r
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, DC 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
☒ |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024
OR
☐ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 001-39603
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in its Charter)
Delaware |
84-3898466 |
|
( State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer |
|
4660 La Jolla Village Drive, Suite 100, San Diego, CA |
92122 |
(Address of principal executive offices) |
(Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (650) 800-3717
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class |
|
Trading Symbol(s) |
|
Name of each exchange on which registered |
Common stock, par value $0.001 per share |
|
REVB |
|
The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC |
Redeemable warrants, each exercisable for a 1/16,800th share of common stock at an exercise price of $193,200.00 per share |
|
REVBW |
|
The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer |
|
☐ |
|
Accelerated filer |
|
☐ |
Non-accelerated filer |
|
☒ |
|
Smaller reporting company |
|
☒ |
Emerging growth company |
|
☐ |
|
|
|
|
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☐
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant was $3,131,850 as of June 30, 2024.
As of March 3, 2025, the registrant had 905,228 shares of common stock, $0.001 par value per share, outstanding.
EXPLANATORY NOTE
On January 28, 2025, we effected the approved 1-for-16 reverse stock split of our outstanding shares of common stock.
On January 25, 2024, we effected the approved 1-for-30 reverse stock split of our outstanding shares of common stock.
On February 1, 2023, we effected the approved 1-for-35 reverse stock split of our outstanding shares of common stock.
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report contains forward-looking statements as defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended. Forward-looking statements are statements that are not historical facts. These forward-looking statements are generally identified by the words “anticipate”, “believe”, “expect”, “estimate”, “plan”, “outlook”, and “project” and other similar expressions. We caution investors that forward-looking statements are based on management’s expectations and are only predictions or statements of current expectations and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause actual results to be materially different from those anticipated by the forward-looking statements. Revelation cautions readers not to place undue reliance on any such forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date they were made. The following factors, among others, could cause actual results to differ materially from those described in these forward-looking statements: the ability of Revelation to meet its financial and strategic goals, due to, among other things, competition; the ability of Revelation to grow and manage growth profitability and retain its key employees; the possibility that the Revelation may be adversely affected by other economic, business, and/or competitive factors; risks relating to the successful development of Revelation’s product candidates; the ability to successfully complete planned clinical studies of its product candidates; the risk that we may not fully enroll our clinical studies or enrollment will take longer than expected; risks relating to the occurrence of adverse safety events and/or unexpected concerns that may arise from data or analysis from our clinical studies; changes in applicable laws or regulations; expected initiation of the clinical studies, the timing of clinical data; the outcome of the clinical data, including whether the results of such study is positive or whether it can be replicated; the outcome of data collected, including whether the results of such data and/or correlation can be replicated; the timing, costs, conduct and outcome of our other clinical studies; the anticipated treatment of future clinical data by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”), the European Medicines Agency (“EMA”) or other regulatory authorities, including whether such data will be sufficient for approval; the success of future development activities for its product candidates; potential indications for which product candidates may be developed; the potential impact that global health crises may have on Revelation’s suppliers, vendors, regulatory agencies, employees and the global economy as a whole; the ability of Revelation to maintain the listing of its securities on NASDAQ; the expected duration over which Revelation’s balances will fund its operations; and other risks and uncertainties described herein, as well as those risks and uncertainties discussed from time to time in other reports and other public filings with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) by Revelation.
Risk Factors Summary
Risks Related to Our Business
Risks Related to the Product Development, Regulatory Approval, Manufacturing and Commercialization of Our Program Products and Product Candidates
i
Risks Related to our Reliance on Third Parties
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
Risks Related to Our Business Operations
General Risk Factors
We are subject to several other risks of which other public companies are subject, including without limitation, the volatility of our common stock price; our ability to comply with corporate governance laws and financial reporting standards; and our ability to maintain an effective system of internal controls.
ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
|
Page |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1. |
1 |
|
Item 1A. |
26 |
|
Item 1B. |
60 |
|
Item 1C. |
60 |
|
Item 2. |
60 |
|
Item 3. |
60 |
|
Item 4. |
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 5. |
61 |
|
Item 6. |
61 |
|
Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
62 |
Item 7A. |
68 |
|
Item 8. |
68 |
|
Item 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
68 |
Item 9A. |
69 |
|
Item 9B. |
69 |
|
Item 9C. |
Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections |
69 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 10. |
70 |
|
Item 11. |
74 |
|
Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
81 |
Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
83 |
Item 14. |
83 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 15. |
84 |
|
Item 16. |
86 |
|
iii
PART I
References in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, unless otherwise noted, “we,” “us,” “our,” “Revelation” and the “Company” refer to Revelation Biosciences, Inc. and its subsidiary.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS.
Overview
Revelation is a clinical-stage life science company that is focused on rebalancing inflammation to optimize health using its proprietary formulation Gemini. We have multiple ongoing programs to evaluate Gemini, including GEM-AKI as a prevention for acute kidney injury (“AKI”), GEM-CKD as a treatment for chronic kidney disease (“CKD”), and GEM-PSI as a prevention for post surgical infection (“PSI”). The Company was incorporated in the state of Delaware on November 20, 2019 (originally as Petra Acquisition, Inc.) and is based in San Diego, California.
Our common stock and warrants sold in our initial public offering (“Public Warrants”) are listed on The Nasdaq Stock Market, LLC (“Nasdaq”) under the ticker symbol “REVB” and “REVBW,” respectively.
Recent Developments
2025 Reverse Stock Split
On January 17, 2025, at a special meeting of stockholders, our stockholders approved a Certificate of Amendment to our Third Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation to effect a reverse stock split of our outstanding shares of common stock at a specific ratio within a range of one-for-two (1-for-2) to a maximum of a one-for-fifty (1-for-50) split. Following the special meeting of stockholders and determination by the Board of Directors on the reverse split ratio, we filed a Certificate of Amendment effective on January 28, 2025, which effected a 1-for-16 reverse stock split of our outstanding shares of common stock as of 12:01 a.m. Eastern Standard Time on January 28, 2025.
2024 Reverse Stock Split
On January 17, 2024, at a special meeting of stockholders, our stockholders approved a Certificate of Amendment to our Third Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation to effect a reverse stock split of our outstanding shares of common stock at a specific ratio within a range of one-for-two (1-for-2) to a maximum of a one-for-fifty (1-for-50) split. On January 22, 2024, we filed the Certificate of Amendment which effected a 1-for-30 reverse stock split of our outstanding shares of common stock as of 12:01 a.m. Eastern Standard Time on January 25, 2024.
2023 Change in Authorized Shares and Reverse Stock Split
On January 30, 2023, at a special meeting of stockholders, our stockholders approved a Certificate of Amendment to our Third Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation to change the authorized common stock from 100,000,000 to 500,000,000 shares and effect a reverse stock split of our outstanding shares of common stock at a specific ratio within a range of one-for-twenty (1-for-20) to a maximum of a one-for-one hundred (1-for-100) split. On January 30, 2023, we filed the Certificate of Amendment which set the authorized common stock to 500,000,000 and effected a 1-for-35 reverse stock split of our outstanding shares of common stock as of 12:01 a.m. Eastern Standard Time on February 1, 2023.
1
Business Strategy and Pipeline
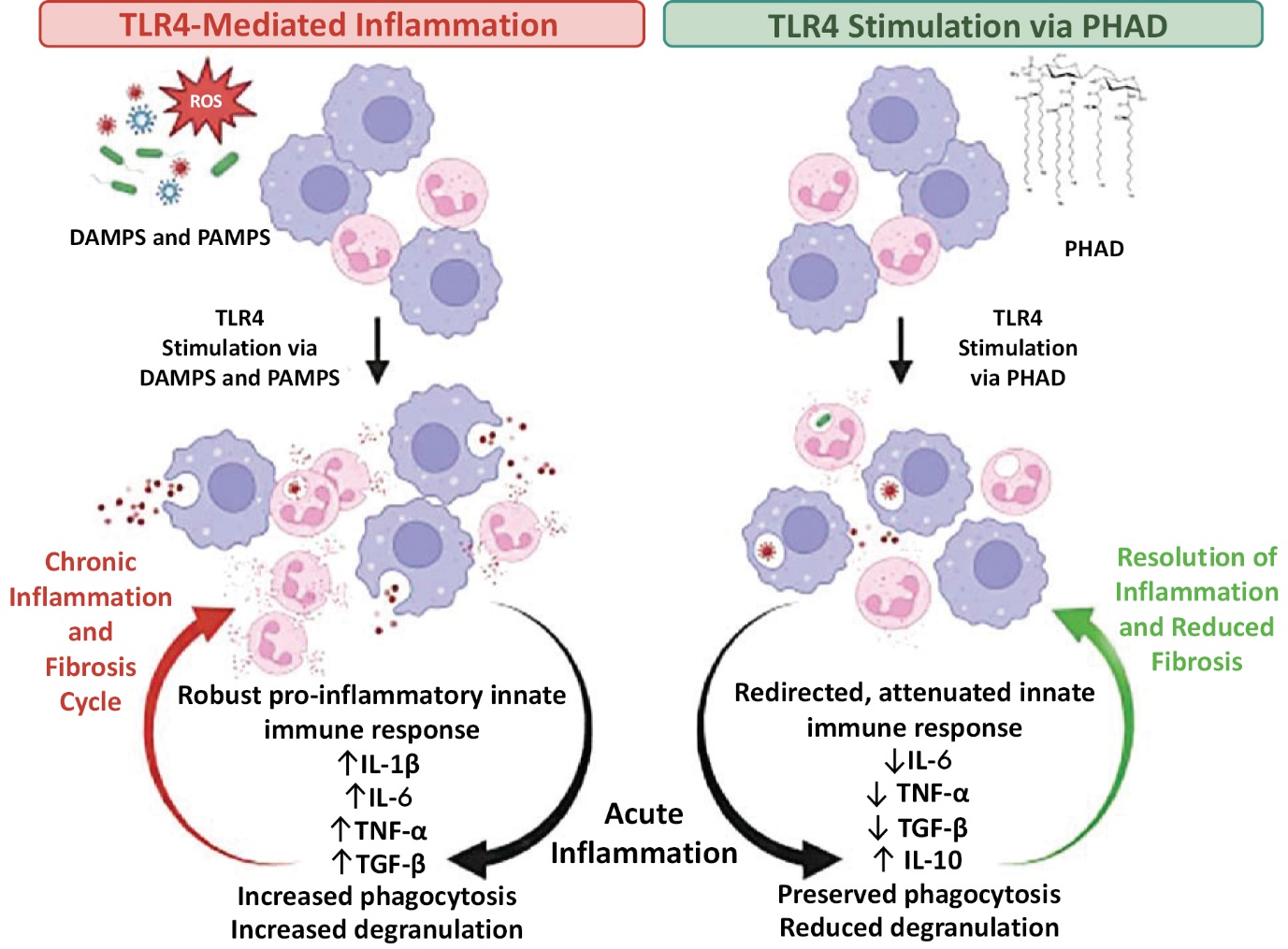
Revelation is developing a pipeline of potential high-value products based on Gemini. Gemini is Revelation’s proprietary formulation of phosphorylated hexaacyl disaccharide (“PHAD®”) an established Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4”) agonist that can stimulate the human body’s innate immune response to prevent and treat disease. Our current Gemini based programs consist of: Gemini-AKI, which is being developed for the prevention of AKI; Gemini-CKD for the treatment of CKD; and Gemini-PSI, which is being developed for the prevention of PSI. Revelation’s pipeline is summarized in the figure below:

The Gemini Platform
Our current therapeutic candidates are all based on our proprietary Gemini formulation of PHAD®, a synthetic version of monophosphoryl lipid A (“MPLA”), that is known to stimulate TLR4. Stimulation of TLR4 via Gemini leads to a more controlled production of varied cytokines and chemokines which modulate the activity of the innate and adaptive immune response, relative to a lipopolysaccharide, a traditional TLR4 agonist. This “Immunostimulatory Preconditioning” with Gemini prepares the body to better guard against a rapid upregulation of multiple pro-inflammatory and microbial gene products and proteins, such as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (“PAMPS”) and damage-associated molecular patterns (“DAMPS”) (damage-associated molecular proteins) (Zwirner 2017, Hernandez 2019, Ismaeli 2002). Modulated activities may include stimulation and recruitment of infection fighting immune cells, reduction of inflammation, and/or regulation of inflammation depending on the degree and nature of the stimulation, which enables the multiple potential product candidates in development.
2
Figure 1: Interaction of PHAD with TLR4
Gemini-AKI
The Gemini-AKI program is being developed as a potential therapy for the prevention of AKI due to external stress or insult (e.g. surgical procedure, chemotherapy toxicity). We believe immunologic preconditioning with Gemini prepares the body to handle biologic stress by redirecting the body’s immune system to have an attenuated response to the stress.
Preclinical studies have demonstrated that preconditioning with PHAD significantly reduces the severity and duration of AKI following an ischemia of the kidney. Additional data from these preclinical studies have been accepted for presentation at The International Conference on Advances in Critical Care Nephrology on March 12, 2024.
During 2024 we conducted a Phase 1 clinical study. safety and biomarker activity data from our Phase 1 clinical study was announced in June of 2024, showing a significant increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL-1RA and IL-10. In January of 2025 we announced the start of our Phase 1b clinical study in CKD patients. The Phase 1b clinical study will support further development of Gemini-AKI. We expect data from our Phase 1b clinic study in the first half of this year.
Gemini-CKD
The Gemini-CKD program is being developed as a potential therapy for preventing the progression of CKD. We believe Gemini may modulate the immune response from a pro-inflammatory state to an anti-inflammatory (protective) state to rebalance the innate immune response and slow down or halt the progressive destruction and scarring of organ tissue, allowing the healing process to take place.
Preclinical studies have demonstrated that Gemini significantly reduces the degree of scar tissue formation in a hyperinflammatory kidney injury model.
In January of 2025 we announced the start of our Phase 1b clinical study in CKD patients. The Phase 1b clinical study will support further development of Gemini-CKD. We expect data from our Phase 1b clinic study in the first half of this year.
3
Gemini-PSI
The Gemini-PSI program is being developed, through a license agreement with Vanderbilt University, as a potential therapy for the prevention or treatment of surgical site infection. We believe immunologic preconditioning with Gemini prepares the body to resist infection by priming the body’s immune system to better and more rapidly respond to pathogen exposure.
Multiple preclinical studies have shown that systemic pretreatment with PHAD results in a significantly augmented immune response leading to significantly reduced duration and severity of infection following bacterial challenge with either gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria.
Our Strategy
Our goal is to become a leading biopharmaceutical company focused on the development of therapeutics that modulate the immune system to prevent and treat conditions with significant unmet needs. The key components of our strategy are to:
Our Corporate History and Team
The Company was incorporated in the state of Delaware on November 20, 2019 (originally as Petra Acquisition, Inc.) and is based in San Diego, California. We have assembled a management team of biopharmaceutical experts with extensive experience in drug development, manufacturing and commercialization of pharmaceutical products along with broad experience in building companies from inception, including La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company, Pluromed, Inc., and Horizon Pharma, Inc. We are also supported by a group of directors and leading investors whose collective experience will assist us in realizing our corporate strategy.
BACKGROUND
Acute Kidney Injury Overview
AKI, also known as acute renal failure, is defined as a rapid loss of kidney function. AKI causes a build-up of waste products in blood and makes it more difficult for kidneys to maintain the correct balance of fluid in the body. AKI can also have a significant impact on other organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs.
Due to its severe nature, AKI represents a significant and increasingly frequent health problem, especially in patients with co-morbidities such as diabetes. Approximately 1% of all hospitalized patients present with AKI upon admission. Of these hospitalizations, rates of AKI increased 165% and 114% for diabetic men and women, respectively from the years 2000 to 2014 (Goyal 2023, Pavkov 2018). During all hospitalizations, the approximate incidence of AKI is 2 to 5%. Development of AKI is even more prevalent in patients admitted to the intensive care unit, occurring in up to 67% of patients admitted (Pavkov 2018, Workeneh 2022).
AKI can develop as a result of many different causes including decreased blood flow to the kidneys, direct damage to the kidneys, or blockage of urine flow through the kidney. AKI inducing events may include shock (low blood pressure), blood or fluid loss (such as bleeding, severe diarrhea), heart attack, heart failure, and other conditions leading to decreased heart function, organ failure (e.g., heart, liver), overuse of pain medicines such as NSAIDs, severe allergic reactions, burns, injury, infection (sepsis), cancer, toxicity (e.g., chemotherapies), hereditary factors, or major surgery.
AKI is of particular concern after cardiac surgery. Published evidence suggests that even slight postoperative increases in serum creatinine levels are associated with a significant increase in the risk of death. Up to 31% of patients undergoing cardiac surgery with no prior CKD develop post operative AKI with a high mortality rate. The average cost to treat AKI is about $42,600 and results in an approximate 4-7 day increase in hospitalization duration (Lysak 2017).
In this surgical setting, ischemia may be initiated intentionally, such as during a procedure that requires cardiopulmonary bypass. Alternatively, ischemia may be the unintentional result of an untoward complication such as intraoperative hypotension. Regardless of etiology, the ischemic event initially leaves the affected area(s) deprived of blood, oxygen, and other nutrients which then can exacerbate to injury when the blood supply returns to the site along with reactive oxygen species and other constituents that cause oxidative stress to the tissues.
There are no approved therapies for preventing AKI, including AKI due to cardiac surgery.
4
Chronic Kidney Disease Overview
Organ damage, due to chronic disease, is a pervasive problem in the United States and world-wide. Organ disease (due to chronic inflammation and subsequent fibrosis, for example) is progressive and ultimately results in loss of function of the organ. Examples of chronic organ and tissue disease include CKD through end-stage renal disease, liver diseases such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, pulmonary fibrotic disease, heart disease, pancreatitis, cancer, and irritable bowel syndrome.
Kidney disease is a major public health problem, affecting ~10% of populations in industrialized countries. AKI, which affects 13.3 million people per year, may lead to CKD. Both AKI and CKD are increasing worldwide. Progression of chronic kidney damage often leads to end stage renal disease with the need for renal replacement therapy (dialysis or transplantation), resulting in significant morbidity and mortality for affected patients.
CKD can be initiated and propagated in several ways. One prevalent condition is the high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes (either Type 1 or Type 2). High blood sugar is toxic to kidney cells creating stress which imitates the inflammatory process leading to the demise of these cells with subsequent fibrosis ultimately resulting in continuous loss of kidney function over time. High arterial blood pressure is another source of stress that initiates the inflammatory process leading to CKD. Other risk factors include heart disease, obesity family history of CKD or older age.
Other causes for CKD include: Glomerulonephritis (inflammation in the glomerulus), polycystic kidney disease, autoimmune diseases (such as systemic lupus erythematosus), vesicoureteral reflux (a condition where urine flows back up to the kidneys), pyelonephritis, interstitial nephritis (inflammation of the tubules), kidney stones, obstruction in kidney or cancer can lead to kidney failure over a period of time, overuse of certain medications, drug (heroin or cocaine) abuse, chemotherapy (such as cisplatin).
Every day more than 360 people begin treatment for kidney failure (dialysis or transplant). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (the “CDC”), more than 1 in 7, that is 15%, of US adults or 37 million people are estimated to have CKD. As many as 9 to 10 adults with CKD as well as about 2 in 5 adults with severe CKD do not know they have the disease. Kidney diseases are the leading cause of death in the United States. The CDC estimates Medicare costs in excess of $87 billion and continues to promote reduced costs including better management of CKD.
Post Surgical Infection Overview
Despite efforts to monitor and prevent infection in hospital care settings, infections arise from a range of different causes including surgery, burn wounds, central line catheters or urinary catheters, and sepsis, as well as long courses of antibiotic treatment, which may lead to the development of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus resistant infection (“MRSA”). According to the most recent prevalence study data published by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention in 2015, approximately 3% of hospital patients suffered at least one infection, and there were approximately 687,000 infection cases in acute care settings resulting in approximately 72,000 deaths. According to the CDC, on any given day about 31 hospital patients has at least one healthcare-associated infection. A World Health Organization cooperative study which included 55 hospitals in 14 countries from four regions, approximately 8.7% of hospitalized patients developed infection within 48 hours of hospitalization (Tikhomirov 1987). The most common healthcare-associated infections are bloodstream infection, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and surgical site infections.
Current Prevention, Treatment, and Detection Options
Prevention and Treatment of AKI
There are currently no therapeutics to prevent or treat AKI. Treatment for AKI requires hospitalization and intensive supportive care until kidney function recovers. In more serious cases, dialysis may be needed to help replace kidney function until kidneys can recover. The main treatment is to address what is causing the acute kidney injury.
Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease
In April 2021, The FDA approved the use of Farxiga (Dapagliflozin) to reduce the risk of kidney function decline, kidney failure, cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adults who are at risk of disease progression. Farxiga was originally approved in 2014 for diabetic control in adults in addition to diet and exercise.
In addition to the approved drug, other treatments include lifestyle changes to control health and weight, medications to control associated diseases such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol and for later stages, filtering the blood with a machine known as dialysis. Avoiding conditions or exposures that can harm the kidneys like certain medications or kidney infections is also beneficial.
Still, at this time, there is a significant unmet need for therapies that slow disease progression and improve outcomes of patients with chronic kidney disease.
5
Prevention of Post Surgical Infection
There are no approved therapies currently available for the prevention of infection outside of pre- and post-surgical administration of antibiotics and commonly recommended procedures for the preventing the transmission of bacteria including hand washing, mask wearing, and cleaning the surgical site pre- and post-surgery.
In the case of antibiotic pretreatment, the typical course of treatment may require an initial empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic, later targeted to an organism if detected, with consideration for the presence of multidrug resistant pathogens, specifically MRSA. Antibiotic resistance has become a major consideration in the need for pretreatment of yet-to-be diagnosed infections, as the number of antibiotic resistant strains have increased, and the over prescription of antibiotics further contributes to resistance.
REVELATION’S PROGRAMS
Gemini Platform
Our current therapeutic candidates are all based on Gemini, our proprietary formulation of PHAD®, a synthetic version of MPLA, that is known to stimulate the innate immune response via TLR4.
The innate immune system is our first line of defense against stress such as trauma, infection and acute and chronic disorders. The innate immune system responds to stress (e.g. infection) by producing and releasing various types of cytokines. Cytokines are proteins that direct different activities in cells and can be inflammatory or protective, meaning they may be able to modulate certain established cellular activities. Toll-like receptors serve a vital role in initiating the innate immune system response by recognizing different molecular patterns associated with pathogens such as bacteria and viruses (e.g. PAMPS: pathogen associated molecular patterns) as well as tissue damage (e.g. DAMPS: damage associated molecular patterns).
Revelation believes immunostimulatory preconditioning with Gemini prepares the body to respond better to stress due to infection, trauma, or other acute and chronic disorders. Modulated activities may include stimulation and recruitment of infection fighting immune cells, reduction of inflammation, and/or regulation of inflammation depending on the degree and nature of the stimulation which enables the multiple potential product indications in development.
6
Figure 1: Interaction of PHAD with TLR4

Source: Revelation Biosciences
Gemini-AKI Program
Overview
Gemini is being evaluated as a potential therapy for the prevention of AKI due to external stress (e.g. surgical procedure, chemotherapy toxicity). We believe immunologic preconditioning with Gemini prepares the body to handle biologic stress by directing the body’s immune system to have an attenuated response to the stress. Gemini is being evaluated as a potential therapy for the prevention of AKI.
Preclinical
Preclinical studies have shown that pretreatment with PHAD results in significantly decreased severity and duration of acute kidney injury due to ischemia.
7
PHAD Pretreatment Reduces AKI in a Unilateral Ischemia/Reperfusion Model1
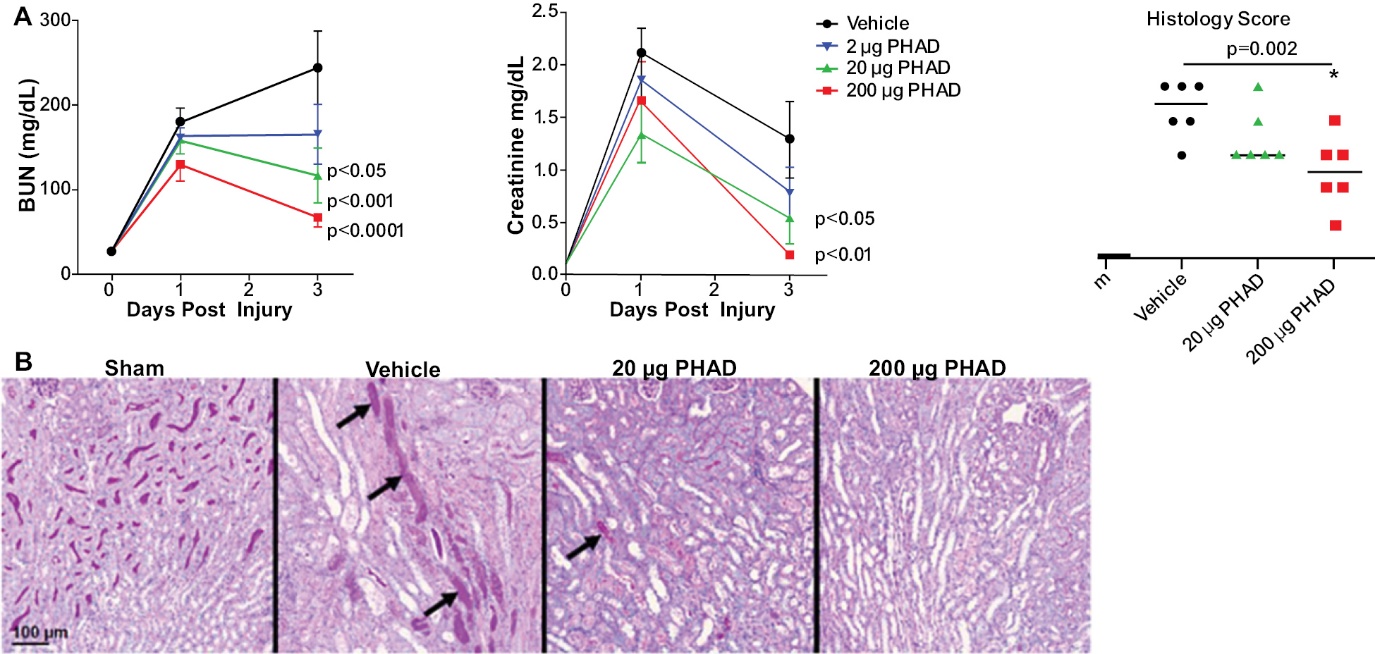
____________
1 Mice pretreated with intravenous PHAD at 2, 20, and 200 µg/mouse or vehicle control, 48 and 24 hours prior to undergoing right nephrectomy followed by clamping of the left renal pedicle for 28 minutes. A) Blood was analyzed for BUN and creatinine at baseline (D0), and post-injury day 1 and 3. Results expressed as means +/-SEM with N = 8. Two-way ANOVA was used to compare differences between PHAD- and vehicle-treated mice over time, with p values indicated; B) Representative images of periodic acid-Schiff staining (PAS) sections of the outer medulla at Day 3 after injury in sham, vehicle- and PHAD-treated mice. Arrows point to casts within the collecting tubules. Scale bar, 100 µm. N = 6. C) Pretreatment with PHAD reduced tubular injury in a dose dependent manner as visualized (PAS). Source: Hernandez A, Patil N, et. al. Pretreatment with a novel Toll-like receptor 4 agonist attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology 2023 324:5, F472 – F482
PHAD Pretreatment Reduces AKI in a Bilateral Ischemia/Reperfusion Model

Mice were pretreated with intravenous PHAD at 200 µg/mouse or vehicle control, 48 and 24 hours prior to undergoing bilateral renal pedicle clamping for 24 minutes. A) Blood was analyzed for BUN and creatinine at baseline (0), and post-injury day 1 and 3. Results expressed as means +/-SEM with N = 10. Two-way ANOVA was used to evaluate between group differences over time (p <0.05 for both BUN and serum creatinine), with p values shown after Sidak’s correction for multiple post hoc between group comparisons at each time point; B) Tubular injury scores in the outer stripe of the outer medulla from PAS-stained sections Day 3 after injury; C) Apoptosis in the outer stripe of the outer medulla from TUNEL stained sections Day 3 after injury. N = 6-7. Source: Hernandez A, Patil N, et. al. Pretreatment with a novel Toll-like receptor 4 agonist attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology 2023 324:5, F472 – F482.
8
Clinical Development Plan
During 2024 we conducted a Phase 1 clinical study. Subsequently, safety and biomarker activity data from our Phase 1 clinical study was announced in June of 2024, showing a significant increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL-1RA and IL-10. In January of 2025 we announced the start of our Phase 1b clinical study in CKD patients. The Phase 1b clinical study will support further development of Gemini-AKI. We expect data from our Phase 1b clinic study in the first half of this year.
The Phase 1b study in CKD patients will be followed by a Phase 1b study in patients undergoing cardiac surgery to establish dose and dosing regimen in preparation for Phase 2. The primary readout will be safety with exploratory endpoints to evaluate biomarkers and rate, duration, and severity of AKI.
Gemini-CKD Program
Overview
Gemini is being evaluated as a potential therapy for preventing the progression of CKD. We believe Gemini may modulate the immune response from a pro-inflammatory state to an anti-inflammatory (protective) state to rebalance the innate immune response and slow down or halt the progressive destruction and scarring of organ tissue, allowing the healing process to take place.
Preclinical
Revelation conducted a nonclinical study to evaluate the potential of Gemini to prevent kidney fibrosis due to excess inflammation. Specifically, a range of daily systemic dosing levels of Gemini were tested in a rat unilateral urethral obstruction (“UUO”) model. The UUO model is appropriate for studying the anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of potential new therapies for acute and chronic kidney disease as complete ureteral obstruction of one kidney results in significant inflammation and subsequent fibrosis of the obstructed kidney over a 7-day period.
The present study consisted of 6 groups with the following outcomes on renal cortical fibrosis as measured by detection of collagen deposition using picrosirius red stained histology sections assessed at three different sampling depths.
Gemini Treatment Reduces Fibrosis in Acute and Chronic Kidney Model (UUO in Rats)

Rats (n=11-12 per treatment group) were subjected to the UUO surgical procedure. Animals were administered either vehicle (Sham, UUO, and Positive control) or Gemini (doses listed are for active ingredient) on days 1-7 post surgery. Kidneys were harvested and analyzed at the end of the treatment period. Composite data represents the average of 3 anatomically distinct depths (10 images/depth/rat/group = ~60-65% of renal cortical area). Treatment with Gemini resulted in a significant dose-dependent reduction in fibrosis. The high dose group (0.9 mg/kg) reduced new collagen deposition (fibrosis) by 58% vs new collagen deposition observed in the no treatment UUO group (normalized to sham group, n=6).
9
Gemini Antifibrotic Effects Likely Mediated by Validated Target Cytokines

Gemini reduced TGF-β and increased IL-10 and NGAL in a dose dependent manner. TGF-β is pro-fibrotic and is directly linked to the propagation of fibrosis. The positive control is an established TGF-β blocker. IL-10 is a key driver for the reduction and resolution of inflammation, and NGAL is an important defense for preventing excessive oxidative damage resulting from injury/ongoing inflammation.
Development Plan
In January of 2025 we announced the start of our Phase 1b clinical study in CKD patients. The Phase 1b clinical study will support further development of Gemini-AKI. We expect data from our Phase 1b clinic study in the first half of this year.
Revelation will continue evaluating the potential of Gemini in additional preclinical models of CKD to identify optimal dosing conditions and conduct the preclinical testing required for chronic dosing in patients.
Gemini-PSI Program
Overview
Gemini is being evaluated as a potential therapy for the prevention or treatment of post surgical infection. We believe immunologic preconditioning with Gemini prepares the body to resist infection by priming the body’s immune system to respond to pathogen exposure more rapidly. In addition to post surgical infection, we believe Gemini may also have utility for post-burn infection, urinary tract infection (e.g. as a result of hospital-based or outpatient catheterization), sepsis, and antibiotic-resistant infection. Revelation is developing Gemini for the prevention of infection through a license agreement with Vanderbilt University.
Preclinical studies
Multiple preclinical studies have shown that pretreatment with PHAD results in significantly augmented immune response with significantly reduced duration and severity of infection following bacterial challenge with either gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria as indicated in the following figures.
10
Pretreatment with PHAD Impart Protection from Gram Negative Bacterial Infection
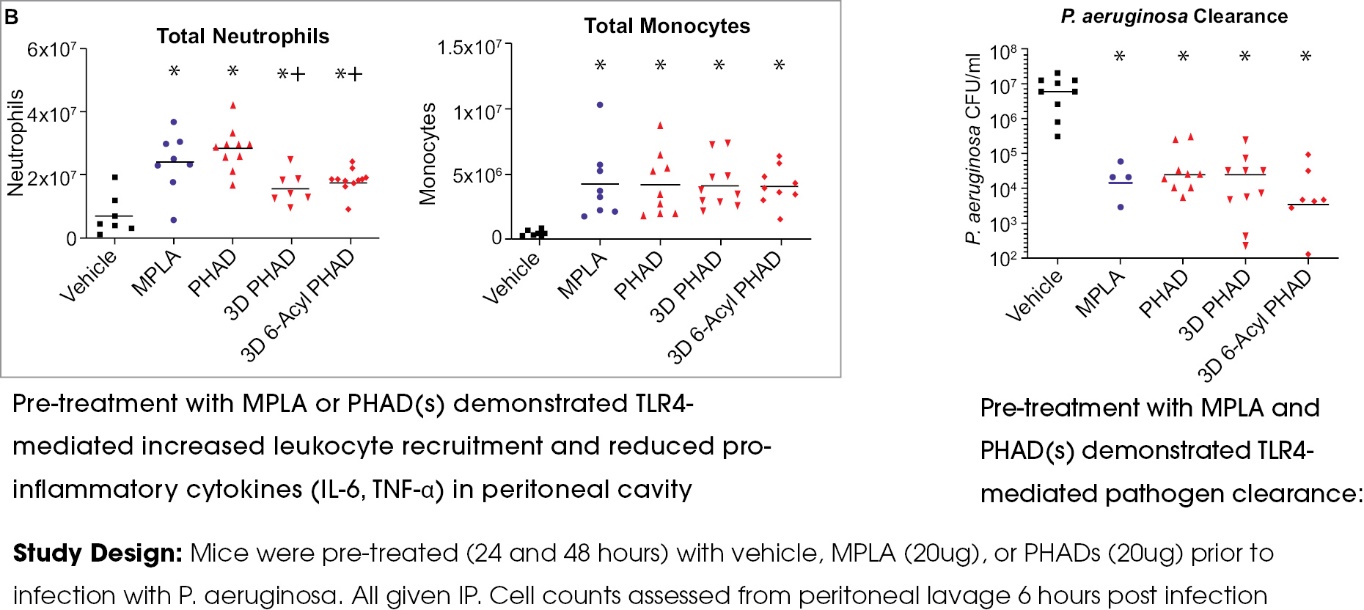
Pretreatment with PHADs Impart Protection from Gram Positive Bacterial Infection

Clinical Development Plan
During 2024 we conducted a Phase 1 clinical study. Subsequently, safety and biomarker activity data from our Phase 1 clinical study was announced in June of 2024, showing a significant increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL-1RA and IL-10. We are evaluating the next steps to be taken in the development of Gemini-PSI.
Competition
The biopharmaceutical industry is intensely competitive and subject to rapid innovation and significant technological advancements. We believe the key competitive factors that will affect the development and commercial success of our Gemini based programs and any future Program Product candidates are efficacy, safety and tolerability profile, reliability, convenience of dosing, price, the level of generic competition, and reimbursement. Our competitors include multinational pharmaceutical companies, specialized biotechnology companies, universities, and other research institutions. A number of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies are pursuing the development or marketing of pharmaceuticals that target the same diseases that we are targeting. Smaller or earlier-stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large, established companies. Given the high incidence of AKI and CKD, and the rate of surgical site infections, it is likely that the number of companies seeking to develop products and therapies for the prevention or treatment of such, will increase.
If Gemini-AKI is approved for prevention of acute kidney injury, we would face competition that could arise from products currently in development.
11
If Gemini-CKD is approved for treatment of chronic kidney disease, we would face competition from currently approved and marketed products including Farxiga®. We would also have future competition that could arise from products currently in development.
If Gemini-PSI is approved for prevention of surgical site infection, we would face competition from currently approved and marketed products including many antibiotics that are effective against non-resistant strains of bacteria. We would also have future competition that could arise from products currently in development.
Many of our competitors have substantially greater financial, technical, human, and other resources than we do and may be better equipped to develop, manufacture, and market technologically superior products. Mergers and acquisitions in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of competitors. In addition, many of these competitors have significantly longer operating histories and greater experience than we have in undertaking preclinical studies and human clinical studies of new pharmaceutical products and in obtaining regulatory approvals of human therapeutic products. Many of our competitors have established distribution channels for the commercialization of their products, whereas we have no such channel or capabilities. In addition, many competitors have greater name recognition and more extensive collaborative relationships. As a result, our competitors may obtain regulatory approval of their products more rapidly than we do or may obtain patent protection or other intellectual property rights that limit our ability to develop or commercialize our Program Products or any future product candidates. Our competitors may also develop and succeed in obtaining approval for drugs that are more effective, more convenient, more widely used and less costly or have a better safety profile than our products and these competitors may also be more successful than we are in manufacturing and marketing their products. If we are unable to compete effectively against these companies, then we may not be able to commercialize our product candidate or any future product candidates or achieve a competitive position in the market. This would adversely affect our ability to generate revenue. Our competitors also compete with us in recruiting and retaining qualified scientific, management and commercial personnel, establishing clinical study sites and enrolling patients for clinical studies, as well as in acquiring technologies complementary to, or necessary for, our programs.
Manufacturing and Supply
We do not own or operate manufacturing facilities for the production of our Program Products or any other product candidates, nor do we have plans to develop our own manufacturing operations in the foreseeable future. We currently rely, and expect to continue to rely, on third parties for the manufacturing of our Program Products or any other product candidates for preclinical and clinical testing, as well as for commercial manufacturing if Gemini or any future product candidate receives marketing approval. Also, there is only one supplier for PHAD®, Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc., with whom we do not have a long-term supply agreement. Currently we have purchased enough material for our planned clinical studies through purchase orders.
Strategic Acquisitions and In-Licensing
We are working to deepen the pipeline of Revelation through both internal organic development of new technologies along with portfolio additions from acquisitions, strategic partnerships and in-licensing of new therapeutic product candidates. From time to time we may enter into discussions regarding potential transactions; however, our focus is on development of our existing pipeline and discussions with third parties to date have not progressed beyond the preliminary stage.
License
On September 29, 2022, we entered into an exclusive worldwide license agreement with Vanderbilt University to develop and commercialize PHAD, for treating or preventing infections. The license grants Revelation the use of issued US patent 11,389,465.
We are obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to (i) develop, commercialize, market and sell licensed products in a manner consistent with a development plan submitted to Vanderbilt by April 2023 and (ii) achieve certain financing, development, regulatory and clinical milestone events, including, among other things, raising $5 million in financing to advance the development program, commencement of various clinical trials by target dates according to the development plan and the filing of an Investigational New Drug Application (“IND”) by the end of 2032.
Under the license agreement we are obligated to make payments to Vanderbilt based upon achievement of certain milestones including achievement of various clinical trial events, regulatory approval and sales levels. In addition, we will pay royalties on sales of products using the licensed patent.
Vanderbilt has the right to terminate the license agreement if the development milestones are not made, subject to a six-month grace period.
12
Sales and Marketing
We currently have no marketing, sales or distribution capabilities. In order to commercialize any products that are approved for commercial sale, we must either develop a sales and marketing infrastructure or collaborate with third parties that have sales and marketing experience.
We may elect to establish our own sales force to market and sell a product for which we obtain regulatory approval if we expect that the geographic market for a product, we develop on our own is limited or that the prescriptions for the product will be written principally by a relatively small number of physicians. If we decide to market and sell any products ourselves, we do not expect to establish direct sales capability until shortly before the products are approved for commercial sale.
We plan to seek third-party support from established pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies for those products that would benefit from the promotional support of a large sales and marketing force. In these cases, we might seek to promote our products in collaboration with marketing partners or rely on relationships with one or more companies with large established sales forces and distribution systems.
Intellectual Property
Our success depends in part on our ability to obtain and maintain proprietary protection for our product candidates, technology, and know-how, to operate without infringing upon the proprietary rights of others and to prevent others from infringing upon our proprietary rights. Our policy is to seek to protect our proprietary position by, among other methods, pursuing and obtaining patent protection in the United States and in jurisdictions outside of the United States related to our proprietary technology, inventions, improvements, and product candidates that are important to the development and implementation of our business. Our patent portfolio is intended to cover our product candidates and components thereof, their methods of use and processes for their manufacture, our kit designs, our proprietary reagents and assays, and any other inventions that are commercially important to our business. We also rely on trade secret protection of our confidential information and know-how relating to our proprietary technology, platforms, and product candidates.
As of March 3, 2025, our patent portfolio includes one patent family directed to MPLA formulations, including Gemini. This patent family includes one U.S. application, one European Patent Organization (“EPO”) application, and one Canadian application. Our portfolio additionally includes a Patent Cooperation Treaty (“PCT”) application directed to methods of using MPLA formulations, including Gemini, as an adjuvant to traditional allergy immunotherapy, such as oral allergy immunotherapy. Regarding our GEM-AKI and GEM-CKD programs, our portfolio also includes a patent family directed to the use of MPLA formulations for the prevention of loss of function associated with acute organ disease and chronic organ disease. This patent family includes one application in the U.S., as well as applications filed in the EPO, China, Japan, South Korea, and Canada. Finally, we have licensed from Vanderbilt University a patent directed to methods of using PHAD for treating or preventing infections.
Our pending and future patent applications may not result in patents being issued which protect our technology or product candidates, or which effectively prevent others from commercializing competitive technologies and product candidates.
Generally, issued patents are granted a term of 20 years from the earliest claimed non-provisional filing date. In certain instances, patent term can be adjusted to recapture a portion of delay incurred by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (the “USPTO”) in examining the patent application (patent term adjustment, or “PTA”) or extended to account for term effectively lost as a result of the FDA regulatory review period (patent term extension, or “PTE”), or both. In addition, we cannot provide any assurance that any patents will be issued from our pending or future applications or that any issued patents will adequately protect our products or product candidates.
We believe that we have certain know-how and trade secrets relating to our technology and product candidates. We rely on trade secrets to protect certain aspects of our technology related to our current and future product candidates. However, trade secrets can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect our trade secrets, in part, by entering into confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors, service providers, and contractors. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems.
Employees
As of March 3, 2025, we had 8 full-time employees and one part-time employee, 5 of whom are engaged in research and development activities or operations and 4 of whom are engaged in general and administrative activities or operations. None of our employees are represented by a labor union or covered by a collective bargaining agreement. We consider our relationship with our employees to be good.
13
Government Regulation
The FDA and other regulatory authorities at federal, state and local levels, as well as in foreign countries, extensively regulate, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, quality control, import, export, safety, effectiveness, labeling, packaging, storage, distribution, recordkeeping, approval, advertising, promotion, marketing, post-approval monitoring and post-approval reporting of drugs. We, along with our vendors, contract research organizations (“CROs”), clinical investigators and contract manufacturing organizations (“CMOs”) will be required to navigate the various preclinical, clinical, manufacturing and commercial approval requirements of the governing regulatory agencies of the countries in which we wish to conduct studies or seek approval of our product candidates. The process of obtaining regulatory approvals of drugs and ensuring subsequent compliance with appropriate federal, state, local and foreign statutes and regulations requires the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources.
In the United States, the FDA regulates drug products under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (“FD&C Act”), its implementing regulations, and other federal, state and local statutes and regulations. Drugs are also subject to other federal, state and local statutes and regulations. If we fail to comply with applicable FDA or other requirements at any time with respect to product development, clinical testing, approval or any other regulatory requirements relating to product manufacture, processing, handling, storage, quality control, safety, marketing, advertising, promotion, packaging, labeling, export, import, distribution, or sale, we may become subject to administrative or judicial sanctions or other legal consequences. These sanctions or consequences could include, among other things, the FDA’s refusal to approve pending applications, issuance of clinical holds for ongoing studies, suspension or revocation of approved applications, warning or untitled letters, product withdrawals or recalls, product seizures, relabeling or repackaging, total or partial suspensions of manufacturing or distribution, injunctions, fines, civil penalties or criminal prosecution.
Our product candidates must be approved for therapeutic indications by the FDA before they may be marketed in the United States. For drug product candidates regulated under the FD&C Act, FDA must approve a New Drug Application (“NDA”). The process generally involves the following:
14
Preclinical studies and the IND process
Preclinical studies include laboratory evaluation of product chemistry and formulation, as well as in vitro and animal studies to assess the potential for adverse events and in some cases to establish a rationale for therapeutic use. The conduct of preclinical studies is subject to federal regulations and requirements, including GLP regulations. An IND sponsor must submit the results of the preclinical tests, together with manufacturing information, analytical data, any available clinical data or literature and a proposed protocol for clinical studies, among other things, to the FDA as part of an IND. An IND is an exemption from the FD&C Act that allows an unapproved product candidate to be shipped in interstate commerce for use in an investigational clinical study and is a request for FDA authorization to administer such investigational product to humans. Such authorization must be secured prior to interstate shipment and administration of any product candidate that is not the subject of an approved application. Some long-term preclinical testing, such as animal tests of reproductive adverse events and carcinogenicity, may continue after the IND is submitted. An IND automatically becomes effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless before that time the FDA raises concerns or questions related to one or more proposed clinical studies and places the study on clinical hold. In such a case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns before the clinical study can begin. As a result, submission of an IND may not necessarily result in the FDA allowing clinical studies to commence.
Clinical studies
Clinical studies involve the administration of the investigational new drug to human subjects — healthy volunteers or patients — under the supervision of qualified investigators in accordance with GCP requirements, which include, among other things, the requirement that all research subjects provide their informed consent in writing before their participation in any clinical study. Clinical studies are conducted under written study protocols detailing, among other things, the objectives of the study, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. A protocol for each clinical study and any subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND. In addition, an IRB at each institution participating in the clinical study must review and approve the plan for any clinical study before it commences at that institution, and the IRB must conduct continuing review and reapprove the study at least annually. The IRB must review and approve, among other things, the study protocol and informed consent information to be provided to study subjects. An IRB may also require the clinical study at the site to be halted, either temporarily or permanently, for failure to comply with the IRB’s requirements, or may impose other conditions. For clinical studies involving an IND, an IRB must operate in compliance with FDA regulations. Additionally, some studies are overseen by an independent group of qualified experts organized by the study sponsor, known as a data safety monitoring board (“DSMB”). This group provides authorization as to whether or not a study may move forward at designated check points based on access that only the DSMB maintains to available data from the study.
Human clinical studies are typically conducted in three sequential phases, which may overlap or be combined:
Progress reports detailing the results of clinical studies involving an IND must be submitted at least annually to the FDA and more frequently if serious adverse events occur. Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical studies may not be completed successfully within any specified period, or at all. Furthermore, the FDA or the sponsor may suspend or terminate a clinical study at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the research subjects are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical study at its institution if the clinical study is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB’s requirements or if the drug or biologic product has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients.
15
Concurrent with clinical studies, the company usually complete additional animal studies, develop additional information about chemistry and physical characteristics of the product candidate, and finalize a process for manufacturing the drug product in commercial quantities in accordance with cGMP requirements. The manufacturing must be capable of consistently producing quality batches of the product candidate and manufacturers must develop, among other things, methods for testing the identity, strength, quality and purity of the final drug product. Additionally, appropriate packaging must be selected and tested, and stability studies must be conducted to demonstrate that the product candidate does not undergo unacceptable deterioration over its shelf life.
In some cases, the FDA may approve an application for a product candidate but require the sponsor to conduct additional clinical studies to further assess the product candidate’s safety and effectiveness after approval. Such post-approval studies are typically referred to as Phase 4 clinical studies. These studies are used to gain additional experience from the treatment of a larger number of patients in the intended treatment group and to further document a clinical benefit in the case of drugs approved under accelerated approval regulations.
U.S. Marketing approval
Assuming successful completion of the required clinical testing, the results of the preclinical and clinical studies, together with detailed information relating to the product’s pharmacology chemistry, manufacture, controls and proposed labeling, among other things, are submitted to the FDA as part of an NDA requesting approval to market the product for one or more indications. FDA approval of the NDA is required before marketing of the product may begin in the United States. Under federal law, the submission of most NDAs is subject to a substantial application user fee, and the sponsor of an approved NDA is also subject to annual product or program fees. These fees may be increased or decreased annually.
The FDA conducts a preliminary review of all NDAs within the first 60 days after receipt before accepting them for filing based on the agency’s threshold determination that they are sufficiently complete to permit substantive review. The FDA may request additional information rather than accept an NDA for filing. In this event, the application must be resubmitted with the additional information, which would also be subject to review before the FDA accepts it for filing. Once the submission is accepted for filing, the FDA begins an in-depth substantive review. The FDA has agreed to specified performance goals in the review of NDAs. Most such applications for non-priority products are reviewed within ten to twelve months after filing, and most applications for priority review products, that is, drugs and biologics that the FDA determines represent a significant improvement over existing therapy, are reviewed in six to eight months after filing. The review process may be extended by the FDA for three additional months to consider certain late-submitted information or clarification regarding information already provided in the submission. The FDA may also refer applications for novel drugs or biological products or products that present difficult questions of safety or efficacy to an advisory committee, typically a panel that includes clinicians and other experts, for review, evaluation and a recommendation as to whether the application should be approved. The FDA is not bound by the recommendations of an advisory committee, but it considers such recommendations carefully when making decisions.
Before approving an NDA, the FDA typically will inspect the facility or facilities where the product is manufactured. The FDA will not approve an application unless it determines that the manufacturing processes and facilities are in compliance with cGMP requirements and adequate to assure consistent production of the product within required specifications. In addition, before approving an NDA, the FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCP and integrity of the clinical data submitted.
The testing and approval process requires substantial time, effort and financial resources, and each may take many years to complete. Data obtained from clinical activities are not always conclusive and may be susceptible to varying interpretations, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. We may encounter difficulties or unanticipated costs in our efforts to develop our product candidates and secure necessary governmental approvals, which could delay or preclude us from marketing our products.
After the FDA’s evaluation of the NDA and inspection of the manufacturing facilities, the FDA may issue an approval letter or a complete response letter. An approval letter authorizes commercial marketing of the drug or biological product with specific prescribing information for specific indications. A complete response letter generally outlines the deficiencies in the submission and may require substantial additional testing or information in order for the FDA to reconsider the application. If and when those deficiencies have been addressed to the FDA’s satisfaction in a resubmission of the NDA, the FDA will issue an approval letter. The FDA has committed to reviewing such resubmissions in two or six months depending on the type of information included. Even with submission of this additional information, the FDA ultimately may decide that the application does not satisfy the regulatory criteria for approval.
16
Even if the FDA approves a product, the agency may limit the approved indications for use for the product, require that contraindications, warnings or precautions be included in the product labeling, require that post-approval studies be conducted to further assess a drug’s safety after approval, require testing and surveillance programs to monitor the product after commercialization, or impose other conditions, including distribution restrictions through a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy or other risk management mechanisms, which can materially affect the potential market and profitability of the product. The FDA may prevent or limit further marketing of a product based on the results of post-market studies or surveillance programs. After approval, some types of changes to the approved product, such as changes in indications, manufacturing changes and labeling, are subject to further testing requirements and FDA review and approval.
Other Regions
Most major markets have different levels of regulatory requirements for medical devices. Modifications to the cleared or approved products may require a new regulatory submission in all major markets. The regulatory requirements, and the review time, vary significantly from country to country. Products can also be marketed in other countries that have minimal requirements for medical devices.
Other U.S. Healthcare Laws and Compliance Requirements
In the United States, our current and future operations are subject to regulation by various federal, state and local authorities in addition to the FDA, including but not limited to, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (“CMS”), other divisions of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (“HHS”) (such as the Office of Inspector General, Office for Civil Rights and the Health Resources and Service Administration), the U.S. Department of Justice, and state and local governments. For example, our clinical research, sales, marketing and scientific/educational grant programs may have to comply with the anti-fraud and abuse provisions of the Social Security Act, the false claims laws, the privacy and security provisions of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (“HIPAA”), and similar state laws, each as amended, as applicable.
The federal Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits, among other things, any person or entity from knowingly and willfully offering, paying, soliciting or receiving any remuneration, directly or indirectly, overtly or covertly, in cash or in kind, to induce or in return for purchasing, leasing, ordering or arranging for the purchase, lease or order of any item or service reimbursable, in whole or in part, under Medicare, Medicaid or other federal healthcare programs. The term remuneration has been interpreted broadly to include anything of value. The Anti-Kickback Statute has been interpreted to apply to arrangements between therapeutic product manufacturers on one hand and prescribers, purchasers, and formulary managers on the other.
There are a number of statutory exceptions and regulatory safe harbors protecting some common activities from prosecution. The exceptions and safe harbors are drawn narrowly and practices that involve remuneration that may be alleged to be intended to induce prescribing, purchasing or recommending may be subject to scrutiny if they do not qualify for an exception or safe harbor. Failure to meet all of the requirements of a particular applicable statutory exception or regulatory safe harbor does not make the conduct per se illegal under the Anti-Kickback Statute. Instead, the legality of the arrangement will be evaluated on a case-by-case basis based on a cumulative review of all of its facts and circumstances. Our practices may not in all cases meet all of the criteria for protection under a statutory exception or regulatory safe harbor. The statutory exceptions and regulatory safe harbors are also subject to change.
Additionally, the intent standard under the Anti-Kickback Statute was amended by the Affordable Care Act, to a stricter standard such that a person or entity no longer needs to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order to have committed a violation. In addition, the Affordable Care Act also codified case law that a claim including items or services resulting from a violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the federal False Claims Act (“FCA”).
17
The federal false claims and civil monetary penalty laws, including the FCA, which imposes significant penalties and can be enforced by private citizens through civil qui tam actions, prohibit any person or entity from, among other things, knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, a false or fraudulent claim for payment to, or approval by, the federal government, including federal healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid; knowingly making, using, or causing to be made or used a false record or statement material to a false or fraudulent claim to the federal government; or knowingly making a false statement to improperly avoid, decrease or conceal an obligation to pay money to the federal government. A claim includes “any request or demand” for money or property presented to the U.S. government. Although we would not submit claims directly to payors, manufacturers can be held liable under these laws if they are deemed to “cause” the submission of false or fraudulent claims by, for example, providing inaccurate billing or coding information to customers or promoting a product off-label. In addition, our future activities relating to the reporting of wholesaler or estimated retail prices for our products, the reporting of prices used to calculate Medicaid rebate information and other information affecting federal, state, and third-party reimbursement for our products, and the sale and marketing of our products, are subject to scrutiny under this law. For example, pharmaceutical companies have been prosecuted under the FCA in connection with their alleged off-label promotion of drugs, purportedly concealing price concessions in the pricing information submitted to the government for government price reporting purposes, and allegedly providing free product to customers with the expectation that the customers would bill federal health care programs for the product.
HIPAA created additional federal criminal statutes that prohibit, among other things, knowingly and willfully executing, or attempting to execute, a scheme to defraud or to obtain, by means of false or fraudulent pretenses, representations or promises, any money or property owned by, or under the control or custody of, any healthcare benefit program, including private third-party payors, willfully obstructing a criminal investigation of a healthcare offense, and knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing or covering up by trick, scheme or device, a material fact or making any materially false, fictitious or fraudulent statement in connection with the delivery of or payment for healthcare benefits, items or services. Like the Anti-Kickback Statute, the Affordable Care Act amended the intent standard for certain healthcare fraud statutes under HIPAA such that a person or entity no longer needs to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order to have committed a violation.
Also, many states have similar, and typically more prohibitive, fraud and abuse statutes or regulations that apply to items and services reimbursed under Medicaid and other state programs, or, in several states, apply regardless of the payor.
In addition, we may be subject to data privacy, data security and data breach notification laws, regulations, standards, and codes of conduct by both the U.S. federal government and the states. These laws, regulations, standards, and codes of conduct may govern the collection, use, disclosure and protection of health-related and other personal information. HIPAA, as amended by the HITECH, imposes requirements relating to the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information. HIPAA requires covered entities to limit the use and disclosure of protected health information to specifically authorized situations and requires covered entities to implement security measures to protect health information that they maintain in electronic form. The federal government may impose civil, criminal, and administrative fines and penalties and/or additional reporting or oversight obligations for a violation of HIPAA’s requirements. Among other things, HITECH makes HIPAA’s privacy and security standards directly applicable to business associates that receive or obtain protected health information in connection with providing a service on behalf of a covered entity.
HITECH also created four new tiers of civil monetary penalties, amended HIPAA to make civil and criminal penalties directly applicable to business associates, and gave state attorneys general new authority to file civil actions for damages or injunctions in federal courts to enforce HIPAA and seek attorneys’ fees and costs associated with pursuing federal civil actions. In addition to HIPAA and HITECH, many state laws govern the privacy and security of health information in specified circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways, are often not pre-empted by federal law, and may have a more prohibitive effect than federal law, thus complicating compliance efforts.
We may develop products that, once approved, may be administered by a physician. Under currently applicable U.S. law, certain products not usually self-administered (including injectable drugs) may be eligible for coverage under Medicare through Medicare Part B. Medicare Part B is the part of Medicare that covers outpatient services and supplies, including certain pharmaceutical products, that are medically necessary to treat a beneficiary’s health condition. As a condition of receiving Medicare Part B reimbursement for a manufacturer’s eligible drugs, the manufacturer is required to participate in other government healthcare programs, including the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program and the 340B Drug Pricing Program. The Medicaid Drug Rebate Program requires pharmaceutical manufacturers to enter into and have in effect a national rebate agreement with the Secretary of HHS as a condition for states to receive federal matching funds for the manufacturer’s outpatient drugs furnished to Medicaid patients. Under the 340B Drug Pricing Program, the manufacturer must extend discounts to entities that participate in the program.
18
In addition, many pharmaceutical manufacturers must calculate and report certain price reporting metrics to the government, such as average sales price and best price. Penalties may apply in some cases when such metrics are not submitted accurately and timely.
Additionally, the Physician Payment Sunshine Act (the “Sunshine Act”) within the Affordable Care Act, and its implementing regulations, require that certain manufacturers of drugs, devices, biological and medical supplies for which payment is available under Medicare, Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (with certain exceptions) report annually to CMS information related to certain payments or other transfers of value made or distributed to physicians and teaching hospitals, or to entities or individuals at the request of, or designated on behalf of, the physicians and teaching hospitals and to report annually certain ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members. This information is made publicly available on a CMS website, and failure to report accurately could result in penalties. In addition, many states also govern the reporting of payments or other transfers of value, many of which differ from each other in significant ways, are often not pre-empted, and may have a more prohibitive effect than the Sunshine Act, thus further complicating compliance efforts.
In order to distribute products commercially, we must comply with state laws that require the registration of manufacturers and wholesale distributors of drug and biological products in a state, including, in certain states, manufacturers and distributors who ship products into the state even if such manufacturers or distributors have no place of business within the state. Some states also impose requirements on manufacturers and distributors to establish the pedigree of product in the chain of distribution, including some states that require manufacturers and others to adopt new technology capable of tracking and tracing product as it moves through the distribution chain. Several state and local laws have been enacted requiring pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies to establish marketing compliance programs, file periodic reports with the state, make periodic public disclosures on sales, marketing, pricing, clinical studies and other activities, and/or register their sales representatives, as well as to prohibit pharmacies and other healthcare entities from providing certain physician prescribing data to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies for use in sales and marketing, and to prohibit certain other sales and marketing practices. In addition, all of our activities are potentially subject to federal and state consumer protection and unfair competition laws.
Ensuring business arrangements with third parties comply with applicable healthcare laws and regulations is a costly endeavor. If our operations are found to be in violation of any of the federal and state healthcare laws described above or any other current or future governmental regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to significant penalties, including without limitation, civil, criminal and/or administrative penalties, damages, fines, disgorgement, imprisonment, exclusion from participation in government programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, injunctions, private “qui tam” actions brought by individual whistleblowers in the name of the government, or refusal to allow us to enter into government contracts, contractual damages, reputational harm, administrative burdens, diminished profits and future earnings, additional reporting obligations and oversight if we become subject to a corporate integrity agreement or other agreement to resolve allegations of non-compliance with these laws, and the curtailment or restructuring of our operations, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our results of operations.
Coverage, Pricing and Reimbursement
Significant uncertainty exists as to the coverage and reimbursement status of any product candidates for which we may obtain regulatory approval. In the United States and in foreign markets, sales of any products for which we receive regulatory approval for commercial sale will depend, in part, on the extent to which third-party payors provide coverage and establish adequate reimbursement levels for such products. In the United States, third-party payors include federal and state healthcare programs, private managed care providers, private health insurers and other organizations.
Adequate coverage and reimbursement from governmental healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid in the United States, and commercial payors are critical to new product acceptance.
Our ability to commercialize any products successfully also will depend in part on the extent to which coverage and adequate reimbursement for these products and related treatments will be available from government health administration authorities, private health insurers and other organizations. Government authorities and third-party payors, such as private health insurers and health maintenance organizations, decide which therapeutics they will pay for and establish reimbursement levels. Coverage and reimbursement by a third-party payor may depend upon a number of factors, including the third-party payor’s determination that use of a therapeutic is:
19
Coverage may also be more limited than the purposes for which the product is approved by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities. Reimbursement may impact the demand for, or the price of, any product for which we obtain regulatory approval.
Third-party payors are increasingly challenging the price, examining the medical necessity, and reviewing the cost-effectiveness of medical products, therapies, and services, in addition to questioning their safety and efficacy. Obtaining reimbursement for our products may be particularly difficult because of the higher prices often associated with branded drugs and drugs administered under the supervision of a physician. We may need to conduct expensive pharmacoeconomic studies in order to demonstrate the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of our products, in addition to the costs required to obtain FDA approvals. Our product candidates may not be considered medically necessary or cost-effective. Obtaining coverage and reimbursement approval of a product from a government or other third-party payor is a time-consuming and costly process that could require us to provide to each payor supporting scientific, clinical and cost-effectiveness data for the use of our product on a payor-by-payor basis, with no assurance that coverage and adequate reimbursement will be obtained. A payor’s decision to provide coverage for a product does not imply that an adequate reimbursement rate will be approved. Further, one payor’s determination to provide coverage for a product does not assure that other payors will also provide coverage for the product. Adequate third-party reimbursement may not be available to enable us to maintain price levels sufficient to realize an appropriate return on our investment in product development. If reimbursement is not available or is available only at limited levels, we may not be able to successfully commercialize any product candidate that we successfully develop.
Different pricing and reimbursement schemes exist in other countries. In the European Union, governments influence the price of pharmaceutical products through their pricing and reimbursement rules and control of national health care systems that fund a large part of the cost of those products to consumers. Some jurisdictions operate positive and negative list systems under which products may only be marketed once a reimbursement price has been agreed. To obtain reimbursement or pricing approval, some of these countries may require the completion of clinical studies that compare the cost effectiveness of a particular product candidate to currently available therapies. Other member states allow companies to fix their own prices for medicines but monitor and control company profits. The downward pressure on health care costs has become intense. As a result, increasingly high barriers are being erected to the entry of new products. In addition, in some countries, cross-border imports from low-priced markets exert a commercial pressure on pricing within a country.
The marketability of any product candidates for which we receive regulatory approval for commercial sale may suffer if the government and third-party payors fail to provide adequate coverage and reimbursement. In addition, emphasis on managed care, the increasing influence of health maintenance organizations, and additional legislative changes in the United States has increased, and we expect will continue to increase, the pressure on healthcare pricing. The downward pressure on the rise in healthcare costs in general, particularly prescription medicines, medical devices and surgical procedures and other treatments, has become very intense. Coverage policies and third-party reimbursement rates may change at any time. Even if favorable coverage and reimbursement status is attained for one or more products for which we receive regulatory approval, less favorable coverage policies and reimbursement rates may be implemented in the future.
Healthcare Reform
In the United States and some foreign jurisdictions, there have been, and continue to be, several legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes regarding the healthcare system that could prevent or delay marketing approval of product candidates, restrict or regulate post-approval activities, and affect the ability to profitably sell product candidates for which marketing approval is obtained. Among policy makers and payors in the United States and elsewhere, there is significant interest in promoting changes in healthcare systems with the stated goals of containing healthcare costs, improving quality and/or expanding access. In the United States, the pharmaceutical industry has been a particular focus of these efforts and has been significantly affected by major legislative initiatives.
20
For example, Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010, or collectively the ACA, has substantially changed healthcare financing and delivery by both governmental and private insurers. Among the ACA provisions of importance to the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, in addition to those otherwise described above, are the following:
Since its enactment, there have been executive, legal and Congressional challenges to certain aspects of the ACA. On June 17, 2021 the U.S. Supreme Court dismissed a challenge on procedural grounds that argued the ACA is unconstitutional in its entirety because the “individual mandate” was repealed by Congress. Further, prior to the U.S. Supreme Court ruling, President Biden issued an executive order that initiated a special enrollment period from February 15, 2021 through August 15, 2021 for purposes of obtaining health insurance coverage through the ACA marketplace. The executive order also instructed certain governmental authorities to review and reconsider their existing policies and rules that limit access to healthcare, including among others, reexamining Medicaid demonstration projects and waiver programs that include work requirements, and policies that create unnecessary barriers to obtaining access to health insurance coverage through Medicaid or the ACA. Additionally, on March 11, 2021, President Biden signed the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 into law, which eliminates the statutory Medicaid drug rebate cap, currently set at 100% of a drug’s average manufacturer price, for single source and innovator multiple source drugs, beginning January 1, 2024.
On August 16, 2022, President Biden signed the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, or IRA, into law, which among other things, extends enhanced subsidies for individuals purchasing health insurance coverage in ACA marketplaces through plan year 2025. The IRA also eliminates the “donut hole” under the Medicare Part D program beginning in 2025 by significantly lowering the beneficiary maximum out-of-pocket cost and through a newly established manufacturer discount program. It is unclear how other healthcare reform measures, if any, will impact our business. Any reduction in reimbursement from Medicare and other government programs may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors. The implementation of cost containment measures or other healthcare reforms may prevent us from being able to generate revenue, attain profitability, or commercialize our products. Such reforms could have an adverse effect on anticipated revenue from product candidates that we may successfully develop and for which we may obtain regulatory approval and may affect our overall financial condition and ability to develop product candidates.
21
Further legislation or regulation could be passed that could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition. Other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted since the ACA was enacted. For example, in August 2011, the Budget Control Act of 2011 was signed into law, which, among other things, included aggregate reductions to Medicare payments to providers, which went into effect beginning on April 1, 2013 and, due to subsequent legislative amendments, will stay in effect through 2032. In January 2013, the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 was signed into law, which, among other things, further reduced Medicare payments to several types of providers, including hospitals, imaging centers and cancer treatment centers, and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years.
More recently, on May 30, 2018, the Trickett Wendler, Frank Mongiello, Jordan McLinn, and Matthew Bellina Right to Try Act of 2017, or the Right to Try Act, was signed into law. The law, among other things, provides a federal framework for certain patients to access certain investigational new drug products that have completed a Phase I clinical trial and that are undergoing investigation for FDA approval. Under certain circumstances, eligible patients can seek treatment without enrolling in clinical trials and without obtaining FDA permission under the FDA expanded access program. There is no obligation for a pharmaceutical manufacturer to make its product candidates available to eligible patients as a result of the Right to Try Act.
Additionally, there has been increasing legislative and enforcement interest in the United States with respect to specialty drug pricing practices. Specifically, there have been several recent U.S. Congressional inquiries and proposed and enacted federal and state legislation designed to, among other things, bring more transparency to drug pricing, reduce the cost of prescription drugs under Medicare, review the relationship between pricing and manufacturer patient programs, and reform government program reimbursement methodologies for drugs. For example, the IRA, among other things, (1) directs HHS to negotiate the price of certain single-source drugs and biologics covered under Medicare and (2) imposes rebates under Medicare Part B and Medicare Part D to penalize price increases that outpace inflation. These provisions took effect progressively in fiscal year 2023, although they may be subject to legal challenges. The IRA permits HHS to implement many of these provisions through guidance, as opposed to regulation, for the initial years. HHS has and will continue to issue and update guidance as these programs are implemented. It is currently unclear how the IRA will be implemented but it is likely to have a significant effect on the pharmaceutical industry. Further, in response to the Biden administration’s October 2022 executive order, on February 14, 2023, HHS released a report outlining three new models for testing by the CMS Innovation Center which will be evaluated on their ability to lower the cost of drugs, promote accessibility, and improve quality of care. It is unclear whether the models will be utilized in any health reform measures in the future. Individual states in the United States have also become increasingly active in passing legislation and implementing regulations designed to control pharmaceutical product pricing, including price or patient reimbursement constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and, in some cases, designed to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing.
We expect additional state, federal and foreign healthcare reform measures to be adopted in the future, any of which could limit the amounts that federal, state and foreign governments will pay for health products, which could result in reduced demand for our products, if approved or additional pricing pressure. For instance, in December 2021, the European Union (“EU”) Regulation No 2021/2282 on Health Technology Assessment, or HTA, amending Directive 2011/24/EU, was adopted. While the Regulation entered into force in January 2022, it will only begin to apply from January 2025 onwards, with preparatory and implementation-related steps to take place in the interim. Once the Regulation becomes applicable, it will have a phased implementation depending on the concerned products. This regulation is intended to boost cooperation among EU member states in assessing health technologies, including new medicinal products, as well as certain high-risk medical devices, and providing the basis for cooperation at the EU level for joint clinical assessments in these areas. The regulation will permit EU member states to use common HTA tools, methodologies, and procedures across the EU, working together in four main areas, including joint clinical assessment of the innovative health technologies with the most potential impact for patients, joint scientific consultations whereby developers can seek advice from HTA authorities, identification of emerging health technologies to identify promising technologies early, and continuing voluntary cooperation in other areas. Individual EU member states will continue to be responsible for assessing non-clinical (e.g., economic, social, ethical) aspects of health technologies, and making decisions on pricing and reimbursement.
Additional Regulation
In addition to the foregoing, local, state and federal laws, including such matters as safe working conditions, manufacturing practices, environmental protection, fire hazard control and hazardous substances, including, in the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Act, the Resource Conservancy and Recovery Act and the Toxic Substances Control Act, affect our business. These and other laws govern our use, handling and disposal of various biological, chemical and radioactive substances used in, and wastes generated by, our operations. If our operations result in contamination of the environment or expose individuals to hazardous or biohazardous substances, we could be liable for damages, environmental remediation, and/or governmental fines. We believe that we are in material compliance with applicable environmental laws and occupational health and safety laws that continued compliance therewith will not have a material adverse effect on our business. We cannot predict, however, how changes in these laws may affect our future operations. We may incur significant costs to comply with such laws and regulations now or in the future.
22
Government Regulation and Product Approval
Government authorities in the United States, at the federal, state and local level, and in other countries extensively regulate, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, including any manufacturing changes, packaging, storage, recordkeeping, labeling, advertising, promotion, distribution, marketing, post-approval monitoring and reporting, import and export of pharmaceutical products, biological products and medical devices, such as those we are developing.
Disclosure of clinical study information
Sponsors of applicable clinical studies of FDA regulated products, including drugs, are required to register and disclose certain clinical study information. Information related to the product, patient population, phase of investigation, study sites and investigators, and other aspects of the clinical study is then made public on the ClinicalTrials.gov website as part of the registration. Sponsors are also obligated to disclose the results of their clinical studies after completion. Disclosure of the results of these studies can be delayed until the new product or new indication being studied has been approved. Competitors may use this publicly available information to gain knowledge regarding the progress of development programs.
Expedited Programs for Serious Conditions
The FDA maintains several programs intended to facilitate and expedite development and review of new drugs and biologics to address unmet medical needs in the treatment of serious or life-threatening diseases or conditions. These programs include Fast Track designation, Breakthrough Therapy designation, Priority Review and Accelerated Approval. These programs can significantly reduce the time it takes for the FDA to review a NDA, but they do not guarantee that a product will receive FDA approval. Even if a product qualifies initially, the FDA may later decide that the product no longer meets the conditions for qualification or decide that the time period for FDA review will not be shortened. In May 2018, the Right to Try Act also established a program to increase access to unapproved, investigational treatments for patients diagnosed with life-threatening diseases or conditions who have exhausted approved treatment options and who are unable to participate in a clinical study.
A new drug or biologic is eligible for Fast Track designation if it is intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs for such disease or condition. Fast Track designation provides increased opportunities for sponsor interactions with the FDA during preclinical and clinical development, in addition to the potential for rolling review once a marketing application is filed, meaning that the agency may review portions of the marketing application before the sponsor submits the complete application, as well as Priority Review, discussed below. In addition, a new drug or biologic may be eligible for Breakthrough Therapy designation if it is intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. Breakthrough Therapy designation provides all the features of Fast Track designation in addition to intensive guidance on an efficient drug development program beginning as early as Phase 1, and FDA organizational commitment to expedited development, including involvement of senior managers and experienced review staff in a cross-disciplinary review, where appropriate.
Any product submitted to the FDA for approval, including a product with Fast Track or Breakthrough Therapy designation, may also be eligible for additional FDA programs intended to expedite the review and approval process, including Priority Review designation and accelerated approval. A product is eligible for Priority Review if it has the potential to provide a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness in the treatment, diagnosis or prevention of a serious disease or condition. Under priority review, FDA will review an application in six months compared to ten months for a standard review. Products are eligible for accelerated approval if they can be shown to have an effect on a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit, or an effect on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality which is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity, or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatment. Accelerated approval is usually contingent on a sponsor’s agreement to conduct additional post-approval studies to verify and describe the product’s clinical benefit. In addition, unless otherwise informed by the FDA, the FDA currently requires, as a condition for accelerated approval, that all advertising and promotional materials that are intended for dissemination or publication be submitted to FDA for review before the initial dissemination or publication.
23
Orphan drugs
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant orphan drug designation to drugs or biologics intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is generally defined as a disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States. Orphan drug designation must be requested before submitting an NDA. After the FDA grants orphan drug designation, the generic identity of the drug or biologic and its potential orphan use are disclosed publicly by the FDA. Orphan drug designation is taken into consideration but generally does not convey any advantage in, or shorten the duration of, the regulatory review and approval process. The first NDA applicant to receive FDA approval for a particular active ingredient to treat a particular disease with FDA orphan drug designation is entitled to a seven-year exclusive marketing period in the United States for that product, for that indication. During the seven-year exclusivity period, the FDA may not approve any other applications to market the same drug or biologic for the same orphan indication, except in limited circumstances, such as a showing of clinical superiority to the product with orphan drug exclusivity in that it is shown to be safer, more effective or makes a major contribution to patient care. This is the case despite an earlier court opinion holding that the Orphan Drug Act unambiguously required the FDA to recognize orphan exclusivity regardless of a showing of clinical superiority. Orphan drug exclusivity does not prevent the FDA from approving a different drug or biologic for the same disease or condition, or the same drug or biologic for a different disease or condition. Among the other benefits of orphan drug designation are tax credits for certain research and a waiver of the NDA application user fee.
Pediatric information and exclusivity
Under the Pediatric Research Equity Act of 2003, an NDA or supplement to an NDA must contain data from pediatric studies that are adequate to assess the safety and effectiveness of the drug or biological product for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations, and to support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the product is safe and effective. The FDA may, on its own initiative or at the request of the applicant, grant deferrals for submission of some or all pediatric data until after approval of the product for use in adults, or full or partial waivers from the pediatric data requirements. Under the Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act, the FDA has additional authority to take action against manufacturers not adhering to pediatric study requirements. Unless otherwise required by regulation, the pediatric data requirements do not apply to products with orphan drug designation.
Pediatric exclusivity is a type of non-patent exclusivity in the United States and, if granted, provides for the attachment of an additional six months of marketing protection to the term of any existing regulatory exclusivity or patent protection, including the non-patent and orphan exclusivity. This six-month exclusivity may be granted if an application sponsor submits pediatric data that fairly respond to a written request from the FDA for such data. The data do not need to show the product to be effective in the pediatric population studied; rather, if the clinical study is deemed to fairly respond to the FDA’s request, the additional protection is granted.
The Hatch-Waxman Act
Abbreviated new drug applications
In seeking approval for a drug through an NDA, applicants are required to list with the FDA each patent that claims to cover the applicant’s product. Upon approval of a drug, each of the patents listed in the application for the drug is then published in the FDA’s Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations, commonly known as the Orange Book. Drugs listed in the Orange Book can, in turn, be cited by potential competitors in support of approval of an abbreviated new drug application (“ANDA”). Generally, an ANDA provides for marketing of a drug product that has the same active ingredients in the same strengths and dosage form as the listed drug and has been shown through bioequivalence testing to be therapeutically equivalent to the listed drug. Other than the requirement for bioequivalence testing, ANDA applicants are not required to conduct or submit results of preclinical or clinical tests to prove the safety or effectiveness of their drug product. Drugs approved in this way are commonly referred to as “generic equivalents” to the listed drug and can often be substituted by pharmacists under prescriptions written for the original listed drug.
The ANDA applicant is required to certify to the FDA concerning any patents listed for the approved product in the FDA’s Orange Book. Specifically, the applicant must certify that:
A certification that the new product will not infringe the already approved product’s listed patents or that such patents are invalid is called a Paragraph IV certification. If the ANDA applicant does not challenge the listed patents, the ANDA will not be approved until all the listed patents claiming the referenced product have expired.
24
If the ANDA applicant has provided a Paragraph IV certification to the FDA, the applicant must also send notice of the Paragraph IV certification to the NDA and patent holders once the ANDA has been accepted for filing by the FDA. The NDA and patent holders may then initiate a patent infringement lawsuit in response to the notice of the Paragraph IV certification. The filing of a patent infringement lawsuit within 45 days after the receipt of a Paragraph IV certification automatically prevents the FDA from approving the ANDA until the earlier of a 30-month period, expiration of the patent, settlement of the lawsuit or a decision in the infringement case that the patent involved is deemed invalid or not infringed.
The ANDA also will not be approved until any applicable non-patent exclusivity, such as exclusivity for obtaining approval of a new chemical entity, listed in the Orange Book for the referenced product has expired. Federal law provides a period of five years following approval of a drug containing no previously approved active ingredients during which ANDAs for generic versions of those drugs cannot be received by the FDA, except that the application may be submitted in four years if it contains a Paragraph IV certification. If there is no listed patent in the Orange Book, there may not be a Paragraph IV certification, and thus, no ANDA may be filed before the expiration of the exclusivity period. Federal law provides for a period of three years of exclusivity following approval of a listed drug that contains previously approved active ingredients but is approved in a new dosage form, route of administration or combination, or for a new use, the approval of which was required to be supported by new clinical studies conducted by or for the sponsor, during which the FDA cannot grant effective approval of an ANDA based on that listed drug.
The FDA must establish a priority review track for certain generic drugs, requiring the FDA to review a drug application within eight months for a drug that has three or fewer approved drugs listed in the Orange Book and is no longer protected by any patent or regulatory exclusivities, or is on the FDA’s drug shortage list. The FDA must also expedite review of “competitor generic therapies” or drugs with inadequate generic competition, including holding meetings with or providing advice to the drug sponsor prior to submission of the application.
Patent term extension
After NDA approval, owners of relevant drug patents may apply for up to a five year patent term extension. The allowable patent term extension is calculated as half of the drug’s testing phase, based on the time between IND application and submission of the NDA, and all of the review phase, based on the time between the NDA submission and approval up to a maximum of five years. The time can be shortened if the FDA determines that the applicant did not pursue approval with due diligence. The total patent term after the extension may not exceed 14 years.
For patents that might expire during the application phase, the patent owner may request an interim patent term extension. An interim patent term extension increases the patent term by one-year and may be renewed up to four times. For each interim patent term extension granted, the post-approval patent term extension is reduced by one-year. The director of the USPTO must determine that approval of the drug covered by the patent for which a patent term extension is being sought is likely.
Interim patent term extensions are not available for a drug for which an NDA has not been submitted.
Section 505(b)(2) new drug applications
Most drug products obtain FDA marketing approval pursuant to an NDA or an ANDA. A third alternative is a special type of NDA, commonly referred to as a Section 505(b)(2) NDA, which enables the applicant to rely, in part, on the FDA’s previous approval of a similar product, or published literature, in support of its application.
Section 505(b)(2) NDAs often provide an alternate path to FDA approval for new or improved formulations or new uses of previously approved products. Section 505(b)(2) permits the filing of an NDA where at least some of the information required for approval comes from studies not conducted by or for the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference. If the Section 505(b)(2) applicant can establish that reliance on the FDA’s previous approval is scientifically appropriate, it may eliminate the need to conduct certain preclinical or clinical studies of the new product. The FDA may also require companies to perform additional studies or measurements to support the change from the approved product. The FDA may then approve the new product for all or some of the label indications for which the referenced product has been approved, as well as for any new indication sought by the Section 505(b)(2) applicant.
To the extent that the Section 505(b)(2) applicant is relying on studies conducted for an already approved product, the applicant is required to certify to the FDA concerning any patents listed for the approved product in the Orange Book to the same extent that an ANDA applicant would. As a result, approval of a Section 505(b)(2) NDA can be stalled until all the listed patents claiming the referenced product have expired, until any non-patent exclusivity, such as exclusivity for obtaining approval of a new chemical entity, listed in the Orange Book for the referenced product has expired, and, in the case of a Paragraph IV certification and subsequent patent infringement suit, until the earlier of a 30-month period, settlement of the lawsuit or a decision in the infringement case that the patent involved is deemed invalid or not infringed.
25
Post-Approval Requirements
Any products manufactured or distributed by us pursuant to FDA approvals are subject to pervasive and continuing regulation by the FDA, including, among other things, requirements relating to record-keeping, reporting of adverse experiences, periodic reporting, product sampling and distribution, and advertising and promotion of the product. After approval, most changes to the approved product, such as adding new indications or other labeling claims, are subject to prior FDA review and approval. There also are continuing user fee requirements, under which FDA assesses an annual program fee for each product identified in an approved NDA. Biologic manufacturers and their subcontractors are required to register their establishments with the FDA and certain state agencies and are subject to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA and certain state agencies for compliance with cGMP, which impose certain procedural and documentation requirements upon us and our third-party manufacturers. Changes to the manufacturing process are strictly regulated, and, depending on the significance of the change, may require prior FDA approval before being implemented. FDA regulations also require investigation and correction of any deviations from cGMP and impose reporting requirements upon us and any third-party manufacturers that we may decide to use. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money and effort in the area of production and quality control to maintain compliance with cGMP and other aspects of regulatory compliance.
The FDA may withdraw approval if compliance with regulatory requirements and standards is not maintained or if problems occur after the product reaches the market. Later discovery of previously unknown problems with a product, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or with manufacturing processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in revisions to the approved labeling to add new safety information; imposition of post-market studies or clinical studies to assess new safety risks; or imposition of distribution restrictions or other restrictions under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy program. Other potential consequences include, among other things:
The FDA closely regulates the marketing, labeling, advertising and promotion of biologic regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in, among other things, adverse publicity, warning letters, corrective advertising and potential civil and criminal penalties. Physicians may prescribe legally available products for uses that are not described in the product’s labeling and that differ from those tested by us and approved by the FDA. Such off-label uses are common across medical specialties. Physicians may believe that such off-label uses are the best treatment for many patients in varied circumstances. The FDA does not regulate the behavior of physicians in their choice of treatments. The FDA does, however, restrict manufacturer’s communications on the subject of off-label use of their products.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS.
The following risk factors are not exhaustive and investors are encouraged to perform their own investigation with respect to the business, prospects, financial condition and operating results of Revelation and our business, prospects, financial condition and operating results. You should carefully consider the following risk factors in addition to the other information included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including our audited financial statements and related notes and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” We may face additional risks and uncertainties that are not presently known to us, or that we currently deem immaterial, which may also impair our business, prospects, financial condition or operating results. The following discussion should be read in conjunction with our audited financial statements and notes to the financial statements included herein.
Unless the context otherwise requires, references herein to “Program Products” refers to Revelation’s GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD, and GEM-PSI programs.
26
Risks Related to Our Business
Although our financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, we have a limited operating history and no products approved for commercial sale. We have incurred net losses since our inception, we anticipate that we will continue to incur significant losses for the foreseeable future, and even if we were to generate revenue, we may never achieve or maintain profitability.
We are a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company with a limited operating history may make it difficult to evaluate the success of our business to date and to assess our future viability. We commenced our operations in May 2020, and, to date, our operations have been limited to organizing and staffing our Company, business planning, raising capital, conducting research and development activities, including early clinical study, and providing general and administrative support for these operations. Investment in biopharmaceutical product development and diagnostic device is highly speculative because it entails substantial upfront capital expenditures and significant risk that any potential product candidate and/or diagnostic device will fail to demonstrate adequate effect and/or an acceptable safety profile, gain regulatory approval or become commercially viable. We currently have no products approved for commercial sale, we have not generated any revenue from product sales to date and we continue to incur significant research and development and other expenses related to our ongoing operations. We have limited experience as a Company conducting clinical studies and no experience as a Company commercializing any products.
We are not profitable and have incurred net losses since our inception. As of December 31, 2024, we had an accumulated deficit of $40.5 million. Consequently, predictions about our future success or viability may not be as accurate as they would be if we had a longer operating history or a history of successfully developing and commercializing pharmaceutical products. We have spent, and expect to continue to spend, significant resources to fund research and development of, conduct clinical studies, and seek regulatory approvals for, our Program Products, and any future product candidates. We expect to incur substantial and increasing operating losses over the next several years as our research, development, preclinical testing and clinical study activities increase. As a result, our accumulated deficit will also increase significantly. We may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays and other unknown factors that may adversely affect our business. The size of our future net losses will depend, in part, on the rate of future growth of our expenses and our ability to generate revenue. Our prior losses and expected future losses have, had and will continue to have a material adverse effect on our stockholders’ equity and working capital.
We do not anticipate that our current cash and cash equivalents balance will be sufficient to sustain operations within one-year after the date that our audited financial statements for December 31, 2024 were issued, which raises substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. In our own required quarterly assessments, we may continue to conclude that there is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern, and future reports from our independent registered public accounting firm may also contain statements expressing substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
If we seek additional financing to fund our business activities in the future and there remains substantial doubt about going concern, investors or other financing sources may be unwilling to provide additional funding on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Our ability to raise more equity capital will depend in part on our ability to amend our certificate of incorporation to authorize additional shares of common stock.
The net losses we incur may fluctuate significantly from quarter-to-quarter such that a period-to-period comparison of our results of operations may not be a good indication of our future performance.
We have no products approved for marketing in any jurisdiction, and our Program Products are in early stages of development. We have never generated any revenue from product sales. Our ability to generate revenue and achieve profitability depends on our ability, alone or with strategic collaboration partners, to successfully complete the development of and obtain the regulatory and marketing approvals necessary to commercialize one or more of our Program Products. We do not anticipate generating revenue from product sales in the next couple of years. Even if we eventually generate product revenue, we may never be profitable and, if we do achieve profitability, we may not be able to sustain or increase profitability on a quarterly or annual basis.
We may not be able to raise additional funding on acceptable terms, or at all. Failure to obtain funding on acceptable terms and on a timely basis may require us to curtail, delay or discontinue our product development efforts or other operations. Raising additional funding may cause dilution to our stockholders.
Developing our Program Products is expensive, and we expect our research and development expenses to increase substantially in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly as we advance our Program Products through clinical studies, manufacturing and regulatory approval. We expect to finance future cash needs through public or private equity or debt offerings or product collaborations. We do not have any committed external source of funds. We cannot guarantee that future financing will be available in sufficient amounts or on terms acceptable to us, if at all, and the terms of any financing may adversely affect the interests or rights of our stockholders. Even if we believe that we have sufficient funds for our current or future operating plans, we may seek additional capital if market conditions are favorable or if we have specific strategic considerations. The issuance of additional securities, whether equity or debt, by us, or the possibility of such issuance, may affect the value of your investment.
27
To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, your ownership interest will be diluted, and the terms of such securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect your rights as a stockholder. Debt financing, if available, may involve covenants restricting our operations or our ability to incur additional debt.
If we do not raise additional capital, we may not be able to expand our operations or otherwise capitalize on our business opportunities, our business and financial condition will be negatively impacted, and we may need to:
Unfavorable global economic conditions, including any adverse macroeconomic conditions or geopolitical events, including the COVID-19 pandemic, the conflict between Ukraine and Russia, and recent bank failures affecting the financial services industry, could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations or liquidity, either directly or through adverse impacts on certain of the third parties on which we rely to conduct certain aspects of our preclinical studies or clinical trials.
Our results of operations could be adversely affected by general conditions in the global economy and in the global financial markets. Global economic and business activities continue to face widespread uncertainties, and global credit and financial markets have experienced extreme volatility and disruptions in the past several years, including severely diminished liquidity and credit availability, rising inflation and monetary supply shifts, rising interest rates, labor shortages, declines in consumer confidence, declines in economic growth, increases in unemployment rates, recession risks, and uncertainty about economic and geopolitical stability. A severe or prolonged economic downturn, or additional global financial or political crises, could result in a variety of risks to our business, including delayed clinical trials or preclinical studies, delayed approval of our product candidates, delayed ability to obtain patents and other intellectual property protection, weakened demand for our product candidates, if approved, or our ability to raise additional capital when needed on acceptable terms, if at all. The extent of the impact of these conditions on our operational and financial performance, including our ability to execute our business strategies and initiatives in the expected timeframe, as well as that of third parties upon whom we rely, will depend on future developments which are uncertain and cannot be predicted. A weak or declining economy also could strain our suppliers, possibly resulting in supply disruption. Any of the foregoing could harm our business and we cannot anticipate all of the ways in which the current economic climate and financial market conditions could adversely impact our business. Furthermore, our stock price may decline due in part to the volatility of the stock market and the general economic downturn.
Risks Related to the Product Development, Regulatory Approval, Manufacturing and
Commercialization of Our Program Products and Product Candidates
If preclinical studies or clinical studies for our Program Products are unsuccessful or delayed, we will be unable to meet our future development goals.
Conducting clinical studies for any product candidates for approval in the United States requires filing an IND and reaching agreement with the FDA on clinical protocols, finding appropriate clinical sites and clinical investigators, securing approvals for such studies from the IRB at each such site, manufacturing clinical quantities of product candidates and supplying drug product or devices to clinical sites. Currently, we do not have an active IND with the FDA in the United States for our Program Products. If our IND is not approved by the FDA, our clinical development timeline may be negatively impacted, and any future clinical programs may be delayed or terminated.
Even if the clinical studies are approved by FDA or other regulatory agencies, clinical study is expensive and can take many years to complete, and its outcome is inherently uncertain. A failure of one or more of our clinical studies can occur at any time during the clinical study process. We do not know whether future clinical studies, if any, will begin on time, need to be redesigned, enroll an adequate number of patients on time or be completed on schedule, if at all. Clinical studies can be delayed, suspended or terminated for a variety of reasons, including failure to (i) generate sufficient positive preclinical and clinical data; (ii) recruit CROs, clinical investigators and patients in a timely manner; (iii) manufacture sufficient quantities at the required quality of Program Products for use in clinical studies; (iv) raise sufficient capital to fund a study; (v) comply with all applicable regulatory requirements, whether in the United States or elsewhere, and (vi) obtain successful regulatory approval from regulatory authorities like the FDA.
28
If we experience delays in completing any clinical study of our Program Products or successfully obtaining regulatory approval, the commercial prospects of our Program Products may be harmed, and our ability to generate product revenues from any of these product candidates will be delayed. In addition, any delays in completing our clinical studies will increase our costs, slow down the development and approval process of our Program Products, and jeopardize our ability to commence product sales and generate revenues. Any of these occurrences may significantly harm our business and financial condition. In addition, many of the factors that cause, or lead to, a delay in the commencement or completion of clinical studies may also ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of our product candidates.
Drug development involves a lengthy and expensive process with uncertain timelines and uncertain outcomes, and the results of prior preclinical or clinical studies are not necessarily predictive of our future results. Our clinical studies may fail to adequately demonstrate the safety and efficacy of our Program Products or any future product candidates.
We are focused on the development of GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD, and GEM-PSI which are in pre-clinical development working towards early clinical trials.
There is a high failure rate for product candidates proceeding through clinical studies. Failure can occur at any time during the clinical study process. Many companies in the pharmaceutical industry have suffered significant setbacks in late-stage clinical studies even after achieving promising results in preclinical testing and earlier-stage clinical studies. Data obtained from preclinical and clinical activities are subject to varying interpretations, which may delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. In addition, we may experience regulatory delays or rejections as a result of many factors, including changes in regulatory policy during the development period of our Program Products. Success in preclinical testing and early clinical studies does not ensure that later clinical studies will generate the same results or otherwise provide adequate data to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of a product candidate. Frequently, product candidates that have shown promising results in early clinical studies have subsequently suffered significant setbacks in later clinical studies. If we are unable to successfully demonstrate the safety and efficacy of our Program Products or other future product candidates and receive the necessary regulatory approvals, our business will be materially harmed.
The Clinical Studies of our Program Products’ have been and are planned to be conducted outside the United States, and the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may not accept data from such studies.
We currently have not conducted any clinical studies in the United States to date. We have conducted and we plan to conduct additional clinical studies outside the United States, including Europe, Australia, or other foreign jurisdictions. The acceptance of clinical study data by the FDA from clinical studies conducted outside the United States may be subject to certain conditions. In cases where data from clinical studies conducted outside the United States are intended to serve as the sole bases for regulatory approval in the United States, the FDA will generally not approve the application on the basis of foreign data alone unless (i) the data are applicable to the United States population and United States medical practices, (ii) the studies were performed by clinical investigators of recognized competence and (iii) the data may be considered valid without the need for an on-site inspection by the FDA or, if the FDA considers such an inspection to be necessary, the FDA is able to validate the data through an on-site inspection or other appropriate means. Additionally, the FDA’s clinical study requirements, including sufficient size of patient populations and statistical powering, must be met. Many foreign regulatory bodies have similar approval requirements. In addition, such foreign studies would be subject to the applicable local laws of the foreign jurisdictions where the studies are conducted. There can be no assurance that the FDA or any comparable foreign regulatory authority will accept data from studies conducted outside of the United States or the applicable jurisdiction. If the FDA or any comparable foreign regulatory authority does not accept such data, it would result in the need for additional studies, which would be costly and time-consuming and delay aspects of our business plan, and may result in our Program Products’ not receiving regulatory approval or clearance for commercialization in the applicable jurisdiction.
29
As an organization, we have never conducted pivotal clinical studies, and we may be unable to do so for any Program Products we may develop.
We will need to successfully complete pivotal clinical studies in order to obtain the approval of the FDA, the EMA or other regulatory agencies to market any of our Program Products. Carrying out later-stage clinical studies and the submission to the FDA of a successful NDA is a complicated process. As an organization, we have not previously conducted any later stage or pivotal clinical studies and have limited experience in preparing, submitting and prosecuting regulatory filings. We may be unable to conduct clinical studies at preferred sites, enlist clinical investigators, enroll sufficient numbers of participants or begin or successfully complete clinical studies in a timely fashion, if at all. In addition, the design of a clinical study can determine whether its results will support approval of a product, and flaws in the design of a clinical study may not become apparent until the clinical study is well advanced. Because we have limited experience as a company designing clinical studies, we may be unable to successfully and efficiently execute and complete necessary clinical studies in a way that leads to successful regulatory submission and approval. We may require more time and incur greater costs than our competitors and may not succeed in obtaining regulatory approvals of product candidates that we develop. Failure to commence or complete, or delays in, our planned clinical studies, could prevent us from or delay us in commercializing our Program Products. We rely on third parties to conduct certain elements of our preclinical and clinical studies and perform other tasks for us. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties, meet expected deadlines or comply with regulatory requirements, we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or commercialize our Program Products.
In addition, Congress recently amended the FDCA to require sponsors of a Phase 3 clinical trial, or other “pivotal study” of a new drug to support marketing authorization, to design and submit a diversity action plan for such clinical trial. The action plan must describe appropriate diversity goals for enrollment, as well as a rationale for the goals and a description of how the sponsor will meet them. Although none of our product candidates has reached Phase 3 of clinical development, we must submit a diversity action plan to the FDA by the time we submit a Phase 3 trial, or pivotal study, protocol to the agency for review, unless we are able to obtain a waiver for some or all of the requirements for a diversity action plan. It is unknown at this time how the diversity action plan may affect the planning and timing of any future Phase 3 trial for our product candidates or what specific information FDA will expect in such plans. However, initiation of such trials may be delayed if the FDA objects to our proposed diversity action plans for any future Phase 3 trial for our product candidates, and we may experience difficulties recruiting a diverse population of patients in attempting to fulfill the requirements of any approved diversity action plan.
We may find it difficult to enroll patients in our clinical studies, which could delay or prevent us from proceeding with clinical studies.
Identifying and qualifying patients to participate in clinical studies of our product candidates is critical to our success. The timing of our clinical studies depends in part on the speed at which we can recruit patients to participate in testing our Program Products, and we may experience delays in our clinical studies if we encounter difficulties in enrollment. Patient enrollment and retention in clinical studies depends on many factors, including the size of the patient population, number and location of the clinical sites, significant adverse events or other side effects observed, if any, the nature of the study protocol, our ability to recruit clinical study investigators with the appropriate competencies and experience, the existing body of safety and efficacy data with respect to the study drug, the number and nature of competing treatments and ongoing clinical studies of competing drugs for the same indication, the proximity of patients to clinical sites, clinicians’ and patients’ perceptions as to the potential advantages of the Program Products being studied in relation to other available therapies, including any drugs that may be approved for the indications we are investigating, the eligibility criteria for the study, our ability to obtain and maintain patient consents and the risk that patients enrolled in clinical studies will drop out of the studies before completion.
In addition, our competitors, some of whom have significantly greater resources than we do, are conducting clinical studies for the same indications and seek to enroll patients in their studies that may otherwise be eligible for our clinical studies or studies, which could lead to slow recruitment and delays in our clinical programs. Further, since the number of qualified clinical investigators is limited, we expect to conduct some of our clinical studies at the same clinical study sites that some of our competitors use, which could further reduce the number of patients who are available for our clinical studies in these sites.
Our inability to enroll sufficient number of patients for our clinical studies would result in significant delays or may require us to abandon one or more clinical studies altogether. If we are unable to enroll sufficient number of patients that will complete clinical testing, we will be unable to seek or gain marketing approval for our Program Products and any future product candidates and our business will be harmed. Even if we are able to enroll a sufficient number of patients in our clinical studies or studies, delays in patient enrollment may result in increased costs or may affect the timing or outcome of our clinical studies, which could prevent completion of these studies and adversely affect our ability to advance the development of our Program Products and any future product candidates.
30
Our Program Products and the administration of our Program Products may cause undesirable side effects or have other properties that could delay or prevent their regulatory approval, limit the commercial profile of an approved label or result in significant negative consequences following marketing approval, if any.
The severity and frequency of undesirable side effects caused by our Program Products, could cause us or regulatory authorities to interrupt, delay or halt clinical studies and could result in a more restrictive label, delay or denial of regulatory approval by the FDA or other regulatory agencies. Results of our studies could reveal a high and unacceptable severity and prevalence of these or other side effects. In such an event, our clinical studies could be suspended or terminated, and the FDA or other regulatory agencies could order us to cease further development of or deny or withdraw approval of our product candidates for any or all targeted indications. Moreover, during the conduct of clinical studies, patients report changes in their health, including illnesses, injuries and discomforts, to their study doctor. Often, it is not possible to determine whether or not the product candidate being studied caused these conditions.
Drug-related, drug product-related, formulation-related and administration-related side effects could affect patient recruitment, the ability of enrolled patients to complete the clinical study or result in potential product liability claims, which could exceed the insurance coverage. Additionally, if one or more of our Program Products receives marketing approval, and we or others later identify undesirable side effects caused by such products, a number of potentially significant negative consequences could result.
If we or others identify undesirable or unacceptable side effects caused by our Program Products or any future product candidates or products:
Interim, topline and preliminary data from our clinical studies that we announce or publish from time to time may change as more patient data become available and are subject to audit and verification procedures that could result in material changes in the final data.
From time to time, we may publicly disclose preliminary or topline data from our clinical studies, which are based on a preliminary analysis of then-available data, and the results and related findings and conclusions are subject to change following a more comprehensive review of the data related to the particular study or studies. We also make assumptions, estimations, calculations and conclusions as part of our analyses of data, and we may not have received or had the opportunity to fully and carefully evaluate all data. As a result, the topline results that we report may differ from future results of the same studies, or different conclusions or considerations may qualify such results, once additional data have been received and fully evaluated. Topline data also remain subject to audit and verification procedures that may result in the final data being materially different from the preliminary data we previously published. As a result, topline data should be viewed with caution until the final data are available. From time to time, we may also disclose interim data from our clinical studies. In addition, we may report interim analyses of only certain endpoints rather than all endpoints. Interim data from clinical studies that we may complete are subject to the risk that one or more of the clinical outcomes may materially change as patient enrollment continues and more patient data become available.
31
In addition, adverse changes between interim data and final data could significantly harm our business and prospects. Additional disclosure of interim data by us or by our competitors in the future could also result in volatility in the price of our common stock after this offering. Further, others, including regulatory agencies, may not accept or agree with our assumptions, estimates, calculations, conclusions or analyses or may interpret or weigh the importance of data differently, which could impact the value of the particular program, the approvability or commercialization of the particular product candidate or product and our Company in general. In addition, the information we choose to publicly disclose regarding a particular study or clinical study is based on what is typically extensive information, and you or others may not agree with what we determine is the material or otherwise, appropriate information to include in our disclosure, and any information we determine not to disclose may ultimately be deemed significant with respect to future decisions, conclusions, views, activities or otherwise regarding a particular drug, drug candidate or our business. If the topline data that we report differ from actual results, or if others, including regulatory authorities, disagree with the conclusions reached, our ability to obtain approval for, and commercialize, our Program Products or any future product candidates may be harmed, which could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Even if we complete the necessary clinical studies, we cannot predict when, or if, we will obtain regulatory approval to commercialize any of our Program Products, and the approval may be for a more narrow indication than we seek or be subject to other limitations or restrictions that limit its commercial profile.
Our Program Products have not received regulatory approval. We do not expect our Program Products or any future product candidate to be commercially available for years, if at all. Our Program Products are, and any future product candidate will be subject to strict regulation by regulatory authorities in the United States and in other countries. We cannot commercialize a product candidate or diagnostic device until the appropriate regulatory authorities have reviewed and approved such product candidate or diagnostic device. Even if our current or future Program Products meet safety and efficacy endpoints in pivotal clinical studies, the regulatory authorities may not complete their review processes in a timely manner, or we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval. Additional delays may result if an FDA Advisory Committee or other regulatory authority recommends non-approval or restrictions on approval. This may include approval of a product candidate for more limited indications than requested or they may impose significant limitations in the form of warnings. In addition, we may experience delays or rejections based upon additional government regulation from future legislation or administrative action, or changes in regulatory authority policy during the period of product development, clinical studies and the review process.
32
Our business depends on the success of our Program Products, including obtaining regulatory approval to market our product candidates in the United States and/or other major foreign markets such as the EU.
We are focusing our time and financial resources in the clinical development of GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD, and GEM-PSI. If we cannot successfully develop, obtain regulatory approval for, and commercialize our Program Products, we may not be able to continue our operations. The future regulatory approval and commercial success of our Program Products are subject to a number of risks, including the following:
Of the large number of drugs and devices in development in the pharmaceutical industry, only a small percentage results in the submission of a marketing authorization to the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities and even fewer are approved for commercialization. Furthermore, even if we do receive regulatory approval to market our Program Products, any such approval may be subject to limitations on the indicated uses or patient populations for which we may market the products. Accordingly, even if we are able to obtain the requisite financing to continue to fund our development programs, we may be unable to successfully develop or commercialize our Program Products.
If we or any of our future development collaborators are unable to develop, or obtain regulatory approval for, or, if approved, successfully commercialize our Program Products, we may not be able to generate sufficient revenue to continue our business.
33
Disruptions at the FDA and other national and foreign government authorities caused by funding shortages or global health concerns, such as COVID-19, could hinder their ability to hire, retain or deploy key leadership and other personnel, or otherwise prevent new or modified products from being developed, approved or commercialized in a timely manner or at all, which could negatively impact our business.
The ability of the FDA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities to review and approve new products can be affected by a variety of factors, including government budget and funding levels, statutory, regulatory, and policy changes, the FDA’s and foreign regulatory authorities’ ability to hire and retain key personnel and accept the payment of user fees, and other events that may otherwise affect the FDA’s and comparable foreign regulatory authorities’ ability to perform routine functions. Average review times at the FDA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities have fluctuated in recent years as a result. In addition, government funding of other government authorities that fund research and development activities is subject to the political process, which is inherently fluid and unpredictable. Disruptions at the FDA and other national and foreign authorities also may slow the time necessary for new biologics or modifications to approved biologics to be reviewed and/or approved by necessary government authorities, which would adversely affect our business. For example, over the last several years, including for 35 days beginning on December 22, 2018, the U.S. government has shut down several times and certain regulatory authorities, such as the FDA, have had to furlough critical FDA employees and stop critical activities.
Separately, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, in March 2020, the FDA announced its intention to postpone most inspections of foreign manufacturing facilities, and on March 18, 2020, the FDA temporarily postponed routine surveillance inspections of domestic manufacturing facilities. Subsequently, in July 2020, the FDA resumed certain on-site inspections of domestic manufacturing facilities subject to a risk-based prioritization system. The FDA utilized this risk-based assessment system to assist in determining when and where it was safest to conduct prioritized domestic inspections. Additionally, on April 15, 2021, the FDA began conducting voluntary remote interactive evaluations of certain drug manufacturing facilities and clinical research sites, among other facilities in circumstances where the FDA determines that such remote evaluation would be appropriate based on mission needs and travel limitations. In May 2021, the FDA outlined a detailed plan to move toward a more consistent state of inspectional operations, and in July 2021, the FDA resumed standard inspectional operations of domestic facilities. Since that time, the FDA has continued to monitor and implement changes to its inspectional activities to ensure the safety of its employees and those of the firms it regulates as it adapts to the evolving COVID-19 pandemic.
Regulatory authorities outside the United States have adopted similar restrictions or other policy measures in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. If a prolonged government shutdown occurs, or if global health concerns continue to prevent the FDA or other regulatory authorities from conducting their regular inspections, reviews, or other regulatory activities, it could significantly impact the ability of the FDA or other regulatory authorities to timely review and process our regulatory submissions, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Even if we obtain regulatory approval for a product candidate, our products and business will remain subject to ongoing regulatory obligations and review.
Even if our Program Products are approved, they will be subject to ongoing regulatory requirements for manufacturing, labeling, packaging, storage, advertising, distribution, promotion, sampling, record-keeping, conduct of post-marketing studies and submission of safety, efficacy and other post-market information, including both federal and state requirements in the United States and comparable requirements outside of the United States. Accordingly, we and others with whom we work must continue to expend time, money and effort in all areas of regulatory compliance, including manufacturing, production and quality control. If a regulatory agency discovers previously unknown problems with a product, such as adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, quality of product or disagrees with the promotion, marketing or labeling of a product, such regulatory agency may impose restrictions on that product or us, including requiring recall or withdrawal of the product from the market.
34
In addition, manufacturers of drug products and their facilities are subject to continual review and periodic inspections by the FDA and other regulatory authorities for compliance with cGMP, regulations and standards. If we or a regulatory agency discover previously unknown problems with a product, such as adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or problems with the facility where the product is manufactured, a regulatory agency may impose restrictions on that product, the manufacturing facility or us, including requiring recall or withdrawal of the product from the market or suspension of manufacturing. If we, our product candidates or the manufacturing facilities for our product candidates fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, or undesirable side effects caused by such products are identified, a regulatory agency may:
The occurrence of any event or penalty described above may inhibit our ability to commercialize our products and generate product revenue.
If one or more of our Program Products is approved for marketing in the United States or other countries, we may be subject, directly or indirectly, to United States or other countries equivalent federal and state healthcare fraud and abuse laws, false claims laws, physician payment transparency laws and health information privacy and security laws. If we are unable to comply, or have not fully complied, with such laws, we could face substantial penalties.
Even if we obtain FDA or other comparable regulatory agencies approval for any of our Program Products and begin commercializing those products in the United States or other countries, our operations may be directly or indirectly through our relationships with physicians, patients, third-party payors and customers, subject to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations that may constrain our business or financial arrangements and relationships through which we research, market, sell and distribute our Program Products. In addition, we may be subject to patient privacy regulation by both the federal government and the states in which we conduct our business. The laws that may affect our ability to operate include, among others, the United States Anti-Kickback Statute, the False Claims Act, the United States Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, and the Sunshine Act and analogous state laws. Ensuring that our internal operations and business arrangements with third parties comply with all applicable healthcare laws and regulations will likely be costly.
Legislative or regulatory healthcare reforms in the United States or other countries may make it more difficult and costly for us to obtain regulatory clearance or approval of our Program Products and to produce, market and distribute our Program Products after clearance or approval is obtained.
From time to time, legislation is drafted and introduced in Congress that could significantly change the statutory provisions governing the regulatory clearance or approval, manufacture and marketing of regulated products or the reimbursement thereof. In addition, FDA or other comparable regulatory agencies regulations and guidance are often revised or reinterpreted by the FDA or other comparable regulatory agencies in ways that may significantly affect our business and our products. Any new regulations or revisions or reinterpretations of existing regulations may impose additional costs or lengthen review times of our Program Products. We cannot determine what effect changes in regulations, statutes, legal interpretation or policies, when and if promulgated, enacted or adopted may have on our business in the future.
35
We face intense competition in an environment of rapid technological change and the possibility that our competitors may develop products and drug delivery systems that are similar, more advanced or more effective than ours, which may adversely affect our financial condition and our ability to successfully market or commercialize our Program Products.
The pharmaceutical industry in which we operate is intensely competitive and subject to rapid and significant technological change. We are currently aware of various existing therapies in the market and in development that may in the future compete with our Program Products.
Even if approved, we will compete with currently approved therapies and therapies further along in development. Our competitors both in the United States and abroad include large, well-established pharmaceutical and generic companies with significantly greater name recognition and an established market share. Our competitors may be able to charge lower prices than we can, which may adversely affect our market acceptance. Many of these competitors have greater resources than we do, including financial, product development, marketing, personnel and other resources.
If our competitors market products that are more effective, safer or cheaper than our products or that reach the market sooner than our products, we may not achieve commercial success. In addition, the biopharmaceutical industry is characterized by rapid technological change. Because our research approach integrates many technologies, it may be difficult for us to stay abreast of the rapid changes in other technologies. If we fail to stay at the forefront of technological change, we may be unable to compete effectively. Technological advances or products developed by our competitors may render our technologies, products or product candidates obsolete, less competitive or not economical. Many of our competitors have substantially greater financial, technical, human and other resources than we do and may be better equipped to develop, manufacture and market technologically superior products. In addition, many of these competitors have significantly longer operating histories and greater experience than we have in undertaking preclinical studies and human clinical studies of new pharmaceutical products and in obtaining regulatory approvals of human therapeutic products. Many of our competitors have established distribution channels for the commercialization of their products, whereas we have no such channel or capabilities. In addition, many competitors have greater name recognition and more extensive collaborative relationships.
As a result, our competitors may obtain regulatory approval of their products more rapidly than we do or may obtain patent protection or other intellectual property rights that limit our ability to develop or commercialize our product candidate or any future product candidates. Our competitors may also develop and succeed in obtaining approval for drugs that are more effective, more convenient, more widely used and less costly or have a better safety profile than our products and these competitors may also be more successful than we are in manufacturing and marketing their products. If we are unable to compete effectively against these companies, then we may not be able to commercialize our product candidate or any future product candidates or achieve a competitive position in the market. This would adversely affect our ability to generate revenue. Our competitors also compete with us in recruiting and retaining qualified scientific, management and commercial personnel, establishing clinical study sites and enrolling patients for clinical studies, as well as in acquiring technologies complementary to, or necessary for, our programs. Our inability to compete effectively in any of these aspects of our business could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Risks Related to our Reliance on Third Parties
We rely on third parties to conduct certain elements of our preclinical and clinical studies and perform other tasks for us. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties, meet expected deadlines or comply with regulatory requirements, we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or commercialize our Program Products.
We currently rely on, and expect to continue to rely on, third parties, such as CROs, clinical data management organizations, medical institutions, consultants and clinical investigators, to conduct our clinical studies and certain aspects of our research and preclinical testing. Any of these third parties may terminate their engagements with us at any time. If we need to enter into alternative arrangements, it will delay our product development activities and such alternative arrangements may not be available on terms acceptable to us.
Our reliance on these third parties for research and development activities will reduce our control over these activities but will not relieve us of our responsibilities. For example, we will remain responsible for ensuring that each of our clinical studies are conducted in accordance with the general investigational plan and protocols for the study. Moreover, the FDA and other regulatory agencies requires us to comply with standards, commonly referred to as current Good Clinical Practices or equivalent, for conducting, recording and reporting the results of clinical studies to assure that data and reported results are credible and accurate and that the rights, integrity and confidentiality of study participants are protected. We also are required to register ongoing clinical studies and post the results of completed clinical.
36
We rely on third parties to manufacture the raw materials, including the active pharmaceutical ingredients that we use to create our therapeutic product candidate, and to manufacture the diagnostic devices, including the antibodies used for testing. Our business could be harmed if existing and prospective third parties fail to provide us with sufficient quantities of these materials and products or fail to do so at acceptable quality levels or prices.
We rely on third party suppliers for certain raw materials necessary to manufacture our product candidates for our preclinical studies and clinical studies and to manufacture our diagnostic tests for our clinical studies. Some of these raw materials and test components are difficult to source. Because there are a limited number of suppliers for these raw materials and components, we may need to engage alternate suppliers to prevent a possible disruption of the manufacture of the materials necessary to produce our Program Products for our clinical studies, and if approved, ultimately for commercial sale. In particular, there is only one supplier for PHAD®, Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc. Although we have secured enough material through a purchase order for our planned clinical trials, we do not have a long-term supply agreement with Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc. We do not have any control over the availability of raw materials and components. If we or our manufacturers are unable to purchase these raw materials or components on acceptable terms, at sufficient quality levels, or in adequate quantities, if at all, the development and commercialization of our product candidates or any future product candidates, would be delayed or there would be a shortage in supply, which would impair our ability to meet our development objectives for our Program Products or generate revenues from the sale of any approved products.
Until such time, if ever, as we establish a manufacturing facility that has been properly validated to comply with FDA or other comparable regulatory agencies cGMP requirements, we will not be able to independently manufacture Program Products for our planned preclinical and clinical programs. We currently rely on a third-party manufacturer for the production of our clinical study materials., GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD, and GEM-PSI have been and for the near-term will be manufactured by a single third-party manufacturer. This manufacturer may not be able to scale production to the larger quantities required for large clinical studies and to commercialize GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD, and GEM-PSI, if approved. Also, the third-party manufacturers may not be able to produce Program Products that meet the quality requirements. In the event that this third-party manufacturer does not successfully carry out its contractual duties, meet expected deadlines or manufacture our products in accordance with regulatory requirements or if there are disagreements between us and this third-party manufacturer, we will not be able to complete, or may be delayed in completing, the clinical studies required. In such instances, we may need to locate an appropriate replacement third-party relationship, which may not be readily available or on acceptable terms, which would cause additional delay or increased expense and would thereby have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We do not have a long-term supply agreement with any third-party manufacturer. Reliance on third-party manufacturers entails risks to which we would not be subject if we manufacture product candidates or products ourselves. For example, if we do not maintain our key manufacturing relationships, we may fail to find replacement manufacturers or develop our own manufacturing capabilities in a timely manner or at all, which could delay or impair our ability to obtain regulatory approval for our products and substantially increase our costs or deplete profit margins, if any. If we do find replacement manufacturers, we may not be able to enter into agreements with them on terms and conditions favorable to us, and there could be a substantial delay before new facilities could be qualified and registered with the FDA and other comparable foreign regulatory authorities. Even if we are able to establish agreements with third-party manufacturers, reliance on third-party manufacturers entails additional risks, including:
37
Certain raw materials necessary for the manufacture of our Program Products, such as our active pharmaceutical ingredient, are available only from a single supplier. Any significant delay in the acquisition or decrease in the availability of these raw materials from our supplier could considerably delay their manufacture, which could adversely impact the timing of any planned studies or the regulatory approvals. The FDA and other comparable foreign regulatory authorities require manufacturers to register manufacturing facilities. The FDA and other comparable foreign regulatory authorities also inspect these facilities to confirm compliance with cGMP.
Contract manufacturers may face manufacturing or quality control problems causing drug substance, drug product, diagnostic test kit production and shipment delays or a situation where the contractor may not be able to maintain compliance with the applicable cGMP requirements. We may have little to no control regarding the occurrence of third-party manufacturer incidents. Any failure to comply with cGMP requirements or other FDA or comparable foreign regulatory requirements could adversely affect our clinical research activities and our ability to develop our Program Products or any future product candidates and market our Program Products following approval.
If our Program Products or any future product candidates are approved by the FDA or other comparable foreign regulatory authorities for commercial sale, we may need to manufacture such product candidate in larger quantities. We intend to use third-party manufacturers for commercial quantities of our Program Products to the extent we advance this product candidate and other product candidates. Our manufacturers may not be able to successfully increase the manufacturing capacity for any of our product candidates in a timely or efficient manner, or at all. If we are unable to successfully increase the manufacturing capacity for a product candidate, the regulatory approval or commercial launch of that product candidate may be delayed or there may be a shortage in the supply of the product candidate.
In addition, the operations of our third-party manufacturers may be subject to earthquakes, power shortages, telecommunications failures, failures or breaches of information technology systems, water shortages, floods, hurricanes, typhoons, fires, extreme weather conditions, medical epidemics, and other natural or man-made disasters or business interruptions. Damage or extended periods of interruption to our facilities due to fire, natural disaster, power loss, communications failure, unauthorized entry or other events could cause us to cease or delay development of some or all of our product candidates. Our ability to obtain clinical supplies of our product candidates could be disrupted if the operations of these suppliers are affected by a man-made or natural disaster or other business interruption.
Our current and anticipated future dependence upon others for the manufacture of our product candidates may adversely affect our future profit margins and our ability to develop our product candidates and commercialize any products that receive regulatory approval on a timely basis.
In some cases, the technical skills or technology required to manufacture our product candidates may be unique or proprietary to the original manufacturer, we may have difficulty transferring such skills or technology to another third party and a feasible alternative many not exist. These factors would increase our reliance on such manufacturer or require us to obtain a license from such manufacturer in order to have another third party manufacture our product candidates. If we are required to change manufacturers for any reason, we will be required to verify that the new manufacturer maintains facilities and procedures that comply with quality standards and with all applicable regulations and guidelines. The delays associated with the verification of a new manufacturer, if we are able to identify an alternative source, could negatively affect our ability to develop product candidates in a timely manner or within budget.
We may not be able to obtain and maintain the third-party relationships that are necessary to develop, commercialize and manufacture some or all of our product candidates.
We expect to depend on collaborators, partners, licensees, clinical investigators, CROs, manufacturers and other third parties to support our discovery efforts, to formulate product candidates, to conduct clinical studies for some or all of our Program Products, to manufacture clinical and commercial scale quantities of our drug substance, drug product, diagnostic test and to market, sell and distribute any products we successfully develop. Any problems we experience with any of these third parties could delay the development, commercialization and manufacturing of our product candidates, which could harm our results of operations.
We cannot guarantee that we will be able to successfully negotiate agreements for, or maintain relationships with, collaborators, partners, licensees, clinical investigators, CROs, manufacturers and other third parties on favorable terms, if at all. If we are unable to obtain or maintain these agreements, we may not be able to clinically develop, formulate, manufacture, obtain regulatory approvals for or commercialize our Program Products and any future product candidates, which will in turn adversely affect our business.
38
We expect to expend substantial management time and effort to enter into relationships with third parties and, if we successfully enter into such relationships, to manage these relationships. In addition, substantial amounts will be paid to third parties in these relationships. However, we cannot control the amount or timing of resources our future contract partners will devote to our research and development programs, product candidates or potential product candidates, and we cannot guarantee that these parties will fulfill their obligations to us under these arrangements in a timely fashion, if at all. In addition, while we manage the relationships with third parties, we cannot control all of the operations of, and any outsourcing used by such third parties. We rely on third parties’ knowledge regarding specific local laws and regulatory requirements in foreign jurisdictions, where applicable.
We depend on our information technology systems and those of our third-party collaborators, service providers, contractors or consultants. Our internal computer systems, or those of our third-party collaborators, service providers, contractors or consultants, may fail or suffer security breaches, disruptions, or incidents, which could result in a material disruption of our development programs or loss of data or compromise the privacy, security, integrity or confidentiality of sensitive information related to our business and have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, financial condition or results of operations.
In the ordinary course of our business, we collect, store and transmit large amounts of confidential information, including intellectual property, proprietary business information and personal information. Our internal technology systems and infrastructure, and those of our current or future third-party collaborators, service providers, contractors and consultants are vulnerable to damage from computer viruses, unauthorized access or use resulting from malware, natural disasters, terrorism, war and telecommunication and electrical failures, denial-of-service attacks, cyber-attacks or cyber-intrusions over the Internet, hacking, phishing and other social engineering attacks, persons inside our organizations (including employees or contractors), loss or theft, or persons with access to systems inside our organization. Attacks on information technology systems are increasing in their frequency, levels of persistence, sophistication and intensity, and they are being conducted by increasingly sophisticated and organized foreign governments, groups and individuals with a wide range of motives and expertise. In addition to extracting or accessing sensitive information, such attacks could include the deployment of harmful malware, ransomware, denial-of-service attacks, social engineering and other means to affect service reliability and threaten the security, confidentiality, integrity and availability of information. The prevalent use of mobile devices that access sensitive information also increases the risk of data security incidents which could lead to the loss of confidential information or other intellectual property. While to our knowledge we have not experienced any material system failure, accident or security breach to date, if such an event were to occur and cause interruptions in our operations or the operations of third-party collaborators, service providers, contractors and consultants, it could result in a material disruption of our development programs and significant reputational, financial, legal, regulatory, business or operational harm. The costs to us to mitigate, investigate and respond to potential security incidents, breaches, disruptions, network security problems, bugs, viruses, worms, malicious software programs and security vulnerabilities could be significant, and while we have implemented security measures to protect our data security and information technology systems, our efforts to address these problems may not be successful, and these problems could result in unexpected interruptions, delays, cessation of service and other harm to our business and our competitive position.
For example, the loss of clinical study data from completed, ongoing or planned clinical studies for our product candidates could result in delays in our regulatory approval efforts and significantly increase our costs to recover or reproduce the data. To the extent that any real or perceived security breach affects our systems (or those of our third-party collaborators, service providers, contractors or consultants), or results in the loss of or accidental, unlawful or unauthorized access to, use of, release of, or other processing of personally identifiable information or damage to our data or applications or other data or applications relating to our technology or product candidates, or inappropriate disclosure of confidential or proprietary information, we could incur liabilities and the further development of our product candidates could be delayed. Such a breach may require notification to governmental agencies, the media or individuals pursuant to various foreign, domestic (federal and state) privacy and security laws, if applicable, including HIPAA, as amended by HITECH, and its implementing rules and regulations, as well as regulations promulgated by the Federal Trade Commission and state breach notification laws. In addition, our liability insurance may not be sufficient in type or amount to cover us against claims related to security breaches, cyberattacks and other related incidents.
Any failure or perceived failure by us or any third-party collaborators, service providers, contractors or consultants to comply with our privacy, confidentiality, data security or similar obligations, or any data security incidents or other security breaches that result in the accidental, unlawful or unauthorized access to, use of, release of, processing of, or transfer of sensitive information, including personally identifiable information, may result in negative publicity, harm to our reputation, governmental investigations, enforcement actions, regulatory fines, litigation or public statements against us, could cause third parties to lose trust in us or could result in claims by third parties, including those that assert that we have breached our privacy, confidentiality, data security or similar obligations, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, financial condition or results of operations. To the extent we maintain individually identifiable health information, we could be subject to fines and penalties (including civil and criminal) under HIPAA for any failure by us or our business associates to comply with HIPAA’s requirements. Moreover, data security incidents and other security breaches can be difficult to detect, and any delay in identifying them may lead to increased harm. While we have implemented data security measures intended to protect our information, data, information technology systems, applications and infrastructure, there can be no assurance that such measures will successfully prevent service interruptions or data security incidents.
39
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
If we are unable to obtain and maintain effective patent rights for our product candidates or any future product candidates, we may not be able to compete effectively in our markets. If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our trade secrets or know-how, such proprietary information may be used by others to compete against us.
Our success will depend in significant part on our and our future licensors’, licensees’ or collaborators’ ability to establish and maintain adequate protection of our owned and licensed intellectual property covering the product candidates we plan to develop, and the ability to develop these product candidates and commercialize the products resulting therefrom, without infringing the intellectual property rights of others. Our Program Products have been developed in-house and are not subject to any third-party license. In addition to taking other steps to protect our intellectual property, we file patent applications to protect inventions we have developed, seeking to protect compositions, methods of use, manufacturing methods, and other aspects of our technology. There can be no assurance that any of these patent applications will issue as patents or, for those applications that do mature into patents, that the claims of these patents will exclude others from making, using or selling our product candidates or products that compete with or are similar to our product candidates.
With respect to patent rights, we cannot be certain whether any of the technology described in our patent applications for any of our product candidates will remain relevant to our future commercial products, whether any of our patent applications will issue as patents, whether any patents that may be issued to us will effectively protect our commercial processes and product candidates, or whether any patents that may be issued to us will effectively prevent others from competing with our products.
In countries where we have not sought and do not seek patent protection, third parties may be able to manufacture and sell our product candidates without our permission, and we may not be able to stop them from doing so.
Publications of discoveries in the scientific literature often lag behind the actual discoveries, and patent applications in the United States and other jurisdictions are typically not published until 18 months after filing or in some cases not at all, until they are issued as a patent. Therefore, we cannot be certain that we or future licensors, licensees or collaborators were the first to make the inventions claimed in our owned or licensed patents or pending patent applications, or that we or future licensors, licensees or collaborators were the first to file for patent protection of such inventions.
Any changes we make to our Program Products or any future product candidates to cause them to have what we view as more advantageous properties may fall outside the coverage of our existing patent applications, and we may need to file new patent applications and/or seek other forms of protection for any such altered product candidates. The patent landscape surrounding the technology underlying our product candidates is crowded, and there can be no assurance that we will be able to secure patent protection that would adequately cover such altered Program Products or any future product candidates.
The patent prosecution process is expensive and time-consuming, and we and our future licensors, licensees or collaborators may not be able to prepare, file and prosecute all necessary or desirable patent applications at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner. It is also possible that we or our future licensors, licensees or collaborators will fail to identify patentable aspects of inventions made in the course of development and commercialization activities before it is too late to obtain patent protection for them. Moreover, in some circumstances, we may not have the right to control the preparation, filing and prosecution of patent applications, or to maintain or enforce the patents, covering technology that we license from or license to third parties and may be reliant on our current or future licensors, licensees or collaborators to perform these activities, which means that these patent applications may not be prosecuted, and these patents may not be enforced or maintained, in a manner consistent with the best interests of our business. If our future licensors, licensees or collaborators fail to establish, maintain, protect or enforce such patents and other intellectual property rights, such rights may be reduced or eliminated. If our future licensors, licensees or collaborators are not fully cooperative or disagree with us as to the prosecution, maintenance or enforcement of any patent rights, such patent rights could be compromised.
Similar to the patent rights of other biotechnology companies, the scope, validity and enforceability of our owned and licensed patent rights generally are highly uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions. The issuance of a patent is not conclusive as to its inventorship, scope, validity or enforceability, and our patents may be challenged in the courts or patent offices in the United States and abroad. In recent years, these areas have been the subject of much litigation in the industry. As a result, the issuance, scope, validity, enforceability and commercial value of our and our current or future licensors’, licensees’ or collaborators’ patent rights are highly uncertain. Our and our future licensors’, licensees’ or collaborators’ future patent applications may not result in patents being issued that protect our technology or product candidates, or that effectively prevent others from commercializing competitive technologies and products. The patent examination process may require us or our future licensors, licensees or collaborators to narrow the scope of the claims of our patent applications, which would limit the scope of patent protection that is obtained, if any. Our and our future licensors’, licensees’ or collaborators’ patent applications cannot be enforced against third parties practicing the technology that is currently claimed in such applications unless and until a patent issues from such applications, and then only to the extent the claims that issue are broad enough to cover the technology being practiced by those third parties.
40
We may not be able to protect our intellectual property rights throughout the world.
Filing, prosecuting, enforcing and defending patents on product candidates in all countries throughout the world would be prohibitively expensive, and we may not protect our intellectual property in some countries outside the United States to the same extent as in the United States. In addition, the laws of some foreign countries do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as federal and certain state laws in the United States.
Consequently, we may not be able to prevent third parties from practicing our inventions in all countries outside the United States, or from selling or importing products made using our inventions in and into the United States or other jurisdictions. Competitors may use technologies in jurisdictions where we have not obtained patent protection to develop their own products and, further, may export otherwise infringing products to territories where we do not have patent protection, or where we do have patent protection, but enforcement is not as strong as that in the United States. These products may compete with our Program Products or any future product candidates and our patents or other intellectual property rights may not effectively prevent them from competing.
Many companies have encountered significant problems in protecting and defending intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions. The legal systems of certain countries, particularly certain developing countries, do not favor the enforcement of patents and other intellectual property protection, particularly those relating to biopharmaceuticals. This could make it difficult for us to stop the infringement of our patents or the marketing of competing products in violation of our proprietary rights. Proceedings to enforce our patent rights in foreign jurisdictions could result in substantial costs and divert our efforts and attention from other aspects of our business, could put our patents at risk of being revoked, invalidated or interpreted narrowly, and could provoke third parties to assert claims against us or our collaborator. We may not prevail in any lawsuits that we initiate, and the damages or other remedies awarded, if any, may not adequately compensate us for the harm to our business.
Different countries impose different requirements for patentability and certain countries have heightened requirements for patentability, requiring more disclosure in the patent application or disfavoring the issuance of broad claims. In addition, certain countries have compulsory licensing laws under which a patent owner may be compelled to grant licenses to third parties. In such countries, we may have limited remedies if patents are infringed or if we are compelled to grant a license to a third party, which could materially diminish the value of those patents. This could limit our potential revenue opportunities. In addition, many countries limit the enforceability of patents against government agencies or government contractors. In these countries, the patent owner may have limited remedies, which could materially diminish the value of such patent. Accordingly, our efforts to enforce intellectual property rights around the world may be inadequate to obtain a significant commercial advantage from the intellectual property that we own or license.
We may not have sufficient patent lifespan to effectively protect our products and business.
All of our patents are in early stages. Patents have a limited lifespan. In the United States, the natural expiration of a patent is generally 20 years after its priority date. Given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after the resulting products are commercialized. As a result, our owned and future in-licensed patents may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing products similar or identical to ours. We expect to seek extensions of patent terms for our issued patents, where available. This includes in the United States under the Hatch-Waxman Act, which permits a patent term extension of up to five years beyond the original expiration date of the patent as compensation for regulatory delays. However, such a patent term extension cannot lengthen the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the product’s approval date. Only one patent applicable to an approved drug is eligible for the extension and the application for the extension must be submitted prior to the expiration of the patent. During the period of patent term extension, the claims of a patent are not enforceable for their full scope but are instead limited to the scope of the approved product. In addition, the applicable authorities, including the FDA in the United States, and any comparable foreign regulatory authorities, may not agree with our assessment of whether such extensions are available, and may refuse to grant extensions to our patents, or may grant more limited extensions than we request. In addition, we may not be granted an extension because of, for example, failing to apply within applicable deadlines, failing to apply prior to the expiration of relevant patents or otherwise failing to satisfy applicable requirements. If this occurs, any period during which we have the right to exclusively market our product will be shorter than we would otherwise have expected, and our competitors may obtain approval of and launch products earlier than might otherwise have been the case.
41
If we are unable to maintain effective proprietary rights for our Program Products or any future product candidates, we may not be able to compete effectively in our markets.
In addition to the protection afforded by any patents that may be granted, we rely on trade secret protection and confidentiality agreements to protect proprietary know-how that is not patentable or that we elect not to patent, processes for which patents are difficult to enforce and any other elements of our product candidate discovery and development processes that involve proprietary know-how, information or technology that is not covered by patents. However, trade secrets can be difficult to protect. We protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by entering into confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors and contractors. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data, trade secrets and intellectual property by maintaining the physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems. While we have confidence in these individuals, organizations and systems, agreements or security measures may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets and intellectual property may otherwise become known or be independently discovered by competitors.
Additionally, our reliance on third parties, including CROs and outside consultants, requires us to share our trade secrets and intellectual property, which increases the possibility that a competitor will discover them or that our trade secrets and intellectual property will be misappropriated or publicly disclosed. The steps that we have already taken to protect our intellectual property may not be sufficient or effective, and our confidentiality, non-disclosure, or invention assignment agreements with employees, consultants, partners, or other parties may be breached and may otherwise not be effective in establishing our rights in intellectual property and in controlling access to our proprietary information. Even if we do detect violations, we may need to engage in litigation to enforce our rights, and such litigation, even if successful, may not restore our proprietary rights or adequately compensate us for the damage to our rights or our business.
We may be involved in lawsuits to protect or enforce our intellectual property, which could be expensive, time-consuming and unsuccessful.
Third parties may infringe our patents or misappropriate or otherwise violate our intellectual property rights. In the future, we may initiate legal proceedings to enforce or defend our intellectual property rights, to protect our trade secrets or to determine the validity or scope of intellectual property rights we own or control. Also, third parties may initiate legal proceedings against us to challenge the validity or scope of intellectual property rights we own, control or license. For example, generic or biosimilar drug manufacturers or other competitors or third parties may challenge the scope, validity or enforceability of our patents, requiring us to engage in complex, lengthy and costly litigation or other proceedings. These proceedings can be expensive and time-consuming and many of our adversaries in these proceedings may have the ability to dedicate substantially greater resources to prosecuting these legal actions than we can. Accordingly, despite our efforts, we may not be able to prevent third parties from infringing upon or misappropriating intellectual property rights we own, control or license, particularly in countries where the laws may not protect those rights as fully as in the United States. Litigation could result in substantial costs and diversion of management resources, which could harm our business and financial results. In addition, if we initiated legal proceedings against a third party to enforce a patent covering a product candidate, the defendant could assert that such patent is invalid or unenforceable, or does not cover their product candidate. Grounds for a validity challenge could be an alleged failure to meet any of several statutory requirements, including lack of novelty, obviousness or non-enablement. Grounds for an unenforceability assertion could be an allegation that someone connected with prosecution of the patent withheld relevant information from the USPTO, or made a misleading statement, during prosecution. In an infringement or declaratory judgment proceeding, a court may decide that a patent owned by or licensed to us is invalid or unenforceable or may refuse to stop the other party from using the subject matter alleged to be infringing on the grounds that our patents do not cover that subject matter. An adverse result in any litigation proceeding could put one or more of our patents at risk of being invalidated, narrowed, held unenforceable or interpreted in such a manner that would allow third parties to enter the market with competing products.
Third-party pre-issuance submission of prior art to the USPTO, or opposition, derivation, revocation, reexamination, inter parties review, post-grant review or interference proceedings, or other patent office proceedings or litigation in the United States or other jurisdictions provoked by third parties or brought by us, may be necessary to determine the inventorship, priority, patentability or validity of inventions with respect to our patents or patent applications. An unfavorable outcome could leave our technology or product candidates without patent protection, could allow third parties to commercialize our technology or product candidates and compete directly with us, or without payment to us. In addition, if the breadth or strength of protection provided by our patents and patent applications is threatened, it could dissuade companies from collaborating with us to license, develop or commercialize current or future product candidates. Even if we successfully defend such litigation or proceeding, we may incur substantial costs and our defense may distract our management and other employees.
42
Furthermore, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation, there is a risk that some of our confidential information could be compromised by disclosure during this type of litigation. In addition, many foreign jurisdictions have rules of discovery that are different than those in the United States and that may make defending or enforcing our patents extremely difficult. There could also be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments. If securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, it could have a material adverse effect on the price of shares of our common stock.
We may infringe the intellectual property rights of others, which could increase our costs and delay or prevent our development efforts.
Our commercial success depends upon our ability to develop, manufacture, market and sell our Program Products and any future product candidates that we may develop and use our proprietary technologies without infringing, misappropriating or otherwise violating the intellectual property and proprietary rights of third parties. The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries are characterized by extensive litigation regarding patents and other intellectual property rights. Third parties may initiate legal proceedings against us alleging that we infringe their intellectual property rights, or we may initiate legal proceedings against third parties to challenge the validity or scope of intellectual property rights controlled by third parties, including in oppositions, interferences, revocations, reexaminations, inter parties review, post-grant review or derivation proceedings before the USPTO or its counterparts in other jurisdictions. These proceedings can be expensive and time-consuming and many of our adversaries in these proceedings may have the ability to dedicate substantially greater resources to prosecuting these legal actions than we can.
We could be found liable for monetary damages, including treble damages and attorneys’ fees, if we are found to have willfully infringed a patent of a third party. A finding of infringement could prevent us from commercializing our Program Products or any future product candidates or force us to cease some of our business operations, which could materially harm our business.
We may not be aware of all third-party intellectual property rights potentially relating to our Program Products or any future product candidates. As to pending third-party applications, we cannot predict with any certainty which claims will issue, if any, or the scope of any claims that may issue. Even if we believe third-party intellectual property claims are without merit, there is no assurance that a court would find in our favor on questions of infringement, validity, enforceability or priority. A court of competent jurisdiction could hold that these third-party patents are valid, enforceable and infringed, which could materially and adversely affect our ability to commercialize any product candidates we may develop and any other product candidates covered by the asserted third-party patents. In order to successfully challenge the validity of any such U.S. patent in federal court, we would need to overcome a presumption of validity. As this burden is a high one requiring us to present clear and convincing evidence as to the invalidity of any such U.S. patent claim, there is no assurance that a court of competent jurisdiction would invalidate the claims of any such U.S. patent. If any third-party patents were successfully asserted against us or our commercialization partners and we were unable to successfully challenge the scope, validity or enforceability of any such asserted patents, then we and our commercialization partners may be prevented from commercializing our product candidates, or may be required to pay significant damages, including treble damages and attorneys’ fees if we are found to willfully infringe the asserted patents, or obtain a license to such patents, which may not be available on commercially reasonable terms, or at all. Even if we were able to obtain a license, it could be non-exclusive, thereby giving our competitors and other third parties’ access to the same technologies licensed to us, and it could require us to make substantial licensing and royalty payments. Any of the foregoing would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and operating results.
Although we have reviewed certain third-party patents and patent filings that we believe may be relevant to our therapeutic candidates or products, we have not conducted a freedom-to-operate search or analysis for any of our therapeutic candidates or products, and we may not be aware of patents or pending or future patent applications that, if issued, would block us from commercializing our therapeutic candidates or products. Thus, we cannot guarantee that our therapeutic candidates or products, or our commercialization thereof, do not and will not infringe any third party’s intellectual property.
43
Changes in United States and international patent law could diminish the value of patents in general, thereby impairing our ability to protect our products.
As is the case with other biotechnology companies, our success is heavily dependent on IP, particularly patents. Obtaining and enforcing patents in the biotechnology industry involve both technological and legal complexity, and therefore obtaining and enforcing biotechnology patents is costly, time-consuming and inherently uncertain. Recent U.S. Supreme Court rulings have narrowed the scope of patent protection available in certain circumstances and weakened the rights of patent owners in certain situations, which may diminish our ability to obtain and enforce patents for our inventions. Depending on decisions by the U.S. Congress, the federal courts, and the USPTO, the laws and regulations governing patents could change in unpredictable ways that would weaken our ability to obtain new patents or to enforce our existing patents and patents that we might obtain in the future. Furthermore, depending on the Supreme Court’s review of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (the “Affordable Care Act”), or legislation to repeal or amend the Affordable Care Act, the twelve years of regulatory exclusivity currently provided to certain biologic products in the United States may be reduced or eliminated. Any such reduction or elimination could impair the length of exclusivity against similar products.
Our inability to protect our trade secrets would harm our business and competitive position.
In addition to seeking patents for some of our technology and product candidates, we also rely substantially on trade secrets, including unpatented know-how, technology and other proprietary materials and information, to maintain our competitive position. We protect these trade secrets, in part, by entering into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to them, such as our employees, corporate collaborators, outside scientific collaborators, contract manufacturers, consultants, advisors and other third parties. However, these steps may be inadequate, we may fail to enter into agreements with all such parties or any of these parties may breach the agreements and disclose our trade secrets and there may be no adequate remedy available for such breach of an agreement. We cannot assure you that our trade secrets will not be disclosed or that we can meaningfully protect our trade secrets. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive and time-consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, some courts both within and outside the United States may be less willing, or unwilling, to protect trade secrets. If a competitor lawfully obtained or independently developed any technology or information that we protect as trade secret, we would have no right to prevent such competitor from using that technology or information to compete with us, which could harm our competitive position.
Intellectual property rights do not necessarily address all potential threats.
The degree of future protection afforded by our intellectual property rights is uncertain because intellectual property rights have limitations and may not adequately protect our business or permit us to maintain our competitive advantage. For example:
44
Should any of these events occur, they could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
If our trademarks and trade names are not maintained and adequately protected, we may not be able to build name recognition in our markets of interest, and our business may be adversely affected.
Failure to obtain trademark registrations in the future could limit our ability to protect and enforce our trademarks and impede our marketing efforts in the countries in which we intend to operate. We may not be able to protect our rights to trademarks and trade names which we may need to build name recognition with potential partners or customers in our markets of interest. As a means to enforce any future trademark rights and prevent infringement, we may be required to file trademark claims against third parties or initiate trademark opposition proceedings. This can be time-consuming and expensive and may strain the financial resources of a company of our size, and we may not ultimately be successful in enforcing our trademark rights. In addition, our registered or unregistered trademarks or trade names may be challenged, infringed, circumvented, declared generic or determined to be infringing on other marks.
Future trademark applications in the United States and in other foreign jurisdictions where we may file may not be allowed or may subsequently be opposed. Even if these applications result in registration of trademarks, third parties may challenge our use or registration of these trademarks in the future. Over the long term, if we are unable to establish name recognition based on our trademarks and trade names, then we may not be able to compete effectively, and our business may be adversely affected.
Risks Related to Our Business Operations
Our future success depends in part on our ability to retain our senior management team, directors and other key employees and to attract, retain and motivate other qualified personnel.
We may not be able to attract or retain qualified directors, personnel and consultants due to the intense competition for such individuals among in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries. If we are not able to attract and retain necessary personnel and consultants to accomplish our business objectives, we may experience constraints that will significantly impede the achievement of our development objectives, our ability to raise additional capital and our ability to implement our business strategy.
Our industry has experienced a high rate of turnover of management personnel in recent years. We are highly dependent on the development, regulatory, commercialization and business development expertise of the members of our executive team, as well as other key employees and consultants. If we lose one or more of our executive officers or other key employees or consultants, our ability to implement our business strategy successfully could be seriously harmed. Any of our executive officers or other key employees or consultants may terminate their employment or consultancy arrangements with us at any time and replacing such individuals may be difficult and time-consuming because of the limited number of individuals in our industry with the necessary breadth of skills and experience. Competition to hire and retain employees and consultants from this limited pool is intense, and we may be unable to hire, train, retain or motivate such individuals. Additionally, we do not currently maintain “key person” life insurance on the lives of our executives or any of our employees. This lack of insurance means that we may not receive adequate compensation for the loss of the services of these individuals. If we are unable to continue to attract and retain high-quality personnel, the rate and success with which we can discover and develop product candidates and our business will be limited.
We will need to expand our organization, and we may experience difficulties in managing this growth, which could disrupt our operations.
We are in the early stages of building the full management team and employee base that we anticipate we will need to complete the development of our Program Products and other future product candidates. As of March 3, 2025, we had 9 employees.
As we advance our preclinical and clinical development programs for our product candidates, seek regulatory approval in the United States and elsewhere and increase the number of ongoing product development programs, we anticipate that we will need to increase our product development, scientific and administrative headcount. We will also need to establish commercial capabilities in order to commercialize any product candidates that may be approved. Such an evolution may impact our strategic focus and our deployment and allocation of resources. Our management, personnel and systems may experience difficulty in adjusting to our growth and strategic focus.
Our ability to manage our operations and growth effectively depends upon the continual improvement of our procedures, reporting systems and operational, financial and management controls. We may not be able to implement administrative and operational improvements in an efficient or timely manner and may discover deficiencies in existing systems and controls. If we do not meet these challenges, we may be unable to execute our business strategies and may be forced to expend more resources than anticipated addressing these issues.
45
We may acquire additional technology and complementary businesses in the future. Acquisitions involve many risks, any of which could materially harm our business, including the diversion of management’s attention from core business concerns, failure to effectively exploit acquired technologies, failure to successfully integrate the acquired business or realize expected synergies or the loss of key employees from either our business or the acquired businesses.
In addition, in order to continue to meet our obligations as a public company and to support our anticipated long-term growth, we will need to increase our general and administrative capabilities. Our management, personnel and systems may not be adequate to support this future growth.
If we are unable to successfully manage our growth and the increased complexity of our operations, our business, financial position, results of operations and prospects may be materially and adversely affected.
We may not be successful in our efforts to identify, discover or license additional product candidates.
Although a substantial amount of our effort will focus on the continued clinical testing, potential approval and commercialization of our lead Program Products, the success of our business also depends upon our ability to identify, discover or license additional product candidates. Our research programs or licensing efforts may fail to yield additional product candidates for clinical development for a number of reasons, including (i) lack of financial or personnel resources to acquire or discover additional product candidates; (ii) product candidates may not succeed in preclinical or clinical testing; (iii) product candidates may be shown to have harmful side effects or may have other characteristics that may make the products unmarketable or unlikely to receive marketing approval; (iv) competitors may develop alternatives that render our product candidates obsolete or less attractive; (v) the market for a product candidate may change during our development program so that such product may become unprofitable to continue to develop; (vi) product candidates may not be capable of being produced in commercial quantities at an acceptable cost, or at all; and (vii) product candidates may not be accepted as safe and effective by patients, the medical community, or third-party payors.
We may be forced to abandon our development efforts for a program or programs that are unsuccessful, or we may not be able to identify, license, or discover additional product candidates, which would have a material adverse effect on our business and could potentially cause us to cease operations. Further, research programs to identify new product candidates require substantial technical, financial and human resources. We may focus our efforts and resources on potential programs or product candidates that ultimately prove to be unsuccessful.
If we fail to comply with environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, we could become subject to fines or penalties or incur costs that could have a material adverse effect on the success of our business.
Our research, development and manufacturing activities and our third-party manufacturers’ and suppliers’ activities involve the controlled storage, use and disposal of hazardous materials, including the components of our product candidates and other hazardous compounds. We and our manufacturers and suppliers are subject to laws and regulations governing the use, manufacture, storage, handling and disposal of these hazardous materials. In some cases, these hazardous materials and various wastes resulting from their use are stored at our and our manufacturers’ facilities pending their use and disposal. We cannot eliminate the risk of contamination, which could cause an interruption of our commercialization efforts, research and development efforts and business operations, environmental damage resulting in costly clean-up and liabilities under applicable laws and regulations governing the use, storage, handling and disposal of these materials and specified waste products. Although we believe that the safety procedures utilized by our third-party manufacturers for handling and disposing of these materials generally comply with the standards prescribed by these laws and regulations, we cannot guarantee that this is the case or eliminate the risk of accidental contamination or injury from these materials. In such an event, we may be held liable for any resulting damages, such liability could exceed our resources, and state or federal or other applicable authorities may curtail our use of certain materials and/or interrupt our business operations. Furthermore, environmental laws and regulations are complex, change frequently and have tended to become more stringent. We cannot predict the impact of such changes and cannot be certain of our future compliance. We do not currently carry biological or hazardous waste insurance coverage.
46
Ongoing healthcare legislative and regulatory reform measures may adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Changes in regulations, statutes or the interpretation of existing regulations could impact our business in the future by requiring, for example: (1) changes to our manufacturing arrangements; (2) additions or modifications to product labeling; (3) the recall or discontinuation of our products; (4) post-marketing approvals or compliance programs or (5) additional record-keeping requirements. If any such changes were to be imposed, they could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
In the United States, there have been and continue to be a number of legislative initiatives to contain healthcare costs. For example, in March 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010, or collectively the ACA, was passed by Congress, which substantially changes the way health care is financed by both governmental and private insurers, and significantly impacts the U.S. pharmaceutical industry. The ACA, among other things, subjected biological products to potential competition by lower-cost biosimilars, addressed a new methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated for drugs that are inhaled, infused, instilled, implanted or injected, increased the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program and extended the rebate program to individuals enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations, established annual fees and taxes on manufacturers of certain branded prescription drugs, and created a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 70% point-of-sale discounts off negotiated prices of applicable brand drugs to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period, as a condition for the manufacturer’s outpatient drugs to be covered under Medicare Part D.
Since its enactment, certain provisions the ACA have been subject to executive, judicial and congressional challenges. On June 17, 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court dismissed the most recent challenge to the ACA on procedural grounds that argued the ACA is unconstitutional in its entirety because the “individual mandate” was repealed by Congress. Thus, the ACA will remain in effect in its current form. Further, prior to the U.S. Supreme Court ruling, President Biden issued an executive order that initiated a special enrollment period from February 15, 2021 through August 15, 2021 for purposes of obtaining health insurance coverage through the ACA marketplace. The executive order also instructed certain governmental authorities to review and reconsider their existing policies and rules that limit access to healthcare, including among others, reexamining Medicaid demonstration projects and waiver programs that include work requirements, and policies that create unnecessary barriers to obtaining access to health insurance coverage through Medicaid or the ACA. On August 16, 2022, President Biden signed the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, or IRA, into law, which among other things, extends enhanced subsidies for individuals purchasing health insurance coverage in ACA marketplaces through plan year 2025. The IRA also eliminates the “donut hole” under the Medicare Part D program beginning in 2025 by significantly lowering the beneficiary maximum out-of-pocket cost and through a newly established manufacturer discount program. It is unclear how other healthcare reform measures of the Biden administration, if any, will impact our business.
Other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted in the United States since the ACA was enacted. On August 2, 2011, the Budget Control Act of 2011, among other things included aggregate reductions of Medicare payments to providers of 2% per fiscal year. These reductions went into effect on April 1, 2013, and, due to subsequent legislative amendments, will stay in effect through 2032 unless additional Congressional action is taken.
On January 2, 2013, the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 was signed into law, which, among other things, further reduced Medicare payments to several types of providers. Additionally, on March 11, 2021, President Biden signed the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 into law, which eliminates the statutory Medicaid drug rebate cap, currently set at 100% of a drug’s average manufacturer price, for single source and innovator multiple source drugs, beginning January 1, 2024. Further, the IRA, among other things, (1) directs HHS to negotiate the price of certain single-source drugs and biologics covered under Medicare and (2) imposes rebates under Medicare Part B and Medicare Part D to penalize price increases that outpace inflation. These provisions will take effect progressively starting in fiscal year 2023, although they may be subject to legal challenges. The IRA permits HHS to implement many of these provisions through guidance, as opposed to regulation, for the initial years. HHS has and will continue to issue and update guidance as these programs are implemented. It is currently unclear how the IRA will be implemented but it is likely to have a significant effect on the pharmaceutical industry. Further, in response to the Biden administration’s October 2022 executive order, on February 14, 2023, HHS released a report outlining three new models for testing by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or CMS, Innovation Center which will be evaluated on their ability to lower the cost of drugs, promote accessibility, and improve quality of care. It is unclear whether the models will be utilized in any health reform measures in the future.
These laws, and future state and federal healthcare reform measures may be adopted in the future, any of which may result in additional reductions in Medicare and other healthcare funding and otherwise affect the prices we may obtain for any of our product candidates for which we may obtain regulatory approval or the frequency with which any such product candidate is prescribed or used.
47
Risks Related to Commercialization of Our Program Products and Product Candidates
As we evolve from a company that is primarily involved in clinical development to a company that is also involved in commercialization, we may encounter difficulties in expanding our operations successfully.
As we advance our Program Products through clinical studies, we will need to expand our development, regulatory, manufacturing, and marketing and sales capabilities and may need to further contract with third parties to provide these capabilities, such as collaborators, distributors, marketers and additional suppliers. We currently have no experience as a Company in or infrastructure for sales, marketing and distribution, and our operations are currently limited to clinical development activities and as our operations expand, we likely will need to manage additional relationships with such third parties.
If our Program Products or any future product candidate is approved, we intend either to establish a sales organization with technical expertise and supporting distribution capabilities to commercialize our Program Products or any future product candidate or to outsource such functions to one or more third parties. Either of these options would be expensive and time-consuming. Some or all of these costs may be incurred in advance of any approval of our Program Products or any future product candidate. In addition, we may not be able to hire a sales force that is sufficient in size or has adequate expertise in the medical markets that we intend to target. Any failure or delay in the development of our internal sales, marketing and distribution capabilities would adversely affect the commercialization of our Program Products and other future product candidates.
Maintaining third-party relationships for these purposes will impose significant added responsibilities on members of our management and other personnel. We must be able to effectively manage our development efforts, recruit and train sales and marketing personnel, effectively manage our participation in the clinical studies in which our product candidates are involved and improve our managerial, development, operational and finance systems, all of which may impose a strain on our administrative and operational infrastructure.
If we enter into arrangements with third parties to perform sales, marketing or distribution services, any product revenues that we receive, or the profitability of these product revenues to us, are likely to be lower than if we were to market and sell any products that we develop without the involvement of these third parties. In addition, we may not be successful in entering into arrangements with third parties to sell and market our products or in doing so on terms that are favorable to us. We likely will have little control over such third parties, and any of them may fail to devote the necessary resources and attention to sell and market our products effectively. If we do not establish sales and marketing capabilities successfully, either on our own or in collaboration with third parties, we will not be successful in commercializing our products.
We may seek to establish commercial collaborations for our Program Products and future product candidates, and, if we are not able to establish them on commercially reasonable terms, we may have to alter our development plans.
Our drug development programs, and the potential commercialization of our product candidates will require substantial additional cash to fund expenses. We may decide to collaborate with other pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies for the development and potential commercialization of our product candidates. For example, we have recently licensed a patent from Vanderbilt University which is the basis of GEM-PSI.
We face significant competition in seeking appropriate collaborators. Whether we reach a definitive agreement for a collaboration will depend, among other things, upon our assessment of the collaborator’s resources and expertise, the terms and conditions of the proposed collaboration and the proposed collaborator’s evaluation of a number of factors. Those factors may include the design or results of clinical studies, the likelihood of approval by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities, the potential market for the subject product candidate, the costs and complexities of manufacturing and delivering such product candidate to patients, the potential of competing products and the existence of uncertainty with respect to our ownership of technology, which can exist if there is a challenge to such ownership without regard to the merits of the challenge and industry and market conditions generally. The collaborators may also consider alternative product candidates or technologies for similar indications that may be available to collaborate on and whether such a collaboration could be more attractive than the one with us for our product candidate.
Collaborations are complex and time-consuming to negotiate and document. In addition, there have been a significant number of business combinations among large pharmaceutical companies that have resulted in a reduced number of potential future collaborators.
48
We may not be able to negotiate collaborations on a timely basis, on acceptable terms, or at all. If we are unable to do so, we may have to curtail the development of the product candidate for which we are seeking to collaborate, reduce or delay its development program or one or more of our other development programs, delay its potential commercialization or reduce the scope of any sales or marketing activities or increase our expenditures and undertake development or commercialization activities at our own expense. If we elect to increase our expenditures to fund development or commercialization activities on our own, we may need to obtain additional capital, which may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. If we do not have sufficient funds, we may not be able to further develop our product candidates or bring them to market and generate product revenue.
We currently have no Program Products approved for marketing. We do not have a marketing and sales organization. If we are unable to establish sales and marketing capabilities or enter into agreements with third parties to market and sell our Program Products, we may be unable to generate any product revenue.
We have no experience selling and marketing our Program Products, and we currently have no marketing or sales organization. To successfully commercialize any product candidates that may result from our development programs, we will need to develop these capabilities, either on our own or with others. If our product candidates receive regulatory approval, we intend to establish a sales and marketing organization independently or by utilizing experienced third parties with technical expertise and supporting distribution capabilities to commercialize our Program Products in major markets, all of which will be expensive, difficult and time consuming. Any failure or delay in the development of our internal sales, marketing and distribution capabilities would adversely impact our ability to commercialize our Program Products.
Our efforts to educate the medical community, including physicians, hospital pharmacists and third-party payors on the benefits of our Program Products may require significant resources and may never be successful. If any of our Program Products are approved but fail to achieve market acceptance among physicians, patients or third-party payors, we will not be able to generate significant revenues from such product, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
It may be difficult for us to profitably sell our Program Products, if and when approved, if coverage and reimbursement for these Program Products are limited by government authorities and/or third-party payor policies.
In addition to any healthcare reform measures which may affect reimbursement, market acceptance and sales of our Program Products, if approved, will depend on, in part, the extent to which the procedures utilizing our Program Products, performed by health care providers, will be covered by third party payors, such as government health care programs, commercial insurance and managed care organizations. In the event health care providers and patients accept our Program Products as medically useful, cost effective and safe, there is uncertainty regarding whether our Program Products will be directly reimbursed, reimbursed through a bundled payment or if the product candidates will be included in another type of value-based reimbursement program. Third party payors determine the extent to which new products will be covered as a benefit under their plans and the level of reimbursement for any covered product or procedure which may utilize a covered product. It is difficult to predict at this time what third party payors will decide with respect to the coverage and reimbursement for our Program Products.
Obtaining coverage and reimbursement approval for a product from a government or other third-party payor is a time-consuming and costly process that could require us to provide supporting scientific, clinical and cost effectiveness data for the use of our products to the payor. Additionally, we may not be able to provide data sufficient to gain acceptance with respect to coverage and reimbursement. We cannot be sure that coverage or adequate reimbursement will be available for our product candidates, if approved. Also, we cannot be sure that reimbursement amounts will not reduce the demand for, or the price of, our future products. If reimbursement is not available, or is available only to limited levels, we may not be able to commercialize our product candidates, or achieve profitably at all, even if approved.
49
Our business entails a significant risk of clinical study and/or product liability and our ability to obtain sufficient insurance coverage could have a material effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects.
Our business exposes us to significant clinical study and/or product liability risks inherent in the development, testing, manufacturing and marketing of therapeutic treatments. Clinical study liability claims could delay or prevent completion of our development programs. If we succeed in marketing products, product liability claims could result in an FDA investigation of the safety and effectiveness of our products, our manufacturing processes and facilities or our marketing programs and potentially a recall of our products or more serious enforcement action, limitations on the approved indications for which they may be used or suspension or withdrawal of approvals. Regardless of the merits or eventual outcome, liability claims may also result in decreased demand for our products, injury to our reputation, costs to defend the related litigation, a diversion of management’s time and our resources, substantial monetary awards to study participants or patients and a decline in our Company valuation. We currently carry insurance coverage to the limit required by clinical sites for our clinical study. We do not anticipate carrying product liability insurance until such time we have a commercially available product. Our current insurance coverage or any other insurance coverage that we may obtain in the future may not provide sufficient coverage against potential liabilities. Furthermore, clinical study and product liability insurance are becoming increasingly expensive. As a result, we may be unable to obtain sufficient insurance at a reasonable cost to protect us against losses caused by clinical study and product liability claims that could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Product liability lawsuits against us could cause us to incur substantial liabilities and to limit commercialization of any products that we may develop.
We face an inherent risk of product liability exposure related to the testing of our product candidates in human clinical studies and will face an even greater risk if we commercialize any resulting products. Product liability claims may be brought against us by subjects enrolled in our clinical studies, patients, or others using our products. If we cannot successfully defend ourselves against claims that our product candidates or products that we may develop caused injuries, we could incur substantial liabilities. Regardless of merit or eventual outcome, liability claims may result in:
Our clinical study liability insurance coverage may not adequately cover all liabilities that we may incur. We may not be able to maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost or in an amount adequate to satisfy any liability that may arise. Our inability to obtain product liability insurance at an acceptable cost or to otherwise protect against potential product liability claims could prevent or delay the commercialization of any products or product candidates that we develop. We intend to expand our insurance coverage for products to include the sale of commercial products if we obtain marketing approval for our product candidates in development, but we may be unable to obtain commercially reasonable product liability insurance for any products approved for marketing. Large judgments have been awarded in class action lawsuits based on drugs that had unanticipated side effects. If we are sued for any injury caused by our products, product candidates or processes, our liability could exceed our product liability insurance coverage and our total assets. Claims against us, regardless of their merit or potential outcome, may also generate negative publicity or hurt our ability to obtain physician endorsement of our products or expand our business.
50
Our employees, contractors, vendors, principal investigators, consultants and future partners may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including noncompliance with regulatory standards and requirements and insider trading.
We are exposed to the risk of fraud or other misconduct by our employees, contractors, vendors, principal investigators, consultants or future partners. Misconduct by these parties could include failures to comply with FDA regulations, to provide accurate information to the FDA, to comply with federal and state healthcare fraud and abuse laws and regulations, to report financial information or data timely, completely or accurately, or to disclose unauthorized activities to us. In particular, sales, marketing and business arrangements in the healthcare industry are subject to extensive laws and regulations intended to prevent fraud, misconduct, kickbacks, self-dealing and other abusive practices. These laws and regulations may restrict or prohibit a wide range of pricing, discounting, marketing and promotion, sales commission, customer incentive programs and other business arrangements. Third-party misconduct could also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of clinical studies, which could result in regulatory sanctions and serious harm to our reputation. Although we have adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, it is not always possible to identify and deter misconduct, and the precautions we take to detect and prevent this activity may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from governmental investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to comply with these laws or regulations. If any such actions are instituted against us resulting from this misconduct and we are not successful in defending ourselves or asserting our rights, those actions could have a significant impact on our business, including the imposition of significant fines or other sanctions. If we or our future partners market products in a manner that violates fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws, or if we or our future partners violate government price reporting laws, we or our future partners may be subject to administrative civil and/or criminal penalties, among other sanctions.
Pharmaceutical and other healthcare companies have been prosecuted under these laws for a variety of promotional and marketing activities, such as: providing free trips, free goods, sham consulting fees and grants and other monetary benefits to prescribers; reporting to pricing services inflated average wholesale prices that were then used by federal programs to set reimbursement rates; engaging in off-label promotion; and submitting inflated best price information to the Medicaid Rebate Program to reduce liability for Medicaid rebates. Ensuring that our internal operations and future business arrangements with third parties comply with applicable healthcare laws and regulations will involve substantial costs. It is possible that governmental authorities will conclude that our business practices do not comply with current or future statutes, regulations, agency guidance or case law involving applicable fraud and abuse or other healthcare laws and regulations.
Our business operations and relationships with investigators, healthcare professionals, consultants, third-party payors, patient organizations and customers are subject to broadly applicable healthcare regulatory laws, which could expose us to penalties.
Healthcare providers, physicians and third-party payors will play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of any product candidate for which we obtain regulatory approval. Our current and future arrangements may expose us to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws that may constrain the business or financial arrangements and relationships through which we would market, sell and distribute our products. Even though we will not control referrals of healthcare services or bill directly to Medicare, Medicaid or other third-party payors, federal and state healthcare laws pertaining to fraud and abuse are and will be applicable to our business. Such laws include, but are not limited to, the following:
51
Pharmaceutical and other healthcare companies have been prosecuted under these laws for a variety of promotional and marketing activities, such as: providing free trips, free goods, sham consulting fees and grants and other monetary benefits to prescribers; reporting to pricing services inflated average wholesale prices that were then used by federal programs to set reimbursement rates; engaging in off-label promotion; and submitting inflated best price information to the Medicaid Rebate Program to reduce liability for Medicaid rebates. Ensuring that our internal operations and future business arrangements with third parties comply with applicable healthcare laws and regulations will involve substantial costs. It is possible that governmental authorities will conclude that our business practices do not comply with current or future statutes, regulations, agency guidance or case law involving applicable fraud and abuse or other healthcare laws and regulations.
The global data protection landscape is rapidly evolving, and we may be affected by or subject to new, amended or existing laws and regulations in the future, including as our operations continue to expand or if we operate in foreign jurisdictions. Several foreign jurisdictions, including the EU, its member states, the United Kingdom, Japan and Australia, among others, have adopted legislation and regulations that increase or change the requirements governing the collection, use, disclosure and transfer of the personal information of individuals in these jurisdictions. Additionally, certain countries have passed or are considering passing laws that require local data residency and/or restrict the international transfer of data. These laws have the potential to increase costs of compliance, risks of noncompliance and penalties for noncompliance.
If our operations are found to be in violation of any of these laws or any other governmental regulations that may apply to us, we may be subject to significant civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, disgorgement, fines, imprisonment, exclusion from government funded healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, additional oversight and reporting obligations, contractual damages, reputational harm, diminished profits and future earnings, and the curtailment or restructuring of our operations. If any of the physicians or other healthcare providers or entities with whom we expect to do business is found not to be in compliance with applicable laws, that person or entity may be subject to significant criminal, civil or administrative sanctions, including exclusions from government funded healthcare programs.
52
Data collection is governed by restrictive regulations governing the collection, use, processing and cross-border transfer of personal information.
We have completed a Phase 2 clinical study in Europe and we will continue to collect, process, use or transfer personal information from individuals located in the European Economic Area (“EEA”) in connection with our business, including in connection with conducting clinical studies in the EEA. Additionally, if any of our product candidates are approved, we may seek to commercialize those products in the EEA. The collection and use of personal health data in the EEA is governed by the provisions of the General Data Protection Regulation ((EU) 2016/679) (“GDPR”), along with other European Union and country-specific laws and regulations. The United Kingdom and Switzerland have also adopted data protection laws and regulations. These legislative acts (together with regulations and guidelines) impose requirements relating to having legal bases for processing personal data relating to identifiable individuals and transferring such data outside of the EEA, including to the United States, providing details to those individuals regarding the processing of their personal data, keeping personal data secure, having data processing agreements with third parties who process personal data, responding to individuals’ requests to exercise their rights in respect of their personal data, reporting security breaches involving personal data to the competent national data protection authority and affected individuals, appointing data protection officers or corporate representatives, conducting data protection impact assessments and record-keeping. The GDPR imposes additional responsibilities and liabilities in relation to personal data that we process and we may be required to put in place additional mechanisms ensuring compliance with the new data protection rules. Failure to comply with the requirements of the GDPR and related national data protection laws of the member states of the EEA and other states in the EEA may result in substantial fines, other administrative penalties and civil claims being brought against us, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. European data protection authorities may interpret the GDPR and national laws differently and may impose additional requirements, which adds to the complexity of processing personal data in or from the EEA or United Kingdom. Guidance on implementation and compliance practices are often updated or otherwise revised. Compliance with the GDPR will be a rigorous and time-intensive process that may increase our cost of doing business or require us to change our business practices, and despite those efforts, there is a risk that we may be subject to fines and penalties, litigation, and reputational harm in connection with our European activities.
In addition, in 2018 California enacted the California Consumer Privacy Act (“CCPA”), which created new individual privacy rights for California consumers (as defined in the law) and places increased privacy and security obligations on entities handling personal data of consumers or households. The CCPA requires covered companies to provide new disclosure to consumers about such companies’ data collection, use and sharing practices, provide such consumers new ways to opt-out of certain sales or transfers of personal information, and provide consumers with additional causes of action. The CCPA went into effect on January 1, 2020, and the California Attorney General commenced enforcement actions for violations on July 1, 2020. Moreover, the California Privacy Rights Act, or CPRA, which was passed in November 2020 and will go into effect on January 1, 2023, with a “look-back” period to January 1, 2022. The CPRA significantly modified the CCPA, resulting in further uncertainty and requiring us to incur additional costs and expenses in an effort to comply. The CCPA and the CPRA, may impact our business activities and exemplifies the vulnerability of our business to the evolving regulatory environment related to personal data and protected health information.
Compliance with U.S. and international data protection laws and regulations could require us to take on more onerous obligations in our contracts, restrict our ability to collect, use and disclose data, or in some cases, impact our ability to operate in certain jurisdictions. Any actual or alleged failure to comply with U.S. or international laws and regulations relating to privacy, data protection, and data security could result in governmental investigations, proceedings and enforcement actions (which could include civil or criminal penalties), private litigation or adverse publicity, harm to our reputation, and could negatively affect our operating results and business. Moreover, clinical study subjects about whom we or our potential collaborators obtain information, as well as the providers who share this information with us, may contractually limit our ability to use and disclose the information or impose other obligations or restrictions in connection with our use, retention and other processing of information, and we may otherwise face contractual restrictions applicable to our use, retention, and other processing of information. Claims that we have violated individuals’ privacy rights, failed to comply with data protection laws, or breached our contractual obligations, even if we are not found liable, could be expensive and time consuming to defend and could result in adverse publicity that could harm our business.
53
Unstable market and economic conditions may have serious adverse consequences on our business and financial condition.
Global credit and financial markets have experienced extreme disruptions at various points over the last few decades, characterized by diminished liquidity and credit availability, declines in consumer confidence, declines in economic growth, increases in unemployment rates and uncertainty about economic stability. If another such disruption in credit and financial markets and deterioration of confidence in economic conditions occurs, our business may be adversely affected. If the equity and credit markets were to deteriorate significantly in the future, it may make any necessary debt or equity financing more difficult to complete, more costly, and more dilutive. Failure to secure any necessary financing in a timely manner and on favorable terms could have a material adverse effect on our growth strategy, financial performance and share price and could require us to delay or abandon development or commercialization plans. In addition, there is a risk that one or more of our service providers, manufacturers or other partners would not survive or be able to meet their commitments to us under such circumstances, which could directly affect our ability to attain our operating goals on schedule and on budget.
We are subject to U.S. and certain foreign export and import controls, sanctions, embargoes, anti-corruption laws, and anti-money laundering laws and regulations. Compliance with these legal standards could impair our ability to compete in domestic and international markets. We can face criminal liability and other serious consequences for violations, which can harm our business.
We are subject to export control and import laws and regulations, including the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, U.S. Customs regulations, various economic and trade sanctions regulations administered by the U.S. Treasury Department’s Office of Foreign Assets Controls, the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977, as amended, the U.S. domestic bribery statute contained in 18 U.S.C. § 201, the U.S. Travel Act, the USA PATRIOT Act, and other state and national anti-bribery and anti-money laundering laws in the countries in which we conduct activities. Anti-corruption laws are interpreted broadly and prohibit companies and their employees, agents, contractors, and other collaborators from authorizing, promising, offering, or providing, directly or indirectly, improper payments or anything else of value to recipients in the public or private sector. We may engage third parties to sell our products sell our products outside the United States, to conduct clinical studies, and/or to obtain necessary permits, licenses, patent registrations, and other regulatory approvals. We have direct or indirect interactions with officials and employees of government agencies or government-affiliated hospitals, universities, and other organizations. We can be held liable for the corrupt or other illegal activities of our employees, agents, contractors, and other collaborators, even if we do not explicitly authorize or have actual knowledge of such activities. Any violations of the laws and regulations described above may result in substantial civil and criminal fines and penalties, imprisonment, the loss of export or import privileges, debarment, tax reassessments, breach of contract and fraud litigation, reputational harm, and other consequences.
Changes in our effective income tax rate could adversely affect our results of operations.
We are subject to income taxes in the United States. Various factors may have favorable or unfavorable effects on our effective income tax rate. These factors include, but are not limited to, interpretations of existing tax laws, changes in tax laws and rates, the accounting for stock options and other stock-based compensation, changes in accounting standards, future levels of research and development spending, changes in the mix and level of pre-tax earnings in different jurisdictions, the outcome of audits or other examinations by the U.S. Internal Revenue Service and tax regulators in other jurisdictions, the accuracy of our estimates for unrecognized tax benefits, the realization of deferred tax assets and changes to our ownership or capital structure. The impact of the above-mentioned factors and others on our effective income tax rate may be significant and could adversely affect our results of operations.
54
Our future growth may depend, in part, on our ability to penetrate foreign markets, where we would be subject to additional regulatory burdens and other risks and uncertainties.
Our future profitability may depend, in part, on our ability to commercialize our product candidates in foreign markets for which we may rely on collaboration with third parties. We are evaluating the opportunities for the development and commercialization of our product candidates in foreign markets. We are not permitted to market or promote any of our product candidates before we receive regulatory approval from the applicable regulatory authority in that foreign market, and we may never receive such regulatory approval for any of our product candidates. To obtain separate regulatory approvals in other countries, we may be required to comply with numerous and varying regulatory requirements of such countries regarding the safety and efficacy of our product candidates and governing, among other things, clinical studies and commercial sales, pricing and distribution of our product candidates, and we cannot predict success in these jurisdictions. We may not obtain foreign regulatory approvals on a timely basis, if at all. If we obtain approval of our product candidates and ultimately commercialize our product candidates in foreign markets, we would be subject to additional risks and uncertainties, including:
Foreign sales of our product candidates could also be adversely affected by the imposition of governmental controls, political and economic instability, trade restrictions and changes in tariffs.
If any of our product candidates is approved for commercialization, we may selectively partner with third parties to market it in certain jurisdictions outside the United States. We expect that we will be subject to additional risks related to international pharmaceutical operations, including:
We have no prior experience in these areas. In addition, there are complex regulatory, tax, labor and other legal requirements imposed by both the EU and many of the individual countries in Europe with which we will need to comply. Many U.S.-based biotechnology companies have found the process of marketing their own products in Europe to be very challenging.
55
Certain legal and political risks are also inherent in foreign operations. There is a risk that foreign governments may nationalize private enterprises in certain countries where we may operate. In certain countries or regions, terrorist activities and the response to such activities may threaten our operations more than in the United States. Social and cultural norms in certain countries may not support compliance with our corporate policies, including those that require compliance with substantive laws and regulations. Also, changes in general economic and political conditions in countries where we may operate are a risk to our financial performance and future growth. Additionally, the need to identify financially and commercially strong partners for commercialization outside the United States who will comply with the high manufacturing and legal and regulatory compliance standards we require is a risk to our financial performance. As we operate our business globally, our success will depend, in part, on our ability to anticipate and effectively manage these and other related risks. There can be no assurance that the consequences of these and other factors relating to our international operations will not have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
In some countries, particularly in Europe, the pricing of prescription pharmaceuticals is subject to governmental control. In these countries, pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can take considerable time after the receipt of marketing approval for a drug. To obtain reimbursement or pricing approval in some countries, we may be required to conduct clinical studies that compare the cost-effectiveness of our product candidates to other available therapies. If reimbursement of our products is unavailable or limited in scope or amount, or if pricing is set at unsatisfactory levels, our business could be harmed, possibly materially.
We face the risk of product liability claims and may not be able to obtain insurance.
Our business exposes us to the risk of product liability claims that are inherent in the development of drugs and diagnostic devices. We may be subject to costly and damaging product liability claims brought against us by clinical study participants, consumers, health care providers, pharmaceutical companies or others selling our products. Our inability to obtain sufficient product liability insurance at an acceptable cost to protect against potential product liability claims could prevent or inhibit the commercialization of pharmaceutical products we develop, alone or with collaborators. While we currently carry clinical study insurance and product liability insurance, the amount of insurance coverage we hold now may not be adequate to cover all liabilities we might incur. We intend to expand our insurance coverage to include the sale of commercial products if we obtain marketing approval for our product candidates in development, but we may be unable to obtain commercially reasonable product liability insurance for any products approved for marketing. If we are unable to obtain insurance at an acceptable cost or otherwise protect against potential product liability claims, we will be exposed to significant liabilities, which may materially and adversely affect our business and financial position. If we are sued for any injury allegedly caused by our Program Products, our liability could exceed our total assets and our ability to pay the liability. A product liability claim or series of claims brought against us would decrease our cash and could cause our stock price to fall.
Our insurance policies are expensive and protect us only from some business risks, which will leave us exposed to significant uninsured liabilities.
We carry insurance for most categories of risk that our business may encounter; however, we may not have adequate levels of coverage. We currently maintain general liability, property, workers’ compensation, clinical study, products liability and directors’ and officers’ insurance, along with an umbrella policy. We may not be able to maintain existing insurance at current or adequate levels of coverage. Any significant uninsured liability may require us to pay substantial amounts, which would adversely affect our cash position and results of operations.
We have no current plans to pay dividends on our shares of common stock.
We do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. If we incur indebtedness in the future to fund our future growth, our ability to pay dividends may be further restricted by the terms of such indebtedness.
Loss of Emerging Grown Company Status
We are no longer an emerging growth company (“EGC”) as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startup Act of 2012, as amended. As a result, we are now subject to additional regulatory and compliance obligations, which may increase our costs, divert management’s attention, and adversely affect our financial condition. These obligations include:
56
Our transition from EGC status became effective on December 31, 2024, as we exceeded the five-year anniversary of our initial public offering. However, we continue to qualify as a smaller reporting company under SEC rules and as defined in the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), which permits certain scaled disclosures but does not alleviate all obligations triggered by the loss of EGC status. Compliance with these requirements may strain our financial and operational resources and could make us less attractive to investors accustomed to EGC reporting standards.
Our common stock price may be volatile and as a result you could lose all or part of your investment.
In addition to volatility associated with equity securities in general, the value of your investment could decline due to the impact of any of the following factors upon the market price of our shares of common stock:
Stock markets in general have experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations, and the market prices of securities have been highly volatile. These fluctuations are often unrelated to operating performance and may adversely affect the market price of our shares of common stock.
Potential future sales pursuant to registration rights granted by the Company and under Rule 144 may depress the market price for our shares of common stock.
The Company has granted a number of its stockholders’ registration rights with respect to their shares of common stock. See the section titled “Registration Rights.” Such future sales of our shares of common stock by our existing stockholders, pursuant to and in accordance with the provisions of any registration statement, may have a depressive effect on the market price of our shares of common stock. Further, in general, under Rule 144 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), a person who has satisfied a minimum holding period of between six months and one-year and any other applicable requirements of Rule 144, may thereafter sell such shares publicly. A significant number of our currently issued and outstanding shares of common stock held by existing stockholders, including officers and directors and other principal stockholders are currently eligible for resale pursuant to and in accordance with the provisions of Rule 144. The possible future sale of our shares by our existing stockholders, pursuant to and in accordance with the provisions of Rule 144, may have a depressive effect on the price of our shares of common stock in the applicable trading marketplace.
FINRA has adopted sales practice requirements, which may also limit a stockholder’s ability to buy and sell our common stock.
The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (“FINRA”) has adopted rules that require that in recommending an investment to a customer, a broker-dealer must have reasonable grounds for believing that the investment is suitable for that customer. Prior to recommending speculative low-priced securities to their non-institutional customers, broker-dealers must make reasonable efforts to obtain information about the customer’s financial status, tax status, investment objectives and other information. Under interpretations of these rules, FINRA believes that there is a high probability that speculative low-priced securities will not be suitable for at least some customers. FINRA requirements make it more difficult for broker-dealers to recommend that their customers buy our shares of common stock, which may limit your ability to buy and sell our stock and have an adverse effect on the market for our shares of common stock.
We face risks related to compliance with corporate governance laws and financial reporting standards.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act, as well as related new rules and regulations implemented by the SEC and the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, require changes in the corporate governance practices and financial reporting standards for public companies. These laws, rules and regulations, including compliance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act relating to internal control over financial reporting, referred to as Section 404, materially increased our legal and financial compliance costs and made some activities more time-consuming and more burdensome.
Anti-takeover provisions contained in our Charter and bylaws, as well as provisions of Delaware law, could impair a takeover attempt.
Our Charter contains provisions that may discourage unsolicited takeover proposals that stockholders may consider to be in their best interests. We are also subject to anti-takeover provisions under Delaware law, which could delay or prevent a change of control.
57
Together, these provisions may make more difficult the removal of management and may discourage transactions that otherwise could involve payment of a premium over prevailing market prices for our securities. These provisions will include:
Our Charter provides that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware and the federal district courts of the United States of America will be the exclusive forums for substantially all disputes between us and our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers, or employees.
Our Charter provides that, subject to limited exceptions, any (i) derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf of under Delaware law, (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any current or former director, officer or other employee of Revelation to its stockholders, (iii) any action asserting a claim against Revelation or any of its directors, officers or other employees arising pursuant to any provision of the Delaware General Corporation Law (“DGCL”), the Charter or the Bylaws of Revelation (in each case, as may be amended from time to time), (iv) any action asserting a claim against Revelation or any of its directors, officers or other employees governed by the internal affairs doctrine of the State of Delaware or (v) any other action asserting an “internal corporate claim,” as defined in Section 115 of the DGCL, in all cases subject to the court’s having personal jurisdiction over all indispensable parties named as defendants shall, to the fullest extent permitted by law, be exclusively brought in the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware or, if such court does not have subject matter jurisdiction thereof, another state or federal court located within the State of Delaware. The Charter also provides that unless a majority of the Board of Revelation, acting on behalf of Revelation, consents in writing to the selection of an alternative forum (which consent may be given at any time, including during the pendency of litigation), the federal district courts of the United States of America, to the fullest extent permitted by law, will be the sole and exclusive forum for the resolution of any action asserting a cause of action arising under the Securities Act. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of Revelation’s capital stock shall be deemed to have notice of and to have consented to the provisions of Revelation’s certificate of incorporation described above. Section 27 of the Exchange Act creates exclusive federal jurisdiction over all suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Exchange Act or the rules and regulations thereunder. As a result, the exclusive forum provision will not apply to suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Exchange Act or any other claim for which the federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction. Section 22 of the Securities Act creates concurrent jurisdiction for state and federal courts over all suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Securities Act or the rules and regulations thereunder.
This choice of forum provision may limit a stockholders ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with Revelation or its directors, officers, or other employees, which, along with potential increased costs of litigating the courts provided by the choice of forum provision, may discourage such lawsuits against Revelation and its directors, officers, and employees. Alternatively, if a court were to find these provisions of Revelation’s Charter inapplicable to, or unenforceable in respect of, one or more of the specified types of actions or proceedings, Revelation may incur additional costs associated with resolving such matters in other jurisdictions, which could adversely affect Revelation’s business and financial condition.
58
If Revelation is not able to comply with the applicable continued listing requirements or standards of Nasdaq, Nasdaq could delist our common stock.
Revelation’s common stock and Public Warrants are listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market listing tier (“Nasdaq Capital Market”) under the symbols “REVB” and “REVBW,” respectively. If Nasdaq delists the Revelation common stock and Public Warrants from trading on its exchange for failure to meet the listing standards such as the minimum public stockholders equity requirement, minimum bid price, for failure to hold an annual stockholders meeting, or any other listing standards, we and our stockholders could face significant material adverse consequences including:
Revelation will continue to incur significant increased expenses and administrative burdens as a public company, which could negatively impact its business, financial condition and results of operations.
As a public company, we are subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, the listing standards of the Nasdaq, and other applicable securities rules and regulations. We expect that the requirements of these rules and regulations will continue to increase our legal, accounting, and financial compliance costs, make some activities more difficult, time-consuming and costly, and place significant strain on our personnel, systems, and resources. For example, the Exchange Act requires, among other things, that we file annual, quarterly, and current reports with respect to our business and results of operations. As a result of the complexity involved in complying with the rules and regulations applicable to public companies, our management’s attention may be diverted from other business concerns, which could harm our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
Revelation’s business and operations could be negatively affected if it becomes subject to any securities litigation or stockholder activism, which could cause Revelation to incur significant expense, hinder execution of business and growth strategy and impact its stock price.
In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities, securities class action litigation has often been brought against that company. Stockholder activism, which could take many forms or arise in a variety of situations, has been increasing recently. Volatility in the stock price of Revelation common stock or other reasons may in the future cause it to become the target of securities litigation or stockholder activism. Securities litigation and stockholder activism, including potential proxy contests, could result in substantial costs and divert management’s and board of directors’ attention and resources from the Revelation’s business. Additionally, such securities litigation and stockholder activism could give rise to perceived uncertainties as to the Combined Entity’s future, adversely affect its relationships with service providers and make it more difficult to attract and retain qualified personnel. Also, Revelation may be required to incur significant legal fees and other expenses related to any securities litigation and activist stockholder matters. Further, its stock price could be subject to significant fluctuation or otherwise be adversely affected by the events, risks and uncertainties of any securities litigation and stockholder activism.
59
Our common stock warrants may be accounted for as warrant liabilities and the changes in value of our warrants could have a material effect on our financial results.
Historically, warrants were reflected on a company’s balance as a component of equity as opposed to liabilities on the balance sheet and the statements of operations did not include subsequent non-cash changes in estimated fair value of the warrants, based on the prevailing application of the Financial Accounting Standards Boar (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) including ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (“ASC 480”) and ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging (“ASC 815”). Based upon the provisions of ASC 480 and ASC 815, the Company accounts for certain types of common stock warrants as current liabilities if the warrant fails the equity classification criteria. Common stock warrants classified as liabilities are initially recorded at fair value on the grant date (based upon option pricing models since in most cases there is no public market for the warrants) and remeasured at each balance sheet date with the offsetting adjustments recorded in change in fair value of warrant liabilities within the consolidated statements of operations. One result of this accounting treatment is that as the market price of the Company’s common stock increases, the value of the warrant liability increases, resulting in a non-cash charge to earnings in the quarter in which the revaluation took place. Conversely, if the common stock price declines, the warrant liability is reduced and the Company recognizes income in the quarter in the amount of the reduction in the liability. Due to specific provisions within the warrant agreement for the Class C Common Stock Warrants (defined below) and the Company’s application of ASC 480 and ASC 815 to the warrant agreement, we assessed our accounting for the Class C Common Stock Warrants (defined below) as a warrant liability. Future issuances of warrants may be accounted for on the same basis.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS.
None.
ITEM 1C. CYBERSECURITY
The Company employs a cybersecurity policy which it believes is appropriate for the potential of cybersecurity threats faced by it. The Company does not have possession of personally identifiable patient information from its clinical trials, nor does it have information with respect to third party credit or banking information. Accordingly, the threat is limited to disruption of ordinary business operations. The Company’s information systems and maintenance are delegated to independent information technology and cybersecurity consultants, with at least 10 years of experience advising similarly situated companies on information technology and cybersecurity risk management, who report to the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, who reports in turn directly to the Board of Directors and the Audit Committee, which is the principal committee charged with the Board’s risk management oversite. The Company has never been affected by cybersecurity incidents.
The Company’s information systems employ storage and recovery services from various third parties, including Microsoft, as its cloud service providers, which provides an additional level of protection from cybersecurity threats.
ITEM 2. PROPERTY.
Our corporate headquarters is located at 4660 La Jolla Village Dr., Suite 100, San Diego, California, where we currently have access to office space on an as-needed basis. We believe that our current space is adequate for our needs. We lease laboratory space located at 11011 Torreyana Rd., Suite 102, San Diego, California, which consists of approximately 2,140 square feet. The lease expires on February 28, 2025 and will continue on a month to month basis. We also believe we will be able to obtain additional space, as needed, on commercially reasonable terms.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS.
None.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES.
Not applicable.
60
PART II
ITEM 5.MARKET FOR COMMON EQUITY AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES.
Market Information
Our common stock and Public Warrants are traded on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbols “REVB” and “REVBW”, respectively.
Holders of Record
As of March 3, 2025, there were approximately 23 stockholders of record of our common stock and 29 holders of record of our warrants. Because many of our securities are held by brokers and other institutions on behalf of stockholders, we are unable to estimate the total number of stockholders represented by these record holders.
Dividends
We have never paid dividends on shares of our common stock, and we do not have any plans to pay dividends in the foreseeable future. Any determination to pay dividends to holders of shares of our common stock will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on many factors, including our financial condition, results of operations, projections, liquidity, earnings, legal requirements, restrictions in the agreements governing any indebtedness we may enter into and other factors that our board of directors deems relevant.
ITEM 6.[RESERVED]
Not applicable.
61
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS.
You should read the following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations in conjunction with our audited financial statements and the notes included elsewhere in this Form 10-K. The following discussion contains forward-looking statements that involve certain risks and uncertainties. Our actual results could differ materially from those discussed in these statements. Factors that could cause or contribute to these differences include those discussed below and elsewhere in this Form 10-K, particularly under the “Risk Factors” and “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements and Risk Factors Summary” sections.
Overview
Revelation is a clinical-stage life science company that is focused on rebalancing inflammation to optimize health using its proprietary formulation Gemini. We are developing a pipeline of potential high-value products based on Gemini. Gemini is our proprietary formulation of PHAD an established TLR4 agonist that can stimulate the human body’s innate immune response to prevent and treat disease. Our current Gemini based programs consist of: GEM-AKI, which is being developed as a potential therapy for the prevention and treatment of acute kidney injury; GEM-CKD, which is being developed as a potential therapy for the prevention and treatment of chronic kidney disease; and GEM-PSI, which is being developed for the prevention and treatment of post surgical infection.
Since our inception, we have devoted substantially all of our resources to organizing and staffing our Company, business planning, raising capital, and research and development of GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI, our product candidates.
We have funded our operations since our inception to December 31, 2024 through the issuance and sale of our capital stock, from which we have raised net proceeds of $56.7 million. Our current cash and cash equivalents balance will not be sufficient to complete all necessary product development or future commercialization efforts. We anticipate that our current cash and cash equivalents balance will not be sufficient to sustain operations within one-year after the date that our audited financial statements for December 31, 2024 were issued, which raises substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
We plan to seek additional funding through public or private equity or debt financings. We may not be able to obtain financing on acceptable terms, or at all. The terms of any financing may adversely affect the holdings or the rights of our stockholders. If we are unable to obtain funding we could be required to delay, reduce or eliminate research and development programs, product portfolio expansion or future commercialization efforts, which could adversely affect our business operations.
We have incurred recurring losses since our inception, including a net loss of $15.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2024 and $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, respectively. As of December 31, 2024 we had an accumulated deficit of $40.5 million. We expect to continue to generate operating losses and negative operating cash flows for the foreseeable future if and as we:
62
Our net losses may fluctuate significantly from quarter-to-quarter and year-to-year, depending on the timing of our clinical studies and our expenditures on other research and development activities.
We have never generated revenue and do not expect to generate revenue from product sales unless and until we successfully complete development and obtain regulatory approval for GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD, GEM-PSI or other product candidates, which we expect will not be for at least several years, if ever. Accordingly, until such time as we can generate significant revenue from sales of GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD, GEM-PSI or other product candidates, if ever, we expect to finance our cash needs through a combination of public or private equity offerings, debt financings or other capital sources, including potential collaborations, licenses and other similar arrangements. However, we may be unable to raise additional funds or enter into such other arrangements when needed on favorable terms or at all. Our failure to raise capital or enter into such other arrangements when needed would have a negative impact on our financial condition and could force us to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or future commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market product candidates that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
Recent Developments
2025 Reverse Stock Split
On January 28, 2025, the Company effected a 1-for-16 reverse stock split of our outstanding shares of common stock, which had been approved at a special meeting of stockholders.
NASDAQ Compliance
As previously reported on October 16, 2024, the Company received a letter from Nasdaq notifying the Company of its noncompliance with Nasdaq Listing Rule 5550(a)(2) by failing to maintain a minimum bid price for its common stock of at least $1.00 per share for 30 consecutive business days. The Company had until February 14, 2025, to regain compliance by having a minimum closing bid price of at least $1.00 per share for at least 10 consecutive business days. On February 19, 2025 the Company received a formal notice from Nasdaq stating that the Company’s common stock will continue to be listed and traded on Nasdaq, due to the Company having regained compliance with the minimum bid price requirement, and all applicable listing standards.
Research and Development
Research and development expenses consist primarily of costs incurred for the development of our product candidates GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI. Our research and development expenses consist primarily of external costs related to clinical development, costs related to contract research organizations, costs related to consultants, costs related to acquiring and manufacturing clinical study materials, costs related to contract manufacturing organizations and other vendors, costs related to the preparation of regulatory submissions, costs related to laboratory supplies and services, and personnel costs. Personnel and related costs consist of salaries, employee benefits and stock-based compensation for personnel involved in research and development efforts.
We expense all research and development expenses in the periods in which they are incurred. We accrue for costs incurred as the services are being provided by monitoring the status of specific activities and the invoices received from our external service providers. We adjust our accrual as actual costs become known.
We expect our research and development expenses to increase substantially for the foreseeable future as we continue the development of GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI and continue to invest in research and development activities. The process of conducting the necessary clinical research and product development to obtain regulatory approval is costly and time consuming, and the successful development of GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI and any future product candidates is highly uncertain. To the extent that our product candidates continue to advance into larger and later stage clinical studies, our expenses will increase substantially and may become more variable.
The actual probability of success for GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI or any future product candidate may be affected by a variety of factors, including the safety and efficacy of our product candidates, investment in our clinical programs, manufacturing capability and competition with other products. As a result, we are unable to determine the timing of initiation, duration and completion costs of our research and development efforts or when and to what extent we will generate revenue from the commercialization and sale of GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI or any future product candidate.
63
General and Administrative
Our general and administrative expenses consist primarily of personnel costs, expenses for outside professional services, including financial advisory, legal, human resource, audit and accounting services and consulting costs. Personnel and related costs consist of salaries, employee benefits and stock-based compensation for personnel involved in executive, finance and other administrative functions. We expect our general and administrative expenses to increase for the foreseeable future as we increase the size of our administrative function to support the growth of our business and support our continued research and development activities. We also anticipate increased expenses as we continue to operate as a public company, including increased expenses related to financial advisory services, audit, legal, regulatory, investor relations costs, director and officer insurance premiums associated with maintaining compliance with exchange listing and SEC requirements.
Other (Expense) Income, Net
Other (expense) income, net primarily consists of the change in fair value of warrant liability, LifeSci Capital LLC judgment expense and reimbursement of legal costs, clinical trial related settlement expenses with A-IR Clinical Research Ltd., foreign currency transaction gains and losses, interest expense and interest income from our cash balances in savings accounts.
Results of Operations
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the periods presented:
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
Change |
|
|||
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Research and development |
|
$ |
3,548,996 |
|
|
$ |
4,145,902 |
|
|
$ |
(596,906 |
) |
General and administrative |
|
|
4,426,113 |
|
|
|
4,510,762 |
|
|
|
(84,649 |
) |
Total operating expenses |
|
|
7,975,109 |
|
|
|
8,656,664 |
|
|
|
(681,555 |
) |
Loss from operations |
|
|
(7,975,109 |
) |
|
|
(8,656,664 |
) |
|
|
681,555 |
|
Total other (expense) income, net |
|
|
(7,063,427 |
) |
|
|
8,536,410 |
|
|
|
(15,599,837 |
) |
Net loss |
|
$ |
(15,038,536 |
) |
|
$ |
(120,254 |
) |
|
$ |
(14,918,282 |
) |
Research and Development Expenses
The following table summarizes our research and development expenses for the periods presented:
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
Change |
|
|||
GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI clinical study expenses |
|
$ |
1,681,731 |
|
|
$ |
209,702 |
|
|
$ |
1,472,029 |
|
Manufacturing expenses |
|
|
390,022 |
|
|
|
697,429 |
|
|
|
(307,407 |
) |
Other program expenses |
|
|
77,679 |
|
|
|
2,190,493 |
|
|
|
(2,112,814 |
) |
Other expenses |
|
|
172,369 |
|
|
|
282,948 |
|
|
|
(110,579 |
) |
Personnel expenses (including stock-based compensation) |
|
|
1,227,195 |
|
|
|
765,330 |
|
|
|
461,865 |
|
Total research and development expenses |
|
$ |
3,548,996 |
|
|
$ |
4,145,902 |
|
|
$ |
(596,906 |
) |
Research and development expenses decreased by $0.6 million, from $4.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 to $3.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2024. The decrease was primarily due to decreases of $2.1 million in other program expenses and $0.3 million in manufacturing expenses, offset by increases of $1.5 million in clinical study expenses related to GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI and $0.5 million in personnel expenses. Other program expenses include pre-clinical costs and clinical preparation costs primarily for programs GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI.
64
General and Administrative Expenses
The following table summarizes our general and administrative expenses for the periods presented:
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
Change |
|
|||
Personnel expenses (including employee stock-based compensation) |
|
$ |
2,768,602 |
|
|
$ |
2,272,005 |
|
|
$ |
496,597 |
|
Legal and professional fees |
|
|
1,274,567 |
|
|
|
1,844,077 |
|
|
|
(569,510 |
) |
Other expenses |
|
|
382,944 |
|
|
|
394,680 |
|
|
|
(11,736 |
) |
Total general and administrative expenses |
|
$ |
4,426,113 |
|
|
$ |
4,510,762 |
|
|
$ |
(84,649 |
) |
General and administrative expenses decreased by $0.1 million, from $4.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 to $4.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2024. The decrease was primarily due to a decrease of $0.6 million in legal and professional fees, offset by an increase of $0.5 million in personnel expenses.
Other (Expense) Income, Net
Other (expense) income, net was $8,536,410 for the year ended December 31, 2023, related to the change in fair value of the warrant liability, foreign currency transaction gains and losses, and interest income from our cash balances in savings accounts. Other (expense) income, net was ($7,063,427) for the year ended December 31, 2024, primarily related to the LifeSci Capital LLC judgment expense and reimbursement of legal costs, clinical trial related settlement expenses with A-IR Clinical Research Ltd. and expenses in connection with the deferred underwriting commissions, offset by interest income from our cash balances in savings accounts.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Since our inception to December 31, 2024, we have funded our operations from the issuance and sale of our common stock, preferred stock and warrants, from which we have raised net proceeds of $56.7 million, of which $12.8 million was received during the year ended December 31, 2024. As of December 31, 2024, we had available cash and cash equivalents of $6.5 million and an accumulated deficit of $40.5 million.
Our use of cash is to fund operating expenses, which consist primarily of research and development expenditures related to our therapeutic product candidates, GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI. We plan to increase our research and development expenses substantially for the foreseeable future as we continue the clinical development of our current and future product candidates. At this time, due to the inherently unpredictable nature of product development, we cannot reasonably estimate the costs we will incur and the timelines that will be required to complete development, obtain marketing approval, and commercialize our current product candidate or any future product candidates. For the same reasons, we are also unable to predict when, if ever, we will generate revenue from product sales or any future license agreements which we may enter into or whether, or when, if ever, we may achieve profitability. Clinical and preclinical development timelines, the probability of success, and development costs can differ materially from expectations. In addition, we cannot forecast the timing and amounts of milestone, royalty and other revenue from licensing activities, which future product candidates may be subject to future collaborations, when such arrangements will be secured, if at all, and to what degree such arrangements would affect our development plans and capital requirements.
We expect to continue to generate substantial operating losses for the foreseeable future as we expand our research and development activities. We will continue to fund our operations primarily through utilization of our current financial resources and through additional raises of capital.
To the extent that we raise additional capital through partnerships or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our product candidates, future revenue streams or research programs or to grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we raise additional capital through public or private equity offerings, the ownership interest of our then-existing stockholders will be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect our stockholders’ rights. If we raise additional capital through debt financing, we may be subject to covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends. If we are unable to obtain adequate financing when needed, we may have to delay, reduce the scope of or suspend one or more of our clinical studies or preclinical studies, research and development programs or commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market our product candidates even if we would otherwise prefer to develop and market such product candidates ourselves.
65
Going Concern
We have incurred recurring losses since our inception, including a net loss of $15.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2024. As of December 31, 2024 we had an accumulated deficit of $40.5 million, a stockholders’ equity of $4.7 million and available cash and cash equivalents of $6.5 million. We expect to continue to incur significant operating and net losses, as well as negative cash flows from operations, for the foreseeable future as we continue to complete all necessary product development or future commercialization efforts. We have never generated revenue and do not expect to generate revenue from product sales unless and until we successfully complete development and obtain regulatory approval for GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD, GEM-PSI or other product candidates, which we expect will not be for at least several years, if ever. We do not anticipate that our current cash and cash equivalents balance will be sufficient to sustain operations within one-year after the date that our audited financial statements for December 31, 2024 were issued, which raises substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
To continue as a going concern, we will need, among other things, to raise additional capital resources. We plan to seek additional funding through public or private equity or debt financings. We may not be able to obtain financing on acceptable terms, or at all. The terms of any financing may adversely affect the holdings or the rights of our stockholders. If we are unable to obtain funding we could be required to delay, reduce or eliminate research and development programs, product portfolio expansion or future commercialization efforts, which could adversely affect our business operations.
The audited consolidated financial statements for December 31, 2024, have been prepared on the basis that we will continue as a going concern, and do not include any adjustments to reflect the possible future effects on the recoverability and classification of assets or the amounts and classification of liabilities that may result from the possible inability for us to continue as a going concern.
Cash Flows
The following table summarizes our cash flows for the periods presented:
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
||
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
$ |
(18,321,276 |
) |
|
$ |
(7,286,286 |
) |
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
(19,171 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|
|
12,847,764 |
|
|
|
14,025,008 |
|
Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
(5,492,683 |
) |
|
$ |
6,738,722 |
|
Net Cash Used in Operating Activities
During the year ended December 31, 2024, net cash used in operating activities was $18.3 million, which consisted of a net loss of $15.0 million and a net change of $3.4 million in our net operating assets and liabilities.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, net cash used in operating activities was $7.3 million, which consisted of a net income of $0.1 million and a net change of $8.1 million comprised of the change in fair value of the warrant liability, stock-based compensation expense and depreciation expense, offset by a net change of $1.0 million in our net operating assets and liabilities.
Net Cash Used in Investing Activities
During the year ended December 31, 2024, net cash used in investing activities consisted of a purchase of lab equipment.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, there was no cash used in investing activities.
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
During the year ended December 31, 2024, net cash provided by financing activities was $12.8 million, from net proceeds of $5.4 million received in connection with the February 2024 Public Offering (defined below), $0.2 million received from exercises of the Class D Common Stock Warrants (defined below), net proceeds of $3.5 million received in connection with the Class D Warrant Inducement (defined below) and net proceeds of $3.7 million received in connection with the Class E Warrant Inducement (defined below).
During the year ended December 31, 2023, net cash provided by financing activities was $14.0 million from the February 2023 Public Offering (defined below).
66
Contractual Obligations and Other Commitments
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2024 and the effects of such obligations are expected to have on our liquidity and cash flow in future periods:
|
|
Less than |
|
|
1 to 3 |
|
|
3 to 5 |
|
|
More than |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||
Operating lease obligations |
|
$ |
10,700 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
10,700 |
|
Total contractual obligations |
|
$ |
10,700 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
10,700 |
|
We have entered into an operating lease for laboratory space in San Diego, California. The table above includes future minimum lease payments under the non-cancelable lease arrangement.
We enter into contracts in the normal course of business with third party service providers and vendors. These contracts generally provide for termination on notice and, therefore, are cancellable contracts and not considered contractual obligations and commitments. We believe that our non-cancelable obligations under these agreements are not material.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2024, we did not have any off-balance sheet arrangements as defined in Item 303(a)(4)(ii) of Regulation S-K.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risk
We are exposed to market risks in the ordinary course of our business.
Interest Rate Risk
Our cash and cash equivalents consist primarily of highly liquid investments in money market funds and cash on hand and have an original maturity date of 90 days or less. The fair value of our cash and cash equivalents would not be significantly affected by either an increase or decrease in interest rates due mainly to the short-term nature of these instruments.
Foreign Currency Risk
Our expenses are generally denominated in the currencies in which our operations are located, which is primarily in the United States, England and Australia. We make payments to vendors for research and development services with payments denominated in foreign currencies including Australian Dollars and British Pounds. We are subject to foreign currency transaction gains or losses on our payments denominated in foreign currencies. To date, foreign currency transaction gains and losses have not been material and we have not had a formal hedging program with respect to foreign currency; however, we may consider doing so in the future. A 10% increase or decrease in currency exchange rates would not have a material effect on our financial results.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
Our management’s discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations is based on our financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with the generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“GAAP”). The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions about future events that affect the amounts of assets and liabilities reported, disclosures about contingent assets and liabilities, and reported amounts of revenue and expenses. These estimates and assumptions are based on management’s best estimates and judgment. Management regularly evaluates its estimates and assumptions using industry experience and other factors; however, actual results could differ materially from these estimates and could have an adverse effect on our consolidated financial statements. While our significant accounting policies are more fully described in the notes to our consolidated financial statements, we believe that the accounting policies discussed below are most critical to understanding and evaluating our historical and future performance.
67
Research and Development Expenses
All research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Research and development costs consist primarily of salaries, employee benefits, costs associated with preclinical studies and clinical trials (including amounts paid to clinical research organizations and other professional services). Payments made prior to the receipt of goods or services to be used in research and development are capitalized until the goods or services are received.
We record accruals for estimated research and development costs, comprising payments for work performed by third party contractors, laboratories, participating clinical trial sites, and others. Some of these contractors bill monthly based on actual services performed, while others bill periodically based upon achieving certain contractual milestones. For the latter, we accrue the expenses as goods or services are used or rendered. Clinical trial site costs related to patient enrollment are accrued as patients enter and progress through the trial. Upfront costs, such as costs associated with setting up clinical trial sites for participation in the trials, are expensed immediately once incurred as research and development expenses.
Stock-based Compensation
We recognize the compensation expense related to stock options, third-party warrants, and restricted stock unit (“RSU”) awards granted, based on the estimated fair value of the awards on the date of grant. The fair value of employee stock options and third-party warrants are generally determined using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model using various inputs, including estimates of historic volatility, term, risk-free rate, and future dividends. The grant date fair value of the stock-based awards, which have graded vesting, is recognized using the straight-line method over the requisite service period of each stock-based award, which is generally the vesting period of the respective stock-based awards. The Company recognizes forfeitures as they occur.
As of December 31, 2024, there were 3 Rollover RSU awards vested and unissued and 64 stock options outstanding.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 2 to our consolidated financial statements for more information about recent accounting pronouncements, the timing of their adoption, and our assessment, to the extent we have made one yet, of their potential impact on our financial condition of results of operations.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK.
We are a smaller reporting company as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act and are not required to provide the information otherwise required under this item.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA.
The financial statements required by this item are set forth at the end of this Annual Report on Form 10-K beginning on page F-1 and are incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE.
None.
68
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our principal executive officer and our principal financial officer, evaluated, as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures. Based on that evaluation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2024, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures as of such date are effective at the reasonable assurance level. The term “disclosure controls and procedures,” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act are recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports we file or submit under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives, and our management necessarily applies its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over our financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Our internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the presentation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP. Internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that our degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In connection with the preparation of this Annual Report, our management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024. In making this assessment, our management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013 framework). Based on such assessment, our management concluded that, as of December 31, 2024, our internal control over financial reporting was effective based on those criteria.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during our most recent quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION.
None.
ITEM 9C. DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS.
Not applicable.
69
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.
Executive Officers and Directors
The following table sets forth information regarding our executive officers and directors, including their ages as of March 3, 2025:
Name |
|
Age |
|
Position |
BOARD OF DIRECTORS |
|
|
|
|
George Tidmarsh, M.D., Ph.D. |
|
65 |
|
Chairman and Director |
James Rolke |
|
56 |
|
Director and Chief Executive Officer |
Jennifer Carver, BSN, MBA |
|
71 |
|
Director |
Jess Roper |
|
60 |
|
Director |
Lakhmir Chawla, M.D. |
|
54 |
|
Director |
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS |
|
|
|
|
James Rolke |
|
56 |
|
Director and Chief Executive Officer |
Chester S. Zygmont, III |
|
44 |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
Our Director and Executive Officers
George Tidmarsh, M.D., Ph.D. — Chairman. Dr. Tidmarsh has been Chairman of the Company since its inception in May 2020. Dr. Tidmarsh received his M.D. and Ph.D. from Stanford University, where he also completed his fellowship training in Pediatric Oncology and Neonatology and is currently Adjunct Faculty of Pediatrics and Neonatology since 2018. He served as clinical faculty at Stanford for a number of years after his fellowship prior to devoting his full time to clinical research and development in order to bring new treatments through the FDA approval process. Since 2018 Dr. Tidmarsh has served as a director and chairman of audit committee of Lucile Packard Foundation for Children’s Health. Since the Company’s inception in 2020 he has also served as chairman at Revelation Biosciences Inc. Prior to joining Revelation, Dr. Tidmarsh was President, Chief Executive Officer, Secretary and a Director of La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company (“La Jolla”) from January 2012 until November 2019. While at La Jolla, Dr. Tidmarsh helped discover the use of angiotensin II for the treatment of shock and led all aspects of development including approval by the FDA and the EMA for the treatment of patients suffering from distributive shock. He also led the development of artesunate for the treatment of severe malaria, which was approved by the FDA. Dr. Tidmarsh has over 30 years of experience in biotechnology, including the successful clinical development of seven FDA-approved drugs. He previously served as the Chief Executive Officer of Horizon Pharma, Inc., a company he founded in 2005, where he continued as CEO until 2008 and Director until 2010. While at Horizon, he invented and led all aspects of development of Duexis, which was approved by the FDA for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. He also founded Threshold Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and held senior positions at Coulter Pharmaceutical, Inc. (acquired by GlaxoSmithKline) and SEQUUS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (acquired by Johnson & Johnson). While at Coulter and SEQUUS, Dr. Tidmarsh led the clinical development of BEXXAR and Doxil, respectively, two FDA-approved anti-cancer agents. We believe that Dr. Tidmarsh is qualified to serve as a director based on his extensive management experience in the biotechnology industry.
James Rolke — Director and Chief Executive Officer. Mr. Rolke cofounded and has been the Chief Executive Officer and a director of Revelation since its inception in May 2020. Mr. Rolke has over 30 years of experience in the biotechnology industry, spanning all areas and phases of drug development. Prior to joining the Company, beginning in 2012, Mr. Rolke was employed at La Jolla in various leadership roles overseeing Research and Development and serving as Chief Scientific Officer from 2017 to 2020. While at La Jolla, Mr. Rolke oversaw the development of multiple technologies including six INDs and two marketing approvals: Giapreza for the treatment of distributive shock (US FDA and EMEA) and artesunate for the treatment of severe malaria. Prior to La Jolla, from July 2009 to January 2012 Mr. Rolke was Chief Technology Officer at Pluromed, Inc. (acquired by Sanofi) and played a key role in the approvals of two medical devices via the 510(k) and premarket approval application approval pathways. Prior to Pluromed, Mr. Rolke held several key positions at biotechnology companies, including Director of Operations at Prospect Therapeutics, Inc., Associate Director of Pharmaceutical Development at Mersana Therapeutics, Inc., Manager of Process Development at GlycoGenesys, Inc., Principal Scientist at Surgical Sealants, Inc., Scientist at GelTex, Inc., and Associate Scientist at Alpha-Beta Technology, Inc. Mr. Rolke received his B.S. in chemistry from Keene State College. We believe that Mr. Rolke is qualified to serve as a director based on his role as our Chief Executive Officer and his extensive management experience in the biotechnology industry.
70
Jennifer Carver, BSN, MBA — Director. Ms. Carver has been a director of the Company since May 2020. Ms. Carver brings over 20 years of industry experience with a focus on small biotech companies and their evolution from early development through commercialization. From 2020 to 2021, Ms. Carver has served as Chief Operating Officer at Kartos Therapeutics (Kartos). Prior to Kartos from 2014, Ms. Carver was employed at La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company in various leadership roles providing leadership through the clinical development, approval and launch of Giapreza and serving as Chief Operating Officer from 2017 to 2019. Prior to La Jolla, Ms. Carver held positions at Spectrum Pharmaceuticals and Allos Therapeutics, leading teams through the development and approval of Belionostat and Folotyn respectively. Her experience in the healthcare industry spans multiple therapeutic areas including oncology, inflammatory disease, shock, iron overload, and anti-infectives. Ms. Carver has played a critical role in negotiating key alliances, evaluation of financing opportunities, and overseeing rapid organizational growth. Ms. Carver earned her B.S.N. and M.B.A. from University of Colorado. We believe that Ms. Carver’s extensive experience working in the biotechnology industry makes her well-qualified to serve as a director.
Jess Roper — Director. Mr. Roper has been a director since October 2020. Mr. Roper has considerable financial and audit experience in the sectors of medical device, life sciences, technology, manufacturing, and financial institutions. Mr. Roper previously served as Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Dexcom, retiring in 2017 following a fulfilling and rewarding career. During his 12-year tenure, Dexcom transitioned from a pre-revenue privately held medical device company to a multi-national publicly traded entity. Mr. Roper previously held financial management positions with two other publicly traded companies and one venture funded company. He has played key roles in two initial public offerings, acquisitions/divestitures, and numerous equity and debt financings. Earlier in his career, Mr. Roper was an auditor with PricewaterhouseCoopers, and a bank and information systems examiner with the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency. He earned a Master of Science in Corporate Accountancy and a Bachelor of Science in Finance. Mr. Roper is a certified public accountant in the state of California. We believe that Mr. Roper is qualified to serve as a director based on his extensive financial and audit experience.
Lakhmir Chawla, M.D. — Director. Dr. Chawla is currently the Chief Executive Officer of Exthera Medical. Previously, Dr. Chawla was the Chief Medical Officer of Silver Creek Pharma where he oversaw the Acute Ischemic Stroke development program and initiation of the ARPEGGIO neuroprotection study. Prior to that, Dr. Chawla was the Chief Medical Officer at La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company where he oversaw the development and conduct of the Phase 3 ATHOS-3 trial. Prior to joining La Jolla, Dr. Chawla was a Professor of Medicine at the George Washington University, where he had dual appointments in the Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine and in the Department of Medicine, Division of Renal Diseases and Hypertension. Dr. Chawla is an internationally renowned expert in the field of acute kidney injury (AKI) and shock. He is the author of over 160 peer-reviewed publications and a recipient of the International Vicenza Award for Critical Care Nephrology; an award that recognizes individuals who have made seminal clinical research advancements that have significantly improved the care of critically ill patients with AKI and have been adopted worldwide. He remains an active investigator in the fields of AKI biomarkers, AKI risk prediction, AKI therapeutics and chronic kidney disease caused by AKI.
Chester S. Zygmont, III — Chief Financial Officer. Mr. Zygmont has been the Company’s Chief Financial Officer since inception. Mr. Zygmont brings over 20 years of experience in finance to the company with a wide range of industry applications. In 2016, Mr. Zygmont Co-Founded Jivanas, a social enterprise that owns and operates a factory in Nepal, that is focused on creating jobs for people at risk for human trafficking. Jivanas has operations in Nepal, Hong Kong, and the USA. During 2013, Mr. Zygmont Co-Founded oOxesis Biotechnology, LLC, a biologics lab that worked on developing therapies for unmet needs. From June 2012 to January 2016, Mr. Zygmont was the Senior Director of Finance, at La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company. During Mr. Zygmont’s tenure at La Jolla, he brought the company to its Nasdaq listing. Prior to La Jolla, Mr. Zygmont served as Managing Director at Z3 Capital, LLC from March 2009 to June 2012. Z3 Capital, LLC, a privately held investment firm, focused on investment acquisition and venture funding for multiple startup companies in real estate, medical device and biotechnology. Mr. Zygmont also served as Vice President at Symmetry Advisors, Inc. a private equity leveraged buyout firm. While at Symmetry, he managed all finance and accounting for its SPAC, was a key player on a $600 million buyout of a portfolio company, and subsequently led the restructuring of its manufacturing division. Mr. Zygmont earned his M.S. in Finance from Baruch College, Zicklin School of Business and his B.A. from Eastern University.
Number and Terms of Office of Officers and Directors
Our Board is divided into three classes, designated Class A, Class B and Class C, with only one class of directors being elected in each year and each class serving a three-year term.
Our officers are appointed by the Board and serve until such person’s successor is appointed or until such person’s earlier resignation, death or removal. Our Board is authorized to appoint persons to the offices set forth in our bylaws as it deems appropriate. Our bylaws provide that our officers may consist of a Chief Executive Officer, President, Secretary, Treasurer, Chief Financial Officer, Vice Presidents and such other offices as may be determined by the Board.
Family Relationships
There are no family relationships among our directors or executive officers.
71
Involvement in Certain Legal Proceedings
None of our directors, executive officers, promoters or control persons has been involved in any events requiring disclosure under Item 401(f) of Regulation S-K.
Board Composition
Classified Board of Directors
In accordance with our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, our board of directors is divided into three classes with staggered three-year terms. At each annual general meeting of stockholders, the successors to the directors whose terms then expire will be elected to serve from the time of election and qualification until the third annual meeting following their election. Our directors are divided among the three classes as follows:
We expect that any additional directorships resulting from an increase in the number of directors will be distributed among the three classes so that, as nearly as possible, each class will consist of one-third of the directors. The division of our board of directors into three classes with staggered three-year terms may delay or prevent a change of our management or a change in control.
Leadership Structure of the Board
Our bylaws and corporate governance guidelines provide our board of directors with flexibility to combine or separate the positions of Chairman of the board of directors and Chief Executive Officer.
Our board of directors has concluded that our current leadership structure is appropriate at this time. However, our board of directors will continue to periodically review our leadership structure and may make such changes in the future as it deems appropriate.
Role of Board in Risk Oversight Process
Risk assessment and oversight are an integral part of our governance and management processes. Our board of directors encourages management to promote a culture that incorporates risk management into our corporate strategy and day-to-day business operations. Management discusses strategic and operational risks at regular management meetings and conducts specific strategic planning and review sessions during the year that include a focused discussion and analysis of the risks facing us. Throughout the year, senior management reviews these risks with the board of directors at regular board meetings as part of management presentations that focus on particular business functions, operations or strategies, and presents the steps taken by management to mitigate or eliminate such risks.
Our board of directors does not have a standing risk management committee, but rather administers this oversight function directly through our board of directors as a whole, as well as through various standing committees of our board of directors that address risks inherent in their respective areas of oversight. While our board of directors is responsible for monitoring and assessing strategic risk exposure, our audit committee is responsible for overseeing our major financial risk exposures and the steps our management has taken to monitor and control these exposures. The audit committee also approves or disapproves any related person transactions. Our nominating and corporate governance committee monitors the effectiveness of our corporate governance guidelines. Our compensation committee assesses and monitors whether any of our compensation policies and programs has the potential to encourage excessive risk-taking.
72
Attendance of Directors at Board Meetings and Annual Meeting of Stockholders
During 2024, the Board of Directors met six times, the Compensation Committee met one time, the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee met one and the Audit Committee met four times. Each director who was on the Board during this timeframe attended at least 100% of the aggregate number of meetings held during his or her term of service. In 2024, the Company held its Annual Meeting of Stockholders which was attended by Mr. Rolke. The Company does not have a policy requiring its directors to attend the Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
Board Committees
Our board of directors has established an audit committee, a compensation committee and a nominating and corporate governance committee. Our board of directors may establish other committees to facilitate the management of our business. The composition and functions of each committee are described below. Members serve on these committees until their resignation or until otherwise determined by our board of directors. Each committee has adopted a written charter that satisfies the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC rules and regulations and the Nasdaq Listing Rules, which are posted on our website. The reference to our website address does not constitute incorporation by reference of the information contained at or available through our website.
Audit Committee
Revelation has a separately-designated standing Audit Committee established in accordance with Section 3(a)(58)(A) of the Exchange Act and Nasdaq listing rules. In addition, the board of directors adopted a written charter for the Audit Committee. The Audit Committee’s duties, will include, but are not limited to:
The composition of the Audit Committee consists of Mr. Roper, Dr. Tidmarsh and Ms. Carver, with Mr. Roper as Chair. Mr. Roper qualifies as an audit committee financial expert, as defined by the SEC rules. In addition, Revelation certified to Nasdaq that the Audit Committee has, and will continue to have, at least one member who has past employment experience in finance or accounting, requisite professional certification in accounting, or other comparable experience or background that results in the individual’s financial sophistication, including being or having been a chief executive officer, chief financial officer or other senior officer with financial oversight responsibilities. It has been determined that Mr. Roper satisfies such requirements.
73
Nominating and Governance Committee
Revelation’s Nominating and Governance Committee is comprised of Ms. Carver and Drs. Tidmarsh and Chawla, each of whom has been determined to be independent under the Nasdaq Listing Rules. The Nominating and Governance Committee adopted a written charter.
Specific responsibilities of the Nominating and Governance Committee include:
Compensation Committee
Revelation has a Compensation Committee established in accordance with the Nasdaq Listing Rules. The Compensation Committee is comprised of Drs. Tidmarsh and Chawla and Mr. Roper, each of whom has been determined to be independent under the Nasdaq Listing Rules and is a “non-employee director” as defined in Rule 16b-3 promulgated under the Exchange Act. The chair of Revelation’s compensation committee is Dr. Chawla.
The Compensation Committee oversees Revelation’s policies relating to compensation and benefits of its officers and employees. The Compensation Committee reviews and approves or recommends corporate goals and objectives relevant to compensation of its executive officers (other than the Chief Executive Officer), evaluates the performance of these officers in light of those goals and objectives and approves the compensation of these officers based on such evaluations. The Compensation Committee also reviews and approves or makes recommendations to the board of directors regarding the issuance of stock options and other awards under Revelation’s stock plans to its executive officers (other than the Chief Executive Officer). The Compensation Committee reviews the performance of the Chief Executive Officer and makes recommendations to the board of directors with respect to his compensation, and the board of directors retains the authority to make compensation decisions relative to the Chief Executive Officer. The Compensation Committee reviews and evaluates, on an annual basis, the compensation committee charter and the compensation committee’s performance.
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
No member of the Compensation Committee has ever been an officer or employee of Revelation. None of Revelation’s executive officers serve, or have served during the last fiscal year, as a member of the compensation committee or other board committee performing equivalent functions of any other entity that has one or more executive officers serving as one of Revelation’s directors or on the Compensation Committee.
Code of Conduct and Ethics
The Revelation Board adopted a Code of Ethics that applies to all its employees including its principal executive and financial officers.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE OFFICER AND DIRECTOR COMPENSATION.
Executive Compensation Overview
Each of the Company’s executive officers receives a base salary to compensate them for services rendered to the Company. The base salary is intended to provide a fixed component of compensation reflecting the executive’s skill set, experience, position and responsibilities.
Effective as of July 27, 2021, the Company entered into separate Executive Employment Agreements with Messrs. Rolke and Zygmont for their service as Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, respectively (collectively, the “Executive Employment Agreements”). The Executive Employment Agreements provide for a term of three years, unless terminated earlier in accordance with their terms.
74
The Executive Employment Agreements provide for an annual base salary of $400,000 for Mr. Rolke and $320,000 for Mr. Zygmont. Messrs. Rolke and Zygmont are also eligible to receive an annual performance bonus targeted at 40% for Mr. Rolke and 35% for Mr. Zygmont of their respective base salaries or as otherwise determined in the sole discretion of the board (each, an “Annual Bonus”), as well as equity incentive grants as determined by the Board in its sole discretion. On January 6, 2025, the Compensation Committee increased the annual base salary for Mr. Rolke to $589,050 and for Mr. Zygmont to $425,250, retroactive to January 1, 2025 and approved payment of the 2024 annual performance bonuses for Mr. Rolke in the amount of $280,500 and Mr. Zygmont in the amount of $162,000. On January 19, 2024, the Compensation Committee increased the annual base salary for Mr. Rolke to $561,000 and for Mr. Zygmont to $405,000, retroactive to January 1, 2024 and approved payment of the 2023 annual performance bonuses for Mr. Rolke in the amount of $237,500 and Mr. Zygmont in the amount of $142,579. On April 13, 2023, the Compensation Committee increased the annual base salary for Mr. Rolke to $475,000 and for Mr. Zygmont to $356,448, retroactive to January 1, 2023. In addition, the Compensation Committee increased Messrs. Rolke and Zygmont annual performance bonus targets to 50% for Mr. Rolke and 40% for Mr. Zygmont of their respective base salaries or as otherwise determined in the sole discretion of the board (each, an “Annual Bonus”).
Pursuant to the Executive Employment Agreements, if his employment is terminated as a result of a “Covered Termination Event” that is not in connection with a change in control of the Company, then each of Messrs. Rolke and Zygmont will be entitled to receive a lump sum payment equal to twelve months of severance payments at his then current base salary, plus a pro-rata portion of his Annual Bonus for the fiscal year in which his termination occurs based on actual achievement of the applicable bonus objectives and/or conditions for such year, plus continuation of medical benefits. If Mr. Rolke’s or Mr. Zygmont’s employment is terminated as a result of a “Covered Termination Event” in connection with a change in control of the Company, then each of Messrs. Rolke and Zygmont will be entitled to receive a lump sum payment equal to one times the sum of his then current base salary, plus his target bonus in effect for the year in which his termination of employment occurs, plus a pro-rata portion of his Annual Bonus for the fiscal year in which his termination occurs based on actual achievement of the applicable bonus objectives and/or conditions for such year, continuation of medical benefits and acceleration of vesting of all outstanding and unvested equity-based awards. “Covered Termination Event” means (i) a dismissal or discharge other than for cause and other than by reason of death or disability, or (ii) a voluntary termination for good reason.
Historically, our executive compensation program has reflected our growth and development-oriented corporate culture. To date, the compensation of our Chief Executive Officer and President and our other executive officers identified in the 2024 and 2023 Summary Compensation Table below, who we refer to as the named executive officers, has consisted of a combination of base salary, bonuses and long-term incentive compensation in the form of restricted common stock awards and incentive stock options. Our named executive officers who are full-time employees, like all other full-time employees, are eligible to participate in our retirement and health and welfare benefit plans. We will continue to evaluate our compensation values and philosophy and compensation plans and arrangements as circumstances merit. At a minimum, we review executive compensation annually with input from a compensation consultant. As part of this review process, we expect the board of directors and the compensation committee to apply our values and philosophy, while considering the compensation levels needed to ensure our executive compensation program remains competitive with our peers. In connection with our executive compensation program, we will also review whether we are meeting our retention objectives and the potential cost of replacing a key employee.
75
Summary Compensation Table
The following table shows the total compensation awarded to, earned by, or paid to during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023 to our executive officers who earned more than $100,000 during each of the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023 and were serving as named executive officers as of such date.
Our named executive officers for 2024 and 2023 who appear in the Summary Compensation Table are:
The following table sets forth, for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, all compensation paid, distributed or earned for services, including salary and bonus amounts, rendered in all capacities by the Company’s named executive officers. The information contained below represents compensation earned by the Company’s officers for their work related to the Company:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-equity |
|
|
|
|
||
Name and Position |
|
Year |
|
Salary |
|
Bonus |
|
Stock-based |
|
Option-based |
|
Annual |
|
Long |
|
All other |
|
Total |
James Rolke |
|
2024 |
|
561,000 |
|
237,500 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
14,726 |
|
813,226 |
CEO |
|
2023 |
|
475,000 |
|
160,000 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
14,250 |
|
649,250 |
Chester S. Zygmont, III |
|
2024 |
|
405,000 |
|
142,579 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
16,427 |
|
564,006 |
CFO |
|
2023 |
|
356,448 |
|
112,000 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
10,693 |
|
479,141 |
____________
76
OUTSTANDING EQUITY AWARDS AT FISCAL YEAR END
Outstanding Equity Awards
The following table provides information regarding the 2021 Equity Incentive Plan awards and the 2020 Equity Incentive Plan awards for each named executive officer outstanding as of December 31, 2024:
|
|
|
|
Option-based Awards |
|
|
|
Stock-based Awards |
|||||||
Name |
|
Date of Grant(1) |
|
Number of |
|
Option |
|
Option |
|
Value of |
|
Number of |
|
Market or |
|
James Rolke, CEO |
|
2/25/2022 |
|
5 |
|
$ |
23,520.00 |
|
2/25/2032 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
Chester S. Zygmont, III, CFO |
|
2/25/2022 |
|
1 |
|
$ |
23,520.00 |
|
2/25/2032 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
____________
(1) The stock options vest 25% on the one-year anniversary of the grant date, and thereafter quarterly over a three-year period, subject to continued service through each such vesting date.
Pay Versus Performance Disclosure
Pay Versus Performance Table
As required by Section 953(a) of the Dodd-Frank Act and Item 402(v) of SEC Regulation S-K, we are providing the following information about the relationship between “compensation actually paid” to our “named executive officers,” within the meaning of such rules, and certain financial performance measures of our Company. The table below provides information regarding compensation actually paid to our CEO, who serves as our principal executive officer (“PEO”), and compensation actually paid to our CFO, our only other non-PEO named executive officer, during each of the past two fiscal years, as well as our total stockholder return and net loss for each of the past two fiscal years.
Year |
|
Summary Compensation Table Total for PEO(1) |
|
|
Compensation Actually Paid to PEO(2)(3) |
|
|
Average Summary |
|
|
Average Compensation Actually Paid to Non-PEO Named Executive Officers(5)(6) |
|
|
Value of Initial Fixed $100 Investment |
|
|
Net Loss |
|
||||||
2024 |
|
$ |
813,226 |
|
|
$ |
813,226 |
|
|
$ |
564,006 |
|
|
$ |
564,006 |
|
|
$ |
0.23 |
|
|
$ |
(15.04 |
) |
2023 |
|
$ |
649,250 |
|
|
$ |
649,250 |
|
|
$ |
479,141 |
|
|
$ |
479,141 |
|
|
$ |
3.07 |
|
|
$ |
(0.12 |
) |
77
|
James Rolke |
|
|
Summary Compensation Table Total for Fiscal 2024 |
$ |
813,226 |
|
Deduct: Stock awards(a) |
|
— |
|
Deduct: Option awards(b) |
|
— |
|
Add: Fiscal year-end value of equity awards granted during the fiscal year that are outstanding and unvested(c) |
|
— |
|
Add: Change in fair value of equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that are outstanding and unvested(d) |
|
— |
|
Add: Change in fair value of equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that vested during the fiscal year(e) |
|
— |
|
Add: Value of dividend equivalents accrued on equity awards during the fiscal year |
|
— |
|
Compensation Actually Paid for Fiscal 2024 |
$ |
813,226 |
|
|
|
|
|
Summary Compensation Table Total for Fiscal 2023 |
$ |
649,250 |
|
Deduct: Stock awards(a) |
|
— |
|
Deduct: Option awards(b) |
|
— |
|
Add: Fiscal year-end value of equity awards granted during the fiscal year that are outstanding and unvested(c) |
|
— |
|
Add: Change in fair value of equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that are outstanding and unvested(d) |
|
— |
|
Add: Change in fair value of equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that vested during the fiscal year(e) |
|
— |
|
Add: Value of dividend equivalents accrued on equity awards during the fiscal year |
|
— |
|
Compensation Actually Paid for Fiscal 2023 |
$ |
649,250 |
|
(a) Represents the total of the amounts reported in the “Stock Awards” column in the Summary Compensation Table for the applicable fiscal year.
(b) Represents the total of the amounts reported in the “Option Awards” column in the Summary Compensation Table for the applicable fiscal year.
(c) Represents the fiscal year-end value of equity awards granted during the applicable fiscal year that are outstanding and unvested as of the end of such applicable fiscal year.
(d) Represents the amount of change as of the end of the applicable fiscal year (from the end of the prior fiscal year) in fair value of any equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that are outstanding and unvested as of the end of such applicable fiscal year.
(e) Represents the amount of change as of the vesting date (from the end of the prior fiscal year) in fair value of any equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that vested during the applicable fiscal year.
Since we do not have a pension plan, all of the foregoing adjustments are equity award adjustments for each applicable fiscal year and include the addition (or subtraction, as applicable) of the following: (i) the fiscal year-end fair value of any equity awards granted in the applicable fiscal year that are outstanding and unvested as of the end of such applicable fiscal year; (ii) the amount of change as of the end of the applicable fiscal year (from the end of the prior fiscal year) in fair value of any equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that are outstanding and unvested as of the end of such applicable fiscal year; (iii) for equity awards that are granted and vest in the same applicable fiscal year, the fair value as of the vesting date; (iv) for equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that vest in the applicable fiscal year, the amount equal to the change as of the vesting date (from the end of the prior fiscal year) in fair value; (v) for equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that are determined to fail to meet the applicable vesting conditions during the applicable fiscal year, a deduction for the amount equal to the fair value at the end of the prior fiscal year; and (vi) the dollar value of any dividends or other earnings paid on equity awards in the applicable fiscal year prior to the vesting date that are not otherwise reflected in the fair value of such award or included in any other component of total compensation for such applicable fiscal year. Adjustments as provided in clauses (iii) and (vi) are inapplicable for all of the fiscal years presented in the table.
The valuation assumptions used to calculate fair values did not materially differ from those disclosed at the time of grant. The value of option awards is based on the fair value as of the end of the covered fiscal year or change in fair value during the covered fiscal year, in each case based on our Black-Scholes option pricing model, the assumptions of which are described in Note 9 to our consolidated financial statements included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2024.
78
|
Chester S. Zygmont, III |
|
|
Summary Compensation Table Total for Fiscal 2024 |
$ |
564,006 |
|
Deduct: Stock awards(a) |
|
— |
|
Deduct: Option awards(b) |
|
— |
|
Add: Fiscal year-end value of equity awards granted during the fiscal year that are outstanding and unvested(c) |
|
— |
|
Add: Change in fair value of equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that are outstanding and unvested(d) |
|
— |
|
Add: Change in fair value of equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that vested during the fiscal year(e) |
|
— |
|
Add: Value of dividend equivalents accrued on equity awards during the fiscal year |
|
— |
|
Compensation Actually Paid for Fiscal 2024 |
$ |
564,006 |
|
|
|
|
|
Summary Compensation Table Total for Fiscal 2023 |
$ |
479,141 |
|
Deduct: Stock awards(a) |
|
— |
|
Deduct: Option awards(b) |
|
— |
|
Add: Fiscal year-end value of equity awards granted during the fiscal year that are outstanding and unvested(c) |
|
— |
|
Add: Change in fair value of equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that are outstanding and unvested(d) |
|
— |
|
Add: Change in fair value of equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that vested during the fiscal year(e) |
|
— |
|
Add: Value of dividend equivalents accrued on equity awards during the fiscal year |
|
— |
|
Compensation Actually Paid for Fiscal 2023 |
$ |
479,141 |
|
(a) Represents the total of the amounts reported in the “Stock Awards” column in the Summary Compensation Table for the applicable fiscal year.
(b) Represents the total of the amounts reported in the “Option Awards” column in the Summary Compensation Table for the applicable fiscal year.
(c) Represents the fiscal year-end value of equity awards granted during the applicable fiscal year that are outstanding and unvested as of the end of such applicable fiscal year.
(d) Represents the amount of change as of the end of the applicable fiscal year (from the end of the prior fiscal year) in fair value of any equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that are outstanding and unvested as of the end of such applicable fiscal year.
(e) Represents the amount of change as of the vesting date (from the end of the prior fiscal year) in fair value of any equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that vested during the applicable fiscal year.
Since we do not have a pension plan, all of the foregoing adjustments are equity award adjustments for each applicable fiscal year and include the addition (or subtraction, as applicable) of the following: (i) the fiscal year-end fair value of any equity awards granted in the applicable fiscal year that are outstanding and unvested as of the end of such applicable fiscal year; (ii) the amount of change as of the end of the applicable fiscal year (from the end of the prior fiscal year) in fair value of any equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that are outstanding and unvested as of the end of such applicable fiscal year; (iii) for equity awards that are granted and vest in the same applicable fiscal year, the fair value as of the vesting date; (iv) for equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that vest in the applicable fiscal year, the amount equal to the change as of the vesting date (from the end of the prior fiscal year) in fair value; (v) for equity awards granted in prior fiscal years that are determined to fail to meet the applicable vesting conditions during the applicable fiscal year, a deduction for the amount equal to the fair value at the end of the prior fiscal year; and (vi) the dollar value of any dividends or other earnings paid on equity awards in the applicable fiscal year prior to the vesting date that are not otherwise reflected in the fair value of such award or included in any other component of total compensation for such applicable fiscal year. Adjustments as provided in clauses (iii) and (vi) are inapplicable for all of the fiscal years presented in the table.
79
The valuation assumptions used to calculate fair values did not materially differ from those disclosed at the time of grant. The value of option awards is based on the fair value as of the end of the covered fiscal year or change in fair value during the covered fiscal year, in each case based on our Black-Scholes option pricing model, the assumptions of which are described in Note 9 to our consolidated financial statements included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2024.
Pay Versus Performance Relationship
In accordance with Item 402(v) of SEC Regulation S-K, we are providing the following descriptions of the relationships between information presented in the Pay versus Performance table above.
Compensation Actually Paid and Company TSR. As demonstrated by the following graph, the amount of compensation actually paid to our NEOs is generally aligned with our cumulative total stockholder return (“TSR”) (assuming reinvestment of dividends) on $100 invested in our common stock over the three fiscal years presented in the table. The overall alignment of compensation actually paid with our cumulative TSR over the period presented is because a significant portion of the compensation actually paid to our NEOs is comprised of equity awards, the value of which is driven by our stock price.
80
Compensation Actually Paid and Net Loss. As demonstrated by the following graph, the amount of compensation actually paid to our NEOs is not necessarily aligned with our net loss for each of the two fiscal years presented in the table.

DIRECTOR COMPENSATION
The general policy of the Board is that compensation for independent directors should be a fair mix between cash and equity-based compensation. Additionally, the Company reimburses directors for reasonable expenses incurred during the course of their performance. There are no long-term incentive or medical reimbursement plans. The Company does not pay directors who are part of management for Board service in addition to their regular employee compensation. The Board determines the amount of director compensation. The Board may delegate such authority to the compensation committee.
The following table sets forth the total cash and equity compensation paid to our non-employee directors for service on our board of directors during 2024:
Name |
|
Fees earned or |
|
Option-based |
|
Total |
George Tidmarsh, M.D., Ph.D. |
|
60,000 |
|
— |
|
60,000 |
Jennifer Carver, BSN, MBA |
|
60,000 |
|
— |
|
60,000 |
Jess Roper |
|
60,000 |
|
— |
|
60,000 |
Lakhmir Chawla, M.D. |
|
60,000 |
|
— |
|
60,000 |
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS.
The following table also sets forth information known to us regarding the beneficial ownership of our common stock as of March 3, 2025:
• each person who is, or is expected to be, the beneficial owner of more than 5% of the outstanding shares of our common stock;
• each of our current officers and directors; and
• all current executive officers and directors of the Company, as a group.
81
Beneficial ownership is determined according to the rules of the SEC, which generally provide that a person has beneficial ownership of a security if he, she or it possesses sole or shared voting or investment power over that security, including options and warrants that are currently exercisable or exercisable within 60 days. Shares of common stock issuable pursuant to options or warrants are deemed to be outstanding for purposes of computing the beneficial ownership percentage of the person or group holding such options or warrants but are not deemed to be outstanding for purposes of computing the beneficial ownership percentage of any other person.
The beneficial ownership of our common stock is based on 905,228 shares of common stock issued and outstanding as of March 3, 2025.
Unless otherwise indicated, we believe that all persons named in the table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock owned by them.
Name |
|
Number of |
|
Beneficial |
||
Directors and Officers of Revelation(1): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
James Rolke(2) |
|
30,142 |
|
|
3.2 |
% |
George F. Tidmarsh M.D., Ph.D.(3) |
|
281 |
|
|
* |
|
Jennifer Carver, BSN, MBA(4) |
|
200 |
|
|
* |
|
Jess Roper(5) |
|
196 |
|
|
* |
|
Lakhmir Chawla, M.D.(6) |
|
181 |
|
|
* |
|
Chester S. Zygmont, III(7) |
|
15,090 |
|
|
1.6 |
% |
All Directors and Officers as a Group (Six Individuals) |
|
46,090 |
|
|
5.0 |
% |
____________
* Less than one percent.
82
ITEM. 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PERSON TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE.
Related Party Policy
Our Code of Ethics requires us to avoid, wherever possible, all related party transactions that could result in actual or potential conflicts of interests, except under guidelines approved by the board of directors (or the audit committee). Related-party transactions are defined as transactions in which (1) the aggregate amount involved will or may be expected to exceed $120,000 in any calendar year, (2) we or any of our subsidiaries is a participant, and (3) any (a) executive officer, director or nominee for election as a director, (b) greater than 5% beneficial owner of our shares of common stock, or (c) immediate family member, of the persons referred to in clauses (a) and (b), has or will have a direct or indirect material interest (other than solely as a result of being a director or a less than 10% beneficial owner of another entity). A conflict of interest situation can arise when a person takes actions or has interests that may make it difficult to perform his or her work objectively and effectively. Conflicts of interest may also arise if a person, or a member of his or her family, receives improper personal benefits as a result of his or her position.
Our audit committee, pursuant to its written charter, will be responsible for reviewing and approving related-party transactions to the extent we enter into such transactions. The audit committee will consider all relevant factors when determining whether to approve a related party transaction, including whether the related party transaction is on terms no less favorable to us than terms generally available from an unaffiliated third-party under the same or similar circumstances and the extent of the related party’s interest in the transaction. No director may participate in the approval of any transaction in which he is a related party, but that director is required to provide the audit committee with all material information concerning the transaction. We also require each of our directors and executive officers to complete a directors’ and officers’ questionnaire that elicits information about related party transactions.
These procedures are intended to determine whether any such related party transaction impairs the independence of a director or presents a conflict of interest on the part of a director, employee or officer.
Director Independence
Our board of directors currently consists of five members. Our board of directors has determined that all of our directors, other than Mr. Rolke, qualify as “independent” directors in accordance with the rules of the SEC and the Nasdaq, Marketplace Rules, or the Nasdaq Listing Rules, which the Company has adopted as its independence standards. Mr. Rolke is not considered independent because he is an executive officer of the Company. Under the Nasdaq Listing Rules, the definition of independence includes a series of objective tests, such as that the director is not, and has not been for at least three years, one of our employees and that neither the director nor any of his or her family members has engaged in various types of business dealings with us. In addition, as required by the Nasdaq Listing Rules, our board of directors has made a subjective determination as to each independent director that no relationships exist that, in the opinion of our board of directors, would interfere with the exercise of independent judgment in carrying out the responsibilities of a director. In making these determinations, our board of directors reviewed and discussed information provided by the directors and us with regard to each director’s relationships as they may relate to us and our management.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
Baker Tilly US, LLP acted as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023 and for the interim periods in such fiscal years. The following table shows the fees that were incurred by the Company for audit and other services provided by Baker Tilly US, LLP for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023.
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
||
Audit Fees(a) |
|
$ |
404,568 |
|
|
$ |
292,833 |
|
Tax Fees(b) |
|
|
15,900 |
|
|
|
29,203 |
|
Other Fees |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Total |
|
$ |
420,468 |
|
|
$ |
322,036 |
|
____________
(a) Audit fees represent fees for professional services provided in connection with the audit of the Company’s annual financial statements and the review of its financial statements included in the Company’s Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, services that are normally provided in connection with statutory or regulatory filings and fees related to our filing of certain Registration Statements.
(b) Tax fees represent fees for professional services related to tax compliance, tax advice and tax planning.
83
Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures
All audit-related services, tax services and other services rendered by Baker Tilly US, LLP were pre-approved by the Company’s Board of Directors. Commencing in 2020, the Audit Committee was charged with all pre-approval activities with respect to the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm. The Audit Committee has adopted a pre-approval policy that provides for the pre-approval of all services performed for the Company by its independent registered public accounting firm. Our independent registered public accounting firm and management are required to periodically report to the Audit Committee regarding the extent of services provided by the independent registered public accounting firm in accordance with this pre-approval policy, and the fees for the services performed to date.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report:
84
|
||
|
||
97(14) |
|
|
99.1(12) |
|
|
99.2(12) |
|
|
99.3(12) |
|
|
101.INS* |
|
XBRL Instance Document – the instance document does not appear in the interactive data file because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document. |
101.SCH* |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Scema Document |
101.CAL* |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
101.DEF* |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
101.LAB* |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
101.PRE* |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
104* |
|
Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) |
The annexes, schedules, and certain exhibits to the Agreement and Plan of Merger have been omitted pursuant to Item 601(b)(2) of Regulation S-K. Revelation hereby agrees to furnish supplementally a copy of any omitted annex, schedule or exhibit to the SEC upon request.
(1) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Current Report on Form S-4 filed, as amended (File No. 333- 259638). |
|
|
(2) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 31, 2023. |
|
|
(3) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 23, 2024. |
|
|
(4) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on July 7, 2023. |
|
|
(5) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 27, 2022. |
|
|
(6) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, as amended (File No. 333-268076). |
|
|
(7) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 13, 2023. |
|
|
(8) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 8, 2024. |
|
|
(9) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 26, 2024. |
|
|
(10) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 6, 2024. |
|
|
(11) |
Previously filed Appendix A to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s definitive proxy statement filed on April 16, 2024. |
|
|
(12) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on March 30, 2023. |
|
|
(13) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 14, 2022. |
|
|
(14) |
Previously filed as an exhibit to Revelation Biosciences, Inc.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on March 22, 2024 |
|
|
* |
Filed herewith. |
|
|
† |
Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan. |
85
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY.
Not applicable.
86
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this Annual Report on Form 10-K to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC. |
|
|
|
|
|
Date: March 6, 2025 |
|
By: |
/s/ James Rolke |
|
|
|
James Rolke |
|
|
|
Chief Executive Officer |
|
|
|
(principal executive officer) |
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Chester S. Zygmont, III and Joseph P. Galda, jointly and severally, their respective attorneys-in-fact, with the power of substitution, for each of them in any and all capacities, to sign any amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and to file the same, with exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, hereby ratifying and confirming all that each of said attorneys-in-fact, or their respective substitute or substitutes, may do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Annual Report on Form 10-K has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Date: March 6, 2025 |
By: |
/s/ James Rolke |
|
|
Chief Executive Officer and Director |
|
|
|
Date: March 6, 2025 |
By: |
/s/ George F.Tidmarsh, MD, PhD |
|
|
Chairman and Director |
|
|
|
Date: March 6, 2025 |
By: |
/s/ Chester S. Zygmont, III |
|
|
Chief Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer |
|
|
|
Date: March 6, 2025 |
By: |
/s/ Jennifer Carver |
|
|
Director |
|
|
|
Date: March 6, 2025 |
By: |
/s/ Jess Roper |
|
|
Director |
|
|
|
Date: March 6, 2025 |
By: |
/s/ Lakhmir Chawla, MD |
|
|
Director |
|
|
|
87
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (PCAOB ID 23) |
|
F-2 |
|
F-4 |
|
|
F-5 |
|
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) |
|
F-6 |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows |
|
F-7 |
|
F-8 – F-28 |
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Revelation Biosciences, Inc.
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Revelation Biosciences, Inc. (the Company) as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of operations, changes in stockholders' equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes (collectively, the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2024, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Going Concern Uncertainty
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has incurred recurring operating losses and has no revenue sources. These conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regard to these matters are also described in Note 1. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
F-2
Critical Audit Matters
Critical audit matters are matters arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. We determined that there are no critical audit matters.
/s/ BAKER TILLY US, LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2021.
San Diego, California
March 6, 2025
F-3
PART I—FINANCIAL INFORMATION
Item 1. Consolidated Financial Statements
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
6,499,018 |
|
|
$ |
11,991,701 |
|
Deferred offering costs |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
71,133 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
66,699 |
|
|
|
84,691 |
|
Total current assets |
|
|
6,565,717 |
|
|
|
12,147,525 |
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
56,332 |
|
|
|
65,084 |
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
6,622,049 |
|
|
$ |
12,212,609 |
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accounts payable |
|
$ |
783,621 |
|
|
$ |
1,359,898 |
|
Accrued expenses |
|
|
1,127,800 |
|
|
|
1,152,460 |
|
Deferred underwriting commissions |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,911,260 |
|
Warrant liability |
|
|
2,246 |
|
|
|
141,276 |
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
1,913,667 |
|
|
|
5,564,894 |
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
1,913,667 |
|
|
|
5,564,894 |
|
Commitments and Contingencies (Note 4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Stockholders’ equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Common Stock, $0.001 par value; 500,000,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023 and 522,223 and 16,484 issued and outstanding at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively |
|
|
522 |
|
|
|
16 |
|
Additional paid-in-capital |
|
|
45,213,498 |
|
|
|
32,114,801 |
|
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
(40,505,638 |
) |
|
|
(25,467,102 |
) |
Total stockholders’ equity |
|
|
4,708,382 |
|
|
|
6,647,715 |
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
|
$ |
6,622,049 |
|
|
$ |
12,212,609 |
|
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
F-4
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
||
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Research and development |
|
$ |
3,548,996 |
|
|
$ |
4,145,902 |
|
General and administrative |
|
|
4,426,113 |
|
|
|
4,510,762 |
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
7,975,109 |
|
|
|
8,656,664 |
|
Loss from operations |
|
|
(7,975,109 |
) |
|
|
(8,656,664 |
) |
Other (expense) income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Change in fair value of warrant liability |
|
|
81,441 |
|
|
|
8,328,937 |
|
Other (expense) income, net |
|
|
(7,144,868 |
) |
|
|
207,473 |
|
Total other (expense) income, net |
|
|
(7,063,427 |
) |
|
|
8,536,410 |
|
Net loss |
|
$ |
(15,038,536 |
) |
|
$ |
(120,254 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net loss per share, basic and diluted |
|
$ |
(87.68 |
) |
|
$ |
(8.44 |
) |
Weighted-average shares used to compute net loss per share, basic and diluted |
|
|
171,510 |
|
|
|
14,246 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
F-5
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
|
|
Series A |
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Equity |
|
|||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2022 (as previously reported) |
|
|
1 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
77,375 |
|
|
$ |
77 |
|
|
$ |
26,399,224 |
|
|
$ |
(25,346,848 |
) |
|
$ |
1,052,453 |
|
Retrospective application of reverse recapitalization |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(72,540 |
) |
|
|
(72 |
) |
|
|
72 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Reverse stock split fractional stock round up |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(23 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Balance at December 31, 2022 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
4,812 |
|
|
$ |
5 |
|
|
$ |
26,399,296 |
|
|
$ |
(25,346,848 |
) |
|
$ |
1,052,453 |
|
Redemption of Series A Preferred Stock |
|
|
(1 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Issuance of common stock from the February 2023 Public Offering |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
6,017 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
33,469 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
33,474 |
|
Class C Pre-Funded Warrants exercise |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
699 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
34 |
|
Alternative cashless exercise of Class C Common Stock Warrants |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,948 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
5,526,282 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,526,287 |
|
RSU awards issued |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
155,721 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
155,721 |
|
Net loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(120,254 |
) |
|
|
(120,254 |
) |
Balance as of December 31, 2023 |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
16,484 |
|
|
$ |
16 |
|
|
$ |
32,114,801 |
|
|
$ |
(25,467,102 |
) |
|
$ |
6,647,715 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2023 (as previously reported) |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
264,537 |
|
|
$ |
265 |
|
|
$ |
32,114,552 |
|
|
$ |
(25,467,102 |
) |
|
$ |
6,647,715 |
|
Retrospective application of reverse recapitalization |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(248,029 |
) |
|
|
(249 |
) |
|
|
249 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Reverse stock split fractional stock round up |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(24 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Balance at December 31, 2023 |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
16,484 |
|
|
$ |
16 |
|
|
$ |
32,114,801 |
|
|
$ |
(25,467,102 |
) |
|
$ |
6,647,715 |
|
Issuance of common stock from the February 2024 Public Offering |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8,029 |
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
5,417,045 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,417,053 |
|
Class D Pre-Funded Warrants exercise |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
77,282 |
|
|
|
78 |
|
|
|
49 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
127 |
|
Alternative cashless exercise of Class C Common Stock Warrants |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
212 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
57,589 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
57,589 |
|
Common stock issued for services |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
653 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
24,999 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
25,000 |
|
Class D Common Stock Warrants exercises |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
6,312 |
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
241,384 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
241,390 |
|
Class D Warrant Inducement exercises |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
159,249 |
|
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
3,501,117 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,501,276 |
|
Class E Common Stock Warrant Inducement exercises |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
254,002 |
|
|
|
254 |
|
|
|
3,687,664 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,687,918 |
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
168,850 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
168,850 |
|
Net loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(15,038,536 |
) |
|
|
(15,038,536 |
) |
Balance as of December 31, 2024 |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
522,223 |
|
|
$ |
522 |
|
|
$ |
45,213,498 |
|
|
$ |
(40,505,638 |
) |
|
$ |
4,708,382 |
|
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
F-6
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
||
Cash flows from operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net loss |
|
$ |
(15,038,536 |
) |
|
|
(120,254 |
) |
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
|
168,850 |
|
|
|
155,721 |
|
Issuance of common stock for services |
|
|
25,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Depreciation expense |
|
|
27,923 |
|
|
|
25,049 |
|
Change in fair value of warrant liability |
|
|
(81,441 |
) |
|
|
(8,328,937 |
) |
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
17,992 |
|
|
|
(11,559 |
) |
Deferred offering costs |
|
|
71,133 |
|
|
|
82,071 |
|
Accounts payable |
|
|
(576,277 |
) |
|
|
749,660 |
|
Accrued expenses |
|
|
(2,935,920 |
) |
|
|
161,963 |
|
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
|
(18,321,276 |
) |
|
|
(7,286,286 |
) |
Cash flows from investing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Purchase of property and equipment |
|
|
(19,171 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
(19,171 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
Cash flows from financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Proceeds from the February 2024 Public Offering, net |
|
|
5,417,053 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Proceeds from the Class D Common Stock Warrants exercises |
|
|
241,390 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Proceeds from Warrant Inducement exercises, net |
|
|
3,501,276 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Proceeds from Class D Pre-Funded Warrants exercise |
|
|
127 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Proceeds from the Class E Common Stock Warrants exercises |
|
|
3,687,918 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Redemption of Series A Preferred Stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(5,000 |
) |
Proceeds from the February 2023 Public Offering, net |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
14,029,974 |
|
Proceeds from Class C Pre-Funded Warrants exercise |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
34 |
|
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|
|
12,847,764 |
|
|
|
14,025,008 |
|
Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
(5,492,683 |
) |
|
|
6,738,722 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period |
|
|
11,991,701 |
|
|
|
5,252,979 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
|
$ |
6,499,018 |
|
|
$ |
11,991,701 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Fair Value of Class G Common Stock Warrants |
|
$ |
2,066,429 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
Fair Value of Class F Common Stock Warrants |
|
$ |
4,104,680 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
Fair Value of Class E Common Stock Warrants in connection with the Class D Warrant Inducement |
|
$ |
4,887,683 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
Incremental fair value of the Class D Common Stock Warrants in connection with the Class D Warrant Inducement |
|
$ |
939,679 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
Equity issuance costs in connection with the Class D Warrant Inducement included in accounts payable |
|
$ |
25,968 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
Fair Value of Class D Common Stock Warrants in connection with the February 2024 Public Offering |
|
$ |
6,269,684 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
Fair Value of Class C Common Stock Warrants in connection with the February 2023 Public Offering |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
13,996,500 |
|
Alternative cashless exercise of Class C Common Stock Warrants |
|
$ |
57,589 |
|
|
$ |
5,526,287 |
|
Deferred offering costs included in accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
66,033 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
F-7
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
1. Organization and Basis of Presentation
Revelation Biosciences, Inc. (collectively with its wholly-owned subsidiaries, referred to as “we,” us,” “our,” “Revelation,” or the “Company”) is a clinical-stage life science company that is focused on rebalancing inflammation to optimize health using its proprietary formulation Gemini. We have multiple ongoing programs to evaluate Gemini, including GEM-AKI as a prevention for acute kidney injury (“AKI”), GEM-CKD as a treatment for chronic kidney disease (“CKD”), and GEM-PSI as a prevention for post surgical infection (“PSI”). The Company was incorporated in the state of Delaware on November 20, 2019 (originally as Petra Acquisition, Inc.) and is based in San Diego, California.
The Company’s common stock and public warrants are listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbols “REVB” and “REVBW”, respectively.
Reverse Stock Splits
On January 17, 2025, the Company filed a Certificate of Amendment of the Third Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation effecting a reverse stock split on January 28, 2025 with a ratio of 1-for-16 (the “2025 Reverse Split”). As a result of the 2025 Reverse Split, every 16 shares of the Company’s issued and outstanding common stock automatically converted into one share of common stock, without any change in the par value per share. No fractional shares were outstanding following the 2025 Reverse Split. Any holder of common stock otherwise entitled to a fractional share as a result of the 2025 Reverse Stock Split because they hold a number of shares not evenly divisible by the 2025 Reverse Stock Split ratio will be rounded down to the nearest whole share. In addition, effective as of the same time as the 2025 Reverse Split, proportionate adjustments were made to all then-outstanding equity awards and warrants with respect to the number of shares of common stock subject to such award or warrant and the exercise price thereof. Furthermore, the number of shares of common stock available for issuance under the Company’s equity incentive plans were proportionately adjusted for the 2025 Reverse Split ratio, such that fewer shares are subject to such plans. All share numbers included herein have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the 1-for-16 Reverse Split (see Note 8).
On January 22, 2024, the Company filed a Certificate of Amendment of the Third Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation effecting a reverse stock split on January 25, 2024 with a ratio of 1-for-30 (the “2024 Reverse Split”). As a result of the 2024 Reverse Split, every 30 shares of the Company’s issued and outstanding common stock automatically converted into one share of common stock, without any change in the par value per share. No fractional shares were outstanding following the 2024 Reverse Split. Any holder who would have received a fractional share of common stock automatically received an additional fraction of a share of common stock to round up to the next whole share. In addition, effective as of the same time as the 2024 Reverse Split, proportionate adjustments were made to all then-outstanding equity awards and warrants with respect to the number of shares of common stock subject to such award or warrant and the exercise price thereof. Furthermore, the number of shares of common stock available for issuance under the Company’s equity incentive plans were proportionately adjusted for the 2024 Reverse Split ratio, such that fewer shares are subject to such plans. All share numbers included herein have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the 1-for-30 Reverse Split (see Note 8).
Nasdaq Compliance
As previously reported on October 16, 2024, the Company received a letter from Nasdaq Stock Market (“Nasdaq”) notifying the Company of its noncompliance with Nasdaq Listing Rule 5550(a)(2) by failing to maintain a minimum bid price for its common stock of at least $1.00 per share for 30 consecutive business days. The Company had until February 14, 2025, to regain compliance by having a minimum closing bid price of at least $1.00 per share for at least 10 consecutive business days. On February 19, 2025 the Company received a formal notice from Nasdaq stating that the Company’s common stock will continue to be listed and traded on Nasdaq, due to the Company having regained compliance with the minimum bid price requirement, and all applicable listing standards.
F-8
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Going Concern
The Company has incurred recurring losses since its inception, including a net loss of $15.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2024. As of December 31, 2024, the Company had an accumulated deficit of $40.5 million, a stockholders’ equity of $4.7 million and available cash and cash equivalents of $6.5 million. The Company expects to continue to incur significant operating and net losses, as well as negative cash flows from operations, for the foreseeable future as it continues to complete all necessary product development or future commercialization efforts. The Company has never generated revenue and does not expect to generate revenue from product sales unless and until it successfully completes development and obtains regulatory approval for GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD, GEM-PSI or other product candidates, which the Company expects will not be for at least several years, if ever. The Company does not anticipate that its current cash and cash equivalents balance will be sufficient to sustain operations within one-year after the date that the Company’s audited financial statements for December 31, 2024 were issued, which raises substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern.
To continue as a going concern, the Company will need, among other things, to raise additional capital resources. The Company plans to seek additional funding through public or private equity or debt financings. The Company may not be able to obtain financing on acceptable terms, or at all. The terms of any financing may adversely affect the holdings or the rights of the Company’s stockholders. If the Company is unable to obtain funding, it could be required to delay, reduce or eliminate research and development programs, product portfolio expansion or future commercialization efforts, which could adversely affect the Company’s business operations.
The audited consolidated financial statements for December 31, 2024, have been prepared on the basis that the Company will continue as a going concern, and does not include any adjustments to reflect the possible future effects on the recoverability and classification of assets or the amounts and classification of liabilities that may result from the possible inability for the Company to continue as a going concern.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements are prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Revelation Biosciences, Inc. and its wholly owned subsidiaries. All intercompany balances and transactions among the consolidated entity have been eliminated in consolidation.
F-9
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions about future events that affect the amounts of assets and liabilities reported, disclosures about contingent assets and liabilities, and reported amounts of expenses. These estimates and assumptions are based on the Company’s best estimates and judgment. The Company regularly evaluates its estimates and assumptions using historical and industry experience and other factors; however, actual results could differ materially from these estimates and could have an adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of three months or less from the purchase date to be cash equivalents. The Company maintains its cash in checking and savings accounts. Income generated from cash held in savings accounts is recorded as interest income. The carrying value of the Company’s savings accounts is included in cash and approximates the fair value.
Concentrations of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to a concentration of credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents. Bank deposits are held by accredited financial institutions and these deposits may at times be in excess of federally insured limits. The Company limits its credit risk associated with cash and cash equivalents by placing them with financial institutions that it believes are of high quality. The Company has not experienced any losses on its deposits of cash or cash equivalents.
Deferred Offering Costs
The Company capitalizes certain legal, professional accounting and other third-party fees that are directly associated with in-process equity financings as deferred offering costs until such financings are consummated. After consummation of the equity financing, these costs are recorded as a reduction of the proceeds generated as a result of the offering. Should the planned equity financing be abandoned, the deferred offering costs will be expensed immediately as a charge to operating expenses in the consolidated statements of operations.
Property and Equipment, Net
Property and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, which is five years. Maintenance and repairs are charged to operating expense as incurred. When assets are sold, or otherwise disposed of, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts, and any gain or loss is included in other income (expense).
Leases
The Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at inception. Lease right-of-use assets represent the right to use an underlying asset for the lease term and lease liabilities represent the obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease. For operating leases with an initial term greater than 12 months, the Company recognizes operating lease right-of-use assets and operating lease liabilities based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term at the commencement date. Operating lease right-of-use assets are comprised of the lease liability plus any lease payments made and excludes lease incentives. Lease terms include options to renew or terminate the lease when the Company is reasonably certain that the renewal option will be exercised or when it is reasonably certain that the termination option will not be exercised. For an operating lease, if the interest rate used to determine the present value of future lease payments is not readily determinable, the Company estimates the incremental borrowing rate as the discount rate for the lease. The Company’s incremental borrowing rate is estimated to approximate the interest rate on a collateralized basis with similar terms and payments, and in similar economic environments. Lease expense for lease payments is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
F-10
Research and Development Expenses
All research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Research and development costs consist primarily of salaries, employee benefits, costs associated with preclinical studies and clinical trials (including amounts paid to clinical research organizations and other professional services). Payments made prior to the receipt of goods or services to be used for research and development expense are capitalized until the goods or services are received.
The Company records accruals for estimated research and development costs, comprising payments for work performed by third party contractors, laboratories, participating clinical trial sites, and others. Some of these contractors bill monthly based on actual services performed. Other contractors bill periodically based upon achieving certain contractual milestones. For the contractors that bill periodically, the Company accrues the expenses as goods or services are used or rendered. Clinical trial site costs related to patient enrollment are accrued as patients enter and progress through the trial. Upfront costs, such as costs associated with setting up clinical trial sites for participation in the trials, are expensed immediately once incurred as research and development expenses.
Patent Costs
Legal costs in connection with approved patents and patent applications are expensed as incurred, as recoverability of such expenditures is uncertain. These costs are recorded in general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of operations.
Stock-based Compensation
The Company recognizes stock-based compensation expense related to stock options, third-party warrants, and Restricted Stock Unit (“RSU”) awards granted, based on the estimated fair value of the stock-based awards on the date of grant. The fair value of employee stock options and third-party warrants are generally determined using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model using various inputs, including estimates of historic volatility, term, risk-free rate, and future dividends. The grant date fair value of the stock-based awards, which have graded vesting, is recognized using the straight-line method over the requisite service period of each stock-based award, which is generally the vesting period of the respective stock-based awards. The Company recognizes forfeitures as they occur.
Income Taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates applied to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be realized. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized as income or loss in the period that includes the enactment date. A valuation allowance is established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized. Interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are included within the provision of income tax. To date, there have been no unrecognized tax benefits balances.
Fair Value
Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. The Company’s valuation techniques used to measure fair value maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The Company follows a fair value hierarchy based on three levels of inputs, of which the first two are considered observable and the last unobservable, that may be used to measure fair value. These levels of inputs are the following:
• Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
• Level 2—Inputs other than Level 1 that are observable, either directly or indirectly, such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in markets that are not active; or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities.
• Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities.
The Company has determined that the measurement of the fair value of the Class C Common Stock Warrants (as defined in Note 5) is a Level 3 fair value measurement and uses the Monte-Carlo simulation model for valuation (see Note 10).
F-11
Warrant Liability
The Company reviews the terms of debt instruments, equity instruments, and other financing arrangements to determine whether there are embedded derivative features, including embedded conversion options that are required to be bifurcated and accounted for separately as a derivative financial instrument. Additionally, in connection with the issuance of financing instruments, the Company may issue freestanding options and warrants.
The Company accounts for its common stock warrants in accordance with ASC 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (“ASC 480”) and ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging (“ASC 815”). Based upon the provisions of ASC 480 and ASC 815, the Company accounts for common stock warrants as current liabilities if the warrant fails the equity classification criteria. Common stock warrants classified as liabilities are initially recorded at fair value on the grant date and revalued at each balance sheet date with the offsetting adjustments recorded in change in fair value of warrant liabilities within the consolidated statements of operations.
The Company values its Class C Common Stock Warrants classified as liabilities using the Monte-Carlo simulation model.
Basic and Diluted Net Loss per Share
The Company follows the guidance in FASB ASC 260, Earnings per Share (“ASC 260”), which establishes standards regarding the computation of earnings per share. Basic and diluted net loss per share of common stock is computed by dividing net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period. In net loss periods, basic net loss per share and diluted net loss per share are identical because the otherwise dilutive potential common shares become anti-dilutive and are therefore excluded. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, there were 960,469 and 2,422 potential shares of common stock excluded from the calculation of diluted net loss per share as their effect is anti-dilutive, respectively (see Note 8). The basic and diluted weighted-average shares used to compute net loss per share in the audited consolidated statements of operations includes the shares issued from the reverse stock split fractional share round down.
Comprehensive Loss
The Company has no components of comprehensive loss other than net loss. Thus, comprehensive loss is the same as net loss for the periods presented.
Segment Reporting
Operating segments are defined as components of an entity about which separate discrete information is available for evaluation by the chief operating decision maker, or decision-making group, in deciding how to allocate resources in assessing performance.
The Company has one operating segment. The Company’s chief operating decision maker, which is the Chief Executive Officer, manages the Company’s operations for the purposes of allocating resources and evaluating financial performance (see Note 12 for further information).
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In November 2023, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2023-07, Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures (“ASU 2023-07”), which improves reportable segment disclosure requirements, primarily through enhanced disclosures about significant segment expenses. The guidance is effective for the Company beginning in the annual reporting period ended December 31, 2024 and interim periods beginning in fiscal year 2025. The Company adopted this standard as of December 31, 2024, which adoption only impacted the Company's segment reporting disclosures (see Note 13 for further information).
F-12
3. Balance Sheet Details
Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets
Prepaid expenses and other current assets consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
Prepaid insurance costs |
|
$ |
17,198 |
|
|
$ |
55,215 |
|
Other prepaid expenses & current assets |
|
|
49,501 |
|
|
|
29,476 |
|
Total prepaid expenses & current assets |
|
$ |
66,699 |
|
|
$ |
84,691 |
|
Property and Equipment, Net
Property and equipment, net consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
Lab equipment |
|
$ |
151,134 |
|
|
$ |
131,963 |
|
Total property and equipment, gross |
|
|
151,134 |
|
|
|
131,963 |
|
Accumulated depreciation |
|
|
(94,802 |
) |
|
|
(66,879 |
) |
Total property and equipment, net |
|
$ |
56,332 |
|
|
$ |
65,084 |
|
Depreciation expense was $27,923 for year ended December 31, 2024 and $25,049 for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Accrued Expenses
Accrued expenses consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
Accrued payroll and related expenses |
|
$ |
835,724 |
|
|
$ |
768,720 |
|
Accrued clinical study expenses |
|
|
183,824 |
|
|
|
10,268 |
|
Accrued professional fees |
|
|
67,049 |
|
|
|
219,888 |
|
Accrued clinical development costs |
|
|
41,203 |
|
|
|
153,584 |
|
Total accrued expenses |
|
$ |
1,127,800 |
|
|
$ |
1,152,460 |
|
F-13
4. Commitments and Contingencies
Lease Commitments
The Company leases 2,140 square feet of laboratory space located at 11011 Torreyana Road, Suite 102, San Diego, California (the “Lease”). In December 2024, the Company signed an amendment extending the Lease until February 28, 2025, with a base monthly rent equal to $5,350. The Company is required to maintain a security deposit of $5,564. The Lease contains customary default provisions, representations, warranties and covenants. In addition to rent, the Lease requires the Company to pay certain taxes, insurance and operating costs relating to the leased premises. The Company has applied the short-term lease exception as the amendment is less than twelve months. The Lease is classified as an operating lease.
Rent expense was $64,200 for the year ended December 31, 2024 and $111,661 for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Future minimum lease payments under the operating lease as of December 31, 2024 is $10,700.
Commitments
The Company enters into contracts in the normal course of business with third party service providers and vendors. These contracts generally provide for termination on notice and, therefore, are cancellable contracts and not considered contractual obligations and commitments.
Contingencies
From time to time, the Company may become subject to claims and litigation arising in the ordinary course of business. The Company is not a party to any material legal proceedings, nor is it aware of any material pending or threatened litigation.
F-14
5. 2023 Public Offering
On February 13, 2023, the Company closed a public offering of 6,017 shares of its common stock, 699 pre-funded warrants to purchase shares of common stock with an exercise price of $0.048 which did not have an expiration date (the “Class C Pre-Funded Warrants”) and 6,450,000 warrants to purchase up to 13,438 shares of common stock with an exercise price of $2,572.80 which expire on February 14, 2028 (the “Class C Common Stock Warrants”) at a combined offering price of $2,318.40 per share of common stock and two Class C Common Stock Warrants, or $2,318.352 per Class C Pre-Funded Warrant and two Class C Common Stock Warrants (the “February 2023 Public Offering”). Net cash proceeds to the Company from the offering were $14.0 million and issuance costs were $1.5 million.
Roth Capital Partners, LLC (“Roth”) was engaged by the Company to act as its exclusive placement agent for the February 2023 Public Offering. The Company paid Roth a cash fee equal to 8.0% of the gross proceeds received by the Company in the public offering, totaling $1.2 million of issuance costs.
The shares of common stock underlying the Class C Pre-Funded Warrants and the shares of common stock underlying the Class C Common Stock Warrants were registered with the SEC on Form S-1 (File No. 333-268576) and was declared effective by the SEC on February 9, 2023.
Between February 14, 2023 and April 6, 2023, the Company received notices of cash exercise for the Class C Pre-Funded Warrants issued in connection with the February 2023 Public Offering for 699 shares of common stock at a total purchase price of $33.64. As of December 31, 2024, there were no Class C Pre-Funded Warrants outstanding.
Using a Monte-Carlo simulation model, the Class C Common Stock Warrants were valued in the aggregate at $14.0 million and included in the issuance costs of the February 2023 Public Offering and treated as a liability (see Note 10).
From March 13, 2023 to December 31, 2024, the Company received notices of alternative cashless exercises for 6,217,640 Class C Common Stock Warrants issued in connection with the February 2023 Public Offering for 5,160 shares of common stock. As of December 31, 2024, there were 232,360 of Class C Common Stock Warrants outstanding to purchase up to 485 shares of common stock.
As part of the Class D Warrant Inducement (defined below) on August 22, 2024, the exercise price of the Class C Common Stock Warrants was reset from $38.24 to $16.00.
6. 2024 Public Offering
On February 5, 2024, the Company closed a public offering of 8,029 shares of its common stock, 77,282 pre-funded warrants to purchase shares of common stock with an exercise price of $0.0016 which did not have an expiration date (the “Class D Pre-Funded Warrants”) and 2,730,000 warrants to purchase up to 170,628 shares of common stock with an exercise price of $72.48 which expire on February 5, 2029 (the “Class D Common Stock Warrants”) at a combined offering price of $72.48 per share of common stock and two Class D Common Stock Warrants, or $72.4784 per Class C Pre-Funded Warrant and two Class D Common Stock Warrants (the “February 2024 Public Offering”). Net cash proceeds to the Company from the offering were $5.4 million and issuance costs were $0.8 million.
Roth was engaged by the Company to act as its exclusive placement agent for the February 2024 Public Offering. The Company paid Roth a cash fee equal to 8.0% of the gross proceeds received by the Company in the public offering, totaling $0.5 million of issuance costs.
The shares of common stock underlying the Class D Pre-Funded Warrants and the shares of common stock underlying the Class D Common Stock Warrants were registered with the SEC on Form S-1 (File No. 333-276232) and was declared effective by the SEC on January 31, 2024.
Between February 5, 2024 and February 13, 2024, the Company has received notices of cash exercise for the Class D Pre-Funded Warrants issued in connection with the February 2024 Public Offering for 77,282 shares of common stock at a total purchase price of $123.65. As of December 31, 2024, there were no Class D Pre-Funded Warrants outstanding.
On August 22, 2024, the Company issued 6,312 shares of common stock in connection with a notice of cash exercise for the Class D Common Stock Warrants issued in connection with the February 2024 Public Offering with a total purchase price of $241,390.
Using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, the Class D Common Stock Warrants were valued in the aggregate at $6.3 million and was included in the issuance costs of the February 2024 Public Offering and treated as equity (see Note 10).
F-15
As part of the Class D Warrant Inducement (defined below) the Company issued common stock to a third party consultant on June 11, 2024, as a result the exercise price of the Class D Common Stock Warrants were reset from $72.48 to $38.24. Additionally, on August 22, 2024, the exercise price of the Class D Common Stock Warrants was reset from $38.24 to $16.00.
As part of the 2025 Reverse Stock Split on January 28, 2025, the exercise price of the Class D Common Stock Warrants was reset from $16.00 to $3.849.
Class D Warrant Inducement
On June 11, 2024, the Company issued 653 shares of common stock to a third party consultant in order to induce the holders of the Class D Common Stock Warrants, as a result the exercise price of the Class D Common Stock Warrants were reduced from $72.48 to $38.24. Further, on August 21, 2024, the Company entered into warrant exercise inducement offer letters with certain holders (the “Class D Holders”) of 2,548,060 existing Class D Common Stock Warrants exercisable for an aggregate of 159,249 shares of its common stock (collectively, the “Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants”), to exercise their warrants at a reduced exercise price of $20.00 per share, in exchange for the Company’s agreement to issue new warrants for $2.00 (the “Class E Common Stock Warrants) as described below. The aggregate net proceeds from the exercise of the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants and the payment of the Class E Common Stock Warrants, as described below, was $3.5 million. The reduction of the exercise price of the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants and the issuance of the Class E Common Stock Warrants (the “Class D Warrant Inducement”) was structured as an at-market transaction under Nasdaq rules.
In consideration for the immediate exercise of the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants for cash and the payment of $2.00 per Class E Common Stock Warrants, the exercising holders received two Class E Common Stock Warrants for each Class D Common Stock Existing Warrant in a private placement pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”). The Class E Common Stock Warrants are exercisable for a period of five years into an aggregate of up to 318,509 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $16.00 per share.
In connection with the Class D Warrant Inducement, the Company entered into a financial advisory services agreement, dated August 21, 2024, with Roth, pursuant to which the Company agreed to pay Roth a cash fee of $267,546 for its services, in addition to reimbursement for certain expenses.
The shares of common stock issued from the exercise of the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants were registered pursuant to a registration statement on Form S-1, as amended (File No. 333-276232), which was declared effective by the SEC on January 31, 2024.
The Class E Common Stock Warrants offered in the private placement were not registered under the Securities Act or applicable state securities laws as of the issuance date, however, as part of the transaction, the Company filed a resale registration statement on Form S-3 with the SEC on September 03, 2024, which was declared effective on September 12, 2024.
The Class D Holders collectively exercised an aggregate of 2,548,060 Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants for 159,249 shares of its common stock. The Class D Warrant Inducement closed on August 22, 2024 with the Company receiving net cash proceeds of approximately $3.5 million consisting of gross cash proceeds of $3.8 million, less cash equity issuance costs of approximately $0.3 million. Note that while all Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants were exercised upon the closing of the Class D Warrant Inducement, certain shares were held in abeyance until September 20, 2024, due to the Class D holders’ exercise limitations. As of December 31, 2024, all underlying shares were issued and there were no shares held in abeyance as of the end of the reporting period that need to be considered.
The lowering of the exercise price of the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants is considered a warrant modification under the guidance of ASC 815-40, Derivatives and Hedging—Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity (“ASC 815-40”). In addition, the warrant modification is consistent with the equity issuance classification under that guidance as the reason for the warrant modification was to induce the Class D Holders of the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants to a cash exercise. As pursuant to the guidance of ASC 480 and ASC 815 the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants were classified as equity instruments before and after the warrant modification. The Company recognized the effect of the warrant modification of approximately $0.9 million as a non-cash equity issuance cost netted against the additional paid-in capital recognized from the associated warrant exercises. The amount of the non-cash equity issuance cost recognized for the warrant modification used the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the incremental fair value of the modified Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants immediately before and after the warrant modification (see Note 10).
Additionally, using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, the Class E Common Stock Warrants issued in connection with the Class D Warrant Inducement are treated as equity and the Company recognized approximately $4.9 million as a non-cash equity issuance cost netted against the additional paid-in capital (see Note 10).
F-16
Total cash and non-cash equity issuance costs recognized in the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants modification and the issuance of the Class E Common Stock Warrants of $5.5 million include cash equity issuance costs of $0.3 million and non-cash equity issuance costs of approximately $5.2 million.
As of December 31, 2024, there are 80,940 Class D Common Stock Warrants outstanding to purchase 5,060 shares of common stock that were not included in the Class D Warrant Inducement.
Class E Warrant Inducement
On December 3, 2024, the Company entered into warrant exercise inducement offer letters (the “December 2024 Inducement Letters”) with the holders of the Class E Common Stock Warrants (the “Class E Holders”) for 4,064,040 existing Class E Common Stock Warrants exercisable for an aggregate of 254,002 shares of common stock (the “Class E Common Stock Existing Warrants”), to exercise their warrants at an exercise price of $16.00 per share, in exchange for the Company’s agreement to issue 4,064,040 Class F Common Stock Warrants for 254,002 shares of its common stock (the “Class F Common Stock Warrants”) and 6,096,060 Class G Common Stock Warrants for 381,004 shares of its common stock (the “Class G Common Stock Warrants”). The aggregate net proceeds from the exercise of the Class E Common Stock Existing Warrants, was $3.7 million.
In consideration for the immediate exercise of the Class E Common Stock Existing Warrants for cash, the exercising holders received one Class F Common Stock Warrants for each Class E Common Stock Existing Warrant and one and a half Class G Common Stock Warrants for each Class E Common Stock Existing Warrant in a private placement pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. The Class F Common Stock Warrants are exercisable for a period of two years as of the date that shareholder approval is obtained into an aggregate of up to 254,002 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $16.00 per share. The Class F Warrants have an alternative cashless exercise provision that allows the holder thereof to receive two shares of common stock without payment of the exercise price. The Class G Common Stock Warrants are exercisable for a period of five years as of the date that Shareholder approval is obtained into an aggregate of up to 381,004 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $16.00 per share.
In connection with the Class E Warrant Inducement, the Company entered into a financial advisory services agreement, dated November 30, 2024, with Roth, pursuant to which the Company agreed to pay Roth a cash fee of $325,000 for its services, in addition to reimbursement for certain expenses.
The shares of common stock issued from the exercise of the Class E Common Stock Existing Warrants were registered pursuant to a registration statement on Form S-3, as amended (File No. 333-281909), which was declared effective by the SEC on September 12, 2024.
The Class F Common Stock Warrants and Class G Common Stock Warrants offered in the private placement were not registered under the Securities Act or applicable state securities laws as of the issuance date, however, as part of the transaction, the Company filed a resale registration statement on Form S-3, as amended (File No. 333-283764) with the SEC on December 19, 2024, which was declared effective on December 20, 2024.
The Class E Holders collectively exercised an aggregate of 4,064,040 Class E Common Stock Existing Warrants to for 254,002 shares of its common stock. The Class F Common Stock Warrants and the Class G Common Stock Warrants closed on December 3, 2024 with the Company receiving net cash proceeds of approximately $3.7 million consisting of gross cash proceeds of $4.1 million, less cash equity issuance costs of approximately $0.4 million.
Using the closing price of our shares of common stock as reported on the date of issuance of the Class F Common Stock Warrants based on the alternative cashless exercise provision issued in connection with the Class E Warrant Inducement are treated as equity and the Company recognized approximately $4.1 million as a non-cash equity issuance cost netted against the additional paid-in capital.
Additionally, using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, the Class G Common Stock Warrants issued in connection with the Class E Warrant Inducement are treated as equity and the Company recognized approximately $2.1 million as a non-cash equity issuance cost netted against the additional paid-in capital (see Note 10).
Total cash and non-cash equity issuance costs recognized in the Class F Common Stock Warrants and the Class G Common Stock Warrants of $6.5 million include cash equity issuance costs of $0.4 million and non-cash equity issuance costs of approximately $6.2 million.
F-17
As of December 31, 2024, there are 1,032,080 Class E Common Stock Warrants outstanding to purchase 64,506 shares of common stock that were not included in the Class E Warrant Inducement.
As part of the 2025 Reverse Stock Split on January 28, 2025, the number of shares of common stock the Class G Common Stock Warrants are exercisable into was reset from 381,004 to 1,621,463 and the exercise price of the Class G Common Stock Warrants was reset from $16.00 to $3.7596.
F-18
7. Preferred Stock
Revelation Authorized Preferred Stock
The Company is authorized under its articles of incorporation, as amended, up to 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock, which may be issued as designated by the Board of Directors without stockholder approval. As of December 31, 2024 and as of the date of this Report, there were no shares of preferred stock issued and outstanding.
Series A Preferred Stock
On December 19, 2022, the Company closed the sale of one share of the Company’s Series A Preferred Stock, par value $0.001 per share, to its Chief Executive Officer for $5,000.00. The outstanding share of Series A Preferred Stock was automatically redeemed for $5,000.00 on January 30, 2023 upon the effectiveness of the Certificate of Amendment implementing the reverse stock split and the increase in authorized shares of common stock of the Company.
8. Common Stock
The Company is authorized under its articles of incorporation, as amended, to issue up to 500,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share.
Common Stock Issuance during the year ended December 31, 2023
On February 13, 2023, the Company issued 6,017 shares of its common stock in connection with the February 2023 Public Offering. The Company received net cash proceeds of $14.0 million.
From February 14, 2023 to April 6, 2023, the Company issued 699 shares of common stock in connection with notices of cash exercise for Class C Pre-Funded Warrants issued in connection with the February 2023 Public Offering with a total purchase price of $33.64.
From March 13, 2023 to June 30, 2023, the Company issued 4,948 shares of common stock in connection with notices of alternative cashless exercise for the Class C Common Stock Warrants issued in connection with the February 2023 Public Offering.
On April 18, 2023, the Company issued 8 shares of common stock in connection with vested Rollover RSU awards.
Common Stock Issuance during the year ended December 31, 2024
On January 29, 2024, the Company issued 212 shares of common stock in connection with notices of alternative cashless exercise for the Class C Common Stock Warrants issued in connection with the February 2023 Public Offering.
On February 5, 2024, the Company issued 8,029 shares of its common stock in connection with the February 2024 Public Offering. The Company received net cash proceeds of $5.4 million.
Between February 5, 2024 and February 13, 2024, the Company issued 77,282 shares of common stock in connection with notices of cash exercise for Class D Pre-Funded Warrants issued in connection with the February 2024 Public Offering with a total purchase price of $123.65.
On June 11, 2024, as part of the Class D Warrant Inducement the Company issued 653 shares of its common stock to a third party consultant for services provided totaling $25,000.
On August 22, 2024, the Company issued 6,312 shares of common stock in connection with a notice of cash exercise for the Class D Common Stock Warrants issued in connection with the February 2024 Public Offering with a total purchase price of $241,390.
Between August 22, 2024 and September 20, 2024, the Company issued 159,249 shares of common stock in connection with notices of cash exercise for the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants issued in connection with the Class D Warrant Inducement with a total purchase price of $3.8 million.
F-19
Between December 3, 2024 and December 6, 2024, the Company issued 254,002 shares of common stock in connection with notices of cash exercise for the Class E Common Stock Existing Warrants issued in connection with the Class E Warrant Inducement with a total purchase price of $4.1 million.
As of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, 522,223 and 16,484 shares of common stock were issued and outstanding, respectively. As of December 31, 2024, no cash dividends have been declared or paid.
The total shares of common stock reserved for issuance are summarized as follows:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
Public Warrants (exercise price of $193,200.00 per share) |
|
|
626 |
|
|
|
626 |
|
Class A Common Stock Warrants (exercise price of $55,272.00 per share) |
|
|
154 |
|
|
|
154 |
|
Class A Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants (exercise price of $55,272.00 per share) |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
22 |
|
Class B Common Stock Warrants (exercise price of $10,080.00 per share) |
|
|
497 |
|
|
|
497 |
|
Class B Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants (exercise price of $12,600.00 per share) |
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
35 |
|
Class C Common Stock Warrants (exercise price of $16.00 per share) |
|
|
485 |
|
|
|
1,014 |
|
Class D Common Stock Warrants (exercise price of $3.849 per share) |
|
|
5,060 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Class E Common Stock Warrants (exercise price of $16.00 per share) |
|
|
64,506 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Class F Common Stock Warrants (alternative cashless exercise) |
|
|
508,006 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Class G Common Stock Warrants (exercise price of $3.7596 per share) |
|
|
381,004 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Rollover Warrants (exercise price of $45,070.73 per share) |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
Rollover RSU awards outstanding |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
Stock options outstanding (minimum exercise price $571.20) |
|
|
64 |
|
|
|
64 |
|
Shares reserved for issuance |
|
|
960,469 |
|
|
|
2,422 |
|
Shares available for future stock grants under the 2021 Equity Incentive Plan |
|
|
10,142 |
|
|
|
1,288 |
|
Total common stock reserved for issuance |
|
|
970,611 |
|
|
|
3,710 |
|
9. Stock-Based Compensation
2021 Equity Incentive Plan
In January 2022, the Board of Directors and the Company’s stockholders adopted the 2021 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2021 Plan”). The 2021 Plan is administered by the Board of Directors. Vesting periods and other restrictions for grants under the 2021 Plan are determined at the discretion of the Board of Directors. Grants to employees, officers, directors, advisors, and consultants of the Company typically vest over one to four years. In addition, the number of shares of stock available for issuance under the 2021 Plan will be automatically increased each January 1, and began on January 1, 2022, by 10% of the aggregate number of outstanding shares of our common stock from the first day of the preceding calendar year to the first day of the current calendar year or such lesser number as determined by our board of directors.
On May 15, 2024 at the Company’s 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, an amendment to the 2021 Equity Incentive Plan to increase the number of shares reserved under the Plan to 10,206 was approved.
Under the 2021 Plan, stock options and stock appreciation rights are granted at exercise prices determined by the Board of Directors which cannot be less than 100% of the estimated fair market value of the common stock on the grant date. Incentive stock options granted to any stockholders holding 10% or more of the Company's equity cannot be granted with an exercise price of less than 110% of the estimated fair market value of the common stock on the grant date and such options are not exercisable after five years from the grant date.
As of December 31, 2024, there were 10,142 shares available for future grants under the 2021 Plan.
Restricted Stock Units
As of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the Company has a total of 3 Rollover RSU awards for shares of common stock outstanding, respectively. As of December 31, 2024, 3 Rollover RSU awards have fully vested but are unissued and no Rollover RSU awards have been forfeited. Each Rollover RSU award converts to one share of common stock.
F-20
Stock Options
The Company has granted stock options which (i) vest fully on the date of grant; (ii) vest 25% on the one-year anniversary of the grant date or the employees hiring date, with the remainder vesting quarterly thereafter; or (iii) vest quarterly over one-year, for grants to Board of Directors, officers and employees. Stock options have a maximum term of 3 or 10 years.
The activity related to stock options during the year ended December 31, 2024 is summarized as follows:
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Weighted-average Exercise Price |
|
|
Weighted-average Remaining Contractual Term (Years) |
|
|||
Outstanding at December 31, 2023 |
|
|
64 |
|
|
$ |
3,555.83 |
|
|
|
|
|
Granted |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
Expired and forfeited |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2024 |
|
|
64 |
|
|
$ |
3,555.83 |
|
|
|
5.8 |
|
Exercisable at December 31, 2024 |
|
|
64 |
|
|
$ |
3,555.83 |
|
|
|
5.8 |
|
For the year ended December 31, 2023, the weighted-average Black-Scholes value per stock option issued during 2023 was $516.21. The fair value of the stock options was estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions:
Volatility |
|
|
144.2 |
% |
Expected term (years) |
|
|
5.04 |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
3.60 |
% |
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
Expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of shares of the Company’s common stock. In determining the expected term of stock options, the Company uses the “simplified” method. Under this method, the expected term is presumed to be the midpoint between the average vesting date and the end of the contractual term. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield for a period consistent with the expected term of the stock options in effect at the time of the grants. The dividend yield assumption is based on the expectation of no future dividend payments by the Company. In addition to assumptions used in the Black-Scholes model, the Company reduces stock-based compensation expense based on actual forfeitures in the period that each forfeiture occurs.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
For the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company recorded stock-based compensation expense for the period indicated as follows:
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
||
General and administrative: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
RSU awards |
|
$ |
97,077 |
|
|
$ |
89,533 |
|
Stock Options |
|
|
58,857 |
|
|
|
56,204 |
|
General and administrative stock-based compensation expense |
|
|
155,934 |
|
|
|
145,737 |
|
Research and development: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
RSU awards |
|
|
7,759 |
|
|
|
7,592 |
|
Stock Options |
|
|
5,157 |
|
|
|
2,392 |
|
Research and development stock-based compensation expense |
|
|
12,916 |
|
|
|
9,984 |
|
Total stock-based compensation expense |
|
$ |
168,850 |
|
|
$ |
155,721 |
|
F-21
10. Warrants
Public Warrants
In connection with our initial public offering, we issued and have outstanding as of December 31, 2024 10,511,597 Public Warrants to purchase an aggregate of 626 shares of common stock with an exercise price of $193,200.00 per share which expire on January 10, 2027 (the “Public Warrants”). The Public Warrants trade on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the ticker symbol REVBW.
The Company may redeem the Public Warrants at a price of $0.01 per Public Warrant upon not less than 30 days’ prior written notice of redemption if, and only if, the reported last sale price of the Company’s common stock equals or exceeds $302,400 per share for any 20 trading days within a 30-trading day period ending on the third business day prior to the notice of redemption to the Public Warrant holders; and if, and only if, there is a current registration statement in effect with respect to the shares of common stock underlying the Public Warrants. If the Company calls the Public Warrants for redemption, management will have the option to require all holders that wish to exercise the Public Warrants to do so on a “cashless basis,” as described in the warrant agreement.
Rollover Warrants
In connection with a private placement on January 31, 2021, Revelation issued warrants to a placement agent to purchase up to 17 shares of common stock with an exercise price of $45,070.73 per share which expire on January 31, 2027, valued on the issuance date in the aggregate at $326,675 (the “Rollover Warrants”).
As of December 31, 2024, there were 7 Rollover Warrants remaining to be exercised or exchanged.
The fair value of the Rollover Warrants were estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
Volatility |
|
|
115 |
% |
Expected term (years) |
|
|
6 |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
0.85 |
% |
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
Class A Common Stock Warrants
In connection with the closing of a private placement on January 25, 2022 (“PIPE Investment”), the Company issued warrants to an institutional investor to purchase up to 154 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $55,272.00 per share (the “Class A Common Stock Warrants”), valued on the PIPE Investment purchase date in the aggregate at $3.6 million and included in the issuance costs of the PIPE Investment and treated as equity. The warrants were exercisable immediately upon issuance, provide for a cash or cashless exercise right and expire on July 25, 2027.
The fair value of the Class A Common Stock Warrants were estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
Volatility |
|
|
47 |
% |
Expected term (years) |
|
|
5 |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
1.54 |
% |
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
Class A Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants
In connection with the PIPE Investment, the Company issued warrants to Roth to purchase an aggregate of 22 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $55,272.00 per share (the “Class A Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants”), valued on the PIPE Investment purchase date in the aggregate at $0.5 million and included in the issuance costs of the PIPE Investment and treated as equity. The warrants were exercisable immediately upon issuance, provide for a cash or cashless exercise right and expire on July 25, 2027.
F-22
The fair value of the Class A Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants were estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
Volatility |
|
|
47 |
% |
Expected term (years) |
|
|
5 |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
1.54 |
% |
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
Class B Common Stock Warrants
In connection with closing of a public offering on July 28, 2022 (“the July 2022 Public Offering”), the Company issued and has outstanding 8,333,334 warrants to purchase an aggregate of 497 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $10,080.00 per share (the “Class B Common Stock Warrants”), valued on the public offering purchase date in the aggregate at $4.5 million and included in the issuance costs of the public offering and treated as equity. The warrants were exercisable immediately upon issuance, provide for a cash or cashless exercise right and expire on July 28, 2027.
The fair value of the Class B Common Stock Warrants were estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
Volatility |
|
|
144 |
% |
Expected term (years) |
|
|
5 |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
2.69 |
% |
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
Class B Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants
In connection with the July 2022 Public Offering, the Company issued warrants to the Placement Agent to purchase up to 35 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $12,600.00 per share (the “Class B Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants”), valued on the public offering purchase date in the aggregate at $0.3 million and included in the issuance costs of the public offering and treated as equity. The warrants were exercisable immediately upon issuance, provide for a cash or cashless exercise right and expire on July 25, 2027.
The fair value of the Class B Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants were estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
Volatility |
|
|
144 |
% |
Expected term (years) |
|
|
5 |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
2.69 |
% |
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
Class C Pre-Funded Warrants
In connection with the February 2023 Public Offering, the Company issued pre-funded warrants to purchase up to 699 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $0.048 per share. Between February 14, 2023 and April 6, 2023, the Company received notices of cash exercise for the Class C Pre-Funded Warrants issued in connection with the February 2023 Public Offering for 699 shares of common stock at a total purchase price of $33.64. As of December 31, 2024, there were no Class C Pre-Funded Warrants outstanding.
Class C Common Stock Warrants
In connection with the February 2023 Public Offering, the Company issued 6,450,000 Class C Common Stock Warrants to purchase up to 13,438 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $2,572.80 per share, valued on the public offering purchase date in the aggregate at $13,996,500 and included in the issuance costs of the public offering and treated as a liability. The warrants were exercisable immediately upon issuance, provide for a cash, cashless exercise right or an alternative cashless exercise right for 0.4 shares of common stock per Class C Common Stock Warrant and expire on February 14, 2028.
The Company evaluated the Class C Common Stock Warrants under ASC 815-40 and concluded that they do not meet the criteria to be classified in stockholders’ equity and accounted for the Class C Common Stock Warrants as current liabilities.
The Company concluded that the multiplier of 0.4 shares of common stock per Class C Common Stock Warrant used in the alternative cashless exercise precludes the Class C Common Stock Warrants from being considered indexed to the Company’s stock. The Company recorded the Class C Common Stock Warrants as current liabilities on the balance sheet at fair value, with subsequent changes in their respective fair values recognized in the consolidated statements of operations at each reporting date.
F-23
Estimating fair values of liability-classified financial instruments requires the development of estimates that may, and are likely to, change over the duration of the instrument with related changes in internal and external market factors. In addition, option-based techniques are highly volatile and sensitive to changes in the trading market price of the Company’s common stock. Because liability-classified financial instruments are initially and subsequently carried at fair value, the Company’s financial results will reflect the volatility in these estimate and assumption changes. Changes in fair value are recognized as a component of other (expense) income in the consolidated statements of operations.
At the date of issuance, the Company valued the Class C Common Stock Warrants using a Monte-Carlo simulation model with a fair value of $14.0 million.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company has received notices of alternative cashless exercises for 6,217,640 Class C Common Stock Warrants issued in connection with the February 2023 Public Offering for 5,160 shares of common stock.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company re-valued 232,360 outstanding Class C Common Stock Warrants to purchase up to 485 shares of common stock using a Monte-Carlo simulation model with a fair value of $2,246. For year ended December 31, 2024, the gain of $0.1 million, resulting from the change in the fair value of the liability for the unexercised warrants was recorded as a change in fair value of the warrant liability in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
As part of the Class D Warrant Inducement on August 22, 2024, the exercise price of the Class C Common Stock Warrants was reset from $38.24 to $16.00.
Class D Pre-Funded Warrants
In connection with the February 2024 Public Offering, the Company issued pre-funded warrants to purchase up to 77,282 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $0.0016 per share. Between February 5, 2024 and February 13, 2024, the Company received notices of cash exercise for the Class D Pre-Funded Warrants issued in connection with the February 2024 Public Offering for 77,282 shares of common stock at a total purchase price of $123.65. As of December 31, 2024, there were no Class D Pre-Funded Warrants outstanding.
Class D Common Stock Warrants
In connection with the February 2024 Public Offering, the Company issued and has outstanding 2,730,000 warrants shares of common stock to purchase up to 170,628 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $72.48 per share, valued on the public offering purchase date in the aggregate at $6.3 million and included in the issuance costs of the public offering and treated as equity. The warrants were exercisable immediately upon issuance, provide for a cash or cashless exercise right and expire on February 5, 2029.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company issued 6,312 shares of common stock in connection with a notice of cash exercise for the Class D Common Stock Warrants issued in connection with the February 2024 Public Offering with a total purchase price of $241,390.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company issued 159,249 shares of common stock in connection with notices of cash exercise for the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants issued in connection with the Class D Warrant Inducement with a total purchase price of $3.8 million.
As part of the Class D Warrant Inducement the Class D Common Stock Warrants the Company issued common stock to a third party consultant on June 11, 2024, as a result the exercise price of the Class D Common Stock Warrants were reset from $72.48 to $38.24. Additionally, on August 22, 2024, the exercise price of the Class D Common Stock Warrants was reset from $38.24 to $16.00.
As part of the 2025 Reverse Stock Split on January 28, 2025, the exercise price of the Class D Common Stock Warrants was reset from $16.00 to $3.849.
As of December 31, 2024 there were 80,940 Class D Common Stock Warrants outstanding to purchase up to 5,060 shares of common stock that were not included in the Class D Warrant Inducement.
The fair value of the Class D Common Stock Warrants were originally estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
Volatility |
|
|
100 |
% |
Expected term (years) |
|
|
5 |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
4.20 |
% |
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
F-24
Modification of the Class D Common Stock Warrants and Class E Common Stock Warrants
As part of the Class D Warrant Inducement, the 2,548,060 Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants to purchase up to 159,249 shares of common stock were modified. Due to the warrant modification the fair value of the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrants were revalued before and after the warrant modification, and as the warrant modification is directly attributable to an equity offering, the Company recognized the effect of the warrant modification of approximately $0.9 million using the Black-Scholes option pricing model.
In connection with the Class D Warrant Inducement, the Company issued 5,096,120 Class E Common Stock Warrants to purchase up to 318,509 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $16.00 per share, valued on the Class D Warrant Inducement date in the aggregate at $4.9 million and included in the issuance costs of the Class D Warrant Inducement and treated as equity. The Class E Common Stock Warrants were exercisable immediately upon issuance, provide for a cash or cashless exercise right and expire on August 22, 2029.
As of December 31, 2024, there are 1,032,080 Class E Common Stock Warrants outstanding to purchase 64,506 shares of common stock that were not included in the Class E Warrant Inducement.
The fair value of the Class D Common Stock Existing Warrant modification and the Class E Common Stock Warrants were estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
Volatility |
|
|
95 |
% |
Expected term (years) |
|
|
5 |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
3.77 |
% |
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
Class F Common Stock Warrants and Class G Common Stock Warrants
In connection with the Class E Warrant Inducement to exercise the Class E Common Stock Existing Warrants, the Company issued 4,064,040 Class F Common Stock Warrants to purchase up to 254,002 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $16.00 per share. The Class F Warrants have an alternative cashless exercise provision that allows the holder thereof to receive two shares of common stock without payment of the exercise price. The Company valued the Class F Common Stock Warrants based on the alternative cashless exercise provision issued and recognized approximately $4.1 million and included in the issuance costs of the Class E Warrant Inducement and treated as equity. The Class F Common Stock Warrants are exercisable for a period of two years from January 17, 2025.
In connection with the Class E Warrant Inducement to exercise the Class E Common Stock Existing Warrants, the Company issued 6,096,060 Class G Common Stock Warrants to purchase up to 381,004 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $16.00 per share, valued on the Class E Warrant Inducement date in the aggregate at $2.1 million and included in the issuance costs of the Class E Warrant Inducement and treated as equity. The Class G Common Stock Warrants are exercisable for a period of five years from January 17, 2025. As part of the 2025 Reverse Stock Split on January 28, 2025, the number of shares of common stock the Class G Common Stock Warrants are exercisable into was reset from 381,004 to 1,621,463 and the exercise price of the Class G Common Stock Warrants was reset from $16.00 to $3.7596.
The fair value of the Class G Common Stock Warrants were estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
Volatility |
|
|
100 |
% |
Expected term (years) |
|
|
5 |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
4.38 |
% |
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
F-25
11. Income Taxes
The Company did not record a provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023 due to a full valuation allowance against its deferred tax assets.
The difference between the provision for income taxes and income taxes computed using the effective U.S. federal statutory rate is as follows:
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Federal tax statutory rate |
|
|
21.0 |
% |
|
|
21.0 |
% |
State tax, net of federal benefit |
|
|
7.2 |
|
|
|
7.2 |
|
Non-taxable change in fair value of warrant liability |
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
1,953.2 |
|
Research and development credits |
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
37.8 |
|
Change in valuation allowance |
|
|
(28.9 |
) |
|
|
(2,019.2 |
) |
Effective tax rate |
|
— % |
|
|
— % |
|
||
Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets are as follows:
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
||
Net operating loss carryforwards |
|
$ |
10,949,394 |
|
|
$ |
7,281,811 |
|
Research and development credits |
|
|
446,160 |
|
|
|
370,145 |
|
Capitalized research and development costs |
|
|
2,122,632 |
|
|
|
1,716,037 |
|
Capitalized start-up costs |
|
|
922,340 |
|
|
|
799,367 |
|
Other, net |
|
|
478,830 |
|
|
|
336,564 |
|
Total gross deferred tax assets |
|
|
14,919,356 |
|
|
|
10,503,924 |
|
Valuation allowance |
|
|
(14,919,356 |
) |
|
|
(10,503,924 |
) |
Net deferred tax assets |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, a full valuation allowance of $14,919,356 and $10,503,924, respectively, was established against its deferred tax assets due to the uncertainty surrounding the realization of such assets. The valuation allowance increased by $4,415,432 and $2,003,941 in 2024 and 2023, respectively, due to the increase in the deferred tax assets by the same amount; primarily due to net operating loss carryforwards and the mandatory capitalization of qualified research and development expenses in 2023.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company had federal and state net operating loss carryforwards of $36,356,115 and $48,464,356, respectively. As of December 31, 2023, the Company had federal and state net operating loss carryforwards of $23,777,049 and $33,468,573, respectively. Federal net operating losses carryforward indefinitely. State net operating loss carryforwards will begin to expire in 2026.
The Company had estimated federal research and development credit carryforwards of $93,915 as of December 31, 2024 and 2023. The federal research tax credit carryforwards will begin to expire in 2040. The Company had estimated state research and development credit carryforwards of $445,880 and $349,658 as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. The California state credits carryforward indefinitely.
Pursuant to Section 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code (“IRC”), utilization of the Company’s federal net operating loss carryforwards and research and development credit carryforwards may be subject to annual limitations in the event of any significant future changes in its ownership structure. These annual limitations may result in the expiration of net operating loss and research and development credit carryforwards prior to utilization. The Company has not completed an IRC Section 382 and 383 analyses regarding the limitation of net operating loss and research and development credit carryforwards.
No liability is recorded on the financial statements related to uncertain tax positions. There are no unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2024 and 2023. The Company does not expect that uncertain tax benefits will materially change in the next 12 months.
The Company’s policy is to record estimated interest and penalties related to uncertain tax benefits as income tax expense. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company had no accrued interest or penalties recorded related to uncertain tax positions.
F-26
The Company is subject to taxation in the U.S. and various state jurisdictions. The Company’s tax returns since inception are subject to examination by the U.S. and various state tax authorities. The Company is not currently undergoing a tax audit in any federal or state jurisdiction.
12. Segment Information
ASC 280, “Segment Reporting,” establishes standards for reporting information about operating segments. Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise about which separate discrete financial information is available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker (“CODM”) in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The Company and the Company’s CODM view the Company’s operations and manage its business on the basis of one reportable segment, which is focused on the prevention and treatment of disease by developing and commercializing therapeutics that modulate the innate immune system (see Note 1 for a brief description of the Company’s business).
The CODM of the Company is the Chief Executive Officer. The CODM assesses the performance of the Company and decides how to allocate resources based upon consolidated net loss that is also reported within the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The measure of segment assets that is reviewed by the CODM is reported within the Consolidated Balance Sheets as consolidated Total assets. The CODM uses consolidated net loss to monitor period-over-period results and decides where to allocate and invest additional resources within the business to continue growth. The following is a summary of the significant expense categories and consolidated net loss details provided to the CODM:
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
2024 |
|
|
2023 |
|
||
Segment operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Research and development: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
GEM-AKI, GEM-CKD and GEM-PSI clinical study expenses |
|
$ |
1,681,731 |
|
|
$ |
209,702 |
|
Manufacturing expenses |
|
|
390,022 |
|
|
|
697,429 |
|
Other program expenses(1) |
|
|
77,679 |
|
|
|
2,190,493 |
|
Other expenses(2) |
|
|
172,369 |
|
|
|
282,948 |
|
Personnel expenses (including stock-based compensation) |
|
|
1,227,195 |
|
|
|
765,330 |
|
General and administrative |
|
|
4,426,113 |
|
|
|
4,510,762 |
|
Change in fair value of warrant liability |
|
|
(81,441 |
) |
|
|
(8,328,937 |
) |
Other (expense) income, net(3) |
|
|
7,144,868 |
|
|
|
(207,473 |
) |
Net loss |
|
$ |
(15,038,536 |
) |
|
$ |
(120,254 |
) |
13. Subsequent Event
2021 Equity Plan Stock Increase
On January 1, 2025, the number of shares of common stock available under the 2021 Plan increased to 156,512 as per the Evergreen Feature in the 2021 Plan.
Restricted Stock Awards Granted
On February 11, 2025, 58,568 Restricted Stock Awards, were granted to employees and the Board of Directors which resulted in a fair value of $0.2 million of stock-based compensation expense based on the Company’s stock price on the date of grant. The grants were granted from shares of the 2021 Plan and either vest 100% on the date of grant or vest 50% on the date of grant, with 50% vesting on the vest one year thereafter.
F-27
Regaining Nasdaq Compliance
As previously reported on October 16, 2024, the Company received a letter from Nasdaq notifying the Company of its noncompliance with Nasdaq Listing Rule 5550(a)(2) by failing to maintain a minimum bid price for its common stock of at least $1.00 per share for 30 consecutive business days. The Company had until February 14, 2025, to regain compliance by having a minimum closing bid price of at least $1.00 per share for at least 10 consecutive business days. On February 19, 2025 the Company received a formal notice from Nasdaq stating that the Company’s common stock will continue to be listed and traded on Nasdaq, due to the Company having regained compliance with the minimum bid price requirement, and all applicable listing standards.
Class F Common Stock Warrant Exercises
As of March 3, 2025, the Company received alternative cashless exercise notices for 3,064,040 Class F Common Stock Warrants to purchase 383,006 shares of common stock issued in connection with the Class E Warrant Inducement.
F-28
EXHIBIT 4.16
DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES REGISTERED UNDER SECTION 12 OF THE EXCHANGE ACT
Authorized and Outstanding Stock
The Charter authorizes the issuance of an aggregate of 505,000,000 shares of capital stock, consisting of 500,000,000 Shares of Common Stock, $0.001 par value per share and 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock, $0.001 par value per share. The outstanding Shares of Common Stock are duly authorized, validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable. Our purpose is to engage in any lawful act or activity for which corporations may be organized under the DGCL. Unless our board of directors determines otherwise, we will issue all shares of our capital stock in uncertificated form.
As of the date of this Prospectus, there were 209,911 Shares of Common Stock outstanding. We have 19,335,611 issued and outstanding warrants, of which 2,964 were warrants issued in private placement transactions, 8,821,050 were warrants issued in public offerings and 10,511,597 Public Warrants. The 2,964 issued and outstanding private warrants consist of 155 Rollover Warrants, 2,464 Class A Common Stock Warrants and 345 Class A Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants. The 8,821,050 issued and outstanding warrants consist of 8,333,334 Class B Common Stock Warrants, 556 Class B Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants and 487,160 Class C Common Stock Warrants. All 19,335,611 warrants are exercisable for a total of 37,708.
Common Stock
Voting Rights
Each holder of the shares of Common Stock is entitled to one vote for each share of Common Stock held of record by such holder on all matters on which stockholders generally are entitled to vote, as provide by the Charter. The holders of the shares of Common Stock do not have cumulative voting rights in the election of directors. Generally, all matters to be voted on by the holders of Common Stock must be approved by a majority (or, in the case of election of directors, by a plurality) of the votes entitled to be cast present in person or represented by proxy, unless otherwise specified by law, the Charter.
Dividend Rights
Subject to preferences that may be applicable to any outstanding preferred stock, the holders of shares of Common Stock are entitled to receive ratably such dividends, if any, as may be declared from time to time by the Revelation Board out of funds legally available therefor.
Rights upon Liquidation, Dissolution and Winding-Up
In the event of any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of Revelation’s affairs, the holders of the shares of Common Stock are entitled to share ratably in all assets remaining after payment of Revelation’s debts and other liabilities, subject to prior distribution rights of preferred stock or any class or series of stock having a preference over the shares of Common Stock, then outstanding, if any.
Preemptive or Other Rights
The holders of shares of Common Stock have no preemptive or conversion rights or other subscription rights. There are no redemption or sinking fund provisions applicable to the shares of Common Stock. The rights, preferences and privileges of holders of shares of Common Stock will be subject to those of the holders of any shares of the preferred stock Revelation may issue in the future.
Preferred Stock
The Charter authorizes the Revelation Board to establish one or more series of preferred stock. Unless required by law or by any stock exchange, and subject to the terms of the Charter, the authorized shares of preferred stock will be available for issuance without further action by holders of Common Stock.
The Revelation Board is able to determine, with respect to any series of preferred stock, designations, powers, preferences and relative, participating, optional or other rights, if any, and the qualifications, limitations or restrictions thereof, if any.
Revelation could issue a series of preferred stock that could, depending on the terms of the series, impede or discourage an acquisition attempt or other transaction that some, or a majority, of the holders of Common Stock might believe to be in their best interests or in which the holders of Common Stock might receive a premium over the market price of the shares of Common Stock. Additionally, the issuance of preferred stock may adversely affect the rights of holders of Common Stock by restricting dividends on the common stock, diluting the voting power of the common stock or subordinating the rights of the common stock to distributions upon a liquidation, dissolution or winding up or other event. As a result of these or other factors, the issuance of preferred stock could have an adverse impact on the market price of Common Stock.
Warrants
Rollover Warrants
On January 31, 2021, Old Revelation issued warrants to purchase shares of its common stock to a placement agent in connection with a prior private placement of its securities. As a result of the merger, these warrants represent the right to purchase an aggregate of 155 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $2,816.92 and expire on January 31, 2026.
Class A Common Stock Warrants and Class A Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants
There are 2,464 Class A Common Stock Warrants and 345 Class A Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants issued and outstanding.
Each Class A Common Stock Warrant has an exercise price of $3,454.50 per share of common stock, is exercisable at any time after the sixth month anniversary of the date of issuance, will expire on July 25, 2027 and is subject to customary adjustments. The Class A Common Stock Warrants may not be exercised if the aggregate number of shares of the Company’s common stock beneficially owned by the holder (together with its affiliates) would exceed 4.99% of the Company’s outstanding common stock immediately after exercise. However, the holder may increase (upon 61 days’ prior notice from the holder to the Company) or decrease such percentage, provided that in no event such percentage exceeds 9.99%. The Class A Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants have substantially the same terms as the Class A Common Stock Warrants.
Class B Common Stock Warrants and Class B Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants
There are 8,333,334 Class B Common Stock Warrants and 556 Class B Placement Agent Common Stock Warrants issued and outstanding.
Each Class B Common Stock Warrant has an exercise price of $630.00 per share of common stock, is exercisable for 1/1,050 of a share of common stock at any time after the date of issuance, will expire on July 28, 2027 and is subject to customary adjustments. The Class B Common Stock Warrants may not be exercised if the aggregate number of shares of the Company’s common stock beneficially owned by the holder (together with its affiliates) would exceed 4.99% of the Company’s outstanding common stock immediately after exercise. However, the holder may increase (upon 61 days’ prior notice from the holder to the Company) or decrease such percentage, provided that in no event such percentage exceeds 9.99%.
Each Class B Placement Agent Common Stock Warrant has an exercise price of $787.50 per share of common stock, is exercisable at any time after the date of issuance, will expire on July 25, 2027 and is subject to customary adjustments.
Class C Common Stock Warrants
There are 487,160 Class C Common Stock Warrants issued and outstanding as of the date of this Prospectus.
Each Class C Common Stock Warrant has an exercise price of 1/30 of a share of common stock at a price of $160.80 per share of common stock, is exercisable for a share of common stock at any time after the date of issuance, will expire on February 14, 2028 and is subject to customary adjustments. Each Class C Common Stock Warrant can be exercised 0.4 shares of common stock per Class C Common Stock Warrant in an alternative cashless exercise. The Class C Common Stock Warrants may not be exercised if the aggregate number of shares of the Company’s common stock beneficially owned by the holder (together with its affiliates) would exceed 4.99% of the Company’s outstanding common stock immediately after exercise. However, the holder may increase (upon 61 days’ prior notice from the holder to the Company) or decrease such percentage, provided that in no event such percentage exceeds 9.99%.
Public Warrants
There are currently outstanding an aggregate of 10,511,597 Public Warrants, which entitle the holder to acquire shares of Common Stock. Each whole Public Warrant will entitle the registered holder to purchase 1/1,050 of a share of common stock at a price of $12,075.00 per share, subject to adjustment as discussed below, beginning 30 days after the closing of the Business Combination, provided that Revelation has an effective registration statement under the Securities Act covering the shares of Common Stock issuable upon exercise of the warrants and a current prospectus relating to them is available (or it permits holders to exercise their warrants on a cashless basis under the circumstances specified in the warrant agreement) and such shares are registered, qualified or exempt from registration under the securities, or blue sky, laws of the state of residence of the holder. The Public Warrants will expire on January 9, 2027, at 5:00 p.m., New York City time, or earlier upon redemption or liquidation.
We will not be obligated to deliver any shares of Common Stock pursuant to the exercise of a Public Warrant and will have no obligation to settle such warrant exercise unless a registration statement under the Securities Act with respect to the shares of Common Stock underlying the warrants is then effective and a prospectus relating thereto is current, subject to Revelation satisfying its obligations described below with respect to registration. No warrant will be exercisable and we will not be obligated to issue shares of Common Stock upon exercise of a warrant unless the shares of Common Stock issuable upon such warrant exercise has been registered, qualified or deemed to be exempt under the securities laws of the state of residence of the registered holder of the warrants. In the event that the conditions in the two immediately preceding sentences are not satisfied with respect to a warrant, the holder of such warrant will not be entitled to exercise such warrant and such warrant may have no value and expire worthless. In no event will we be required to net cash settle any warrant. In the event that a registration statement is not effective for the exercised warrants, the purchaser of a unit containing such warrant will have paid the full purchase price for the unit solely for the shares of Common Stock underlying such unit.
If a registration statement covering the shares of Common Stock issuable upon exercise of the warrants is not effective by the ninetieth (90th) business day after the Closing, warrant holders may, until such time as there is an effective registration statement and during any period when we will have failed to maintain an effective registration statement, exercise warrants on a “cashless basis” in accordance with Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act or another exemption. Notwithstanding the above, if the shares of Common Stock are at the time of any exercise of a warrant not listed on a national securities exchange such that they satisfy the definition of a “covered security” under Section 18(b)(1) of the Securities Act, we may, at our option, require holders of public warrants who exercise their warrants to do so on a “cashless basis” in accordance with Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act and, in the event we so elect, we will not be required to file or maintain in effect a registration statement, and in the event we do not so elect, we will use our best efforts to register or qualify the shares under applicable blue sky laws to the extent an exemption is not available.
Redemption of Warrants
Once the warrants become exercisable, Revelation may call the warrants for redemption for cash:
• in whole and not in part;
• at a price of $0.01 per warrant;
• upon not less than 30 days’ prior written notice of redemption (the “30-day redemption period”) to each warrant holder; and • if, and only if, the closing price of the common stock equals or exceeds $18,900.00 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock capitalizations, reorganizations, recapitalizations and the like and for certain issuances of shares of Common Stock and equity-linked securities for capital raising purposes in connection with the closing of our initial business combination as described elsewhere in this prospectus) for any 20 trading days within a 30-trading day period ending three business days before we send to the notice of redemption to the warrant holders.
If and when the warrants become redeemable by Revelation for cash, Revelation may exercise its redemption right even if it is unable to register or qualify the underlying securities for sale under all applicable state securities laws.
We have established the last of the redemption criterion discussed above to prevent a redemption call unless there is at the time of the call a significant premium to the warrant exercise price. If the foregoing conditions are satisfied and Revelation issues a notice of redemption of the warrants, each warrant holder will be entitled to exercise his, her or its warrant prior to the scheduled redemption date. However, the price of the shares of Common Stock may fall below the $18,900.00 redemption trigger price (as adjusted for stock splits, stock capitalizations, reorganizations, recapitalizations and the like and for certain issuances of shares of Common Stock and equity-linked securities for capital raising purposes in connection with the closing of our initial business combination as described elsewhere in this prospectus) as well as the $12,075.00 per share warrant exercise price after the redemption notice is issued.
If Revelation calls the warrants for redemption, our management will have the option to require any holder that wishes to exercise his, her or its warrant to do so on a “cashless basis.” In determining whether to require all holders to exercise their warrants on a “cashless basis,” our management will consider, among other factors, our cash position, the number of warrants that are outstanding and the dilutive effect on our stockholders of issuing the maximum number of shares of Common Stock issuable upon the exercise of our warrants. If our management takes advantage of this option, all holders of warrants would pay the exercise price by surrendering their warrants for that number of shares of Common Stock equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (x) the product of the number of shares of Common Stock underlying the warrants, multiplied by the excess of the “fair market value” (defined below) of our shares of Common Stock over the exercise price of the warrants by (y) the fair market value. The “fair market value” will mean the average closing price of the shares of Common Stock for the 10 trading days ending on the third trading day prior to the date on which the notice of redemption is sent to the holders of warrants. If our management takes advantage of this option, the notice of redemption will contain the information necessary to calculate the number of shares of Common Stock to be received upon exercise of the warrants, including the “fair market value” in such case. Requiring a cashless exercise in this manner will reduce the number of shares to be issued and thereby lessen the dilutive effect of a warrant redemption. We believe this feature is an attractive option to us if we do not need the cash from the exercise of the warrants after our initial business combination. If we call our warrants for redemption and our management does not take advantage of this option, the holders of the Private Warrants and their permitted transferees would still be entitled to exercise their Private Warrants for cash or on a cashless basis using the same formula described above that other warrant holders would have been required to use had all warrant holders been required to exercise their warrants on a cashless basis, as described in more detail below.
A holder of a warrant may notify us in writing in the event it elects to be subject to a requirement that such holder will not have the right to exercise such warrant, to the extent that after giving effect to such exercise, such person (together with such person’s affiliates), to the warrant agent’s actual knowledge, would beneficially own in excess of 4.9% or 9.8% (as specified by the holder) of the Shares of Common Stock outstanding immediately after giving effect to such exercise.
If the number of outstanding shares of Common Stock is increased by a share capitalization payable in shares of Common Stock, or by a split-up of common stock or other similar event, then, on the effective date of such share capitalization, split-up or similar event, the number of shares of Common Stock issuable on exercise of each warrant will be increased in proportion to such increase in the outstanding Shares of Common Stock. A rights offering to holders of common stock entitling holders to purchase shares of Common Stock at a price less than the fair market value will be deemed a share capitalization of a number of shares of Common Stock equal to the product of (i) the number of shares of Common Stock actually sold in such rights offering (or issuable under any other equity securities sold in such rights offering that are convertible into or exercisable for shares of Common Stock) multiplied by (ii) one (1) minus the quotient of (x) the price per shares of Common Stock paid in such rights offering and divided by (y) the fair market value.
For these purposes (i) if the rights offering is for securities convertible into or exercisable for shares of Common Stock, in determining the price payable for shares of Common Stock, there will be taken into account any consideration received for such rights, as well as any additional amount payable upon exercise or conversion and (ii) fair market value means the volume weighted average price of shares of Common Stock as reported during the ten (10) trading day period ending on the trading day prior to the first date on which the shares of Common Stock trades on the applicable exchange or in the applicable market, regular way, without the right to receive such rights.
In addition, if Revelation, at any time while the Warrants are outstanding and unexpired, pays a dividend or makes a distribution in cash, securities or other assets to the holders of common stock on account of such Shares of Common Stock (or other shares of capital stock into which the warrants are convertible), other than (a) as described above, (b) certain ordinary cash dividends, (c) to satisfy the redemption rights of the holders of Common Stock in connection with the Closing, (d) to satisfy the redemption rights of the holders of common stock in connection with a stockholder vote to amend the Current Charter to modify the substance or timing of the obligation to redeem 100% of Common Stock if it does not complete its initial business combination within 12 months from the closing of its IPO or to provide for redemption in connection with a business combination, or (e) in connection with the redemption of Petra’s public shares upon its failure to complete its initial business combination, then the warrant exercise price will be decreased, effective immediately after the effective date of such event, by the amount of cash and/or the fair market value of any securities or other assets paid on each share of common stock in respect of such event.
If the number of outstanding Shares of Common Stock is decreased by a consolidation, combination, reverse share split or reclassification of Shares of Common Stock or other similar event, then, on the effective date of such consolidation, combination, reverse share split, reclassification or similar event, the number of Shares of Common Stock issuable on exercise of each warrant will be decreased in proportion to such decrease in outstanding Shares of Common Stock.
Whenever the number of Shares of Common Stock purchasable upon the exercise of the warrants is adjusted, as described above, the warrant exercise price will be adjusted by multiplying the warrant exercise price immediately prior to such adjustment by a fraction (x) the numerator of which will be the number of Shares of Common Stock purchasable upon the exercise of the warrants immediately prior to such adjustment, and (y) the denominator of which will be the number of Shares of Common Stock so purchasable immediately thereafter.
In case of any reclassification or reorganization of the outstanding Shares of Common Stock (other than those described above or that solely affects the par value of such Shares of Common Stock), or in the case of any merger or consolidation of us with or into another corporation (other than a consolidation or merger in which we are the continuing corporation and that does not result in any reclassification or reorganization of our outstanding Shares of Common Stock), or in the case of any sale or conveyance to another corporation or entity of the assets or other property of us as an entirety or substantially as an entirety in connection with which we are dissolved, the holders of the warrants will thereafter have the right to purchase and receive, upon the basis and upon the terms and conditions specified in the warrants and in lieu of the Shares of Common Stock immediately theretofore purchasable and receivable upon the exercise of the rights represented thereby, the kind and amount of shares of new common stock or other securities or property (including cash) receivable upon such reclassification, reorganization, merger or consolidation, or upon a dissolution following any such sale or transfer, that the holder of the warrants would have received if such holder had exercised their warrants immediately prior to such event. If less than 70% of the consideration receivable by the holders of Shares of Common Stock in such a transaction is payable in the form of Shares of Common Stock in the successor entity that is listed for trading on a national securities exchange or is quoted in an established over-the-counter market, or is to be so listed for trading or quoted immediately following such event, and if the registered holder of the warrant properly exercises the warrant within thirty days following public disclosure of such transaction, the warrant exercise price will be reduced as specified in the warrant agreement based on the Black-Scholes Warrant Value (as defined in the warrant agreement) of the warrant. The purpose of such exercise price reduction is to provide additional value to holders of the warrants when an extraordinary transaction occurs during the exercise period of the warrants pursuant to which the holders of the warrants otherwise do not receive the full potential value of the warrants.
The Warrants have been issued in registered form under a warrant agreement between Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company, as warrant agent, and us. The warrant agreement provides that the terms of the warrants may be amended without the consent of any holder to cure any ambiguity or correct any defective provision, and that all other modifications or amendments will require the vote or written consent of the holders of at least 50% of the then outstanding Public Warrants, and, solely with respect to any amendment to the terms of the Private Warrants, a majority of the then outstanding Private Warrants. You should review a copy of the warrant agreement, which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, for a complete description of the terms and conditions applicable to the warrants.
The Warrants may be exercised upon surrender of the warrant certificate on or prior to the expiration date at the offices of the warrant agent, with the exercise form on the reverse side of the warrant certificate completed and executed as indicated, accompanied by full payment of the exercise price (or on a cashless basis, if applicable), by certified or official bank check payable to us, for the number of Warrants being exercised. The warrant holders do not have the rights or privileges of holders of Common Stock and any voting rights until they exercise their warrants and receive Shares of Common Stock. After the issuance of Shares of Common Stock upon exercise of the warrants, each holder will be entitled to one vote for each share held of record on all matters to be voted on by stockholders.
No fractional shares will be issued upon exercise of the Warrants. If, upon exercise of the Warrants, a holder would be entitled to receive a fractional interest in a share, we will, upon exercise, round down to the nearest whole number the number of Shares of Common Stock to be issued to the warrant holder.
Description of Securities in this Offering
We are offering shares of our common stock and warrants to purchase up to shares of common stock. We are also offering pre-funded warrants to those purchasers whose purchase of shares of common stock in this offering would result in the purchaser, together with its affiliates and certain related parties, beneficially owning more than 4.99% (or, at the election of the purchaser, 9.99%) of our outstanding shares of common stock following the consummation of this offering in lieu of the shares of common stocks that would result in such excess ownership. Each pre-funded warrant will be exercisable for one share of common stock. No warrant for fractional shares of common stock will be issued, rather warrants will be issued only for whole shares of common stock. We are also registering the shares of common stock issuable from time to time upon exercise of the pre-funded warrants and warrants offered hereby.
Common Stock
Voting Rights
Each holder of the shares of Common Stock is entitled to one vote for each share of Common Stock held of record by such holder on all matters on which stockholders generally are entitled to vote, as provide by the Charter. The holders of the shares of Common Stock do not have cumulative voting rights in the election of directors. Generally, all matters to be voted on by the holders of Common Stock must be approved by a majority (or, in the case of election of directors, by a plurality) of the votes entitled to be cast present in person or represented by proxy, unless otherwise specified by law, the Charter.
Dividend Rights
Subject to preferences that may be applicable to any outstanding preferred stock, the holders of shares of Common Stock are entitled to receive ratably such dividends, if any, as may be declared from time to time by the Revelation Board out of funds legally available therefor.
Rights upon Liquidation, Dissolution and Winding-Up
In the event of any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of Revelation’s affairs, the holders of the shares of Common Stock are entitled to share ratably in all assets remaining after payment of Revelation’s debts and other liabilities, subject to prior distribution rights of preferred stock or any class or series of stock having a preference over the shares of Common Stock, then outstanding, if any.
Preemptive or Other Rights
The holders of shares of Common Stock have no preemptive or conversion rights or other subscription rights. There are no redemption or sinking fund provisions applicable to the shares of Common Stock. The rights, preferences and privileges of holders of shares of Common Stock will be subject to those of the holders of any shares of the preferred stock Revelation may issue in the future.
Class D Common Stock Warrants
The following is a summary of certain terms and provisions of the warrants that are being offered hereby is not complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by, the provisions of the warrant, the form of which will be filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. Prospective investors should carefully review the terms and provisions of the form of warrant for a complete description of the terms and conditions of the warrants.
Duration and Exercise Price
Each Class D Common Stock Warrant offered hereby will have an exercise price equal to $ . The warrants will be immediately exercisable and may be exercised until the fifth anniversary of the issuance date. The number of Class D Common Stock Warrants outstanding, and the exercise price of those securities, will be adjusted proportionately in the event of a reverse or forward stock split of our common stock, a recapitalization or reclassification of our common stock, payment of dividends or distributions in common stock to our common stock holders, or similar transactions. In the event that the Company effects a rights offering to its common stock holders or a pro rata distribution of its assets among its common stock holders, then the holder of the Class D Common Stock Warrants will have the right to participate in such distribution and rights offering to the extent of their pro rata share of the Company’s outstanding common stock assuming they owned the number of shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of their Class D Common Stock Warrants. In the event of a “Fundamental Transaction” by the Company, such as a merger or consolidation of it with another company, the sale or other disposition of all or substantially all of the Company’s assets in one or a series of related transactions, a purchase offer, tender offer or exchange offer, or any reclassification, reorganization or recapitalization of the Company’s common stock, then the Class D Common Stock Warrant holder will have the right to receive, for each share of common stock issuable upon the exercise of the Class D Common Stock Warrant, at the option of the holder, the number of shares of common stock of the successor or acquiring corporation or of the Company, if it is the surviving corporation, and any additional consideration payable as a result of the Fundamental Transaction, that would have been issued or conveyed to the Class D Common Stock Warrant holder had the holder exercised the Class D Common Stock Warrant immediately preceding the closing of the Fundamental Transaction. In lieu of receiving such common stock and additional consideration in the Fundamental Transaction, the Class D Common Stock Warrant holder may elect to have the Company or the successor entity purchase the Class D Common Stock Warrant holder’s Public Warrant for its fair market value measured by the Black Scholes method.
In the event of the implementation of a reverse stock split, holders of the Class D Common Stock Warrants will be able to reset the exercise price of the Class D Common Stock Warrants based on the average of the five (5) VWAPs immediately prior to the date that is six trading days immediately following the reverse stock split.
If while the Class D Common Stock Warrants are outstanding, the Company issues or sells, or is deemed to have issued or sold, any common stock and/or common stock equivalents other than in connection with certain exempt issuances, with a purchase price per share less than the exercise price in effect immediately prior to such issuance or sale or deemed issuance or sale, then immediately after such issuance or sale or deemed issuance or sale, the exercise price then in effect will be reduced to an amount equal to the new issuance price.
The Company will promptly notify the Class D Common Stock Warrants holders in writing of any adjustment to the exercise price or to the number of the outstanding Class D Common Stock Warrants, declaration of a dividend or other distribution, a special non-recurring cash dividend on or a redemption of the common stock, the authorization of a rights offering, the approval of the stockholders required for any proposed reclassification of the common stock, a consolidation or merger by the Company, sale of all or substantially all of the assets of the Company, any compulsory share exchange, or the authorization of any voluntary or involuntary dissolution, liquidation, or winding up of the Company.
The Class D Common Stock Warrants contain a contractual provision stating that all questions concerning the construction, validity, enforcement and interpretation of the Class D Common Stock Warrants are governed by and construed and enforced in accordance with the internal laws of the State of New York, without regard to the principles of conflicts of law.
There is no trading market available for the Class D Common Stock Warrants on any securities exchange or nationally recognized trading system, and we do not intend to list the Class D Common Stock Warrants on any securities exchange or nationally recognized trading system.
Exercisability
The warrants will be exercisable, at the option of each holder, in whole or in part, by delivering to us a duly executed exercise notice accompanied by payment in full for the number of shares of our common stock purchased upon such exercise (except in the case of a cashless exercise as discussed below). A holder (together with its affiliates) may not exercise any portion of such holder’s warrants to the extent that the holder would own more than 4.99% of the outstanding common stock immediately after exercise, except that upon at least 61 days’ prior notice from the holder to us, the holder may increase the amount of ownership of outstanding stock after exercising the holder’s warrants up to 9.99% of the number of shares of our common stock outstanding immediately after giving effect to the exercise, as such percentage ownership is determined in accordance with the terms of the warrants.
Cashless Exercise
If, at the time a holder exercises its warrants, a registration statement registering the issuance or resale of the shares of common stock underlying the warrants under the Securities Act is not then effective or available for the issuance of such shares, then in lieu of making the cash payment otherwise contemplated to be made to us upon such exercise in payment of the aggregate exercise price, the holder may elect instead to receive upon such exercise (either in whole or in part) the net number of shares of common stock determined according to a formula set forth in the warrant.
Transferability
Subject to applicable laws, a warrant may be transferred at the option of the holder upon surrender of the warrant to us together with the appropriate instruments of transfer.
Fractional Shares
No fractional shares of common stock will be issued upon the exercise of the warrants. Rather, the number of shares of common stock to be issued will, at our election, either be rounded up to the nearest whole number or we will pay a cash adjustment in respect of such final fraction in an amount equal to such fraction multiplied by the exercise price.
Trading Market
There is no established trading market for the warrants, and we do not expect an active trading market to develop. We do not intend to apply to list the warrants on any securities exchange or other trading market. Without a trading market, the liquidity of the warrants will be extremely limited.
Right as a Stockholder
Except as otherwise provided in the warrants or by virtue of the holder’s ownership of shares of our common stock, such holder of warrants does not have the rights or privileges of a holder of our common stock, including any voting rights, until such holder exercises such holder’s warrants.
Waivers and Amendments
No term of the warrants may be amended or waived without the written consent of the holders of the warrants purchased in this offering.
Pre-funded Warrants
The following summary of certain terms and provisions of the pre-funded warrants that are being offered hereby is not complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by, the provisions of the pre-funded warrant, the form of which will be filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. Prospective investors should carefully review the terms and provisions of the form of pre-funded warrant for a complete description of the terms and conditions of the pre-funded warrants.
Duration and Exercise Price
Each pre-funded warrant offered hereby will have an initial exercise price per share of common stock equal to $0.0001. The pre-funded warrants will be immediately exercisable and will expire when exercised in full. The exercise price and number of shares of common stock issuable upon exercise is subject to appropriate adjustment in the event of share dividends, share splits, reorganizations or similar events affecting our shares of common stock and the exercise price. Subject to the rules and regulations of the applicable trading market, we may at any time during the term of the pre-funded warrant, subject to the prior written consent of the holders, reduce the then current exercise price to any amount and for any period of time deemed appropriate by our board of directors.
Exercisability
The pre-funded warrants will be exercisable, at the option of each holder, in whole or in part, by delivering to us a duly executed exercise notice accompanied by payment in full for the number of shares of common stock purchased upon such exercise (except in the case of a cashless exercise as discussed below). A holder (together with its affiliates) may not exercise any portion of the pre-funded warrant to the extent that the holder would own more than 4.99% of the outstanding shares of common stock immediately after exercise, except that upon at least 61 days’ prior notice from the holder to us, the holder may increase the amount of beneficial ownership of outstanding shares after exercising the holder’s pre-funded warrants up to 9.99% of the number of our shares of common stock outstanding immediately after giving effect to the exercise, as such percentage ownership is determined in accordance with the terms of the pre-funded warrants. Purchasers of pre-funded warrants in this offering may also elect prior to the issuance of the pre-funded warrants to have the initial exercise limitation set at 9.99% of our outstanding shares of common stock.
Cashless Exercise
In lieu of making the cash payment otherwise contemplated to be made to us upon such exercise in payment of the aggregate exercise price, the holder may elect instead to receive upon such exercise (either in whole or in part) the net number of shares of common stock determined according to a formula set forth in the pre-funded warrants.
Fractional Shares
No fractional shares of common stock will be issued upon the exercise of the pre-funded warrants. Rather, at the Company’s election, the number of shares of common stock to be issued will be rounded up to the nearest whole number or the Company will pay a cash adjustment in an amount equal to such fraction multiplied by the exercise price.
Transferability
Subject to applicable laws, a pre-funded warrant may be transferred at the option of the holder upon surrender of the pre-funded warrants to us together with the appropriate instruments of transfer.
Trading Market
There is no trading market available for the pre-funded warrants on any securities exchange or nationally recognized trading system, and we do not expect a trading market to develop. We do not intend to list the pre-funded warrants on any securities exchange or nationally recognized trading market. Without a trading market, the liquidity of the pre-funded warrants will be extremely limited. The shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of the pre-funded warrants are currently traded on the Nasdaq.
Right as a Shareholder
Except as otherwise provided in the pre-funded warrants or by virtue of such holder’s ownership of shares of common stock, the holders of the pre-funded warrants do not have the rights or privileges of holders of our shares of common stock, including any voting rights, until they exercise their pre-funded warrants.
The pre-funded warrants will provide that holders have the right to participate in distributions or dividends paid on our shares of common stock.
Fundamental Transaction
In the event of a fundamental transaction, as described in the pre-funded warrants and generally including any reorganization, recapitalization or reclassification of our shares of common stock, the sale, transfer or other disposition of all or substantially all of our properties or assets, our consolidation or merger with or into another person, the acquisition of more than 50% of our outstanding shares of common stock, or any person or group becoming the beneficial owner of 50% of the voting power represented by our outstanding shares of common stock, the holders of the pre-funded warrants will be entitled to receive upon exercise of the pre-funded warrants the kind and amount of securities, cash or other property that the holders would have received had they exercised the pre-funded warrants immediately prior to such fundamental transaction on a net exercise basis.
Our Transfer Agent and Warrant Agent
The transfer agent and warrant agent is and will be Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company.
Anti-Takeover Effects of the Charter and Bylaws and Certain Provisions of Delaware Law
The Charter and the DGCL contain provisions that are summarized in the following paragraphs and that are intended to enhance the likelihood of continuity and stability in the composition of our board of directors. These provisions are intended to avoid costly takeover battles, reduce our vulnerability to a hostile or abusive change of control and enhance the ability of our board of directors to maximize stockholder value in connection with any unsolicited offer to acquire us. However, these provisions may have an anti-takeover effect and may delay, deter or prevent a merger or acquisition of Revelation by means of a tender offer, a proxy contest or other takeover attempt that a stockholder might consider in its best interest, including those attempts that might result in a premium over the prevailing market price for the Shares of Common Stock held by stockholders.
Authorized but Unissued Capital Stock
Delaware law does not require stockholder approval for any issuance of shares that are authorized and available for issuance. However, the listing requirements of Nasdaq, which would apply so long as the shares of Common Stock remain listed on Nasdaq, require stockholder approval of certain issuances equal to or exceeding 20% of the then outstanding voting power or the then outstanding number of Shares of Common Stock. These additional shares may be used for a variety of corporate purposes, including future public offerings, to raise additional capital or to facilitate acquisitions. Additionally, the number of authorized shares of any series of common stock or preferred stock may be increased or decreased (but not below the number of shares thereof outstanding) by the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority in voting power, irrespective of the provisions of Section 242(b)(2) of the DGCL.
The Revelation Board may generally issue shares of one or more series of preferred stock on terms designed to discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of Revelation or the removal of our management. Moreover, our authorized but unissued shares of preferred stock will be available for future issuances in one or more series without stockholder approval and could be utilized for a variety of corporate purposes, including future offerings to raise additional capital, to facilitate acquisitions and employee benefit plans.
One of the effects of the existence of authorized and unissued and unreserved Shares of Common Stock or preferred stock may be to enable Revelation’s board of directors to issue shares to persons friendly to current management, which issuance could render more difficult or discourage an attempt to obtain control of Revelation by means of a merger, tender offer, proxy contest or otherwise, and thereby protect the continuity of our management and possibly deprive our stockholders of opportunities to sell their Shares of Common Stock at prices higher than prevailing market prices.
Vacancies and Newly Created Directorships
The Charter provides that, subject to the rights granted to one or more series of preferred stock then outstanding, any newly-created directorship on the board of directors that results from an increase in the number of directors and any vacancies on our board of directors will be filled solely only by the affirmative vote of a majority of the remaining directors, even if less than a quorum, by a sole remaining director or by the stockholders.
Special Stockholder Meetings
The Charter provides that special meetings of our stockholders may be called at any time only by the board of directors acting pursuant to a resolution approved by the affirmative vote of a majority of the directors then in office, subject to the rights of holders of any series of preferred stock then outstanding.
Stockholder Action by Written Consent
Pursuant to Section 228 of the DGCL, any action required to be taken at any annual or special meeting of the stockholders may be taken without a meeting, without prior notice, and without a vote if a consent or consents in writing, setting forth the action so taken, is or are signed by the holders of outstanding stock having not less than the minimum number of votes that would be necessary to authorize or take such action at a meeting at which all shares of our stock entitled to vote thereon were present and voted, the certificate of incorporation provides otherwise. In accordance with Section 228, the Charter prohibits action by written consent.
Section 203 of the DGCL
Revelation is subject to the provisions of Section 203 of the DGCL, which we refer to as “Section 203” regulating corporate takeovers. In general, Section 203 prohibits a publicly held Delaware corporation from engaging, under certain circumstances, in a business combination with an interested stockholder for a period of three years following the date the person became an interested stockholder unless:
• prior to the date of the transaction, Revelation’s board of directors approved either the business combination or the transaction that resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder;
• upon completion of the transaction that resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder, the interested stockholder owned at least 85% of the voting stock of the corporation outstanding at the time the transaction commenced, excluding for purposes of determining the voting stock outstanding, but not the outstanding voting stock owned by the interested stockholder, (1) shares owned by persons who are directors and also officers and (2) shares owned by employee stock plans in which employee participants do not have the right to determine confidentially whether shares held subject to the plan will be tendered in a tender or exchange offer; or
• at or subsequent to the date of the transaction, the business combination is approved by Revelation’s board of directors and authorized at an annual or special meeting of stockholders, and not by written consent, by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the outstanding voting stock that is not owned by the interested stockholder.
Generally, a business combination includes a merger, asset or stock sale, or other transaction resulting in a financial benefit to the interested stockholder. An interested stockholder is a person who, together with affiliates and associates, owns or, within three years prior to the determination of interested stockholder status, did own 15% or more of a corporation’s outstanding voting stock. The Petra Board expects the existence of this provision to have an anti-takeover effect with respect to transactions Revelation’s board of directors does not approve in advance. The Petra Board also anticipates that Section 203 may discourage attempts that might result in a premium over the market price for the Shares of Common Stock held by stockholders.
The provisions of Delaware law and the provisions of the Charter and Revelation’s Bylaws could have the effect of discouraging others from attempting hostile takeovers and as a consequence, they might also inhibit temporary fluctuations in the market price of Common Stock that often result from actual or rumored hostile takeover attempts. These provisions might also have the effect of preventing changes in Revelation’s management. It is also possible that these provisions could make it more difficult to accomplish transactions that stockholders might otherwise deem to be in their best interests.
Dissenters’ Rights of Appraisal and Payment
Under the DGCL, with certain exceptions, our stockholders will have appraisal rights in connection with a merger or consolidation in which we are a constituent entity. Pursuant to the DGCL, stockholders who properly demand and perfect appraisal rights in connection with such merger or consolidation will have the right to receive payment of the fair value of their shares as determined by the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware, plus interest, if any, on the amount determined to be the fair value, from the effective time of the merger or consolidation through the date of payment of the judgment.
Stockholders’ Derivative Actions
Under the DGCL, any of our stockholders may bring an action in our name to procure a judgment in our favor, also known as a derivative action, provided that the stockholder bringing the action is a holder of our shares at the time of the transaction to which the action relates or such stockholder’s stock thereafter devolved by operation of law. To bring such an action, the stockholder must otherwise comply with Delaware law regarding derivative actions.
Exclusive forum for certain lawsuits
Our Charter requires, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, that (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf, (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any director, officer or other employee to us or our stockholders, (iii) any action asserting a claim against us, our directors, officers or employees arising pursuant to any provision of the DGCL or our Charter or bylaws, or (iv) any action asserting a claim against us, our directors, officers or employees governed by the internal affairs doctrine may be brought only in the Court of Chancery in the State of Delaware, except any claim (A) as to which the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware determines that there is an indispensable party not subject to the jurisdiction of the Court of Chancery (and the indispensable party does not consent to the personal jurisdiction of the Court of Chancery within ten days following such determination), (B) which is vested in the exclusive jurisdiction of a court or forum other than the Court of Chancery or (C) for which the Court of Chancery does not have subject matter jurisdiction, as to which the Court of Chancery and the federal district court for the District of Delaware shall have concurrent jurisdiction. If an action is brought outside of Delaware, the stockholder bringing the suit will be deemed to have consented to service of process on such stockholder’s counsel. Although we believe this provision benefits us by providing increased consistency in the application of Delaware law in the types of lawsuits to which it applies, a court may determine that this provision is unenforceable, and to the extent it is enforceable, the provision may have the effect of discouraging lawsuits against our directors and officers, although our stockholders will not be deemed to have waived our compliance with federal securities laws and the rules and regulations thereunder.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, our Charter provides that the exclusive forum provision will not apply to suits brought to enforce a duty or liability created by the Exchange Act or any other claim for which the federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction. Section 27 of the Exchange Act creates exclusive federal jurisdiction over all suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Exchange Act or the rules and regulations thereunder. Additionally, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the federal courts shall be the exclusive forum for the resolution of any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under the Securities Act against us or any of our directors, officers, other employees or agents. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in our securities shall be deemed to have notice of and consented to these provisions. We note, however, that there is uncertainty as to whether a court would enforce this provision and that investors cannot waive compliance with the federal securities laws and the rules and regulations thereunder. Section 22 of the Securities Act creates concurrent jurisdiction for state and federal courts over all suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Securities Act or the rules and regulations thereunder.
Limitations on Liability and Indemnification of Officers and Directors
The DGCL authorizes corporations to limit or eliminate the personal liability of directors to corporations and their stockholders for monetary damages for breaches of directors’ fiduciary duties, subject to certain exceptions. The Charter includes a provision that eliminates the personal liability of directors for monetary damages to the corporation or its stockholders for any breach of fiduciary duty as a director, except to the extent such exemption from liability or limitation thereof is not permitted under the DGCL. The effect of these provisions is to eliminate the rights of us and our stockholders, through stockholders’ derivative suits on our behalf, to recover monetary damages from a director for breach of fiduciary duty as a director, including breaches resulting from grossly negligent behavior.
However, exculpation does not apply to any director if the director has breached such director’s duty of loyalty, acted in bad faith, knowingly or intentionally violated the law, authorized illegal dividends, redemptions or repurchases or derived an improper benefit from his or her actions as a director.
The limitation of liability provision in the Charter may discourage stockholders from bringing a lawsuit against directors for breach of their fiduciary duty. These provisions also may have the effect of reducing the likelihood of derivative litigation against directors and officers, even though such an action, if successful, might otherwise benefit us and our stockholders. In addition, your investment may be adversely affected to the extent we pay the costs of settlement and damage awards against directors and officers pursuant to these indemnification provisions.
There is currently no pending material litigation or proceeding involving any of our directors, officers or employees for which indemnification is sought.
Listing
The Common Stock and Public Warrants of Revelation are listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “REVB” and “REVBW”.
Exhibit 14.2

INSIDER TRADING POLICY
(dated January 10, 2021)
I. INTRODUCTION
Federal and state laws prohibit buying, selling or making other transfers of securities by persons who have material information that is not generally known or available to the public. These laws also prohibit persons with such material nonpublic information from disclosing this information to others who trade.
Revelation Biosciences, Inc. (the “Company”) has adopted the following policy (this “Policy”) regarding trading in securities by directors, officers, employees and consultants who have Material Nonpublic Information (as defined below).
You are responsible for ensuring that you do not violate federal or state securities laws or this Policy. We designed this Policy to promote compliance with the federal securities laws and to protect the Company and you from the serious liabilities and penalties that can result from violations of these laws.
If you violate the insider trading laws, you may have to pay civil fines for up to three times the profit gained or loss avoided by such trading, as well as criminal fines of up to $5 million. You also may have to serve a jail sentence of up to 20 years. In addition, the Company may face civil penalties up to the greater of $1 million, or three times the profit gained or loss avoided as a result of your insider trading violations, as well as criminal fines of up to $25 million.
Both the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) and The Nasdaq Stock Market (“Nasdaq”) are very effective at detecting and pursuing insider trading cases. The SEC has successfully prosecuted cases against employees trading through foreign accounts, trading by family members and friends, and trading involving only a small number of shares. Therefore, it is important that you understand the breadth of activities that constitute illegal insider trading. This Policy sets out the Company’s policy in the area of insider trading and should be read carefully and complied with fully.
This Policy will be reviewed, evaluated and revised by the Company from time to time in light of regulatory changes, developments in the Company’s business and other factors.
1
II. POLICIES AND PROCEDURES
A. Trading Policy
1. You may not buy or sell a company’s securities when you have Material Nonpublic Information about that company. This Policy against “insider trading” applies to trading in Company securities, as well as to trading in the securities of other companies, such as the Company’s customers and suppliers or a firm with which the Company is negotiating a major transaction.
2. You may not convey Material Nonpublic Information about the Company or another company to others. You also may not suggest that anyone purchase or sell any company’s securities while you are aware of Material Nonpublic Information about that company. These practices, known as “tipping,” also violate the U.S. securities laws and can result in the same civil and criminal penalties that apply if you engage in insider trading directly, even if you do not receive any money or derive any benefit from trades made by persons to whom you passed Material Nonpublic Information. This Policy against “tipping” applies to information about the Company and its securities, as well as to information about other companies. This Policy does not restrict legitimate business communications on a “need to know” basis.
3. It is against Company policy for you to engage in short-term or speculative transactions in Company securities. As such, you may not engage in: (a) short-term trading (generally defined as selling Company securities within six months following a purchase); (b) short sales (selling Company securities you do not own); (c) transactions involving publicly traded options or other derivatives, such as trading in puts or calls with respect to Company securities (unless in connection with approved hedging transactions); and (d) unless approved by legal counsel, hedging transactions. Additionally, because securities held in a margin account or pledged as collateral may be sold without your consent, if you fail to meet a margin call or if you default on a loan, a margin or foreclosure sale may result in unlawful insider trading. Because of this danger, you should exercise caution when including Company securities in a margin account or pledging Company securities as collateral for a loan.
The foregoing restrictions apply to all directors, officers, employees and consultants. These restrictions also apply to anyone that lives in your household (other than household employees). The SEC and federal prosecutors may presume that trading by family members is based on information you supplied and may treat any such transactions as if you had traded yourself. There is no exception for small transactions or transactions that may seem necessary or justifiable for independent reasons, such as the need to raise money for an emergency expenditure.
For purposes of this Policy, references to “trading” and “transactions” includes, among other things:
2
Directors, officers, employees and consultants should consult the CFO if they have any questions.
B. What is “Material Nonpublic Information”?
1. Material Information
Material information generally means information that a reasonable investor would consider important in making an investment decision to buy, hold, or sell securities. Either positive or negative information may be material. Depending on the circumstances, common examples of information that may be material include:
3
Federal and Nasdaq investigators will scrutinize a questionable trade after the fact with the benefit of hindsight, so you should always err on the side of deciding that the information is material and not trade. If you have questions regarding specific transactions, please contact the CFO.
2. Nonpublic Information
Nonpublic information is information that is not generally known or available to the public. We consider information to be available to the public only when:
C. Unauthorized Disclosure
All directors, officers, employees and consultants must maintain the confidentiality of Company information for competitive, security and other business reasons, as well as to comply with securities laws. All information you learn about the Company or its business plans is potentially nonpublic information until it is publicly disclosed. You should treat this information as confidential and proprietary to the Company. You may not disclose it to others, such as family members, other relatives, or business or social acquaintances.
Also, legal rules govern the timing and nature of our disclosure of material information to outsiders or the public. Violation of these rules could result in substantial liability for you, the Company and its management.
4
For this reason, we permit only specifically designated representatives of the Company to discuss the Company with the news media, securities analysts and investors and only in accordance with the Company’s policies and/or guidelines. If you receive inquiries of this nature, refer them to the CFO. At any time when the Company does not have an active CFO, the duties and responsibilities assigned to the CFO under this policy shall be performed by the principal financial officer.
D. When and How to Trade Company Stock
1. Overview
Directors, officers and certain other employees and consultants who are so designated from time to time (such officers and designated employees and consultants, “Restricted Employees”) are for purposes of this Policy required to comply with the restrictions covered below. Even if you are not a director or a Restricted Employee, however, following the procedures listed below may assist you in complying with this Policy.
2. Blackout Periods
From time to time due to certain developments relating to Material Nonpublic Information, the Company may implement special blackout periods during which the Company may notify particular individuals that they should not engage in any transactions involving the purchase or sale of Company securities or the securities of another company. If you are subject to a special blackout period, you should not trade in the applicable company’s securities during such time and you should not disclose to others the fact that you are prohibited from trading.
However, it is not the Company’s policy to impose special blackout periods every time that Material Nonpublic Information exists, or every time that a Company employee may be in the possession of Material Nonpublic Information. Thus, the absence of a special blackout should not be interpreted as permission to trade. In addition, if you are subject to the Company’s pre-clearance policy (described below), you must pre-clear transactions even if you initiate them while a special blackout period is not in place.
Even if a special blackout period is in place, you may exercise Company stock options if no shares are to be sold – you may not, however, effect sales of stock issued upon the exercise of stock options (including same-day sales and cashless exercises). Generally, all pending purchase and sale orders regarding Company securities that could be executed while a special blackout period is not in place must be cancelled before a special blackout period is implemented so as to avoid any purchases and sales during such period.
In light of these restrictions, if you expect a need to sell Company stock at a specific time in the future, you may wish to consider entering into a prearranged Rule 10b5‑1(c) trading plan, as discussed below.
3. Pre-clearance
The Company requires its directors and Restricted Employees to contact the CFO in advance of effecting any purchase, sale or other trading of Company securities and to obtain prior approval of the transaction.
5
Transactions involving the CFO must be approved the CEO or the chairman of the Audit Committee The pre-clearance policy applies to directors and Restricted Employees even if they are initiating a transaction while a special blackout period is not in place. The pre-clearance policy also applies to anyone that lives in the household (other than household employees) of a director or Restricted Employee.
If a transaction is approved under the pre-clearance policy, the transaction must be executed by the end of the second full trading day after the approval is obtained, but regardless may not be executed if you acquire Material Nonpublic Information concerning the Company during that time. If a transaction is not completed within the period described above, the transaction must be approved again before it may be executed.
If a proposed transaction is not approved under the pre-clearance policy, you may not transact in Company stock, and you should not inform anyone within or outside of the Company of the restriction. Any transaction under a Rule 10b5-1 trading plan (discussed below) will not require pre-clearance at the time of the transaction.
E. Rule 10b5-1 Trading Plans
Rule 10b5-1 provides a defense from insider trading liability if trades occur pursuant to a pre-arranged trading plan that meets specified conditions. It is possible to pre-arrange trades in Company securities by entering into a written trading plan. Trading plans can be established for a single trade or a series of trades. A plan must either specify the number of securities to be bought or sold, along with the price and the date, or provide a written formula for determining this information. Alternatively, a trading plan can delegate investment discretion to a third party, such as a broker, who then makes trading decisions without further input from the person implementing the plan. Because the SEC rules on trading plans are complex, you should consult with your broker and be sure you fully understand the limitations and conditions of the rules before you establish a trading plan.
All Rule 10b5-1 trading plans must be reviewed and approved in advance by the Board.
F. Noncompliance
Anyone who fails to comply with this Policy will be subject to appropriate disciplinary action, up to and including termination of employment.
Questions about these guidelines should be directed to the CFO at czygmont@revbiosciences.com.
6
Exhibit 23.1
CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
We hereby consent to the incorporation by reference in the Registration Statements on Form S-3 (File Nos. 333-283764, 333-281909, and 333-280908) and Form S‑8 (File Nos. 333-280313, 333-273933, and 333‑265329) of Revelation Biosciences, Inc. of our report dated March 6, 2025, relating to the consolidated financial statements, which includes an explanatory paragraph relating to the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern and appears on page F‑2 of this annual report on Form 10‑K for the year ended December 31, 2024.
/s/ BAKER TILLY US, LLP
San Diego, CA
March 6, 2025
Exhibit 31.1
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO SECTION 302 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
I, James Rolke, certify that:
1. |
I have reviewed this annual report on Form 10-K of Revelation Biosciences, Inc.; |
|
|
|
|
2. |
Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report; |
|
|
|
|
3. |
Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report; |
|
|
|
|
4. |
The registrant’s other certifying officer and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a–15(e)) for the registrant and have: |
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; |
|
|
|
|
(b) |
designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles; |
|
|
|
|
(c) |
evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and |
|
|
|
|
(d) |
disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and |
|
|
|
5. |
The registrant’s other certifying officer and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions): |
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
all significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and |
|
|
|
|
(b) |
any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting. |
By: |
/s/ James Rolke |
|
|
James Rolke |
|
|
Chief Executive Officer and Director |
|
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
Date: |
March 6, 2025 |
|
Exhibit 31.2
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO SECTION 302 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
I, Chester S. Zygmont, III, certify that:
1. |
I have reviewed this annual report on Form 10-K of Revelation Biosciences, Inc.; |
|
|
|
|
2. |
Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report; |
|
|
|
|
3. |
Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report; |
|
|
|
|
4. |
The registrant’s other certifying officer and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a–15(e)) for the registrant and have: |
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; |
|
|
|
|
(b) |
designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles; |
|
|
|
|
(c) |
evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and |
|
|
|
|
(d) |
disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and |
|
|
|
5. |
The registrant’s other certifying officer and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions): |
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
all significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and |
|
|
|
|
(b) |
any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting. |
By: |
/s/ Chester S. Zygmont, III |
|
|
Chester S. Zygmont, III |
|
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
|
(Principal Financial Officer and |
|
|
|
|
Date: |
March 6, 2025 |
|
Exhibit 32.1
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with this Annual Report on Form 10-K of Revelation Biosciences, Inc. (the “Company”) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), the undersigned, in the capacity and on the date indicated below, hereby certifies pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to his knowledge:
By: |
/s/ James Rolke |
|
|
James Rolke |
|
|
Chief Executive Officer and Director |
|
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
Date: |
March 6, 2025 |
|
Exhibit 32.2
REVELATION BIOSCIENCES, INC.
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with this Annual Report on Form 10-K of Revelation Biosciences, Inc. (the “Company”) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), the undersigned, in the capacity and on the date indicated below, hereby certifies pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to his knowledge:
By: |
/s/ Chester S. Zygmont, III |
|
|
Chester S. Zygmont, III |
|
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
|
(Principal Financial Officer and |
|
|
|
|
Date: |
March 6, 2025 |
|