combination is intended to support the growth of our institutional funding sources, as well as to strengthen our big data analytics and fintech R&D.
In September 2020, our wholly owned subsidiary Geerong (HK) acquired, from China Smartpay Group Holdings Limited (“China Smartpay”), a Hong Kong listed company, 35% equity interest in Keen Best, a wholly-owned subsidiary of China Smartpay, incorporated in the British Virgin Islands holding 100% equity interests in certain PRC entities engaging in microcredit business.
In November 2020, the outstanding loan balance of our and the VIE Group’s legacy P2P lending business was reduced to zero.
On April 1, 2021, our wholly consolidated VIE, Jiayin Technology, entered into a framework acquisition agreement with Shanghai Bweenet and its shareholders, pursuant to which, Jiayin Technology agreed, subject to certain conditions, to subscribe for certain equity interests of Shanghai Bweenet and acquire certain equity interests held by current shareholders of Shanghai Bweenet, for an aggregate consideration of RMB95.0 million. Following the completion of the transaction, Jiayin Technology owned 95% of the equity interests of Shanghai Bweenet.
On December 29, 2021, Jiayin Technology entered into a share acquisition framework agreement with Shenzhen Rongxinbao, an independent third-party licensed financing guarantee company, pursuant to which, Jiayin Technology agreed to transfer 95% equity interest of Shanghai Bweenet to Shenzhen Rongxinbao for an aggregate consideration of RMB93.3 million. Following the completion of the proposed transaction, Jiayin Technology no longer owned any equity interest in Shanghai Bweenet.
On December 29, 2021, Jiayin Finance entered into a sale agreement to transfer its 70% equity interest held in Shanghai Zhundian Enterprise Service Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Zhundian”) (formerly known as “Shanghai Limahui E-Commerce Co., Ltd”) to Shenzhen Rongxinbao, an independent third-party licensed financing guarantee company.
On January 28, 2022, Shanghai Niwodai Internet Services Co., Ltd. changed its corporate name to Shanghai Wuxingjia Information Technology Co., Ltd., which was further deregistered on April 11, 2024.
In August 2022, Hainan Yinke, was incorporated as a wholly-owned PRC subsidiary of Geerong Yunke. Hainan Yinke provides guarantee services to borrowers facilitated by us and the VIE Group.
In April 2023, we disposed our 100% equity interest in Fuzhou Zhuoqun Jieneng Information Technology Co., Ltd and its subsidiaries.
Our principal executive offices are located at 18th Floor, Building No. 1, Youyou Century Plaza, 428 South Yanggao Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai 200122, People’s Republic of China. Our telephone number at this address is +86 21-6190-6826. Our registered office in the Cayman Islands is located at the offices of Maples Corporate Services Limited at PO Box 309, Ugland House, Grand Cayman, KY1-1104, Cayman Islands. Our agent for service of process in the United States is Cogency Global Inc., located at 10 East 40th Street, 10th Floor, New York NY, 10016.
We and the VIE Group are one of the leading fintech platforms in China committed to facilitating effective, transparent, secure and fast connections between underserved individual borrowers and financial institutions. We and the VIE Group operate a highly secure and open platform with a comprehensive risk management system and a proprietary and effective risk assessment model which employs advanced big data analytics and sophisticated algorithms to accurately assess the risk profiles of potential borrowers. Our and the VIE Group’s online platform embraces significant opportunities presented by a financial system that leaves many creditworthy individuals underserved. We and the VIE Group provide borrowers with fast and convenient access to credit at affordable and competitive rates.
We and the VIE Group strategically focus on facilitating consumer loans primarily with a term of no more than 12 months, as we and the VIE Group believe such loan facilitation services are best positioned to generate attractive returns for our and the VIE Group’s funding partners, and at the same time, capture the financing needs of qualified borrowers. With a highly scalable capital-light business model, we and the VIE Group have been able to grow our and the VIE Group’s platform and reinforce our and the VIE Group’s strengths through network effects.
Our and the VIE Group’s borrowers are typically creditworthy individuals with stable salary income and/or credit history but underserved by traditional financial institutions. We and the VIE Group primarily utilize diverse online borrower acquisition channels including online advertising channels such as websites, search engines, app stores, information feeds as well as online partnerships with online traffic marketplaces which have access to quality borrowers. Our and the VIE Group’s online average borrower acquisition cost per new borrower was RMB433.4 (US$59.4) in 2024, representing 5.1% of the average loan principal borrowed by our and the VIE Group’s borrowers in 2024.
We and the VIE Group operate a highly secure and open platform with a proprietary and effective risk assessment model and a comprehensive risk management system. We and the VIE Group build our and the VIE Group’s risk assessment model based on our and the VIE Group’s first-hand and proprietary user and transaction data generated from our and the VIE Group’s loan process as well as multiple layers of background and behavioral data from third-party sources. Our and the VIE Group’s model employs advanced big data analytics and sophisticated algorithms to accurately assess the risk profiles of potential borrowers. We and the VIE Group have also established reliable systematic risk management procedures. To supplement our and the VIE Group’s risk management efforts, we and the VIE Group also selectively collaborate with expert consultants with strong credit assessment capabilities to help us further screen and re-assess the creditworthiness of applicants and identify creditworthy potential borrowers based on desensitized user data.
The loans that we and the VIE Group facilitate are funded by institutional funding partners, including commercial banks, trusts, consumer finance companies and microcredit companies. In 2024, we and the VIE Group facilitated an aggregate loan volume of RMB100.8 billion (US$13.8 billion), funded by 48 institutional funding partners. We and the VIE Group generate a substantial majority of our and the VIE Group’s total revenues from services we and the VIE Group provided to institutional funding partners and cooperated financing guarantee companies. As a leading technology platform, we and the VIE Group do not use our and the VIE Group’s own capital to invest in loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform in Mainland China.
Our and the VIE Group’s Users
Borrowers
We and the VIE Group target the large and growing number of creditworthy individual borrowers in China who are underserved by traditional financial institutions and receptive to online finance solutions. Our and the VIE Group’s borrowers typically belong to the young urban working class with stable salary and/or credit history.
From the launch of our and the VIE Group’s business through December 31, 2024, we and the VIE Group had successfully facilitated loan transactions for over 17.3 million borrowers. The number of our and the VIE Group’s borrowers grew by 13.2 times from approximately 0.2 million in 2016 to approximately 2.8 million in 2024. We and the VIE Group strategically target the young generation and cultivate their loyalty on our and the VIE Group’s platform, aiming to capture the vast growth opportunities as our and the VIE Group’s borrowers enter into different stages of their lives and qualify for higher credit limits. In 2024, 44.7% of our and the VIE Group’s borrowers were between 20 and 35 years of age.
Institutional Funding Partners
The loans that we and the VIE Group facilitate are funded by institutional funding partners, including commercial banks, trusts, consumer finance companies and microcredit companies.
In 2024, we and the VIE Group had 48 institutional funding partners. We and the VIE Group expect these institutional funding partners to provide stable funding to borrowers on our and the VIE Group’s platform, which will allow us to increase our and the VIE Group’s loan facilitation volume and generate more revenue. We and the VIE Group will further develop our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with institutional funding partners in 2025.
Our and the VIE Group’s Services
Loan Facilitation Services Offered to Borrowers
We and the VIE Group facilitate primarily standard loan facilitation services online, which are all unsecured consumer loans to our and the VIE Group’s borrowers. All of the loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform feature fixed interest rates. To provide a transparent platform, interest rates, service fees and other charges are all clearly disclosed to borrowers upfront. We and the VIE Group strategically design our and the VIE Group’ loan facilitation services to target borrowers with different types of available credentials and therefore different credit limits varying from RMB500 to RMB150,000.
We and the VIE Group believe that our and the VIE Group’s dedication and devotion to superior user service is a significant contributor to our and the VIE Group’s growth. To better serve our and the VIE Group’s borrowers, we and the VIE Group adopt user-oriented business practices, including offering user service hotlines and online user service support on our and the VIE Group’s mobile apps and WeChat account. We and the VIE Group also offer clear and concise guidelines on our and the VIE Group’s website and within our and the VIE Group’s app to guide borrowers throughout the transaction process. In addition, we and the VIE Group provide an online discussion forum, where our and the VIE Group’s current and potential borrowers can communicate with each other and our and the VIE Group’s user service agents. Finally, our and the VIE Group’s user service team frequently reaches out to our and the VIE Group’s users to seek their feedback. We and the VIE Group maintain a user complaint feedback channel to improve our and the VIE Group’s products and services.
Services Offered to Institutional Funding Partners and Licensed Financing Guarantee Companies
We and the VIE Group introduce borrowers to institutional funding partners, including commercial banks, trusts, consumer finance companies and microcredit companies, and provide preliminary risk assessment services as well as other services to them. The service arrangement between our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners and us varies depending on the type of institutional funding partners. For institutional funding partners with a license to extend loans, such as banks, online micro-credit companies, they typically extend loans with their own funds directly to the borrowers introduced by us. In 2024, we and the VIE Group facilitated an aggregate loan volume of RMB100.8 billion (US$13.8 billion), funded by 48 institutional funding partners.
We and the VIE Group also provide guarantee services through our and VIE Group’s licensed financing guarantee subsidiaries or through cooperation with third-party licensed financing guarantee companies. Under the guarantee services through our and VIE Group’s licensed financing guarantee subsidiaries, such subsidiaries are obligated to place deposits directly to institutional funding partners with an agreed percentage of outstanding loan balance subject to guarantee. We and the VIE Group record deposits to funding banks under restricted cash, and deposits to institutional funding partners other than funding banks under prepaid expenses and other current assets, net on the consolidated balance sheets, respectively. Under the cooperation with the third-party licensed financing guarantee companies, such companies initially reimburse the loan principal and interest to the institutional funding partners upon borrower’s default. Although we and the VIE Group do not have direct contractual obligation to the institutional funding partners for defaulted principal and interest, we and the VIE Group provide back-to-back guarantee to the third-party licensed financing guarantee companies. As of December 31, 2023 and 2024, the maximum potential future payments, including all outstanding principal and interest for which we and the VIE Group provides primary guarantee, were RMB13.7 billion and RMB2.8 billion (US$0.4 billion), respectively. For certain off-balance sheet loans facilitated between borrowers and institutional funding partners, we and the VIE Group may provide commitment letters to the institutional funding partners or the third-party licensed financing guarantee companies to cover any residual obligation of the third-party licensed financing guarantee companies. As of December 31, 2023 and 2024, the outstanding loan balance for which we and the VIE Group provide commitment letter was RMB20.9 billion and RMB29.2 billion (US$4.0 billion), respectively.
Our and the VIE Group’s Platform and Transaction Processes
We and the VIE Group provide a streamlined and smooth user experience for borrowers. The process on our and the VIE Group’s mobile apps and website is designed to be simple, seamless and efficient while our and the VIE Group’s platform leverages sophisticated, proprietary technologies to make it possible.
Transaction Process for Institutional Funding Partners
Our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners provide us with pre-determined criteria for borrowers and we and the VIE Group will use our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment model to assess the applicants in our and the VIE Group’s platform and select qualified applicants for the institutional funding partners for further approval. Institutional funding partners will assess the applicants through their own credit assessment process and once they approve the loans, our and the VIE Group’s system will generate a multilateral loan agreement among the borrower, the institutional funding partner, guarantor and us, which will become effective immediately. We and the VIE Group will then instruct the institutional funding partner to transfer the funding to the borrower’s account directly and we and the VIE Group are also not involved in the repayment of principal and interest between borrowers and institutional funding partners.
The following diagram illustrates the typical loan facilitation process flow and cash flow.

Transaction Process for Borrowers
Application
An applicant can submit a loan application after he or she has registered a user account using a valid mobile phone number. First-time applicants are required to present their PRC identity cards to us via their phone camera or webcam for identity verification. The images of their identity cards will be automatically captured and recognized by our and the VIE Group’s authentication module and authenticated against personal identity data in the database of the Ministry of Public Security of China. In addition, based on the instructions within our and the VIE Group’s apps or on our and the VIE Group’s website, applicants are also required to do specific poses facing the front camera to complete automatic biometric recognition. Our and the VIE Group’s system authenticates the face recognition result against the database of the Ministry of Public Security of China to detect if it matches the identity card provided by the applicant.
In addition to the identity card, applicants are required to provide basic personal information, including educational level, marital status, occupation, address and bank account information for our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment. Applicants also authorize us to collect data from third parties for purposes of credit assessment.
If the applicants have previously applied for loans through our and the VIE Group’s platform, they do not need to go through the procedures again, but may supplement or update their personal information if there are any changes.
Credit Assessment and Approval
Our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment model automatically computes a credit score for the applicant upon receipt of his or her credit information. If the applicants have previously applied for loans on our and the VIE Group’s platform, their credit scores may be adjusted upwards or downwards based on their performance of repayment obligations and updated personal information. Please see “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—Credit Assessment and Risk Management System” for a detailed description of our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment and risk management system. For funds provided by institutional funding partners, we and the VIE Group use a variety of technological tools to pre-screen the applicants and qualified applicants still need approvals from the institutional funding partners.
Funding
For funds provided by institutional funding partners, upon confirmation of the loan amount by the borrower and credit approval from the institutional funding partners, our and the VIE Group’s system will generate a multilateral loan agreement among the borrower, the institutional funding partner, guarantor and us, which will become effective immediately. We and the VIE Group will then instruct the institutional funding partner to transfer the funding to the borrower’s account directly.
Credit Assessment and Risk Management System
We and the VIE Group operate a highly secure and open platform with proprietary and effective credit assessment model and comprehensive risk management system. Leveraging advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence and big data analytics, we and the VIE Group continuously refine, test, and optimize our and the VIE Group’s model as our and the VIE Group’s platform continues to accumulate and collect more credit data in our and the VIE Group’s operations.
Our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment model and risk management system have undergone significant evolution. We and the VIE Group have been building an online credit assessment model since the launch of our and the VIE Group’s online platform in December 2015. We and the VIE Group no longer offer offline loan products since February 2018 and have fully automated data collection and risk management methodologies accordingly. With data accumulation and model optimization, we currently utilize a proprietary intelligent system known as Mingjian, which has achieved risk management throughout the life cycle of loans, involving the application stage, customer management stage, risk monitoring and early warning stage empowering multiple operating processes.
Data Collection and Pre-processing
The first step of our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment process is to collect data from the applicant for prescreening. The list below presents the typical types of data that we and the VIE Group use as input for our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment.
•
Identity authentication information;
•
Data directly provided by the applicant, such as age, geographical region and work-related information;
•
Behavioral data of applicants when applying for loans;
•
Historical credit data collected through our and the VIE Group’s platform;
•
Data regarding fraud cases.
We and the VIE Group feed the raw, unstructured data that we and the VIE Group collect into our and the VIE Group’s data pre-processing module to generate high quality structured data as input for our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment modules. Our and the VIE Group’s data pre-processing procedures involve data cleaning, data normalization and feature extraction.
Credit Assessment Model
Our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment system includes three main modules-authentication module, anti-fraud module and scorecard module. We and the VIE Group continuously optimize these models and strengthen our risk management capability.
The authentication module is a personal information authentication system that verifies and authenticates the identity of the applicant through the information provided by the applicant and third parties. With OCR and facial recognition technologies, the authentication module is able to automatically verify the identity card provided by applicants and their self-taken video against the Ministry of Public Security identity card database. We and the VIE Group also cross check the personal and credit information, against data from third parties to verify the authenticity of the data. Using the proprietary intelligent risk management system, we and the VIE Group have achieved the whole process life cycle risk control of pre-loan risk screening, risk monitoring and pre-warning in 2021.
We and the VIE Group have a large database of past fraud accounts information and sophisticated rules in detecting fraudulent behaviors. We and the VIE Group have been working closely with multiple partners in a joint effort to identify emerging fraudulent schemes, scams, trends, threats, and criminal organizations and have accumulated massive data relating to fraud. The database we and the VIE Group maintain enables us to fine-tune the rules we and the VIE Group set and enhance our and the VIE Group’s fraud detection capabilities. Utilizing graph mining technology, this module analyzes each applicant’s social proximity or relationships, to known fraudsters in our and the VIE Group’s database to determine the applicant’s likelihood of also being a fraudster. We and the VIE Group also continuously evolve this module to detect fraud clusters across device, environment, behavior and social dimensions. We and the VIE Group also maintain a blacklist after detecting any fraudulent borrowers. We and the VIE Group put the transaction link into the anti-fraud control, according to the customer risk level using different means of verification, in order to achieve the whole process risk management. We and the VIE Group have independently developed and built the knowledge graph platform known as Xingkong in 2021, on which multi-relational graphs are built based on the graph database technology and potential risks are identified. We and the VIE Group also incorporate the transaction process into the anti-fraud module as different means of verification are adopted according to the risk level of the borrowers. During the year of 2024, We and the VIE Group established an AI-powered comprehensive anti-fraud defense system through self-developed intelligent platforms, including the Qimingxing Intelligent Warning System and the Mingrui Document Verification System.
After a prospective borrower has passed the fraud detection module, we and the VIE Group initiate a credit review using our and the VIE Group’s proprietary scorecard module to generate a score for the prospective borrower, which ultimately drives the decision on whether to extend credit and the amount to be extended. Our and the VIE Group’s scorecard module utilizes historical credit data collected through our and the VIE Group's platform and data we and the VIE Group collected from the borrower, such as the credit card transaction record and repayment history. We and the VIE Group are authorized by the borrower to collect. We and the VIE Group generally assign the highest score for borrowers who demonstrate the most solid financial position and consistent repayment history. We and the VIE Group started using the scorecard module since 2016 and it evolved over time as our and the VIE Group’s product mix evolved and our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment capabilities improve. As part of our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment efforts, we and the VIE Group also adapt our and the VIE Group’s scorecard module to our and the VIE Group’s borrower base, which shifted from offline to online and has evolved as We and the VIE Group engage borrowers through different channels from time to time. Our and the VIE Group’s scorecard module analyzes a different set of data for each loan application compared to earlier versions of the module and we and the VIE Group continually test, validate and optimize it by changing the types of data it analyzes and the relative weights of various types of data. In particular, as the quality and availability of various data from third parties which is input in our and the VIE Group’s scorecard module changes over time, we and the VIE Group refine our and the VIE Group’s scorecard module accordingly. At the same time, deep learning algorithms, techniques and graphs are introduced to model and maximize the value of data mining to optimize access strategies and grant credit lines, and effectively extract high-quality customers. In 2021, based on the traditional scorecard module and original learning algorithm, we and the VIE Group have incorporated advanced learning algorithms, NLP technology and multi-relational graphs into the feature engineering and model construction to maximize the value of data mining, optimize access strategies and effectively identify creditworthy borrowers. Continuously refined by machine learning algorithms and the high volume of transaction data we and the VIE Group collect, especially proprietary credit repayment records, our and the VIE Group’s scorecard module currently analyzes a large number of variables for each loan application and enables us to better differentiate between creditworthy borrowers and lower quality borrowers. We and the VIE Group also enhanced the stability of our and the VIE Group’s scorecard module in view of increased amounts of loan applications we and the VIE Group receive. As our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment capabilities evolve, we and the VIE Group are increasingly capable of identifying creditworthy borrowers, some of which we and the VIE Group were unable to identify previously. We and the VIE Group also benefit from the growth of our and the VIE Group’s platform and the larger pool of borrower applicants our and the VIE Group’s platform attracts, among which we and the VIE Group are able to identify more creditworthy borrowers. As such, the credit scores generated by our and the VIE Group’s scorecard module are not directly comparable across different time periods. Currently, the credit scores of our and the VIE Group’s borrowers range from 0 to 100, while 100 represents the lowest credit risk associated with the borrower and 0 represents the highest. We and the VIE Group generally reject borrowers with a credit score lower than 0, who we and the VIE Group believe have low repayment willingness or capability.
Set forth below is a breakdown of loan facilitation volume by the range of the credit scores of our and the VIE Group’s borrowers as of the time of the loan facilitation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
Credit Risk Level |
|
(in RMB
millions) |
|
|
% |
|
|
(in RMB
millions) |
|
|
% |
|
|
(in RMB
millions) |
|
|
% |
|
60+ |
|
|
48,669 |
|
|
|
87.7 |
|
|
|
78,827 |
|
|
|
89.5 |
|
|
|
89,423 |
|
|
|
88.7 |
|
40-60 |
|
|
6,574 |
|
|
|
11.8 |
|
|
|
7,718 |
|
|
|
8.8 |
|
|
|
9,569 |
|
|
|
9.5 |
|
20-40 |
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
1,538 |
|
|
|
1.7 |
|
|
|
1,055 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
|
0-20 |
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
0.0 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
802 |
|
|
|
0.8 |
|
Total |
|
|
55,509 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
|
|
88,083 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
|
|
100,849 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
Risk Management Team
We and the VIE Group have a risk management committee, comprised of nine members, that meets regularly to examine the credit, liquidity and operational risks on our and the VIE Group’s platform. Our and the VIE Group’s risk management team is responsible for designing and implementing the risk management and credit assessment policies and processes, loan performance analysis, credit model validation and credit decisioning performance. Our and the VIE Group’s risk management team engages in various risk management activities, including reporting on performance trends, monitoring of loan concentrations and stability, performing economic stress tests on loans, randomly auditing loan decisions by our and the VIE Group’s credit assessment model and conducting peer benchmarking and external risk assessments.
Guarantee Arrangements
Starting from the fourth quarter of year 2022, we and the VIE Group provide guarantee services through our and the VIE Group’s own licensed financing guarantee subsidiaries or through cooperation with third-party licensed financing guarantee companies. Under guarantee services through our and the VIE Group’s licensed financing guarantee subsidiaries, such subsidiaries are obligated to place deposits directly to institutional funding partners with an agreed percentage of outstanding loan balance subject to guarantee. Starting from year 2024, a majority of the new guarantee services provided by us are through our own licensed financing guarantee subsidiary. Under the cooperation with the third-party licensed financing guarantee companies, such companies initially reimburse the loan principal and interest to the institutional funding partners upon borrower’s default. Although we and the VIE Group do not have direct contractual obligation to the institutional funding partners for defaulted principal and interest, we and the VIE Group provide back-to-back guarantee to the licensed financing guarantee companies. As agreed in the back-to-back guarantee contract, we and the VIE Group would compensate the third-party licensed financing guarantee companies for actual losses incurred by them on defaulted principal and interest. When the third-party licensed financing guarantee companies are required to place deposits to the institutional funding partners as part of the arrangement, we and the VIE Group will also be obligated to place back-to-back deposits to them of the same amount and with the same settlement terms. The deposit amount is typically set at an agreed percentage of outstanding loan balance subject to guarantee. In 2024, a subsidiary of us entered into a one-year agreement with an overseas third-party funding partner to guarantee its principal and interest income with a pre-agreed rate. The maximum potential future payments under such agreement is US$3 million. As of December 31, 2023 and 2024, the maximum potential future payments, including all outstanding principal and interest for which we and the VIE Group provide primary guarantee, were RMB13.7 billion and RMB2.8 billion (US$0.4 billion), respectively.
For certain off-balance sheet loans facilitated between borrowers and institutional funding partners, we and the VIE Group may provide commitment letters to the institutional funding partners or the licensed financing guarantee companies to cover any residual obligation of the third-party licensed financing guarantee companies. The fair value of guarantee liabilities of us and the VIE Group as a secondary guarantor was inconsequential and no compensation was accrued by us and the VIE Group during 2022 and 2023. During 2024, we and the VIE Group accrued guarantee liabilities of RMB3.1 million arising from secondary guarantee. The net risk exposure arising from the commitment letter provided by us and the VIE Group as of December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024 was inconsequential.
Overseas Development
Leveraging on the proprietary technology and operation experience accumulated in China, we are exploring business opportunities in other developing countries with a significant size of low-to mid- income population. We believe that these low-to mid- income populations is currently underserved by local financial systems similar to the financial market situation in China and our credit assessment and risk management system can be readily deployed in these countries. In 2024, we and the VIE Group disposed of the subsidiaries in Nigeria.
The technical expertise and operational experience we have accumulated in China continues to support the growth of our overseas business. With our proprietary credit assessment and risk management system, we aim to provide more accessible financial solutions to low-and-middle income groups in multiple developing countries.
In recent years, we increased our investments in Indonesia to explore more business opportunities in local markets.
We plan to further explore overseas markets, to expand our customer base. In the future, we plan to broaden our financing channels through partnerships with local banks and other financial institutions. With our risk management technologies and the localization capabilities, we will be able to deliver more accessible and convenient financial services to better serve our customers.
Our and the VIE Group’s Technology and IT Infrastructure
The success of our and the VIE Group’s business is dependent on our and the VIE Group’s strong technological capabilities that support us in delivering superior user experience, safeguarding information on our and the VIE Group’s platform, increasing operational efficiency and enabling innovations. Principal components of our and the VIE Group’s technology system include:
•
Big data analytics capabilities. Leveraging a massive borrower base, we and the VIE Group have been continuously improving our and the VIE Group’s data mining and user behavior analytics capabilities, which enable us to build a comprehensive credit profile for each borrower as the basis for our and the VIE Group’s quick and accurate credit decisions. Our and the VIE Group’s data mining and analytics capabilities also allow us to empower numerous aspects of our and the VIE Group’s operations, such as management of the loan lifecycle for borrowers, proprietary fraud detection, graph mining, risk management and financial modeling.
•
Artificial Intelligence technologies. We and the VIE Group put together a dedicated team focusing on internal Artificial Intelligence technologies development. Based on the comprehensive range of voice, image and video data collected through our and the VIE Group’s platform, we and the VIE Group have strengthened our and the VIE Group’s data-centric machine learning technologies. We and the VIE Group also achieved important milestones in the areas of human-computer interaction, OCR and facial recognition, which have been utilized in our and the VIE Group’s risk management system and enabled us to build up a secured and stable platform.
•
Highly automated process. Throughout the life cycle of the loan products facilitated by us and the VIE Group, we and the VIE Group maintain a highly automated management process to monitor the registration, application, verification, credit assessment, decision making, funding and collections. Our and the VIE Group’s user-friendly apps gives borrowers convenient access to our and the VIE Group’s product features and help them find the loan products that match their needs.
•
Data security. We and the VIE Group maintain an effective cyber security system to monitor and manage the traffic to our and the VIE Group’s platform on a real-time basis. Our and the VIE Group’s system is designed to automatically defect suspicious activities and an alert will be instantly sent to our and the VIE Group’s IT team. To minimize the risk of a cyber-attack, we and the VIE Group keep and constantly update an internal blacklist of malicious IP addresses. For our and the VIE Group’s daily operation, we and the VIE Group collect and store certain personal information, including sensitive information such as people’s ID card numbers and bank accounts information. We and the VIE Group retrieve such information only upon user’s consent and store all data in an encrypted form. We and the VIE Group also implement multiple layers of security to insulate our and the VIE Group’s databases from unauthorized access and use sophisticated security protocols for communication among applications.
•
Stability. We and the VIE Group utilize multiple data centers in different cities and maintain data redundancy through a real-time multi-layer data backup system to ensure the reliability of our and the VIE Group’s network. We and the VIE Group have implemented a disaster recovery program which enables us to react appropriately in an emergency and instantly start transferring our and the VIE Group’s data to a back-up data center if needed.
•
Scalability. With modular architecture, our and the VIE Group’s platforms can be easily expanded as data storage requirements and user visits increase. In addition, load balancing technology helps us improve distribution of workloads across multiple computing components, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing response time.
Intellectual Property
We and the VIE Group regard our patents, trademarks, domain names, copyrights, know-how, proprietary technologies and similar intellectual property as critical to our success, and we and the VIE Group rely on patents, trademarks, copyrights and trade secret law and confidentiality, invention assignment and non-compete agreements with our employees and others to protect our proprietary rights. We and the VIE Group have registered 3 patents and 186 trademarks in the PRC. We and the VIE Group are the registered holder of 29 domain names, including www.jiayintech.cn. We and the VIE Group also have 126 copyrights for our and the VIE Group’s proprietary techniques in connection with our and the VIE Group’s systems.
Competition
Online consumer finance market is an evolving industry in China. We and the VIE Group face competition from other online consumer finance platforms, online platforms that engage in online loan facilitation and traditional financial institutions. We and the VIE Group compete with other online consumer finance platforms directly for borrowers, institutional funding partners and online investors. In addition, we and the VIE Group compete with other online platforms that engage in online lending businesses for borrowers. We and the VIE Group also compete with traditional financial institutions, including credit card issuers, consumer finance business units in commercial banks and other consumer finance companies. Some of our and the VIE Group’s larger competitors have substantially broader products or service offerings and richer financial resources to support heavy spending on sales and marketing. We and the VIE Group believe that our and the VIE Group’s ability to compete effectively for funding partners and borrowers depends on many factors, including our and the VIE Group’s ability to attract and retain borrowers and institutional funding partners and borrower experience on our and the VIE Group’s platform, the effectiveness of our and the VIE Group’s risk management system, the returns and reliance offered to funding partners, our and the VIE Group’s marketing and selling efforts and the strength and reputation of our and the VIE Group’s brand.
In addition, as our and the VIE Group’s business continues to grow rapidly, we and the VIE Group face significant competition for talents, including management, engineers, product managers and risk management personnel. The success of our and the VIE Group’s growth strategy depends in part on our and the VIE Group’s ability to retain existing personnel and attract additional talents.
Seasonality
We and the VIE Group experience seasonality in our and the VIE Group’s business, which reflects the seasonal fluctuations in internet usage and consumer behavior patterns. For instance, during national holidays in China, particularly during Chinese New Year, we and the VIE Group typically observe reduced borrowing activity from individual borrowers. Additionally, our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners may be affected by liquidity seasonality in the banking system, notably in the first and fourth quarters. The seasonality our institutional funding partners experience may impact our and the VIE Group’s business and loan facilitation volume during those periods. However, the seasonal trends and patterns we and the VIE Group have experienced in the past may not necessarily apply to, or indicate, our future operating results.
Regulation
This section sets forth a summary of the most significant laws, regulations and rules that affect our and the VIE Group’s business activities in the PRC and our and the VIE Group’s shareholders’ rights to receive dividends and other distributions from us.
Regulations Relating to Online Consumer Finance Services
Due to the relatively brief history of the online consumer finance industry in China, the regulatory framework governing our and the VIE Group’s industry has not developed comprehensively. Even though few specific regulations on online consumer finance industry have been issued in the past few years, detailed guidance and interpretation has yet to be promulgated by the regulators.
Regulations Relating to Cooperation with Institutional Funding Partners
On July 18, 2015, the Guidelines on Promoting the Healthy Development of Online Finance Industry, or the Guidelines, were promulgated by ten PRC regulatory authorities, including the PBOC, the MIIT and the CBRC. Pursuant to the Guidelines, a company that provides online lending information intermediary services shall function clearly as an information intermediary and provide information services rather than provide credit enhancement services or engage in illegal fund-raising.
On December 1, 2017, the Office of the Leading Group for the Special Campaign against Internet Financial Risks and the Office of the Leading Group for the Special Campaign against Online Lending Risks jointly issued the Circular on Regulating and Rectifying of “Cash Loan” Services, or Circular 141. Circular 141 sets out the principles and general requirements for the conduct of “cash loan” business by banking financial institutions (for the purpose of Circular 141, including banks, trust companies and consumer financial companies). Circular 141 focuses on regulating the “cash loans” with features of no user scenario, specified uses of loan proceeds, specified customer base, or collateral, etc. Circular 141 sets forth several general principles with respect to the regulation of “cash loan” business, including: (i) no organization or individual may conduct the “cash loan” lending business without obtaining relevant approval; (ii) the aggregated borrowing costs of borrowers charged by institutions in the form of interest and various fees should be annualized and subject to the limit on interest rate of private lending provided by the judicial department; (iii) institutions engaged in cash, among others, loan business must follow the “know-your-customer” process and prudentially assess and determine the borrower’s suitability, credit limit and cooling-off period, etc.; and (iv) all institutions engaged in cash, among others, loan business must enhance their internal risk control and prudentially use the “data-driven” risk management models.
The Circular 141 also sets forth several requirements on banking financial institutions participating in “cash loan” business, including, among other things, (i) such banking financial institutions shall not extend loans jointly with any third-party institution which has not obtained approvals for the lending business, or fund such institution for the purpose of extending loans in any form; (ii) with respect to the loan business conducted in cooperation with third-party institutions, such banking financial institutions shall not outsource the core business (including the credit assessment and risk control), and shall not accept any credit enhancement service whether or not in a disguised form (including the commitment to taking default risks) provided by any third-party institutions with no guarantee qualification and (iii) such banking financial institutions must require and ensure that the third-party institutions shall not collect any interests or fees from the borrowers. Moreover, Circular 141 also sets forth certain specific requirements related to online small loan companies and banking financial institutions in cash loan business. Any violation of the Circular 141 may result in penalties, including but not limited to suspension of operation, orders to make rectification, condemnation, revocation of license, order to cease business operation, and criminal liabilities.
On July 12, 2020, the Interim Measures for the Administration of Online Lending by Commercial Banks came into effect, or the Commercial Banks Online Lending Measure, which formulates the regulation regime for online lending business conducted by commercial banks. For example, the Commercial Banks Online Lending Measures require that a commercial bank shall not grant an individual with a credit line more than RMB200,000 and the term of the personal credit loan extended under such credit shall not exceed one year in the case of repayment of the principal due in a lump sum. Meanwhile, reading of the loan contract by a borrower shall be mandatory in the loan application process and reasonable time limit shall be set therefor.
In addition, the Commercial Banks Online Lending Measures set several rules for commercial banks to collaborate with external institutions on online lending, including: (i) commercial banks shall conduct pre-admission assessments on cooperative external institutions and manage such external institutions by a name list; (ii) commercial banks shall not accept any credit enhancement services directly or in disguised form, from third parties without qualification to provide guarantee, credit insurance or guarantee insurance; (iii) commercial banks shall independently conduct the credit approval, contract execution and other core risk control business; (iv) the collaboration agreement between the commercial banks and the cooperative external institutions shall be executed in writing and specify the cooperation scope, data confidentiality, transitional arrangement for change or termination of the matters under cooperation, the commitment of the external institutions for cooperating with the commercial bank in accepting the inspection by the banking regulatory authorities, and the cooperative external institutions (except for an insurance company or an institution with guarantee qualification) shall not charge any interest or expense to the borrower in any form; and (v) the commercial banks shall fully disclose, in conspicuous place of relevant page, the information of the cooperative external institutions, the information of the cooperative product, as well as rights and responsibilities of the commercial bank and the cooperative external institutions.
The Commercial Banks Online Lending Measures set forth a transitional period of these measures, which is two years from the date on which the Commercial Banks Online Lending Measures is implemented. The business newly increased in the transitional period shall comply with the requirement therein, and a plan to rectify the online lending business within such transitional period shall be formulated and submitted to the banking regulatory authority within one month from the implementation date. The Commercial Banks Online Lending Measures shall also apply as reference to the online lending business conducted by consumer finance companies and auto finance companies (except for the above-mentioned requirements on the terms of personal credit loan).
On February 19, 2021, the CBIRC further issued the Notice of Further Regulating Online Loan Business of Commercial Banks, also known as Circular 24, which provides that the commercial banks shall independently carry out the risk management of online loans and are forbidden from outsourcing the material procedures of loan management. Circular 24 will also apply by analogy to branches of foreign banks, trusts, consumer finance companies and auto finance companies. Circular 24 also provides for the transition periods, and further requirements may be imposed by CBIRC and its local counterparts based on the provisions of Circular 24.
In February 2021, the CBIRC, the PBOC, the Ministry of Education, the Office of the Central Cyberspace Affairs Commission and the Ministry of Public Security jointly issued the Notice on Further Strengthening the Regulation and Management Work of Internet Consumer Loan for College Students, or the Notice on Internet Consumer Loan for College Students. The Notice on Internet Consumer Loan for College Students provides that the microcredit companies are prohibited to provide internet consumer loans to college students. In addition, it sets forth several requirements on the banking financial institutions participating in internet consumer loans for college students, including without limitation: (i) the banking financial institutions and its cooperative institution shall not conduct online precision marketing aimed at college students, and shall complete necessary filings and reports with relevant authorities before offline promotion in campus; (ii) the banking financial institutions shall strictly check credit qualifications and the identities of college students and their use of loans, conduct comprehensive credit assessment, and receive the written confirm from the second repayment sources (such as parents, guardians, or other administrator of the college students) that they agree such internet consumer loan provided to such college student and they will guarantee the repayment of such internet consumer loan; and (iii) all credit information of internet consumer loan for college students shall be submitted to the financial credit information database in a timely, complete and accurate manner, and college students who do not agree to submit such credit information shall not be extended the loan.
On December 31, 2021, the PBOC, the MIIT, the CAC, the CBIRC, the CSRC, the SAFE, and the State Intellectual Property Office jointly issued the Measures for the Management of Online Marketing of Financial Products (Draft for Comments), or the Draft Measures for Online Marketing, to further regulate Financial Institutions or their cooperation with third-party internet platform operators entrusted by them. Financial Institutions refer to institutions engaged in financial business approved by relevant financial department. Financial products refer to products and services designed, developed and sold by Financial Institutions, including but not limited to deposits, loans, asset management products, insurance, payments, precious metals, etc.
The Draft Measures for Online Marketing also requires that: (i) Financial Institutions shall undertake the responsibility if entrusted to third-party internet platform operators to carry out online marketing of financial products. The third-party Internet platform operators shall bear the relevant responsibility if not perform their fiduciary duties as agreed, and damage the rights and interests of financial consumers or cause other adverse effects; (ii) the third-party Internet platform operators shall not intervene or disguise their involvement in the sales of financial products business, including but not limited to interactive consultation with consumers on financial products, financial consumer suitability assessment, sales contract signing, fund transfer, etc. without the approval of the financial management, and shall not disguise their participation in the financial business revenue sharing by setting various fee mechanisms linked to loan size and interest scale; (iii) Financial Institutions using third-party Internet platforms for cyberspace business premises, should ensure business independence, technical security, data and personal information security. Third-party Internet platform operators should adhere to the information technology services propriety, shall not be disguised as financial business activities, shall not help the cooperation of financial institutions to circumvent regulation by technical means; (iv) Financial Institutions should sign written cooperation agreements with third-party Internet platform operators; (v) Financial Institutions shall continuously evaluate the compliance and security of third-party Internet platform operators and the performance of agreements, and promptly identify, evaluate and prevent risks resulting from default or operational failure of third-party Internet platform operators; (vi) Financial Institutions and third-party Internet platforms should take the necessary technical security measures to safeguard the confidentiality and integrity of data transmission and prevent other institutions and individuals from illegally decrypting, intercepting and storing relevant data; and (vii) Third-party Internet platform operators should obtain the appropriate financial business qualifications or financial information services business qualifications when using financial-related words in their website, mobile Internet applications, small programs, self-media. While the Draft Measures for Online Marketing had been released for consultation purpose, there is still uncertainty regarding the Draft Measures for Online Marketing as to its final content, its adoption timeline or effective date, its final interpretation and implementation, and other aspects.
On January 15, 2022, the CBIRC issued the Guidelines on Regulating the Management of Market-regulated Pricing of Banking Services, or the Guidelines on the Management of Market-regulated Pricing, which took effect on May 1, 2022. According to the Guidelines on the Management of Market-regulated Pricing, banks shall fully understand the service contents and price standards provided by online platforms and other institutional funding partners, agree in the cooperation agreement the requirements for the service prices disclosure, responsibilities and obligations for resolving disputes among three parties, prohibit institution partners from charging any fees from customers in the name of banks and terminate cooperating with any institution partners whose service charges do not match the quality in a timely manner.
In addition, on July 12, 2022, the CBIRC issued the Notice on Strengthening Management of Online Lending Business of Commercial Banks and Improving the Quality and Efficiency of Financial Services, which stipulates that (i) if commercial banks engage in online lending business through cooperating with other institutions to obtain customers, conduct payment and settlement services, they shall strengthen the management of core risk control and shall not reduce risk control standards due to business cooperation; (ii) if commercial banks cooperate with an institution providing personal information process services, they shall effectively and properly carry out security assessment on the cooperative institution, including but not limited to the compliance system for protection of personal information, supervision mechanism, information processing standards and safety and security measures; (iii) commercial banks shall regulate its cooperation in online lending business with third-party institutions, signing cooperation agreements and clarifying the rights and responsibilities of each party for co-financing, IT cooperation and other businesses by category and shall not mix other services in the loan agreement or the capital contribution agreement. Commercial banks shall regularly assess the comprehensive financing costs for the loans cooperating with other institutions and shall restrict or terminate the cooperation if the cooperative institutions or their related parties pool the loan funds in violation of PRC laws, set unfair and unreasonable conditions for cooperation, fail to provide the necessary information for loan management, charge service fees not matching the service quality, or violate other provisions on online lending; (vi) commercial banks shall strengthen the compliance management of the marketing and promotional activities of the cooperative institutions, and clearly agreeing on relevant prohibited behaviors in the cooperation agreement.
On April 3, 2025, the National Administration of Financial Regulation issued the Notice on Strengthening the Supervision of Online Lending Business and Promoting Financial Services, effective from October 1, 2025.
It mandates, among other things, the following key provisions: (i) bank headquarters shall maintain and publicly disclose on their official websites and mobile applications a whitelist of partnered online lending platforms; (iii) online lending platforms are prohibited from charging interest or other fees to borrowers; (iv) credit enhancement service providers are prohibited from charging service or consultation fees, as such practices are deemed to increase credit enhancement fees in a disguised form; and (v) banks and online lending platforms must fully disclose key information, including but not limited to lenders, annualized interest rates, credit enhancement providers and fees, annualized funding costs, post-default interest and costs, and must clearly state that no other fees will be charged to borrowers. These requirements also apply to consumer finance companies and trust companies engaged in online lending business.
As our institutional funding partners include commercial banks, consumer finance companies, and trust companies, they are required to evaluate and review us as mandated by the Commercial Banks Online Lending Measure, the Notice on Strengthening the Supervision of Online Lending Business and Promoting Financial Services and the subsequent requirements issued by the CBIRC. If any of our institutional funding partners identifies any inadequacies in our evaluation and review, they may terminate their cooperation with us, which could materially and adversely affect our business and operating results. Furthermore, as an intermediary between institutional funding partners and borrowers, we cannot assure you that all the institutional funding partners we cooperate with have been and will continue to be in strict compliance with the Commercial Banks Online Lending Measure or other requirements issued by the CBIRC.
Regulations on Loans
The Civil Code of PRC, which was promulgated by the National People's Congress in May 2020 and became effective in January 2021, requires that the interest rates charged under a loan agreement must not violate applicable provisions of the PRC laws and regulations. In the meantime, it also provides that the interest shall not be deducted from the proceeds of the loan in advance, and if the interest is deducted from the proceeds in advance, the loan shall be repaid and the interest shall be calculated based on the actual loan amount.
The Provisions of the Supreme People’s Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Law in the Trial of Private Lending Cases, or the Private Lending Judicial Interpretations, issued by the Supreme People’s Court, which came into effect on September 1, 2015, provided that agreements between lenders and borrowers on loans with interest rates below 24% per annum are valid and enforceable. As to the loans with interest rates per annum between 24% (exclusive) and 36% (inclusive), if the interest on the loans has already been paid to the lender, and so long as such payment has not damaged the interest of the state, the community and any third parties, the courts will turn down the borrower’s request to demand the return of the excess interest payment. If the annual interest rate of a private loan is higher than 36%, the agreement on the excess part of the interest is invalid, and if the borrower requests the lender to return the part of interest exceeding 36% of the annual interest that has been paid, the courts will support such requests. In addition, on August 4, 2017, the Supreme People’s Court issued the Several Opinions on Further Strengthening the Judicial Work in the Finance Sector, which provided that (i) if the total amount of interest, compounded interest, default interest and other fees charged by a lender under a loan contract substantially exceeds the actual loss of such lender, the request by the debtor under such loan contract to reduce or to adjust the part of the aforementioned fees exceeding the amount accrued at an annual rate of 24% will be upheld; and (ii) in the context of private lending disputes, if the online lending information intermediaries and lenders circumvent the statutory limit of the interest rate by charging intermediary fees, such fees shall be deemed invalid.
The Supreme People’s Court amended the Provisions of the Supreme People’s Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Law in the Trial of Private Lending Cases on August 20, 2020, and then again on January 1, 2021. Under these amendments, if the service fees or other fees that we and the VIE Group charge are deemed to be loan interest or fees related to loans (inclusive of any default rate and default penalty and any other fee), then in the event that the sum of the annualized interest that lenders charge and fees we and the VIE Group and our and the VIE Group’s business partners charge exceed four times the one-year Loan Prime Rate at the time of the establishment of the agreement, the borrower may refuse to pay the portion that exceeds the limit. In that case, PRC courts will not uphold our and the VIE Group’s request to demand the payment of fees that exceed the limit from the borrower. The aforementioned one-year Loan Prime Rate refers to the one-year Loan Prime Rate issued by the National Bank Interbank Funding Center. These new limits replace the upper limits on interest rates of 24% and 36% described in the Private Lending Judicial Interpretations. Moreover, if the lender and the borrower agree on both the overdue interest rate and the liquidated damages or other fees, the lender may choose to claim any or all of them, but the portion of the total exceeding the limit shall not be supported by the people’s court. The new limits apply to new first-instance cases of private lending disputes accepted by the people’s court after August 20, 2020. As to the cases in which the loan contract was established before August 20, 2020, if the lender requests that the court apply the old limits of 24% and 36% for calculating the loan interest accrued from the establishment of the loan contracts up to August 19, 2020, such request will be supported by the court, but the loan interest accrued from August 20, 2020 to the date of the loan repayment shall be calculated by applying the new limit of four times the one-year Loan Prime Rate at the time of the filing of the lawsuit.
On December 29, 2020, the Supreme People’s Court also issued the Reply Regarding the Scope of Application of the New Private Lending Judicial Interpretation, which provides that the two amendments are not applicable to disputes arising from the relevant financial business of micro-credit companies, licensed financing guarantee companies, and five other types of local financial organizations which are regulated by local financial authorities.
On July 20, 2020, the Supreme People’s Court and the NDRC jointly released the Opinions on Providing Judicial Services and Safeguards for Accelerating the Improvement of the Socialist Market Economic System for the New Era. This document states that if the interest and fees, including compound interests, penalty interests and liquid damages, claimed by one party to the loan contract exceed the upper limit under judicial protection, the claim will not be supported by the court, and if the parties to the loan disguise the financing cost in an attempt to circumvent the upper limit, the rights and obligations of all parties to the loan will be determined by the actual loan relationship. In addition, this document indicates that the relevant governmental authorities should promptly revise and improve the judicial interpretation of the legal issues for private lending trial cases and significantly reduce the upper limit of private lending rates under judicial protection. The timetable and other details of the regulatory revisions proposed by this document remain uncertain.
In March 2021, the PBOC releases the Announcement No.3, or the Announcement, to ensure orderly competition in the loan market and protect the legitimate rights and interests of financial consumers, all loan products are required to expressly list their annualized interest rates, specifically: (i) all lending institutions are required to display the annualized rate of each loan product prominently on the website, mobile app, poster, and any other channels where the product is marketed, and specify the annualized rate in the loan contract. Daily and monthly interest rates may also be displayed if necessary, but not more prominently than the annualized interest rates; (ii) lending institutions include but are not limited to depository financial institutions, automobile finance companies, consumer finance companies, micro-lending companies, and internet platforms that advertise or display loan services; (iii) the annualized rate of a loan should be calculated as the annualized ratio of total costs (to borrower) to outstanding principal amount. The costs include interest and other fees and charges directly related to the loan. The amount of principal should be specified in the loan contract or other loan certificates. If the loan is repaid in installments, the outstanding principal amount should be the balance after each repayment; and (iv) the calculation of the annualized interest rate may be based on compound interest or simple interest. The calculation based on compound interest is equivalent to that of the internal rate of return, and the simple-interest approach should be specified as such.
Regulations on Financial Guarantee
The Regulations on the Administration of Financing Guarantee Companies, or the Financing Guarantee Regulations, was promulgated by the State Council on August 2, 2017 and took effect on October 1, 2017. According to the Financing Guarantee Regulations, the establishment of financing guarantee companies should be subject to the approval of the competent government authority, and unless otherwise stipulated, no entity is allowed to operate the financing guarantee business without such approval. If any entity operates the financing guarantee business without such approval, the entity may be subject to penalties, including termination or suspension of business, fines of RMB500,000 to RMB1,000,000, confiscation of illegal gains if any, and if the violation constitutes a criminal offense, criminal liability shall be imposed in accordance with the applicable laws and regulations. The maximum amount of outstanding guarantee liabilities of a financing guarantee company may not exceed ten times of its net assets.
In addition, on October 9, 2019, CBIRC issued the Notice on Printing and Distributing the Supplementary Provisions on the Supervision and Management of Financing Guarantee Companies, which provides that any entity providing client referral or credit assessment services to the lending institutions may not provide financing guarantee services in a direct or a disguised form without the regulatory approval. If any entity operates financing guarantee business without appropriate approval, its business operations will be banned by the regulatory authorities and it will be required to properly settle existing business.
On July 14, 2020, the CBIRC issued the Guidelines for Off-Site Supervision of Financing Guarantee Companies, or the Off-Site Supervision Guidelines, which took effect on September 1, 2020. The Off-Site Supervision Guidelines provides, among others, that (i) the relevant regulatory authorities and CBIRC shall collect data and non-data information from the financing guarantee companies and banks respectively; (ii) financing guarantee companies shall establish and implement an off-site supervision information report system and submit data and non-data information timely according to the requirements of the competent regulatory authorities; and (iii) for the off-site supervision, the competent regulatory authorities shall mainly focus on the external operating environment, corporate governance, internal control, risk management capabilities, guarantee business, associated guarantee risks, asset quality, liquidity indicators and investment conditions of financing guarantee companies.
On December 31, 2021, the PBOC issued the Regulations on Local Financial Supervision and Management (draft for comment), or the Draft Regulations on Local Financial Supervision and Management. The Draft Regulations on Local Financial Supervision and Management stipulate: (i) In addition to the establishment of regional equity markets, the establishment of other Local Financial Organizations shall be approved by the provincial local financial supervision and management departments while the establishment of regional equity markets should be publicized by the provincial people's government, and reported to the State Council securities supervision and management agencies for the record.
Local Financial Organizations refer to the establishment of microfinance companies, financing guarantee companies, regional equity markets, financial leasing companies, commercial factoring companies, local asset management companies and other institutions engaged in local financial business; (ii) Local Financial Organizations should serve the local, in principle, and shall not carry out business across the provinces; (iii) The financial management department of the State Council and local financial supervision and management departments should strengthen the monitoring, identification and disposal of illegal financial activities; (iv) Local Financial Organizations established before the implementation of the Draft Regulations on Local Financial Supervision and Management, shall meet the prescribed conditions within the period specified by the local financial supervision and management departments. While the Draft Regulations on Local Financial Supervision and Management had been released for consultation purpose, there is still uncertainty regarding the Draft Regulations on Local Financial Supervision and Management as to its final content, its adoption timeline or effective date, its final interpretation and implementation, and other aspects.
Regulations on Sharing Information of and Imposing Disciplinary Measures on Discredited Parties subject to Enforcement
The Several Provisions on Announcement of the List of Discredited Parties Subject to Enforcement promulgated by the Supreme People’s Court on July 16, 2013, and amended on February 28, 2017, or Several Provisions, provides the framework for collecting and sharing information of discredited parties which are subject to law enforcement actions. According to the Several Provisions, where a party subject to enforcement fails to perform the obligations determined in a valid legal document but he/she has the capacity to perform, under any of the following circumstances, a people’s court shall record him/her in the list of discredited parties subject to enforcement, and impose credit-related disciplinary measures pursuant to the law in cases if: (i) he/she hinders or resists enforcement by way of forging evidence, violence or coercion; (ii) he/she circumvents enforcement by way of false lawsuit, false arbitration or concealment or removal of properties; (iii) there is a violation of property reporting system; (iv) there is a violation of order to restrict consumption; or (v) he/she refuses to perform settlement agreement for enforcement without a valid reason.
The Several Provisions further provide that people’s courts at all levels shall record the information of the discredited parties subject to enforcement in the database of the Supreme People’s Court, and announce such information to the public on a unified basis through such database. Furthermore, the people’s court at all levels may, based on the actual conditions of the locality, announce the list of discredited parties subject to enforcement by way of newspapers, radio, television, Internet, bulletin board of the court, and may hold press conference or engage other methods for announcement of implementation status of lists of discredited parties subject to enforcement by these courts and courts within their respective jurisdictions.
In accordance with the Notice on Issuing the Memorandum of Cooperation on Jointly Imposing Disciplinary Measures against Discredited Parties Subject to Enforcement promulgated by the NDRC and other government agencies on January 20, 2016, or the Joint Disciplinary Measures Memorandum, the NDRC will, on the basis of the national credit information sharing platform, establish a system for joint disciplinary measures against discredited acts. Through said system, Supreme People’s court shall provide other governmental agencies who have signed this Joint Disciplinary Measures Memorandum with the information of discredited parties subject to enforcement, and update such information according to the relevant provisions. Other governmental agencies shall obtain the information of discredited parties subject to enforcement via said system, implement or assist in implementing the disciplinary measures specified in the Joint Disciplinary Measures Memorandum, and report the information on implementation of such measures to the Supreme People’s Court and the NDRC via said system. The disciplinary measures for the discredited parties include, among others, (i) restrictions on participation in government procurement; (ii) restrictions on establishment of insurance companies and financing guarantee companies; (iii) provision of relevant information as a prudent reference for all financial institutions when financial institutions approve credit applications; (iv) restrictions on support of subsidy or social security funds; (v) provision of reference for accreditation of preferential policies; (vi) for individuals, restrictions on serving as legal representative, director or supervisor of wholly state-owned enterprises, legal representative of public institutions, public servants or staff members of public institutions; (vii) for individuals, restrictions on luxurious consumptions, including but not limited to taking airplanes, luxurious sleeping compartments on trains, higher star-rated hotels, night clubs or golf courses, and other consumption unnecessary for living and working.
Regulations on Illegal Fund-Raising
The Measures for the Banning of Illegal Financial Institutions and Illegal Financial Business Operations promulgated by the State Council in July 1998 and revised in 2011, and the Circular on Relevant Issues Concerning the Penalty on Illegal Fund-Raising issued by the General Office of the State Council in July 2007, explicitly prohibit illegal public fund-raising.
According to Regulations on Preventing and Dealing with Illegal Fundraising, which came into effect in May 2021 and replaced the Measures for the Banning of Illegal Financial Institutions and Illegal Financial Business Operations, illegal fundraising involves collecting funds from non-specific targets with promised principal and interest or other investment returns, without lawful permission from the State Council’s financial management departments or in violation of China’s financial management rules. Provincial-level governments should have overall responsibility for anti-illegal fundraising efforts within their respective administrative regions, and local governments should build necessary work mechanisms. Financial and non-banking payment institutions should report large-value and suspicious transactions as required, and analyze and identify related accounts having suspected association with illegal fundraising.
We and the VIE Group provide loan facilitation services and are not a party to the loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform. We and the VIE Group rely on third-party payment platforms in handling funds transfer and settlement.
Regulations on Anti-money Laundering
The PRC Anti-money Laundering Law, which became effective in January 2007, and was recently amended in November 2024 and came into effect in January 2024, stipulates that institutions engaged in financial business as determined and announced by the administrative department of anti-money laundering under the State Council shall comply with the anti-money laundering obligations. The PBOC and other regulatory authorities issued a series of administrative regulations and rules to specify the anti-money laundering obligations of financial institutions and special non-financial institutions.
In cooperation with our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners, we and the VIE Group have adopted various policies and procedures, including “know-your-customer” procedures, customer due diligence, and customer screening procedures, for anti-money laundering purposes. However, as the detailed anti-money laundering regulations of loan facilitators have not been published, it remains to be observed as to how the anti-money laundering requirements will be interpreted and implemented and whether loan service providers like us must abide by the rules and procedures set forth in the PRC Anti-money Laundering Law that are applicable to nonfinancial institutions with anti-money laundering obligations. We and the VIE Group cannot assure you that our and the VIE Group’s existing anti-money laundering policies and procedures will be deemed to be in full compliance with any anti-money laundering laws and regulations that may become applicable to us in the future.
Regulations Relating to Corporation and Foreign Investment
The establishment, operation and management of corporate entities in the PRC are governed by the Company Law of the PRC, or the Company Law, which was promulgated by the SCNPC on December 29, 1993 and became effective on July 1, 1994, and was amended on December 25, 1999, August 28, 2004, October 27, 2005, December 28, 2013 and October 26, 2018 respectively. Pursuant to the Company Law, companies are classified into two categories, namely limited liability companies and limited companies by shares. The Company Law also applies to foreign-invested limited liability companies and companies limited by shares. According to the Company Law, the provisions otherwise prescribed by the laws on foreign investment shall prevail.
Furthermore, the Company Law of the PRC (Revised in 2023), or the Revised Company Law, was promulgated by the SCNPC on December 29, 2023 and will take effect on July 1, 2024. The major revisions made by the Revised Company Law include improvement of the system for the establishment and exit of companies, optimization of organizational structures of companies, improvement of the capital system of companies, strengthening the responsibilities of the controlling shareholder and senior management, enhancing the social responsibilities of companies, etc.
Investments in the PRC by foreign investors and foreign-invested enterprises are regulated by the Special Administrative Measures for Access of Foreign Investment (Negative List) (2024 Version), or the 2024 Negative List. The establishment of wholly foreign-owned enterprises is generally allowed in industries not included in the 2024 Negative List. Industries not listed in the 2024 Negative List are generally open to foreign investments unless specifically restricted by other applicable Chinese regulations. Under the 2024 Negative List, foreign equity in companies providing value-added telecommunications services, excluding e-commerce, domestic multi-party communications, data collection and transmission services, and call centers, should not exceed 50%.
The National People’s Congress adopted the Foreign Investment Law of the PRC on March 15, 2019 and its implementation regulation later on December 26, 2019, which became effective on January 1, 2020 and replaced three then existing laws on foreign investments in China, namely, the PRC Equity Joint Venture Law, the PRC Cooperative Joint Venture Law and the Wholly Foreign-owned Enterprise Law, together with their implementation rules and ancillary regulations. The Foreign Investment Law of the PRC embodies an expected PRC regulatory trend to rationalize its foreign investment regulatory regime in line with prevailing international practice and the legislative efforts to unify the corporate legal requirements for both foreign and domestic invested enterprises in China. The Foreign Investment Law of the PRC establishes the basic framework for the access to, and the promotion, protection and administration of foreign investments in view of investment protection and fair competition. Pursuant to the Foreign Investment Law of the PRC, China will grant national treatment to foreign invested entities, except for those foreign invested entities that operate in industries that fall within “restricted” or “prohibited” categories as prescribed in the “negative list” to be released or approved by the State Council.
Furthermore, the Interim Administrative Measures for the Record-filing of the Incorporation and Change of Foreign-invested Enterprises (amended in 2018) was replaced by Measures for the Reporting of Foreign Investment Information, or the Foreign Investment Information Measures. Since January 1, 2020, for foreign investors carrying out investment activities directly or indirectly in the PRC, foreign investors or foreign-invested enterprises shall submit investment information through the Enterprise Registration System and the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System operated by the State Administration for Market Regulation. Foreign investors or foreign-invested enterprises shall disclose their investment information by submitting reports for their establishments, modifications and cancellations and their annual reports in accordance with the Foreign Investment Information Measures. If a foreign-invested enterprise investing in the PRC has finished submitting its reports for its establishment, modifications and cancellation and its annual reports, the relevant information will be shared by the competent market regulation department to the competent commercial department, and does not require such foreign-invested enterprise to submit the reports separately.
Regulations Relating to Internet Companies
Regulations on Value-Added Telecommunication Services
The Telecommunications Regulations of the PRC, or the Telecommunications Regulations, promulgated by the State Council on September 25, 2000 and amended on July 29, 2014 and February 6, 2016, provide a regulatory framework for telecommunication service providers in the PRC. The Telecommunications Regulations require telecommunication service providers to obtain an operating license prior to the commencement operations. The Telecommunications Regulations categorize telecommunication services into basic telecommunication services and value-added telecommunication services. According to the Catalog of Telecommunication Business, attached to the Telecommunications Regulations, both information services and online data processing and transaction processing services provided via fixed network, mobile network and Internet fall within value-added telecommunication services.
In July 2017, the MIIT promulgated the Administrative Measures on Telecommunication Business Operating Licenses. Under these regulations, a commercial operator of value-added telecommunication services must first obtain a license for value-added telecommunication service business, or VATS License, from the MIIT or its provincial level counterparts.
In July 2006, the Ministry of Information Industry of the PRC, the predecessor of the MIIT, issued the Circular on Strengthening the Administration of Foreign Investment in the Operation of Value-added Telecommunication Business, which prohibits holders of telecommunication business licenses from leasing, transferring or selling their licenses in any form, or providing any resource, sites or facilities, to any foreign investor intending to conduct such business in China.
Regulation on Mobile Internet Applications Information Services
In addition to the Telecommunications Regulations and other regulations above, mobile application information service providers are especially regulated by the Administrative Provisions on Mobile Internet Applications Information Services, or the APP Provisions, which were promulgated by the CAC, on June 28, 2016 and amended on June 14, 2022. According to the APP Provisions, the CAC and its local counterparts shall be responsible for the supervision and administration of nationwide or local mobile application information, respectively.
Under the APP Provisions, the APP information service providers shall satisfy relevant qualifications required by laws and regulations, strictly fulfill their responsibilities of information security management, and perform the following duties: (i) verify identities with the registered users through mobile phone numbers etc.; (ii) establish a mechanism for examining the content of the information; (iii) obtain an internet news and information services license or other administrative licenses for information services. In particular, the APP Provisions stipulate the obligations in relation to cyber security, data security and personal information protection, emphasizing the necessity for personal information collection and the fact that users shall not be denied the use of the basic function services of certain applications merely on account of their refusal to provide unnecessary personal information.
The APP Provisions also set out the requirements for application distribution platforms, which include, among others, (i) filing the required information with the local network information administration authority within 30 days from the time the platform has become operational; and (ii) establishing classification management systems. If the applications violate the amended provisions, relevant laws and regulations, and service agreements, the application distribution platform shall take such measures as giving warnings, suspension of services, removal of the application from the platform, etc. It shall also keep relevant records and report the breach to competent authorities.
The MIIT issued the Notice on the Further Special Rectification of Apps Infringing upon Users’ Personal Rights and Interests, or the Further Rectification Notice, on July 22, 2020. The notice requires that certain conducts of app service providers should be inspected with respect to (i) collecting personal information without the user’s consent, collecting or using personal information beyond the necessary scope of providing services, and forcing users to receive advertisements; (ii) requesting user’s permission in a compulsory and frequent manner, or frequently launching third-parties apps; and (iii) deceiving and misleading users into downloading apps or providing personal information. The notice also set forth that the period for the regulatory specific inspection on apps and that the MIIT will order the non-compliant entities to modify their business within five business days, or otherwise to make public announcement to remove the apps from the app stores and impose other administrative penalties.
We and the VIE Group have implemented necessary programs in our and the VIE Group’s mobile application to make sure the collection, protection and preservation of user information are in compliance with the APP Provisions in all material aspects.
Regulations on Internet Security
Internet information in China is regulated and restricted from a national security standpoint. The SCNPC, has enacted the Decisions on Maintaining Internet Security on December 28, 2000 and further amended on August 27, 2009, which may subject violators to criminal punishment for any effort to: (i) gain improper entry into a computer or system of strategic importance; (ii) disseminate politically disruptive information; (iii) leak state secrets; (iv) spread false commercial information; or (v) infringe intellectual property rights.
Pursuant to the Cyber Security Law of the PRC promulgated by the SCNPC on November 7, 2016 and effective on June 1, 2017, network operators, including Internet information service providers, shall comply with laws and regulations and fulfill their obligations to safeguard security of the network when conducting business and providing services, and take all necessary measures pursuant to laws, regulations and compulsory national requirements to safeguard the safe and stable operation of the networks, respond to network security incidents effectively, prevent illegal and criminal activities, and maintain the integrity, confidentiality and usability of network data.
The Measures for Cybersecurity Review were jointly issued on December 28, 2021 and took effect on February 15, 2022. The measures provide detailed rules regarding cyber security review, and any operator in violation of the regulations shall be penalized in accordance with the Cyber Security Law of the PRC, and the PRC Data Security Law. The Measures for Cybersecurity Review specifies that the procurement of network products and services by operator of critical information infrastructure and the activities of data process carried out by online platform operator that raise or may raise “national security” concerns are subject to strict cyber security review by Office of Cyber Security Review established by the CAC. In addition, online platform operators that possesses the personal data of at least one million users must apply for a review by the Cyber Security Review Office, if they plan listing of companies in foreign countries. The CAC may voluntarily conduct cyber security review if any network products and services, activities of data process or listing of companies overseas affects or may affect national security.
The Administrative Provisions for Text Message and Voice Call Service (Draft for Comments) were published to solicit public comments on August 31, 2020. It provides that no entity or individual can send commercial text messages or make commercial calls to users without user consent. In case of violation, the relevant governmental authorities may order to make rectification, impose warnings or fines, make public announcements, or enforce other administrative measures. Under severe circumstances, the relevant governmental authorities may revoke the telecommunication licenses and phone number sources of the violating entity or individual.
The Ministry of Public Security issued the Guiding Opinions on Implementing the Network Security Level Protection System and Critical Information Infrastructure Security Protection System on July 22, 2020, which stipulate that internet operators shall cooperate with public security authorities to crack down on illegal and criminal online activities. In the event of online crimes, material cyber security threats and incidents, the internet operators shall promptly report to and provide necessary assistance to the public security authorities.
The PRC Data Security Law became effective on September 1, 2021. It establishes a data protection system based on the category and security level of the data in terms of its importance for economic and social development and the potential harm caused by illegal use of such data to national security, public interest or rights and interests of individuals and organizations. Competent governmental authorities shall be responsible to formulate lists for “key data”.
Higher level of protection shall apply to “national core data” which refers to data that are vital to national security, economy, people’s livelihood and major public interests. According to the PRC Data Security Law, data activities affecting or likely to affect national security will be subject to national security review under the data security review system. The data relating to safeguarding national security and interests and performance of international obligations shall be subject to export control of China. In addition, the PRC Data Security Law provides that key data processors shall appoint a data security officer and establish a management department to take charge of data security, and such processors shall evaluate the risk of their data activities periodically and file assessment reports with the relevant regulatory authorities. Furthermore, data transaction intermediary service providers shall check the sources of the data, the identities of parties involved in the data transactions and keep records accordingly. Violation of the PRC Data Security Law may subject the relevant entities or individuals to warning, fines, suspension of business for rectification, revocation of permits or business licenses, and/or even criminal liabilities.
On July 30, 2021, the State Council promulgated the Safe Protection Regulations which took effect on September 1, 2021. Pursuant to the Safe Protection Regulations, critical information infrastructure refers to important network infrastructure and information system in public telecommunications, information services, energy sources, transportation and other critical industries and domains, in which any destruction or data leakage will have severe impact on national security, the nation’s welfare, the people’s living and public interests. The Safe Protection Regulations provide specific requirements for the responsibilities and obligations of the operator: (i) the operator shall establish and improve the cyber security protection system and responsibility system, and ensure the input of manpower, financial and material resources; (ii) the operator shall set up a special security management department, and review the security background of the person in charge of the special security management department and the personnel in key positions; (iii) the operator shall guarantee the operation funds of the special security management department, allocate corresponding personnel, and have the personnel of the special security management department participate in the decision-making relating to cyber security and informatization; (iv) the operators shall give priority to the purchase of safe and reliable network products and services; network products and services procured that may affect the national security shall be subject to the security review in accordance with the national provisions on network security. The Safe Protection Regulations clarity the measures for dealing with the failure of key information infrastructure operators to perform their responsibilities for security protection, such as imposing fines.
The Administrative Provisions on Security Vulnerability of Network Products, or the Provisions was jointly promulgated by the MIIT, the CAC and the Ministry of Public Security on July 12, 2021 and became effective on September 1, 2021. Network product providers, network operators as well as organizations or individuals engaging in the discovery, collection, release and other activities of network product security vulnerability are subject to the Provisions and shall establish channels to receive information of security vulnerability of their respective network products and shall examine and fix such security vulnerability in a timely manner. Network product providers are required to report relevant information of security vulnerability of network products with the MIIT within two days and to provide technical support for network product users. Network operators shall take measures to examine and fix security vulnerability after discovering or acknowledging that their networks, information systems or equipment have security loopholes. According to the Provisions, the breaching parties may be subject to monetary fine as regulated in accordance with the Cyber Security Law of the PRC.
On September 30, 2024, the State Council released the Network Data Regulation, which serves as a comprehensive framework to enforce compliance with mandates outlined in the Cyber Security Law of the PRC, the PRC Data Security Law, and Personal Information Protection Law. The Network Data Regulation introduces several key obligations, including the requirement for network data handlers to specify the purpose and method of personal information handling, as well as the types of personal information involved, before such information is processed. It also clarifies definitions for important data, outlines the obligations of important data handlers, expands contractual requirements for data sharing between data handlers, and introduces a new exemption for regulatory obligations regarding cross-border data transfers.
We and the VIE Group have, in accordance with relevant provisions on the state network security and the requirements of the state’s system for classified protection of information security, conducted the record-filing of class determination and class testing of information system, possessed perfect network security facility and management system such as firewall, intrusion detection, data encryption and disaster recovery, etc.
Regulations on Privacy Protection
The Several Provisions on Regulating the Market Order of Internet Information Services, issued by the MIIT in December 2011, provide that an Internet information service provider may not collect any user personal information or provide any such information to third parties without the consent of a user. An Internet information service provider must expressly inform the users of the method, content and purpose of the collection and processing of such user personal information and may only collect such information necessary for the provision of its services. An Internet information service provider is also required to properly maintain the user personal information, and in case of any leak or likely leak of the user personal information, online information service providers must take immediate remedial measures and, in severe circumstances, make an immediate report to the telecommunication regulatory authority.
In addition, pursuant to the Decision on Strengthening the Protection of Online Information issued by the SCNPC in December 2012 and the Order for the Protection of Telecommunication and Internet User Personal Information issued by the MIIT in July 2013, any collection and use of user personal information must be subject to the consent of the user, abide by the principles of legality, rationality and necessity and be within the specified purposes, methods and scopes.
Pursuant to the Ninth Amendment to the Criminal Law of the PRC issued by the SCNPC in August 2015 and became effective in November, 2015 any Internet service provider that fails to fulfill the obligations related to Internet information security administration as required by applicable laws and refuses to rectify upon orders shall be subject to criminal penalty. On May 8, 2017, the Supreme People’s Court and the Supreme People’s Procuratorate released the Interpretations on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Law in the Handling of Criminal Cases Involving Infringement of Citizens’ Personal Information, or the Personal Information Judicial Interpretations, which became effective on June 1, 2017. The Personal Information Judicial Interpretations provide more practical conviction and sentencing criteria for the infringement of citizens’ personal information and mark a milestone for the criminal protection of citizens’ personal information.
The Civil Code of PRC, which was issued by the National People’s Congress on May 28, 2020 and became effective from January 1, 2021, provides that personal information of natural persons is protected by law. The Civil Code of the PRC defines the processing of personal information as the collection, storage, use, processing, transmittal, provision and disclosure of personal information. Furthermore, according to the Civil Code of PRC, any entity that engages in the processing of personal information must follow the principles of lawfulness, fairness, and necessity and may not overuse personal information, and they must obtain the consent of the natural person or his or her guardian, except as otherwise provided by laws and regulations.
On August 20, 2021, the SCNPC issued the Personal Information Protection Law, which came into effect from November 1, 2021. The Personal Information Protection Law reiterates the circumstances under which a personal information processor could process personal information and the requirements for such circumstances, such as when (i) the individual’s consent has been obtained; (ii) the processing is necessary for the conclusion or performance of a contract to which the individual is a party; (iii) the processing is necessary to fulfill statutory duties and statutory obligations; (iv) the processing is necessary to respond to public health emergencies or protect natural persons’ life, health and property safety under emergency circumstances; (v) the personal information that has been made public is processed within a reasonable scope in accordance with this law; (vi) personal information is processed within a reasonable scope to conduct news reporting, public opinion-based supervision, and other activities in the public interest; or (vii) under any other circumstance as provided by any law or regulation. It also stipulates the obligations of a personal information processor. The Personal Information Protection Law clarifies the definition of “Sensitive Personal Information”, which means personal information that, once leaked or illegally used, may give rise to discrimination against individuals or seriously endanger personal or property security, including information on race, ethnicity, religious beliefs, personal biometric features, medical health, financial accounts, and personal whereabouts, among others. To process sensitive personal information based on an individual’s consent, a personal information processor shall obtain the separate consent from the individual. Where any law or administrative regulation provides that written consent shall be obtained for processing sensitive personal information, such provision shall prevail. In terms of cross-border transmission of personal information, pursuant to the Personal Information Protection Law, a personal information processor, providing personal information to any party outside the territory of the PRC, shall notify individuals of the overseas recipient’s identity, contact information, processing purposes, processing methods, categories of personal information, the methods in which individuals exercise the rights over the overseas recipient, and other matters, and obtain individuals’ separate consent. Furthermore, critical information infrastructure operators and the personal information processors that process the personal information reaching or exceeding the threshold specified by the national cyberspace administration in terms of quantity shall store domestically the personal information collected and generated within the territory of the PRC. Where it is truly necessary to provide the information abroad, the security assessment organized by the national cyberspace administration shall be passed, unless otherwise regulated by laws, administrative regulations, or provisions issued by the national cyberspace administrative authorities. The Personal Information Protection Law provides that if an overseas organization or individual engages in personal information processing activities that damage the rights and interests relating to personal information of citizens of the PRC or compromise national security or public interests of the PRC, the national cyberspace administration may include it or him in a list of those the provision of personal information to whom is restricted or prohibited, make an announcement, and take measures such as restricting or prohibiting the provision of personal information to it or him. On the other hand, personal information processors shall themselves, on the basis of the purposes of the processing of personal information, processing methods, categories of personal information, the impacts on individuals, and potential security risks, among others, take necessary measures to ensure that personal information processing activities comply with the provisions of laws and administrative regulations, and prevent unauthorized access to as well as the leakage, tampering or loss of personal information.
While we and the VIE Group have taken measures to protect the confidential information that we and the VIE Group have access to, our and the VIE Group’s security measures could be breached. Any accidental or willful security breaches or other unauthorized access to our and the VIE Group’s platform could cause confidential information of lenders and borrowers to be stolen and used for criminal purposes. Security breaches or unauthorized access to confidential information could also expose us to liability related to the loss of information, time-consuming and expensive litigation and negative publicity. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry—If we and the VIE Group are unable to protect the confidential information of our and the VIE Group’s users and adapt to the relevant regulatory framework regarding protection of such information, our and the VIE Group’s business and operations may be adversely affected.”
Regulations on Internet Advertising
The Advertising Law of the PRC, promulgated by the SCNPC on October 27, 1994 and last amended on April 29, 2021, sets out certain content requirements for advertisements in the PRC, including the prohibition of false or misleading content, superlatives wording, destabilizing content or content that involves obscenity, superstition, violence, discrimination or infringement of the public interest. Advertisers, advertising agents and advertising distributors are required to ensure that the contents of the advertisements they prepare or publish are truthful and fully comply with applicable laws. In providing advertising services, advertising operators and advertisement publishers shall review the supporting documents provided by the advertisers for the advertisements and verify that the contents of the advertisements comply with applicable PRC laws and regulations.
The Interim Measures for Administration of Internet Advertising, or the Internet Advertising Measures, were promulgated by the State Administration for Industry and Commerce of the PRC and became effective on September 1, 2016. According to the Internet Advertising Measures, Internet advertisers are responsible for the authenticity of the content of advertisements. Internet advertisements shall be distinguishable and prominently marked as “advertisements” in order to enable consumers to identify them as advertisements. It is required that publishing and circulating advertisements through the Internet shall not affect the normal use of the Internet by users. It is not allowed to induce users to click on the content of advertisements by any fraudulent means, or to attach advertisements or advertising links in the emails without permission.
On February 25, 2023, the State Administration for Market Regulation, or the SAMR promulgated the Administrative Measures for Internet Advertising, which came to effect on May 1, 2023 and replaced the Internet Advertising Measures. Pursuant to the Administrative Measures for Internet Advertising, internet advertisers are responsible for the authenticity of the contents of the advertisements and may publish advertisements on their own through their own websites or through the internet media they own, or entrust internet advertising operators or advertisement publishers to publish advertisements. The Administrative Measures for Internet Advertising also provides that internet advertisement shall be identifiable, enabling consumers to identify it as an advertisement. Internet platform operators shall take measures to prevent and deter illegal advertisements in the course of providing internet information services. In addition, users shall not be deceived or misled into clicking or viewing advertisements by: (i) false system or software updates, bug reports, removals, notifications and other prompts; (ii) false signals such as play, start, pause, stop and return; (iii) false reward promises; and (iv) other ways to deceive or mislead users. The administrative department of market regulation is the relevant local administrative authority to supervise and punish any illegal acts in internet advertising. Any violation of the Administrative Measures for Internet Advertising, may be subject to fines, prohibition of advertisements for a period of time or revocation of business licenses and other penalties.
Regulations on Intellectual Property Rights
The PRC has adopted comprehensive legislation governing intellectual property rights, including copyrights, patents, trademarks and domain names.
Copyright. Copyright in the PRC, including copyrighted software, is principally protected under the PRC Copyright Law and related regulations and rules. Under the PRC Copyright Law, the term of protection for copyrighted software is 50 years.
Patent. The PRC Patent Law provides for patentable inventions, utility models and designs, which must meet three conditions: novelty, inventiveness and practical applicability. The China National Intellectual Property Administration is responsible for examining and approving patent applications. A patent is valid for twenty years in the case of an invention, ten years in the case of utility models and fifteen years in case of designs.
Trademark. The PRC Trademark Law promulgated on August 23, 1982 and most recently revised on April 23, 2019 and became effective on November 1, 2019, and its implementation rules promulgated on August 3, 2002 and revised on April 29, 2014, protect registered trademarks. The PRC Trademark Law has adopted a “first-to-file” principle with respect to trademark registration. The Trademark Office under the China National Intellectual Property Administration is responsible for the registration and administration of trademarks throughout the PRC, and grants a term of 10 years to registered trademarks and another 10 years if requested upon expiry of the initial or extended term.
Trademark license agreements must be filed with the Trademark Office for record.
Domain Name. Domain names are protected under the Administrative Measures on the Internet Domain Names promulgated by the MIIT and effective on November 1, 2017. The MIIT is the major regulatory authority responsible for the administration of the PRC Internet domain names. The registration of domain names in PRC is on a “first-apply-first-registration” basis. A domain name applicant will become the domain name holder upon the completion of the application procedure. Our and the VIE Group’s major domain name “niwodai.com” has been registered.
Regulations Relating to Mergers and Acquisitions and Overseas Listings
Six PRC regulatory authorities, including the CSRC, jointly adopted the Regulations on Mergers and Acquisitions of Domestic Enterprises by Foreign Investors, or the M&A Rules, which became effective in September 2006 and were amended on June 22, 2009. The M&A Rules, among other things, require offshore SPVs formed for overseas listing purposes through acquisitions of PRC domestic companies and controlled by PRC companies or individuals, to obtain the approval of the CSRC prior to publicly listing their securities on an overseas stock exchange.
On February 17, 2023, the CSRC promulgated the Trial Administrative Measures and five supporting guidelines, which became effective on March 31, 2023. Pursuant to the Trial Administrative Measures, PRC domestic enterprises that directly or indirectly offer or list their securities in an overseas market, which include (i) any PRC company limited by shares, and (ii) any offshore company that conducts its business operations primarily in China and contemplates to offer or list its securities in an overseas market based on its onshore equities, assets or similar interests, are required to complete the filing with the CSRC. Specifically, (i) where PRC domestic enterprises conduct overseas initial public offering or listing, or offer and list securities in other overseas markets upon completion of overseas offering and listing, PRC domestic enterprises shall file with the CSRC within three business days after its application for overseas offering and listing is submitted; and (ii) where PRC domestic enterprises offer securities in the same overseas market upon completion of overseas offering and listing, PRC domestic enterprises shall file with the CSRC within three business days after completion of offering. In addition, PRC domestic enterprises are required to report detailed information of material events after the completion of overseas offering and listing within three business days after the relevant events occur and are announced, including (i) change of control right; (ii) investigation, penalties or other measures imposed by overseas securities regulatory authorities or competent departments; (iii) change of listing status or listing board; and (iv) voluntary termination of listing or compulsory termination of listing. Failure to complete the filing under the Trial Administrative Measures may subject a PRC domestic enterprise to rectification ordered by the CSRC, warning, and fine of RMB1 million to RMB10 million.
On February 24, 2023, the CSRC and other relevant government authorities promulgated the Provisions on Confidentiality and Archives Management, which became effective on March 31, 2023. Pursuant to the Provision on Confidentiality and Archives Management, PRC domestic enterprises that seek to offer and list securities in overseas markets shall establish confidentiality and archives management system. The PRC domestic enterprises shall obtain approval from the competent authority and file with the confidential administration department at the same level when providing or publicly disclosing documents and materials related to state secrets or secrets of the governmental authorities to the underwriters or other agencies or the offshore regulatory authorities, and shall complete corresponding procedures when providing or publicly disclosing documents and materials which may adversely influence national security and the public interest.
Regulations Relating to Foreign Exchange
Regulations on Foreign Currency Exchange
The principal regulations governing foreign currency exchange in China are the Foreign Exchange Administration Regulations, most recently amended in August 2008. Under the Foreign Exchange Administration Regulations, payments of current account items, such as profit distributions, interest payments and trade and service-related foreign exchange transactions, can be made in foreign currencies without prior approval from the SAFE by complying with certain procedural requirements. By contrast, approval from or registration with appropriate regulatory authorities is required where Renminbi is to be converted into foreign currency and remitted out of China to pay capital account items, such as direct investment, repayment of foreign currency-denominated loans, repatriation of investment and investment in securities outside of China.
On March 30, 2015, the SAFE promulgated SAFE Circular 19, which was partially abolished on December 30, 2019, to expand the reform nationwide. Under SAFE Circular 19, the foreign exchange capital in the capital account of foreign-invested enterprises upon the confirmation of rights and interests of monetary contribution by the local branches of the SAFE (or the book-entry registration of monetary contribution by the banks) can be settled at the banks based on the actual operation needs of the enterprises.
The proportion of discretionary settlement of foreign exchange capital of foreign-invested enterprises is currently 100%. The SAFE can adjust such proportion in due time based on the circumstances of international balance of payments. On June 9, 2016, the SAFE promulgated the SAFE Circular 16, SAFE Circular 16 continue to prohibit foreign-invested enterprises from, among other things, using Renminbi fund converted from its foreign exchange capitals for expenditure beyond its business scope, investment and financing (except for security investment or guarantee products issued by bank), providing loans to non-affiliated enterprises or constructing or purchasing real estate not for self-use. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—PRC regulation of loans to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore holding companies and governmental administration of currency conversion may delay or prevent us from using the proceeds of further offerings to make loans to or make additional capital contributions to our PRC subsidiaries, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand our business.”
On January 26, 2017, the SAFE issued the Circular on Further Improving Reform of Foreign Exchange Administration and Optimizing Genuineness and Compliance Verification, or SAFE Circular 3, which stipulates several capital control measures with respect to the outbound remittance of profit from domestic entities, including (i) under the principle of genuine transaction, banks shall check board resolutions regarding profit distribution, the original version of tax filing records and audited financial statements; and (ii) domestic entities shall hold income to account for previous years’ losses before remitting the profits. Moreover, pursuant to SAFE Circular 3, domestic entities shall make detailed explanations of the sources of capital and utilization arrangements, and provide board resolutions, contracts and other proof when completing the registration procedures in connection with an outbound investment.
On April 14, 2020, SAFE issued the Notice on Optimizing Foreign Exchange Administration to Support the Development of Foreign-related Business. It stipulates that on the premise of ensuring the true and compliant use of funds and compliance with the existing regulations on use of income under the capital account, enterprises which satisfy the criteria are allowed to use income under the capital account, such as capital funds, foreign debt and overseas listing for domestic payment, without prior provision of proof materials for veracity to the bank for each transaction. The authority to process the deregistration of qualified overseas loans under domestic guarantee and overseas lending shall be delegated to banks.
Regulations on Foreign Exchange Registration of Offshore Investment by PRC Residents
The SAFE promulgated the Circular on Relevant Issues Relating to PRC Resident’s Investment and Financing and Roundtrip Investment through Special Purpose Vehicles, or SAFE Circular 37, on July 4, 2014, which replaced the former circular commonly known as “SAFE Circular 75.” SAFE Circular 37 requires PRC residents to register with local branches of the SAFE in connection with their direct establishment or indirect control of an offshore entity, for the purpose of offshore investment and financing, with such PRC residents’ legally owned assets or equity interests in domestic enterprises or offshore assets or interests, referred to in SAFE Circular 37 as a “special purpose vehicle”. SAFE Circular 37 further requires amendment to the registration in the event of any significant changes with respect to the special purpose vehicle, such as increase or decrease of capital contributed by PRC residents, share transfer or exchange, merger, division or other material event.
On February 13, 2015, the SAFE promulgated the Circular on Further Simplifying and Improving the Administration of the Foreign Exchange Concerning Direct Investment, or SAFE Circular 13, the attachment of which was partially abolished on December 30, 2019. After SAFE Circular 13 became effective on June 1, 2015, instead of applying for approvals regarding foreign exchange registrations of foreign direct investment and offshore direct investment from the SAFE, entities and individuals will be required to apply for such foreign exchange registrations from qualified banks. The qualified banks, under the supervision of the SAFE, will directly examine the applications and conduct the registration.
In the event that a PRC shareholder holding interests in a special purpose vehicle fails to fulfill the required SAFE registration, the PRC subsidiaries of that special purpose vehicle may be prohibited from making profit distributions to the offshore parent and from carrying out subsequent cross-border foreign exchange activities, and the special purpose vehicle may be restricted in its ability to contribute additional capital into its PRC subsidiaries. Furthermore, failure to comply with the various SAFE registration requirements described above could result in liability under PRC law for evasion of foreign exchange controls. Mr. Dinggui Yan, Mr. Guanglin Zhang and Mr. Yuanle Wu, who directly or indirectly hold shares in our Cayman Islands holding company and who are known to us as being PRC residents, have completed their SAFE registration pursuant to SAFE Circular 37.
Regulations on Employee Share Incentive Plans of Overseas Publicly-Listed Company
Pursuant to the Circular on Issues Concerning the Foreign Exchange Administration for Domestic Individuals Participating in Share Incentive Plan of Overseas Publicly-Listed Company, issued by the SAFE in February 2012, individuals participating in any share incentive plan of any overseas publicly listed company who are PRC citizens or non-PRC citizens who reside in China for a continuous period of not less than one year, subject to a few exceptions, are required to register with the SAFE through a domestic qualified agent, which could be a PRC subsidiary of such overseas publicly listed company, and complete certain other procedures.
We and our executive officers and other employees who are PRC citizens or non-PRC citizens who reside in China for a continuous period of not less than one year and have been granted options are subject to these regulations. Failure by these individuals to complete their SAFE registrations may subject us and them to fines and other legal sanctions. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—Any failure to comply with PRC regulations regarding the registration requirements for employee share incentive plans may subject the PRC plan participants or us to fines and other legal or administrative sanctions.”
The SAT has issued certain circulars concerning employee share options and restricted shares. Under these circulars, our and the VIE Group’s employees working in China who exercise share options will be subject to PRC individual income tax. Our PRC subsidiaries have obligations to file documents related to employee share options with relevant tax authorities and to withhold individual income taxes of those employees who exercise their share options. If our and the VIE Group’s employees fail to pay or we and the VIE Group fail to withhold their income taxes according to relevant laws and regulations, we and the VIE Group may face sanctions imposed by the tax authorities or other PRC regulatory authorities.
Regulations on Dividend Distribution
Under our current corporate structure, our Cayman Islands holding company may rely on dividend payments from our PRC subsidiaries, which are wholly foreign-owned enterprises incorporated in China, to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have. The principal regulations governing distribution of dividends of foreign-invested enterprises is the Company Law of the PRC. Under the Company Law of the PRC, companies in China may pay dividends only out of their retained earnings, if any, determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. In addition, companies in China are required to set aside 10% of its after-tax profit each year, if any, to fund certain statutory reserve funds until the cumulative amount of such statutory reserves reaches 50% of its registered capital. The aforementioned registered capital refers to the total amount of share capital of all issued shares or the total amount of capital contribution subscribed by all shareholders, as registered with the registration authority. Furthermore, companies in China may allocate a portion of its after-tax profits based on PRC accounting standards to a discretionary surplus fund at their discretion. The statutory reserve funds and the discretionary surplus funds are not distributable as cash dividends. After our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE have generated retained earnings and met the requirements for appropriation to the statutory reserves and until such reserves reach 50% of its registered capital, respectively, our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE can distribute dividends upon approval of the shareholders.
Regulations Relating to Employment
The PRC Labor Law and the PRC Labor Contract Law require that employers must execute written employment contracts with full-time employees. All employers must compensate their employees with wages equal to at least the local minimum wage standards. Violations of the PRC Labor Law and the PRC Labor Contract Law may result in the imposition of fines and other administrative sanctions, and serious violations may result in criminal liabilities.
Enterprises in China are required by PRC laws and regulations to participate in certain employee benefit plans, including social insurance funds, namely a pension fund, a medical insurance fund, an unemployment insurance fund, a work-related injury insurance fund and a maternity insurance fund, and a housing provident fund, and contribute to the funds in amounts equal to certain percentages of salaries, including bonuses and allowances, of the employees as specified by the local government from time to time at locations where they operate their businesses or where they are located. According to the Social Insurance Law of the PRC and Interim Regulation on the Collection and Payment of Social Insurance Premiums, an employer that fails to make social insurance contributions may be ordered to rectify the non-compliance and pay the required contributions within a stipulated deadline and be subject to a late fee of up to 0.05% or 0.2% per day, as the case may be. If the employer still fails to rectify the failure to make social insurance contributions within the stipulated deadline, it may be subject to a fine ranging from one to three times the amount overdue. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry—Increases in labor costs in the PRC may adversely affect our business and results of operations.” In addition, the Individual Income Tax Law of the PRC requires companies operating in China to withhold individual income tax on employees’ salaries based on the actual salary of each employee upon payment.
Prior to March 2018, we and the VIE Group failed to make adequate contributions to employee benefit plans or adequate employee individual income tax withholdings, as required by applicable PRC laws and regulations. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—Failure to make adequate contributions to various employee benefit plans and withhold individual income tax on employees’ salaries as required by PRC regulations may subject us to penalties.” We and the VIE Group have recorded accruals for the estimated underpaid amounts in our and the VIE Group’s financial statements. Since March 2018, we and the VIE Group have made adequate payments for the social welfare and housing provident fund and withholding individual tax for our and the VIE Group’s employees in accordance with relevant laws and regulations.
Regulations Relating to Tax
Dividend Withholding Tax
Pursuant to the Enterprise Income Tax Law of the PRC, or the EIT Law and its implementation rules, which became effective on January 1, 2008 and amended on December 29, 2018, if a non-resident enterprise has not set up an organization or establishment in the PRC, or has set up an organization or establishment but the income derived has no actual connection with such organization or establishment, it will be subject to a withholding tax on its PRC-sourced income at a rate of 10%. Pursuant to the Arrangement between the Mainland China and the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region for the Avoidance of Double Taxation and Tax Evasion on Income, the withholding tax rate in respect to the payment of dividends by a PRC resident enterprise to a Hong Kong resident enterprise is reduced to 5% from a standard rate of 10% if the Hong Kong enterprise directly holds at least 25% of the PRC enterprise. Pursuant to the Circular on Issues Concerning the Application of the Dividend Clauses of Tax Agreements issued by the SAT, or SAT Circular 81, a Hong Kong resident enterprise must meet the following conditions, among others, in order to enjoy the reduced withholding tax: (i) it must directly own the required percentage of equity interests and voting rights in the PRC resident enterprise; and (ii) it must have directly owned such percentage in the PRC resident enterprise throughout the 12 months prior to receiving the dividends. There are also other conditions for enjoying the reduced withholding tax rate according to other relevant tax rules and regulations. In October 2019, the SAT promulgated the Announcement of the State Taxation Administration on Issuing the Measures for the Administration of Non-resident Taxpayers’ Enjoyment of Treaty Benefits, or SAT circular 35, which became effective on January 1, 2020, replacing the Administrative Measures for Non-Resident Taxpayers to Enjoy Treatments under Tax Treaties. SAT Circular 35 provides that non-resident enterprises are not required to obtain pre-approval from the relevant tax authority in order to enjoy the reduced withholding tax rate. Instead, non-resident enterprises and their withholding agents may, by self-assessment and on confirmation that the prescribed criteria to enjoy the tax treaty benefits are met, file the Information Reporting Form for Non-resident Taxpayers Claiming Treaty Benefits and directly apply the reduced withholding tax rate when performing tax filings, and collect and retain relevant supporting documents, which will be subject to post-tax filing examinations by the relevant tax authorities. Accordingly, Geerong (HK) may be able to enjoy the 5% withholding tax rate for the dividends they receive from our and the VIE Group’s PRC subsidiaries, if it satisfies the conditions prescribed under SAT Circular 81 and other relevant tax regulations and rules. However, according to SAT Circular 81 and SAT Circular 35, if the relevant tax authorities consider the transactions or arrangements we and the VIE Group have are for the primary purpose of enjoying a favorable tax treatment, the relevant tax authorities may adjust the favorable withholding tax in the future. According to the Circular on Several Issues regarding the “Beneficial Owner” in Tax Treaties, which was issued on February 3, 2018 by the SAT, effective as of April 1, 2018, when determining the applicant’s status of the “beneficial owner”, several factors in connection with dividends, interests or royalties in the tax treaties, including without limitation, whether the applicant is obligated to pay more than 50% of his or her income in twelve months to residents of third country or region, whether the business operated by the applicant constitutes actual business activities, and whether the counterparty country or region to the tax treaties levy no tax, grant tax exemption on relevant incomes or levy tax at an extremely low rate, will be taken into account. The applicant’s status will be analyzed in light of actual circumstances of specific cases. This circular further provides that applicants who intend to prove his or her status of the “beneficial owner” shall submit the relevant documents to the relevant tax bureau according to SAT Circular 35.
Enterprise Income Tax
The EIT Law and its implementing rules are the principal regulations governing enterprise income tax in the PRC. The EIT Law imposes a uniform enterprise income tax rate of 25% on all resident enterprises in the PRC, including foreign-invested enterprises. Under the EIT Law, an enterprise established outside China with its “de facto management body” located within China is considered a “resident enterprise”, which means that it is treated in a manner similar to a PRC domestic enterprise for enterprise income tax purposes. The implementing rules of the EIT Law define “de facto management body” as a managing body that in practice exercises “substantial and overall management and control over the production and operations, personnel, accounting, and properties” of the enterprise.
The SAT issued the Circular on Issues Concerning the Identification of Chinese-Controlled Offshore Incorporated Enterprises as Resident Enterprises in Accordance With the Actual Standards of Organizational Management, or SAT Circular 82 in 2009. According to SAT Circular 82, a Chinese-controlled offshore incorporated enterprise will be regarded as a PRC resident enterprise by virtue of having a “de facto management body” in China and will be subject to PRC enterprise income tax on its worldwide income only if all of the following criteria are met:(i) the senior executives and core management departments in charge of the day-to-day operations have their presence mainly in China; (ii) decisions relating to the enterprise’s financial and human resource matters are made or are subject to approval by organizations or personnel in China; (iii) the enterprise’s primary assets, accounting books and records, company seals, and board and shareholders meeting minutes are located or maintained in China; and (iv) 50% or more of voting board members or senior executives habitually reside in China.
If we were to be considered a PRC resident enterprise, we would be subject to PRC enterprise income tax at the rate of 25% on our global income. In such case, our profitability and cash flow may be materially reduced as a result of our global income being taxed under the EIT Law. We believe that none of our entities outside of China is a PRC resident enterprise for PRC tax purposes. However, the tax resident status of an enterprise is subject to determination by the PRC tax authorities and it remains to be observed with respect to the interpretation of the term “de facto management body.”
In the event that we are considered to be a PRC resident enterprise, interest paid to our overseas shareholders or ADS holders who are non-PRC resident enterprises as well as gains realized by such shareholders or ADS holders from the transfer of our shares or ADSs may be regarded as PRC-sourced income and as a result be subject to PRC withholding tax at a rate of up to 10%, subject to any reduction or exemption set forth in relevant tax treaties, and similarly, dividends paid to our overseas shareholders or ADS holders who are non-PRC resident individuals, as well as gains realized by such shareholders or ADS holders from the transfer of our shares or ADSs, may be regarded as PRC-sourced income and as a result be subject to PRC withholding tax at a rate of 20%, subject to any reduction or exemption set forth in relevant tax treaties.
SAT issued the Bulletin on Issues of Enterprise Income Tax on Indirect Transfers of Assets by Non-PRC Resident Enterprises, or SAT Bulletin 7, on February 3, 2015, which replaced or supplemented certain previous rules under the circular commonly known as “SAT Circular 698.” Under SAT Bulletin 7, an “indirect transfer” of assets, including equity interests in a PRC resident enterprise, by non-PRC resident enterprises may be re-characterized and treated as a direct transfer of PRC taxable assets, if such arrangement does not have a reasonable commercial purpose and was established for the purpose of avoiding payment of PRC enterprise income tax. As a result, gains derived from such indirect transfer may be subject to PRC enterprise income tax. According to SAT Bulletin 7, “PRC taxable assets” include assets attributed to an establishment in China, immoveable properties in China, and equity investment in PRC resident enterprises. In respect of an indirect offshore transfer of assets of a PRC establishment, the relevant gain is to be regarded as effectively connected with the PRC establishment and therefore included in its enterprise income tax filing, and would consequently be subject to PRC enterprise income tax at a rate of 25%. Where the underlying transfer relates to the immoveable properties in China or to equity investment in a PRC resident enterprise, which is not effectively connected to a PRC establishment of a non-resident enterprise, a PRC enterprise income tax at 10% would apply, subject to available preferential tax treatment under applicable tax treaties or similar arrangements, and the party who is obligated to make the transfer payments has the withholding obligation. If SAT Bulletin 7 was determined by the tax authorities to be applicable to some of our transactions involving PRC taxable assets, our offshore subsidiaries conducting the relevant transactions might be required to spend valuable resources to comply with SAT Bulletin 7 or to establish that the relevant transactions should not be taxed under SAT Bulletin 7. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—We face uncertainty with respect to indirect transfers of equity interests in PRC resident enterprises by their non-PRC holding companies.”
Under applicable PRC laws, payers of PRC-sourced income to non-PRC residents are generally obligated to withhold PRC income taxes from the payment. In the event of a failure to withhold, the non-PRC residents are required to pay such taxes on their own. Failure to comply with the tax payment obligations by the non-PRC residents will result in penalties, including full payment of taxes owed, fines and default interest on those taxes.
PRC Value-Added Tax
In November 2011, the MOF and the SAT promulgated the Pilot Plan for Imposition of Value-Added Tax to Replace Business Tax, pursuant to which, a VAT was imposed to replace the business tax in the transport and shipping industry and some of the modern service industries in certain pilot regions from January 1, 2012. The pilot plan for replacing business tax with VAT was expanded to all regions and industries as of May 1, 2016 according to the Circular on Fully Promoting the Pilot Plan for Replacing Business Tax with Value-Added Tax promulgated by the MOF and the SAT in March 2016. Entities or individuals conducting business in the service industry in the PRC are required to pay a valued-added tax, or VAT, at a rate of 6% or 3% with respect to revenues derived from the provision of online information services. A taxpayer is allowed to offset the qualified input VAT paid on taxable purchases against the output VAT chargeable on the revenue from services provided.
C.
Organizational Structure
The following diagram illustrates the corporate structure of us and the consolidated VIE, including the names, places of incorporation and the proportion of ownership interests in our and the consolidated VIE’s significant subsidiaries and consolidated affiliated entities and their subsidiaries as of the date of this annual report:

(1)
Jiayin Southeast Asia Holdings Limited was established in February 2018 to develop and operate our overseas business.
(2)
Jiayin Technology is owned as to 58% by Mr. Dinggui Yan, our founder, director and chief executive officer, 27% by Shanghai Jinmushuihuotu Investment Center (Limited Partnership), or Jinmushuihuotu Investment, 12% by Mr. Guanglin Zhang, and 3% by Mr. Yuanle Wu, who both are employees of our company. Jinmushuihuotu Investment is established in connection with the share incentive plan of Jiayin Technology. See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—B. Compensation—Share Incentive Plans—2019 Share Incentive Plan.” The general partner of Jinmushuihuotu Investment is Shanghai Jinmushuihuotu Marketing and Planning Co., Ltd., or Jinmushuihuotu Marketing, which is controlled by Mr. Dinggui Yan.
(3)
Jiayin Technology entered into Contractual Arrangements with Shanghai Kunjia. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure—Contractual Arrangements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the shareholders of Jiayin Technology.”
(4)
Jiangxi Yunkaijianming became our wholly-owned subsidiary after the business combination in September 2019.
(5)
Shanghai Jiajie became our wholly-owned subsidiary after the business combination in July 2019.
(6)
Chuangzhen Software was established in April 2020.
(7)
Jiayin Shuke was established in January 2021.
(8)
Hainan Yinke was established in August 2021.
(9)
Guangxi Chuangzhen was established in January 2022.
(10)
Shanghai Jirongzhicheng was established in November 2024.
Risks Relating to the Consolidated VIE and China Operations
We are subject to risks and uncertainties relating to our corporate structure, including, but not limited to, the following:
•
Jiayin Group Inc. is a Cayman Islands holding company primarily operating in China through its subsidiaries and contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology. Investors in the ADSs thus are not purchasing, and may never hold, equity interests in the consolidated VIE. The interpretation and application of current and future PRC laws, regulations, and rules relating to such agreements that establish the VIE structure for the majority of our and the consolidated VIE’s operations in China, including potential future actions by the PRC government remains to be observed, which could affect the enforceability of our contractual arrangements with Jiayin Technology and, consequently, significantly affect the financial condition and results of operations of Jiayin Group Inc. If the PRC government finds such agreements non-compliant with relevant PRC laws, regulations, and rules, or if these laws, regulations, and rules or the interpretation thereof change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our beneficial interest in Jiayin Technology or forfeit our rights under the contractual arrangements;
•
The PRC government has authority to exert influence on the China operations of an offshore holding company, such as us. Changes in China’s economic, political or social conditions, or government policies may cause our and the consolidated VIE’s underlying operations in China to become prohibitive, which could materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business, financial condition, and results of operations;
•
We and the consolidated VIE are subject to extensive and evolving legal development, non-compliance with which, or changes in which, may materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s business and prospects, and may result in a material change in our and the consolidated VIE’s operations and/or the value of our ADSs or could significantly limit or completely hinder our and the consolidated VIE’s ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of our securities to significantly decline or be worthless;
•
It is unclear whether we and the consolidated VIE will be subject to the oversight of the CAC and how such oversight may impact us. Our and the consolidated VIE’s business could be interrupted or we and the consolidated VIE could be subject to liabilities which may materially and adversely affect the results of our and the consolidated VIE’s operation and the value of your investment;
•
The PRC government’s oversight over our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations could result in a material adverse change in our and the consolidated VIE’s operations and the value of our ADSs;
•
The approval, filing or other requirements of the CSRC, the CAC or other PRC government authorities may be required under PRC law in connection with our future offering;
•
The interpretation and enforcement of PRC laws and regulations could limit the legal protections available to you and us, significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer our ADSs, cause significant disruption to our and the consolidated VIE’s business operations, and severely damage our and the consolidated VIE’s reputation, which would materially and adversely affect our and the consolidated VIE’s financial condition and results of operations and cause our ADSs to significantly decline in value or become worthless;
•
We rely on Contractual Arrangements with Jiayin Technology and shareholders of Jiayin Technology for certain business operations, which may not be as effective as direct ownership in providing operational control, and these contractual arrangements have not been tested in a court of law; and
•
Any failure by Jiayin Technology or shareholders of Jiayin Technology to perform their obligations under our Contractual Arrangements with them would have a material adverse effect on our business.
For further details on the regulatory, liquidity, and enforcement risks relating to our corporate structure and the fact that we conduct substantially all of our operations in China, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure” and “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China.” You should also carefully consider other risks described under “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors” and other information contained in this annual report on Form 20-F, before you decide whether to purchase the ADSs.
Contractual Arrangements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the Shareholders of Jiayin Technology
Due to PRC legal restrictions on foreign ownership and investment in, among other areas, value-added telecommunications services, which include the operations of Internet content providers, or ICPs, we, similar to all other entities with foreign incorporated holding company structures operating in our industry in China, currently conduct these activities mainly through Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries over which we exercise effective control through Contractual Arrangements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and its shareholders.
The Contractual Arrangements allow us to:
•
exercise effective control over Jiayin Technology
•
receive substantially all of the economic benefits of Jiayin Technology; and
•
have an exclusive call option to purchase all or part of the equity interests in and/or assets of Jiayin Technology when and to the extent permitted by laws.
As a result of these Contractual Arrangements, we are the primary beneficiary of Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries for accounting purposes, and, therefore, have consolidated the financial results of Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries in our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
In the opinion of King & Wood Mallesons, our PRC legal counsel:
•
the ownership structure of Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries is not in violation of existing PRC laws, regulations and rules currently in effect; and
•
each of the VIE contractual agreements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the shareholders of Jiayin Technology is valid, binding and enforceable upon each party to such agreements in accordance with their terms and applicable PRC laws and regulations currently in effect.
As of and for the year ended December 31, 2024 and till the date of this annual report, the Company is not aware of any notice from the PRC government that the PRC government holds the opinion that the ownership structure of Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and its subsidiaries is illegal, or any of the VIE contractual agreements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the shareholders of Jiayin Technology governed by PRC laws are illegal. However, King & Wood Mallesons has also advised us that there are substantial uncertainties regarding the interpretation and application of PRC laws, rules and regulations and there can be no assurance that the PRC government will take a view that is consistent with the opinion of our PRC legal counsel, King & Wood Mallesons, in the future.
The following is a summary of the currently effective Contractual Arrangements by and among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and the shareholders of the Jiayin Technology.
Agreements that provide us with effective control over Jiayin Technology
Power of Attorney. Pursuant to the power of attorney issued by Jiayin Technology and its shareholders, each shareholder of Jiayin Technology, has irrevocably appointed the board of directors of Shanghai Kunjia to act as such shareholder’s exclusive attorney-in-fact to exercise all shareholder rights, including the right to attend and vote on shareholder’s meetings and appoint legal representatives, directors, supervisors and executive officers. In addition, the board of directors of Shanghai Kunjia is also entitled to appropriate, use or otherwise dispose of all dividends and other distributions. Furthermore, all activities of the board of directors of Shanghai Kunjia in connection with the equity interest of Jiayin Technology shall be considered activities of the shareholders of Jiayin Technology, including in the execution of the exclusive call option agreement. The board of directors of Shanghai Kunjia may delegate the power of attorney prescribed under this power of attorney to others without prior approval or notification. Jiayin Technology disclaims all rights and powers entrusted to the directors of Shanghai Kunjia. The power of attorney will remain in force for so long as the shareholder remains a shareholder of Jiayin Technology.
Equity Pledge Agreement. Pursuant to the equity interest pledge agreements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and each of the shareholders of Jiayin Technology, the shareholders of Jiayin Technology have pledged all of their equity interest in Jiayin Technology as a continuing first priority security interest, as applicable, to respectively guarantee Jiayin Technology’ performance of its obligations under the relevant Contractual Arrangements, which include the exclusive consultation and service agreement, exclusive call option agreement and power of attorney agreement provided that the guaranteed obligation shall not exceed the expected market capitalization of Jiayin Technology, which is US$20 billion, multiplied by their respective shareholding percentage.
If Jiayin Technology breaches its contractual obligations under these agreements, Shanghai Kunjia, as pledgee, will be entitled to certain rights regarding the pledged equity interests. In the event of such breaches, Shanghai Kunjia’s rights include forcing the auction or sale of all or part of the pledged equity interests of Jiayin Technology and receiving proceeds from such auction or sale in accordance with PRC law to the extent the rights of Shanghai Kunjia under the Contractual Arrangements are satisfied. In the event of significant decrease in value of the equity interest of Jiayin Technology, in addition to the foregoing remedies, Shanghai Kunjia is also entitled to entrust notary with the proceeds from such auction or sale, or requiring the shareholders, as pledgor, to provide other forms of security acceptable to Shanghai Kunjia. It is also agreed that any subscription of additional registered capital of Jiayin Technology or any equity interests transferred among those shareholders will automatically be subject to this agreement and the shareholders will be obligated to register pledge of such equity interest in ten business days. During the term of the applicable equity interest pledges, such shareholder will not dispose of the pledged equity interests or create or allow any encumbrance on the pledged equity interests. Each equity interest pledge will remain effective until the full performance of the contractual agreements, including the settlement of payment by Jiayin Technology and its shareholders and indemnification of any losses caused by Jiayin Technology, if applicable, and termination of such contractual agreements. We have registered pledges of equity interest in Jiayin Technology with the relevant office of the administration for industry and commerce in accordance with the PRC Property Rights Law.
Agreement that allows us to receive economic benefits from Jiayin Technology
Exclusive Consultation and Service Agreement. Pursuant to the Exclusive Consultation and Service Agreement between Shanghai Kunjia and Jiayin Technology, Shanghai Kunjia has the exclusive right to provide Jiayin Technology with consulting and other services. Without Shanghai Kunjia’s prior written consent, Jiayin Technology may not accept any services subject to this agreement from any third party. In exchange, Shanghai Kunjia is entitled to receive a service fee on a quarterly basis and at an amount equivalent to all of its net income. Shanghai Kunjia has the right to determine the service fee to be charged to Jiayin Technology under this agreement by considering, among other things, the complexity of the services, the actual time that may be spent and cost that may be incurred for providing such services, as well as the value and comparable price on the market of the service provided. Shanghai Kunjia will exclusively enjoy all the rights, property rights and intellectual property rights created as a result of the performance of this agreement. Without prior written consent of Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology shall not enter into any transactions which may materially affect Jiayin Technology’s assets, liabilities, business operations, equity interests and other legal interests. Unless Shanghai Kunjia terminates this agreement in advance or otherwise required by law, this agreement will remain effective for ten years and automatically extend for another ten years upon any expiration date. Jiayin Technology may not terminate this agreement unilaterally.
Agreement that provides us with the option to purchase the equity interests in Jiayin Technology
Exclusive Call Option Agreement. Pursuant to the exclusive call option agreements among Shanghai Kunjia, Jiayin Technology and shareholders of Jiayin Technology, Jiayin Technology and each of their shareholders have irrevocably granted Shanghai Kunjia an exclusive option to purchase, or have its designated person or persons to purchase, at its discretion at any time, to the extent permitted under PRC law, all or part of such shareholder’s equity interests in the applicable, or all or part of the assets, of Jiayin Technology for RMB1, or the minimum purchase price as permitted by PRC laws. Shareholders of Jiayin Technology promise to make all efforts to enable Shanghai Kunjia to exercise its option, including but not limited to resignation and granting options and right to earnings of Shanghai Kunjia. Without Shanghai Kunjia’s prior written consent, Jiayin Technology and its shareholders have agreed that they shall not amend its articles of association, increase or decrease the registered capital, sell or otherwise dispose of its assets or beneficial interest, create or allow any encumbrance on its assets or other beneficial interests, provide any loans or guarantees and etc. Jiayin Technology and its shareholders undertake to appoint persons designated by Shanghai Kunjia as directors of Jiayin Technology. Unless Shanghai Kunjia terminates this agreement in advance or otherwise required by law, this agreement will remain effective for ten years and automatically extend for another ten years upon any expiration date. Jiayin Technology may not terminate this agreement unilaterally.
D.
Property, Plants and Equipment
Our and the VIE Group’s principal executive offices are located on leased premises comprising 11,160 square meters in Shanghai, China. We and the VIE Group lease our premises mainly from unrelated third parties under operating lease agreements.
On December 17, 2024, we entered into a definitive agreement to purchase certain commercial property located in Shanghai, China (the “Commercial Property”) of approximately 43,500 square meters for total cash consideration of approximately RMB1.35 billion (US$184.9 million). In March 2025, we paid all consideration for and obtained title to, the Commercial Property. The Commercial Property will primarily be used as our new headquarters to meet the demand arising from the continuing growth of our businesses.
Our and the VIE Group’s servers are primarily hosted at third-party Internet data centers. We and the VIE Group believe that we will be able to obtain adequate facilities, principally through leasing, to accommodate our future expansion plans.
Not applicable.
ITEM 5. OPERATING AND FINANCIAL REVIEW AND PROSPECTS
The following discussion and analysis of our and the VIE Group’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our and the VIE Group’s consolidated financial statements and the related notes thereto included elsewhere in this annual report on Form 20-F. This discussion may contain forward-looking statements based upon current expectations that involve risks and uncertainties. Our and the VIE Group’s actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including those set forth under “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors” or in other parts of this annual report on Form 20-F. For discussion of year-over-year comparisons between 2023 and 2022 that are not included in this annual report on Form 20-F, refer to "Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects" found in our Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2023, that was filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 29, 2024.
Overview
We and the VIE Group are a leading fintech platform in China committed to facilitating effective, transparent, secure and fast connections between underserved individual borrowers and financial institutions. We and the VIE Group operate a highly secure and open platform with a comprehensive risk management system and a proprietary and effective risk assessment model which employs advanced big data analytics and sophisticated algorithms to accurately assess the risk profiles of potential borrowers. Our and the VIE Group’s online platform embraces significant opportunities presented by a financial system that leaves many creditworthy individuals underserved. We and the VIE Group provide borrowers with fast and convenient access to credit at affordable and competitive rates. We and the VIE Group do not use our and the VIE Group’s own capital to invest in loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform in Mainland China.
We and the VIE Group offer loan products with fixed terms and repayment schedules generally ranging from RMB500 to RMB150,000 via our and the VIE Group’s apps and our and the VIE Group’s website. We and the VIE Group strategically focused on facilitating loans primarily with a term of no more than 12 months, as we and the VIE Group believe such loan products facilitated by us and the VIE Group are best positioned to generate attractive returns, and at the same time, capture the financing needs of qualified borrowers.
We and the VIE Group introduce borrowers to our and the VIE Group’s institutional funding partners, including commercial banks, trusts, consumer finance companies and micro-credit companies, and provide preliminary risk assessment services as well as other services to them. For institutional funding partners with a license to extend loans, such as banks, online micro-credit companies, they typically extend loans with their own funds directly to the borrowers introduced by us. In 2024, we and the VIE Group facilitated an aggregate loan volume of RMB100.8 billion (US$13.8 billion), funded by 48 institutional funding partners. We and the VIE Group also provide guarantee services through our own licensed financing guarantee subsidiary or through cooperation with third-party licensed financing guarantee companies. Under the guarantee services through our and VIE Group’s licensed financing guarantee subsidiaries, such subsidiaries are obligated to place deposits directly to institutional funding partners with an agreed percentage of outstanding loan balance subject to guarantee. We and the VIE Group record deposits to funding banks under restricted cash, and deposits to institutional funding partners other than funding banks under prepaid expenses and other current assets, net on the consolidated balance sheets, respectively. Under the cooperation with third-party licensed financing guarantee companies, such companies initially reimburses the loan principal and interest to the institutional funding partners upon borrower’s default. Although we and the VIE Group do not have direct contractual obligation to the institutional funding partners for defaulted principal and interest, we and the VIE Group provide back-to-back guarantee to the third-party licensed financing guarantee companies. As of December 31, 2023 and 2024, the maximum potential future payments, including all outstanding principal and interest for which our and the VIE Group provide primary guarantee, were RMB13.7 billion and RMB2.8 billion (US$0.4 billion), respectively.
Our and the VIE Group’s net revenue increased by 6.1% from RMB5,466.9 million in 2023 to RMB5,801.0 million (US$794.7 million) in 2024. Our net income was RMB1,056.5 million (US$144.7 million), compared with RMB1,297.6 million in 2023.
General Factors Affecting Our and the VIE Group’s Results of Operations
Economic Conditions
The demand for online consumer finance service is dependent upon overall economic conditions in China. General economic factors, including the interest rate environment, regional salary and disposable income levels and unemployment rates, may affect borrowers’ willingness to seek loans and funding partners’ ability and desire to invest in loans. For example, significant increases in interest rates could cause potential borrowers to defer obtaining loans as they wait for interest rates to stabilize or decrease. Additionally, a slowdown in the economy, such as a rise in the unemployment rate and a decrease in real income, may affect individuals’ level of disposable income. This may negatively affect borrowers’ repayment capability, which in turn may decrease their willingness to seek loans and potentially cause an increase in default rates. If actual or expected default rates increase generally in China or in the online consumer finance market, investors may delay or reduce their investments in loan products in general.
Regulatory Environment in China
The regulatory environment for the online consumer finance industry in China is evolving, with new legislation and trial programs being instituted in the recent years, creating both challenges and opportunities that could affect our and the VIE Group’s financial performance. PRC government officials from a number of agencies and departments have expressed support for the development of the online consumer finance industry in China, and have also expressed the need for strengthening the regulation and supervision of the industry.
Unfavorable changes in any of these general industry conditions could negatively affect demand for our and the VIE Group’s services. As the regulatory regime is evolving, and the interpretation and enforcement of related laws and regulations remains to be observed, it results in difficulties in determining whether our and the VIE Group’s existing practices may be interpreted to violate any applicable laws and regulations, and any such violation could materially and adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s business, financial condition and results of operation.
Furthermore, due to the lack of clarity in certain key definitions under these regulations, there remain uncertainties including the possibility that regulatory authorities may disagree with our and the VIE Group’s interpretation. For example, it is still uncertain whether our and the VIE Group’s cooperation model with institutional funding partners will be influenced by the CBIRC Circular 37. As our and the VIE Group’s future revenue, profit and working capital rely on the amount of loans facilitated on our and the VIE Group’s platform and the corresponding service fees we and the VIE Group are entitled to collect from such loans, if we and the VIE Group were required by regulatory action to cease or reduce offering loan facilitation services to individual borrowers or funding loans with institutional funding partners, we and the VIE Group might need to take various measures in order to maintain the current scale or growth of our and the VIE Group’s business while adhering to our and the VIE Group’s interpretations of these regulations. These measures might include providing technology services to third-party companies, expanding our and the VIE Group’s overseas businesses, diversifying our and the VIE Group’s funding channels and strengthening our and the VIE Group’s cooperation with financial institutions, which may not be available on reasonable terms in a timely manner, or at all, and all of these measures may not be sufficient to maintain our and the VIE Group’s business growth, and may not generate sufficient revenue or cash inflows to offset decreases in the outstanding principal of our and the VIE Group’s platform, or may not otherwise result in the intended benefits.
We and the VIE Group will continue to make efforts to ensure that we and the VIE Group are compliant with the existing laws, regulations and governmental policies relating to our and the VIE Group’s industry and to comply with new laws and regulations or changes under existing laws and regulations that may arise in the future. While new laws and regulations or changes to existing laws and regulations could make loans more difficult to be accepted by institutional funding partners or borrowers on terms favorable to us, or at all, these events could also provide new product and market opportunities.
Ability to Acquire Borrowers Cost Effectively
Our and the VIE Group’s ability to increase the loan volume facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform largely depends on our and the VIE Group’s ability to attract borrowers through sales and marketing efforts. Our and the VIE Group’s sales and marketing efforts include those related to borrower acquisition and retention, and general marketing. We and the VIE Group intend to continue to dedicate significant resources to our and the VIE Group’s sales and marketing efforts and constantly seek to improve the effectiveness of these efforts.
Effectiveness of Risk Control Framework
Our and the VIE Group’s ability to effectively evaluate a borrower’s risk profile and likelihood of default affects our and the VIE Group’s relationships with our and the VIE Group’s funding partners. If the effectiveness of our and the VIE Group’s risk control framework decreases and borrower default rates increase, our and the VIE Group’s funding partners may reduce or stop their collaboration with us, which would adversely affect our and the VIE Group’s funding source and in turn reduce the amount of loans of we and the VIE Group can facilitate, both of which could have significant impact on our and the VIE Group’s results of operations.
Ability to Attract and Retain Institutional Funding Partners and to Compete Effectively
Our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations depend on our and the VIE Group’s ability to attract and retain institutional funding partners and to compete effectively in the markets in which we and the VIE Group operate. Reinforcing long-standing relationships with our institutional funding partners ensures that we have sufficient and sustainable funding to meet borrower demands and thus is key to our success. Furthermore, retaining the existing and expanding the base of institutional funding partners is critical to secure a stable stream of funds and to increase the volume of loans facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform, driving the growth of our and the VIE Group’s future operations.
The online consumer finance industry in China is intensely competitive, and we and the VIE Group expect that competition to persist and intensify in the future. In addition to competing with other online consumer finance platforms, we and the VIE Group also compete with other types of financial products and companies that attract borrowers and/or funding partners. With respect to borrowers, we and the VIE Group primarily compete with traditional financial institutions, such as online consumer finance business units in commercial banks, credit card issuers and other online consumer finance companies. If we and the VIE Group are unable to compete effectively, the demand for our and the VIE Group’s products and services could stagnate or substantially decline, we and the VIE Group could experience reduced revenues or our and the VIE Group’s platform could fail to maintain or achieve more widespread market acceptance, any of which could harm our and the VIE Group’s business and results of operations.
Credit Performance Data
Our and the VIE Group’s operating results and financial condition are directly affected by the performance of the loans we and the VIE Group facilitate. We and the VIE Group closely monitor key loan performance data, including the data set out below, to track the lifetime performance of our and the VIE Group’s loans and adjust our and the VIE Group’s risk management strategies accordingly.
M3+ Delinquency Rate by Vintage
We and the VIE Group refer to loans facilitated during a specified time period as a vintage. We and the VIE Group define “M3+ Delinquency Rate by Vintage” as the total amount of principal for all loans in a vintage for which any repayment was more than 90 days past due as of a particular date, less the total amount of past due principal recovered for such loans, and divided by the total amount of principal for all loans in such vintage. We and the VIE Group calculate M3+ Delinquency Rate by Vintage for quarter vintage as the weighted average of the M3+ Delinquency Rate by Vintage for each month in such quarter by loan facilitation volume.
The following chart and table display the historical cumulative M3+ Delinquency Rate by Vintage for loan products facilitated through our and the VIE Group’s platform.

Delinquency Rate by Balance
We and the VIE Group define the delinquency rates by balance as the total outstanding principal for loans where the longest past due period of a repayment was 1 to 30, 31 to 60, 61 to 90, 91 to 180 and more than 180 calendar days as of a certain date as a percentage of the total outstanding principal for the loans on our and the VIE Group’s platform. We and the VIE Group consider our and the VIE Group’s delinquency rate by balance as an indicator of our and the VIE Group’s loan performance and quality of our and the VIE Group’s assets in general. The following table provides the delinquency rate by balance for all outstanding loans on our and the VIE Group’s platform as of the respective dates indicated.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Delinquent for |
|
As of |
|
1-30 days |
|
|
31-60 days |
|
|
61-90 days |
|
|
91-180 days |
|
|
More than
180 days |
|
|
|
(%) |
|
December 31, 2020 |
|
|
1.47 |
|
|
|
0.88 |
|
|
|
0.70 |
|
|
|
1.66 |
|
|
|
1.81 |
|
December 31, 2021 |
|
|
1.31 |
|
|
|
0.90 |
|
|
|
0.72 |
|
|
|
1.78 |
|
|
|
2.12 |
|
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
1.01 |
|
|
|
0.67 |
|
|
|
0.51 |
|
|
|
1.18 |
|
|
|
2.02 |
|
December 31, 2023 |
|
|
1.13 |
|
|
|
0.90 |
|
|
|
0.68 |
|
|
|
1.48 |
|
|
|
2.07 |
|
December 31, 2024 |
|
|
1.02 |
|
|
|
0.79 |
|
|
|
0.53 |
|
|
|
1.16 |
|
|
|
2.36 |
|
Components of Results of Operations
Net Revenue
Our and the VIE Group’s net revenue is derived from fees charged for providing services, including loan facilitation services, guarantee services, and other revenues. In accordance with the agreements with our and the VIE Group’s borrowers and institutional funding partners, we and the VIE Group collect service fees from customers in facilitating loan transactions. In addition, we and the VIE Group charge other fees contingent on future events, such as variable consideration due to borrowers’ actual repayment to institutional funding partners.
Our and the VIE Group’s net revenue is presented net of VAT. Our and the VIE Group’s net revenue is recognized as revenues from loan facilitation services, revenues from releasing of guarantee liabilities and other revenues.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
|
% |
|
|
|
(in thousands, except for percentages) |
|
Net revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue from loan
facilitation services |
|
|
2,881,725 |
|
|
|
88.1 |
|
|
|
3,489,184 |
|
|
|
63.8 |
|
|
|
4,011,776 |
|
|
|
549,611 |
|
|
|
69.2 |
|
Revenue from the releasing
of guarantee liabilities |
|
|
47,141 |
|
|
|
1.4 |
|
|
|
1,393,081 |
|
|
|
25.5 |
|
|
|
1,357,705 |
|
|
|
186,005 |
|
|
|
23.4 |
|
Other revenue |
|
|
342,548 |
|
|
|
10.5 |
|
|
|
584,608 |
|
|
|
10.7 |
|
|
|
431,551 |
|
|
|
59,122 |
|
|
|
7.4 |
|
Total |
|
|
3,271,414 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
|
|
5,466,873 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
|
|
5,801,032 |
|
|
|
794,738 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
Revenue from loan facilitation services
We and the VIE Group provide service through the facilitation of loan transactions between borrowers and institutional funding partners. Our and the VIE Group’s service mainly consist of performing credit assessment on the borrowers and referring qualified borrowers to the institutional funding partners and facilitating the execution of loan agreements between the parties. We and the VIE Group assesses ability and intention to pay the service fees of the customers when they become due and determines if the collection of the service fees is probable, based on historical experiences as well as the credit due diligence performed before cooperation.
We and the VIE Group determine the total transaction price to be the service fees chargeable according to the contracts, net of value-added tax. Under certain agreements, the transaction price includes variable consideration due to borrowers’ actual repayment to institutional funding partners. We and the VIE Group estimate variable consideration for these contracts using the expected value approach on the basis of historical information. We and the VIE Group identify one performance obligation under ASC Topic 606, as we and the VIE Group do not retain any further obligations after the facilitation of a loan.
We and the VIE Group recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies the service/ performance obligation by transferring the promised service (that is, an asset) to customers based on the underlying contract terms excluding consideration of impairment of contract assets or accounts receivable. Revenues from loan facilitation services are recognized at the time a loan is facilitated between the institutional funding partners and the borrower and the principal loan balance is transferred to the borrower, at which time the facilitation service is considered completed.
From 2020 to 2022, the institutional funding partners typically engage third-party non-performing loan management entities to assist on the subsequent collection. We and the VIE Group are in turn engaged by such non-performing loan management entities to provide information including risk profile and collection methods or plans for the borrowers on its platform to the non-performing loan management entity based on the historical records and experiences that we and the VIE Group have as of the date when each loan is successfully extended to borrower. Revenue from technical services is recognized at the time a loan is successfully facilitated by the institutional funding partner as the technical services are completed at that time. We and the VIE Group no longer provided this service since 2023.
Revenue from releasing of guarantee liabilities
We and the VIE Group started to provide primary guarantee since the fourth quarter of 2022. We recognized the stand-ready guarantee liabilities on a gross basis and amortize the entire amount into “revenue from releasing of guarantee liabilities” over the term of the guarantee. See “—E. Critical Accounting Estimates—Guarantee liabilities” for more details.
Other Revenue
Investor referral
We and the VIE Group provide referral services in respect of investment products offered by the third-party financial service providers on Youdao wealth platform, a proprietary platform operated by us. We and the VIE Group consider the financial service providers to be our customers, and receives service fees from the customers primarily based on the transaction volume of the investment successfully subscribed by online investors. After the online investors subscribe the products referred by us, We and the VIE Group do not retain any further obligations.
The price for each referral charged to the financial service providers is a fixed charge rate as pre-agreed in the service contract. Revenue is recognized when the online investors successfully subscribed to investment products from financial service providers.
Others
Other revenues primarily include service fees charged to the third-party financial service providers for the referral service of borrowers, and interest income generated from loan services to individuals overseas.
Interest income generated from oversea individuals is recognized over the terms of loans receivable using the effective interest rate method under ASC Topic 310. Interest income is not recorded when reasonable doubt exists as to the full, timely collection of interest income or principal. Interest collected upfront at the loan inception is recorded as deferred revenue.
The following table sets forth the breakdown of our and the VIE Group’s other revenue, both in absolute amount and as a percentage of our and the VIE Group’s total net revenue for the periods presented:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
|
% |
|
|
|
(in thousands, except for percentages) |
|
Other revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investor referral |
|
|
269,256 |
|
|
|
8.2 |
|
|
|
342,181 |
|
|
|
6.3 |
|
|
|
228,488 |
|
|
|
31,302 |
|
|
|
3.9 |
|
Others |
|
|
73,292 |
|
|
|
2.3 |
|
|
|
242,427 |
|
|
|
4.4 |
|
|
|
203,063 |
|
|
|
27,820 |
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
Total other revenue |
|
|
342,548 |
|
|
|
10.5 |
|
|
|
584,608 |
|
|
|
10.7 |
|
|
|
431,551 |
|
|
|
59,122 |
|
|
|
7.4 |
|
Operating Costs and Expenses
Our and the VIE Group’s operating costs and expenses primarily consist of facilitation and servicing expenses, sales and marketing expenses, general and administrative expenses, research and development expenses, and allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets, loans receivable and others. We and the VIE Group expect our and the VIE Group’s operating expenses to be in line with our and the VIE Group’s business development. The following table sets forth our and the VIE Group’s operating costs and expenses both in absolute amount and as a percentage of our and the VIE Group’s total net revenue for the periods presented:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
|
% |
|
|
|
(in thousands, except for percentages) |
|
Operating cost and
expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Facilitation and servicing |
|
|
565,227 |
|
|
|
17.3 |
|
|
|
2,011,553 |
|
|
|
36.8 |
|
|
|
2,033,511 |
|
|
|
278,590 |
|
|
|
35.1 |
|
Allowance for uncollectible
receivables, contract assets,
loans receivable and others |
|
|
32,053 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
|
72,764 |
|
|
|
1.3 |
|
|
|
12,204 |
|
|
|
1,672 |
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
1,081,382 |
|
|
|
33.1 |
|
|
|
1,538,913 |
|
|
|
28.1 |
|
|
|
1,913,868 |
|
|
|
262,199 |
|
|
|
33.0 |
|
General and administrative |
|
|
194,039 |
|
|
|
5.9 |
|
|
|
214,856 |
|
|
|
3.9 |
|
|
|
220,993 |
|
|
|
30,276 |
|
|
|
3.8 |
|
Research and development |
|
|
216,694 |
|
|
|
6.6 |
|
|
|
296,317 |
|
|
|
5.4 |
|
|
|
372,441 |
|
|
|
51,024 |
|
|
|
6.4 |
|
Total operating cost and
expenses |
|
|
2,089,395 |
|
|
|
63.9 |
|
|
|
4,134,403 |
|
|
|
75.5 |
|
|
|
4,553,017 |
|
|
|
623,761 |
|
|
|
78.5 |
|
The following table sets forth our and the VIE Group’s operating cost and expenses paid to related parties both in absolute amounts and as a percentage of our and the VIE Group’s total net revenue for the periods presented:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
|
% |
|
|
|
(in thousands, except for percentages) |
|
Operating cost and expenses
incurred with related
parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Facilitation and servicing |
|
|
124,071 |
|
|
|
3.8 |
|
|
|
115,888 |
|
|
|
2.1 |
|
|
|
74,549 |
|
|
|
10,213 |
|
|
|
1.3 |
|
General and administrative |
|
|
2,103 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
482 |
|
|
|
0.0 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
- |
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
4,873 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
630 |
|
|
|
0.0 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
- |
|
Research and development |
|
|
4,373 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
1,074 |
|
|
|
0.0 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
- |
|
Total |
|
|
135,420 |
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
|
|
118,074 |
|
|
|
2.1 |
|
|
|
74,549 |
|
|
|
10,213 |
|
|
|
1.3 |
|
Facilitation and Servicing
Facilitation and servicing expenses primarily consist of variable expenses including costs related to back-to-back guarantee service fee to third-party companies, credit assessment, user and system support, payment processing services and collection, associated with facilitating and servicing loans, salaries and benefits and share-based compensation for the personnel who work on credit checking, data processing and analysis, loan facilitation, user and system support.
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing expenses primarily consist of variable marketing and promotional expenses, including those expenses related to acquisition and retention of borrowers and institutional funding partners, and general brand and awareness building. Salaries and benefits expenses as well as share-based compensation related to our and the VIE Group’s sales and marketing personnel and other expenses related to our sales and marketing team are also included in the sales and marketing expenses. Borrower acquisition expenses include charges by third-party online channels for online marketing services such as search engine marketing, search engine optimization, information feeds, and referral fees charged by other parties relating to borrower acquisition.
General and Administrative
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and benefits and share-based compensation related to accounting and finance, business development, legal, human resources and other personnel, as well as professional service fees related to various corporate activities.
Research and Development
Research and development expenses primarily consist of salaries and other compensation expenses for employees engaged in research and development activities, technology infrastructure expenses and server expenses.
Share-Based Compensation
The following table sets forth the effect of share-based compensation expenses on our and the VIE Group’s operating cost and expenses line items, both in an absolute amount and as a percentage of total net revenue for the periods presented.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
|
% |
|
|
|
(in thousands, except for percentages) |
|
Share-based compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Facilitation and servicing |
|
|
2,408 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
4,921 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
8,035 |
|
|
|
1,101 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
General and administrative |
|
|
33,740 |
|
|
|
0.8 |
|
|
|
31,464 |
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
|
|
25,879 |
|
|
|
3,546 |
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
Research and development |
|
|
6,038 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
6,823 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
10,557 |
|
|
|
1,446 |
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
362 |
|
|
|
0.0 |
|
|
|
11,145 |
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
14,651 |
|
|
|
2,007 |
|
|
|
0.3 |
|
Total share-based
compensation |
|
|
42,548 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
|
54,353 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
|
59,122 |
|
|
|
8,100 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
|
Taxation
Cayman Islands
Jiayin Group Inc. is incorporated in the Cayman Islands. Under the current laws of the Cayman Islands, Jiayin Group Inc. is not subject to income or capital gains taxes. In addition, dividend payments are not subject to withholdings tax in the Cayman Islands.
Hong Kong
The first 2.0 million Hong Kong dollars of profits that our subsidiary incorporated in Hong Kong earned are subject to be taxed at an income tax rate at 8.25%, while the remaining profits will continue to be taxed at the existing tax rate of 16.5%. Additionally, payments of dividends by the subsidiary incorporated in Hong Kong to us are not subject to any Hong Kong withholding tax.
PRC
Under the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law, or the EIT Law, the standard enterprise income tax rate for domestic enterprises and foreign invested enterprises is 25%. A “high and new technology enterprise” (HNTE) is entitled to a favorable statutory tax rate of 15% and such qualification is reassessed by relevant governmental authorities every three years. Geerong Yunke and Jiayin Shuke were entitled for a preferential income tax rate of 15% from 2022 to 2024 as they are qualified as HNTE. Chuangzhen Software has been qualified as an eligible software enterprise. As a result of this qualification, it is entitled to a tax holiday of a full exemption for year 2020 and 2021 which its taxable income is greater than zero, followed by a three-year 50% exemption. From 2022, Guangxi Chuangzhen Information Technology Co., Ltd. benefits from a preferential tax rate of 9% as it falls within the encouraged industries catalogue in western China. From 2023, Hainan Yinke Financing Guarantee Co., Ltd. benefits from a preferential tax rate of 15% as it is registered in Hainan Free Trade Port and engaged in encouraged business activities.
We and the VIE Group is subject to VAT at the rate of 6% or 3% given that they are classified as a general tax payer. Entities that are VAT general taxpayers are allowed to offset qualified input VAT paid to suppliers against their output VAT liabilities.
Dividends paid by our wholly foreign-owned subsidiary in China to our intermediary holding company in Hong Kong will be subject to a withholding tax rate of 10%, unless the relevant Hong Kong entity satisfies all the requirements under the Arrangement between the Mainland China and the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region for the Avoidance of Double Taxation and Tax Evasion on Income and receives approval from the relevant tax authority. If our Hong Kong subsidiary satisfies all the requirements under the tax arrangement, then the dividends paid to the Hong Kong subsidiary would be subject to withholding tax at the standard rate of 5%.
If our holding company in the Cayman Islands or any of our subsidiaries outside of China were deemed to be a “resident enterprise” under the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law, it would be subject to enterprise income tax on its worldwide income at a rate of 25%.
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth a summary of our and the VIE Group’s consolidated results of operations for the periods presented, both in absolute amount and as a percentage of our and the VIE Group’s total operating revenues for the periods presented. This information should be read together with our and the VIE Group’s consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this annual report. The results of operations in any period are not necessarily indicative of our and the VIE Group’s future trends.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
% |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
|
% |
|
|
|
(in thousands, except for percentages) |
|
Net revenue |
|
|
3,271,414 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
|
|
5,466,873 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
|
|
5,801,032 |
|
|
|
794,738 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
Operating cost and expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
Facilitation and servicing |
|
|
(565,227 |
) |
|
|
(17.3 |
) |
|
|
(2,011,553 |
) |
|
|
(36.8 |
) |
|
|
(2,033,511 |
) |
|
|
(278,590 |
) |
|
|
(35.1 |
) |
Allowance for uncollectible
receivables, contract assets,
loans receivable and others |
|
|
(32,053 |
) |
|
|
(1.0 |
) |
|
|
(72,764 |
) |
|
|
(1.3 |
) |
|
|
(12,204 |
) |
|
|
(1,672 |
) |
|
|
(0.2 |
) |
Sales and marketing |
|
|
(1,081,382 |
) |
|
|
(33.1 |
) |
|
|
(1,538,913 |
) |
|
|
(28.1 |
) |
|
|
(1,913,868 |
) |
|
|
(262,199 |
) |
|
|
(33.0 |
) |
General and administrative |
|
|
(194,039 |
) |
|
|
(5.9 |
) |
|
|
(214,856 |
) |
|
|
(3.9 |
) |
|
|
(220,993 |
) |
|
|
(30,276 |
) |
|
|
(3.8 |
) |
Research and development |
|
|
(216,694 |
) |
|
|
(6.6 |
) |
|
|
(296,317 |
) |
|
|
(5.4 |
) |
|
|
(372,441 |
) |
|
|
(51,024 |
) |
|
|
(6.4 |
) |
Total operating cost and
expenses |
|
|
(2,089,395 |
) |
|
|
(63.9 |
) |
|
|
(4,134,403 |
) |
|
|
(75.5 |
) |
|
|
(4,553,017 |
) |
|
|
(623,761 |
) |
|
|
(78.5 |
) |
Income from operations |
|
|
1,182,019 |
|
|
|
36.1 |
|
|
|
1,332,470 |
|
|
|
24.5 |
|
|
|
1,248,015 |
|
|
|
170,977 |
|
|
|
21.5 |
|
Gain from de-recognition of
liabilities |
|
|
117,021 |
|
|
|
3.6 |
|
|
|
280,231 |
|
|
|
5.1 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Loss from disposal of subsidiaries |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(2,012 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(14,431 |
) |
|
|
(1,977 |
) |
|
|
(0.2 |
) |
Impairment of long-term
investments |
|
|
(15,078 |
) |
|
|
(0.5 |
) |
|
|
(91,236 |
) |
|
|
(1.7 |
) |
|
|
(51,923 |
) |
|
|
(7,113 |
) |
|
|
(0.9 |
) |
Interest income, net |
|
|
281 |
|
|
|
0.0 |
|
|
|
12,895 |
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
18,281 |
|
|
|
2,504 |
|
|
|
0.3 |
|
Other income, net |
|
|
43,447 |
|
|
|
1.4 |
|
|
|
14,834 |
|
|
|
0.3 |
|
|
|
95,426 |
|
|
|
13,073 |
|
|
|
1.6 |
|
Income before income taxes and
share of income from equity
method investments |
|
|
1,327,690 |
|
|
|
40.6 |
|
|
|
1,547,182 |
|
|
|
28.4 |
|
|
|
1,295,368 |
|
|
|
177,464 |
|
|
|
22.3 |
|
Income tax expense |
|
|
(155,398 |
) |
|
|
(4.7 |
) |
|
|
(247,616 |
) |
|
|
(4.5 |
) |
|
|
(238,900 |
) |
|
|
(32,729 |
) |
|
|
(4.1 |
) |
Share of income (loss) from equity
method investments |
|
|
7,940 |
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
(1,990 |
) |
|
|
0.0 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Net income |
|
|
1,180,232 |
|
|
|
36.1 |
|
|
|
1,297,576 |
|
|
|
23.9 |
|
|
|
1,056,468 |
|
|
|
144,735 |
|
|
|
18.2 |
|
Year Ended December 31, 2024 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2023
Net revenue. Our and the VIE Group’s net revenue increased from RMB5,466.9 million in 2023 to RMB5,801.0 million (US$794.7million) in 2024.
Revenue from loan facilitation services increased from RMB3,489.2 million in 2023 to RMB4,011.8 million (US$549.6 million) in 2024, primarily attributed to the increase in the facilitation volume from RMB88.1 billion to RMB100.8 billion (US$13.8 million).
Revenue from the releasing of guarantee liabilities decreased from RMB1,393.1 million in 2023 to RMB1,357.7 million (US$186.0 million) in 2024, primarily due to the decrease in average outstanding loan balances for which we and the VIE Group provided guarantee services.
Revenue from other revenue decreased from RMB584.6 million in 2023 to RMB431.5 million (US$59.1 million) in 2024, primarily due to the decrease in revenue from investor referral service.
Operating costs and expenses. Our and the VIE Group’s total operating costs and expenses increased from RMB4,134.4 million in 2023 to RMB4,553.0 million (US$623.8 million) in 2024, primarily due to increased loan facilitation volume and partially offset by decreased expenses related to financial guarantee services.
•
Facilitation and servicing expenses. Our and the VIE Group’s facilitation and servicing expenses increased from RMB2,011.6 million in 2023 to RMB2,033.5 million (US$278.6 million) in 2024, primarily due to increased loan facilitation volume and partially offset by the decreased expenses related to financial guarantee services.
•
Allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets, loans receivable and others. Our and the VIE Group’s allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets, loans receivable and others decreased from RMB72.8 million in 2023 to RMB12.2 million (US$1.7 million) in 2024, primarily due to the decrease in loans receivable as a result of disposal of Nigeria entities in 2024.
•
Sales and marketing expenses. Our and the VIE Group’s sales and marketing expenses increased from RMB1,538.9 million in 2023 to RMB1,913.9 million (US$262.2 million) in 2024, primarily due to an increase in borrower acquisition expenses.
•
General and administrative expenses. Our and the VIE Group’s general and administrative expenses increased from RMB214.9 million in 2023 to RMB221.0 million (US$30.3 million) in 2024, primarily driven by increases in professional service fees.
•
Research and development expenses. Our and the VIE Group’s research and development expenses increased from RMB296.3 million in 2023 to RMB372.4 million (US$51.0 million) in 2024, primarily due to higher employee compensation and benefit expenses.
Interest income, net. We and the VIE Group recognized interest income of RMB12.9 million in 2023 and RMB18.3 million (US$2.5 million) in 2024, respectively.
Other income, net. Our and the VIE Group’s other income decreased from RMB14.8 million in 2023 to RMB95.4 million (US$13.1 million) in 2024.
Income before income taxes and share of gain from equity method investments. As a result of foregoing, we and the VIE Group recognized income before income taxes and share of gain from equity method investments of RMB1,547.2 million and RMB1,295.4 million (US$177.5 million) in 2023 and 2024, respectively.
Income tax expense. We and the VIE Group recognized tax expenses of RMB247.6 million in 2023 and RMB238.9 million (US$32.7 million) in 2024.
Net income. As a result of foregoing, we and the VIE Group recorded net income of RMB1,297.6 million and RMB1,056.5 million (US$144.7 million) in 2023 and 2024, respectively.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See note 2 to the consolidated financial statements for details on recent accounting pronouncements and our adoption of certain accounting rules.
Inflation
As of the date of this annual report, inflation in China has not materially impacted our and the VIE Group’s results of operations. According to the National Bureau of Statistics of China, the year-over-year percent changes in the consumer price index for December 2022, 2023 and 2024 were increase of 1.8%, decrease of 0.3% and decrease of 0.1%, respectively. Although we and the VIE Group have not been materially affected by inflation in the past, we and the VIE Group can provide no assurance that we and the VIE Group will not be affected by higher rates of inflation in China in the future.
B.
Liquidity and Capital Resource
Our and the VIE Group’s primary source of liquidity has been cash provided by operating activities, and funds provided by our and the VIE Group’s shareholders, including through capital contributions and loans from related parties, which has historically been sufficient to meet our and the VIE Group’s working capital and substantially all of our and the VIE Group’s capital expenditure requirements. As of December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, we and the VIE Group had RMB291.0 million, RMB370.2 million and RMB540.5 million (US$74.0 million), respectively, in cash and cash equivalents. In May 2019, we completed our initial public offering in which we issued and sold an aggregate of 4,025,000 ADSs, representing 16,100,000 class A ordinary shares, resulting in net proceeds to us of approximately US$35.0 million. Our and the VIE Group’s cash and cash equivalents primarily consist of cash on hand and demand deposits which are highly liquid and have original maturities of three months or less and are unrestricted as to withdrawal or use. We and the VIE Group believe that our and the VIE Group’s current cash and cash equivalents and our and the VIE Group’s anticipated cash flows from operations will be sufficient to meet our and the VIE Group’s anticipated working capital requirements and capital expenditures for the next 12 months. We and the VIE Group may, however, need additional capital in the future to fund our and the VIE Group’s continued operations. If we and the VIE Group determine that our and the VIE Group’s cash requirements exceed the amount of cash and cash equivalents we and the VIE Group have on hand at the time, we and the VIE Group may seek to issue equity or debt securities or obtain credit facilities. The issuance and sale of additional equity would result in further dilution to our and the VIE Group’s shareholders. The incurrence of indebtedness would result in increased fixed obligations and could result in operating covenants that might restrict our and the VIE Group’s operations. We and the VIE Group cannot assure you that financing will be available in amounts or on terms acceptable to us, if at all.
Although we consolidate the results of the VIE Group, we only have access to cash balances or future earnings of the VIE Group through our contractual arrangements with them. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure” For restrictions and limitations on liquidity and capital resources as a result of our corporate structure, see “—Holding Company Structure.”
As a Cayman Islands exempted company and offshore holding company, we are permitted under PRC laws and regulations to provide funding to our wholly foreign-owned subsidiaries in China only through loans or capital contributions, subject to the approval of government authorities and limits on the amount of capital contributions and loans. In addition, our wholly foreign-owned subsidiaries in China may provide Renminbi funding to their respective subsidiaries through capital contributions and entrusted loans, and to the VIE Group only through entrusted loans. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—PRC regulation of loans to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore holding companies and governmental administration of currency conversion may delay or prevent us from using the proceeds of further offerings to make loans to or make additional capital contributions to our PRC subsidiaries, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand our business.” and “Item 14. Material Modifications to the Rights of Security Holders and Use of Proceeds.”
The following table sets forth a summary of our and the VIE Group’s cash flows for the period presented:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
Summary Consolidated Cash Flow Data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash provided by
operating activities |
|
|
133,592 |
|
|
|
389,588 |
|
|
|
1,425,488 |
|
|
|
195,292 |
|
Net cash used in
investing activities |
|
|
(22,949 |
) |
|
|
(105,850 |
) |
|
|
(783,520 |
) |
|
|
(107,342 |
) |
Net cash used in
financing activities |
|
|
(12,566 |
) |
|
|
(193,481 |
) |
|
|
(332,687 |
) |
|
|
(45,578 |
) |
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted
cash at beginning of year |
|
|
184,567 |
|
|
|
293,041 |
|
|
|
372,628 |
|
|
|
51,050 |
|
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted
cash at end of year |
|
|
293,041 |
|
|
|
372,628 |
|
|
|
677,855 |
|
|
|
92,865 |
|
Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was RMB1,425.5 million (US$195.3 million) in 2024, primarily due to net income of RMB1,056.5 million (US$144.7 million), mainly adjusted for gain on recovery of Long-term investment of RMB69.0 million (US$9.5 million), share-based compensation of RMB59.1 million (US$8.1 million), impairment of long-term investments of RMB51.9 million (US$7.1 million), non-cash lease expenses of RMB23.6 million(US$3.2 million), depreciation and amortization of RMB17.9 million (US$2.4 million), allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets, loans receivable and others of RMB12.2 million (US$1.7 million), and changes in working capital. Changes in working capital were primarily due to (i) an increase in accounts receivable and contract assets of RMB886.5 million (US$121.4 million) in connection with uncollected service fees, which was in line with the increasing facilitation volume, (ii) a decrease in deferred guarantee income of RMB657.4 million (US$90.1 million) due to the decrease in average outstanding loan balances for which we and the VIE Group provided guarantee services, and (iii) a decrease in contingent guarantee liabilities of RMB728.2 million (US$99.8 million), as a result of lower outstanding loan balances subject to the guarantee services, partially offset by (i) a decrease in prepaid expenses and other current assets of RMB1,494.5 million (US$204.7 million) due to the back-to-back guarantee arrangements, (ii) a decrease in financial assets receivable of RMB701.7 million (US$96.1 million), (iii) an increase in accrued expenses and other liabilities of RMB190.6 million (US$26.1 million), and (iv) an increase in tax payable of RMB124.8 million (US$17.1 million).
Net cash provided by operating activities was RMB389.6 million in 2023, primarily due to net income of RMB1,297.6 million, mainly adjusted for gain from de-recognition of liabilities of RMB280.2 million, impairment of long-term investments of RMB91.2 million, allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets, loans receivable and others of RMB72.8 million, share-based compensation of RMB54.4 million, non-cash lease expenses of RMB21.0 million, depreciation and amortization of RMB9.5 million, and changes in working capital. Changes in working capital were primarily due to (i) an increase in accounts receivable and contract assets of RMB497.5 million in connection with uncollected service fees, which was in line with the increasing facilitation volume, (ii) an increase in prepaid expenses and other current assets of RMB1,890.4 million due to the back-to-back guarantee arrangements, and (iii) an increase in financial assets receivable of RMB917.8 million, partially offset by (i) an increase in deferred guarantee income of RMB821.6 million, (ii) an increase in contingent guarantee liabilities of RMB933.9 million as we and the VIE group began to provide primary guarantee to certain loans facilitated since late 2022, (iii) an increase in accrued expenses and other liabilities of RMB445.0 million, and (iv) an increase in tax payable of RMB219.3 million.
Net cash provided by operating activities was RMB133.6 million in 2022, primarily due to net income of RMB1,180.2 million, mainly adjusted for gain from de-recognition of other payable associated with disposal of Shanghai Caiyin of RMB117.0 million, allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets, loans receivable and others of RMB32.1 million, share-based compensation of RMB42.5 million, depreciation and amortization of RMB10.0 million, and changes in working capital. Changes in working capital were primarily due to (i) an increase in accounts receivable and contract assets of RMB1,232.3 million in connection with uncollected service fees, (ii) an increase in prepaid expenses and other current assets of RMB456.2 million and (iii) an increase in financial assets receivable of RMB292.3 million, partially offset by (i) an increase in accrued expenses and other liabilities of RMB444.1 million, and (ii) an increase in deferred guarantee income of RMB276.5 million, and an increase in tax payable of RMB223.8 million.
Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities was RMB783.5 million (US$107.3 million) in 2024, primarily due to purchase of property, equipment and software of RMB739.1 million (US$101.3 million), loans to related parties of RMB120.0 million (US$16.4 million), acquisition of long-term investments of RMB97.6 million (US$13.4 million), and net investment and collection in loans receivable of RMB23.3 million (US$3.2 million), partially offset by loan repayments from related parties of RMB130.1 million (US$17.8 million) and proceeds from recovery of long-term investments of RMB69.0 million (US$9.5 million).
Net cash used in investing activities was RMB105.9 million in 2023, primarily due to acquisition of long-term investments of RMB77.5 million, disposal of subsidiaries, net of cash disposed of RMB68.7 million, partially offset by net collection loans receivable of RMB53.8 million, and loan repayments from related parties of RMB31.2 million.
Net cash used in investing activities was RMB22.9 million in 2022, primarily due to loans to related parties of RMB56.4 million and purchase of property, equipment and software of RMB17.5 million, partially offset by loan repayments from related parties of RMB50.9 million.
Financing Activities
Net cash used in financing activities was RMB332.7 million (US$45.6 million) in 2024, primarily due to dividend distributed to shareholders of RMB301.2 million (US$41.3 million) and repurchase of ordinary shares of RMB53.3 million (US$7.3 million), partially offset by loans from related parties of RMB27.3 million (US$3.7 million).
Net cash used in financing activities was RMB193.5 million in 2023, primarily due to dividend distributed to shareholders of RMB156.7 million and repurchase of ordinary shares of RMB38.1 million.
Net cash used in financing activities was RMB12.6 million in 2022, primarily due to repurchase of ordinary shares of RMB14.8 million.
Material Cash Requirements
Our and the VIE Group’s material cash requirements as of December 31, 2024 and any subsequent interim period primarily include our and the VIE Group’s payment of purchase of commercial property, employee’s payroll and welfare expenses, taxes and other various selling, general and administrative expenses to support our daily business operations, capital expenditures and operating lease obligations.
Our and the VIE Group’s operating lease obligations consist of the commitments under the lease agreements for our and the VIE Group’s office premises. Our and the VIE Group’s leasing expense was RMB29.2 million, RMB22.7 million and RMB25.3 million (US$3.5 million) in 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. The majority of our and the VIE Group’s operating lease commitments are related to our and the VIE Group’s office lease agreements in China.
Other than those discussed above, we and the VIE Group did not have any significant capital and other commitments, long-term obligations as of December 31, 2024.
Capital Expenditures
We and the VIE Group made capital expenditures of RMB17.5 million, RMB31.5 million and RMB739.1 million (US$101.3 million) in 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. In 2024, our and the VIE Group’s capital expenditures were mainly used for purchase of certain commercial property, equipment, including servers, computers and other office equipment, and office renovation. We and the VIE Group will continue to make capital expenditures to meet the expected growth of our and the VIE Group’s business.
Holding Company Structure
Jiayin Group Inc. is a holding company with no material operations of its own. We conduct our operations primarily through our subsidiaries, consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries in China. As a result, Jiayin Group Inc.’s ability to pay dividends depends upon dividends paid by our PRC subsidiaries. If our existing PRC subsidiaries or any newly formed ones incur debt on their own behalf in the future, the instruments governing their debt may restrict their ability to pay dividends to us. In addition, relevant PRC laws and regulations permit the PRC companies, such as our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE, to pay dividends only out of their retained earnings, if any, as determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations.
Each of our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE that is in retained earnings position as of the end of each year is required to set aside 10% of its after-tax profits each year, if any, to fund certain statutory reserve funds until such reserve funds reach 50% of its registered capital. Furthermore, each of our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE may allocate a portion of its after-tax profits based on PRC accounting standards to a discretionary surplus fund at their discretion. The statutory reserve funds and the discretionary funds are not distributable as cash dividends. After our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE have generated retained earnings and met the requirements for appropriation to the statutory reserves and until such reserves reach 50% of its registered capital, respectively, our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE can distribute dividends upon approval of the shareholders. Remittance of dividends by a wholly foreign-owned company out of China is subject to examination by the banks designated by SAFE.
C.
Research and Development, Patents and Licenses, etc.
See “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—Intellectual Property.”
Other than as disclosed elsewhere in this annual report, we are not aware of any trends, uncertainties, demands, commitments or events for the period from January 1, 2024 to December 31, 2024 that are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on our net revenues, income, profitability, liquidity or capital resources, or that would cause reported financial information not necessarily to be indicative of future operating results or financial conditions.
E.
Critical Accounting Estimates
We and the VIE group prepare our and the VIE Group’s consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP, which requires us to make judgments, estimates and assumptions. We and the VIE group continually evaluate these estimates and assumptions based on the most recently available information, our and the VIE Group’s own historical experiences and various other assumptions that we and the VIE group believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. Since the use of estimates is an integral component of the financial reporting process, actual results could differ from our and the VIE Group’s expectations as a result of changes in our estimates. Some of our and the VIE Group’s accounting policies require a higher degree of judgment than others in their application and require us to make significant accounting estimates. An accounting estimate is considered critical if it is made basing on assumptions about matters that are highly uncertain at the time such estimate is made, and if different accounting estimates that reasonably could have been used, or changes in the accounting estimates that are reasonably likely to occur periodically, could materially impact the consolidated financial statements. We believe that the following critical accounting estimates involve the most significant judgments used in the preparation of our financial statements.
Allowance for credit losses
We recognize an allowance for our financial assets, mainly accounts receivable and contract assets, financial assets receivable, receivables from the third-party asset management companies and amount due from related parties based on estimate of the expected credit losses over the contractual term of these financial assets.
Allowances for the above-mentioned financial assets are driven by estimated default rate of respective counterparties. With the assistant of a third-party valuation firm, we estimate the default rate based on loss rate with forward looking factors. External factors, such as CPI and GDP are also applied based on regular review and updated on a timely basis once we become aware of any new patterns. Estimates can vary over time due to changes in the factors noted above and management’s judgments regarding these factors; further, exposures can be difficult to estimate, particularly in situations in which the Company has limited experience or transparency with certain counterparties. Our estimate of the key assumptions related to credit losses did not change significantly throughout the periods presented.
As of December 31, 2024, allowance for accounts receivable and contract assets is RMB3.2 million (US$0.4 million) and reversal of allowance for financial assets receivable is RMB6.0 million (US$0.8 million). If change in various factors constituting the estimate of loss rate result in 5 percentage point increase/decrease in the overall estimate loss rate, it would result in an increase/decrease of RMB1.1 million (US$0.2 million) and RMB 0.1 million (US$0 million) for allowance for accounts receivable and contract assets and financial assets receivable, respectively.
Guarantee liabilities
We provide guarantee services directly or cooperating with third-party financing guarantee companies for certain loans we facilitated. We recognize a stand-ready guarantee liability at fair value at inception of guarantee, which is released into guarantee revenue over the term of the guarantee. We also separately record a contingent guarantee liability based on estimate of future payout by us upon borrowers’ default, which is ultimately determined by the estimated default rate of underlying loans subject to guarantee. We estimate the borrower’s default rate based on historical default rate of underlying loans subject to guarantee on a pool basis according to the historical delinquency data by vintage and adjusted by our current risk and business strategies which we believe it could have potential impacts into the future periods, if any. The contingent guarantee is revalued at each period end to reflect updated estimation for future pay-out. There are significant judgments and estimations by management in determining the estimated default rate with the underlying assumptions, which led to judgment and subjectivity. As of December 31, 2024, outstanding balance for deferred guarantee income and contingent guarantee liabilities is RMB229.5million (US$31.4 million) and RMB213.6million (US$29.3 million), respectively. As of December 31, 2024, outstanding balance for contingent guarantee liabilities is RMB213.6 million (US$29.3 million). If change in various factors constituting the estimate of default rate result in 5 percentage point increase/decrease in the overall estimate default rate, it would result in an increase/decrease of RMB10.7 million (US$1.5 million) for contingent guarantee liability.
F.
Off-balance Sheet Arrangements
We and the VIE Group have not entered into any derivative contracts that are indexed to our and the VIE Group’s shares and classified as shareholder’s equity or that are not reflected in our and the VIE Group’s consolidated financial statements. Furthermore, we and the VIE Group do not have any retained or contingent interest in assets transferred to an unconsolidated entity that serves as credit, liquidity or market risk support to such entity. We do not have any variable interest in any unconsolidated entity that provides financing, liquidity, market risk or credit support to us or engages in leasing, hedging or product development services with us.
See “Forward-Looking Statements” at the beginning of this annual report.
ITEM 6. DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND EMPLOYEES
A.
Directors and Senior Management
The following table provides information regarding our directors and executive officers as of the date of this annual report.
|
|
|
|
|
Directors and Executive Officers |
|
Age |
|
Position/Title |
Dinggui Yan |
|
56 |
|
Founder, director and chief executive officer |
Yi Feng |
|
48 |
|
Chief technology officer |
Chunlin Fan |
|
49 |
|
Chief financial officer |
Yifang Xu |
|
47 |
|
Director and chief risk officer |
Libin Wang |
|
38 |
|
Director and vice president of finance |
Yuhchang Hwang |
|
70 |
|
Independent Director |
Meng Rui |
|
57 |
|
Independent Director |
Mr. Dinggui Yan is our founder, and has served as our director since 2015, and as our chief executive officer since 2016. He has also been the chief executive officer of Shanghai Wuxingjia since 2014, and the chairman and general manager of Jiayin Technology since 2011. Prior to founding our company, Mr. Yan served as the general manager of Beijing Tianrongxin Network Safety Technology Co., Ltd. in the region of Zhejiang from 2007 to 2010. From 2000 to 2006, Mr. Yan served as the general manager of Shanghai Tongtian Information Technology Co., Ltd. Mr. Yan received a doctorate degree from University of Geneva in 2023, a master’s degree from China Europe International Business School in 2016, and a bachelor’s degree from Xidian University in 1990.
Mr. Yi Feng has served as our chief technology officer since November 2021. Mr. Feng has over 18 years of technology leadership experience in internet and financial services. He joined Jiayin in 2021. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Feng had held senior technology roles at well-known firms such as Fidelity, Lufax, Trip.com and Oracle since 2006. Mr. Feng received his master’s degree of computer science from University of Pennsylvania in 2006, another master’s degree in computer science from University of Texas at Austin in 2002 and a bachelor’s degree in computer science from Sun Yat-Sen University in 2000.
Mr. Chunlin Fan previously served as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer from January 2016 to January 2021. Prior to rejoining the Company in May 2022, Mr. Fan worked as the Chief Financial Officer of LinkDoc Technology Limited from January 2021 to March 2022. Mr. Fan worked as the Chief Financial Officer and leader of the strategic development department at Shanghai Richtech Engineering Co., Ltd. from 2014 to 2016. Mr. Fan also served a wide range of international corporations including Microsoft, Nomura, Macquarie, ICBCI, Deloitte and Shenyin & Wanguo Investment Co. Ltd. Mr. Fan received his MBA from University of Michigan’s Ross School of Business in 2007, and a bachelor’s degree in engineering from Shanghai Jiaotong University in 1998.
Ms. Yifang Xu has served as our director since May 2019. Ms. Xu has been our chief risk officer since July 2018. Prior to joining our company, Ms. Xu worked as a director in risk management department at Ant Financial Services Group from 2016 to 2018, leading various lending business solution consultancy and delivery in risk management to consumer banks and leading fin-tech lending companies. From 2015 to 2016, Ms. Xu served as a chief operating officer at Shanghai Fujin Finance and Information Service Corporation, commonly known as Huasheng Finance. From 2004 to 2015, Ms. Xu held various positions in Capital One Financial Corporation (NYSE: COF) in risk management, product management and distribution channel management with credit card business and direct banking, including senior analyst, manager, senior manager and department director. Ms. Xu received her MBA from Kellogg School of Management, Northwestern University in 2004, a master’s degree in economics from University of International Business and Economics in 2000, and a bachelor’s degree in economics from Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics in 1997.
Mr. Libin Wang has served as our director since May 2019. Mr. Wang has been our vice president of finance since 2018. He served as a financial supervisor in our company from 2017 to 2018, and as our asset management supervisor from 2015 to 2017. Prior to joining our company, Mr. Wang worked at China Sino-Trans Shipping Agency Shanghai Co., Ltd. and its subsidiaries from 2008 to 2014, responsible for financial-related work. Mr. Wang received his master’s degree in accounting from Fudan University in 2015 and his bachelor’s degree in financial management from Shanghai Second Polytechnic University in 2008.
Mr. Yuhchang Hwang has served as our director since May 2019. Since 2013, Mr. Hwang has been working at China Europe International Business School as a professor in accounting, the department chair in finance and accounting, and a co-director of China Europe International Business School center on China innovation. He has also served as an emeritus professor in Arizona State University since 2013, and served as its assistant professor and a tenured associate professor from 1987 to 1995 and 1995 to 2001, respectively. Since 2015, Mr. Hwang has been an independent director, chair of the compensation committee, and member of the audit committee and strategy committee of Shanghai Jahwa United Co., Ltd. (SSE: 600315), and the chair of its nominating committee since 2018. Mr. Hwang has also worked as an independent director of Red Avenue New Materials Group Co., Ltd. (SSE: 603650) since 2016, and the chair of its audit committee, compensation committee and nominating committee since 2017. Mr. Hwang has also served as an independent director, chair of the compensation committee and member of the audit committee and nominating committee of Opple Lighting Co., Ltd. (SSE: 603515) since 2017. From January 2018 to May 2018, Mr. Hwang worked as an independent director, chair of the compensation committee and member of the audit committee of Chongqing Iron & Steel Company Limited (SEHK: 1053). From 2015 to 2017, Mr. Hwang was as an independent director, chair of the audit committee, and member of the compensation committee and strategy committee of Shanghai Tianji Technology Co., Ltd. (SZSE: 300245). From 2012 to 2018, Mr. Hwang worked as an independent director, chair of the audit committee, and member of the compensation committee and strategy committee of Baoshan Iron & Steel Co., Ltd. (SSE: 600019). Mr. Hwang received his Ph.D. in business administration from University of California, Berkeley in 1987, and a master’s degree in science from National Chengchi University in 1979.
Mr. Meng Rui has served as our director since May 2019. Mr. Rui has been a professor of finance and accounting at China Europe International Business School since 2012, and has held the title of Zhongkun Group chair in finance at China Europe International Business School since 2015. Mr. Rui is also a tenured professor at the Chinese University of Hong Kong and held various positions in the Chinese University of Hong Kong from 2002 to 2012, including a senior research associate of the Institute of Economics and Finance from 2005 to 2012, a deputy director of the Center for Institutions and Governance from 2005 to 2012, and a program director of master of accountancy and executive master of professional accountancy from 2003 to 2012. From 1997 to 2002, Mr. Rui served as a deputy director of the China accounting and finance center at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University. He also serves as an independent director of COSCO Shipping Energy Transportation Co., Ltd. (SEHK: 1138, SSE:600026) since 2016, an independent director and chairman of the audit committee of Shanghai Winner Information Technology Co., Inc. (SZSE: 300609) since 2017, an independent director of Shang Gong Group Co., Ltd. (SSE: 600843) since 2017, an independent director of China Education Group (SEHK: 839) since 2017 and an independent director of Country Garden Service Holding Company Limited (SEHK: 6098) since 2018. From 2015 to 2018, Mr. Rui worked as an independent director of Midea Group Co., Ltd. (SZSE: 000333). Mr. Rui is also a member of various professional committees, including but not limited to American Finance Association, Financial Management Association, American Accounting Association and Hong Kong Securities Institute. He is also a vice president of Hong Kong Financial Engineering Association. Mr. Rui received his Ph.D. in business administration and MBA in 1997 and 1996, respectively, both from University of Houston, a master’s degree in economics from Oklahoma State University in 1993, and a bachelor’s degree in international economics from University of International Relations in 1990.
In 2024, we paid an aggregate of RMB30.6 million (US$4.2 million) in cash and benefits to our executive officers and directors. We have not set aside or accrued any amount to provide pension, retirement or other similar benefits to our directors and executive officers. Our PRC subsidiaries, the consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries are required by law to make contributions equal to certain percentages of each employee’s salary for his or her pension insurance, medical insurance, unemployment insurance and other statutory benefits and a housing provident fund. Our board of directors may determine compensation to be paid to the directors and the executive officers. The compensation committee will assist the directors in reviewing and approving the compensation structure for the directors and the executive officers.
Employment Agreements and Indemnification Agreements
We entered into employment agreements with our executive officers. Each of our executive officers is employed for a specified time period, which will be automatically extended unless either we or the executive officer gives prior written notice to terminate such employment. We may terminate the employment for cause, at any time, without notice or remuneration, for certain acts of the executive officer, including but not limited to the commitments of any serious or persistent breach or non-observance of the terms and conditions of the employment, conviction of a criminal offense other than one which in the opinion of the board does not affect the executive’s position, willful disobedience of a lawful and reasonable order, misconducts being inconsistent with the due and faithful discharge of the executive officer’s material duties, guilty of fraud or dishonesty, or habitual neglect of his or her duties. An executive officer may terminate his or her employment at any time with a three-month prior written notice.
Each executive officer has agreed to hold, both during and after the employment agreement expires or is earlier terminated, in strict confidence and not to use or disclose to any person, corporation or other entity without written consent, any confidential information, except for the benefit of us. Each executive officer has also agreed to assign to our company all his or her all inventions, improvements, designs, original works of authorship, formulas, processes, compositions of matter, computer software programs, databases, mask works, concepts and trade secrets which the executive officer may solely or jointly conceive or develop or reduce to practice, or cause to be conceived or developed or reduced to practice, during the period of the executive officer’s employment with us that are either related to the scope of the employment or make use of the resources of the company. In addition, all executive officers have agreed to be bound by non-competition and non-solicitation restrictions set forth in their agreements. Specifically, each executive officer has agreed to devote all his or her working time, attention and skills to our business and use best efforts to perform his or her duties. Moreover, each executive officer has agreed not to, for a certain period following termination of his or her employment or expiration of the employment agreement: (i) carry on or be engaged, concerned or interested directly or indirectly whether as shareholder, director, employee, partner, agent or otherwise carry on any business in direct competition with us, (ii) solicit or entice away or attempt to solicit or entice away any of our customer, client, representative or agent, or (iii) employ, solicit or entice away or attempt to employ, solicit or entice away any of our officer, manager, consultant or employee.
We have entered into indemnification agreements with our directors and executive officers, pursuant to which we agree to indemnify our directors and executive officers against certain liabilities and expenses incurred by such persons in connection with claims made by reason of their being such a director or officer.
Share Incentive Plans
We maintain share incentive plans in order to attract, motivate, retain and reward talent, provide additional incentives to our officers, employees, directors and other eligible persons, and promote the success of our business and the interests of our shareholders.
2016 Share Incentive Plan
In September 2016, Jiayin Technology adopted the 2016 Share Incentive Plan, which allowed Jiayin Technology to grant share-based awards of such company to our founders, employees and officers. The total number of outstanding shares of Jiayin Technology is 50,000,000 and the maximum number of shares that may be issued pursuant to all awards under the 2016 plan is 13,500,000 shares of Jiayin Technology. In September 2016 and October 2018, 13,321,500 and 2,851,600 share options to purchase the respective number of shares of Jiayin Technology were granted to certain of our employees and officers, among which 4,848,900 options were subsequently canceled, at exercise prices of RMB3.5 per share, which have vesting periods of 4.5 years. All 13,500,000 shares of Jiayin Technology underlying the 2016 Share Incentive Plan is held by Jinmushuihuotu Investment, and upon the exercise of the share options, our employees and officers become a limited partner of Jinmushuihuotu Investment, which allows such grantees to enjoy beneficial ownership in Jiayin Technology representing the respective awards granted. As of the date of this annual report, the sole general partner of Jinmushuihuotu Investment is Jinmushuihuotu Marketing, which is controlled by Mr. Dinggui Yan. All outstanding options granted under the 2016 Share Incentive Plan have been canceled or replaced with options granted under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan.
The 2016 Share Incentive Plan has been terminated when all options granted hereunder were canceled.
2019 Share Incentive Plan
In February 2019, we adopted our 2019 Share Incentive Plan, which permits the grant of options to purchase our ordinary shares. The 2019 Share Incentive Plan was adopted to replace our 2016 Share Incentive Plan. All outstanding options granted under the 2016 Share Incentive Plan have been canceled or replaced with options granted under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan. The maximum number of ordinary shares may be subject to equity awards pursuant to the 2019 Share Incentive Plan is 54,000,000 initially. In connection with the adoption of 2019 Plan, we cancelled 2,377,000 and 1,169,000 share options granted in September 2016 and October 2018, respectively. As of December 31, 2024, we had granted options to purchase an aggregate 73,938,000 Class A ordinary shares (excluding options that were forfeited, cancelled, or exercised after the relevant grant date) and RSUs to receive an aggregate of 21,480,000 Class A ordinary shares (excluding RSUs that were forfeited, cancelled, or vested after the relevant grant date), pursuant to the 2019 Share Incentive Plan. On April 28, 2025, our board of directors increased the aggregate number of Class A Ordinary Shares reserved for issuance pursuant to awards granted under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan by 24,000,000 additional Class A Ordinary Shares.
We established Dream Glory L.P. to hold shares underlying potential awards granted pursuant to our 2019 Share Incentive Plan. In December 2017, 2,700 ordinary shares were issued to in view of the establishment of the 2019 Share Incentive Plan, which were transferred subsequently to Dream Glory L.P. In February 2019, we entered into a shareholding entrustment agreement with Dream Glory L.P., pursuant to which Dream Glory L.P. is entrusted to hold the shares in connection with the 2019 Share Incentive Plan as a nominal holder and Dream Glory L.P. accepts such shareholding entrustment retrospectively. Dream Glory L.P. will use its reasonable best effort to facilitate the exercise of the awards granted under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan and transfer a certain number of ordinary shares held by Dream Glory L.P. to a grantee of the awards or to the depositary bank or its nominee for deposit as evidence for ADSs in settlement of any award in lieu of ordinary shares upon our instruction for free. Dream Glory L.P. is entitled to rights as a member of Jiayin Group Inc. except that Dream Glory L.P. irrevocably agrees that it will (i) abstain from voting on any general meetings of members, or acting as any function at a general meeting, or (ii) not sale, transfer, pledge or otherwise encumbrance of the Ordinary Shares of the Company without our written consent, and sale, transfer, pledge or otherwise encumbrance of the ordinary shares as instructed by us in writing.
Such 2,700 ordinary shares with a par value of US$0.0001 each were subsequently sub-divided into 54,000,000 ordinary shares with a par value of US$0.000000005 each. Dream Glory L.P. is a limited partnership established in the British Virgin Islands. The general partner of Dream Glory L.P. is New Dream, which is controlled by Mr. Dinggui Yan.
The following paragraphs summarize the terms of the 2019 Share Incentive Plan.
Plan Administration. Our board of directors or a committee appointed by our board of directors acts as the plan administrator. The board of directors or the committee may also delegate one or more members of our board of directors to grant or amend awards or take other administrative actions.
Types of Awards. The 2019 Share Incentive Plan authorizes the grant of options to purchase ordinary shares, the award of restricted shares and the award of RSUs.
Award Agreements. Each award under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan shall be evidenced by an award agreement between the award recipient and our company, which may be any written notice, agreement, terms and conditions, contract or other instrument or document evidencing such award.
Eligibility. The plan administrator may select among the following eligible individuals to whom an award may be granted: (i) our employees and (ii) directors who are not our employees; provided however that awards shall not be granted to non-employee directors who are resident of any country in the European Union and any other country, which pursuant to the applicable laws, does not allow grants to non-employee.
Term of Awards. Each award under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan shall vest or be exercised not more than ten years after the date of grant unless extended by the plan administrator. Each share award is subject to earlier termination as set forth in the 2019 Share Incentive Plan. The award is only exercisable before the eligible individual’s termination of service with us, except as determined otherwise by the plan administrator or set forth in the award agreement. Any awards that are outstanding on the tenth anniversary of the 2019 Share Incentive Plan shall be terminated automatically.
Vesting Schedule and Other Restrictions. The plan administrator has discretion in determining the individual vesting schedules and other restrictions applicable to the awards granted under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan, including vesting conditions related to our operation performance, the grantee’s department performance and his individual performance.
The vesting schedule is set forth in the award agreement.
Exercise Price and Purchase Price. The plan administrator has discretion in determining the price of the awards, which can be fixed or variable related to the fair market value of the underlying ordinary shares and are subject to a number of limitations.
Termination. The 2019 Share Incentive Plan shall expire on the tenth anniversary of the effective date of the 2019 Share Incentive Plan.
Amendment, Suspension or Termination. No amendment, modification or termination of the 2019 Share Incentive Plan shall, without the prior written consent of the award recipients, adversely affect in any material way any award that has been granted or awarded prior to such amendment, suspension or termination. Subject to the above, the plan administrator may at any time terminate, amend or modify the 2019 Share Incentive Plan, except where shareholder approval is required to comply with applicable laws or where the amendment relates to (i) any increases in the number of shares available under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan (other than any adjustment permitted under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan), or (ii) an extension of the term of the 2019 Share Incentive Plan or the exercise period for an option beyond ten years from the date of grant. To the extent permissible under the applicable laws, our board of directors may decide to follow home country practice not to seek shareholder approval for any amendment or modification of the 2019 Share Incentive Plan.
Transfer Restrictions. Subject also to all the transfer restrictions under the applicable laws and regulations and the restrictions set forth in the applicable award agreement, all awards are non-transferable and will not be subject in any manner to sale, transfer, anticipation, alienation, assignment, pledge, encumbrance or charge except for certain exceptions set forth in the plan.
Options. The following table summarizes the outstanding options we granted to our directors and executive officers under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name |
|
Position |
|
Ordinary
Shares
Underlying
Options
Awarded
|
|
Option
Exercise
Price
|
|
Grant Date |
|
Expiration
Date
|
Chunlin Fan |
|
Chief financial officer |
|
* |
|
RMB3.5 |
|
November 25, 2019 |
|
November 24, 2029 |
Yifang Xu |
|
Director and chief risk officer |
|
* |
|
RMB3.5 |
|
November 25, 2019 |
|
November 24, 2029 |
Libin Wang |
|
Director and vice president of finance |
|
* |
|
RMB3.5 |
|
November 25, 2019 |
|
November 24, 2029 |
* Less than 1% of our outstanding shares.
RSUs. The following table summarizes the outstanding RSUs which are legally granted to our directors and executive officers under the 2019 Share Incentive Plan.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name |
|
Position |
|
Ordinary Shares
Underlying
RSUs Legally Grant
|
|
Legally Grant Date |
Yifang Xu |
|
Director and chief risk officer |
|
5,600,000 |
|
September 5, 2022 |
Libin Wang |
|
Director and vice president of finance |
|
3,360,000 |
|
October 25, 2022 |
Yi Feng |
|
Chief technology officer |
|
3,200,000 |
|
September 5, 2022 |
Chunlin Fan |
|
Chief financial officer |
|
2,400,000 |
|
April 19, 2023 |
Our board of directors consists of five directors. A director is not required to hold any shares in our company to qualify to serve as a director. A director who is in any way, whether directly or indirectly, interested in a contract, transaction or arrangement, or a proposed contract, transaction or arrangement, with our company is required to declare the nature of his interest at a meeting of our directors. A general notice given to our directors by any director to the effect that he is a member, shareholder, director, partner, officer or employee of any specified company or firm and is to be regarded as interested in any contract, transaction or arrangement which may thereafter be made with that company or firm, shall be deemed to be a sufficient declaration of interest with respect to any such contract, transaction or arrangement so made or entered into, and after such notice it shall not be necessary for such director to give any further or special notice relating to any particular contract, transaction or arrangement. A director may vote in respect of any contract, transaction or arrangement, or any proposed contract, transaction or arrangement, notwithstanding that he may be interested therein and if he does so his vote shall be counted and he may be counted in the quorum at any meeting of the directors at which any such contract, transaction or arrangement is considered and voted upon.
Our board of directors may exercise all of the powers of our company to borrow money, to mortgage or charge its undertaking, property and uncalled capital, or any part thereof, and to issue debentures, debenture stock or other securities whenever money is borrowed or as security for any debt, liability or obligation of our company or of any third-party. None of our directors has a service contract with us that provides for benefits upon termination of service.
Committees of the Board of Directors
We have established an audit committee, a compensation committee and a nominating and corporate governance committee under the board of directors. We have adopted a charter for each of the three committees. Each committee’s members and functions are described below.
Audit Committee. Our audit committee consists of Mr. Yuhchang Hwang and Mr. Meng Rui, and is chaired by Mr. Yuhchang Hwang. Mr. Yuhchang Hwang and Mr. Meng Rui satisfy the “independence” requirements of Rule 5605(a)(2) of the Nasdaq Stock Market Rules and meets the independence standards under Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act. Our board of directors has also determined that each of Mr. Yuhchang Hwang and Mr. Meng Rui qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” within the meaning of the SEC rules and possesses financial sophistication within the meaning of the Listing Rules of the Nasdaq Stock Market. The audit committee oversees our accounting and financial reporting processes and the audits of the financial statements of our company. The audit committee is responsible for, among other things:
•
selecting our independent registered public accounting firm and pre-approving all auditing and non-auditing services permitted to be performed by our independent registered public accounting firm;
•
reviewing with our independent registered public accounting firm any audit problems or difficulties and management’s response and approving all proposed related party transactions, as defined in Item 404 of Regulation S-K;
•
discussing the annual audited financial statements with management and our independent registered public accounting firm;
•
annually reviewing and reassessing the adequacy of our audit committee charter;
•
meeting separately and periodically with the management and our internal auditor and our independent registered public accounting firm;
•
reporting regularly to the full board of directors; and
•
such other matters that are specifically delegated to our audit committee by our board of directors from time to time.
Compensation Committee. Our compensation committee consists of Mr. Yuhchang Hwang, Ms. Yifang Xu and Mr. Libin Wang, and is chaired by Mr. Libin Wang. Mr. Yuhchang Hwang satisfies the “independence” requirements of Rule 5605(a)(2) of the Nasdaq Stock Market Rules. Our compensation committee assists the board in reviewing and approving the compensation structure, including all forms of compensation, relating to our directors and executive officers. Our chief executive officer may not be present at any committee meeting during which his compensation is deliberated upon. The compensation committee is responsible for, among other things:
•
reviewing and approving to the board with respect to the compensation for our chief executive officer;
•
overseeing and making recommendations with respect to the compensation for our officers and employees other than the chief executive officer;
•
reviewing and recommending to the board with respect to the compensation and benefits of our directors
•
selecting, or receiving advise from compensation and benefits consultants, legal counsel or other advisors after taking into consideration all factors relevant to that person’s independence from management; and
•
reviewing and administrating all long-term incentive compensation, stock option, annual bonuses, employee pension and welfare benefit plans.
Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee. Our nominating and corporate governance committee consists of Mr. Dinggui Yan, Mr. Yifang Xu and Mr. Libin Wang, and is chaired by Mr. Dinggui Yan. The nominating and corporate governance committee assists the board in selecting individuals qualified to become our directors and in determining the composition of the board of directors and its committees.
The nominating and corporate governance committee is responsible for, among other things:
•
identifying and recommending nominees for election or re-election to our board of directors or for appointment to fill any vacancy;
•
reviewing the performance of each incumbent director and considering the results of such evaluation when determining whether or not to recommend the retention of such director;
•
advising the board policies and procedures with respect to corporate governance matters
•
monitoring compliance with our code of business conduct and ethics, including reviewing the adequacy and effectiveness of our procedures to ensure proper compliance;
•
evaluating its own performance on an annual basis; and
•
reporting to the board on its findings and actions periodically.
Duties of Directors
Under Cayman Islands law, our directors owe fiduciary duties to our company, including a duty of loyalty, a duty to act honestly, and a duty to act in what they consider in good faith to be in our best interests. Our directors must also exercise their powers only for a proper purpose. Our directors also owe to our company a duty to exercise the skill they actually possess and such care and diligence that a reasonably prudent person would exercise in comparable circumstances. It was previously considered that a director need not exhibit in the performance of his duties a greater degree of skill than may reasonably be expected from a person of his knowledge and experience. However, English and Commonwealth courts have moved towards an objective standard with regard to the required skill and care and these authorities are likely to be followed in the Cayman Islands. In fulfilling their duty of care to us, our directors must ensure compliance with our memorandum and articles of association, as amended and restated from time to time. Our company has the right to seek damages if a duty owed by our directors is breached. In limited exceptional circumstances, a shareholder may have the right to seek damages in our name if a duty owed by our directors is breached.
The functions and powers of our board of directors include, among others:
•
convening shareholders’ annual general meetings and reporting its work to shareholders at such meetings;
•
declaring dividends and distributions;
•
appointing officers and determining the term of office of officers;
•
exercising the borrowing powers of our company and mortgaging the property of our company; and
•
approving the transfer of shares of our company, including the registering of such shares in our share register.
Terms of Directors and Executive Officers
Unless otherwise determined by our company in general meeting, our company shall have not less than three directors, and there shall be no maximum number of directors. Our directors may be elected by an ordinary resolution of our shareholders, or by a resolution of our board of directors (whether to fill a casual vacancy or as an addition to the existing board). Our directors are not subject to a term of office and hold office until the expiration of his or her term or his or her successor shall have been elected and qualified, or until his or her office is otherwise vacated. A director may be removed from office by special resolution, notwithstanding anything in our amended and restated memorandum and articles of association or in any agreement between the Company and such director (but without prejudice to any claim for damages under such agreement). In addition, a director will be removed from office automatically if, among other things, the director (i) becomes bankrupt or makes any arrangement or composition with his creditors; (ii) dies or is found to be or becomes of unsound mind; (iii) resigns by notice in writing to our company; (iv) without special leave of absence from our board of directors, is absent from three consecutive meetings of the board and the board resolves that his office be vacated; (v) is prohibited by any applicable law from being a director; or (vi) is removed from office pursuant to any other provision of our amended and restated memorandum and articles of association. The compensation of our directors may be determined by the board of directors or by an ordinary resolution. There is no mandatory retirement age for directors.
Our officers are appointed by and serve at the discretion of our board of directors.
We and the VIE Group had 796, 925 and 1,028 employees as of December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. As of December 31, 2024, 1,004 of our and the VIE Group’s employees were located in Shanghai, 15 in Beijing, 7 in certain other city in China, and 2 in Singapore. The following table sets forth the breakdown of our and the VIE Group’s employees as of December 31, 2024 by function:
|
|
|
|
|
Functions |
|
Number of
Employees |
|
Facilitation and servicing department |
|
|
119 |
|
General and administrative department |
|
|
186 |
|
Sales and marketing department |
|
|
307 |
|
Research and development department |
|
|
416 |
|
Total |
|
|
1,028 |
|
We and the VIE Group believe we and the VIE Group offer our and the VIE Group’s employees competitive compensation packages and dynamic work environment that encourages initiatives. As a result, we and the VIE Group have generally been able to attract and retain qualified personnel and maintain a stable core management team. We and the VIE Group plan to hire more experienced and talented employees in the areas such as big data analytics, risk management and operation management as we and the VIE Group expand our and the VIE Group’s business.
As required by PRC regulations, we and the VIE Group participate in various statutory employee benefit plans, including social insurance funds, namely a pension contribution plan, a medical insurance plan, an unemployment insurance plan, a work-related injury insurance plan and a maternity insurance plan, and a housing provident fund. We and the VIE Group are required under PRC law to make contributions to employee benefit plans at specified percentages of the salaries, bonuses and certain allowances of our and the VIE Group’s employees, up to a maximum amount specified by the local government from time to time. In addition, we and the VIE Group purchased the liability insurance and additional commercial health insurance for our and the VIE Group’s senior management.
We and the VIE Group believe that we and the VIE Group maintain a good working relationship with our and the VIE Group’s employees, and we and the VIE Group have not experienced any major labor disputes.
The following table sets forth information concerning the beneficial ownership of our ordinary shares as of March 31, 2025 by:
•
each of our directors and executive officers;
•
each person known to us to beneficially own more than 5% of our ordinary shares.
Our total number of ordinary shares outstanding as of March 31, 2025 was 213,478,184, which includes 54,000,000 ordinary shares held by Dream Glory. L.P. as an entrusted shareholder of shares issued in view of our 2019 Share Incentive Plan, of which 22,454,240 are shares underlying the options and 31,200,000 are underlying the RSUs entitled under our 2019 Share Incentive Plan and the remaining 345,760 are reserved for future issuance. Dream Glory L.P. will not vote such ordinary shares it held at general meetings of our company.
Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with the rules and regulations of the SEC. In computing the number of shares beneficially owned by a person and the percentage ownership of that person, we have included shares that the person has the right to acquire within 60 days, including through the exercise of any option, warrant, or other right or the conversion of any other security. These shares, however, are not included in the computation of the percentage ownership of any other person.
We have adopted a dual class ordinary share structure. The calculations in the table below are based on 213,478,184 ordinary shares (being the sum of 105,478,184 Class A ordinary shares (excluding the 2,621,816 Class A ordinary shares in the form of ADSs the issuer repurchased under its share repurchase program and held as treasury shares) and 108,000,000 Class B ordinary shares) of the issuer as of March 31, 2025.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ordinary Shares Beneficially Owned as of March 31, 2025 |
|
|
|
Class A
ordinary
shares |
|
|
Class B
ordinary
shares |
|
|
Percentage
of total
ordinary
share on an
as-converted basis |
|
|
Percentage
of aggregate
voting
power** |
|
Directors and Executive Officers: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dinggui Yan(1) |
|
|
1,360,000 |
|
|
|
108,000,000 |
|
|
|
51.2 |
|
|
|
91.2 |
|
Yifang Xu(2) |
|
|
4,454,776 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2.1 |
|
|
|
0.0 |
|
Libin Wang |
|
* |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
|
Chunlin Fan |
|
* |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
|
Yi Feng |
|
* |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
|
Yuhchang Hwang |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Meng Rui |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Directors and Executive Officers as a Group |
|
|
8,576,928 |
|
|
|
108,000,000 |
|
|
|
54.6 |
|
|
|
91.2 |
|
Principal Shareholders: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Dream Capital Holdings Limited(1) |
|
|
1,360,000 |
|
|
|
108,000,000 |
|
|
|
51.2 |
|
|
|
91.2 |
|
Sunshinewoods Holdings Limited(3) |
|
|
23,446,492 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
11.0 |
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
Dream Glory L.P.(4) |
|
|
26,180,004 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
12.3 |
|
|
|
— |
|
* Beneficially owns less than 1% of our total outstanding shares.
** For each person and group included in this column, percentage of voting power is calculated by dividing the voting power beneficially owned by such person or group by the voting power of all of our Class A and Class B ordinary shares as a single class. In respect of all matters subject to a shareholders’ vote, each Class A ordinary share is entitled to one vote, and each Class B ordinary share is entitled to ten votes, voting together as one class. Each Class B ordinary share is convertible into one Class A ordinary share at any time by the holder thereof. Class A ordinary shares are not convertible into Class B ordinary shares under any circumstances. Upon any transfer of Class B ordinary shares by a holder to any person or entity which is not an affiliate of such holder, such Class B ordinary shares shall be automatically and immediately converted into the equivalent number of Class A ordinary shares.
(1)
Represents 1,360,000 Class A ordinary shares and 108,000,000 Class B ordinary shares held by New Dream Capital Holdings Limited, or New Dream, a limited liability company established in the British Virgin Islands. New Dream is wholly owned by Mr. Dinggui Yan and Mr. Dinggui Yan is the sole director of New Dream. The registered address of New Dream is Sertus Incorporations (BVI) Limited, Sertus Chambers, P.O. Box 905, Quastisky Building, Road Town, Tortola, British Virgin Islands.
(2)
Represents the Class A ordinary shares held directly by Ms. Yifang Xu, including 4,454,776 Class A ordinary shares which were vested from RSUs. With respect to such 4,454,776 Class A ordinary shares, Ms. Yifang Xu has given an irrevocable proxy to vote such ordinary shares to the plan administrator of our 2019 Share Incentive Plan, and as a result, such ordinary shares are excluded from the voting power of Ms. Yifang Xu. The business address of Ms. Yifang Xu is 18th Floor, Building No. 1, Youyou Century Plaza, 428 South Yanggao Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai 200122, People’s Republic of China.
(3)
Represents 23,446,492 ordinary shares held by Sunshinewoods Holdings Limited, or Sunshinewoods, a limited liability company established in the British Virgin Islands. Sunshinewoods is wholly owned by Mr. Guanglin Zhang, an employee of our company. Mr. Guanglin Zhang is the sole director of Sunshinewoods. The registered address of Sunshinewoods is Sertus Incorporations (BVI) Limited, Sertus Chambers, P.O. Box 905, Quastisky Building, Road Town, Tortola, British Virgin Islands.
(4)
Represents 26,180,004 ordinary shares held by Dream Glory L.P., a limited partnership established in the British Virgin Islands, which in accordance with the shareholding entrustment agreement entered into between Dream Glory L.P. and us, does not have any voting or investment power. Dream Glory L.P. is established to hold shares underlying potential awards granted pursuant to our share incentive plan. The general partner of Dream Glory L.P. is New Dream, which is controlled by Mr. Dinggui Yan. The registered address of Dream Glory L.P. is Sertus Chambers, P.O. Box 905, Quastisky Building, Road Town, Tortola, British Virgin Islands.
As of March 31, 2025, a total of 14,024,545 ADSs, representing 56,098,180 Class A ordinary shares, were held by holders of record in the United States, representing approximately 26.3% of our total outstanding shares. None of our outstanding Class B ordinary shares were held by holders of record in the United States.
We are not aware of any arrangement that may, at a subsequent date, result in a change of control of our company.
F.
Disclosure of A Registrant’s Action to Recover Erroneously Awarded Compensation ITEM 7.
Not applicable.
MAJOR SHAREHOLDERS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—E. Share Ownership.”
B.
Related Party Transactions
Transactions with Jiayin Zhuoyue
We and the VIE group engaged Shanghai Jiayin Zhuoyue Enterprise Management Co., Ltd. (“Jiayin Zhuoyue”, formerly known as “Shanghai Jiayin Zhuoyue Wealth Management Co., Ltd.”) to refer online investors to us. We and the VIE group paid Jiayin Zhuoyue referral service fees. Jiayin Zhuoyue is controlled by Mr. Dinggui Yan, our founder, director and chief executive officer.
We and the VIE group incurred RMB122.9 million, RMB115.5 million and RMB74.5 million (US$10.2 million) of referral service fees to Jiayin Zhuoyue in 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
Amounts due to Jiayin Zhuoyue was RMB0.4 million, RMB11.3 million and RMB27.0 million (US$3.7 million) as of December 31, 2022, 2023, and 2024, respectively.
Transactions with Shanghai Jiayin
Shanghai Jiayin is controlled by Mr. Dinggui Yan, our founder, director and chief executive officer.
In 2022, we and the VIE group provided interest free loans to Shanghai Jiayin with a total amount of RMB35.0 million. As of December 31, 2022, the loan has been collected.
In 2024, we and the VIE group provided interest free loans to Shanghai Jiayin with a total amount of RMB120.0 million. As of December 31, 2024, the loan has been collected.
We and the VIE group rented certain space for annual rental and related fees was of RMB12.5 million, RMB2.5 million and nil in 2022, 2023 and 2024.
Transactions with Aguila Information, S.A.P.I. de C.V. (“Aguila Information”)
We are engaged by Aguila Information to provide business and operational support services. On January 5, 2021, Aguila Information was deconsolidated by us and deemed as our related party. (See note 6 to the consolidated financial statements on page F-31 for further details.)
We charged RMB6.6 million, nil and nil from Aguila Information for the service fees provided in 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. As of December 31, 2022, the outstanding balance of the service fees receivable was RMB13.5 million, which was fully accrued of credit losses.
In 2022, we provided interest free loans to Aguila Information with a total amount of RMB4.2 million. As of December 31, 2022, the loan has been collected.
Transactions with GAYANG (Hongkong) Co., Limited(“GAYANG”)
GAYANG is controlled by Mr. Dinggui Yan, our founder, director and chief executive officer. In October and November 2021, we entered into a loan contract with GAYANG, pursuant to which we provided a total amount of RMB10.6 million to GAYANG for an annual interest rate of 8%, with the term of 360 days. We accrued RMB171,111 and RMB637,976 of interest in 2021 and 2022 respectively. In July 2022, we collected RMB1.4 million of the loan. In November 2022, we provided an interest bearing loan to GAYANG for its daily operation with principal of RMB17.2 million (US$2.4 million) and fixed interest rate of 8% after a three-months free of interest duration. As of December 31, 2022, the loans have an outstanding balance of RMB27.2 million, among which, RMB10.0 million was accrued of credit losses. In February 2023, the outstanding balance of RMB17.2 million has been collected.
Transactions with Keen Best
In 2020, we, through our subsidiary, Geerong (HK) and another independent purchaser entered into a share purchase agreement with China Smartpay Group Holdings Limited (“China Smartpay”), to acquire 35 ordinary shares of Keen Best Investment Limited (“Keen Best”), representing 35% equity interest in Keen Best, a wholly-owned subsidiary of China Smartpay for an amount of RMB92.0 million.
For the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, we recognized we and the VIE Group’s proportionate share of the equity investee’s net loss into earnings in the amount of RMB1.2 million, RMB2.0 million and nil, respectively. In 2023, the VIE group provided non-interest bearing loans to Keen Best with a total amount of RMB13.9 million. Keen Best is one of our affiliate enterprises. The loan has been fully repaid as of December 31, 2023.
As of December 31, 2023, we were no longer able to exert significant influence over Keen Best. Considering the business forecast of the investee, we fully impaired this investment in 2023.
In 2024, we received RMB69.0 million (US$9.5 million) for our equity investments in Keen Best and recorded in Other income, net in the consolidated statements of operations.
Transactions with Sunshinewoods
In 2024, we borrowed interest bearing loans from Sunshinewoods for our daily operation with principal of RMB27.5 million (US$3.8 million) and fixed interest rate of 8%, with term of 360 days. As of December 31, 2024, the outstanding loan balance was RMB22.2 million (US$3.0 million).
Dividends Paid to Dream Glory L.P. and New Dream
In August 2024, the Board of Directors of the Company approved a dividend of US$ 0.125 per ordinary share, which was paid in September 2024 to shareholders of record as of the close of business on August 27, 2024. As of December 31, 2024, the unpaid dividends distributed to Dream Glory L.P. and New Dream was RMB23.9 million (US$3.3 million) and RMB16.9 million (US$2.3 million), respectively.
Transactions with Jiayin Technology Service (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.(“Jiayin Technology Service”)
In 2024, we provided loan facilitation services to Jiayin Technology Service, who funded loans through a trust as the sole beneficiary. Jiayin Technology Service is controlled by Mr. Dinggui Yan, our founder, director and chief executive officer.
We and the VIE group incurred nil, nil and RMB31.0 million (US$4.2 million) of loan facilitation services fee in 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
Amounts due from Jiayin Technology Service was nil, nil and RMB4.4 million (US$0.6 million) as of December 31, 2022, 2023, and 2024, respectively.
Contractual Arrangements with Jiayin Technology and Its Shareholders
See “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure.”
Collaboration Agreement with Shanghai Caiyin
See “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure.”
Share Incentive Plan
See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—B. Compensation—Share Incentive Plans.”
Employment Agreements and Indemnification Agreements
See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—B. Compensation—Employment Agreements and Indemnification Agreements.”
C.
Interest of Experts and Counsel
Not applicable.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL INFORMATION
A. Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information
We have appended consolidated financial statements filed as part of this annual report.
Legal Proceedings
We are currently not a party to any material legal or administrative proceedings. We may from time to time be subject to various legal or administrative claims and proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business. Litigation or any other legal or administrative proceeding, regardless of the outcome, is likely to result in substantial cost and diversion of our resources, including our management’s time and attention.
Dividend Policy
In March 2018, Jiayin Technology paid a cash dividend of RMB400 million to its shareholders. Jiayin Group Inc. has not previously declared or paid cash dividends on our Class A ordinary shares.
On March 28, 2023, our Board approved and adopted a dividend policy, under which the Company may choose to declare and distribute cash dividend twice each fiscal year, starting from 2023, at an aggregate amount of no less than 15% of the net income after tax of the Company in the previous fiscal year on a consolidated basis. The determination to make dividend distributions in any particular fiscal year will be made at the discretion of the Board based upon factors such as our results of operations, cash flow, general financial condition, capital requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors as the Board may deem relevant. On July 10, 2023, our board of directors approved the payment of a cash dividend of US$0.10 per ordinary share, or US$0.40 per ADS. ("July 2023 Dividend") The aggregate amount of cash distributed for the July 2023 Dividend was approximately US$21.5 million. On January 8, 2024, our board of directors approved the payment of a cash dividend of US$0.10 per ordinary share, or US$0.40 per ADS. ("January 2024 Dividend"). The aggregate amount of cash distributed for the January 2024 Dividend was US$21.2 million. On August 16, 2024, our board of directors approved the payment of a cash dividend of US$0.125 per ordinary share, or US$0.50 per ADS ("August 2024 Dividend"). The aggregate amount of cash distributed for the August 2024 Dividend was US$26.6 million. On November 19, 2024, our board of directors approved and adopted an amended dividend policy (the “Amended Dividend Policy”) to replace the prior dividend policy in its entirety, with immediate effect. Under the Amended Dividend Policy, we may choose to declare and distribute a cash dividend once each fiscal year, starting from 2025, at an aggregate amount of no less than 15% of our net income after tax in the previous fiscal year. On March 27, 2025, in order to provide investors with higher returns, our board of directors approved and adopted a further adjustment to the Amended Dividend Policy to increase the annual dividend amount such that we may choose to declare and distribute a cash dividend once each fiscal year, starting from 2025, at an aggregate amount of around 30% of our net income after tax in the previous fiscal year. The determination to make dividend distributions in any particular fiscal year will be made at the discretion of our board of directors based upon factors such as our results of operations, cash flow, general financial condition, capital requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant.
We are a holding company incorporated in the Cayman Islands. In order for us to distribute any dividends to our shareholders and ADS holders, we may rely on dividends distributed by our PRC subsidiaries. Certain payments from our PRC subsidiaries to us may be subject to PRC withholding income tax. In addition, relevant PRC laws and regulations permit the PRC companies, such as our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE, to pay dividends only out of their retained earnings, if any, as determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. Each of our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE that is in retained earnings position as of the end of each year is required to set aside at least 10% of its after-tax profits each year, if any, to fund certain statutory reserve funds until such reserve funds reach 50% of its registered capital. Furthermore, each of our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE may allocate a portion of its after-tax profits based on PRC accounting standards to a discretionary surplus fund at their discretion. The statutory reserve funds and the discretionary surplus funds are not distributable as cash dividends. After our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE have generated retained earnings and met the requirements for appropriation to the statutory reserves and until such reserves reach 50% of its registered capital, respectively, our PRC subsidiaries and the consolidated VIE can distribute dividends upon approval of the shareholders See “Item 3.
Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—We rely on dividends and other distributions on equity paid by our PRC subsidiaries to fund any cash and financing requirements we may have, and any limitation on the ability of our PRC subsidiaries to make payments to us could have a material adverse effect on our ability to conduct our business.”
Our board of directors has discretion as to whether to distribute dividends, subject to certain requirements of Cayman Islands law. In addition, our shareholders may by ordinary resolution declare a dividend, but no dividend may exceed the amount recommended by our directors. Under Cayman Islands law, a Cayman Islands company may pay a dividend out of either profit or share premium account, provided that in no circumstances may a dividend be paid if this would result in the company being unable to pay its debts as they fall due in the ordinary course of business. Even if our board of directors decides to pay dividends, the form, frequency and amount will depend upon our future operations and earnings, capital requirements and surplus, general financial condition, contractual restrictions and other factors that the board of directors may deem relevant. Any dividend declared on our ordinary shares shall be payable equally to holders of Class A and Class B ordinary shares. If we pay any dividends on our ordinary shares, we will pay those dividends which are payable in respect of the underlying Class A ordinary shares represented by our ADSs to the depositary, as the registered holder of such Class A ordinary shares, and the depositary then will pay such amounts to our ADS holders in proportion to the underlying Class A ordinary shares represented by the ADSs held by such ADS holders, subject to the terms of the deposit agreement, including the fees and expenses payable thereunder. Cash dividends on our ordinary shares, if any, will be paid in U.S. dollars.
B. Significant Changes
Except as disclosed elsewhere in this annual report, we have not experienced any significant changes since the date of our audited consolidated financial statements included in this annual report.
ITEM 9. THE OFFER AND LISTING
A.
Offer and Listing Details
Our ADSs, each representing four of our Class A ordinary shares, have been listed on the Nasdaq Stock Market since May 10, 2019. Our ADSs trade under the symbol “JFIN.”
Not applicable.
Our ADSs have been listed on the NASDAQ Global Market since May 10, 2019 under the symbol “JFIN”.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
ITEM 10. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Not applicable.
B.
Memorandum and Articles of Association
We are a Cayman Islands exempted company with limited liability and our corporate affairs are governed by our memorandum and articles of association, as amended from time to time and the Companies Act (As Revised) of the Cayman Islands, which we refer to as the Companies Act below, and the common law of the Cayman Islands.
The following are summaries of material provisions of our currently effective memorandum and articles of association and of the Companies Act, insofar as they relate to the material terms of our ordinary shares.
General
All of our issued and outstanding Class A and Class B ordinary shares are fully paid and non-assessable. Our shareholders who are non-residents of the Cayman Islands may freely hold and vote their ordinary shares.
Dividends
The holders of our ordinary shares are entitled to receive such dividends as may be declared by our board of directors subject to our memorandum and articles of association and the Companies Act. In addition, our shareholders may by ordinary resolution declare a dividend, but no dividend may exceed the amount recommended by our directors. Under Cayman Islands law, dividends may be paid only out of profits or share premium, provided that, immediately after the payment, we will be able to pay our debts as they become due in the ordinary course of business.
Register of Members
Under Cayman Islands law, we must keep a register of members and there must be entered therein:
•
the names and addresses of the members, together with a statement of the shares held by each member, and such statement shall confirm (i) the amount paid or agreed to be considered as paid, on the shares of each member, (ii) the number and category of shares held by each member, and (iii) whether each relevant category of shares held by a member carries voting rights under the articles of association of the company, and if so, whether such voting rights are conditional;
•
the date on which the name of any person was entered on the register as a member; and
•
the date on which any person ceased to be a member.
Under Cayman Islands law, the register of members of our company is prima facie evidence of the matters set out therein (i.e. the register of members will raise a presumption of fact on the matters referred to above unless rebutted) and a member registered in the register of members will be deemed as a matter of Cayman Islands law to have legal title to the shares as set against its name in the register of members.
If the name of any person is incorrectly entered in or omitted from the register of members, or if default is made or unnecessary delay takes place in entering on the register the fact of any person having ceased to be a member, the person or member aggrieved or any member or the company itself may apply to the Grand Court of the Cayman Islands for an order that the register be rectified, and the Court may either refuse such application or it may, if satisfied of the justice of the case, make an order for the rectification of the register.
Voting Rights
In respect of all matters subject to a shareholders’ vote, each registered holder of Class A ordinary shares is, on a poll, entitled to one vote per share, and each registered holder of Class B ordinary shares is, on a poll, entitled to ten votes per share. Holders of Class A ordinary shares and Class B ordinary shares shall, at all times, vote together on all resolutions submitted to a shareholders’ vote. Holders of our ordinary shares have the right to receive notice of, attend, speak and vote at general meetings of our company. At any general meeting a resolution put to the vote of the meeting shall be decided on a show of hands, unless a poll is (before or on the declaration of the result of the show of hands) demanded by the chairman of the meeting or by one or more shareholders present in person or by proxy (or, if a corporation or other non-natural person, by its duly authorized representative or proxy) who together hold shares which carry in aggregate not less than ten percent of the votes attaching to all issued and outstanding shares of our company that carry the right to vote at the general meeting. An ordinary resolution to be passed by the shareholders requires the affirmative vote of a simple majority of the votes cast in a general meeting, while a special resolution requires the affirmative vote of no less than two-thirds of the votes cast in a general meeting. Both ordinary resolutions and special resolutions may also be passed by a unanimous written resolution signed by all the shareholders of our company, as permitted by the Companies Act and our memorandum and articles of association.
A special resolution will be required for important matters such as a change of name or making changes to our memorandum and articles of association.
General Meetings and Shareholder Proposals
As a Cayman Islands exempted company, we are not obliged by the Companies Act to call shareholders’ annual general meetings. Our memorandum and articles of association provide that we may (but are not obliged to) in each year hold a general meeting as our annual general meeting in which case we will specify the meeting as such in the notices calling it, and the annual general meeting will be held at such time and place as may be determined by our directors.
Cayman Islands law provides shareholders with only limited rights to requisition a general meeting, and does not provide shareholders with any right to put any proposal before a general meeting. However, these rights may be provided in a company’s articles of association. Our memorandum and articles of association allow any two or more of our shareholders, who together hold shares which carry in aggregate not less than ten percent of all votes attaching to all of the issued and outstanding shares of our company, to requisition an extraordinary general meeting of our shareholders, in which case the directors are obliged to call such meeting and to put the resolutions so requisitioned to a vote at such meeting.
A quorum required for a meeting of shareholders consists of one or more shareholders, who together hold shares which carry in aggregate not less than one-third (1/3rd) of all votes attaching to all issued and outstanding shares of our company that carry the right to vote at such general meeting, present in person or by proxy or, if a corporation or other non-natural person, by its duly authorized representative. Advance notice of at least seven calendar days is required for the convening of our annual general meeting and other shareholders meetings.
Conversion
Each Class B ordinary share is convertible into one Class A ordinary share at any time at the option of the holder thereof. Class A ordinary shares are not convertible into Class B ordinary shares under any circumstances. Upon any direct or indirect sale, transfer, assignment or disposition of Class B ordinary shares by a holder to any person or entity which is not an affiliate of such holder or the direct or indirect transfer or assignment of the voting power attached to such number of Class B ordinary shares through voting proxy or otherwise to any person or entity which is not an affiliate of such holder, such Class B ordinary shares shall be automatically and immediately converted into the equivalent number of Class A ordinary shares.
Transfer of Ordinary Shares
Subject to the restrictions in our memorandum and articles of association as set out below, any of our shareholders may transfer all or any of his or her ordinary shares by an instrument of transfer in the usual or common form or any other form approved by our board.
Our board of directors may, in its absolute discretion, decline to register any transfer of any ordinary share which is not fully paid up or on which we have a lien. Our directors may also decline to register any transfer of any ordinary share unless:
•
the instrument of transfer is lodged with us, accompanied by the certificate for the ordinary shares to which it relates and such other evidence as our board of directors may reasonably require to show the right of the transferor to make the transfer;
•
the instrument of transfer is in respect of only one class of shares;
•
the instrument of transfer is properly stamped, if required;
•
in the case of a transfer to joint holders, the number of joint holders to whom the ordinary share is to be transferred does not exceed four; and
•
the ordinary shares transferred are free of any lien in favor of us.
If our directors refuse to register a transfer they are obligated to, within two calendar months after the date on which the instrument of transfer was lodged, send to each of the transferor and the transferee notice of such refusal. The registration of transfers of shares or of any class of shares may, after compliance with any notice requirement of the designated stock exchange, be suspended at such times and for such periods (not exceeding in the whole thirty (30) days in any calendar year) as our board of directors may determine.
Liquidation
On the winding up of our company, if the assets available for distribution among our shareholders shall be more than sufficient to repay the whole of the share capital at the commencement of the winding up, the surplus shall be distributed among our shareholders in proportion to the par value of the shares held by them at the commencement of the winding up, subject to a deduction from those shares in respect of which there are monies due, of all monies payable to our company for unpaid calls or otherwise. If our assets available for distribution are insufficient to repay all of the paid-up capital, the assets will be distributed so that, as nearly as may be, the losses are borne by our shareholders in proportion to the par value of the shares held by them. We are an exempted company with limited liability incorporated under the Companies Act, and under the Companies Act, the liability of our members is limited to the amount, if any, unpaid on the shares respectively held by them. Our memorandum of association contains a declaration that the liability of our members is so limited.
Calls on Ordinary Shares and Forfeiture of Ordinary Shares
Our board of directors may from time to time make calls upon shareholders for any amounts unpaid on their ordinary shares in a notice served to such shareholders at least fourteen calendar days prior to the specified time and place of payment. The ordinary shares that have been called upon and remain unpaid on the specified time are subject to forfeiture, subject to certain terms and conditions.
Redemption, Repurchase and Surrender of Ordinary Shares
We may issue shares on terms that such shares are subject to redemption, at our option or at the option of the holders thereof, on such terms and in such manner as may be determined, before the issue of such shares, by our board of directors or by a special resolution of our shareholders. Our company may also repurchase any of our shares provided that the manner and terms of such purchase have been approved by our board of directors or by ordinary resolution of our shareholders, or are otherwise authorized by our memorandum and articles of association. Under the Companies Act, the redemption or repurchase of any share may be paid out of our company’s profits or out of the proceeds of a fresh issue of shares made for the purpose of such redemption or repurchase, or out of capital (including share premium account and capital redemption reserve) if the company can, immediately following such payment, pay its debts as they fall due in the ordinary course of business. In addition, under the Companies Act no such share may be redeemed or repurchased (a) unless it is fully paid up, (b) if such redemption or repurchase would result in there being no shares outstanding, or (c) if the company has commenced liquidation. In addition, our company may accept the surrender of any fully paid share for no consideration.
Variations of Rights of Shares
If at any time the share capital is divided into different classes of shares, all or any of the rights attached to any class of shares may, subject to any rights or restrictions for the time being attached to the shares of that class, be varied either with the unanimous written consent of the holders of the issued shares of that class or with the sanction of a special resolution passed at a separate meeting of the holders of the shares of that class. The rights conferred upon the holders of the shares of any class issued with preferred or other rights shall not, unless otherwise expressly provided by the terms of issue of the shares of that class, be deemed to be varied by the creation or issue of further shares ranking pari passu with or subsequent to the shares of that class or the redemption or purchase of any shares of any class by the Company. The rights of the holders of shares shall not be deemed to be varied by the creation or issue of shares with preferred or otherwise rights including, without limitation, the creation of shares with enhanced or weighted voting rights.
Inspection of Books and Records
Holders of our ordinary shares will have no general right under Cayman Islands law to inspect or obtain copies of our register of members or our corporate records (other than a right to receive copies of our memorandum and articles of association, special resolutions passed by our shareholders and our registered of mortgages and charges). However, we will provide our shareholders with annual audited financial statements. Under Cayman Islands law, the names of current directors can be obtained from a search conducted at the Registrar of Companies in the Cayman Islands.
Changes in Capital
Our shareholders may from time to time by ordinary resolutions:
•
increase the share capital by such sum, to be divided into shares of such classes and amount, as the resolution prescribes;
•
consolidate and divide all or any of our share capital into shares of a larger amount than our existing shares
•
sub-divide our existing shares, or any of them into shares of a smaller amount than that fixed by our memorandum of association; provided that in the subdivision the proportion between the amount paid and the amount, if any, unpaid on each reduced share will be the same as it was in case of the share from which the reduced share is derived; and
•
cancel any shares which, at the date of the passing of the resolution, have not been taken or agreed to be taken by any person and diminish the amount of our share capital by the amount of the shares so canceled.
However, no alteration contemplated above, or otherwise, may be made to the par value of the Class A ordinary shares or Class B ordinary shares unless an identical alteration is made to the par value of the Class B ordinary shares and Class A ordinary shares, as the case may be.
Subject to the Companies Act, our shareholders may by special resolution reduce our share capital and any capital redemption reserve in any manner authorized by law.
We have not entered into any material contracts other than in the ordinary course of business and other than those described in this annual report.
See “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—Regulation—Regulations Relating to Foreign Exchange.”
The following summary of Cayman Islands, the PRC and U.S. federal income tax consequences of an investment in the ADSs or Class A ordinary shares is based upon laws and relevant interpretations thereof in effect as of the date of this annual report, all of which are subject to change. This summary does not deal with all possible tax consequences relating to an investment in the ADSs or Class A ordinary shares, such as the tax consequences under state, local and other tax laws, or tax laws of jurisdictions other than the Cayman Islands, the PRC and the United States. To the extent that the discussion relates to matters of Cayman Islands tax law, it represents the opinion of Maples and Calder (Hong Kong) LLP, our Cayman Islands legal counsel. To the extent that the discussion relates to matters of the PRC tax law, it represents the opinion of King & Wood Mallesons, our PRC legal counsel.
Cayman Islands Taxation
The Cayman Islands currently levies no taxes on individuals or corporations based upon profits, income, gains or appreciation and there is no taxation in the nature of inheritance tax or estate duty. There are no other taxes likely to be material to us levied by the government of the Cayman Islands except for stamp duties which may be applicable on instruments executed in, or, after execution, brought within the jurisdiction of the Cayman Islands. The Cayman Islands is not party to any double tax treaties that are applicable to any payments made to or by our company. There are no exchange control regulations or currency restrictions in the Cayman Islands.
Payments of dividends and capital in respect of our Class A ordinary shares or ADSs will not be subject to taxation in the Cayman Islands and no withholding will be required on the payment of a dividend or capital to any holder of our Class A ordinary shares or ADSs, nor will gains derived from the disposal of our Class A ordinary shares or ADSs be subject to Cayman Islands income or corporate tax.
People’s Republic of China Tax Considerations
Under the EIT Law, an enterprise established outside the PRC with a “de facto management body” within the PRC is considered a PRC resident enterprise for PRC enterprise income tax purposes and is generally subject to a uniform 25% enterprise income tax rate on its worldwide income as well as tax reporting obligations. Under the Implementation Rules of the Enterprise Income Tax Law, a “de facto management body” is defined as a body that has material and overall management and control over the manufacturing and business operations, personnel and human resources, finances and properties of an enterprise. In addition, SAT Circular 82 issued in April 2009 specifies that certain offshore-incorporated enterprises controlled by PRC enterprises or PRC enterprise groups will be classified as PRC resident enterprises if all of the following conditions are met: (a) senior management personnel and core management departments in charge of the daily operations of the enterprises have their presence mainly in the PRC; (b) their financial and human resources decisions are subject to determination or approval by persons or bodies in the PRC; (c) major assets, accounting books and company seals of the enterprises, and minutes and files of their board’s and shareholders’ meetings are located or kept in the PRC; and (d) half or more of the enterprises’ directors or senior management personnel with voting rights habitually reside in the PRC. If the PRC tax authorities deem our company or any of our overseas subsidiaries as a PRC resident enterprise for PRC enterprise income tax purposes, a number of unfavorable PRC tax consequences could follow. We or the overseas subsidiaries, as the case may be, would be subject to the PRC enterprise income tax at the rate of 25% on worldwide income. Also, a 10% withholding tax would be imposed on dividends we pay to our non-PRC enterprise shareholders and any gains realized by our non-PRC enterprise shareholders on the transfer of ADS or Class A ordinary shares are also subject to a withholding tax rate of 10%. The withholding tax rate could potentially increase to 20% on dividends we pay to our non-PRC individual shareholders and any gains realized by such non-PRC individual shareholders on the transfer of ADS or Class A ordinary shares. These rates may be reduced by an applicable tax treaty.
SAT issued the Bulletin on Issues of Enterprise Income Tax on Indirect Transfers of Assets by Non-PRC Resident Enterprises, or SAT Bulletin 7, on February 3, 2015, which replaced or supplemented certain previous rules under the circular commonly known as “SAT Circular 698.” Under SAT Bulletin 7, an “indirect transfer” of assets, including equity interests in a PRC resident enterprise, by non-PRC resident enterprises may be re-characterized and treated as a direct transfer of PRC taxable assets, if such arrangement does not have a reasonable commercial purpose and was established for the purpose of avoiding payment of PRC enterprise income tax. As a result, gains derived from such indirect transfer may be subject to PRC enterprise income tax. According to SAT Bulletin 7, “PRC taxable assets” include assets attributed to an establishment in China, immoveable properties in China, and equity investment in PRC resident enterprises. In respect of an indirect offshore transfer of assets of a PRC establishment, the relevant gain is to be regarded as effectively connected with the PRC establishment and therefore included in its enterprise income tax filing, and would consequently be subject to PRC enterprise income tax at a rate of 25%. Where the underlying transfer relates to the immoveable properties in China or to equity investment in a PRC resident enterprise, which is not effectively connected to a PRC establishment of a non-resident enterprise, a PRC enterprise income tax at a rate of 10% would apply, subject to available preferential tax treatment under applicable tax treaties or similar arrangements, and the party who is obligated to make the transfer payments has the withholding obligation. It remains to be observed as to the implementation details of SAT Bulletin 7. If SAT Bulletin 7 were determined by the tax authorities to be applicable to some of our transactions involving PRC taxable assets, our offshore subsidiaries conducting the relevant transactions might be required to spend valuable resources to comply with SAT Bulletin 7 or to establish that the relevant transactions should not be taxed under SAT Bulletin 7. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—We face uncertainty with respect to indirect transfers of equity interests in PRC resident enterprises by their non-PRC holding companies.”
Pursuant to the Arrangement between the Mainland China and the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region for the Avoidance of Double Taxation and Tax Evasion on Income, or the Tax Arrangement, where a Hong Kong resident enterprise which is considered a non-PRC tax resident enterprise directly holds at least 25% of a PRC enterprise, the withholding tax rate in respect of the payment of dividends by such PRC enterprise to such Hong Kong resident enterprise is reduced to 5% from a standard rate of 10%. Pursuant to SAT Circular 81, a resident enterprise of the counter-party to such Tax Arrangement should meet the following conditions, among others, in order to enjoy the reduced withholding tax under the Tax Arrangement: (i) it must directly own the required percentage of equity interests and voting rights in such PRC resident enterprise; and (ii) it should directly own such percentage in the PRC resident enterprise anytime in the 12 months prior to receiving the dividends.
United States Federal Income Tax Considerations
The following discussion summarizes the material United States federal income tax consequences to a United States Holder (as defined below), under current law, of an investment in our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares. This discussion is based on the federal income tax laws of the United States as of the date of this annual report, including the United States Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, existing and proposed Treasury regulations promulgated thereunder, judicial authority, published administrative positions of the United States Internal Revenue Service, or the IRS, and other applicable authorities, all as of the date of this annual report. All of the foregoing authorities are subject to change, which change could apply retroactively and could significantly affect the tax consequences described below. We have not sought any ruling from the IRS with respect to the statements made and the conclusions reached in the following discussion and there can be no assurance that the IRS or a court will agree with our statements and conclusions. This discussion, moreover, does not address the United States federal estate, gift, Medicare, or alternative minimum tax considerations, or any state, local or non-United States tax considerations, relating to the ownership or disposition of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares. Except as specifically described below, this discussion does not address any of the consequences of holding our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares through a bank, financial institution or other entity, or a branch thereof, located, organized or resident outside the United States, including withholding taxes or reporting obligations applicable to accounts maintained with non-United States financial institutions (through which a United States Holder may hold our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares), and does not describe any tax consequences arising in respect of the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (“FATCA”) regime.
This discussion applies only to a United States Holder (as defined below) that holds our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares as capital assets for United States federal income tax purposes (generally, property held for investment). The discussion neither addresses the tax consequences to any particular investor nor describes all of the tax consequences applicable to persons in special tax situations, such as:
•
banks and certain other financial institutions;
•
regulated investment companies;
•
real estate investment trusts;
•
brokers or dealers in stocks and securities, or currencies;
•
persons that use or are required to use a mark-to-market method of accounting;
•
certain former citizens or residents of the United States subject to Section 877 of the Code;
•
entities subject to the United States anti-inversion rules;
•
tax-exempt organizations or entities (including private foundations);
•
persons whose functional currency is other than the United States dollar;
•
persons holding ADSs or Class A ordinary shares as part of a straddle, hedging, conversion or integrated transaction;
•
persons that actually or constructively own ADSs or Class A ordinary shares representing 10% or more of our total voting power or value;
•
persons who acquired ADSs or Class A ordinary shares pursuant to the exercise of an employee equity grant or otherwise as compensation;
•
partnerships or other pass-through entities, or persons holding ADSs or Class A ordinary shares through such entities;
•
persons required to accelerate the recognition of any item of gross income with respect to our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares as a result of such income being recognized on an applicable financial statement; or
•
persons that held, directly, indirectly or by attribution, ADSs or Class A ordinary shares or other ownership interests in us prior to our initial public offering.
If a partnership (including an entity or arrangement treated as a partnership for United States federal income tax purposes) holds our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares, the tax treatment of a partner in the partnership generally will depend upon the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. A partnership or partner in a partnership holding our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares should consult its tax advisors regarding the tax consequences of investing in and holding our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares.
THE FOLLOWING DISCUSSION IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT A SUBSTITUTE FOR CAREFUL TAX PLANNING AND ADVICE. HOLDERS SHOULD CONSULT THEIR TAX ADVISORS WITH RESPECT TO THE APPLICATION OF THE UNITED STATES FEDERAL INCOME TAX LAWS TO THEIR PARTICULAR SITUATIONS, AS WELL AS ANY TAX CONSEQUENCES ARISING UNDER THE UNITED STATES FEDERAL ESTATE OR GIFT TAX LAWS OR THE LAWS OF ANY STATE, LOCAL OR NON-UNITED STATES TAXING JURISDICTION OR UNDER ANY APPLICABLE TAX TREATY.
For purposes of the discussion below, a “United States Holder” is a beneficial owner of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares that is, for United States federal income tax purposes:
•
an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States;
•
a corporation created or organized in or under the laws of the United States, any state thereof or the District of Columbia;
•
an estate, the income of which is subject to United States federal income taxation regardless of its source; or
•
a trust, if (i) a court within the United States is able to exercise primary jurisdiction over its administration and one or more United States persons (as defined in the Code) have the authority to control all of its substantial decisions or (ii) a valid election is in place under applicable Treasury Regulations to treat such trust as a domestic trust.
The discussion below assumes that the representations contained in the deposit agreement and any related agreement are true and that the obligations in such agreements will be complied with in accordance with their terms.
ADSs
If you own our ADSs, then you generally should be treated as the owner of the underlying Class A ordinary shares represented by those ADSs for United States federal income tax purposes. Accordingly, deposits or withdrawals of Class A ordinary shares for ADSs generally are not expected to be subject to United States federal income tax.
Passive Foreign Investment Company
General
Based on the market price of our ADSs, the value of our assets and the nature and composition of our income and assets, we do not believe that we were a passive foreign investment company, or PFIC, for United States federal income tax purposes for our taxable year ended December 31, 2024. However, we believe that were a PFIC for our taxable year ended December 31, 2023.
The determination of PFIC status is based on an annual determination that cannot be made until the close of a taxable year and involves extensive factual investigation, including ascertaining the fair market value of all of our assets on a quarterly basis and the character of each item of income that we earn. Moreover, the application of the PFIC rules is subject to uncertainty in several respects, and we cannot assure you that the United States Internal Revenue Service, or the IRS, will agree with any determination we make. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that we will not be treated as a PFIC for any taxable year or that the IRS will not take a contrary position to any determination we make. We will be a PFIC, for United States federal income tax purposes for any taxable year if, applying applicable look-through rules, either:
•
at least 75% of our gross income for such year is passive income; or
•
at least 50% of the value of our assets (generally determined based on a quarterly average) during such year is attributable to assets that produce or are held for the production of passive income.
For this purpose, passive income generally includes dividends, interest, and certain types of rents and royalties. In addition, cash, cash equivalents, securities held for investment purposes, and certain other similar assets are generally categorized as passive assets. We will be treated as owning a proportionate share of the assets and earning a proportionate share of the income of any other corporation in which we own, directly or indirectly, at least 25% (by value) of the stock.
Although the law in this regard is unclear, we treat the consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries as being owned by us for United States federal income tax purposes, because we exercise effective control over the operation of these entities and because we are entitled to substantially all of their economic benefits, and, as a result, we consolidate their results of operations in our consolidated U.S. GAAP financial statements. If it were determined, however, that we are not the owner of the consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries for United States federal income tax purposes, the composition of our income and assets would change and we may be more likely to be treated as a PFIC for one or more taxable years.
Changes in the value of our assets and/or the nature and composition of our income or assets may cause us to be or become a PFIC. The determination of whether we will be a PFIC for any taxable year may depend in part upon the value of our goodwill and other unbooked intangibles not reflected on our balance sheet (which may depend upon the market price of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares from time to time, which may fluctuate significantly) and also may be affected by how, and how quickly, we spend our liquid assets and the cash we generated from our operations and raised in any offering. In estimating the value of our goodwill and other unbooked intangibles, we have taken into account our market capitalization. Among other matters, if our market capitalization declines, we may be more likely to be a PFIC because our liquid assets and cash (which are for this purpose considered assets that produce passive income) may then represent a greater percentage of the value of our overall assets. Further, while we believe our classification methodology and valuation approach are reasonable, it is possible that the IRS may challenge our classification or valuation of our goodwill and other unbooked intangibles, which may result in our being or becoming a PFIC for one or more taxable years.
A United States Holder that holds our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares in any taxable year in which we are a PFIC will be required to file an annual report containing such information as the United States Treasury Department may require.
You are strongly encouraged to consult your tax advisors regarding the application of the PFIC rules to an investment in our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares and the availability, application and consequences of the elections discussed below.
U.S. Holders During 2023
The following discussion summarizes the consequences for U.S. Holders of our ADSs and Class A ordinary shares during any taxable year during which we are/were treated as a PFIC (as we believe we were for our taxable year ended December 31, 2023). U.S. Holders of our ADSs and Class A ordinary shares during our taxable year ended December 31, 2023 (or any other taxable year during which we are a PFIC) are strongly encouraged to consult their tax advisors regarding the application of the PFIC rules and the availability and consequences of the elections discussed below.
Deemed Sale Election. As we believe that we were treated as a PFIC for our taxable year ended December 31, 2023, if you held our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares during our taxable year ended December 31, 2023, we generally will continue to be treated as a PFIC with respect to you for all succeeding years during which you hold our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares, unless we were to cease to be a PFIC (as we believe we have for our taxable year ended December 31, 2024) and you make a “deemed sale” election with respect to such ADSs or Class A ordinary shares. If such election is made, you will be deemed to have sold such ADSs or Class A ordinary shares at their fair market value and any gain from such deemed sale would be subject to the rules described in the following two paragraphs. After the deemed sale election, so long as we do not become a PFIC in a subsequent taxable year, such ADSs or Class A ordinary shares with respect to which such election was made will not be treated as shares in a PFIC and, as a result, you will not be subject to the rules described below with respect to any “excess distribution” you receive from us or any gain from a sale or other taxable disposition of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares. You are strongly urged to consult your tax advisors as to the possibility and consequences of making a deemed sale election if such an election becomes available to you.
Mark-to-Market Election. As we believe that we were a PFIC for our taxable year ended December 31, 2023, if you held our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares during our taxable year ended December 31, 2023 (or any other taxable year during which we are a PFIC), if no “deemed sale” election (as discussed above) has been made, unless you make a “mark-to-market” election (as discussed below), you generally will be subject to special and adverse tax rules with respect to any “excess distribution” that you receive from us and any gain that you recognize from a sale or other disposition, including a pledge, of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares. For this purpose, distributions that you receive in a taxable year that are greater than 125% of the average annual distributions that you received during the shorter of the three preceding taxable years or your holding period for the ADSs or Class A ordinary shares will be treated as an excess distribution. Under these rules:
•
the excess distribution or recognized gain will be allocated ratably over your holding period for the ADSs or Class A ordinary shares;
•
the amount of the excess distribution or recognized gain allocated to the taxable year of distribution or gain, and to any taxable years in your holding period prior to the first taxable year in which we were a PFIC, will be treated as ordinary income; and the amount of the excess distribution or recognized gain allocated to each other taxable year will be subject to the highest tax rate in effect for individuals or corporations, as applicable, for each such year and the resulting tax will be subject to the interest charge generally applicable to underpayments of tax.
As we believe that we were a PFIC for our taxable year ended December 31, 2023, if you held our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares during our taxable year ended December 31, 2023 (or any other taxable year during which we are a PFIC), if any of our non-United States subsidiaries that are corporations (or other corporations in which we directly or indirectly own equity interests) is also a PFIC for such taxable year, you would be treated as owning a proportionate amount (by value) of the shares of each such non-United States corporation classified as a PFIC (each such corporation, a lower tier PFIC) for purposes of the application of these rules. You should consult your tax advisors regarding the application of the PFIC rules to any of our lower tier PFICs.
As we believe that we were a PFIC for our taxable year ended December 31, 2023, if you held our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares during our taxable year ended December 31, 2023 (or any other taxable year during which we are a PFIC), in lieu of being subject to the tax and interest-charge rules discussed above, you may make an election to include gain on our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares as ordinary income under a mark-to-market method, provided that such ADSs or Class A ordinary shares constitute “marketable stock.” Marketable stock is stock that is regularly traded on a qualified exchange or other market, as defined in applicable Treasury regulations. Our ADSs, but not our ordinary shares, are listed on the Nasdaq, which is a qualified exchange for these purposes. Consequently, as long as our ADSs remain listed on the Nasdaq and are regularly traded, and you are a United States Holder of such ADSs, we expect that the mark-to-market election would be available to you for each taxable year for which we are a PFIC, but no assurances are given in this regard.
If you make a mark-to-market election, it will be effective for the taxable year for which the election is made and all subsequent taxable years unless our ADSs are no longer regularly traded on a qualified exchange or other market, or the IRS consents to the revocation of the election. United States Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the availability of the mark-to-market election, and whether making the election would be advisable in such United States Holder’s particular circumstances.
Because a mark-to-market election cannot be made for any lower-tier PFICs that we may own, if we were a PFIC for any taxable year, a United States Holder that makes a mark-to-market election with respect to our ADSs may continue to be subject to the tax and interest charges under the general PFIC rules with respect to such United States Holder’s indirect interest in any investments held by us that are treated as an equity interest in a PFIC for United States federal income tax purposes.
QEF Election. In certain circumstances, a shareholder in a PFIC may avoid the adverse tax and interest-charge regime described above by making a “qualified electing fund” election to include in income its share of the PFIC’s income on a current basis. However, if we were a PFIC (as we believe we were for our taxable year ended December 31, 2023), you would be able to make a qualified electing fund election with respect to our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares only if we agreed to furnish you annually with a PFIC annual information statement as specified in the applicable Treasury regulations. We currently do not intend to prepare or provide the information that would enable you to make a qualified electing fund election.
A United States Holder that holds or has held our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares in any taxable year in which we are or were a PFIC will be required to file an annual report containing such information as the United States Treasury Department may require.
You are strongly encouraged to consult your tax advisors regarding the application of the PFIC rules to an investment in our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares and the availability, application and consequences of the elections discussed above.
U.S. Holders Acquiring ADSs or Class A Ordinary Shares After 2023
The following discussion summarizes the consequences for U.S. Holders of our ADSs and Class A ordinary shares that acquire their ADSs or Class A ordinary shares in taxable years after 2023. As discussed above, we do not believe that we were a PFIC for United States federal income tax purposes for our taxable year ended December 31, 2024. As further discussed above, the determination of PFIC status is based on an annual determination that cannot be made until the close of a taxable year and involves extensive factual investigation, including ascertaining the fair market value of all of our assets on a quarterly basis and the character of each item of income that we earn. Moreover, the application of the PFIC rules is subject to uncertainty in several respects, and we cannot assure you that the IRS will agree with any determination we make. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that we will not be treated as a PFIC in 2024, 2025 or any subsequent taxable year or that the IRS will not take a contrary position to any determination we make. If we are treated as a PFIC in 2024, 2025, or in any subsequent taxable year, the treatment of U.S. Holders of our ADSs and Class A ordinary shares during such taxable years is generally described above under “—Passive Foreign Investment Company—U.S. Holders During 2023.” U.S. Holders of our ADSs and Class A ordinary shares during our taxable years ended December 31, 2024 and/or December 31, 2025 (or any subsequent taxable year) are strongly encouraged to consult their tax advisor regarding the application of the PFIC rules and the availability and consequences of the elections discussed above in any taxable year in which we are treated as a PFIC.
Dividends and Other Distributions on our ADSs or Class A Ordinary Shares. Subject to the passive foreign investment company rules discussed above, the gross amount of any distribution that we make to you with respect to our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares (including any amounts withheld to reflect PRC or other withholding taxes) will be taxable as a dividend, to the extent paid out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under United States federal income tax principles. Such income (including any withheld taxes) will be includable in your gross income on the day actually or constructively received by you, if you own our Class A ordinary shares, or by the depositary, if you own our ADSs. Because we do not intend to determine our earnings and profits on the basis of United States federal income tax principles, any distribution paid generally will be reported as a “dividend” for United States federal income tax purposes. Such dividends will not be eligible for the dividends-received deduction allowed to qualifying corporations under the Code.
Dividends received by a non-corporate United States Holder may qualify for the lower rates of tax applicable to “qualified dividend income,” if the dividends are paid by a “qualified foreign corporation” and other conditions discussed below are met. A non-United States corporation (other than a corporation that is a PFIC for the taxable year in which the dividend is paid or the preceding taxable year) generally will be treated as a qualified foreign corporation (i) with respect to dividends paid by that corporation on shares (or American depositary shares backed by such shares) that are readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States or (ii) if such non-United States corporation is eligible for the benefits of a qualifying income tax treaty with the United States that includes an exchange of information program. However, a non-United States corporation will not be treated as a qualified foreign corporation if it is a passive foreign investment company in the taxable year in which the dividend is paid or the preceding taxable year. As discussed above under “––Passive Foreign Investment Company––General,” we do not believe that we were a PFIC for United States federal income tax purposes for our taxable year ended December 31, 2024. However, we believe that we were a PFIC for our taxable year ended December 31, 2023.
Under a published IRS Notice, common or ordinary shares, or American depositary shares representing such shares (such as our ADSs), are considered to be readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States if they are listed on the Nasdaq, as our ADSs are (but not our ordinary shares). Based on existing guidance, it is unclear whether the Class A ordinary shares will be considered to be readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States, because only our ADSs, and not the underlying Class A ordinary shares, are listed on a securities market in the United States. We believe, but we cannot assure you, that dividends we pay, if any, on the Class A ordinary shares that are represented by our ADSs, but not on the ordinary shares that are not so represented, will, subject to applicable limitations, be eligible for the reduced rates of taxation. In addition, if we are treated as a PRC resident enterprise under the PRC tax law (see “Item 10. Additional Information—E. Taxation—People’s Republic of China Tax Considerations”), then we may be eligible for the benefits of the income tax treaty between the United States and the PRC. If we are eligible for such benefits, then dividends that we pay on our Class A ordinary shares, regardless of whether such shares are represented by our ADSs, would be eligible for the reduced rates of taxation, subject to applicable limitations (including ineligibility for reduced rates as a result of our being a PFIC for the taxable year in which the dividend is paid or the preceding taxable year).
Even if dividends would be treated as paid by a qualified foreign corporation, a non-corporate United States Holder will not be eligible for reduced rates of taxation if it does not hold our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares for more than 60 days during the 121-day period beginning 60 days before the ex-dividend date (disregarding certain periods of ownership while the United States Holder’s risk of loss is diminished) or if such United States Holder elects to treat the dividend income as “investment income” pursuant to Section 163(d)(4) of the Code. In addition, the rate reduction will not apply to dividends of a qualified foreign corporation if the non-corporate United States Holder receiving the dividend is obligated to make related payments with respect to positions in substantially similar or related property. This disallowance applies even if the minimum holding period has been met. Non-corporate United States Holders will not be eligible for reduced rates of taxation on any dividends received from us if we are a PFIC in the taxable year in which such dividends are paid or in the preceding taxable year.
You should consult your tax advisors regarding the availability of the lower tax rates applicable to qualified dividend income for any dividends that we pay with respect to our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares, as well as the effect of any change in applicable law after the date of this annual report.
Subject to certain conditions and limitations (including a minimum holding period requirement), any PRC withholding taxes imposed on dividends paid to you with respect to our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares (at a rate not exceeding the applicable rate provided in the United States–PRC income tax treaty in the case of a United States Holder that is eligible for the benefits of such treaty) generally will be treated as foreign taxes eligible for deduction or credit against your United States federal income tax liability, subject to the various limitations and disallowance rules that apply to foreign tax credits generally. For purposes of calculating the foreign tax credit limitation, dividends paid to you with respect to our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares will be treated as income from sources outside the United States and generally will constitute passive category income. However, Treasury regulations that apply to taxes paid or accrued in taxable years beginning on or after December 28, 2021 (the “Foreign Tax Credit Regulations”) impose additional requirements for foreign taxes to be eligible for a foreign tax credit, and there can be no assurance that those requirements will be satisfied.
A notice from the Internal Revenue Service indicates that the Internal Revenue Service is considering proposing amendments to the Foreign Tax Credit Regulations and also allows taxpayers to defer the application of many aspects of the Foreign Tax Credit Regulations until further notice.
Instead of claiming a foreign tax credit, United States Holders may be able to deduct any non-U.S. withholding taxes on dividends in computing your taxable income, subject to generally applicable limitations under United States law (including that a United States Holder is not eligible for a deduction for otherwise creditable foreign income taxes paid or accrued in a taxable year if such United States Holder claims a foreign tax credit for any foreign income taxes paid or accrued in the same taxable year). The rules relating to the determination of the foreign tax credit are complex, and you should consult your tax advisors regarding the availability of a foreign tax credit in your particular circumstances.
Disposition of our ADSs or Class A Ordinary Shares
You will recognize gain or loss on a sale or exchange of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares in an amount equal to the difference between the amount realized on the sale or exchange and your adjusted tax basis in our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares. Subject to the discussion under “—Passive Foreign Investment Company—U.S. Holders During 2023” above (which may be applicable to U.S. Holders acquiring our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares after 2023 as described above), such gain or loss generally will be capital gain or loss. Capital gains of a non-corporate United States Holder, including an individual, that has held our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares for more than one year currently may be eligible for reduced tax rates. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations.
Any gain or loss that you recognize on a disposition of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares generally will be treated as United States-source income or loss for foreign tax credit limitation purposes. However, if we are treated as a PRC resident enterprise for PRC tax purposes and PRC tax is imposed on gain from the disposition of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares (see “Item 10. Additional Information—E. Taxation—People’s Republic of China Tax Considerations”), then a United States Holder that is eligible for the benefits of the income tax treaty between the United States and the PRC may elect to treat the gain as PRC-source income for foreign tax credit purposes, subject to certain limitations. If such an election is made, the gain so treated will be treated as a separate class or “basket” of income for foreign tax credit purposes. You should consult your tax advisors regarding the proper treatment of gain or loss, as well as the availability of a foreign tax credit, in your particular circumstances.
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
Information reporting to the IRS and backup withholding generally will apply to dividends in respect of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares, and the proceeds from the sale or exchange of our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares, that are paid to you within the United States (and in certain cases, outside the United States), unless you furnish a correct taxpayer identification number and make any other required certification, generally on IRS Form W-9, or you otherwise establish an exemption from information reporting and backup withholding. Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Amounts withheld as backup withholding generally are allowed as a credit against your United States federal income tax liability, and you may be entitled to obtain a refund of any excess amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules if you file an appropriate claim for refund with the IRS and furnish any required information in a timely manner.
United States Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the application of the information reporting and backup withholding rules.
Information with Respect to Foreign Financial Assets
United States Holders who are individuals (and certain entities closely held by individuals) generally will be required to report our name, address and such information relating to an interest in our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares as is necessary to identify the class or issue of which our ADSs or Class A ordinary shares are a part. These requirements are subject to exceptions, including an exception for ADSs or Class A ordinary shares held in accounts maintained by certain financial institutions and an exception applicable if the aggregate value of all “specified foreign financial assets” (as defined in the Code) does not exceed US$75,000 at any point during the taxable year or US$50,000 on the last day of the taxable year.
United States Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the application of these information reporting rules.
F.
Dividends and Paying Agents
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
We are subject to periodic reporting and other informational requirements of the Exchange Act as applicable to foreign private issuers, and are required to file reports and other information with the SEC. Specifically, we are required to file annually an annual report on Form 20-F within four months after the end of each fiscal year, which is December 31. All information filed with the SEC can be obtained over the internet at the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov or inspected and copied at the public reference facilities maintained by the SEC at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. You can request copies of documents, upon payment of a duplicating fee, by writing to the SEC. As a foreign private issuer, we are exempt from the rules under the Exchange Act prescribing the furnishing and content of quarterly reports and proxy statements, and officers, directors and principal shareholders are exempt from the reporting and short-swing profit recovery provisions contained in Section 16 of the Exchange Act.
We will furnish Citibank, N.A., the depositary of our ADSs, with our annual reports, which will include a review of operations and annual audited consolidated financial statements prepared in conformity with U.S. GAAP, and all notices of shareholders’ meetings and other reports and communications that are made generally available to our shareholders. The depositary will make such notices, reports and communications available to holders of ADSs and, upon our request, will mail to all record holders of ADSs the information contained in any notice of a shareholders’ meeting received by the depositary from us.
For a listing of our subsidiaries, see “Item 4. Information on the Company—C. Organizational Structure.”
J.
Annual Report to Security Holders ITEM 11.
Not applicable.
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Foreign Currency Risk
Substantially all of our revenues and our expenses are denominated in Renminbi. The functional currency of our company, Jiayin Group Inc. is the U.S. dollar. The functional currency of our subsidiaries in the PRC, the consolidated VIE and its subsidiaries is the Renminbi. We use Renminbi as our reporting currency. Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are translated into the functional currency at the rates of exchange ruling at the balance sheet date. Transactions in currencies other than the functional currency during the year are converted into functional currency at the applicable rates of exchange prevailing when the transactions occurred. Transaction gains and losses are recognized in the statements of comprehensive income.
We do not believe that we currently have any significant direct foreign exchange risk and have not used any derivative financial instruments to hedge exposure to such risk. Although in general our exposure to foreign exchange risks should be limited, the value of your investment in our ADSs will be affected by the exchange rate between U.S. dollar and RMB because the value of our business is effectively denominated in Renminbi, while our ADSs will be traded in U.S. dollars.
The conversion of Renminbi into foreign currencies, including U.S. dollars, is based on rates set by the PBOC. Since June 2010, the PRC government has allowed the RMB to appreciate slowly against the U.S. dollar, though there have been periods when the Renminbi has depreciated against the U.S. dollar. In particular, on August 11, 2015, the PBOC allowed the Renminbi to depreciate by approximately 2% against the U.S. dollar. Since then, the Renminbi has fluctuated against the U.S. dollar, at times significantly and unpredictably. From August 11, 2015 until the end of 2016, the Renminbi depreciated against the U.S. dollar by approximately 10%. During 2020, the Renminbi appreciated approximately by 6% against the U.S. dollar. During 2021, the Renminbi appreciated approximately by 2% against the U.S. dollar. During 2022, the Renminbi depreciated approximately by 8% against the U.S. dollar. In later 2023, the Renminbi appreciated approximately by 3% against the U.S. dollar and gradually depreciated approximately 2% against the U.S. dollar in early 2024. It is difficult to predict how market forces or PRC or U.S. government policy may impact the exchange rate between the Renminbi and the U.S. dollar in the future. It is difficult to predict how long the current situation may last and when and how the relationship between the Renminbi and the U.S. dollar may change again.
To the extent that we need to convert U.S. dollars into Renminbi for our operations, appreciation of the Renminbi against the U.S. dollar would have an adverse effect on the Renminbi amount we receive from the conversion. Conversely, if we decide to convert Renminbi into U.S. dollars for the purpose of making payments for dividends on our ordinary shares or ADSs or for other business purposes, appreciation of the U.S. dollar against the Renminbi would have a negative effect on the U.S. dollar amounts available to us.
Interest Rate Risk
We have not been exposed to material risks due to changes in market interest rates, and we have not used any derivative financial instruments to manage our interest risk exposure. However, we cannot provide assurance that we will not be exposed to material risks due to changes in market interest rate in the future.
The fluctuation of interest rates may affect the demand for loan services on our platform. For example, a decrease in interest rates may cause potential borrowers to seek lower-priced loans from other channels. A high interest rate environment may lead to an increase in competing investment options and dampen online investors’ desire to invest on our platform. We do not expect that the fluctuation of interest rates will have a material impact on our financial condition. However, we cannot provide assurance that we will not be exposed to material risks due to changes in market interest rate in the future.
We may invest our cash in interest-earning instruments. Investments in both fixed rate and floating rate interest earning instruments carry a degree of interest rate risk. Fixed rate securities may have their fair market value adversely impacted due to a rise in interest rates, while floating rate securities may produce less income than expected if interest rates fall.
ITEM 12. DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES OTHER THAN EQUITY SECURITIES
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
D.
American Depositary Shares
Fees and Charges Our ADS holders May Have to Pay
As an ADS holder, you will be required to pay the following fees under the terms of the deposit agreement:
|
|
|
Service |
|
Fees |
• Issuance of ADSs (e.g., an issuance of ADS upon a deposit of Class A ordinary shares, upon a change in the ADS(s)-to-Class A Ordinary Share(s) ratio, or for any other reason), excluding ADS issuances as a result of distributions of Class A ordinary shares)
|
|
Up to U.S. 5¢ per ADS issued |
|
|
|
• Cancellation of ADSs (e.g., a cancellation of ADSs for delivery of deposited property, upon a change in the ADS(s)-to-Class A ordinary share(s) ratio, or for any other reason)
|
|
Up to U.S. 5¢ per ADS canceled |
|
|
|
• Distribution of cash dividends or other cash distributions (e.g., upon a sale of rights and other entitlements)
|
|
Up to U.S. 5¢ per ADS held |
|
|
|
• Distribution of ADSs pursuant to (i) stock dividends or other free stock distributions, or (ii) exercise of rights to purchase additional ADSs
|
|
Up to U.S. 5¢ per ADS held |
|
|
|
• Distribution of securities other than ADSs or rights to purchase additional ADSs (e.g., upon a spin-off)
|
|
Up to U.S. 5¢ per ADS held |
|
|
|
|
|
Up to U.S. 5¢ per ADS held on the applicable record date(s) established by the depositary bank |
|
|
|
• Registration of ADS Transfers (e.g., upon a registration of the transfer of registered ownership of ADSs, upon a transfer of ADSs into DTC and vice versa, or for any other reason).
|
|
Up to U.S. 5¢ per ADS (or fraction thereof) transferred. |
|
|
|
• Conversion of ADSs of one series for ADSs of another series (e.g., upon conversion of Partial Entitlement ADSs for Full Entitlement ADSs, or upon conversion of Restricted ADSs into freely transferable ADSs, and vice versa).
|
|
Up to 5¢ per ADS (or fraction thereof) converted. |
As an ADS holder you will also be responsible to pay certain charges such as:
•
taxes (including applicable interest and penalties) and other governmental charges; the registration fees as may from time to time be in effect for the registration of Class A ordinary shares on the share register and applicable to transfers of Class A ordinary shares to or from the name of the custodian, the depositary bank or any nominees upon the making of deposits and withdrawals, respectively;
•
certain cable, telex and facsimile transmission and delivery expenses;
•
the expenses and charges incurred by the depositary bank in the conversion of foreign currency
•
the fees and expenses incurred by the depositary bank in connection with compliance with exchange control regulations and other regulatory requirements applicable to Class A ordinary shares, ADSs and ADRs; and
•
the fees, charges, costs and expenses incurred by the depositary bank, the custodian, or any nominee in connection with the ADR program.
ADS fees and charges for (i) the issuance of ADSs, and (ii) the cancellation of ADSs are charged to the person for whom the ADSs are issued (in the case of ADS issuances) and to the person for whom ADSs are canceled (in the case of ADS cancellations). In the case of ADSs issued by the depositary bank into DTC, the ADS issuance and cancellation fees and charges may be deducted from distributions made through DTC, and may be charged to the DTC participant(s) receiving the ADSs being issued or the DTC participant(s) holding the ADSs being canceled, as the case may be, on behalf of the beneficial owner(s) and will be charged by the DTC participant(s) to the account of the applicable beneficial owner(s) in accordance with the procedures and practices of the DTC participants as in effect at the time. ADS fees and charges in respect of distributions and the ADS service fee are charged to the holders as of the applicable ADS record date. In the case of distributions of cash, the amount of the applicable ADS fees and charges is deducted from the funds being distributed. In the case of (i) distributions other than cash and (ii) the ADS service fee, holders as of the ADS record date will be invoiced for the amount of the ADS fees and charges and such ADS fees and charges may be deducted from distributions made to holders of ADSs. For ADSs held through DTC, the ADS fees and charges for distributions other than cash and the ADS service fee may be deducted from distributions made through DTC, and may be charged to the DTC participants in accordance with the procedures and practices prescribed by DTC and the DTC participants in turn charge the amount of such ADS fees and charges to the beneficial owners for whom they hold ADSs. In the case of (i) registration of ADS transfers, the ADS transfer fee will be payable by the ADS Holder whose ADSs are being transferred or by the person to whom the ADSs are transferred, and (ii) conversion of ADSs of one series for ADSs of another series, the ADS conversion fee will be payable by the Holder whose ADSs are converted or by the person to whom the converted ADSs are delivered.
In the event of refusal to pay the depositary bank fees, the depositary bank may, under the terms of the deposit agreement, refuse the requested service until payment is received or may set off the amount of the depositary bank fees from any distribution to be made to the ADS holder. Certain depositary fees and charges (such as the ADS services fee) may become payable shortly after the closing of the ADS offering. Note that the fees and charges you may be required to pay may vary over time and may be changed by us and by the depositary bank. You will receive prior notice of such changes.
The depositary bank may reimburse us for certain expenses incurred by us in respect of the ADR program, by making available a portion of the ADS fees charged in respect of the ADR program or otherwise, upon such terms and conditions as we and the depositary bank agree from time to time.
PART II
ITEM 13. DEFAULTS, DIVIDEND ARREARAGES AND DELINQUENCIES
None.
ITEM 14. MATERIAL MODIFICATIONS TO THE RIGHTS OF SECURITY HOLDERS AND USE OF PROCEEDS
See “Item 10. Additional Information—B. Memorandum and Articles of Association” for a description of the rights of securities holders, which remain unchanged.
ITEM 15. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management has performed an evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of the end of the period covered by this report, as required by Rule 13a-15(b) under the Exchange Act.
Based upon that evaluation, our management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2024, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective in ensuring that the information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file and furnish under the Exchange Act was recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that the information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to our management, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the exchange Act), under the supervision and with the participation of our chairman of the board of directors, chief executive officer and chief financial officer, our management conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on the criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013), issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). Based on this assessment, our management determined that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2024.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies and procedures may deteriorate.
For risks and uncertainties related to our internal control, see “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry— If we fail to implement and maintain an effective system of internal controls over financial reporting, we may be unable to accurately report our results of operations, meet our reporting obligations or prevent fraud.”
Attestation Report of the Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Our independent registered public accounting firm, Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Certified Public Accountants LLP, has issued an attestation report on our internal control over financial reporting, which is included on page F-4 of this annual report.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal controls over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by this annual report on Form 20-F that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 16A. AUDIT COMMITTEE FINANCIAL EXPERT
Our board of directors has determined that each of Mr. Yuhchang Hwang and Mr. Meng Rui qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” within the meaning of the SEC rules and possesses financial sophistication within the meaning of the Listing Rules of the Nasdaq Stock Market. Mr.Yuhchang Hwang and Mr. Meng Rui satisfy the “independence” requirements of Rule 5605(a)(2) of the Nasdaq Stock Market Rules and meets the independence standards under Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act.
The audit committee will oversee our accounting and financial reporting processes and the audits of the financial statements of our company.
ITEM 16B. CODE OF ETHICS
Our board of directors adopted a code of business conduct and ethics that applies to our directors, officers and employees in December 2018. We have posted a copy of our code of business conduct and ethics on our website at https://ir.jiayin-fintech.com/.
ITEM 16C. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The following table sets forth the aggregate fees by categories specified below in connection with certain professional services rendered by Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Certified Public Accountants LLP and Marcum Asia CPAs LLP, our principal external auditors, for the periods indicated. Marcum Asia CPAs LLP served as our independent auditor in 2022 and Deloitte Touche Certified Public Accountants LLP served as our independent auditor since 2023.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
(US$’000) |
|
|
(US$’000) |
|
Audit Fee |
|
1022 |
|
|
|
1,763 |
|
Audit-related Fee (1) |
|
|
278 |
|
|
|
50 |
|
Predecessor auditor |
|
|
230 |
|
|
|
125 |
|
(1) “Audit related fees” represents the aggregate fees billed for assurance and related services by our principal auditors that are not reported as audit fees.
The policy of our audit committee is to pre-approve all audit and non-audit services provided by Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Certified Public Accountants LLP and its affiliates.
ITEM 16D. EXEMPTIONS FROM THE LISTING STANDARDS FOR AUDIT COMMITTEES
Not applicable.
ITEM 16E. PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES BY THE ISSUER AND AFFILIATED PURCHASERS
On June 13, 2022, our board of directors authorized a share repurchase plan under which we may repurchase our ordinary shares with an aggregate value of US$10 million during the 12-month period beginning on June 13, 2022. The share repurchase plan was publicly announced on June 16, 2022. On June 7, 2023, our board of directors approved to extend the share repurchase plan for a period of 12-months period beginning on June 13, 2023 and ending on June 12, 2024. Pursuant to the extended share repurchase plan, we may repurchase our ordinary shares through June 12, 2024 with an aggregate value not exceeding the remaining balance under share repurchase plan. In March 2024, our board of directors approved an adjustment to the existing share repurchase plan, pursuant to which the aggregate value of ordinary shares authorized for repurchase under the plan shall not exceed US$30 million. On June 4, 2024, our board of directors approved to further extend the share repurchase plan for another period of 12 months, commencing on June 13, 2024 and ending on June 12, 2025. Pursuant to the extended share repurchase plan, we may repurchase our ordinary shares through June 12, 2025 with an aggregate value not exceeding the remaining balance under the share repurchase plan. As of March 31, 2025, we had repurchased approximately 3.8 million of our ADSs for approximately US$16.8 million under this share repurchase plan.
The following table summarizes the shares repurchase activity for the periods indicated.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period |
|
Total Number of
ADSs Purchased |
|
|
Average Price Paid
Per ADS |
|
|
Total Number of
ADSs Purchased
as Part of the
Publicly
Announced Plan |
|
|
Approximate
Dollar Value of
ADSs that May
Yet Be Purchased
under the Plan |
June 2022 |
|
|
225,301 |
|
|
|
US$2.1 |
|
|
|
225,301 |
|
|
US$29.5million |
September 2022 |
|
|
683,738 |
|
|
|
US$2.4 |
|
|
|
683,738 |
|
|
US$27.9million |
December 2022 |
|
|
589,553 |
|
|
|
US$2.3 |
|
|
|
589,553 |
|
|
US$26.5million |
June 2023 |
|
|
339,948 |
|
|
|
US$6.1 |
|
|
|
339,948 |
|
|
US$24.4million |
September 2023 |
|
|
400,092 |
|
|
|
US$4.8 |
|
|
|
400,092 |
|
|
US$22.5million |
December 2023 |
|
|
592,422 |
|
|
|
US$5.1 |
|
|
|
592,422 |
|
|
US$19.4million |
June 2024 |
|
|
508,788 |
|
|
|
US$6.5 |
|
|
|
508,788 |
|
|
US$16.1million |
September 2024 |
|
|
205,362 |
|
|
|
US$5.5 |
|
|
|
205,362 |
|
|
US$15.0million |
December 2024 |
|
|
287,270 |
|
|
|
US$6.5 |
|
|
|
287,270 |
|
|
US$13.1million |
Total |
|
|
3,832,474 |
|
|
|
US$4.4 |
|
|
|
3,832,474 |
|
|
|
There were no other purchases of any class of registered equity securities of the Company by the Company or, to our knowledge, by any affiliated purchaser.
ITEM 16F. CHANGE IN REGISTRANT’S CERTIFYING ACCOUNTANT
On December 20, 2023(the “Dismissal Date”), our audit committee resolved to approve the dismissal of Marcum Asia and the appointment of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Certified Public Accountants LLP (“Deloitte”) as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm.
Marcum Asia CPAs LLP or Marcum Asia, has served as our independent registered public accounting firm since 2021, and the reports of Marcum Asia of our consolidated financial statements have contained no adverse opinion or disclaimer of opinion and were not qualified as to uncertainty, audit scope or accounting principle. During each of the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2022, and in the subsequent interim period through the Dismissal Date, there has been no (i) disagreements as defined in Item 16F(a)(1)(iv) of Form 20-F between us and Marcum Asia on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedure, which disagreements if not resolved to the satisfaction of Marcum Asia would have caused them to make reference to the disagreements in their audit reports, or (ii) reportable events as defined in Item 16F(a)(1)(v) of Form 20-F other than the material weaknesses identified as of December 31, 2021 and 2022, respectively, as reported in the Company’s 2021 and 2022 annual reports on Form 20-F filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange of Commission (the “SEC”) on April 29, 2022 and April 28, 2023, respectively.
During our fiscal years ended December 31, 2021 and 2022 and until the engagement of Deloitte, neither we nor anyone on our behalf has consulted with Deloitte on either (i) the application of accounting principles to a specified transaction, either completed or proposed, or the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on our financial statements, and neither a written report nor oral advice was provided to the us by Deloitte which Deloitte concluded as an important factor considered by the Company in reaching a decision as to any accounting, auditing or financial reporting issue, or (ii) any matter that was the subject of a disagreement, as that term is defined in Item 16F(a)(1)(iv) of Form 20-F (and the related instructions thereto) or a reportable event as set forth in Item 16F(a)(1)(v)(A) through (D) of Form 20-F.
ITEM 16G. CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
As a Cayman Islands company listed on Nasdaq, we are subject to the Nasdaq corporate governance listing standards. However, Nasdaq rules permit a foreign private issuer like us to follow the corporate governance practices of its home country. Certain corporate governance practices in the Cayman Islands, which is our home country, may differ significantly from the Nasdaq corporate governance listing standards. We currently follow and intend to continue to follow Cayman Islands corporate governance practices in lieu of the corporate governance requirements of Nasdaq that listed companies must have: (i) a majority of the board be independent; (ii) an audit committee of at least three independent directors; (iii) a nominating and corporate governance committee composed entirely of independent directors; and (iv) hold an annual meeting of shareholders no later than one year after the end of our fiscal year. Also, our home country practice does not require us to hold an annual meeting of shareholders no later than one year after the end of its fiscal year and does not require us to seek shareholder approval for amending our share incentive plans. To the extent we choose to follow home country practice in the future, our shareholders may be afforded less protection than they otherwise would enjoy under the Nasdaq corporate governance listing standards applicable to U.S. domestic issuers. See “Item 3. Key Information—D. Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our American Depositary Shares—We are a foreign private issuer within the meaning of the rules under the Exchange Act, and as such we are exempt from certain provisions applicable to U.S. domestic public companies.”
ITEM 16H. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
ITEM 16I. DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS
Not applicable.
ITEM 16J. INSIDER TRADING POLICIES
Our board of directors have established insider trading policies and procedures governing the purchase, sale and other dispositions of our securities by our directors, officers, employees and other relevant persons to promote compliance with applicable insider trading laws, rules and regulations, and the listing standards of Nasdaq.
ITEM 16K. CYBERSECURITY
Risk Management and Strategy
We have implemented comprehensive cybersecurity risk assessment procedures to ensure the effectiveness of cybersecurity management, strategy, governance, and reporting of cybersecurity risks. We have also integrated cybersecurity risk management into our overall enterprise risk management system.
We have developed a comprehensive cybersecurity threat defense system to address both internal and external threats. This system encompasses various levels, including network, host, and application security, and incorporates systematic security capabilities for threat defense, monitoring, analysis, response, deception, and countermeasures. We strive to manage cybersecurity risks and protect sensitive information through various means, such as technical safeguards, procedural requirements, an intensive program of monitoring on our corporate network, continuous testing of aspects of our security posture internally and with outside vendors, a robust incident response program, and regular cybersecurity awareness training for employees. We annually engage third-party companies to conduct security testing on important information systems and customer-facing applications. Our cybersecurity department regularly monitors the performance of our mobile applications, platforms and infrastructure to enable us to respond quickly to potential problems, including potential cybersecurity threats.
As of the date of this annual report, we have not experienced any material cybersecurity incidents or identified any material cybersecurity threats that have affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect us, our business strategy, results of operations or financial condition.
Governance
Under our board’s supervision, the Chief Technology Officer is responsible for overseeing the Company’s cybersecurity risk management and be informed on risks from cybersecurity threats. The Chief Technology Officer shall review, approve and maintain oversight of the disclosure (i) on Form 6-K for material cybersecurity incidents (if any) and (ii) related to cybersecurity matters in the periodic reports (including annual report on Form 20-F) of the Company. Our Chief Technology Officer has over 18 years of experience as a technology leader in internet and financial services sectors.
He is specialized in securing and ensuring compliance of complex technology environments across well-known enterprises. In addition, at the management level, we have established a risk management committee, which consists of nine executives and is chaired by our Chief Risk Officer to oversee and manage cybersecurity related matters and formulate policies as necessary. The chairman and members of the risk management committee have rich working experience in banks and prominent internet companies, bringing valuable expertise in dealing with confidentiality-related cybersecurity issues. Our risk management committee members report to the chairman on a monthly basis regarding its assessment, identification, and management on material risks from cybersecurity threats that occur in the ordinary course of our business operations. If a cybersecurity incident occurs, our risk management committee will promptly organize relevant personnel for internal assessment and, depending on the situation, seek the opinions of external experts and legal advisors. If it is determined that the incident could potentially be a material cybersecurity event, our risk management committee will promptly report the investigation and assessment results to our Chief Risk Officer within 24 hours and our Chief Risk Officer will decide on the relevant response measures and whether any disclosure is necessary. If such disclosure is determined to be necessary, our risk management committee shall promptly prepare disclosure material for review and approval by our Chief Risk Officer before it is disseminated to the public.
PART III
ITEM 17. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
We have elected to provide financial statements pursuant to Item 18.
ITEM 18. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The consolidated financial statements of Jiayin Group Inc. are included at the end of this annual report.
ITEM 19. EXHIBITS
|
|
Exhibit
Number |
Description of Document |
|
|
1.1 |
Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association of the Registrant (incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the registration statement on Form F-1 (File No. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
2.1 |
Form of Registrant’s Specimen American Depositary Receipt (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
2.2 |
Registrant’s Specimen Certificate for Ordinary Shares (incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the registration statement on Form F-1 (File No. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
2.3 |
Form of Deposit Agreement among the Registrant, the depositary and holders of the American Depositary Shares (incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit (a) to the registration statement on Form F-6 (File No. 333-229579), as amended, initially filed with the SEC on February 8, 2019) |
|
|
2.4 |
Description of Securities (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.4 of our annual report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-38806), filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 29, 2022) |
|
|
4.1 |
2016 Share Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
4.2 |
2019 Share Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of our registration statement on Form S-8 (file no. 333-233615), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 4, 2019) |
|
|
4.3 |
Form of Indemnification Agreement with the Registrant’s directors and executive officers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
4.4 |
Form of Employment Agreement between the Registrant and an executive officer of the Registrant (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
4.5 |
Power of Attorney Agreement concerning Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd. among Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd., Dinggui Yan, Guanglin Zhang, Yuanle Wu, Shanghai Jinmushuihuotu Investment Center (Limited Partnership) and Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd., dated October 15, 2018 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
4.6 |
Equity Pledge Agreement concerning Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd. among Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd., Dinggui Yan and Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd., dated October 15, 2018 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
4.7 |
Equity Pledge Agreement concerning Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd. among Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd., Guanglin Zhang and Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd., dated October 15, 2018 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
Exhibit
Number |
Description of Document |
|
|
|
|
4.8 |
Equity Pledge Agreement concerning Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd. among Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd., Yuanle Wu and Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd., dated October 15, 2018 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
4.9 |
Equity Pledge Agreement concerning Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd. among Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd., Jinmushuihuotu Investment Center (Limited Partnership) and Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd., dated October 15, 2018 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
4.10 |
Exclusive Call Option Agreement concerning Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd. among Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd., Dinggui Yan, Guanglin Zhang, Yuanle Wu, Shanghai Jinmushuihuotu Investment Center (Limited Partnership) and Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd., dated October 15, 2018 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
4.11 |
Exclusive Consultation and Service Agreement between Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd. and Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd., dated June 29, 2018 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
4.12 |
Collaboration Agreement between Shanghai Caiyin Asset Management Co., Ltd. and Shanghai Wuxingjia Finance Information Services Co., Ltd., dated December 1, 2015 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 of our registration statement on Form F-1 (file no. 333-228896), as amended, initially filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 19, 2018) |
|
|
4.13 |
Equity Transfer Agreement concerning Shanghai Caiyin Asset Management Co., Ltd. among Shanghai Jiayin Finance Services Co., Ltd., Shenzhen Rongxinbao Non-financial Guarantee Co., Ltd. and Shanghai Wuxingjia Finance Information Services Co., Ltd. dated September 16, 2019 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to our Form 6-K (file no. 001-38806), filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 16, 2019) |
|
|
4.14 |
Supplementary Agreement to Collaboration Agreement dated December 1, 2015 between Shanghai Caiyin Asset Management Co., Ltd. and Shanghai Wuxingjia Finance Information Services Co., Ltd., dated September 16, 2019 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.3 to our Form 6-K (file no. 001-38806), filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 16, 2019) |
|
|
4.15 |
Agreement among Shenzhen Rongxinbao Non-financial Guarantee Co., Ltd., Shanghai Wuxingjia Finance Information Services Co., Ltd. and Shanghai Jiayin Finance Services Co., Ltd. dated October 16, 2019 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to our Form 6-K (file no. 001-38806), filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 24, 2019) |
|
|
4.16 |
Framework Acquisition Agreement among Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Bweenet Network Technology Co., Ltd., Tang Chuanfa, Liu Ning, Wang Peiqiong, Zhao Wu and Cui Junying dated April 1, 2021 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to our Form 6-K (file no. 001-38806), filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 5, 2021) |
|
|
4.17 |
Share Acquisition Framework Agreement among Shenzhen Rongxinbao Non-Financial Guarantee Co., Ltd., Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd. and Shanghai Bweenet Network Technology Co., Ltd. dated December 29, 2021 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to our Form 6-K (file no. 001-38806), filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on January 3, 2022) |
|
|
4.18 |
Share Acquisition Framework Agreement among Shenzhen Rongxinbao Non-Financial Guarantee Co., Ltd. And Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd. dated April 4, 2023 (English Translation) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.18 of our annual report on Form 20-F (File No. 001-38806), filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 29, 2023) |
4.19*† |
Property Transfer Agreement among Shanghai Jirongzhicheng Enterprise Development Co., Ltd., Geerong Yunke Information Technology Co., Ltd. and the seller, dated December 17, 2024 |
|
|
* Filed with this annual report on Form 20-F.
** Furnished with this annual report on Form 20-F.
† Portions of this exhibit have been omitted in accordance with Item 601(b)(10) of Regulation S-K.
SIGNATURES
The registrant hereby certifies that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form 20-F and that it has duly caused and authorized the undersigned to sign this annual report on its behalf.
|
|
|
|
Jiayin Group Inc. |
|
|
By: |
/s/ Dinggui Yan |
|
|
|
|
Name: |
Dinggui Yan |
Title: |
Director and Chief Executive Officer |
Date: April 28, 2025
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
REPORTS OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Jiayin Group Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Jiayin Group Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income, changes in shareholders' equity, and cash flows, for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes and financial statement schedule (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2024, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated April 28, 2025, expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Convenience Translation
Our audits also comprehended the translation of Renminbi amounts into United States dollar amounts and, in our opinion, such translation has been made in conformity with the basis stated in Note 2(g). Such United States dollar amounts are presented solely for the convenience of readers outside the People’s Republic of China.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit matter does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Management’s estimation of expected default rate primarily applied in accounting for guarantee liabilities and guarantee revenues – refer to note 2(k) and 2(q) to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
The Group provides guarantee service for certain loans it facilitates. The Group recognizes a stand-ready guarantee liability for its guarantee exposure at the inception, which is released into guarantee revenue over the term of the guarantee. The Group estimates the fair value of stand-ready guarantee liabilities based on expected default rate of underlying loans subject to guarantee on a pool basis according to the historical delinquency data by vintage, adjusted by specific risk characteristics for borrowers from various channels, and other pertinent information in assessing future performance of the loan portfolio.
We identified the estimation of expected default rate as a critical audit matter because of the significant judgments required by management when developing the estimation. This required a high degree of auditor judgment and an increased extent of effort, including the need to involve our fair value specialists and information technology (IT) specialists when performing audit procedures to evaluate the reasonableness of management’s methodologies and assumptions used in estimation.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
- We tested the operating effectiveness of the controls over estimation of expected default rate, including management’s controls over the historical delinquency data and the adjustments, if any, to the delinquency rate.
- We evaluated the relevance of the historical delinquency data as an input and, with the assistance of our IT specialists, tested on a sample basis the accuracy of such data by comparing it with original data retrieved from the operating system.
- With the assistance of our internal fair valuation specialists, we evaluated the reasonableness of the valuation methodology and evaluated the assumptions used in the model for expected default rate.
- We evaluated observable data close to the report issue date to evaluate whether the assumptions used by management are appropriate.
/s/ Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Certified Public Accountants LLP
Shanghai, the People’s Republic of China
April 28, 2025
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2023.
REPORTS OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Jiayin Group Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Jiayin Group Inc. and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2024 of the Company and our report dated April 28, 2025, expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements and included an explanatory paragraph regarding the translation of Renminbi amounts into United States dollar amounts for the convenience of readers outside the People’s Republic of China.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Certified Public Accountants LLP
Shanghai, the People’s Republic of China
April 28, 2025
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and Board of Directors of
Jiayin Group Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income, changes in shareholders’equity and cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2022, and the related notes and schedules of Jiayin Group Inc. (the “Company”) (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the results of the Company’s operations and its cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2022, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Change in Accounting Principle
We were not engaged to audit the retrospective adjustment as described in Note 2(z), and accordingly, we do not express an opinion or any other form of assurance about whether such retrospective adjustment is appropriate and has been properly applied.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) ("PCAOB") and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audit we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Marcum Asia CPAs LLP
Marcum Asia CPAs LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor from 2021 to 2023.
New York, New York
April 28, 2023
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2023 AND 2024
(Amounts in thousands, except for share and per share data)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Note 2(g)) |
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
370,193 |
|
|
|
540,523 |
|
|
|
74,051 |
|
Restricted cash |
|
|
2,435 |
|
|
|
137,332 |
|
|
|
18,814 |
|
Amounts due from related parties |
|
|
509 |
|
|
|
4,411 |
|
|
|
604 |
|
Accounts receivable and contract assets, net (net of allowance
for credit losses of RMB17,953 and RMB21,200 as of
December 31, 2023 and 2024, respectively) |
|
|
2,103,545 |
|
|
|
2,986,755 |
|
|
|
409,184 |
|
Financial assets receivable, net (net of allowance for credit losses
of RMB7,207 and RMB1,250 as of December 31, 2023 and 2024, respectively) |
|
|
991,628 |
|
|
|
293,483 |
|
|
|
40,207 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets, net (net of allowance for
credit losses of RMB13,205 and RMB771 as of December 31, 2023
and 2024, respectively) |
|
|
1,921,547 |
|
|
|
377,978 |
|
|
|
51,784 |
|
Deferred tax assets, net |
|
|
61,174 |
|
|
|
72,405 |
|
|
|
9,919 |
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
40,332 |
|
|
|
44,397 |
|
|
|
6,082 |
|
Right-of-use assets |
|
|
49,659 |
|
|
|
52,759 |
|
|
|
7,228 |
|
Long-term investments, net |
|
|
101,481 |
|
|
|
162,267 |
|
|
|
22,230 |
|
Other non-current assets |
|
|
2,263 |
|
|
|
737,583 |
|
|
|
101,048 |
|
TOTAL ASSETS |
|
|
5,644,766 |
|
|
|
5,409,893 |
|
|
|
741,151 |
|
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities including amounts of the consolidated VIEs without
recourse to the Company (Note 2(b)): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred guarantee income |
|
|
886,862 |
|
|
|
229,503 |
|
|
|
31,442 |
|
Contingent guarantee liabilities |
|
|
933,947 |
|
|
|
213,644 |
|
|
|
29,269 |
|
Payroll and welfare payables |
|
|
94,856 |
|
|
|
144,065 |
|
|
|
19,737 |
|
Amounts due to related parties |
|
|
11,325 |
|
|
|
89,947 |
|
|
|
12,323 |
|
Tax payables |
|
|
568,819 |
|
|
|
687,034 |
|
|
|
94,123 |
|
Accrued expenses and other liabilities |
|
|
720,538 |
|
|
|
866,409 |
|
|
|
118,696 |
|
Lease liabilities |
|
|
47,958 |
|
|
|
51,677 |
|
|
|
7,080 |
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES |
|
|
3,264,305 |
|
|
|
2,282,279 |
|
|
|
312,670 |
|
Commitments and Contingencies (Note 15) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class A ordinary shares (US$0.000000005 par value; 2,108,100,000
shares authorized, 108,100,000 shares issued as of December 31,
2023 and December 31, 2024; 104,129,944 and 105,478,184 shares
outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2024,
respectively) |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Class B ordinary shares (US$0.000000005 par value; 116,000,000 shares
authorized, 108,000,000 and 108,000,000 shares issued and
outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2024, respectively) |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Treasury stock (3,970,056 and 2,621,816 shares as of
December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2024, respectively) |
|
|
(35,443 |
) |
|
|
(28,889 |
) |
|
|
(3,958 |
) |
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
901,932 |
|
|
|
909,649 |
|
|
|
124,621 |
|
Retained earnings |
|
|
1,525,841 |
|
|
|
2,241,414 |
|
|
|
307,072 |
|
Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income |
|
|
(10,189 |
) |
|
|
7,099 |
|
|
|
973 |
|
Total Jiayin Group shareholder’s equity |
|
|
2,382,141 |
|
|
|
3,129,273 |
|
|
|
428,708 |
|
Non-controlling interests |
|
|
(1,680 |
) |
|
|
(1,659 |
) |
|
|
(227 |
) |
TOTAL SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
2,380,461 |
|
|
|
3,127,614 |
|
|
|
428,481 |
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
5,644,766 |
|
|
|
5,409,893 |
|
|
|
741,151 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2022, 2023 AND 2024
(Amounts in thousands, except for share and per share data)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
US$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Note 2(g)) |
|
Net revenue (including revenue from related parties of
RMB6,567, nil and RMB31,034 for 2022, 2023
and 2024, respectively) |
|
|
3,271,414 |
|
|
|
|
5,466,873 |
|
|
|
|
5,801,032 |
|
|
|
794,738 |
|
Operating costs and expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Facilitation and servicing |
|
|
(565,227 |
) |
|
|
|
(2,011,553 |
) |
|
|
|
(2,033,511 |
) |
|
|
(278,590 |
) |
Sales and marketing |
|
|
(1,081,382 |
) |
|
|
|
(1,538,913 |
) |
|
|
|
(1,913,868 |
) |
|
|
(262,199 |
) |
General and administrative |
|
|
(194,039 |
) |
|
|
|
(214,856 |
) |
|
|
|
(220,993 |
) |
|
|
(30,276 |
) |
Research and development |
|
|
(216,694 |
) |
|
|
|
(296,317 |
) |
|
|
|
(372,441 |
) |
|
|
(51,024 |
) |
Allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets,
loans receivable and others |
|
|
(32,053 |
) |
|
|
|
(72,764 |
) |
|
|
|
(12,204 |
) |
|
|
(1,672 |
) |
Total operating costs and expenses |
|
|
(2,089,395 |
) |
|
|
|
(4,134,403 |
) |
|
|
|
(4,553,017 |
) |
|
|
(623,761 |
) |
Income from operations |
|
|
1,182,019 |
|
|
|
|
1,332,470 |
|
|
|
|
1,248,015 |
|
|
|
170,977 |
|
Gain from de-recognition of liabilities |
|
|
117,021 |
|
|
|
|
280,231 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Loss from disposal of subsidiaries |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
(2,012 |
) |
|
|
|
(14,431 |
) |
|
|
(1,977 |
) |
Impairment of long-term investments |
|
|
(15,078 |
) |
|
|
|
(91,236 |
) |
|
|
|
(51,923 |
) |
|
|
(7,113 |
) |
Interest income, net |
|
|
281 |
|
|
|
|
12,895 |
|
|
|
|
18,281 |
|
|
|
2,504 |
|
Other income, net |
|
|
43,447 |
|
|
|
|
14,834 |
|
|
|
|
95,426 |
|
|
|
13,073 |
|
Income before income taxes and
share of income (loss) from equity
method investments |
|
|
1,327,690 |
|
|
|
|
1,547,182 |
|
|
|
|
1,295,368 |
|
|
|
177,464 |
|
Income tax expense |
|
|
(155,398 |
) |
|
|
|
(247,616 |
) |
|
|
|
(238,900 |
) |
|
|
(32,729 |
) |
Share of income (loss) from equity method investments |
|
|
7,940 |
|
|
|
|
(1,990 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Net income |
|
|
1,180,232 |
|
|
|
|
1,297,576 |
|
|
|
|
1,056,468 |
|
|
|
144,735 |
|
Net income (loss) attributable to non-controlling interests |
|
|
574 |
|
|
|
|
(43 |
) |
|
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
|
(1 |
) |
Net income attributable to Jiayin Group Inc. |
|
|
1,179,658 |
|
|
|
|
1,297,619 |
|
|
|
|
1,056,478 |
|
|
|
144,736 |
|
Net income per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Basic |
|
|
5.48 |
|
|
|
|
6.06 |
|
|
|
|
4.97 |
|
|
|
0.68 |
|
- Diluted |
|
|
5.48 |
|
|
|
|
6.06 |
|
|
|
|
4.97 |
|
|
|
0.68 |
|
Weighted average shares used in calculating net income
per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Basic |
|
|
215,259,640 |
|
|
|
|
213,996,233 |
|
|
|
|
212,433,169 |
|
|
|
212,433,169 |
|
- Diluted |
|
|
215,259,640 |
|
|
|
|
213,996,233 |
|
|
|
|
212,433,169 |
|
|
|
212,433,169 |
|
Net income |
|
|
1,180,232 |
|
|
|
|
1,297,576 |
|
|
|
|
1,056,468 |
|
|
|
144,735 |
|
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax of nil |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
|
14,802 |
|
|
|
|
(7,133 |
) |
|
|
|
(3,171 |
) |
|
|
(434 |
) |
Comprehensive income |
|
|
1,195,034 |
|
|
|
|
1,290,443 |
|
|
|
|
1,053,297 |
|
|
|
144,301 |
|
Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to
non-controlling interests |
|
|
534 |
|
|
|
|
(99 |
) |
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
Total comprehensive income attributable to
Jiayin Group Inc. |
|
|
1,194,500 |
|
|
|
|
1,290,542 |
|
|
|
|
1,053,276 |
|
|
|
144,298 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2022, 2023 AND 2024
(Amounts in thousands, except for share and per share data)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issued Class A
Ordinary
shares |
|
|
Issued Class B
Ordinary
shares |
|
|
Treasury
stock |
|
|
Additional
paid-in
capital |
|
|
(Accumulated
deficit)
Retained earnings |
|
|
Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
(Loss) Income |
|
|
Non-controlling
interests |
|
|
Total shareholder's
equity |
|
|
|
Number |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
Number |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
Number |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Balance at
January 1, 2022 |
|
|
108,100,000 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
108,000,000 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
840,580 |
|
|
|
(794,762 |
) |
|
|
(17,954 |
) |
|
|
(2,115 |
) |
|
|
25,749 |
|
Net income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,179,658 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
574 |
|
|
|
1,180,232 |
|
Share-based
compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
42,548 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
42,548 |
|
Exercise of share
options |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
237,988 |
|
|
|
1,008 |
|
|
|
1,176 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,184 |
|
Vest of Restricted
Share Units |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,383,784 |
|
|
|
13,742 |
|
|
|
(13,742 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Repurchase of
ordinary shares |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(5,994,368 |
) |
|
|
(24,012 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(24,012 |
) |
Foreign currency
translation
adjustments |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
14,842 |
|
|
|
(40 |
) |
|
|
14,802 |
|
Balance at
December 31, 2022 |
|
|
108,100,000 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
108,000,000 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
(2,372,596 |
) |
|
|
(9,262 |
) |
|
|
870,562 |
|
|
|
384,896 |
|
|
|
(3,112 |
) |
|
|
(1,581 |
) |
|
|
1,241,503 |
|
Net income (loss) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,297,619 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(43 |
) |
|
|
1,297,576 |
|
Dividend to
shareholders |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(156,674 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(156,674 |
) |
Repurchase of
ordinary shares |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(5,329,848 |
) |
|
|
(50,438 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(50,438 |
) |
Share-based
compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
54,353 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
54,353 |
|
Exercise of share
options |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
660,950 |
|
|
|
4,301 |
|
|
|
(3,027 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,274 |
|
Vest of Restricted
Share Units |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,071,438 |
|
|
|
19,956 |
|
|
|
(19,956 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Foreign currency
translation
adjustments |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(7,077 |
) |
|
|
(56 |
) |
|
|
(7,133 |
) |
Balance at
December 31, 2023 |
|
|
108,100,000 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
108,000,000 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
(3,970,056 |
) |
|
|
(35,443 |
) |
|
|
901,932 |
|
|
|
1,525,841 |
|
|
|
(10,189 |
) |
|
|
(1,680 |
) |
|
|
2,380,461 |
|
Net income (loss) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,056,478 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
|
1,056,468 |
|
Dividend to
shareholders |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(340,905 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(340,905 |
) |
Repurchase of
ordinary shares |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(4,005,680 |
) |
|
|
(45,020 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(45,020 |
) |
Share-based
compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
59,122 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
59,122 |
|
Exercise of share
options |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
193,920 |
|
|
|
1,731 |
|
|
|
(1,562 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
169 |
|
Vest of Restricted
Share Units |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,160,000 |
|
|
|
49,843 |
|
|
|
(49,843 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
De-consolidation of
subsidiaries |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
20,490 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
20,490 |
|
Foreign currency
translation
adjustments |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(3,202 |
) |
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
(3,171 |
) |
Balance at
December 31, 2024 |
|
|
108,100,000 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
108,000,000 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
(2,621,816 |
) |
|
|
(28,889 |
) |
|
|
909,649 |
|
|
|
2,241,414 |
|
|
|
7,099 |
|
|
|
(1,659 |
) |
|
|
3,127,614 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2022, 2023 AND 2024
(Amounts in thousands, except for share and per share data)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Note2(g)) |
|
Cash flows from operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
|
1,180,232 |
|
|
|
1,297,576 |
|
|
|
1,056,468 |
|
|
|
144,735 |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash flows from
operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets,
loans receivable and others |
|
|
32,053 |
|
|
|
72,764 |
|
|
|
12,204 |
|
|
|
1,672 |
|
Share-based compensation |
|
|
42,548 |
|
|
|
54,353 |
|
|
|
59,122 |
|
|
|
8,100 |
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
9,961 |
|
|
|
9,461 |
|
|
|
17,873 |
|
|
|
2,449 |
|
Non-cash lease expenses |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
21,033 |
|
|
|
23,557 |
|
|
|
3,227 |
|
Loss from disposal of property, equipment and software |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(191 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Share of (income) loss in equity method investments |
|
|
(7,940 |
) |
|
|
1,990 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Impairment of long-term investments |
|
|
15,078 |
|
|
|
91,236 |
|
|
|
51,923 |
|
|
|
7,113 |
|
Gain from de-recognition of liabilities |
|
|
(117,021 |
) |
|
|
(280,231 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Loss from disposal of subsidiaries |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,012 |
|
|
|
14,431 |
|
|
|
1,977 |
|
Gain on recovery of long-term investment |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(69,018 |
) |
|
|
(9,455 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable and contract assets |
|
|
(1,232,326 |
) |
|
|
(497,470 |
) |
|
|
(886,457 |
) |
|
|
(121,444 |
) |
Financial assets receivable |
|
|
(292,342 |
) |
|
|
(917,775 |
) |
|
|
701,666 |
|
|
|
96,128 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
(456,221 |
) |
|
|
(1,890,443 |
) |
|
|
1,494,509 |
|
|
|
204,748 |
|
Amounts due from/to related parties |
|
|
12,437 |
|
|
|
10,759 |
|
|
|
11,266 |
|
|
|
1,543 |
|
Deferred tax assets |
|
|
(22,322 |
) |
|
|
(66 |
) |
|
|
(18,806 |
) |
|
|
(2,576 |
) |
Other non-current assets |
|
|
(516 |
) |
|
|
(504 |
) |
|
|
186 |
|
|
|
25 |
|
Right-of-use assets |
|
|
7,903 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Deferred guarantee income |
|
|
276,518 |
|
|
|
821,644 |
|
|
|
(657,359 |
) |
|
|
(90,058 |
) |
Contingent guarantee liabilities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
933,947 |
|
|
|
(728,172 |
) |
|
|
(99,759 |
) |
Payroll and welfare payables |
|
|
25,502 |
|
|
|
17,695 |
|
|
|
49,625 |
|
|
|
6,799 |
|
Tax payables |
|
|
223,762 |
|
|
|
219,348 |
|
|
|
124,845 |
|
|
|
17,104 |
|
Accrued expenses and other liabilities |
|
|
444,064 |
|
|
|
445,045 |
|
|
|
190,564 |
|
|
|
26,107 |
|
Operating Lease |
|
|
(7,778 |
) |
|
|
(22,595 |
) |
|
|
(22,939 |
) |
|
|
(3,143 |
) |
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
|
133,592 |
|
|
|
389,588 |
|
|
|
1,425,488 |
|
|
|
195,292 |
|
Cash flows from investing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchase of property, equipment and software |
|
|
(17,468 |
) |
|
|
(31,542 |
) |
|
|
(739,130 |
) |
|
|
(101,260 |
) |
Disposal of property, equipment and software |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
840 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
0 |
|
Disposal of subsidiaries, net of cash disposed of
nil, RMB68,747 and RMB2,683 |
|
— |
|
|
|
(68,747 |
) |
|
|
(2,683 |
) |
|
|
(368 |
) |
Acquisition of long-term investments |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(77,533 |
) |
|
|
(97,577 |
) |
|
|
(13,368 |
) |
Proceeds from recovery of long-term investments |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
69,018 |
|
|
|
9,455 |
|
Investment in loans receivable, net |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
53,803 |
|
|
|
(23,257 |
) |
|
|
(3,186 |
) |
Loans to related parties |
|
|
(56,416 |
) |
|
|
(13,904 |
) |
|
|
(120,003 |
) |
|
|
(16,440 |
) |
Repayments from related parties |
|
|
50,935 |
|
|
|
31,233 |
|
|
|
130,110 |
|
|
|
17,825 |
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
(22,949 |
) |
|
|
(105,850 |
) |
|
|
(783,520 |
) |
|
|
(107,342 |
) |
Cash flows from financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loans from related parties |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
27,335 |
|
|
|
3,745 |
|
Repayment of loans from related parties |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(5,755 |
) |
|
|
(788 |
) |
Dividend distributed to shareholders |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(156,674 |
) |
|
|
(301,175 |
) |
|
|
(41,261 |
) |
Repurchase of ordinary shares |
|
|
(14,750 |
) |
|
|
(38,081 |
) |
|
|
(53,261 |
) |
|
|
(7,297 |
) |
Proceeds from exercise of options |
|
|
2,184 |
|
|
|
1,274 |
|
|
|
169 |
|
|
|
23 |
|
Net cash used in financing activities |
|
|
(12,566 |
) |
|
|
(193,481 |
) |
|
|
(332,687 |
) |
|
|
(45,578 |
) |
Effect of foreign exchange rate changes on cash, cash equivalents
and restricted cash |
|
|
10,397 |
|
|
|
(10,670 |
) |
|
|
(4,054 |
) |
|
|
(557 |
) |
Net change in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash |
|
|
108,474 |
|
|
|
79,587 |
|
|
|
305,227 |
|
|
|
41,815 |
|
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash at beginning of the year |
|
|
184,567 |
|
|
|
293,041 |
|
|
|
372,628 |
|
|
|
51,050 |
|
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash at end of the year |
|
|
293,041 |
|
|
|
372,628 |
|
|
|
677,855 |
|
|
|
92,865 |
|
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2022, 2023 AND 2024
(Amounts in thousands, except for share and per share data)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Note2(g)) |
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income taxes paid, net |
|
|
1,900 |
|
|
|
40,895 |
|
|
|
118,679 |
|
|
|
16,259 |
|
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disposal consideration settled by other payable related
to the disposal of Shanghai Caiyin (see Note 7) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
75,646 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Disposal consideration settled by accounts
receivable (see Note 7) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
108,190 |
|
|
|
33,307 |
|
|
|
4,563 |
|
Non-cash right-of-use assets in exchange for new
lease liabilities |
|
|
12,655 |
|
|
|
46,954 |
|
|
|
24,683 |
|
|
|
3,382 |
|
Disposal consideration settled by payables related to the
disposal of Fujian Zhuoqun (see Note 7) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
316,224 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Payables for share repurchase (see Note 10) |
|
|
9,262 |
|
|
|
21,619 |
|
|
|
13,378 |
|
|
|
1,833 |
|
Payables for dividend to shareholders (see Note 14) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
40,793 |
|
|
|
5,589 |
|
Long-term receivable from disposal consideration
related to disposal of Giasun and Quark (see Note 7) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
18,814 |
|
|
|
2,578 |
|
Reconciliation to amounts on consolidated balance sheets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
291,018 |
|
|
|
370,193 |
|
|
|
540,523 |
|
|
|
74,051 |
|
Restricted cash |
|
|
2,023 |
|
|
|
2,435 |
|
|
|
137,332 |
|
|
|
18,814 |
|
Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash |
|
|
293,041 |
|
|
|
372,628 |
|
|
|
677,855 |
|
|
|
92,865 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Amounts in thousands, except for share and per share data)
1.
ORGANIZATION AND PRINCIPAL ACTIVITIES
Jiayin Group Inc. (the “Company”) is an exempted company incorporated with limited liabilities in the Cayman Islands under the laws of the Cayman Islands in December 2017.
The Company, its consolidated subsidiaries and the consolidated variable interest entities (“VIEs”) (collectively referred to as the “Group”) provide online consumer finance service in the People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) by connecting institutional funding partners with borrowers through a proprietary internet platform.
As of December 31, 2024 the Company’s significant subsidiaries and its consolidated VIEs are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name |
Date of
incorporation/
establishment or
acquisition
|
Place of
incorporation/
establishment
|
Percentage
of direct or indirect
ownership
|
|
Principal activities |
Subsidiaries |
|
|
|
|
|
Jiayin Holdings Limited |
January 2018 |
BVI |
100% |
|
Investment Holding |
|
Geerong (HK) Limited (formerly known as “Jiayin
(HK) Limited”)
|
January 2018 |
Hong Kong |
100% |
|
Investment Holding |
Jiayin Southeast Asia Holdings Limited |
February 2018 |
BVI |
100% |
|
Investment Holding |
|
Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd.
(“Shanghai Kunjia”)*
|
June 2018 |
Shanghai |
100% |
|
Investment Holding |
Geerong Yunke Information Technology Co., Ltd. |
July 2019 |
Shanghai |
100% |
|
Technology
development
and consumer finance
services
|
|
Jiangxi Yunkaijianming Technology Co., Ltd. (formerly known as “Geerong Yun
(Shanghai) Technology Development Co., Ltd.”)
|
September 2019 |
Jiangxi |
100% |
|
Technology
development
and consumer finance
services
|
Shanghai Chuangzhen Software Co., Ltd. |
April 2020 |
Shanghai |
100% |
|
Technology service |
|
Shanghai Jirongzhicheng Enterprise
Development Co., Ltd.
|
November 2024 |
Shanghai |
100% |
|
Commercial service |
Hainan Yinke Financing Guarantee Co., Ltd. |
August 2021 |
Hainan |
100% |
|
Guarantee service |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIEs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shanghai Jiayin Technology Co., Ltd.
("Jiayin Technology", formerly known as "Shanghai
Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd.")
|
June 2015 |
Shanghai |
* |
|
Technology service |
|
Shanghai Jiajie Internet Information Services Co., Ltd.
(formerly known as "Shanghai Jiajie Finance
Information Services Co., Ltd.")
|
July 2019 |
Shanghai |
* |
|
Technology
development
and consumer finance
services
|
Jiayin Shuke Information Technology Co., Ltd. |
January 2021 |
Shanghai |
* |
|
Technology service |
|
Guangxi Chuangzhen Information Technology
Co., Ltd.
|
January 2022 |
Guangxi |
* |
|
Technology service |
* Shanghai Kunjia is the primary beneficiary of the VIEs.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The accompanying consolidated financial statements of the Group have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”).
(b)
Principles of consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the financial information of the Company, its wholly owned subsidiaries and its consolidated VIEs. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated upon consolidation.
Variable interest entity
The VIE Arrangement with Shanghai Kunjia, the WFOE
In order to comply with the PRC laws and regulations currently in effect, which place certain restrictions and conditions on foreign ownership of certain areas of businesses, the Group operates relevant business in the Chinese mainland through its VIEs. In June 2018, the Company, through its wholly owned foreign invested subsidiary, Shanghai Kunjia or WFOE, entered into a series of contractual arrangements (“VIE agreements”) with Jiayin Technology and its respective shareholders that enable the Company to (1) have power to direct the activities that most significantly affects the economic performance of the VIEs, and (2) receive the economic benefits of the VIEs that could be significant to the VIEs.
Despite the lack of technical majority direct voting interest, there exists a parent subsidiary relationship between Shanghai Kunjia and the VIEs through the aforementioned agreements. The following is a summary of the VIE agreements:
The agreements that provide the Company effective control over the VIEs include:
Powers of Attorney:
Pursuant to the Power of Attorney, each of the four shareholders have signed power of attorney with WFOE to irrevocably authorize the board of directors / Executive Directors of WFOE and their successors to act as his or her attorney-in-fact to exercise all of his or her rights as a shareholder of Jiayin Technology including, but not limited to, the right (1) to make and sign the relevant shareholders’ general meeting decision on behalf of the shareholders of Jiayin Technology; (2) in accordance with the law and Jiayin Technology’s Charter of shareholders exercise the right to enjoy all the rights of shareholders, including but not limited to the right of shareholders to vote, sell or transfer or pledge or dispose of all or any part of Jiayin Technology’s shares; and (3) designate and appoint the legal representative, chairman, director, supervisor, general manager and other senior management of Jiayin Technology as the authorized representative of the Group. This power of attorney is irrevocable and continues to be in force during the period when the authorized person is a shareholder of WFOE, from the date of signature of this power of attorney.
Exclusive Purchase Agreement:
Pursuant to the Exclusive Purchase Agreement among WFOE, Jiayin Technology and the four shareholders of Jiayin Technology, the four shareholders and Jiayin Technology shall irrevocably grant WFOE, to purchase or appoint one or more persons from WFOE at any time to purchase all or part of the shares which is not subject to legal restriction or assets held by the four shareholders or Jiayin Technology. Except for WFOE and the designated person, no third party shall have the right to purchase shares and assets or other shares and assets related to the four shareholders. The consideration of the purchase should be RMB1 or the lowest price permitted by the PRC laws. The effective time period of this agreement is ten years, and will be automatically extended to further years.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(b)
Principles of consolidation - continued
Variable interest entity - continued
The VIE Arrangement with Shanghai Kunjia, the WFOE - continued
The agreements that transfer economic benefits to the Company include:
Exclusive Consultation and Service Agreement:
Pursuant to the Exclusive Consultation and Service Agreement between WFOE and Jiayin Technology, WFOE has the exclusive right to provide Jiayin Technology with consulting and other services. Without WFOE’s prior written consent, Jiayin Technology may not accept any services subject to this agreement from any third party. WFOE has the right to determine the service fee to be charged to Jiayin Technology under this agreement by considering, among other things, the complexity of the services, the actual cost that may be incurred for providing such services, as well as the value and comparable price on the market of the service provided. WFOE will have the exclusive ownership of all intellectual property rights created as a result of the performance of this agreement. Unless WFOE terminates this agreement in advance or otherwise provided by law, this agreement will remain effective for ten years and shall automatically extend the term of this agreement prior to its expiration. Jiayin Technology may not terminate this agreement unilaterally.
Equity Pledge Agreement:
Pursuant to the Equity Pledge Agreement among WFOE, Jiayin Technology and the four shareholders, in order to ensure that Jiayin Technology and its shareholders will fulfill the obligations under the power of attorney, the exclusive consultation and service agreement, and the exclusive purchase agreement (collectively “the Main Agreement”), the four shareholders have pledged 100% equity interest in Jiayin Technology to WFOE. According to the Main Agreement, the pledgee has the right to charge the service fee to Jiayin Technology. Those shareholders and WFOE also agree that without a prior written consent of the pledgee, they shall not transfer the shares or set up any pledge or other form of guarantee which may affect the rights and interests of the pledgee.
These contractual arrangements allow the Company, through its wholly owned subsidiary WFOE, to effectively control the VIEs, and to derive substantially all of the economic benefits from them. Accordingly, the Company has consolidated the financial results of the VIEs. The Company believes that the contractual arrangements with the VIEs are in compliance with PRC law and are legally enforceable. However, uncertainties in the PRC legal system could limit the Company’s ability to enforce the contractual arrangements.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(b)
Principles of consolidation - continued
Variable interest entity - continued
The VIE Arrangement with Shanghai Kunjia, the WFOE - continued
The following condensed financial statement balances and amounts of the Company’s VIEs, were included in the accompanying consolidated financial statements after the elimination of intercompany balances and transactions among the Company, its subsidiaries and its VIEs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
81,384 |
|
|
|
5,439 |
|
Restricted cash |
|
|
2,435 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
|
97,187 |
|
|
|
54,404 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets, net |
|
|
31,101 |
|
|
|
29,822 |
|
Deferred tax assets, net |
|
|
13,935 |
|
|
|
18,550 |
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
9,538 |
|
|
|
6,531 |
|
Right-of-use assets |
|
|
17,271 |
|
|
|
24,643 |
|
Other non-current assets |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
511 |
|
TOTAL ASSETS |
|
|
252,851 |
|
|
|
139,900 |
|
Payroll and welfare payables |
|
|
41,189 |
|
|
|
64,442 |
|
Tax payables |
|
|
24,249 |
|
|
|
25,935 |
|
Accrued expenses and other liabilities |
|
|
220,770 |
|
|
|
184,996 |
|
Lease liabilities |
|
|
16,647 |
|
|
|
23,521 |
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES |
|
|
302,855 |
|
|
|
298,894 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Net revenue |
|
|
972,029 |
|
|
|
473,239 |
|
|
|
280,566 |
|
Operating income (loss) |
|
|
52,204 |
|
|
|
(1,140,806 |
) |
|
|
(1,274,173 |
) |
Net income (loss) |
|
|
164,741 |
|
|
|
(868,605 |
) |
|
|
(1,265,296 |
) |
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
|
|
8,807 |
|
|
|
(1,095,655 |
) |
|
|
(1,368,916 |
) |
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
(7,265 |
) |
|
|
(74,100 |
) |
|
|
(1,274 |
) |
Net cash used in financing activities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
The VIEs contributed 30%, 9% and 5% of the Group’s consolidated revenue for years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. As of December 31, 2023 and 2024, the VIEs accounted for an aggregate of 4% and 3% of the consolidated total assets, and 9% and 13% of the consolidated total liabilities, respectively.
There are no terms in any arrangements, considering both explicit arrangements and implicit variable interests that require the Company or its subsidiaries to provide financial support to the VIEs. However, if the VIEs were ever to need financial support, the Group may, at its option and subject to statutory limits and restrictions, provide financial support to its VIEs through loans to the shareholders of the VIEs or entrustment loans to the VIEs.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(b)
Principles of consolidation - continued
Variable interest entity - continued
The VIE Arrangement with Shanghai Kunjia, the WFOE - continued
The Group believes that there are no assets held in the VIEs that can be used only to settle obligations of the VIEs, except for registered capital and the PRC statutory reserves. As the VIEs are incorporated as limited liability companies under the PRC Company Law, creditors of the VIEs do not have recourse to the general credit of the Company for any of the liabilities of the VIEs. Relevant PRC laws and regulations restrict the VIEs from transferring a portion of their net assets, equivalent to the balance of its statutory reserve and its share capital, to the Company in the form of loans and advances or cash dividends. See Note 16 for disclosure of restricted net assets.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results may differ from these estimates. Changes in estimates are recorded in the period they are identified.
The Group bases its estimates on historical experience and various other factors believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Significant accounting estimates reflected in the Group’s financial statements include expected credit loss for financial guarantee in scope of ASC 326, allowance for credit losses on financial assets receivable, loan receivables, accounts receivables and contract assets, amount due from related parties and other receivables, valuation allowances for deferred tax assets, fair value measurement and impairment of investments, determination on the standalone selling price of each identified performance obligation and variable consideration for revenue recognition.
Fair value is considered to be the price that would be received from selling an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. When determining the fair value measurements for assets and liabilities required or permitted to be recorded at fair value, the Group considers the principal or most advantageous market in which it would transact and considers assumptions that market participants would use when pricing the asset or liability.
Authoritative literature provides a fair value hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three broad levels. The level in the hierarchy within which the fair value measurement in its entirety falls is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement as follows:
Level 1 applies to assets or liabilities for which there are quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2 applies to assets or liabilities for which there are inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in markets with insufficient volume or infrequent transactions (less active markets); or model-derived valuations in which significant inputs are observable or can be derived principally from, or corroborated by, observable market data.
Level 3 applies to assets or liabilities for which there are unobservable inputs to the valuation methodology that are significant to the measurement of the fair value of the assets or liabilities.
The carrying values of financial instruments, which consist of cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, accounts receivable and contract assets, financial assets receivable, other receivables included in other current assets, certain investments, which are approximate to the fair values mainly due to the short-term nature of these instruments.
The Group does not have any assets or liabilities that are recorded at fair value subsequent to initial recognition on a recurring basis other than the investment in convertible debt accounted for as available-for-sale debt security, which is classified as a level 2 fair value measurement. Fair value measurement on a nonrecurring basis as of December 31, 2023 and 2024 included that used in impairment of an equity investment (see Note 6) which was classified as a Level 3 fair value.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(e)
Certain risks and concentrations
Financial instrument that potentially exposes the Group to significant concentration of credit risk primarily includes cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, accounts receivable and contract assets, financial assets receivable, loans receivable, and amounts due from related parties. As of December 31, 2023 and 2024, there were 97% and 99% of the Group’s cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash held in major financial institutions located in the PRC, respectively, and the rest were held in overseas major financial institutions which management considers to be of high credit quality. Accounts receivable, contract assets and financial assets receivable are typically unsecured and are derived from revenue earned from customers in the PRC. The risk with respect to accounts receivable and contract assets, and financial assets receivable is mitigated by credit evaluations the Group performs on its customers and its ongoing monitoring process of outstanding balances. Credit risk of loans receivable is controlled by the application of credit approvals, credit limits and monitoring procedures.
As of December 31, 2024, Customer A accounted for 28% of accounts receivable and contract assets.
(f)
Foreign currency translation
The functional currency of the Company is dollars (“US$”). The functional currency of the Group’s subsidiaries and VIEs in the PRC is Renminbi (“RMB”). The functional currency of subsidiaries outside of PRC is typically their local currency. The determination of the respective functional currency is based on the criteria stated in Accounting Standard Codification (“ASC”) Topic 830, Foreign Currency Matters. The Group also uses RMB as its reporting currency. Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are translated into the functional currency at the rates of exchange ruling at the balance sheet date. Transactions in currencies other than the functional currency are measured and recorded in the functional currency at the exchange rate prevailing on the transaction date. Transaction gains and losses are recognized in earnings.
Assets and liabilities are translated using the exchange rates in effect on the balance sheet date. Equity amounts are translated at historical exchange rates. Revenues, expenses, gains and losses are translated using the average rates for the year. Translation adjustments are reported as cumulative translation adjustments and are shown as a separate component in the statements of comprehensive income.
(g)
Convenience translation
The Group’s financial statements are stated in RMB. Translations of balances in the consolidated balance sheets, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity and cash flows from RMB into US dollars as of and for the year ended December 31, 2024 are included solely for the convenience of the readers and have been made at the rate of US$1.00=RMB7.2993, representing the noon buying rate set forth in the H.10 statistical release of the U.S. Federal Reserve Board on December 31, 2024. No representation is made that the RMB amounts could have been, or could be, converted, realized or settled into US$ at that rate or at any other rate.
The Renminbi (“RMB”) is not a freely convertible currency. The State Administration for Foreign Exchange, under the authority of the Peoples Bank of China, controls the conversion of RMB into other currencies. The value of the RMB is subject to changes in central government policies, international economic and political developments affecting supply and demand in the China Foreign Exchange Trading System market. The Group’s cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash denominated in RMB amounted to RMB357,118 and RMB669,464 as of December 31, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
(i)
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents consist of cash on hand and demand deposits which are highly liquid and have original maturities of three months or less and are unrestricted as to withdrawal or use.
Restricted cash represents restricted deposits placed in funding banks in relation to the guarantee services provided by the Group.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
Primary guarantee
Starting from the fourth quarter of year 2022, the Group provides guarantee services through its own licensed financing guarantee subsidiaries or through cooperation with third-party licensed financing guarantee companies for loans facilitated to the institutional funding partners. Under guarantee services through its own licensed financing guarantee subsidiaries, the Group is obligated to place deposits directly to institutional funding partners with an agreed percentage of outstanding loan balance subject to guarantee. The Group records deposits to funding banks under “restricted cash” and deposits to institutional funding partners other than funding banks under “Prepaid expenses and other current assets, net” on the consolidated balance sheets, respectively. Starting from year 2024, majority of the new guarantee services provided by the Group are through its own licensed financing guarantee subsidiary. Under the cooperation with licensed financing guarantee companies, these licensed financing guarantee companies initially reimburses the loan principal and interest to the institutional funding partners upon borrower’s default. Although the Group does not have direct contractual obligation to the institutional funding partners for defaulted principal and interest, the Group provides back-to-back guarantee to the licensed financing guarantee companies. As agreed in the back-to-back guarantee contract, the Group would compensate the licensed financing guarantee companies for actual losses incurred by them on defaulted principal and interest. When the licensed financing guarantee companies are required to place deposits to the institutional funding partners as part of the arrangement, the Group will also be obligated to place back-to-back deposits to the licensed financing guarantee companies of the same amount and with the same settlement terms. The deposit amount is typically set at an agreed percentage of outstanding loan balance subject to guarantee. The Group’s deposits to licensed financing guarantee companies are recorded under "Prepaid expenses and other current assets, net" on the consolidated balance sheets. Given that the Group effectively takes on all of the credit risk of the borrowers, the Group recognizes a stand-ready obligation for its guarantee exposure at the inception of guarantee in accordance with ASC Topic 460 with an associated financial assets receivable. The initial fair value of stand-ready guarantee liabilities based on expected default rate of underlying loans subject to guarantee on a pool basis according to the historical delinquency data by vintage, adjusted by specific risk characteristics for borrowers from various channels, and other pertinent information in assessing future performance of the loan portfolio. The Group also records a contingent guarantee liability with an allowance for credit losses pursuant to ASC Topic 326 Current expected credit loss (“CECL”). Subsequent to the initial recognition, the ASC 460 stand-ready guarantee is released into guarantee revenue on a straight-line basis over the term of the guarantee, while the contingent guarantee is reduced by the payouts made by the Group to compensate the institutional funding partners/licensed financing guarantee companies upon borrowers’ default. Allowance for credit losses under CECL model was included under “Allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets, loans receivable and others” and revalued at each period end to reflect updated estimation for future net pay-out. In 2024, a subsidiary of the Group entered into an one-year agreement with an oversea third-party funding partner to guarantee its principle and interests income with a pre-agreed rate. The maximum potential future payments under such agreement was US$3 million. In February 2025, the Company additionally provided oversesa guarantees in an aggregate amount of US$12,000. As of December 31, 2023 and 2024, the maximum potential future payments, including all outstanding principal and interests for which the Group provides primary guarantee, were RMB13,694,236 and RMB2,776,650, respectively.
The following table summarizes the aging of the Group’s contractual amounts of the outstanding principle and interests subject to guarantee:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0-30 days |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
past due |
|
|
Current |
|
|
Total loans |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
December 31, 2023 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
13,694,236 |
|
|
|
13,694,236 |
|
December 31, 2024 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,776,650 |
|
|
|
2,776,650 |
|
In connection with the above back-to-back guarantee arrangements with the institutional funding partners and licensed financing guarantee companies, the Group also engages third-party companies to provide back-to-back guarantee services to the Group, pursuant to which the third-party companies are obligated to compensate the Group at an amount equal to the compensation the Group paid to the institutional funding partners and the third-party licensed financing guarantee companies. The Group pays a service fee to the third-party companies, which is typically set as a pre-agreed percentage of loan volume. As part of the arrangement, the Group also requests for a back-to-back deposit from the third-party companies. The Group records the deposits received from the third-party companies under "Accrued expenses and other liabilities” on the consolidated balance sheets.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(k)
Guarantee arrangement - continued
Primary guarantee - continued
The Group records an estimated receivable for the amount determined to be probable of recovery (if any) from the third-party companies under “Prepaid expenses and other current assets” on the consolidated balance sheets in accordance with ASC326-20, with a corresponding amount recorded under “Allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets, loans receivable and others”. The corresponding service fee have been included in “Facilitation and servicing expenses” on the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company recorded contingent guarantee liabilities and corresponding recoverable assets of RMB205,775, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2024, the net payout for contingent guarantee liabilities was RMB2,301,314. In February 2025, the Company additionally provided oversesa guarantees in an aggregate amount of US$12,000.
Deferred guarantee income and Expected credit loss under ASC 326
The following table sets forth the activities of the Group’s obligations associated with the deferred guarantee income for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2024:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Opening balances |
|
|
276,518 |
|
|
|
886,862 |
|
Fair value of guarantee liabilities at inception of new loans |
|
|
2,296,882 |
|
|
|
781,808 |
|
Release of guarantee liabilities |
|
|
(1,475,238 |
) |
|
|
(1,439,167 |
) |
Disposal of subsidiary |
|
|
(211,300 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Ending balances |
|
|
886,862 |
|
|
|
229,503 |
|
*The Group disposed of a financing guarantee subsidiary and transferred out the remaining guarantee obligation to a third party company in April 2023. For more details, please refer to Note 7.
Financial assets receivable
Financial assets receivable is recognized at loan inception which is equal to the stand-ready guarantee liability recorded at fair value in accordance with ASC 460. The financial assets receivable is accounted for as a financial asset, and reduced upon the receipt of the service fee payment. At each reporting date, the Group estimates an allowance for credit losses primarily based on expectations of lifetime credit losses based on historical default experience, known or inherent risks in the portfolio, current economic conditions and macroeconomics forecasts as well as other factors surrounding the credit risk of specific type of customers. If the carrying amounts of the financial assets receivable exceed the expected cash to be received, an impairment loss is recorded for the irrecoverable financial assets receivable and is recorded in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income. Credit loss (Reversal of credit loss) of nil, RMB7,207 and RMB(5,957) were recorded in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income during the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
The following table presents the Group’s financial assets receivable as of December 31, 2023 and 2024:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Financial assets receivable |
|
|
998,835 |
|
|
|
294,733 |
|
Allowance for credit losses of financial assets receivable |
|
|
(7,207 |
) |
|
|
(1,250 |
) |
Financial assets receivable, net |
|
|
991,628 |
|
|
|
293,483 |
|
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(k)
Guarantee arrangement - continued
Secondary guarantee
For certain off-balance sheet loans facilitated between borrowers and institutional funding partners, guarantee services are provided by third-party guarantee companies who charge guarantee service fees directly from borrowers. Upon borrowers’ default, the third-party guarantee companies compensate institutional funding partners for unpaid principal and interest. In certain contracts, the Group provides commitment letter of balance complements to the institutional funding partners in the event that the guarantee companies are unable to fully reimburse the institutional funding partners. In some other contracts, the guarantee companies require a third-party company to act as counter guarantor and require the Group to provide a commitment letter of balance complements to compensate third-party guarantee companies in the event that the counter guarantor are unable to fully reimburse the guarantee companies or when the deposits are below the required threshold. The fair value of guarantee liabilities of the Group as a secondary guarantor was inconsequential and no compensation was accrued by the Group during the years of 2022 and 2023. During the year of 2024, the Group accrued guarantee liabilities of RMB3,051 arising from secondary guarantee. As of December 31, 2023 and 2024, the outstanding loan balance for which the Group provides secondary guarantee was RMB20,893,308 and RMB29,151,751, respectively.
(l)
Current Expected Credit Losses
The Group’s in-scope assets are primarily loans receivable, accounts receivable and contract assets, financial assets receivable from institutional funding partners and licensed financing guarantee companies, receivables from the third-party asset management company and amounts due from related parties. ASC Topic 326 also requires the expected credit losses related to guarantee contracts be recorded separately from and in addition to the stand ready guarantee liability accounted for in accordance with ASC Topic 460. The guarantee obligation is separated into the expected credit losses of the guarantee contracts accounted for in accordance with ASC Topic 326, and deferred guarantee income.
In establishing the allowance for loans receivable, the Group considers historical losses, delinquency rate and other factors in pooling basis upon the use of the CECL Model in accordance with ASC topic 326. The Group writes off loans receivable as a reduction to the allowance for loans receivable when the loan principal and interest are deemed to be uncollectible. In general, loans receivable are identified as uncollectible when it is determined to be not probable that the balance can be collected.
The Group estimates the allowance for accounts receivables and contract assets based on expected net accumulated loss rates for terms during which losses of such service fees are expected to occur, which are consistent with the terms during which the Group expects to collect service fees.
The Group establishes an allowance for amounts due from related parties and receivables from the third-party asset management company that are based on historical experience and other factors surrounding the credit risk of specific customers.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(m)
Property and equipment
Property and equipment is generally stated at historical cost and depreciated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Depreciation and amortization expense of long-lived assets are included in either facilitation and servicing expenses, selling and marketing expenses, general and administrative expenses, or research and development expenses as appropriate. Property and equipment consist of the following and depreciation is calculated on a straight-line basis over the following estimated useful lives are:
|
|
|
|
|
Category |
|
Estimated useful life |
|
Electronic equipment |
|
3-5 years |
|
|
|
|
|
Office equipment & Furniture |
|
3-5 years |
|
|
|
|
|
Motor vehicles |
|
4-10 years |
|
|
|
|
|
Leasehold improvement |
|
Shorter of the lease term or expected useful life |
|
|
|
|
|
Software |
|
10 years |
Equity Investments Accounted for Using the Equity Method
Investments in entities in which the Group can exercise significant influence and holds an investment in voting common stock or in-substance common stock (or both) of the investee but does not own a majority equity interest or control are accounted for using the equity method of accounting in accordance with ASC 323. Under the equity method, the Group adjusts the carrying amount of the investments to recognize the Group’s proportionate share of each equity investee’s net income or loss into earnings after the date of investment. The Group evaluates the equity method investments for impairment under ASC 323. An impairment loss on equity method investments is recognized in earnings when the decline in value is determined to be other-than-temporary.
Equity securities without readily determinable fair values
Equity securities without readily determinable fair values and over which the Group has neither significant influence nor control through investments in common stock or in-substance common stock are measured and recorded using a measurement alternative that measures the securities at cost minus impairment, if any, plus or minus changes resulting from qualifying observable price changes.
Available-for-sale debt securities
Investments in debt securities that do not meet the criteria of held-to-maturity or trading securities are classified as available-for-sale, which are measured at fair value with changes in fair value with the unrealized gains or losses recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) as a component of shareholders’ equity (deficit).
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(o)
Valued-added taxes (“VAT”)
The Group is subject to VAT at the rate of 6% or 3% given that they are classified as a general tax payer. Entities that are VAT general taxpayers are allowed to offset qualified input VAT paid to suppliers against their output VAT liabilities.
(p)
Share-based compensation
Share-based payment transactions with employees are measured based on the grant date fair value of the equity instrument issued and recognized as compensation expense on a graded vesting basis, over the requisite service period, with a corresponding impact reflected in additional paid-in capital. For grants of options and restricted stock units (“RSUs”) subject to service-based and company performance-based vesting conditions, the fair value is established based on the market price on the date of the grant.
The expected term represents the period that share-based awards are expected to be outstanding, giving consideration to the contractual terms of the share-based awards, vesting schedules and expectations of future employee exercise behavior. Volatility is estimated based on annualized standard deviation of daily stock price return of comparable companies for the period before valuation date and with similar span as the expected expiration term. The Group adopted ASU 2016-09 and accounts for forfeitures of the share-based awards when they occur. Previously recognized compensation cost for the awards is reversed in the period that the award is forfeited. Amortization of share-based compensation is presented in the same line item in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income as the cash compensation of those employees receiving the award.
Modifications of the terms or conditions of the awards are treated as an exchange of the original awards for new awards. Incremental compensation cost is measured and recognized as the excess, if any, of the fair value of the modified award over the fair value of the original award immediately before the terms are modified. When the Group cancels unvested options and restricted share units (“RSUs”), the remaining unrecognized expenses are recognized immediately on the cancellation date.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
The Group has adopted ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) and all subsequent ASUs that modified ASC Topic 606 on January 1, 2018.
The core principle of the guidance is that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. To achieve that core principle, the Group applies the following steps:
•
Step 1: Identify the contract (s) with a customer
•
Step 2: Identify the performance obligations in the contract
•
Step 3: Determine the transaction price
•
Step 4: Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract
•
Step 5: Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation
Loan facilitation services
The Group provides service through its facilitation of loan transactions between borrowers and institutional funding partners. The Group’s service mainly consist of performing credit assessment on the borrowers, referring qualified borrowers to the institutional funding partners, and facilitating the execution of loan agreements between the parties.
The Group identifies the loan facilitation service as one performance obligation under ASC Topic 606, as the Group does not retain any further obligations after the facilitation of a loan. The Group follows the guidance on immaterial promises when identifying performance obligations and concludes that promises related to post-facilitation service, if any, are immaterial in the context of the contract and do not constitute a performance obligation.
The Group assesses ability and intention to pay the service fees of the customers when they become due and determines if the collection of the service fees is probable, based on historical experiences as well as the credit due diligence performed before cooperation. The Group determines the total transaction price to be the service fees chargeable according to the contracts, net of value-added tax, which are normally settled through third-party licensed financing guarantee companies. Under certain agreements, the transaction price includes variable consideration due to borrowers’ actual repayment to institutional funding partners. The Group estimates variable consideration for these contracts using the expected value approach on the basis of historical information.
The Group recognizes revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies the service/ performance obligation by transferring the promised service (that is, an asset) to customers based on the underlying contract terms excluding consideration of impairment of contract assets or accounts receivable. Revenues from loan facilitation services are recognized at the time a loan is facilitated between the institutional funding partners and the borrower and the principal loan balance is transferred to the borrower, at which time the facilitation service is considered completed.
In some cases, the institutional funding partners engage third-party licensed financing guarantee companies to provide guarantee on the performance of the loans the Group facilitates. The Group may, at the request of the institutional funding partner or the third-party licensed financing guarantee company to provide back-to-back guarantee. See details of guarantee arrangement accounting in Note 2(k).
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(q)
Revenue Recognition – continued
From 2020 to 2022, the institutional funding partners typically engaged third-party non-performing loan management entities to assist on the subsequent collection. The Group was in turn engaged by such non-performing loan management entities to provide information including risk profile and collection methods or plans for the borrowers on its platform to the non-performing loan management entity based on the historical records and experiences that the Group had as of the date when each loan is successfully extended to borrower. The Group no longer provided this service since 2023.
Revenue from technical services is recognized at the time a loan is successfully facilitated by the institutional funding partner as the technical services are completed at that time.
Guarantee revenue
The stand-ready guarantee liabilities are released into guarantee revenue over the term of the guarantee (see accounting policy for Guarantee arrangement 2(k)).The Group started to provide primary guarantee since the fourth quarter of 2022. For the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, revenue from the releasing of guarantee liabilities were RMB47,141, RMB1,393,081 and RMB1,357,705, respectively.
Other revenue
Investor referral
The Group provides referral services in respect of investment products offered by the third-party financial service providers on Youdao wealth platform, a proprietary platform operated by the Group. The Group considers the financial service providers to be its customers, and receives service fees from the customers primarily based on the transaction volume of the investment successfully subscribed by online investors. After the online investors subscribe the products referred by the Group, the Group does not retain any further obligations. The price for each referral charged to the financial service providers is at a fixed rate as pre-agreed in the service contract. Revenue is recognized when the online investors successfully subscribed to investment products from financial service providers.
Others
Other revenues primarily include service fees charged to the third-party financial service providers for the referral service of borrowers, and interest income generated from loan services to oversea individuals.
Interest income generated from oversea individuals is recognized over the terms of loans receivable using the effective interest rate method under ASC Topic 310. Interest income is not recorded when reasonable doubt exists as to the full, timely collection of interest income or principal. Interest collected upfront at the loan inception is recorded as deferred revenue.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(q)
Revenue Recognition - continued
The following table illustrates the disaggregation of revenue by product and services the Group offered in 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively, net of VAT and surcharges:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Revenue from loan facilitation
services |
|
At a point in time |
|
|
2,881,725 |
|
|
|
3,489,184 |
|
|
|
4,011,776 |
|
Revenue from the releasing of
guarantee liabilities |
|
Overtime |
|
|
47,141 |
|
|
|
1,393,081 |
|
|
|
1,357,705 |
|
Other revenue - investor
referral |
|
At a point in time |
|
|
269,256 |
|
|
|
342,181 |
|
|
|
228,488 |
|
Other revenue - others |
|
At a point in time/Overtime |
|
|
73,292 |
|
|
|
242,427 |
|
|
|
203,063 |
|
Total net revenue |
|
|
|
|
3,271,414 |
|
|
|
5,466,873 |
|
|
|
5,801,032 |
|
Accounts receivable and contract assets
Contract assets represent the Group’s right to consideration in exchange for services that the Group has transferred to the customer before payment is due. The Group only recognizes accounts receivable and contract assets to the extent that the Group believes it is probable that it will collect substantially all of the consideration to which it will be entitled to in exchange for the services transferred to the customer.
Accounts receivable and contract assets are stated at the historical carrying amount net of write-offs and allowance for collectability in accordance with ASC Topic 326. The Group established an allowance for receivables and contract assets based on estimates, which incorporate historical experience and other factors surrounding the credit risk of specific type of customers. The Group evaluates and adjusts its allowance for receivables and contract assets on a quarterly basis or more often as necessary. Revenue recognized for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024 from performance obligations satisfied (or partially satisfied) in prior periods pertaining to adjustments to variable consideration due to the change of estimated receivables, change of estimated prepayment rate and referral fees was immaterial.
Practical expedients
The Group determines that the acquisition cost paid based on the amount of loans facilitated represents costs to obtain a contract qualifying for capitalization since these payments are directly related to sales achieved during a period. The Group elects to expense such expenses when incurred as the amortization period would have been less than a year.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(r)
Employee defined contribution plan
Full time employees of the Group in the PRC participate in a government mandated multi-employer defined contribution plan pursuant to which certain pension benefits, medical care, unemployment insurance, employee housing fund and other welfare benefits are provided to employees. Chinese labor regulations require that the Group makes contributions to the government for these benefits based on a certain percentage of the employee’s salaries. The Group has no legal obligation for the benefits beyond the contributions. The total amount that was expensed as incurred was RMB68,145, RMB94,300 and RMB114,374 for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
(s)
Facilitation and servicing expense
Facilitation and servicing expenses primarily consist of variable expenses including costs related to back-to-back guarantee service fee to third-party companies, credit assessment, user and system support, payment processing services and collection, associated with facilitating and servicing loans, salaries and benefits and share-based compensation for the personnel who work on credit assessment, data processing and analysis, loan facilitation, user and system support.
(t)
Sales and marketing expenses
Sales and marketing expenses primarily consist of variable marketing and promotional expenses, including those expenses related to acquisition and retention of borrowers and institutional funding partners, and general brand and awareness building. Salaries and benefits expenses as well as share-based compensation related to the Group’s sales and marketing personnel and other expenses related to the Group’s sales and marketing team are also included in the sales and marketing expenses. The Group’s borrower acquisition expenses include charges by third-party online channels for online marketing services such as search engine marketing, search engine optimization, information feeds, and referral fees charged by other parties relating to borrower acquisition. The Group expenses all advertising costs as incurred and classifies these costs under sales and marketing expenses. For the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, the advertising expenses were RMB8,437, RMB12,658 and RMB12,855, respectively.
(u)
Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses primarily consist of salaries and other compensation expenses for employees engaged in research and development activities, technology infrastructure expenses and server expenses.
Government grants are primarily referred to the amounts received from various levels of local governments from time to time which are granted for general corporate purposes and to support its ongoing operations in the region. The grants are determined at the discretion of the relevant government authority and there are no restrictions on their use. The government subsidies are recorded as other income in the period the cash is received and when all the conditions for their receipt have been satisfied. The government grants received by the Group amount to RMB22,306, RMB15,398 and RMB28,165 for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
Current income taxes are provided for in accordance with the laws of the relevant tax authorities.
Deferred income taxes are provided using assets and liabilities method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined on the basis of the differences between financial statements and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax assets are recognized to the extent that these assets are more likely than not to be realized. In making such a determination, the management consider all positive and negative evidence, including future reversals of projected future taxable income and results of recent operation. Deferred tax assets are then reduced by a valuation allowance through a charge to income tax expense when, in the opinion of management, it is more like than not that a portion of or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
The Group accounts for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in the consolidated financial statements by applying a two-step process to determine the amount of the benefit to be recognized. First, the tax position must be evaluated to determine the likelihood that it will be sustained upon external examination by the taxing authorities. If the tax position is deemed more-likely-than-not to be sustained (defined as a likelihood of more than fifty percent of being sustained upon an audit, based on the technical merits of the tax position), the tax position is then assessed to determine the amount of benefits to recognize in the consolidated financial statements. The amount of the benefits that may be recognized is the largest amount that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Interest and penalties on income taxes will be classified as a component of the provisions for income taxes.
The Group is subject to tax in local and foreign jurisdictions. As a result of its business activities, the Group will file tax returns that are subject to examination by the relevant tax authorities. Tax returns of the Group's major subsidiaries in PRC, Hong Kong, Singapore, Indonesia and Nigeria remain subject to examination by relevant tax authorities for five years, seven years, four years, five years and indefinite years, respectively, from the date of filing.
In accordance with the EIT Law, dividends, which arise from profits of foreign invested enterprises (“FIEs”) earned after January 1, 2008, are subject to a 10% withholding income tax.
Comprehensive income is defined to include all changes in equity of the Group during a period arising from transactions and other events and circumstances excluding transactions resulting from investments by shareholders and distributions to shareholders. During the periods presented, comprehensive income is reported on the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income, and other comprehensive loss includes foreign currency translation adjustments and fair value changes of available-for-sale debt securities.
Basic income per share is computed by dividing net income attributable to holders of ordinary shares by the weighted average number of ordinary shares outstanding during the period.
Diluted income per ordinary share reflects the potential dilution that could occur if securities or other contracts to issue ordinary shares were exercised or converted into ordinary shares. Ordinary share equivalents of stock options are calculated using the treasury stock method. Ordinary share equivalents are excluded from the computation in income periods should their effects be anti-dilutive.
The Group uses the management approach to determine operating segment. The management approach considers the internal organization and reporting used by the Group’s chief operating decision maker (‘‘CODM’’) for making decisions, allocation of resource and assessing performance.
The Group operates and manages its business as a single operating and reportable segment. The Group’s CODM has been identified as the Chief Executive Officer who reviews the consolidated net income when making decisions about allocating resources and assessing performance of the Group. Significant segment expenses are the same as these presented under the operating costs and expenses in the consolidated statements of operations, and the difference between net revenue less the significant segment expenses and consolidated net income are the other segment items. The CODM reviews and utilizes these financial metrics together with non-financial metrics to make operation decisions, such as the determination of the fee rate at which the Company charges for its services and the allocation of budget between operating costs and expense.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(z)
Segment reporting - continued
The Group’s long-lived assets are substantially all located in the PRC and substantially all of the Group’s revenues are derived from within the PRC. Therefore, no geographical segments are presented.
(aa) Operating leases
The Group leases administrative office spaces under operating leases and accounts for the leases under ASC 842. The Group determines whether an arrangement constitutes a lease and records lease liabilities and right-of-use assets on its consolidated balance sheets at the lease commencement. The Group measures its lease liabilities based on the present value of the total lease payments not yet paid discounted based on the more readily determinable of the rate implicit in the lease or its incremental borrowing rate, which is the estimated rate the Group would be required to pay for a collateralized borrowing equal to the total lease payments over the term of the lease. The Group estimates its incremental borrowing rate based on an analysis of publicly traded debt securities of companies with credit and financial profiles similar to its own. As of December 31, 2024, the Group’s operating leases had a weighted average remaining lease term of 2.3 years and a weighted average discount rate of 4.11%. The Group measures right-of-use assets based on the corresponding lease liability adjusted for payments made to the lessor at or before the commencement date, and initial direct costs it incurs under the lease. The Group considers only payments that are fixed and determinable at the time of lease commencement. The Group begins recognizing operating lease expense when the lessor makes the underlying asset available to the Group. After considering the factors that create an economic incentive, the Group did not include renewal option periods in the lease term for which it is not reasonably certain to exercise.
Additionally, the Group elects not to recognize lease with lease term of 12 months or less at the commencement date in the consolidated balance sheets and records its operating lease expense in its consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Operating lease expenses (including fixed lease cost and short-term lease cost) were RMB29,229, RMB22,654 and RMB25,327 for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. Total lease expense related to short-term leases was RMB7,158, RMB1,621 and RMB1,770 for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
(ab) Treasury shares
The Group accounts for treasury shares using the cost method. Under this method, the cost incurred to purchase the shares is recorded in the treasury shares account in the consolidated balance sheets.
(ac) Dividends
Dividends of the Company are recognized when declared.
(ad) Recent accounting pronouncements
Recent adopted Accounting pronouncement
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures” (“ASU 2023-07”). ASU 2023-07 intends to improve reportable segment disclosure requirements, enhance interim disclosure requirements and provide new segment disclosure requirements for entities with a single reportable segment. The Group adopted this guidance on January 1, 2024 and it did not have material impact on the Group’s consolidated financial statements.
2.
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
(ad) Recent accounting pronouncements - continued
Recent Accounting pronouncement Not Yet Adopted
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU No. 2023-09, Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures (Topic 740). The ASU requires disaggregated information about a reporting entity’s effective tax rate reconciliation as well as additional information on income taxes paid. The ASU is effective on a prospective basis for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is also permitted for annual financial statements that have not yet been issued or made available for issuance. The Group has evaluated this ASU and expects to add additional disclosures to the consolidated financial statements, once adopted.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU No.2024-03, Income Statement—Reporting Comprehensive Income—Expense Disaggregation Disclosures (Subtopic 220-40). The amendments in this update intend to improve the disclosures about a public business entity’s expenses and address requests from investors for more detailed information about the types of expenses (including purchases of inventory, employee compensation, depreciation, amortization, and depletion) in commonly presented expense captions(such as cost of sales, selling, general and administrative expenses, and research and development). In January 2025, the FASB issued ASU No. 2025 - 01, which clarifies the effective date of ASU No. 2024 - 03. The guidance is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2027. Early adoption is permitted. The Group is currently evaluating the impact from the adoption of this ASU on its consolidated financial statements.
3.
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE AND CONTRACT ASSETS, NET
Accounts receivable consists of the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Accounts receivable: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable |
|
|
1,645,005 |
|
|
|
2,694,476 |
|
Less: Allowance for credit losses |
|
|
(13,752 |
) |
|
|
(19,574 |
) |
Total accounts receivable |
|
|
1,631,253 |
|
|
|
2,674,902 |
|
The movement of allowance for uncollectible accounts receivable for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024 are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Balance at the beginning of the year |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,539 |
|
|
|
13,752 |
|
Current year credit losses |
|
|
2,539 |
|
|
|
13,752 |
|
|
|
5,822 |
|
Current year write off |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(2,539 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Balance at end of the year |
|
|
2,539 |
|
|
|
13,752 |
|
|
|
19,574 |
|
Contract assets consists of the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Contract assets |
|
|
476,493 |
|
|
|
313,479 |
|
Less: Allowance for credit losses |
|
|
(4,201 |
) |
|
|
(1,626 |
) |
Contract assets, net |
|
|
472,292 |
|
|
|
311,853 |
|
Provision (Reversal) for credit loss of RMB4,201 and RMB(2,575) were recorded for contract assets for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
4.
PREPAID EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS
Prepaid expenses and other current assets consisted of the followings:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Receivable from third party companies* |
|
|
933,947 |
|
|
|
205,775 |
|
Security deposits, net of credit loss** |
|
|
906,720 |
|
|
|
129,590 |
|
Others*** |
|
|
80,880 |
|
|
|
42,613 |
|
|
|
|
1,921,547 |
|
|
|
377,978 |
|
*The balances represent the receivable from the third party companies in relation to the back-to-back guarantee services provided to the Group (see Note 2(k)).
**The balances represent security deposits set aside as requested by certain institutional funding partners for provision of the primary guarantee. Starting from year 2024, majority of the new guarantee services provided by the Group is through its own licensed financing guarantee subsidiary. Under these agreements, the deposits are placed in funding banks, which are recorded under “Restricted cash” (see Note 2(k)). ”As of December 31, 2023 and 2024, allowance for credit loss were RMB6,838 and RMB771, respectively. Provision (Reversal) for credit loss of RMB6,838 and RMB(6,067), were recorded for security deposits for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
4.
PREPAID EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS - continued
***Other includes the following balances of loans receivable::
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Loans receivable |
|
|
9,149 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Less: Allowance for credit losses |
|
|
(6,367 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Loans receivable, net |
|
|
2,782 |
|
|
|
— |
|
The movement of allowance for loans receivable for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024 are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Balance at beginning of the year |
|
|
(27,255 |
) |
|
|
(17,991 |
) |
|
|
(6,367 |
) |
Current year credit losses |
|
|
(18,609 |
) |
|
|
(40,766 |
) |
|
|
(18,935 |
) |
Current year write off |
|
|
27,665 |
|
|
|
29,133 |
|
|
|
12,805 |
|
Disposal of a subsidiary |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
9,056 |
|
Foreign currency exchange |
|
|
208 |
|
|
|
23,257 |
|
|
|
3,441 |
|
Balance at end of the year |
|
|
(17,991 |
) |
|
|
(6,367 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
5.
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment, net consisted of the followings:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Leasehold improvement |
|
|
8,093 |
|
|
|
8,093 |
|
Motor vehicles |
|
|
4,103 |
|
|
|
4,103 |
|
Electronic equipment |
|
|
103,599 |
|
|
|
125,361 |
|
Office equipment & furniture |
|
|
7,907 |
|
|
|
7,535 |
|
Software |
|
|
1,407 |
|
|
|
1,407 |
|
Total costs |
|
|
125,109 |
|
|
|
146,499 |
|
Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization |
|
|
(84,777 |
) |
|
|
(102,102 |
) |
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
40,332 |
|
|
|
44,397 |
|
For the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, depreciation expenses were RMB7,668, RMB9,461 and RMB17,782 respectively.
In December 2024, the Group entered into a definitive agreement to purchase certain commercial property for a total consideration of approximately RMB1,353,638. The Group paid the down payment of RMB714,576 in 2024 and recorded in other non-current assets on the consolidated balance sheets. In March 2025, the Group paid remaining consideration and completed the purchase of, and obtained title to, the commercial property.
6.
LONG-TERM INVESTMENTS, NET
On January 5, 2021, Noble Fintech disposed its 6% of the equity interests in Aguila Information, S.A.P.I. de C.V. (“Aguila Information”) to a certain minority shareholder. Following the completion of the transaction, the equity interest of Aguila Information owned by the Group decreased from 51% to 45%. The Group thus deconsolidated Aguila Information and applied equity method to account for the investment in Aguila Information. For the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2022, the Group recognized the Group’s proportionate share of the equity investee’s net gain into earnings in the amount of RMB8,457 and RMB9,151 in accordance with ASC Topic 323. The Group received dividend return of the long-term equity investment of RMB2,586 in June 2021. As of December 31, 2021 and 2022, the balance of this investment was RMB5,819 and RMB15,078.
As there was disagreement between the Group and Aguila Information on business strategy, the Group determined that this investment was not recoverable and full impairment amounted to RMB15,078 was provided in the year ended December 31, 2022.
In 2020, the Group, through its subsidiary, Geerong, and another independent purchaser entered into a share purchase agreement with China Smartpay Group Holdings Limited (“China Smartpay”), to acquire 35 ordinary shares of Keen Best Investment Limited (“Keen Best”), representing 35% equity interest in Keen Best, a wholly-owned subsidiary of China Smartpay for an amount of RMB91,957. For the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, the Group recognized the Group’s proportionate share of the equity investee’s net loss into earnings in accordance with ASC Topic 323 in the amount of RMB1,211, RMB1,990 and nil, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Group was no longer able to exert significant influence over Keen Best and reclassified the investment from equity method to measurement alternative, i.e. cost less impairment, plus or minus qualifying observable price changes. Considering the business forecast of the investee, the Group fully impaired this investment in 2023. In 2024, the Group received a distribution upon unwind of Keen Best of RMB69,018 and recorded in “Other income, net” in the consolidated statements of operations.
The Group purchased two convertible notes totaling RMB51,006 in 2022 and 2023 from PT Rumah Inovasi JET, which is entitled to certain redemption rights and conversion rights on or before the maturity date. The Group accounts for its investments in as “available-for-sale” and measured the fair value at each period end. The unrealized holding gains and losses for available-for-sale securities are reported in other comprehensive income until realized.
In 2023, the Group purchased 8% equity interest of Emprende Conmovi, S.A. DE C.V., Sofom, Enr (“EPD”), a Mexico Fintech company for consideration of US$0.5. During the year of 2023, the Group lent two loans of RMB44,709 with the annual interest rate of 10% to EPD. The Group does not have the ability to exert the significant influence the operations of this entity and accounts for this investment using measurement alternative, and loans at amortized cost, respectively.
During the year of 2024, performance of EPD was below forecast and there were increased uncertainties around the local regulation environment. The Group took these indicators into consideration when assessing the recoverability of this investment and fully impaired the investment of RMB51,923 as of December 31, 2024.
In 2024, the Group lent several loans totaling RMB97,577 with annual interest rate of 10% to PT Telekomunikasi Andalan Indonesia (“Teleko”). The Group accounts for this investment at amortized cost.
7.
DISPOSALS AND DISSOLUTION OF SUBSIDIARIES
In September, 2019, Shanghai Wuxingjia Information Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai Wuxingjia) entered into an agreement (the “Agreement”) with Shenzhen Rongxinbao, and Shanghai Jiayin, which wholly owns the equity interest of Shanghai Caiyin. Pursuant to the Agreement, Shanghai Jiayin agreed to transfer all of its equity interest in Shanghai Caiyin to Shenzhen Rongxinbao and the Group revised the terms of its collaboration with Shanghai Caiyin. As a result, the Group deconsolidated Shanghai Caiyin. Major line items of Shanghai Caiyin as of August 31, 2019 included cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, contract assets, liabilities from the investor assurance program and tax payable. As Shanghai Caiyin was in net deficit position as of August 31, 2019 due to its collaboration with the Group, the Group also agreed to waive Shanghai Caiyin’s payables to the Group of RMB1,973,613 and pay a total transaction price of RMB1,078,686, of which RMB372,085 is contingent upon Shanghai Caiyin’s liability status in the period preceding December 30, 2022 subject to the cap amount of RMB372,085, RMB255,064 and RMB117,021 on December 30, in each of the three years ending 2022, respectively. The remaining amount of the equity transfer consideration shall be settled through the service fee Shenzhen Rongxinbao collected on behalf of the Group.
For the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2022, “Gain from de-recognition of liabilities” of RMB138,043 and RMB117,021 were derived from the release of contingent consideration payable recorded as gain from de-recognition of liabilities on the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income. As of December 31, 2021, the payable related to the disposal of Shanghai Caiyin was RMB322,028 which consisted of fixed consideration payable of RMB205,007 and contingent consideration payable of RMB117,021. As of December 31, 2022, the payable balance was RMB188,300 which was all related to fixed consideration payable. In 2023, RMB108,190 has been settled with the receivables from Shenzhen Rongxinbao, RMB75,646 was settled in the Company’s disposal of Fujian Zhuoqun as disclosed below and the remaining RMB 4,464 was settled through cash payment.
Further in November 2023, the Group decided to dissolve Shanghai Wuxingjia. The book value of Shanghai Wuxingjia were mainly consisted of VAT and income tax payable accrued in previous years related to terminated P2P business. Upon receipt of the tax de-registration from the tax authority, the tax liabilities of approximately RMB280,231 were deemed to be waived, resulting in the recognition of a gain from de-recognition of liabilities on the consolidated statements of operation and comprehensive income. The remaining administrative procedures to dissolve Shanghai Wuxingjia were completed in April 2024.
In 2023, Jiayin Technology disposed of its 100% equity interest of Fujian Zhuoqun to Shenzhen Rongxinbao for an aggregate consideration of RMB391,870, in which RMB316,224 was settled by the existing payables the Group owed to Fujian Zhuoqun, RMB75,646 was settled with the existing payables the Group owed to Shenzhen Rongxinbao in connection with the disposal of Shanghai Caiyin in 2019. As a result, the Group recognized disposal loss of RMB2,012 upon the closing for the year ended December 31, 2023.
In August 2024, the Group disposed of its 100% equity interest of Giasun Technology Nigeria Limited (“Giasun”) and Quark Financials Nigeria Limited (“Quark”) to Fortunify International Holdings Pte. Ltd. (“Fortunify”). The total consideration was of RMB21,866, which was net-settled by the receivables from Giasun and Quark. The consideration would be due in March 2028. The Group recorded the consideration at its present value of RMB18,814 as “Other non-current assets” on the consolidated statements and recognized disposal loss of RMB14,431 arising from the transaction.
The Company assessed and considered the revenue streams of these transactions did not represent a strategic shift that has a major effect on the Company’s operation and financial results. Therefore, none of these transactions are qualified as discontinued operations under ASC 205-20.
8.
SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION
The following table presents the classification of the Group’s share-based compensation expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Facilitation and servicing |
|
|
2,408 |
|
|
|
4,921 |
|
|
|
8,035 |
|
General and administrative |
|
|
33,740 |
|
|
|
31,464 |
|
|
|
25,879 |
|
Research and development |
|
|
6,038 |
|
|
|
6,823 |
|
|
|
10,557 |
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
362 |
|
|
|
11,145 |
|
|
|
14,651 |
|
Total |
|
|
42,548 |
|
|
|
54,353 |
|
|
|
59,122 |
|
Share Options
In September 2016, Jiayin Technology approved an employee incentive plan (the “2016 Plan”) and utilized a limited liability partnership (“LLP”) as a vehicle to hold 13,500,000 shares that will be used under the 2016 Plan. The shares were contributed by the Founder and a company controlled by the Founder is the general partner (“GP”) of the LLP. The 2016 Plan allows the grantees to hold options to purchase LLP shares from the GP or the designated persons to indirectly hold the equity shares of Jiayin Technology.
Options have a 4.5-year life and vest at 15%, 25%, 30%, and 30% respectively at each anniversary. The awards are in substance share-based expenses incurred by the controlling Founder on behalf of the Company. The related expenses are reflected in the Group’s consolidated financial statements as share-based compensation expenses with an offsetting to additional paid-in capital. Given the shares owned by the LLP for the purpose of the 2016 Plan are existing outstanding shares of Jiayin Technology, the option does not have dilution effect on income per share.
In February 2019, the Group adopted the 2019 Share Incentive Plan (“2019 Plan”), effectively upon the completion of the Company’s initial public offering (“IPO”) to replace the 2016 Plan on a 4:1 ratio. The 2019 Plan contains performance vesting condition related to the operation results of the Group and the business department the grantee belongs to, as well as the grantee’s individual performance. The modification did not result in any incremental value. The shares to be issued under the 2019 Plan can be either new shares or treasury shares.
In August 2021, the Group granted one batch options equivalent of 108,400 share options of Jiayin Group with the exercise price of RMB0.875 per Ordinary Shares to a then employee pursuant to the 2019 Plan. The options were fully exercised in 2021.
No options were granted during the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024.
8.
SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION – continued
The summary of the Share Option activities is as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of
Options
(in ‘000s) |
|
|
Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price |
|
|
Weighted
Average
Remaining
Contract Life |
|
|
Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
Years |
|
|
RMB |
|
Options outstanding at December 31, 2023 |
|
|
58 |
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
|
|
2.00 |
|
|
|
894 |
|
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised |
|
|
(48 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options outstanding at December 31, 2024 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Options exercisable at December 31, 2024 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Options vested or expected to be vested at
December 31, 2024 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Total share-based compensation cost for the Share Options amounted to RMB6,855, RMB4,380 and RMB39 for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. As of December 31, 2024, there was nil in total unrecognized compensation cost, net of estimated forfeitures, related to non-vested stock options.
Restricted Share Units ("RSUs”)
The Group granted RSUs under 2019 plan which vested upon satisfaction of both service-based vesting conditions and performance-based vesting conditions. Performance-based RSUs vest in certain installments after the grant letter date, pending certification of performance achievement by the management and continued service. The fair value of performance-condition awards is based on the closing market price of the Group’s common stock on the grant date. The Group recorded share-based compensation expense for RSUs over the requisite service period when the performance condition is probable to meet and accounted for forfeitures as they occur.
The summary of the RSUs activities in 2024 is as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of
RSUs
(in ‘000s) |
|
|
Weighted
Average
Grant-Date
Fair Value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RMB |
|
Unvested at December 31, 2023 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Granted |
|
|
1,290 |
|
|
|
45.80 |
|
Vested |
|
|
(1,290 |
) |
|
|
(45.80 |
) |
Canceled/Forfeited |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Unvested at December 31, 2024 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Total share-based compensation cost for the RSUs amounted to RMB35,693, RMB49,973 and RMB59,083 for the year ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2024, 1,290 share units were exercised with an aggregate intrinsic value of RMB59,083. As of December 31, 2024, there was nil in total unrecognized compensation cost related to RSUs.
Income (loss) by tax jurisdictions:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Income from Mainland China operations |
|
|
1,393,173 |
|
|
|
1,631,882 |
|
|
|
1,286,327 |
|
(Loss) Income from non-Mainland China operations |
|
|
(65,483 |
) |
|
|
(84,700 |
) |
|
|
9,041 |
|
Income before income taxes and share of income
from equity method investments |
|
|
1,327,690 |
|
|
|
1,547,182 |
|
|
|
1,295,368 |
|
Income tax expense consists of the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Current income tax expense: |
|
|
177,720 |
|
|
|
207,567 |
|
|
|
210,472 |
|
Deferred income tax (benefit) expense: |
|
|
(22,322 |
) |
|
|
40,049 |
|
|
|
28,428 |
|
Total income tax expense |
|
|
155,398 |
|
|
|
247,616 |
|
|
|
238,900 |
|
Cayman Islands
Jiayin Group Inc. is incorporated in the Cayman Islands. Under the current laws of the Cayman Islands, Jiayin Group Inc. is not subject to income or capital gains taxes. In addition, dividend payments are not subject to withholdings tax in the Cayman Islands.
Hong Kong
The Company subsidiary, Geerong (HK) Limited, is located in Hong Kong. The first 2.0 million Hong Kong dollars of profits it earned are subject to be taxed at an income tax rate at 8.25%, while the remaining profits will continue to be taxed at the existing tax rate, 16.5%. Additionally, payments of dividends by the subsidiary incorporated in Hong Kong to the Company are not subject to any Hong Kong withholding tax. No income tax provision has been made in the consolidated financial statements as it has no assessable income for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
PRC
Under the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Enterprise Income Tax (“EIT Law”), the Group’s subsidiaries and VIEs incorporated in the PRC are subject to statutory rate of 25%. High-technology enterprises may obtain a preferential tax rate of 15% provided they meet the related criteria. An enterprise’s qualification as a “high and new technology enterprise” (“HNTE”) is reassessed by the relevant PRC governmental authorities every three years. Geerong Yunke Information Technology Co., Ltd. and Jiayin Shuke Information Technology Co., Ltd. was entitled for a preferential income tax rate of 15% from 2022 to 2024 as they are qualified as HNTE. Shanghai Chuangzhen Software Co., Ltd. has been qualified as an eligible software enterprise. As a result of this qualification, it is entitled to a tax holiday of a full exemption for year 2020 and 2021 in which its taxable income is greater than zero, followed by a three-year 50% exemption. From 2022, Guangxi Chuangzhen Information Technology Co., Ltd. benefits from a preferential tax rate of 9% as it falls within the encouraged industries catalogue in western China. From 2023, Hainan Yinke Financing Guarantee Co., Ltd. benefits from a preferential tax rate of 15% as they are registered in Hainan and engaged in encouraged business activities.
Indonesia
The Group’s subsidiary incorporated in Indonesia is subject to Indonesia Income (“CIT”) law. In accordance with the CIT law, an Indonesian resident is subject to worldwide income tax. Corporate income tax is calculated based on corporate taxable income (income less deductible expenses / expenses after fiscal adjustment), and the applicable CIT rate is 25%. Based on Government Regulation No.1 Year 2020 Jo No.30 Year 2020, Corporate Income Tax was adjusted from 22% to 20% for fiscal year 2021 and 2022, and next is adjusted to 22% since 2023.
9.
INCOME TAXES – continued
Nigeria
The Group’s subsidiary incorporated in Nigeria is subject to Nigerian Company Income Tax (“NCIT”) law. In accordance with the NCIT law, a Nigerian Company is subject to worldwide income tax. Corporate income tax is calculated based on corporate taxable income (income less deductible expenses / expenses after fiscal adjustment), and the applicable NCIT rate is 30%. In August 2024, Quark and Giasun were disposed of by the Group (see Note 7).
Global Anti-base Erosion Rules
In December 2021, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (“OECD”) introduced the Global Anti-Base Erosion (GloBE) Rules, which set out global minimum tax rules designed to ensure that large multinational businesses with group annual revenue of EUR 750 million or more pay a minimum effective rate of tax of 15% on profits in all their operating countries (referred to as “Pillar Two Rules”). Countries may also implement their own domestic minimum tax regimes. Global minimum tax rules have been enacted in certain jurisdictions in which we are subject to income taxes. To provide transitional relief for Pillar Two tax compliance and administrative burden, the OECD has introduced a Framework for Transitional Country-by-Country Reporting Safe Harbor applicable for a transition period covering the years ended December 31, 2024 to December 31, 2026.
The Group has reviewed its corporate structure in light of the introduction of Pillar Two model rules in various jurisdictions. While such new rules introduce complexity into the Group’s calculation of income tax expense, Pillar Two did not have a material impact to the Group’s tax expense in 2024.
The following table sets forth the significant components of the deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Deferred tax assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accrued expenses |
|
|
43,423 |
|
|
|
69,343 |
|
Property, plant and equipment |
|
|
95 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Unrealized exchange difference |
|
|
4,191 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Allowance for uncollectible receivables, contract assets,
loans receivable and others |
|
|
9,240 |
|
|
|
3,607 |
|
Net loss carryforward |
|
|
20,295 |
|
|
|
25,668 |
|
Deferred income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
255 |
|
Gross deferred tax assets |
|
|
77,244 |
|
|
|
98,873 |
|
Valuation allowances |
|
|
(16,070 |
) |
|
|
(26,468 |
) |
Deferred tax assets, net |
|
|
61,174 |
|
|
|
72,405 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Deferred tax liabilities
Dividend withholding tax |
|
|
40,115 |
|
|
|
70,450 |
|
9.
INCOME TAXES – continued
Deferred tax assets and liabilities have been offset where the Group has a legally enforceable right to do so, and intends to settle on a net basis. The deferred tax liabilities were recorded in accrued expenses and other liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets.
Changes in valuation allowance are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Balance at beginning of the year |
|
|
(73,189 |
) |
|
|
(16,070 |
) |
Additions |
|
|
(4,676 |
) |
|
|
(11,151 |
) |
Reversals |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
375 |
|
Disposal of subsidiaries |
|
|
61,790 |
|
|
|
378 |
|
Balance at end of the year |
|
|
(16,070 |
) |
|
|
(26,468 |
) |
The Group assesses the available positive and negative evidence to estimate if sufficient future taxable income will be generated to use the existing deferred tax assets. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon its ability to generate sufficient future taxable income within the carry-forward periods provided for in the tax law and during the periods in which the temporary differences become deductible. When assessing the realization of deferred tax assets, the Group has considered possible sources of taxable income including (i) future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, (ii) future taxable income exclusive of reversing temporary differences and carry-forwards, (iii) future taxable income arising from implementing tax planning strategies, and (iv) specific known trend of profits expected to be reflected within the industry. On the basis of this evaluation, valuation allowances of RMB16,070, and RMB26,468 have been established for deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2024 respectively, based on a more likely than not threshold due to accumulated loss and uncertainty of sufficient profit generated in future years for certain subsidiaries within the Group. The amount of the deferred tax assets considered realizable, however, could be adjusted if estimates of future taxable income during the carry forwards period are reduced or increased or if objective negative evidence in the form of cumulative losses is no longer present and additional weight may be given to subjective evidence such as our projections for growth.
At December 31, 2024, tax loss carry-forward amounted to RMB79,716, and would expire in calendar year 2026 to 2029 if not utilized, while tax loss of RMB60,344 can be carried forward indefinitely. The Group operates its business through its subsidiaries and VIEs. The Group does not file consolidated tax returns, therefore, losses from individual subsidiaries or the VIEs may not be used to offset other subsidiaries’ or VIEs’ earnings within the Group.
Under U.S. GAAP, undistributed earnings are presumed to be transferred to the Company and are subject to the withholding taxes. Prior to December 31, 2022, the Group intended to indefinitely reinvest the PRC subsidiaries’ accumulated profits for expansion of its PRC business and no withholding tax was recorded for those accumulated profits. Starting from March 2023, the Group decided to transfer a portion of the annual profits generated by its PRC subsidiaries to their overseas parent company for dividend distribution purposes. The Group accrues withholding taxes on the profits that it does not intend to indefinitely invest. During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2024, the Group accrued corresponding deferred tax liabilities of RMB 40,115 and RMB47,234, respectively. The remaining undistributed earnings of the Group’s PRC subsidiaries that the Group intends to indefinitely reinvest was RMB 2,420,395 as of December 31, 2024.
A deferred tax liability should be recorded for taxable temporary differences attributable to the excess of financial reporting amounts over tax basis amounts, including those differences attributable to a more than 50% interest in a domestic subsidiary. However, recognition is not required in situations where the tax law provides a means by which the reported amount of that investment can be recovered tax-free and the enterprise expects that it will ultimately use that means the Group does not accrue deferred tax liabilities on the earnings of the VIEs given that the Group’s VIEs had accumulated deficits as of December 31, 2023 and 2024.
9.
INCOME TAXES – continued
Reconciliations of the differences between PRC statutory income tax rate and the Group’s effective income tax rate for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024 are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Statutory income tax rate |
|
|
25.00 |
% |
|
|
25.00 |
% |
|
|
25.00 |
% |
Non-taxable income |
|
|
(0.71 |
)% |
|
|
0.00 |
% |
|
|
(1.33 |
)% |
Non-deductible expense |
|
|
1.23 |
% |
|
|
2.09 |
% |
|
|
2.00 |
% |
Disposal of subsidiaries |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(4.50 |
)% |
|
|
0.03 |
% |
Research and Development expense super deduction |
|
|
(2.09 |
)% |
|
|
(4.13 |
)% |
|
|
(5.45 |
)% |
Effect of tax holiday * |
|
|
(10.99 |
)% |
|
|
(7.05 |
)% |
|
|
(6.31 |
)% |
Different tax rate of entities operating in other
jurisdiction |
|
|
0.55 |
% |
|
|
0.03 |
% |
|
|
0.07 |
% |
Valuation allowance |
|
|
0.32 |
% |
|
|
0.30 |
% |
|
|
0.83 |
% |
Withholding tax |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5.34 |
% |
|
|
3.65 |
% |
True up |
|
|
(1.68 |
)% |
|
|
(1.05 |
)% |
|
|
(0.05 |
)% |
Effective tax rate |
|
|
11.63 |
% |
|
|
16.03 |
% |
|
|
18.44 |
% |
*The effect of the tax holiday on the income per share is as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Tax saving amount due to HNTE status, software enterprise and other jurisdiction |
|
|
139,441 |
|
|
|
108,922 |
|
|
|
81,726 |
|
Income per share effect-basic and diluted |
|
|
0.65 |
|
|
|
0.51 |
|
|
|
0.38 |
|
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of total unrecognized tax benefits for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2024 is as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Balance at beginning of the year |
|
|
240,319 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Increase related to current year tax positions |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Release related to de-recognition of liabilities |
|
|
(240,319 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Balance at end of the year |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the unrecognized tax benefit was fully released upon the de-recognition of liabilities (see Note 7).
The Group recognizes interest expenses and penalty charges related to uncertain tax positions as necessary in the provision for income taxes. For the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024, no interest expense or penalty was accrued in relation to the unrecognized tax benefit. The Group has a liability for accrued interest of nil and nil as of December 31, 2023 and 2024, respectively.
ASC 740 states that a tax benefit from an uncertain tax position may be recognized when it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including resolutions of any related appeals or litigation processes, on the basis of the technical merits. The Group record unrecognized tax benefits as liabilities in accordance with ASC 740 and adjust these liabilities when the Group’s judgment changes as a result of the evaluation of new information not previously available. However, due to the uncertain and complex application of tax regulations, it is possible that the ultimate resolution of uncertain tax positions may result in liabilities which could be materially different from these estimates. In such an event, the Group will record additional tax expense or tax benefit in the period in which such resolution occurs.
10.
ORDINARY SHARES AND TREASURY STOCK
On May 10, 2019, the Group completed its IPO on the NASDAQ Global Market. In this offering, 4,025,000 ADSs, representing 16,100,000 ordinary shares, were issued at a price of US$10.50 per ADS. One ADS represents four Class A ordinary shares.The aggregate proceeds received by the Group from the IPO, net of issuance costs, were approximately RMB234,354. Upon completion of IPO, the 216,100,000 outstanding ordinary shares with par value of US$0.000000005 per share were split into 100,100,000 Class A ordinary shares and 116,000,000 Class B ordinary shares, with each Class A ordinary share being entitled to one vote and each Class B ordinary share being entitled to ten votes on all matters that are subject to shareholder vote. All classes of ordinary shares are entitled to the same dividend right. All of the Class B ordinary shares were held by the Founder of the Company. In 2020, 8,000,000 Class B ordinary shares were converted into Class A ordinary shares.
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2024, the Group repurchased 5,329,848 and 4,005,680 Class A ordinary shares on the open market for an aggregate cash consideration of US$7,060 (RMB50,438) and US$6,316 (RMB45,020) respectively. The weighted average price of these shares repurchased was US$1.32 per share and US$1.58 per share respectively. As of December 31, 2024, 2,621,816 ordinary shares are considered not outstanding and therefore were accounted for under the cost method and included in treasury stock as a component of the shareholder’s equity.
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted net income per share attribute to ordinary shareholders:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Net income attributable to ordinary shareholders
– basic and diluted |
|
|
1,179,658 |
|
|
|
1,297,619 |
|
|
|
1,056,478 |
|
Weighted average number of ordinary shares
outstanding – basic and diluted |
|
|
215,259,640 |
|
|
|
213,996,233 |
|
|
|
212,433,169 |
|
Basic and diluted net income per share
attributable to ordinary shares |
|
|
5.48 |
|
|
|
6.06 |
|
|
|
4.97 |
|
As economic rights and obligations are applied equally to both Class A and Class B ordinary shares, earnings are allocated between the two classes of ordinary shares evenly with the same allocation on a per share basis.
The Group does not have shares with a dilutive effect for the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024.
On March 28, 2023, the Board of Directors of the Company approved and adopted a dividend policy, under which the Company may choose to declare and distribute cash dividend twice each fiscal year, starting from 2023, at an aggregate amount of no less than 15% of the net income after tax of the Company in the previous fiscal year.
In July 2023, the Board of Directors of the Company approved a dividend of US dollar 0.10 per ordinary share, which was paid in August, 2023 to shareholders of record as of the close of business on July 28, 2023. The aggregate amount of cash distributed for the dividends was US$21,474 (equivalent to RMB156,674).
In January 2024, the Board of Directors of the Company approved a dividend of US dollar 0.10 per ordinary share, which was paid in January 2024 to shareholders of record as of the close of business on January 19, 2024. The aggregate amount of cash distributed for the dividends was US$21,213 (equivalent to RMB151,887).
In August 2024, the Board of Directors of the Company approved a dividend of US dollar 0.125 per ordinary share, which was paid in September 2024 to shareholders of record as of the close of business on August 27, 2024. The aggregate amount of cash distributed for the dividends was US$26,589 (equivalent to RMB189,018).
13.
ACCRUED EXPENSES AND OTHER LIABILITIES
Accrued expenses and other liabilities consisted of the followings:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Deposits* |
|
|
309,832 |
|
|
|
266,870 |
|
Accrued expenses |
|
|
313,041 |
|
|
|
467,032 |
|
Deferred tax liabilities |
|
|
40,115 |
|
|
|
70,450 |
|
Others |
|
|
57,550 |
|
|
|
62,057 |
|
|
|
|
720,538 |
|
|
|
866,409 |
|
*The balances represent deposits held by the Group related to the back-to-back guarantee service from the third-party companies.
14.
RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The table below sets forth the major related parties and their relationships with the Group, with which the Group entered into transactions during the years ended December 31, 2022, 2023 and 2024:
|
|
|
Name of related parties |
|
Relationship with The Group |
Shanghai Jiayin Finance Services Co., Ltd.
(“Shanghai Jiayin”) |
|
Entity controlled by Mr. Yan,
the Founder and Chairman of the Group
|
|
Shanghai Jiayin Zhuoyue Corporate Management Co., Ltd.
(“Jiayin Zhuoyue”)
|
|
Entity controlled by Mr. Yan,
the Founder and Chairman of the Group
|
|
GAYANG (Hongkong) Co., Ltd.
(“GAYANG”)
|
|
Entity controlled by Mr. Yan,
the Founder and Chairman of the Group
|
|
New Dream Capital Holdings Limited
(“New Dream Capital”)
|
|
Entity controlled by Mr. Yan,
the Founder and Chairman of the Group
|
Dream Glory L.P. |
|
Entity controlled by Mr. Yan,
the Founder and Chairman of the Group
|
|
Sunshinewoods Holdings Limited
(“Sunshinewoods”)
|
|
A principal shareholder |
|
Jiayin Technology Service (Shanghai) Co.,Ltd
(“Jiayin Technology”)
|
|
Entity controlled by Mr. Yan,
the Founder and Chairman of the Group
|
|
Aguila Information, S.A.P.I. de C.V.
(“Aguila Information”)
|
|
Subsidiary of Company’s equity investee |
Keen Best Investments Ltd. (“Keen Best”) |
|
Affiliate enterprise |
|
|
|
Subsidiary shareholder |
|
The minority shareholder of the subsidiaries of the Group |
14.
RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS - continued
The Group entered into the following significant transactions with its related parties:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nature of transactions |
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Services provided by related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jiayin Zhuoyue (1) |
|
|
122,946 |
|
|
|
115,538 |
|
|
|
74,549 |
|
Shanghai Jiayin (2) |
|
|
12,474 |
|
|
|
2,536 |
|
|
— |
|
Total |
|
|
135,420 |
|
|
|
118,074 |
|
|
|
74,549 |
|
Services provided to related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aguila Information (3) |
|
|
6,567 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Jiayin Technology Service (8) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
31,034 |
|
Total |
|
|
6,567 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
31,034 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nature of transactions |
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Loans to related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shanghai Jiayin (4) |
|
|
35,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
120,000 |
|
GAYANG (5) |
|
|
17,243 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Aguila Information (6) |
|
|
4,173 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Keen Best (7) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
13,904 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Subsidiary shareholder |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
Total |
|
|
56,416 |
|
|
|
13,906 |
|
|
|
120,003 |
|
Loans from related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sunshinewoods (9) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
27,335 |
|
Total |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
27,335 |
|
14.
RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS - continued
(1)
Jiayin Zhuoyue refers investors to the Group and charged referral service fees.
(2)
Shanghai Jiayin rented office space to the Group and charged other related service fee, which is calculated dependent on its usage of the underlying office space from April 2022 with lease period of 12 months.
(3)
The Group provides business and operational support services to Aguila Information and charged corresponding service fees. On January 5, 2021. Aguila Information was deconsolidated by the Group and deemed as our related party (see Note 6).
(4)
The amount in 2022 represents loans that were non-interest bearing, unsecured, and due on demand, and were fully collected as of December 31, 2022. The amount in 2024 represents loans to Shanghai Jiayin in November 2024 that were non-interest bearing, unsecured, and due in 1 year, and were fully collected as of December 31, 2024.
(5)
The amount represents loans to GAYANG in 2021 and 2022. In 2021, the loans comprise non-interest bearing loan of RMB20,664 and interest bearing loan with principal of RMB10,642 and fixed annual interest rate of 8%. In 2021, RMB11,471 of non-interest bearing loan has been collected and RMB171 interest has been accrued. In 2022, the amount represents interest bearing loan with principal of RMB17,243 and fixed interest rate of 8% after a three-months free of interest duration. In 2022, RMB9,193 of non-interest bearing loan and RMB1,408 of interest bearing loan has been collected and RMB638 interest has been accrued. In 2023, RMB17,302 of non-interest bearing loan has been collected.
(6)
The amount represents non-interest bearing loans to Aguila Information in 2022, which were fully collected as of December 31, 2022.
(7)
The amount represents non-interest bearing loans to Keen Best in May 2023, which have been fully collected as of December 31, 2023.
(8)
The Company provides loan facilitation services to Jiayin Technology, who funded loans through a trust as the sole beneficiary.
(9)
The amount represents loans that were unsecured and due in 1 year, with principal of RMB27,335 and fixed annual interest rate of 8%.
14.
RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS - continued
The following table present amounts due from and due to related parties as of December 31, 2023 and 2024:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
Amounts due from related parties |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jiayin Technology (1) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,411 |
|
Shanghai Jiayin (2) |
|
|
500 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Subsidiary shareholder (2) |
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Total |
|
|
509 |
|
|
|
4,411 |
|
Amounts due to related parties |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jiayin Zhuoyue (3) |
|
|
11,325 |
|
|
|
27,002 |
|
Dream Glory L.P. (4) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
23,887 |
|
Sunshinewoods (5) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
22,152 |
|
New Dream Capital(4) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
16,906 |
|
Total |
|
|
11,325 |
|
|
|
89,947 |
|
(1)
The amount represented uncollected service fees for services provided to related parties.
(2)
The amounts represented outstanding loans receivable from related parties.
(3)
The amount represented unsettled service fees for services provided by related parties.
(4)
The amounts represented unpaid dividends distributed to shareholders.
(5)
The amount represented loans payable to related parties.
15.
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Capital and other commitments
The Group entered into a definitive agreement on December 17, 2024 to purchase certain commercial property located in Shanghai, China for total cash consideration of approximately RMB1.35 billion. As of December 31, 2024, the Group’s commitments related to the certain commercial property was RMB639,062, which was settled in March 2025. Except this, the Group did not have any other significant capital, other commitments or long term obligations as of December 31, 2024.
Contingencies
The Group are currently not a party to any material legal or administrative proceedings. The Group may from time to time be subject to various legal or administrative claims and proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business. Litigation or any other legal or administrative proceeding, regardless of the outcome, is likely to result in substantial cost and diversion of the Group’s resources, including the Group’s management’s time and attention.
The Company’s ability to pay dividends is primarily dependent on the Company receiving distributions of funds from its subsidiaries. Relevant PRC statutory laws and regulations permit payments of dividends by the VIEs and subsidiaries of the VIEs incorporated in PRC only out of their retained earnings, if any, as determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. The consolidated results of operations reflected in the consolidated financial statements prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP differ from those reflected in the statutory financial statements of the Company’s subsidiaries.
Under PRC law, the Company’s subsidiaries, VIEs and the subsidiaries of the VIEs located in the PRC (collectively referred as the “PRC entities”) are required to provide for certain statutory reserves, namely a general reserve, an enterprise expansion fund and a staff welfare and bonus fund. The PRC entities are required to allocate at least 10% of their after tax profits on an individual company basis as determined under PRC accounting standards to the statutory reserve and has the right to discontinue allocations to the statutory reserve if such reserve has reached 50% of registered capital on an individual company basis. In addition, the registered capital of the PRC entities is also restricted.
Amounts restricted that include paid in capital and statutory reserve funds, as determined pursuant to PRC GAAP, is RMB 1,030,271 as of December 31, 2024.
Dividend distribution
On March 27, 2025, the Group adopted an adjustment to its dividend policy, pursuant to which the Group may declare and to distribute a cash dividend once each fiscal year, starting from 2025, at an aggregate amount of around 30% of the Group's net income after tax in the previous fiscal year.
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION—FINANCIAL STATEMENTS SCHEDULE I
CONDENSED FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF PARENT COMPANY BALANCE SHEETS
(AMOUNT IN THOUSANDS)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
804 |
|
|
|
298 |
|
|
|
41 |
|
Amounts due from subsidiaries and VIEs |
|
|
190,018 |
|
|
|
191,103 |
|
|
|
26,181 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
2,627 |
|
|
|
2,506 |
|
|
|
343 |
|
Total current assets |
|
|
193,449 |
|
|
|
193,907 |
|
|
|
26,565 |
|
Investments in subsidiaries and VIEs |
|
|
2,269,730 |
|
|
|
3,101,038 |
|
|
|
424,840 |
|
Total assets |
|
|
2,463,179 |
|
|
|
3,294,945 |
|
|
|
451,405 |
|
Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amounts due to subsidiaries and VIEs |
|
|
55,763 |
|
|
|
111,406 |
|
|
|
15,263 |
|
Accrued expenses and other liabilities |
|
|
25,275 |
|
|
|
54,266 |
|
|
|
7,434 |
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
81,038 |
|
|
|
165,672 |
|
|
|
22,697 |
|
Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ordinary shares |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Treasury stock |
|
|
(35,443 |
) |
|
|
(28,889 |
) |
|
|
(3,958 |
) |
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
901,932 |
|
|
|
909,649 |
|
|
|
124,621 |
|
Retained earnings |
|
|
1,525,841 |
|
|
|
2,241,414 |
|
|
|
307,072 |
|
Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income |
|
|
(10,189 |
) |
|
|
7,099 |
|
|
|
973 |
|
Total equity |
|
|
2,382,141 |
|
|
|
3,129,273 |
|
|
|
428,708 |
|
Total liabilities and equity |
|
|
2,463,179 |
|
|
|
3,294,945 |
|
|
|
451,405 |
|
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION—FINANCIAL STATEMENTS SCHEDULE I
CONDENSED FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF PARENT COMPANY STATEMENTS OF
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(AMOUNT IN THOUSANDS)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
Operating costs and expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
(6,494 |
) |
|
|
(4,546 |
) |
|
|
(3,736 |
) |
|
|
(512 |
) |
Total operating costs and expenses |
|
|
(6,494 |
) |
|
|
(4,546 |
) |
|
|
(3,736 |
) |
|
|
(512 |
) |
Loss from operations |
|
|
(6,494 |
) |
|
|
(4,546 |
) |
|
|
(3,736 |
) |
|
|
(512 |
) |
Interest (expense) income, net |
|
|
(76 |
) |
|
|
1,098 |
|
|
|
(5 |
) |
|
|
(1 |
) |
Other expenses, net |
|
|
(13,445 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Loss before income taxes and equity in subsidiaries
and share of income from VIEs |
|
|
(20,015 |
) |
|
|
(3,448 |
) |
|
|
(3,741 |
) |
|
|
(513 |
) |
Equity in earnings of subsidiaries and share of income from VIEs |
|
|
1,199,673 |
|
|
|
1,301,067 |
|
|
|
1,060,219 |
|
|
|
145,249 |
|
Net income |
|
|
1,179,658 |
|
|
|
1,297,619 |
|
|
|
1,056,478 |
|
|
|
144,736 |
|
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Change in cumulative foreign currency translation adjustment |
|
|
14,842 |
|
|
|
(7,077 |
) |
|
|
(3,202 |
) |
|
|
(438 |
) |
Other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
14,842 |
|
|
|
(7,077 |
) |
|
|
(3,202 |
) |
|
|
(438 |
) |
Comprehensive income |
|
|
1,194,500 |
|
|
|
1,290,542 |
|
|
|
1,053,276 |
|
|
|
144,298 |
|
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION—FINANCIAL STATEMENTS SCHEDULE I
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF PARENT COMPANY CASH FLOW STATEMENTS
(AMOUNT IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT FOR SHARE AND PER SHARE DATA
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
RMB |
|
|
US$ |
|
Cash flows from operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
|
1,179,658 |
|
|
|
1,297,619 |
|
|
|
1,056,478 |
|
|
|
144,736 |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash
used in operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share of income from subsidiaries and VIEs |
|
|
(1,199,673 |
) |
|
|
(1,301,067 |
) |
|
|
(1,060,219 |
) |
|
|
(145,249 |
) |
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
2,293 |
|
|
|
1,698 |
|
|
|
1,344 |
|
|
|
184 |
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amounts due from/to subsidiaries and VIEs |
|
|
(2,151 |
) |
|
|
(11,332 |
) |
|
|
4,046 |
|
|
|
554 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
(2,680 |
) |
|
|
(1,060 |
) |
|
|
(1,223 |
) |
|
|
(167 |
) |
Return on equity method investments |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
157,672 |
|
|
|
303,652 |
|
|
|
41,600 |
|
Accrued expenses and other liabilities |
|
|
636 |
|
|
|
780 |
|
|
|
(3,563 |
) |
|
|
(487 |
) |
Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities |
|
|
(21,917 |
) |
|
|
144,310 |
|
|
|
300,515 |
|
|
|
41,171 |
|
Cash flows from financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from exercise of options |
|
|
8,783 |
|
|
|
1,274 |
|
|
|
169 |
|
|
|
23 |
|
Repurchase of ordinary shares |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(38,081 |
) |
|
|
(53,261 |
) |
|
|
(7,297 |
) |
Loans from subsidiaries |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
38,081 |
|
|
|
53,261 |
|
|
|
7,297 |
|
Dividend distributed to shareholders |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(156,674 |
) |
|
|
(301,175 |
) |
|
|
(41,261 |
) |
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
|
|
8,783 |
|
|
|
(155,400 |
) |
|
|
(301,006 |
) |
|
|
(41,238 |
) |
Effect of foreign exchange rate changes on
cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
13,840 |
|
|
|
3,327 |
|
|
|
(15 |
) |
|
|
(2 |
) |
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
706 |
|
|
|
(7,763 |
) |
|
|
(506 |
) |
|
|
(69 |
) |
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
|
|
7,861 |
|
|
|
8,567 |
|
|
|
804 |
|
|
|
110 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents at end of the year |
|
|
8,567 |
|
|
|
804 |
|
|
|
298 |
|
|
|
41 |
|
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION—FINANCIAL STATEMENTS SCHEDULE I
NOTES TO SCHEDULE I
1.
Schedule I has been provided pursuant to the requirements of Rule 12-04(a) and 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X, which require condensed financial information as to the financial position, changes in financial position and results of operations of a parent company as of the same dates and for the same periods for which audited consolidated financial statements have been presented when the restricted net assets of consolidated subsidiaries exceed 25 percent of consolidated net assets as of the end of the most recently completed fiscal year.
2.
The condensed financial information has been prepared using the same accounting policies as set out in the consolidated financial statements except that the equity method has been used to account for investments in its subsidiaries and VIEs. The Company records its investments in subsidiaries and VIEs under the equity method of accounting as prescribed in ASC Topic 323, Investments—Equity Method and Joint Ventures. Such investments are presented on the Condensed Balance Sheets as “Investment in subsidiaries and VIEs” and share of their earnings as “Equity in earnings of subsidiaries and VIEs” on the Condensed Statements of Comprehensive Income.
3.
Certain information and footnote disclosures normally included in financial statements prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP have been condensed or omitted. The footnote disclosure certain supplemental information relating to the operations of the Company and, as such, these statements should be read in conjunction with the notes to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements.
4.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2024, there were no material contingencies, significant provisions of long-term obligations, mandatory dividend or redemption requirements of redeemable stocks or guarantees of the Company.
5.
Translations of balances in the additional financial information of Parent Company- Financial Statements Schedule I from RMB into US$ as of and for the year ended December 31, 2024 are solely for the convenience of the readers and were calculated at the rate of US$1.00= RMB7.2993, representing the noon buying rate set forth in the H.10 statistical release of the U.S. Federal Reserve Board on December 31, 2024. No representation is made that the RMB amounts could have been, or could be, converted, realized or settled into US$ at that rate or at any other rate.
EX-4.19
2
jfin-ex4_19.htm
EX-4.19
EX-4.19
Exhibit 4.19
*** Certain information in this document has been excluded pursuant to Item 601(b)(10) of Regulation S-K. Such excluded information is not material and is the type the registrant treats as private or confidential. Such omitted information is indicated by brackets (“[Redacted]”) in this exhibit. ***
Property Transfer Agreement
Party A: [Redacted]
Address: [Redacted]
Legal Representative: [Redacted]
Party B: Shanghai Jirongzhicheng Enterprise Development Co., Ltd.
Address: Zone C, F/25 (physically structured as F/21), Building 1, No.428 Yanggao South Road, China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone
Legal Representative: Zhang Guanglin
Party C: Jirong Yunke Information Technology Co., Ltd.
Address: Room 1513, 15/F, No.3553 Zhongshan North Road, Putuo District, Shanghai
Legal Representative: Zhang Guanglin
The parties listed above shall be individually referred to as “a Party” and collectively as “the Parties”.
Whereas:
(1)
Party A is the owner of the buildings located at [Redacted], with a gross floor area of [43,490.48] square meters (hereinafter referred to as the “Target Properties”);
(2)
Party A hereby intends to transfer, and Party B has the intention to purchase, the Target Properties. Party A and Party C (an affiliate of Party B) have entered into a Letter of Intent dated [Redacted] in relation to the purchase and sale of the Target Properties, pursuant to which Party C has paid an Earnest Money of [Redacted] to Party A.
(3)
Party C and Party B have each executed a Commitment of Satisfaction with Due Diligence dated [Redacted], respectively, whereby both Party C and Party B undertake that they fully acknowledge and accept the current status and defects of the Target Properties and are willing to purchase the Target Properties.
NOW, THEREFORE, the Parties, having reached mutual agreement through negotiation, hereby agree as follows with respect to the Target Properties:
1.1
Unless otherwise specified, the following terms in this Agreement shall have the meanings set forth below:
|
|
|
“Target Property 1”
“Target Property 2”
“Target Properties”
|
[Redacted]
[Redacted]
Means Target Property 1 and Target Property 2 collectively.
|
“This Project” |
Means the transaction in which Party A intends to transfer the Target Properties to Party B;
|
“This Transaction” |
Means Party B’s purchase of the Target Properties owned by Party A in accordance with the provisions of this Agreement;
|
“Letter of Intent” |
Means the Letter of Intent signed by and between Party A and Party C in relation to this Project on [Redacted];
|
“Earnest Money” |
Means the sum of [Redacted] paid by Party C to Party A as earnest money in accordance with the Letter of Intent; |
|
|
“Transfer Price” |
Has the meaning set forth in Article 3.1 hereof; |
|
|
“Transaction Office” |
Means the Real Estate Transaction Office of Shanghai Pudong New Area;
|
“Real Estate Purchase and Sale Agreement” |
Means the standard-form Real Estate Purchase and Sale Agreement executed in respect of the Target Properties in accordance with the title transfer regulations of the Transaction Office, which is used to apply for and complete title transfer with the Transaction Office;
|
|
“Ownership Certificate”
|
Means the Shanghai Certificate of Real Estate Ownership;
|
|
|
“Laws” |
Means any applicable laws, regulations, decrees, ordinances, rules, judgments, injunctions, treaties and/or orders issued by any competent authorities in China, excluding, for the purposes of this Agreement, the laws of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, the Macao Special Administrative Region and Taiwan;
|
“Yuan/10,000 Yuan” |
Means RMB Yuan/10,000 Yuan unless otherwise specified. |
In this Agreement, unless the context otherwise requires:
(1)
any reference to any document, agreement or contract (including this Agreement) or to any part or provision thereof shall include all amendments, modifications, supplements or updates thereto as made from time to time;
(2)
the word “including” shall be construed as being followed by “but not limited to”;
(3)
any reference to a clause shall refer to a clause of this Agreement, and not to any clause of another document forming part hereof; and any reference to an exhibit shall refer to an exhibit to this Agreement;
(4)
the table of contents, headings and sub-headings are inserted for convenience only, and shall not be considered in the construction of this Agreement;
(5)
unless otherwise specified herein, any reference to “writing” and “written form” shall include all methods of reproducing text in a legible, durable manner, including email and fax;
(6)
unless otherwise specified, if a period is specified to commence on a particular day or on the day when a specific act or event occurs, that day shall not be counted toward that period;
(7)
unless otherwise explicitly stated, any reference herein to a year, month or day shall refer to the corresponding year, month or day of the Gregorian calendar.
ARTICLE II
TARGET PROPERTIES
2.1
Basic Information of Target Properties
(1)
The Target Properties refer to spaces within [Redacted] located at [Redacted], Shanghai, with a gross floor area of 43,490.48 square meters, as registered under the Ownership Certificate Number [Redacted].
Specifically, [Redacted]. The room numbers and use details of the Target Properties are set forth in Exhibit 1, and the floor plans/site plans and a copy of the Certificate of Real Estate Ownership are included in Exhibit 2.
(2)
The Target Properties are partially leased at the time this Agreement is executed and comes into effect, and the relevant lease agreements are listed in Exhibit 3.
(3)
Party A has disclosed to Party B and Party C that at the time this Agreement comes into effect, Target Property 2 is “unsaleable”, and Party A is coordinating with the competent authorities of Pudong New Area to transition it to a “saleable” state. The Parties acknowledge that if it is ultimately determined that Target Property 2 cannot be transitioned to a “saleable” state, no Party shall be liable for breach of contract for such inability to transition. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the inability to transition Target Property 2 to a “saleable” state shall not affect the transaction involving Target Property 1 and the performance of the relevant terms.
Party B and Party C have completed its due diligence investigation of the Target Properties, is satisfied with the investigation results, and fully accepts the current status of the Target Properties.
ARTICLE III
TRANSFER OF TARGET PROPERTIES
3.1
Transfer Prices for the Target Properties
The Parties acknowledge that the total Transfer Price for Target Property 1 shall be RMB [1,268,138,000] (in words: [RMB One Billion Two Hundred and Sixty-Eight Million One Hundred and Thirty-Eight Thousand Yuan Only]), inclusive of a 5% value-added tax, with a tax-exclusive base price of RMB [1,207,750,476.19]. Notwithstanding any national changes to the value-added tax rate, the total Transfer Price shall remain unchanged.
The Parties acknowledge that the total Transfer Price for Target Property 2 shall be RMB [85,500,000] (in words: [RMB Eighty-Five Million Five Hundred Thousand Yuan Only]), inclusive of a 5% value-added tax, with a tax-exclusive base price of RMB [81,428,571.43]. Notwithstanding any national changes to the value-added tax rate, the total Transfer Price shall remain unchanged.
The Parties acknowledge that the Transfer Price and floor area of each unit within the Target Properties shall be as set forth in Exhibit 1.
3.2
Terms of Payment of Transfer Prices
3.2.1 Target Property 1: to be paid in two installments:
(1) First installment: Party B shall pay [55]% of the total Transfer Price for Target Property 1, i.e.[697,475,900] (including an Earnest Money of [Redacted]), to Party A within five (5) working days from the Effective Date hereof. More specifically, Party C shall return to Party A the original receipt of the Earnest Money within the said period, and agrees that the Earnest Money of [Redacted] paid by Party C shall be credited towards the Transfer Price for Target Property 1 payable by Party B, and the rest of the first installment, i.e. [647,475,900], shall also be paid by Party B to Party A within the said period. Party B and Party C shall negotiate financial settlement issues in relation to the transfer of the Earnest Money independently, which shall have nothing to do with Party A and shall not affect the validity and performance of this Agreement.
(2) Second installment: Party B shall pay the remaining [45]% of the total Transfer Price for Target Property 1, i.e. [570,662,100], to Party A within sixty (60) working days from the Effective Date hereof.
3.2.2 Target Property 2: to be paid in two installments:
(1) First installment: Party B shall pay [20]% of the total Transfer Price for Target Property 2, i.e. [17,100,000], to Party A within five (5) working days from the Effective Date hereof.
(2) Second installment: Party B shall pay the remaining [80]% of the total Transfer Price for Target Property 2, i.e. [68,400,000], to Party A within five (5) working days after Target Property 2 is transitioned to a “saleable” state.
3.2.3 The information of Party A’s receiving account is as follows:
Bank: [Redacted]
Account Name: [Redacted]
Account Number: [Redacted]
3.2.4 If Party B’s payment of the Transfer Price for Target Property 1 is financed by a loan, in respect of such loan:
(1) Party B shall confirm that it has been fully aware of the financing bank’s lending policies prior to its execution of this Agreement;
(2) Party B shall comply with the following provisions in respect of its loan application and other matters:
A. Party B shall, within five working days after this Agreement comes into effect, submit a loan application to the bank and provide all required supporting documentation;
B. Party B shall transfer the loan amount to Party A’s designated account specified in Article 3.2.3;
C. If Party B’s loan application is not approved or is approved for an amount less than the applied sum, Party B shall make up the shortfall through self-financing. Should Party B fail to pay the full amounts specified in Article 3.2.1 hereof, it shall be deemed in breach for late payment under Article 8.2 hereof.
(3) Any expenses incurred in connection with securing such loan shall be borne by Party B.
ARTICLE IV
TITLE TRANSFER OF TARGET PROPERTIES
4.1 Party A and Party B shall submit a title transfer application for Target Property 1 to the Transaction Office within ten (10) working days upon Party B’s payment of 55% of the total Transfer Price for Target Property 1 in accordance with Article 3.2.1 hereof and submission of an executed and effective loan agreement to Party A, or upon Party B’s full payment of the total Transfer Price for Target Property 1 without utilizing loan financing. The Parties acknowledge that Party A and Party B shall, at the time this Agreement enters into force, sign the Shanghai Real Property Purchase and Sale Agreement or the Real Estate Purchase and Sale Agreement (in such form and content as then prescribed by the Transaction Office (the same hereinafter)) at the request of the Transaction Office to complete the title transfer procedures. For the avoidance of doubt, Party A and Party B acknowledge that the Shanghai Real Property Purchase and Sale Agreement or the Real Estate Purchase and Sale Agreement signed by and between Party A and Party B in such case shall be used solely for applying for and completing the title transfer of Target Property 1 with the Transaction Office, and the rights and obligations of Party A and Party B in relation to the transfer of Target Property 1 shall be still subject to this Agreement.
4.2 Party A and Party B shall submit a title transfer application for Target Property 2 to the Transaction Office within ten (10) working days after the underground parking spaces within Target Property 2 have been designated as “saleable”, the title transfer application process for Target Property 1 has been completed, and Party A has received the full Transfer Price for Target Property 2. The Parties acknowledge that Party A and Party B shall, at the time this Agreement enters into force, sign the Parking Space Sale Agreement (in such form and content as then prescribed by the Transaction Office (the same hereinafter)) at the request of the Transaction Office to complete the title transfer procedures.
For the avoidance of doubt, Party A and Party B acknowledge that the Parking Space Sale Agreement signed by and between Party A and Party B in such case shall be used solely for applying for and completing the title transfer of Target Property 2 with the Transaction Office, and the rights and obligations of Party A and Party B in relation to the transfer of Target Property 2 shall be still subject to this Agreement. Where Party A and Party B ultimately confirm that Target Property 2 cannot be transitioned to a “saleable” state, the relevant clauses of this Agreement regarding the transfer of Target Property 2 and the executed Parking Space Sale Agreement shall automatically terminate, without prejudice to the validity of the provisions in Article 5.7 hereof governing the use of Target Property 2.
ARTICLE V
DELIVERY OF TARGET PROPERTIES AND RELEVANT PROVISIONS
5.1
Party A and Party B acknowledge that Target Property 1 will be delivered on an “as is” basis. Within five working days upon Party B’s full payment of the total Transfer Price for Target Property 1, Party A and Party B shall each appoint a representative authorized in writing to the site of Target Property 1 to complete handover of Target Property 1 on an “as is” basis and jointly sign a Confirmation of Property Delivery. The signing of the Confirmation of Property Delivery (in the form attached hereto as Exhibit 4) shall constitute conclusive evidence of the completion of delivery of Target Property 1, and the risks in relation to Target Property 1 shall transfer to Party B upon the delivery thereof to Party B.
Party A and Party B acknowledge that after Target Property 1 is delivered on an “as is” basis, Party A shall conduct renovations of Target Property 1 according to the Decoration and Renovation Delivery Standards (see Exhibit 6 for details) at the cost of Party A, and then re-deliver the renovated property, which delivery does not involve the transfer of the ownership of Target Property 1. Unless otherwise specified, the term “delivery” as used hereinafter shall mean the first delivery on an “as is” basis.
5.2
Party A and Party B acknowledge that Target Property 2 will be delivered on an “as is” basis. Within five working days upon Party B’s payment of 20% of the total Transfer Price for Target Property 2, Party A and Party B shall each appoint a representative authorized in writing to the site of Target Property 2 to complete handover of Target Property 2 on an “as is” basis and jointly sign a Confirmation of Parking Space Delivery (in the form attached hereto as Exhibit 4). The signing of the Confirmation of Parking Space Delivery shall constitute conclusive evidence of the completion of delivery of Target Property 2, and the risks in relation to Target Property 2 shall transfer to Party B upon the delivery thereof to Party B.
5.3
Party A and Party B acknowledge that the Target Properties are transferred subject to existing leases (details of such leases are set forth in Exhibit 3). After the Target Properties are transferred to Party B, Party B shall assume all the rights and obligations of the lessor under such leases. The cut-off time for apportionment of the rental income from the Target Properties shall be the handover date specified in the Handover Confirmation, with rent accrued on and before the handover date to be attributable to Party A, and rent accrued on and after the day following the handover date to be attributable to Party B. Party A shall, within 5 working days after the handover date, transfer to Party B in full all security deposits paid by tenants and, with respect to the rent prepaid by tenants, allocate and transfer to Party B the portion of prepaid rent attributable to Party B, calculated using the day following the handover date as the cut-off date. In addition, Party A shall notify tenants in writing of the change in the leased properties’ right-holder (including change in the counterparty and the account receiving rent payments), and actively assist Party B in contract replacements, lease renewals and tenant communications. Should Party A receive any rent payments, rental-related fees, or other amounts (including insurance proceeds) pertaining to the Target Properties on or after the day following the handover date, Party A shall promptly transfer such amounts to Party B and provide Party B with the details thereof. In case of any tenant dispute, Party A shall actively cooperate with Party B toward resolution. Party A warrants that as of the Effective Date hereof, it has fully performed its obligations under the corresponding leases.
5.4
Upon the effectiveness hereof, [Redacted] shall be the designated property management company for the Target Properties. Commencing from the day (inclusive) immediately following the execution by Party A and Party B of the Confirmation of Property Delivery or the Confirmation of Parking Space Delivery, all principal’s rights and obligations concerning the Target Properties under the property management agreement shall be assumed by Party B, and Party A shall actively assist Party B in effecting a replacement of the contract with the property management company.
5.5
Party A and Party B acknowledge that the purposes of rooms (units) within the Target Properties include “office”, “retail”, and “special use”, as detailed in Exhibit 1. Party A makes no warranty as to the suitability of the Target Properties for any other purposes. The premises and the Owners’ Committee office (together, the “Special-Purpose Premises”) listed below shall be owned collectively by all owners and are excluded from the pricing for this Transaction. Party B may use the Special-Purpose Premises for their intended purposes upon the completion of this Transaction, provided that the usability thereof shall not affect the validity of this Transaction, and Party A accepts no liability to Party B in that regard.
[Redacted]
5.6 Party A and Party B acknowledge that starting from the day (inclusive) following the handover date, all rights and interests arising from the Target Properties, whether under policy or contract, shall vest in Party B, including those under service contracts, renewed insurance policies or otherwise. Notwithstanding any consideration paid by Party A for such rights and interests, Party A agrees that Party B is entitled to receive all services provided by the counterparties to such contracts, at no additional cost, within the scope of such consideration.
5.7 Party A and Party B acknowledge that subject to Party B’s payment of the first installment under Article 3.2.2 hereof and completion of the delivery process under Article 5.2 hereof, Party A agrees that Party B has the right to use Target Property 2. Should Target Property 2 ultimately prove untradeable, the transfer of Target Property 2 shall convert from a transfer of ownership to a transfer of right-of-use, with a right-of-use term of 20 years from the date of delivery of Target Property 2, and the first installment paid by Party B under Article 3.2.2 hereof shall constitute consideration for such right-of-use. Upon the expiration of the right-of-use term, the Parties shall renew the right-of-use in accordance with the provisions hereof (with no additional fees payable by Party B for such right-of-use).
ARTICLE VI
APPORTIONMENT OF TAXES AND OTHER EXPENSES
6.1
In accordance with Chinese Laws and regulations, Party A and Party B shall each bear their respective taxes and fees (including but not limited to property tax, urban land use tax, deed tax, value-added tax, stamp duty, and handling fees) incurred in connection with the title transfer of the Target Properties and the completion of procedures by Party A and Party B with the Transaction Office for transferring the Ownership Certificate of the Target Properties to Party B. In the absence of such Laws and regulations, Party A and Party B shall share such taxes and fees equally.
6.2
Party A shall, in accordance with the relevant national regulations, pay the maintenance funds for the Target Properties within 3 months of the completion of the title transfer of Target Property 1, provided that Party B shall reimburse Party A for any portion of the maintenance funds that Party B is responsible for but has been paid by Party A on its behalf. Party B shall reimburse Party A for any Shanghai Commercial Housing Maintenance Fund paid by Party A on its behalf, within 5 working days of receiving the official receipt of such payment.
6.3
Neither Party A nor Party B shall delay any tax or fee payment, thereby maliciously impeding the timely completion of the ownership transfer of the Target Properties.
ARTICLE VII
REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES
7.1
In respect of this Transaction, Party A represents and warrants to Party B as follows:
(1)
Party A is the sole legal titleholder of the Target Properties. Except for the disclosed fact that Target Property 2 is in an “unsaleable” state at the time this Agreement takes effect, the Target Properties are not subject to any other restrictions on rights, and this transfer has been effected in full compliance with the Laws and regulations, with all necessary procedures and process duly completed. Furthermore, except for the disclosed status of Target Property 2, there are no other circumstances that may affect the validity of this Agreement;
(2)
At the time this Agreement takes effect, the Target Properties are not subject to any mortgages, guarantees, or other external security interests;
(3)
At the time this Agreement takes effect, the Target Properties are not subject to judicial seizure resulting from litigation or arbitration disputes;
(4)
In accordance with the Laws, regulations, policies and other relevant provisions in force as of the Effective Date hereof, the Target Properties are free from any illegal construction or unauthorized reconstruction, modification, decoration, quality problems and other issues, and are in compliance with the relevant regulations in terms of floor area ratio, fire safety, water supply and drainage, environmental protection and other aspects;
(5)
In accordance with the Laws, regulations, policies and other relevant provisions in force as of the Effective Date hereof, there are no outstanding or payable land transfer fees for the Target Properties.
7.2
In respect of this Transaction, Party B represents and warrants to Party A as follows:
(1)
The funds used by Party B to pay the Transfer Prices and other amounts originate from legal and compliant sources;
(2)
Party B meets the eligibility requirements for purchasing the Target Properties as provided by the relevant Laws and policies;
(3)
Party B has completed all necessary due diligence on the Target Properties, fully understands and accepts the conditions thereof, and opts to purchase the Target Properties out of free will;
(4)
Party B shall be solely responsible for the use and renovation of the Target Properties after its purchase thereof, and Party A shall accept no liability in that regard.
ARTICLE VIII
BREACH OF CONTRACT AND DISSOLUTION
8.1
General Breach of Contract
Unless otherwise provided herein, if either Party breaches this Agreement, the non-breaching party shall have the right to seek one or more of the following remedies to protect its rights, which remedies available to the non-breaching party are cumulative and shall not affect other rights and remedies the non-breaching party may be entitled to under the law:
(1)
requiring specific performance by the breaching party;
(2)
requiring the breaching party to compensate the non-breaching party for the economic losses it has suffered;
(3)
other remedies as provided in this Agreement or by the applicable Laws.
8.2
Material Breach by Party B:
8.2.1
If Party B commits any of the following breaches, Party A shall have the right to require Party B to cure such breach immediately. Should Party B fail to cure such breach within thirty (30) days of receiving a written notice to cure from Party A (or such other extended period as agreed in writing by the Parties), Party A shall have the right to dissolve this Agreement by written notice to Party B:
(1)
Party B fails to pay the Transfer Prices to Party A in accordance with Article 3.2 hereof;
(2)
Party B fails to complete the title transfer procedures for the Target Properties in accordance with Article 4 hereof;
(3)
Party B fails to complete the handover procedures for the Target Properties in accordance with Articles 5.1 and 5.2 hereof;
(4)
Party B violates any of the representations and warranties under Article 7 hereof;
(5)
Party B unilaterally requests the dissolution hereof, other than under any of the circumstances where Party B has the right to dissolve this Agreement as provided by law or agreed in this Agreement.
8.2.2
Where Party A dissolves this Agreement in accordance with Article 8.2.1 hereof, Party B shall pay Party A a sum equal to 20% of the total Transfer Prices as liquidated damages. In such case, Party A shall have the right to deduct such sum from any amounts (including the Earnest Money) already paid by Party B for this Transaction, and any remaining balance after such deduction shall be returned to Party B without interest. Additionally, if Party B fails to pay the Transfer Prices to Party A in accordance with Article 3.2 hereof, for each day of delay, Party B shall also pay Party A liquidated damages in an amount equal to one thousandth of the outstanding payables.
If Party B fails, due to reasons attributable to Party B, to complete the title transfer procedures for the Target Properties in accordance with Article 4 hereof or to complete the handover procedures for the Target Properties in accordance with Articles 5.1 and 5.2 hereof, for each day of delay, Party B shall also pay Party A liquidated damages in an amount equal to one thousandth of the total Transfer Prices. From the day (inclusive) immediately following the handover date as specified in Article 5.1 or 5.2 until the date of dissolution hereof, the rental income from the Target Properties shall be attributable to Party A; where any such rental income has been paid to Party B pursuant to Article 5.3, Party A shall have the right to demand refund of the corresponding rental income from Party B.
8.3 Material Breach by Party A:
8.3.1 If Party A commits any of the following breaches, Party B shall have the right to require Party A to cure such breach immediately. Should Party A fail to cure such breach within thirty (30) days of receiving a written notice to cure from Party B (or such other extended period as agreed in writing by the Parties), Party B shall have the right to dissolve this Agreement by written notice to Party A:
(1)
Party A fails to complete the title transfer procedures for the Target Properties in accordance with Article 4 hereof;
(2)
Party A fails to complete the handover procedures for the Target Properties in accordance with Articles 5.1 and 5.2 hereof;
(3)
Party A violates any of the representations and warranties under Article 7 hereof;
(4)
Party A unilaterally requests the dissolution hereof, other than under any of the circumstances where Party A has the right to dissolve this Agreement as provided by law or agreed in this Agreement.
8.3.2 Where Party B dissolves this Agreement in accordance with Article 8.3.1 hereof, Party A shall pay Party B a sum equal to 20% of the total Transfer Prices as liquidated damages, and shall, on the termination date hereof, return to Party B any amounts (including the Earnest Money) already paid by Party B. Additionally, if Party A fails, due to reasons attributable to Party A, to complete the title transfer procedures for the Target Properties in accordance with Article 4 hereof or to complete the handover procedures for the Target Properties in accordance with Articles 5.1 and 5.2 hereof, for each day of delay, Party A shall also pay Party B liquidated damages in an amount equal to one thousandth of the total Transfer Prices.
From the day (inclusive) immediately following the handover date as specified in Article 5.1 or 5.2 until the date of dissolution hereof, the rental income from the Target Properties shall be attributable to Party B, and Party B shall have the right to require Party A to fulfil the corresponding obligations under Article 5.3.
8.4 For the avoidance of doubt, the Parties acknowledge that:
(1)
If any Party breaches this Agreement, the non-breaching party shall hold the breaching party liable for breach of contract in accordance with this Agreement, rather than in accordance with the Shanghai Real Property Purchase and Sale Agreement, the Real Estate Purchase and Sale Agreement, or the Parking Space Sale Agreement.
(2)
If this Agreement is terminated or dissolved, the Shanghai Real Property Purchase and Sale Agreement or the Real Estate Purchase and Sale Agreement, and the Parking Space Sale Agreement already concluded for the Target Properties hereunder shall automatically terminate.
8.5 In the event that Party B’s payment of the second installment of the Transfer Price for Target Property 1 is financed by a loan, if the title transfer for Target Property 1 has been completed, but the full Transfer Price for Target Property 1 is not received by Party A within the agreed time frame, which results in the dissolution of this Agreement, in addition to other provisions set forth herein, Party A and Party B shall act as follows:
(1) Party B shall, at Party A’s request, cooperate in handling the title reversion procedures, signing the relevant documents, and completing the procedures for dissolution of the loan guarantee agreement and for deregistration of mortgage, so as to ensure transfer of the title back to Party A’s name without mortgage. All taxes and other expenses incurred in connection with title reversion shall be borne by Party B. If Party B fails to cooperate as required above, Party B shall, for each day from the date Party B fails to complete the title reversion procedures until the date such procedures are completed, pay Party A liquidated damages in an amount equal to three ten-thousandths (0.03%) of the total Transfer Prices for the Target Properties.
(2) Party A shall cooperate with Party B to complete the procedures for dissolution of the loan agreement and the loan guarantee agreement and for deregistration of mortgage, and shall, at Party B’s request, repay to the bank or Party B the loan principal already disbursed to Party A’s account. In the event of any delay in such repayment, Party A shall pay Party B a late fee equal to one thousandth of the outstanding payables for each day of delay.
9.1
For the purposes of this Agreement, force majeure refers to any event, circumstance or condition that is unforeseeable, unavoidable, and beyond a Party’s reasonable control, and which is wholly or partially unavoidable or insurmountable by the affected Party despite its exercise of reasonable and prudent measures, thereby directly or indirectly preventing the performance of any material obligations hereunder, including but not limited to natural disasters, wars, fires, explosions, earthquakes, terrorist attacks, and similar occurrences.
9.2
If a force majeure event occurs after this Agreement comes into effect and prevents either Party from performing its obligations hereunder, the obligations of the affected Party shall, to the extent of the impact of such force majeure event and subject to the provisions of the applicable Laws, be wholly or partially exempted. The affected Party shall give written notice to the other Party within fifteen (15) days after it becomes aware or should have become aware of the event, providing reasonable details regarding its nature and scope, and shall make every effort to mitigate or prevent any losses the other Party may suffer as a result of the force majeure event. If a force majeure event prevents performance of this Agreement for more than one hundred and eighty (180) consecutive days, either Party shall have the right to terminate this Agreement.
10.1
All notices given by one Party to any other Party hereunder shall be delivered in person, by fax, by prepaid courier service, or by email to the following address of the other Party:
To Party A: [Redacted]
Address: [Redacted]
Postal Code: [Redacted]
Fax: [Redacted]
E-mail: [Redacted]
Addressee: [Redacted]
To Party B: Shanghai Jirongzhicheng Enterprise Development Co., Ltd.
Address: 26/F, Building No.1, Youyou Century Plaza, No.428 Yanggao South Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai
Postal Code: 200127
Fax: [Redacted]
E-mail: [Redacted]
Addressee: [Redacted]
To Party C: Jirong Yunke Information Technology Co., Ltd.
Address: 26/F, Building No.1, Youyou Century Plaza, No.428 Yanggao South Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai
Postal Code: 200127
Fax: [Redacted]
E-mail: [Redacted]
Addressee: [Redacted]
10.2
Any Party shall promptly notify the other Parties in writing of any change in its address as set forth above, and any notices given thereafter shall be delivered to the newly notified address.
10.3
Unless there is evidence of earlier service, all notices or other communications given by one Party to the other Parties hereunder shall be deemed served:
(1)
if delivered in person, at the time of delivery to the above address;
(2)
if sent by fax, at the time shown on the transmission confirmation report from the sender’s fax machine;
(3)
if sent by prepaid courier service, on the third (3rd) working day after dispatch;
(4)
if sent by registered airmail, on the fifth (5th) working day after dispatch;
(5)
if sent by email, at the time when a legible email is received.
ARTICLE XI
CONFIDENTIALITY
11.1
The Parties shall keep confidential this Agreement and all non-public information received in relation hereto (hereinafter referred to as the “Confidential Information”), and shall not disclose such information to any third party.
11.2
This Article does not apply to the disclosure of the following information:
(1)
information that is publicly available (other than through a violation of this Article);
(2)
information required to be disclosed by the Laws and regulations governing listed companies, or by judicial, government, or regulatory authorities, or by court decisions;
(3)
information disclosed by one Party to its professional advisors, provided that such Party shall ensure that the advisors are bound by confidentiality obligations equivalent to those set forth herein;
(4)
information that needs to be disclosed separately or in conjunction with this Agreement in one Party’s due performance hereof; information obtained by one Party from a third party subject to no confidentiality obligations;
(6)
information already in a Party’s possession prior to the commencement of negotiations for this Agreement; and
(7)
information disclosed by a Party to its affiliates for internal reporting purposes, provided that such affiliates undertake to comply with the confidentiality obligations set forth herein, and that the disclosing Party remains jointly and severally liable for its affiliates’ performance of their confidentiality obligations.
For the avoidance of doubt, any disclosure of the above information [except for information specified in paragraphs (1) and (2) of this Article 11.2] shall be subject to the receiving party maintaining the confidentiality of such information, and the receiving party may use such information solely for the purpose for which it is disclosed.
11.3
The above confidentiality obligations shall survive the termination of this Agreement.
ARTICLE XII
APPLICABLE LAW AND DISPUTE RESOLUTION
12.1
The conclusion, effectiveness, interpretation and performance of this Agreement shall be governed by the Laws and regulations currently in force in China.
12.2
The Parties shall first attempt to resolve through friendly negotiation any dispute arising out of or in connection with this Agreement, including the formation, interpretation, effectiveness, termination or performance of this Agreement. If the Parties fail to reach an agreement through negotiation, any Party may submit the dispute to a people’s court of competent jurisdiction in the locality where the Target Properties are situated for resolution through litigation.
ARTICLE XIII
MISCELLANEOUS
13.1
The Parties acknowledge that if, before Party A and Party B completes the transfer of the Ownership Certificate of the Target Properties to Party B, the Parties to this Transaction receive any materials indicating disapproval from a state-owned assets supervision agency or any authority of the Government of Pudong New Area or another government, this Transaction shall terminate automatically, without any Party incurring any liability for breach of contract. However, Party A shall, within five working days from the date of receiving such disapproval materials, refund all amounts already paid by Party B (including the Earnest Money) without interest and via the original payment method; if, as of the date of receiving such disapproval materials, the loan applied for by Party B for this Transaction has been disbursed, Party A shall repay the loan principal to the bank or Party B at the request of Party B. In the event of any delay in such repayment, Party A shall pay Party B a late fee equal to one thousandth of the outstanding payables for each day of delay.
In the event that Party A requires Party B’s cooperation in handling any procedures, all associated taxes and fees shall be borne by Party A, and any losses (including loan losses) suffered by Party B as a result shall be dealt with as otherwise agreed by Party A and Party B.
13.2
The Parties acknowledge that Party B and Party C shall bear joint and several liability to Party A for the relevant obligations, warranties, and responsibilities under this Transaction.
This Agreement and its Exhibit constitute the entire understanding and agreement between the Parties with respect to the subject matter hereof, and supersede any prior written or oral agreements reached between the Parties on the same subject matter. The Parties acknowledge that in the event of any conflict between this Agreement and the Shanghai Real Property Purchase and Sale Agreement or the Real Estate Purchase and Sale Agreement to be executed for this Transaction, the provisions of this Agreement shall prevail.
13.4
Restrictions on Assignment
No Party hereto may assign any of its rights, interests or obligations hereunder without the prior written consent of the other Parties.
This Agreement (including its Exhibits) shall come into effect as of the date when the legal representatives or authorized representatives of the Parties sign and affix their respective common seals, and when the Parties receive an original copy or a scanned copy of the fully executed version of this Agreement (the date on which the last Party signs to acknowledge its receipt of a paper copy or a scanned copy (whichever is earlier)) (hereinafter referred to as the “Effective Date”). The scanned copy shall have the same legal effect as the original paper copy and be legally binding upon the Parties.
This Agreement shall be executed in six copies, with each Party holding two copies. Each copy shall be deemed an original and have the same legal effect.
No term of this Agreement shall be modified except in writing and duly signed by the Parties.
[End of Body]
Exhibits:
1.
Table of Conditions and Unit Prices for Units within Target Properties
2.
Floor Plans of Target Properties and Copy of Ownership Certificate
3.
Table of Existing Leases Concerning Targe Properties (As of Effective Date)
4.
Confirmation of Property Delivery (Form), Confirmation of Parking Space Delivery (Form)
5.
Real Estate Purchase and Sale Agreement (Form)
6.
Decoration and Renovation Delivery Standards IN WITNESS WHEREOF, this Agreement has been duly executed and delivered by the Parties as of the date first above written.
[Signature Page]
Party A:
[Redacted]
Company seal: /s/ [Redacted]
Authorized Representative: /s/ [Redacted]
December 17th, 2024
Party B:
Shanghai Jirongzhicheng Enterprise Development Co., Ltd.
Company seal: /s/ [Name of Shanghai Jirongzhicheng Enterprise Development Co., Ltd]
Authorized Representative: /s/ [Redacted]
Party C:
Jirong Yunke Information Technology Co., Ltd.
Company seal: /s/ [Name of Jirong Yunke Information Technology Co., Ltd]
Authorized Representative: /s/ [Redacted]
Exhibit 1: Table of Conditions and Unit Prices for Units within Target Properties
Exhibit 2: Floor Plans of Target Properties and Copy of Ownership Certificate
Exhibit 3: Table of Existing Leases Concerning Targe Properties (As of Effective Date)
Exhibit 4: Confirmation of Property Delivery (Form), Confirmation of Parking Space Delivery (Form)
Exhibit 5: Real Estate Purchase and Sale Agreement (Form)
Exhibit 6: Decoration and Renovation Delivery Standards
EX-8.1
3
jfin-ex8_1.htm
EX-8.1
EX-8.1
Exhibit 8.1
LIST OF SUBSIDIARIES AND CONSOLIDATED VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES OF
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
|
|
|
|
Name |
Place of
incorporation/
establishment |
Subsidiaries |
|
Jiayin Holdings Limited |
BVI |
Geerong (HK) Limited (formerly known as “Jiayin (HK) Limited”) |
Hong Kong |
Jiayin Southeast Asia Holdings Limited |
BVI |
Shanghai Kunjia Technology Co., Ltd. |
Shanghai |
Geerong Yunke Information Technology Co., Ltd. |
Shanghai |
|
Jiangxi Yunkaijianming Technology Co., Ltd.
(formerly known as “Geerong Yun (Shanghai) Technology Development Co., Ltd.”)
|
Jiangxi |
Shanghai Chuangzhen Software Co., Ltd. |
Shanghai |
Shanghai Jirongzhicheng Enterprise Development Co., Ltd. |
Shanghai |
Hainan Yinke Financing Guarantee Co., Ltd. |
Hainan |
|
|
VIEs |
|
|
Shanghai Jiayin Technology Co., Ltd.
(formerly known as "Shanghai Jiayin Finance Technology Co., Ltd.”)
|
Shanghai |
|
Shanghai Jiajie Internet Information Services Co., Ltd.
(formerly known as “Shanghai Jiajie Finance Information Services Co., Ltd.”)
|
Shanghai |
Jiayin Shuke Information Technology Co., Ltd. |
Shanghai |
Guangxi Chuangzhen Information Technology Co., Ltd. |
Guangxi |
EX-11.2
4
jfin-ex11_2.htm
EX-11.2
EX-11.2
Exhibit 11.2
JIAYIN GROUP INC.
(THE “COMPANY”)
STATEMENT OF POLICIES
GOVERNING MATERIAL, NON-PUBLIC INFORMATION AND
THE PREVENTION OF INSIDER TRADING
Adopted by the Board of Directors of the Company on March 20, 2025
This Statement of Policies Governing Material, Non-Public Information and the Prevention of Insider Trading (this “Statement”) of the Company consists of three sections: Section I provides an overview; Section II sets forth the Company’s policies prohibiting insider trading; and Section III explains insider trading.
I.
SUMMARY
The Company’s American depositary shares (the “ADSs”) representing the Class A ordinary shares are currently trading on the Nasdaq Stock Market (“Nasdaq”). Pursuant to United States securities laws, it is illegal for any person, either personally or on behalf of others, to trade in securities on the basis of “material”, “non-public” information (defined below). It is also illegal to communicate (i.e., to “tip”) material, non-public information to others so that they may trade in securities on the basis of that information. These illegal activities are commonly referred to as “insider trading.” Preventing insider trading is necessary to comply with the United States federal securities laws and to preserve the reputation and integrity of the Company as well as that of all persons affiliated with it.
The Company considers strict compliance with the policies (the “Policy”) set forth in this Statement to be a matter of utmost importance. Violation of this Policy could cause extreme embarrassment and possible legal liability to you and the Company. Knowing or willful violations of this Statement or its spirit will be grounds for immediate dismissal from the Company. Violation of the Policy might expose the violator to severe criminal penalties and civil liabilities. Penalties for insider trading violations include civil fines of up to three times the profit realized by the violator, criminal fines of up to $5 million and civil liability to those damaged by the trading, as well as the attorney’s fees of persons injured.
While the regulatory authorities concentrate their efforts on the individuals who trade or who tip inside information to others who trade, the U.S. federal securities laws also impose potential liability on companies and other “controlling persons” if they fail to take reasonable steps to prevent insider trading by the violator. “Controlling persons”
includes employers (i.e., the Company), its directors, officers and managerial and supervisory personnel. The concept is broader than what would normally be encompassed by a reporting chain. Individuals may be considered “controlling persons” with respect to any other individual whose behavior they have the power to influence. Liability can be imposed only if two conditions are met. First, it must be shown that the “controlling person” knew or recklessly disregarded the fact that a violation was likely. Second, it must be shown that the “controlling person” failed to take appropriate steps to prevent the violation from occurring. For this reason, the Company’s supervisory personnel are directed to take appropriate steps to ensure that those they supervise, understand and comply with the requirements set forth in this Policy
This Statement applies to all officers, directors, employees and advisors (e.g., accountants, attorneys, investment bankers and consultants) of the Company and its subsidiaries or any consolidated entities or any other person or entity (a) over which an individual mentioned above exercises influence or control of its investment decisions, or (b) which effects a transaction in the Company’s securities, which securities are in fact beneficially owned by any of the individuals mentioned above (“Insider(s)”). Every Insider must review this Statement, and execute and return the Certificate of Compliance attached as Exhibit A hereto to the Compliance Officer, or confirm receipt of and future adherence to this Statement by other reasonable means, within seven (7) days or such longer period as permitted by the Company after you receive this Statement.
The failure of any Insider to comply with this Policy may subject him or her to sanctions by the Company, including dismissal for cause, whether or not the failure to comply results in a violation of law. The matters set forth in this Policy are guidelines only and are not intended to replace your responsibility to understand and comply with the legal prohibition on insider trading. Appropriate judgment should be exercised in connection with all securities trading.
Questions regarding the Statement should be directed to the Compliance Officer.
II.
POLICIES PROHIBITING INSIDER TRADING
For purposes of this Statement, while the terms “purchase” and “sell” of securities exclude the acceptance of options granted by the Company thereof and the exercise of options that does not involve the sale of securities, the cashless exercise of options does involve the sale of securities and therefore is subject to the policies set forth below.
A. No Trading with Material Insider Information–No Insider shall purchase or sell any securities of the Company while in possession of material, non-public information relating to the Company, its ADSs or other securities (the “Material Insider Information”) or during certain periods.
If you possess Material Insider Information, you must wait for the later of (i) forty eight (48) hours after public disclosure of the Material Insider Information by the Company, or (ii) one full Trading Day on Nasdaq following such public disclosure before trading the Company’s ADSs or other securities. The term “Trading Day” is defined as a day on which Nasdaq is open for trading. Nasdaq’s regular trading hours are from 9:30 a.m. to 4:00 p.m., New York City time, Monday through Friday.
In addition, no Insider shall purchase or sell any securities of the Company, regardless of whether such Insider possesses any Material Insider Information, (1) during any period commencing at the close of trading on the last day of the last month of each fiscal quarter and ending at the close of trading on the second Trading Day following the date upon which the Company’s earnings statement for that fiscal quarter is released to the public; or (2) without the prior clearance by the Compliance Officer, during any period designated as a “limited trading period.” The Compliance Officer may declare limited trading periods at the times that he deems appropriate, and need not provide any reason for making a declaration. If the Compliance Officer declares a limited trading period, a member of the Legal Department will notify the persons affected by the blackout as to when the blackout period begins and when it ends. The existence of a limited trading period may not be announced other than to those who are aware of the event giving rise to the blackout period. As long as the event remains material and non-public, no person aware of the event or notified of the event-specific blackout period may trade in the Company’s securities. Any person made aware of the existence of a limited trading period should not disclose the existence of the blackout period to any other person. The failure of the Compliance Officer to designate a person as being subject to a limited blackout period will not relieve that person of the obligation not to trade while aware of Material Insider Information.
Furthermore, beginning from the close of trading on December 31 of each fiscal year, no Insider shall purchase or sell any security of the Company until the close of trading on the second Trading Day following the date of the Company’s release of its financial results for the fiscal year ended on December 31 of the prior year.
In order to assist Company directors, officers and other employees in complying with this Policy, the Company will deliver an e-mail (or other communication) notifying all directors, officers and employees subject to the quarterly blackout period when the quarterly blackout period will begin and when it ends. The Company’s delivery or non-delivery of these e-mails (or other communication) does not relieve any persons from their obligation to only trade in the Company’s securities in full compliance with this Policy.
A person who is subject to a blackout period and who has an unexpected and urgent need to sell the Company’s stock in order to generate cash may, in appropriate circumstances, be permitted to sell the Company’s stock even during the blackout period. Hardship exceptions may be granted only by the Compliance Officer and must be requested at least two business days in advance of the proposed trade. A hardship exception may be granted only if the Compliance Officer concludes that the person requesting the exception is not in possession of Material, Insider Information. Hardship exceptions are granted infrequently and only in exceptional circumstances.
This Policy continues to apply to transactions in Company securities even after employment or service with the Company has ended. If a director, officer or other employee is in possession of Material Insider Information when employment or service terminates, the securities laws still prohibit trading in the Company’s securities until that information has become public or is no longer material.
Certain Exceptions. The foregoing restrictions on trading in the Company’s securities do not apply to:
•
Transferring shares to an entity that does not involve a change in the beneficial ownership of the shares (for example, to an inter vivos trust of which you are the sole beneficiary during your lifetime).
•
The exercise of stock options for cash under our stock plans (including any net-settled stock option exercise); however, the sale of any such stock acquired upon such exercise, including as part of a cashless exercise of an option, is subject to this Policy.
•
The exercise of a tax withholding right pursuant to which you elect to have the Company withhold shares of restricted stock, shares underlying restricted stock units or shares subject to an option to satisfy tax withholding requirements.
•
Trades by Insiders that occur in connection with a registered primary or secondary underwritten offering of the Company.
•
The execution of transactions pursuant to a trading plan that complies with Rule 10b5-1 under the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (a “Trading Plan”), and which has been approved by the Company.
Please see Section II.B below.
Please see Section III below for an explanation of the Material Insider Information.
Additionally, no Insider may purchase or sell securities of another company at any time when the Insider has material non-public information about that company, including, without limitation, any of the suppliers, customers or partners of the Company, its subsidiaries or consolidated entities, when that information was obtained, in whole or in part, as a result of the Insider’s employment or relationship to the Company.
B.
10b5-1 Trading Plans. Any director, officer or employee of the Company who wishes to implement, modify or terminate a Trading Plan must first pre-clear any such action with the Compliance Officer. A Trading Plan can only be established when you do not possess material, non-public information. Therefore, a director, officer or employee of the Company may enter into or modify a Trading Plan only when he or she is not in a blackout period or otherwise not in possession of material, non-public information. A Trading Plan is a pre-established plan that directs one’s broker to buy or sell securities according to pre-established parameters. In addition, the Trading Plan must not permit the holder of the account to exercise any subsequent influence over how, when, or whether the purchases or sales are made. The Company reserves the right to withhold approval of any Trading Plan that the Company determines is not consistent with the rules regarding such plans. Notwithstanding any approval of a Trading Plan, the Company assumes no liability for the consequences of any transaction made pursuant to such plan.
Transactions effected pursuant to a pre-approved Trading Plan will not require further approval at the time of the transaction if the plan complies with Rule 10b5-1 by specifying the dates, prices and amounts of the contemplated trades, or by establishing a formula for determining such dates, prices and amounts. However, the Trading Plan should be structured to avoid purchases or sales shortly before known announcements, such as quarterly or annual earnings announcements. Even though transactions executed in accordance with a properly formulated Trading Plan are exempt from the insider trading rules, the trades may nonetheless occur at times shortly before we announce material news, and the investing public and media may not understand the nuances of trading pursuant to a Trading Plan. This could result in negative publicity for you and the Company if the SEC or Nasdaq were to investigate your trades.
Any Trading Plan adopted by a director, officer or employee must comply with the requirements set forth in the Requirements for Trading Plans attached as Exhibit B hereto.
Approval of a Trading Plan by the Compliance Officer does not constitute legal advice to the requesting party. The rules regarding Trading Plans are complex and you must fully comply with them.
You should consult with your legal advisor before proceeding.
C. Blackout Periods. The Company’s announcement of its quarterly and annual financial results has the potential to have a material effect on the market for the Company’s securities. Therefore, to avoid even the appearance of trading while aware of Material Insider Information, all directors, officers and employees of the Company, and all employees of subsidiaries and consolidated entities of the Company with a title of director or above, as well the household and family members (as described in Section G, below), and trusts, corporations and other entities controlled by any of such persons, are prohibited from trading in the Company’s securities outside of four Trading Windows per year, each commencing with the close of trading on the second Trading Day following the date upon which the Company’s financial results for the prior fiscal quarter is released to the public and closing on the last day of the last month of each fiscal quarter.
Furthermore, all transactions in the Company’s securities (including without limitation, acquisitions and dispositions of the ADSs and the sale of ordinary shares issued upon exercise of stock options, but excluding the acceptance of options granted by the Company and the exercise of options that does not involve the sale of securities) by officers, directors and employees designated by the Company from time to time must be pre-approved by the Compliance Officer (other than pursuant to a pre-approved Trading Plan in compliance with Rule 10b5-1). A pre-clearance request shall be submitted to the Compliance Officer at least five business days in advance of the proposed transaction. If the Compliance Officer is the requester, his/her pre-clearance request shall be submitted to the Company’s Chief Executive Officer or his delegate for approval. The person requesting pre-clearance will be asked to certify that he or she is not in possession of Material Insider Information. The Compliance Officer is under no obligation to approve a transaction submitted for pre-clearance and may determine not to permit the transaction. Approval for transactions of the Company’s securities will generally be granted only during a Trading Window and the transaction may only be performed during the Trading Window in which the approval is granted and in any event within two business days from the date of approval.
If the Company’s earnings statement for a fiscal quarter or fiscal year is released on a Trading Day more than four hours before Nasdaq closes, then such date of disclosure shall be considered the first Trading Day following such public disclosure.
Please note that trading in Company securities during the Trading Window is not a “safe harbor,” and all Insiders should strictly comply with all other policies set forth in this Statement. Further, no director, officer or other employee, however, may buy or sell Company securities, even during the quarterly window periods, if he or she is in possession of Material Insider Information or has been notified by the Company of the imposition of a limited trading period.
When in doubt, do not trade! Check with the Compliance Officer first.
D. No Tipping - No Insider shall directly or indirectly disclose any Material Insider Information to anyone who trades in securities (so-called “tipping”), and no Insider may make buy or sell recommendations on the basis of Material Insider Information.
E. Confidentiality - No Insider shall communicate any Material Insider Information to anyone outside the Company under any circumstances unless approved by the Compliance Officer in advance, or to anyone within the Company other than on a need-to-know basis.
F. No Comment - No Insider shall discuss any internal matters or developments of the Company with anyone outside of the Company, except as required in the performance of regular corporate duties. Unless you are expressly authorized to the contrary, if you receive any inquiries about the Company or its securities by the financial press, investment analysts or others, or any requests for comments or interviews, you should decline to comment and direct the inquiry or request to the Compliance Officer.
G. Transactions by Family Members - This Policy also applies to your family members who reside with you, anyone else who lives in your household and any family members who do not live in your household but whose transactions in the Company’s securities are directed by you or are subject to your influence or control (such as relatives who consult with you before they trade in the Company’s securities). You are responsible for the transactions of these other persons, and, therefore, you should make them aware of the need to confer with you before they trade in the Company’s securities.
H. Transactions by Entities that You Influence or Control - This Policy also applies to any entities that you influence or control, including any corporations, partnerships or trusts, and transactions by these controlled entities should be treated for the purposes of this Policy and applicable securities laws as if they were for your own account.
I. “Twenty-Twenty Hindsight” - Before engaging in any transaction, you should carefully consider how enforcement authorities and others might view the transaction in hindsight after the occurrence of a negative event.
J. Corrective Action - If any potentially Material Insider Information is inadvertently disclosed, any Insider should notify the Compliance Officer immediately so that the Company can determine whether or not corrective action, such as general disclosure to the public, is warranted.
K. No Short Sales, Hedging or Speculative Transactions - No Insider, whether or not he or she possesses Material Insider Information, may trade in options, warrants, puts and calls or similar instruments on the Company’s securities or sell such securities “short” (i.e., selling stock that is not owned and borrowing the shares to make delivery). Such activities may put the personal gain of the Insider in conflict with the best interests of the Company and its stockholders or otherwise give the appearance of impropriety. No Insider may engage in any transactions (including prepaid variable forward contracts, equity swaps, collars and exchange funds) that are designed to hedge or offset any decrease in the market value of the Company’s equity securities.
L. Margin Accounts and Pledges - Securities purchased on margin may be sold by the broker without the customer’s consent if the customer fails to meet a margin call. Similarly, securities held in an account which may be borrowed against or are otherwise pledged (or hypothecated) as collateral for a loan may be sold in foreclosure if the borrower defaults on the loan. Accordingly, if an Insider purchases securities on margin or pledges them as collateral for a loan, a margin sale or foreclosure sale may occur at a time when the Insider is aware of Material Insider Information or otherwise are not permitted to trade in the Company’s securities. The sale, even though not initiated at the Insider’s request, is still a sale for the Insider’s benefit and may subject the Insider to liability under the insider trading rules if made at a time when the Insider is aware of Material Insider Information. Similar cautions apply to a bank or other loans for which the Insider has pledged stock as collateral.
Therefore, no Insider, whether or not in possession of Material Insider Information, may purchase the Company’s securities on margin, or borrow against any account in which the Company’s securities are held, or pledge the Company’s securities as collateral for a loan, without first obtaining pre-clearance. Request for approval must be submitted to the Compliance Officer (or his/her designee) at least two weeks prior to the execution of the relevant documents. The Compliance Officer is under no obligation to approve any request for pre-clearance and may determine not to permit the arrangement for any reason. Approvals will be based on the particular facts and circumstances of the request, including, but not limited to, the percentage amount that the securities being pledged represent of the total number of the Company’s securities held by the person making the request and the financial capacity of the person making the request. Notwithstanding the pre-clearance of any request, the Company assumes no liability for the consequences of any transaction made pursuant to such request.
M. Policy Effective Time - For all Insiders, this Policy continues in effect until the opening of the first Trading Window after termination of employment or other relationship with the Company, except that the pre-approval requirements set forth herein continue to apply to directors and officers of the Company for six months after the termination of their status as a director or officer.
N. Legal Effect of this Policy - The Company’s Policy with respect to insider trading and the disclosure of confidential information, and the procedures that implement this Policy, are not intended to serve as precise recitations of the legal prohibitions against insider trading and tipping which are highly complex, fact specific and evolving. Certain of the procedures are designed to prevent even the appearance of impropriety and in some respects may be more restrictive than the securities laws. Therefore, these procedures are not intended to serve as a basis for establishing civil or criminal liability that would not otherwise exist.
(Remainder of the page intentionally left blank)
III.
EXPLANATION OF INSIDER TRADING
As noted above, “insider trading” refers to the purchase or sale of securities while in possession of “material” and “non-public” information relating to such securities. “Securities” include not only stocks, bonds, notes and debentures, but also options, warrants and similar instruments. “Purchase” and “sale” are defined broadly under the United States federal securities law. “Purchase” includes not only the actual purchase of securities, but any contract to purchase or otherwise acquire securities. “Sale” includes not only the actual sale of securities, but any contract to sell or otherwise dispose of securities. These definitions extend to a broad range of transactions including conventional cash-for-stock transactions, the grant and exercise of stock options and acquisitions and exercises of warrants or puts, calls or other options related to the securities. It is generally understood that insider trading includes the following:
Trading by Insiders while in possession of Material Insider Information;
Trading by persons other than Insiders while in possession of Material Insider Information where the information either was given in breach of an Insider’s fiduciary duty to keep it confidential or was misappropriated; or
Communicating or tipping Material Insider Information to others, including recommending the purchase or sale of the securities while in possession of such information.
As noted above, for purposes of this Statement, the terms “purchase” and “sell” of securities exclude the acceptance of options granted by the issuer thereof and the exercise of options that does not involve the sale of securities. Among other things, the cashless exercise of options does involve the sale of securities and therefore is subject to the policies set forth in this Statement.
What Facts are Material?
The materiality of a fact depends upon the circumstances. A fact is considered “material” if it could reasonably be expected to affect the decision of a reasonable investor to buy, sell or hold the Company’s securities or where the fact is likely to have a significant effect on the market price of the Company’s securities. Material Insider Information can be positive or negative and can relate to virtually any aspect of a company’s business or to any type of securities, debt or equity.
Examples of Material Insider Information include (but are not limited to) information concerning:
• dividends;
• corporate earnings or earnings forecasts; • changes in financial condition or asset value;
• negotiations for the mergers or acquisitions or dispositions of significant subsidiaries or assets;
• significant new contracts or the loss of a significant contract;
• significant new products or services;
• significant marketing plans or changes in such plans;
• capital investment plans or changes in such plans;
• material litigation, administrative action or governmental investigations or inquiries about the Company or any of its affiliated companies, officers or directors;
• significant borrowings or financings;
• defaults on borrowings;
• new equity or debt offerings;
• significant personnel changes;
• changes in accounting methods and write-offs; and
• any substantial change in industry circumstances or competitive conditions which could significantly affect the Company’s earnings or prospects for expansion.
A good general rule of thumb: when in doubt, do not trade. One convenient rule of thumb in making this determination is to ask yourself, “Would the person on the other side of this transaction still want to complete the trade at this price if he or she knew what I know about the Company?” If the answer is “no,” you probably possess Material Insider Information.
What is Non-public?
Information is “non-public” if it has not been disclosed in a manner that allows it to be widely disseminated. In order for information to be considered public, it must be widely disseminated in a manner making it generally available to investors and confirmed by a reasonably reliable source. Wide dissemination generally occurs through a press release or in the Company’s filing with the United States Security and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), or through such media as Dow Jones, Reuters Economic Services, The Wall Street Journal, Bloomberg, Associated Press, or United Press International. Reasonable confirmation generally includes confirmation by officers, directors and employees who have been authorized by the Company to speak on its behalf.
The circulation of rumors, even if accurate and reported in the media, does not constitute effective public dissemination.
In addition, even after a public announcement, a reasonable period of time must lapse in order for the market to react to the information. Generally, one should allow approximately forty eight (48) hours following publication as a reasonable waiting period before such information is deemed to be public.
Who is an Insider?
Insiders include all officers, directors, employees, consultants and advisors (e.g. accountants, attorneys, investment bankers and consultants) of the Company and its subsidiaries or consolidated entities or any other person or entity (a) over which an individual mentioned above exercises influence or control of its investment decisions, or (b) which effects a transaction in the Company’s securities, which securities are in fact beneficially owned by any of the individuals mentioned above. Insiders have independent fiduciary duties to their company and its stockholders not to trade on Material Insider Information relating to the company’s securities. In addition, family members and friends of Insiders who receive Material Insider Information about the Company may also fall under the definition of Insiders of the Company.
It should be noted that trading by an Insider’s family members can be the responsibility of such Insider under certain circumstances and could give rise to legal and Company-imposed sanctions.
Trading by Persons Other than Insiders
Insiders are also prohibited from disclosing Material Insider Information, or making a recommendation or expressing an opinion regarding the Company’s securities based on such information, to others who might use the information to trade in the Company’s securities. Both the Insider who communicated the Material Insider Information and the person who receives and uses such information (the “Tippee”) may be liable under the United States federal securities law.
Persons other than Insiders also can be liable for insider trading, including Tippees who trade on Material Insider Information tipped to them or individuals who trade on Material Insider Information which has been misappropriated. Tippees inherit an Insider’s duties and are liable for trading on Material Insider Information illegally tipped to them by an Insider. Similarly, just as Insiders are liable for the insider trading of their Tippees, so are Tippees who pass the information along to others who trade. In other words, a Tippee’s liability for insider trading is no different from that of an Insider. Tippees can obtain Material Insider Information by receiving overt tips from others or through, among other things, conversations at social, business, or other gatherings.
Penalties for Engaging in Insider Trading
Penalties for trading on or tipping Material Insider Information can extend significantly beyond any profits made or losses avoided, both for individuals engaging in such unlawful conduct and their employers.
The SEC and the United States Department of Justice have made the civil and criminal prosecution of insider trading violations a top priority. Enforcement remedies available to the government or private plaintiffs under the United States federal securities law include:
SEC administrative sanctions;
securities industry self-regulatory organization sanctions;
civil injunctions;
damage awards to private plaintiffs;
disgorgement of all profits;
civil fines for the violator of up to three times the amount of profit gained or loss avoided;
civil fines for the employer or other controlling person of a violator (i.e., where the violator is an employee or other controlled person) of up to the greater of US$1,000,000 or three times the amount of profit gained or loss avoided by the violator;
criminal fines for individual violators of up to US$1,000,000 (US$2,500,000 for an entity); and
jail sentences of up to 10 years.
In addition, insider trading could result in serious sanctions by the Company, including immediate dismissal. Insider trading violations are not limited to violations of the United States federal securities law: other federal and state civil or criminal laws, such as the laws prohibiting mail and wire fraud and the United States Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act (RICO), may also be violated upon the occurrence of insider trading.
(Remainder of the page intentionally left blank)
Exhibit A
CERTIFICATION OF COMPLIANCE
TO: Compliance Officer
FROM: ______________________________
RE: JIAYIN GROUP INC.STATEMENT OF POLICIES OF GOVERNING MATERIAL, NON-PUBLIC INFORMATION AND THE PREVENTION OF INSIDER TRADING
I have received, reviewed, and understand the above-referenced Statement of Policies (the “Policy”) and hereby undertake, as a condition to my present and continued employment at or association with Jiayin Group Inc., to comply fully with the Policy.
I hereby certify that I have adhered to the Policy during the time period that I have been employed by or associated with Jiayin Group Inc.
I agree to adhere to the Policy in the future.
______________________________
Name:
Title:
______________________________
Date:
Exhibit B
REQUIREMENTS FOR TRADING PLANS
For transactions under a Trading Plan to be exempt from (A) the prohibitions in the Policy with respect to transactions made while aware of Material Insider Information and (B) the pre-clearance procedures and blackout periods established under the Policy, the Trading Plan must comply with the affirmative defense set forth in Rule 10b5‑1 under the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and must meet the following requirements:
1.
The Trading Plan must be in writing and signed by the person adopting the Trading Plan.
2.
The Trading Plan must be adopted at a time when:
a.
the person adopting the Trading Plan is not aware of any Material Insider Information; and
b.
there is no quarterly, special or other trading blackout in effect with respect to the person adopting the plan.
3.
The Trading Plan should be structured to avoid purchases or sales shortly before known announcements, such as quarterly or annual earnings announcements. Even though transactions executed in accordance with a properly formulated Trading Plan are exempt from the insider trading rules, the trades may nonetheless occur at times shortly before the Company announces Material Insider Information, and the investing public and media may not understand the nuances of trading pursuant to a Trading Plan. This could result in negative publicity for the Company if the SEC or Nasdaq were to investigate these trades.
4.
The Trading Plan must be entered in good faith and not as part of a plan or scheme to evade the prohibitions of Rule 10b5‑1, and the person adopting the Trading Plan must act in good faith with respect to such Trading Plan.
5.
The individual adopting the Trading Plan may not have entered into or altered a corresponding or hedging transaction or position with respect to the securities subject to the Trading Plan and must agree not to enter into any such transaction while the Trading Plan is in effect.
6.
The Trading Plan shall be subject to an applicable cooling-off period (the “Applicable Cooling-off Period”):
a.
If the person adopting the Trading Plan is a director or officer of the Company, the first trade under the Trading Plan may not occur until after the later of (a) 90 calendar days after adoption of the Trading Plan and (b) two business days following the disclosure of the Company’s financial results in (i) a Form 6-K for the completed fiscal quarter in which the Trading Plan is adopted, in case the Trading Plan is adopted in the first, second or third quarter of a calendar year and (ii) a Form 20-F for the year in which the Trading Plan is adopted, in case the Trading Plan is adopted in the fourth quarter of a calendar year (but, in any event, this required cooling-off period is subject to a maximum of 120 days after adoption of the Trading Plan); or
b.
If the person adopting the Trading Plan is not a director or officer of the Company, the first trade under the Trading Plan may not occur until after 30 calendar days after the adoption of the Trading Plan.
7.
If the person adopting the Trading Plan is a director or officer of the Company, such director or officer must include a representation in the Trading Plan certifying that, on the date of adoption of the plan:
a.
The individual director or officer is not aware of any Material Insider Information about the security underlying the plan or the Company; and
b.
The individual director or officer is adopting the plan in good faith and not as part of a plan or scheme to evade the prohibitions of Rule 10b-5 under the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
8.
The Trading Plan must have a minimum term of one year (starting from when trades may first occur in accordance with these requirements).
9.
Regarding modifications:
a.
The Trading Plan may only be modified when the person modifying the Trading Plan is not aware of Material Insider Information.
b.
The Trading Plan may only be modified when there is no quarterly, special or other blackout in effect with respect to the person modifying the plan.
c.
The first trade under the modified Trading Plan may not occur until after the expiration of the Applicable Cooling-off Period. The existing plan would remain in effect until the modified plan comes into effect.
d.
The modified Trading Plan must have a minimum duration of one year from the time when trades may first occur under the modified plan in accordance with these requirements.
10.
The person adopting the Trading Plan shall not have any other Trading Plan outstanding, except as permitted under Rule 10b5-1(c)(1)(ii)(D).
11.
Within the one year preceding the modification or adoption of a Trading Plan, a person may not have otherwise modified or adopted a plan more than once.
12.
If the person that adopted the Trading Plan terminates the plan prior to its stated duration, he or she may not trade in the Company’s securities until after the later of (a) the commencement of the next Trading Window and (b) 30 calendar days after termination.
13.
The Company must be promptly notified of any modification or termination of the Trading Plan, including any suspension of trading under the plan.
14.
The Company must have authority to require the suspension or cancellation of the Trading Plan at any time.
15.
The person adopting the Trading Plan must not exercise any subsequent influence over how, when or whether the purchases or sales are made. If the Trading Plan grants discretion to a broker or other person with respect to the execution of trades under the plan:
a.
trades made under the Trading Plan must be executed by someone other than the broker or other person that executes trades in other securities for the person adopting the Trading Plan;
b.
the person adopting the Trading Plan may not confer with the person administering the Trading Plan regarding the Company or its securities; and
c.
the person administering the Trading Plan must provide prompt notice to the Company of the execution of a transaction pursuant to the plan.
16.
All transactions under the Trading Plan must be in accordance with applicable law.
17.
The Trading Plan (including any modified Trading Plan) must meet such other requirements as the Compliance Officer may determine.
18.
The Trading Plan must be submitted to the Company’s Compliance Officer with an executed certificate stating that the Trading Plan complies with Rule 10b5-1 and the criteria set forth above.
EX-12.1
5
jfin-ex12_1.htm
EX-12.1
EX-12.1
Exhibit 12.1
Certification by Chief Executive Officer
Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
I, Dinggui Yan, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this annual report on Form 20-F of Jiayin Group Inc. (the “Company”);
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the Company as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The Company’s other certifying officers and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the Company and have:
(a)
Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the Company, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b)
Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c)
Evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d)
Disclosed in this report any change in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by the annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting; and
5. The Company’s other certifying officers and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the Company’s auditors and the audit committee of the Company’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a)
All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the Company’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b)
Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
|
|
|
Date: April 28, 2025 |
|
|
By: |
|
/s/ Dinggui Yan |
Name: |
|
Dinggui Yan |
Title: |
|
Chief Executive Officer |
EX-12.2
6
jfin-ex12_2.htm
EX-12.2
EX-12.2
Exhibit 12.2
Certification by Chief Financial Officer
Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
I, Chunlin Fan, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this annual report on Form 20-F of Jiayin Group Inc. (the “Company”);
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the Company as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The Company’s other certifying officers and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the Company and have:
(a)
Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the Company, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b)
Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c)
Evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d)
Disclosed in this report any change in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by the annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting; and
5. The Company’s other certifying officers and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the Company’s auditors and the audit committee of the Company’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a)
All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the Company’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b)
Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
|
|
|
|
Date: April 28, 2025
|
|
|
By: |
|
/s/ Chunlin Fan |
Name: |
|
Chunlin Fan |
Title: |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
EX-13.1
7
jfin-ex13_1.htm
EX-13.1
EX-13.1
Exhibit 13.1
Certification by Chief Executive Officer
Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
In connection with the annual report of Jiayin Group Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2024 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Dinggui Yan, Chief Executive Officer of the Company, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to my knowledge:
1.
The Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
2.
The information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: |
|
April 28, 2025 |
|
|
By: |
|
/s/ Dinggui Yan |
Name: |
|
Dinggui Yan |
Title: |
|
Chief Executive Officer |
EX-13.2
8
jfin-ex13_2.htm
EX-13.2
EX-13.2
Exhibits 13.2
Certification by Chief Financial Officer
Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
In connection with the annual report of Jiayin Group Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2024 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Chunlin Fan, Chief Financial Officer of the Company, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to my knowledge:
1.
The Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
2.
The information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: |
|
April 28, 2025 |
|
|
By: |
|
/s/ Chunlin Fan |
Name: |
|
Chunlin Fan |
Title: |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
EX-15.1
9
jfin-ex15_1.htm
EX-15.1
EX-15.1
Exhibit 15.1

INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM’S CONSENT
We consent to the incorporation by reference in the Registration Statement of Jiayin Group Inc. on Form F-3 (FILE NO. 333-279990) and Form S-8 (FILE NO. 333-233615) of our report dated April 28, 2023, with respect to our audit of the consolidated financial statements of Jiayin Group Inc. for the year ended December 31, 2022 appearing in the Annual Report on Form 20-F of Jiayin Group Inc. for the year ended December 31, 2024.
/s/ Marcum Asia CPAs LLP
Marcum Asia CPAs LLP
New York, New York
April 28, 2025
NEW YORK OFFICE • 7 Penn Plaza • Suite 830 • New York, New York • 10001
Phone 646.442.4845 • Fax 646.349.5200 • www.marcumasia.com Jiayin Group Inc. 18th Floor, Building No. 1, Youyou Century Plaza 428 South Yanggao Road, Pudong New Area Shanghai 200122 People’s Republic of China
EX-15.2
10
jfin-ex15_2.htm
EX-15.2
EX-15.2

Our ref SQG/745172-000001/31562556v2
28 April 2025
Dear Sirs
Jiayin Group Inc.
We have acted as legal advisers as to the laws of the Cayman Islands to Jiayin Group Inc., an exempted company incorporated in the Cayman Islands with limited liability (the “Company”), in connection with the filing by the Company with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) of an annual report on Form 20-F for the year ended 31 December 2024 (the “Annual Report”).
We hereby consent to the reference to our firm under the heading “Item 10. Additional Information—E. Taxation—Cayman Islands Taxation” in the Annual Report. We further consent to the incorporation by reference of the summary of our opinion under the heading “Item 10. Additional Information—E. Taxation—Cayman Islands Taxation” in the Annual Report, into (a) the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (No. 333-233615) pertaining to the Company’s 2019 Share Incentive Plan, and (b) the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-3 (No. 333-279990).
We consent to the filing with the SEC of this consent letter as an exhibit to the Annual Report. In giving such consent, we do not thereby admit that we come within the category of persons whose consent is required under Section 7 of the Securities Act of 1933, or under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, in each case, as amended, or the regulations promulgated thereunder.
Yours faithfully
/s/ Maples and Calder (Hong Kong) LLP
Maples and Calder (Hong Kong) LLP 18th Floor, Building No.

EX-15.3
11
jfin-ex15_3.htm
EX-15.3
EX-15.3
April 28, 2025
Jiayin Group Inc.
1, Youyou Century Plaza
428 South Yanggao Road, Pudong, New Area, Shanghai 200122
People’s Republic of China
Attention: The Board of Directors
Dear Sirs or Madam,
Re: Jiayin Group Inc.
We, King & Wood Mallesons, consent to the reference to our firm under the captions of “Item 3. Key Information—Approvals Required from the PRC Authorities for Offering Securities to Foreign Investors” “Item 3.D—Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure” “Item 4.C—Organizational Structure” and “Item 10.E—Taxation—People’s Republic of China Tax Considerations” in the annual report of Jiayin Group Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2024 (the “Annual Report”), which will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof. We further consent to the incorporation by reference of the summary of our opinion under the captions of “Item 3. Key Information—Approvals Required from the PRC Authorities for Offering Securities to Foreign Investors” “Item 3.D—Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Corporate Structure” “Item 4.C—Organizational Structure” and “Item 10.E—Taxation—People’s Republic of China Tax Considerations” in the Annual Report into (a) the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (No. 333-233615) pertaining to the Company’s 2019 Share Incentive Plan, and (b) the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-3 (No. 333-279990).
In giving such consent, we do not thereby admit that we come within the category of persons whose consent is required under Section 7 of the Securities Act of 1933, or under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, in each case, as amended, or the regulations promulgated thereunder.
Yours faithfully,
/s/ King & Wood Mallesons We consent to the incorporation by reference in Registration Statement No.
King & Wood Mallesons

EX-15.4
12
jfin-ex15_4.htm
EX-15.4
EX-15.4
Exhibit 15.4

CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
333-279990 on Form F-3 and Registration Statement No. 333-233615 on Form S-8 of our reports dated April 28, 2025, relating to the financial statements of Jiayin Group Inc. and the effectiveness of Jiayin Group Inc.'s internal control over financial reporting appearing in this Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2024.
/s/ Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Certified Public Accountants LLP
Shanghai, China
April 28, 2025












